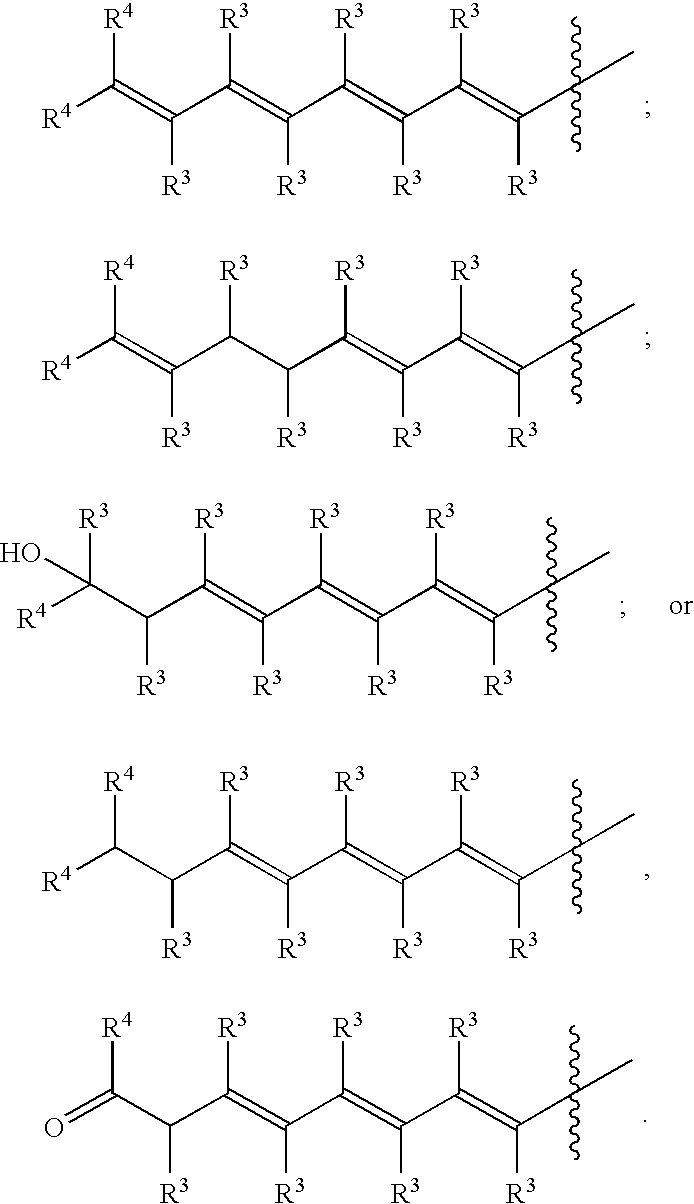
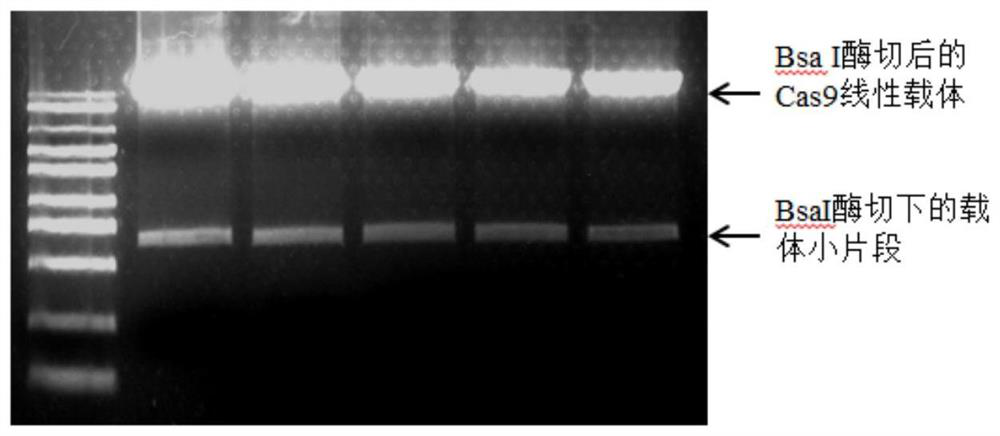
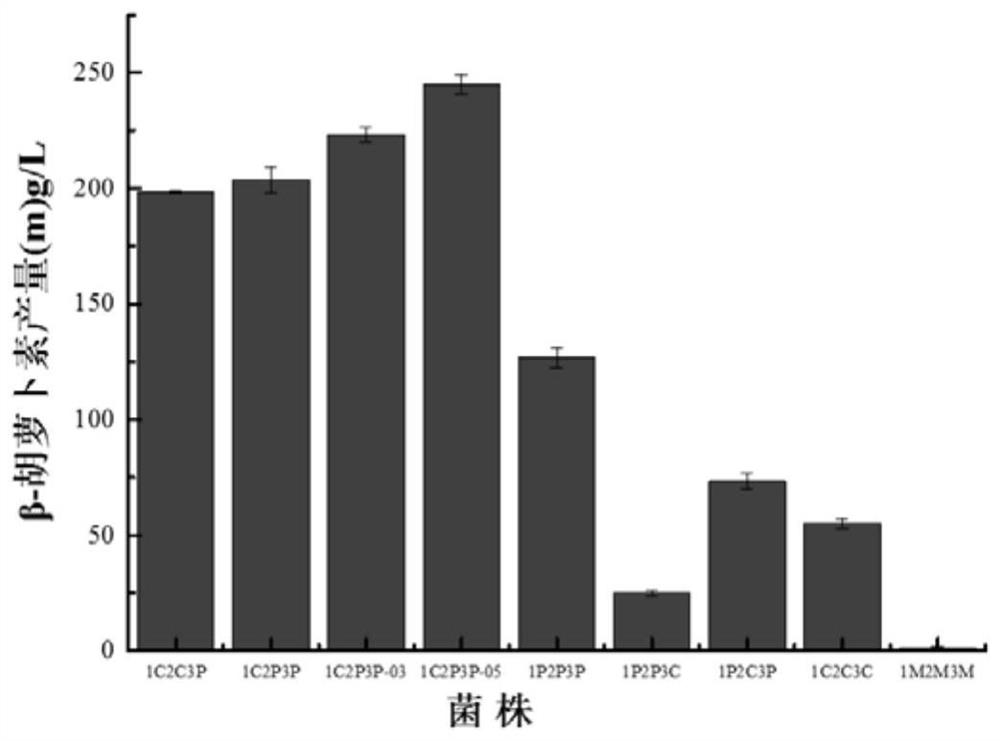
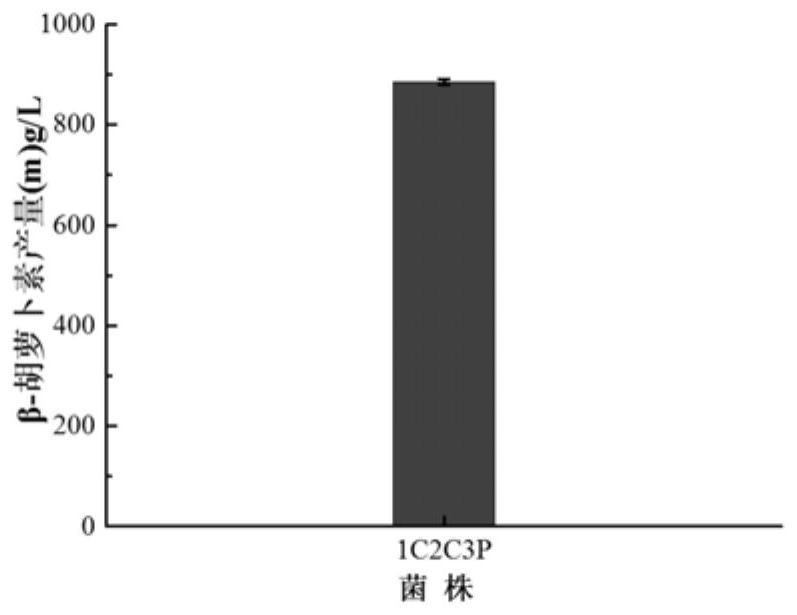
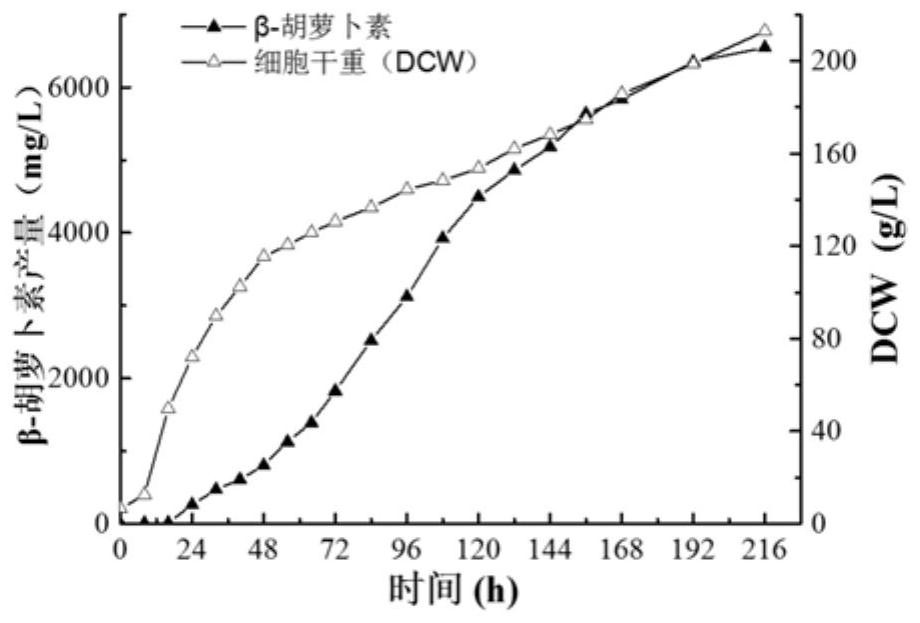
Patents
Literature
62 results about "Carotene synthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
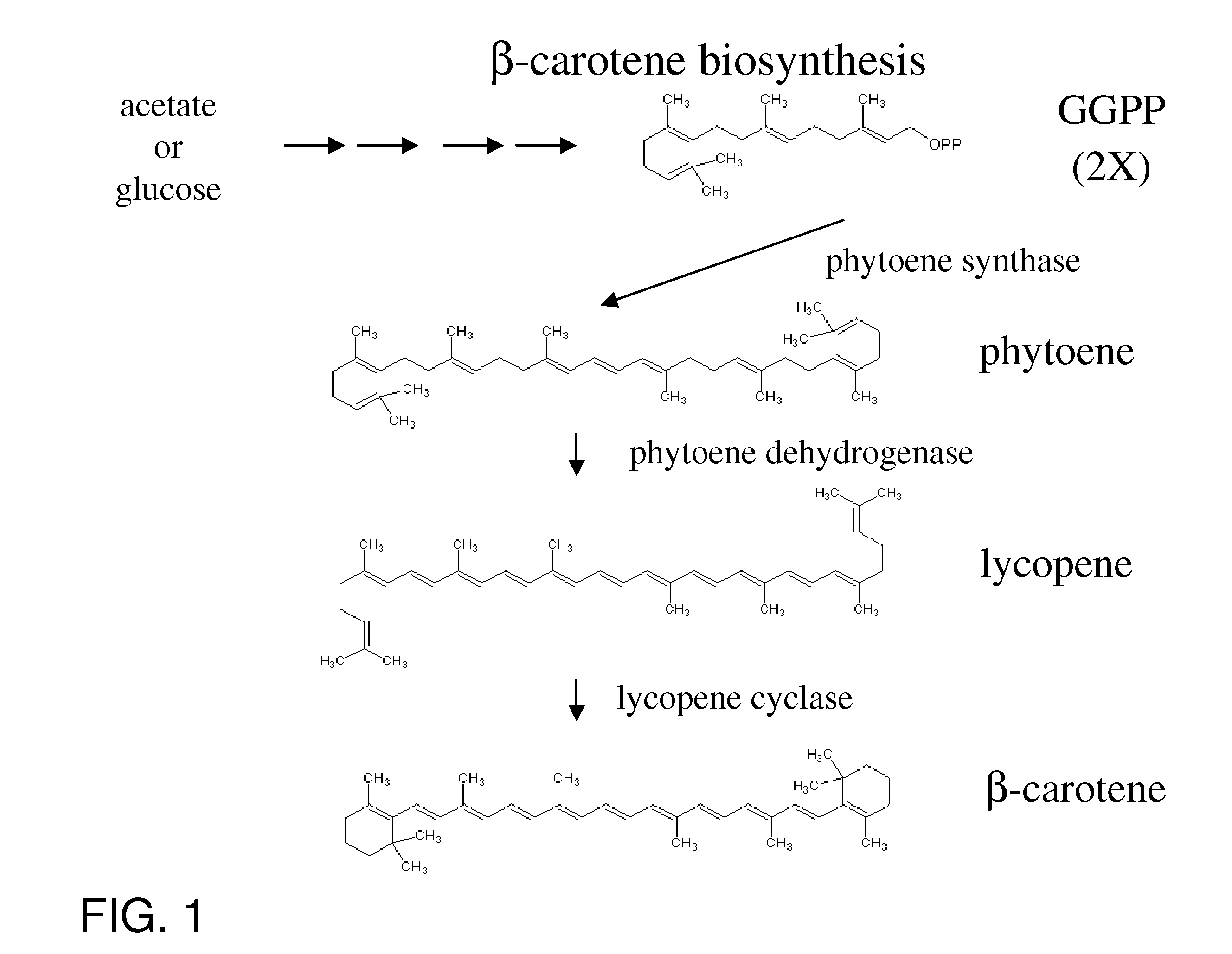
Recombinant bacterium for producing beta-carotene as well as construction method and application of recombinant bacterium
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium for producing beta-carotene as well as a construction method and application of the recombinant bacterium. The construction method comprises the following steps: respectively constructing superstrong gene expression modules of protein phytoene synthetase / lycopene cyclase coded by beta-carotene synthetic genes optimized by codons, phytoene dehydrogenase, protein geranyl diphosphate synthase coded by MAV (micro aerial vehicle) pathway genes and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase; assembling the gene expression modules in vitro, so as to obtain four plasmids of the gene expression modules, integrating the plasmids into a host bacteria genome which does not produce beta-carotene and screening orange single colonies, so as to obtain the recombinant bacterium for producing beta-carotene. The recombinant bacterium disclosed by the invention is adopted for producing beta-carotene by fermental cultivation, and the yield of beta-carotene can reach 26.03mg / g DCW. Therefore, the recombinant bacterium has high performance of producing beta-carotene.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
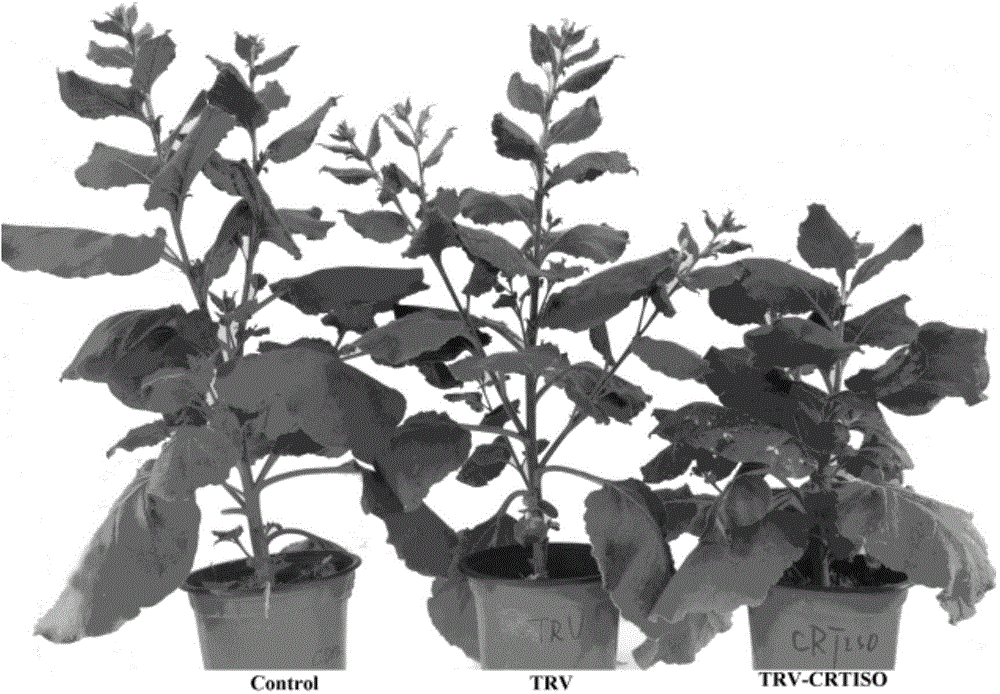
Tobacco carotenoid isomerase gene and is application
ActiveCN104152473AIncrease contentIncreased resistance to photoinhibitionGenetic engineeringFermentationBiotechnologyBeta-Carotene
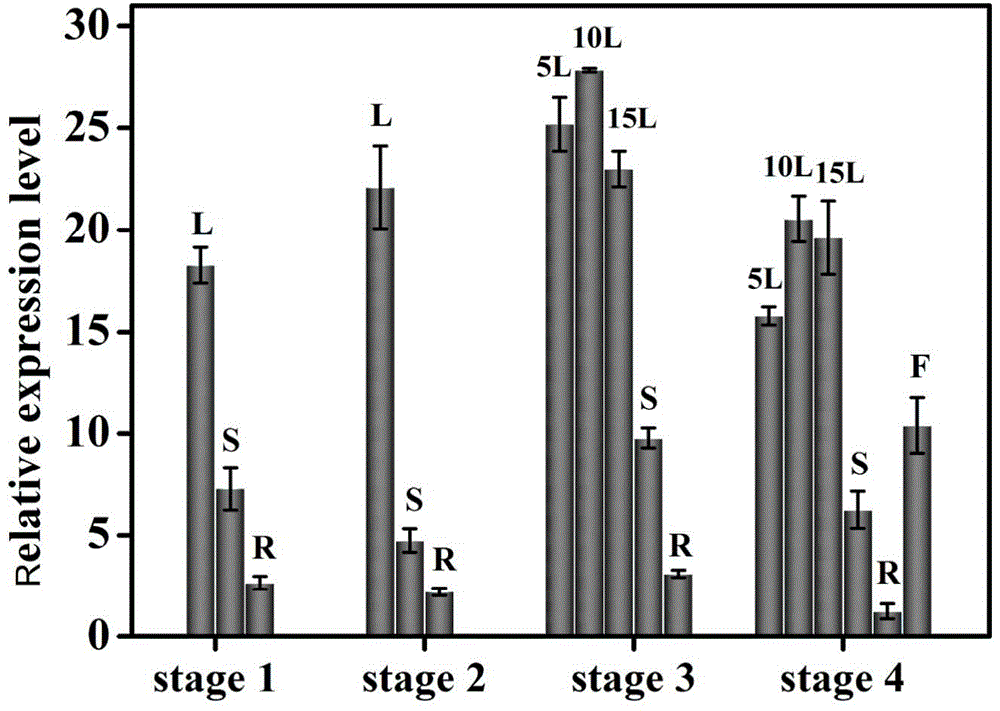
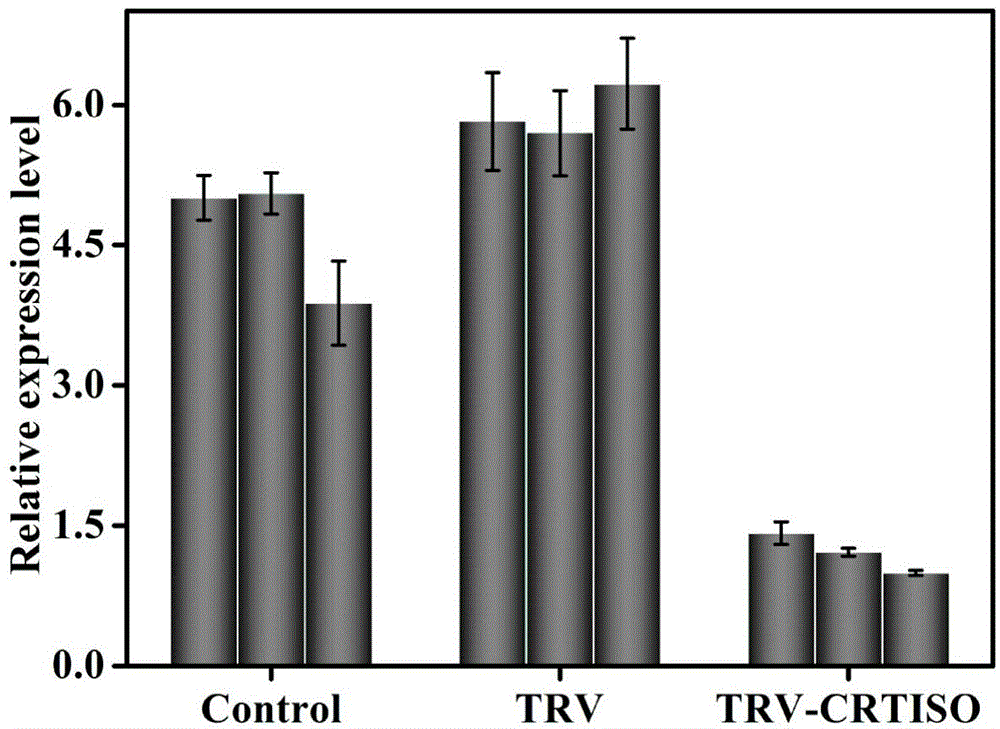
The invention discloses a tobacco carotenoid isomerase gene. The base sequence of the tobacco carotenoid isomerase gene is represented by SEQIDNO:1. In tobacco, a key carotenoid synthesis gene NtCRTISO is cloned, and the gene can be inhibited to effectively improve the carotenoid content of tobacco leaf and improve the photoinhibition resistance of tobacco plants. The invention discloses an important function of the CRTISO gene in tobacco in carotenoid synthesis. The CRTISO gene plays a great role in the regulation of the composition of carotenoid. A method for improving the content of carotenoid, especially beta-carotene, in the tobacco is searched, and a good theoretic guidance is provided for the improvement of the molecules of the plants.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Method for positioning and synthesizing terpenoids by means of Yarrowia lipolytica way
ActiveCN110106209AHigh synthetic yieldImprove the added value of the applicationMicroorganism based processesFermentationHMG-CoA reductaseAlpha-farnesene
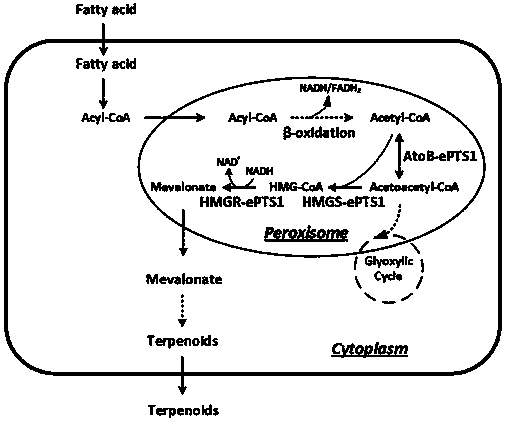
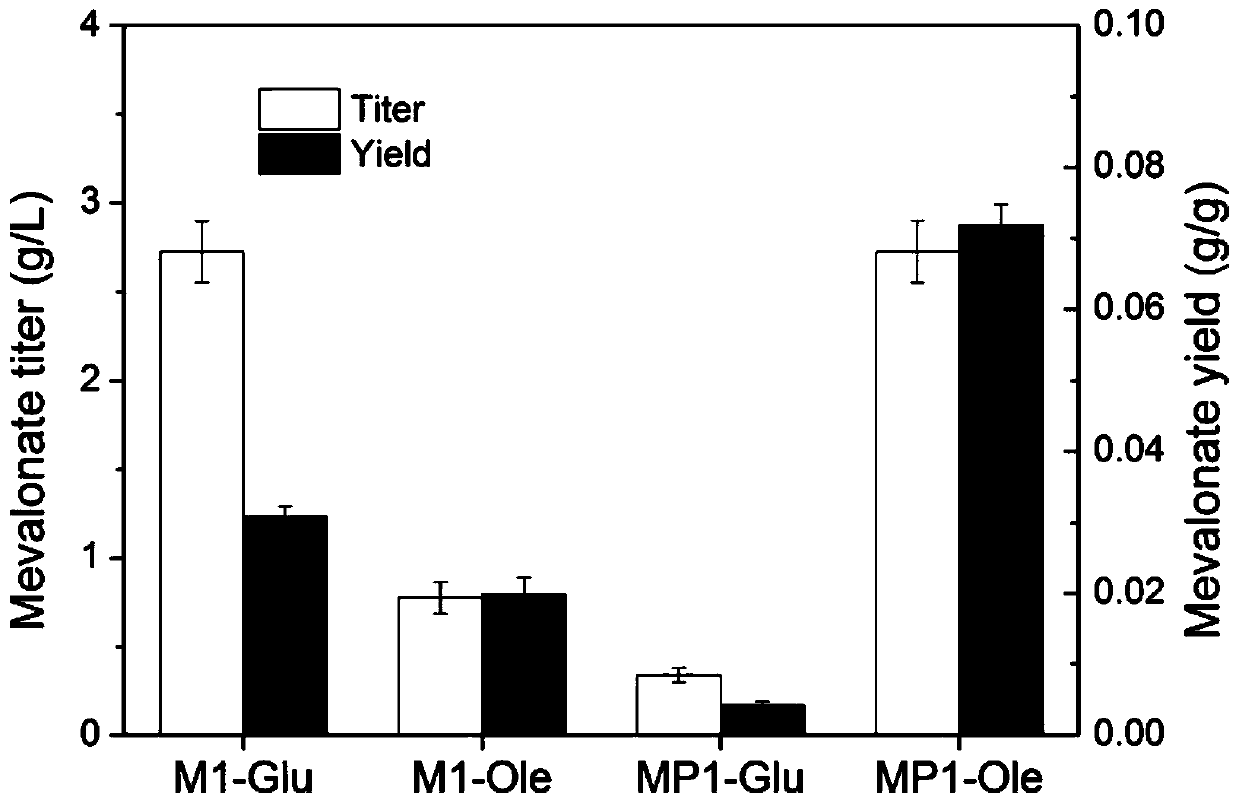
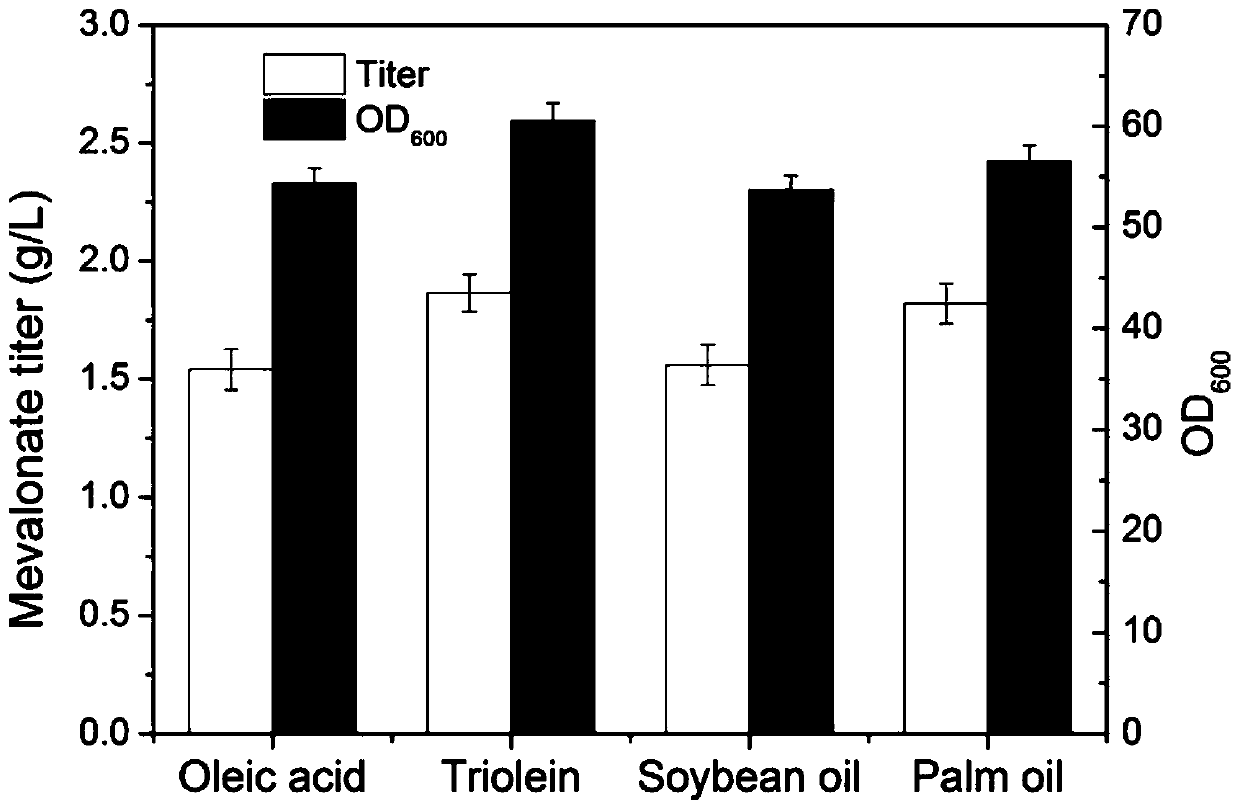
The invention discloses a method for positioning and synthesizing terpenoids by means of the Yarrowia lipolytica way. The method comprises the steps that an acetoacetyl coenzyme A thiolase, HMG-CoA synthetase and HMG-CoA reductase in the synthetic route of mevalonic acid in Yarrowia lipolytica are over-expressed and positioned to the peroxisome, and engineering bacteria MP1 are obtained; on the basis of the engineering bacteria MP1, the alpha-farnesene synthesis way is expressed, and engineering bacteria FP1 are obtained; or, the beta-carotene synthesis way is expressed, and engineering bacteria CP1 are obtained; or, the linalool synthesis way is expressed, engineering bacteria LP1 are obtained; the bacteria FP1 or CP1 or LP1 can synthesize the terpenoids under the aerobatic condition by means of a culture medium containing fatty acid or grease, and the yield of the synthesized terpenoids is higher compared with a traditional method. According to the method, fatty acid, grease and cheap food waste oil can be used for generating mevalonic acid downstream terpenoids, and the considerable application prospect and the economic value are achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
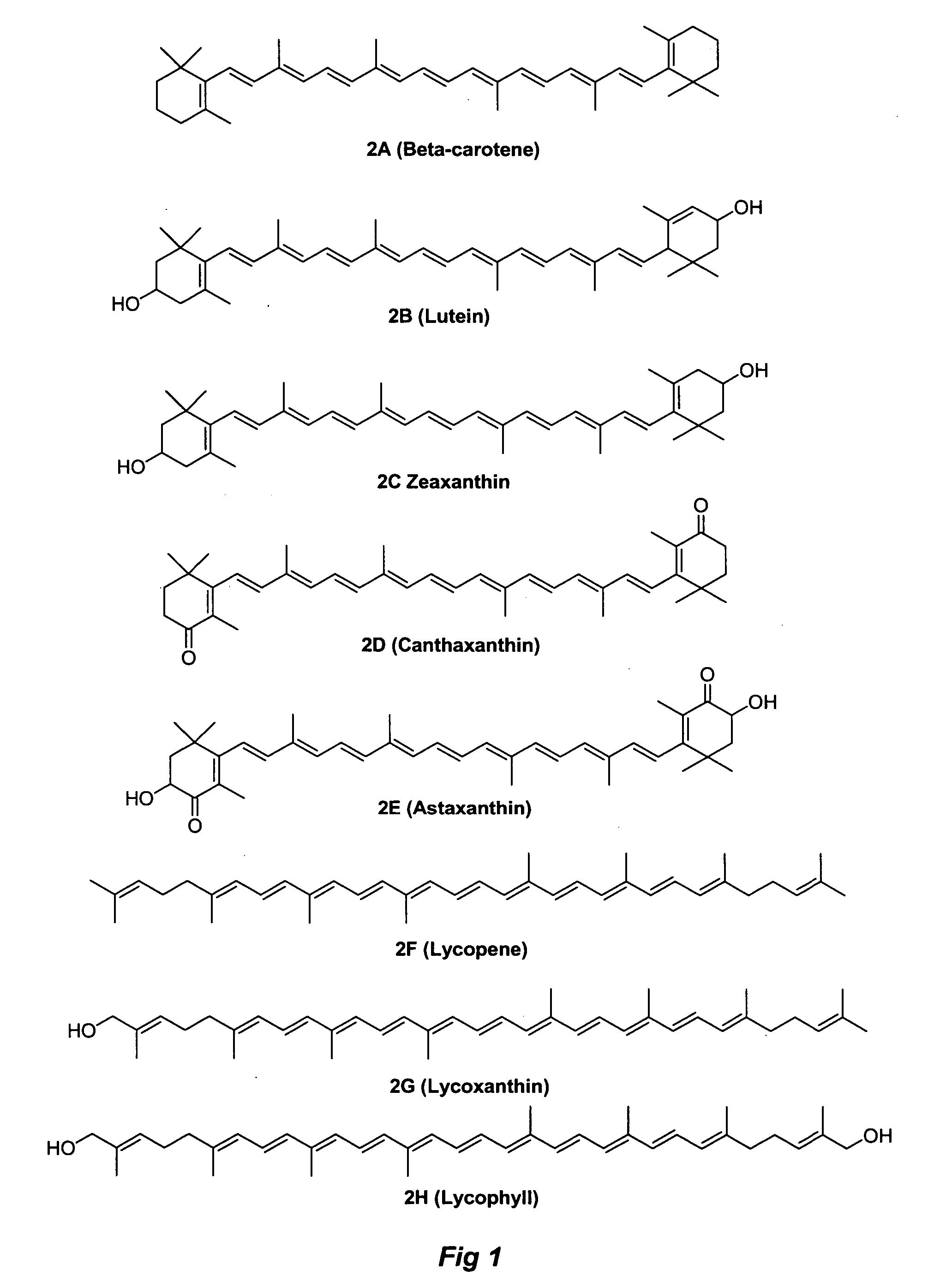
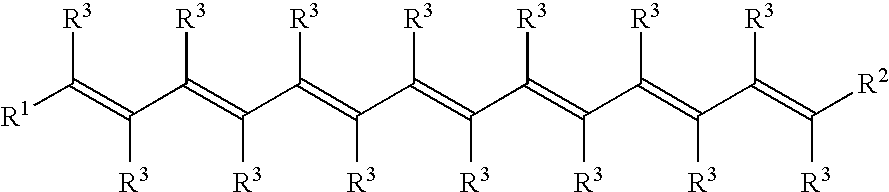
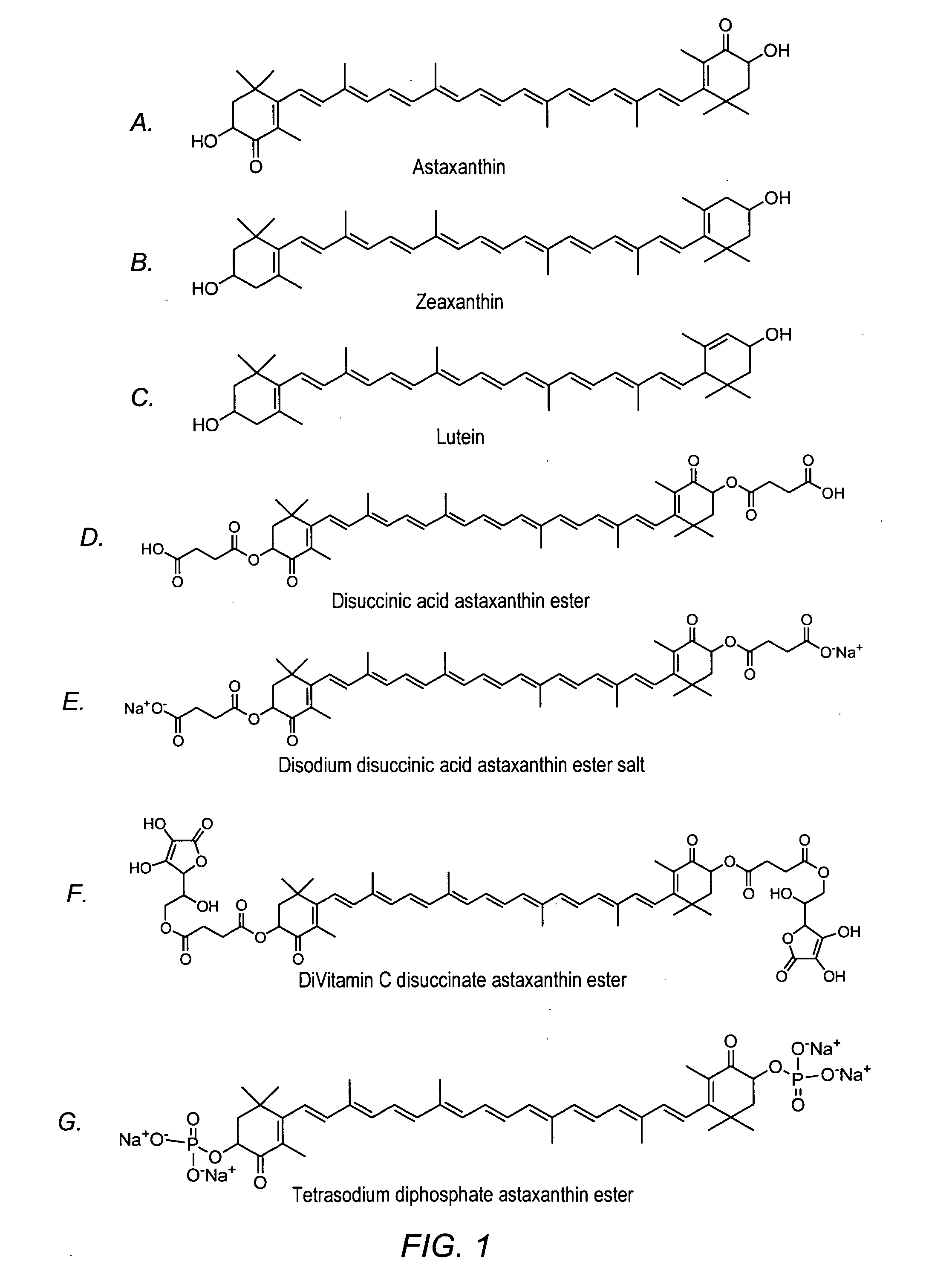
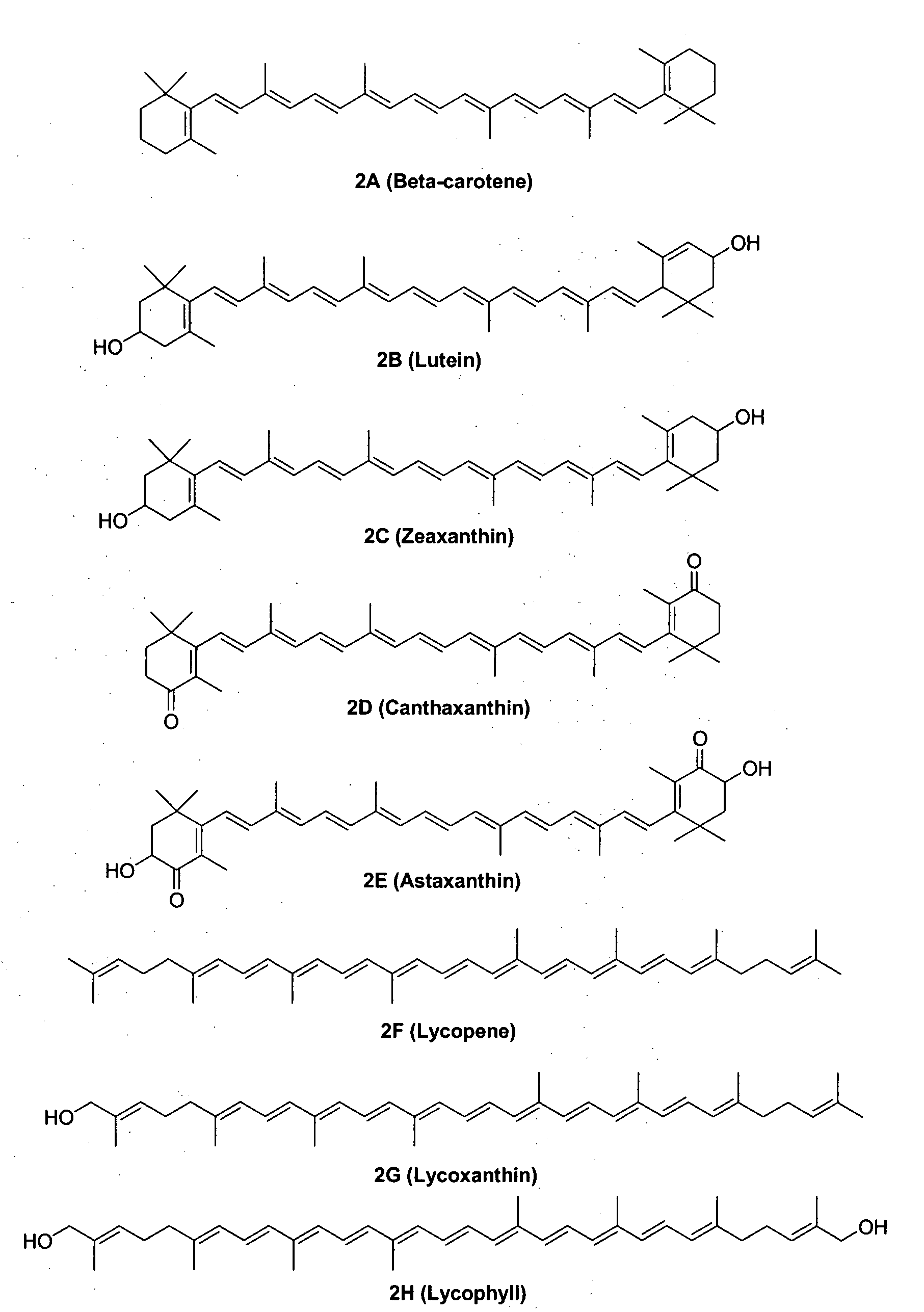
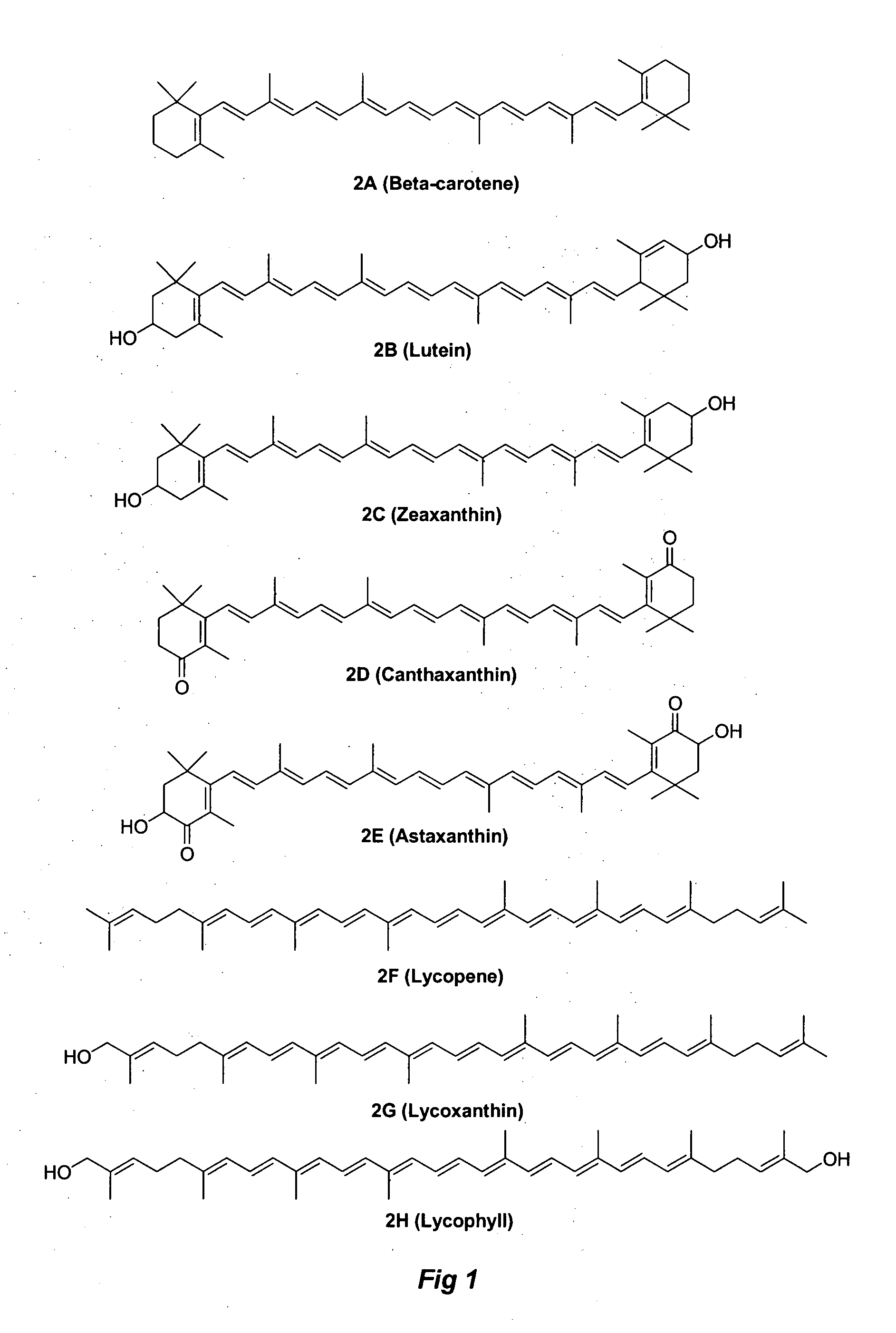
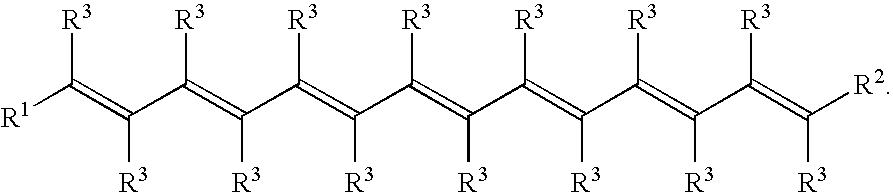
Water-dispersible carotenoids, including analogs and derivatives
A method used for synthesizing intermediates for use in the synthesis of carotenoid synthetic intermediates, carotenoid analogs, and / or carotenoid derivatives. The analog, derivative, or intermediate may be administered such that a subject's risk of experiencing diseases associated with reactive oxygen species, reactive nitrogen species, radicals and / or non-radicals may be thereby reduced. The analog or analog combination may be administered to a subject for the inhibition and / or amelioration of any disease that involves production of reactive oxygen species, reactive nitrogen species, radicals and / or non-radicals. In some embodiments, the invention may include methods for synthesizing chemical compounds including an analog or derivative of a carotenoid. The carotenoid analog or derivative may be synthetic. In some embodiments, a carotenoid analog or derivative may include at least one substituent. The substituent may enhance the solubility of the carotenoid analog or derivative such that the carotenoid analog or derivative at least partially dissolves in water.
Owner:LOCKWOOD SAMUEL F +1
Methods for synthesis of carotenoids, including analogs, derivatives, and synthetic and biological intermediates
InactiveUS20080221377A1Organic compound preparationGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsDiseaseSolubility
A method for synthesizing intermediates for use in the synthesis of carotenoid synthetic intermediates, carotenoid analogs, and / or carotenoid derivatives. The carotenoid analog, derivative, or intermediate may be administered to a subject for the inhibition and / or amelioration of any disease that involves production of reactive oxygen species, reactive nitrogen species, radicals and / or non-radicals. In some embodiments, the invention may include methods for synthesizing chemical compounds including an analog or derivative of a carotenoid. Carotenoid analogs or derivatives may include acyclic end groups. In some embodiments, a carotenoid analog or derivative may include at least one substituent. The substituent may enhance the solubility of the carotenoid analog or derivative such that the carotenoid analog or derivative at least partially dissolves in water.
Owner:CARDAX PHARMA
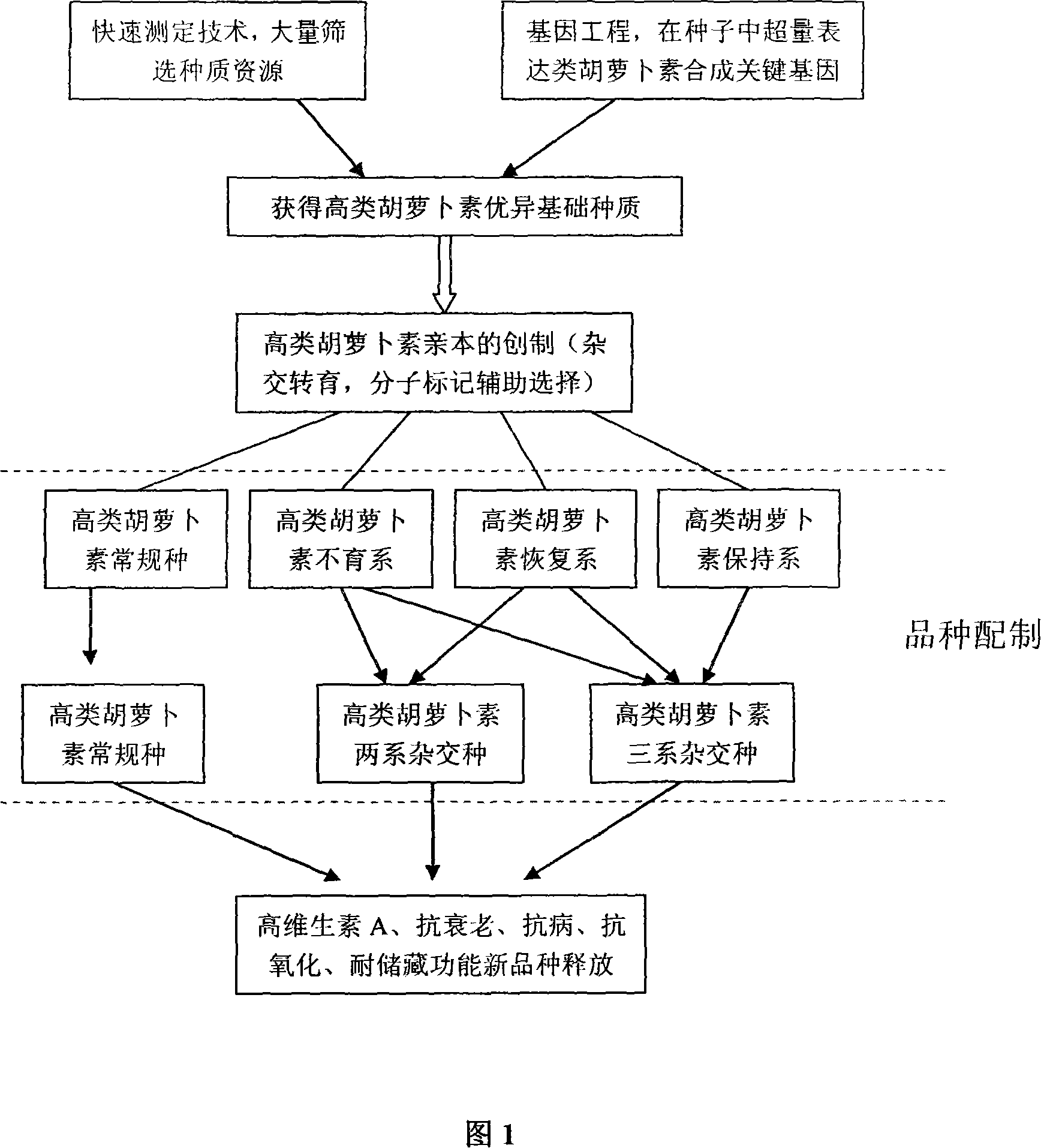
Breeding method of oil-bearing crop with high content of vitamin A having functions of antisenescence, disease-resistant and oxidation resistance
InactiveCN101138314ASimple methodThe result is accurateOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by optical meansHplc methodNutrition
A cultivation method of oil plant, which contains rich vitamin A and is anti-aging, disease resistant and oxidation resistant relates to the oil plant breeding technology. The method is that the spectrophotometer is used for selecting large amounts of seed resource or the gene engineering technology is used for over-expressing the crucial genes of synthesizing the carotenoid; the basic germ plasm of seeds selected contain the carotenoid which is higher than 60Mu ggFW-1; the basic germ plasm with high carotenoid content is taken as the donor and the high-quality seeds are taken as the acceptor; the conventional breeding technology is used for hybridizing to obtain high-quality breeds with high carotenoid; the HPLC method is used for detecting the carotenoid content of the breeding seeds to control the content in the range of 60-300Mu ggFW-1. The selecting method of the present invention is simple with high efficiency, accurate results, low cost and reliable resources. The plant oil squeezed from the oil plant cultivated with the method of the present invention contains rich vitamin A and is characterized by high nutrition and anti-aging, disease resistant and deterioration resistant functions.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
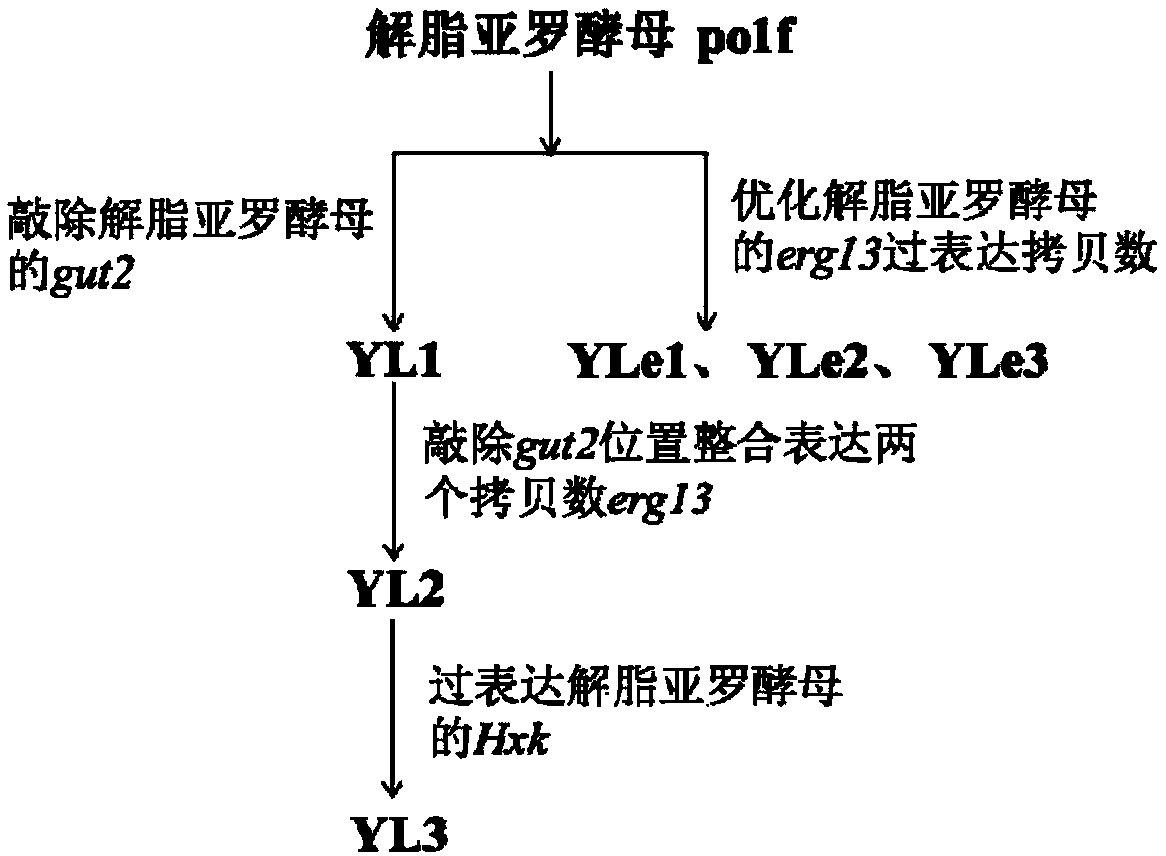
Genetic engineering bacteria producing beta- carotene and construction method of genetic engineering bacteria
ActiveCN109609579AIncrease storage capacityIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBeta-CaroteneHexokinase
The invention discloses genetic engineering bacteria producing beta- carotene and a construction method of the genetic engineering bacteria. The construction method comprises the following steps of firstly knocking out alpha-glycerophosphate dehydrogenase gut2 genes in a glycolysis way in a beta-carotene synthetizing pathway in yarrowia lipolytica, then performing free expression on beta-hydroxyl-beta-methylglutaric acid erg13 genes having two endogenous copy numbers of the yarrowia lipolytica, and then performing integrant expression on the erg13 genes having two endogenous copy numbers of the yarrowia lipolytica at the position where the gut2 genes are knocked out; and performing free expression on endogenous hexokinase Hxk genes of the yarrowia lipolytica, and screening positive transformants to obtain the engineering bacterial strains producing beta-carotene yarrowia lipolytica. The bacterial strains are subjected to fermentation, culturing, extraction and separation, the beta-carotene is purified, and the content of the beta-carotene can reach 26.6mg / g cell dry weight.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Carotene Synthase Gene and Uses Therefor
Described herein is a novel three domain gene from Schizochytrium, denoted carotene synthase, that encodes a protein with three different enzymatic activities: phytoene dehydrogenase (PD), phytoene synthase (PS), and lycopene cyclase (LC). Also described is the isolated gene encoding the carotene synthase, homologues thereof, the enzyme encoded by such gene, biologically active portions and homologues thereof, recombinant nucleic acid molecules, microorganisms and plants that have been genetically modified to increase or decrease the action of such gene, and methods of producing carotenoids and derivatives thereof or methods of producing microorganisms and lipid products lacking pigmentation using the knowledge of the carotene synthase described herein.
Owner:MARTEK BIOSCIENCES CORP
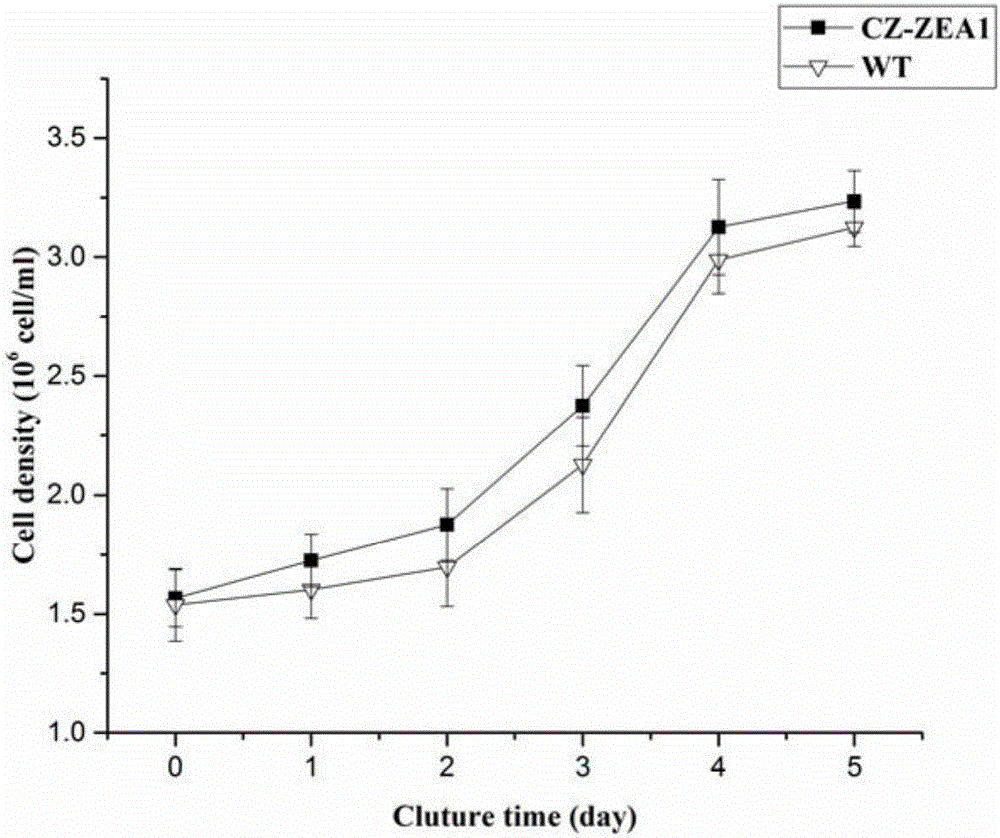
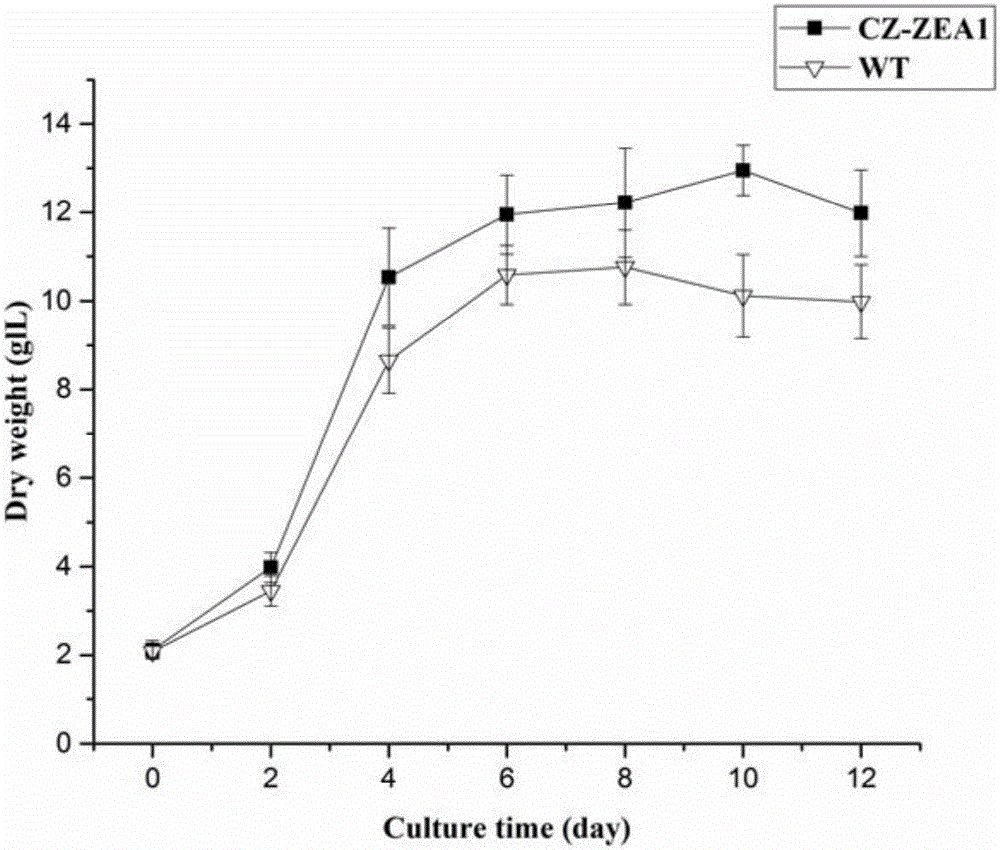
Mutant chlorella strain capable of producing zeaxanthine and beta-carotene and culturing method thereof
The invention provides a mutant chlorella strain capable of realizing high yield of zeaxanthine and other carotenoids essential to the human body, and a culturing method thereof. The culturing method comprises the following steps: subjecting Chlorella zofingiensis ATCC 30412 to nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis; then coating a Kuhl solid medium containing DPA with treated chlorella cells for culture; selecting a single chlorella colony from the Kuhl solid medium and culturing the single chlorella colony on a Kuhl liquid medium; adding glucose in the middle and later periods of logarithm for induction of carotenoid synthesis; and detecting the variety changes and content of carotenoids in the obtained chlorella body so as to obtain the strain which can realize high yield of zeaxanthine, xanthophyll and beta-carotene and is named as CZ-ZEA1. Under the induction condition that the concentration of glucose is 30 g / L, the biomass of the CZ-ZEA1 is 12.95 g / L, and the contents of zeaxanthine, xanthophyll and beta-carotene reach 2.176 mg / g, 1.10 mg / g and 1.211 mg / g, respecitively. The mutant chlorella strain is an edible alga species and contains high-content optimally-proportioned carotenoids essential to the human body, especially zeaxanthine rare in nature; so the mutant chlorella strain is an ideal new-resource functional foodstuff for preventing deterioration and lesion of the eyes of middle aged and old people and has good development and application prospects.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Recombinant bacillus subtilis expressing C30 carotenoid
ActiveCN105838731ARelieves Colitis SymptomsBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementDendritic cellGenetic engineering
The invention relates to recombinant bacillus subtilis capable of synthesizing carotenoid 4,4'-diaponeurosporene with 30 carbon atoms (C30), and belongs to the biotechnology genetic engineering field. A bacillus subtilis expression plasmid pMK3-crtmn (which is capable of expressing C30 carotenoid synthases Crtm and Crtn in bacillus subtilis) containing C30 carotenoid synthase genes crtm and crtn is successfully constructed, and is successfully electro-transformed into bacillus subtilis WB800. The WB800 strain after transformation turns from the original color of white to yellow. A pigment component extracted from the recombinant WB800 is identified as 4,4'-diaponeurosporene by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). 4,4'-diaponeurosporene can stimulate maturation of dendritic cells, and generated cytokines (IL-6, IL-10, IL-12p70 and TNF[alpha]) have the amount increased, and moreover and have stronger ability to stimulate proliferation of T lymphocytes. With oral administration of the bacillus subtilis capable of synthesizing 4,4'-diaponeurosporene, the dextran sulphate sodium (DSS)-induced mice colitis symptoms can be significantly reduced. The bacillus subtilis capable of producing 4,4'-diaponeurosporene is expected to be developed as probiotics for prevention of colitis.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Genetically engineered bacterium for improving yield of beta-carotene and application thereof
ActiveCN113151340AEasy to storeIncrease supplyFungiMicroorganism based processesLipid BodyEngineered genetic
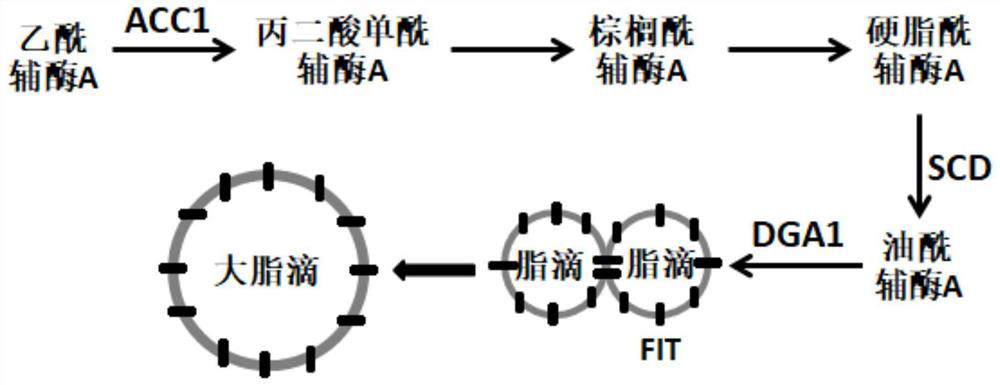
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium capable of increasing the yield of beta-carotene and application thereof, and the genetically engineered bacterium contains a beta-carotene synthetic pathway related gene, a phosphoketolase pathway related gene and a lipid droplet synthetic pathway related gene. A beta-carotene synthetic pathway is covered; a phosphoketolase pathway is increased, the carbon loss is reduced, and more precursor substance acetyl coenzyme A for synthesizing beta-carotene is generated from a carbon source; the supply of a reducing power substance NADPH and an energy substance ATP is increased; and a lipid droplet synthesis pathway is also increased, and the storage of beta-carotene can be increased by increasing the content and volume of intracellular lipid droplets. The highest yield of the beta-carotene of the genetically engineered bacterium reaches 7.8g / L, and the yield of the beta-carotene is remarkably improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU WISDOM BIO TECH
Carotene synthase gene and uses therefor
Described herein is a novel three domain gene from Schizochytrium, denoted carotene synthase, that encodes a protein with three different enzymatic activities: phytoene dehydrogenase (PD), phytoene synthase (PS), and lycopene cyclase (LC). Also described is the isolated gene encoding the carotene synthase, homologues thereof, the enzyme encoded by such gene, biologically active portions and homologues thereof, recombinant nucleic acid molecules, microorganisms and plants that have been genetically modified to increase or decrease the action of such gene, and methods of producing carotenoids and derivatives thereof or methods of producing microorganisms and lipid products lacking pigmentation using the knowledge of the carotene synthase described herein.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
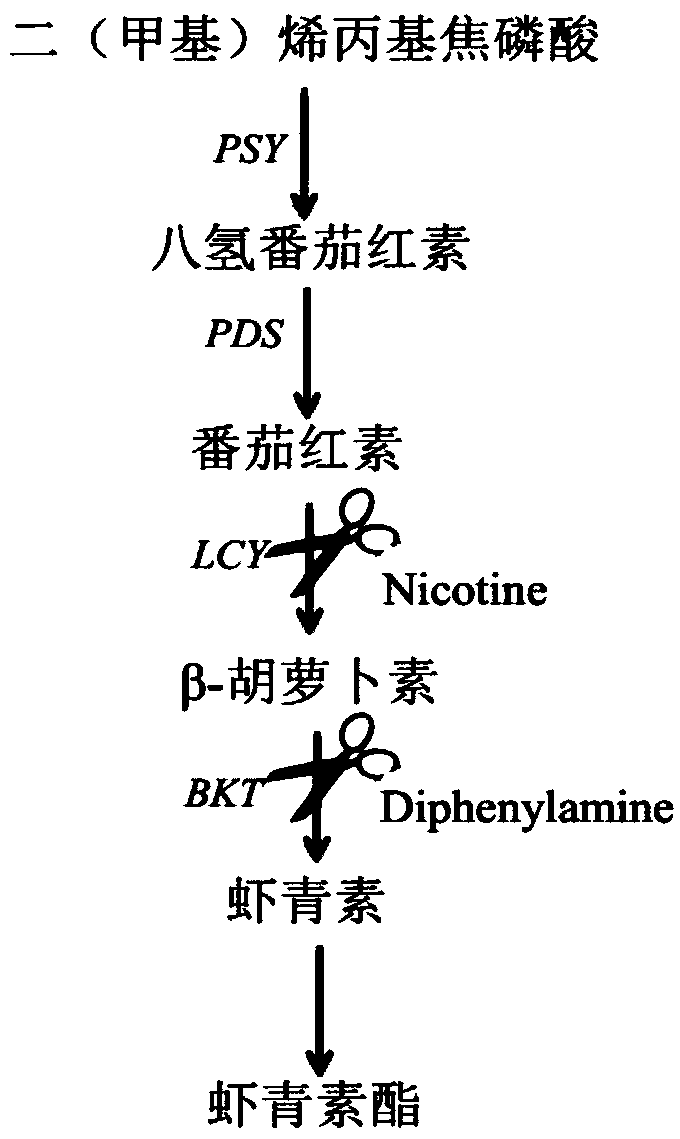
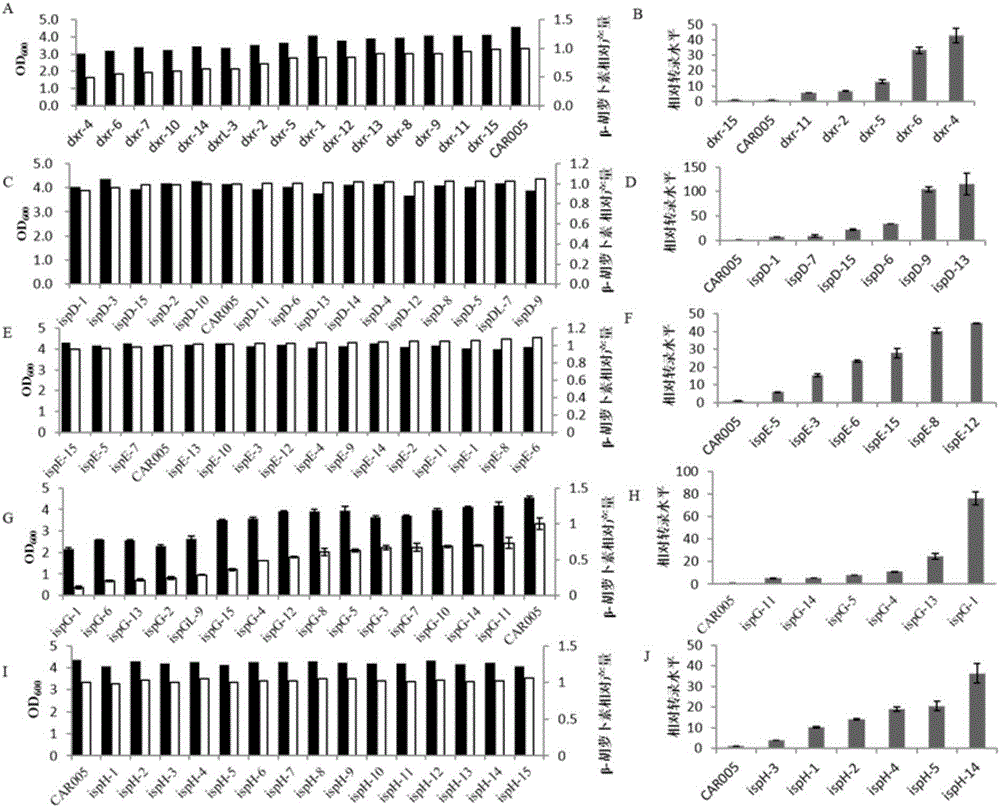
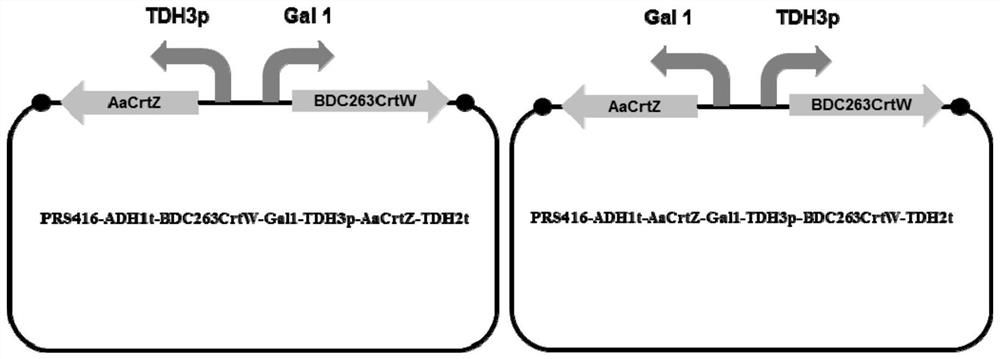
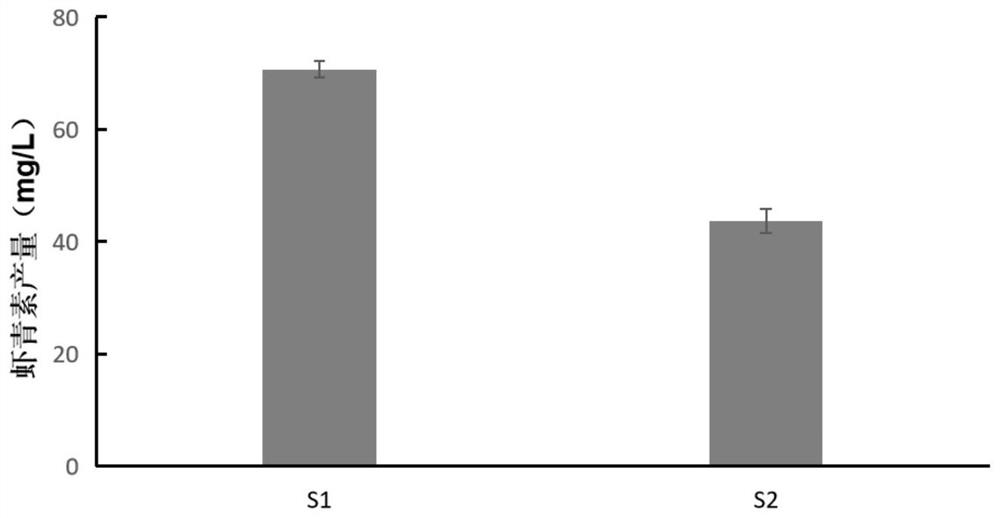
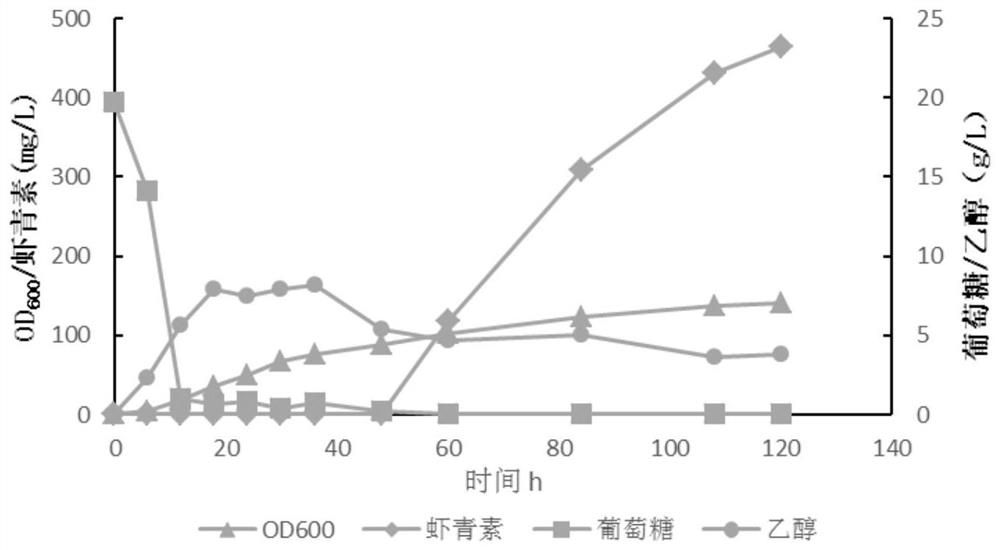
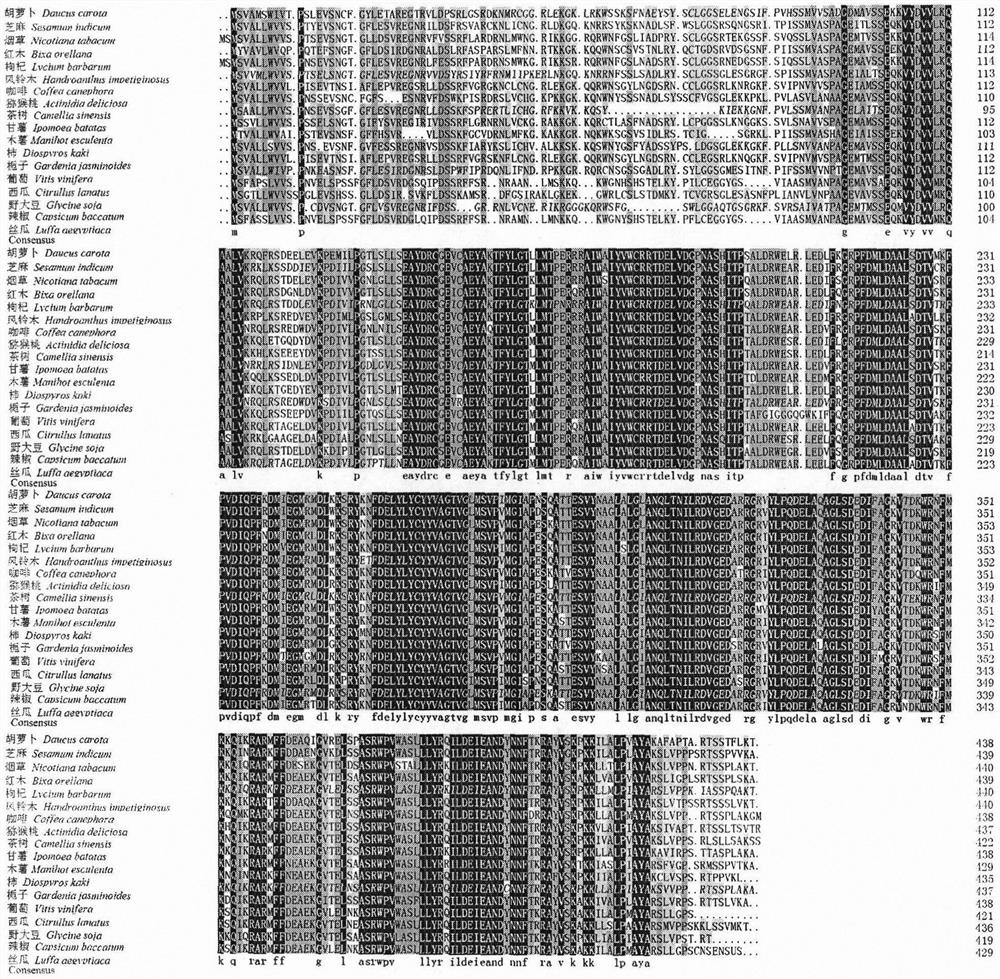
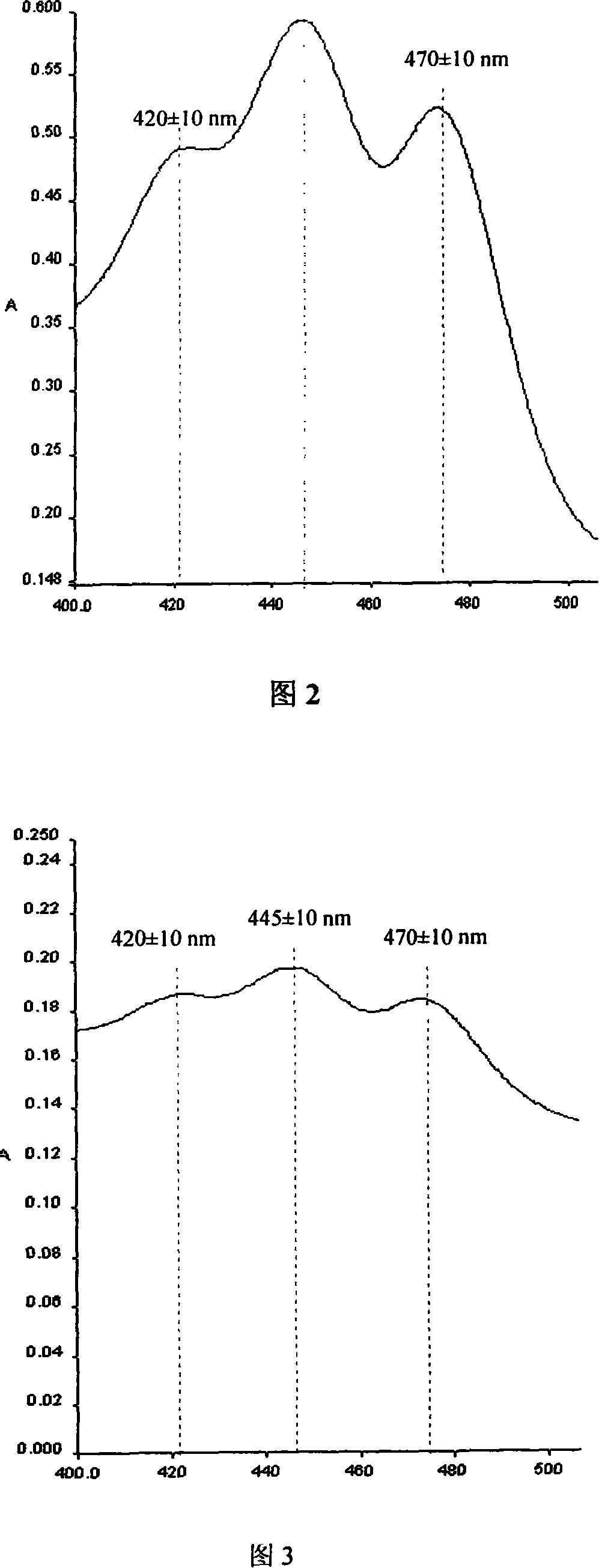
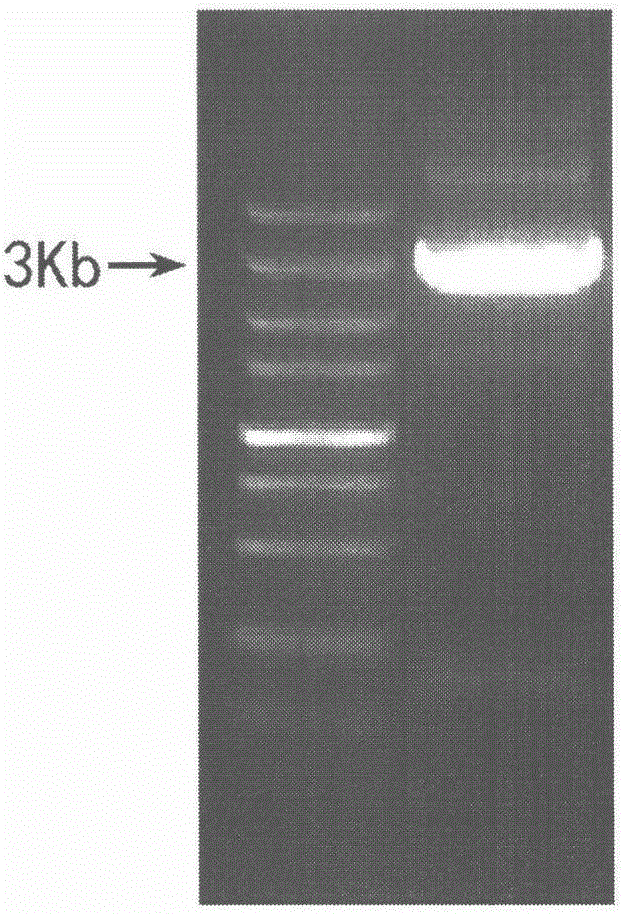
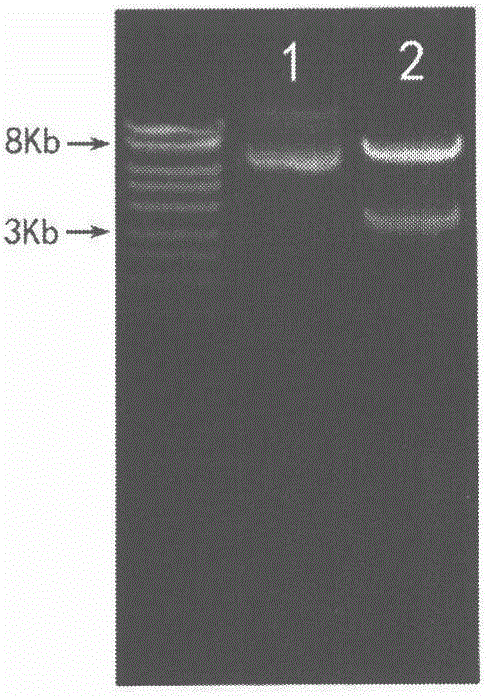
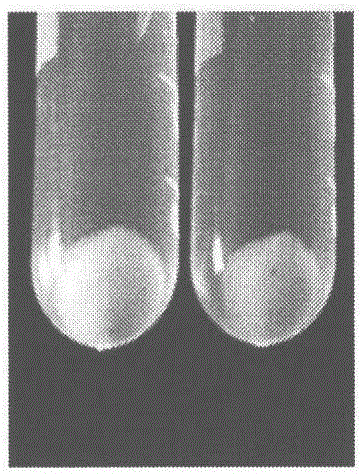
[Beta]-carotenoid ketolase mutant, recombinant expression vector, genetic engineering bacterium and application thereof
ActiveCN106520712AHigh catalytic activityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
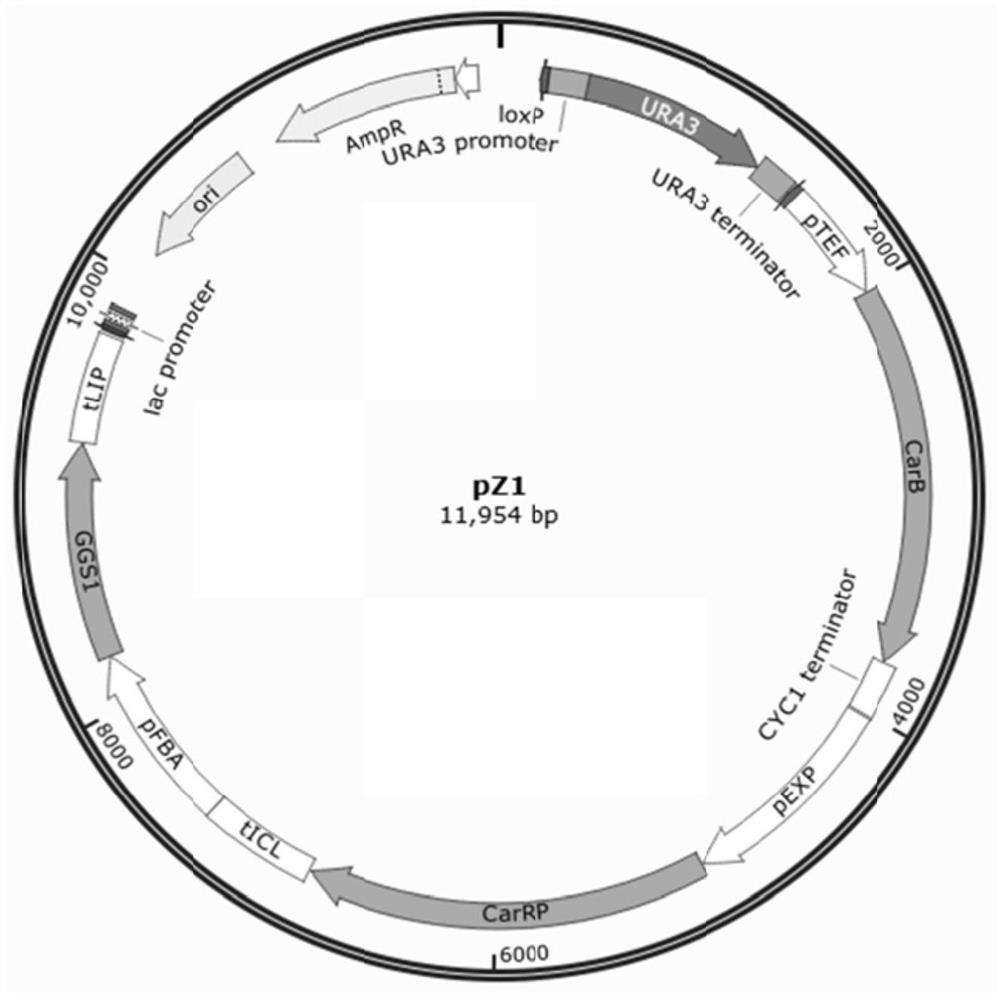
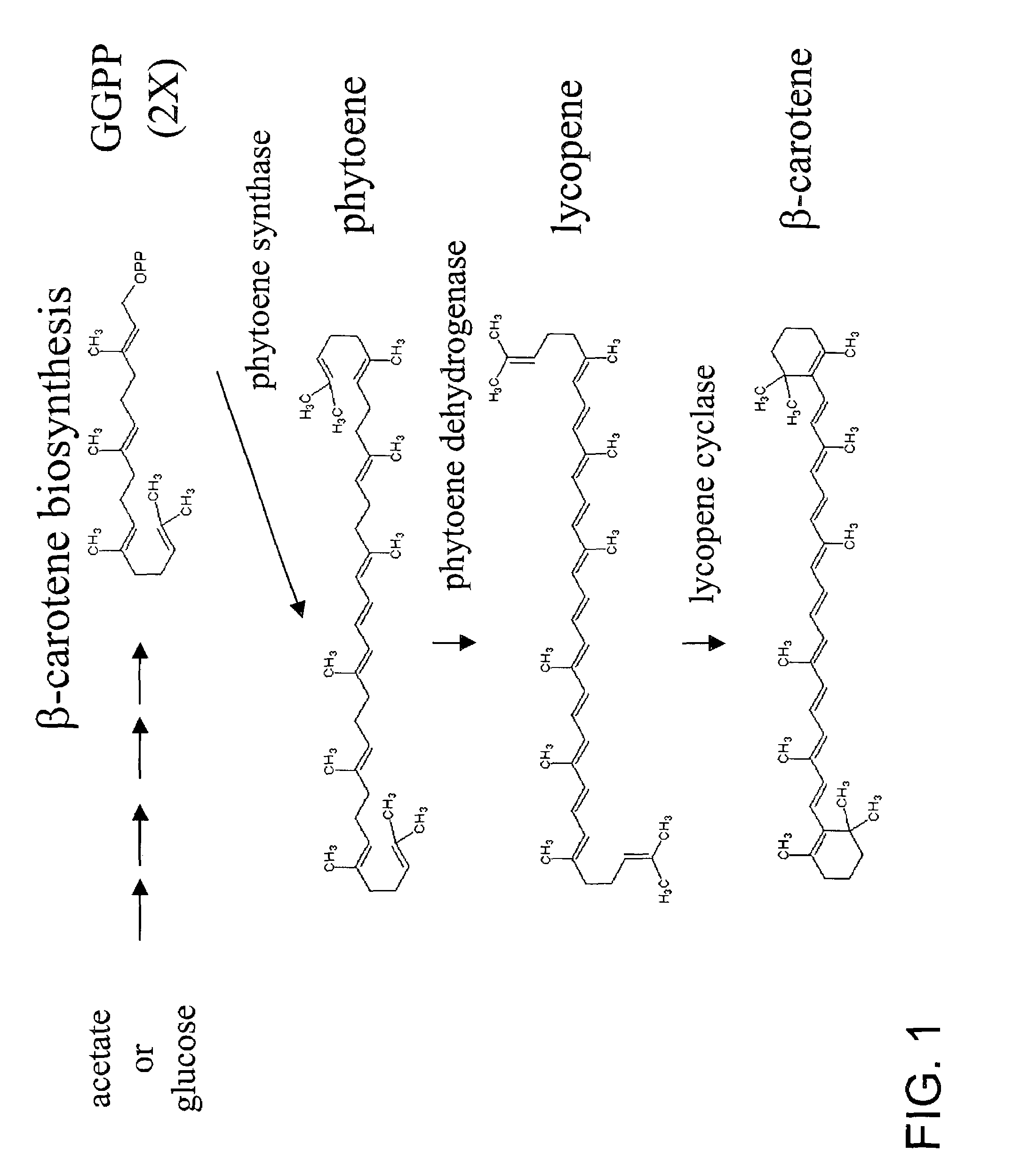
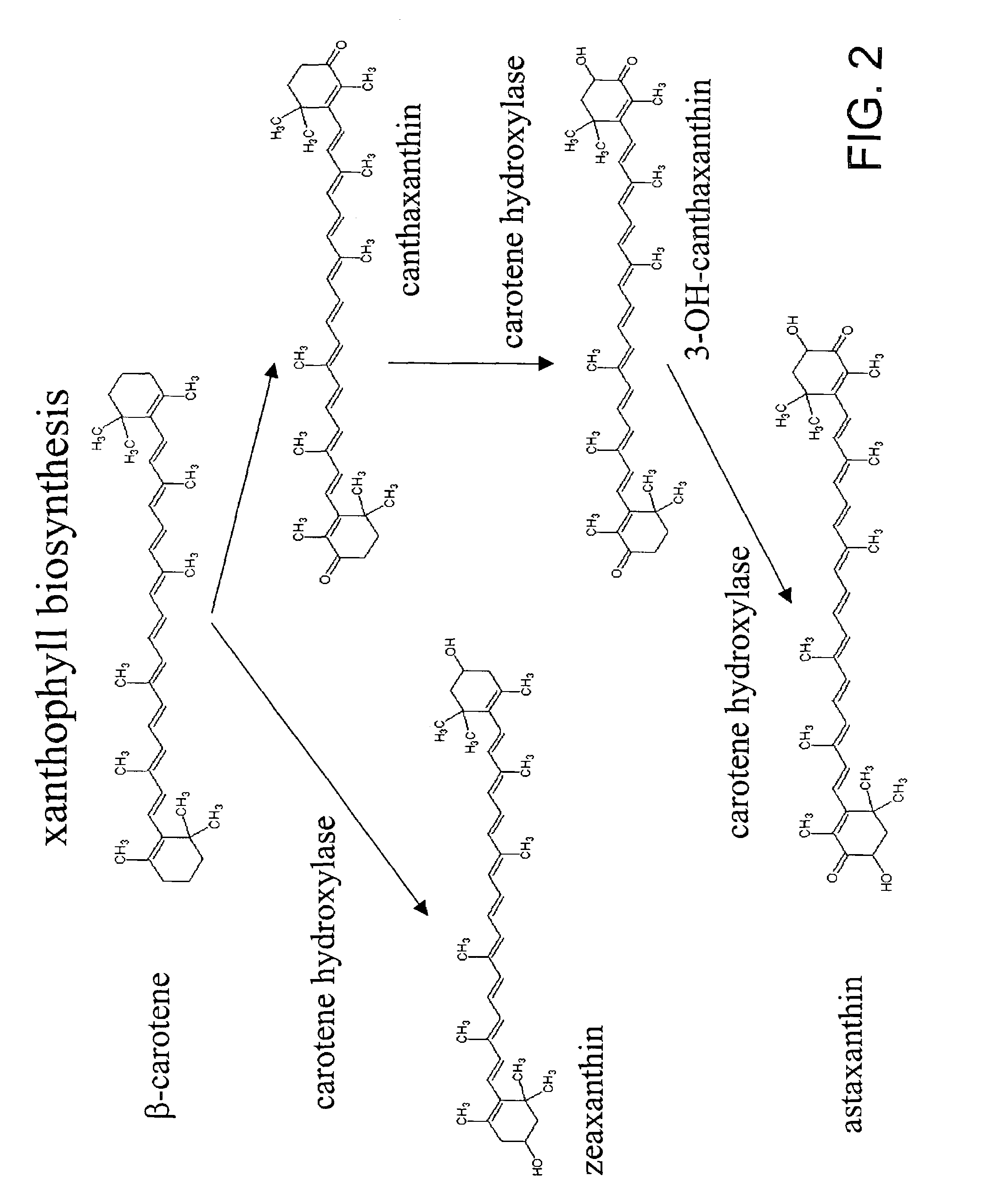
The invention provides a [beta]-carotenoid ketolase mutant, which is obtained through a directed evolution means, nucleotide sequences for encoding the mutant, a recombinant expression vector containing a mutant gene, expression in saccharomyces cerevisiae and application of a genetic engineering bacterium in the synthesis of keto-carotenoids. According to the invention, a mutant strain with catalytic activity on [beta]-carotenoid enhanced is screened by virtue of a high-throughput screening method, and through gene sequencing analysis, mutant sites are subjected to combined mutation, so that the catalytic activity is further enhanced; and the screened mutant strain is applied to the production of saccharomyces cerevisiae keto-carotenoids.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Carotenoid synthetic route Tagetes erecta violaxanthin de-epoxidase (TeVDE1) gene and application
The invention discloses a carotenoid synthetic route Tagetes erecta violaxanthin de-epoxidase (TeVDE1) gene. The TeVDE1 is characterized in that the nucleotide sequence of the TeVDE1 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1 in a sequence table, the amino acid sequence of the TeVDE1 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 2 in the sequence table. The TeVDE1 gene is obtained from tagetes erecta petal tissue in a clone mode. Real-time quantification analysis and a xanthophyll content determination result show that the expression quantity of the TeVDE1 gene in Tagetes erecta flower buds is high, and the expression level of the TeVDE1 is related to the xanthophyll content. The SEQ ID NO: 1 gene has an effect on xanthophyll synthetic accumulation, and the TeVDE1 obtained from the pigment tagetes erecta in a clone mode can be used for increasing the pigment contents of xanthophylls and other carotenoid.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Fermentation medium beneficial to synthesis of saccharomyces cerevisiae carotenoid
ActiveCN112553096APromote growthPromote accumulationFungiMicroorganism based processesZinc ionCarotenoid synthesis
The invention discloses a fermentation medium beneficial to synthesis of saccharomyces cerevisiae carotenoid. The culture medium comprises a saccharomyces cerevisiae basic culture medium and copper ions. The fermentation medium provided by the invention significantly improves the accumulation of recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae carotenoid (by 10 times). According to the invention, transcriptomics reveals that the addition of zinc ions and copper ions in the culture medium can significantly promote the synthesis of the carotenoid, and the zinc ions, copper ions and the carotenoid have a synergistic enhancement effect.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
Medlar carotenoid synthase gene lycB and plasmid comprising the gene
InactiveCN1884546AIncrease contentImprove nutritional qualityEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyNucleotide
This invention exposed a kind of synthase gene lycB of medlar carotenoids as well as the plasmid that includes this gene. The synthase gene lycB of medlar carotenoids has the nucleotide sequence indicated in the SEQ ID No. 1 sequence listing. The synthase gene lycB of medlar carotenoids in this invention can help to control the metabolism and accumulation of carotenoids in plant by the gene engineering approach, create the strains with higher carotenoids content, improve the nutrition of fruit and vegetable and realize the production of natual carotenoids in factory.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
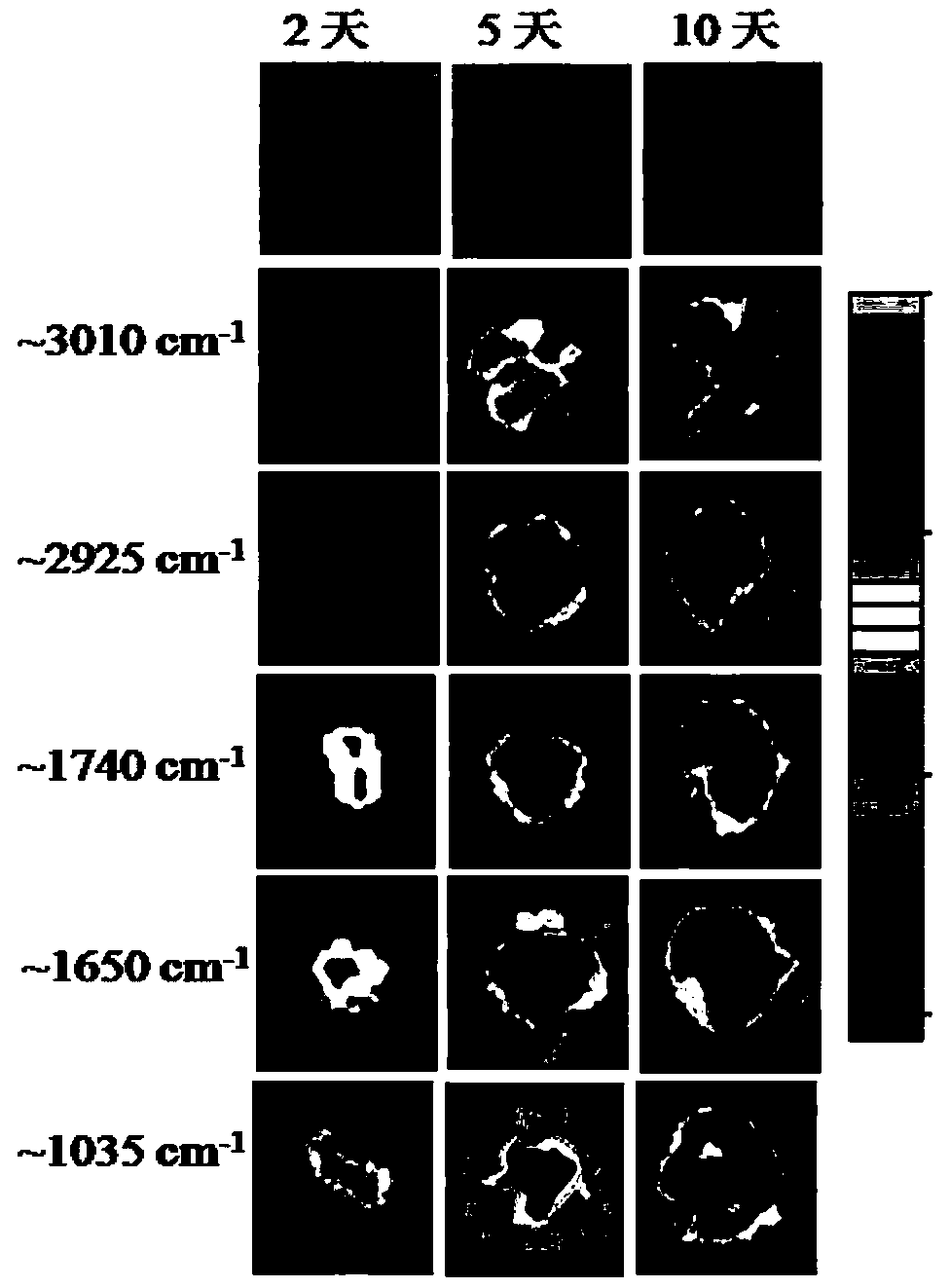
Research method for synthetic process of haematococcus pluvialis astaxanthin based on infrared spectroscopy microscopic imaging technology
InactiveCN108918456ASolve the problem that high-throughput measurement cannot be taken into account at the same timeResolve resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansBeta-CaroteneLycopene
The invention discloses a research method for the synthetic process of haematococcus pluvialis astaxanthin based on an infrared spectroscopy microscopic imaging technology. The method comprises the following steps that inoculation and culture are carried out on haematococcus pluvialis; an inhibitor performs treatment on haematococcus pluvialis strains; the infrared spectroscopy of the astaxanthin,beta-carotene and lycopene are collected; the infrared microscopic spectroscopy of haematococcus pluvialis cells are detected; and comparison and analysis of imaging of the microscopic infrared spectroscopy are carried out. According to the method, the infrared microscopic spectroscopy imaging technology is utilized, the haematococcus pluvialis cells are treated by combining the inhibitor synthesized by carotenoid, and high-spatial-resolution in-situ observation is carried out on the contents of various components of the haematococcus pluvialis cells in the astaxanthi accumulation process, sothat the effects of the components in the synthesis path of the astaxanthin can be conveniently analyzed. The method has important significance in research of the synthesis path of the carotenoid inthe haematococcus pluvialis cells and large-scale breeding of the haematococcus pluvialis for production of the astaxanthin.
Owner:ANHUI SCI & TECH UNIV
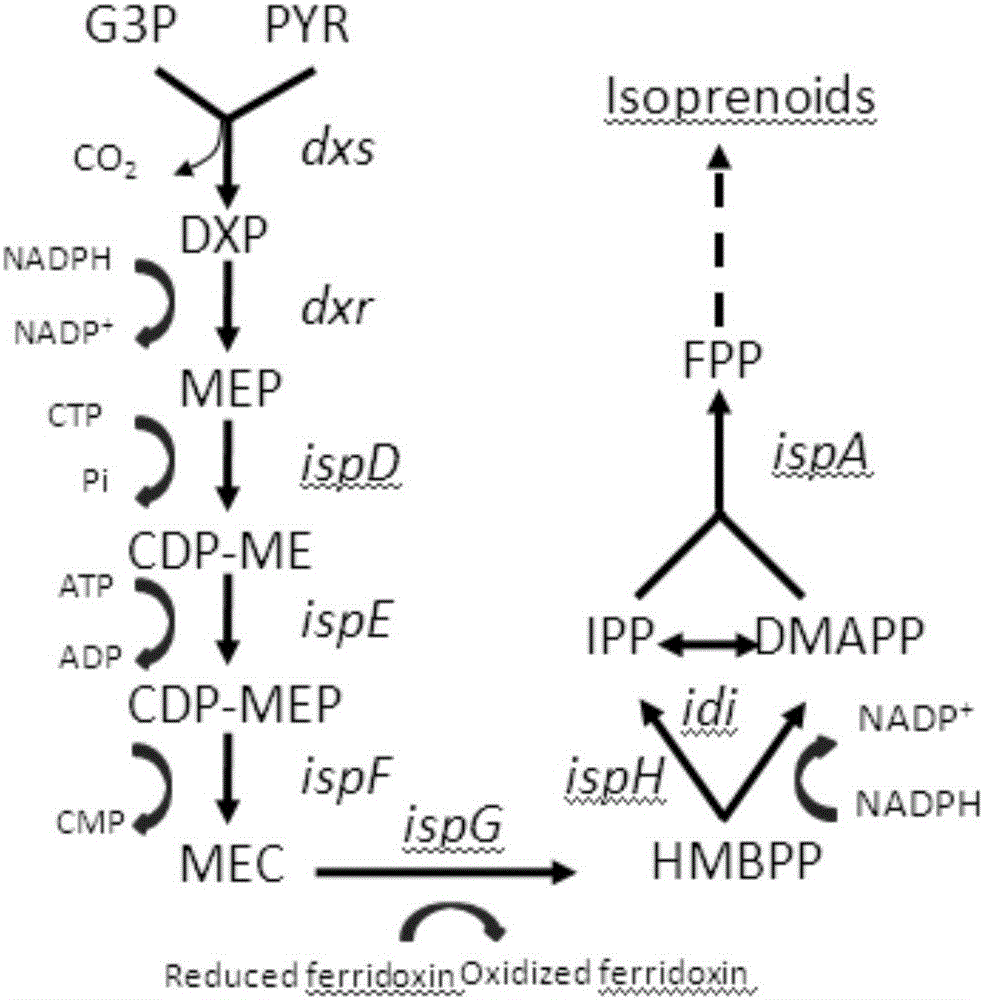
Recombination microorganism for producing beta-carotene, construction method and application
ActiveCN106434507AImprove synthesis abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliMicroorganism
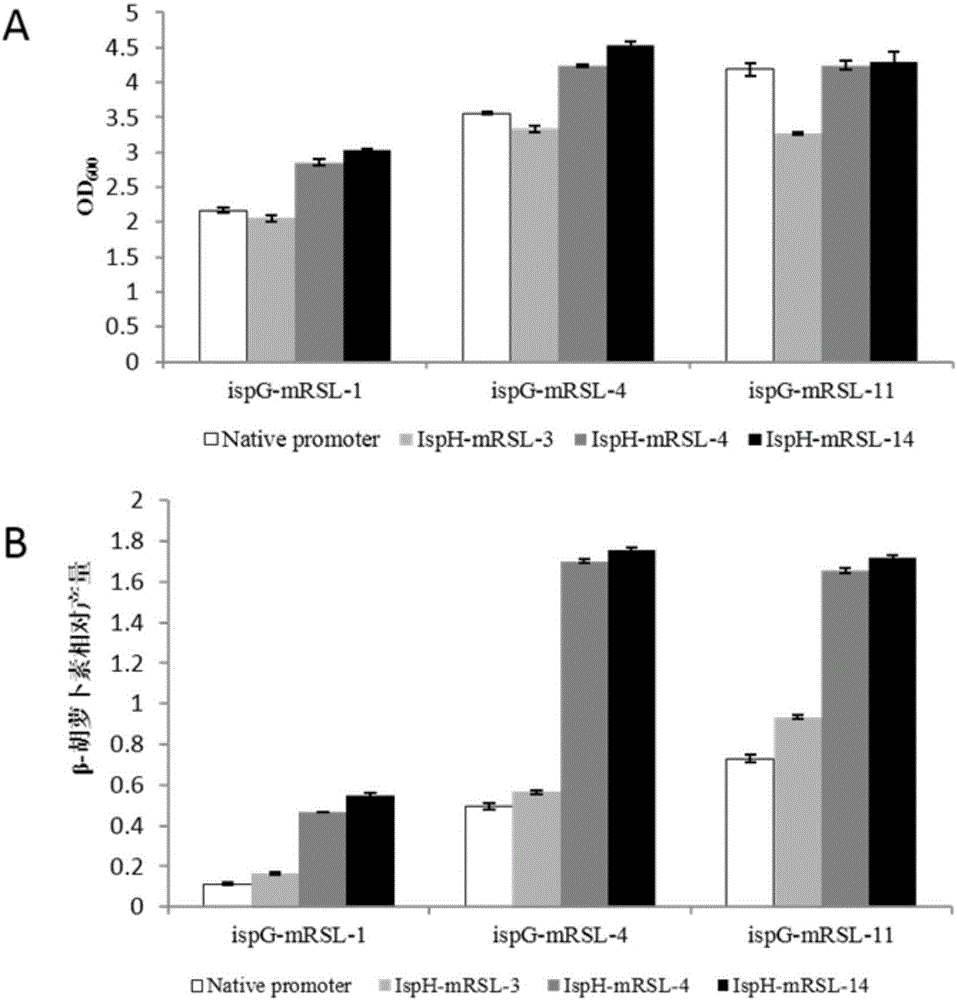
The invention discloses a method for finding and removing MEP route rate-limiting step and an application thereof in production of terpene compound. The invention provides a method for constructing recombinant bacteria. The expression and / or activity of (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methyl-2-butenyl-pyrophosphoric acid synthetase gene ispG and (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methyl-2-butenyl-pyrophosphoric acid reductase gene ispH for producing beta-carotene escherichia coli are promoted, so as to obtain the recombinant bacteria. An experiment proves that the cytotoxicity is caused by the intracellular accumulation of MEP route intermediate HMBPP in the recombinant escherichia coli having a certain beta-carotene compounding capacity and the coordinative expression for ispG and ispH genes can effectively increase the capacity of the recombinant escherichia coli for compounding the terpene compound.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Medlar carotenoid synthase gene PSY and plasmid comprising the gene
InactiveCN1884547AIncrease contentImprove nutritional qualityEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyNucleotide
This invention exposed a kind of synthase gene PSY of medlar carotenoids as well as the plasmid that includes this gene. The synthase gene PSY of medlar carotenoids has the nucleotide sequence indicated in the SEQ ID No. 1 sequence listing. The synthase genes PSY of medlar carotenoids in this invention can help to control the metabolism and accumulation of carotenoids in plant by the gene engineering approach, create the strains with higher carotenoids content, improve the nutrition of fruit and vegetable and realize the production of natual carotenoids in factory.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
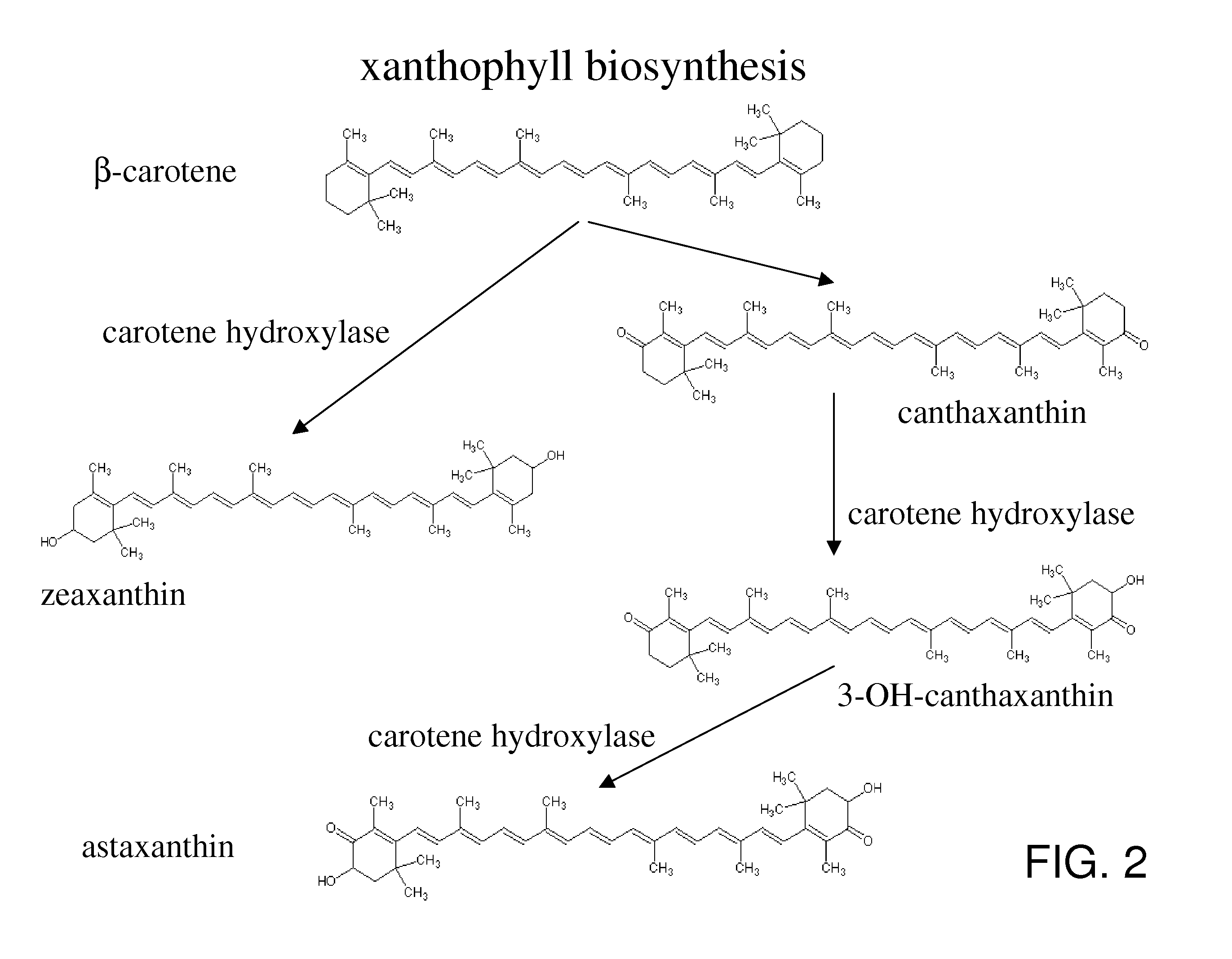
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing astaxanthin, and application of recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae
ActiveCN113699052AIncrease productionHigh purityFungiMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneAstaxanthin
The invention discloses recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing astaxanthin, and application of the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae. According to the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae disclosed by the invention, a [beta]-carotene ketolase gene CrtW is subjected to constitutive expression, a [beta]-carotene hydroxylase gene CrtZ is subjected to inducible expression, an intermediate product [beta]-carotene is synthesized into the astaxanthin, and the copy number ratio of the [beta]-carotene ketolase gene CrtW to the [beta]-carotene hydroxylase gene CrtZ is (3: 1)-(3: 2). When the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae provided by the invention is used for producing the astaxanthin, the shake flask fermentation yield of the astaxanthin can reach 14.70 mg / g DCW, and the purity of the astaxanthin can reach 96.69%.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM (SICHUAN) CO LTD +1
Cucumber carotenoid phytoene synthetase gene
InactiveCN102776211AIncrease contentImprove nutritional qualityEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionAmpicillinPrenylation
The invention discloses a cucumber carotenoid phytoene synthetase gene. All cucumber carotenoids are synthesized by isoprenoid compounds or terpenoids. The length of the nucleotide sequence SEQ ID of the cucumber carotenoid phytoene synthetase gene is 1479bp, and the cucumber carotenoid phytoene synthetase gene has a specific nucleotide sequence. The gene-coded polypeptide of claim 1 comprises 422 amino acids, has the molecular weight of 47393.507Da, the isoelectric point of 6.545, the charge of 0.777 when the pH value is 7.0, and has a specific amino acid sequence. The recombinant plasmid pT-PSY of the gene of claim 1 has the length of 4515bp, comprises ampicillin selection markers, and has a specific nucleotide sequence. The invention is used for cloning cucumber carotenoid phytoene synthetase genes.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
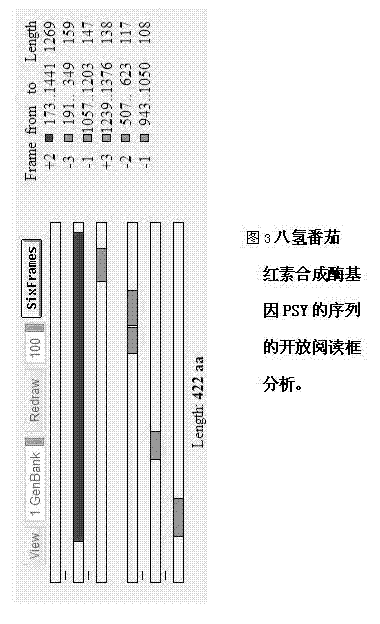
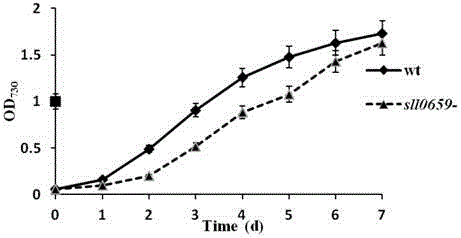
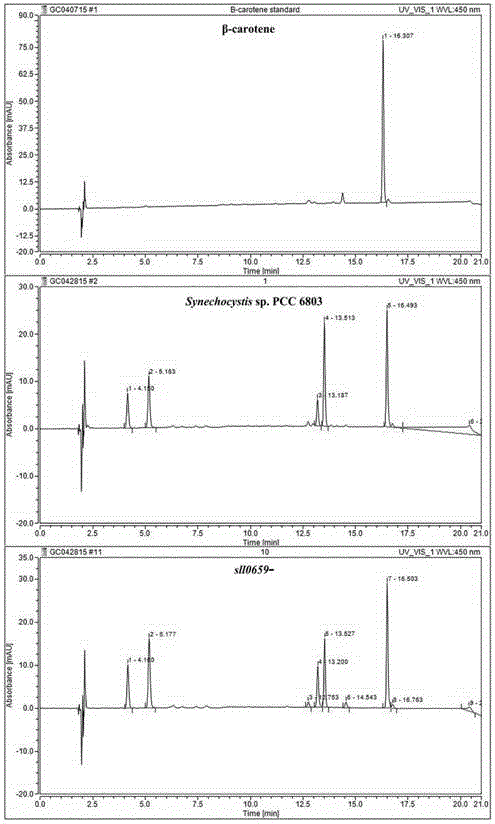
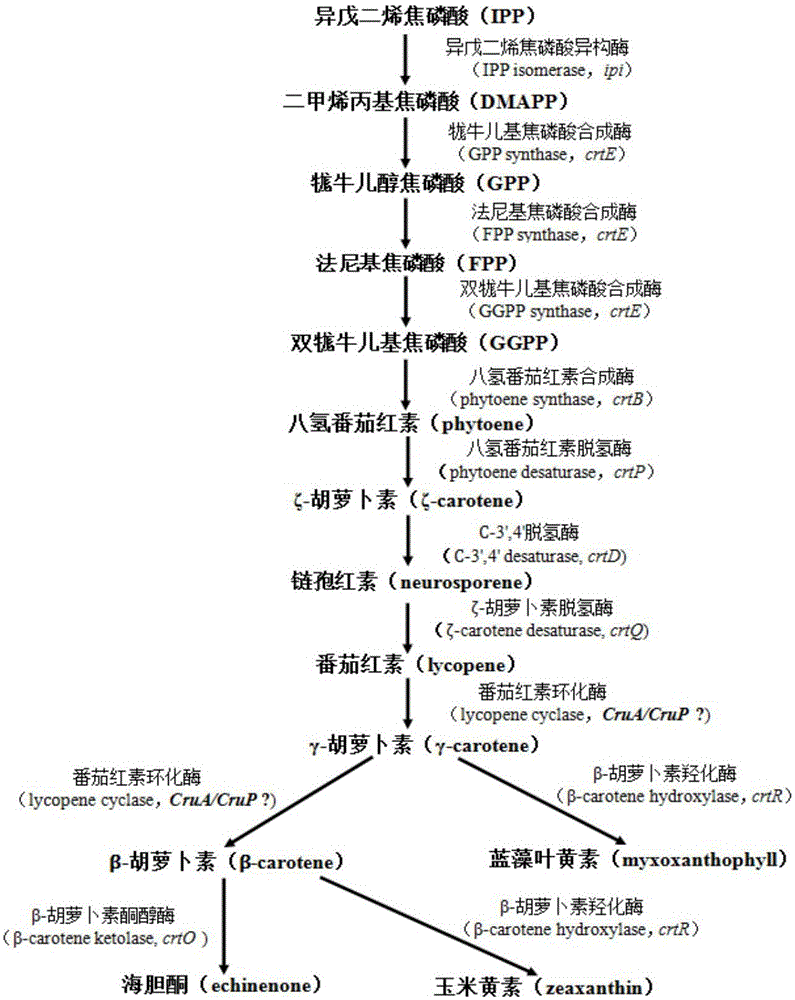
Application of sll0659 gene to synthesis of synechocystis carotenoids
ActiveCN105087627AIncrease Lutein ContentReduce percentageBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBeta-CaroteneAlpha-Carotene
The invention relates to application of a sll0659 gene to synthesis of synechocystis carotenoids. The nucleotide sequence of the sll0659 gene is shown in SEQ ID No.1. The invention provides application of the sll0659 gene in synechocystis PCC6803, which has an important effect on synthesis of synechocystis PCC6803 beta-carotene. By knocking out the sll0659 gene in synechocystis PCC6803, the lutein content of the synechocystis PCC6803 is increased by 22.3%, zeaxanthin content is increased by 31.3%, the echinenone content is reduced by 34.3%, and the percentage content of beta-carotene is reduced by 1.3%. Meanwhile, HPLC detection results show when synechocystis PCC6803 involved in the invention is compared with wild synechocystis PCC6803, an obvious peak exists in the carotenoid components in the sll0659 gene knockout mutant, and the obvious peak is determined to be alpha-carotene by contrasting the obvious peak with a standard product and detecting.
Owner:BIOTECH RES CENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
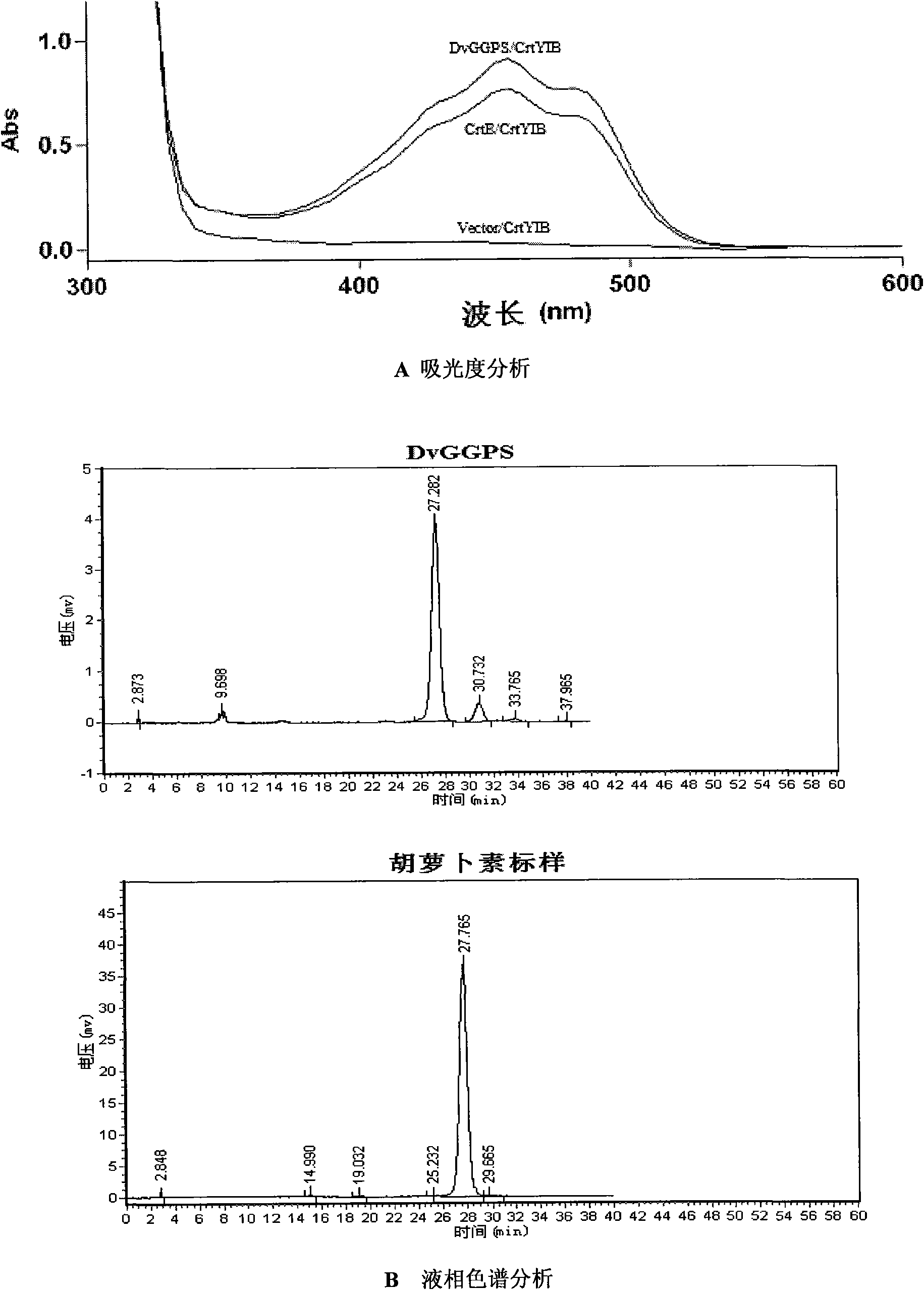
Synthetase gene relative to carotene synthesis, coded protein and application thereof
The invention relates to a synthetase gene relative to carotene synthesis, a coded protein and an application thereof. The synthetase gene DvGGPS relative to carotene synthesis performs the function of geranyl synthetase in E.coli and provides a needed precursor GGPP for carotene synthesis for a downstream gene in a carotene synthesis way. Meanwhile, the pronucleus bacterial strain containing theDvGGPS gene of the invention has great potential on the aspect of using gene engineering to produce carotene.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Methods for synthesis of carotenoids, including analogs, derivatives, and synthetic and biological intermediates
InactiveUS20060293545A1Organic compound preparationGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsCarotene synthesisSolubility
A method for synthesizing intermediates for use in the synthesis of carotenoid synthetic intermediates, carotenoid analogs, and / or carotenoid derivatives. The carotenoid analog, derivative, or intermediate may be administered to a subject for the inhibition and / or amelioration of any disease that involves production of reactive oxygen species, reactive nitrogen species, radicals and / or non-radicals. In some embodiments, the invention may include methods for synthesizing chemical compounds including an analog or derivative of a carotenoid. Carotenoid analogs or derivatives may include acyclic end groups. In some embodiments, a carotenoid analog or derivative may include at least one substituent. The substituent may enhance the solubility of the carotenoid analog or derivative such that the carotenoid analog or derivative at least partially dissolves in water.
Owner:CARDAX PHARMA
Wheat carotenoid synthesis route key gene Lcye mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN111171129AReduce yellow pigment contentReduced expression levelPlant peptidesIsomerasesProteinCarotene synthesis
The invention discloses a wheat carotenoid synthesis route key gene Lcye mutant and an application thereof. The invention provides the following proteins: a protein obtained by replacing the 253th-site serine of a Lcye-D1 protein with phenylalanine, or a derived protein which is obtained through replacement and / or deletion and / or addition of one or several amino acid residues on the Lcye-D1 protein and has the same capacity as the Lcye-D1 protein, or a protein which as 99% or above, 95% or above, 90% or above, 85% or above or 80% or above of homology with an amino acid sequence restricted by the Lcye-D1 protein and has the same functions as the Lcye-D1 protein, or a fusion protein which is obtained through connecting a label with an N end and / or a C end of the Lcye-D1 protein. According tothe wheat carotenoid synthesis route key gene Lcye mutant disclosed by the invention, the functions of a Lcye gene are verified, and a theory basis and germplasm resources are also provided for colorproperty improvement of flour and products thereof.
Owner:CROP RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing astaxanthin, and application of recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae
ActiveCN113699053AHigh-yielding orderImprove metabolic fluxFungiMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneAstaxanthin
The invention discloses recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing astaxanthin, and application of the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae. According to the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae disclosed by the invention, a [beta]-carotene ketolase gene CrtW is subjected to constitutive expression, a [beta]-carotene hydroxylase gene CrtZ is subjected to inducible expression, and an intermediate product [beta]-carotene is synthesized into the astaxanthin. According to the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae, a constitutive promoter is used for regulating and controlling the CrtW gene to be firstly expressed, the inducible promoter is used for regulating and controlling the CrtZ gene to be expressed subsequently, so that the metabolic flux of the synthesis path of the astaxanthin of the saccharomyces cerevisiae is obviously improved, the yield of the astaxanthin reaches 464.90 mg / L, and the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae has a good industrial development prospect.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM (SICHUAN) CO LTD +1
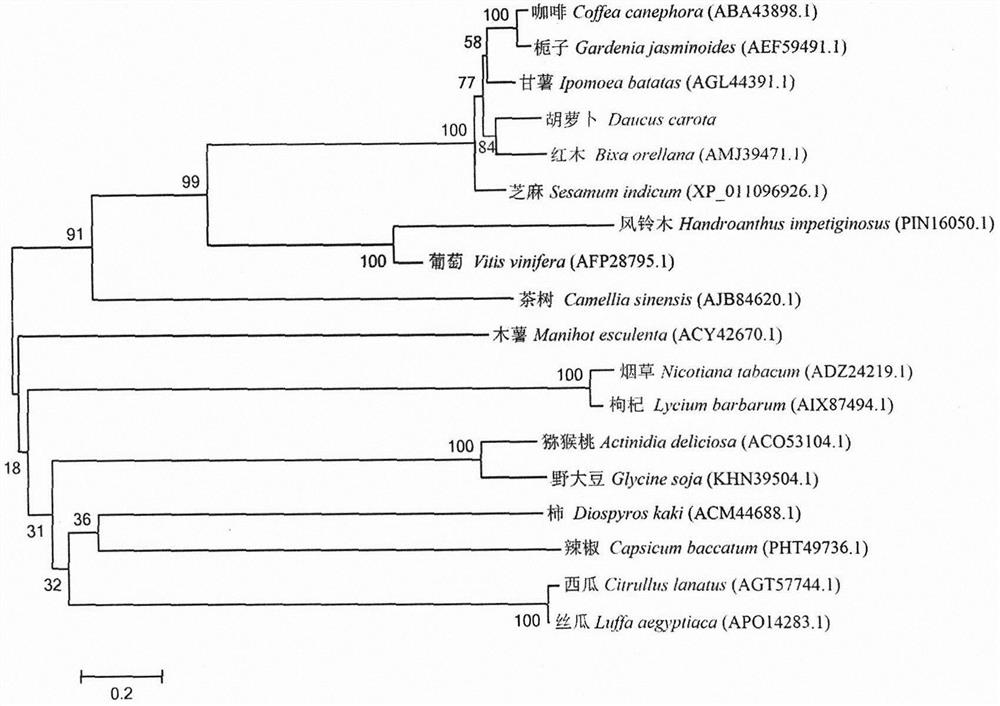
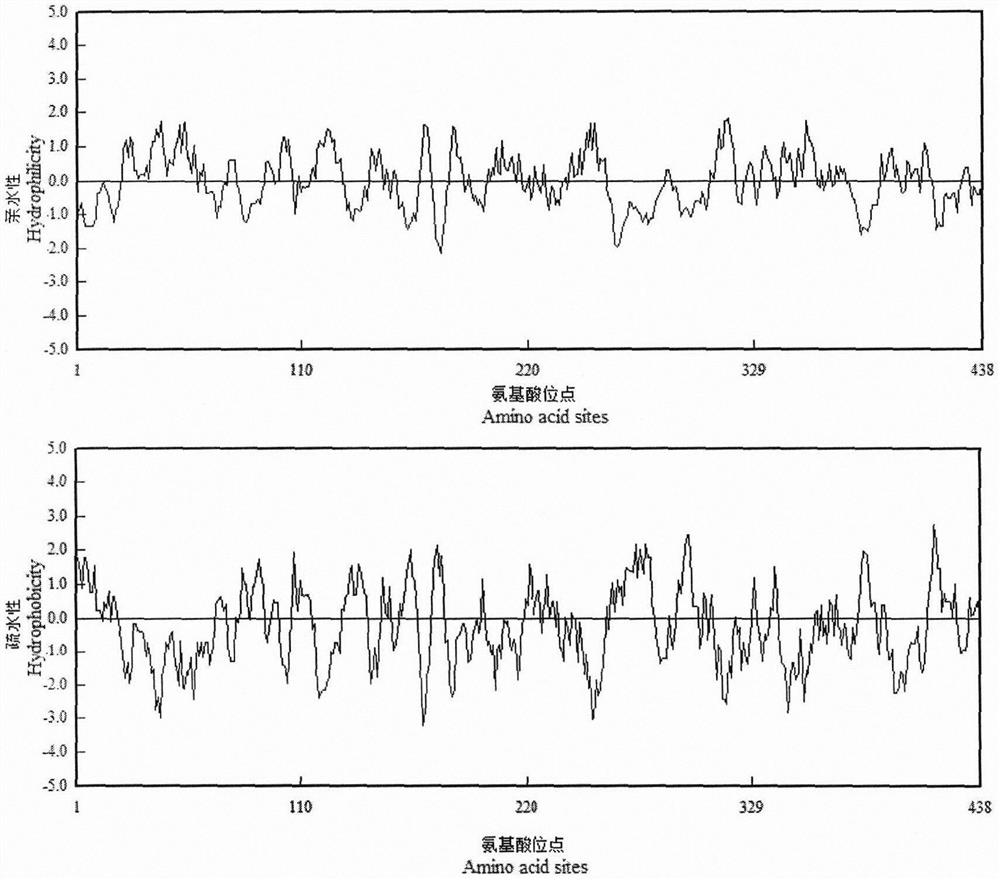
PSY2 gene sequence related to carrot carotenoid synthesis and application thereof
A PSY2 gene is a key gene participating in carotenoid synthesis. A new PSY gene DcPSY2 is cloned from carrots. The open reading frame length of the gene is 1317bp, and 438 amino acids are encoded. Theprotein encoded by DcPSY2 belongs to hydrophilic protein. The protein is closest to the evolutionary relationship of leguminous rosewood PSY and has high conservative property. Fluorescent quantitative expression analysis shows that the relative expression level of the DcPSY2 gene reaches a peak value after treatment for 2h under high temperature and high salt stress, and the relative expressionlevel is significantly different from that of a control group (P is less than 0.05). Under low temperature and drought stress, the expression level of the DcPSY2 gene of the carrots is increased mostobviously after treatment for 1h. The DcPSY2 gene of the carrots is cloned from the carrots by using a polymerase amplification technology, and the DcPSY2 gene of the carrots responds to the adversitystress of carrot plants.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
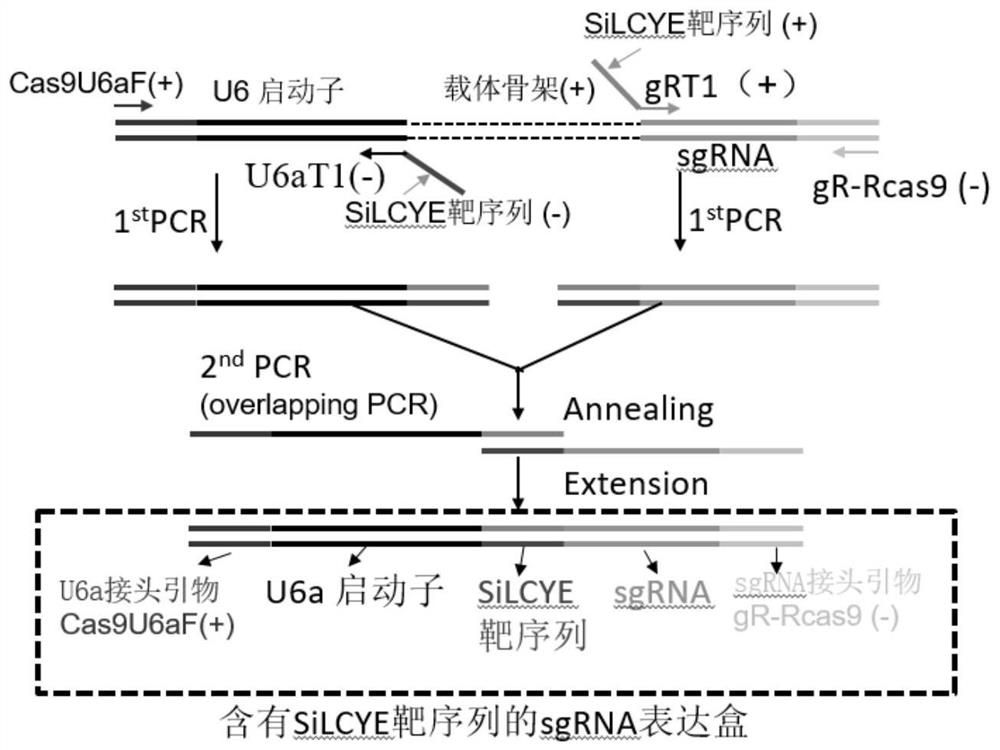
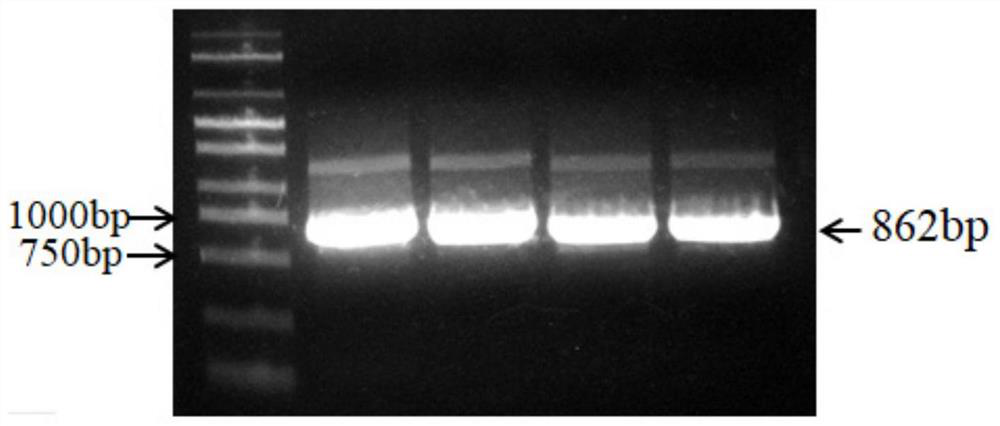
Function and application of SiLCYE in regulating and controlling anabolism of millet carotenoids such as zeaxanthin
The invention discloses a method for increasing the content of zeaxanthin or / and lutein stearate or / and antheraxanthin in millet. The method comprises the following steps of inhibiting or reducing the expression quantity of a protein coding gene in the millet, and / or inhibiting or reducing the activity and / or content of the protein in the millet, so as to increase the content of the zeaxanthin or / and the lutein stearate or / and the antheraxanthin in the millet, wherein the protein is SiLCYE protein. SiLCYE is cloned through a homologous cloning technology. An amino acid sequence of the SiLCYE is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1, and a coding sequence of the SiLCYE is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. An edited strain of SiLCYE genes is obtained through a CRISPR-Cas9 editing technology, and the regulation and control effects of the two genes in the metabolic reaction of the millet carotenoids are determined through metabonomics analysis. An experimental basis and gene resources are provided for revealing a metabolic pathway regulation and control mechanism of the millet carotenoids and cultivating new germplasm of the millet which is rich in carotenoid and high in nutritional quality.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Construction method and application of strain for efficiently synthesizing beta-carotene
ActiveCN114277040AIncrease productionApplicable to biosynthesisFungiMicroorganism based processesEngineered geneticBiology
The invention discloses a construction method and application of a strain for efficiently synthesizing beta-carotene, and belongs to the field of metabolic engineering. According to the construction method, related genes synthesized from acetyl coenzyme A to mevalonic acid in a beta-carotene synthesis route are expressed in yeast cytoplasm, and related genes synthesized from IPP and DMAPP to beta-carotene are overexpressed in yeast peroxisome. Related genes synthesized from mevalonic acid to IPP and DMAPP are over-expressed in cytoplasm or peroxisome. The yield of beta-carotene in the engineering strain constructed by the method is obviously improved. After the genetic engineering strain constructed by the invention is fermented for 9 days, the dry weight of thalli in fermentation liquor can reach 213g / L, and the yield of beta-carotene can reach 6.5 g.L <-1 >. The engineering strain constructed by the invention can efficiently synthesize beta-carotene, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
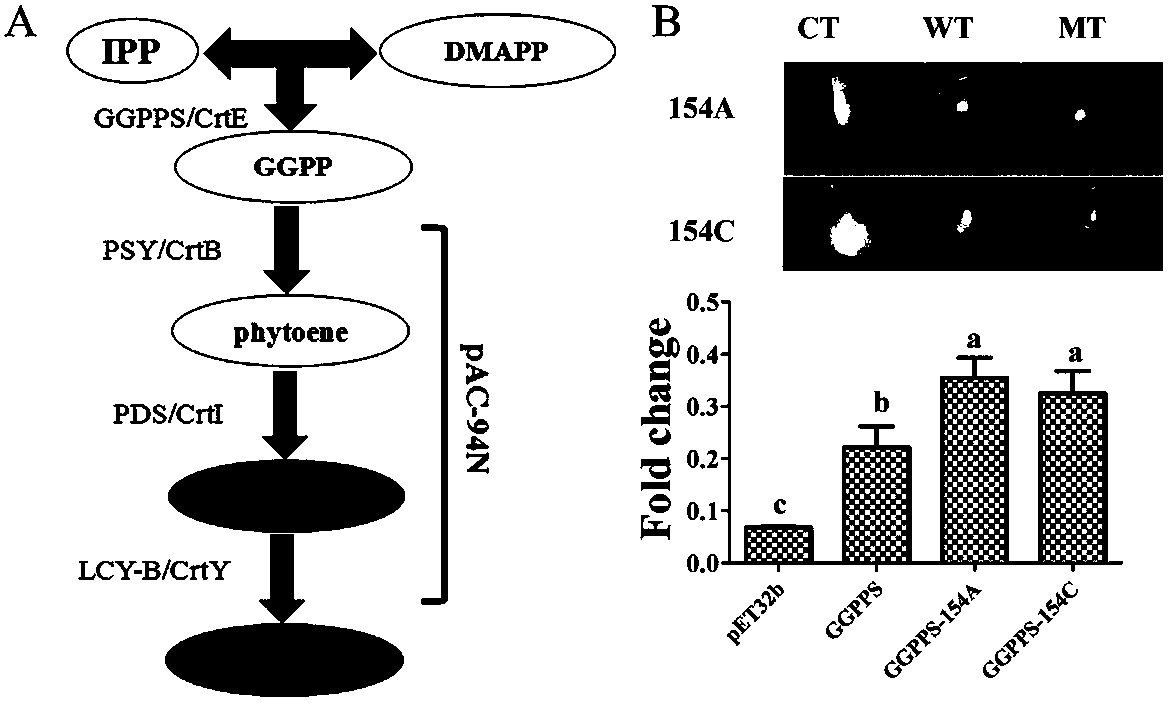
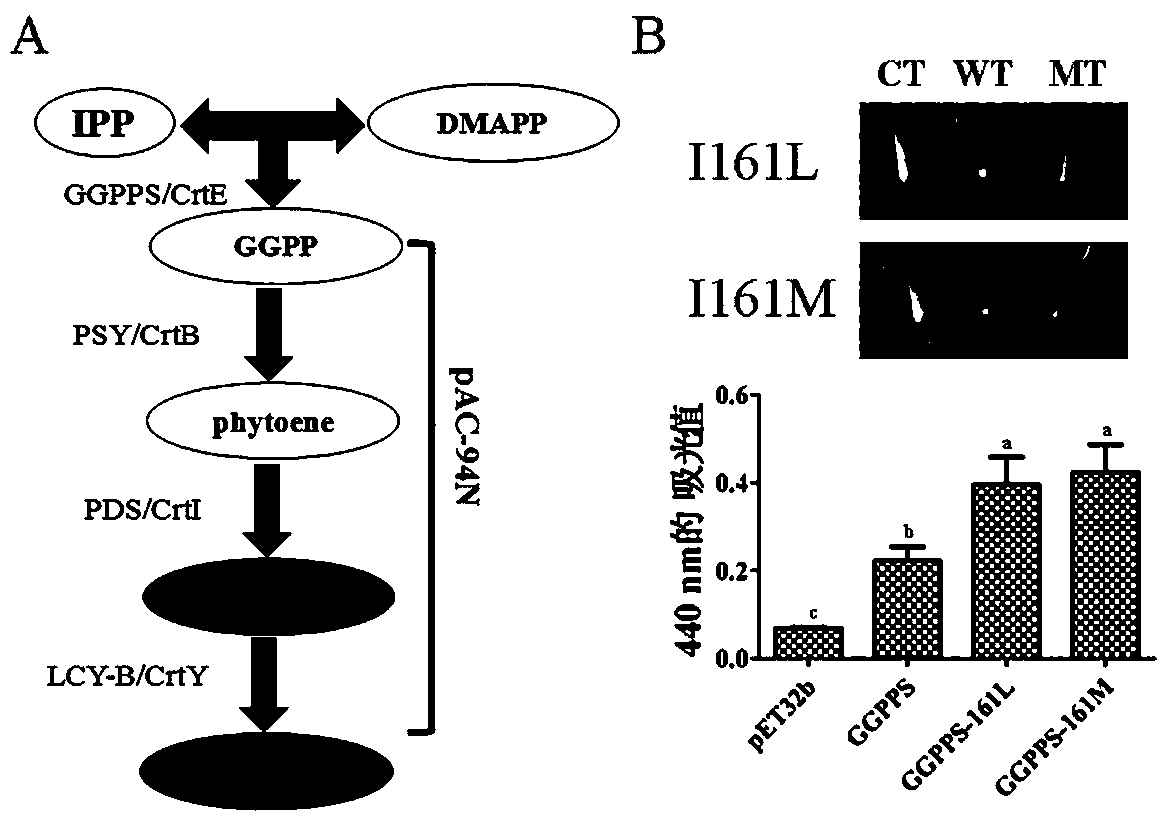
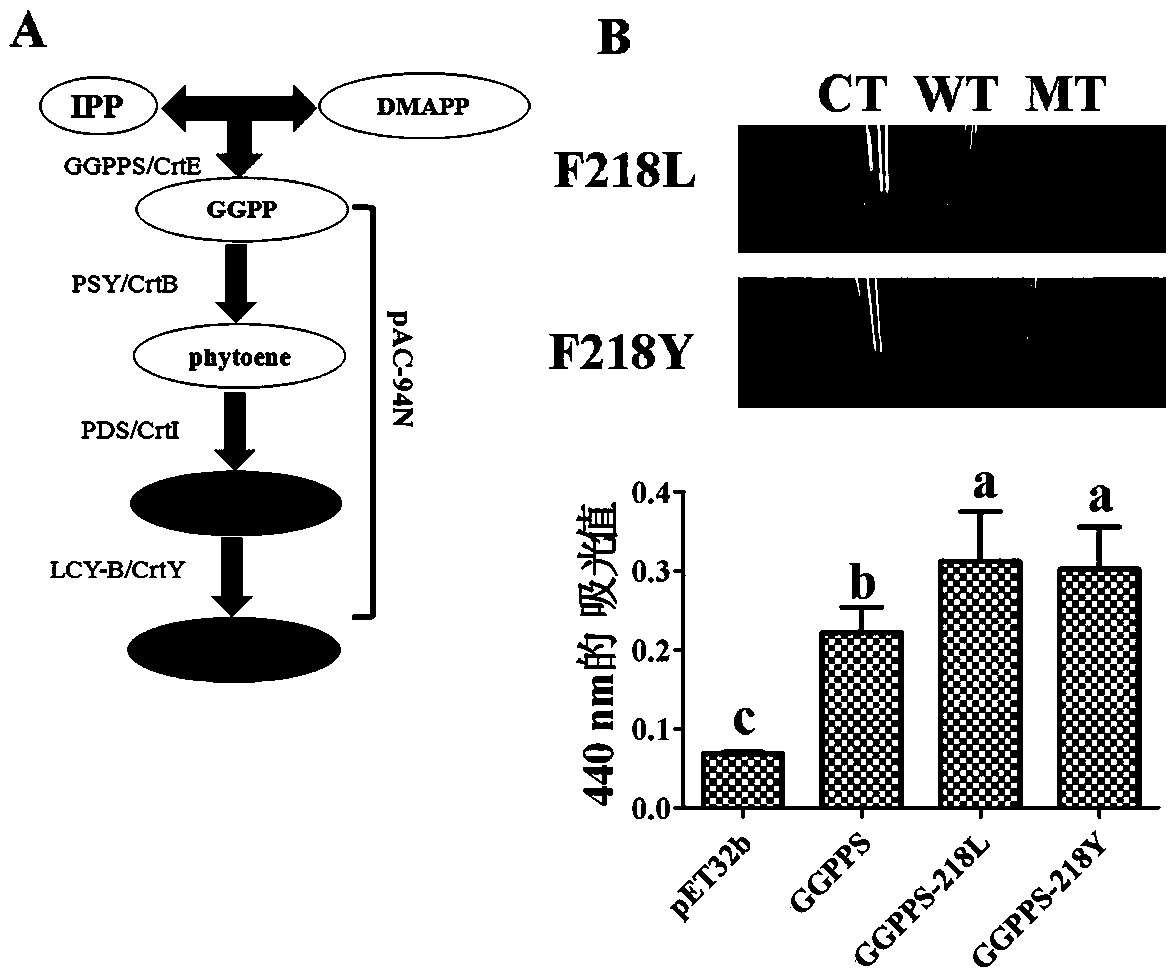
Directed five-site mutant protein GGPPS in enzyme pocket and on enzyme molecule surface
The invention belongs to the technical field of tobacco gene engineering, and particularly relates to patent application matters of a directional mutant protein GGPPS. 154, 161 and 218 sites of an existing GGPPS protein are positioned in a catalytic pocket of an enzyme, and 209 and 233 sites are positioned on an enzyme molecule surface; based on the five sites, the invention provides a GGPPS-series directional mutant protein, which comprises a series of single-site mutant proteins, a double-site mutant protein, a three-site mutant protein, a four-site mutant protein and a five-site mutant protein. The inventor constructs a 'small and fine' mutant library by using a CAST technology, and performs detailed analysis on the amino acid mutation type of a specific site through further screening on the basis of directed evolution requirements. Preliminary experiment results show that after amino acid mutation at the specific site, the synthesis amount of beta-carotene is obviously increased, and a certain technical foundation is laid for further cultivation of new crop varieties.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

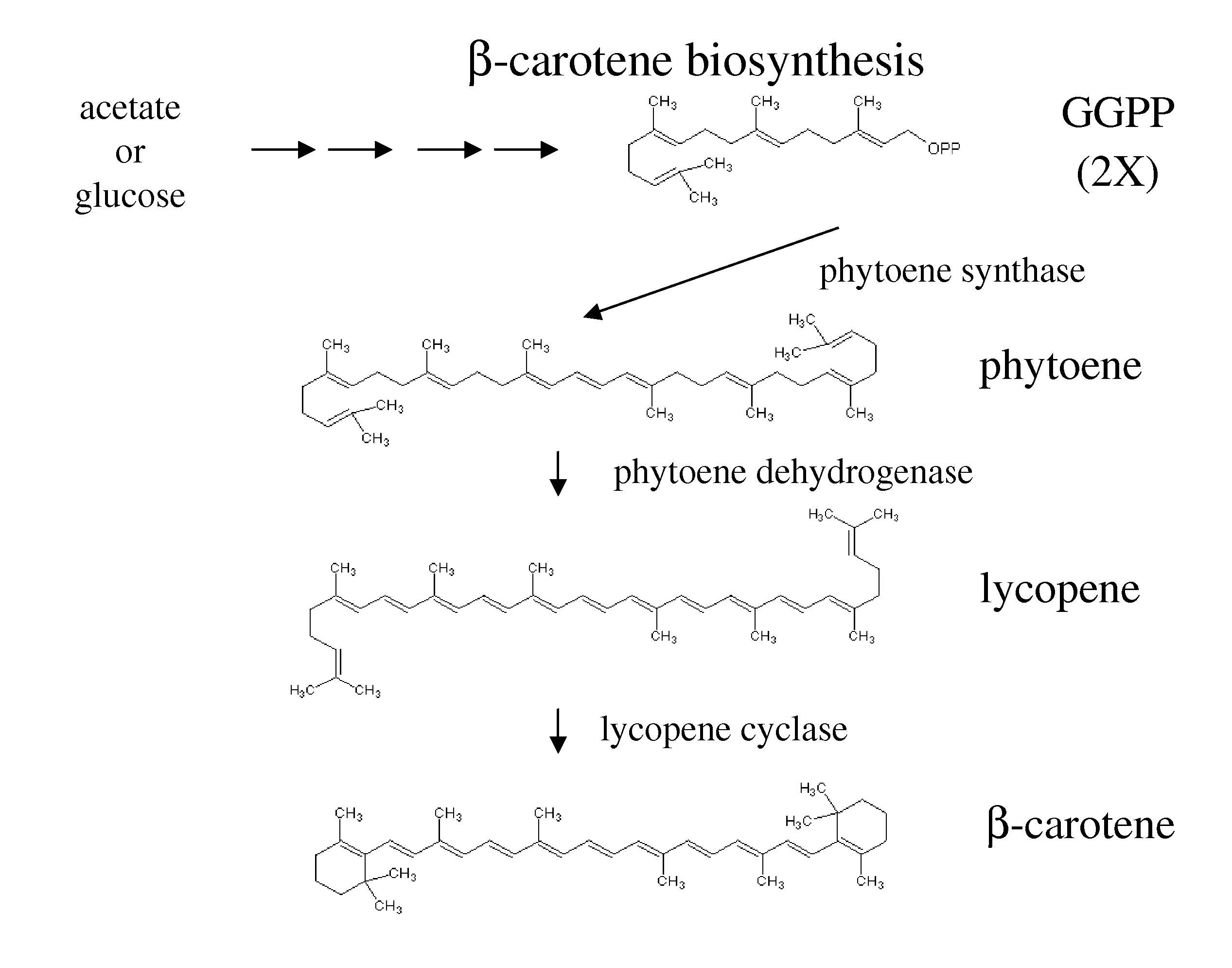

![[Beta]-carotenoid ketolase mutant, recombinant expression vector, genetic engineering bacterium and application thereof [Beta]-carotenoid ketolase mutant, recombinant expression vector, genetic engineering bacterium and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/93c7ac42-d802-432b-97fd-2c06a5e54273/HDA0001132334350000011.png)
![[Beta]-carotenoid ketolase mutant, recombinant expression vector, genetic engineering bacterium and application thereof [Beta]-carotenoid ketolase mutant, recombinant expression vector, genetic engineering bacterium and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/93c7ac42-d802-432b-97fd-2c06a5e54273/HDA0001132334350000012.png)
![[Beta]-carotenoid ketolase mutant, recombinant expression vector, genetic engineering bacterium and application thereof [Beta]-carotenoid ketolase mutant, recombinant expression vector, genetic engineering bacterium and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/93c7ac42-d802-432b-97fd-2c06a5e54273/HDA0001132334350000013.png)