Process for preparing conjugated fatty acid
A technology of fatty acid and fatty acid salt, applied in the field of preparing conjugated fatty acid, to achieve the effect of broadening the scope of application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
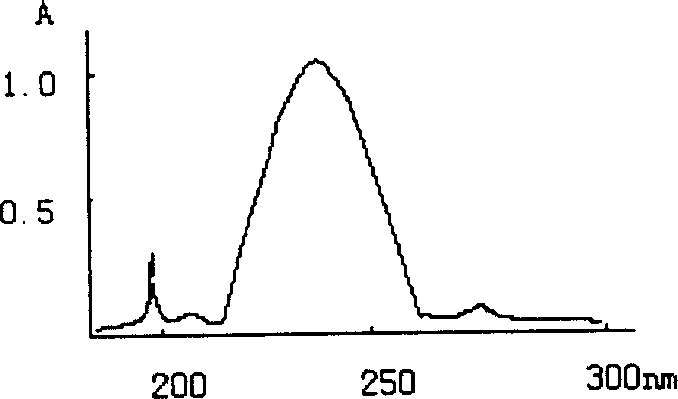
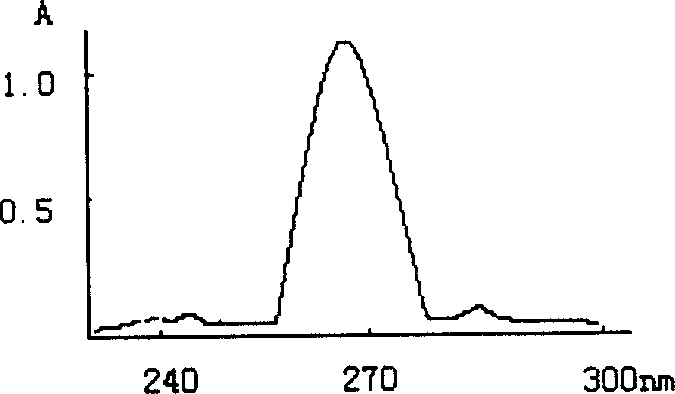
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Optimization of isomerization conditions
[0023] 1.1 Effect of linoleic acid concentration on conjugated linoleic acid
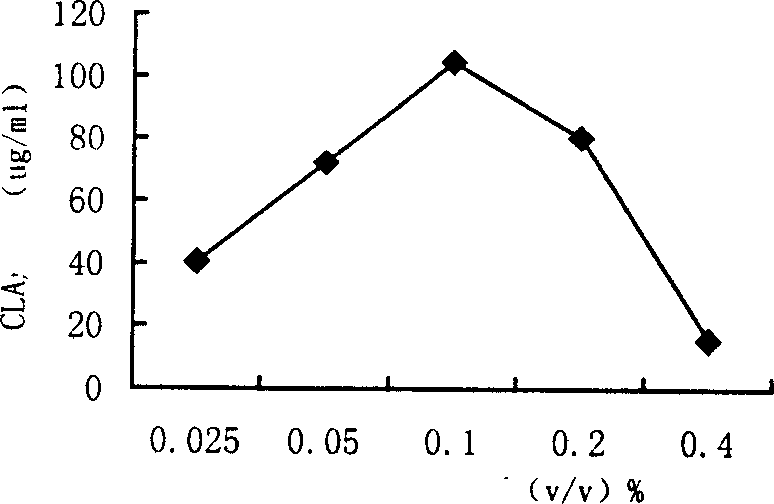
[0024] CLA is the product of isomerization of linoleic acid by lactic acid bacteria, so the concentration of substrate linoleic acid is one of the most important factors determining the formation of CLA. Due to the high concentration of unsaturated fatty acids have inhibitory effect on bacterial growth and metabolism, and this inhibitory effect on G + The lactic acid bacteria are particularly obvious, so respectively add different amounts of linoleic acid in the culture medium, and measure the output of CLA after cultivating for 24 hours. It is found that the amount of CLA formed by adding 0.1% (v / v) linoleic acid is the largest ( image 3 ), when the concentration of linoleic acid was higher than 0.4%, the number of bacteria was significantly reduced.
[0025] 1.2 Effect of culture time on CLA production
[0026] At present, it is generally belie...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Comparison of Isomerization of Different Forms of Fatty Acids
[0029] The specific isomerase produced by lactic acid bacteria can isomerize 9c and 12c unsaturated fatty acids to form 9c and 11t conjugated fatty acids. In order to understand the effect of this enzyme on unsaturated fatty acid derivatives containing 9c and 12c structures, select Linoleic acid, sodium linoleate, and corn oil were used as substrates to study the level of isomerization. The three substrates were added to the MRS medium at 0.1% respectively, 10% of the strains were added, mixed evenly, and cultured at 30° C. for 42 hours. In the linoleic acid group, conjugated linoleic acid was directly extracted with n-hexane; in the sodium linoleate group, the pH was first adjusted to 2.0 with concentrated sulfuric acid, and then conjugated linoleic acid was extracted with n-hexane; in the corn oil group, sodium hydroxide was first used to After saponification and neutralization with concentrated sulfuric a...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Comparison of different isomerization methods
[0038] Isomerase in lactic acid bacteria is a catalyst for bioisomerization to form conjugated fatty acids. In order to understand the isomerization level of lactic acid bacteria in the cultivation process, lactic acid bacteria cells, and crude enzyme solution of lactic acid bacteria cells, three methods and The relationship formed by the CLA.
[0039] Isomerization method of lactic acid bacteria during cultivation: add 10% lactic acid bacteria strains and 0.1% linoleic acid to MRS medium, mix well, and culture at 30° C. for 42 hours.
[0040] Isomerization method of lactic acid bacteria: culture lactic acid bacteria in MRS medium for 24 hours, collect the bacteria by centrifugation, add pH 7.0 phosphate buffer to the washed bacteria to make a bacterial suspension, and add 0.1% linoleic acid, mix well, and stand at 30°C for 12h.
[0041] Isomerization method of crude enzyme solution of lactic acid bacteria: After culturi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com