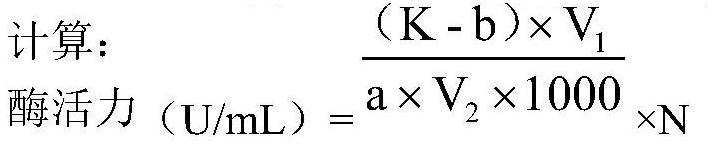Cutinase mutant capable of efficiently degrading polyethylene glycol terephthalate and application of cutinase mutant
A technology of polyethylene terephthalate and mutants, applied in the field of environmental science, can solve the problem of low efficiency of cutinase degradation of PET, and achieve the effects of improved efficiency, improved half-life and good industrial prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0103] Preparation of variants
[0104] Cutinase variants of the invention can be prepared using any mutagenesis procedure known in the art (eg, site-directed mutagenesis, synthetic gene construction, semi-synthetic gene construction, random mutagenesis, shuffling, etc.).
[0105] Site-directed mutagenesis is a technique for introducing one or more (eg, several) mutations at one or more defined sites in the polynucleotide encoding the parent Cutinase.
[0106] Site-directed mutagenesis can be accomplished in vitro by PCR involving the use of oligonucleotide primers containing the desired mutation. In vitro site-directed mutagenesis can also be performed by cassette mutagenesis, which involves cleavage by restriction enzymes at sites in the plasmid containing the polynucleotide encoding the parental cutinase and subsequent insertion of oligonucleotides containing the mutation into acid linkages in polynucleotides. Typically, the restriction enzymes that digest the plasmid and...
Embodiment 1
[0156] Embodiment 1: Construction of TfC mutant recombinant plasmid
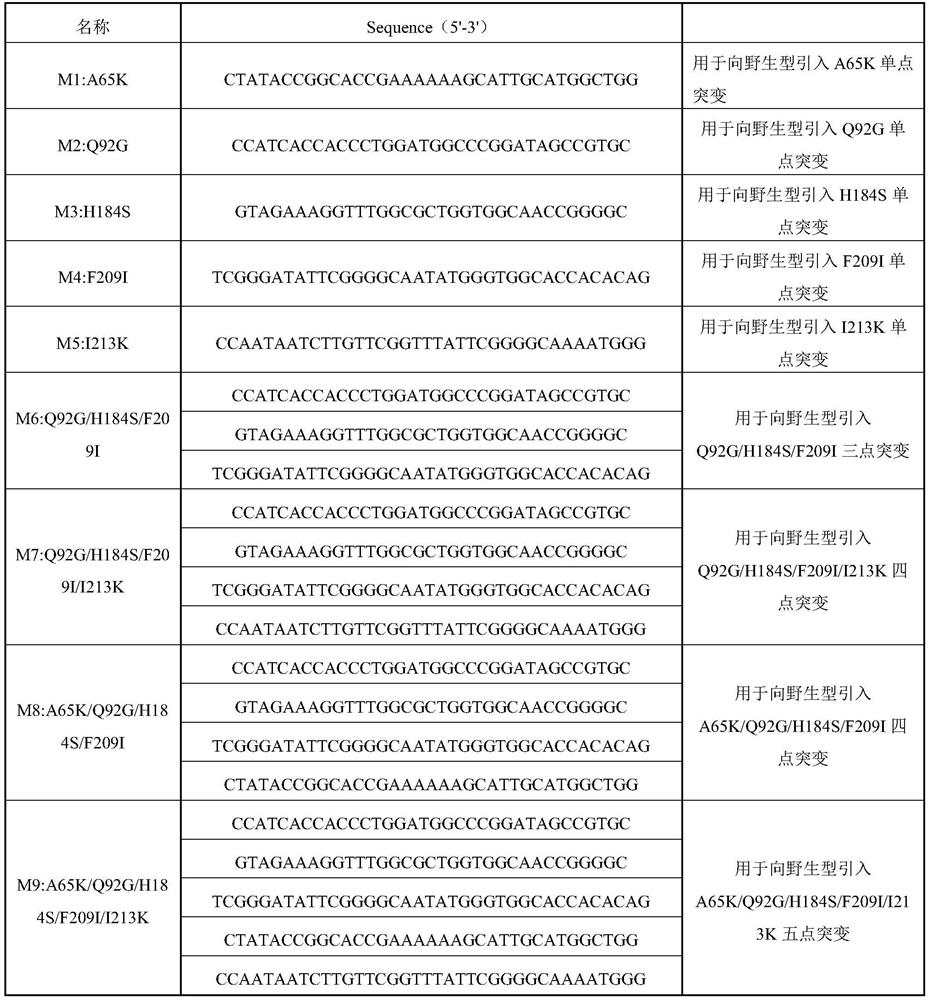
[0157] (1) Insert wild-type cutinase (the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 11) into the NdeI site and XhoI site of pET24a by restriction endonucleases point to obtain pET24a-TfC; then use site-directed mutagenesis (site-directed mutagenesis), with the pET24a-TfC plasmid as a template, carry out PCR with the primers shown in Table 1 respectively, and obtain the target gene mutation fragment (primers are shown in Table 1 ). The target fragment was ligated with the pET-24a expression vector by Megawhop PCR to obtain a recombinant plasmid. The constructed recombinant plasmid was transformed into Escherichia coli JM109 to obtain the transformation product; the transformation product was spread on LB solid medium (containing 40 μg / mL kanamycin), and cultured upside down in a constant temperature incubator at 37°C for 8 After ~12 hours, transformant...
Embodiment 2
[0164] Example 2: Performance of TfC mutants
[0165] The wild-type and TfC mutants were used to determine the enzyme activity, protein concentration and heat resistance.
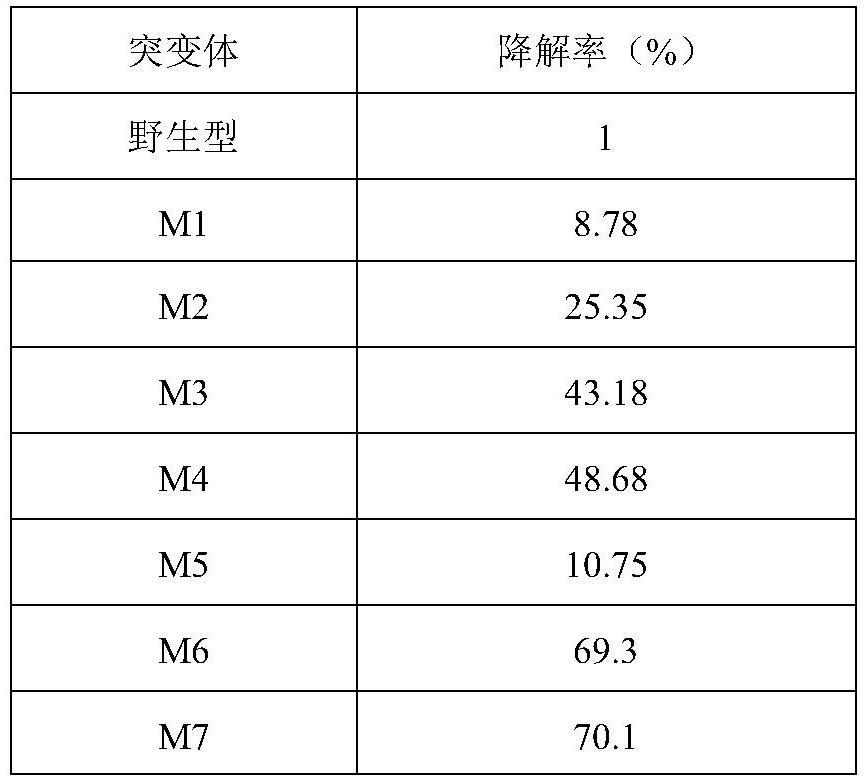
[0166] As shown in Table 2, compared with the wild-type TfC, the activities of the nine TfC mutants have been significantly improved, such as the mutant M5 increased from 86.5U / mL to 150.4U / mL, an increase of 73.87%. At the same time, the expression of the mutants has also been improved to varying degrees, for example, the mutant M2 has increased from 0.10 mg / mL of the wild type to 0.59 mg / mL, which is 4.9 times higher than that of the wild type.
[0167] Compared with the wild-type TfC, the thermal stability of the nine TfC mutants at 60°C has been significantly improved, from 96h to 102-150h compared with the wild-type, and the half-life of the mutant M6 has been increased from 96h to 150h .
[0168] Table 2 Enzyme activity and concentration of TfC mutants
[0169] mutant Enzyme activity ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com