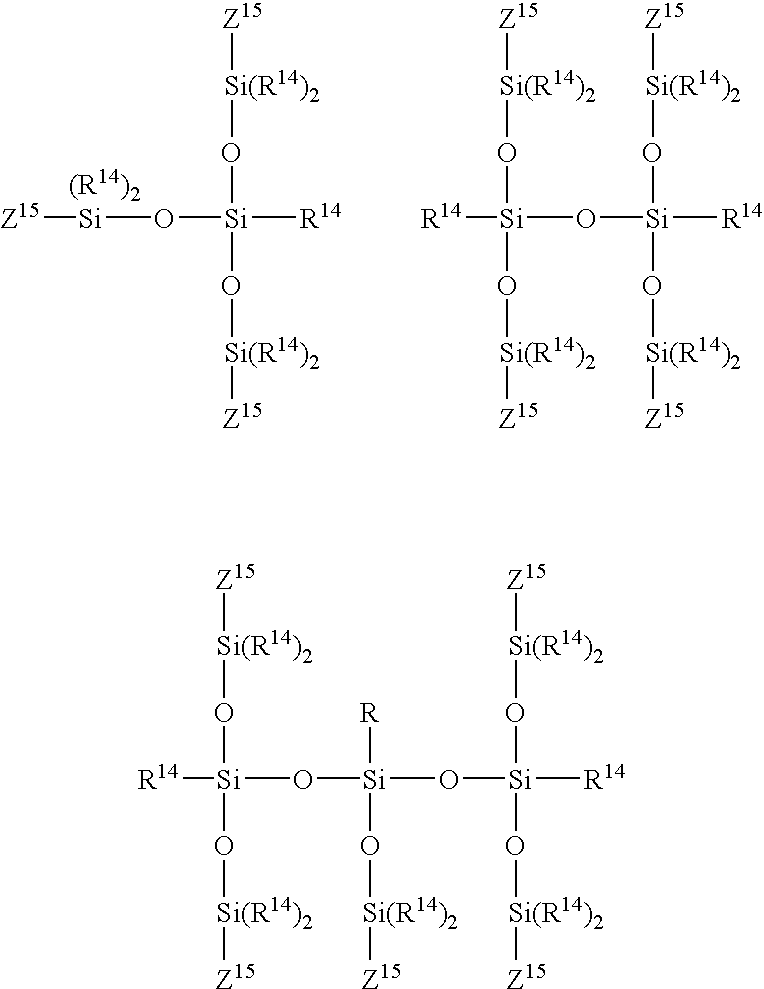Patents
Literature
58results about How to "Meet high-speed operation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
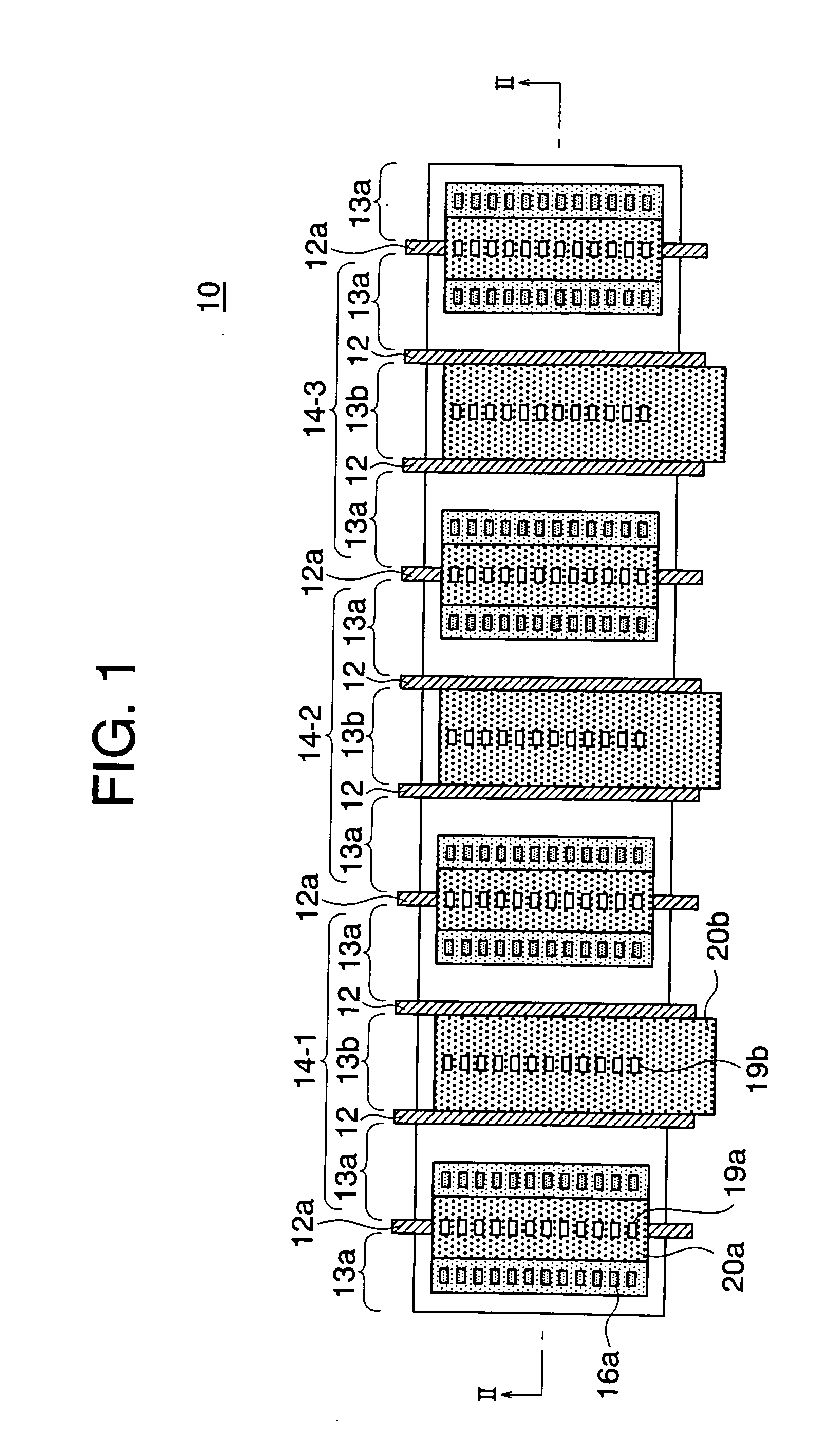
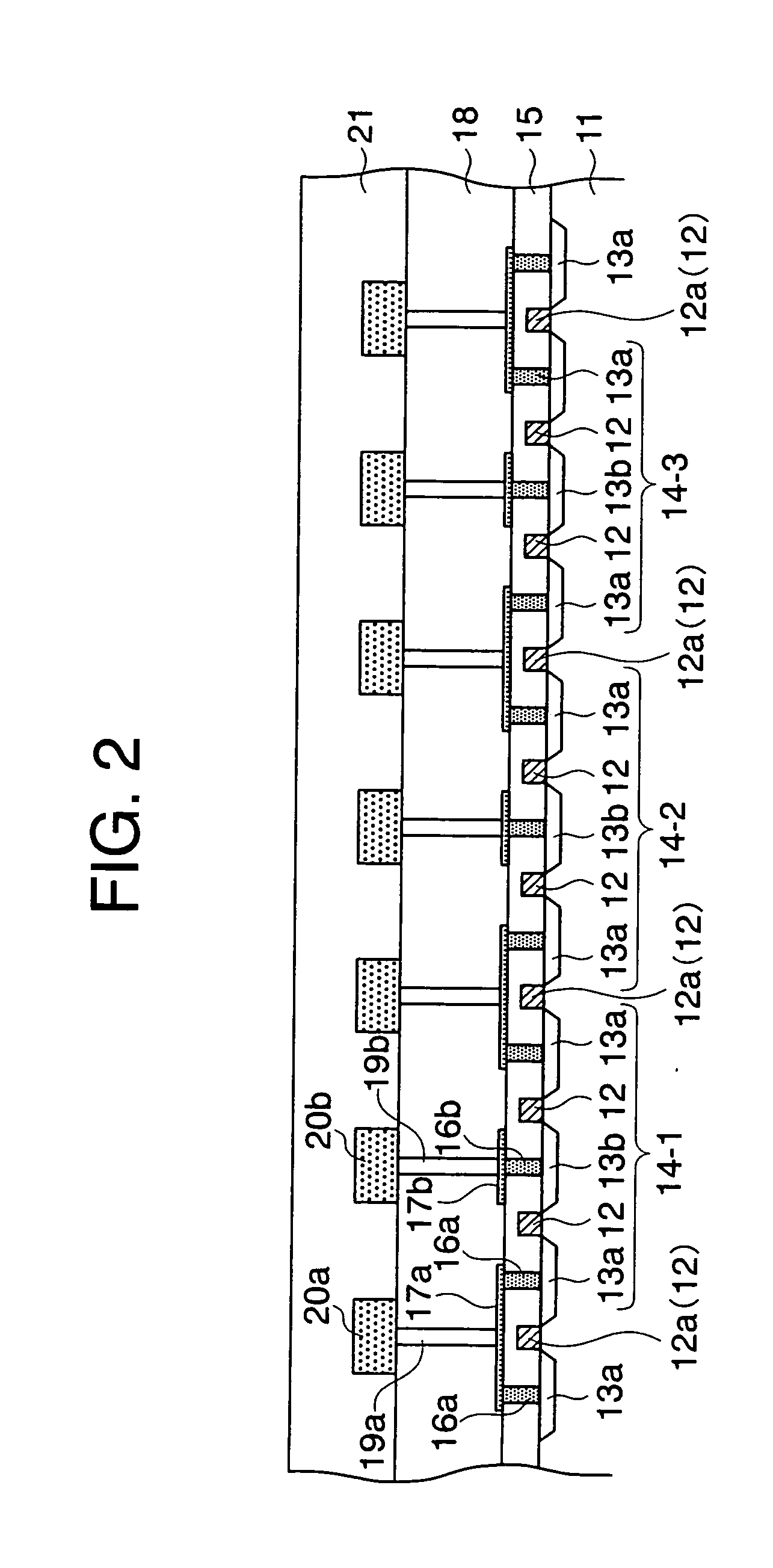
Semiconductor device and method for controlling semiconductor device
ActiveUS20090134468A1Meet high-speed operationGuaranteed uptimeTransistorSolid-state devicesInsulation layerMemory circuits
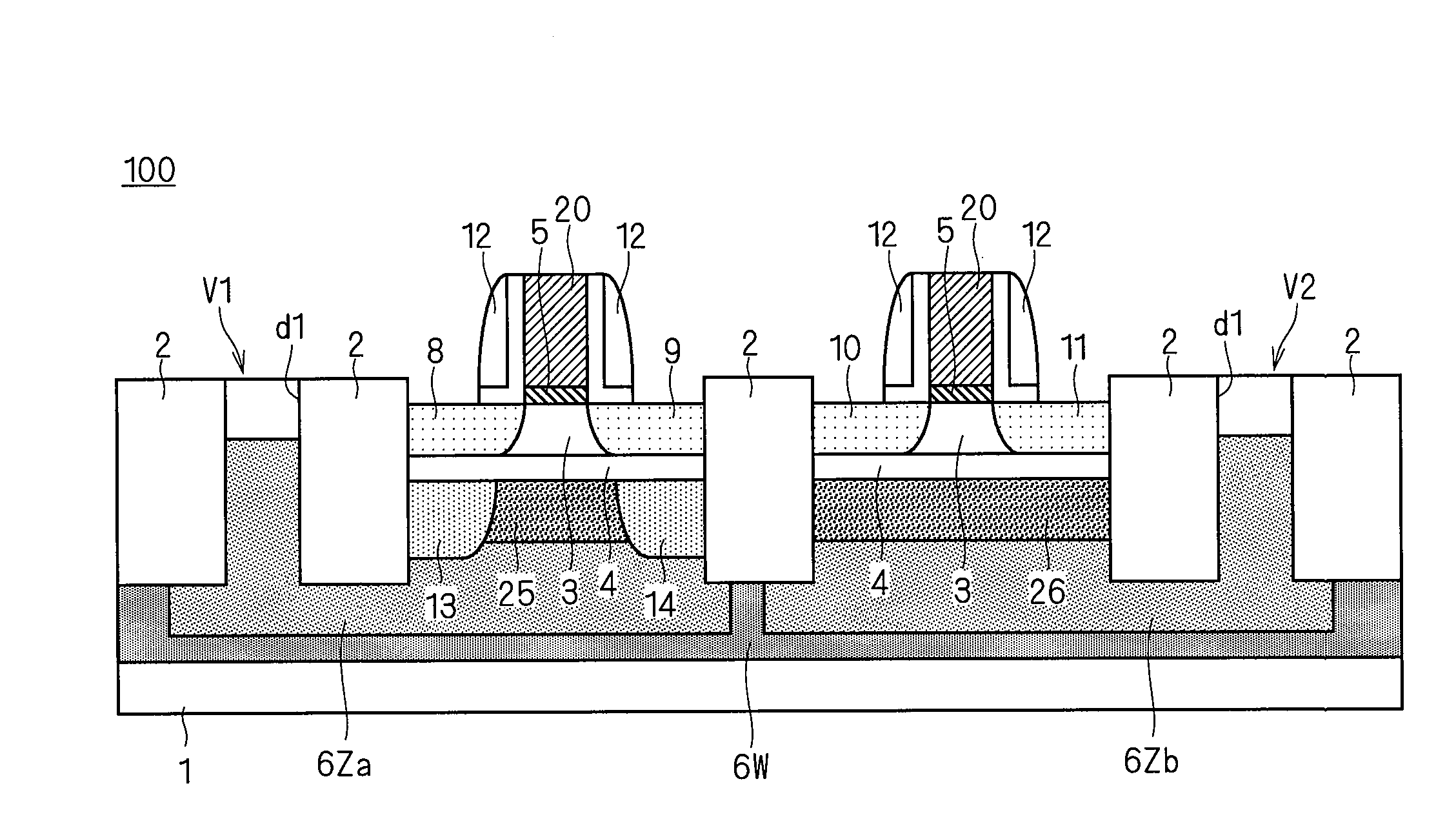
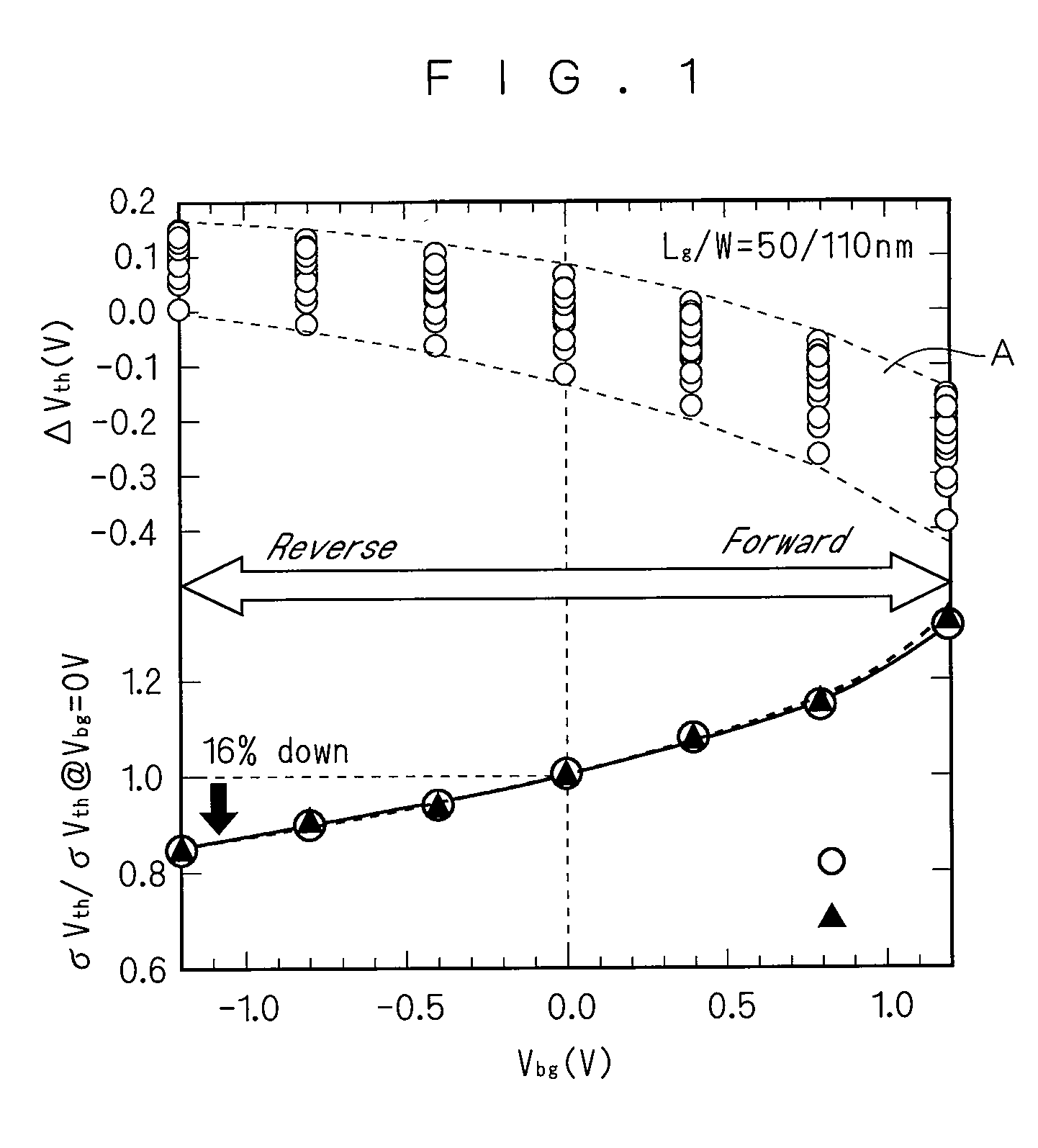
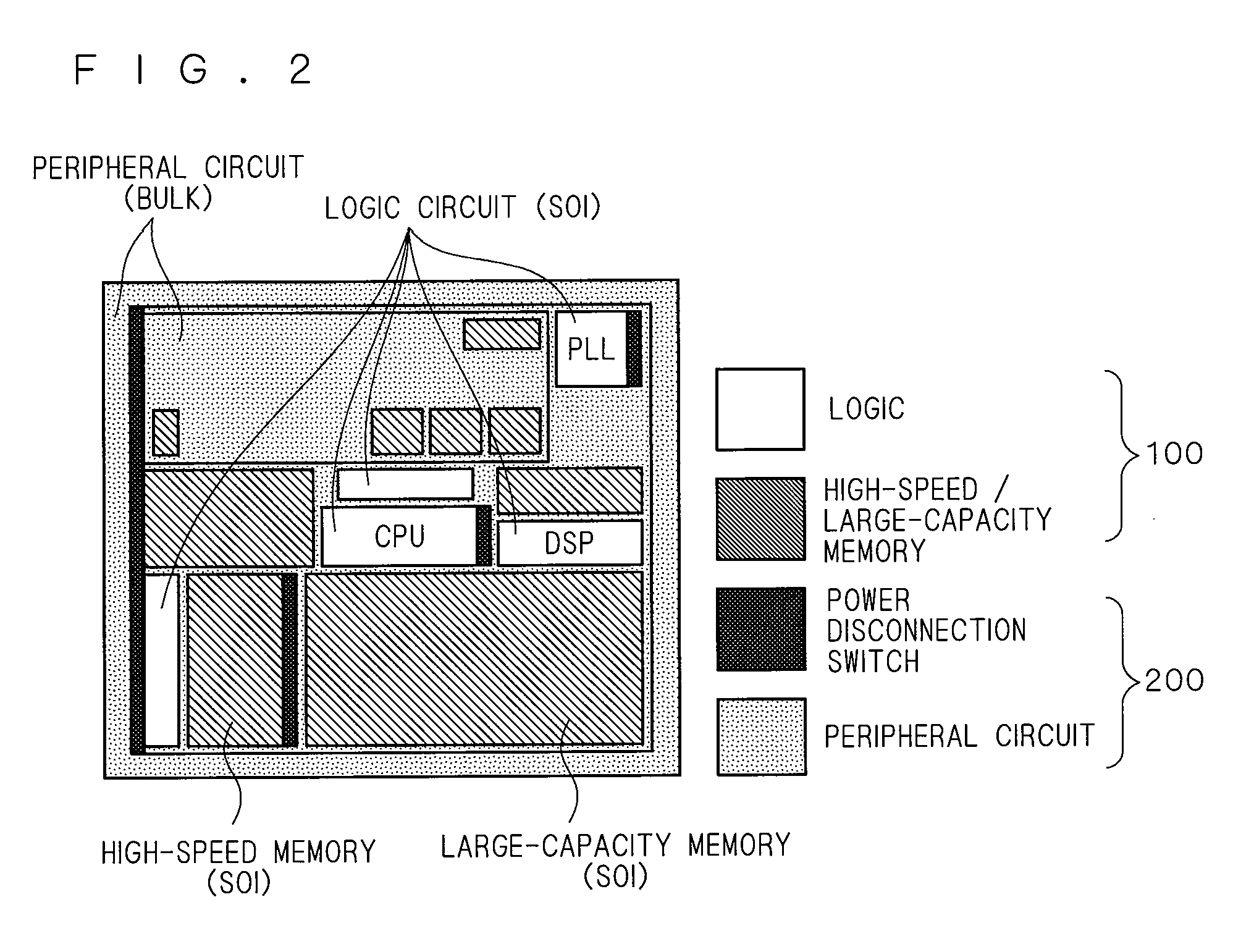
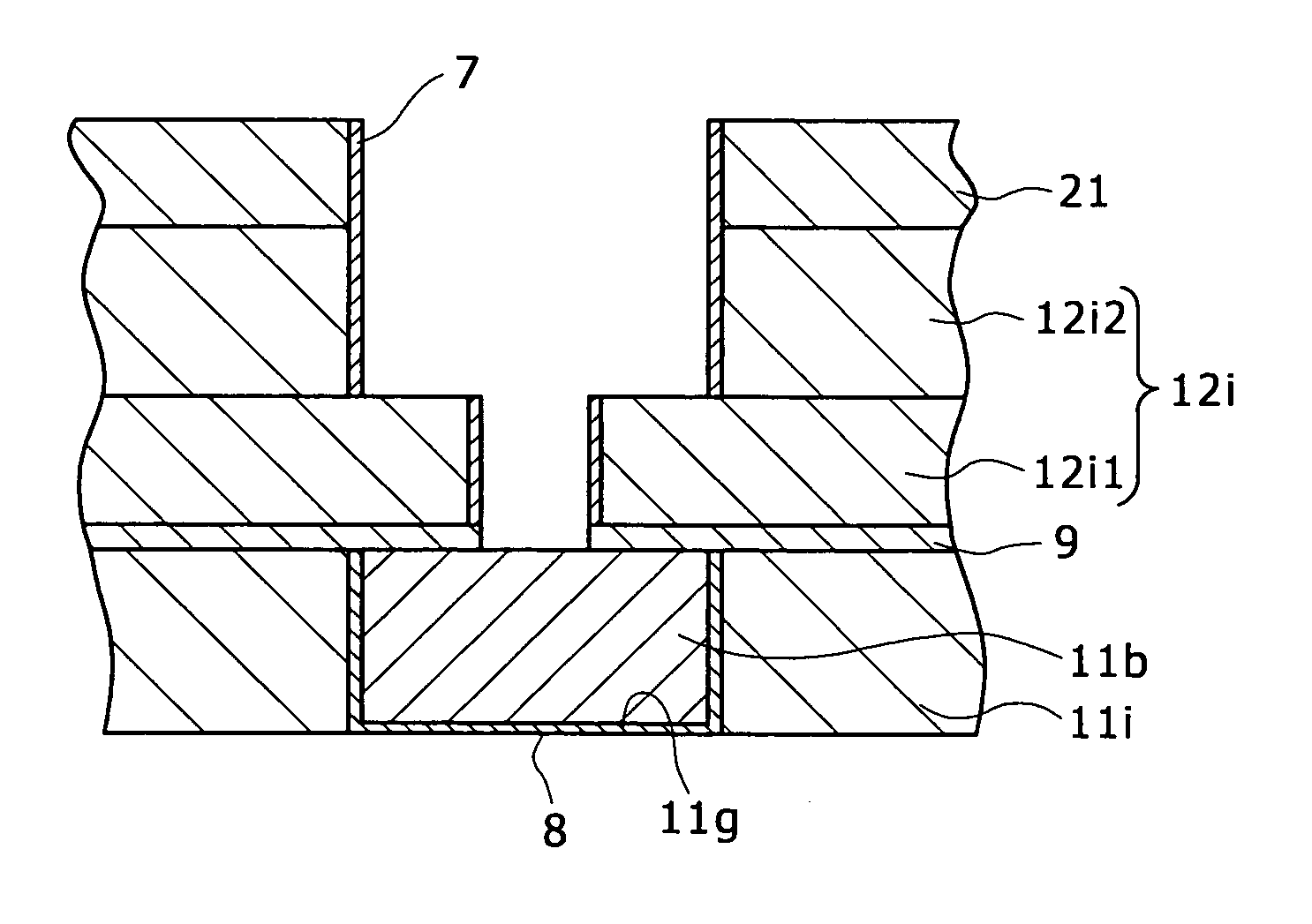
To provide a semiconductor device having a thin-film BOX-SOI structure and capable of realizing a high-speed operation of a logic circuit and a stable operation of a memory circuit. A semiconductor device according to the present invention includes a semiconductor support substrate, an insulation layer having a thickness of at mast 10 nm, and a semiconductor layer. In an upper surface of the semiconductor layer, a first field-effect transistor including a first gate electrode and constituting a logic circuit is formed. Further, in the upper surface of the semiconductor layer, a second field-effect transistor including a second gate electrode and constituting a memory circuit is formed. At least three well regions having different conductivity types are formed in the semiconductor support substrate. In the presence of the well regions, a region of the semiconductor support substrate below the first gate electrode and a region of the semiconductor support substrate below the second gate electrode are electrically separated from each other.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
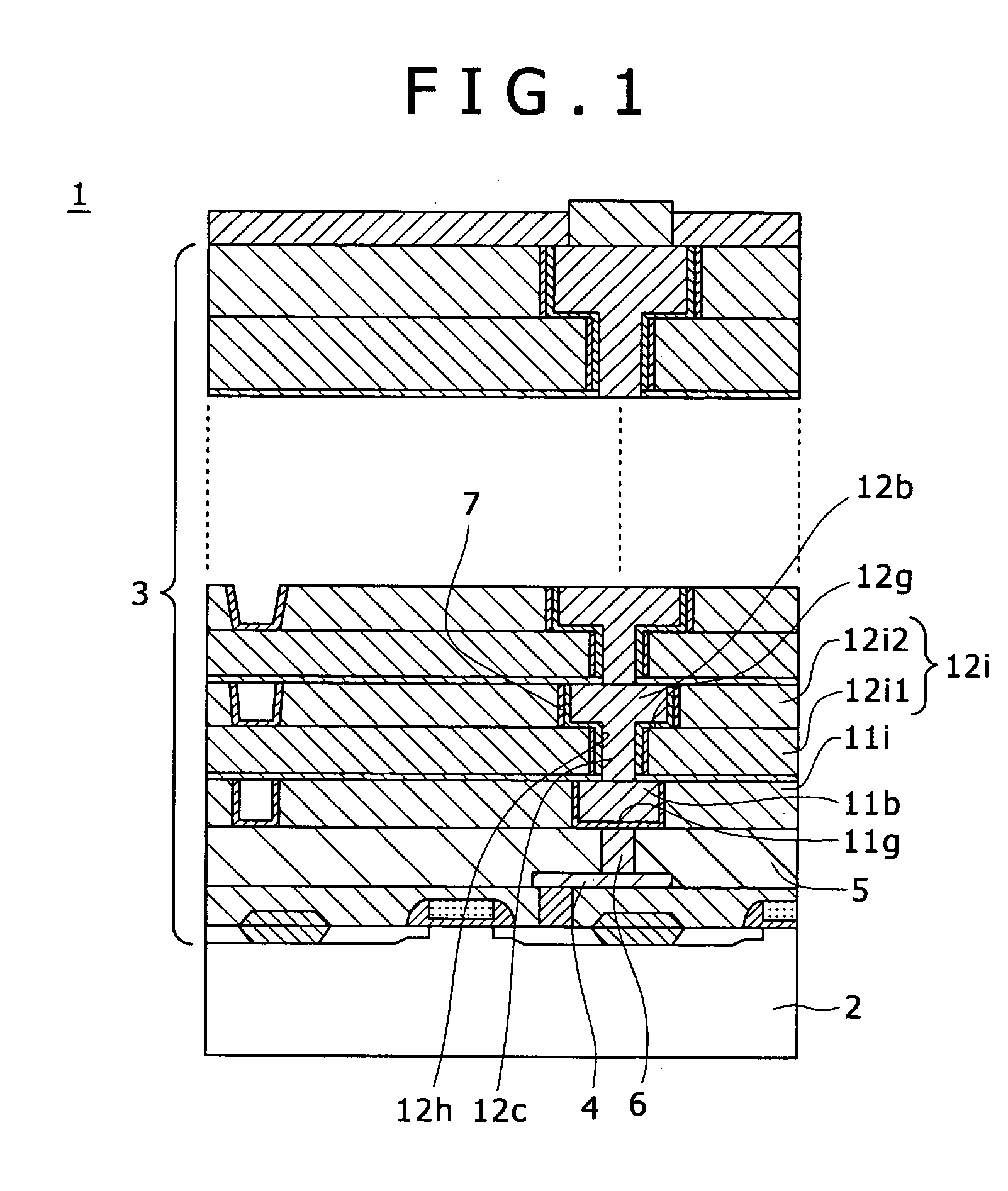
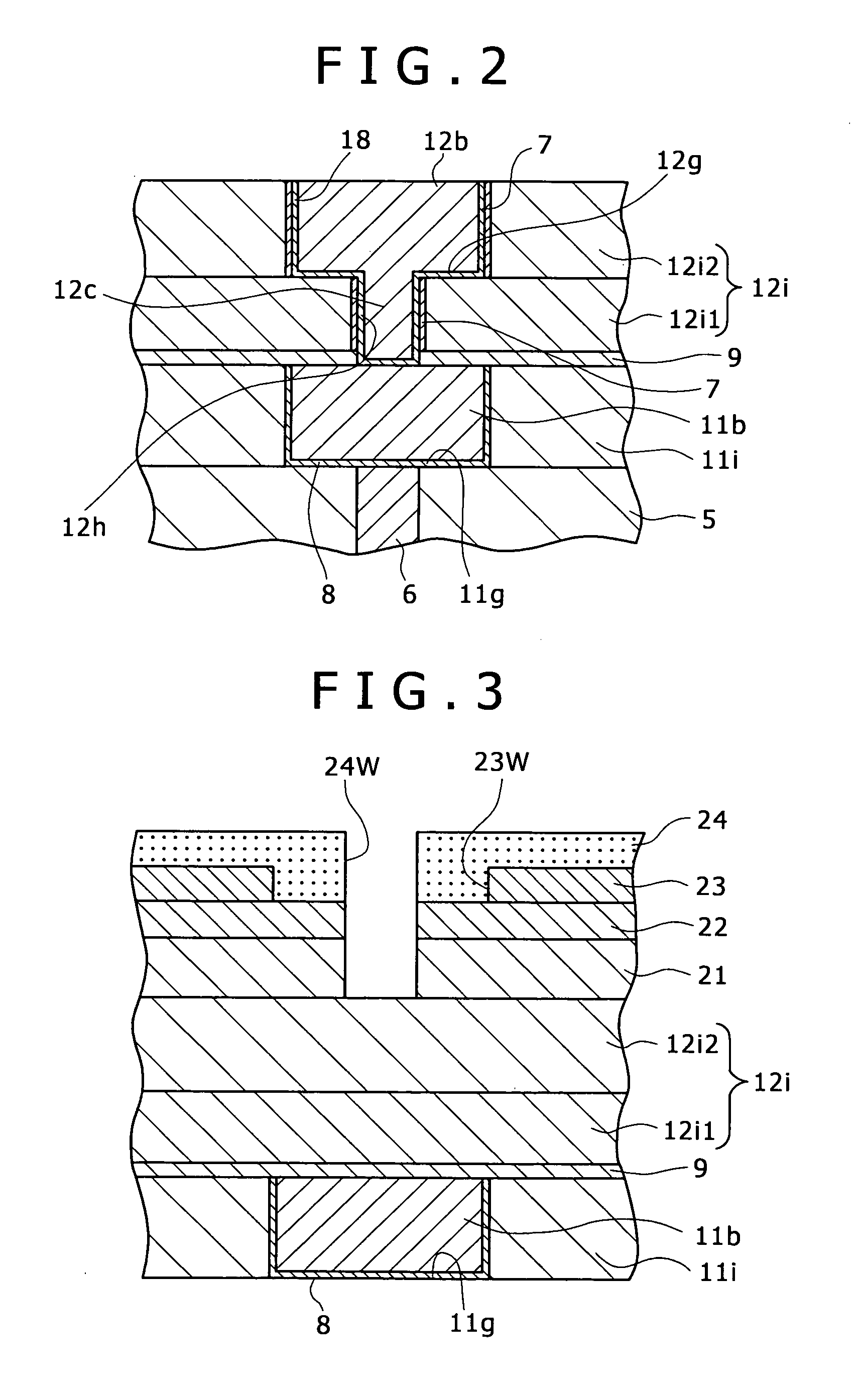
Multi-layer wiring structure, semiconductor apparatus having multi-layer wiring structure, and methods of manufacturing them
InactiveUS20060019485A1Low resistance contactStable, highly reliable high-density buried wiringSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorInsulation layer
A multi-layer wiring structure including an upper layer wiring (second buried wiring) connected to a buried wiring (first buried wiring) in lower layer wiring grooves (first wiring grooves) through connection conductors, wherein a protective film capable of enduring a cleaning treatment with hydrogen radicals or hydrogen plasma applied to the surface of the first buried wiring at the time of forming the connection conductors is formed on the inside surfaces of the wiring grooves to be filled with he second buried wiring and the wiring connection holes to be filled with the connection conductors which surfaces are liable to be eroded upon exposure to the atmosphere used in the cleaning treatment, whereby erosion of the insulation layers at the time of the cleaning is obviated, sufficient cleaning can be performed, and deterioration of characteristics can be improved.
Owner:SONY CORP
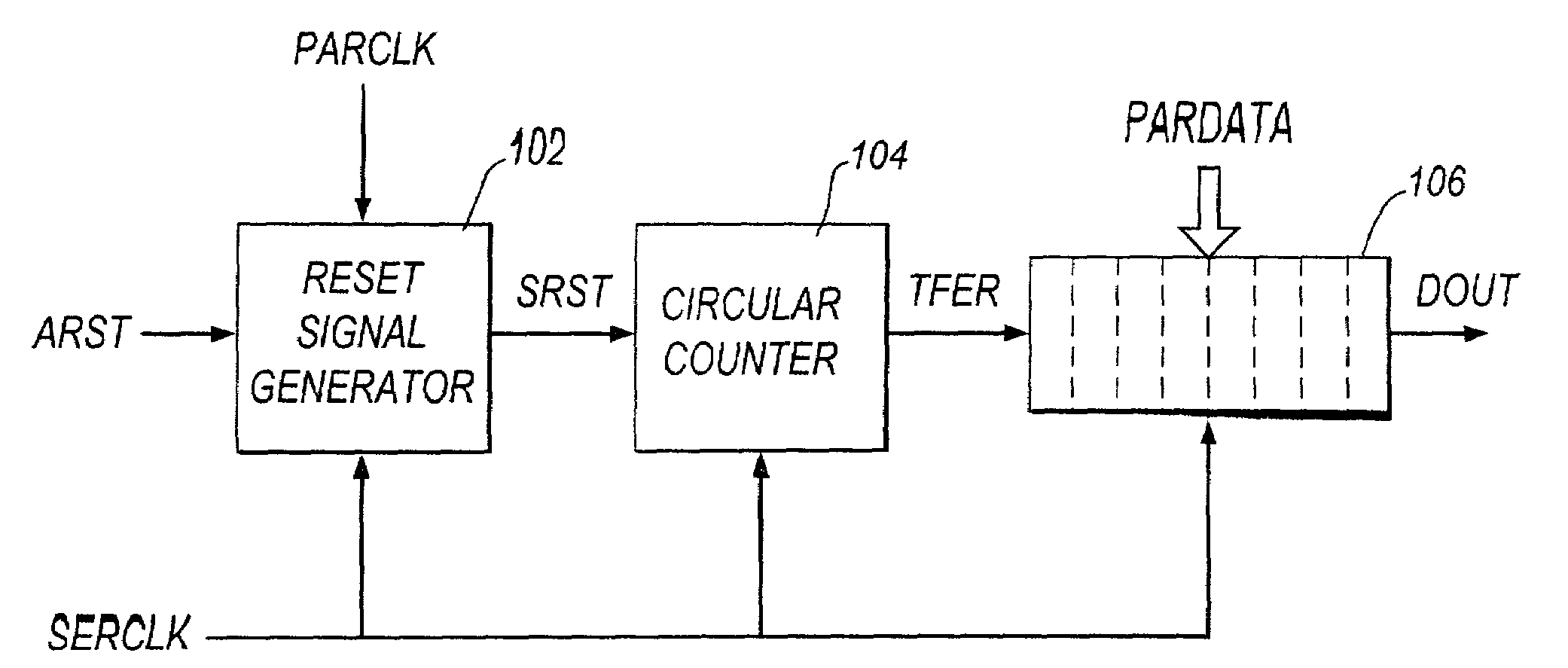
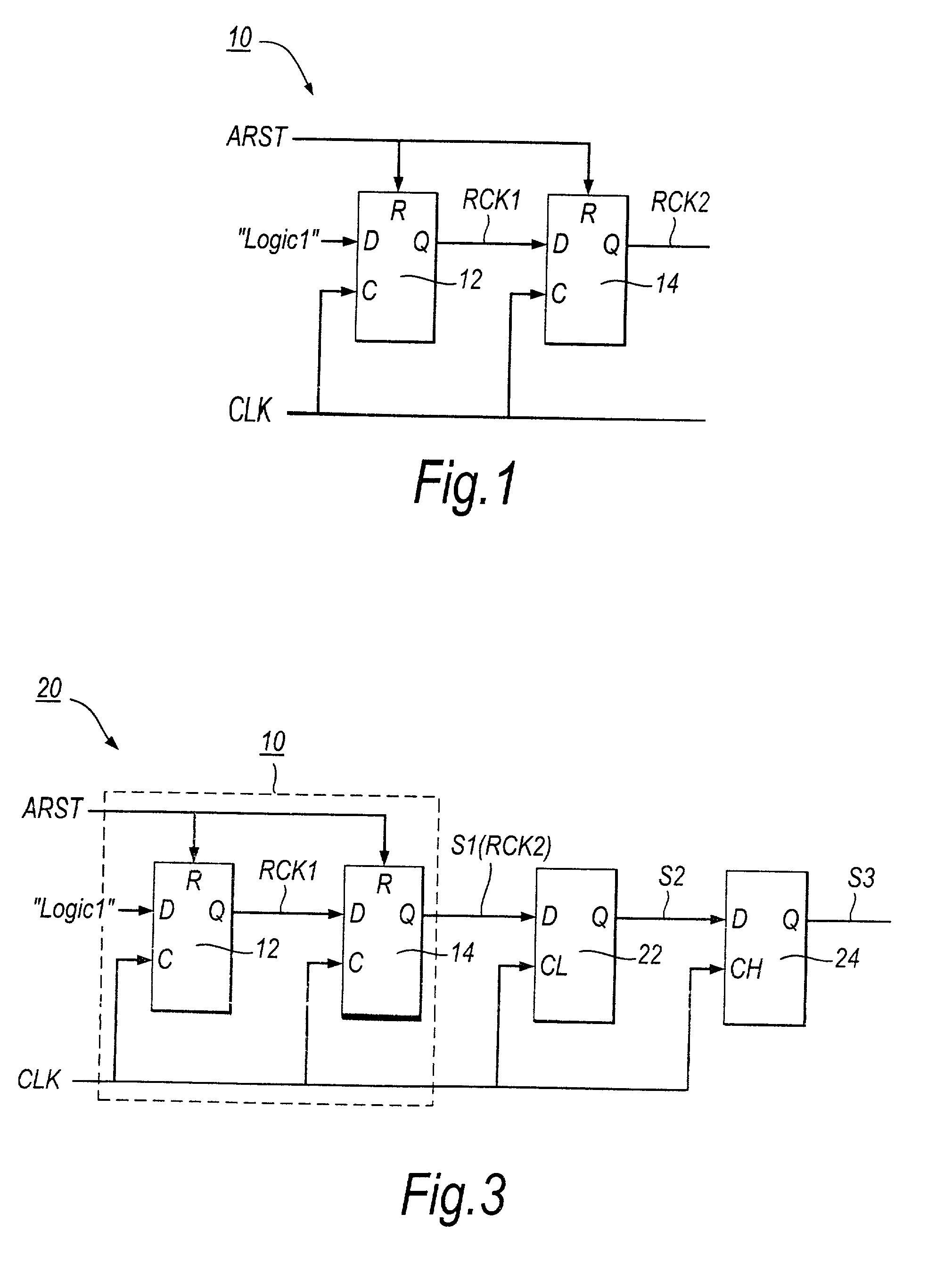
Processing high-speed digital signals
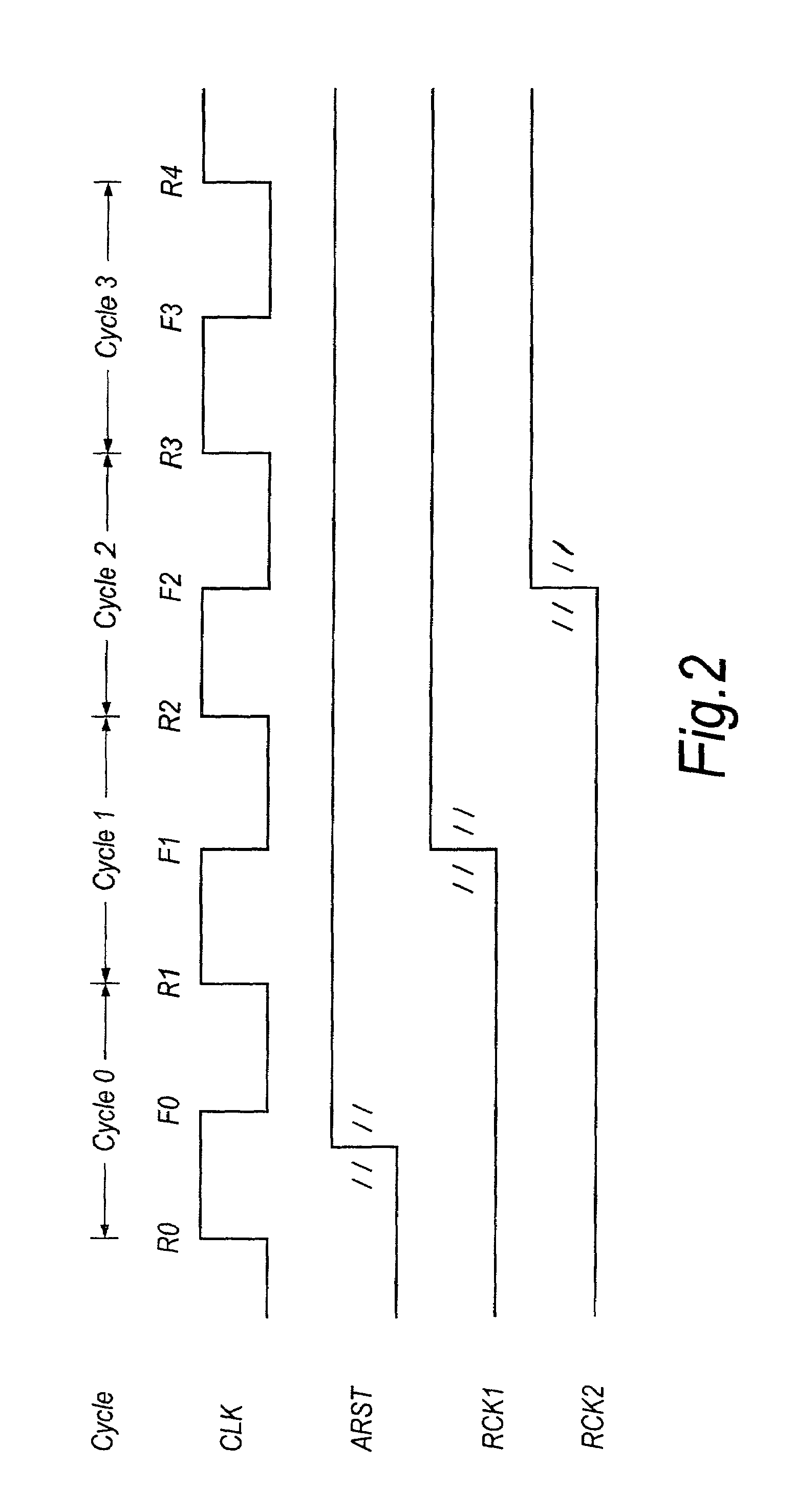
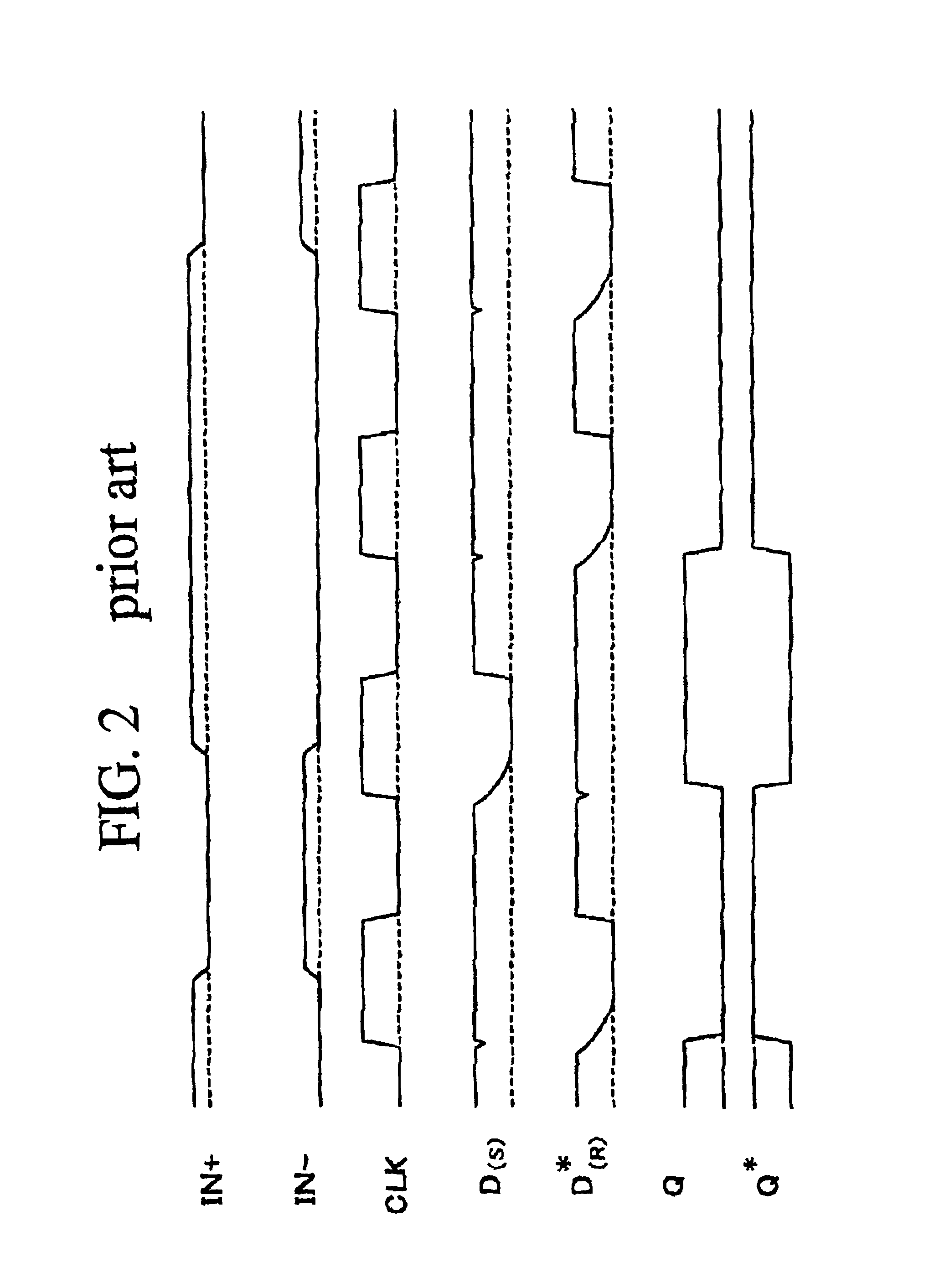
ActiveUS7187738B2Reduce controlMeet high-speed operationChannel dividing arrangementsPulse automatic controlData synchronizationData stream
A first transparent latch receives a first synchronised signal changing its logic state synchronously with respect to a clock signal. A second transparent latch receives a second synchronised signal output by the first latch. When the clock signal has a first logic state the first latch has a non-responsive state and the second latch has a responsive state, and when the clock signal has a second logic state the first latch has the responsive state and the second latch has the non-responsive state. The change in logic state of a third synchronised signal output by the second latch is guaranteed to occur in a particular half-cycle of the clock signal, irrespective of process / voltage / temperature (PVT) variations of the circuitry. Clock recovery circuitry may have rising-edge and falling-edge latches; circulating control pattern verification circuitry; data synchronising circuitry for converting parallel data clocked by a first clock signal into serial data clocked by a second clock signal asynchronous with the first clock signal; and data recovery circuitry for producing an offset clock signal which suits a data eye shape of a received serial data stream.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Semiconductor device and method of fabricating the same
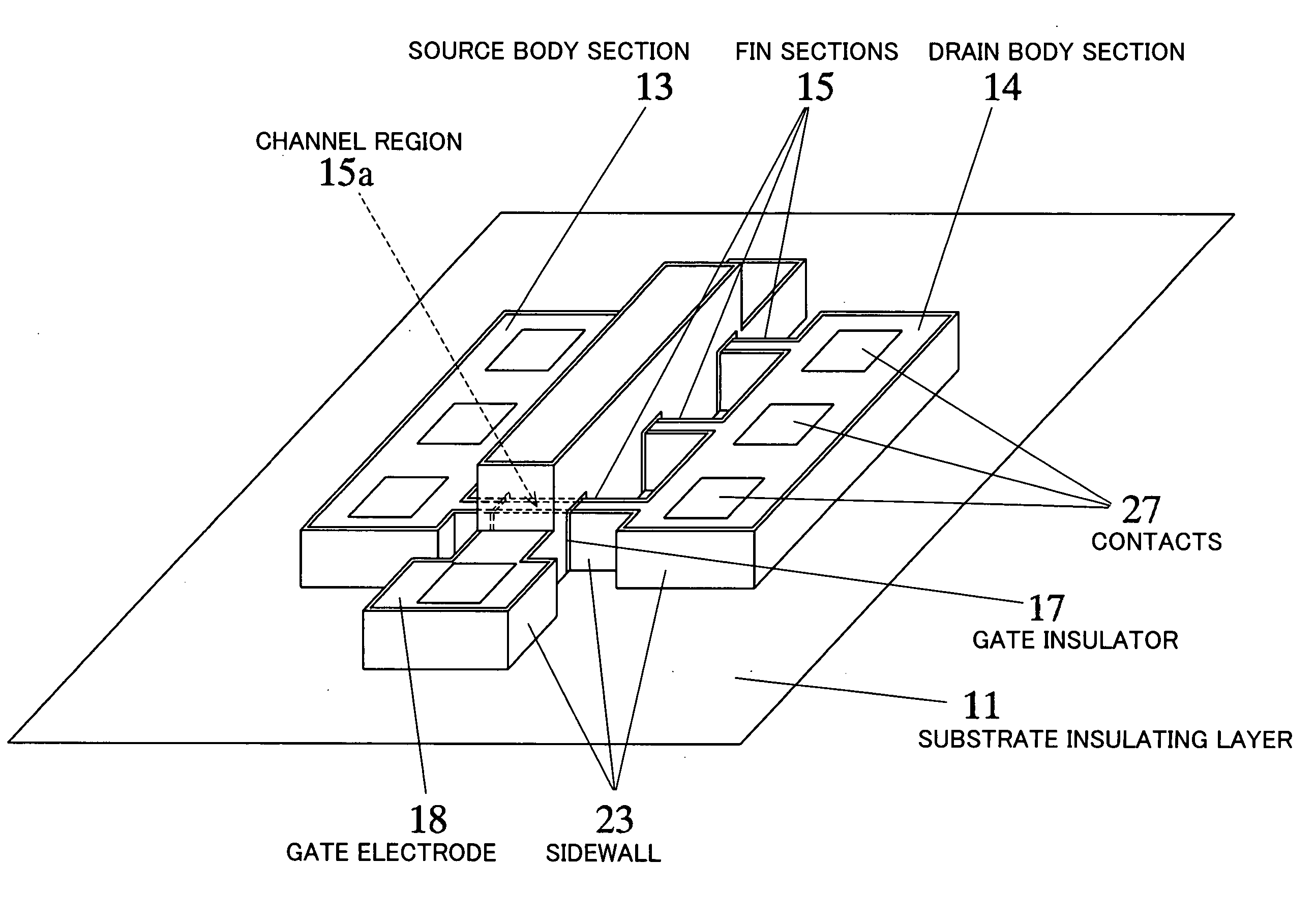
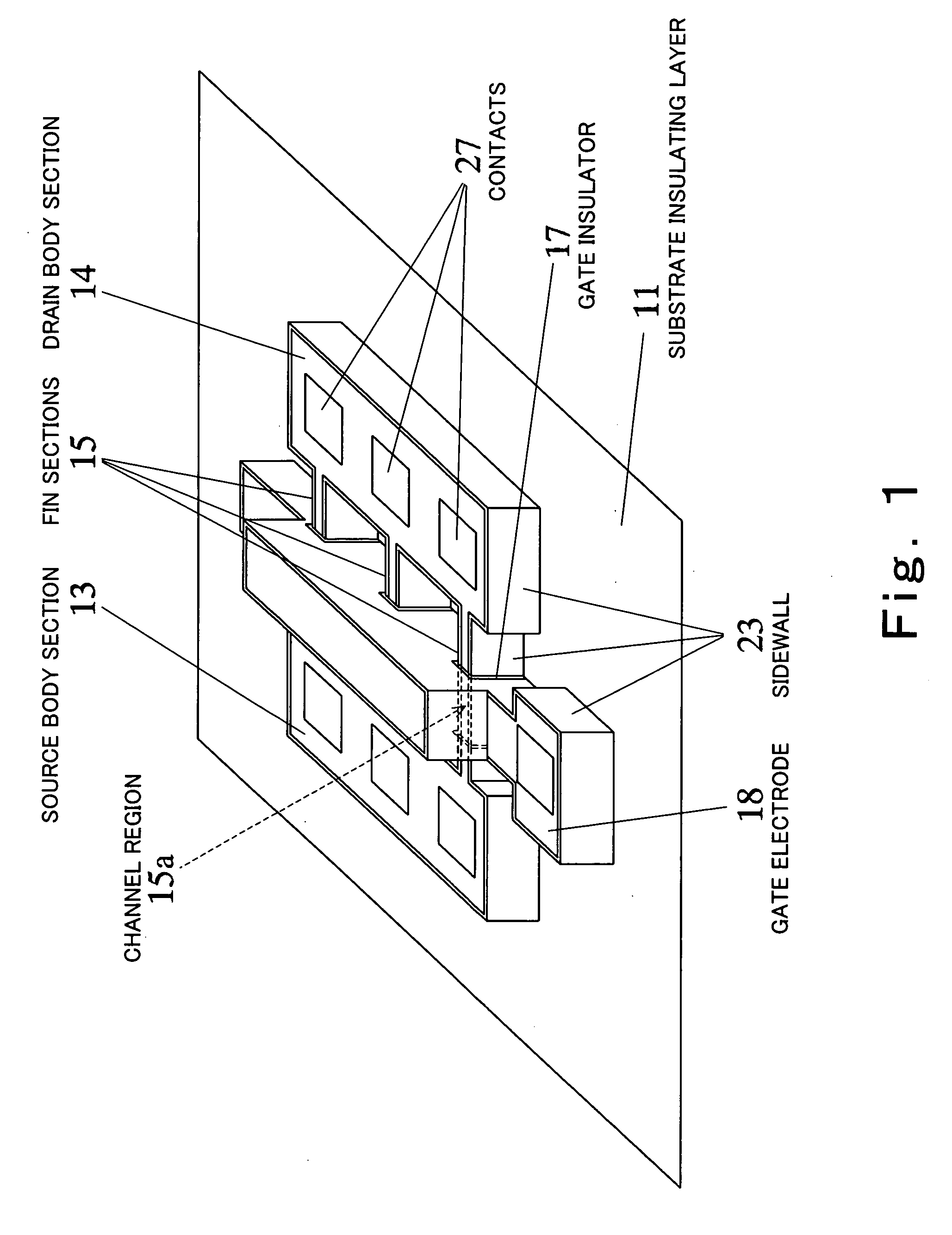
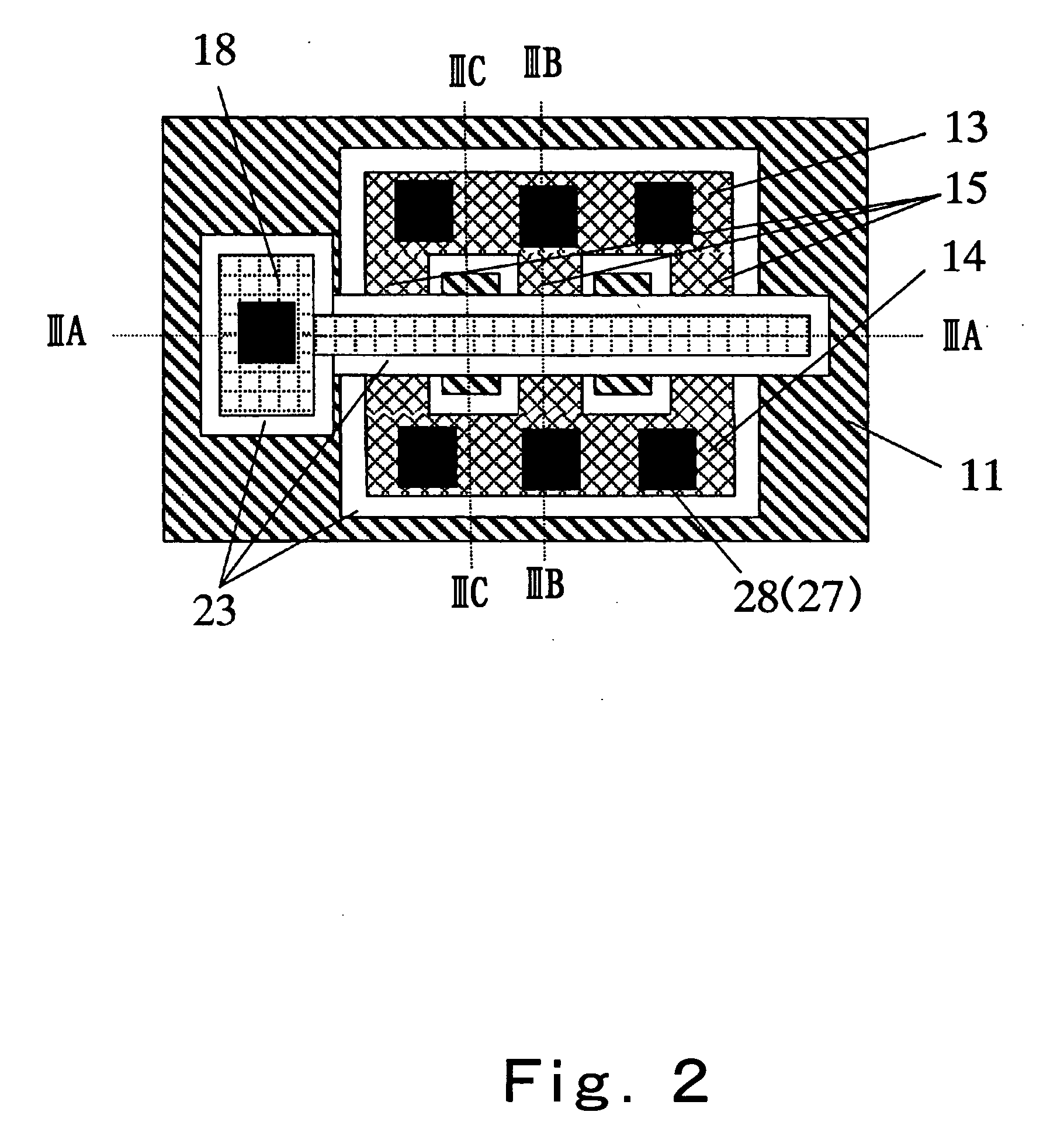
InactiveUS20070052041A1Easily fabricateReduce difficultyTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringRidge
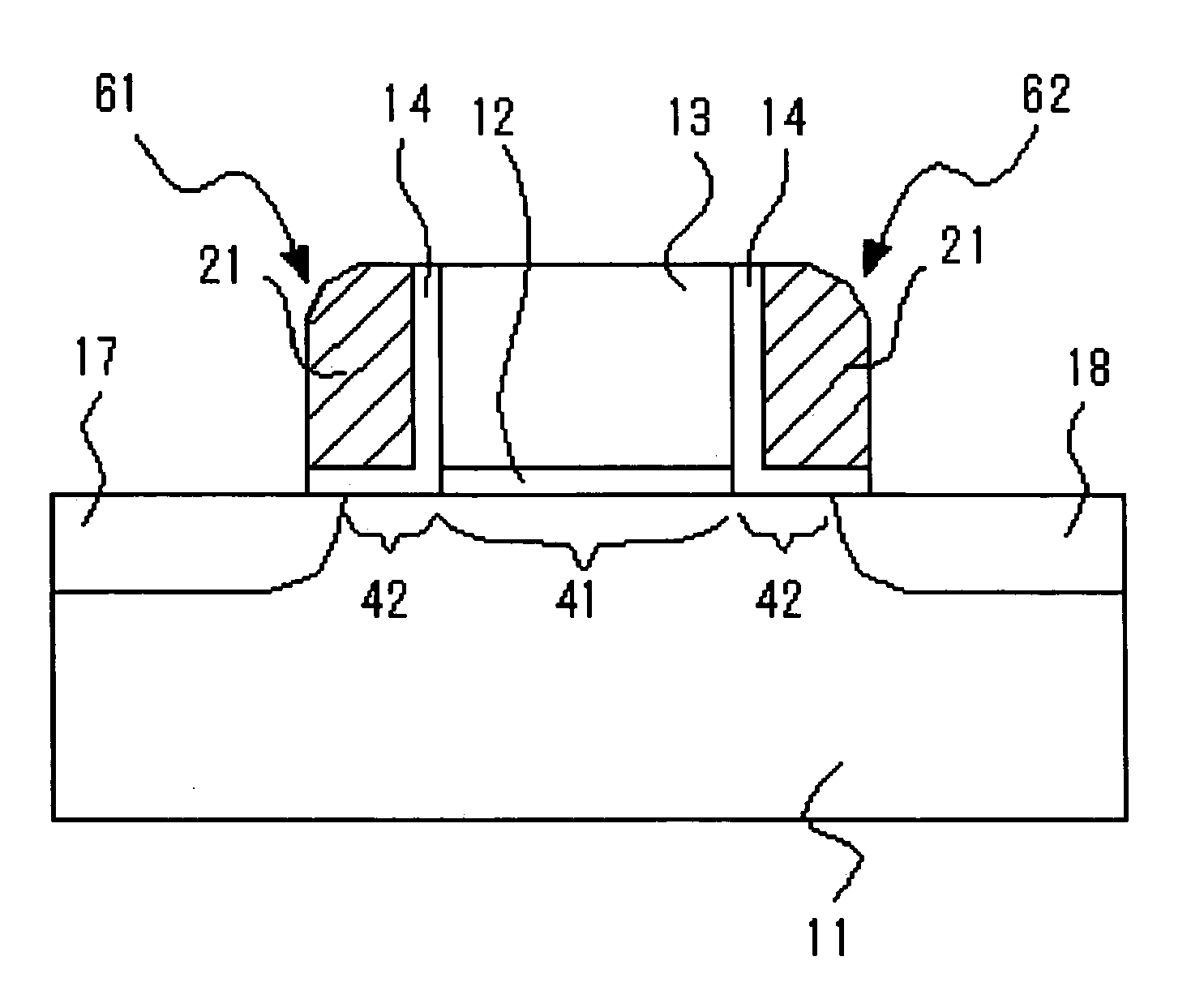
A semiconductor device according to this invention includes: a first insulating layer (11); a first body section (13) including an island-shaped semiconductor formed on the first insulating layer; a second body section (14) including an island-shaped semiconductor formed on the first insulating layer; a ridge-shaped connecting section (15) formed on the first insulating layer to interconnect the first body section and the second body section; a channel region (15a) formed by at least a part of the connecting section in lengthwise direction of the connecting section; a gate electrode (18) formed to cover a periphery of the channel region, with a second insulating layer intervening therebetween; a source region formed to extend over the first body section and a portion of the connecting section between the first body section and the channel region; and a drain region formed to extend over the second body section and a portion of the connecting section between the second body section and the channel region, wherein a semiconductor forming the channel region has a lattice strain.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
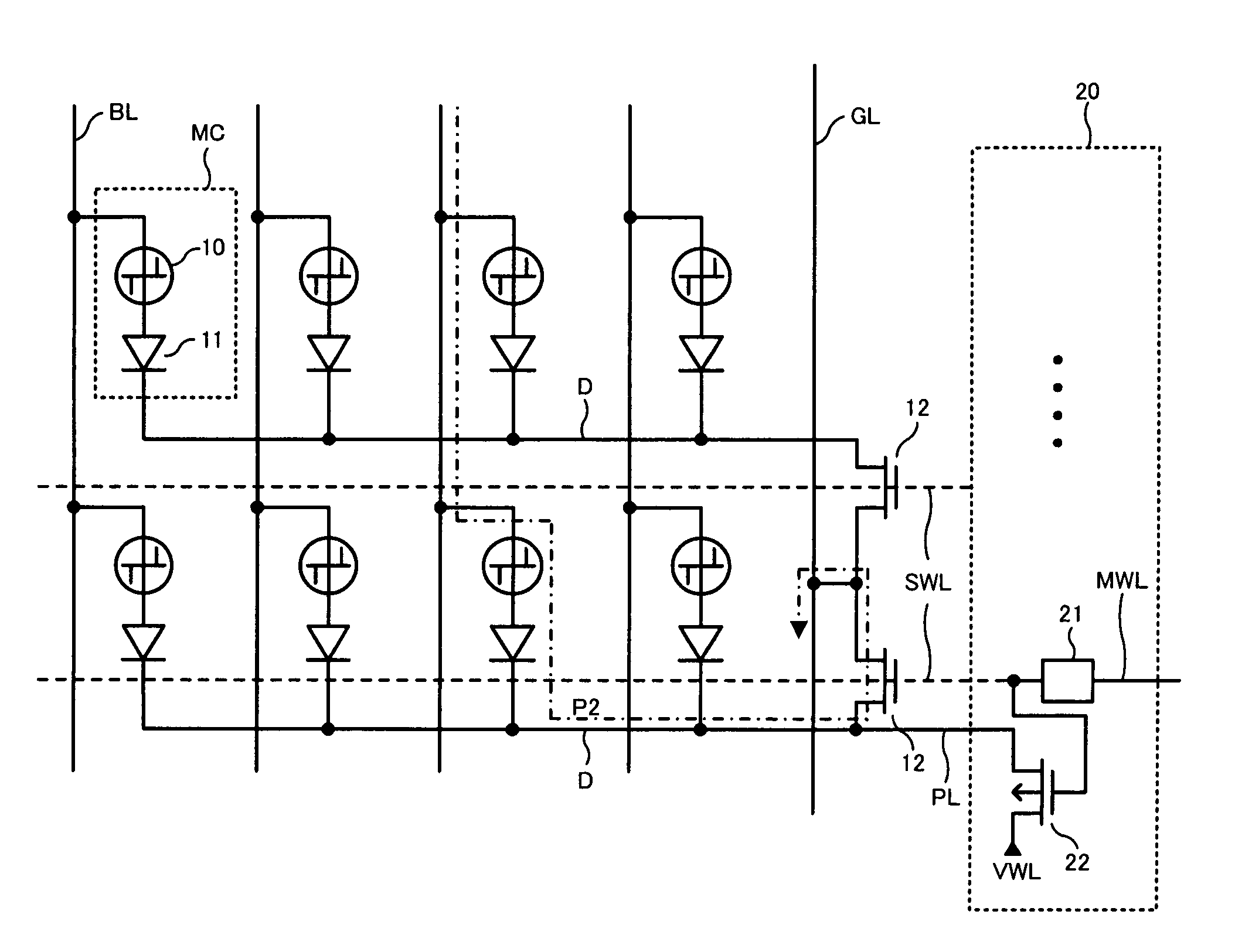
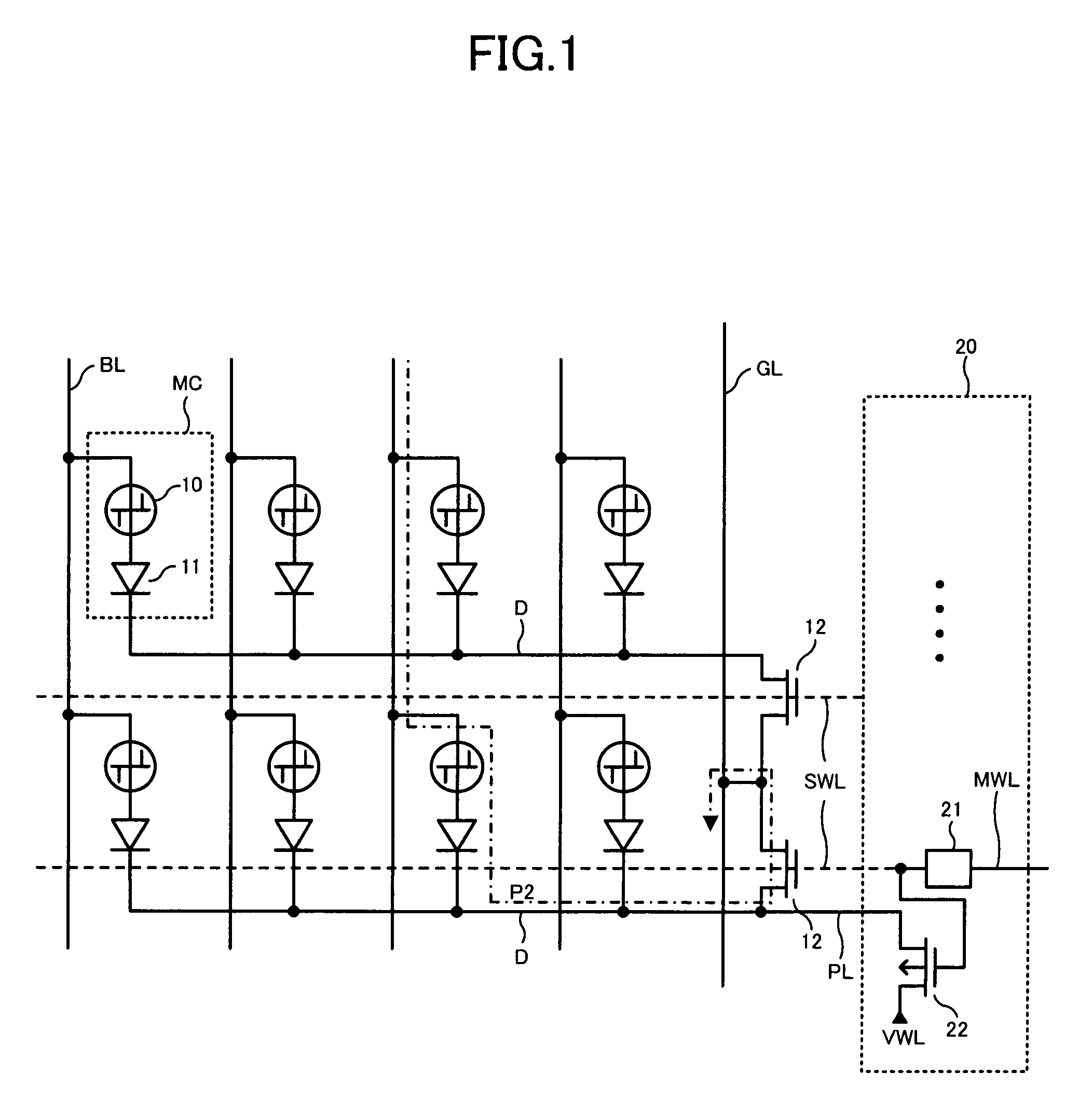
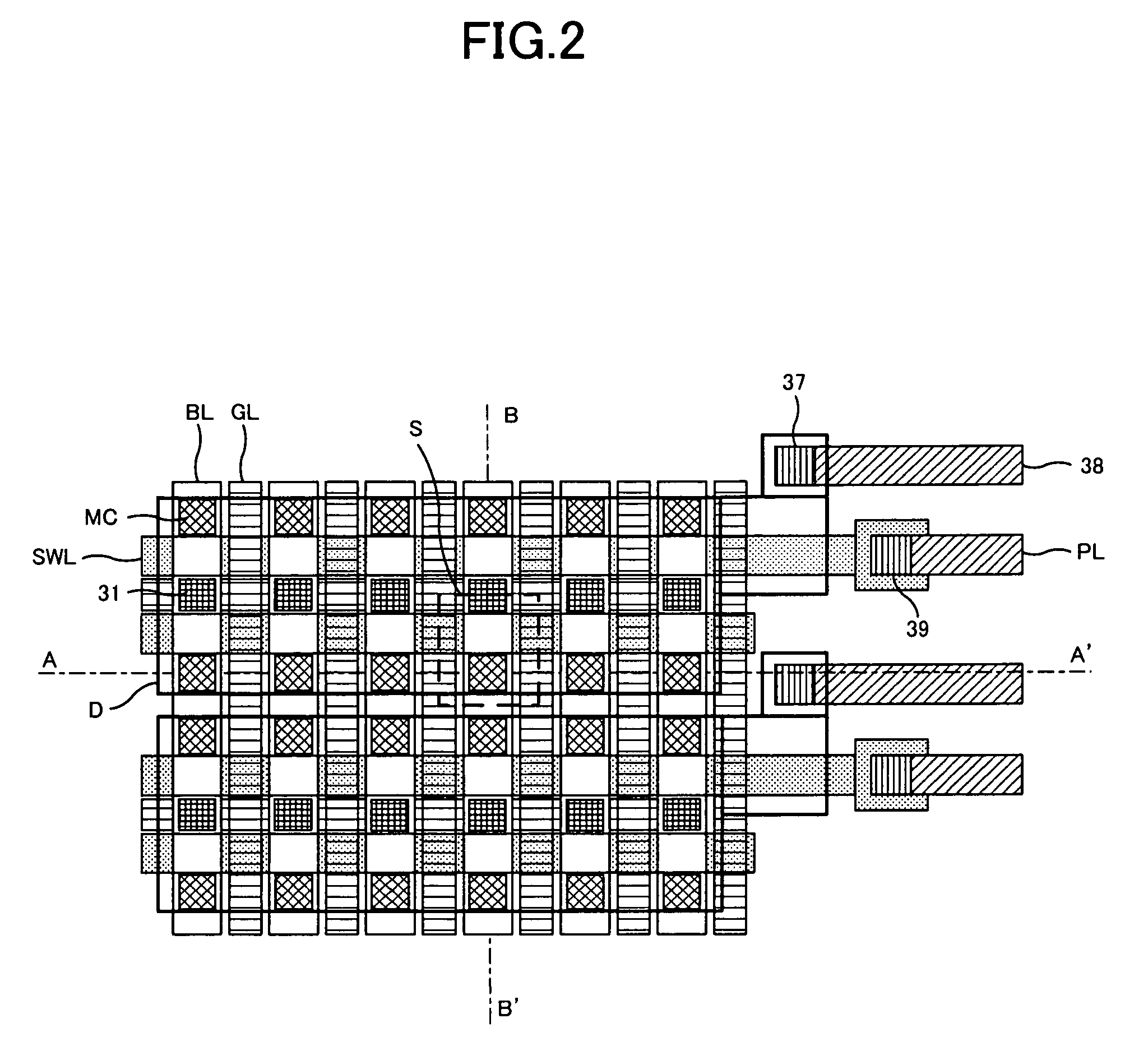
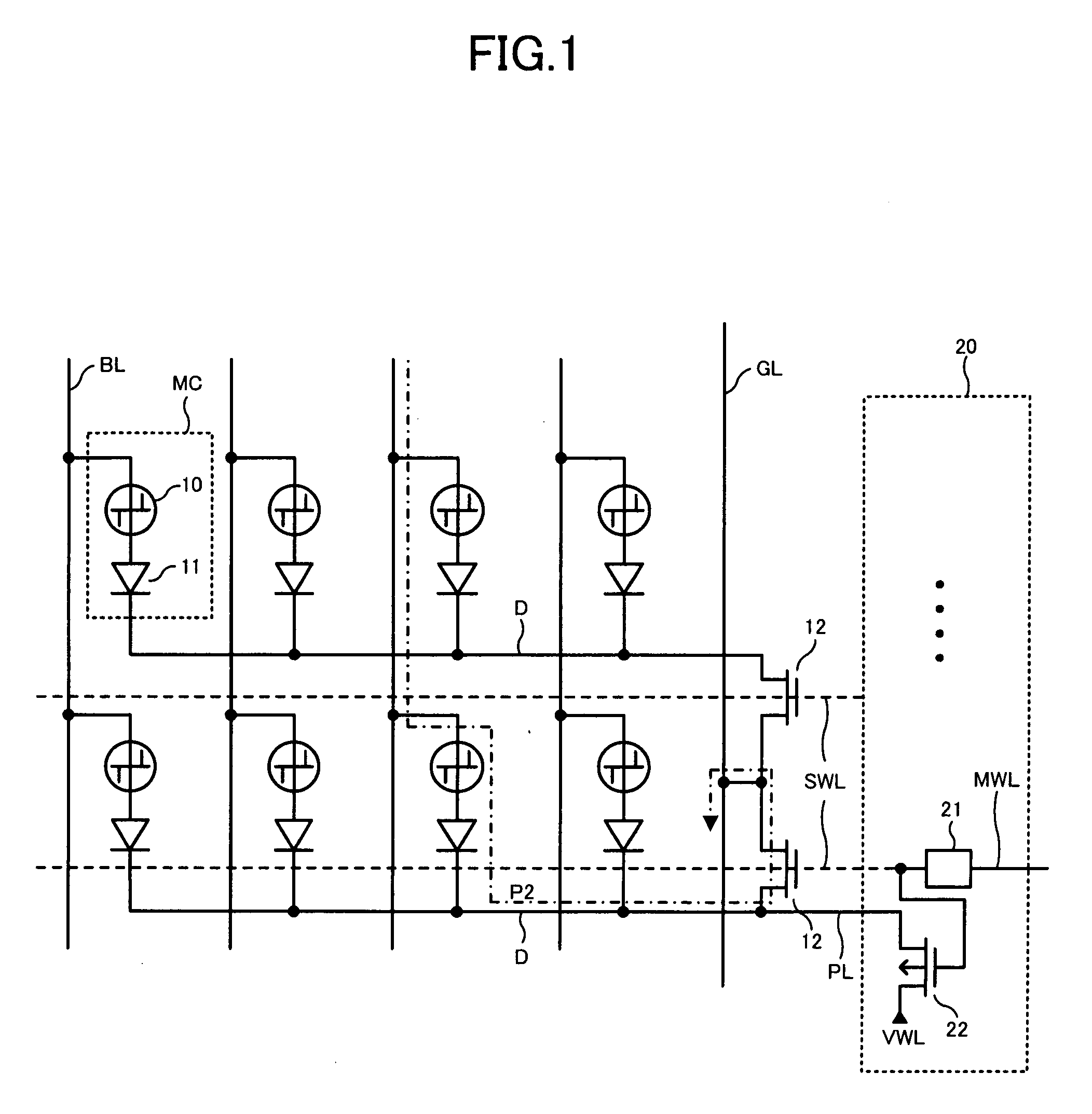
Phase change memory device
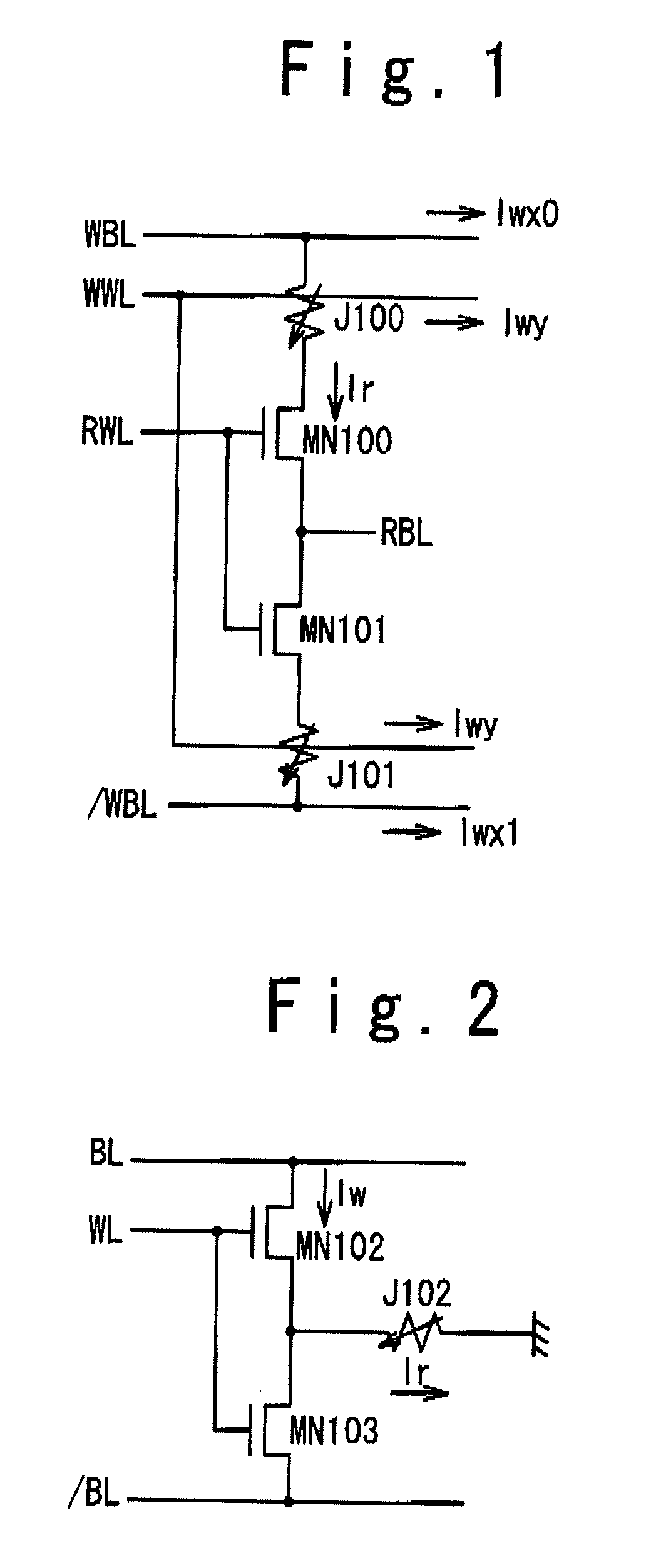
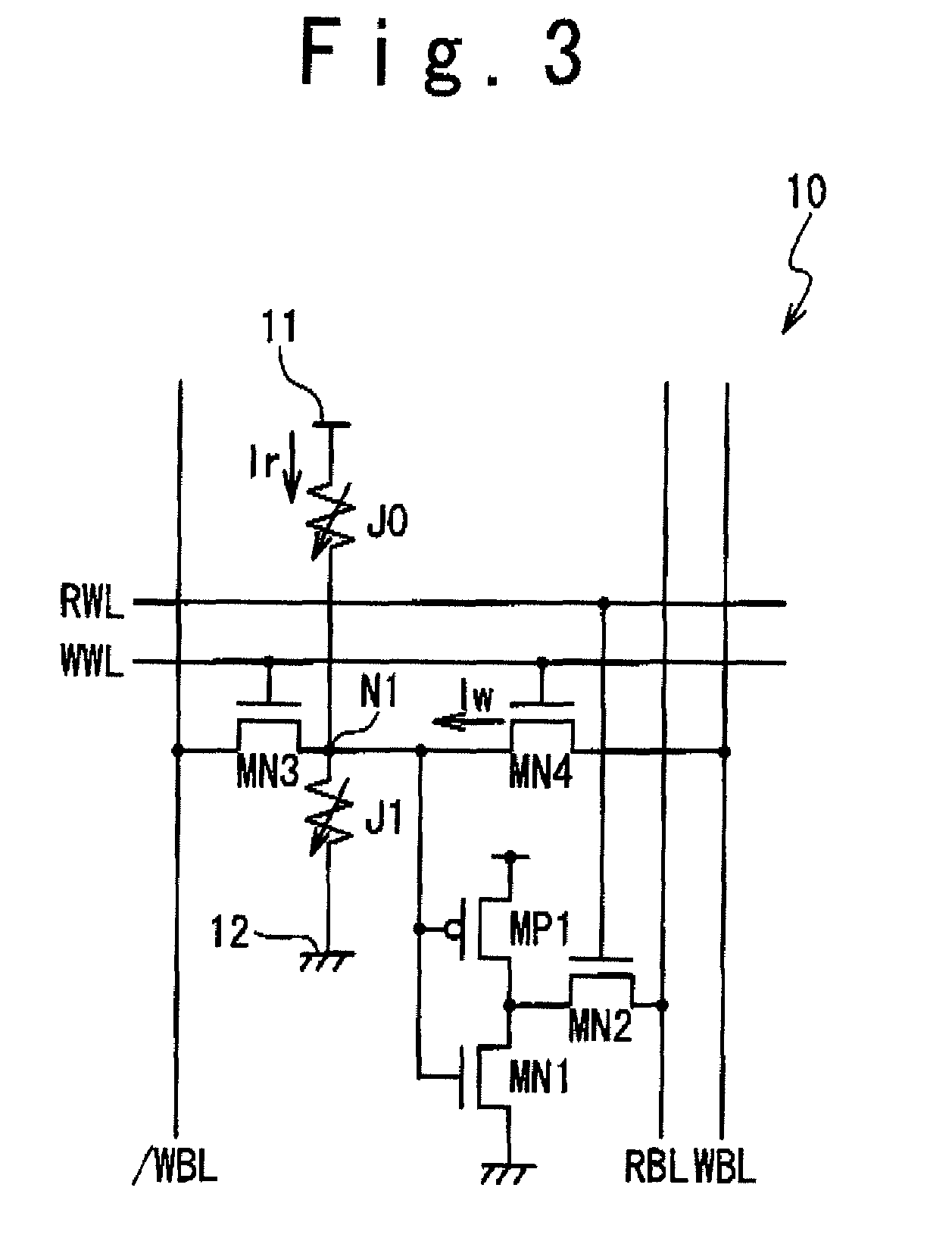
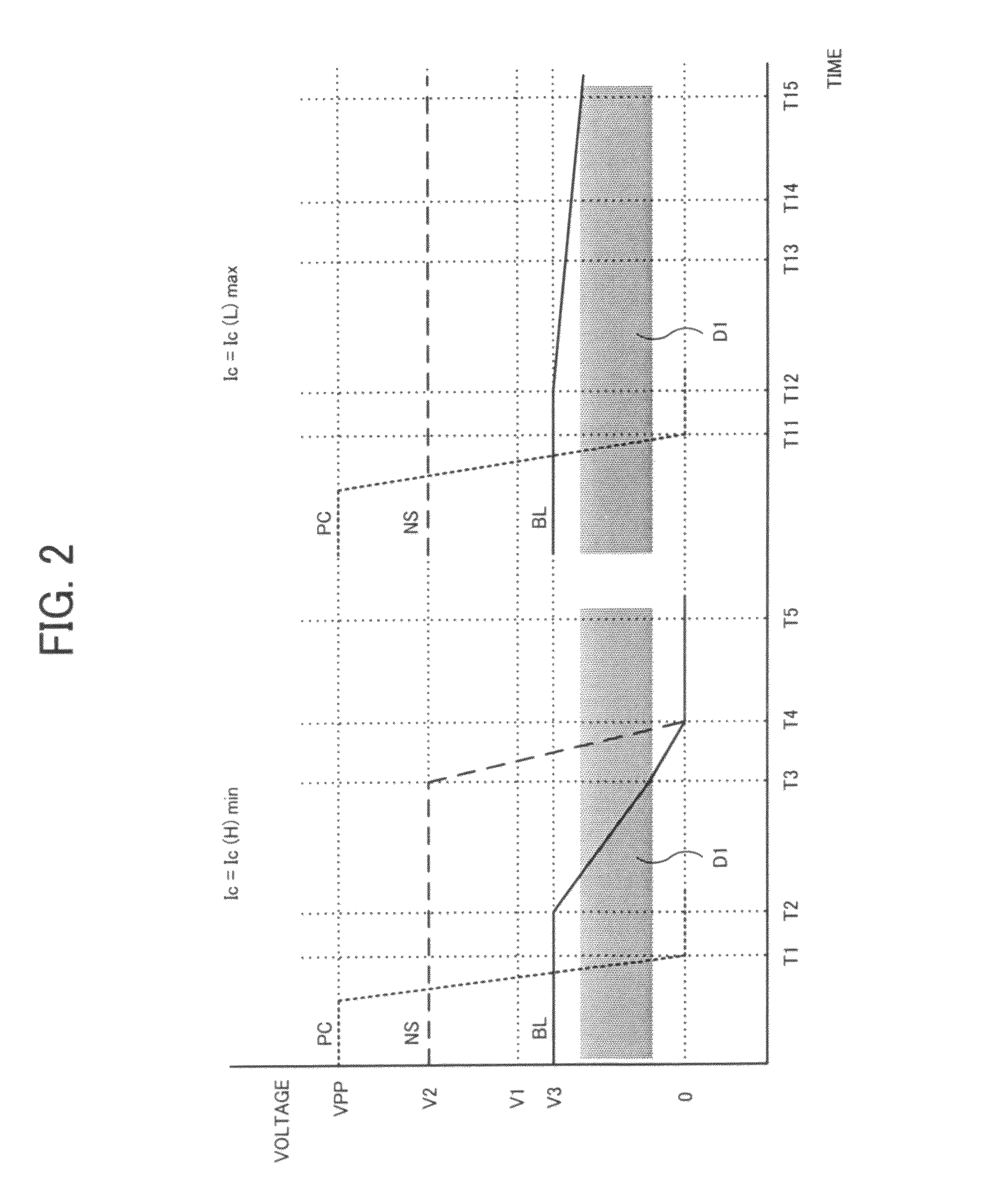
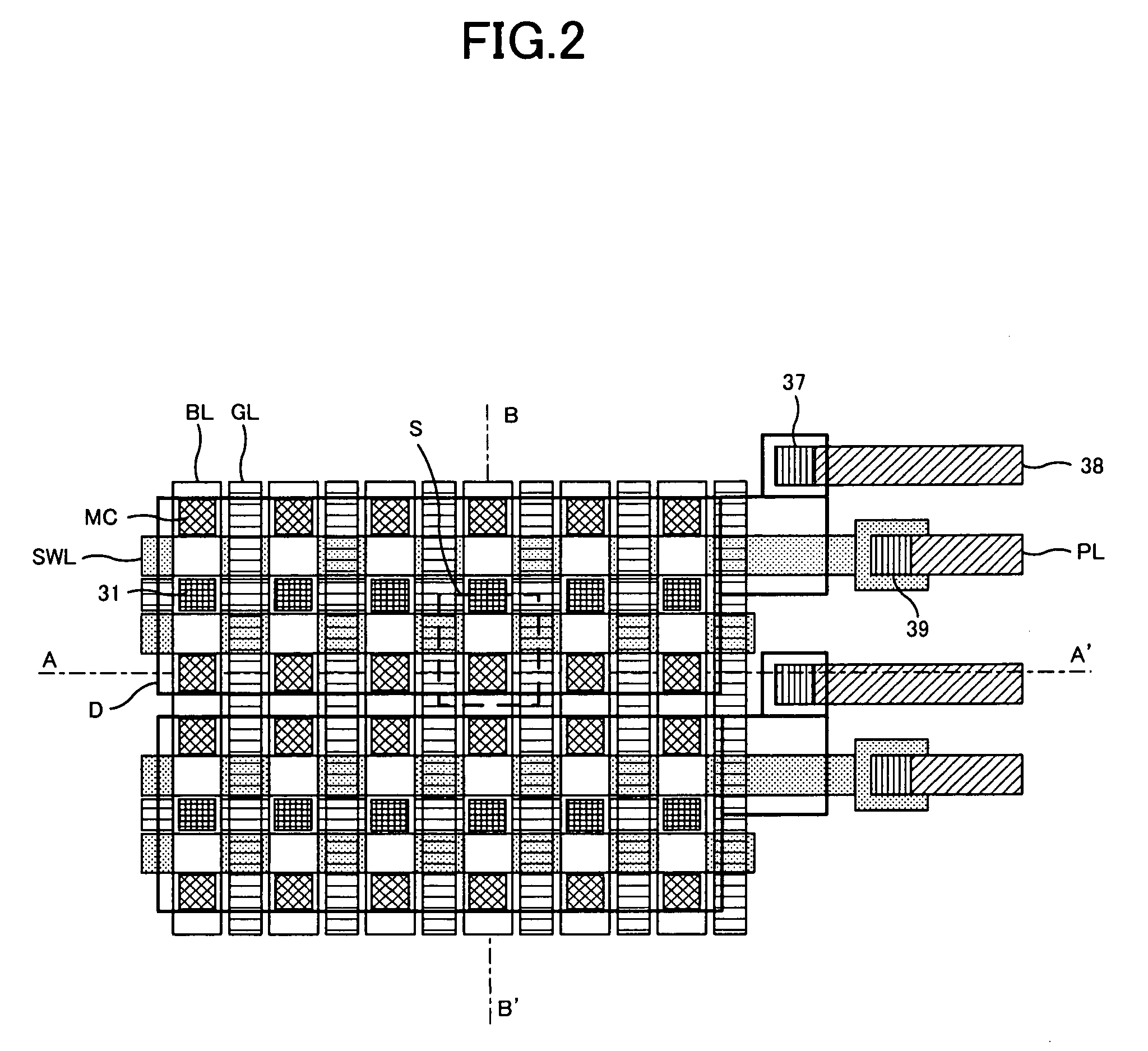
A phase change memory device comprises: a phase change element for rewritably storing data by changing a resistance state; a memory cell arranged at an intersection of a word line and a bit line and formed of the phase change element and a diode connected in series; a select transistor formed in a diffusion layer below the memory cell, for selectively controlling electric connection between an anode of the diode and a ground line in response to a potential of the word line connected to a gate; and a precharge circuit for precharging the diffusion layer below the memory cell corresponding to a non-selected word line to a predetermined voltage and for disconnecting the diffusion layer below the memory cell corresponding to a selected word line from the predetermined voltage.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
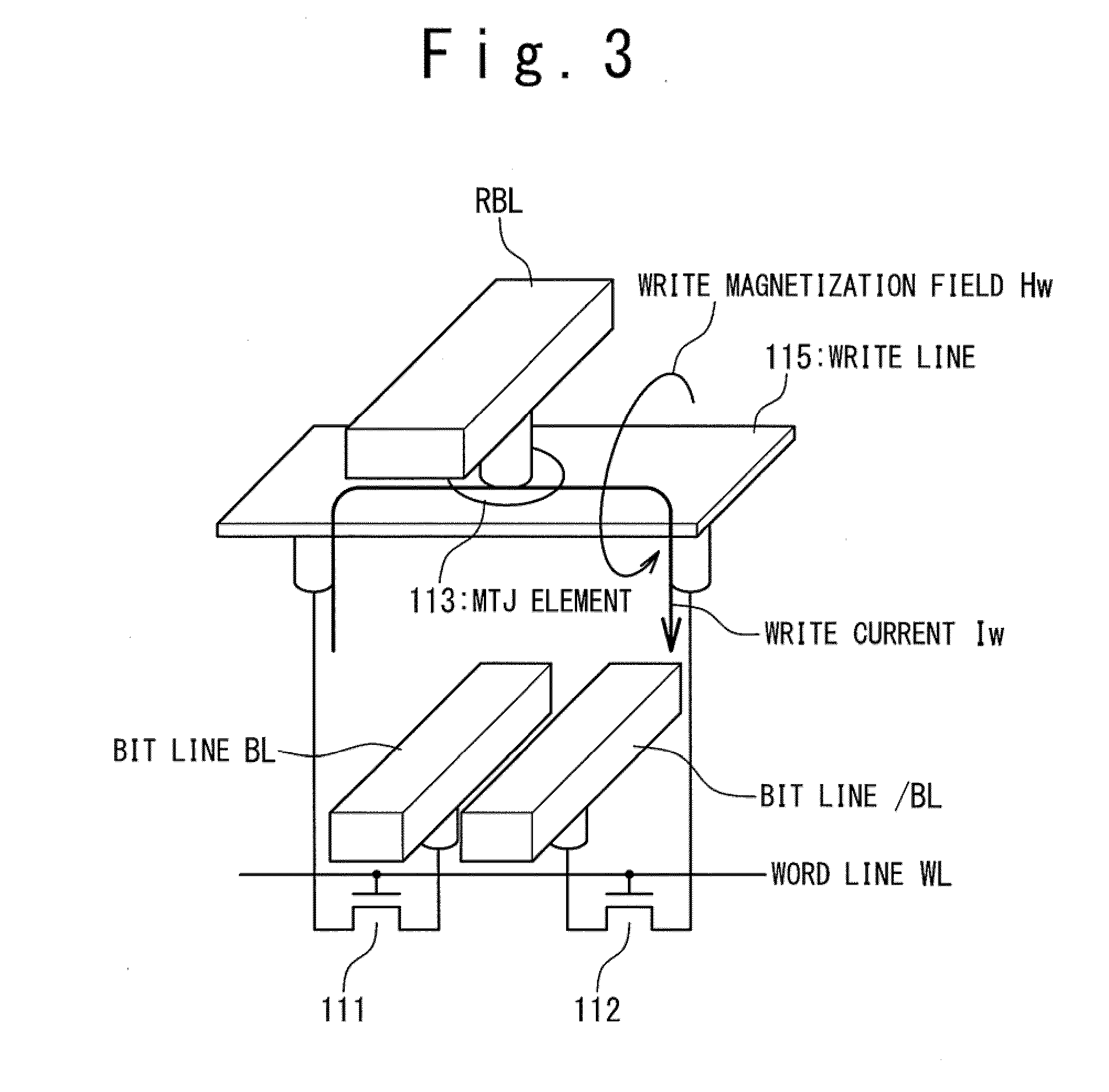
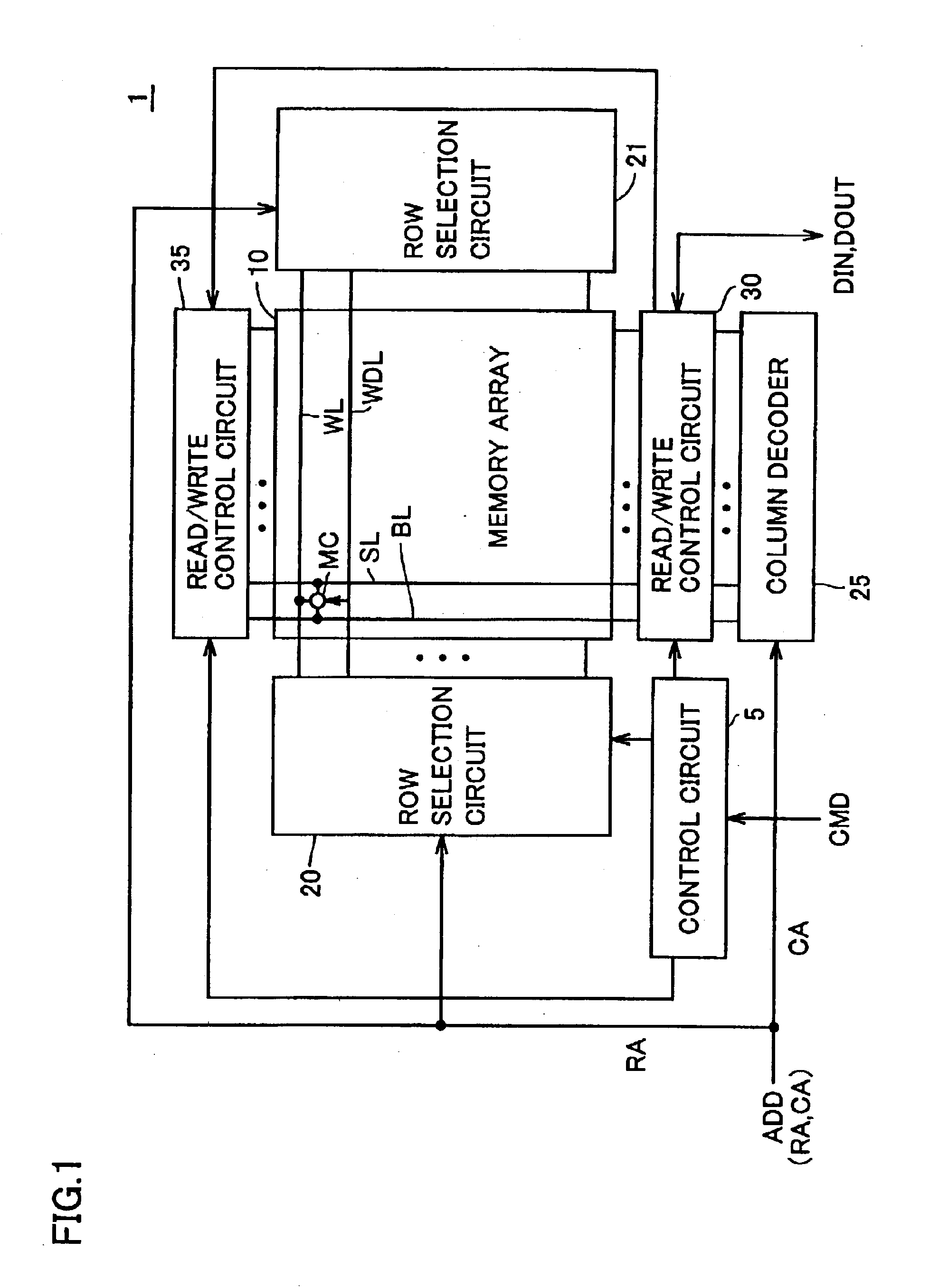
Magnetic ramdom access memory and operating method of the same
ActiveUS20070159876A1High-speed read operationMeet high-speed operationDigital storageStatic random-access memoryAudio power amplifier
A semiconductor memory device is provided with a memory array including memory cells arranged in rows and columns; and a sense amplifier circuit. Each of the memory cells includes at least one magnetoresistive element storing data, and an amplifying member used to amplify a signal generated by a current through the at least one magnetoresistive element. The sense amplifier circuit identifies data stored in the at least one magnetoresistive element in response to an output signal of the amplifying member.
Owner:NEC CORP
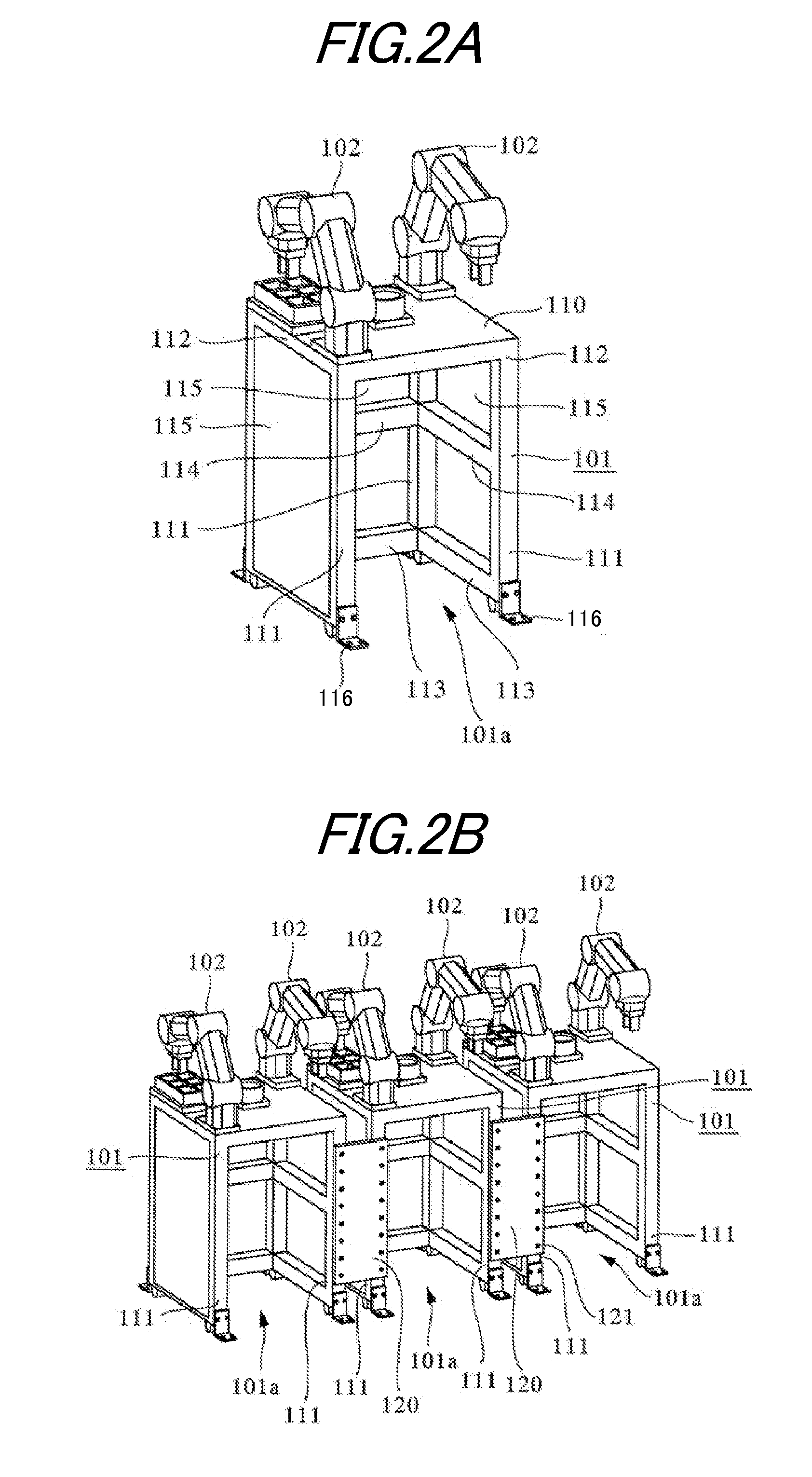
Robotic cell
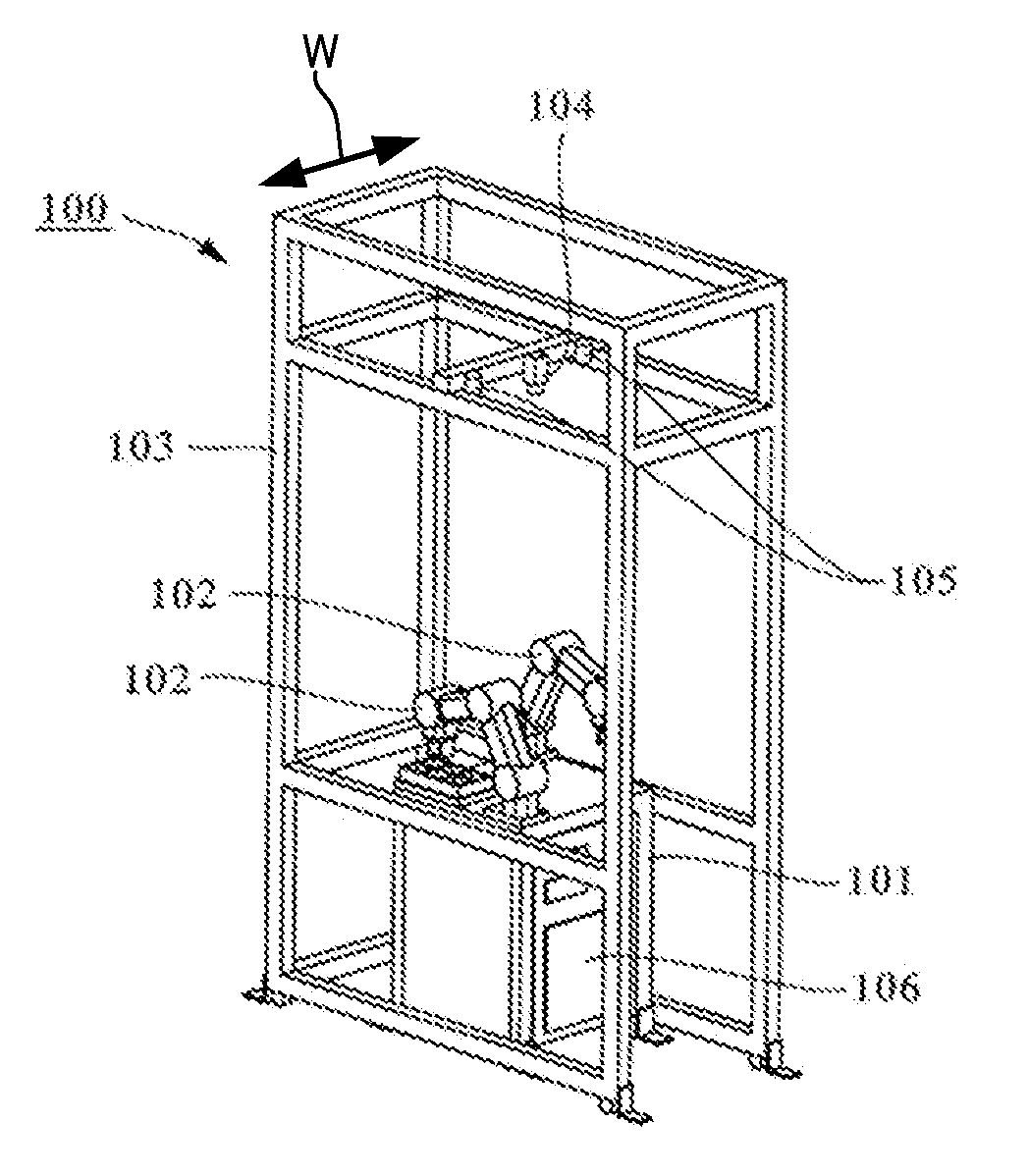
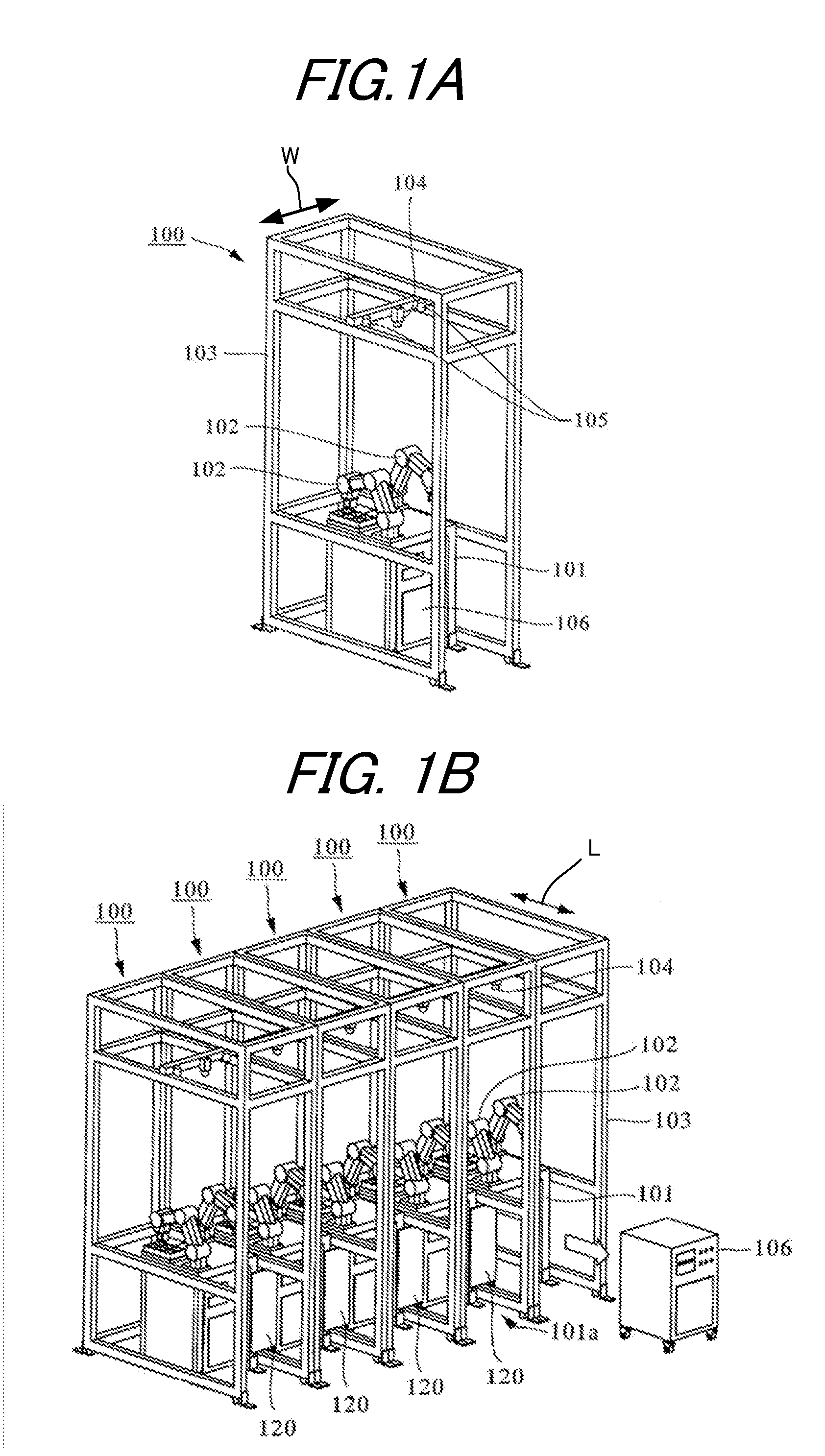
InactiveUS20110258847A1Improve maintainabilityImprove rigidityProgramme-controlled manipulatorAssembly machinesPower controllerMaintainability
A robotic cell enables a robotic station to be downsized and both high maintainability and high rigidity to be attained. To this end, the robotic cell for assembling parts by using multiple robots includes multiple booths for housing multiple trestles, on each of which a pair of robotic arms are mounted, with the trestles adjoining one another. Each trestle has an opening portion on one side surface thereof, through which a power controller box is carried in and out. To compensate for a decrease in rigidity of the trestle due to the opening portion, a connecting member is used for coupling two trestles adjacent to each other across the respective booths. Both end portions of each connecting member are fastened to the both trestles with screws, respectively.
Owner:CANON KK
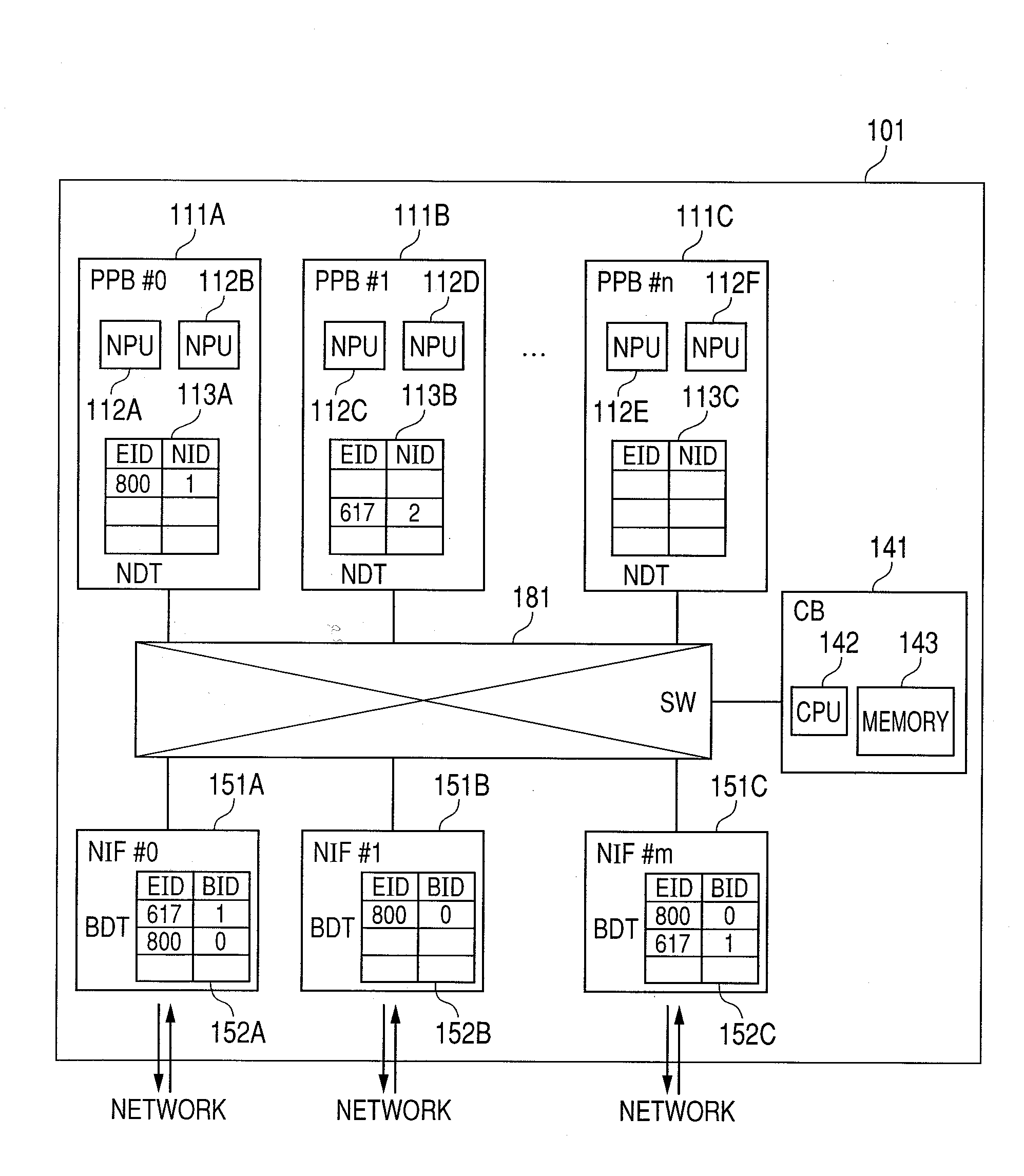
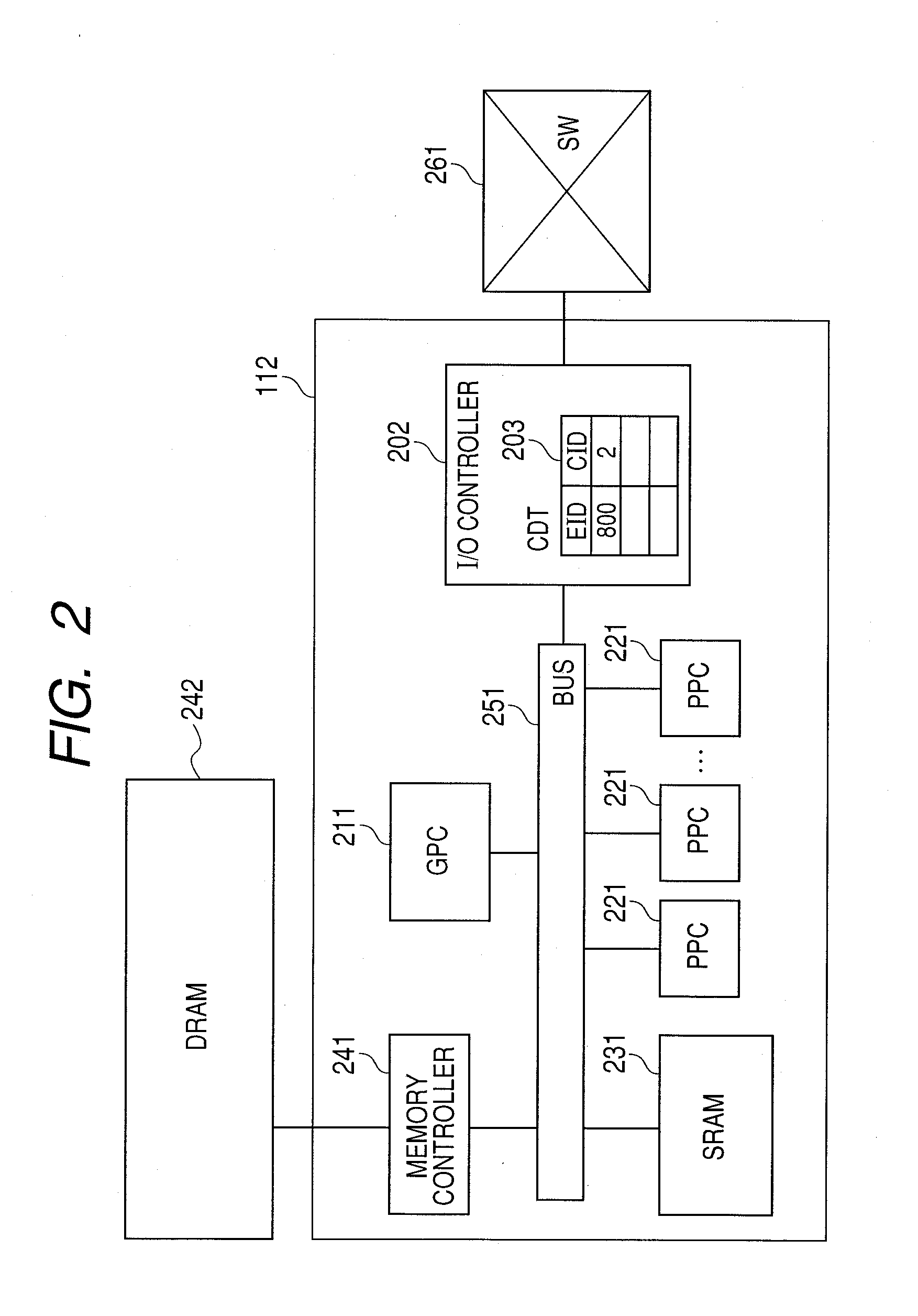
Packet processing device by multiple processor cores and packet processing method by the same
InactiveUS20100215050A1Flexible programmingIncrease speedProgram control using stored programsGeneral purpose stored program computerPacket processingParallel computing
A packet processing device includes multiple processor cores and memory connected to the multiple processor cores, upon reception of a load request of a program, selects a processor core to which the program has not yet been loaded, loads the program to the selected processor core, retains first association information that associates attribute information specified by the load request with the processor core to which the program has been loaded, upon reception of the packet, specifies the attribute information corresponding to the received packet, and transfers the received packet to the processor core corresponding to the specified attribute information.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS20070176233A1Operation of circuitReduce power consumptionSwitching accelaration modificationsReliability increasing modificationsLow voltageActive state
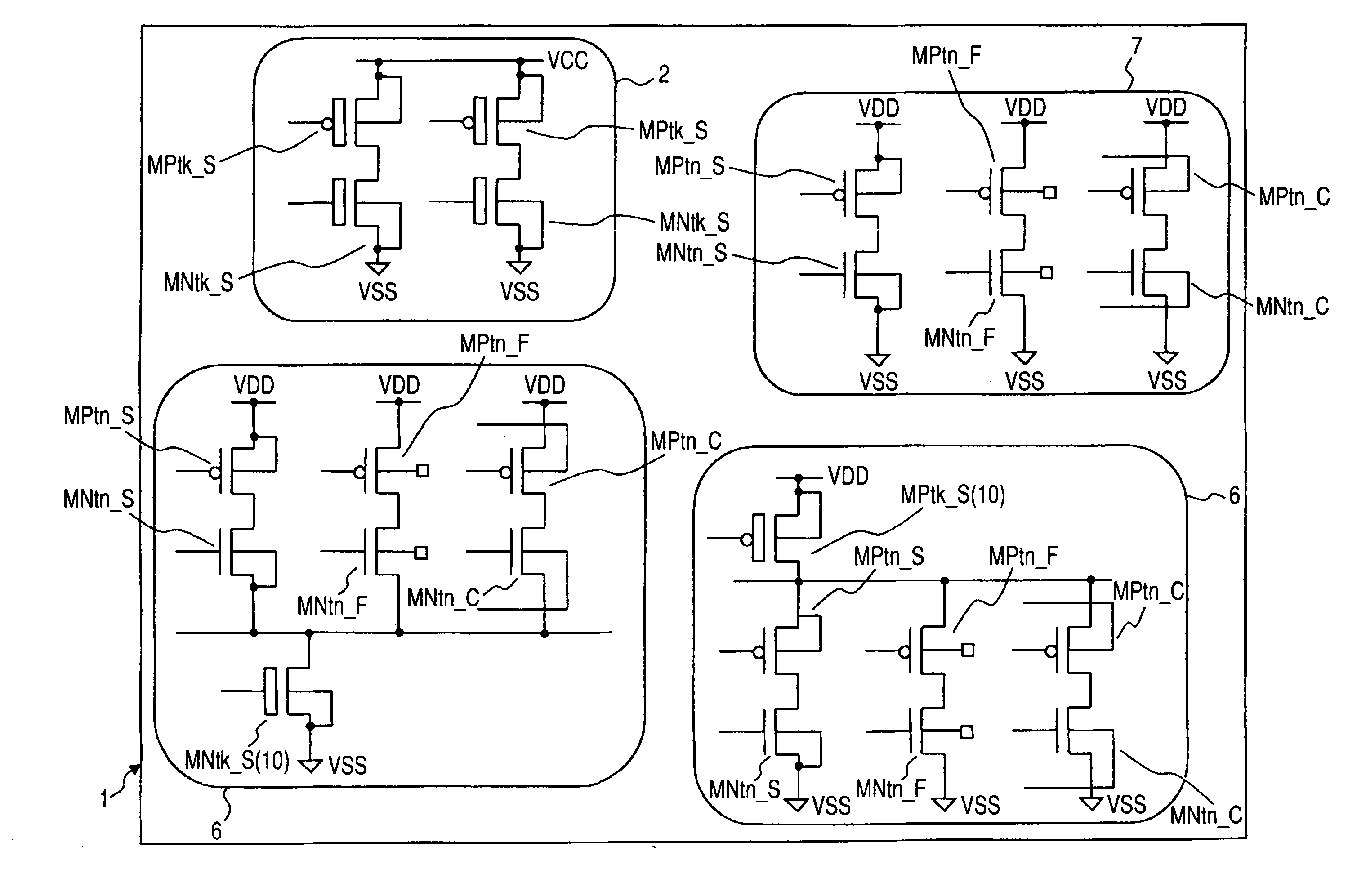
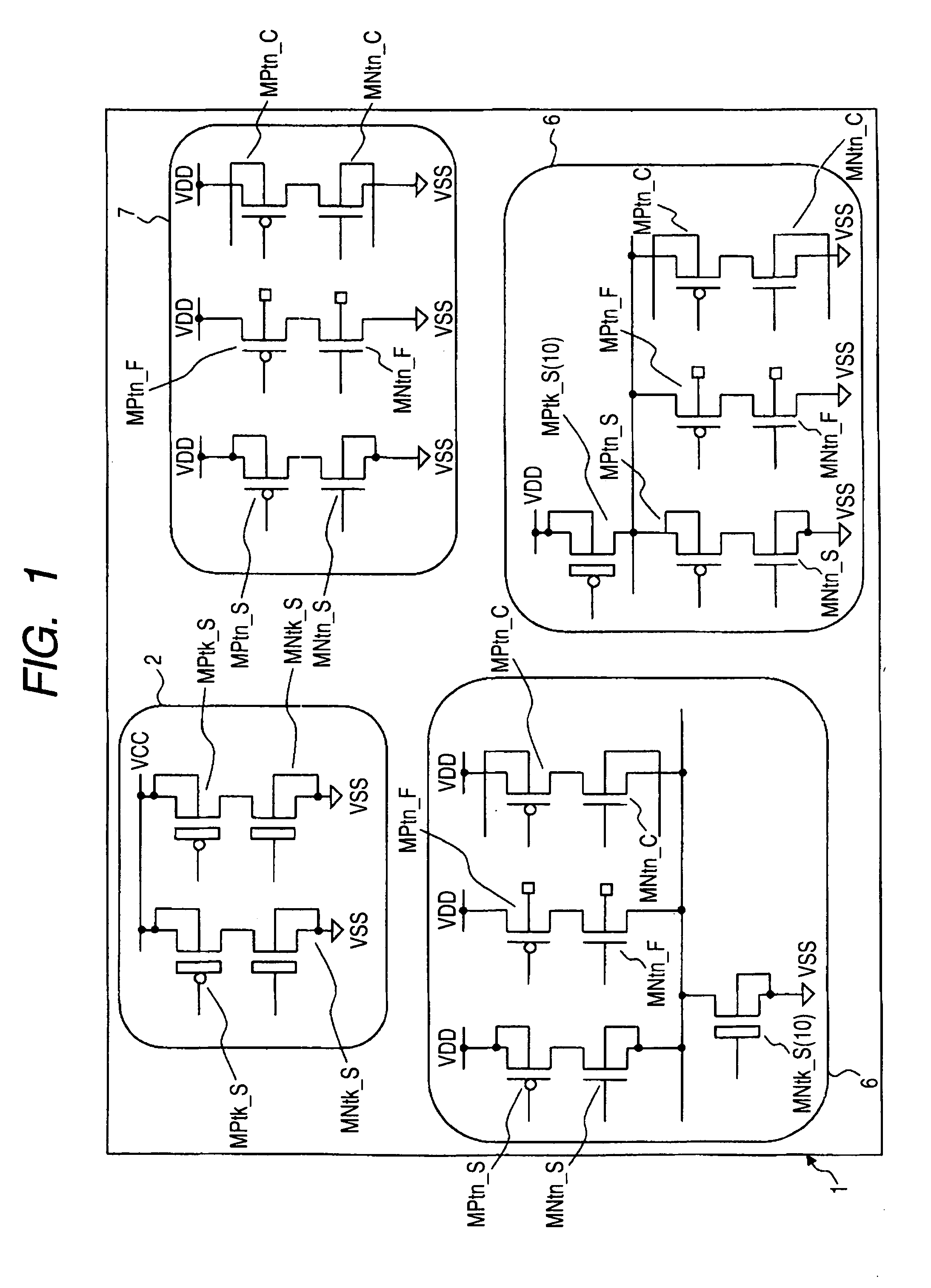
A plurality of MOS transistors each having an SOI structure includes, in mixed form, those brought into body floating and whose body voltages are fixed and variably set. When a high-speed operation is expected in a logic circuit in which operating power is relatively a low voltage and a switching operation is principally performed, body floating may be adopted. Body voltage fixing may be adopted in an analog system circuit that essentially dislikes a kink phenomenon of a current-voltage characteristic. Body bias variable control may be adopted in a logic circuit that requires the speedup of operation in an active state and needs low power consumption in a standby state. Providing in mixed form the transistors which are subjected to the body floating and the body voltage fixing and which are variably controlled in body voltage, makes it easier to adopt an accurate body bias according to a circuit function and a circuit configuration in terms of the speedup of operation and the low power consumption.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
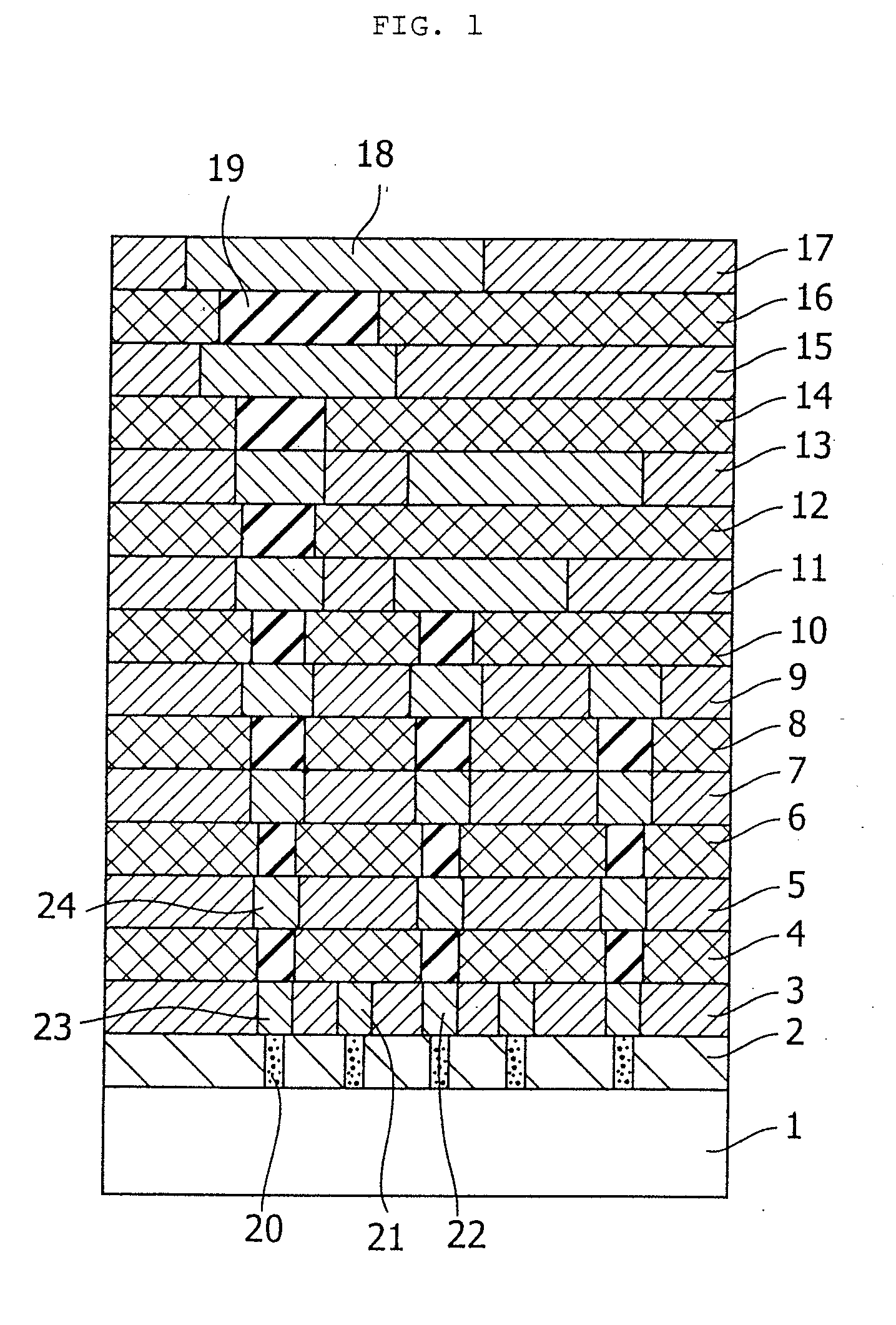
Composition for forming porous film, porous film and method for forming the same, interlevel insulator film, and semiconductor device
InactiveUS20040219372A1Promote decompositionMechanical strength is securedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectricDevice material
Provided are a composition for forming film which can form porous film excelling in dielectric constant, adhesiveness, uniformity of the film, mechanical strength and having low hygroscopicity; porous film and a method for forming the film; and a high-performing and highly reliable semiconductor device comprising the porous film inside. More specifically, provided is a composition for forming porous film, the composition comprising siloxane polymer and one or more quaternary ammonium salts represented by following formula (1) or (2): [(R<1>)4N]+[R<2>X]<-> (1) Hk[(R<1>)4N]m<+>Y<-> (2) wherein X represents CO2, OSO3 or SO3; Y represents SO4, SO3, CO3, O2C-CO2, NO3 or NO2; and k is 0 or 1, m is 1 or 2 and n is 1 or 2 in proviso that n=1 requires k=0 and m=1, and n=2 requires k=O and m=2, or k=1 and m=1.
Owner:RPX CORP
Semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS7714606B2Meet high-speed operationReduce power consumptionSwitching accelaration modificationsReliability increasing modificationsLow voltageEngineering
A plurality of MOS transistors each having an SOI structure includes, in mixed form, those brought into body floating and whose body voltages are fixed and variably set. When a high-speed operation is expected in a logic circuit in which operating power is relatively a low voltage and a switching operation is principally performed, body floating may be adopted. Body voltage fixing may be adopted in an analog system circuit that essentially dislikes a kink phenomenon of a current-voltage characteristic. Body bias variable control may be adopted in a logic circuit that requires the speedup of operation in an active state and needs low power consumption in a standby state. Providing in mixed form the transistors which are subjected to the body floating and the body voltage fixing and which are variably controlled in body voltage, makes it easier to adopt an accurate body bias according to a circuit function and a circuit configuration in terms of the speedup of operation and the low power consumption.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Integrated semiconductor nonvolatile storage device
ActiveUS7723779B2Improve performanceIncrease currentSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesComputer architectureSemiconductor storage devices
An object of the present invention is to provide an integrated semiconductor nonvolatile storage device that can be read at high speed and reprogrammed an increased number of times.In the case of conventional nonvolatile semiconductor storage devices having a split-gate structure, there is a tradeoff between the read current and the maximum allowable number of reprogramming operations. To overcome this problem, an integrated semiconductor nonvolatile storage device of the present invention is configured such that memory cells having different memory gate lengths are integrated on the same chip. This allows the device to be read at high speed and reprogrammed an increased number of times.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor storage device
ActiveUS20100097845A1High-speed write operationRun at high speedNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsElectrical connectionSemiconductor storage devices
A semiconductor storage device is provided with a memory array including a plurality of memory cells. The plurality of memory cells includes: first and third memory cells arranged along one of an even-numbered row and an odd-numbered row, and a second memory cell arranged along the other. Each of the plurality of memory cells includes: a first transistor comprising first and second diffusion layers; a second transistor comprising third and fourth diffusion layers; and a magnetoresistance element having one of terminals thereof connected to an interconnection layer which provides an electrical connection between the second and third diffusion layers. The fourth diffusion layer of the first memory cell is also used as the first diffusion layer of the second memory cell. In addition, the fourth diffusion layer of the second memory cell is also used as the first diffusion layer of the third memory cell.
Owner:NEC CORP
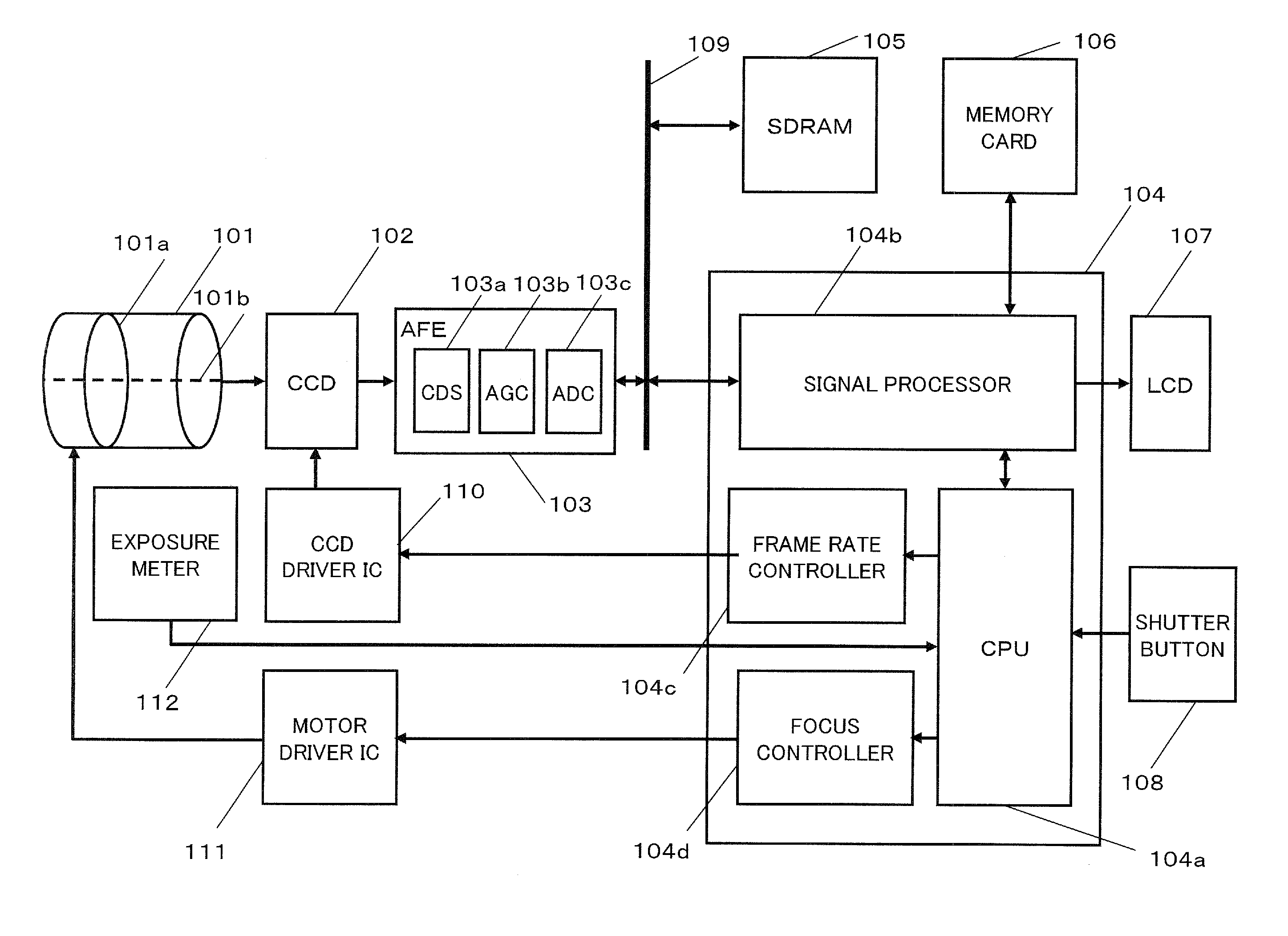
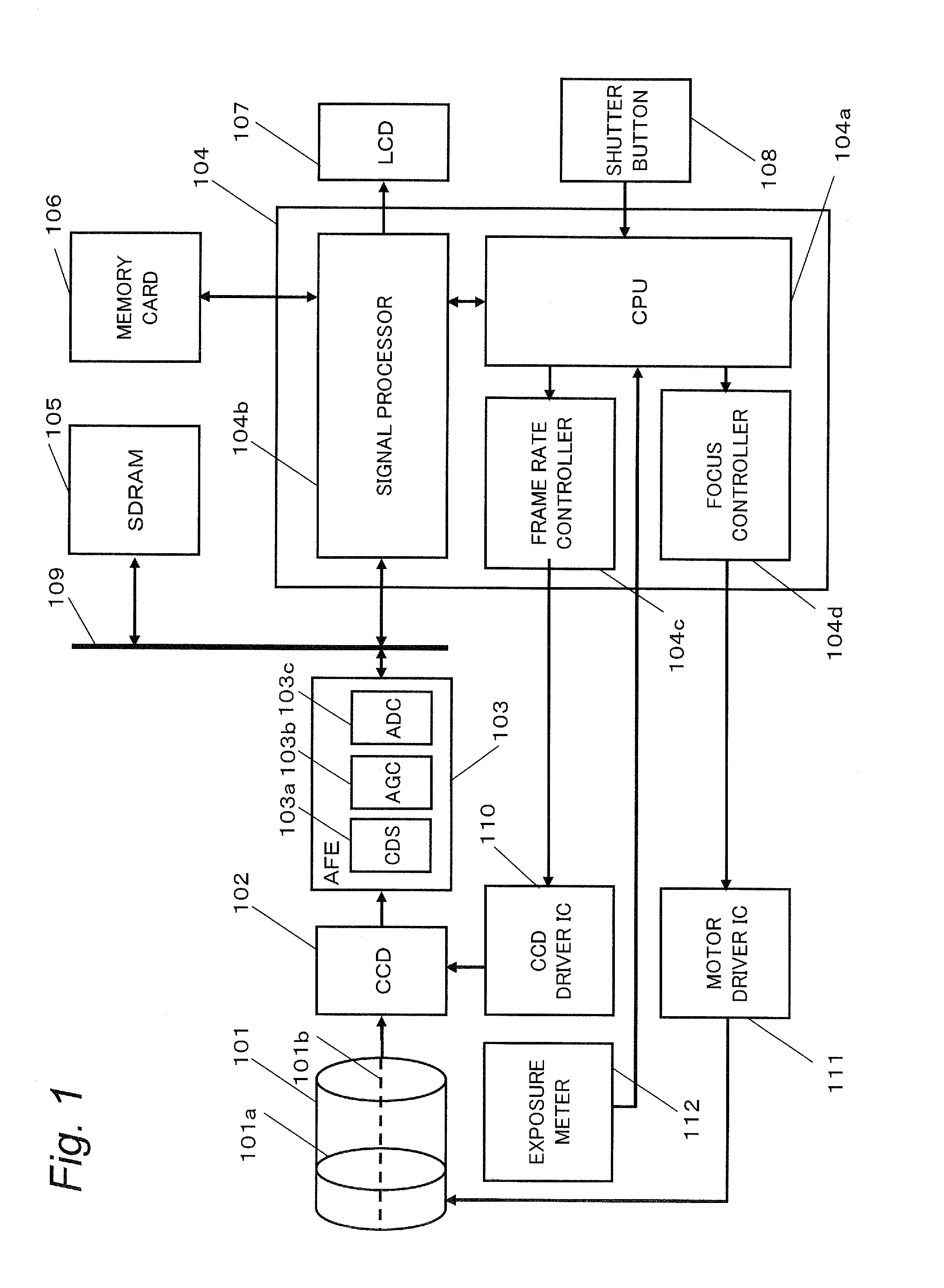
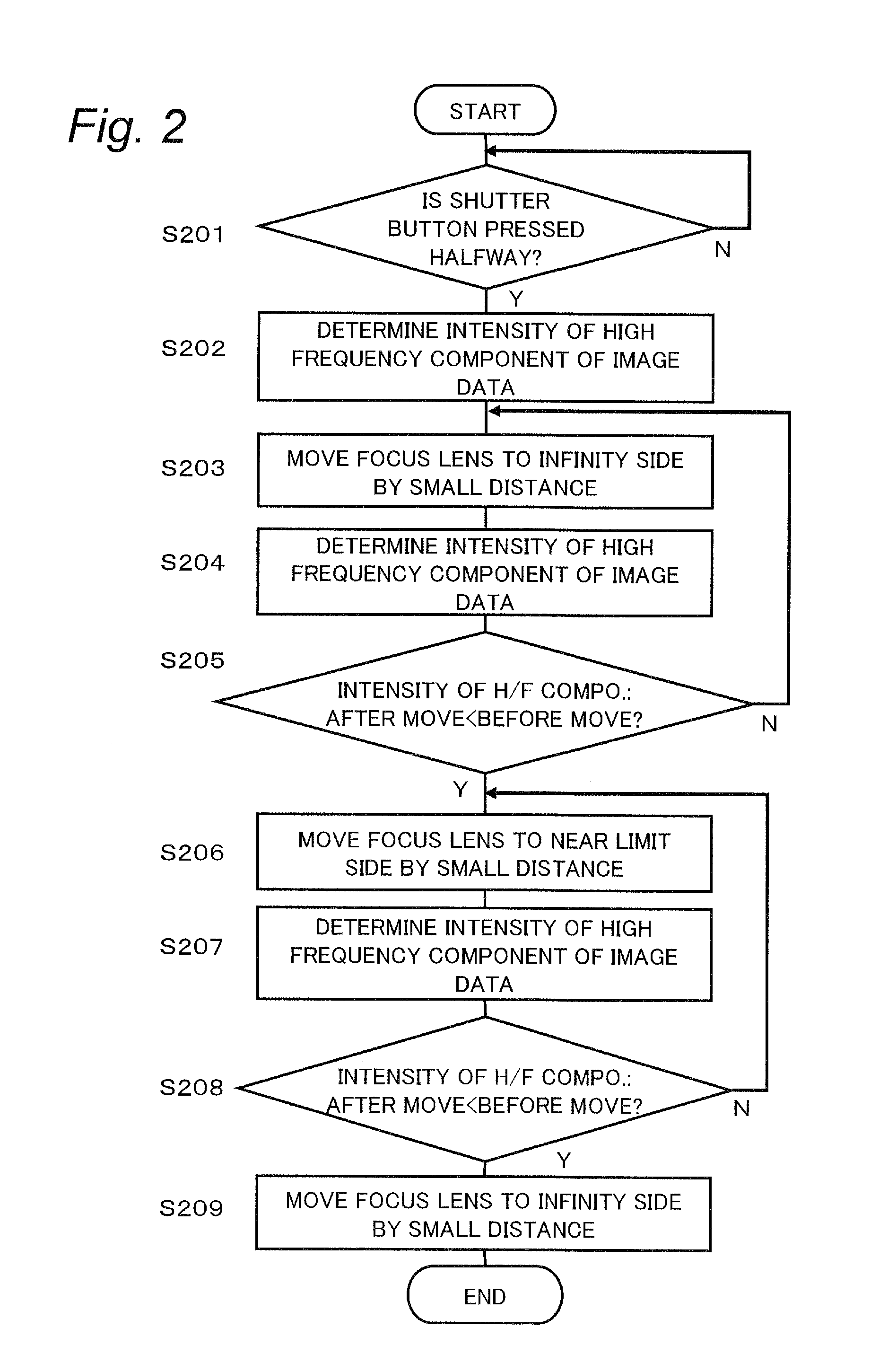
Imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20100171844A1Shortage of exposure timeRead frame rateTelevision system detailsColor television detailsAudio power amplifierImaging equipment
An imaging apparatus includes an imaging unit operable to output an image signal of a subject, an amplifier unit operable to amplify the image signal output by the imaging unit, a gain adjusting unit operable to adjust a gain of the amplifier unit, and a frame rate adjusting unit operable to set a read frame rate of the imaging unit for a normal operation period to a first frame rate, and set the read frame rate for a focus operation period to a second frame rate which is larger than the first frame rate. When the frame rate adjusting unit changes the read frame rate of the imaging unit from the first frame rate to the second frame rate, the gain adjusting unit adjusts the gain of the amplifier unit so that a substantially equivalent exposure amount is maintained before and after the change in the read frame rate.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Magnetoresistance effect element and magnetic memory
ActiveUS20130141966A1High magneto-resistive ratioLow constantMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesFilm planeMagnetic memory
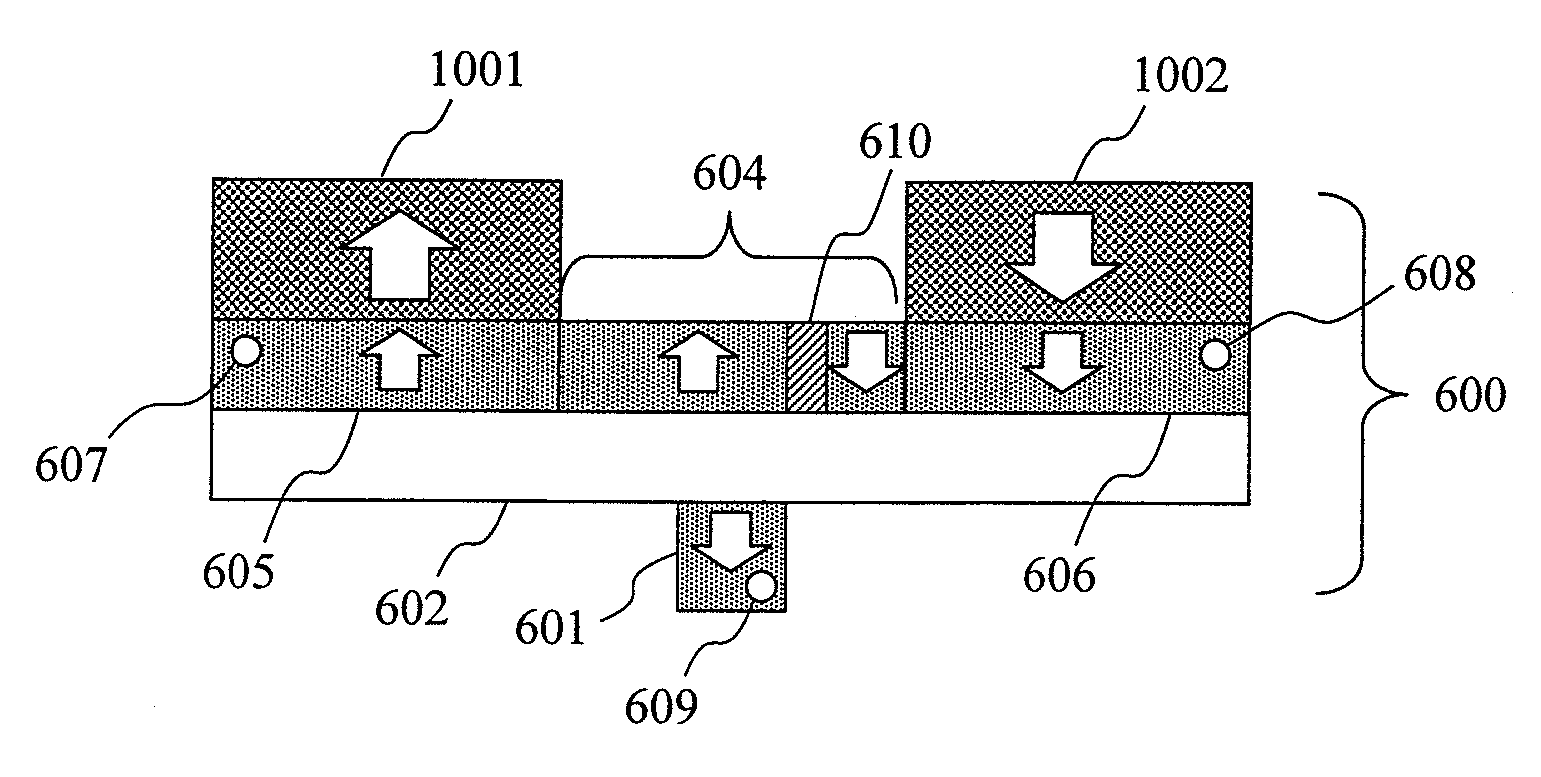
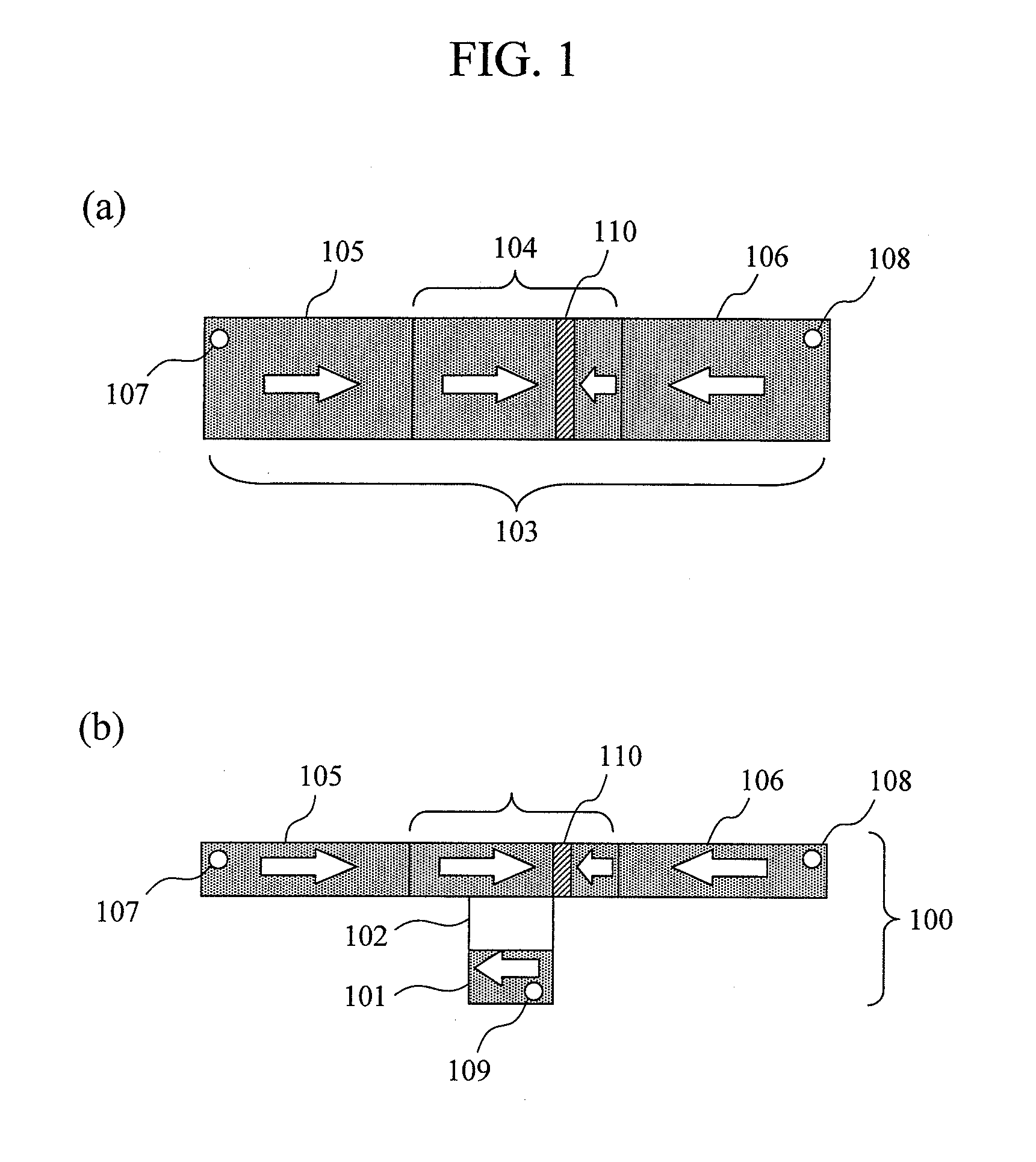
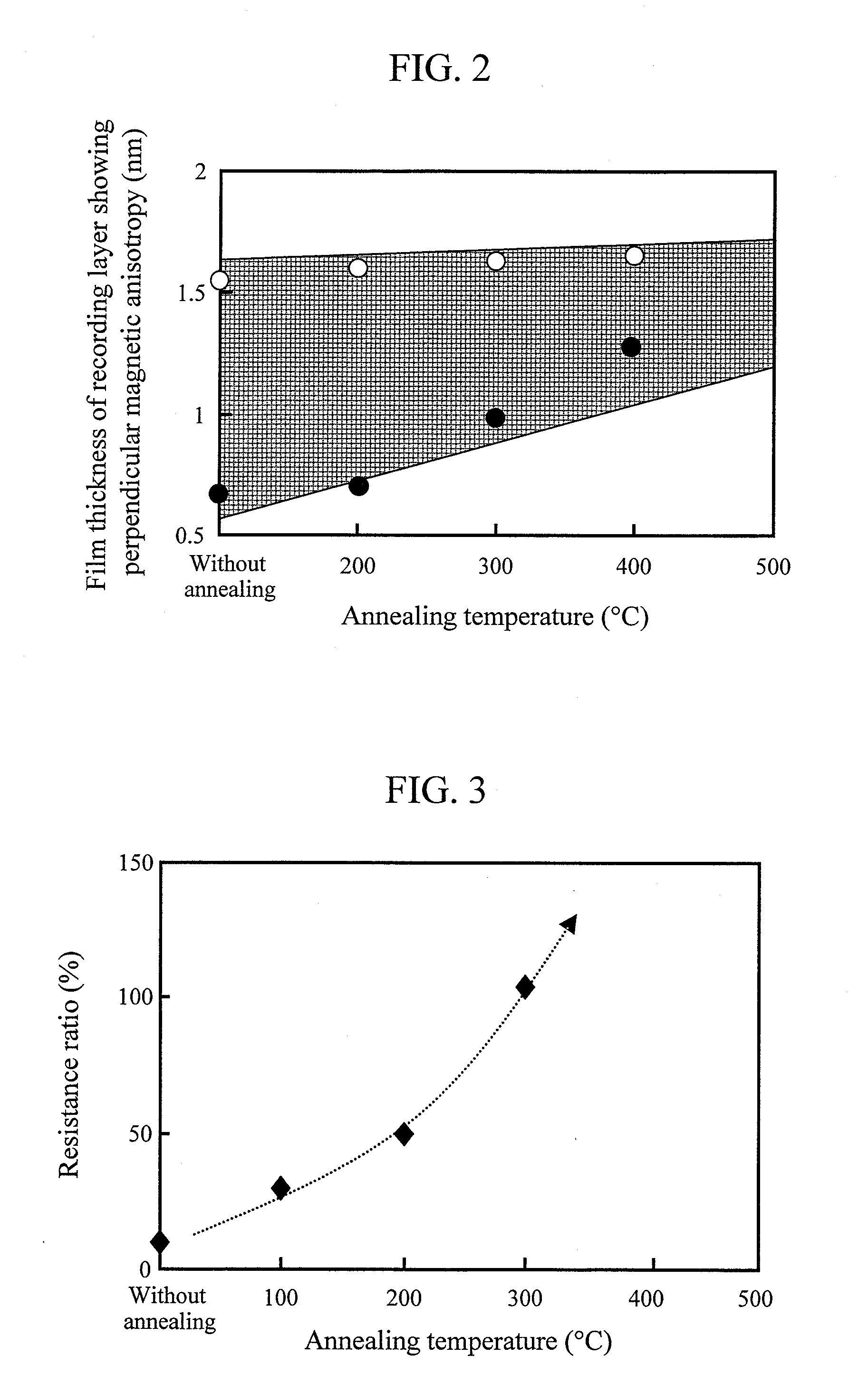
Provided are a magnetoresistance effect element with a stable magnetization direction perpendicular to film plane and a controlled magnetoresistance ratio, in which writing can be performed by magnetic domain wall motion, and a magnetic memory including the magnetoresistance effect element. The magnetoresistance ratio is controlled by forming a ferromagnetic layer of the magnetoresistance effect element from a ferromagnetic material including at least one type of 3d transition metal or a Heusler alloy. The magnetization direction is changed from a direction in the film plane to a direction perpendicular to the film plane by controlling the film thickness of the ferromagnetic layer on an atomic layer level.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
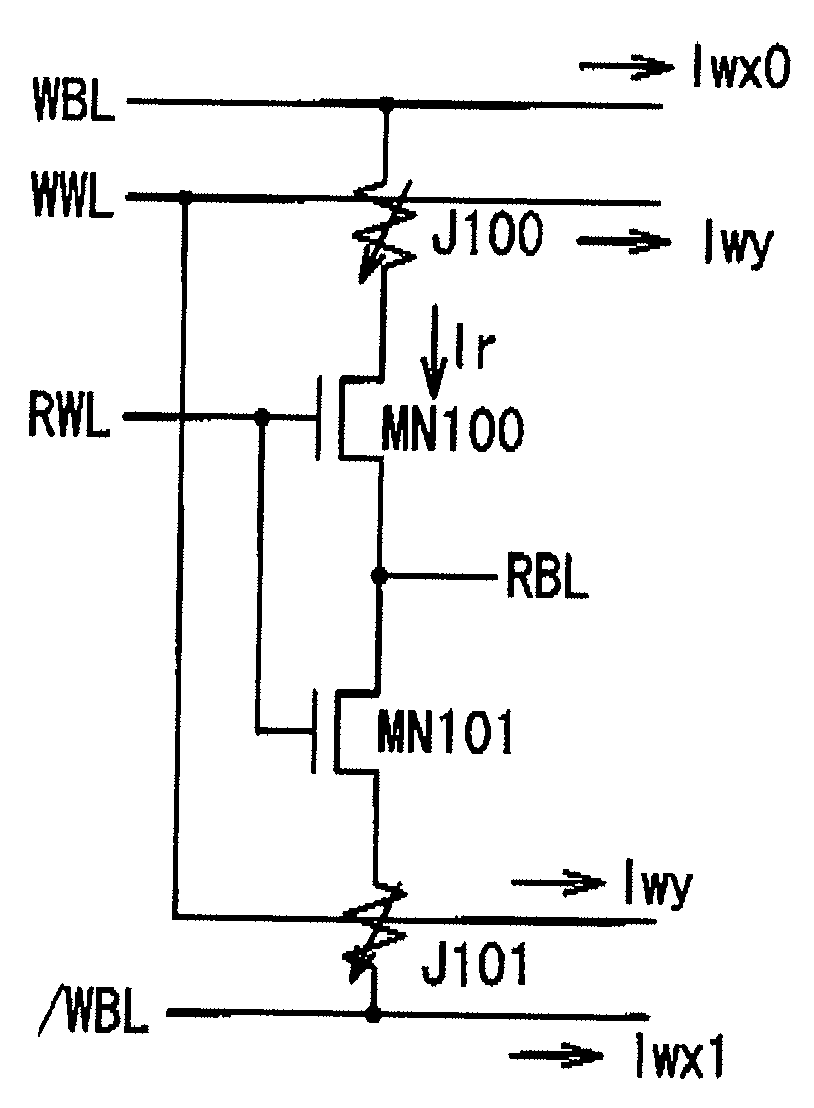
Semiconductor storage
InactiveUS7187588B2Effective restraint of interferenceSolve the lack of functionTransistorSolid-state devicesCharge retentionSemiconductor storage devices
A semiconductor storage device includes a semiconductor substrate, a gate insulating film formed on the semiconductor substrate, a single gate electrode formed on the gate insulating film, two charge holding portions formed on both sides of the gate electrode, source / drain regions respectively corresponding to the charge holding portions, and a channel region disposed under the single gate electrode. A memory function implemented by these two charge holding portions and a transistor operation function implemented by the gate insulating film is separated from each other for securing sufficient memory function as well as easily suppressing short channel effect by making the gate insulating film thinner.
Owner:SHARP KK
High speed sampling receiver with reduced output impedance
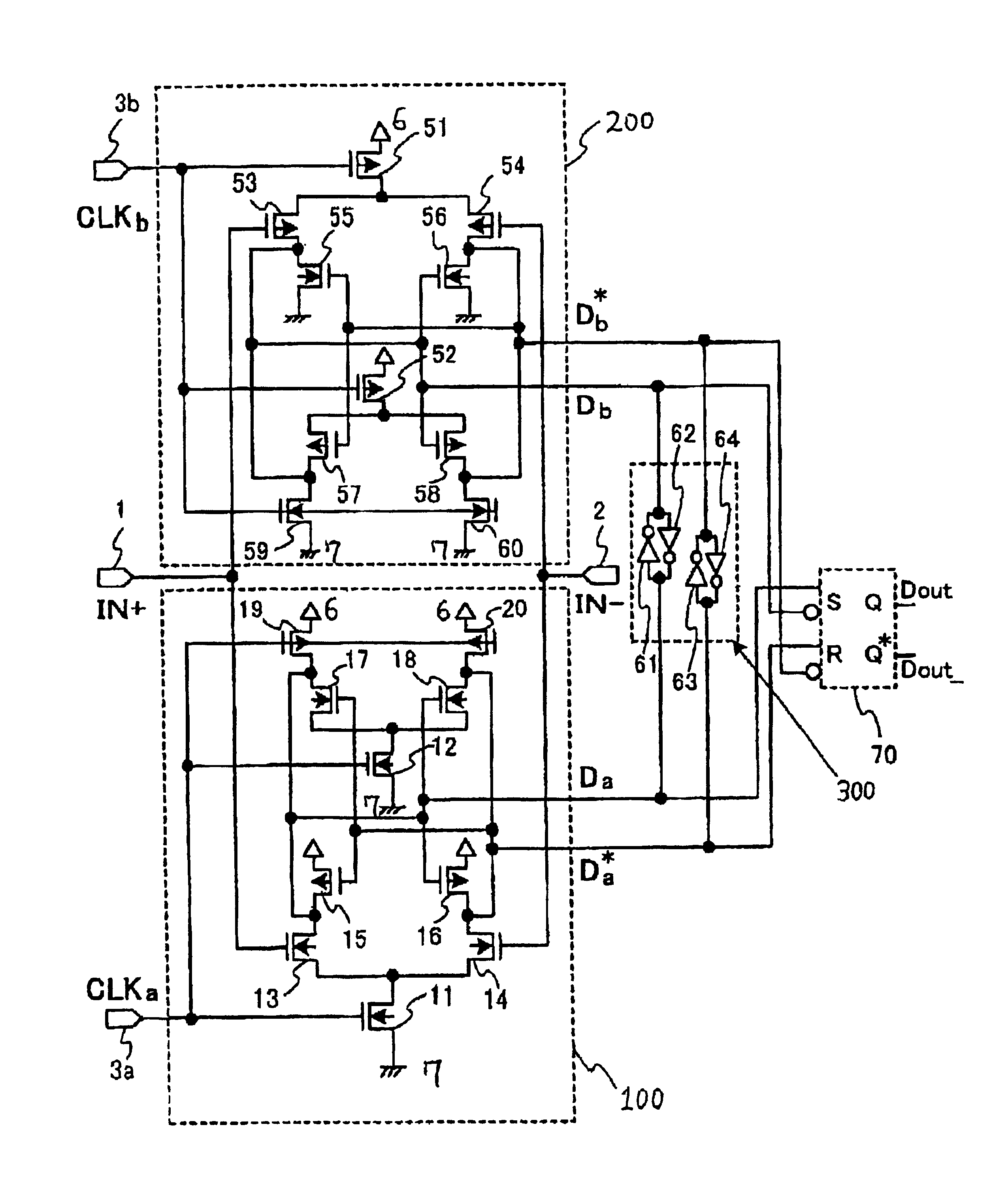
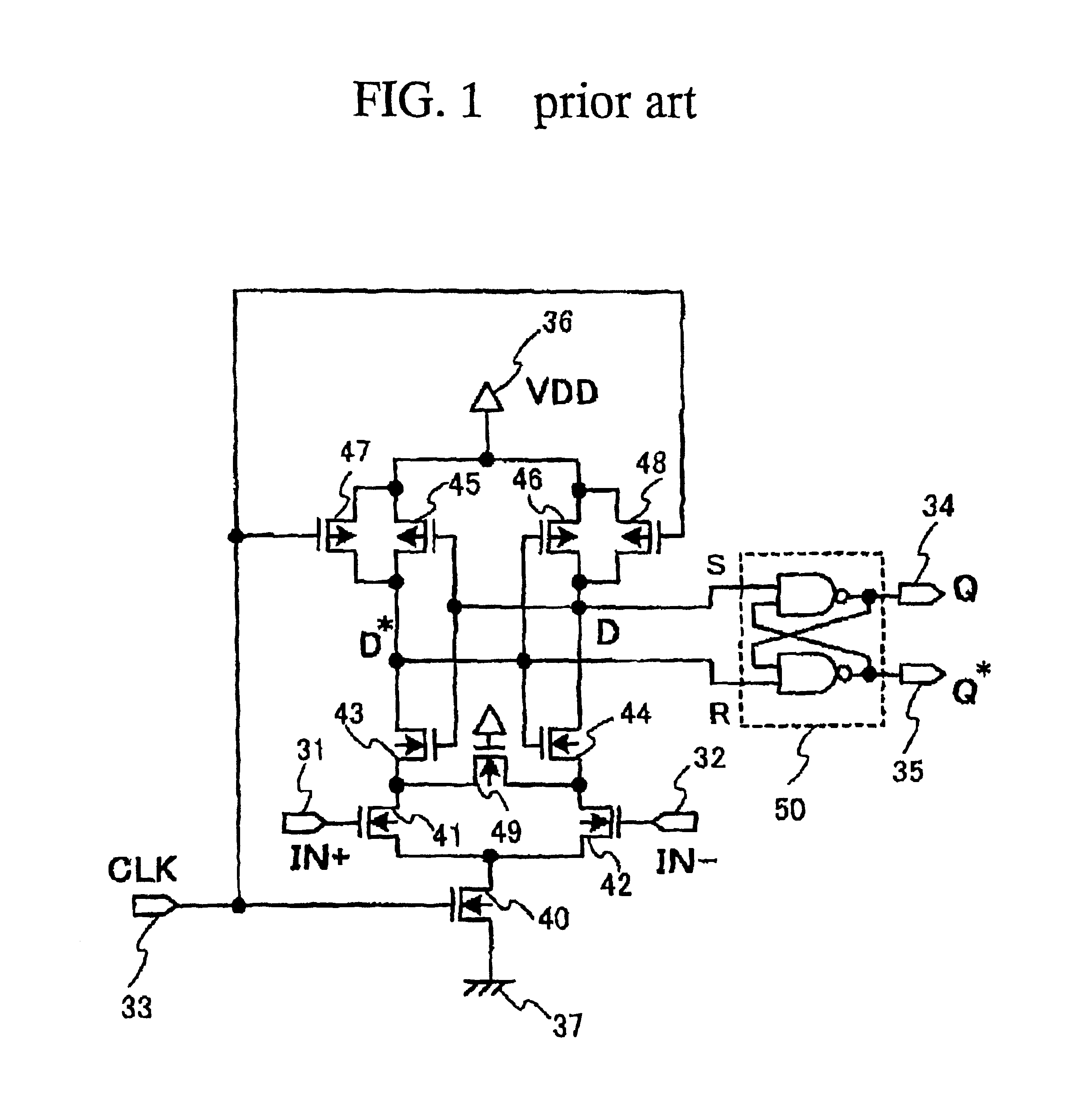
InactiveUS6922083B2Enlarged common mode levelHigh latch operationCurrent/voltage measurementLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsBistable circuitsEngineering
A sampling receiver includes: at least one slave latch circuit; and at least one master latch circuit which further includes: at least one differential input transistor pair, and at least one bistable circuit. Output terminals of the at least one differential input transistor pair and output terminals of the at least one bistable circuit are coupled to the at least one slave latch circuit but in parallel to each other with reference to the at least one slave latch circuit for the purpose of reducing an output impedance to allow the sampling receiver to exhibit a high speed latch operation.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Apparatus for cutting and stacking a multi-form web
InactiveUS6267034B1Reduce stepsContinuous operationMechanical working/deformationStock shearing machinesEngineeringWeb handling
A high speed rotary cutter assembly for transversely cutting a moving web, comprising a cutting roll and an anvil roll rotating at web speed which are selectively movable toward and away from one another to set the rotary cutter assembly in operative and idle modes, respectively. The invention also extends to a web handling device for forming a continuous multi-form web into a stack, comprising a folder assembly laying successive forms of the web in a superposed relationship on a table to form a stack. A temporary stack support assembly is extended along an arcuate descending path between the folder assembly and the table when the stack is completed for temporarily holding the incoming folded product until the completed stack on the table has been ejected.
Owner:RDP MARATHON
Porous insulating film, method for producing the same, and semiconductor device using the same
ActiveUS7968471B2Low specific inductive capacityImprove stabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsUnsaturated hydrocarbon
The present invention provides a process of producing a porous insulating film effective as an insulating film constituting a semiconductor device and a process of producing a porous insulating film having high adhesion to a semiconductor material, which is in contact with the upper and lower interfaces of the insulating film. Gas containing molecule vapor of at least one or more organic silica compounds, which have a cyclic silica skeleton in its molecule and have at least one or more unsaturated hydrocarbon groups bound with the cyclic silica skeleton is introduced into plasma to grow a porous insulating film on a semiconductor substrate.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
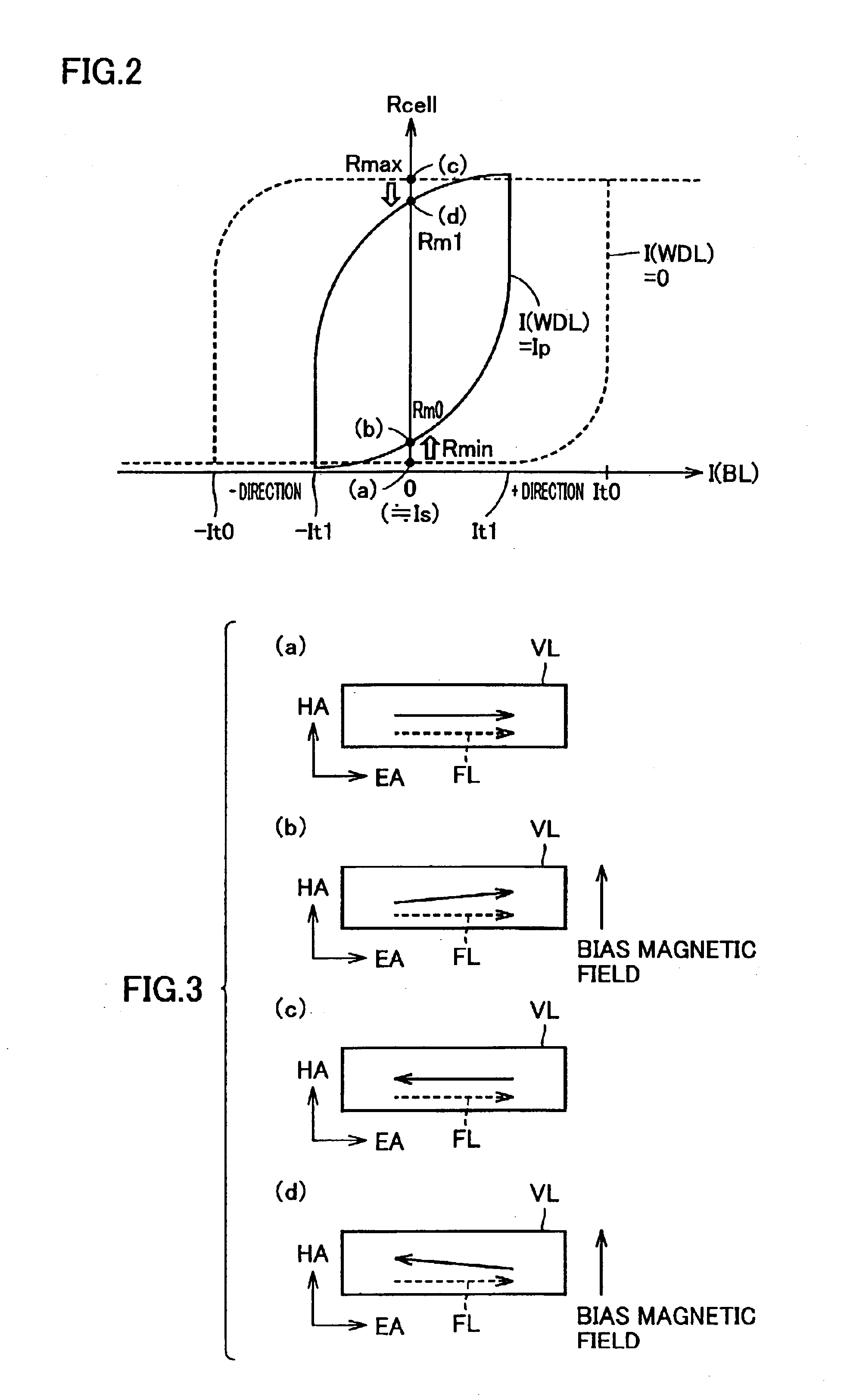
Thin film magnetic memory device conducting read operation by a self-reference method
InactiveUS6856565B2Increase speedHigh-speed read operationMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesAudio power amplifierMagnetization
In read operation, a current from a current supply transistor flows through a selected memory cell and a data line. Moreover, a bias magnetic field having such a level that does not destroy storage data is applied to the selected memory cell. By application of the bias magnetic field, an electric resistance of the selected memory cell changes in the positive or negative direction depending on the storage data level. A sense amplifier amplifies the difference between voltages on the data line before and after the change in electric resistance of the selected memory cell. Data is thus read from the selected memory cell by merely accessing the selected memory cell. Moreover, since the data line and the sense amplifier are insulated from each other by a capacitor, the sense amplifier can be operated in an optimal input voltage range regardless of magnetization characteristics of the memory cells.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
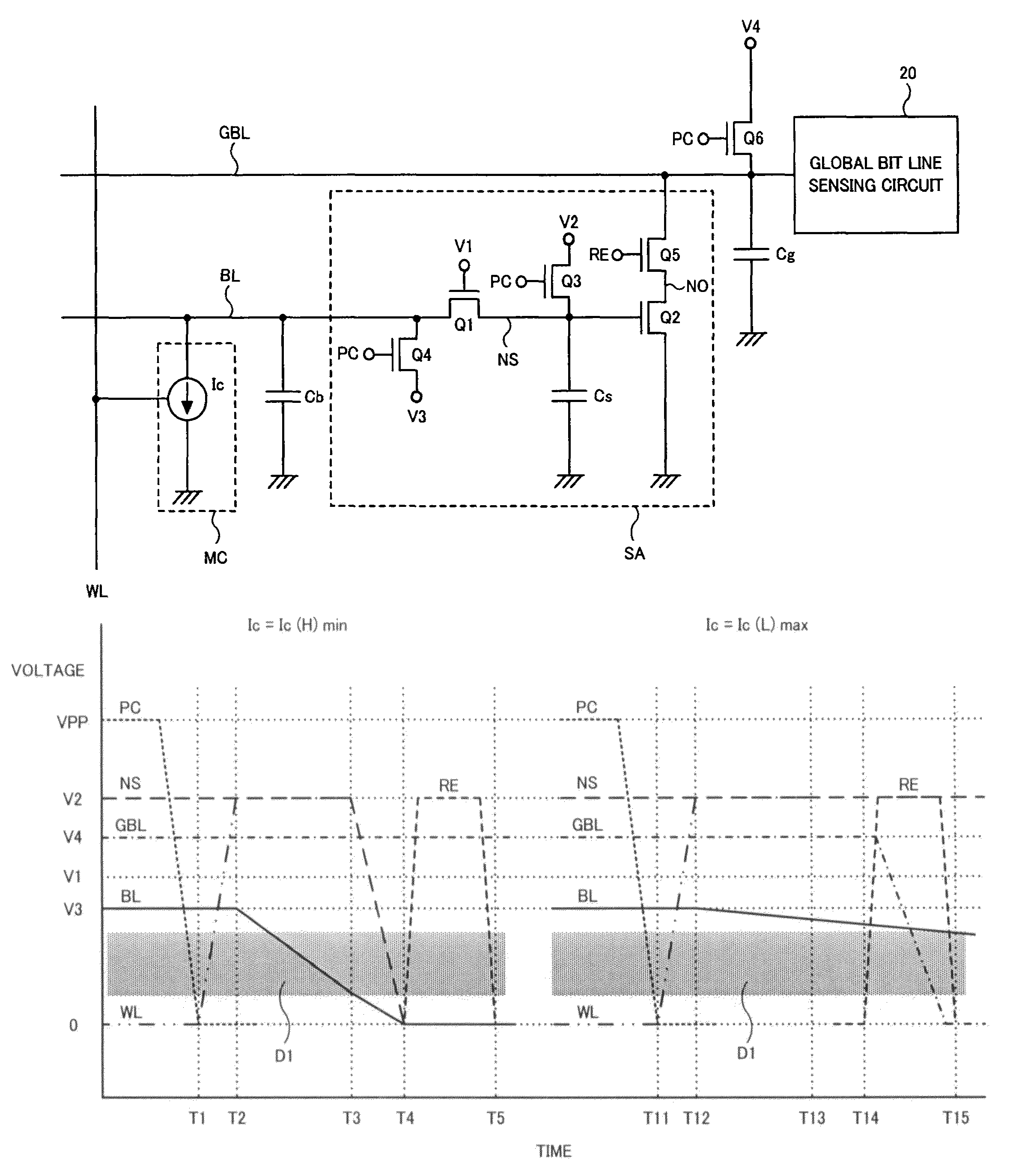
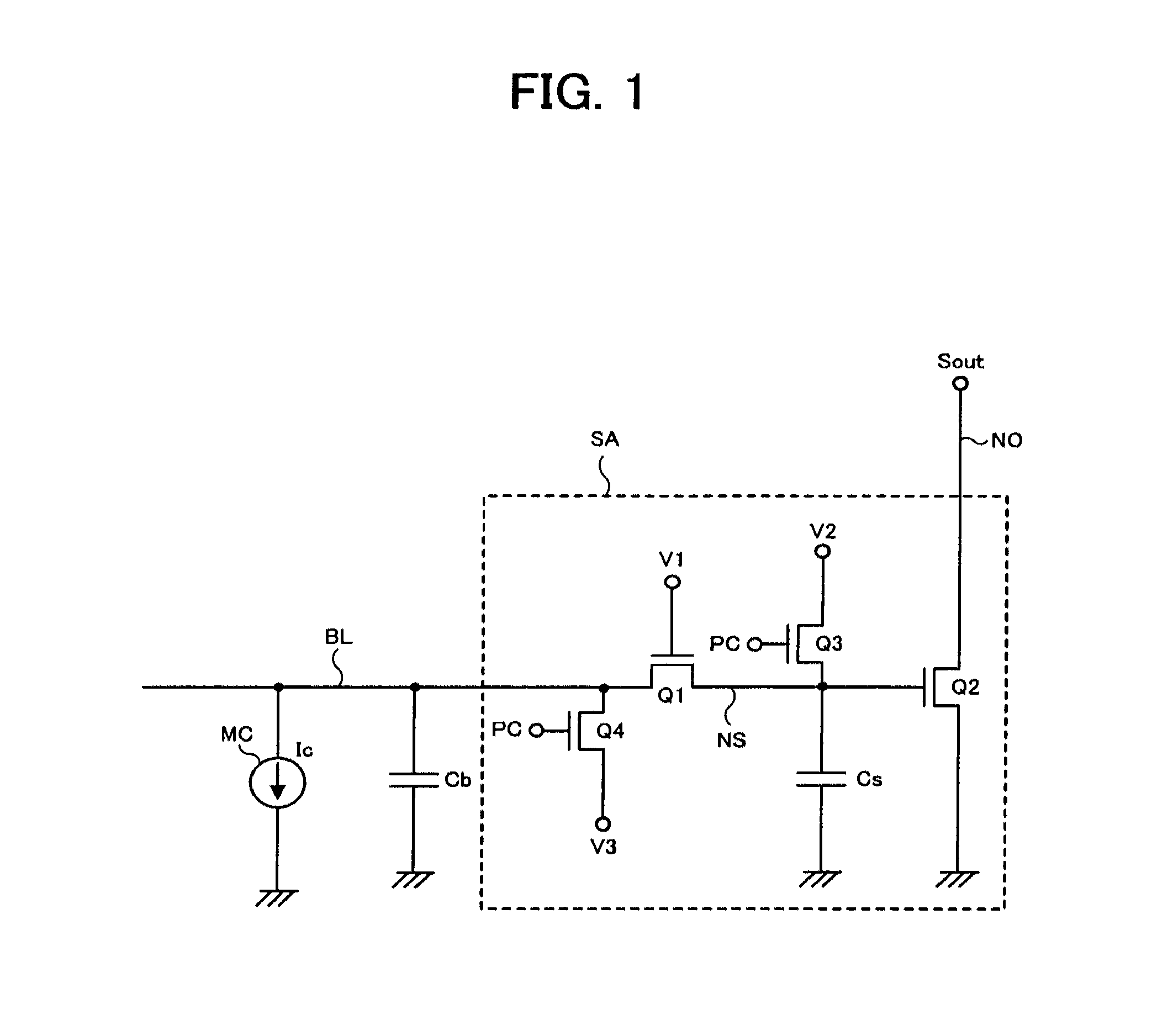
Semiconductor device having current change memory cell
InactiveUS8588019B2Improve current drive capabilityReduced operating requirementsElectric analogue storesDigital storageBit lineSemiconductor
A semiconductor device comprises a first transistor connected between a bit line and a sense node, and a second transistor amplifying a signal of the sense node. A first potential applied to a gate of the first transistor, a second potential supplied to the sense node, and a third potential supplied to the bit line are controlled so that the first potential applied to a gate of the first transistor is between the second and third potentials, the second potential is set larger than the third potential, and a predetermined potential obtained by subtracting a threshold voltage of the first transistor from the first potential is smaller than the third potential and higher than a low potential supplied to the second transistor. A potential of the bit line transitions from the third potential toward the low potential in accordance with data of a current change memory cell.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
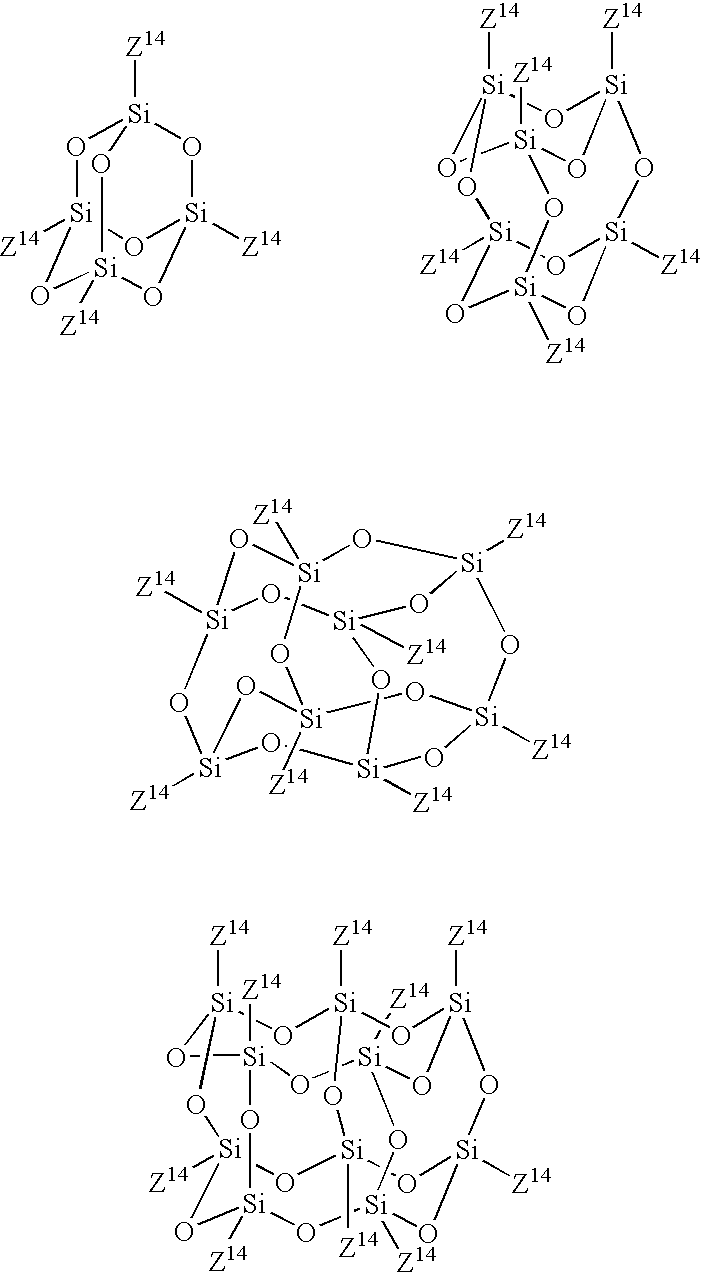
Composition for forming porous film, porous film and method for forming the same, interlevel insulator film, and semiconductor device
InactiveUS20070178319A1Hygroscopic property be decreaseDecrease parasitic capacitanceLayered productsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsOligomerSemiconductor
The present invention is a composition for forming a porous film obtainable by hydrolysis and condensation, in an acidic or alkaline condition, of a mixture of 100 parts by weight of one or more compounds selected of the group consisting of hydrolysable silicon compounds represented by Formulas (1) and (2) as described herein and partially hydrolyzed and condensed products of the hydrolysable silicon compounds represented by Formulas (1) and (2), and 0.1 to 20 parts by weight of one or more cross-linking agents selected from the group consisting of structure-controlled cyclic or multi-branched oligomers represented by Formulas (3) to (8) as described herein.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Data output circuit with improved overvoltage/surge protection
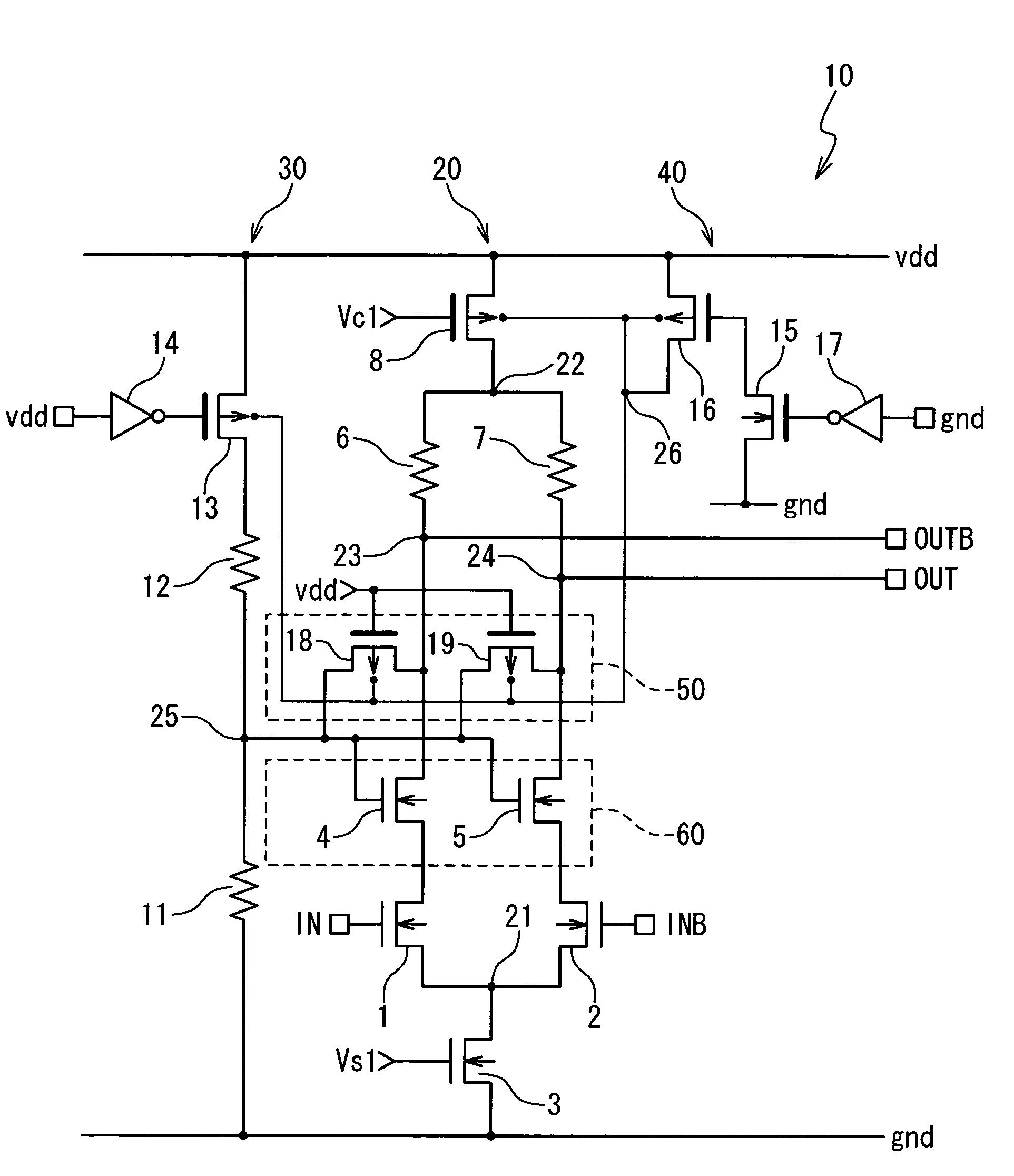
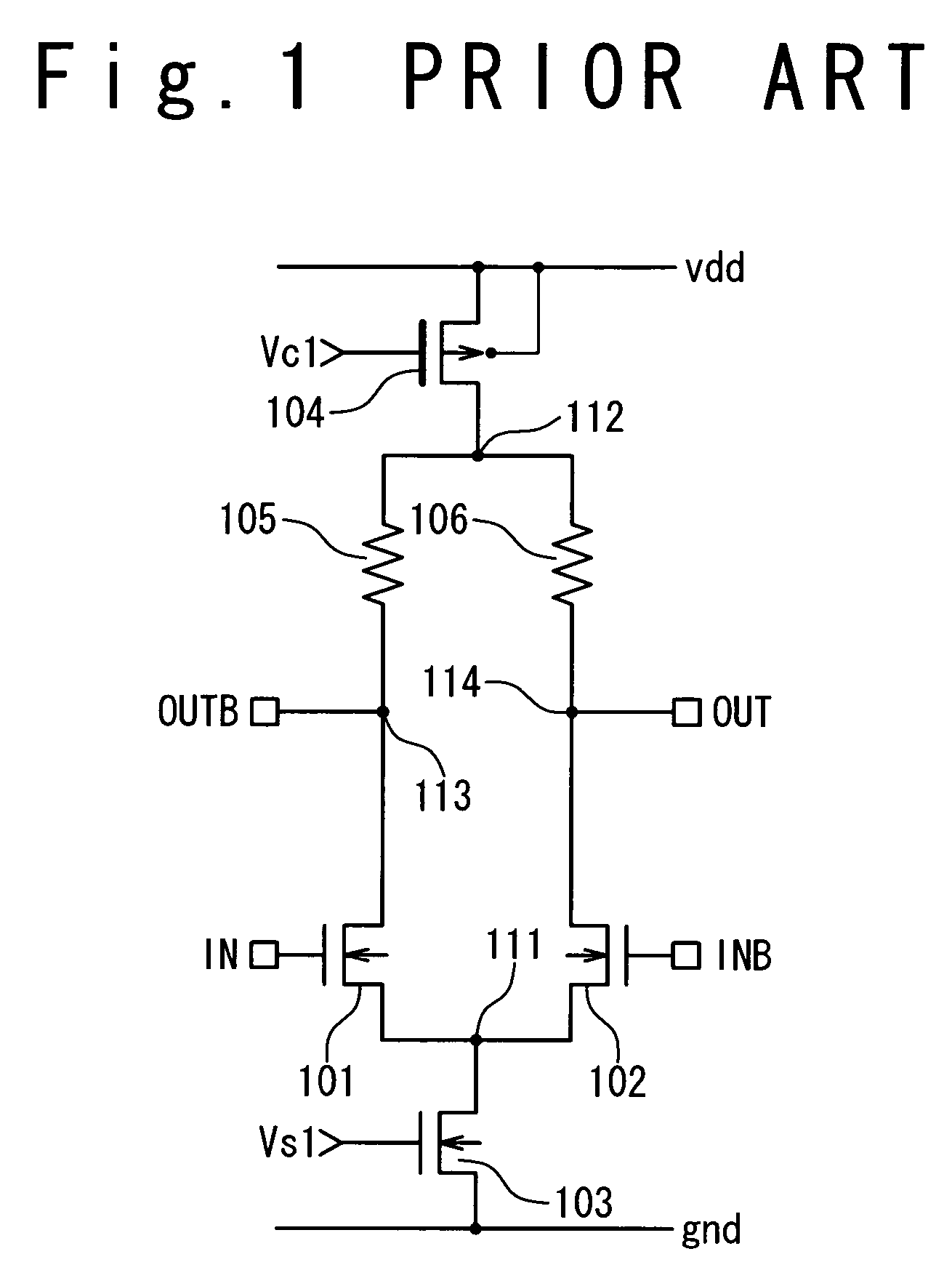
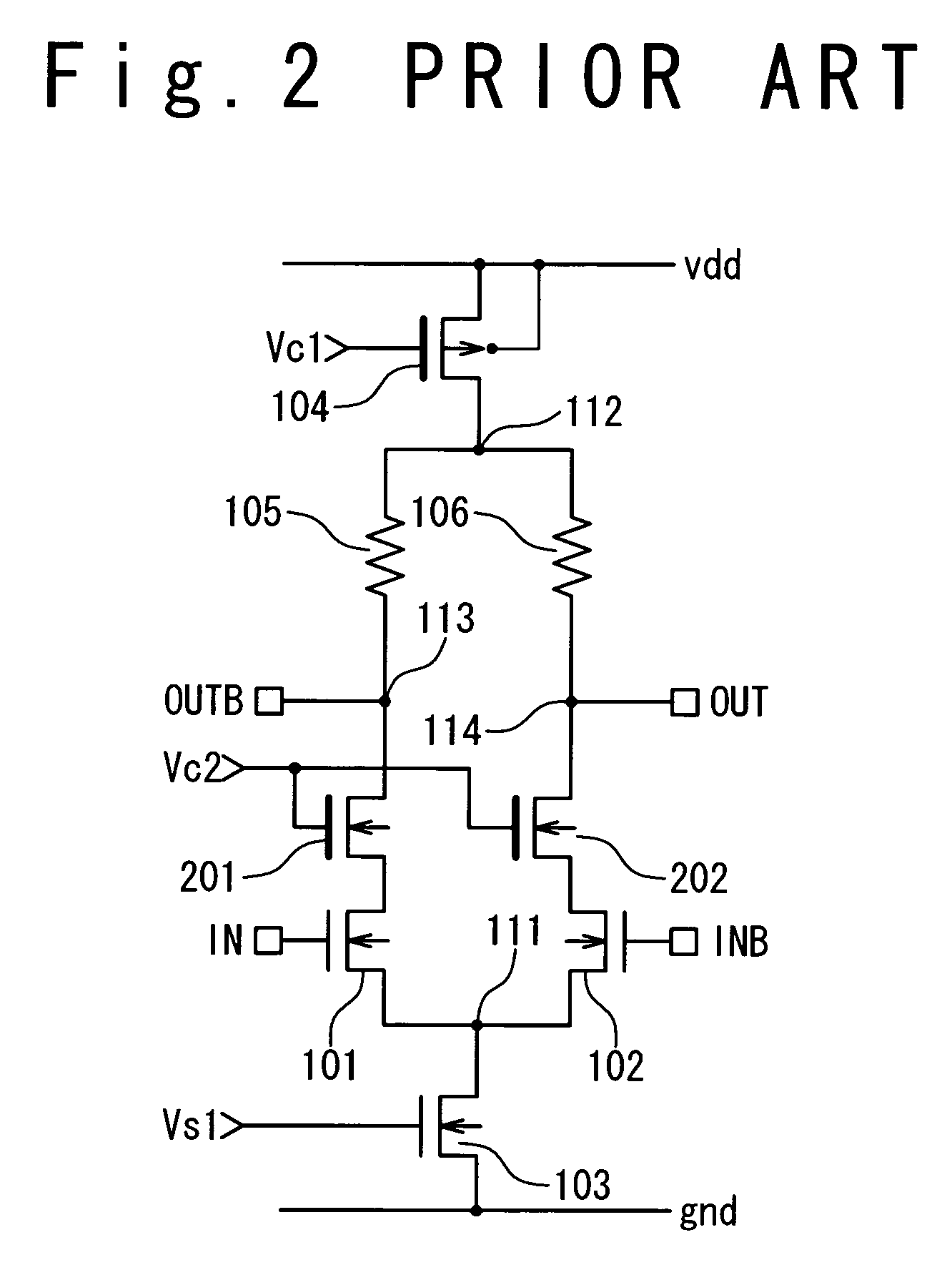
ActiveUS7245155B2Meet high-speed operationEffective protectionTransistorLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsOvervoltageGround line
A data output circuit is composed of first and second differential MOS transistors, first and second cascade MOS transistors, first and second outputs, and first and second resistor elements. The first and second differential MOS transistors receive first and second input voltages on the gates, respectively, sources of the differential MOS transistors being commonly connected. The first cascade MOS transistor is connected between the first differential MOS transistor and the first output, and the second cascade MOS transistor is connected between the second differential MOS transistor and the second output, gates of the first and second cascade MOS transistors being commonly connected. The first transistor element is connected between a ground line and the commonly connected gates, and the second transistor element is connected between a power supply line and the commonly connected gates.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
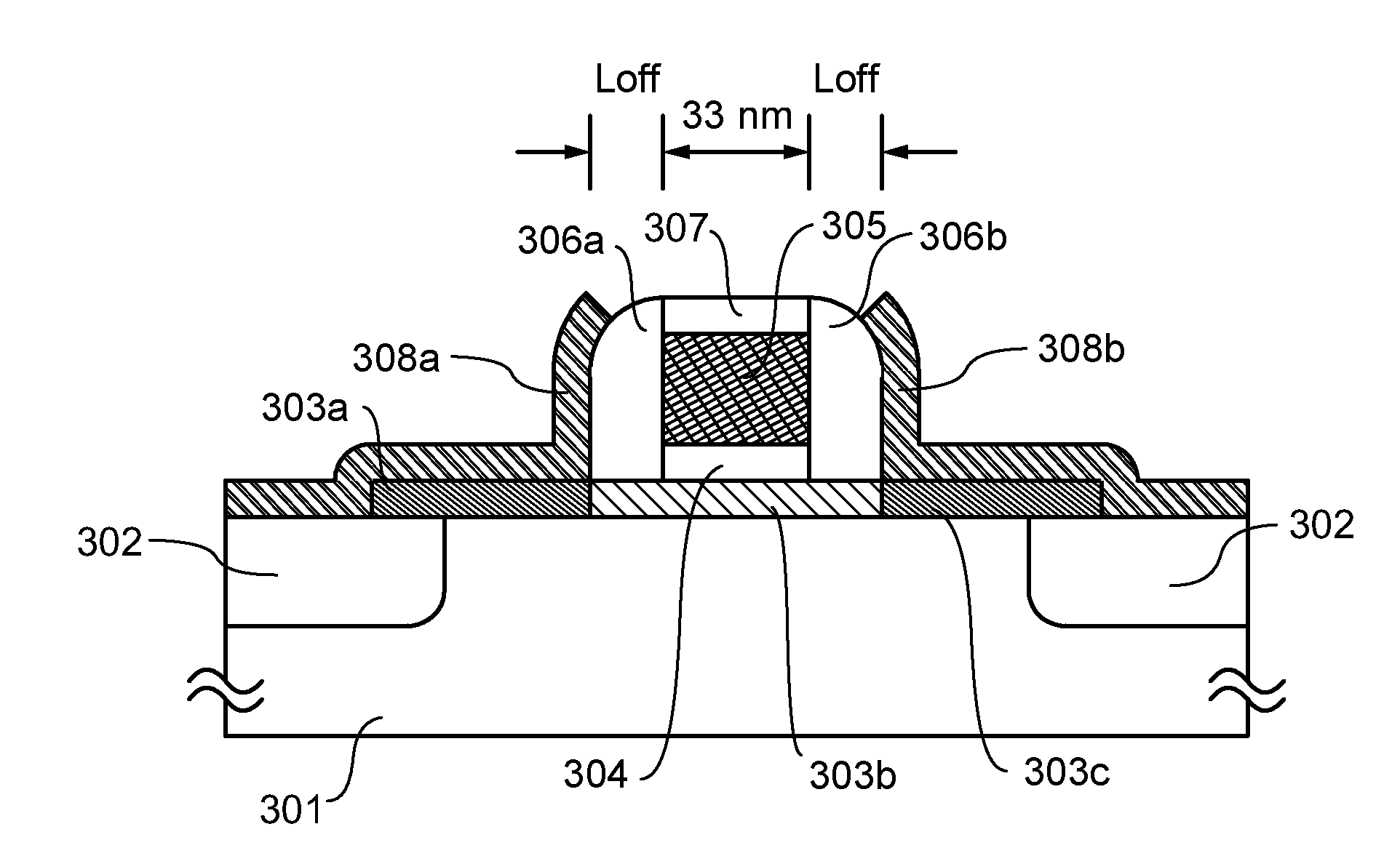
Semiconductor device having a dummy gate
ActiveUS20060220066A1Meet high-speed operationImprove controllabilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDevice materialSemiconductor
A semiconductor device includes a plurality of MOS transistors, wherein each of the MOS transistors has a drain region, a pair of source regions sandwiching therebetween the drain region, and a pair of normal gates each overlying a space between the drain region and a corresponding one of the source regions. A plurality of dummy gates are provided each between adjacent two of the MOS transistors. The dummy gate electrodes are maintained at an equi-potential with the adjacent drain regions. MOS transistors include a row of pMOS transistors and nMOS transistors, wherein each of pMOS transistors and a corresponding nMOS transistor configure a CMOS gate, and a plurality of CMOS gates configure a ring oscillator.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
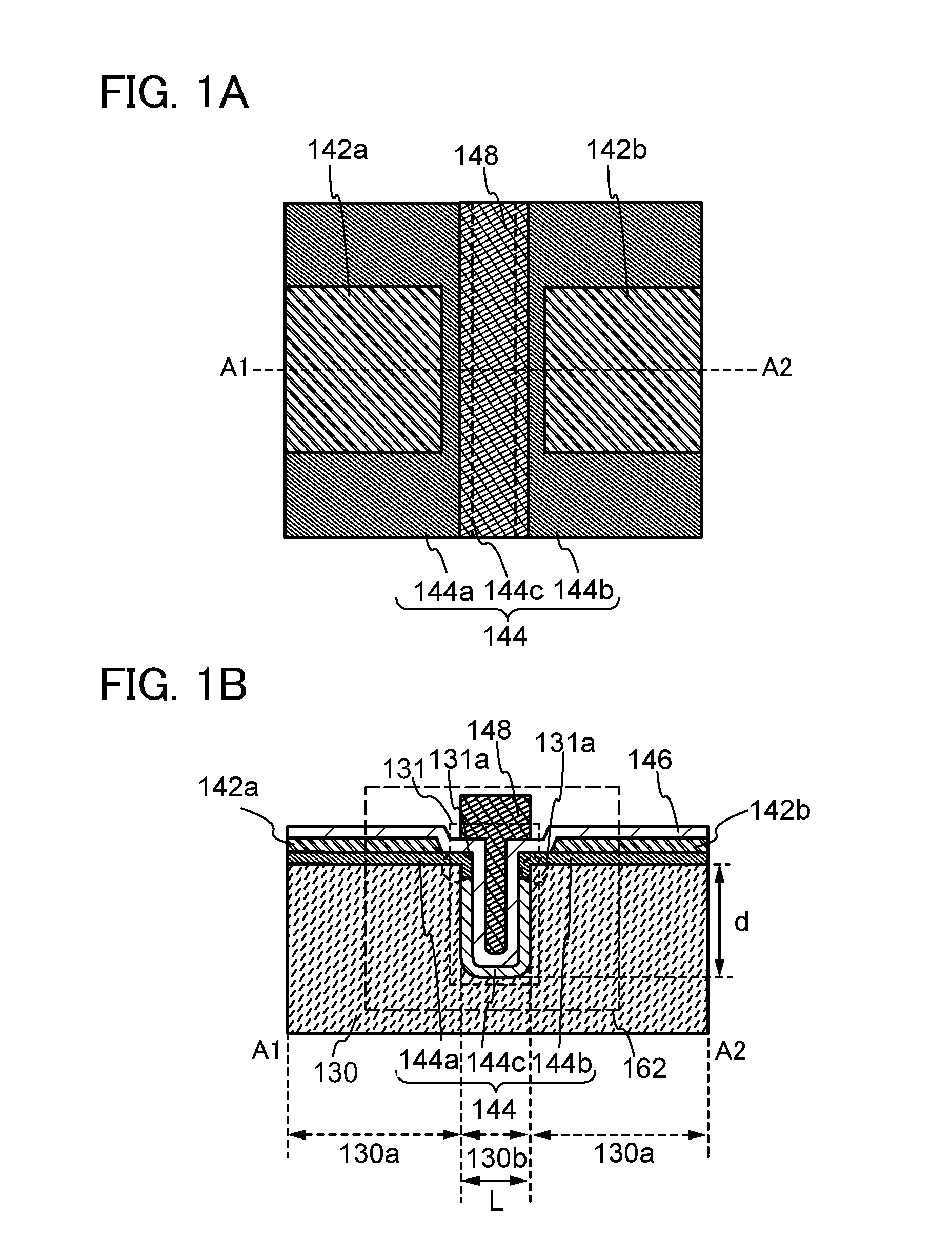
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20120286270A1Good ohmic contactResistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMiniaturizationEngineering
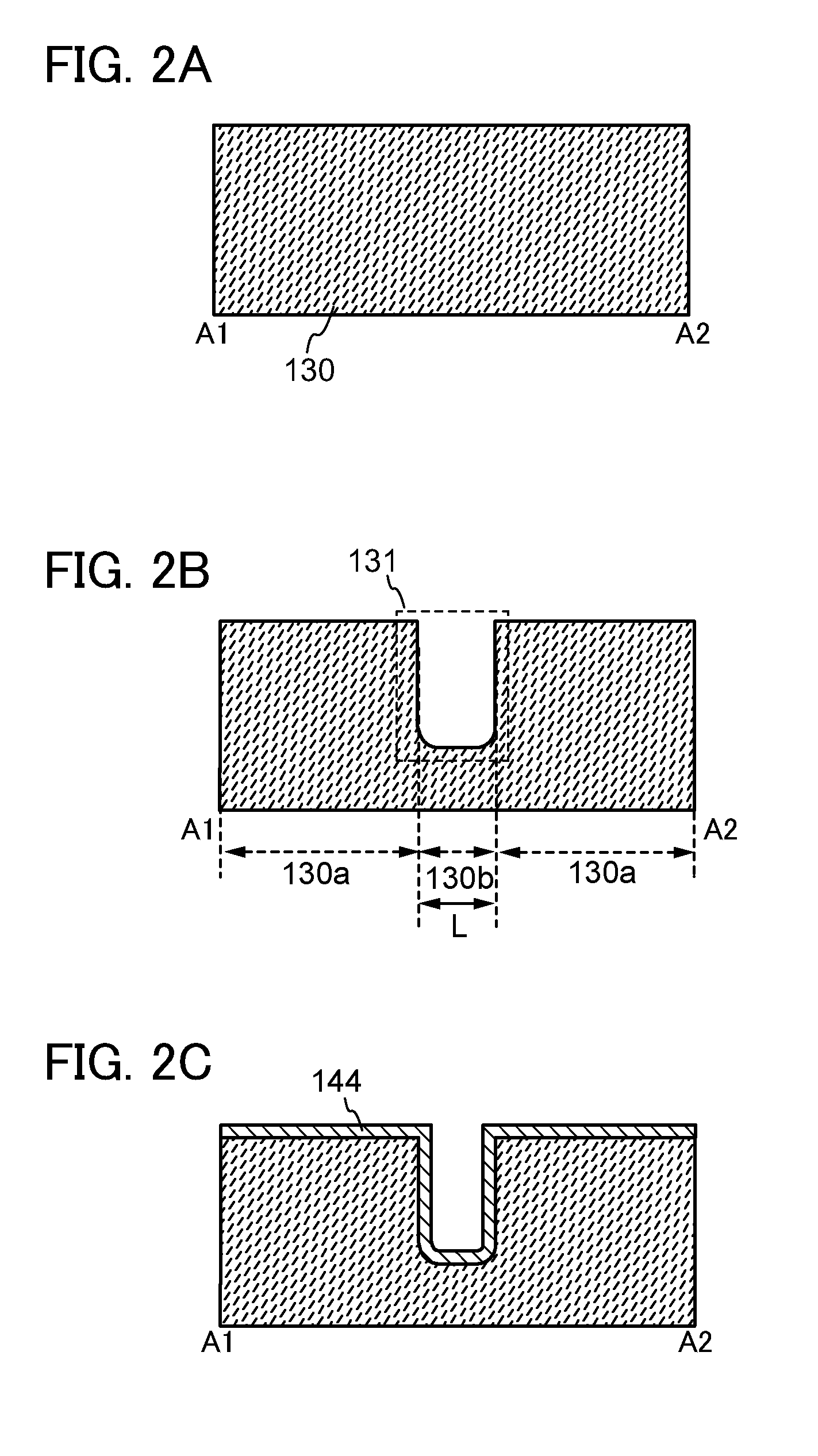
It is an object to provide a semiconductor device in which a short-channel effect is suppressed and miniaturization is achieved, and a manufacturing method thereof. A trench is formed in an insulating layer and impurities are added to an oxide semiconductor film in contact with an upper end corner portion of the trench, whereby a source region and a drain region are formed. With the above structure, miniaturization can be achieved. Further, with the trench, a short-channel effect can be suppressed setting the depth of the trench as appropriate even when a distance between a source electrode layer and a drain electrode layer is shortened.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Railway vehicle and stone sweeping machine thereof
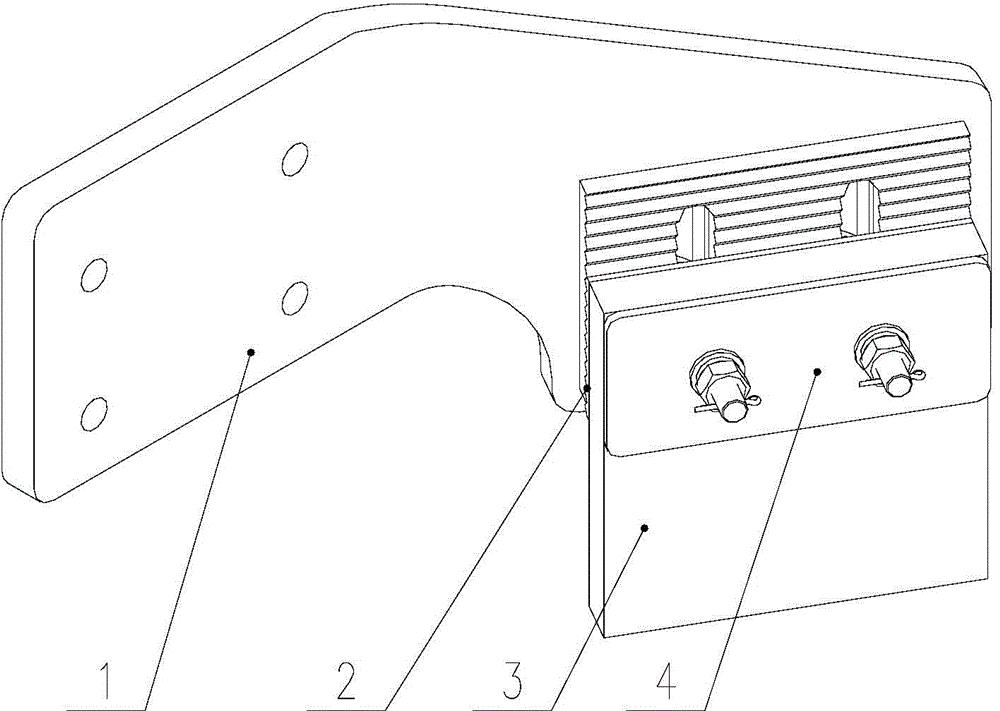
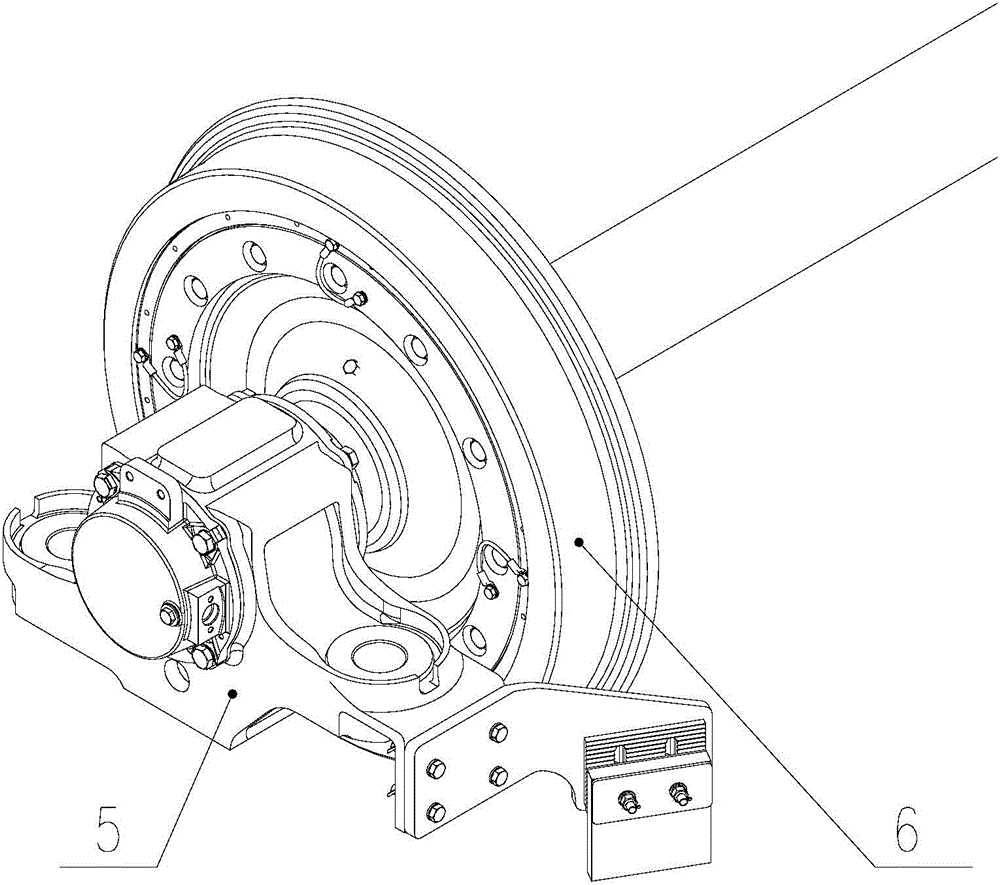
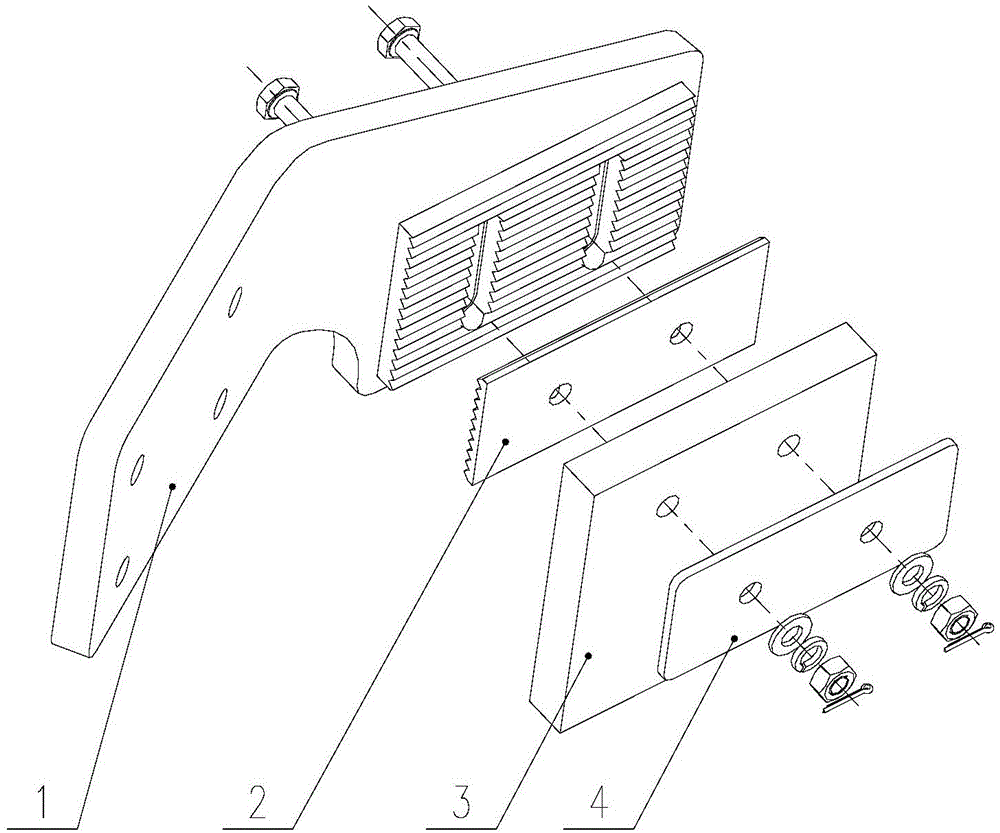
InactiveCN104149809AReduce distance variationMeet high-speed operationRailway wheel guards/bumpersEngineering
The invention discloses a stone sweeping machine. The stone sweeping machine is characterized in that a support of the stone sweeping machine is fixed onto the front end surface of an axle box, and a stone sweeping structure is fixed to the front side of a wheel set by the aid of the support. The stone sweeping machine can be repositioned, can be fixed onto the axle box and can be guaranteed against being affected by vibration of a primary spring, change of the distance from the stone sweeping machine to a rail surface can be greatly reduced, accordingly, obstacle removing effects can be improved, and high-speed running of a railway vehicle can be effectively guaranteed. The stone sweeping machine has the advantages that the stone sweeping machine is mounted on the axle box and is simple in structure, and good stone sweeping effects can be realized; the support of the stone sweeping machine with the structure is free of weld rib plates, and accordingly weld cracks can be prevented; the distance from a rubber plate to the rail surface can be adjusted via end teeth, and accordingly the stone sweeping machine is safe and reliable. The invention further discloses the railway vehicle with the stone sweeping machine.
Owner:ZHUZHOU ELECTRIC LOCOMOTIVE CO
Semiconductor device including trench with at least one of an edge of an opening and a bottom surface being round
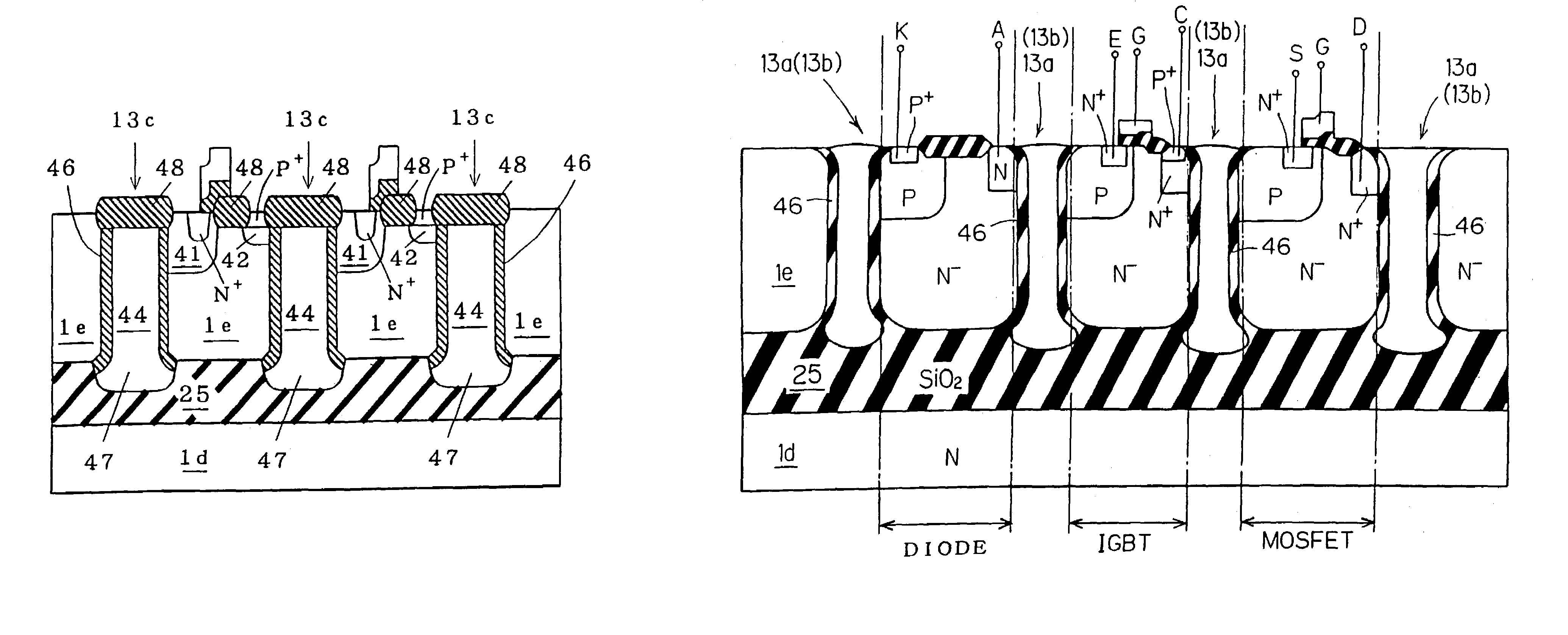
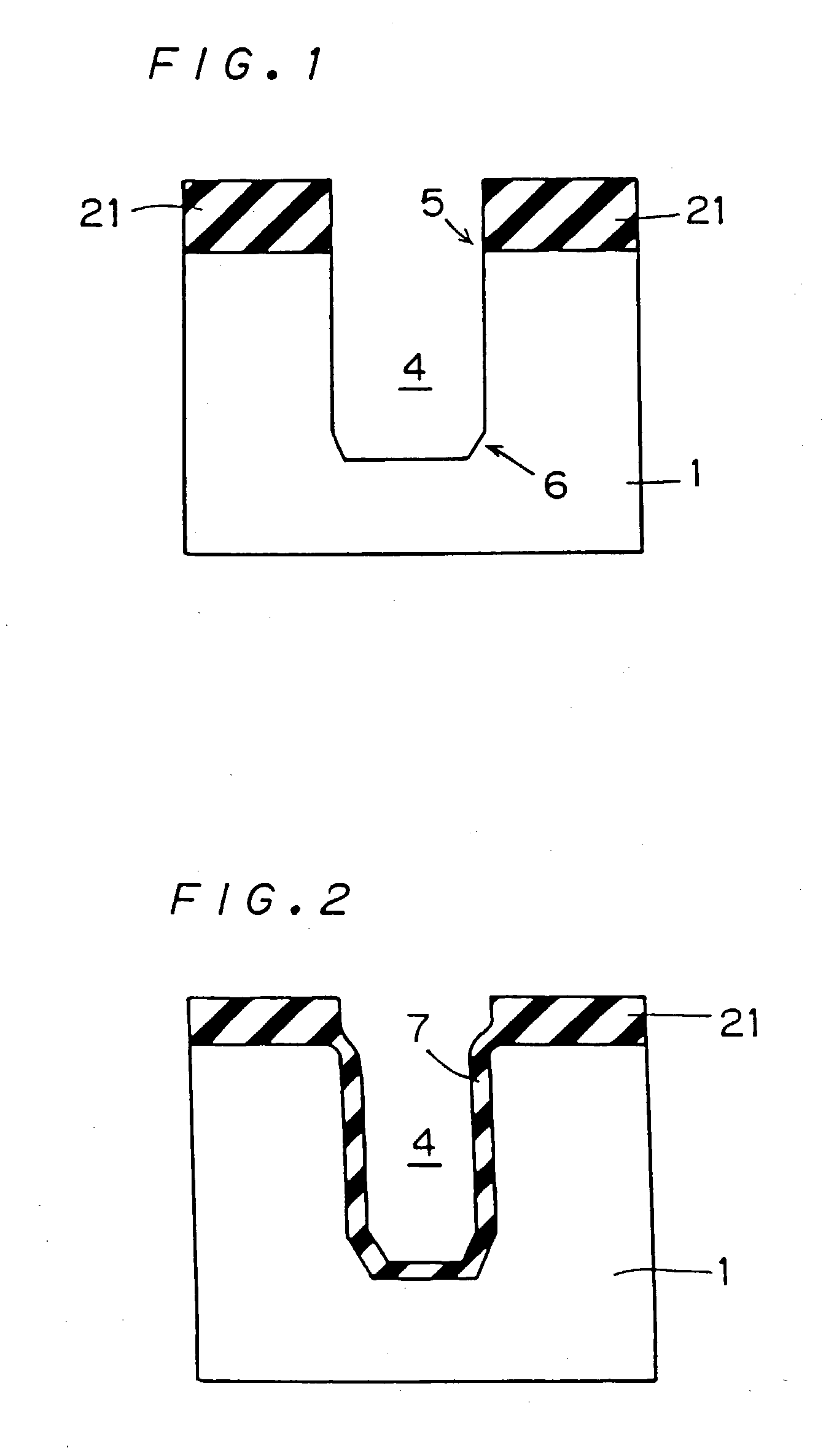
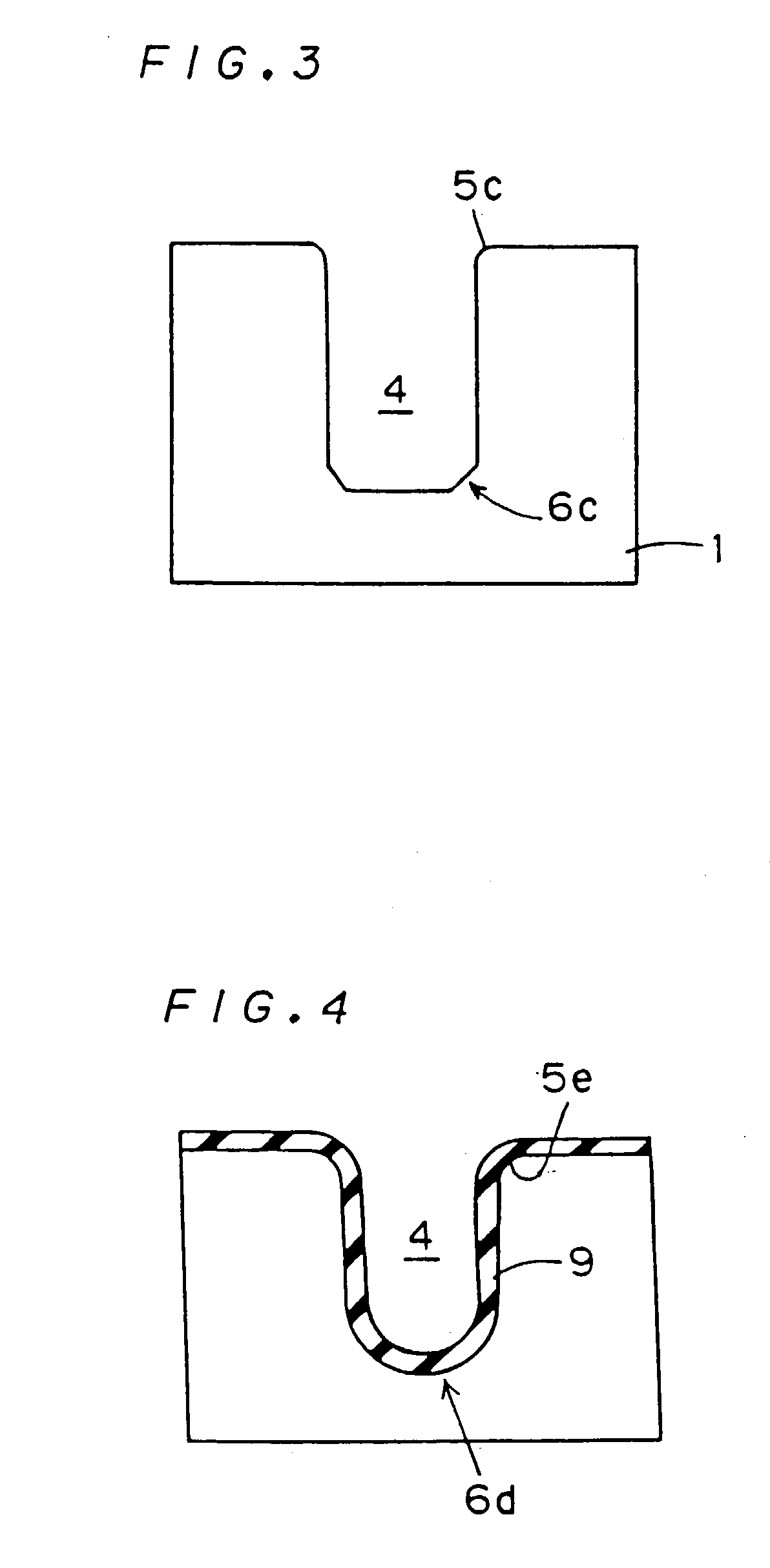
InactiveUS7067874B2Improve featuresMeet high-speed operationTransistorThyristorEngineeringSemiconductor device
A semiconductor device that includes an insulating substrate, a plurality of semiconductor layers arranged to be isolated from one another on the insulating substrate, and a semiconductor element independently provided on the semiconductor layers. Further, a trench may extend from the main surface to the substrate and have an inner wall covered with an insulating film. At least one of an edge on the side of the substrate and an edge on the side opposite thereof of the semiconductor layer has a rounded surface. Further, an angle between a line tangent to a surface having a smallest radius of curvature of the rounded surface of the edge and the main surface ranges from 30° to 60° at a section of the edge.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Printed circuit board
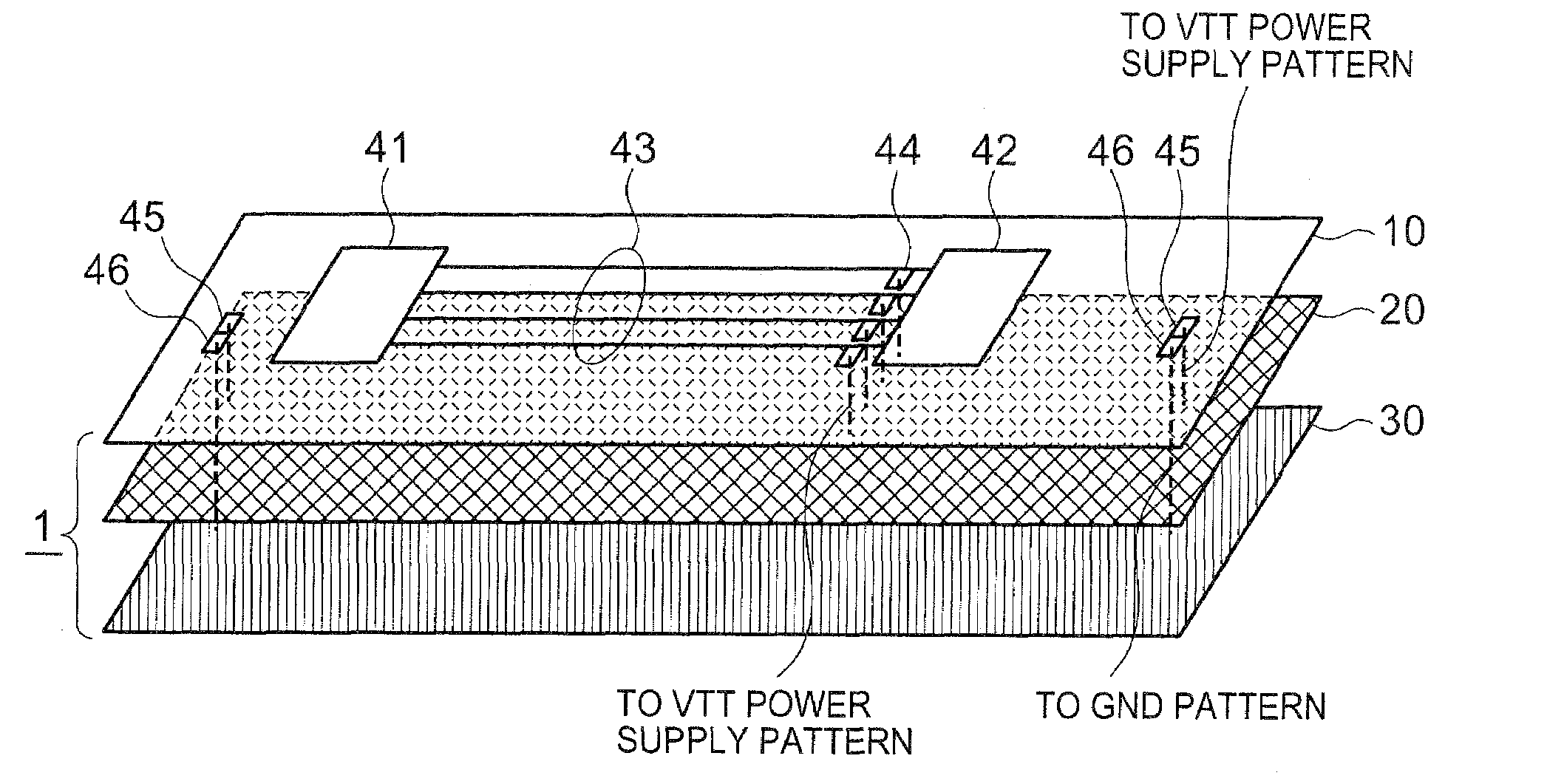
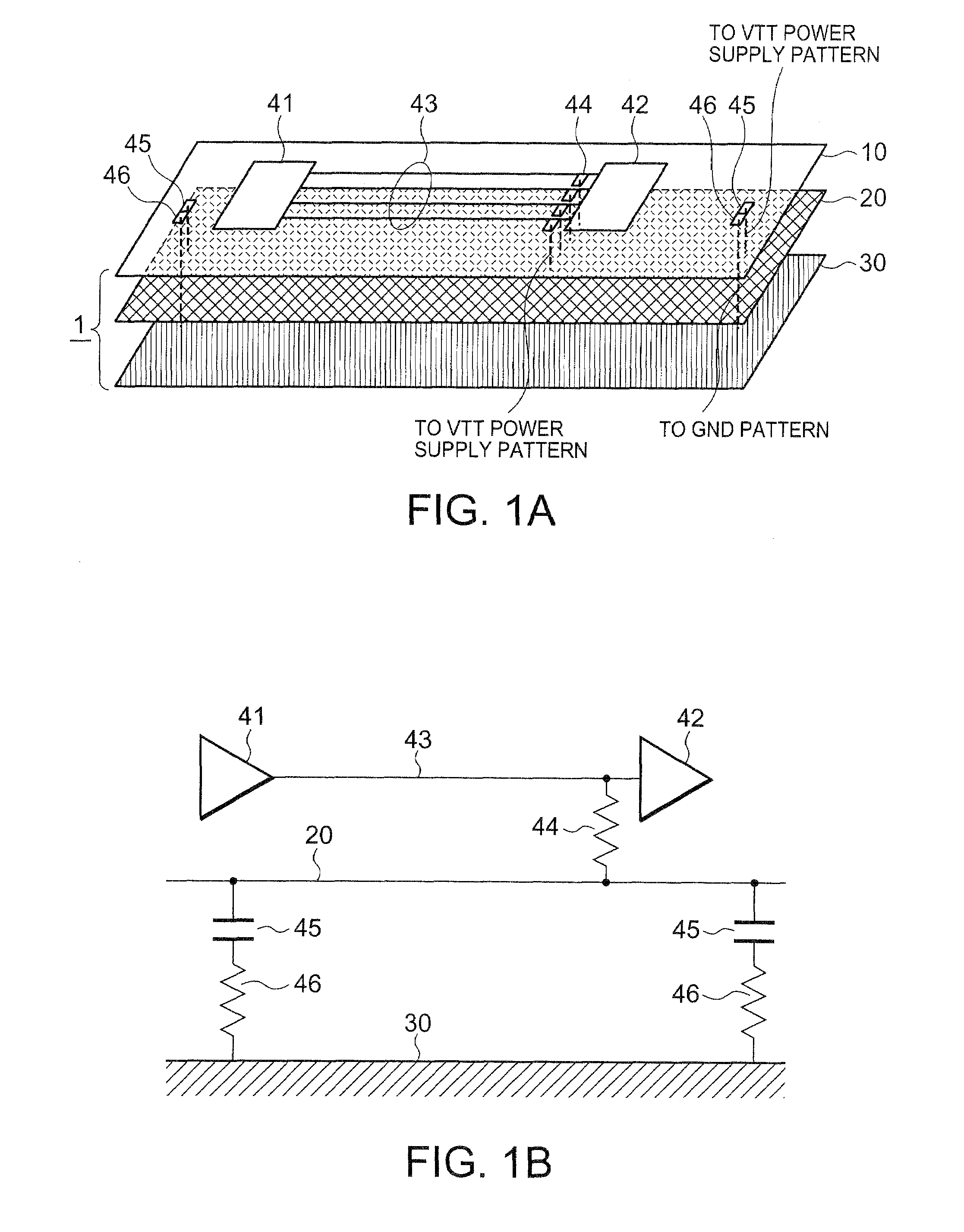
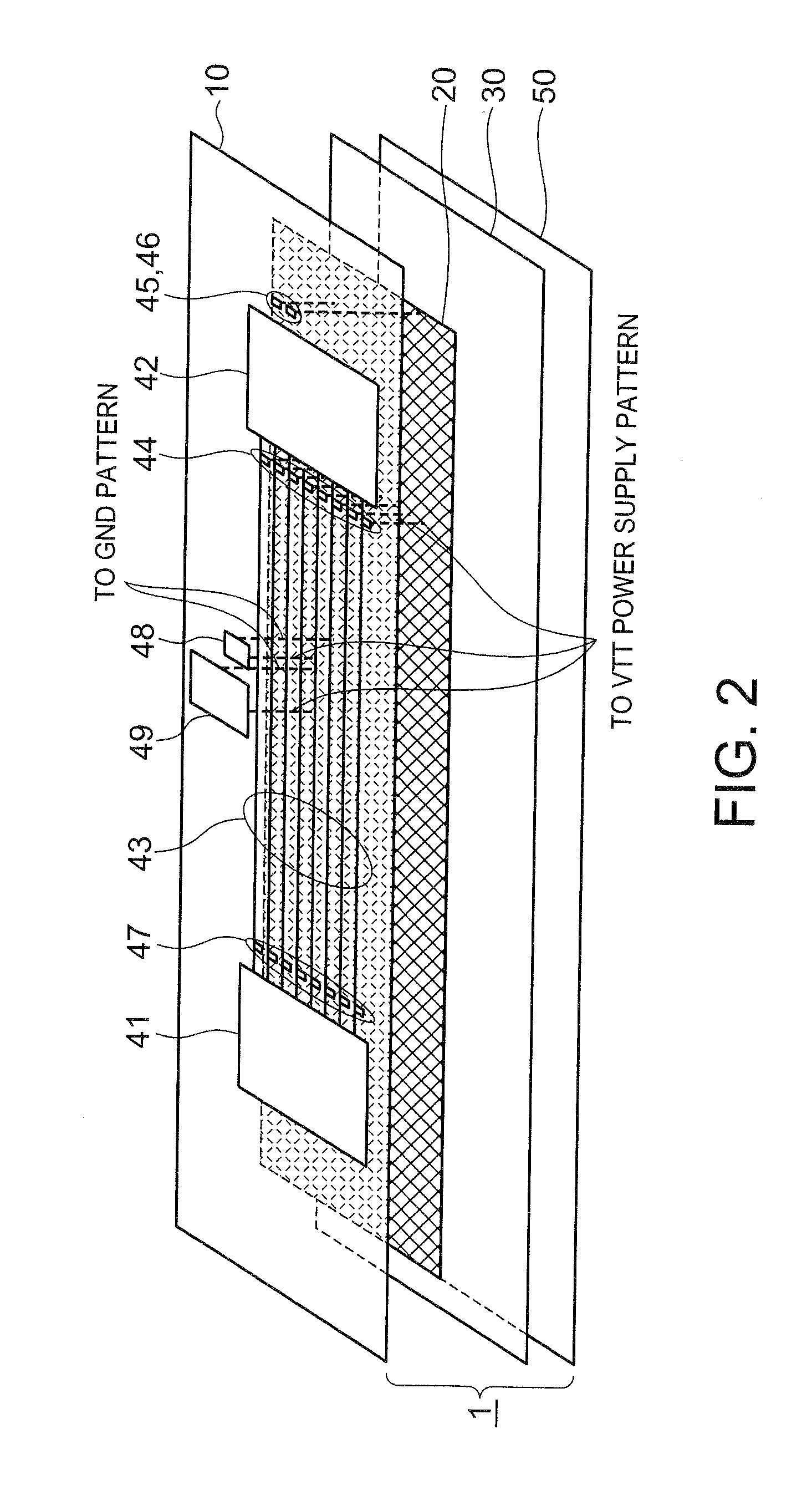
InactiveUS20080002373A1Guaranteed uptimeReduce high frequency noiseCross-talk/noise/interference reductionPrinted circuit aspectsMemory busEngineering
A printed circuit board comprises a high-speed DRAM and a memory controller mounted thereon. The high-speed DRAM is connected to the memory controller by memory bus wiring. The printed circuit board further comprises a power supply pattern connected to the memory bus wiring via a parallel terminal end resistor. A series circuit is formed by serially connecting, between the power supply pattern and a ground pattern, a capacitor and a resistor having a resistance value substantially equal to a characteristic impedance of the power supply pattern.
Owner:NEC CORP
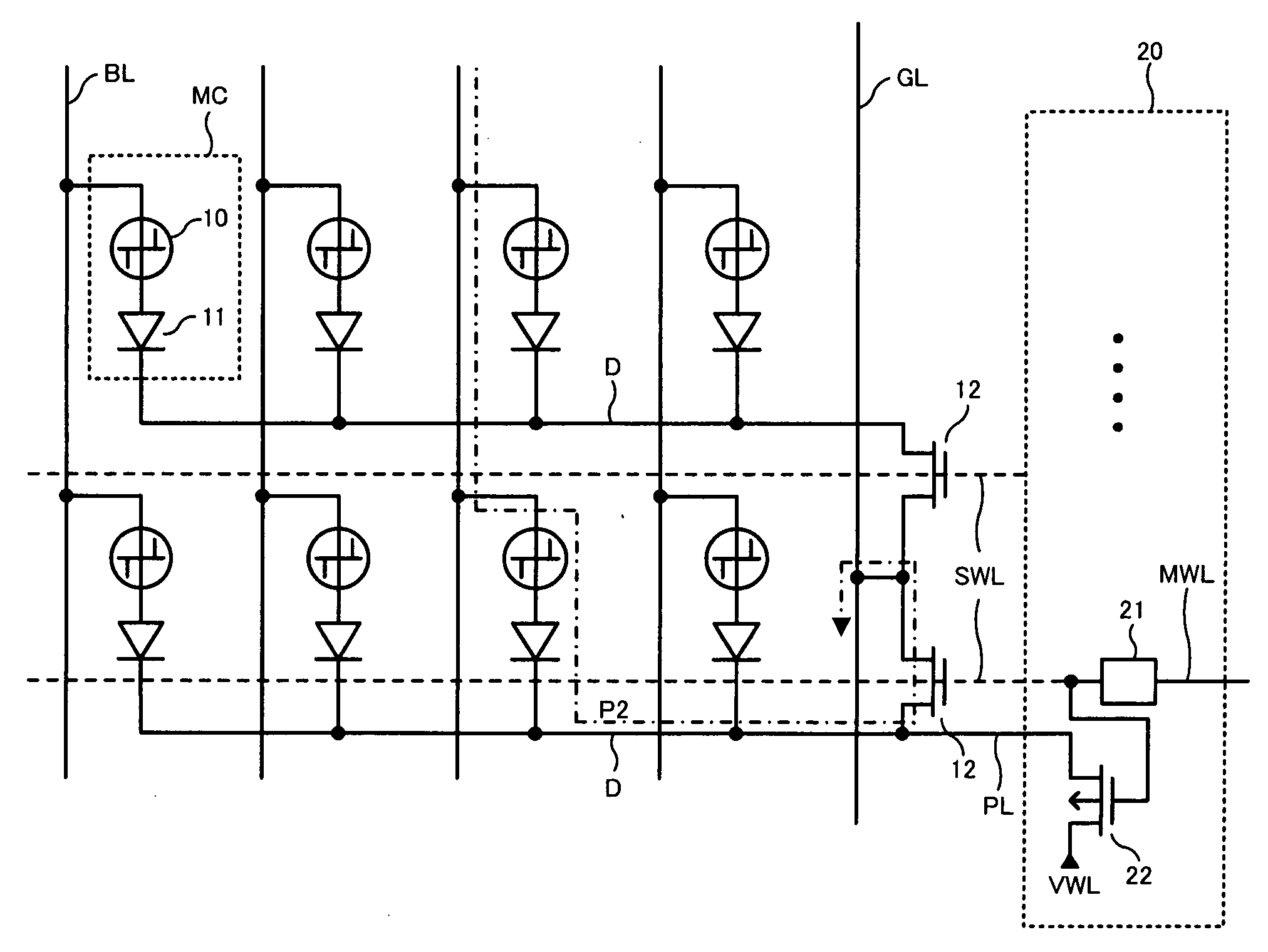
Phase change memory device
ActiveUS20080316806A1Decrease in reading speedHigh-speed read operationDigital storageBit lineElectricity
A phase change memory device comprises: a phase change element for rewritably storing data by changing a resistance state; a memory cell arranged at an intersection of a word line and a bit line and formed of the phase change element and a diode connected in series; a select transistor formed in a diffusion layer below the memory cell, for selectively controlling electric connection between an anode of the diode and a ground line in response to a potential of the word line connected to a gate; and a precharge circuit for precharging the diffusion layer below the memory cell corresponding to a non-selected word line to a predetermined voltage and for disconnecting the diffusion layer below the memory cell corresponding to a selected word line from the predetermined voltage.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
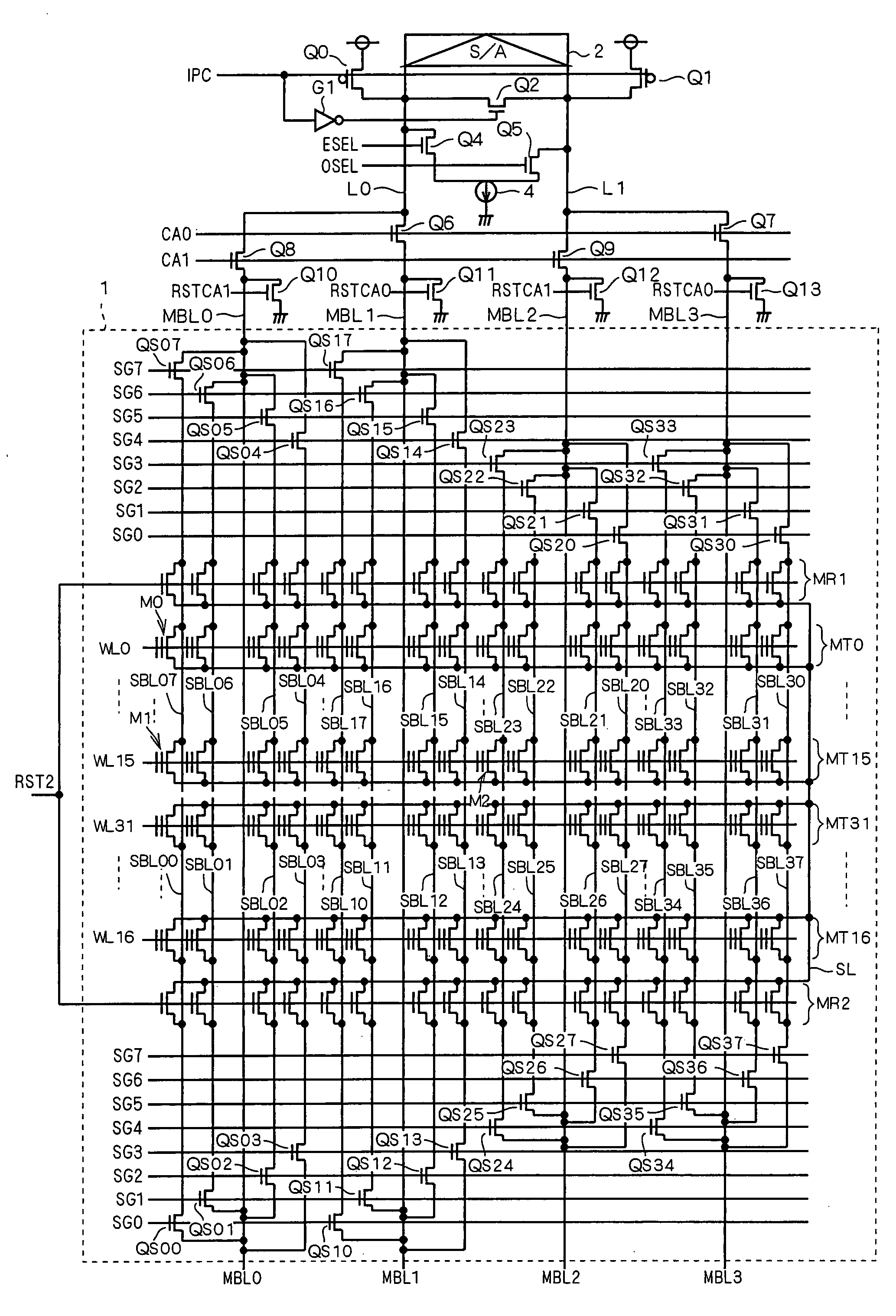
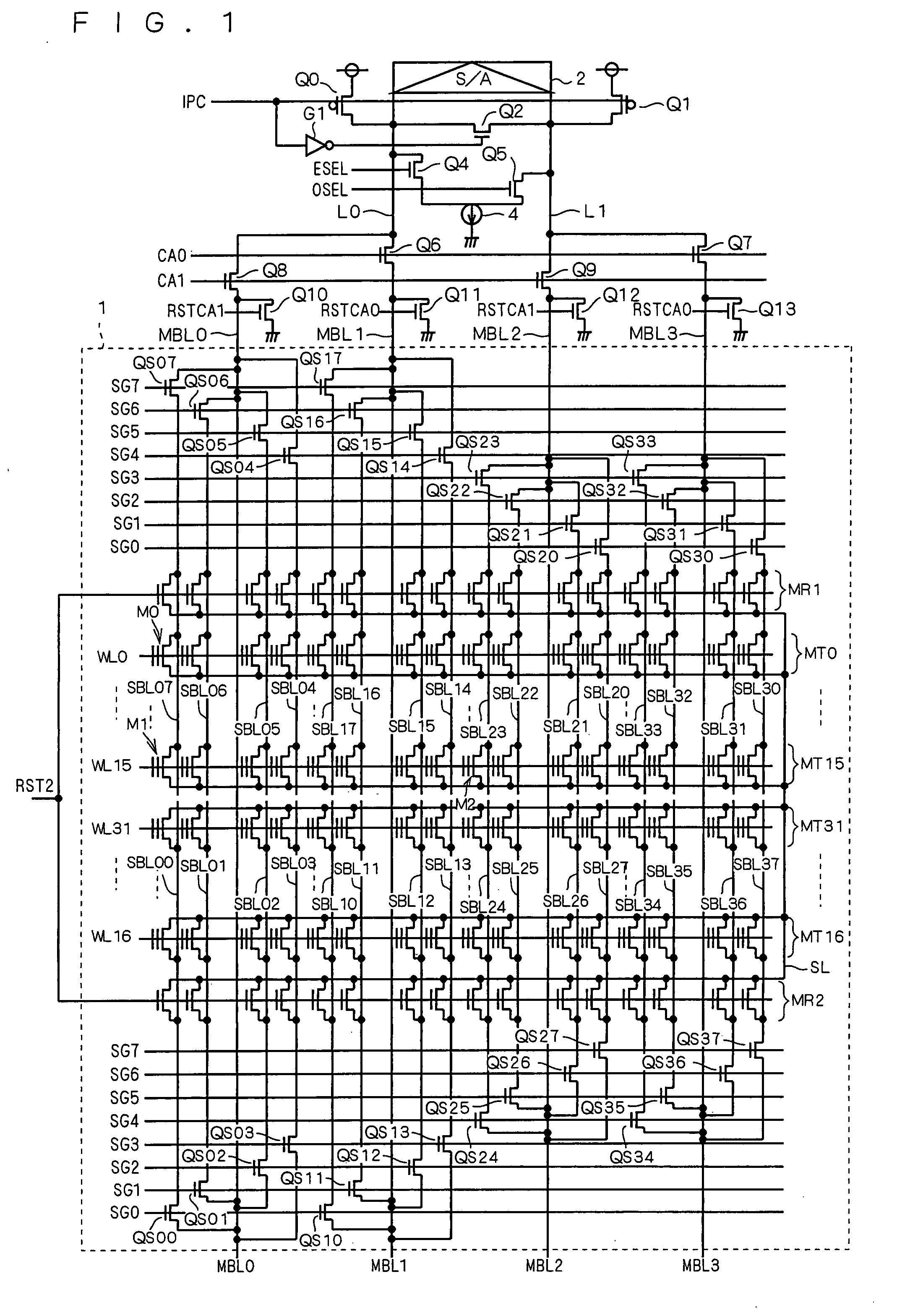
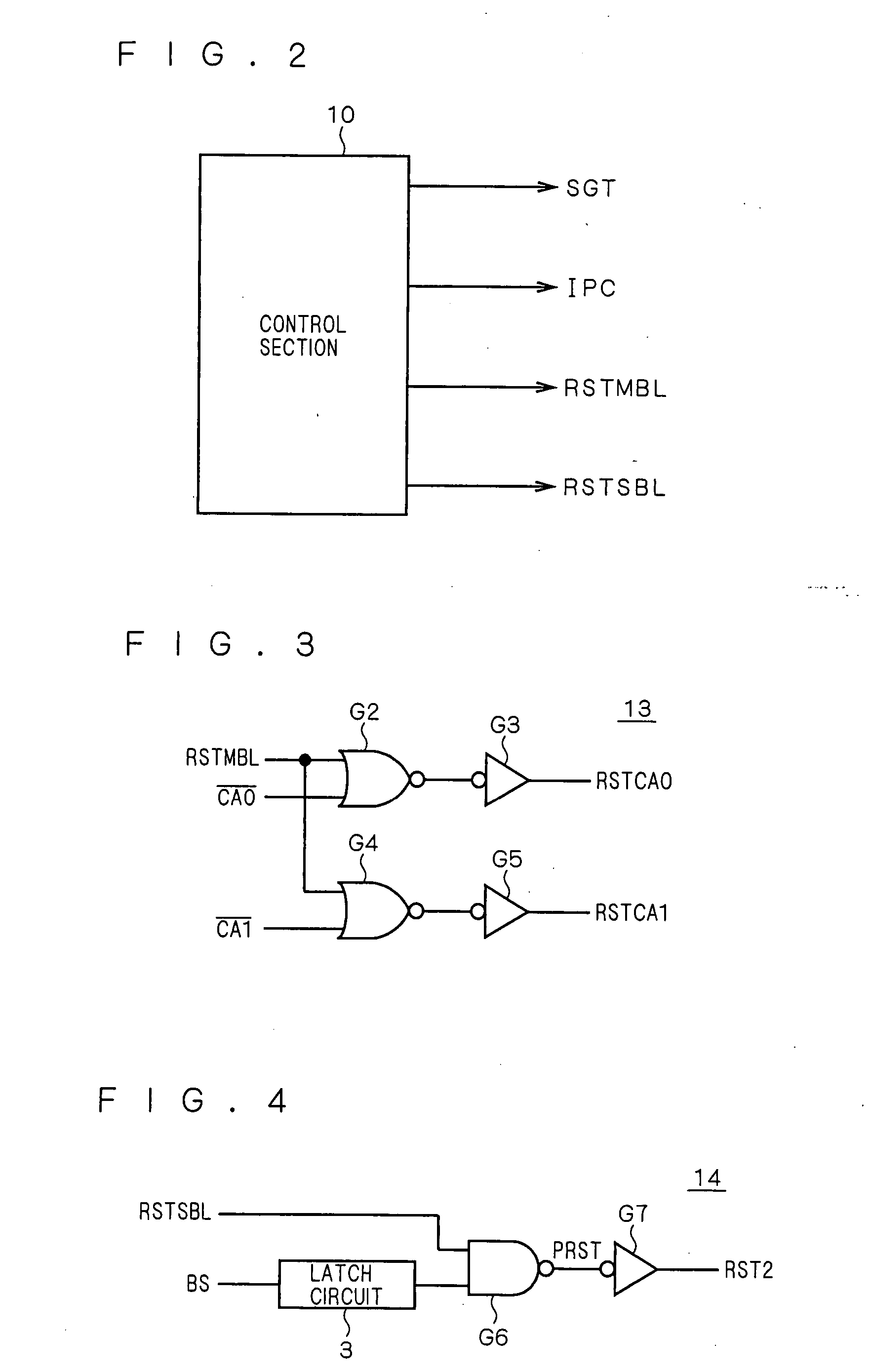
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device that achieves speedup in read operation
InactiveUS20070195601A1Speedup in read operationReduce stepsRead-only memoriesDigital storageTime segmentEngineering
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com