Patents
Literature
219 results about "Hosting environment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
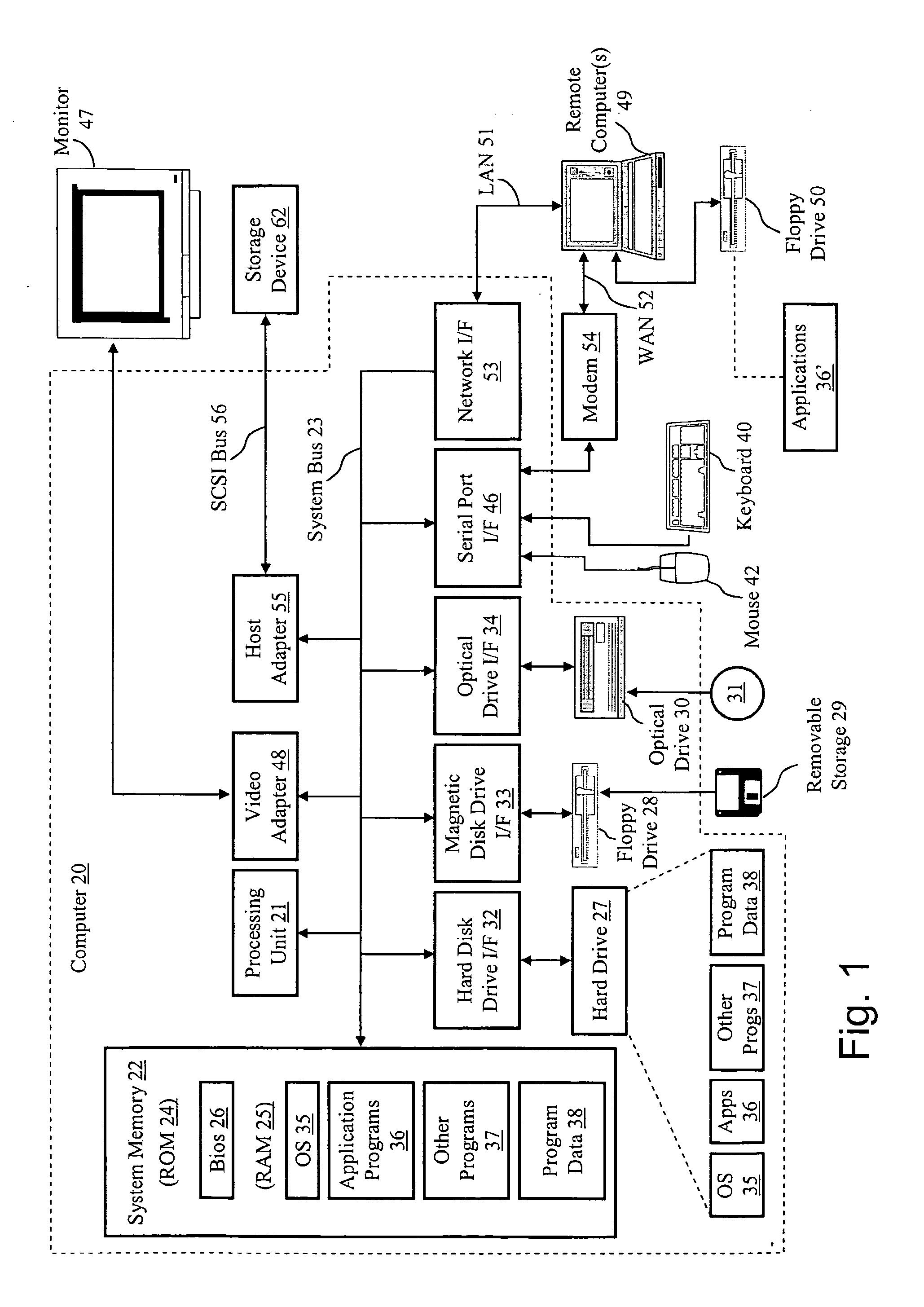
Hosting environment is a term used in telecommunication and Internet businesses. Hosting is a relatively new form of business between a vendor and a telecom operator.
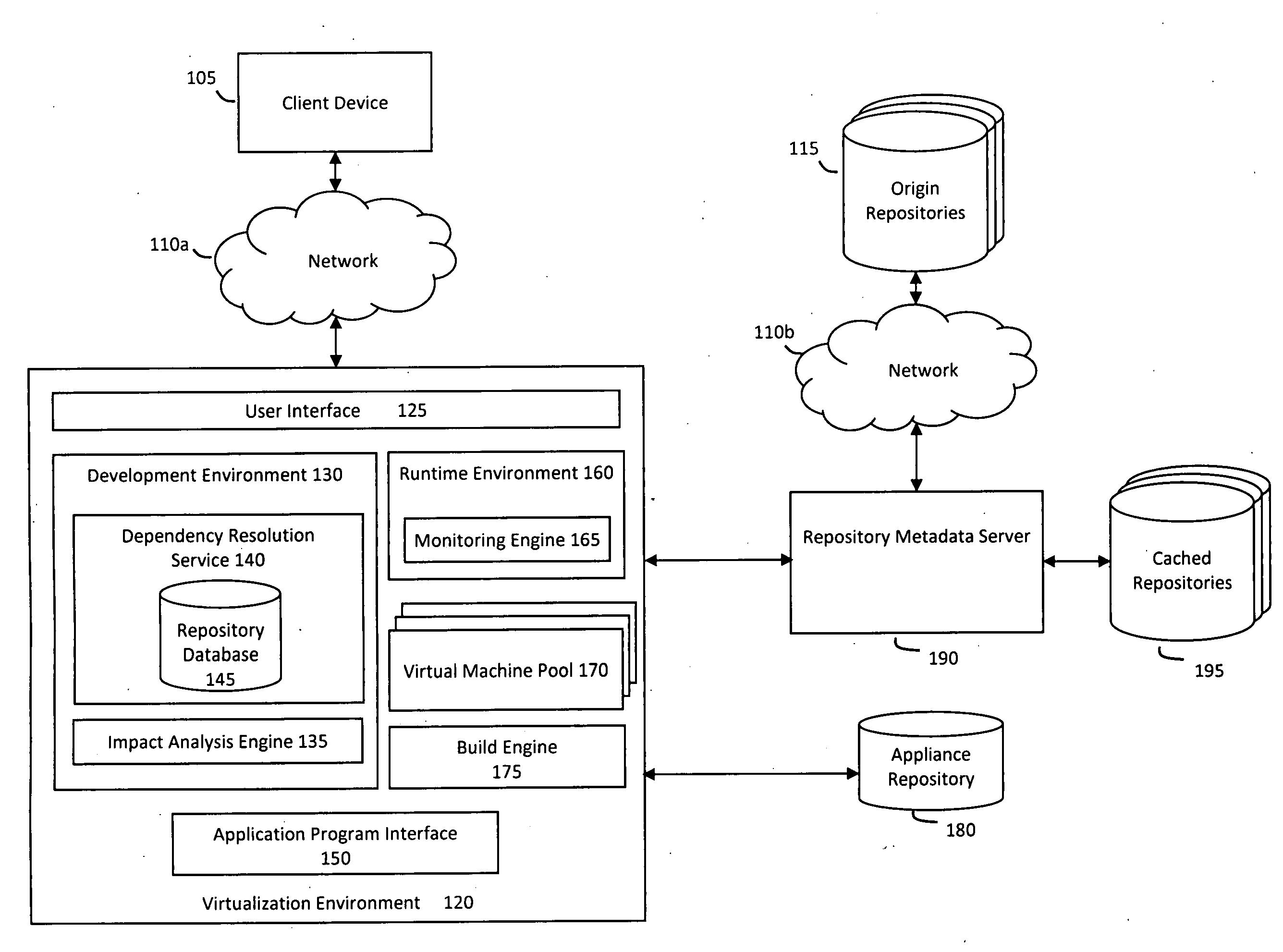
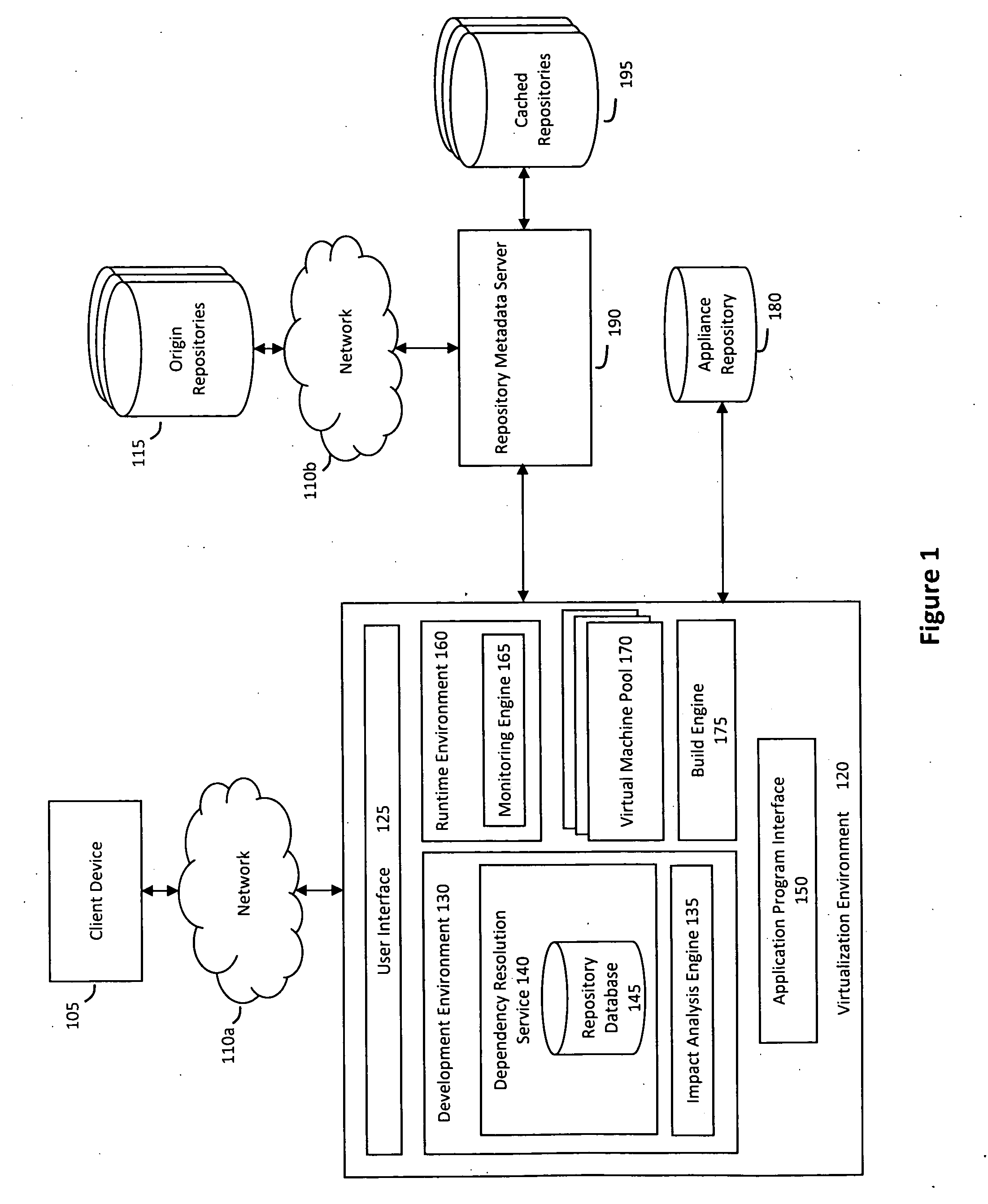
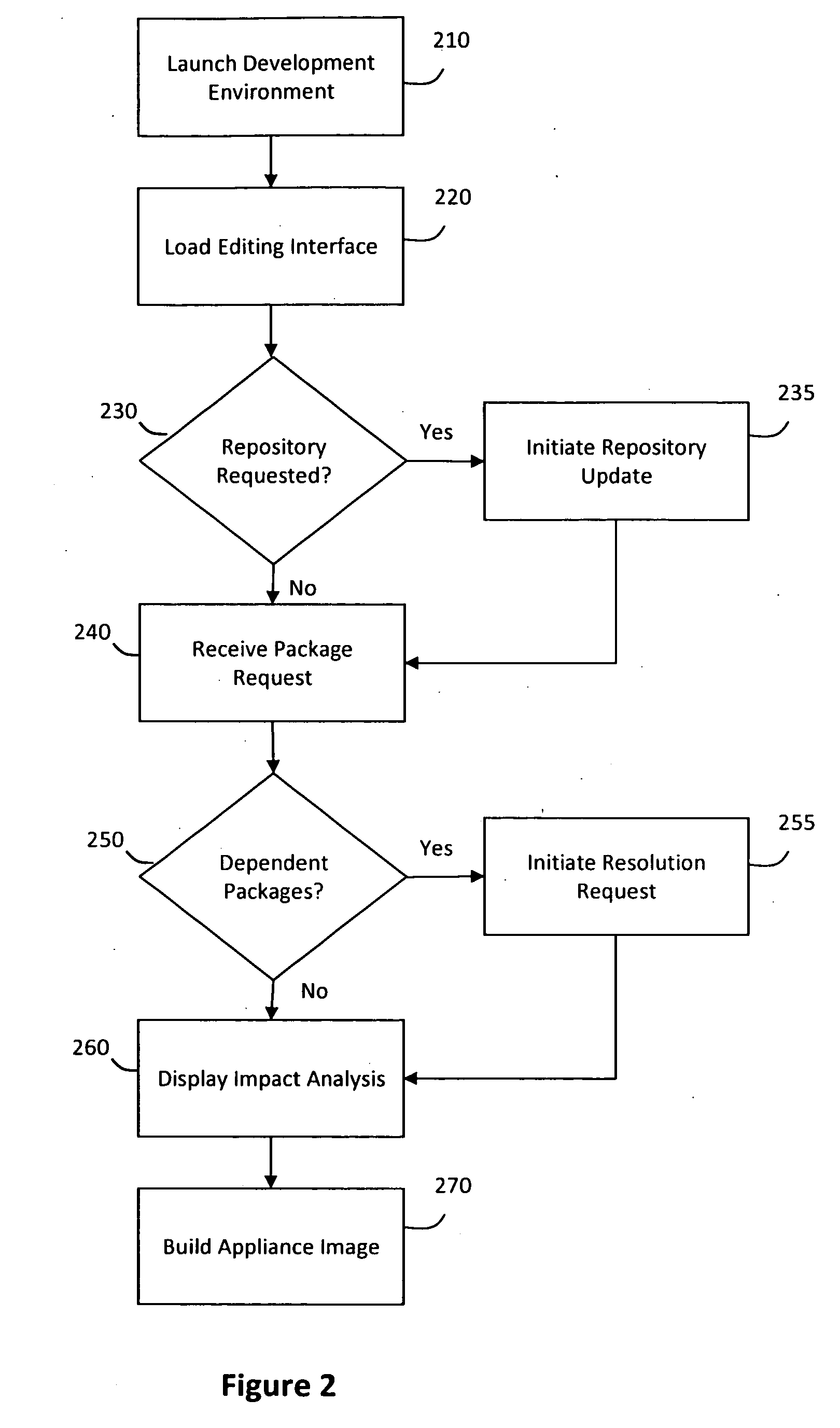
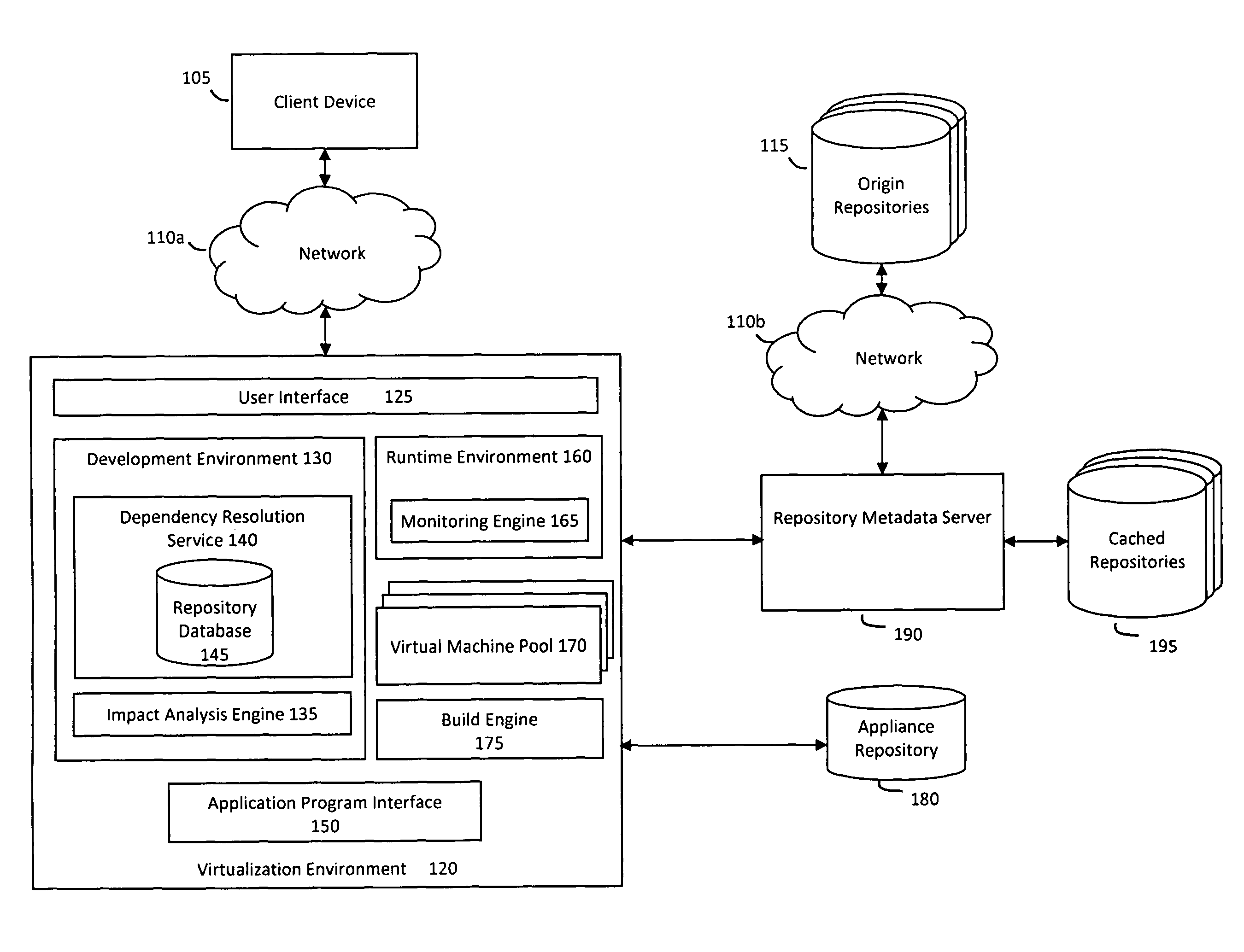
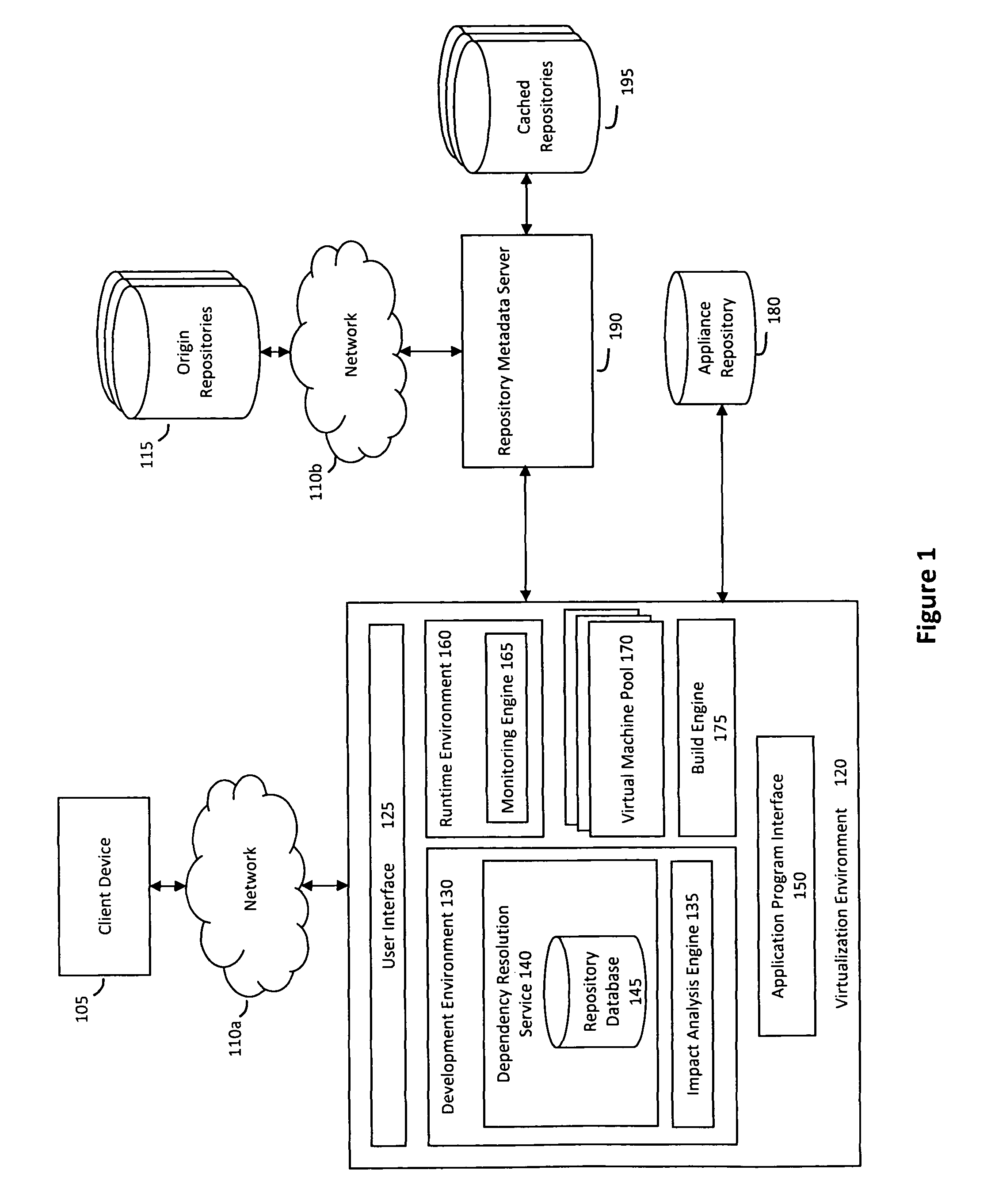
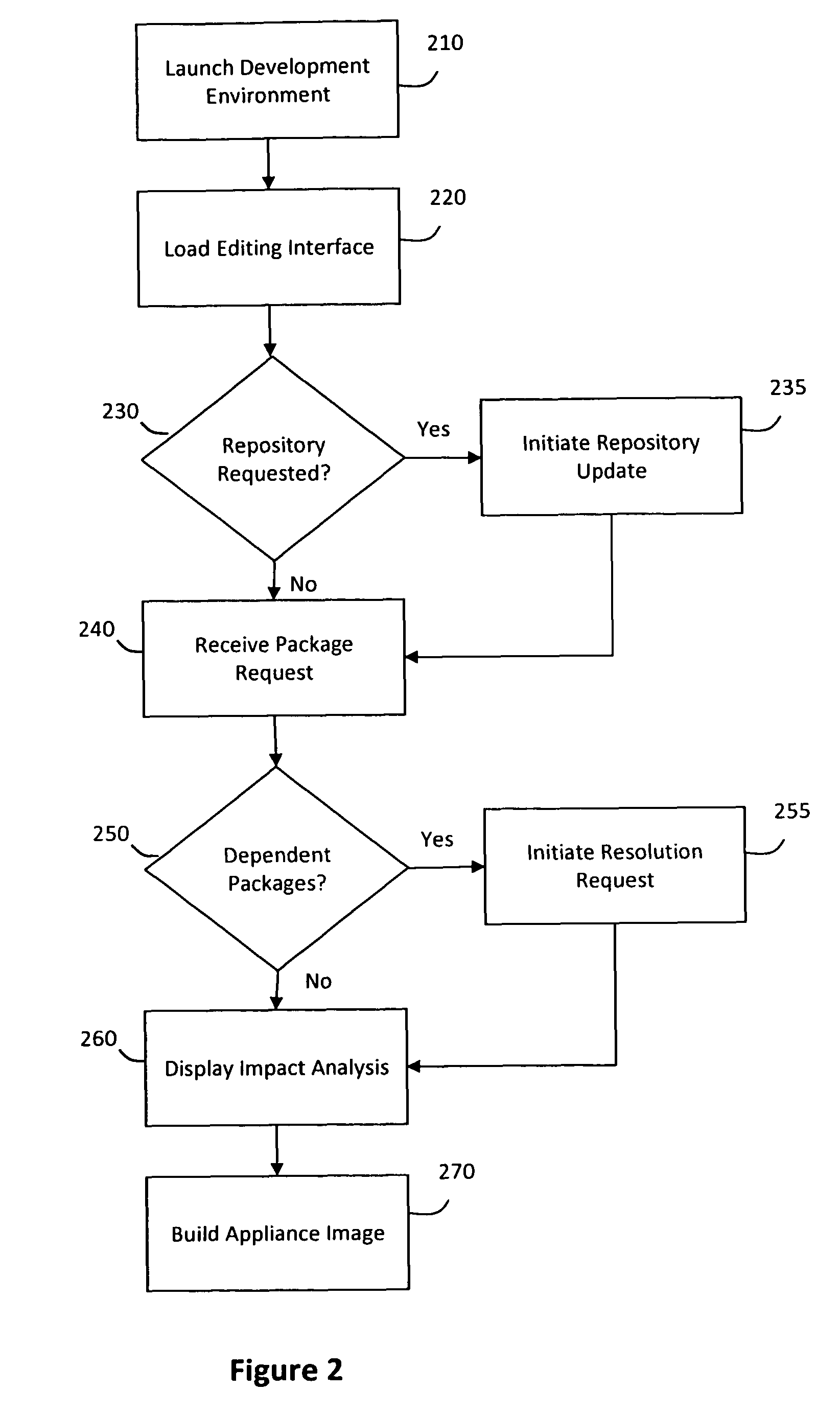
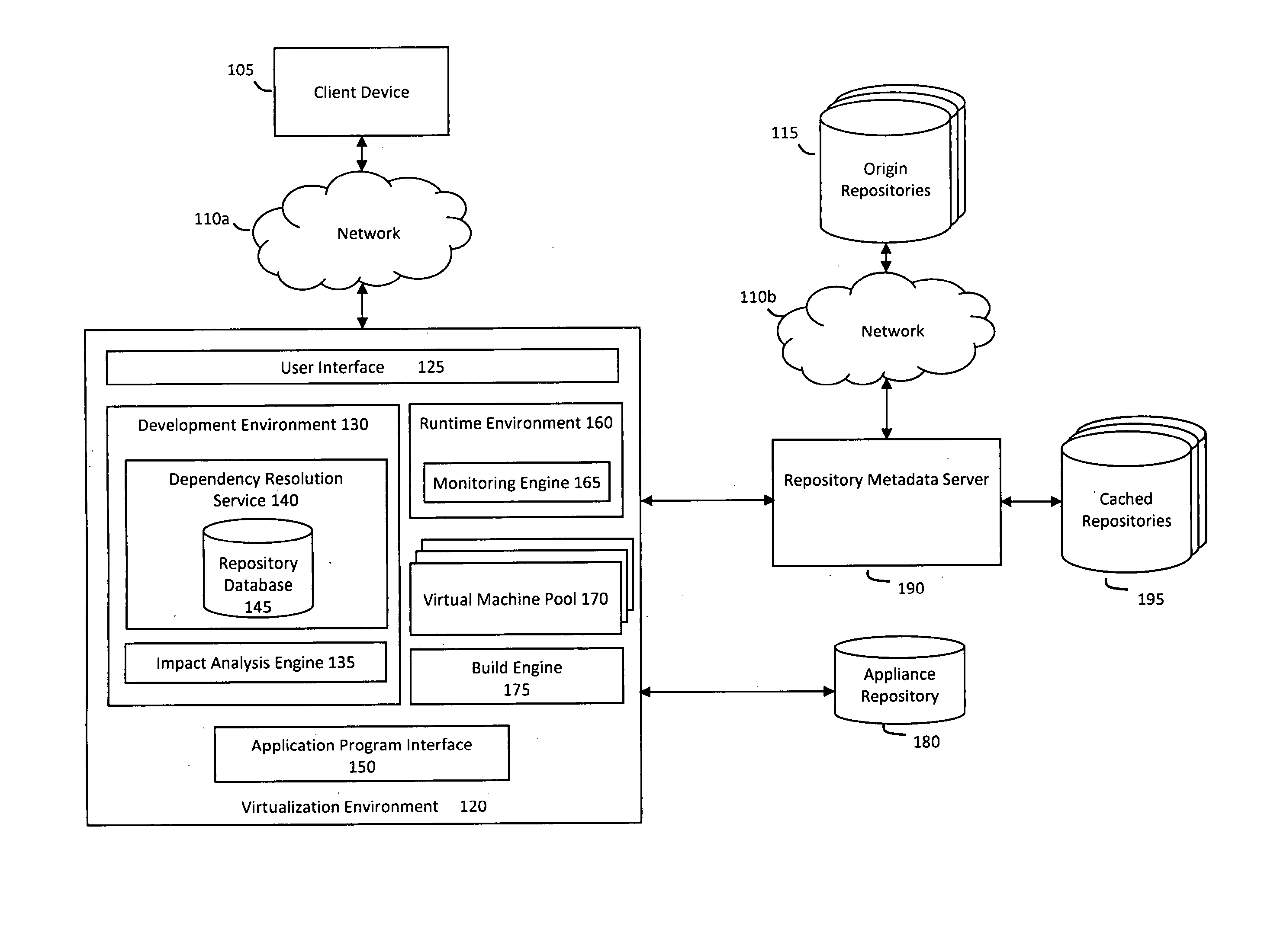
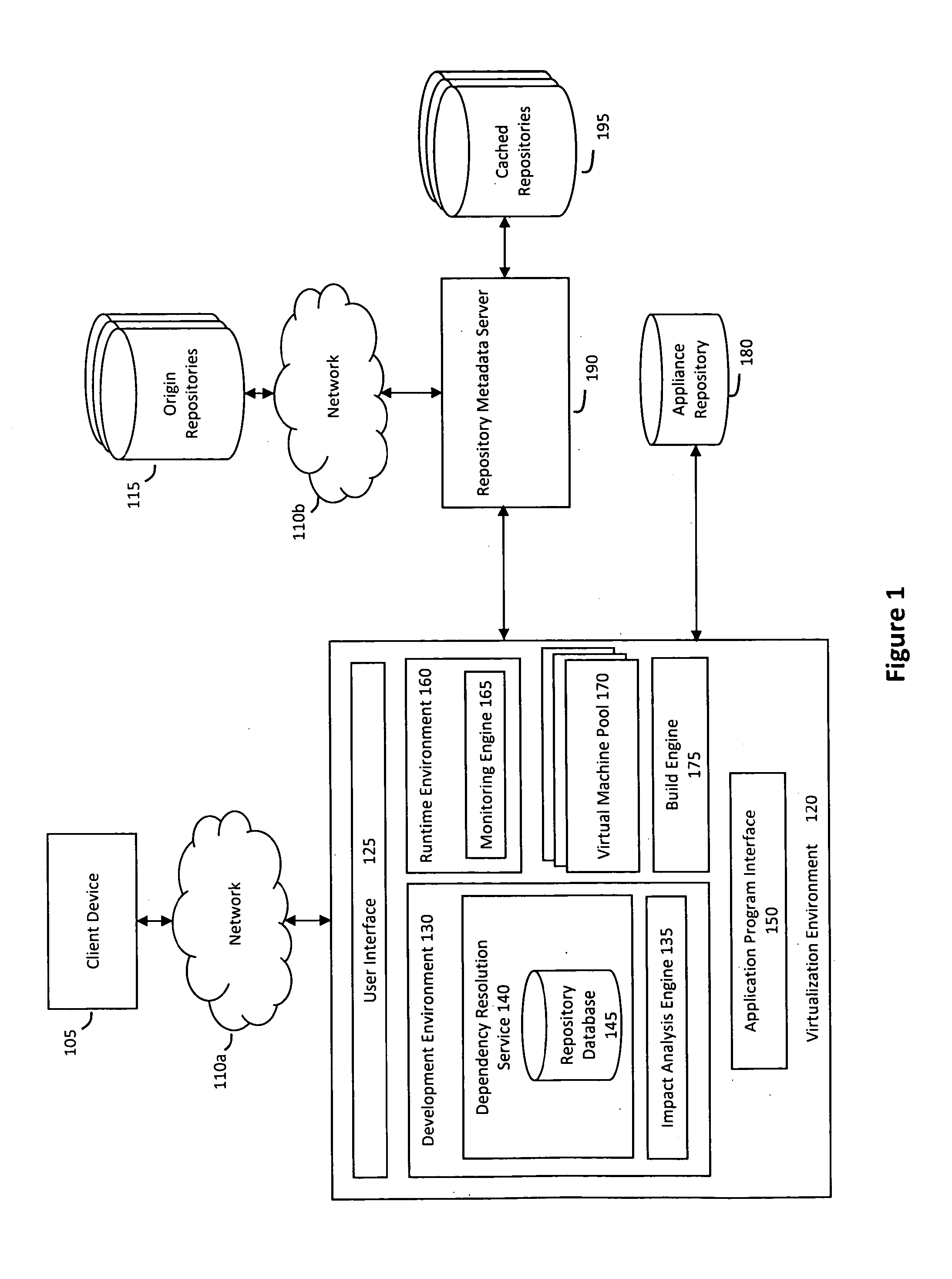
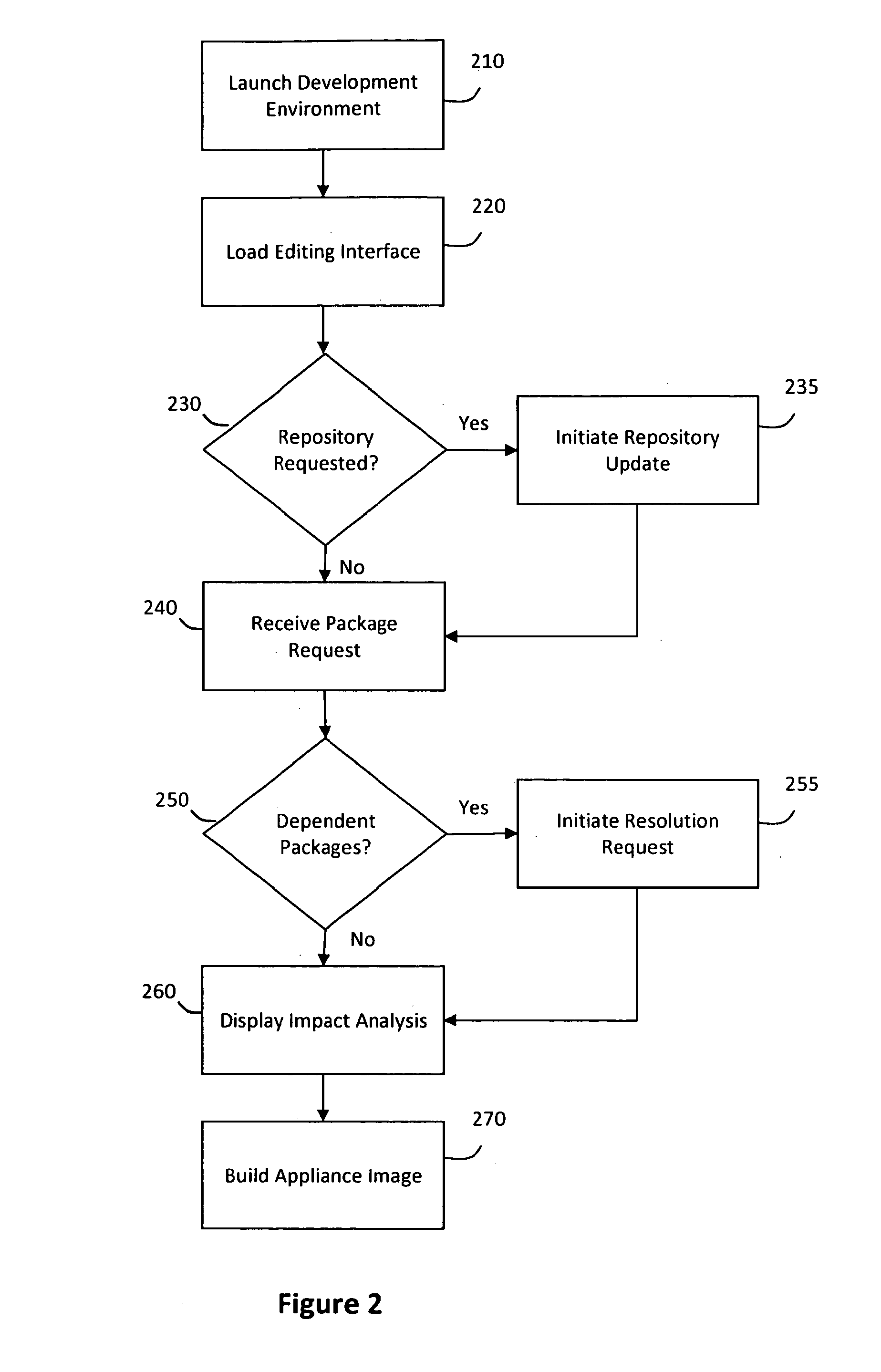
System and method for efficiently building virtual appliances in a hosted environment
ActiveUS20090300057A1Drawback can be addressedMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsFile systemHosting environment
A system and method for efficiently building virtual appliances in a hosted environment is provided. In particular, a plurality of image archives may be stored in a build database, with each image archive including a file system having a directory structure and a plurality of files installed within the directory structure. In response to a build request containing an image description, a build engine may create a file system layout defining a directory structure for an image. The build engine may then copy the file system for one of the image archives to the file system layout for the image, wherein the copied file system may provide a subset of the file system for the image. The build engine may then build the image, which may include a file system having various files installed within various directories in accordance with the directory structure defined for the image.
Owner:SUSE LLC
Systems and methods for providing seamless software compatibility using virtual machines
ActiveUS20060010433A1Specific program execution arrangementsMemory systemsModem deviceOperational system
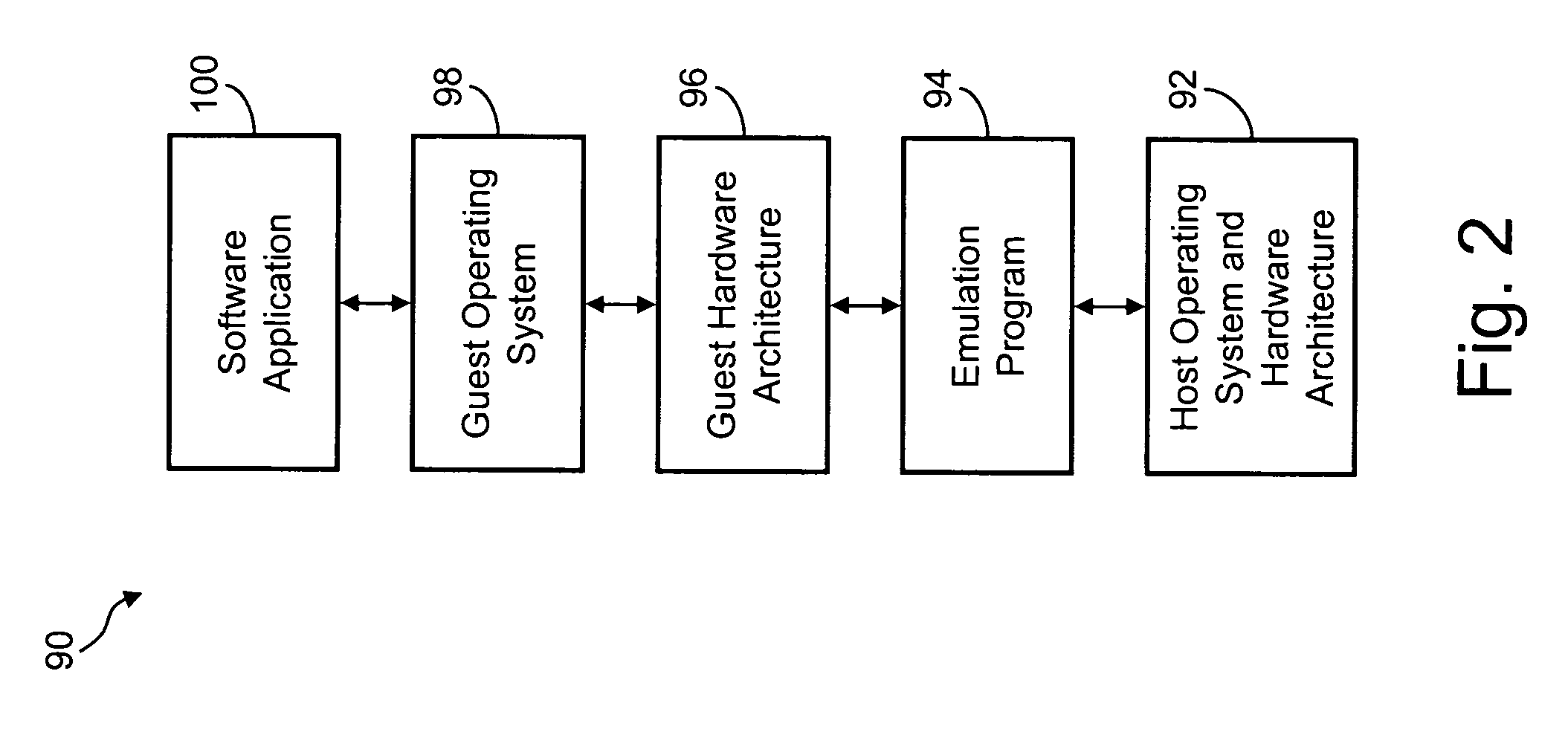
Certain embodiments of the present invention are directed to a system for and method of providing seamless software compatibility by using virtual machines to provide an improved, more seamless method of user interaction with one or more virtual machines (VMs) that are resident on a host computer system. Several embodiments of the present invention provide a means in the host environment for directly invoking one or more guest operating system (OS) applications or files and displaying them in the host environment, rather than in a separate VM window. Furthermore, each embodiment of the present invention allows the possibility of multiple applications on multiple OSs (i.e., legacy or modem OSs), respectively, to run simultaneously and with the appearance of running seamlessly in the host environment.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Securing stored content for trusted hosts and safe computing environments
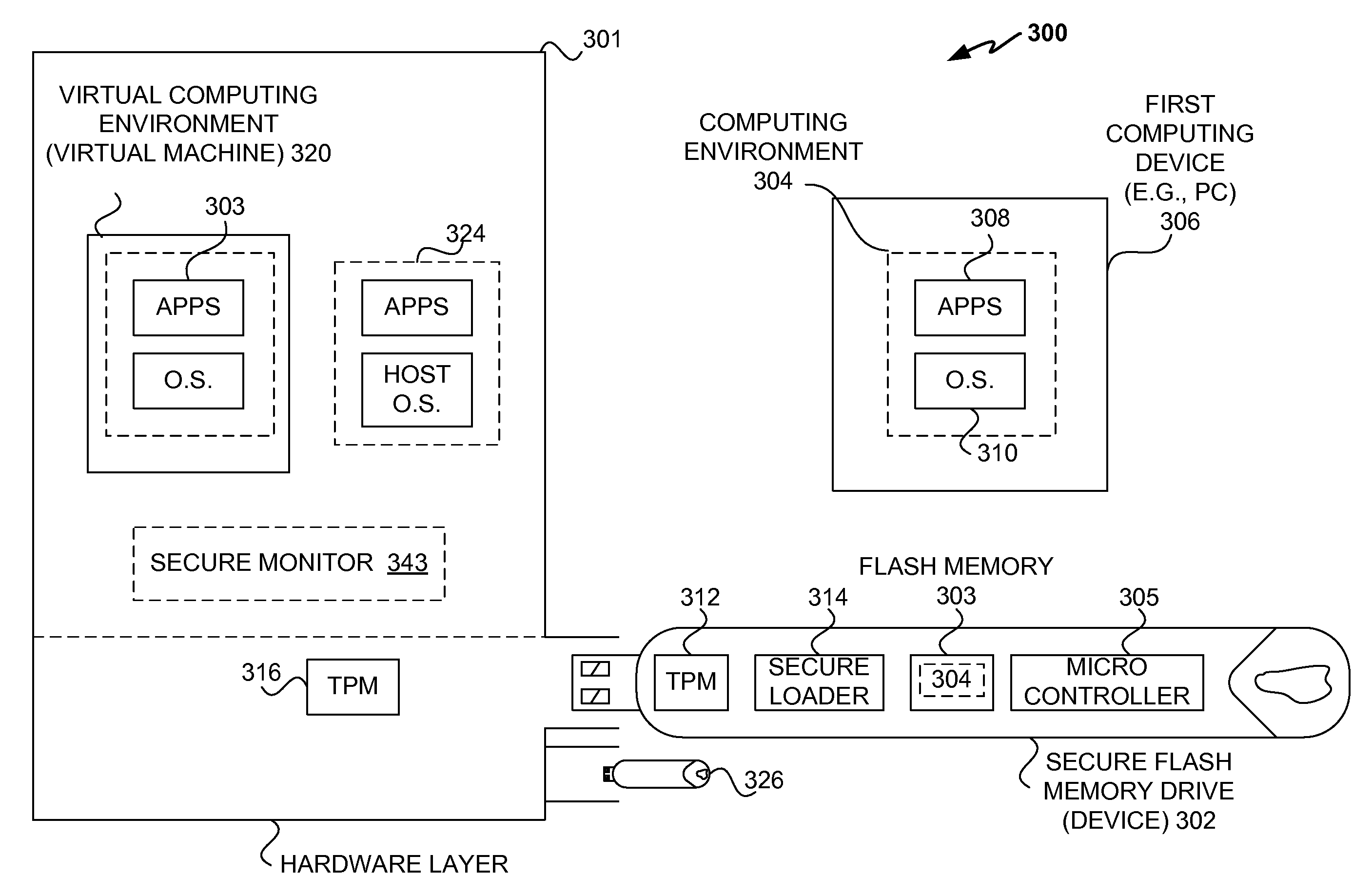
InactiveUS20090049510A1Safe computing environmentEasy to usePublic key for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsHosting environmentComputer science
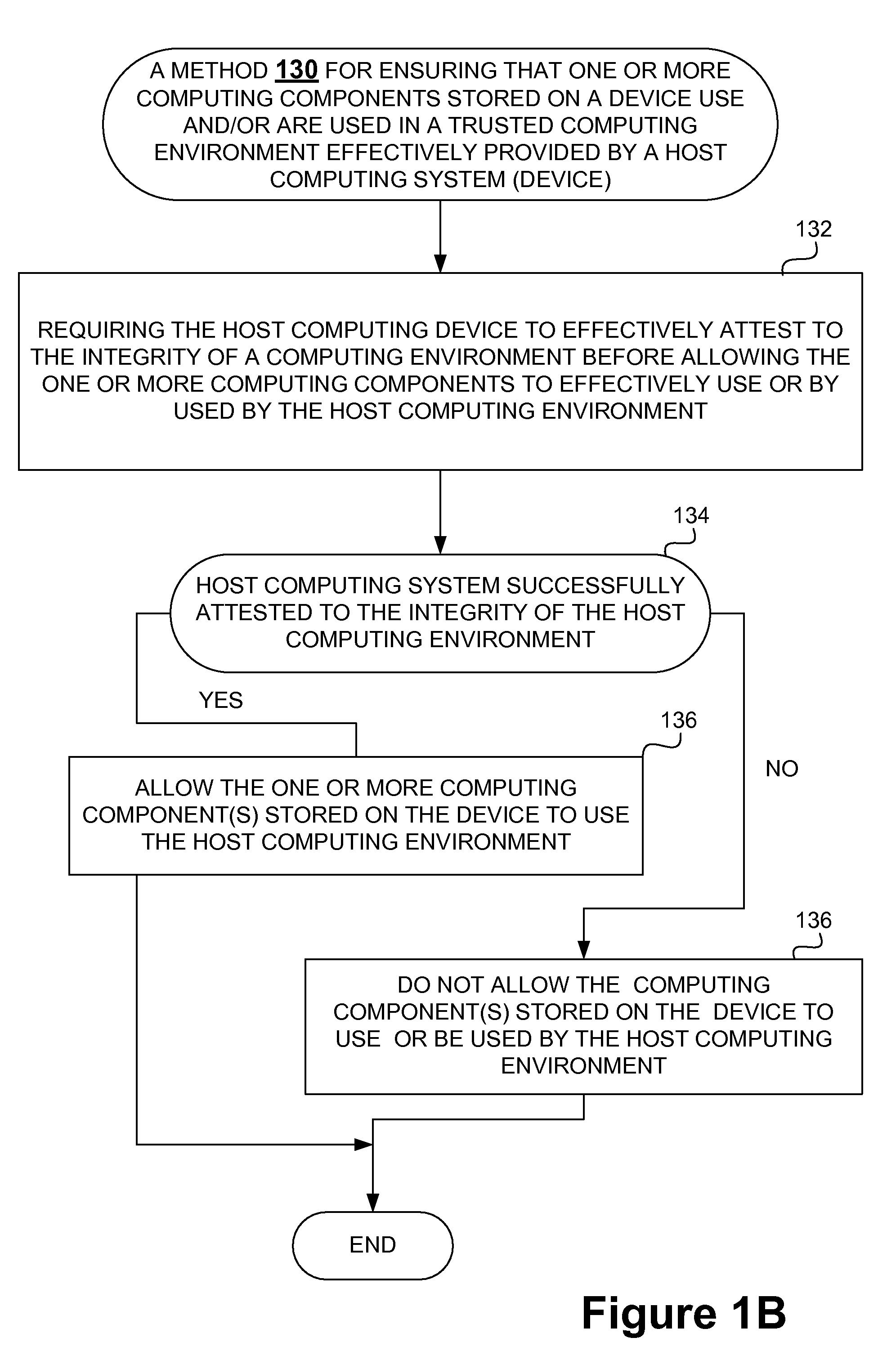
Techniques for protecting content to ensure its use in a trusted environment are disclosed. The stored content is protected against harmful and / or defective host (or hosted) environments. A trusted security component provided for a device can verify the internal integrity of the stored content and the host before it allows the content to come in contact with the host. As a counter part, a trusted security component provided for the host can verify and attest to the integrity of the host and / or specific host computing environment that can be provided for the content stored in the device. The trusted security component provided for a device effectively verify the host integrity based on the information attested to by the trusted security component provided for the host. If the trusted security component trusts the host, it allows the trusted host to provide a trusted host computing environment trusted to be safe for the content stored in the device. A trusted host can effectively provide a safe virtual environment that allows a content representing a copy (or image) of an original computing environment to operate on the host computing system to give a similar appearance as the original computing environment.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
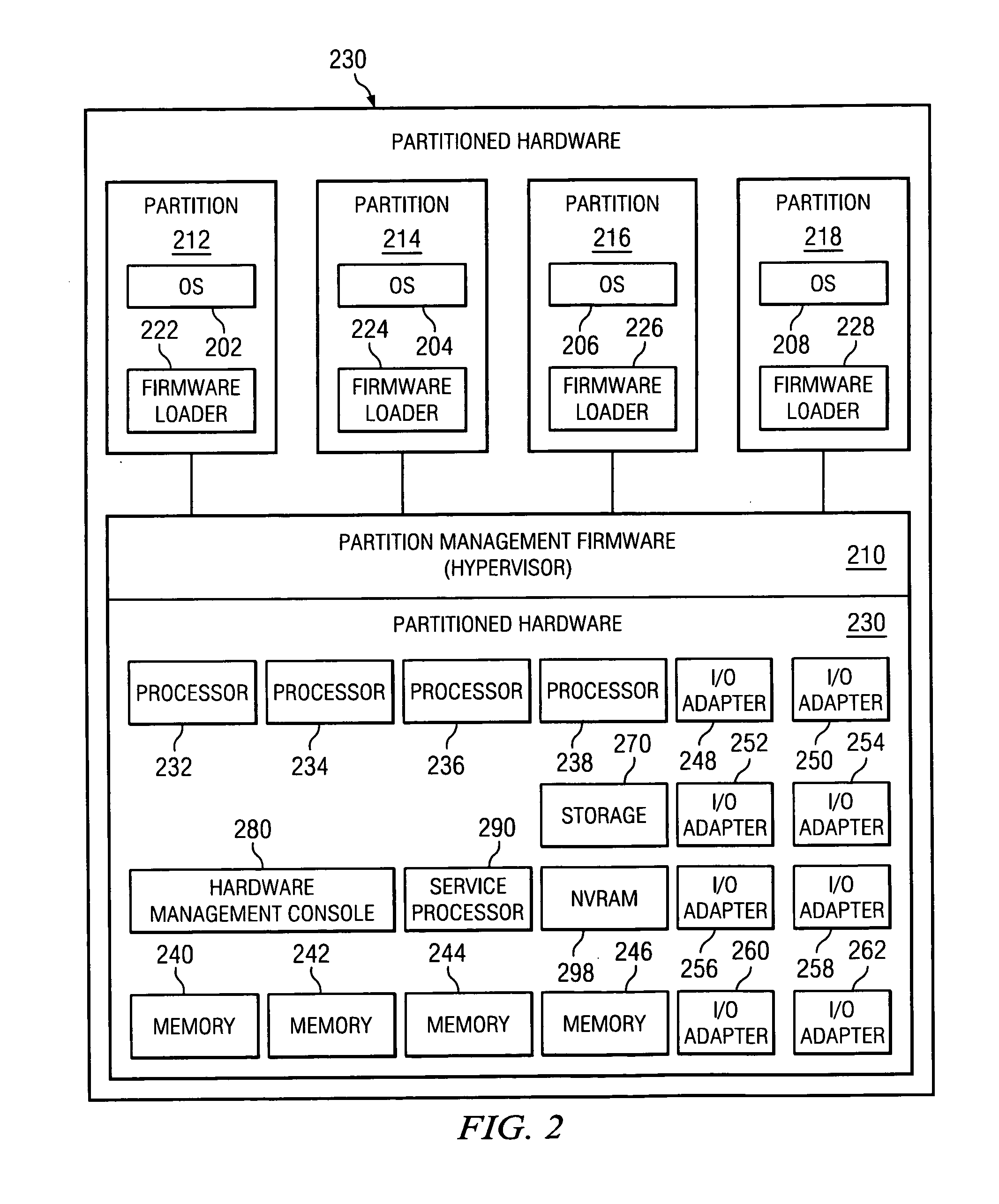
System and method for adapting a system configuration of a first computer system for hosting on a second computer system
ActiveUS8219653B1Digital computer detailsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationOperational systemHosting environment
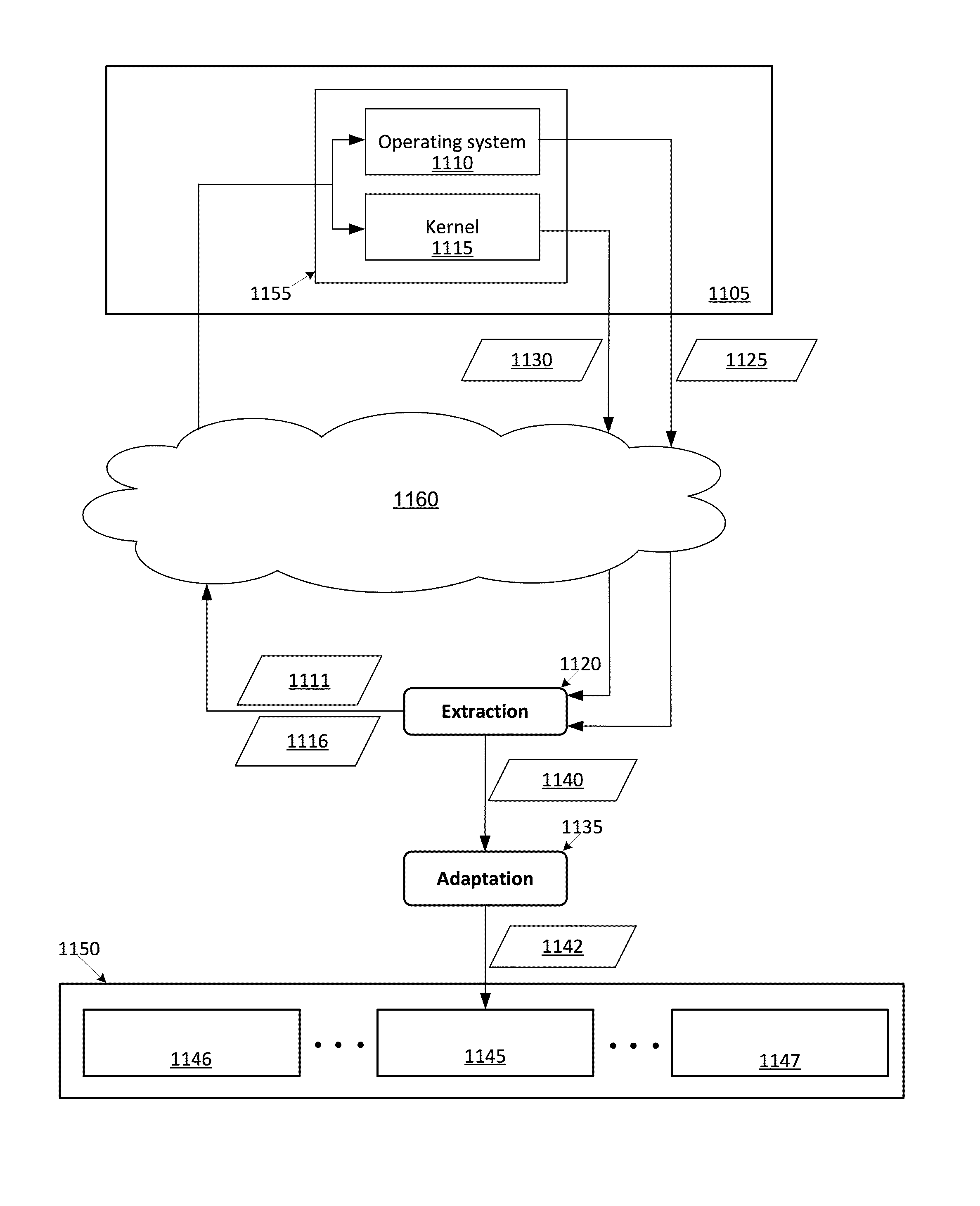
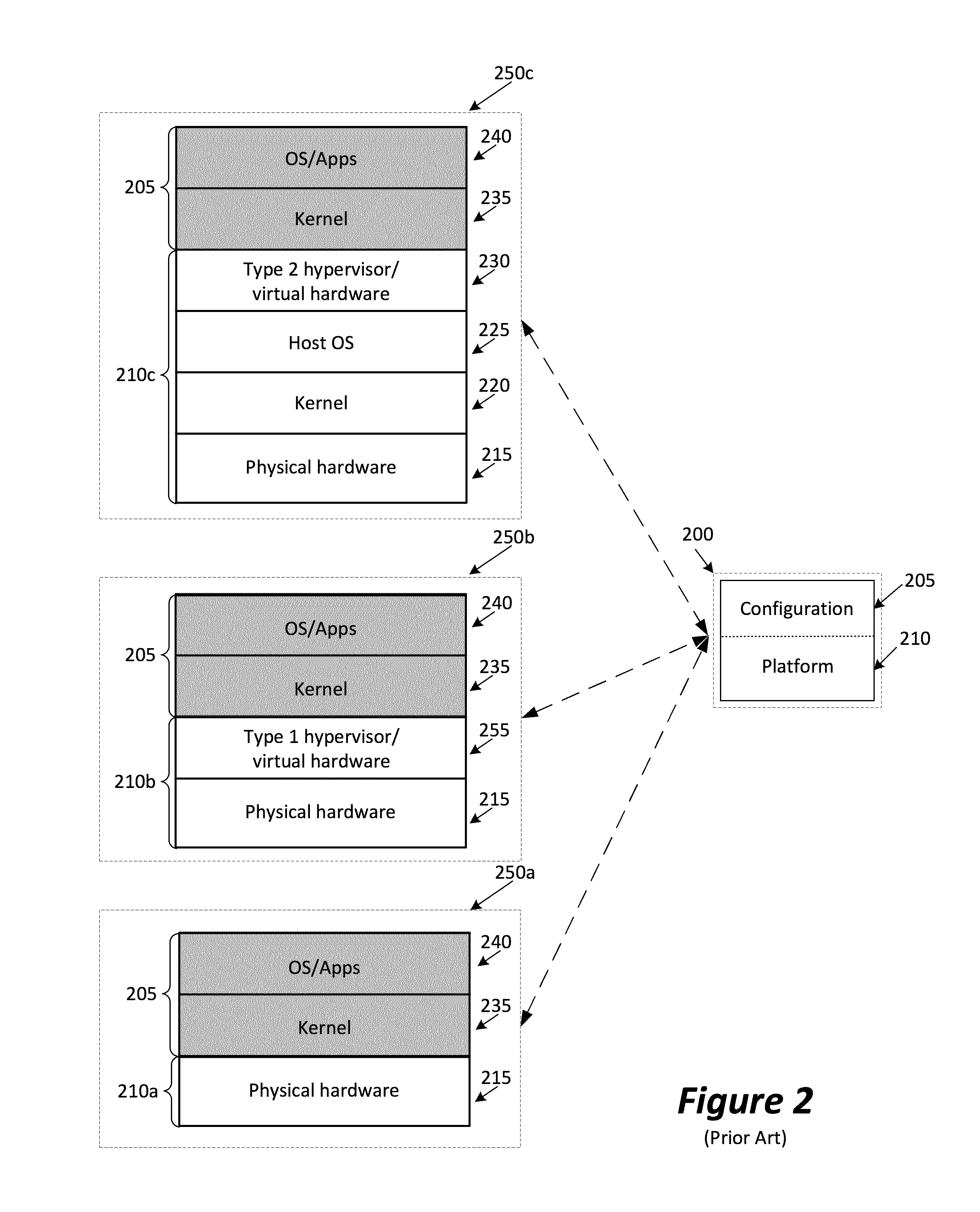
Some embodiments provide a method for a server hosting environment having several nodes. Each node is for using one or more hypervisors in order to host several configurations of several computer systems. The method receives a first configuration of a computer system. The first configuration includes an operating system that directly accesses hardware of the computer system. The method generates a second configuration that is based on the first configuration. The second configuration includes the first configuration modified to be operable on a particular hypervisor of a particular node in the several nodes. The method installs the second configuration on the particular node in order to allow the particular node to operate on the second configuration in conjunction with the particular hypervisor. The second configuration accesses a set of virtual hardware provided by the particular hypervisor.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
System and method for modeling and dynamically deploying services into a distributed networking architecture
InactiveUS20060029054A1Avoid disadvantagesMultiplex system selection arrangementsCircuit switching systemsHosting environmentNetwork architecture
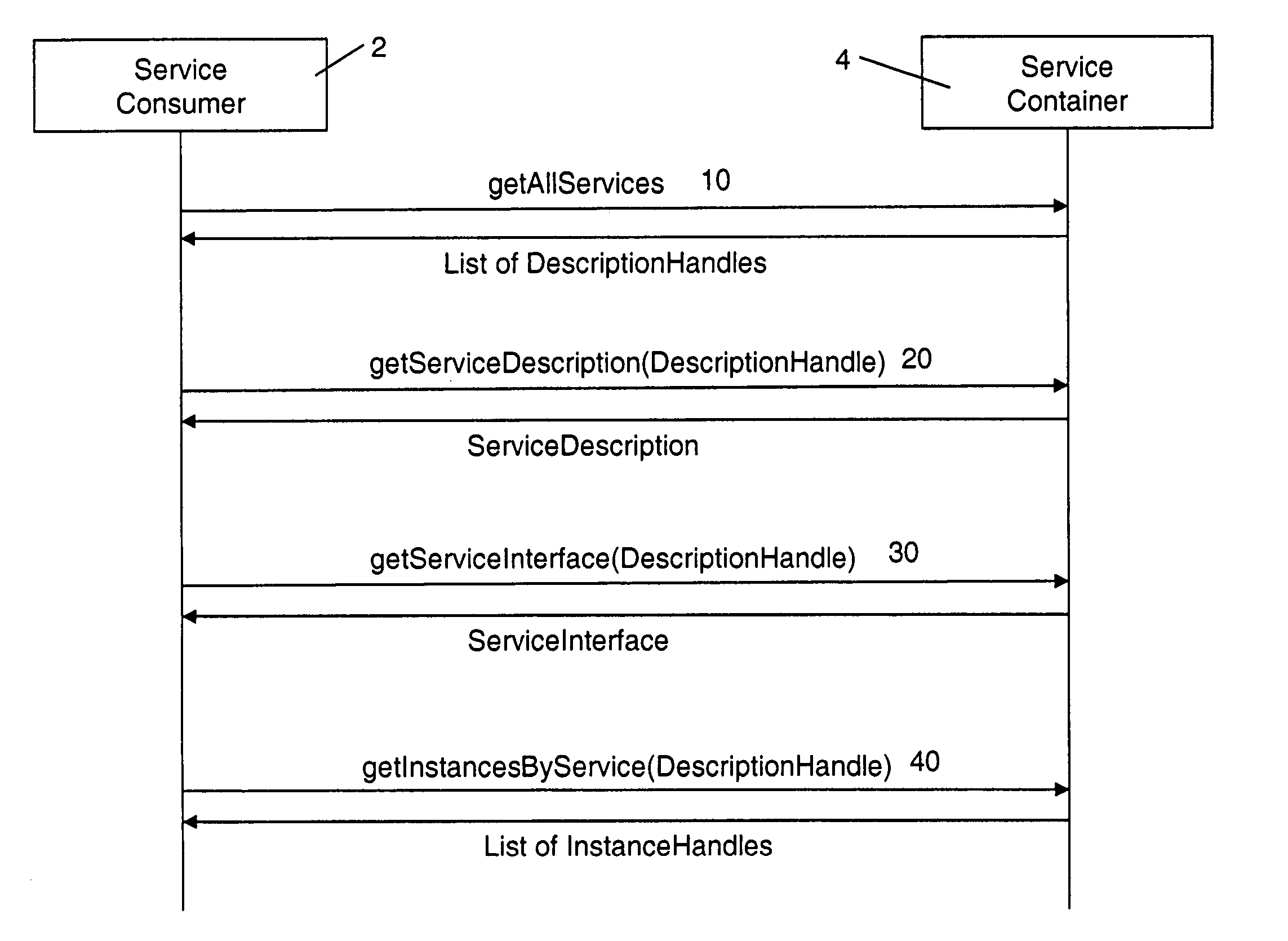
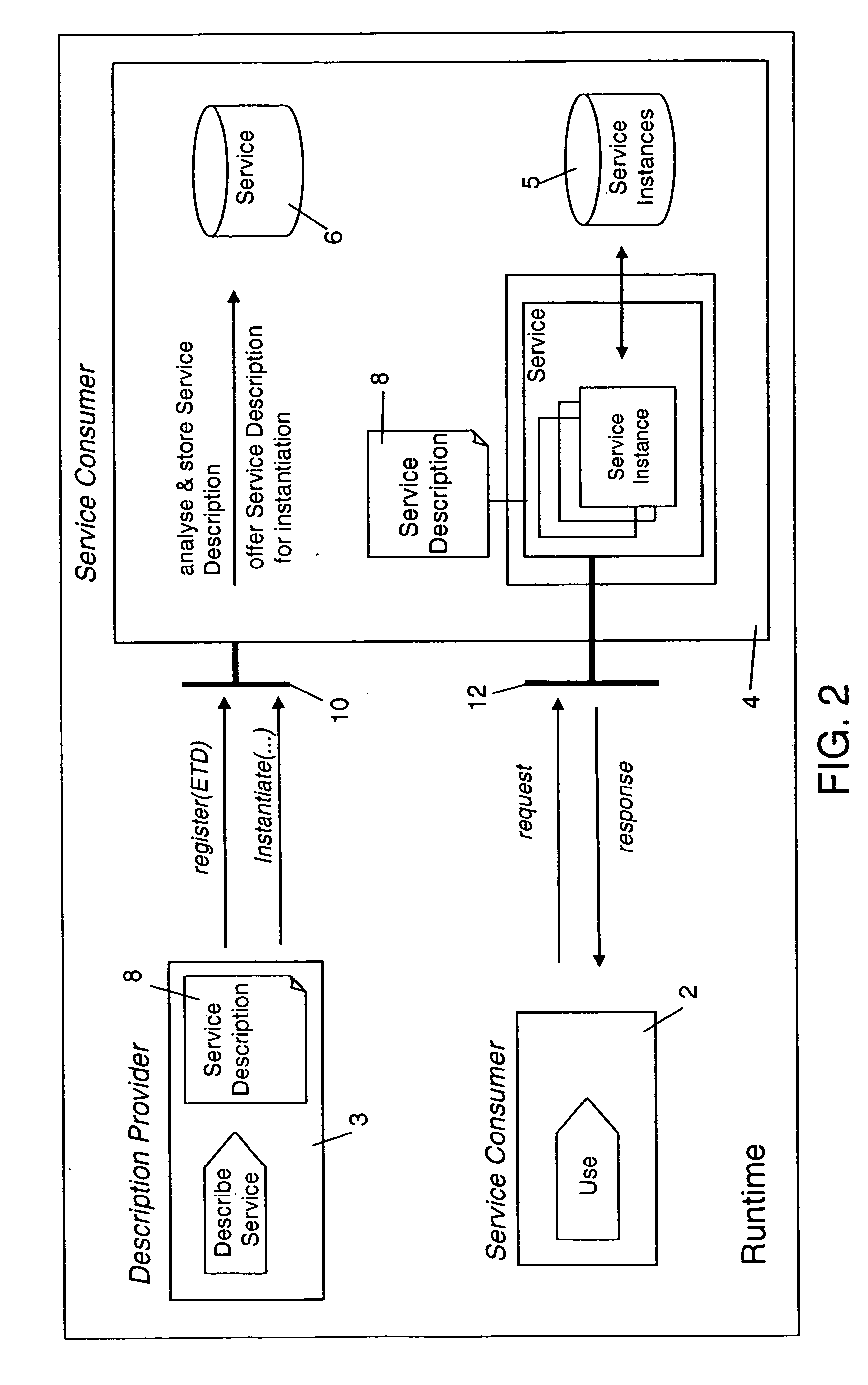
The present invention describes a new system and method for modeling and dynamically deploying services into a distributed networking architecture, especially in a service-oriented architecture. The service container being part of distributed networking architecture exposes its functionality as services. It provides a registration service for deploying service descriptions. Having created a new service description in any declarative description language (i.e. a description of a (stateful) service e.g. a stateful Web service), the description provider invokes the registration service at the service container that allows to register (i.e. deploy) that new service description during runtime without restarting service container. The service container is responsible to analyze and check the submitted new service description for validity, to store the service description and to make it available for interested services consumers for instantiation. If a new service has been successfully registered, a new service interface for accessing that new service is automatically created by the service container. Interested services consumers may query the hosting environment for the available services being hosted and to subsequently instantiate a new service. A service consumer may then invoke any exposed service operation on a given service instance which generally follows a request response pattern.
Owner:IBM CORP
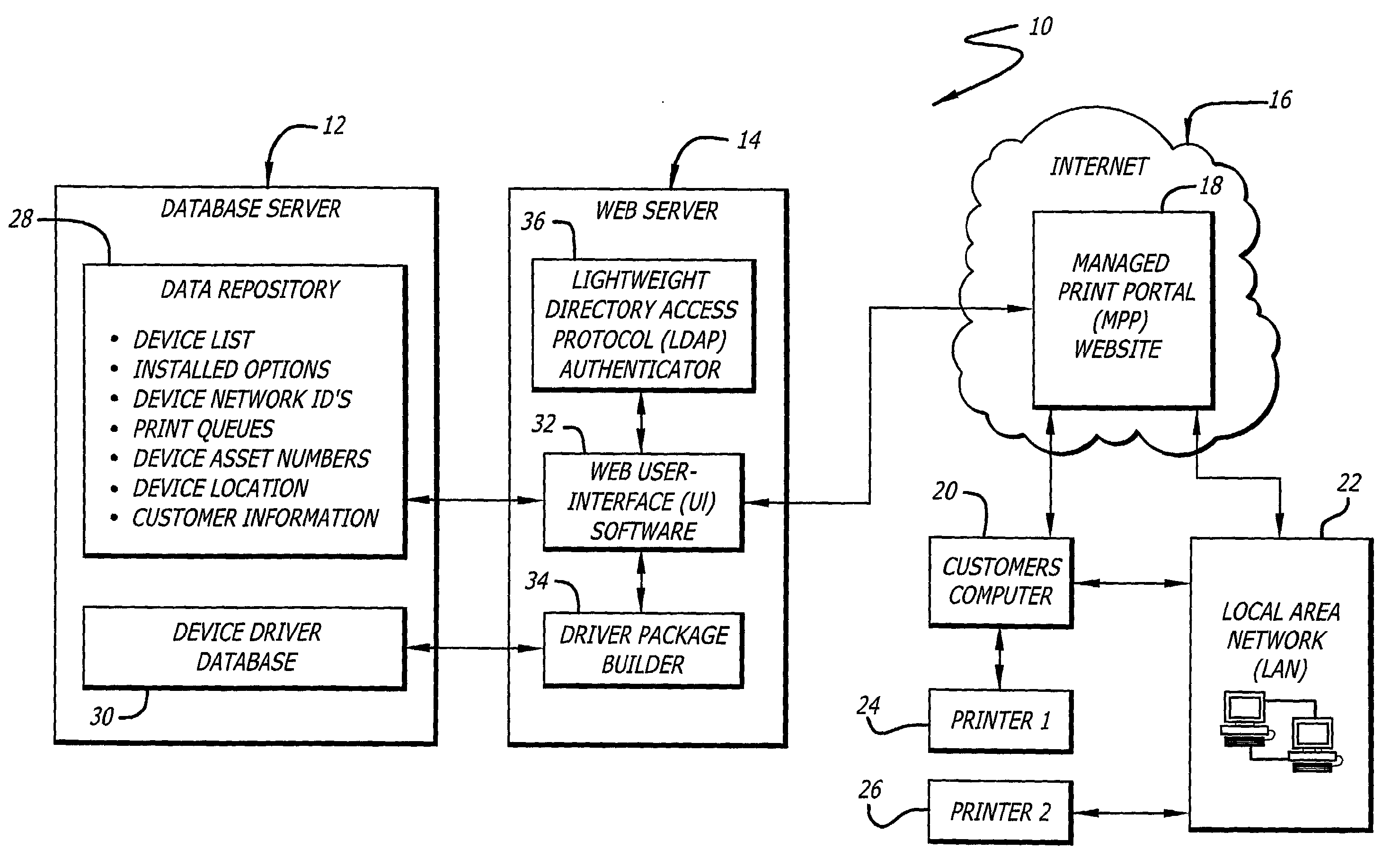
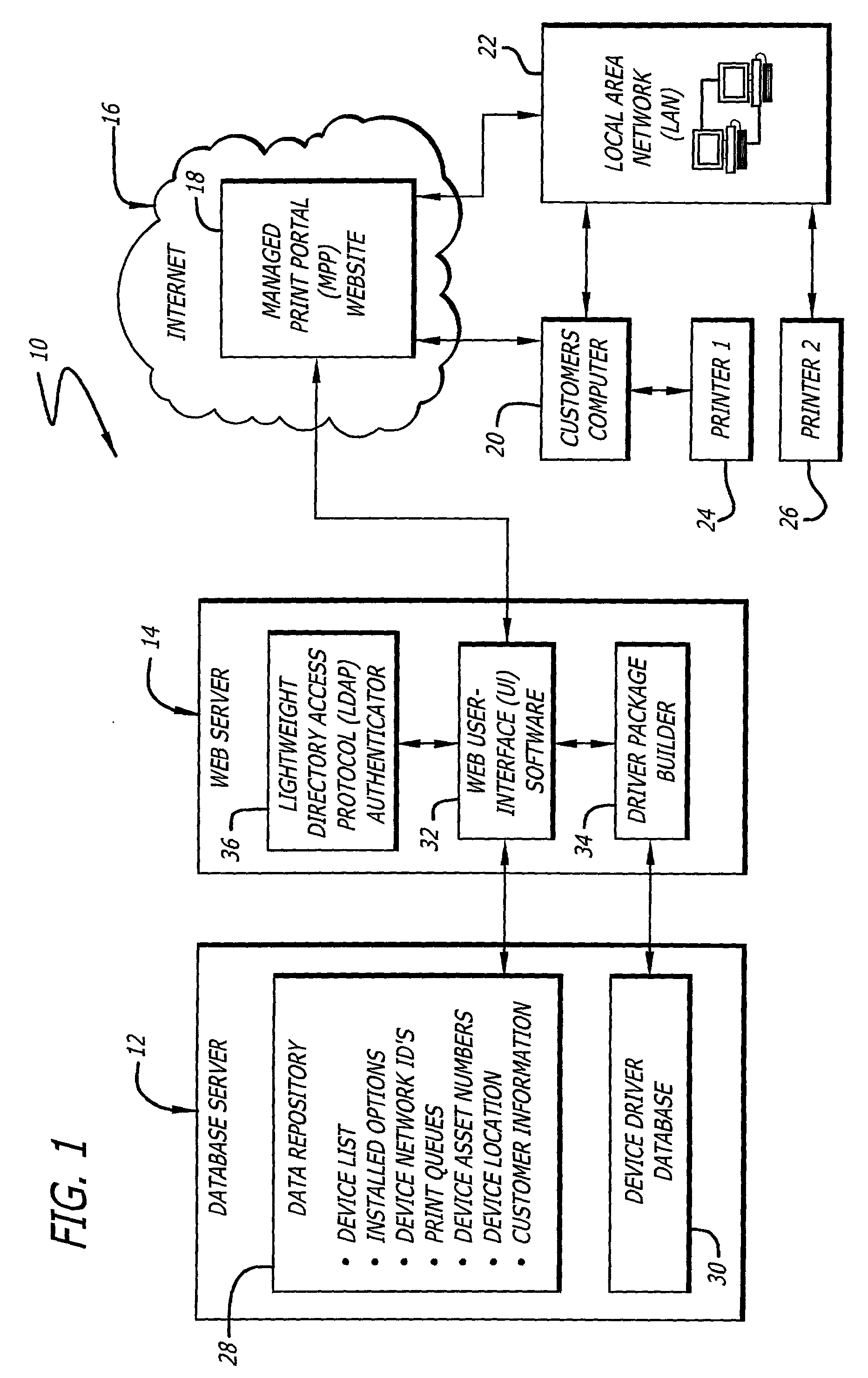
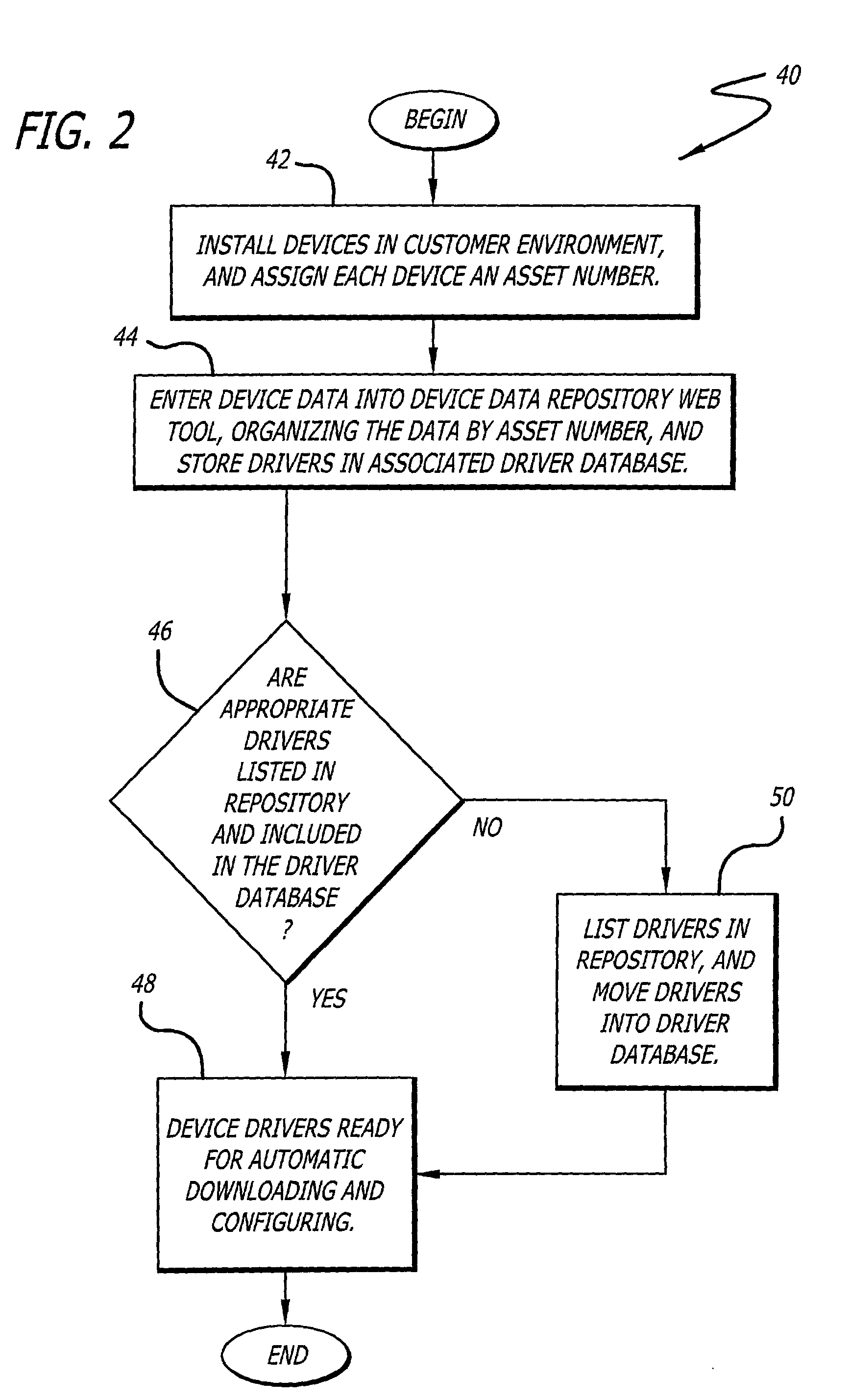
System and method for efficiently installing and configuring device drivers in managed environments
A system for facilitating selection, installation, and configuration of device drivers in a managed environment. The system includes a first mechanism for automatically accessing information about a device for which a driver is to be installed on a computer connected thereto and providing a signal in response thereto. The information includes device type and operational capabilities. A second mechanism selects a driver for the device and installs and automatically configures the driver on the computer based on the signal. In a specific embodiment, the first mechanism includes a database that maintains the information, which is organized according to an asset identification number. The information includes first and second portions. The first portion of information is obtained and entered in the database upon installation of the device. The second portion of the information includes operating system and language information pertaining to the computer. The second mechanism includes a website portal accessible by via the computer for enabling downloading of the driver. The second portion of the information is obtained from headers that are automatically supplied to website portal user-interface software by a browser running on the computer and accessing the website portal. The user-interface software runs on the website portal and enables the user to enter the asset identification number into the website portal. The asset number enables the website portal to automatically select and / or build an appropriate driver package.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Conformance specification and checking for hosting services
InactiveUS20150261842A1Fulfil requirementsEasy to manageDigital data processing detailsRelational databasesProgramming languageHosting environment
One or more requirements of a target hosting environment are captured in a specification. The specification is automatically checked against a source content of a source environment with a conformance checker, where the source content is to be migrated to the target hosting environment. It is determined whether the source content conforms to the specification.
Owner:IBM CORP
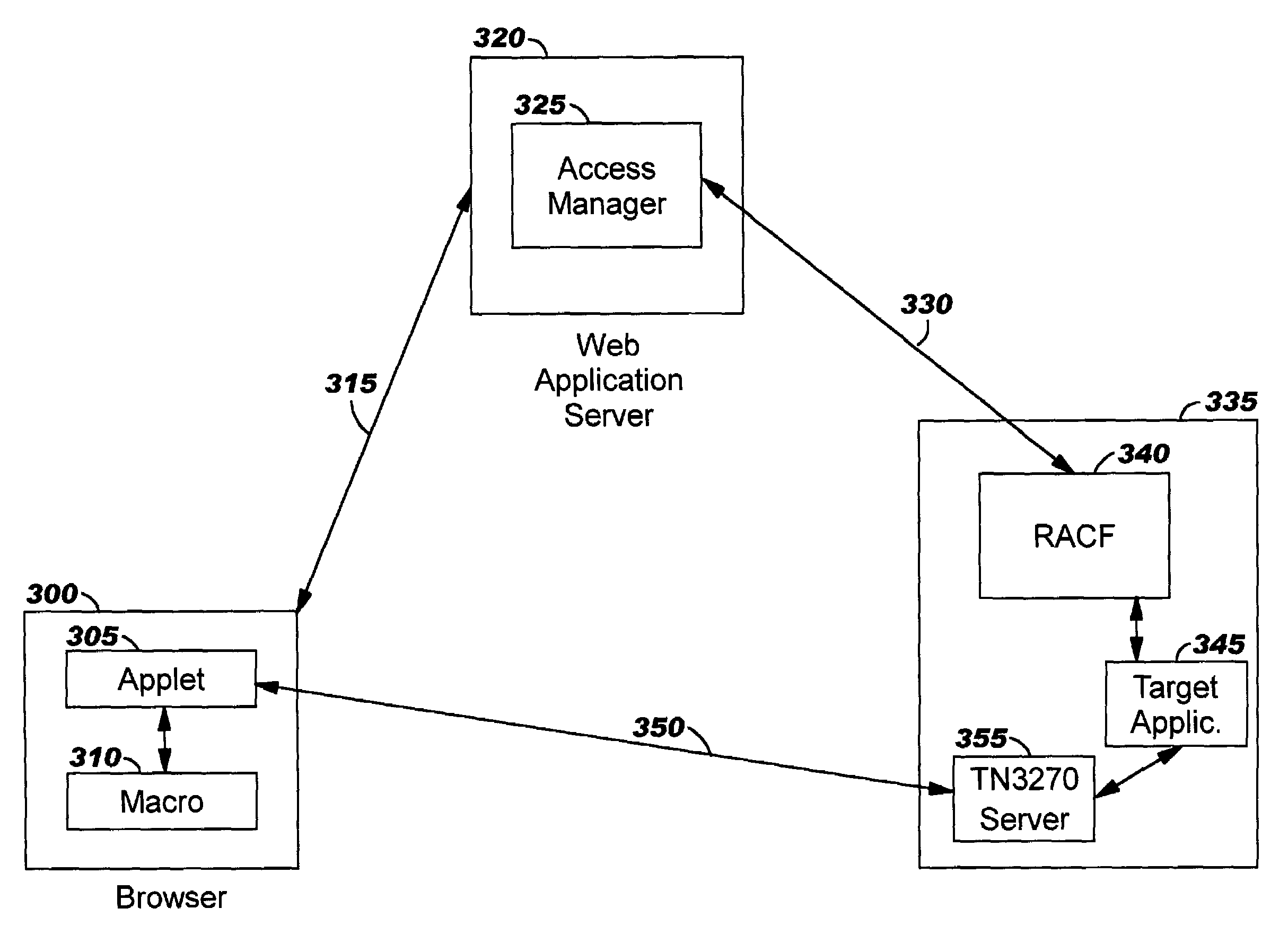
Integrating legacy application/data access with single sign-on in a distributed computing environment
ActiveUS7426642B2Conveniently and securely accessDigital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsModem deviceData stream
The present invention provides methods, systems, computer program products, and methods of doing business whereby legacy host application / system access is integrated with single sign-on in a modem distributed computing environment. A security token used for signing on to the modem computing environment is leveraged, and is mapped to user credentials for the legacy host environment. These user credentials are programmatically inserted into a legacy host data stream, thereby giving the end user the look and feel of seamless access to all applications / systems, including not only modem computing applications / systems but also those residing on (or accessible through) legacy hosts. In addition to providing users with the advantages of single sign-on, the disclosed techniques enable limiting the number of user identifiers and passwords an enterprise has to manage.
Owner:HULU
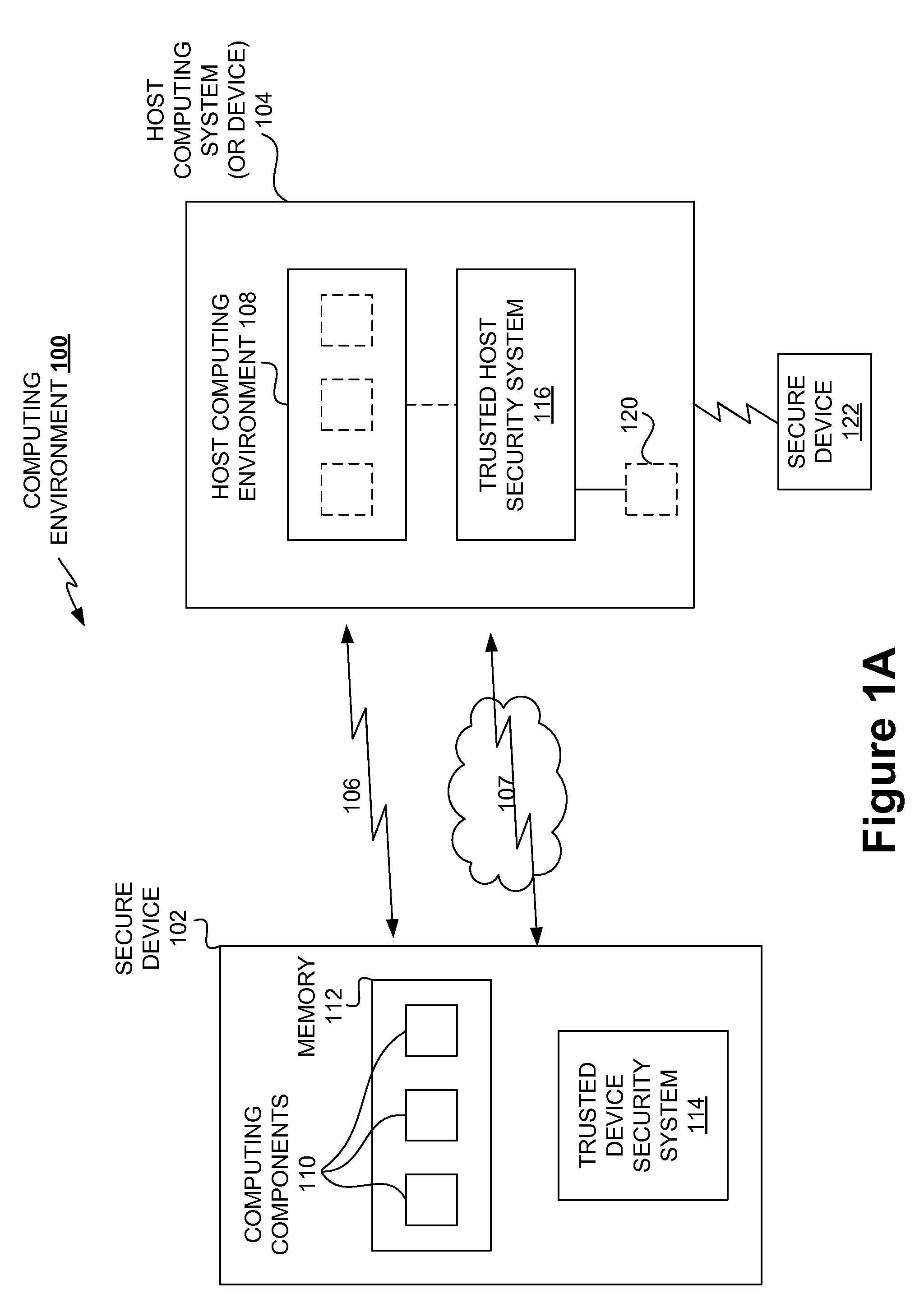
System for providing secure and trusted computing environments
ActiveUS7716720B1Provide partEnvironment safetyDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationTrusted ComputingComputer module
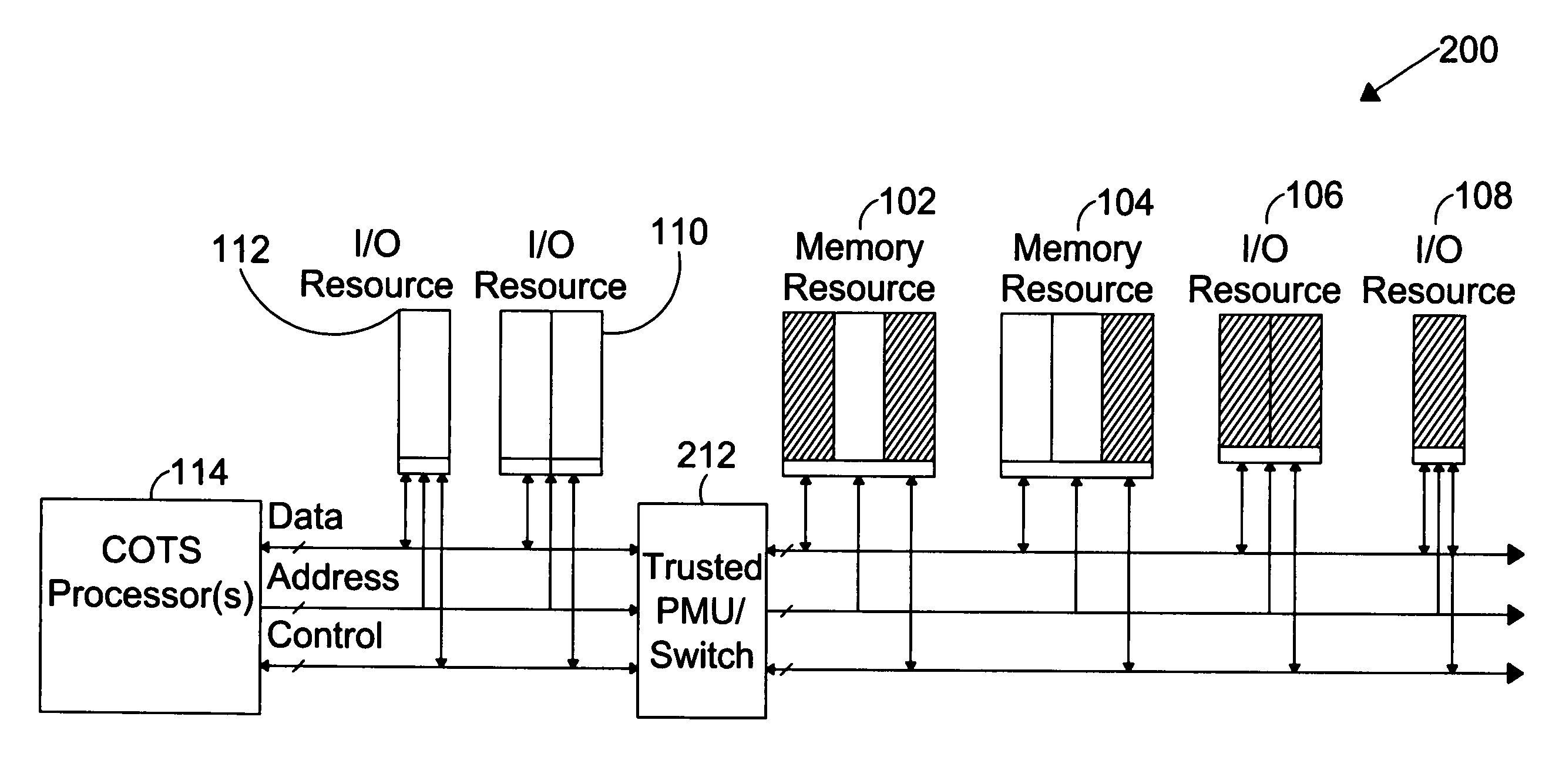
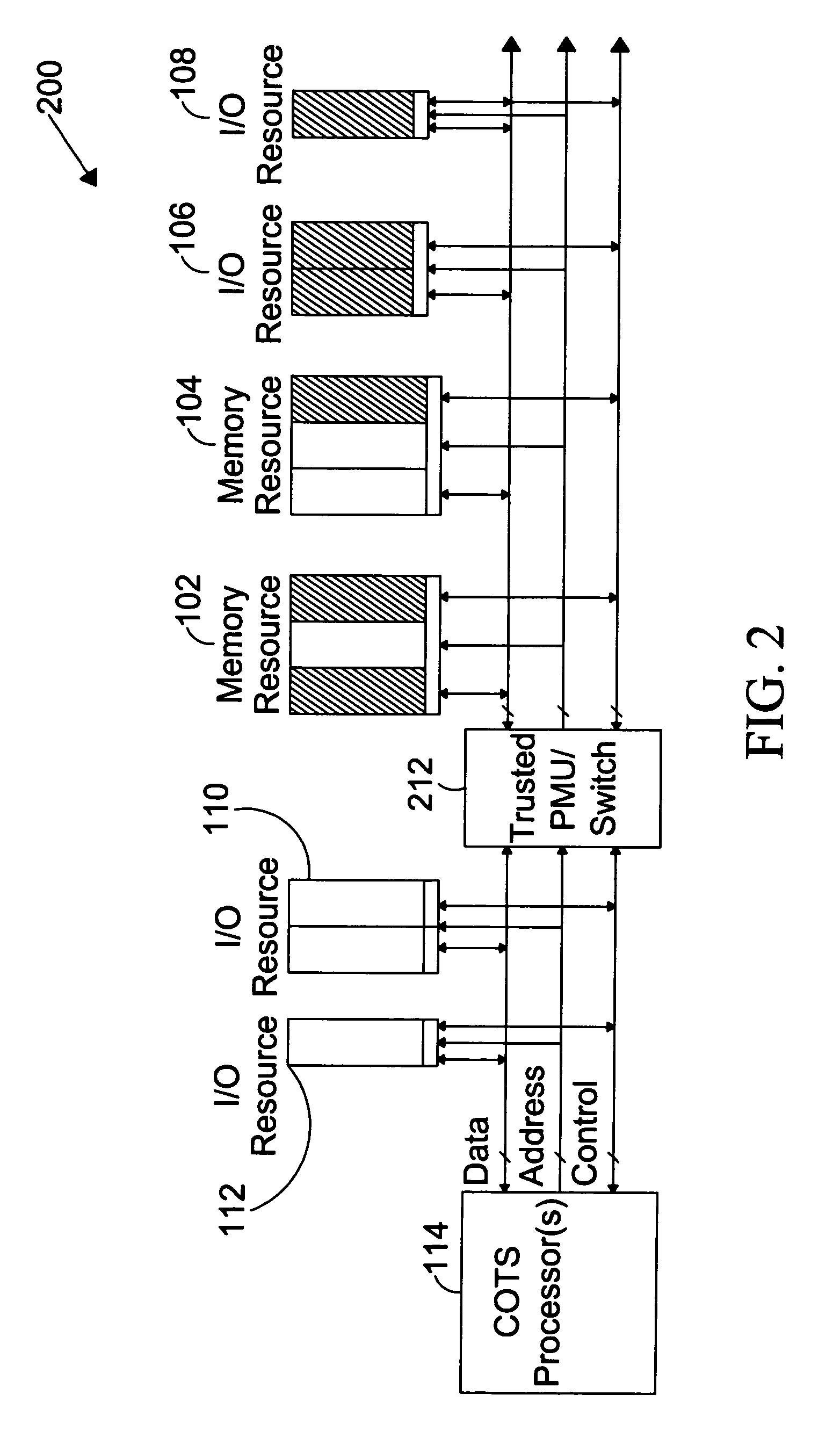
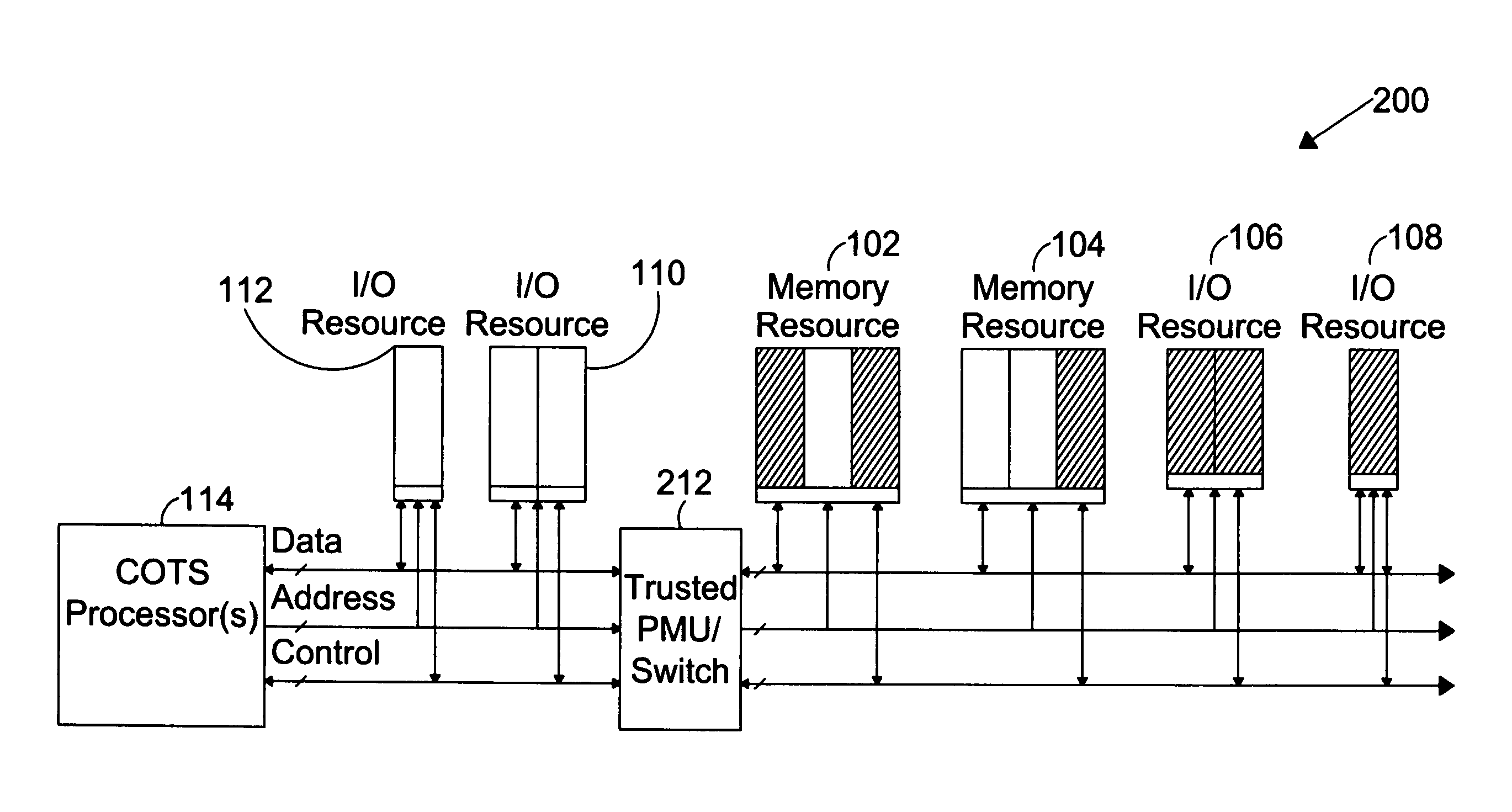
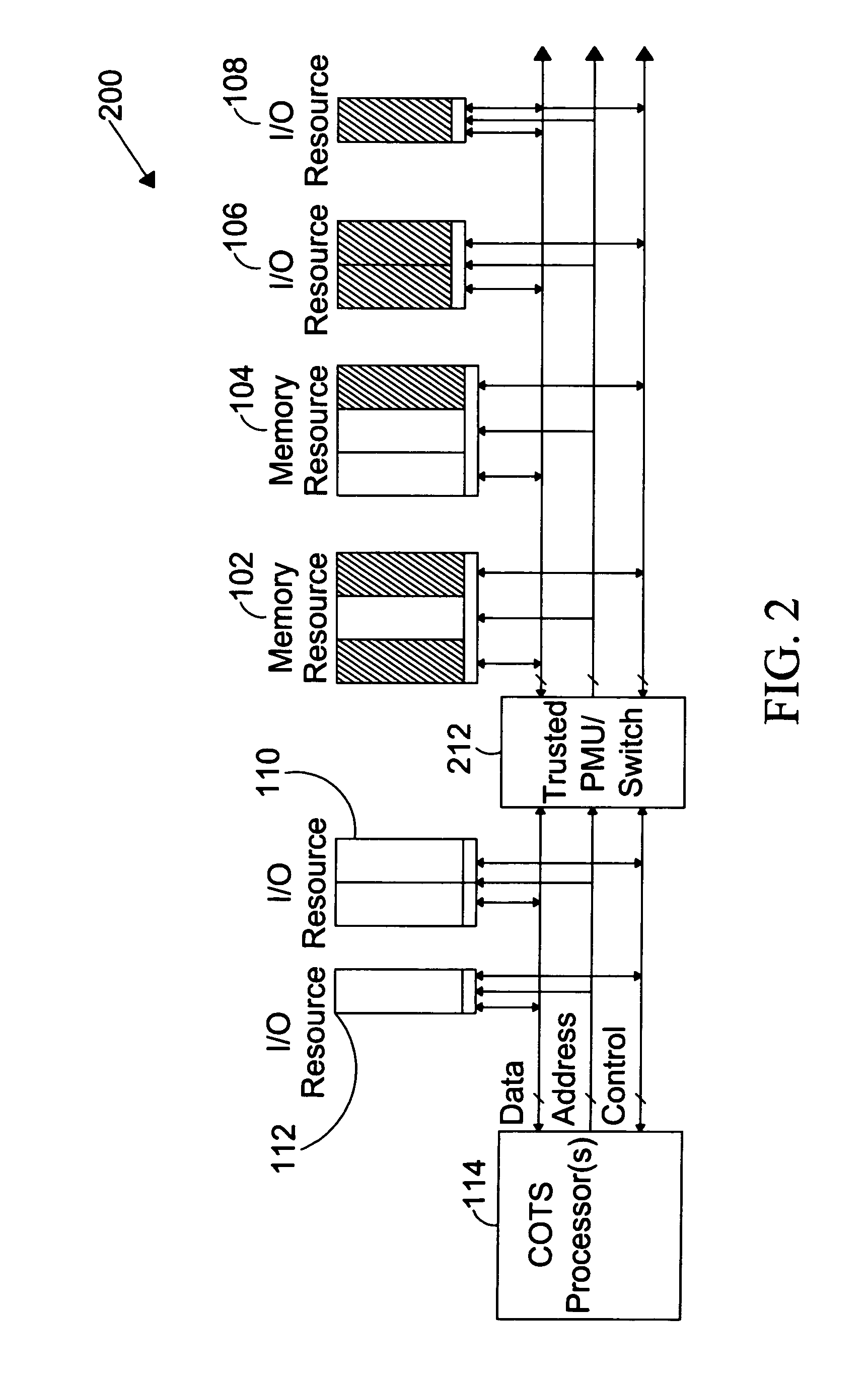
The present invention is directed to a system for providing a trusted environment for untrusted computing systems. The system may include a HAC subsystem managing shared resources and a trusted bus switch for controlling a COTS processor to access the shared resources. The shared resources such as memory and several I / O resources reside on the trusted side of the trusted bus switch. Alternatively, the system may include a SCM as an add-on module to an untrusted host environment. Only authenticated applications including COTS OS execute on the SCM while untrusted applications execute on the untrusted host environment. The SCM may control secure resource access from the untrusted host through a plug-in module interface. All secure resources may be maintained on the trusted side of the plug-in module interface.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Methods and systems for operating secure digital management aware applications
ActiveUS9935772B1Prevent loss and theftKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageCloud baseHosting environment
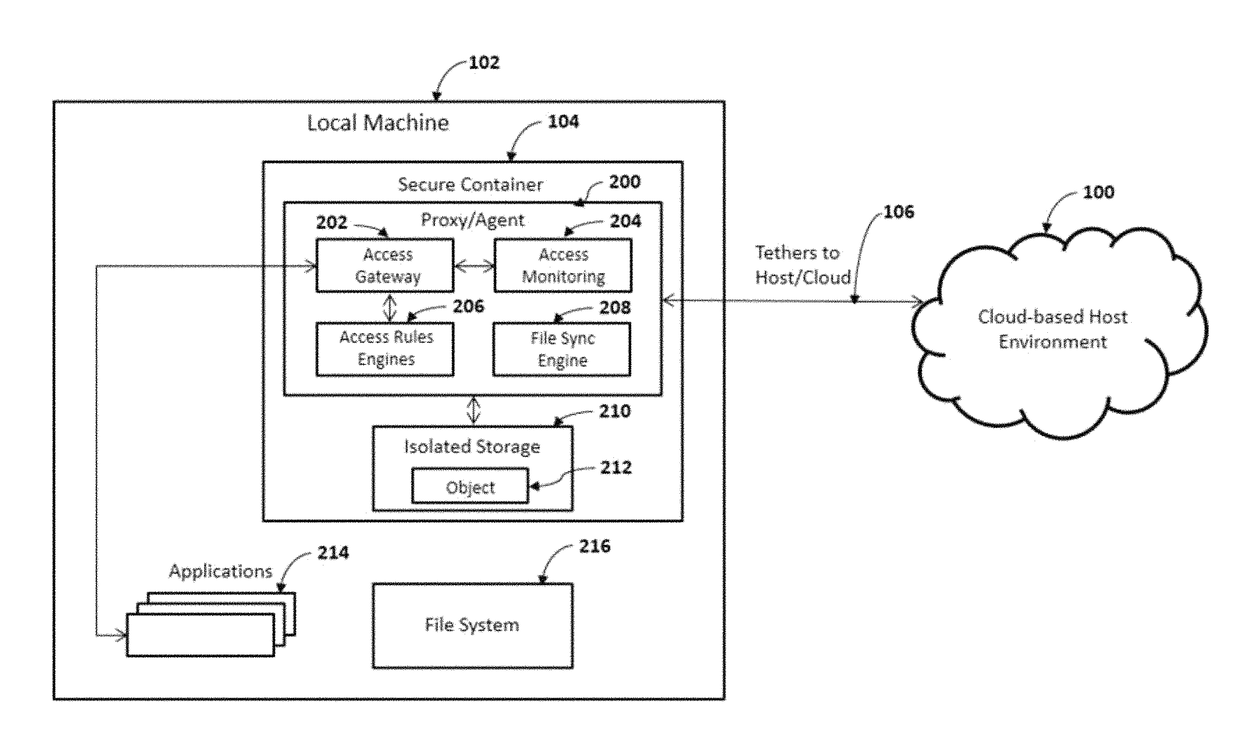
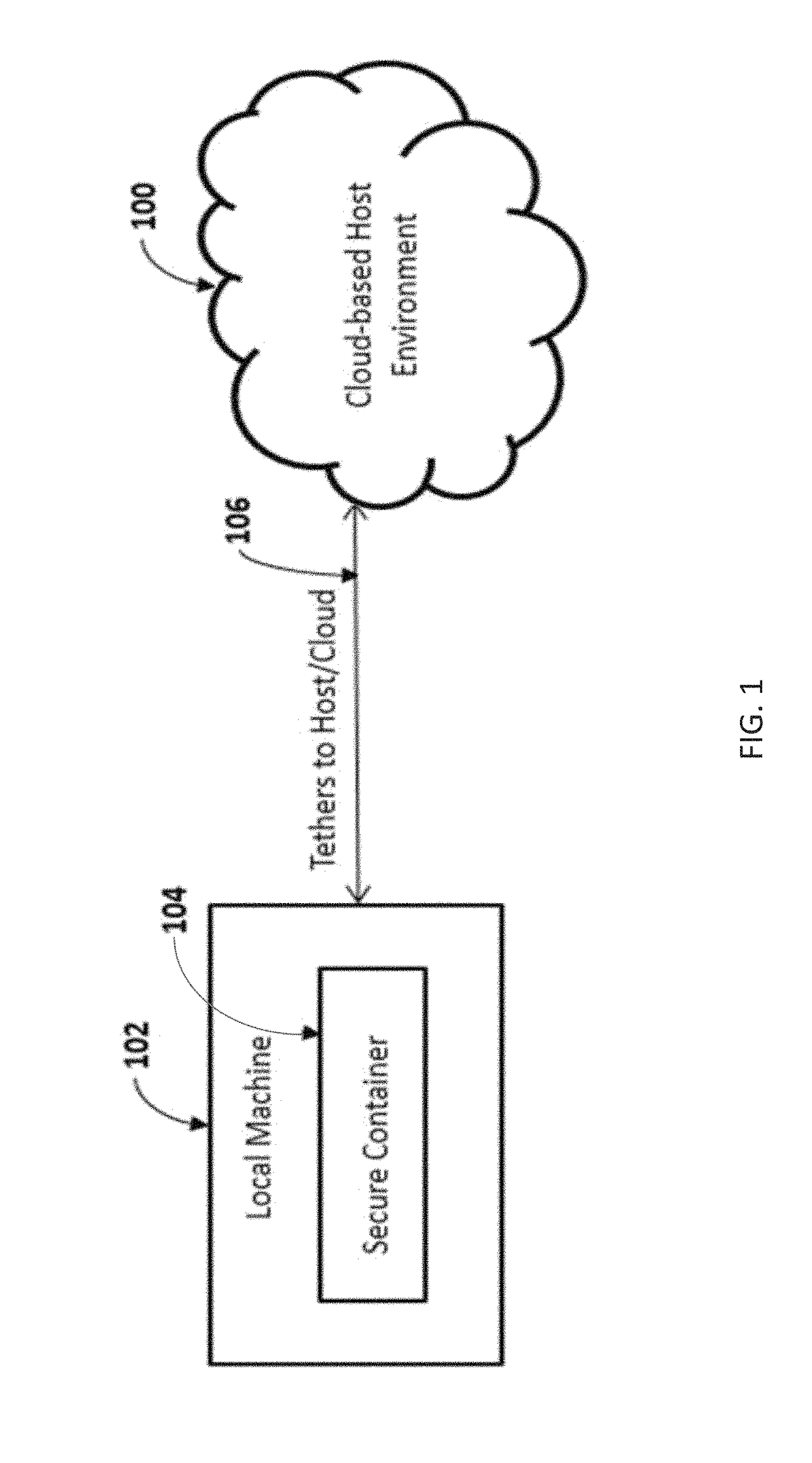
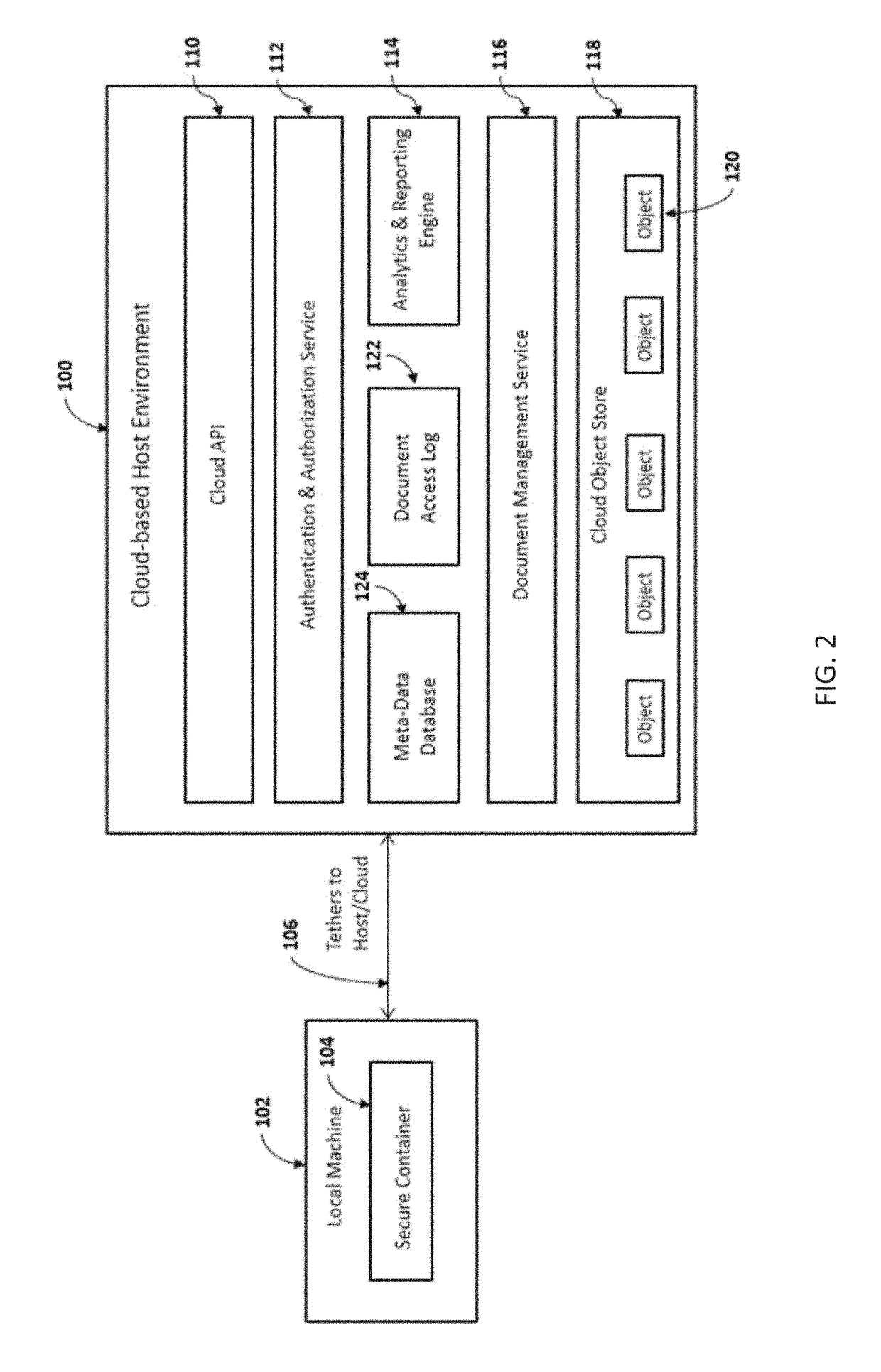
A system and method for servicing secure data object management aware applications using a cloud-based host environment and a local secure container. The cloud-based host environment creates a controlled digital object from a master digital object, and activates a tether associated with the controlled digital object. The tether includes an access permission, and optionally an operation permission (e.g., view, delete, store, edit, and copy) and a command (e.g., timeout, destroy). The controlled digital object is stored to an isolated storage of the secure container. The tether contents control access and manipulation of the controlled digital object. Certain conditions (e.g., timeout period reached, anomalous data access pattern detected), cause the controlled digital object to be destroyed and / or the tether to be inactivated. In accordance with applicable law, the cloud-based host environment utilizes the tether to detect, identify, and / or thwart unauthorized host environments in possession of the controlled digital object.
Owner:MADISETTI VIJAY K +2
Accessing network resources outside a security boundary
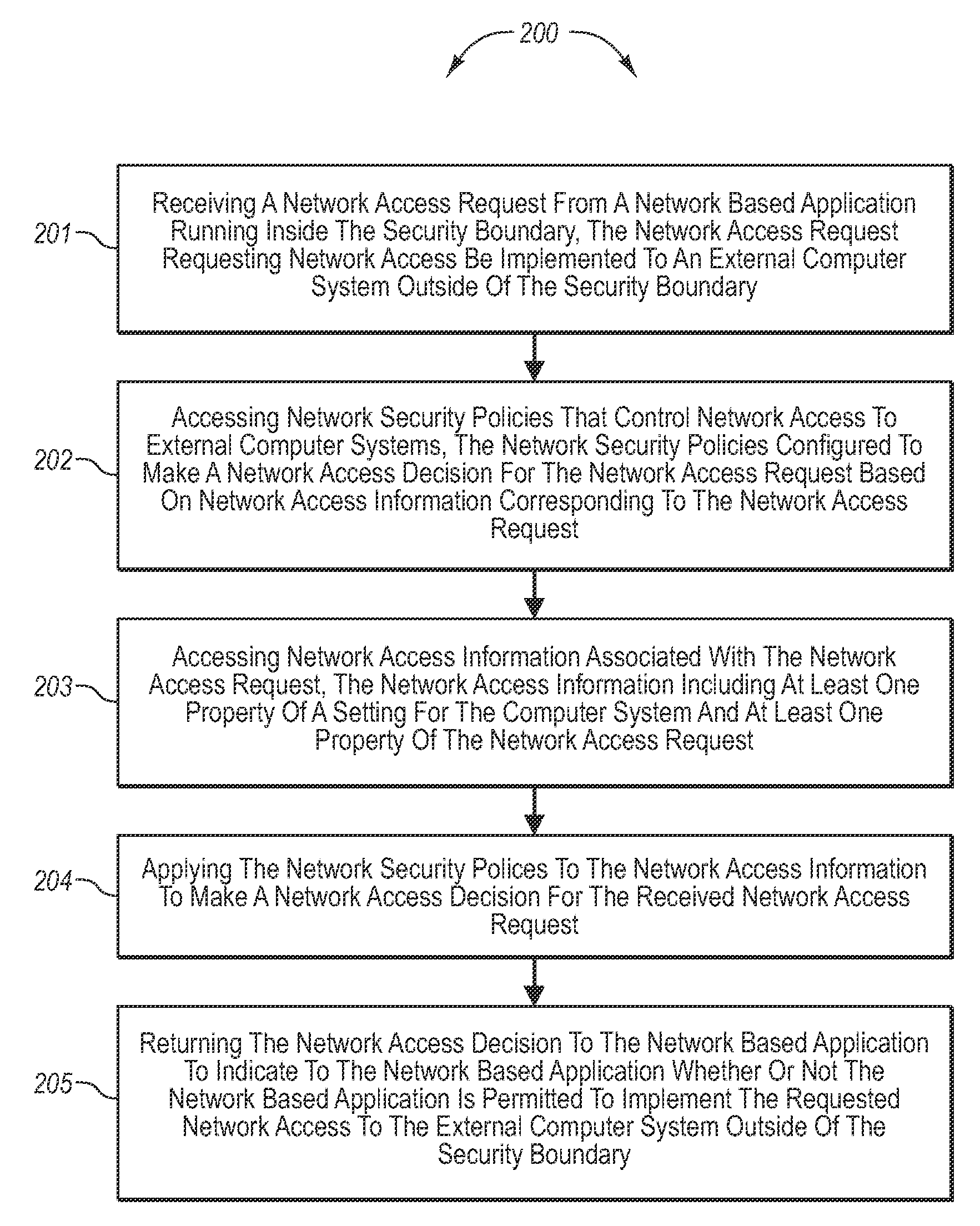
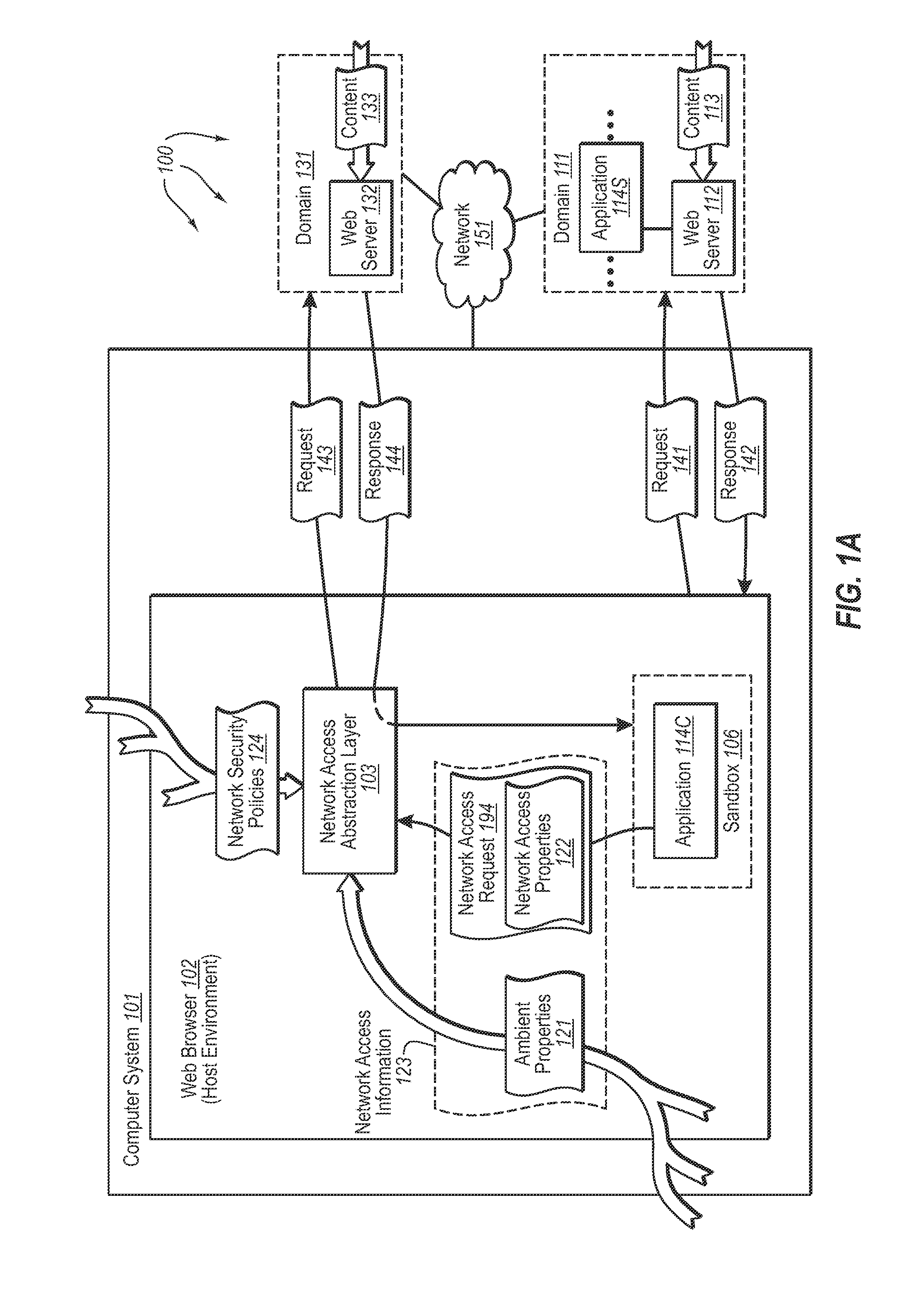
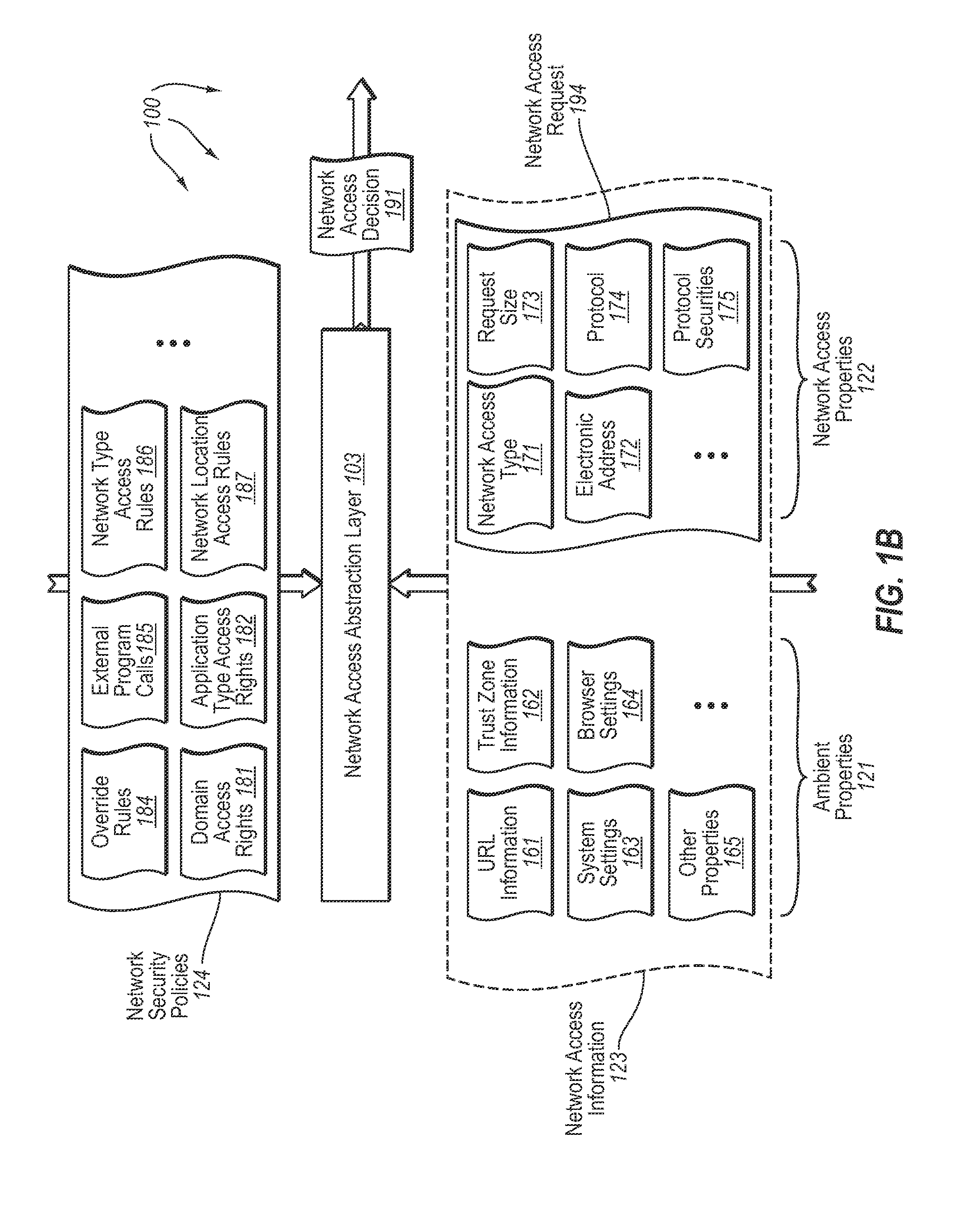
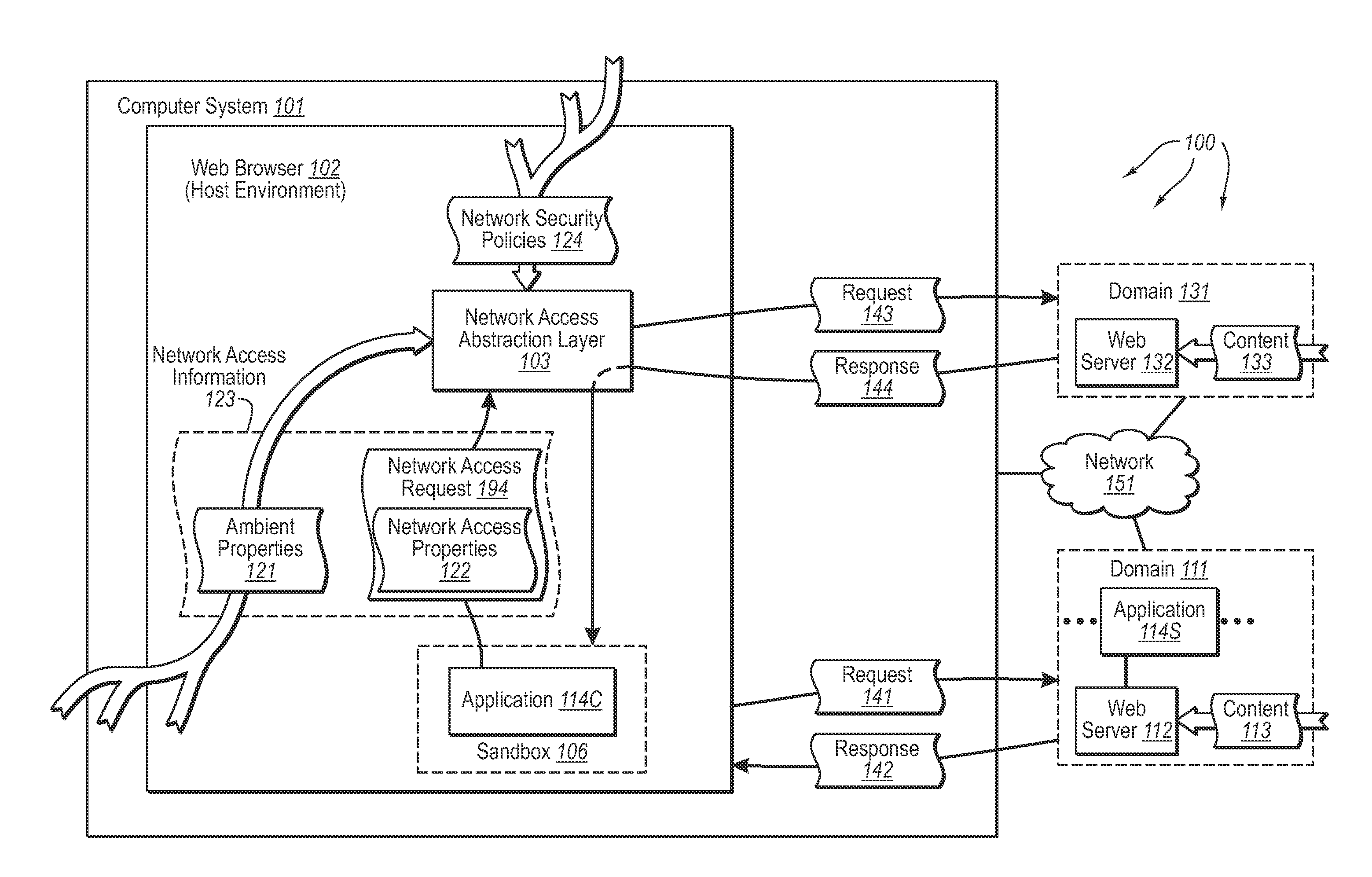
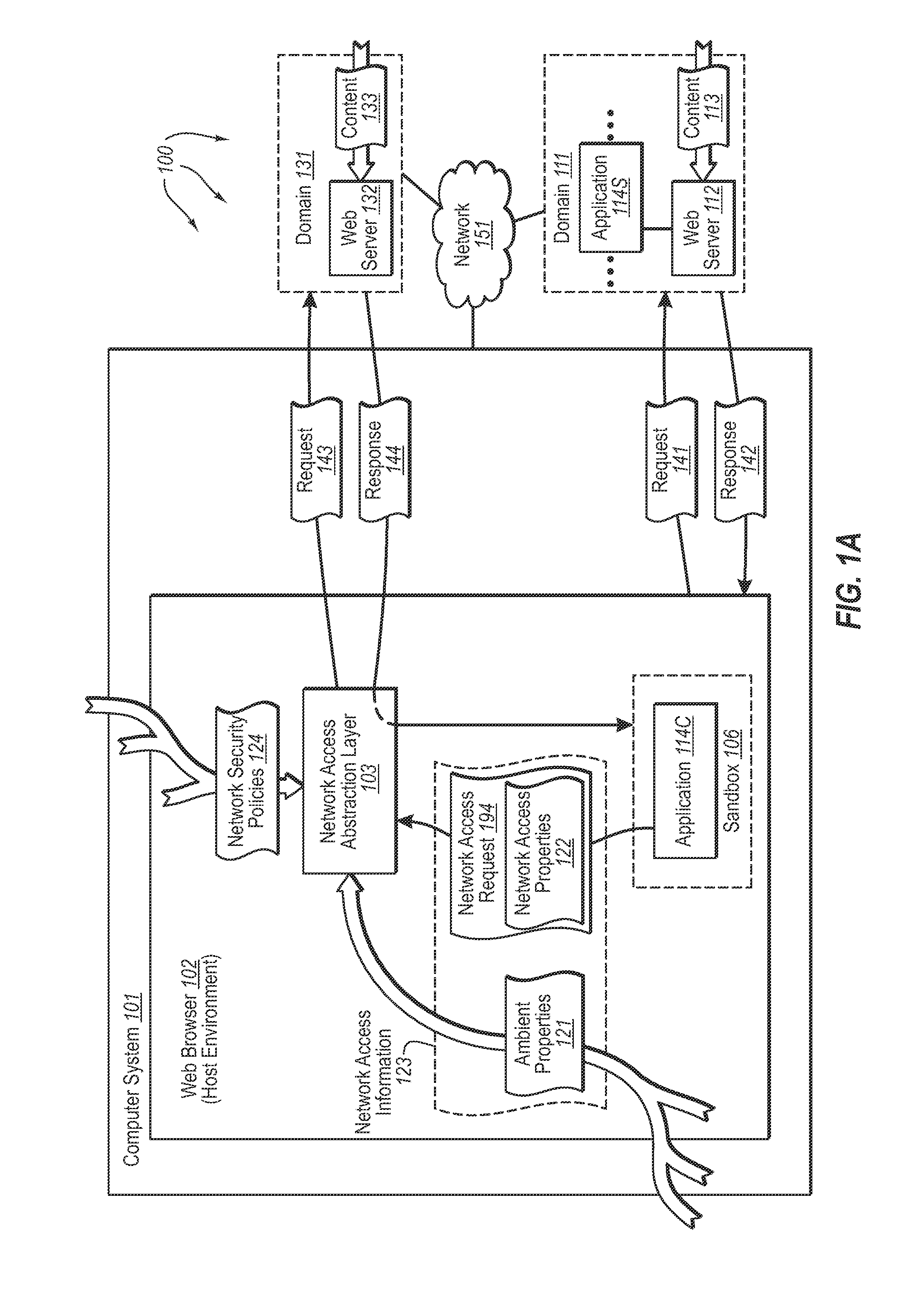
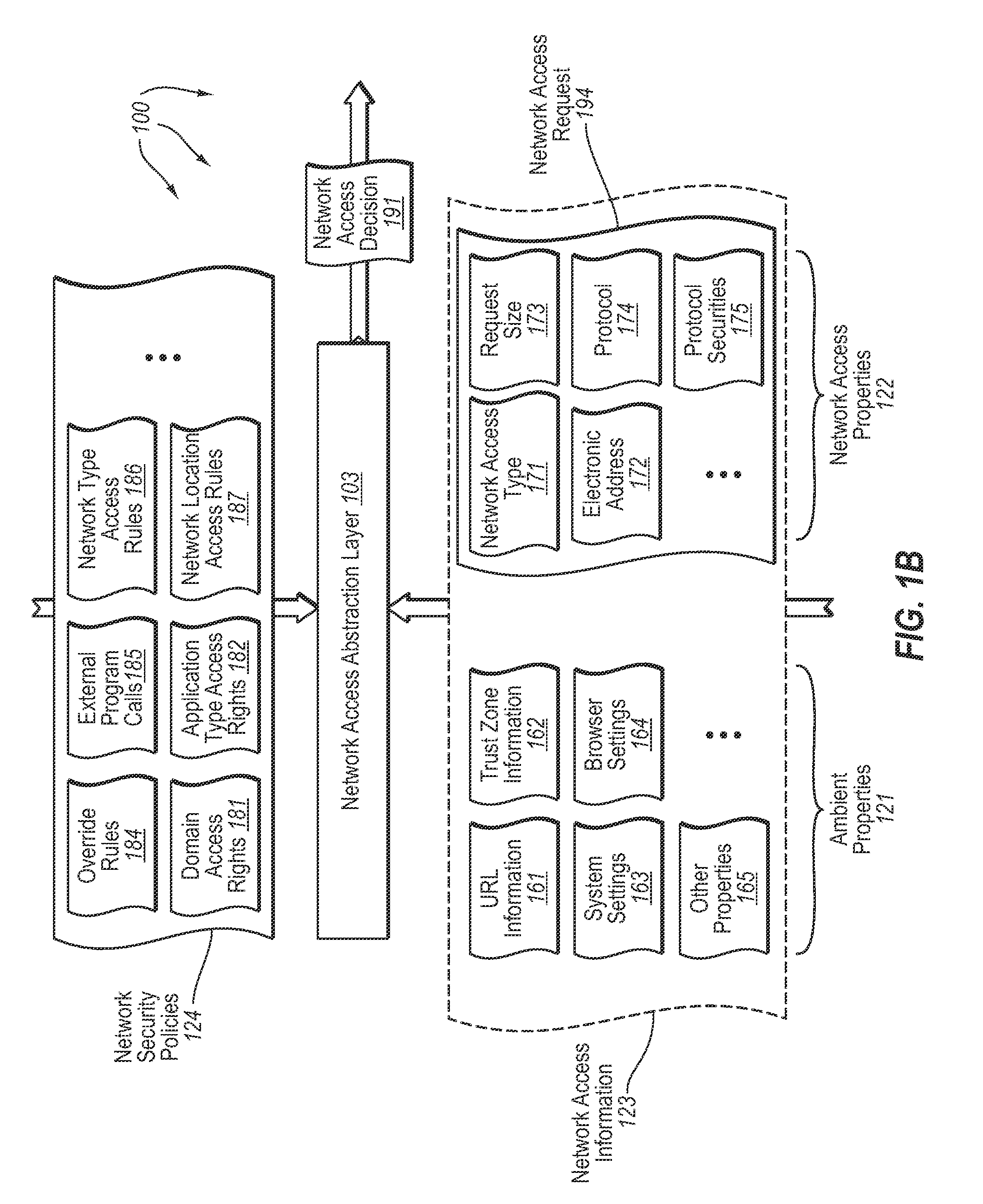
InactiveUS20080189757A1Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsHosting environmentClient system
The present invention extends to methods, systems, and computer program products for accessing network resources outside a security boundary. The present invention can provide a modules running within a security boundary (e.g., sandboxed client-side scripts) access to network resources at computer systems other than the computer system where the module originated. When network access is permitted, the properties of network request can be adjusted so that security information of the client system and the originating computer system for the module are not divulged. Thus, a module can obtain content for inclusion in a Web page from third party servers in a more secure meaner. Network e access decisions can be made based on ambient data already accessible to a host environment such that network access decisions can be made in a more automated manner.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
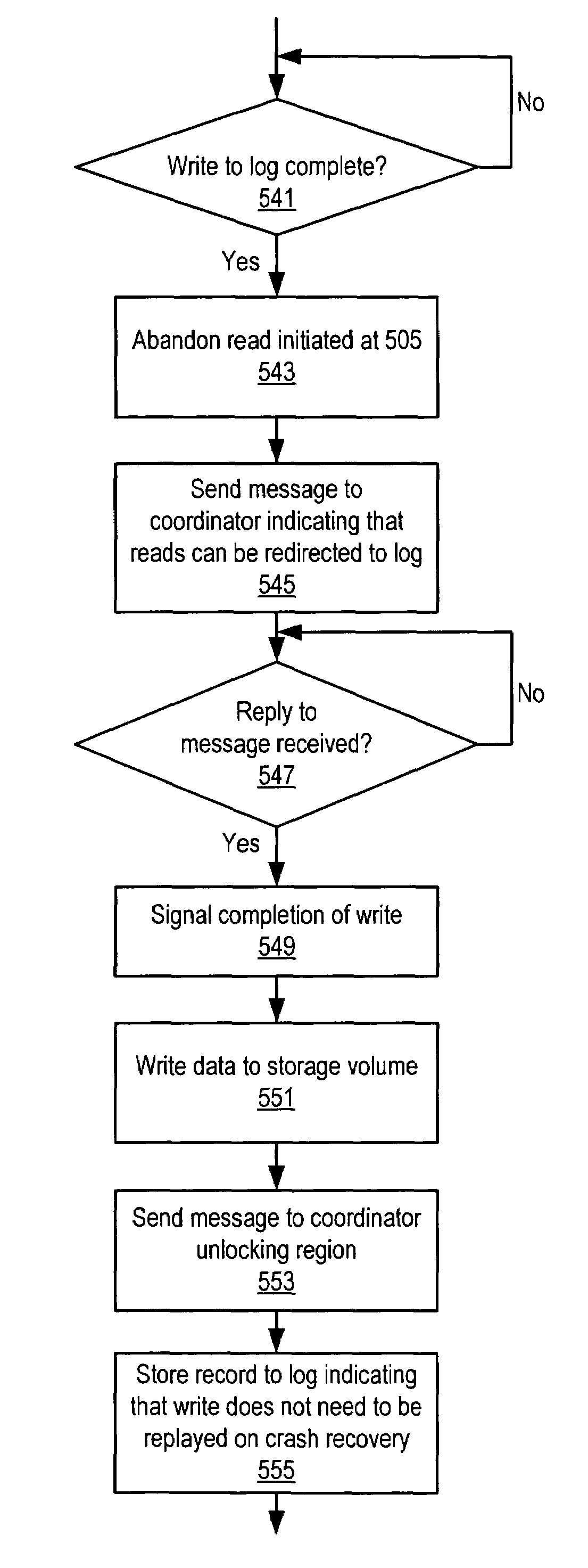
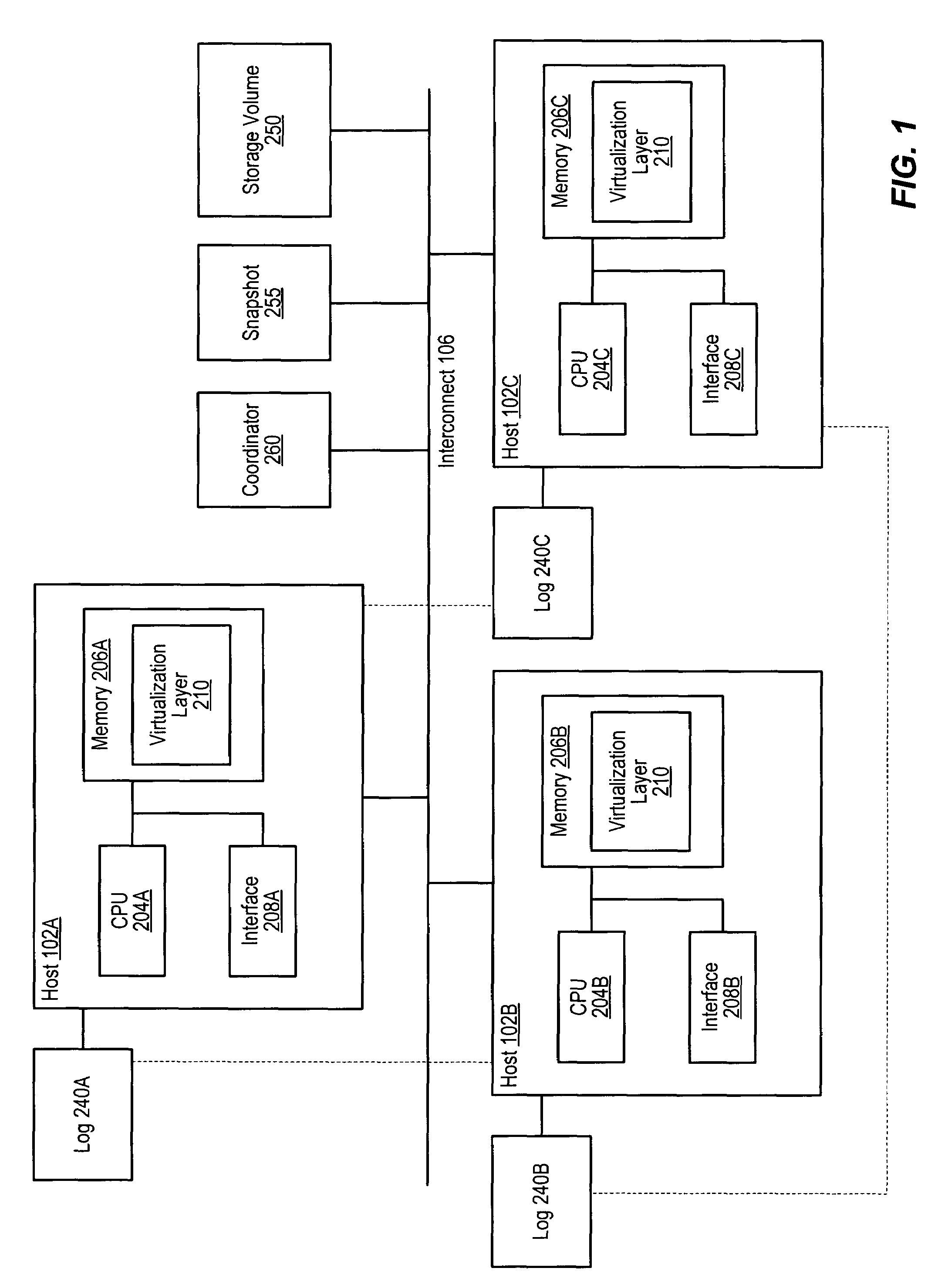
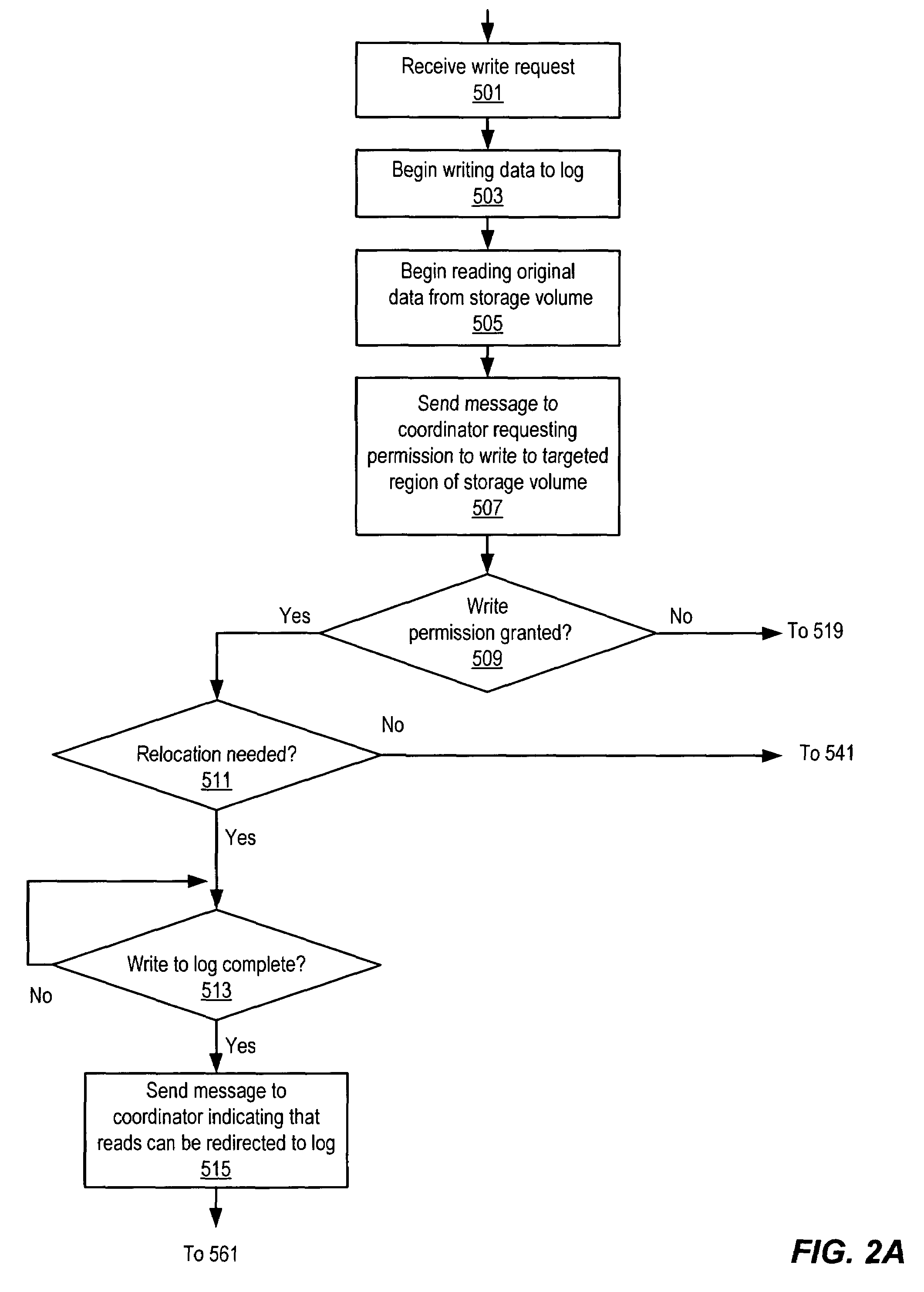
Coordinated distributed log-based snapshots in a multi-host environment
ActiveUS7328226B1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsHosting environmentApplication software
A method for coordinating access to a storage volume between several hosts, each of which has an associated log, may involve: one of the hosts requesting permission from a coordinator to perform a write to a region of the storage volume; the host storing write data for the write to an associated log; and the coordinator sending a response granting permission to perform the write to the host, where the response indicates whether an old version of data in the region of the storage volume should be relocated to a COW (Copy On Write) snapshot volume. The host may signal completion of the write to an application that initiated the write prior to performing the write to the region of the storage volume and subsequent to both storing the write data to the associated log and receiving the response from the coordinator.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
System and method for efficiently building virtual appliances in a hosted environment
ActiveUS8176094B2Drawback can be addressedError detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsFile systemImage description
A system and method for efficiently building virtual appliances in a hosted environment is provided. In particular, a plurality of image archives may be stored in a build database, with each image archive including a file system having a directory structure and a plurality of files installed within the directory structure. In response to a build request containing an image description, a build engine may create a file system layout defining a directory structure for an image. The build engine may then copy the file system for one of the image archives to the file system layout for the image, wherein the copied file system may provide a subset of the file system for the image. The build engine may then build the image, which may include a file system having various files installed within various directories in accordance with the directory structure defined for the image.
Owner:SUSE LLC
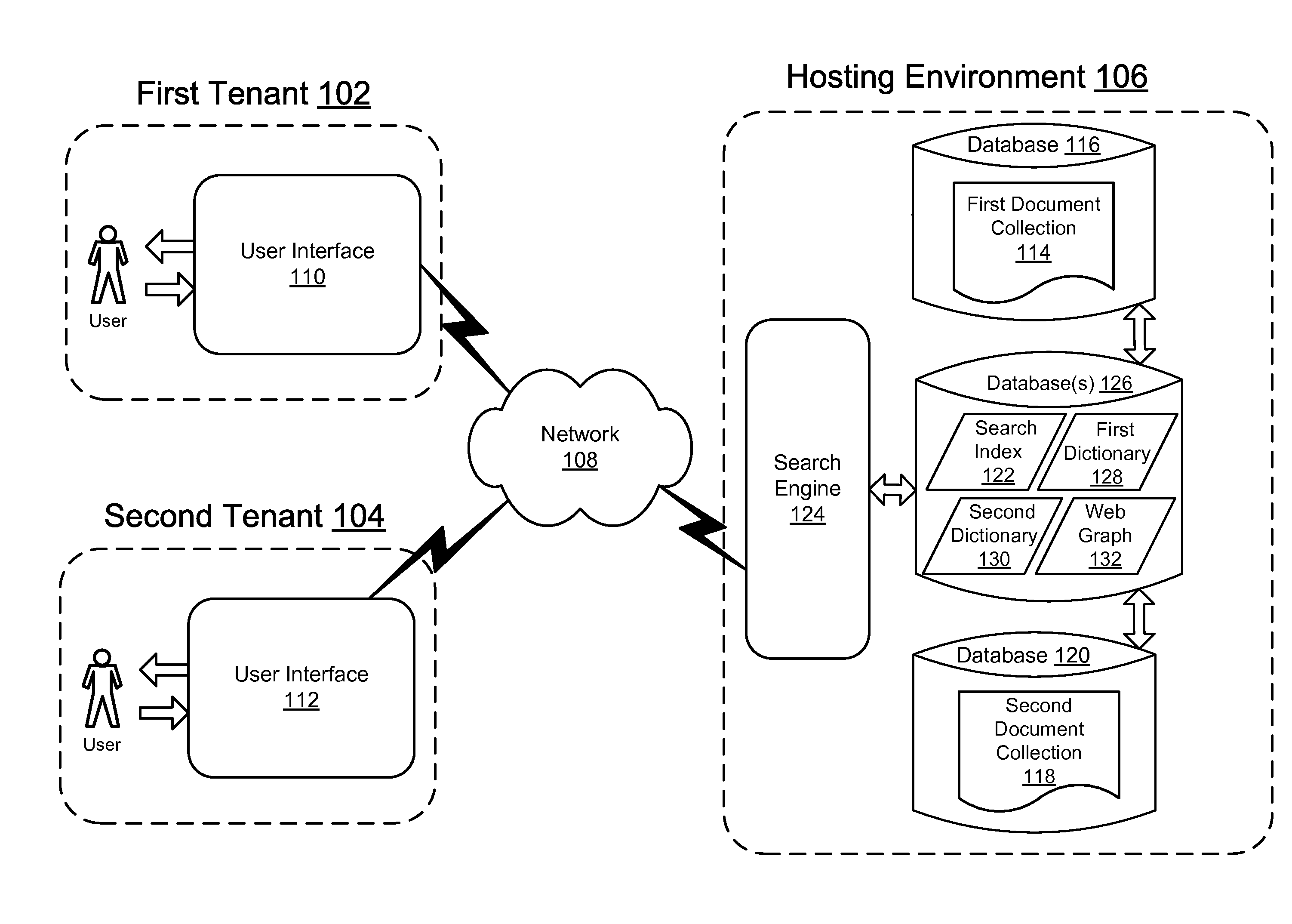
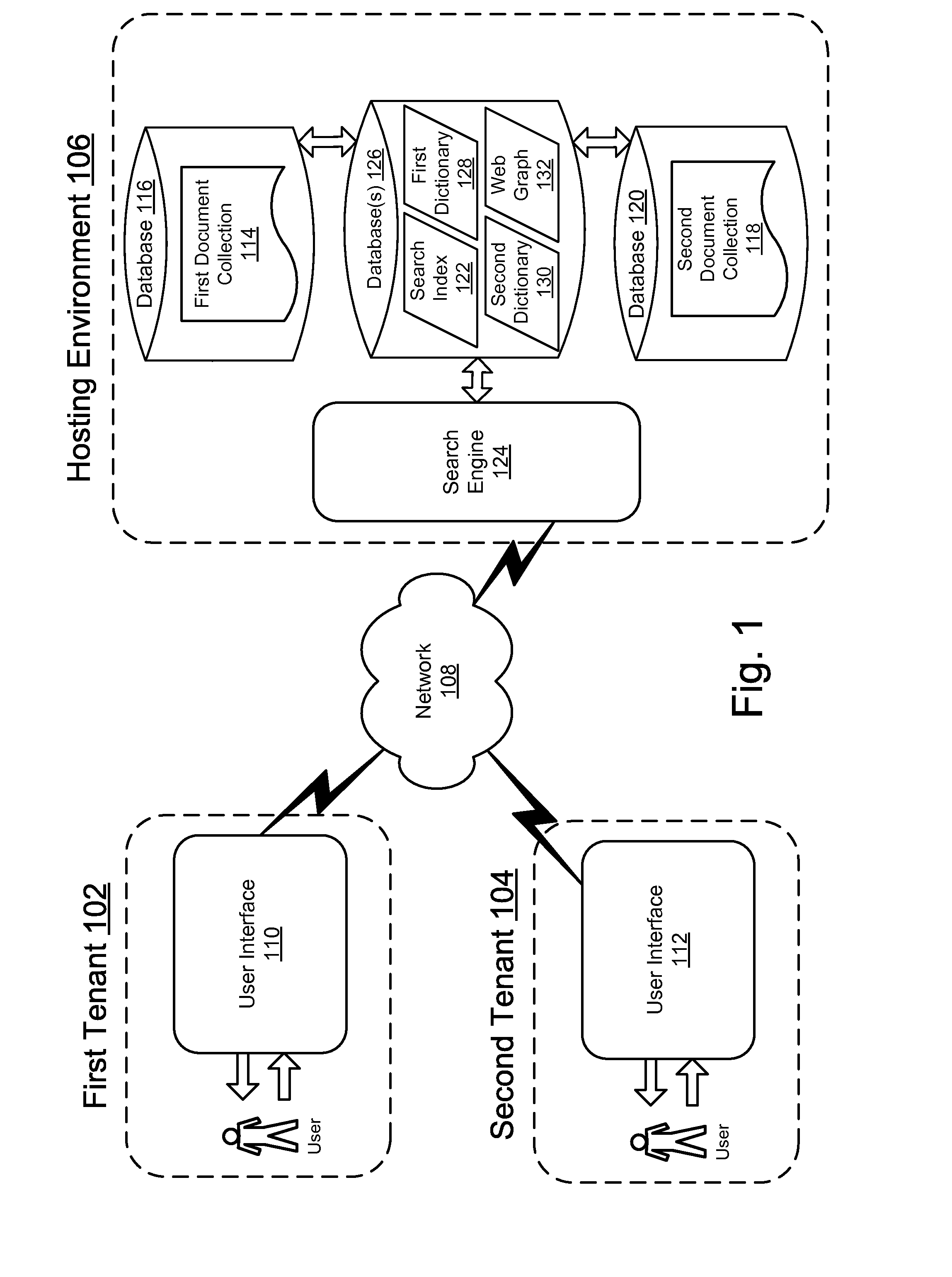
Tenantization of search result ranking
This disclosure describes methods and systems for searching documents in a multi-tenant hosting environment. According to embodiments, to conserve hardware resources, a plurality of documents associated with a plurality of tenants may be mapped to the same search index in the multi-tenant hosting environment. In order to search documents associated only with a single tenant in the multi-tenant hosting environment, a tenant identifier is prepended to every key stored in the search index that is associated with the plurality of documents of the single tenant. Moreover, where one document links to another document within the multi-tenant hosting environment, the link is stored in a web graph when a source tenant identifier matches a target tenant identifier for the link. According to embodiments, when conducting a search, the link is resolved only if the link is stored in the web graph.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
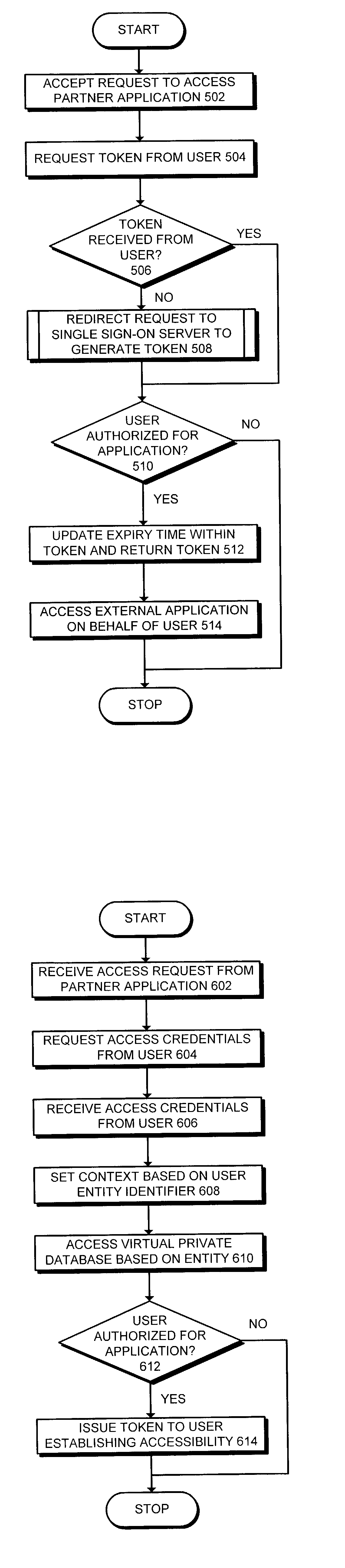
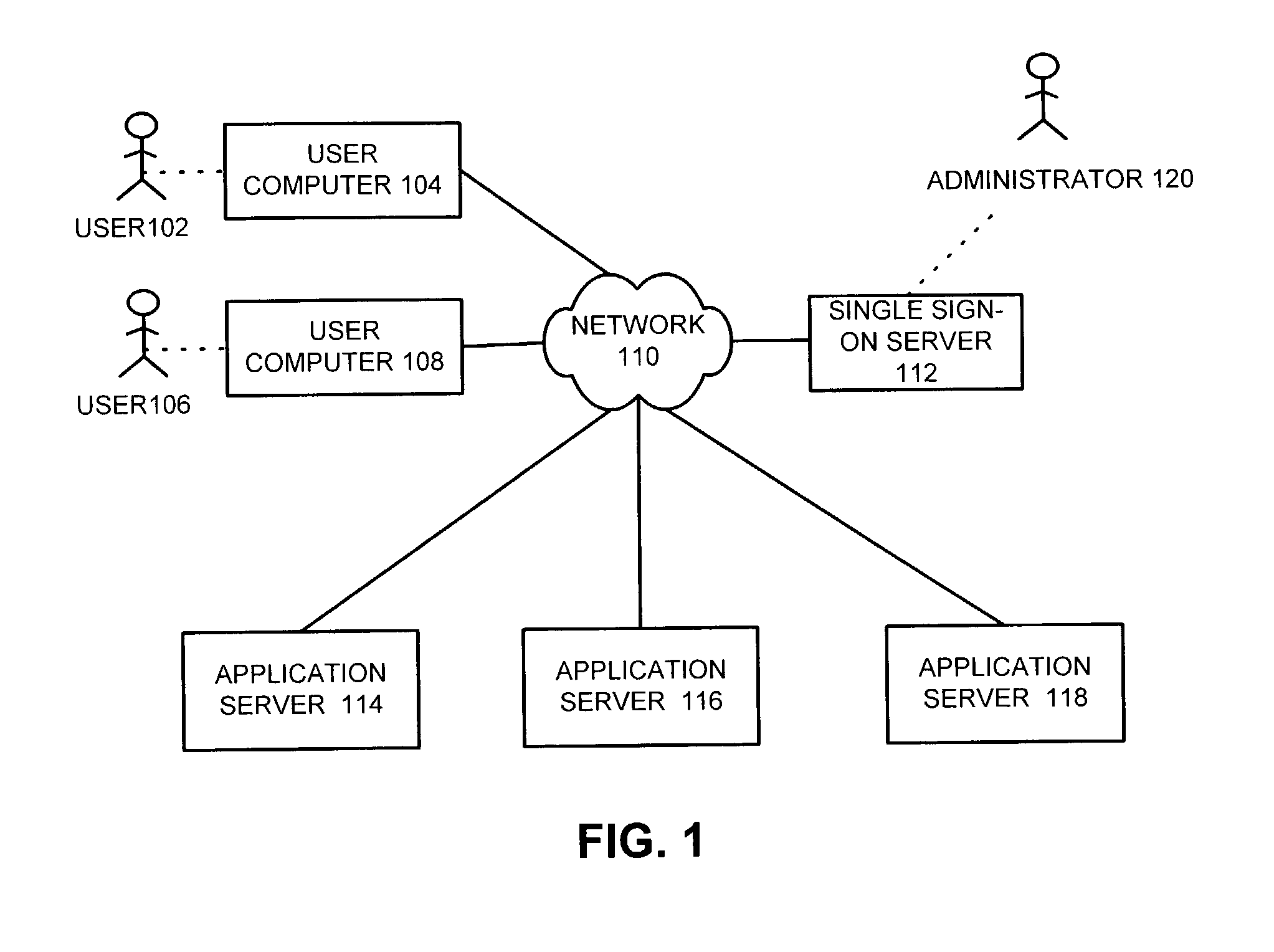
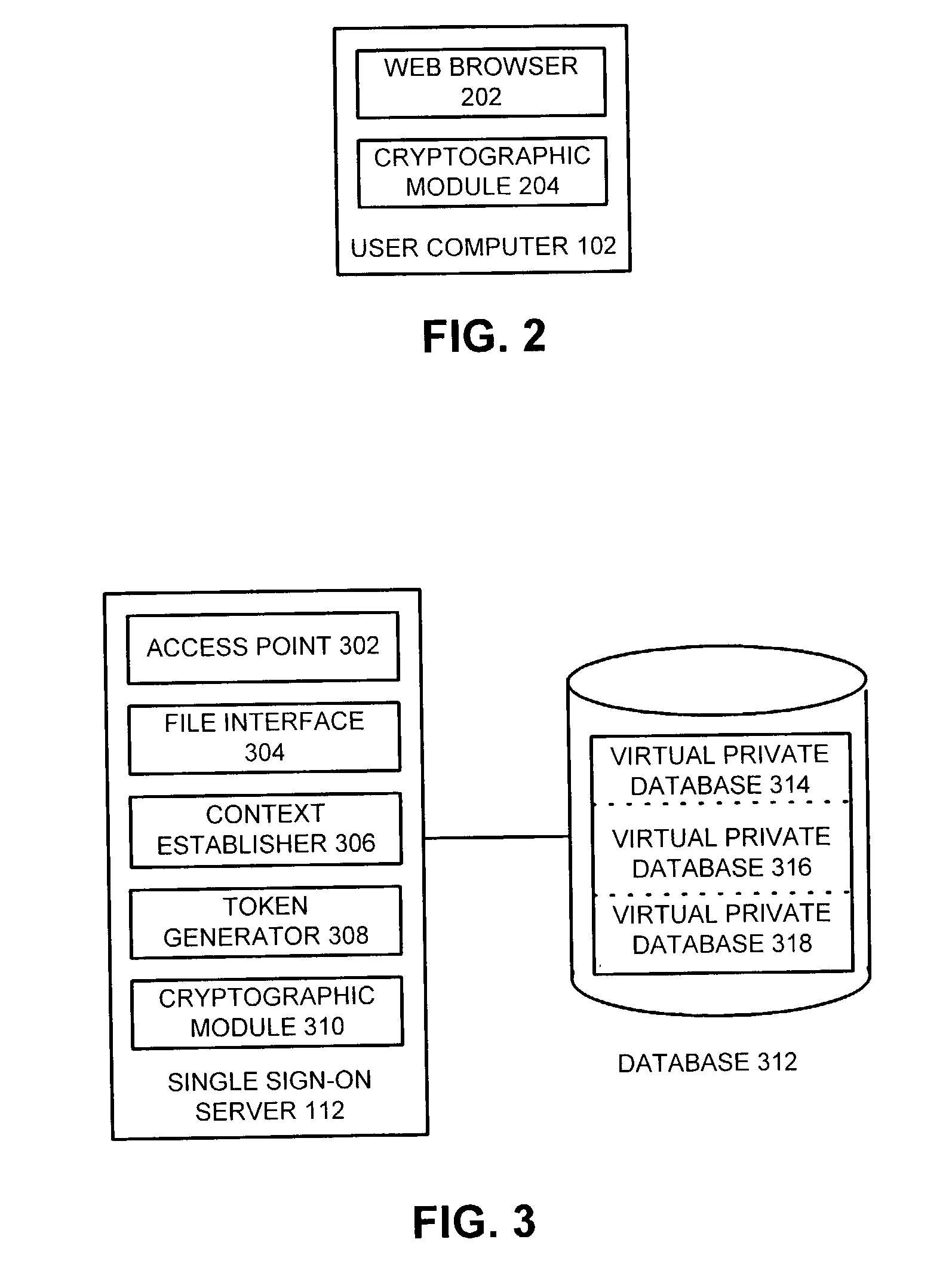
Method and apparatus to facilitate single sign-on services in a hosting environment
ActiveUS7174383B1Facilitates single sign-on servicePrevent tamperingMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionEntity identifierApplication server
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that facilitates single sign-on services in a hosting environment. The system operates by first receiving a request from a user to access a partner application at an application server. The system then determines if the user holds a token granting access to this partner application. If the user does not hold this token, the system redirects the request to a single sign-on server. This single sign-on server requests a user authentication credential from the user. Upon receiving the user authentication credential, including an entity identifier, the single sign-on server verifies if the user is authorized to access the partner application based on the entity identifier. If the user is authorized to access the partner application, the single sign-on server issues a token to the user, which grants the user access to the partner application.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System and method for efficiently building virtual appliances in a hosted environment
ActiveUS20130297922A1Drawback can be addressedDigital computer detailsProgram controlFile systemHosting environment
A system and method for efficiently building virtual appliances in a hosted environment is provided. In particular, a plurality of image archives may be stored in a build database, with each image archive including a file system having a directory structure and a plurality of files installed within the directory structure. In response to a build request containing an image description, a build engine may create a file system layout defining a directory structure for an image. The build engine may then copy the file system from one of the image archives to the file system layout of the image, wherein the copied file system may provide a subset of the file system for the image. The build engine may then build the image, which may include a file system having various files installed within various directories in accordance with the directory structure defined for the image.
Owner:SUSE LLC
System for providing secure and trusted computing environments through a secure computing module
ActiveUS7734933B1Provide partUnauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringTrusted ComputingHosting environment
The present invention is directed to a system for providing a trusted environment for untrusted computing systems. The system may include a HAC subsystem managing shared resources and a trusted bus switch for controlling a COTS processor to access the shared resources. The shared resources such as memory and several I / O resources reside on the trusted side of the trusted bus switch. Alternatively, the system may include a SCM as an add-on module to an untrusted host environment. Only authenticated applications including COTS OS execute on the SCM while untrusted applications execute on the untrusted host environment. The SCM may control secure resource access from the untrusted host through a plug-in module interface. All secure resources may be maintained on the trusted side of the plug-in module interface.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Accessing network resources outside a security boundary
InactiveUS7870596B2Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionHosting environmentDecision taking
The present invention extends to methods, systems, and computer program products for accessing network resources outside a security boundary. The present invention can provide a modules running within a security boundary (e.g., sandboxed client-side scripts) access to network resources at computer systems other than the computer system where the module originated. When network access is permitted, the properties of network request can be adjusted so that security information of the client system and the originating computer system for the module are not divulged. Thus, a module can obtain content for inclusion in a Web page from third party servers in a more secure meaner. Network e access decisions can be made based on ambient data already accessible to a host environment such that network access decisions can be made in a more automated manner.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
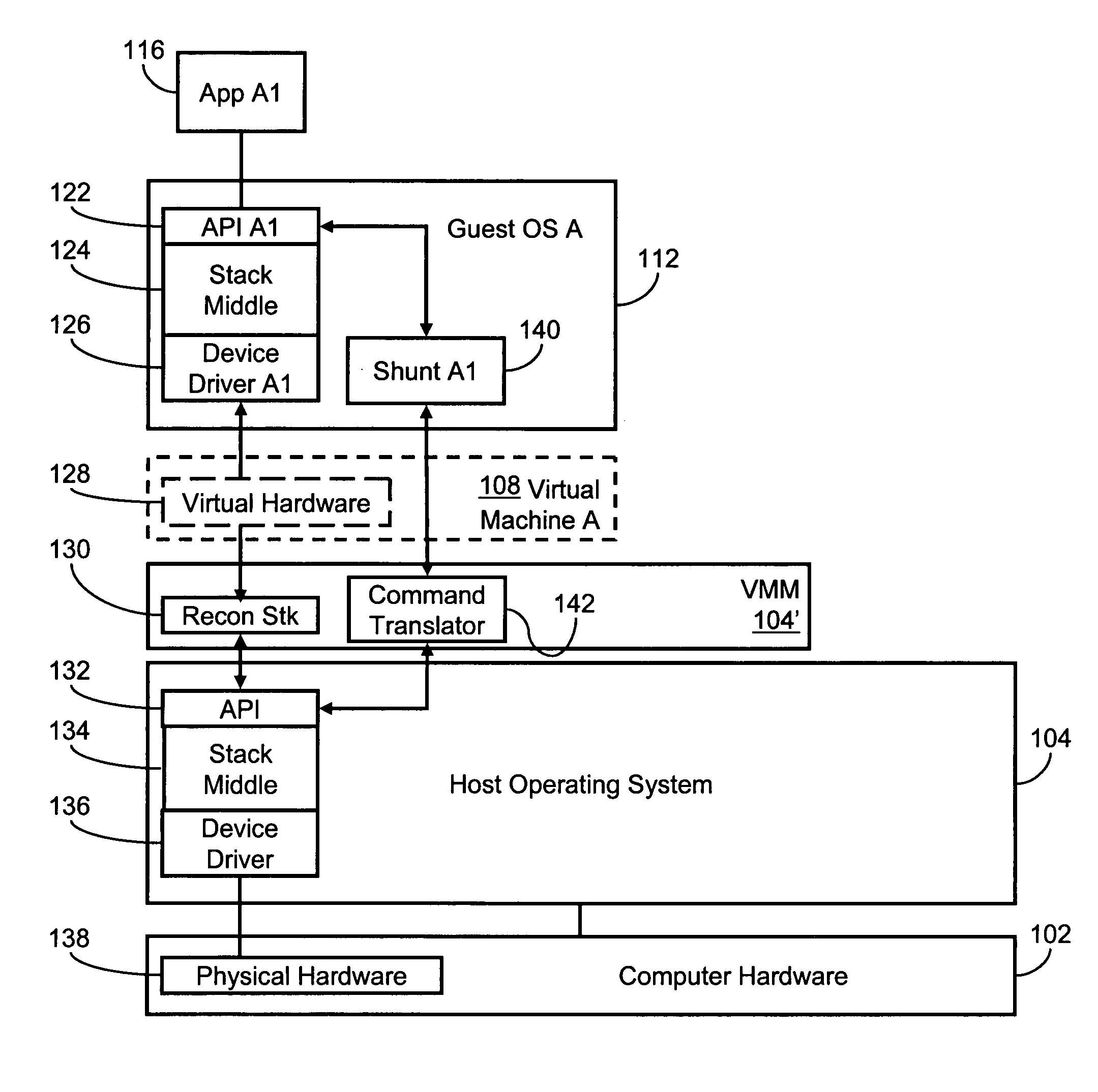
Systems and methods for stack-jumping between a virtual machine and a host environment
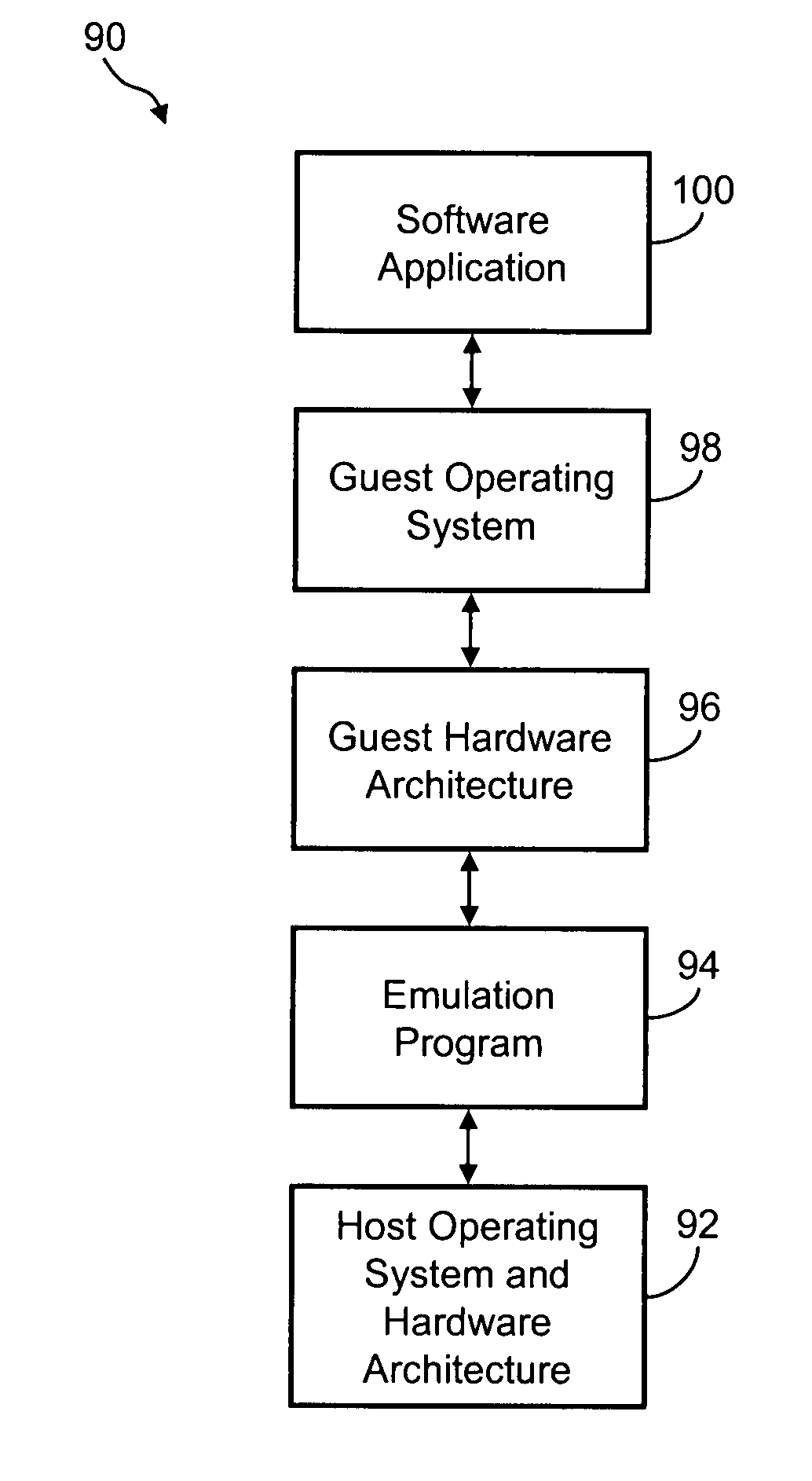
ActiveUS20060005186A1Reduce overheadOperation efficiency can be improvedMultiprogramming arrangementsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationVirtualizationOperational system
Several embodiments of the present invention provide a means for reducing overhead and, thus, improving operating efficiency in virtualized computing systems. Certain of these embodiments are specifically directed to providing a bypass mechanism for jumping directly from a first stack in the guest operating system to a second stack in the host operating system for a virtual machine environment. More specifically, certain embodiments of the present invention are directed to a system for and method of eliminating redundancy in execution of certain virtual machine commands and executing host environment equivalents by using bypass mechanisms, thereby bypassing redundant software layers within the guest and host stacks. For some of these embodiments, the bypass mechanism operates at a high-level component of the stack or, alternatively, the bypass mechanism operates at a low-level component of the stack.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
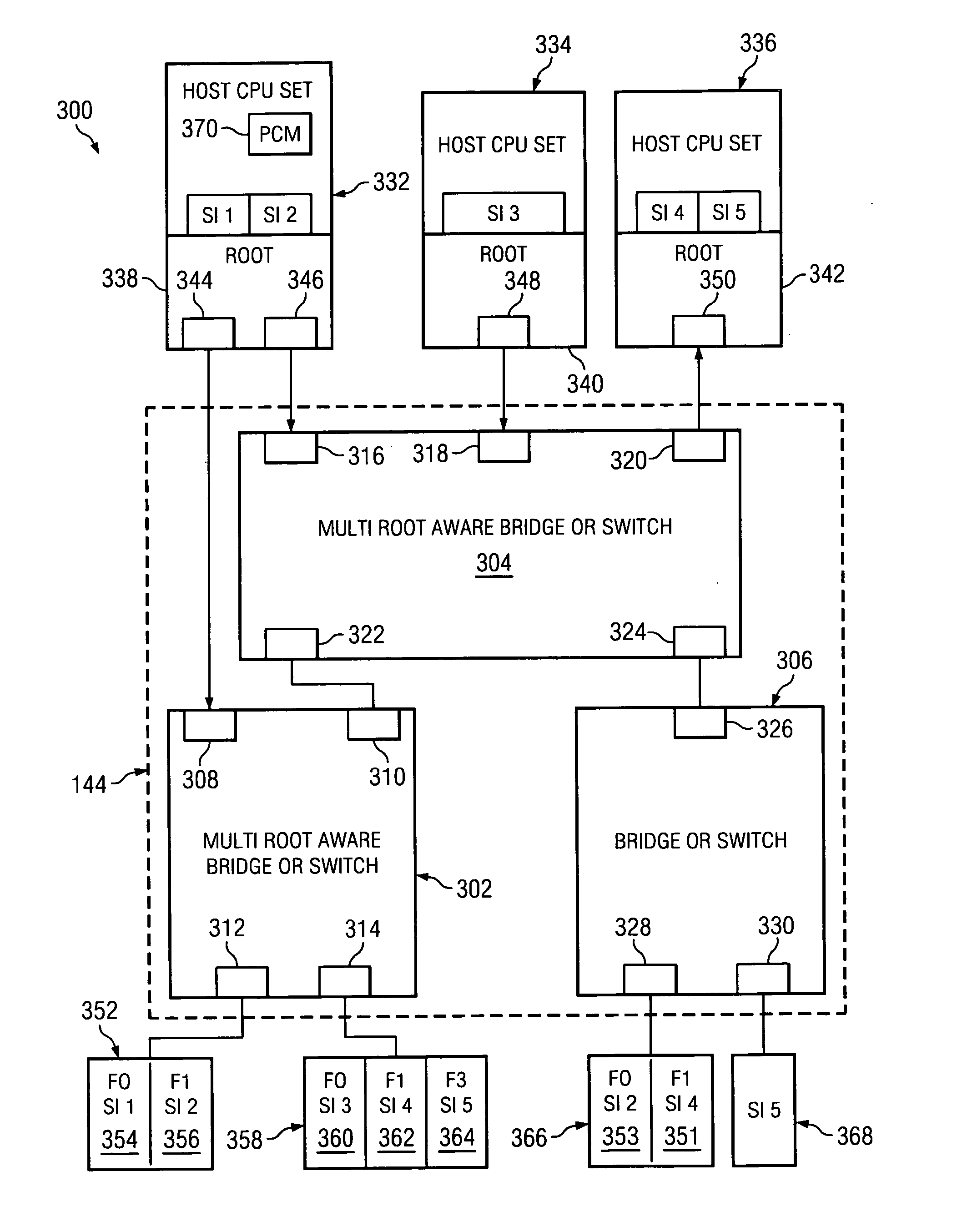
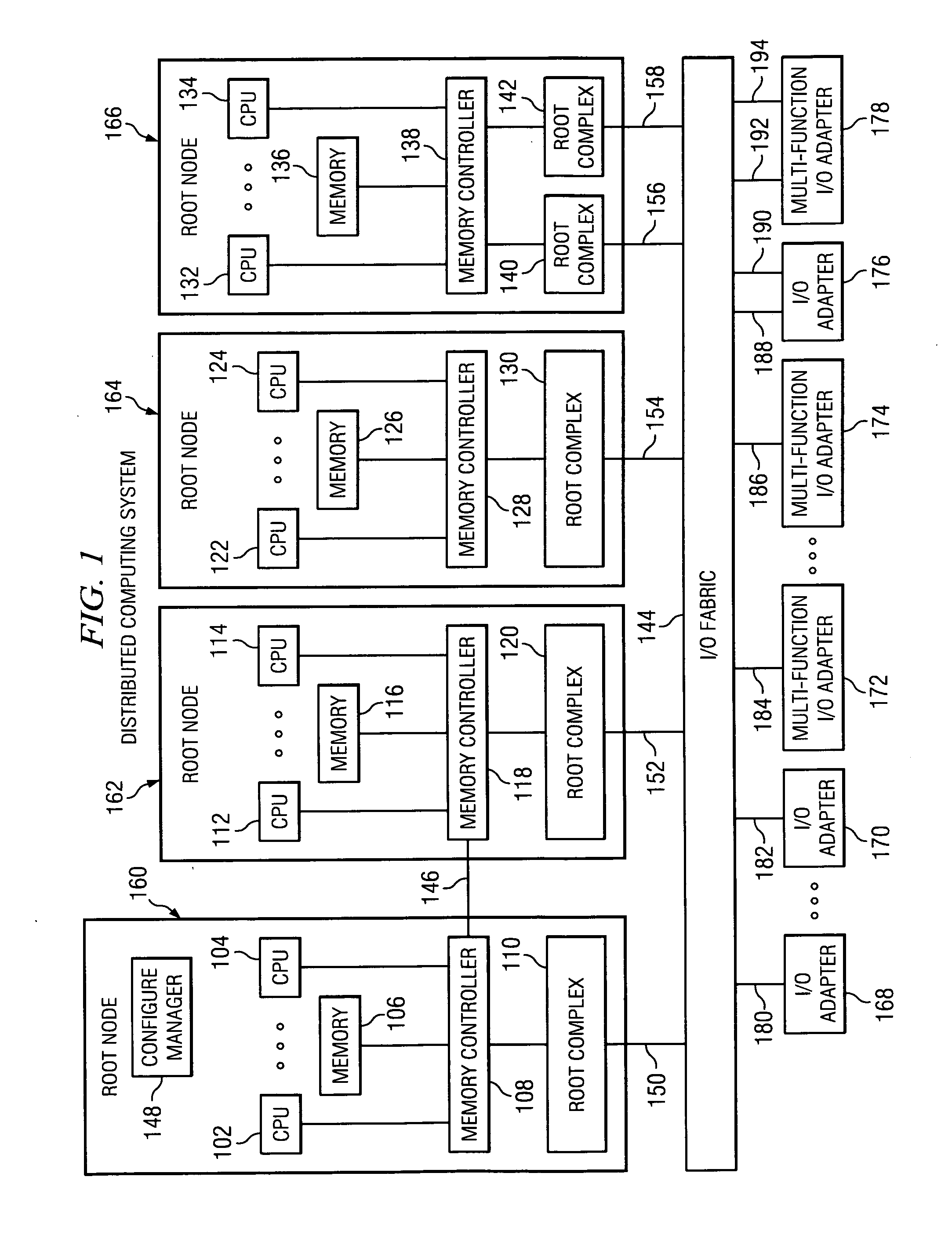
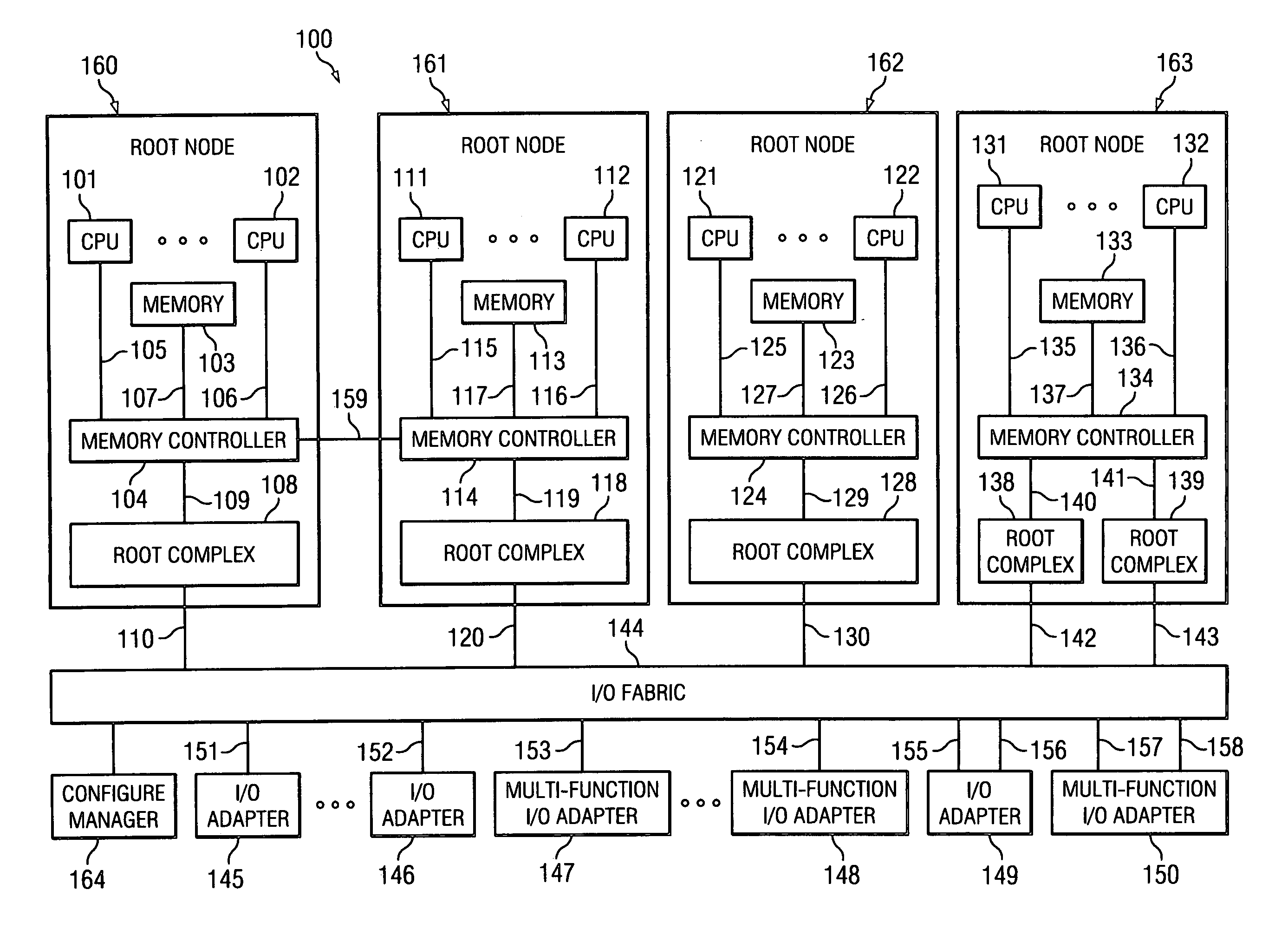
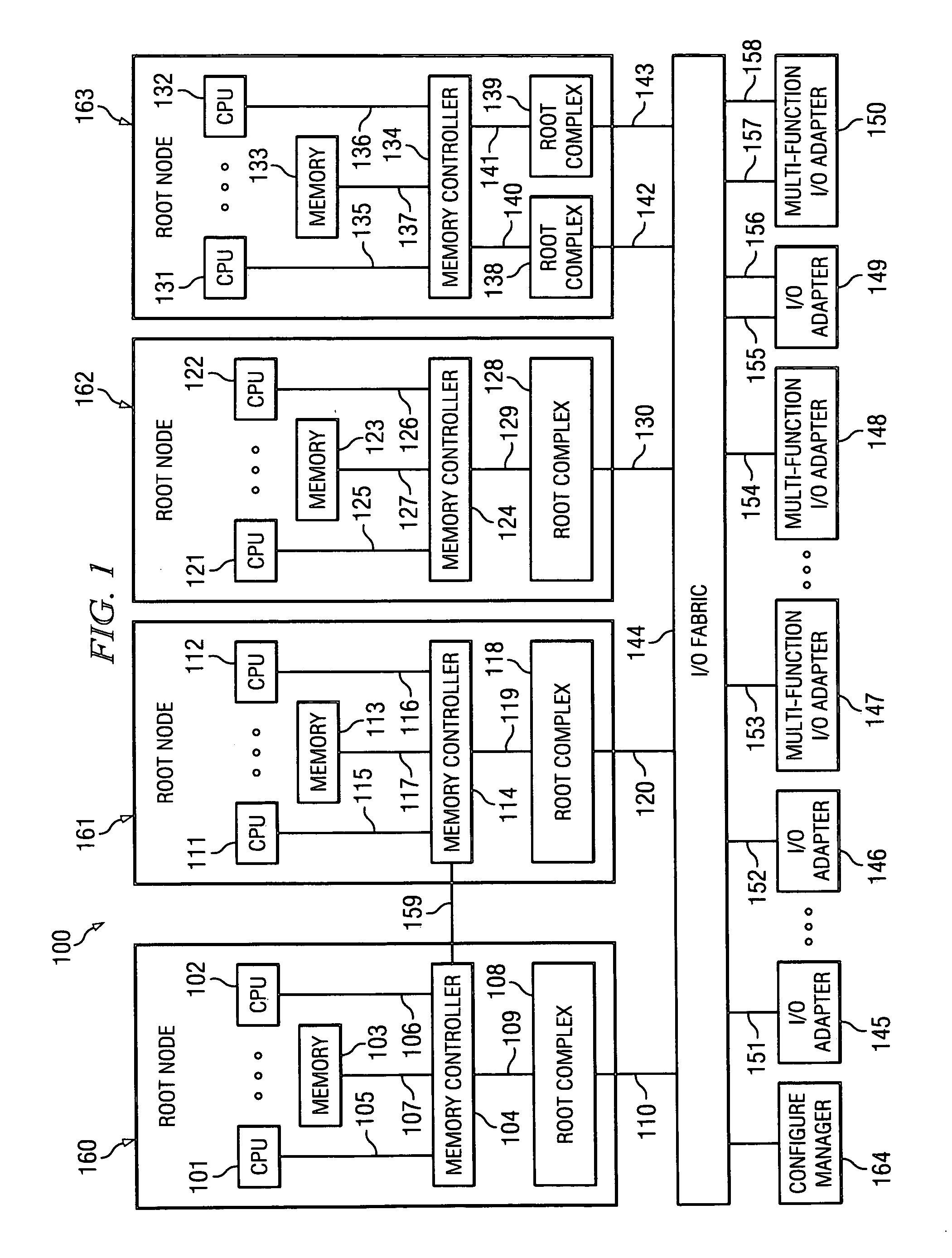
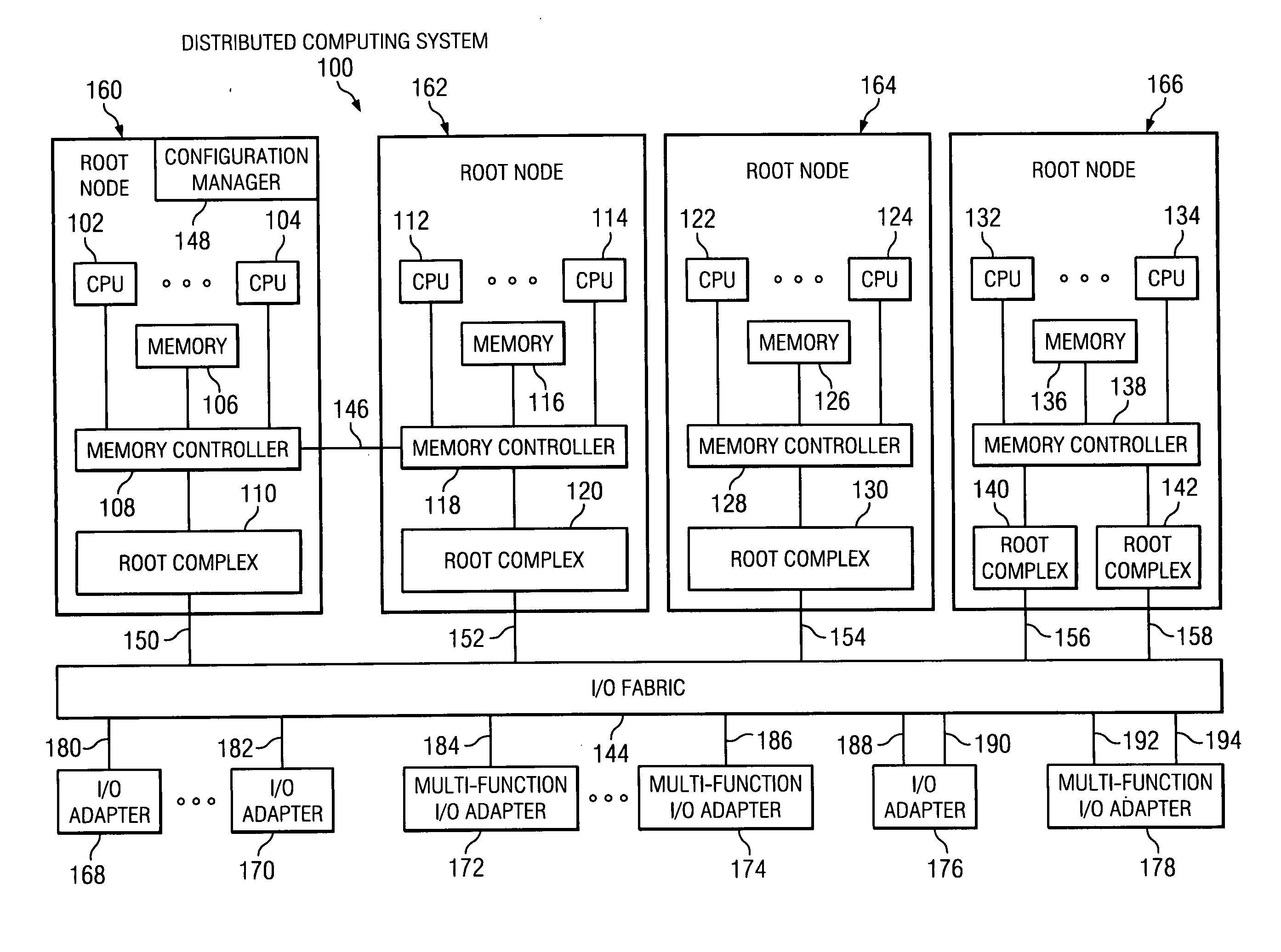
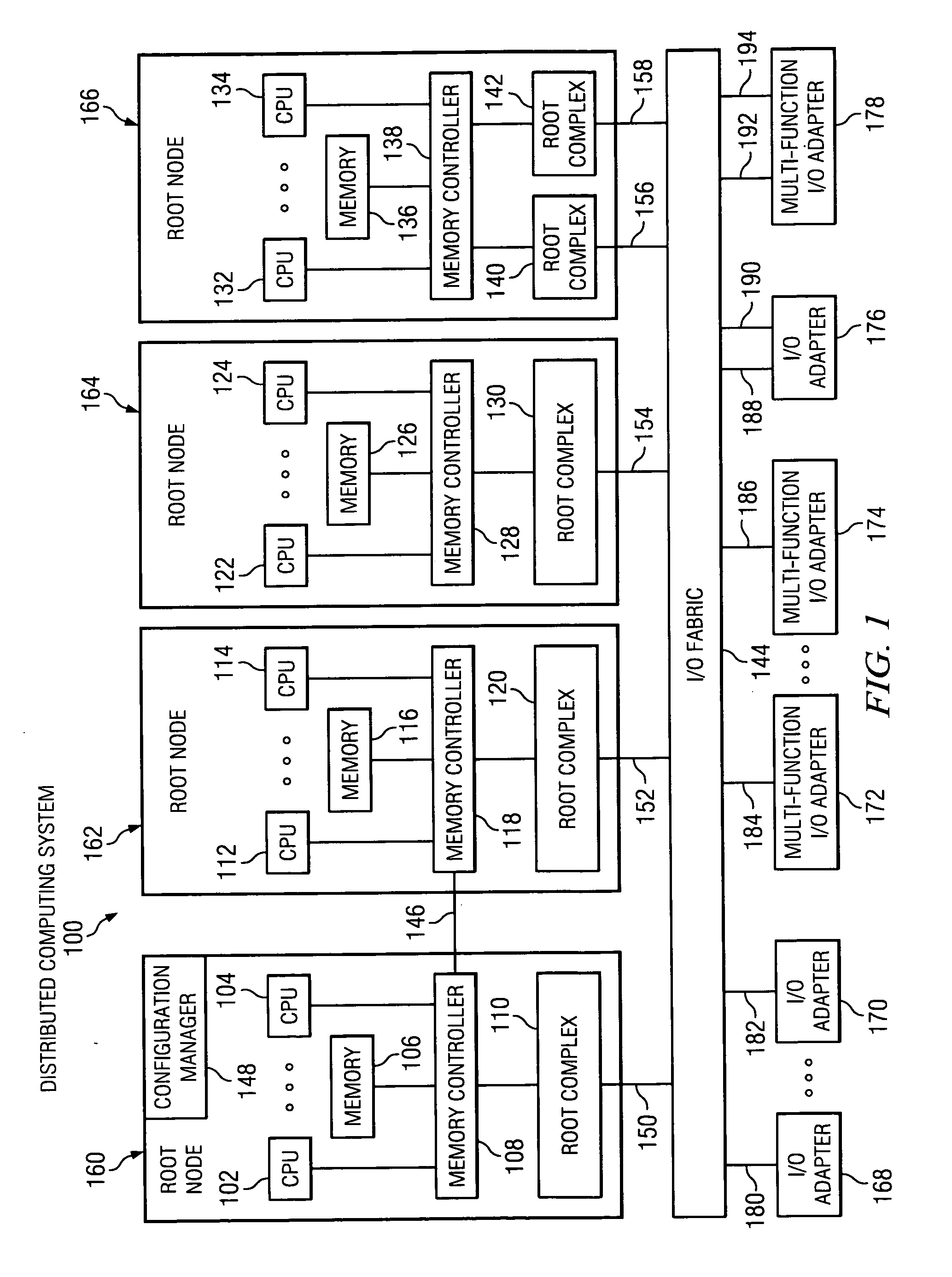
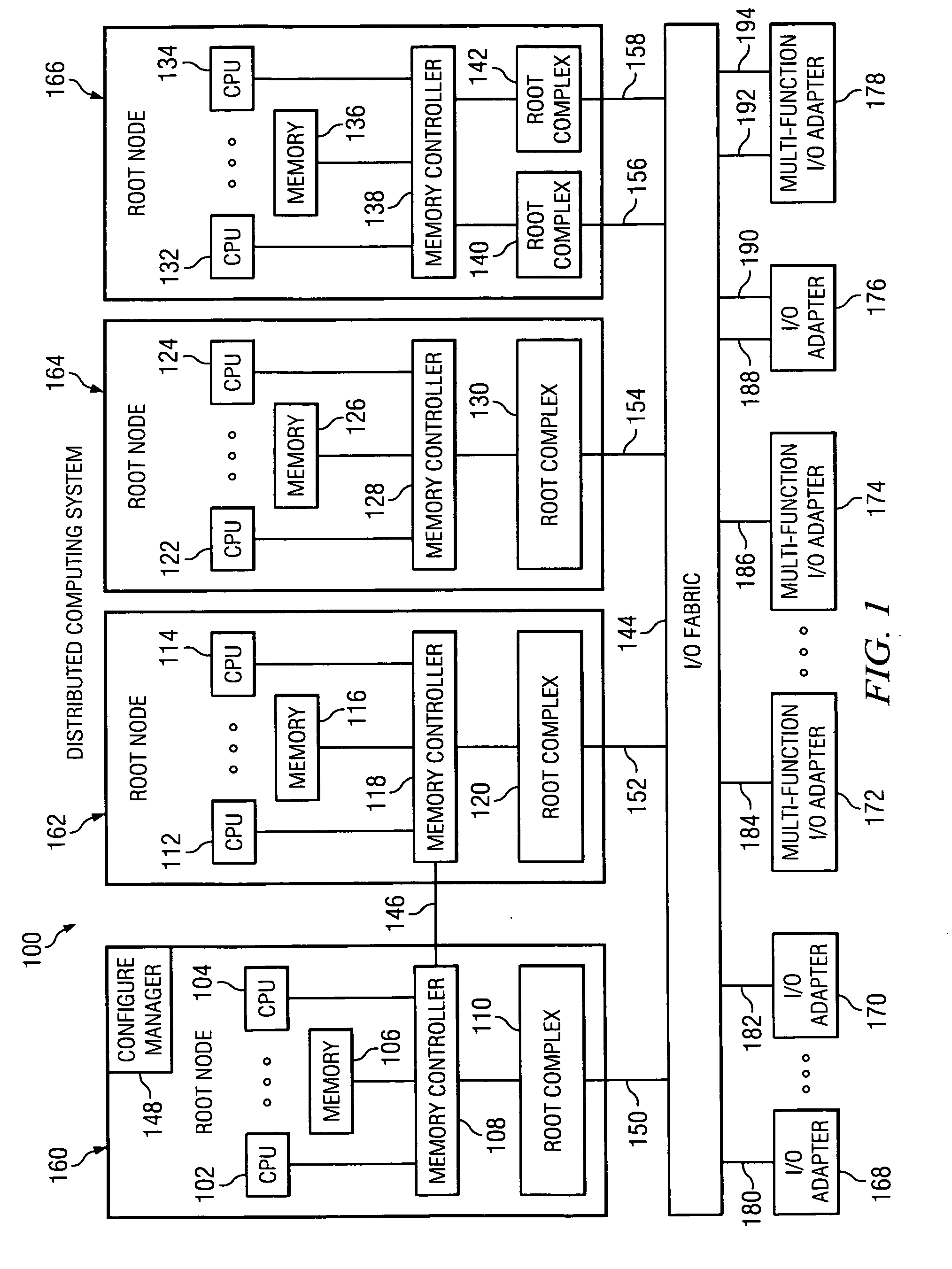
Method using a master node to control I/O fabric configuration in a multi-host environment
InactiveUS20070097949A1Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationComputerized systemHosting environment
A method is directed to use of a master root node, in a distributed computer system provided with multiple root nodes, to control the configuration of routings through an I / O switched-fabric. One of the root nodes is designated as the master root node or PCI Configuration Manager (PCM), and is operable to carry out the configuration while each of the other root nodes remains in a quiescent or inactive state. In one useful embodiment pertaining to a system of the above type, that includes multiple root nodes, PCI switches, and PCI adapters available for sharing by different root nodes, a method is provided wherein the master root node is operated to configure routings through the PCI switches. Respective routings are configured between respective root nodes and the PCI adapters, wherein each of the configured routings corresponds to only one of the root nodes. A particular root node is enabled to access each of the PCI adapters that are included in any configured routing that corresponds to the particular root node. At the same time, the master root node writes into a particular root node only the configured routings that correspond to the particular root node. Thus, the particular root node is prevented from accessing an adapter that is not included in its corresponding routings.
Owner:IBM CORP
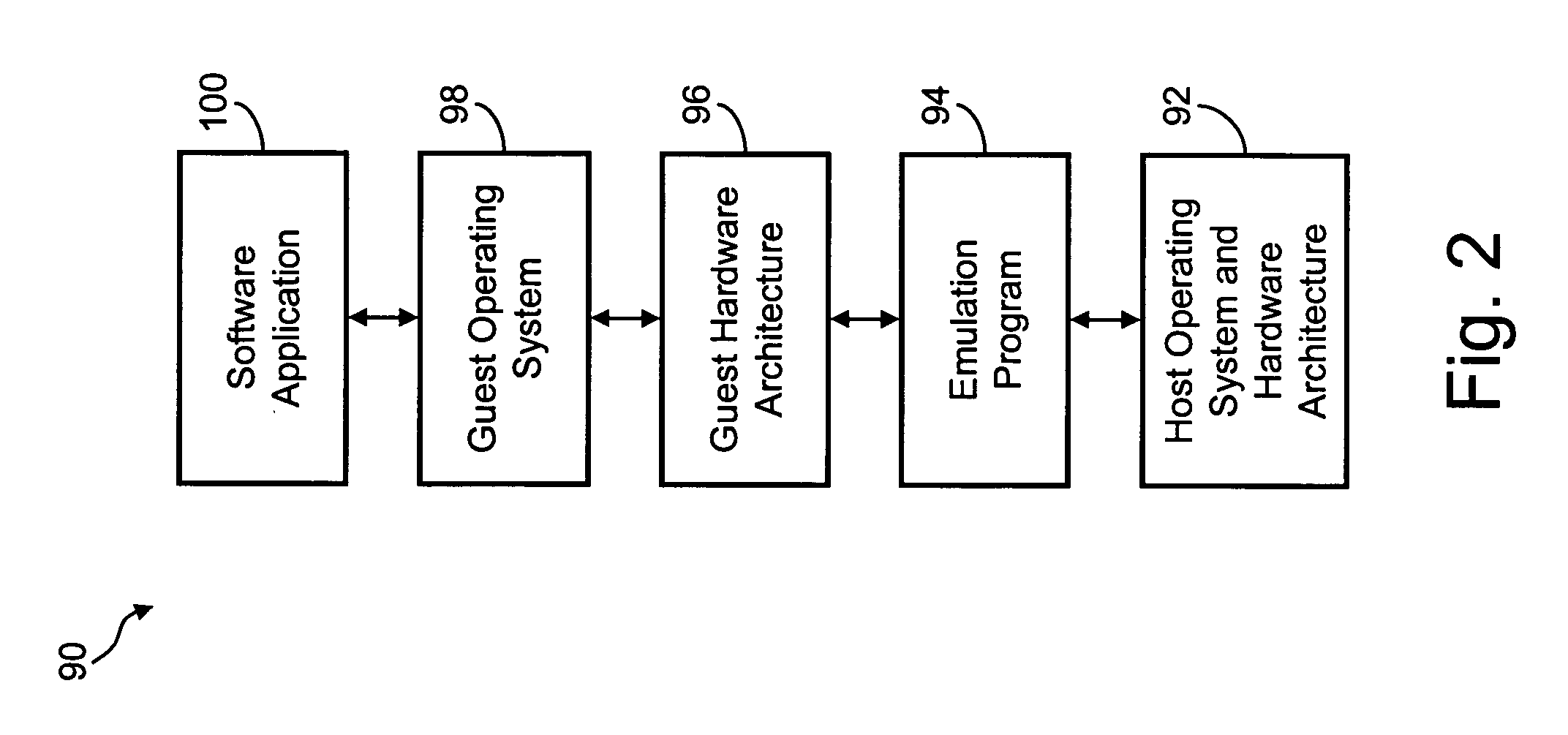
Method of measuring performance of an emulator and for adjusting emulator operation in response thereto
InactiveUS6882968B1Consistent and accurate outputHardware monitoringGenerating/distributing signalsParallel computingHosting environment
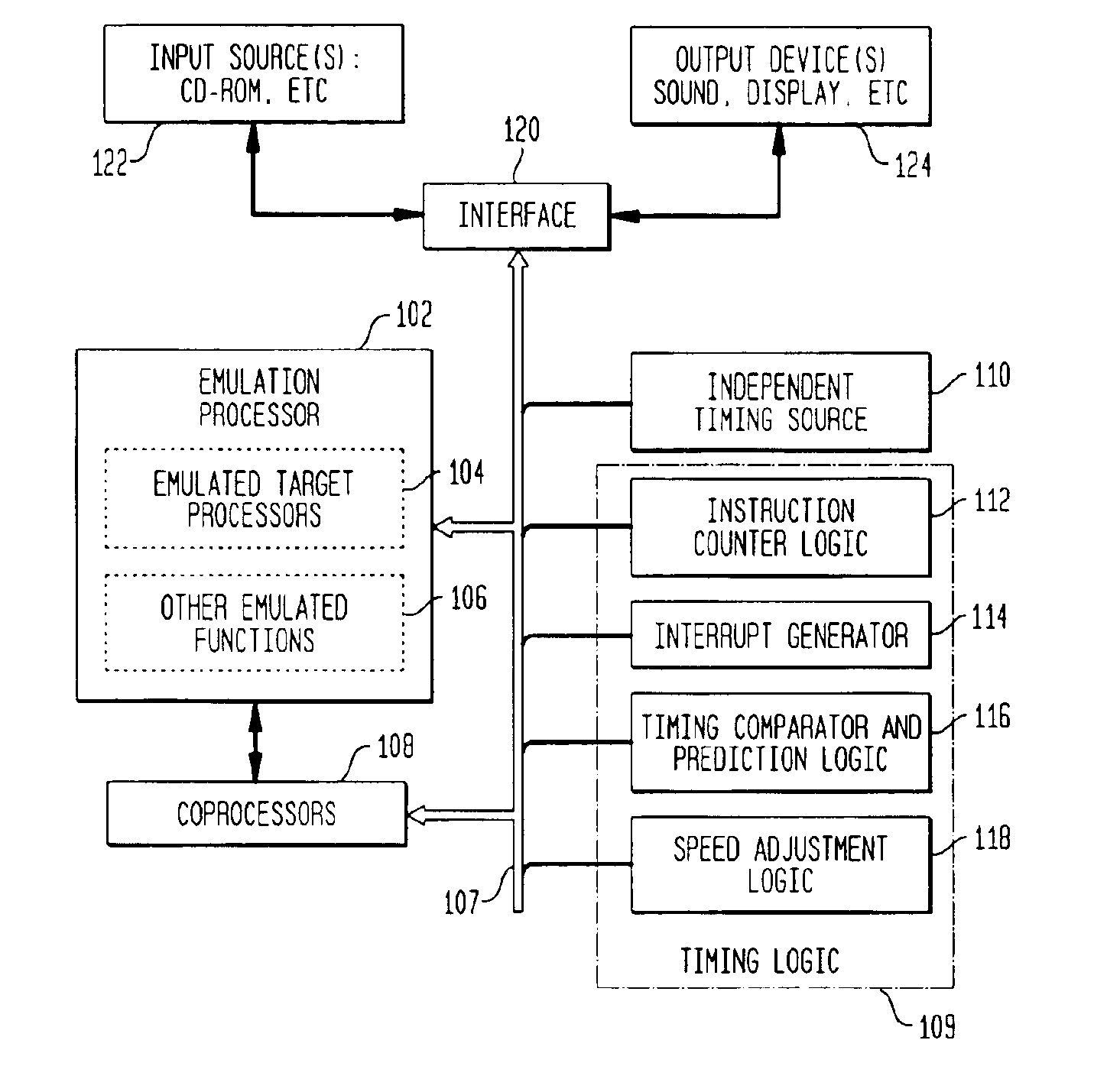
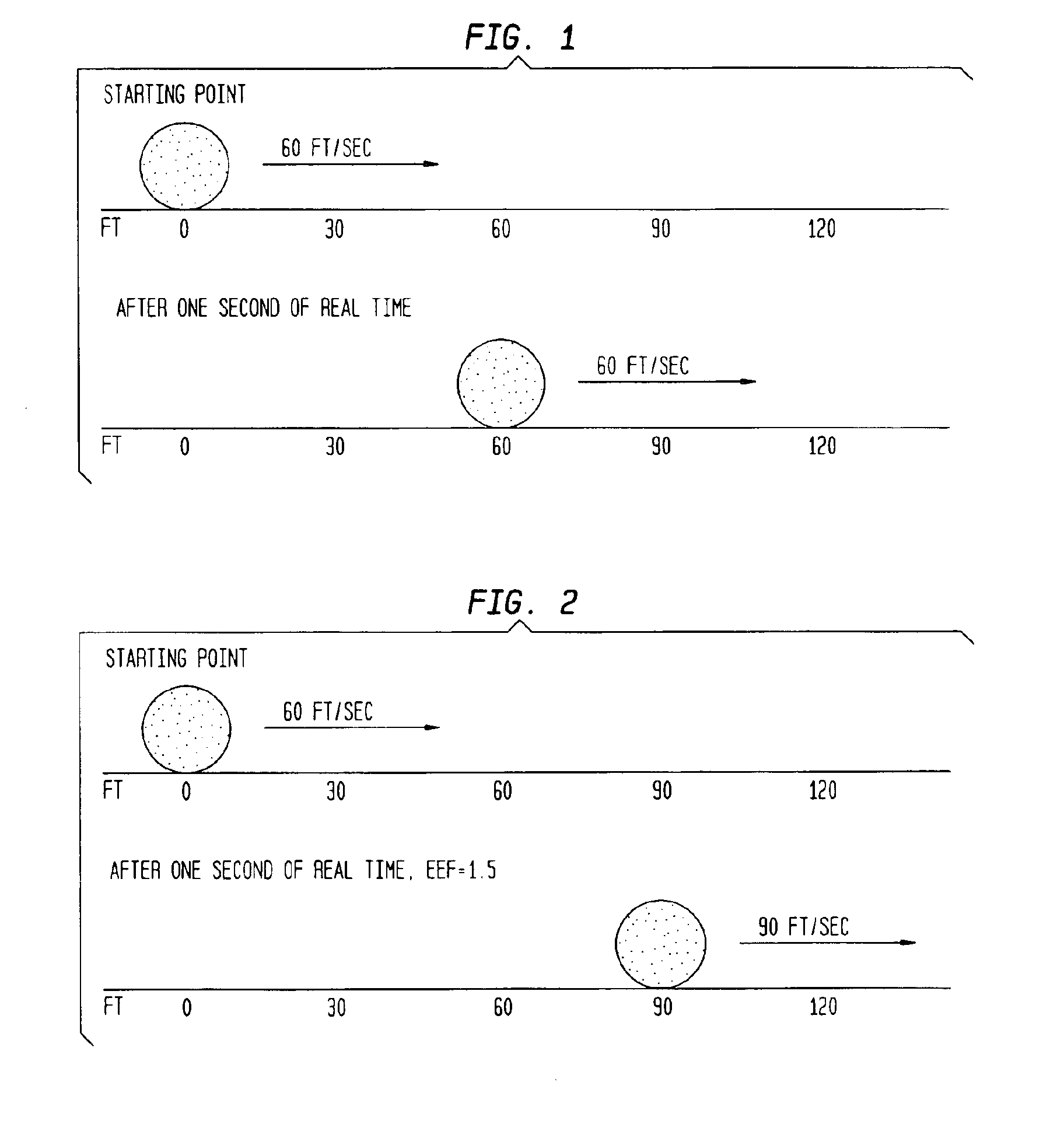
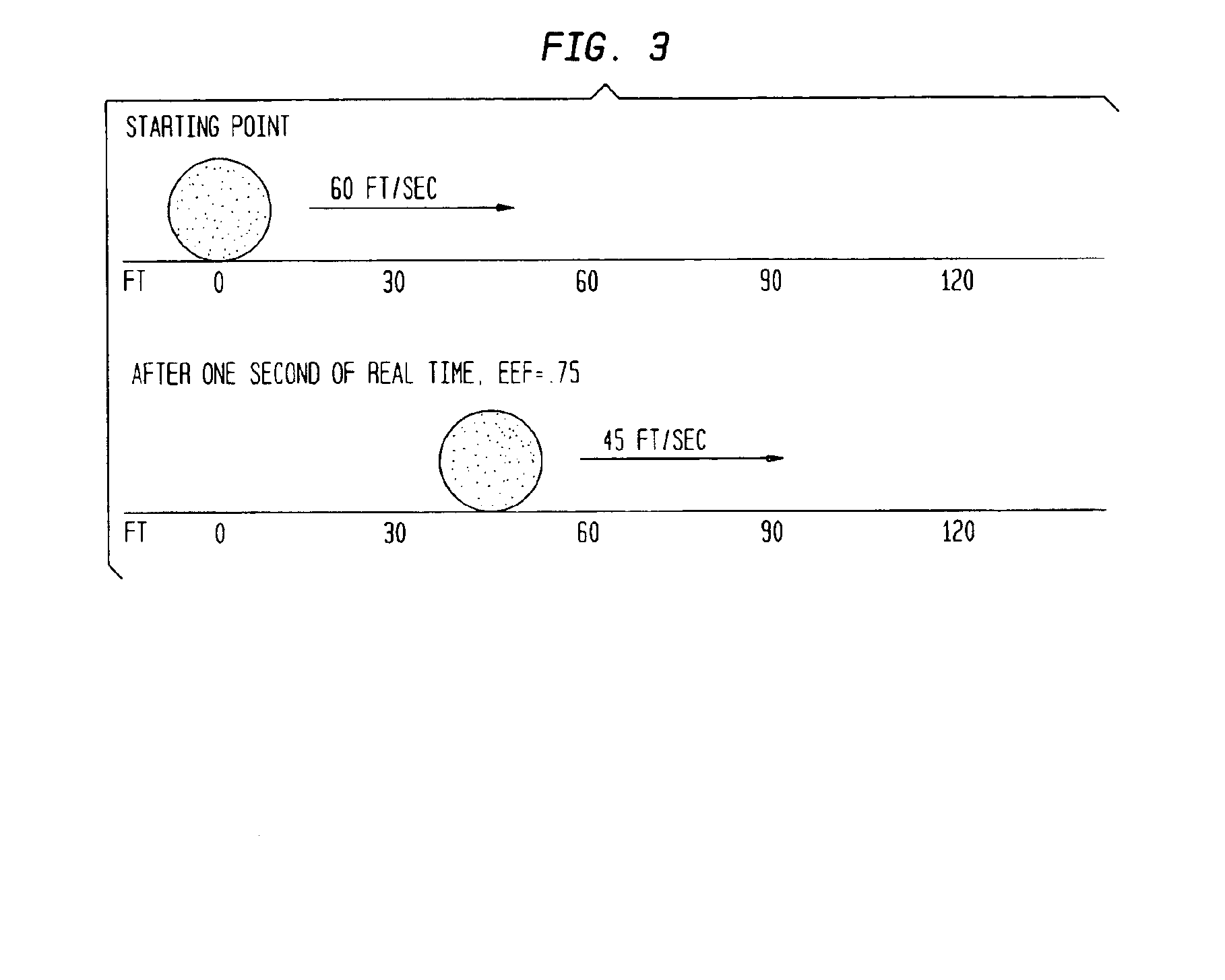
A method which simulates the operating speed of an emulated target system with a consistent rate of instruction execution on a plurality of host systems with varied and variable instruction execution speeds. An arbitrary “time quantum” is selected as a referent and is multiplied by the target's speed of instruction cycle execution to determine the quantity of instructions the target system executes in the specified time period. When non-native code is executed on the host system, a counter is used to track the number of instructions executed and to interrupt when that target quantity is reached. A processor-activity-independent timing source is queried to determine the time elapsed; that measurement is then compared to the original “time quantum.” The resulting ratio is a timing reference that is independent of the operating speed characteristics of any particular host system. This reference is used to predict the operational speed of the host system and to adjust factors in the host computer and emulation process to more accurately match the target system before executing the next block of instructions and repeating the process. In certain embodiments, the time quantum is dynamically adjusted to avoid sampling frequencies, which may conflict or resonate with timing frequencies of other system activities or to place a greater or lesser load on the host system. This process results in more consistent, accurate simulation of the target system's speed on a variety of host system configurations, within the limitations and flexibility of the host environment.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Dynamic management of addresses to an input/output (I/O) device
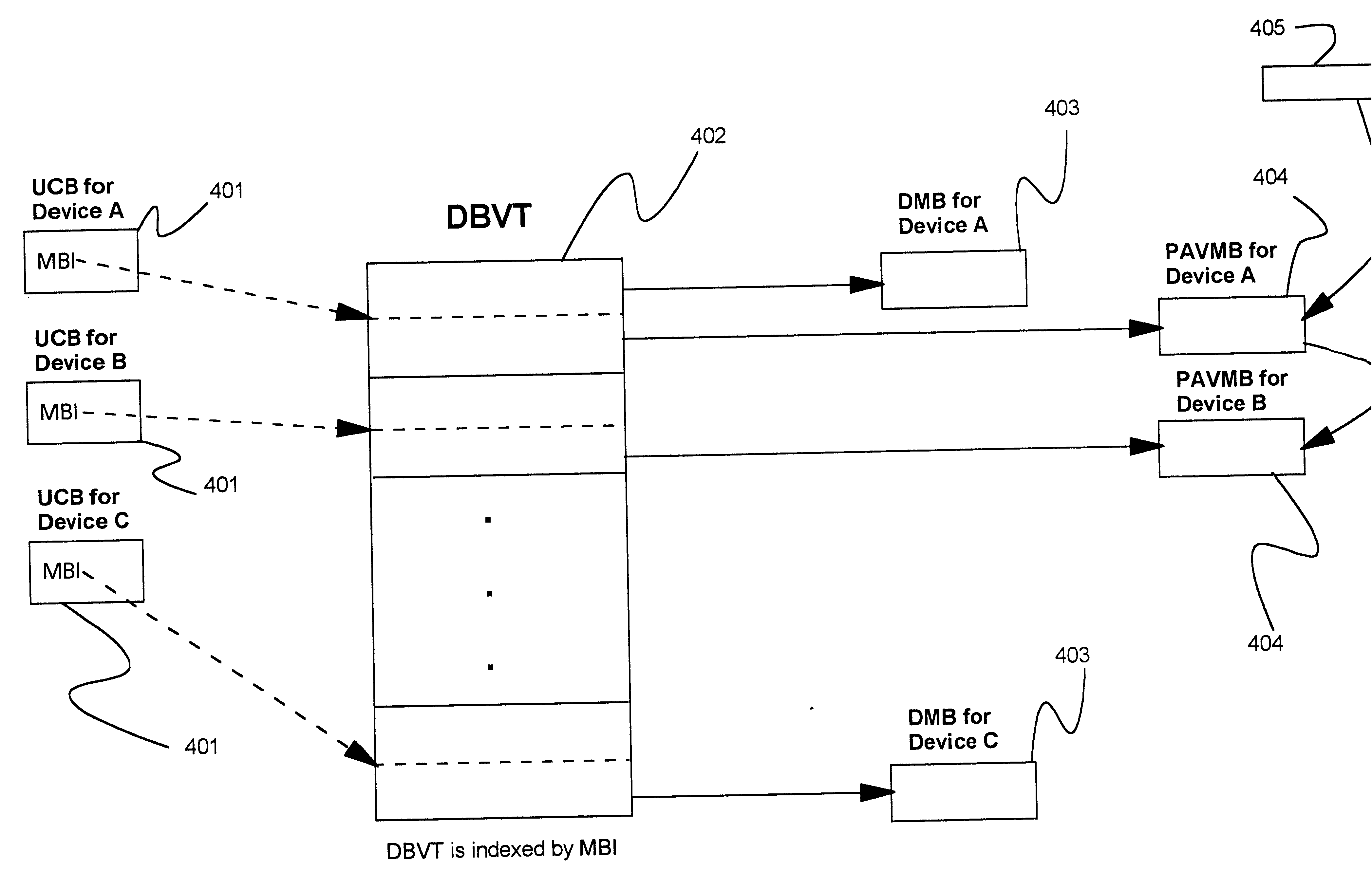
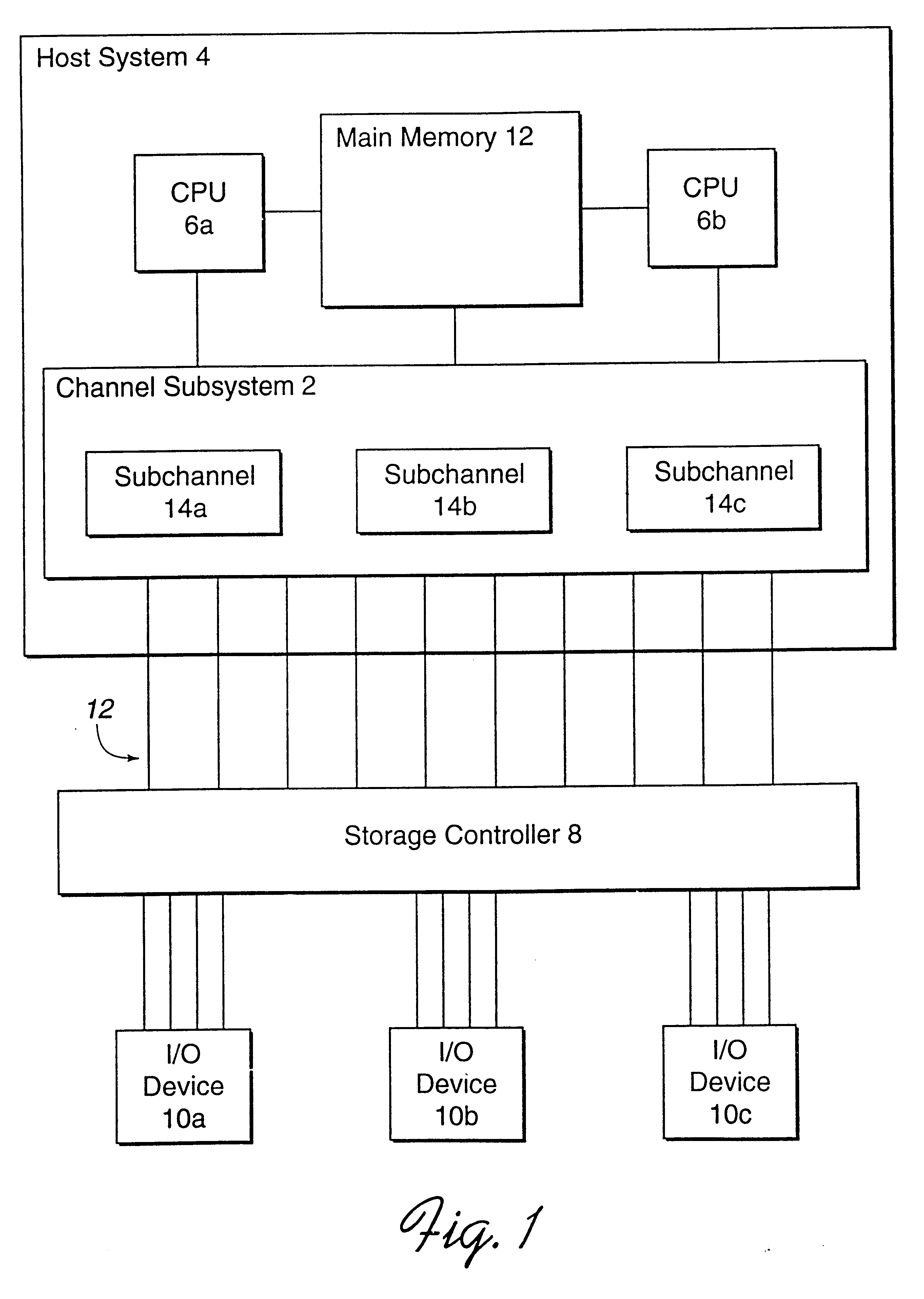
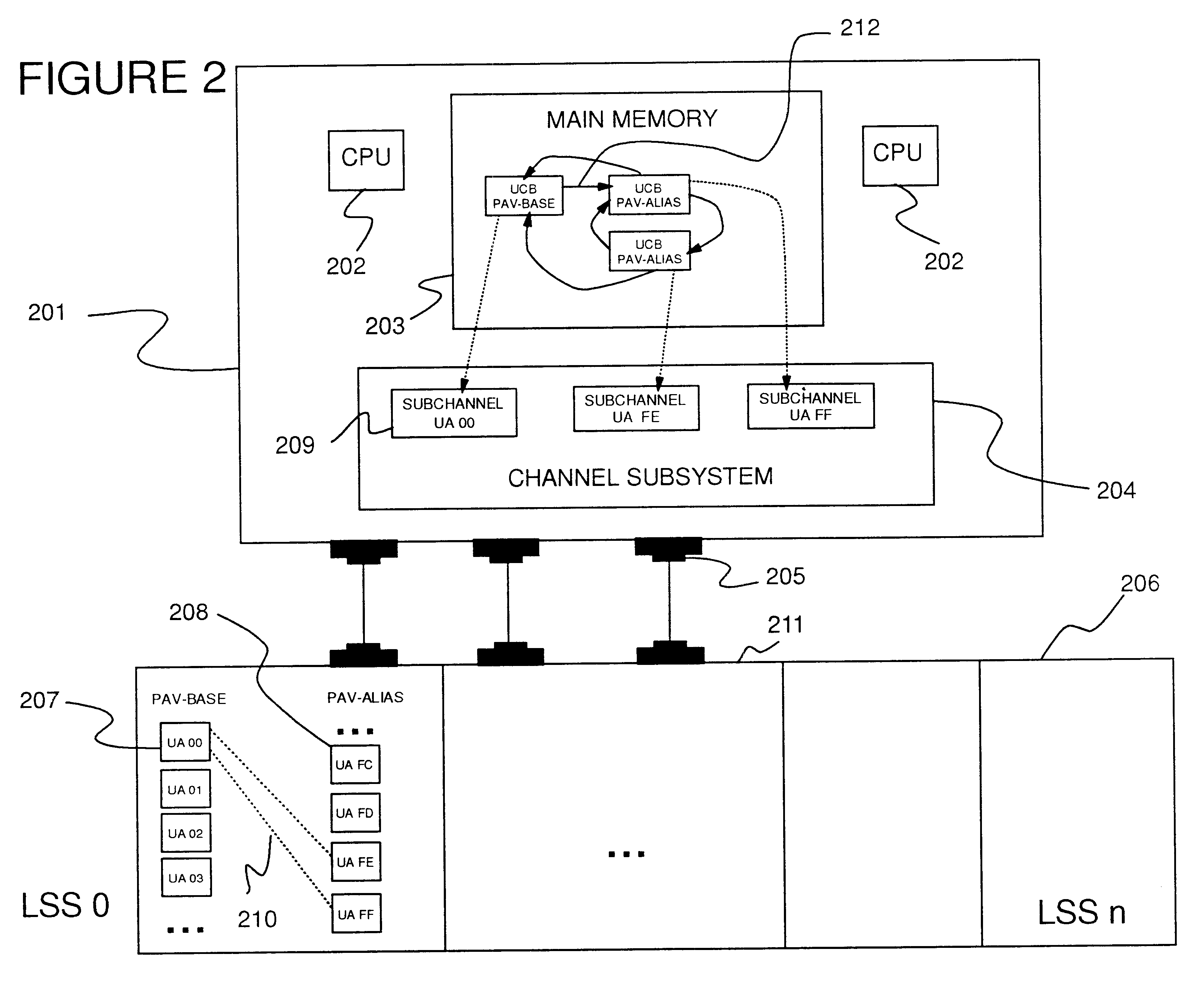
InactiveUS6622177B1Increase profitMultiple digital computer combinationsInput/output processes for data processingDirect-access storage deviceHosting environment
Disclosed is a method and computer program device for dynamically managing the assignment of alias addresses to base addresses referencing an input / output (I / O) device, such as a direct access storage device (DASD). Two distinct methods are disclosed. In one method, alias addresses are assigned based on the performance of the I / O devices. In this method, alias addresses are assigned to highly utilized devices, as indicated by device performance data, in order to maximize the efficient utilization of I / O device resources. In a second method, workload management principles are utilized to assign alias addresses. In this method, a correlation is made between each I / O device and the service classes utilizing each device. As in the first method, performance data is generated for each I / O device. Alias addresses are assigned to I / O devices experiencing queue delays as indicated by their performance data, if the device is associated with a service class that has failed to meet one or more processing goals. These methods may operate on a single host, or in a multi-host environment. The methods may be operated individually, or concurrently. Methods are disclosed to manage contention between concurrently operating assignment methods, and between multiple hosts concurrently operating one or more assignment methods.
Owner:IBM CORP
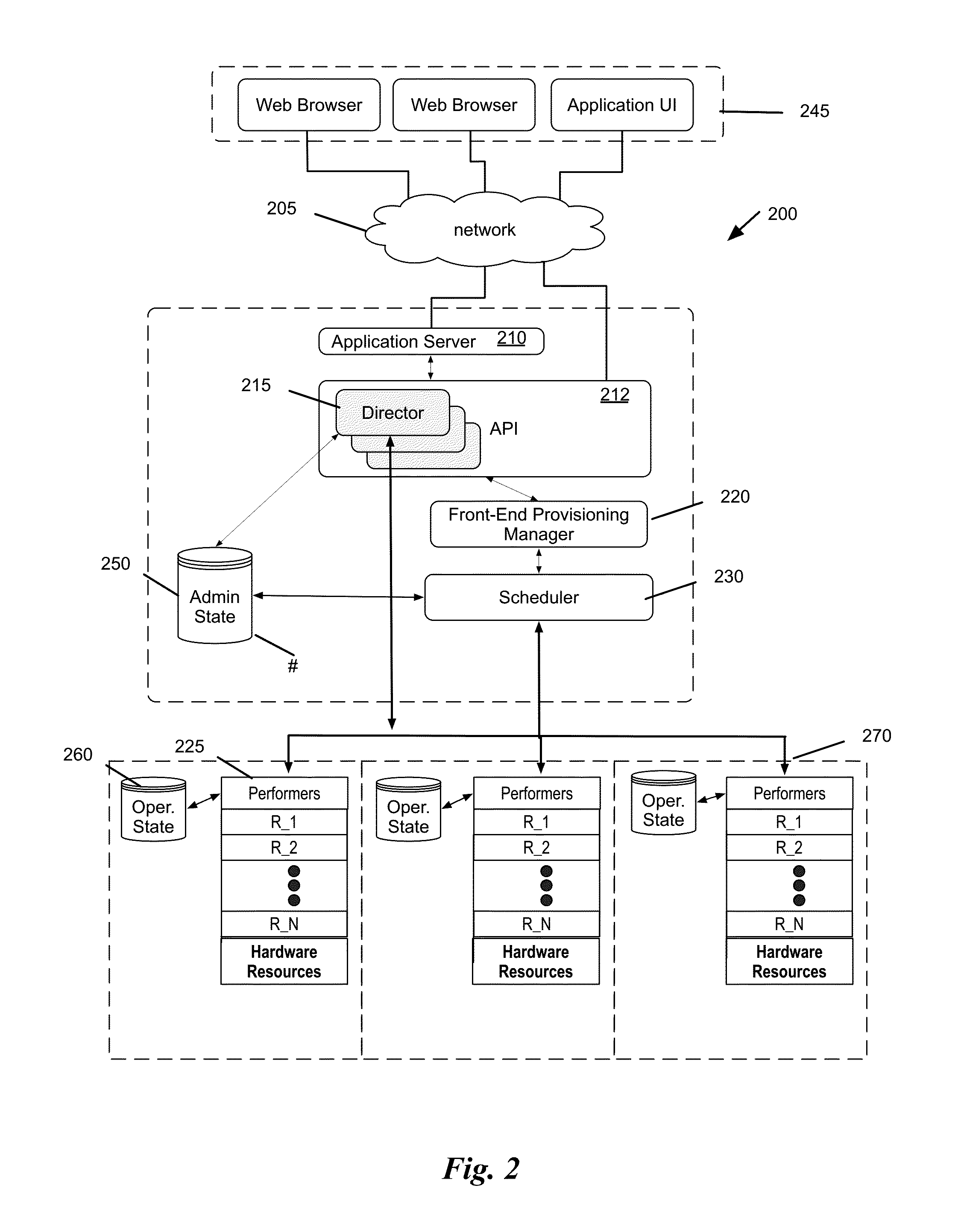
System and method for distributed management of cloud resources in a hosting environment
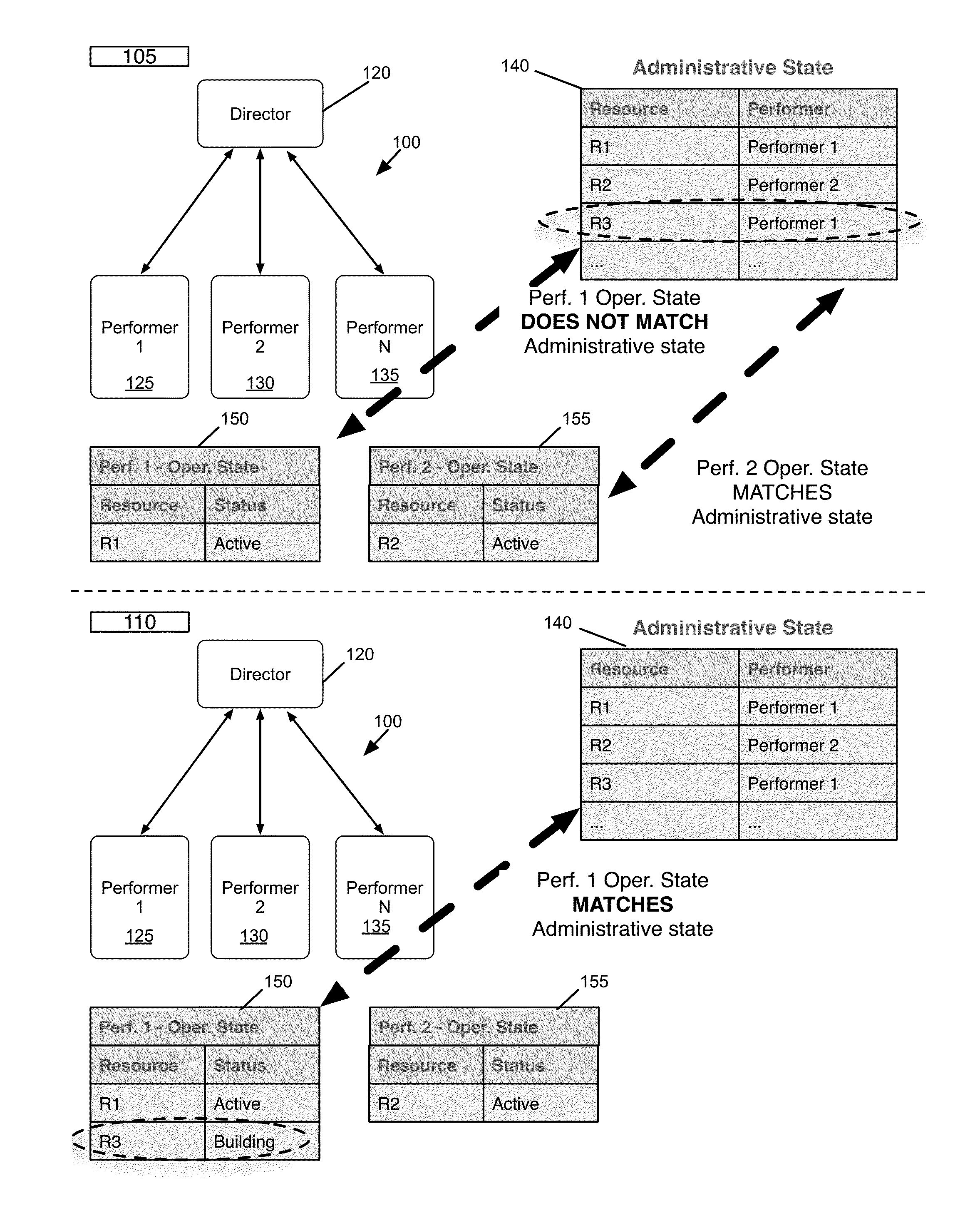
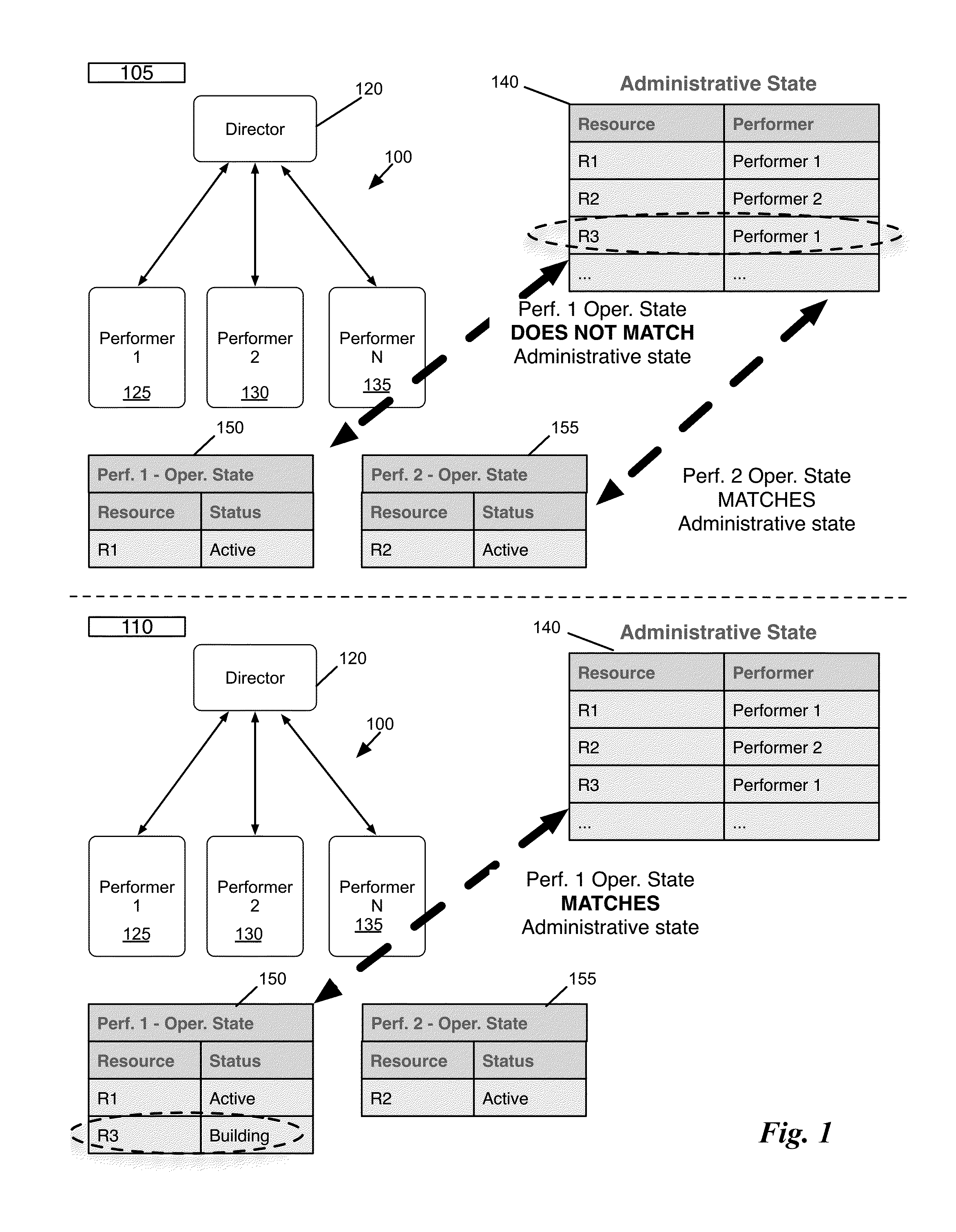
ActiveUS9350681B1Efficient managementDigital computer detailsData switching networksHosting environmentCloud resources
Some embodiments provide a method of managing cloud resources on several of nodes of a hosting system. The method receives a cloud resource configuration. The method identifies a particular node from the several nodes to host the cloud resource configuration. The method sets an administrative state of the hosting system to reflect the hosting of the cloud resource configuration on the particular node. The administrative state includes information for each node in the hosting system. Each node includes a performer operating on the node that manages an operational state of the node based on the administrative state of the node.
Owner:OPEN INVENTION NEWTORK LLC
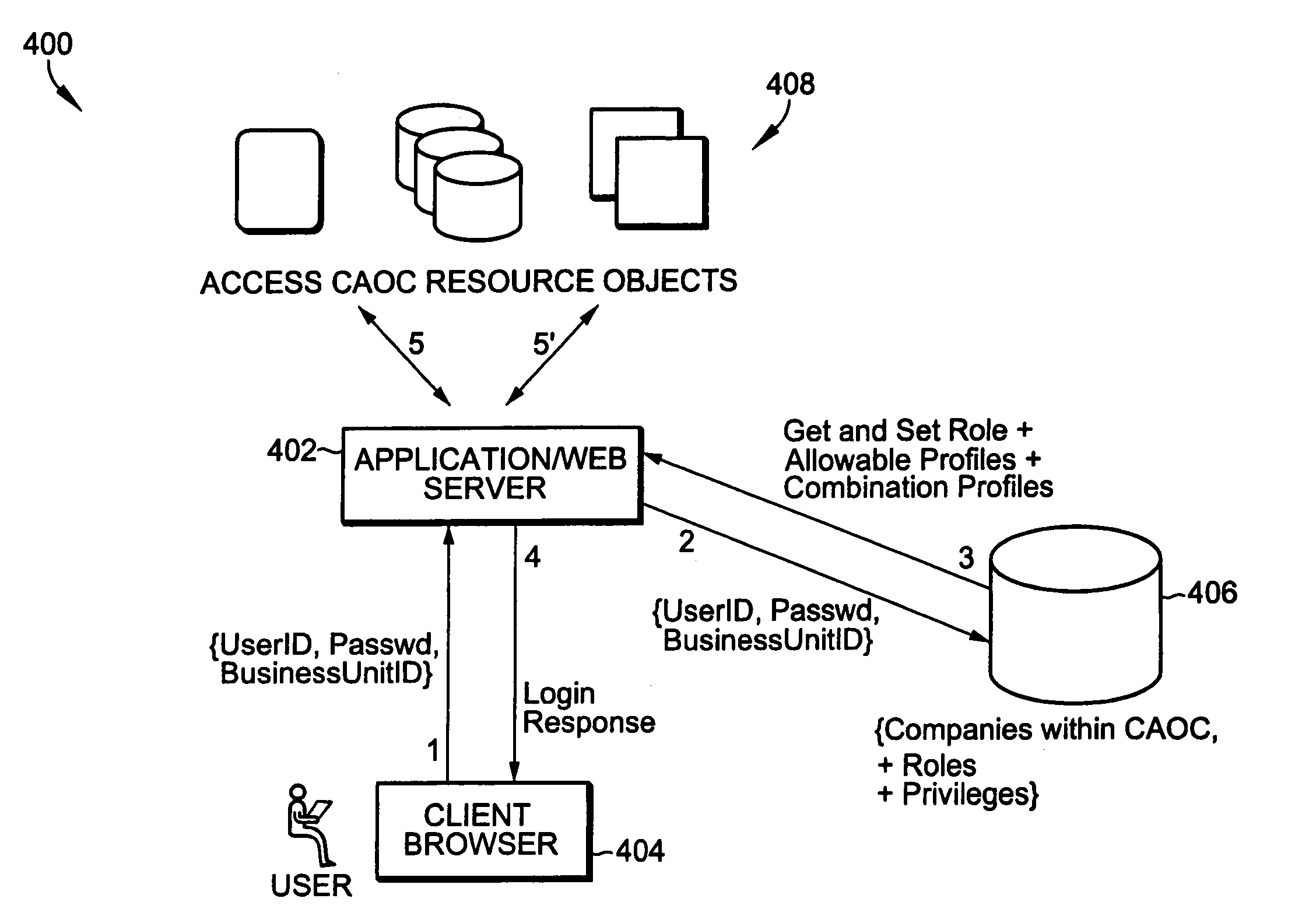
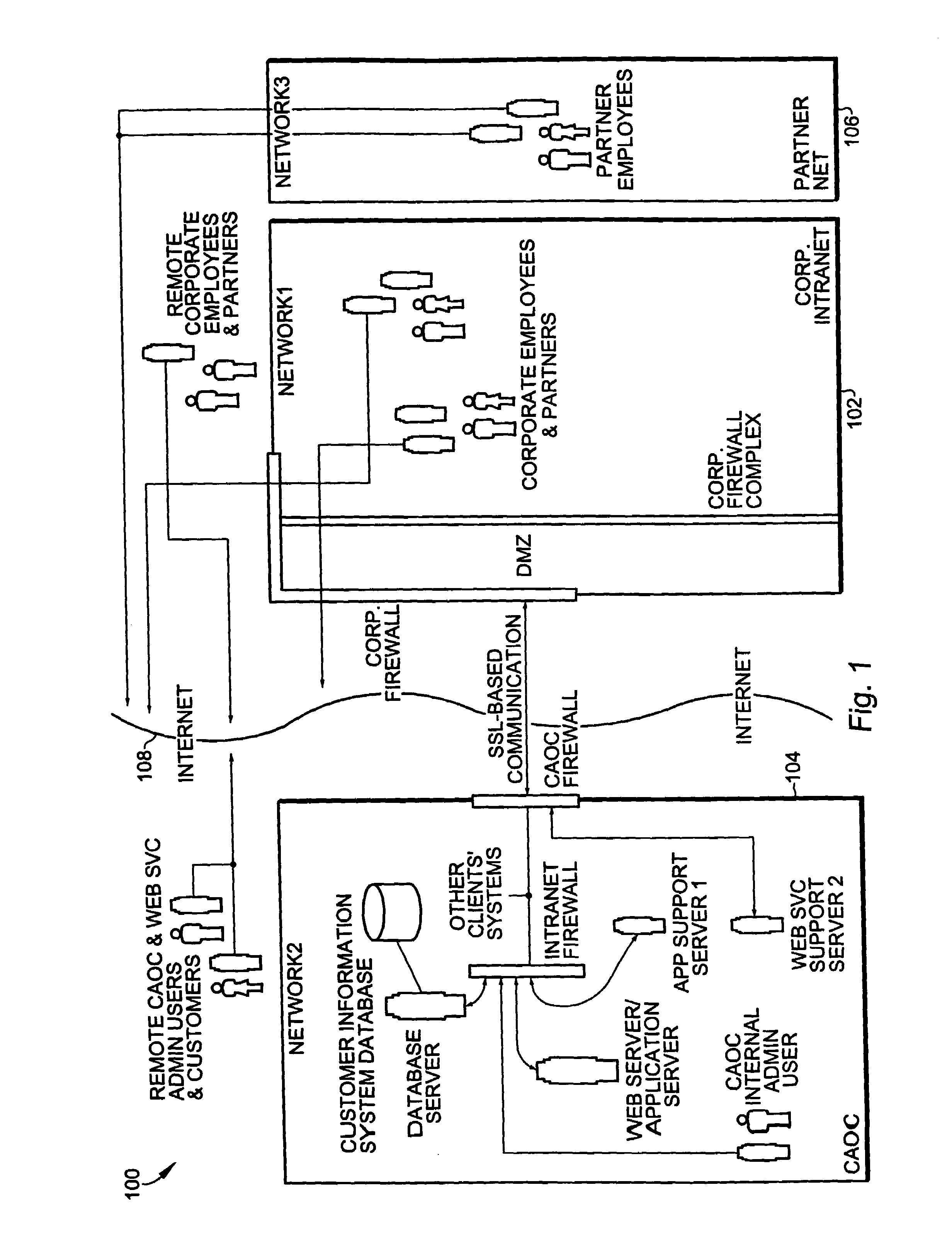
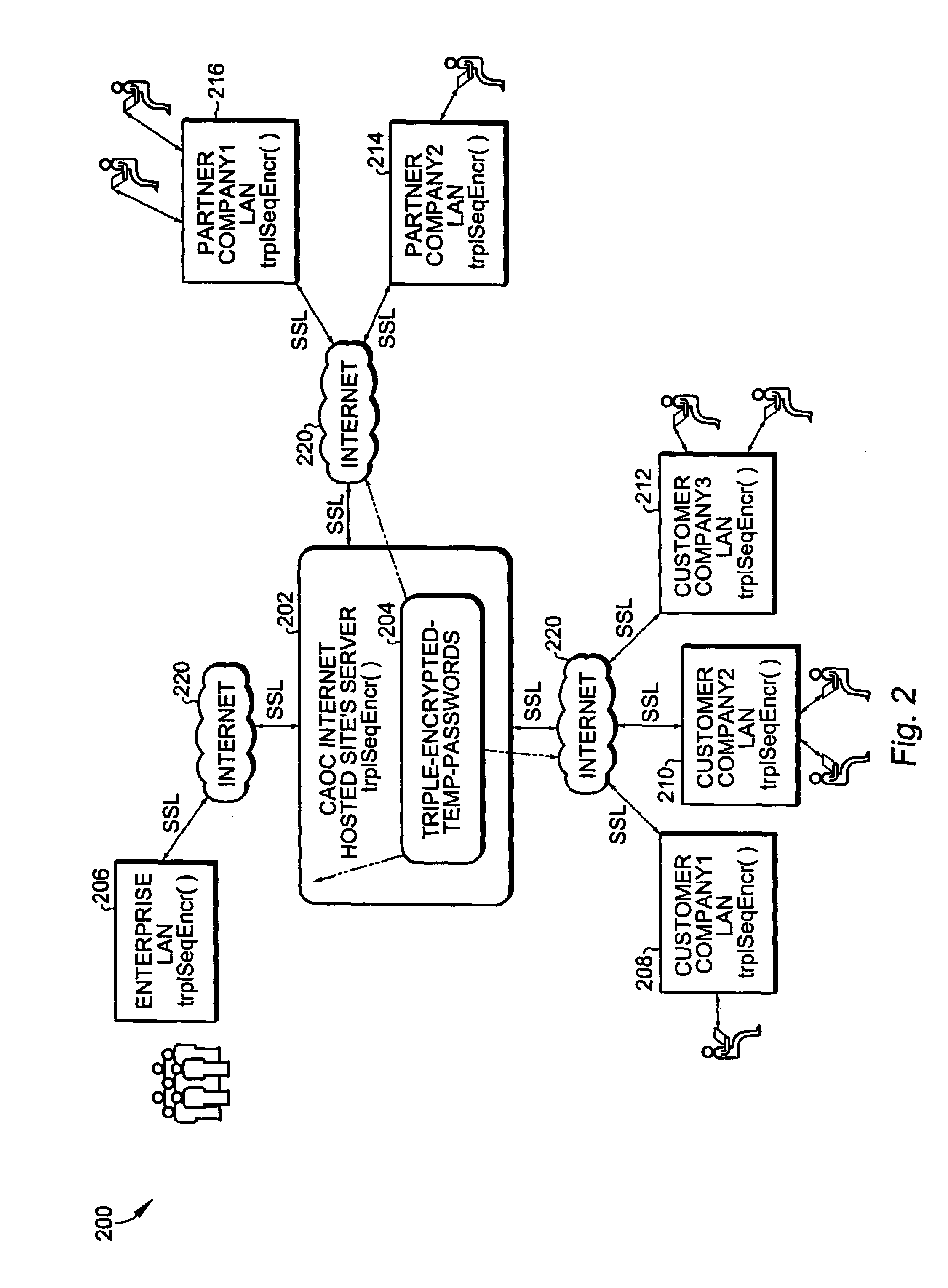
Role-based access using combinatorial inheritance and randomized conjugates in an internet hosted environment
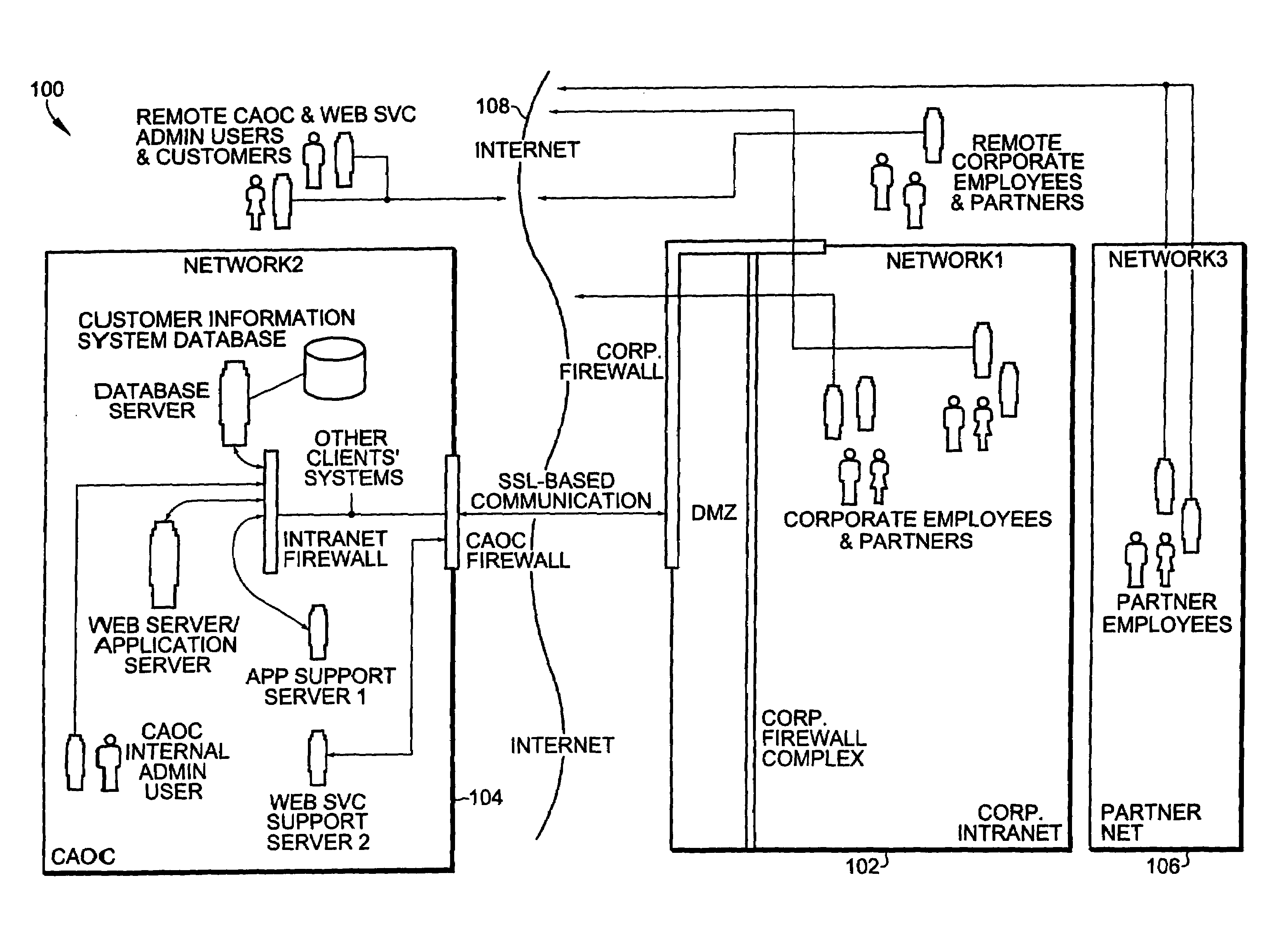
ActiveUS7730523B1Improve functionalityHigh processDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsPasswordWeb service
A method for remote services authentication in an internet hosted environment includes a high level process and functionality for a secure, practical and logically optimized inter-network authentication mechanism by employees, partners and customers of an enterprise into the hosted Internet site. The lightweight authentication and authorization mechanism can be most effectively implemented in Java as part of the application or web server servlet. The method for remote services authentication includes initial secure password establishment, subsequent authentication and authorization, as well as authentication and authorization upon resuming previously run sessions with the hosted server using Internet cookies.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
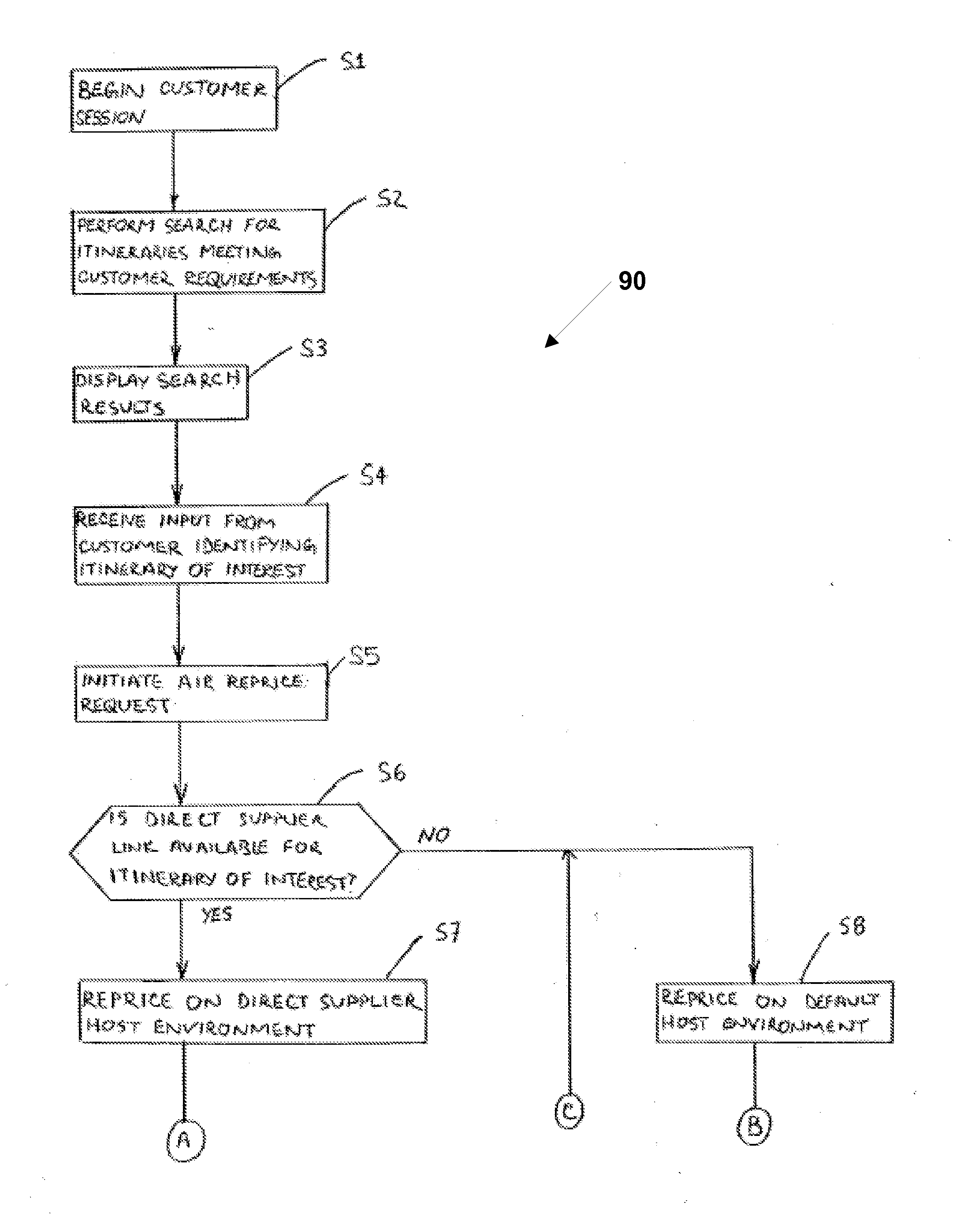
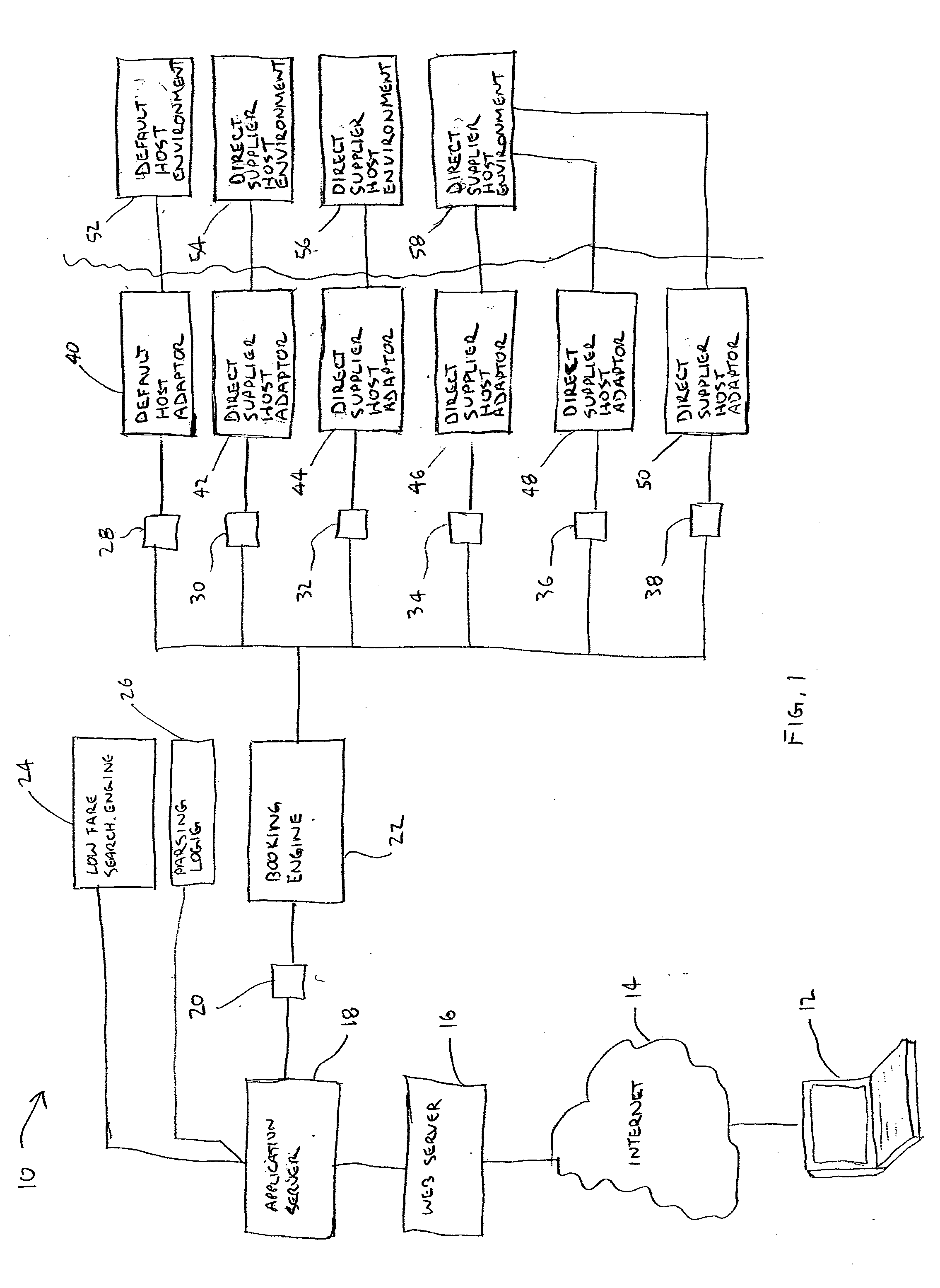
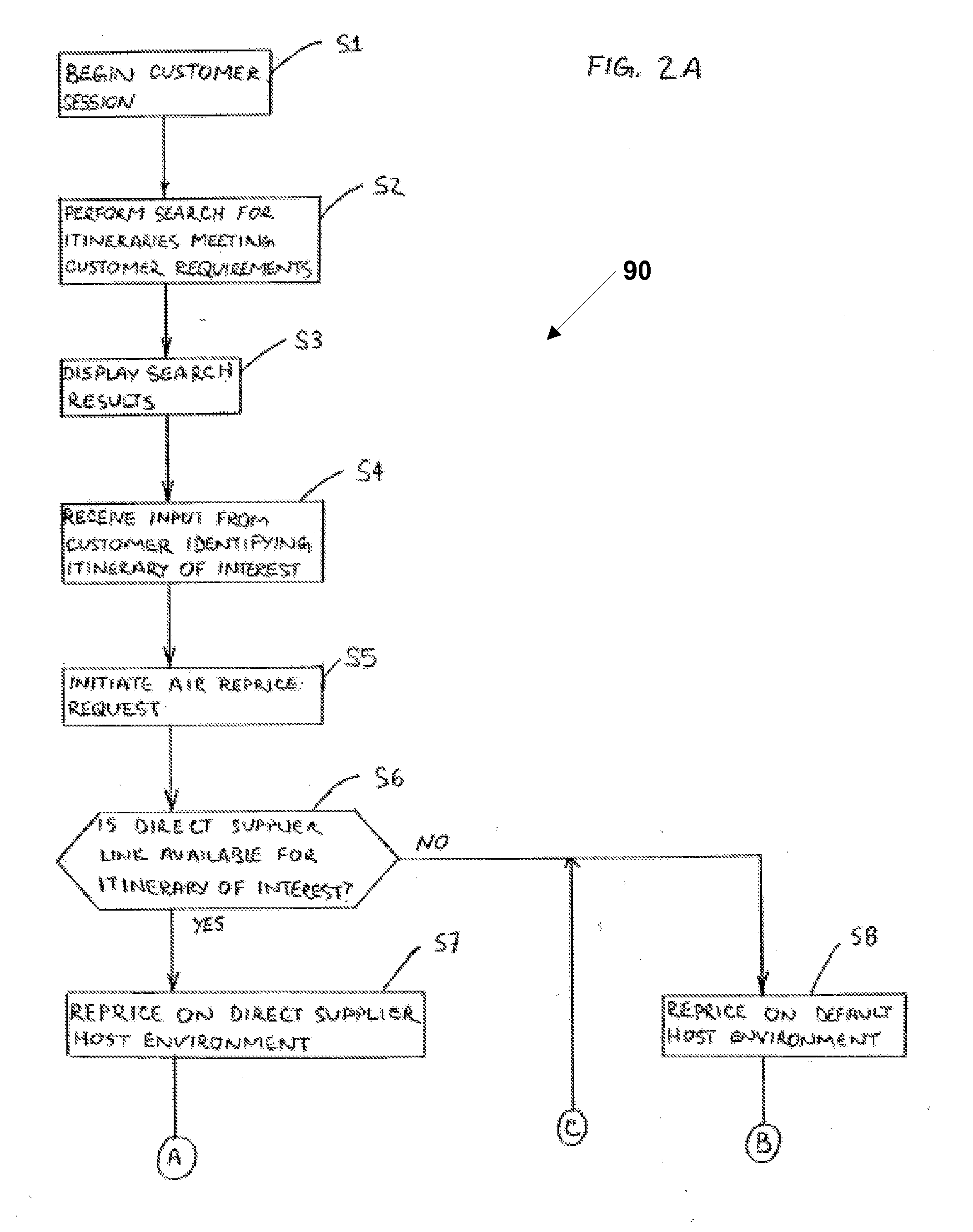
Booking engine for booking airline tickets on multiple host environments
A system and method of booking an itinerary on at least one of a multiplicity of host environments include a plurality of host adaptor modules. Each host adaptor module is configured to interact with one of the plurality of host ticketing environments. A booking engine is provided for receiving commands related to booking the air travel itinerary and determining an appropriate host ticketing environment for processing the commands based on a number of predefined criteria. When the booking engine receives a command it forwards the command to a first host adaptor module which is associated with first host ticketing environment selected by the booking engine for processing the command. The host adaptor module receives the command and issues the command to said first host ticketing environment. The first host adaptor module in turn receives a response from the first host ticketing environment and determines whether the response comports with an expected response. If the response does not comport with the expected response, the booking engine identifies a second appropriate host environment for processing the command and forwards the command to a second host adaptor module associated with the second host ticketing environment. The second host adaptor module then issues the command to the second host ticketing environment.
Owner:ORBITZ
Methods and apparatus for persistence of authentication and authorization for a multi-tenant internet hosted site using cookies
ActiveUS7650505B1Improve functionalityHigh processUser identity/authority verificationWeb servicePassword
A method for remote services authentication in an internet hosted environment includes a high level process and functionality for a secure, practical and logically optimized inter-network authentication mechanism by employees, partners and customers of an enterprise into the hosted Internet site. The lightweight authentication and authorization mechanism can be most effectively implemented in Java as part of the application or web server servlet. The method for remote services authentication includes initial secure password establishment, subsequent authentication and authorization, as well as authentication and authorization upon resuming previously run sessions with the hosted server using Internet cookies.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
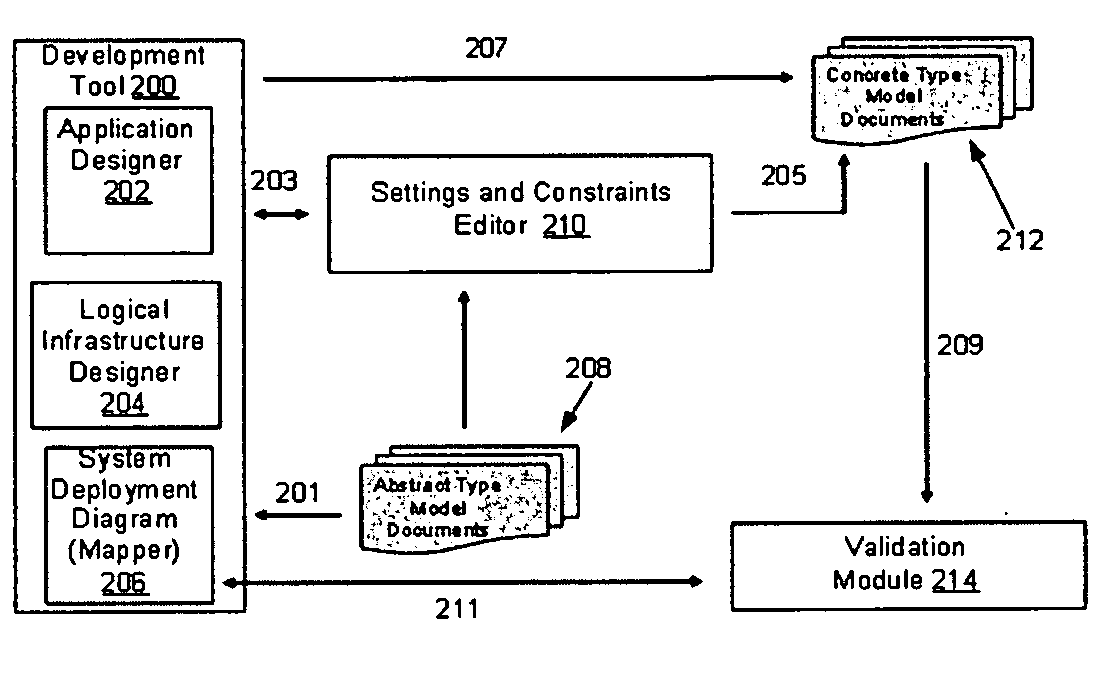
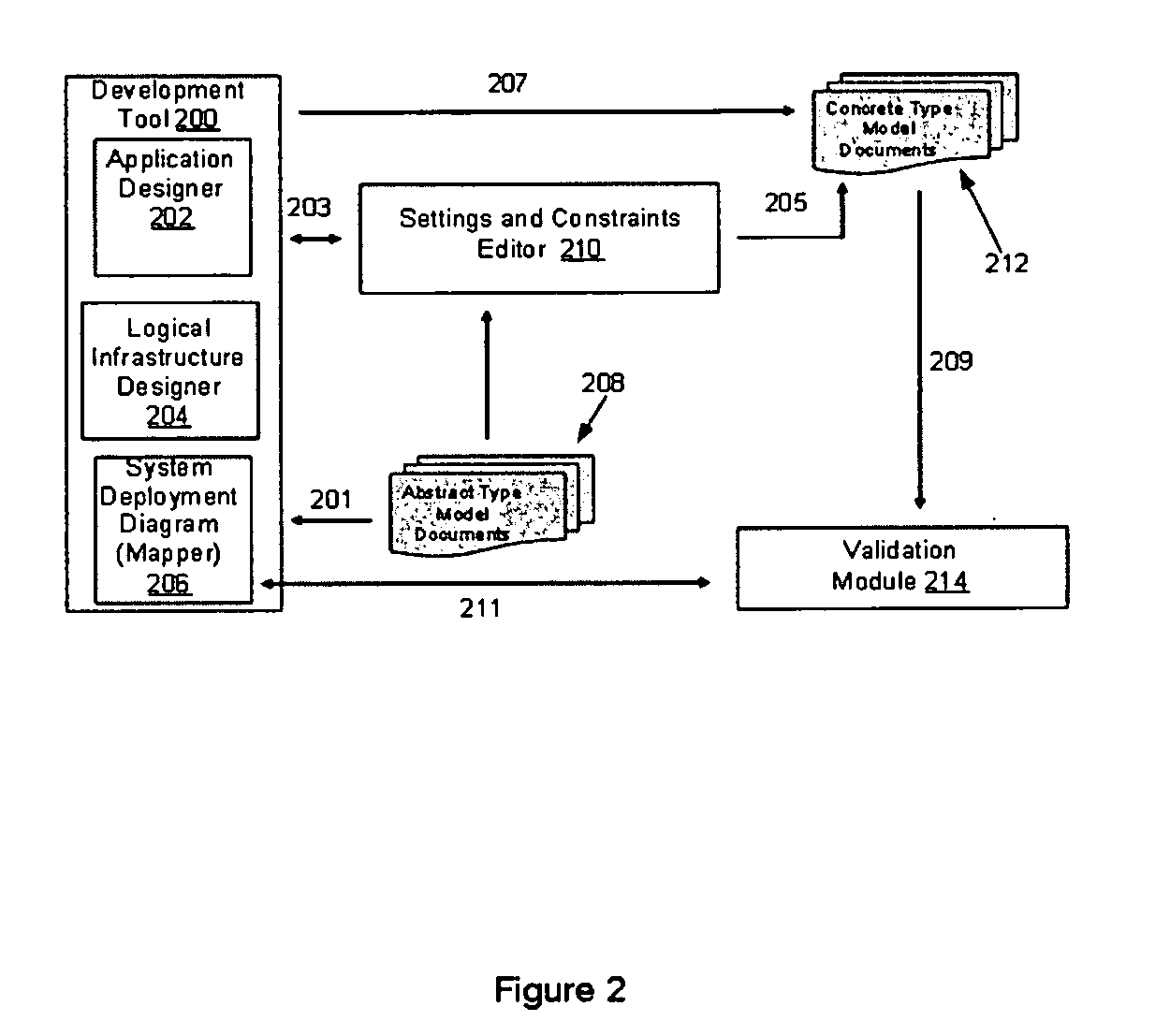
Settings and constraints validation to enable design for operations
ActiveUS20050251783A1Reduce modificationDigital computer detailsRequirement analysisHosting environmentDesign systems
Systems and methods for designing systems that include computer applications hosted on hosting environments are disclosed. The hosting environments are modeled to include hosting environment settings and constraints placed on applications. The applications are also modeled to include application settings and constraints placed on the hosting environments. Hosting environment and application models are then used to validate designs by confirming that settings are in compliance with the constraints.
Owner:SERVICENOW INC
Broadcast of shared I/O fabric error messages in a multi-host environment to all affected root nodes
ActiveUS20070027952A1Transmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsHosting environmentPCI Express
A method, mechanism and computer usable medium is provided for distributing I / O fabric errors to the appropriate root nodes in a multi-root environment. The case where the I / O fabric is attached to more than one root node and where each root can potentially share with the other roots the I / O adapter (IOA) resources which are attached to the I / O is addressed. Additionally, a method, mechanism and computer usable medium is provided by which errors detected in an I / O fabric may be routed to all root nodes which may be affected by the error, while not being reported to the root nodes that will not be affected by those errors. In particular, distributed computing system which uses the PCI Express protocol to communicate over the I / O fabric is addressed.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for confirming identity of a master node selected to control I/O fabric configuration in a multi-host environment
InactiveUS20070101016A1Multiple digital computer combinationsElectric digital data processingHosting environmentDistributed computing
In a distributed computer system having multiple root nodes, a challenge protocol is provided, for use in determining or confirming the root node in which a PCI Configuration Manager (PCM) actually resides. This node is referred to as the master node. The challenge procedure is activated whenever the identity of the PCM, which is determined by the root node in which it resides, appears to be uncertain. The challenge procedure resolves this uncertainty, and enables the PCM to continue to configure routings throughout the system. In a useful embodiment, a method is directed to a distributed computer system of the above type which is further provided with PCI switches and with adapters that are available for sharing by different nodes. The method includes the steps of selecting a first one of the root nodes to be master root node, and operating the first root node to query the configuration space of a particular one of the PCI switches. The method further includes detecting information indicating that a second root node is considered to be the master root node for the particular switch. A challenge protocol is implemented in response to this detected information, to seek confirmation that the first root node is the master root node. The configuration space querying procedure is continued if the first root node is confirmed to be the master root node, and is otherwise aborted.
Owner:IBM CORP
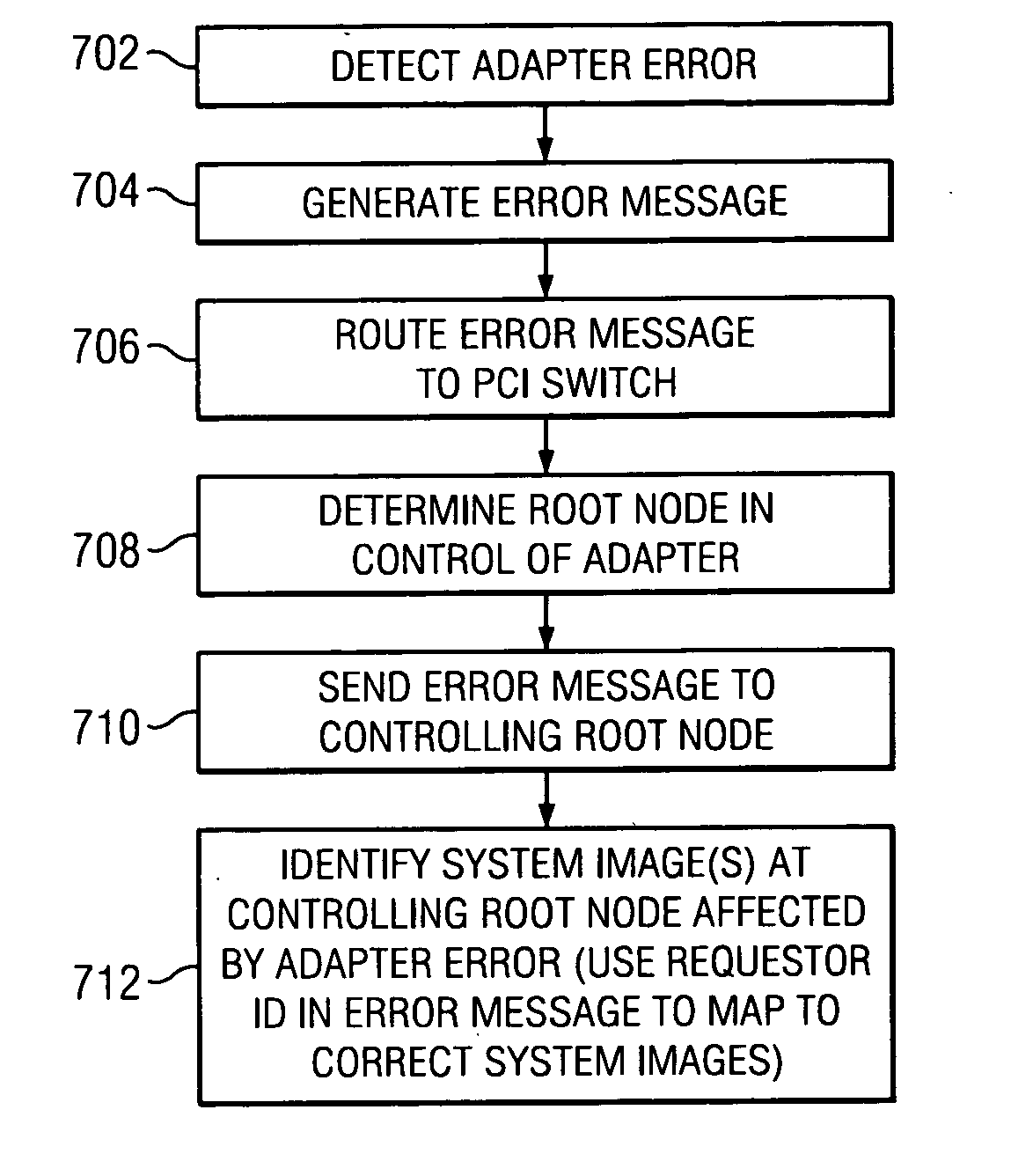
Method of routing I/O adapter error messages in a multi-host environment
A method and apparatus is provided for routing error messages in a distributed computer system comprising multiple root nodes, and further comprising one or more PCI switches and one or more I / O adapters, wherein each root node includes one or more system images. In one useful embodiment, a method is provided for routing I / O error messages to root nodes respectively associated with the errors contained in the messages. The method includes detecting occurrence of an error at a specified one of the adapters, wherein the error affects one of the system images, and generating an error message at the specified adapter. The method further comprises routing the error message from the specified adapter to the particular root node that includes the affected system image. The error message is then selectively processed at the particular root node, in order to identify the affected system image. Usefully, the step of routing the error message includes using a bus / device / function number associated with the error, together with a routing table located in one of the PCI switches, to route the error message to the correct root node and system image.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com