Preparation method of grating with continuously changing diffraction efficiency
A diffraction efficiency and grating technology, applied in the field of waveguide optical diffraction elements, can solve problems such as poor uniformity of the outgoing beam
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
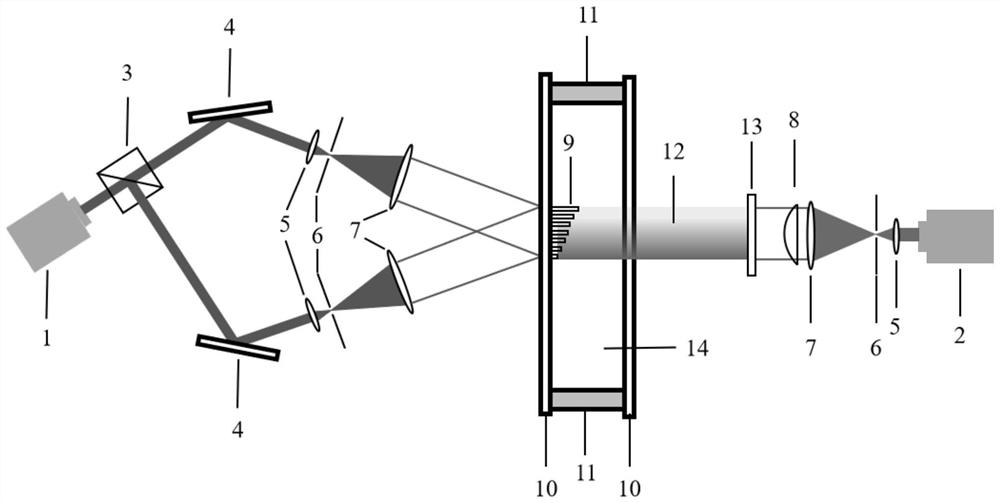
[0039] Such as figure 1 with Figure 7 As shown, after the light of wavelength a is emitted by the laser 1, it is split into two beams through the beam splitter 3. The two beams are reflected by the reflector 4 and form a certain angle, and then pass through the beam expander lens 5, The filter pinhole 6 and the collimating lens 7 interfere with each other after beam expansion, filtering and collimation.
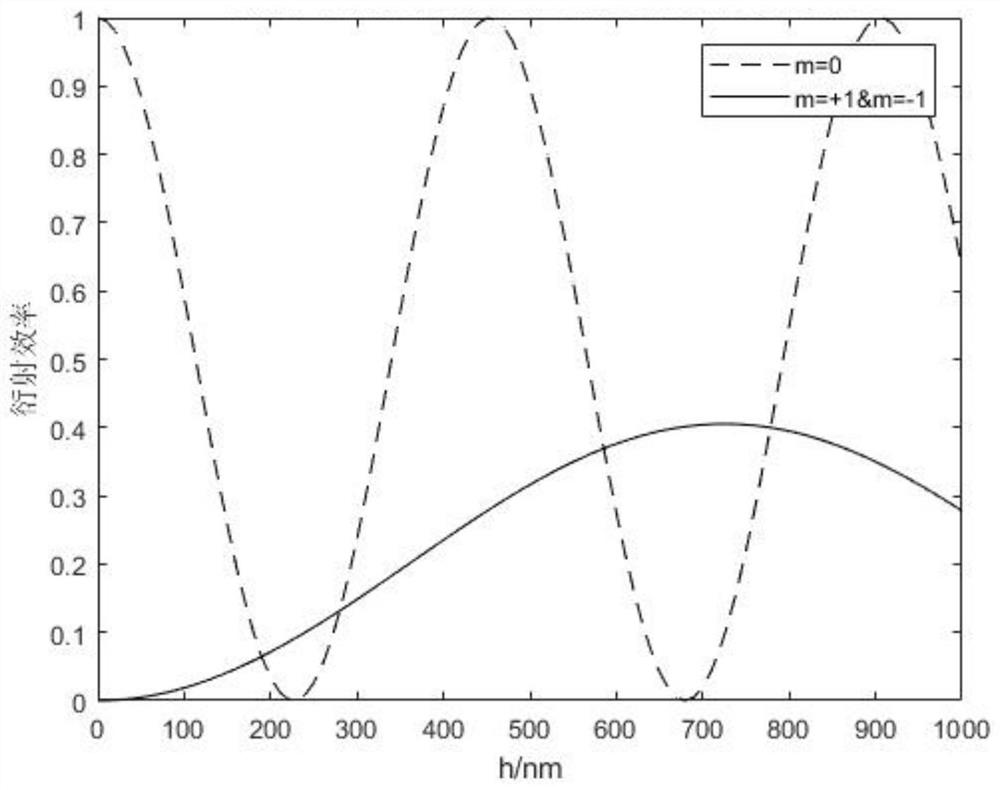
[0040] After the light of wavelength b is emitted by the laser 2, it passes through the beam expander lens 5, the filter pinhole 6 and the collimator lens 7, after beam expansion, filtering and collimation, the light intensity of the obtained expanded beam has a Gaussian distribution. In order to obtain a light beam with uniform light intensity, it should go through the shaping lens 8 to make its light intensity uniform. After the light beam with the uniformly distributed light intensity of the wavelength b is superimposed on the neutral filter 13 of the continuously variable t...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Such as Figure 4 with Figure 7 As shown, after the light of wavelength a is emitted by the laser 1, it is split into two beams through the beam splitter 3. The two beams are reflected by the reflector 4 and form a certain angle, and then pass through the beam expander lens 5, The filter pinhole 6 and the collimating lens 7 interfere with each other after beam expansion, filtering and collimation.
[0053] After the light of wavelength b is emitted by the laser 2, it passes through the beam expander lens 5, the filter pinhole 6 and the collimator lens 7, after beam expansion, filtering and collimation, the light intensity of the obtained expanded beam has a Gaussian distribution. In order to obtain a light beam with uniform light intensity, it should go through the shaping lens 8 to make its light intensity uniform. After the light beam with the uniformly distributed light intensity of the wavelength b is superimposed on the neutral filter 13 of continuously changing tran...
Embodiment 3
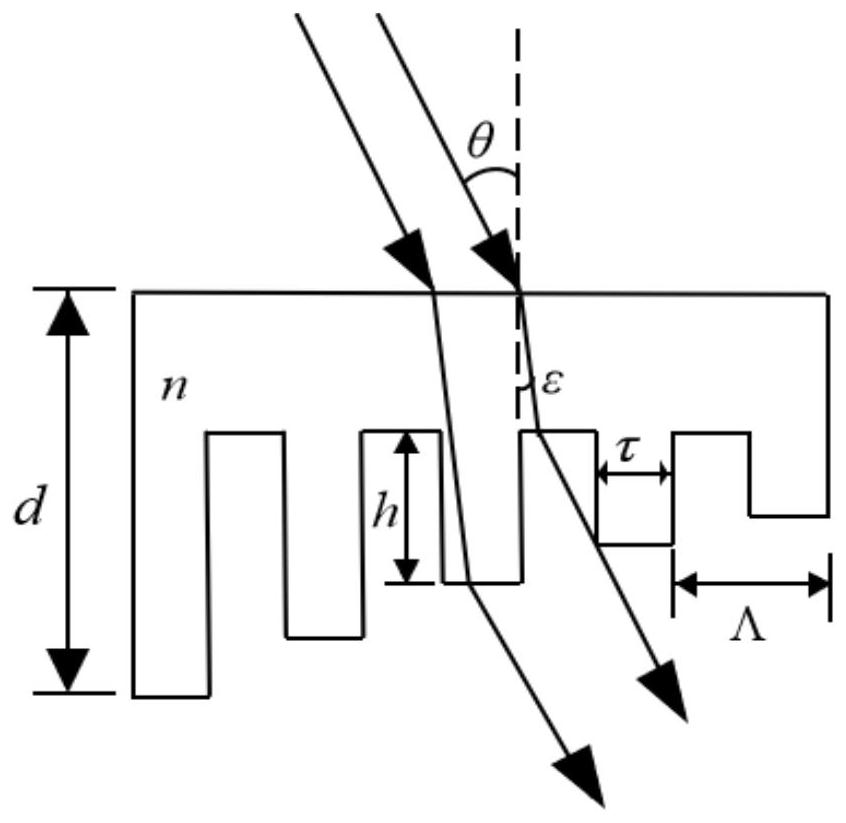
[0071] Such as Picture 8 As shown, after the light of wavelength a is emitted by the laser 1, it passes through the beam expander lens 5, the filter pinhole 6 and the collimator lens 7 for beam expansion, filtering and collimation, and then passes through the wedge plate 15 and occurs behind the wedge plate. Interference of equal thickness.
[0072] After the light of wavelength b is emitted by the laser 2, it passes through the beam expander lens 5, the filter pinhole 6 and the collimator lens 7, after beam expansion, filtering and collimation, the light intensity of the obtained expanded beam has a Gaussian distribution. In order to obtain a light beam with uniform light intensity, it should go through the shaping lens 8 to make its light intensity uniform. After the light beam with the uniformly distributed light intensity of the wavelength b is superimposed on the neutral filter 13 of continuously changing transmittance, the light 12 with the continuous light intensity chang...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com