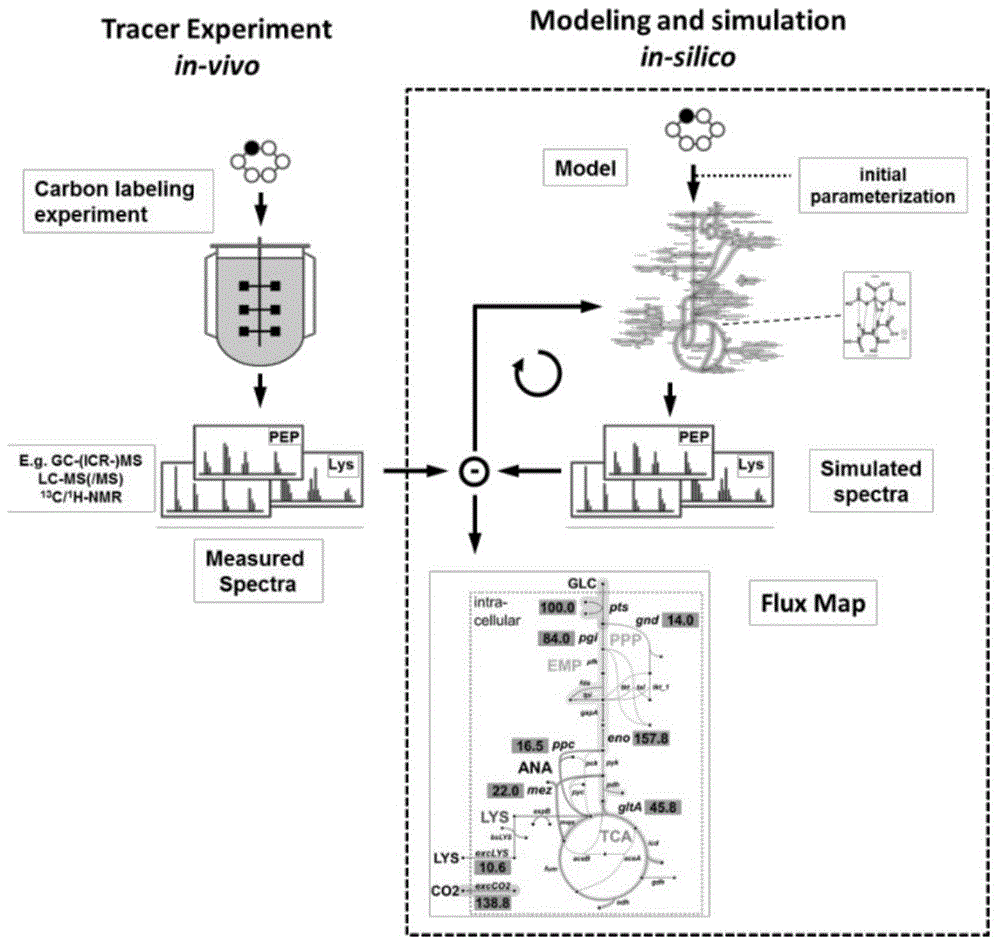
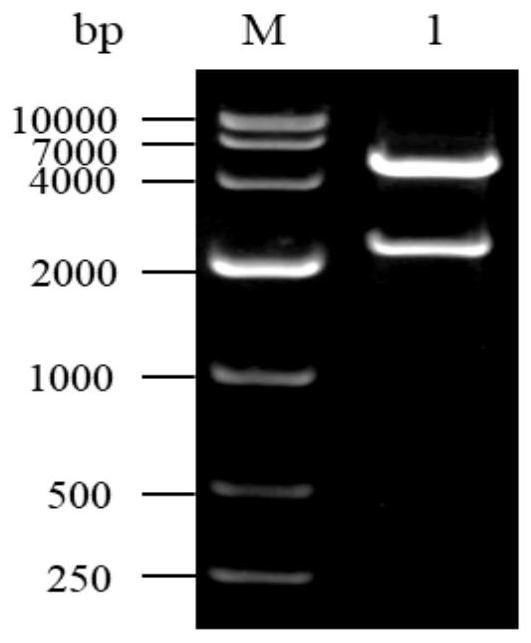
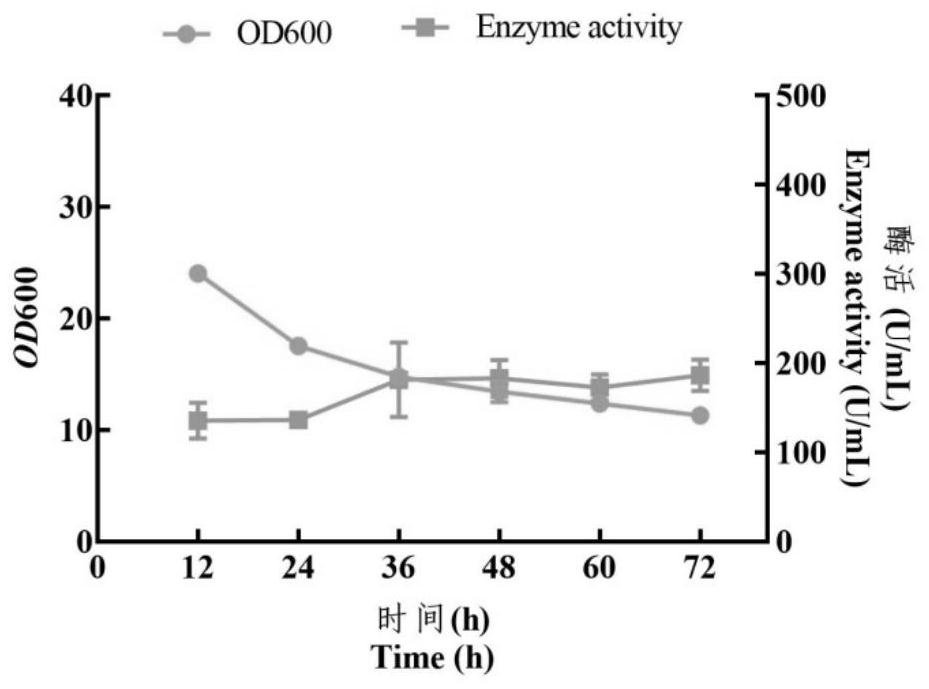
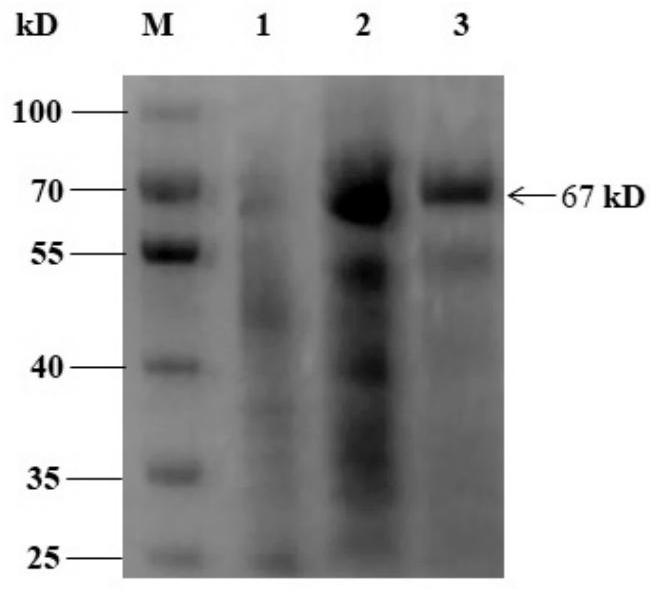
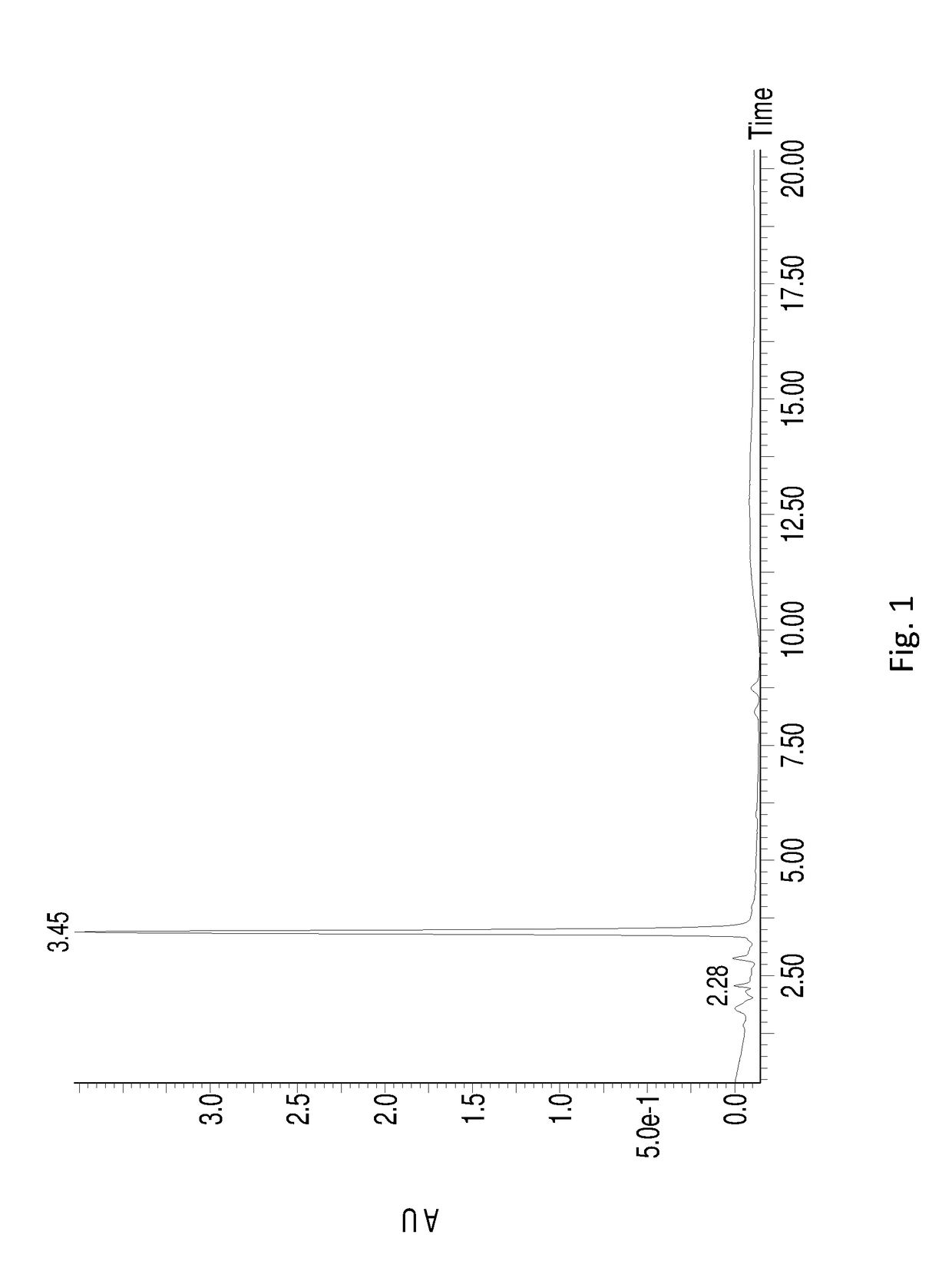
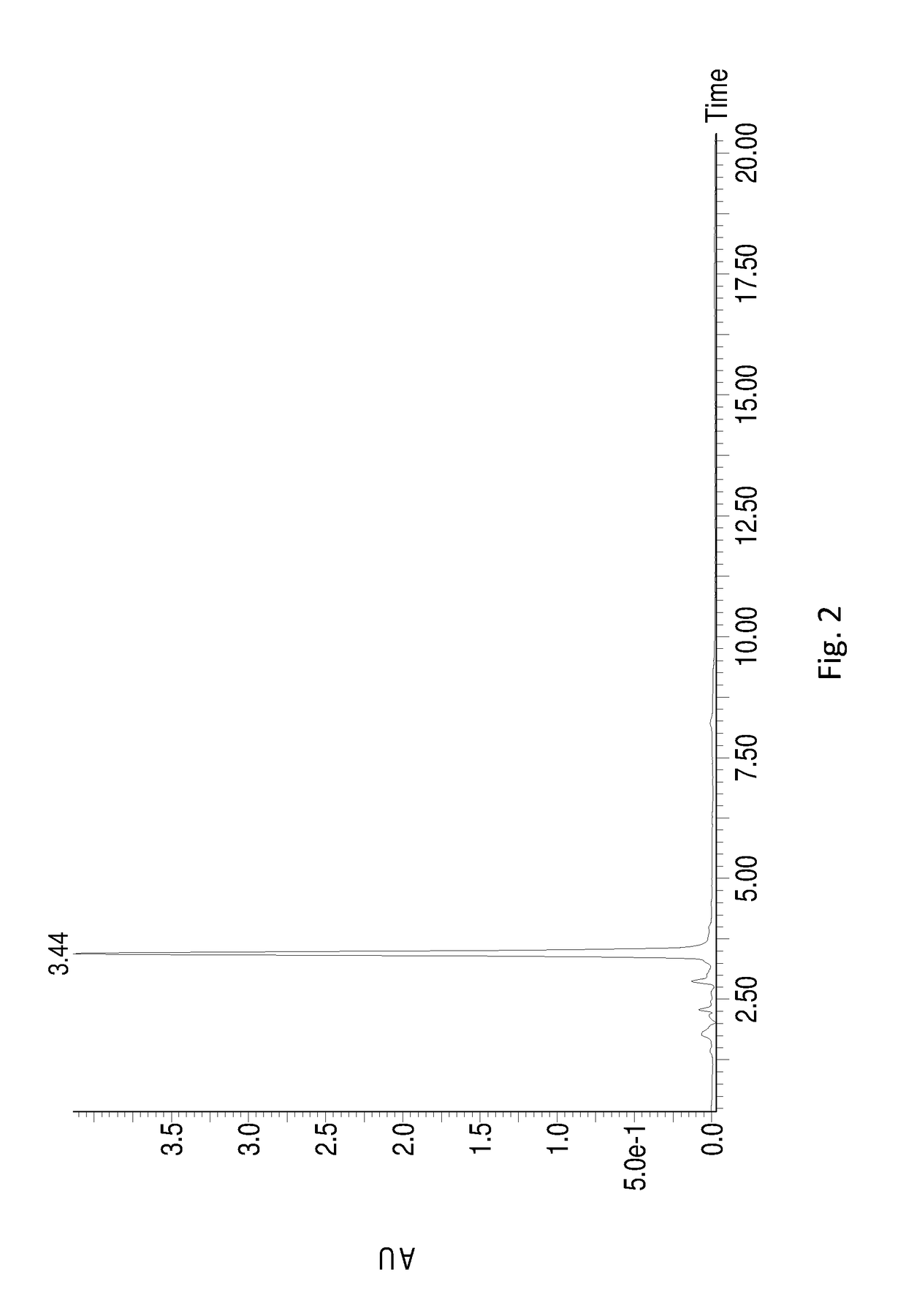
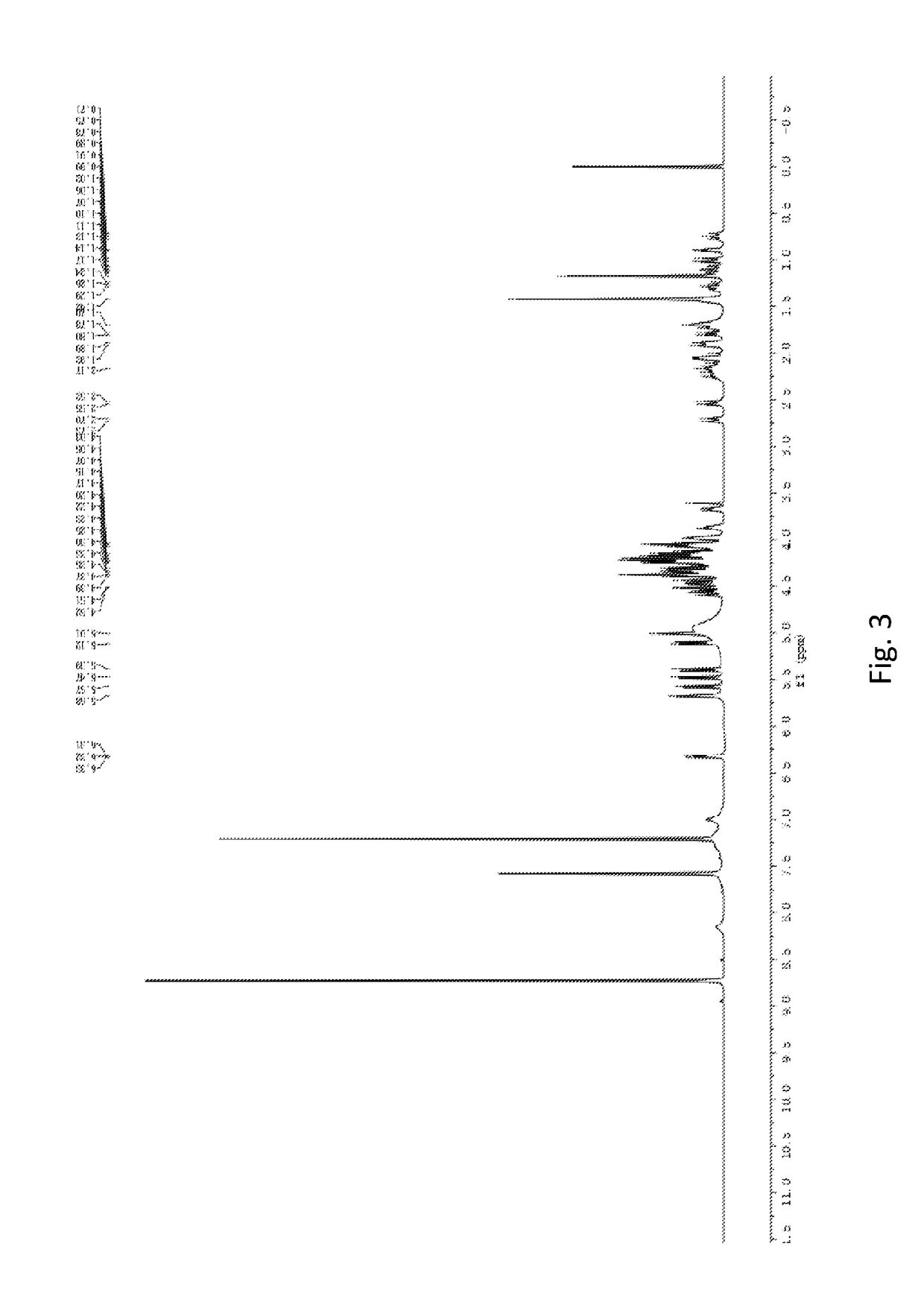
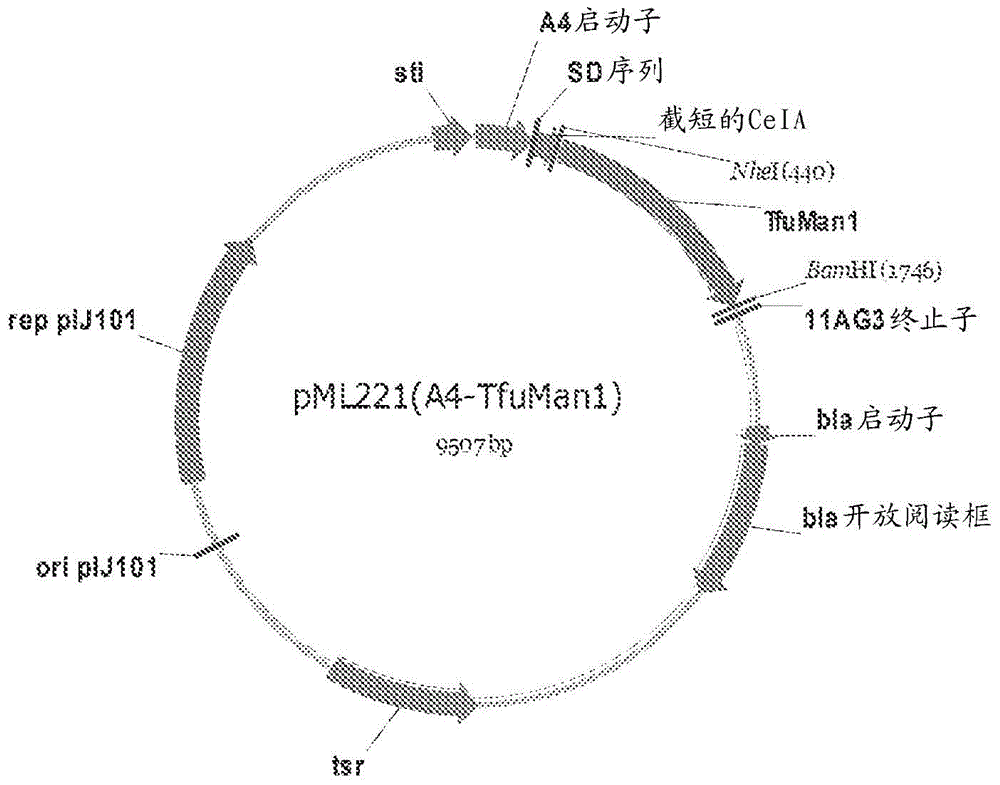
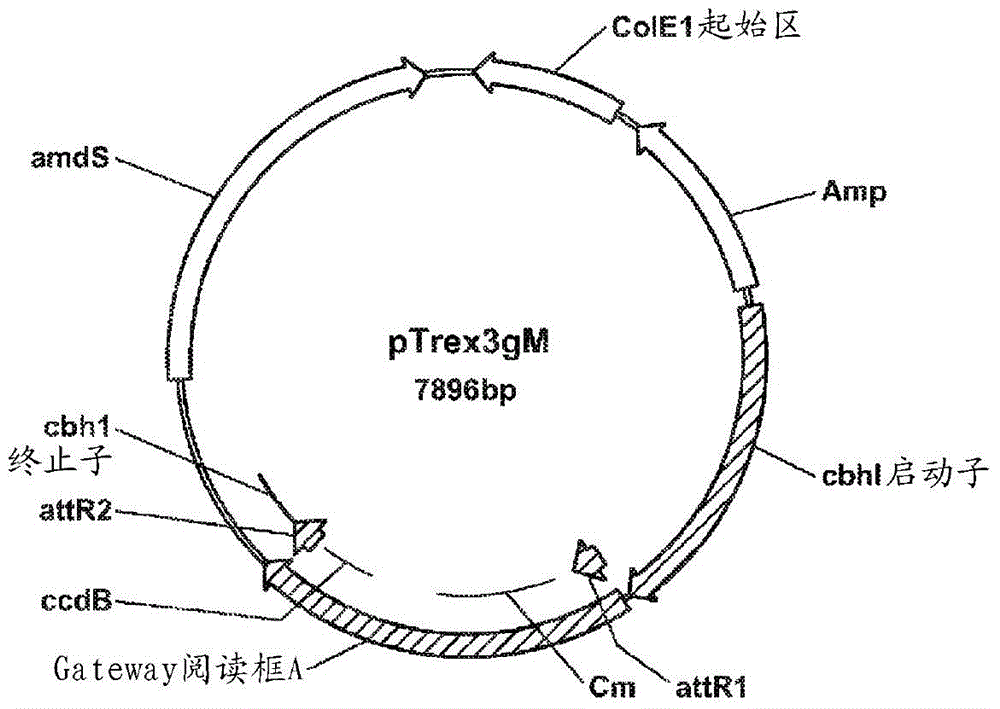
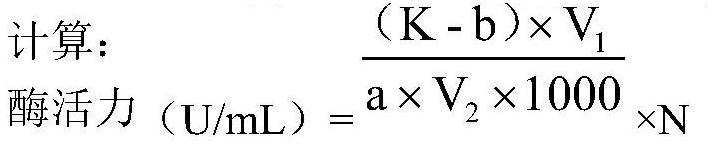Patents
Literature
40 results about "Thermobifida fusca" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
High-temperature cow dung decomposition agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105154373APromote growthGrowth inhibitionBio-organic fraction processingFungiBacillus licheniformisThermomyces lanuginosus
The invention discloses a high-temperature cow dung decomposition agent which is prepared from cow dung and a compound microbial agent through fermentation and drying, wherein cow dung particles in the high-temperature cow dung decomposition agent are loaded with compound bacteria of bacillus subtilis, bacillus licheniformis, in-situ composting geobacillus toebii, thermomyces lanuginosus and thermobifida fusca. In addition, the living bacteria count is not lower than 48+ / - 100 millions / g, the high-temperature cow dung decomposition agent is 50-650 [mu]m in average particle size, lower than 15% in moisture content and 6.0-8.0 in pH. The compound microbial agent in the decomposition agent generates plenty of cellulase, hemicellulase and protease, so that cow dung is rapidly decomposed into a simple inorganic nitrogen source and a carbon source, further, plant growth is promoted and soil fertility is improved. Fermentation is carried out under the high temperature environment, so that mesophilic plant pathogen growth is inhibited effectively, and cow dung products fermented through the decomposition agent can be directly used as organic fertilizer to be applied to soil.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently secreting, expressing and reconstructing cutinase and method for constructing same
ActiveCN101792729AIncrease productionReduce pollutionBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliBiotechnology
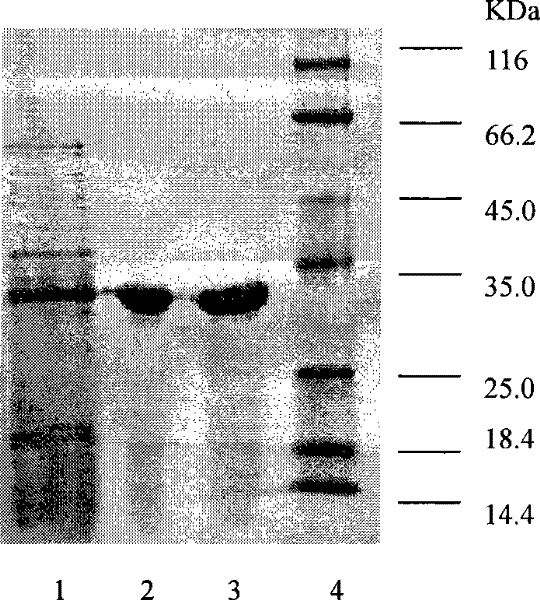
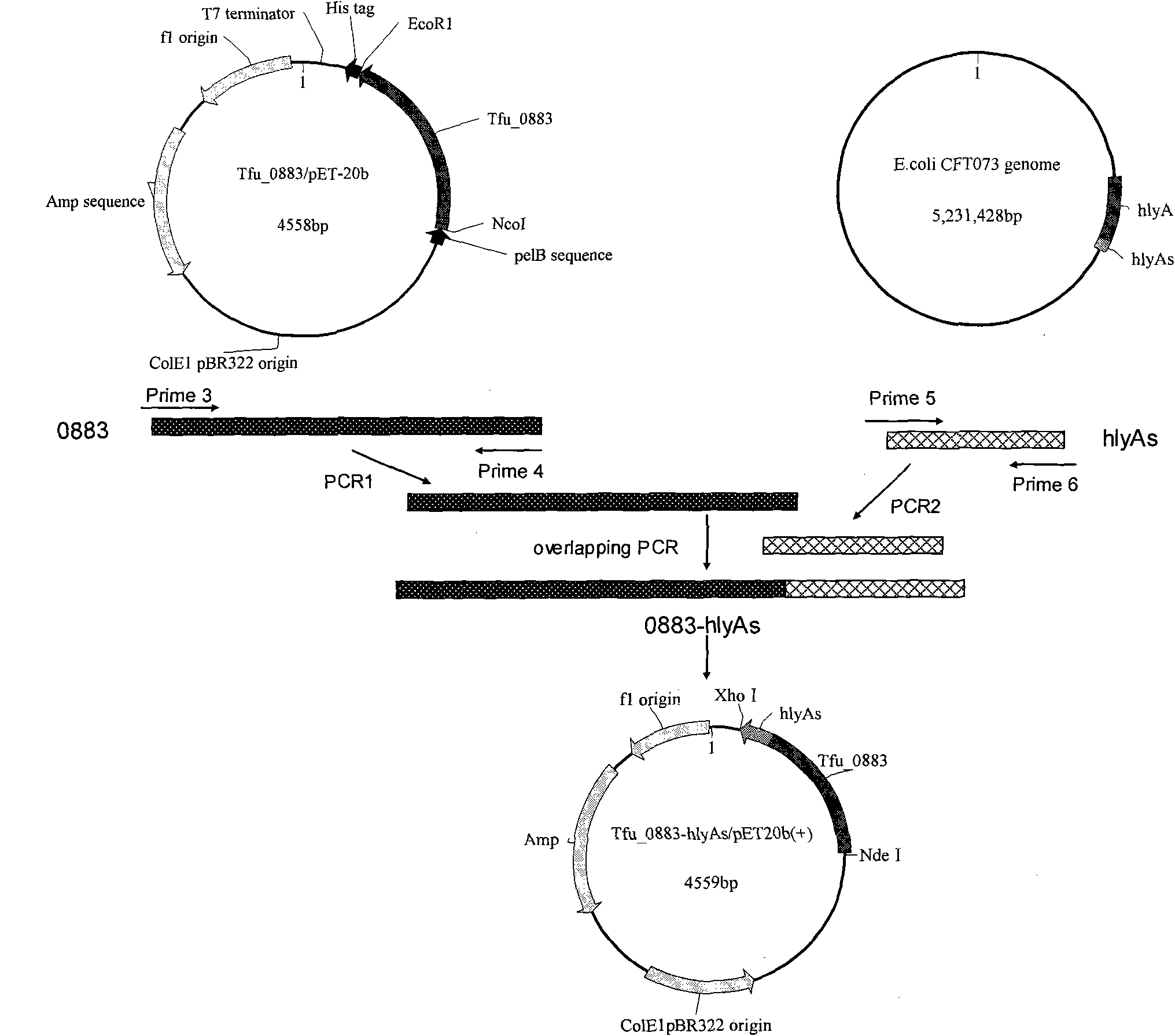
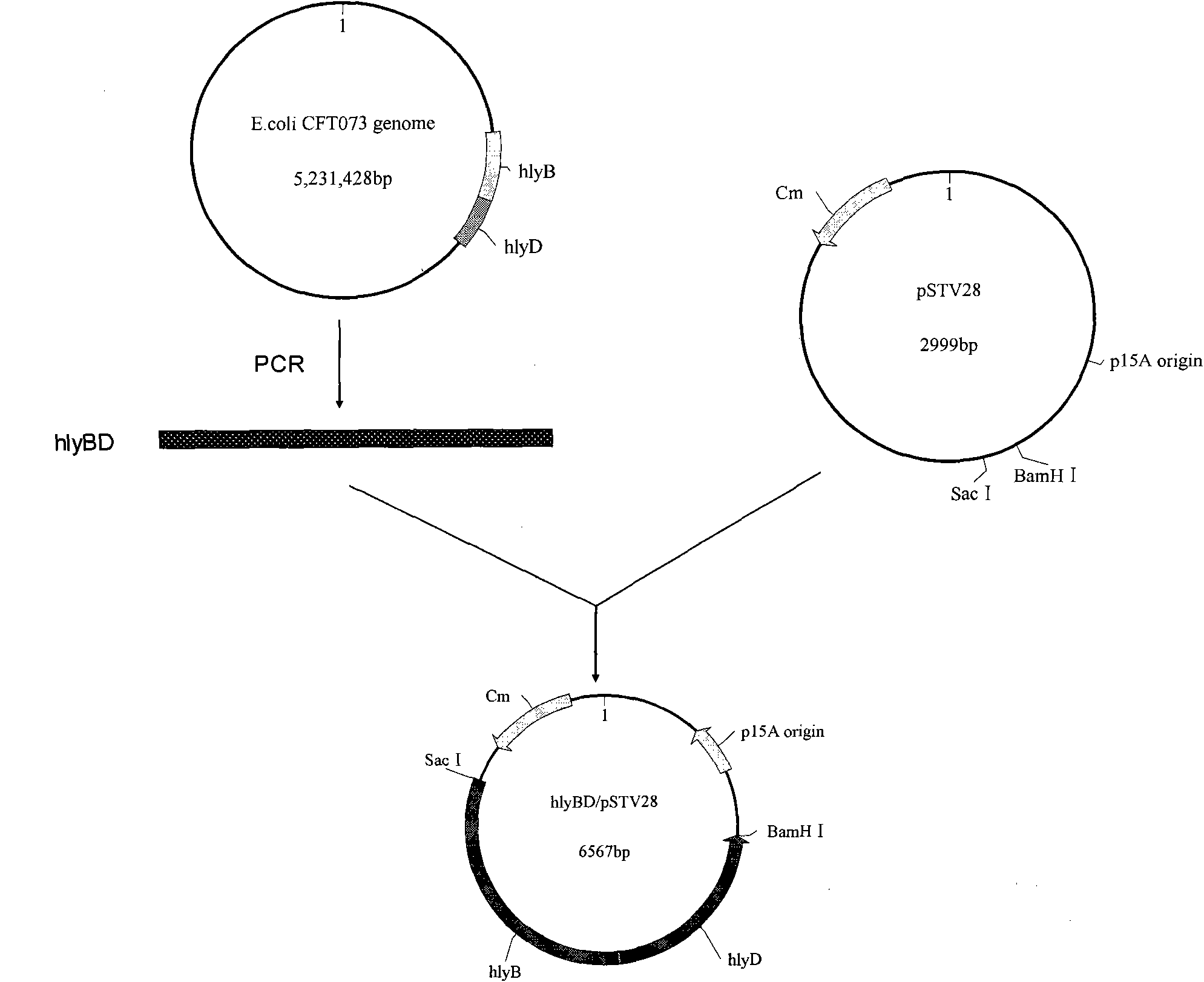
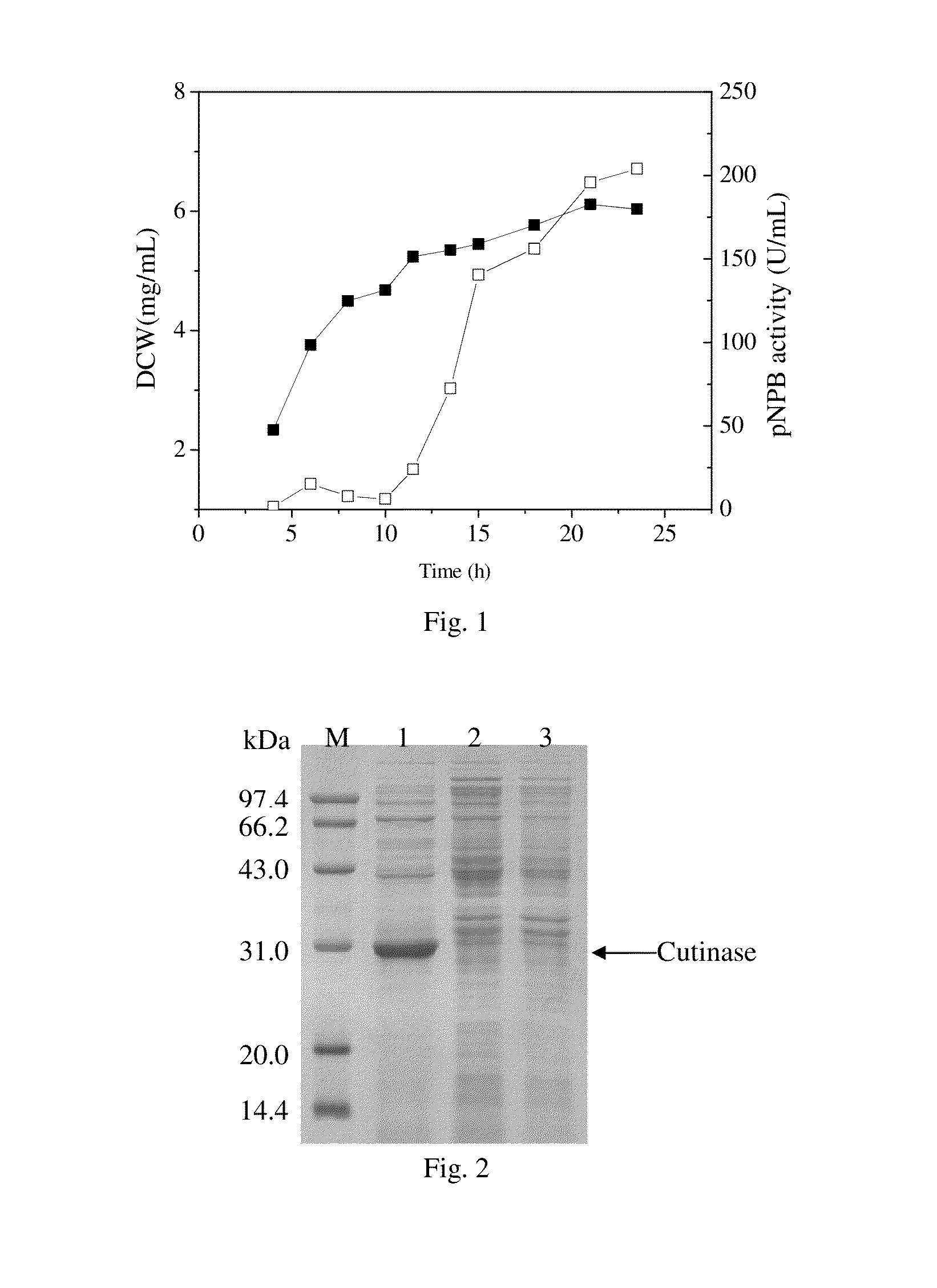
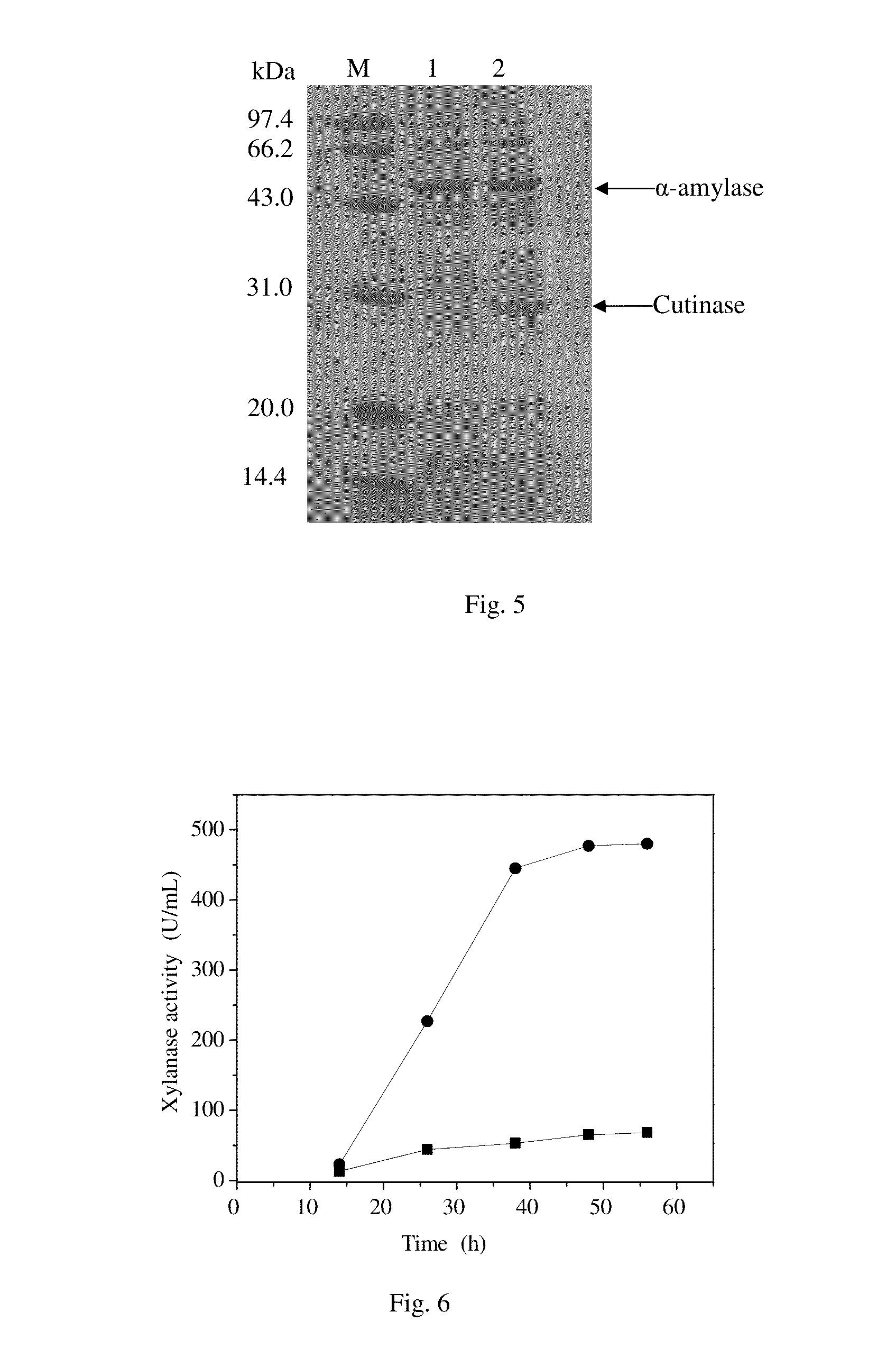
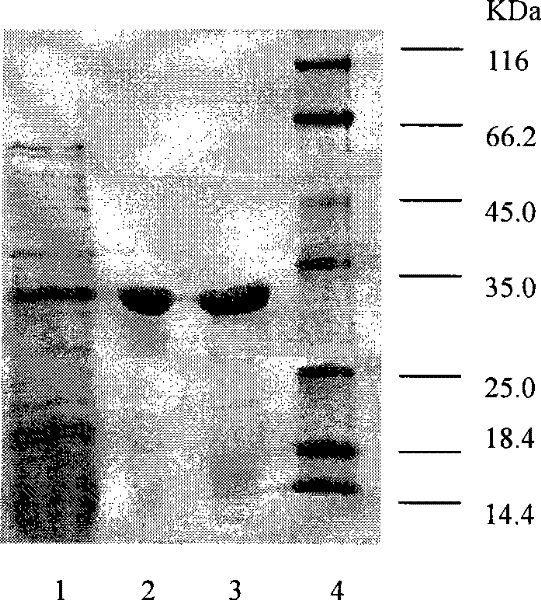
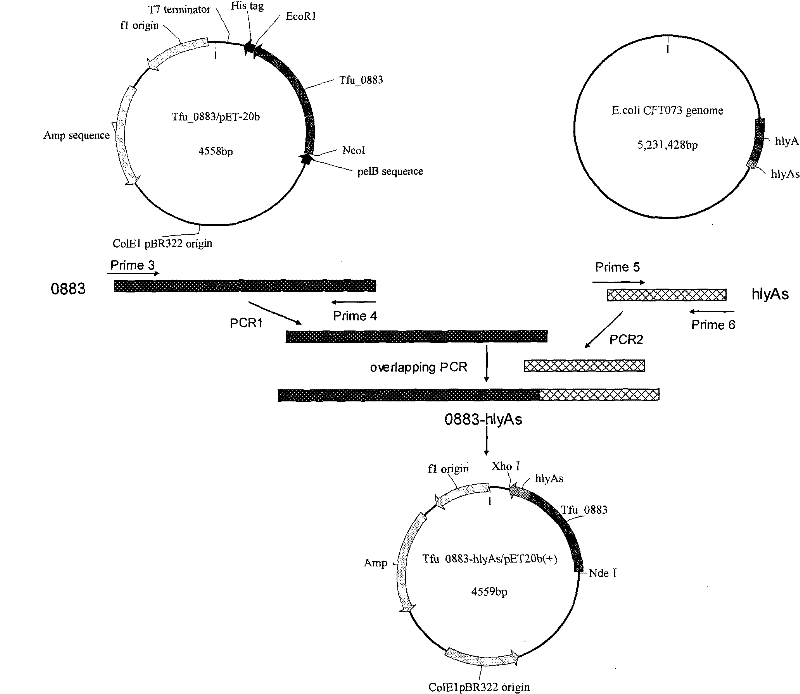
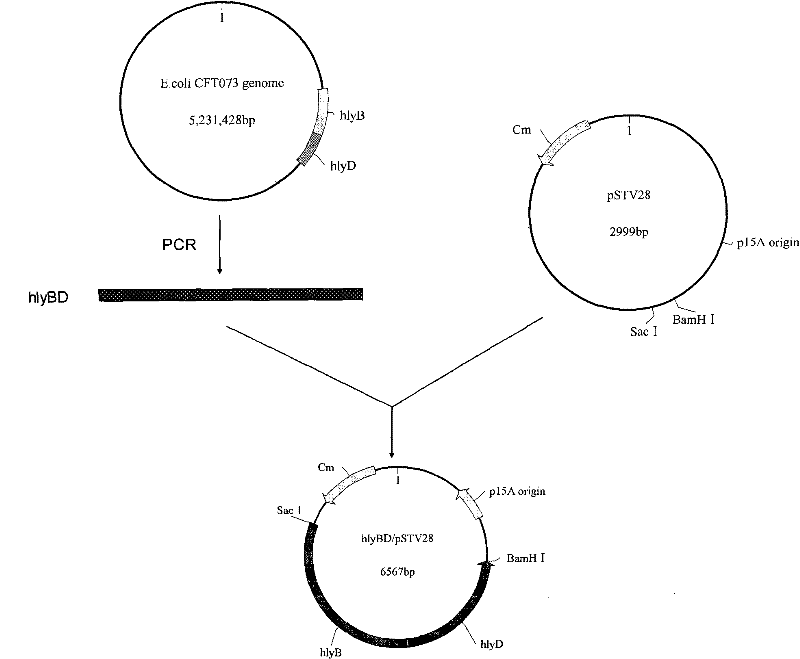
The invention relates to genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently secreting, expressing and reconstructing cutinase and a method for constructing the same, belonging to the field of the bioengineering technology. The genetically engineered bacteria are escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) which carry two recombinant plasmids, and the recombinant plasmids are respectively plasmid pSTV28 carrying the specific genes in the Alpha-hemolysin A (hly A) pathway and plasmid pET20b(+) containing the cutinase-hly As genes. The method for constructing the genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently secreting, expressing and reconstructing cutinase comprises the following steps: constructing two key recombinant plasmids and transforming the constructed recombinant plasmids in the escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) to obtain the genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently secreting, expressing and reconstructing cutinase. The cutinase is produced by using the genetically engineered bacteria through culturing liquid and inducing and expressing the cutinase. The cutinase Tfu_0883 for thermophilic monospore bacteria of Thermobifida Fusca WSH03-11 is used as the report protein. The shaking flask fermentation shows that the extracellular output of the cutinase is 306U / mL which is 1.7 times of the output of the cutinase which adopts the II-type secreting pathway in the preliminary working process in the research laboratory. The cutinase is secreted and expressed efficiently.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Heat resistance cutinase and its coding gene and expression
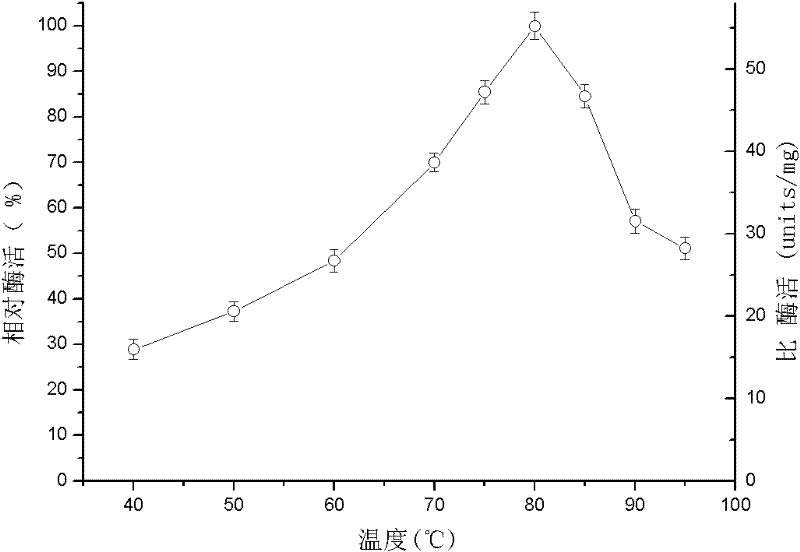
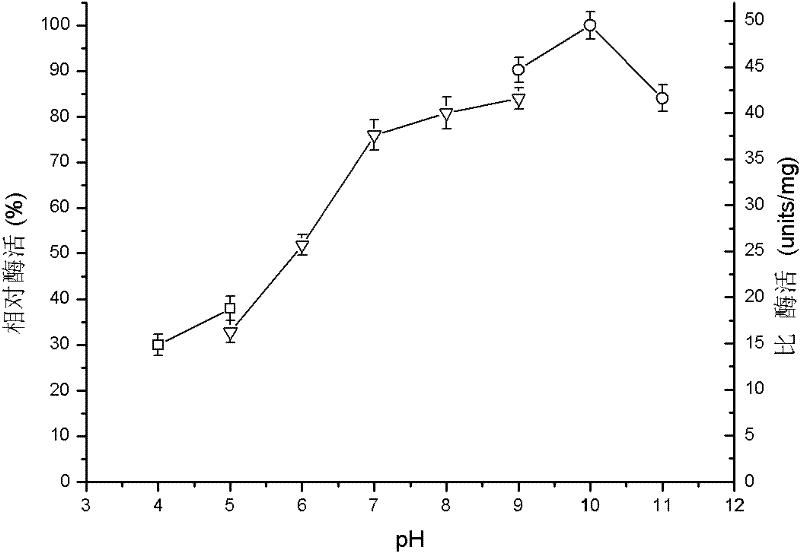
A heat-resistant cutinase and its coding gene and expression belong to the technical field of bioengineering. The present invention provides a bacterial cutinase different from fungal cutinase, its encoding gene and expression system, including extracting the total DNA of Thermobifida fusca WSH03-11, designing primers, and PCR amplification to obtain the gene encoding heat-resistant cutinase, It has the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, the full length is 906 nucleotides, and it encodes 301 amino acids. The plasmid pET20b(+) is used as the expression vector, and E.coli BL21 Rosetta(DE3)PlysS is used as the expression vector. The host can realize the high-efficiency expression of the heat-resistant cutinase gene. This cutinase has good thermal stability and has a good hydrolysis effect on cutin, triglyceride and various soluble synthetic esters, and can be widely used in textile, detergent and other industries.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Compound microbial agent for promoting fermentation of pig manure composting
InactiveCN107058179AShort fermentation timeThe promotion effect is obviousBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaBiotechnologyEnterobacter agglomerans
The invention discloses a compound microbial agent for promoting fermentation of pig manure composting. The compound microbial agent is prepared from thermobifida fusca, ureibacillus thermophaericus, pantoea agglomerans, gibsonii, bacillus amyloliquefaciens, bacillus pumilus and a liquid culture medium. Compared with other treatment methods, the fermentation time of the compound microbial agent on the pig manure composting is shorter, and more obvious facilitation effect on fermentation of the pig manure composting is obtained.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Complete-biological synthesis method of adipic acid
ActiveCN105112436AImprove product qualityReduce pollutionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliSynthesis methods
The present invention discloses a complete-biological synthesis method of adipic acid. The complete-biological synthesis method comprises: carrying out metabolic transformation on Thermobifida fusca to obtain a mutant strain B6 capable of producing adipic acid; determining the synthesis pathway of the adipic acid, transforming the gene of the pathway into escherichia coli, carrying out modular expression, and balancing the expression of a heterologous metabolic pathway; and regulating the expression level of the heterologous gene and the flow ratio of different modules to improve the accumulation of the adipic acid. According to the present invention, the bio-manufacturing of the adipic acid and the precursor thereof has characteristics of less pollution, high product quality, good development prospect, and the like.
Owner:黄山科宏生物香料股份有限公司
Organic fertilizer fermentation inoculant and application
The invention discloses an organic fertilizer fermentation inoculant and application. The inoculant is composed of a primary fermentation inoculant body and a secondary fermentation inoculant body. The primary fermentation inoculant body comprises bacillus subtilis, bacillus licheniformis, trichoderma viride, aspergillus oryzae, pseudomonas, trichoderma koningii, geotrichum candidum, long spiny shells, ascomycetes, thermomyces lanuginosus and thermobifida fusca. The secondary fermentation inoculant body comprises halophilic bacteria, alkalophilic bacteria, azotobacter chroococcum, bacillus megatherium, streptomyces griseus, bacillus thuringiensis, brevibacillus laterosporus and bacillus mucilaginosus. Time for fermenting organic fertilizer with cow dung as the raw material can be effectively shortened, and diseases and insect pests in the fertilizer can be eliminated. Meanwhile, alkalophilic bacteria and bacillus thuringiensis are added so that the fermentation inoculant can adapt to saline-alkali soil and can prevent diseases and insect pests of plants, and the prepared organic fertilizer can improve the soil structure, reduces the salt content and the pH value in soil, improves soil fertility and is particularly beneficial to improvement of saline-alkali soil.
Owner:SHANDONG SUNWAY LANDSCAPE TECH
Maize straw high-temperature decomposition agent and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN105254353APromote growthGrowth inhibitionBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationCelluloseBacillus licheniformis
The invention discloses a maize straw high-temperature decomposition agent. The maize straw high-temperature decomposition agent is prepared by fermenting and then drying maize straw powder and complex microbial inoculants. The maize straw powder particles in the maize straw high-temperature decomposition agent are loaded with a bacterium mixture containing thermomyces lanuginosus, thermobifida fusca, thermopolyspora flexuosa, streptomyces thermoviolaceus, in-situ composting bacillus licheniformis and bacillus subtilis. Living bacteria count is not lower than 48+ / -1 hundred million / g. The average grain diameter of the maize straw high-temperature decomposition agent is 150-650 micrometers, water content is lower than 15%, and pH is 6.0-8.0. By the adoption of the decomposition agent, the lignocelluloses substance and the protein substance in maize straw can be degraded quickly to achieve straw decomposing, and rich simple inorganic carbon sources and nitrogen sources are generated. Decomposed maize straw is made into organic fertilizer to effectively promote the growth of plants and improve the fertility of soil. Soil improvement and environment management are facilitated, and sustainable development of agriculture is achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Activity expression and application of thermobifida fusca xylose isomerase in wine brewing yeast
The invention discloses a method for extraction of xylose isomerases by taking brown hot crack loving spore fungus as sources and the activity expression and application of the brown hot crack loving spore fungi xylose isomerases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The molecule weight of the brown hot crack loving spore fungi xylose isomerases is 43 kilodaltons; the most suitable reaction temperature of the xylose isomerases is 80 to 85 DEG C; and the most suitable reaction pH of the xylose isomerases is 7.0. The xylose isomerases can convert xyloses into xyluloses under normal biochemical reaction conditions; genes of the xylose isomerases can be recombined into the Saccharomyces cerevisiae in which the activity expression is realized, and the xyloses or other carbon sources such as lignocellulose hydrolysate and so on can be utilized for production of various fermentation products such as alcohols and so on. The method utilizes the genetic engineering means to expand substrates which are converted by the alcohols and has important theoretical significance and application value on full utilization of lignocellulose resources.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
A mutant of cutinase and its preparation method
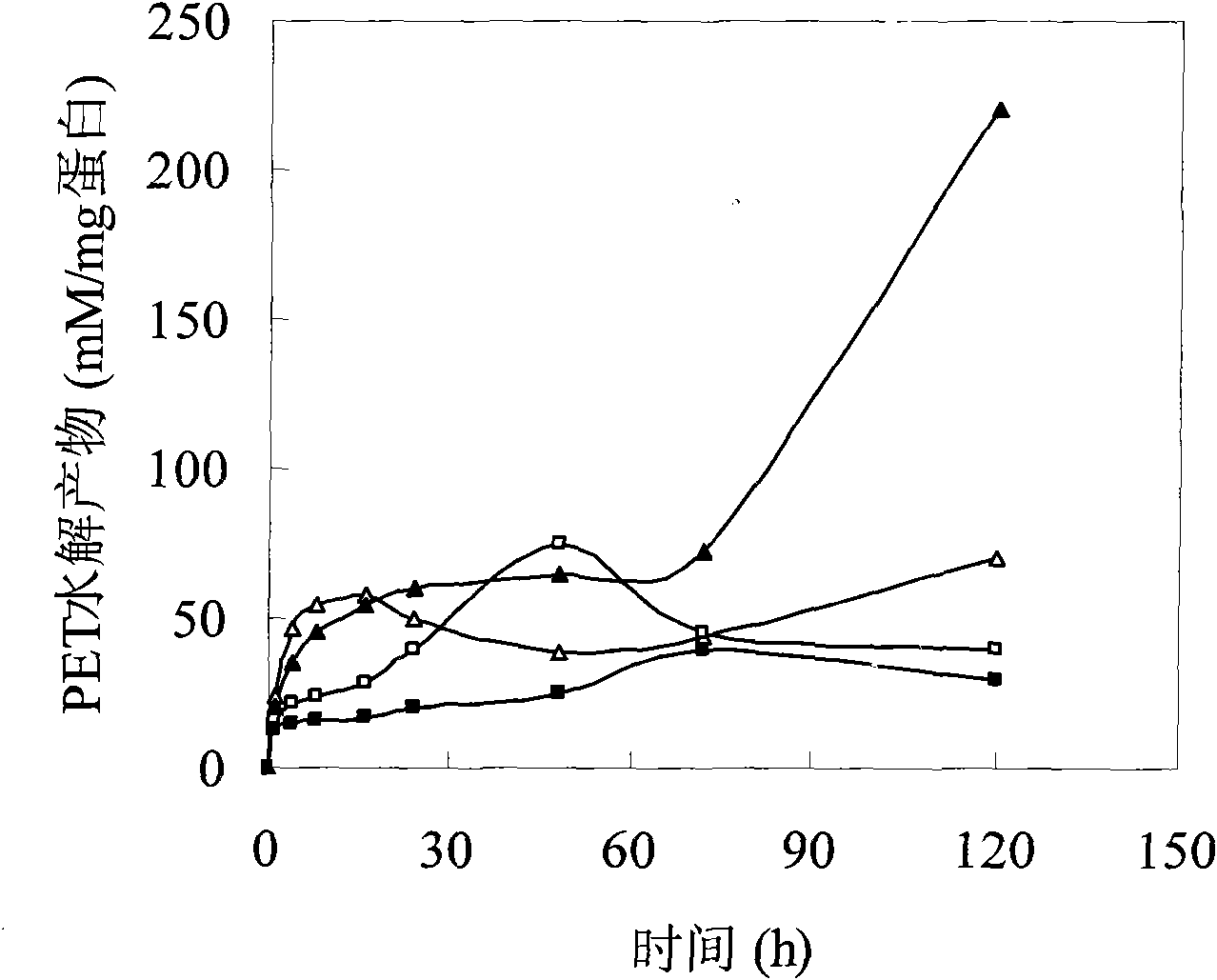
The invention provides a mutant of themobifida fusca cutinase and a preparation method thereof. The mutant comprises one or more substituents adjacent to amino acid residues corresponding to the active center of cutinase of thermobifida fusca. I218A, Q132A / T101A and W195A / F249A can improve catalyzing efficiency to cotton fiber. The catalyzing efficiency of mutant I218A to keratin is improved by 50% compared with that of the original cutinase. The catalyzing efficiency of Q132A / T101A on synthetic fibre ethylene glycol terephthalate (PET) is improved by 3 times compared with the original cutinase. The three types of mutants have wide application prospect in pre-treatment of textile fiber.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A mutant of cutinase and its preparation method
The present invention provides a mutant of Thermobifida fusca cutinase and a preparation method thereof. The mutant includes one or two active center sites of cutinase corresponding to Thermobifida fusca The substitution of nearby amino acid residues, I218A, Q132A / T101A and W195A / F249A all improved the catalytic efficiency of cotton fiber, and the catalytic efficiency of mutant I218A to cutin was 50% higher than that of procutinase; The catalytic efficiency of fiber ethylene terephthalate (PET) is 3 times higher than that of procutinase, and these three mutants have broad application prospects in textile fiber pretreatment.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Glucose isomerase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN102443578ASolve technical problemsSignificant technological progressMicroorganism based processesIsomerasesBiotechnologyHalf-life
The invention discloses a glucose isomerase mutant and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of enzyme genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. According to the invention, a high temperature glucose isomerase gene (NCBI coding: CP000088) is obtained from total DNA of thermobifida fusca, and after site-directed mutagenesis, high efficiency expression of the glucose isomerase gene with a high conversion rate is realized, with the plasmid pT7-7 or a vector that can express glucose isomerase as an expression vector and E. coli BL21 (DE3) or a bacterial strain that can express glucose isomerase as an expression host; the glucose isomerase gene has altogether 1158 nucleotide and encodes 385 amino acids; expression plasmid is constructed in the invention, glucose isomerase is expressed through conversion of bacteria or yeast, and an obtained recombinase mutant has activity of glucose isomerase and has a conversion rate of 60% at a temperature of 70 DEG C, 7% higher than the conversion rate of a parent; optimum temperature of the recombinant glucose isomerase is 80 DEG C, an optimum pH is 10, and the half life of the recombinant glucose isomerase at a temperature of 70 DEG C is no less than 30 h. The recombinant glucose isomerase is particularly applicable to production of F55 high-fructose syrup in the industry of foodstuffs.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for Enhancing Extracellular Secretion of Recombinant Proteins in Escherichia coli by Co-expressing Thermobifida Fusca Cutinase
The present invention provides a method of increasing extracellular secretion of secretory proteins by co-expressing the secretory proteins with a mature cutinase. Cutinase can improve the permeability of E. coli cell membrane without destroying the membrane, and thus facilitate cross-membrane transfer of the secretory proteins co-expressed in E. coli. Increased extracellular secretion of target proteins can shorten cell culture time, reduce the formation of inclusion bodies and increase production of target proteins.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Trehalose synthase mutant and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a trehalose synthase mutant and a preparation method and application thereof and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. The 271st Gln codon near the active center of trehalose synthase of trehalose synthase of Thermobifida fusca YX is converted into the Met codon, the 220th Ile codon is converted into the Val codon, the 228th Val codon is converted into the Ile codon, the 290th Cys codon is converted into Val codon, the 294th Phe codon is converted into the Tyr codon, and the 332nd Ile codon is converted into the Phe codon, so as to respectively obtain mutants Q271M, I220V, V228I, C290V, F294T and I332F. Based on the I220V, amphimutation is carried out to obtain mutants I220V / Q271M, I220V / V228I, I220V / C290V, I220V / F294Y and I220V / I332F. The mutants can be used for improving the trehalose conversion rate prepared by trehalose synthase and have relatively high industrial value.
Owner:湖南金代科技发展有限公司
Trehalose synthase with increased maltose conversion rate, method for preparing trehalose synthase and application thereof
Owner:HUNAN JINDAI TECH DEV CO LTD
Cutinase mutant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101775382AHigh catalytic efficiencyHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesTextile fiberPolyethylene terephthalate
The invention provides a thermobifida fusca cutinase mutant and a preparation method thereof. The mutant comprises one or two substitutes corresponding to amino acid residue near the active central site of the thermobifida fusca cutinase, the catalysis efficiency of I218A, Q132A / T101A and W195A / F249A on cotton fibers is increased, wherein the catalysis efficiency of the mutant I218A on ceratine is increased by 50 percent compared with the prior cutinase, the catalysis efficiency of the Q132A / T101A on synthetic fibers and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is increased by three times compared with the prior cutinase, and the three mutants have a broad application prospect in the preprocessing textile fibers.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
High-temperature cutinase and gene order thereof
ActiveCN101250509BEfficient expressionHas cutinase activityHydrolasesFermentationEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
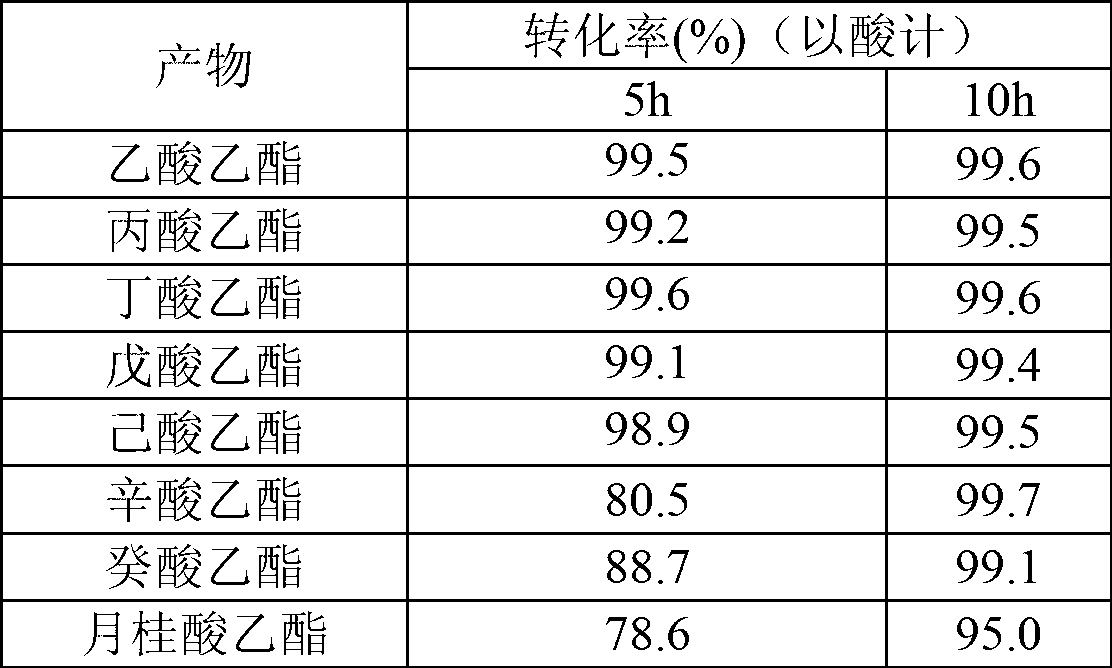
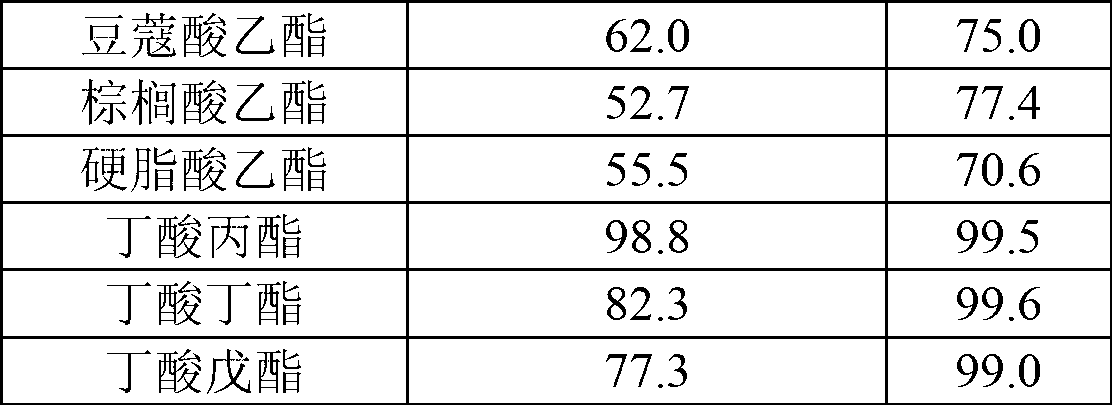
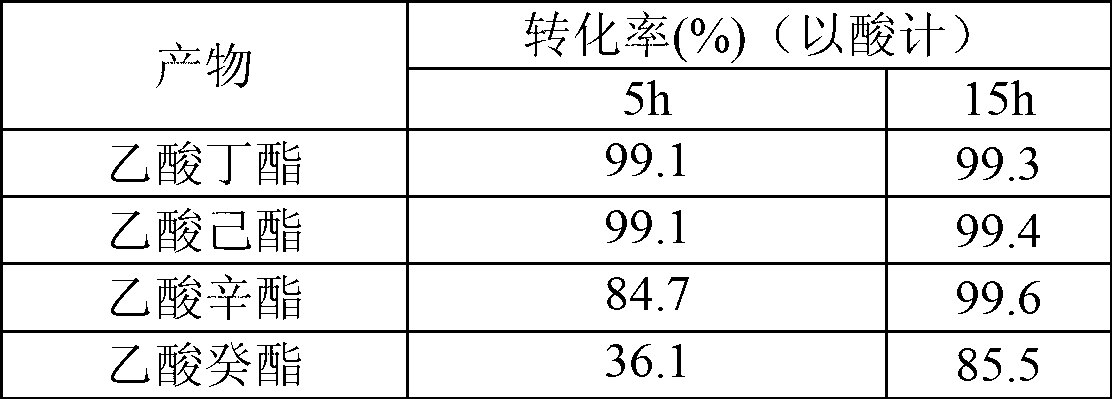
Method for synthesizing ester by using cutinase
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing ester by using cutinase. The Thermobifida fusca cutinase is added in a reaction system of acid and alcohol, wherein the cutinase is from Thernobifida fusca and the NCBI (national center of biotechnology information) number is AAZ54920 and AAZ54921; and the reaction system is as follows: the reaction solvent is an organic solvent, the additive amount of water is 0.03-0.08%, and the addition amount of enzyme is 10-80U / mL. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in technology and has the advantages of simple process, high conversion rate, wide application scope, and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Cutinase mutant capable of efficiently degrading polyethylene glycol terephthalate and application of cutinase mutant
ActiveCN114317489AExtended half-lifeImprove the efficiency of degrading PETHydrolasesPlastic recyclingCutinaseBinding site
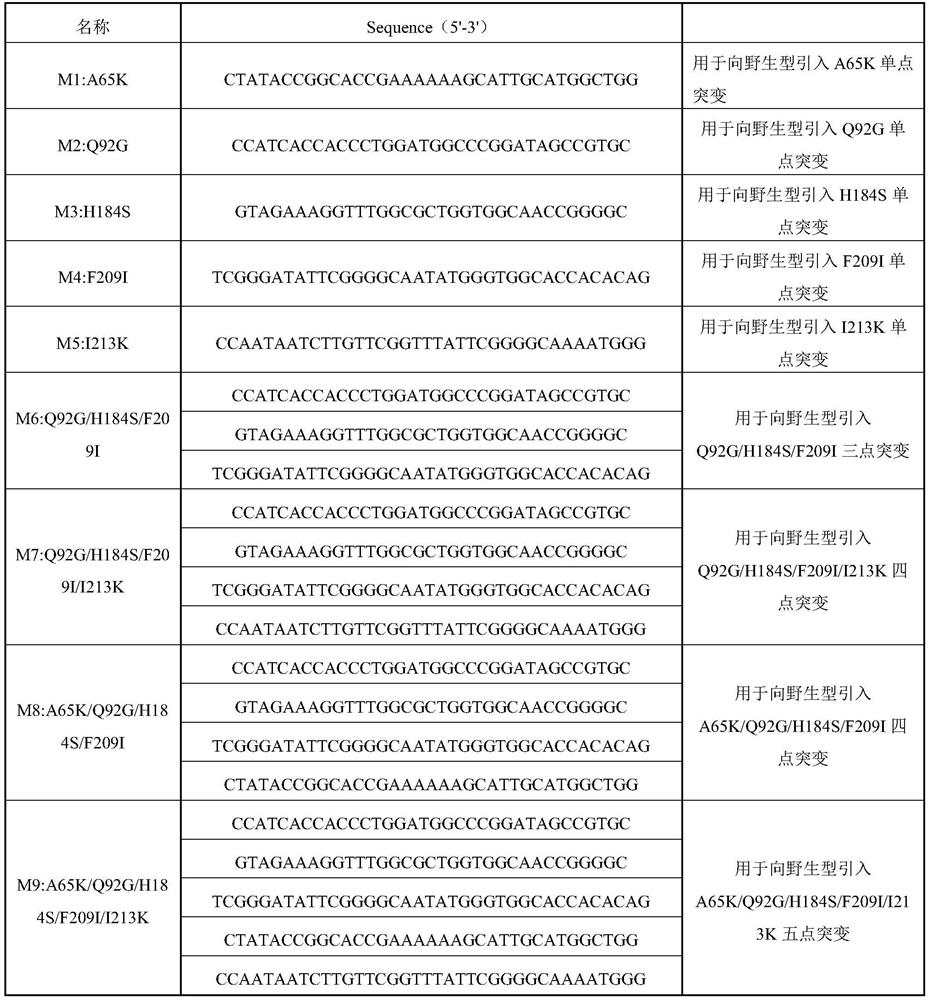
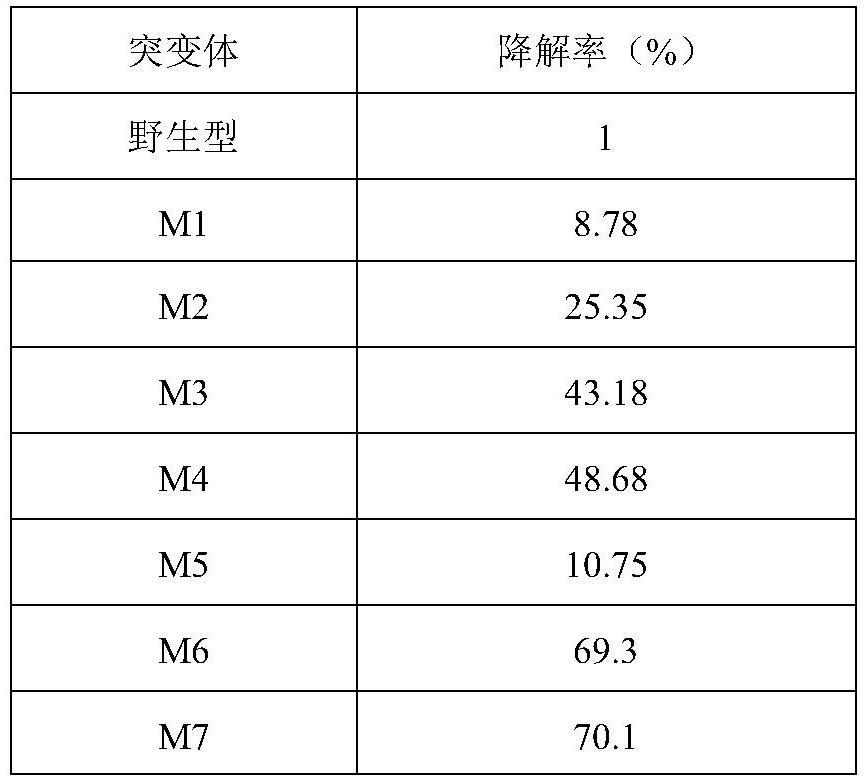
The invention discloses a cutinase mutant capable of efficiently degrading polyethylene glycol terephthalate and application of the cutinase mutant, and belongs to the field of environmental science. The cutinase TfC derived from Thermobifida fusca is modified to obtain a series of mutants, the mutants are subjected to single-point or multi-point mutation near a substrate binding site of the TfC, the 65th site, the 92th site, the 184th site, the 209th site and the 213th site of the TfC are subjected to mutation, and nine mutants are constructed. Compared with wild TfC, the 9 TfC mutants (M1-M9) have the advantages that the enzyme activity and the half-life period at 60 DEG C are obviously improved, the PET degradation efficiency is obviously improved, and the industrial prospect is good.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Detergent compositions containing thermobifida fusca lipase and methods of use thereof
The present compositions and methods relate to a lipase cloned from Thermobifida fusca, polynucleotides encoding the lipase, and methods of use thereof. The compositions and methods have particular application in detergent cleaning compositions and methods.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Improved Cellulase Variants
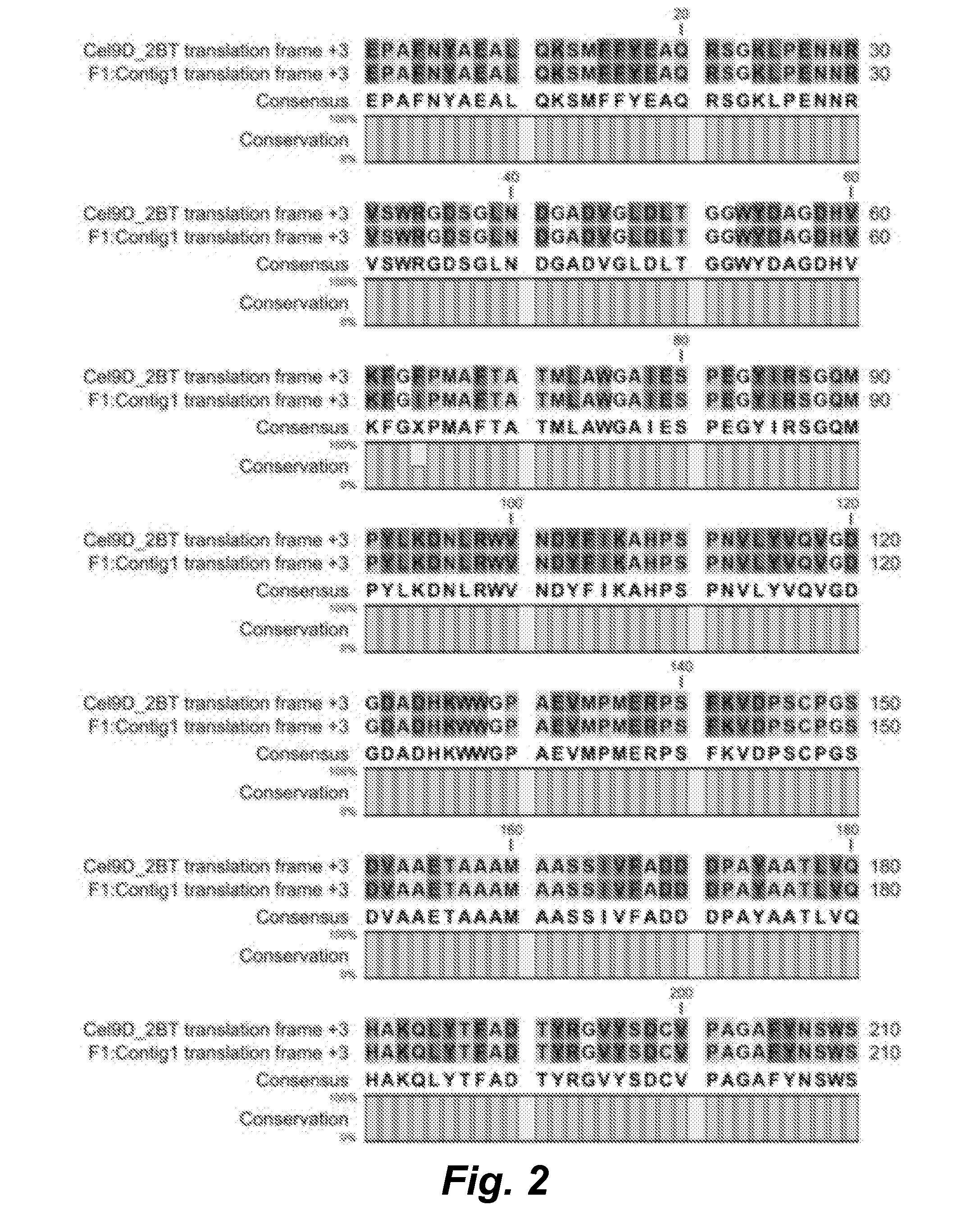
This invention provides novel variant cellulolytic enzymes having improved activity and / or stability. In certain embodiments the variant cellulotyic enzymes comprise a glycoside hydrolase with or comprising a substitution at one or more positions corresponding to one or more of residues F64, A226, and / or E246 in Thermobifida fusca Cel9A enzyme. In certain embodiments the glycoside hydrolase is a variant of a family 9 glycoside hydrolase. In certain embodiments the glycoside hydrolase is a variant of a theme B family 9 glycoside hydrolase.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Method for promoting degradation of agricultural waste by thermobifida fusca
The invention provides a method for promoting the utilization of a xylan-containing substrate by thermobifida fusca. The thermobifida fusca generates xylanase to decompose xylan to produce xylo-oligosaccharide and xylose. The method comprises a step of controlling the content of xylo-oligosaccharide in a reaction system. Besides, the invention further provides a method for improving the utilization efficiency of a xylan-containing substrate by the thermobifida fusca. The method includes a step of culturing the thermobifida fusca by utilizing a substrate containing xylan; and the thermobifida fusca can produce xylanase and cellulase. And the method further comprises a step of adding thermomyces lanoginosus in the culture process.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Novel constitutive promoter, recombinant bacillus licheniformis and application of recombinant bacillus licheniformis
ActiveCN112795569AAchieve secretory expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus licheniformisHigh activity
The invention discloses a novel constitutive promoter, recombinant bacillus licheniformis and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering and enzyme engineering. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a strong constitutive promoter P2 from bacillus licheniformis and a target gene of maltotriose amylase from Thermobifida fusca NTU22 through PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), constructing a recombinant plasmid pHY-P2-tfa, and transforming the recombinant plasmid pHY-P2-tfa into bacillus licheniformis, so as to obtain the recombinant bacillus licheniformis. According to the invention, food-safe bacillus licheniformis is taken as an expression host, and a novel high-activity promoter P2 is utilized to realize recombinant expression of maltotriose amylase. The mixed carbon source maltodextrin of 60 g / L, glucose of 10 g / L and the fermentation condition of 42 DEG C are more beneficial to enzyme production, and the highest enzyme activity of recombinant bacterium fermentation reaches 578.47 U / mL.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method of converting RB to RD by using cutinase under stepwise changing temperatures
ActiveUS20180073049A1Increase conversion rateHigh speedSugar derivativesHydrolasesCutinaseReaction rate
The present invention provides a method to produce RD by using a cutinase to catalyze the esterification of RB under stepwise cooling temperatures, which is related to the field of biosynthesis of organic compounds. The method uses a cutinase from Thermobifida fusca to catalyze the esterification of RB and sophorose to produce RD. The stepwise cooling temperatures are used to reduce the heat inactivation of the enzyme as well as to improve the mass transfer. The method catalyzes the esterification of RB to produce RD in a solvent such as methanol, DMSO and DMF. The reaction is safe, efficient and highly selective. In addition, the method uses stepwise additions of substrate RB and cooling temperatures for the esterification reaction. In this way, it speeds up the initial reaction rate, increases the amount of solved RB as it is converted to RD, and improves the mass transfer to further increase the reaction speed. In summary, the method uses moderate reaction conditions, and has a high yield and a simple purification procedure.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Compositions and methods of use
The present compositions and methods relate to a beta-mannanase from Thermobifida fusca, polynucleotides encoding the beta-mannanase, and methods of make and / or use thereof. Formulations containing the beta-mannanase are suitable for use in hydrolyzing lignocellulosic biomass substrates, especially those comprising a measurable level of galactoglucomannan (GGM) and / or glucomannan (GM).
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Method for enhancing extracellular secretion of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli by co-expressing Thermobifida fusca cutinase
The present invention provides a method of increasing extracellular secretion of secretory proteins by co-expressing the secretory proteins with a mature cutinase. Cutinase can improve the permeability of E. coli cell membrane without destroying the membrane, and thus facilitate cross-membrane transfer of the secretory proteins co-expressed in E. coli. Increased extracellular secretion of target proteins can shorten cell culture time, reduce the formation of inclusion bodies and increase production of target proteins.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for producing chitinase through fermentation of thermobifida fusca
InactiveCN105779421AHigh temperature resistantLarge pH tolerance rangeMicroorganism based processesGlycosylasesChitinaseMicrobiology
The invention discloses a method for producing chitinase through fermentation of thermobifida fusca.The method includes the steps of culturing thermobifida fusca in a fermentation culture medium at a temperature of 50-55 DEG C and a rotating speed of 200-240 r / min for 20-24 hours to prepare a first-grade seed solution, transferring the first-grade seed solution into a fermentation culture medium at an inoculum size of 2-3% to be cultured at a temperature of 50-55 DEG C and a rotating speed of 200-240 r / min for 20-24 hours to prepare a second-grade seed solution, and transferring the second-grade seed solution into a fermentation culture medium at an inoculum size of 2-3% to be cultured at a temperature of 50-55 DEG C and a rotating speed of 200-240 r / min for 50-54 hours to obtain a chitinase product.Thermobifida fusca is easy to culture, rapid in growth and short in fermentation time, and produced chitinase is high in activity, resistant to high temperature and large in pH tolerance range.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Trehalose synthase mutant
ActiveCN108977427AReduce inhibitionMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesGlucose polymersD-Glucose
The invention discloses trehalose synthase mutant, and belongs to the field of gene engineering and enzyme engineering. According to the trehalose synthase mutant, a trehalose synthase derived from Thermobifida fusca YX is modified, so that the inhibition effect of the glucose on the activity of the trehalose synthase in the catalytic synthesis of trehalose is weakened when the synthase takes industrial-grade maltose (containing 10% of glucose) as a substrate, when the industrial-grade maltose (containing 10% of glucose) is taken as the substrate, the conversion rate of the trehalose producedby a wild enzyme is 62.2%, and the conversion rate of the trehalose produced by the mutant G52H and the mutant G52H / H134N can reach 74.8% and 82.3% correspondingly. The trehalose synthase mutant has the advantages that even if certain glucose is contained in the substrate, the conversion efficiency of the trehalose prepared by the trehalose synthase is still not greatly influenced, and a high industrial value is achieved.
Owner:湖南金代科技发展有限公司
Heat resistance cutinase and its coding gene and expression
The invention relates to heat resistant exogenous enzyme, and the coding gene and the expression formula thereof, and belongs to the biological engineering technical technology. The invention provides the bacteria exogenous enzyme different from the accurate exogenous enzyme, and the coding gene and the expression formula thereof. The exogenous enzyme comprises the abstraction of Thermobifida fusca WSH03-11 genomic DNA, the design of primer, and the gene of the heat resistant exogenous enzyme obtained by PCR augmenting, the exogenous enzyme is provided with SEQ ID NO: 1 showed nucleotide sequence, the total length is 906 nucleotides, the coding is 301 amino acids, so as to take plasmid pET20b (+) as the expression carrier, and to take E.coli BL21 Rosetta (DE3) PlysS as expression host, and the high-efficient expression of the heat resistant exogenous enzyme agene can be realized. The thermal stability of the exogenous enzyme is good, and the invention which has good hydrolytic action to cutin, triglyceride and various solubility synthesized greases can be widely used in industries such as spinning and cleaning agent.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently secreting, expressing and reconstructing cutinase and method for constructing same
ActiveCN101792729BIncrease productionReduce pollutionBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention relates to genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently secreting, expressing and reconstructing cutinase and a method for constructing the same, belonging to the field of the bioengineering technology. The genetically engineered bacteria are escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) which carry two recombinant plasmids, and the recombinant plasmids are respectively plasmid pSTV28 carrying the specific genes in the Alpha-hemolysin A (hly A) pathway and plasmid pET20b(+) containing the cutinase-hly As genes. The method for constructing the genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently secreting, expressing and reconstructing cutinase comprises the following steps: constructing two key recombinant plasmids and transforming the constructed recombinant plasmids in the escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) to obtain the genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently secreting, expressing and reconstructing cutinase. The cutinase is produced by using the genetically engineered bacteria through culturing liquid and inducing and expressing the cutinase. The cutinase Tfu_0883 for thermophilic monospore bacteria of Thermobifida Fusca WSH03-11 is used as the report protein. The shaking flask fermentation shows that the extracellular output of the cutinase is 306U / mL which is 1.7 times of the output of the cutinase which adopts the II-type secreting pathway in the preliminary working process in the research laboratory. The cutinase is secreted and expressed efficiently.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for producing heat-resistant superoxide dismutase (SOD) by using thermobifida fusca
InactiveCN104694497AImprove heat resistanceSolve the shortcomings of heat intoleranceMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesBio engineeringOrganic chemistry
The invention relates to a method for producing superoxide dismutase (SOD) by using thermobifida fusca and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. According to the method, SOD is produced from thermobifida fusca under the condition of liquid-state fermentation and is an ectoenzyme. The yield of heat-resistant SOD can reach 2500U / ml to the maximum, so that the method has a good industrial application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com