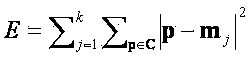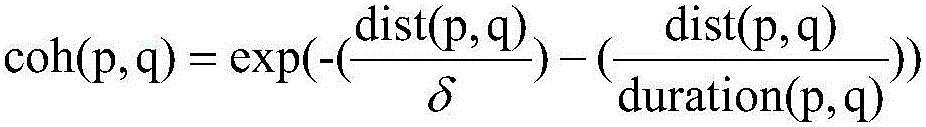Patents
Literature
75 results about "Spatial complexity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Spatial complexity is hypothesized to promote biodiversity by reducing the potential for competitive exclusion; whereas, models show that weak trophic interactions can enhance stability and maintain biodiversity by dampening destabilizing oscillations associated with strong interactions.
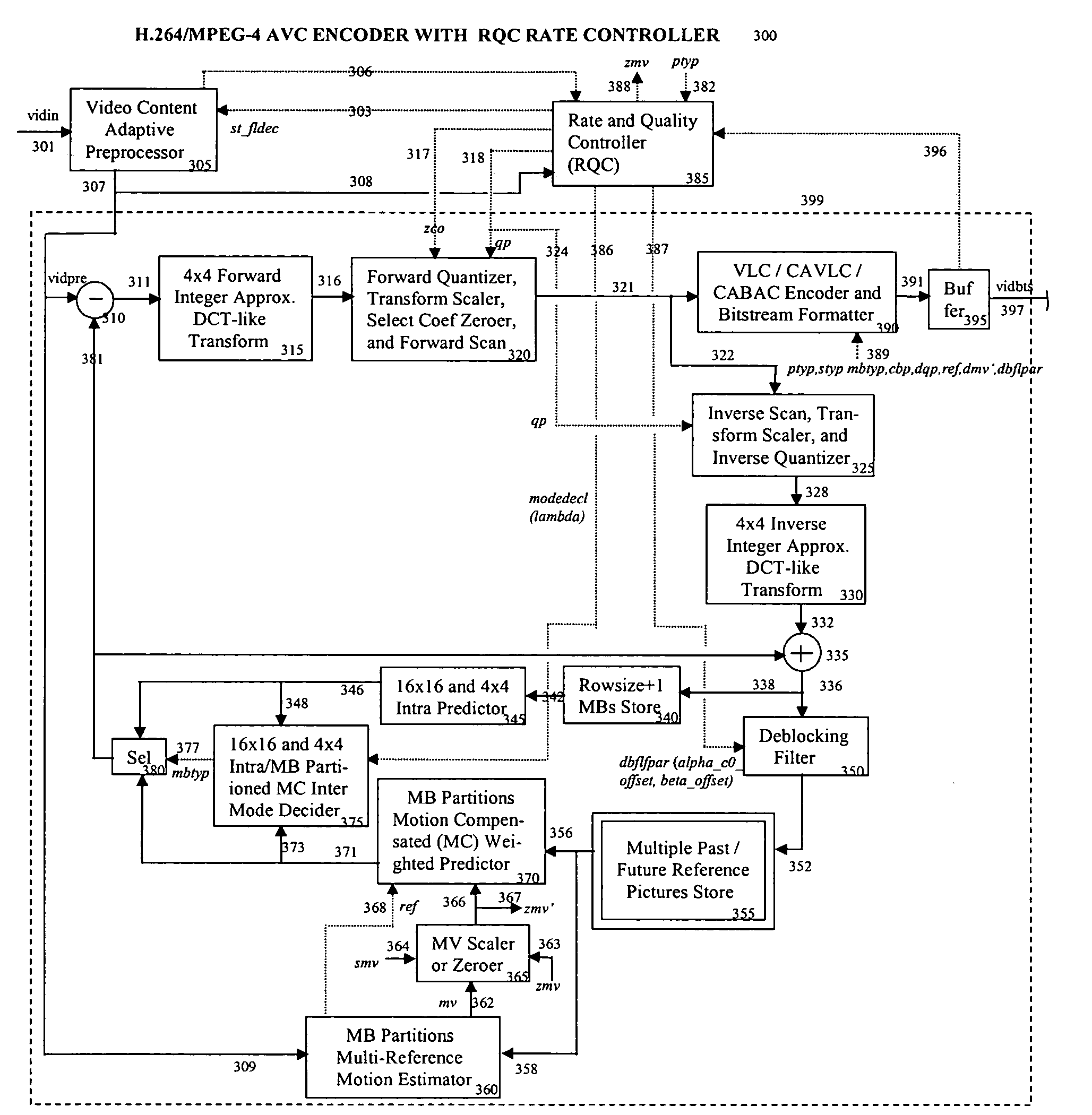
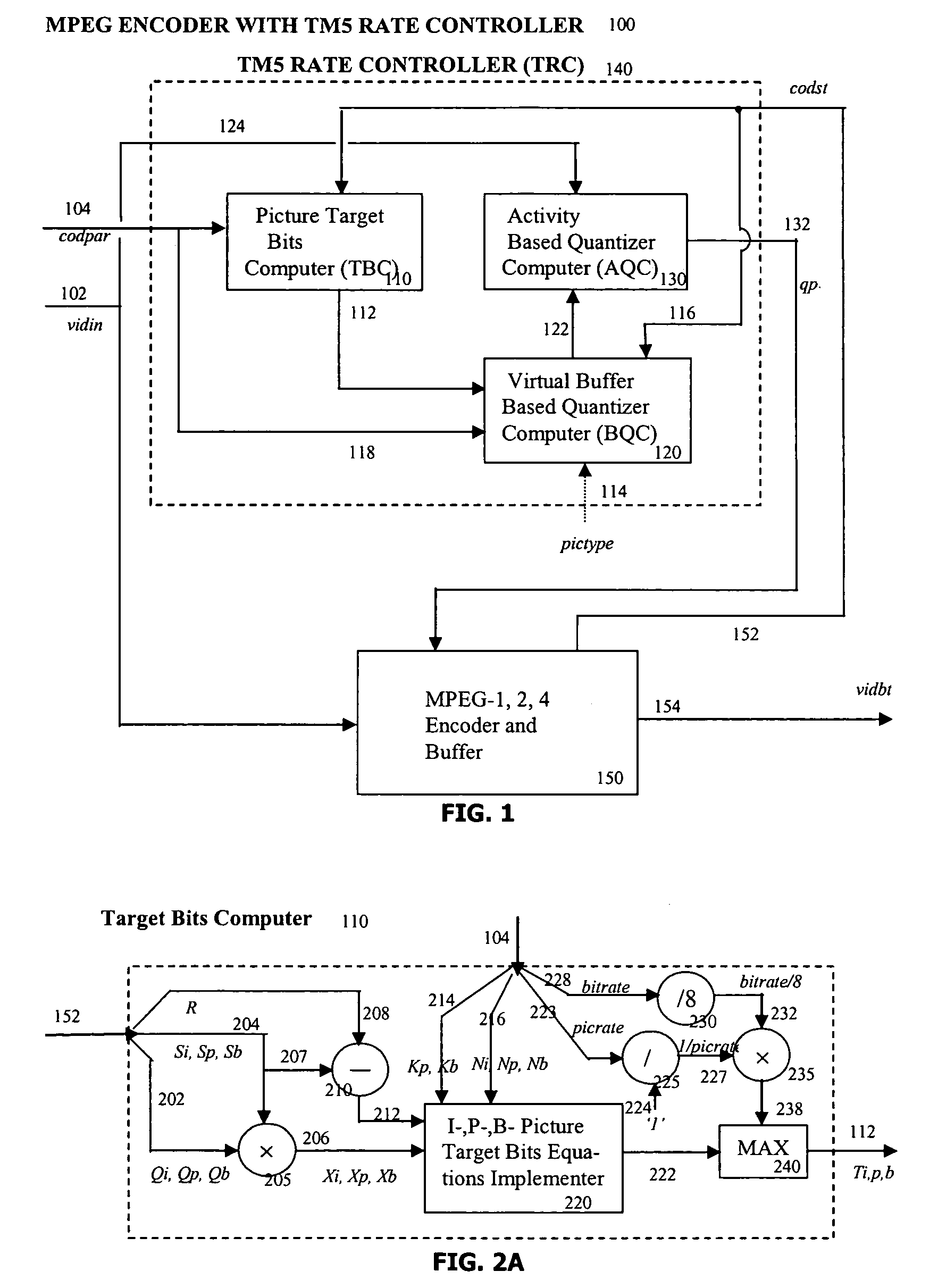
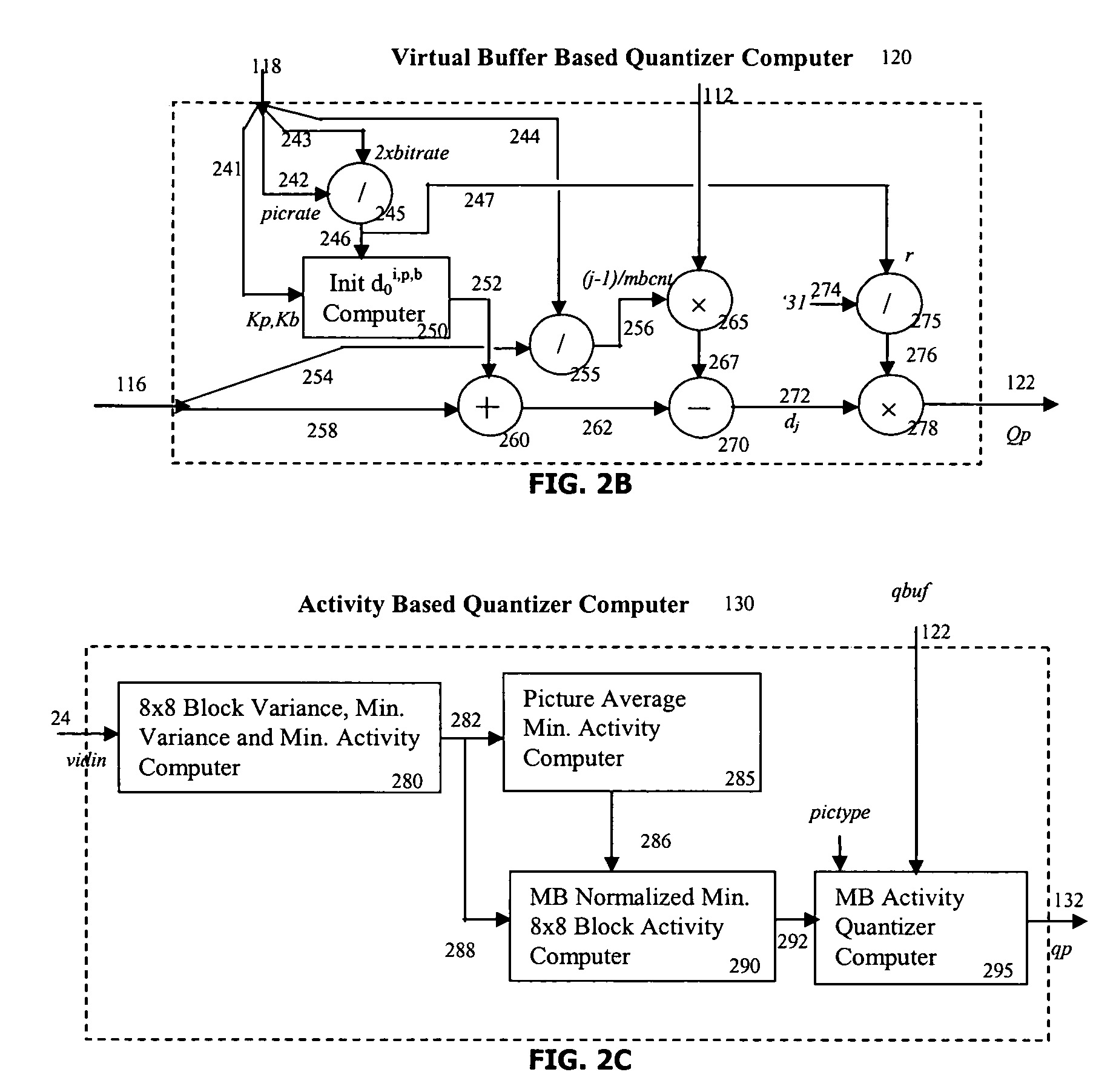
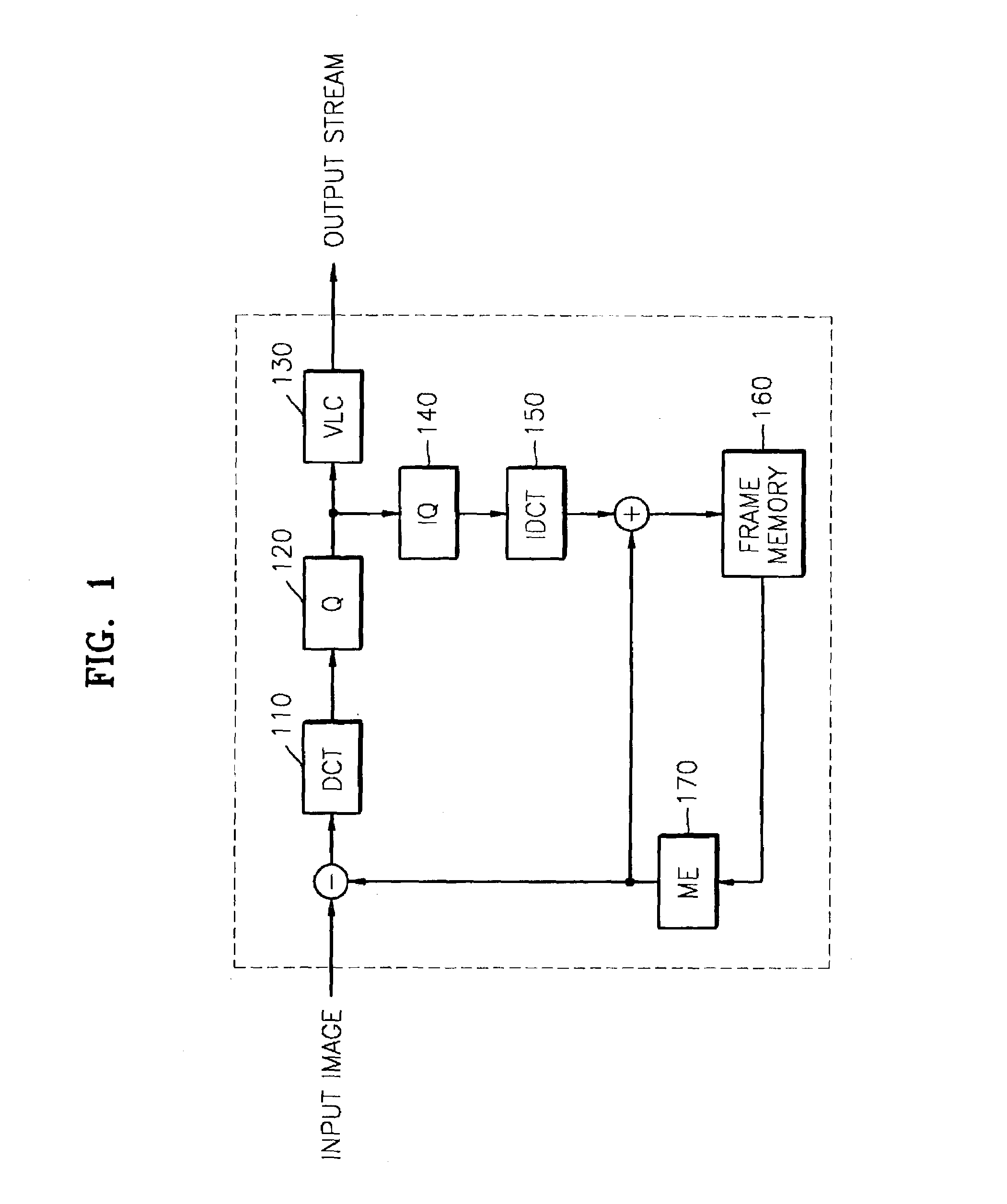
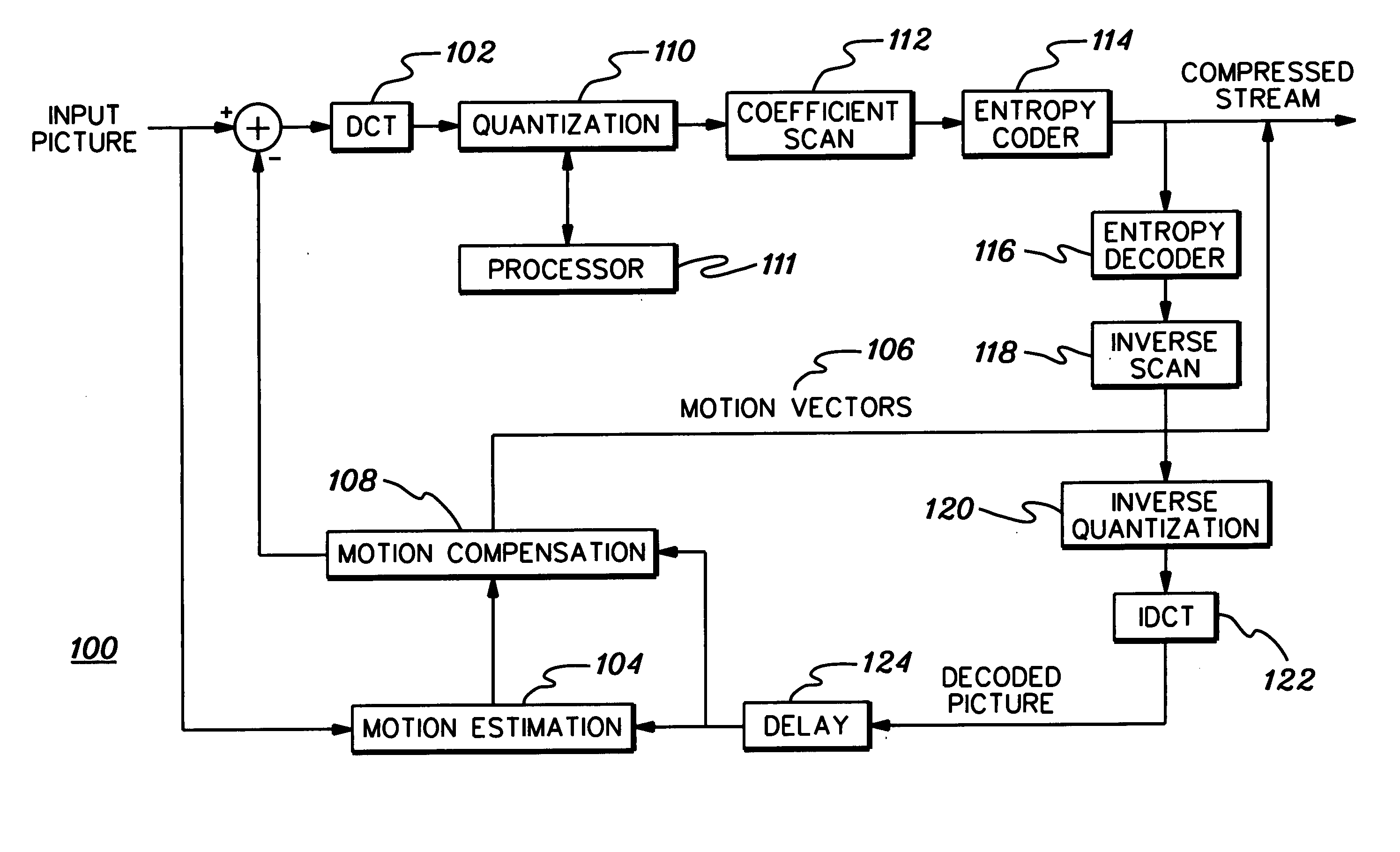
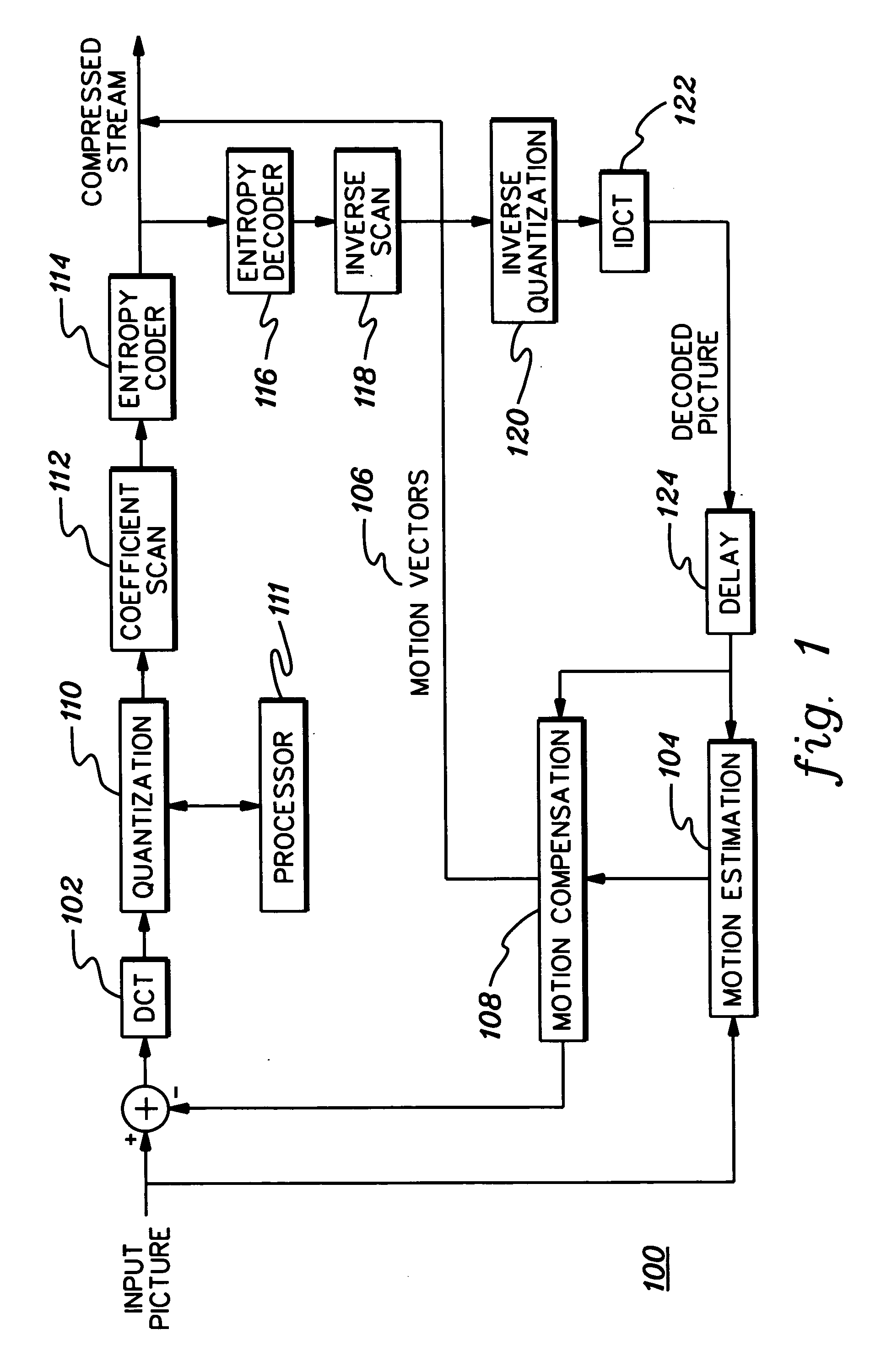
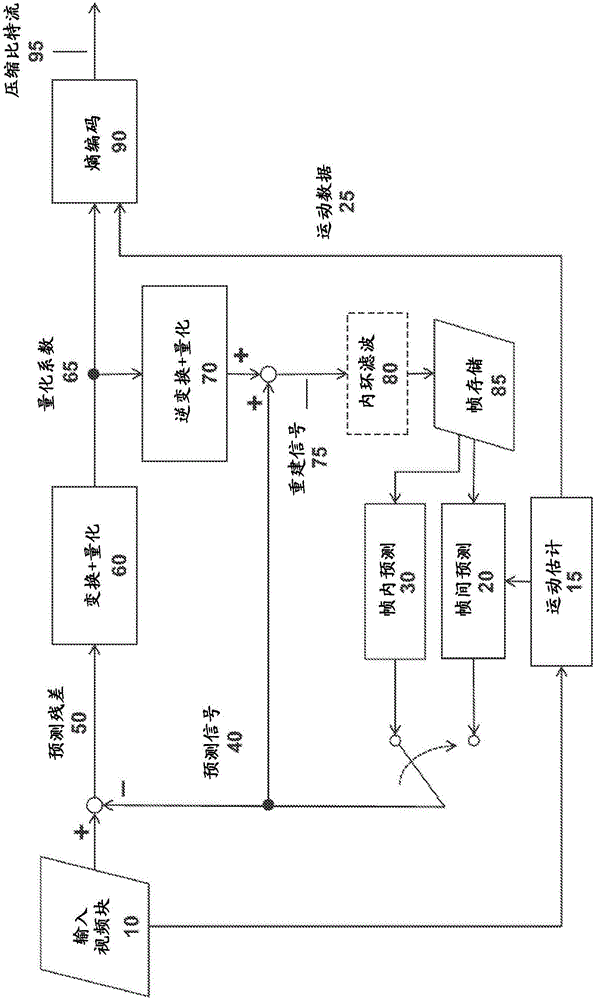
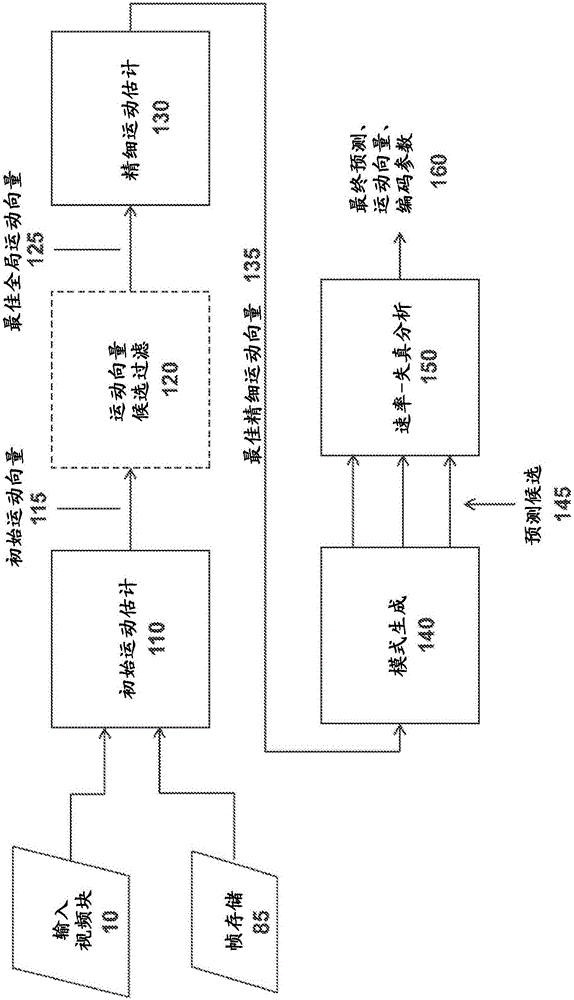
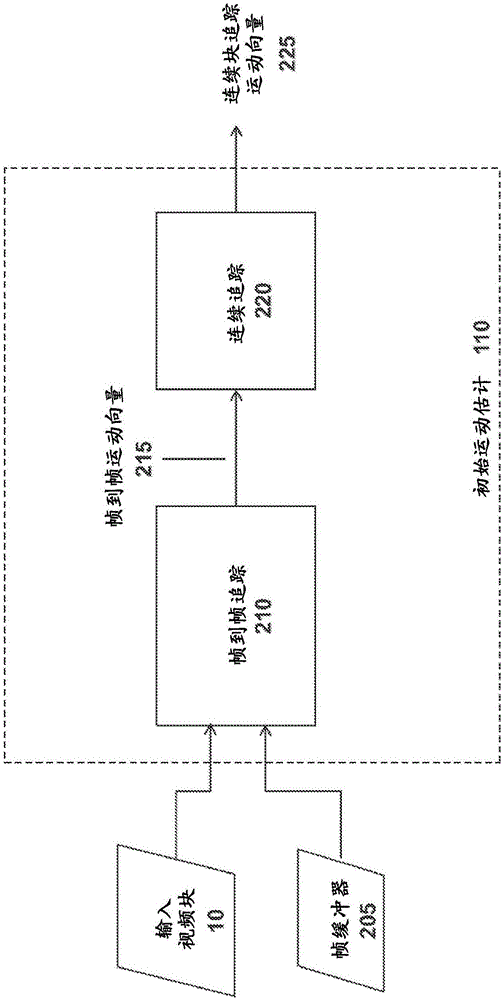
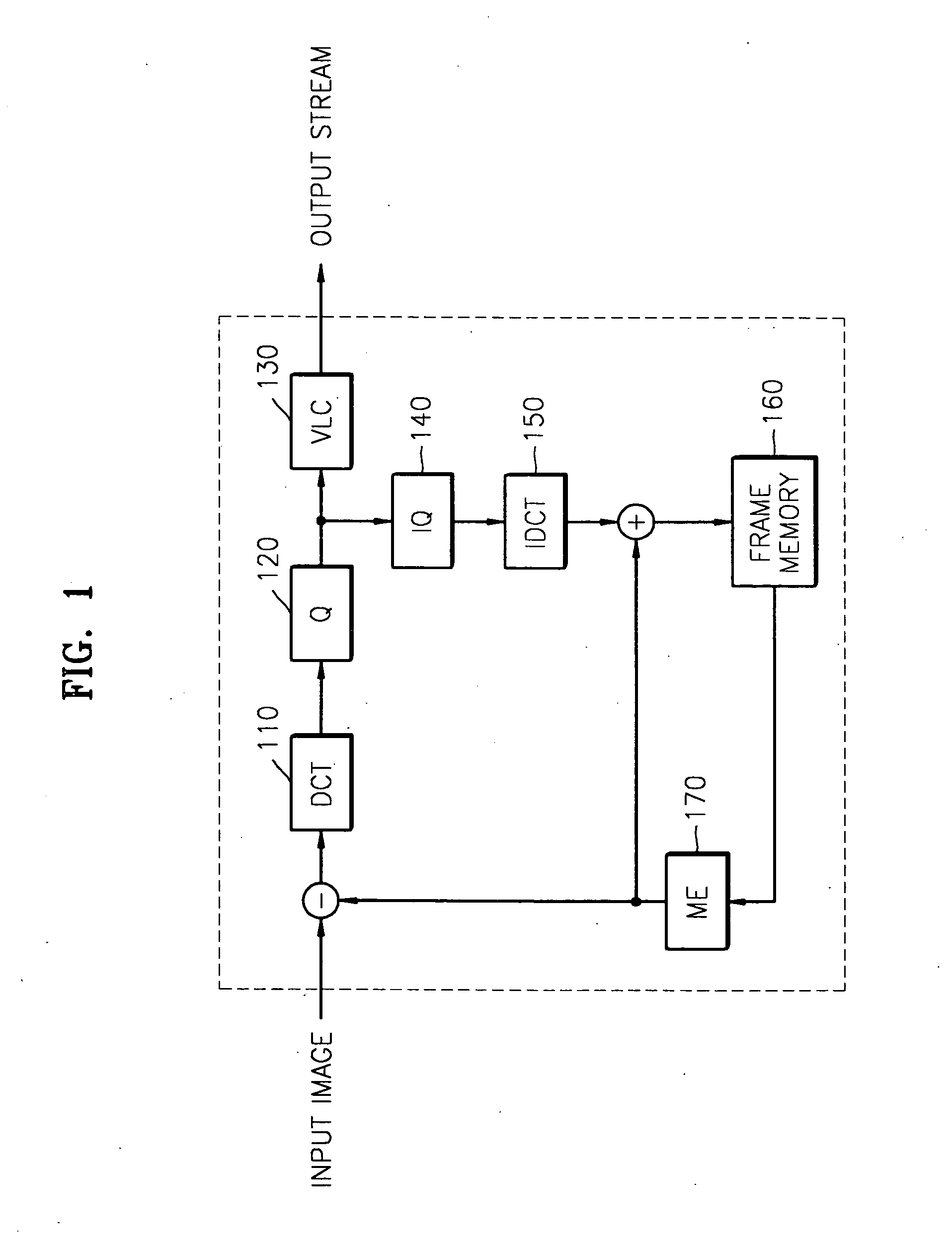
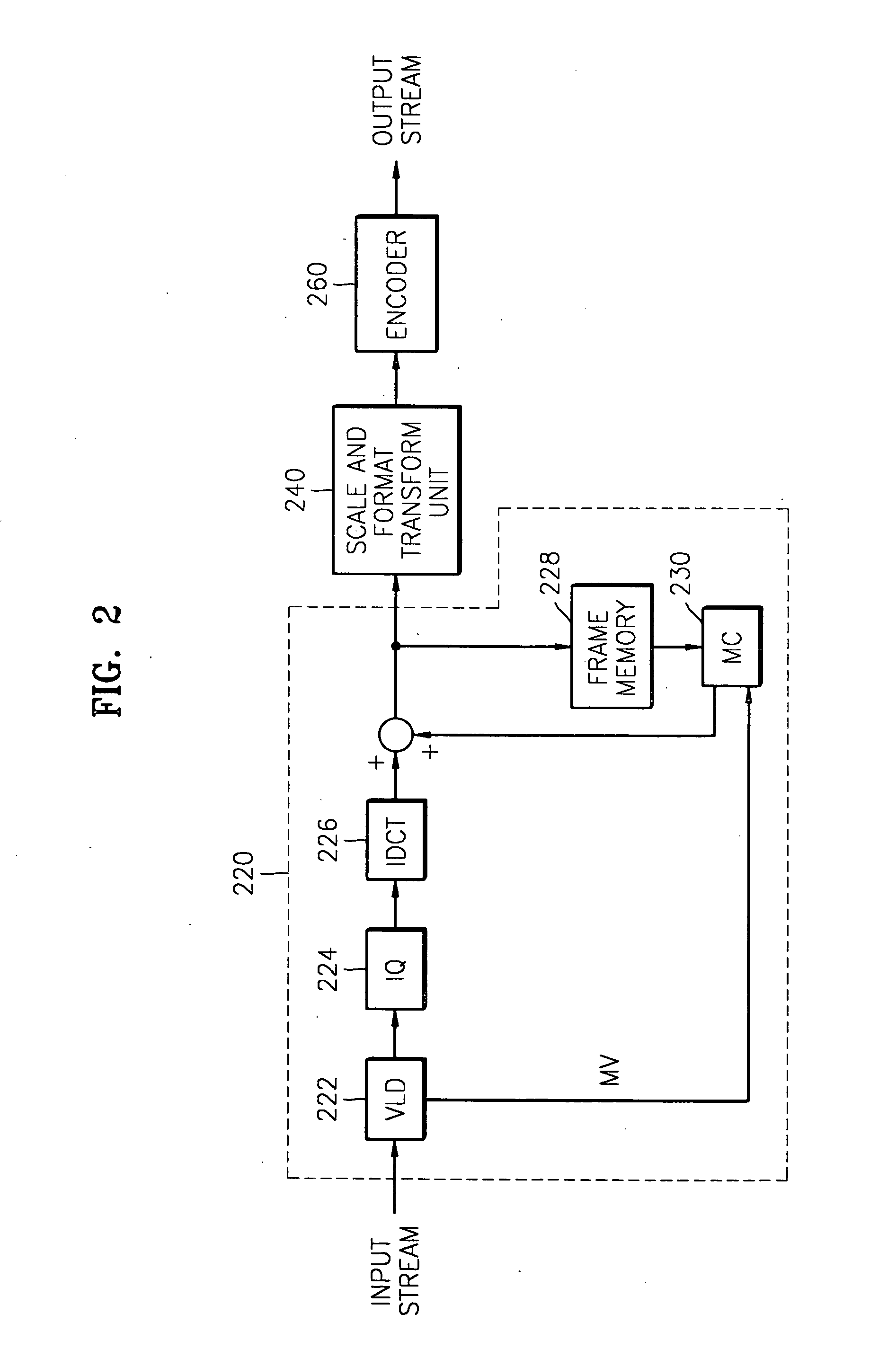
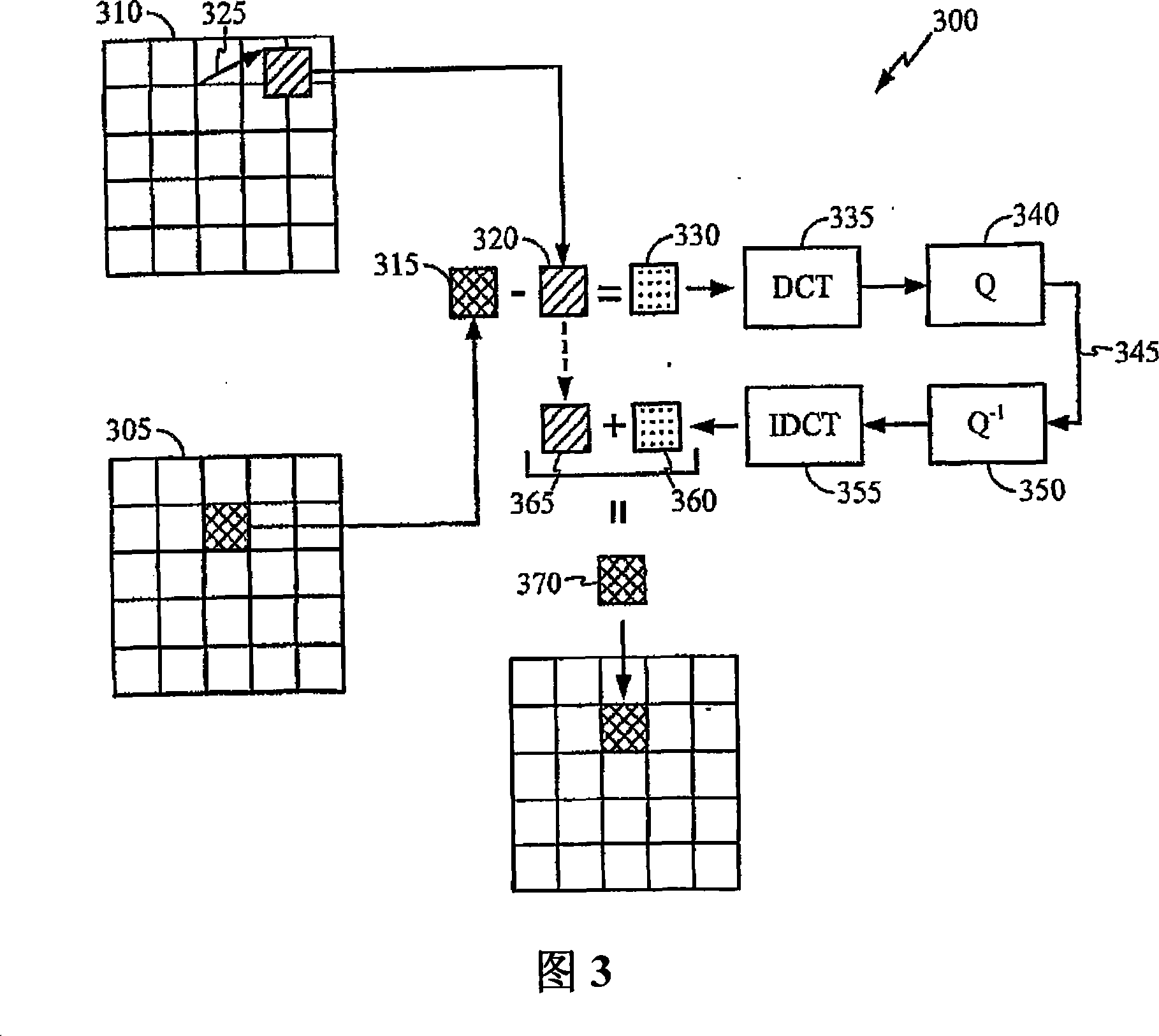
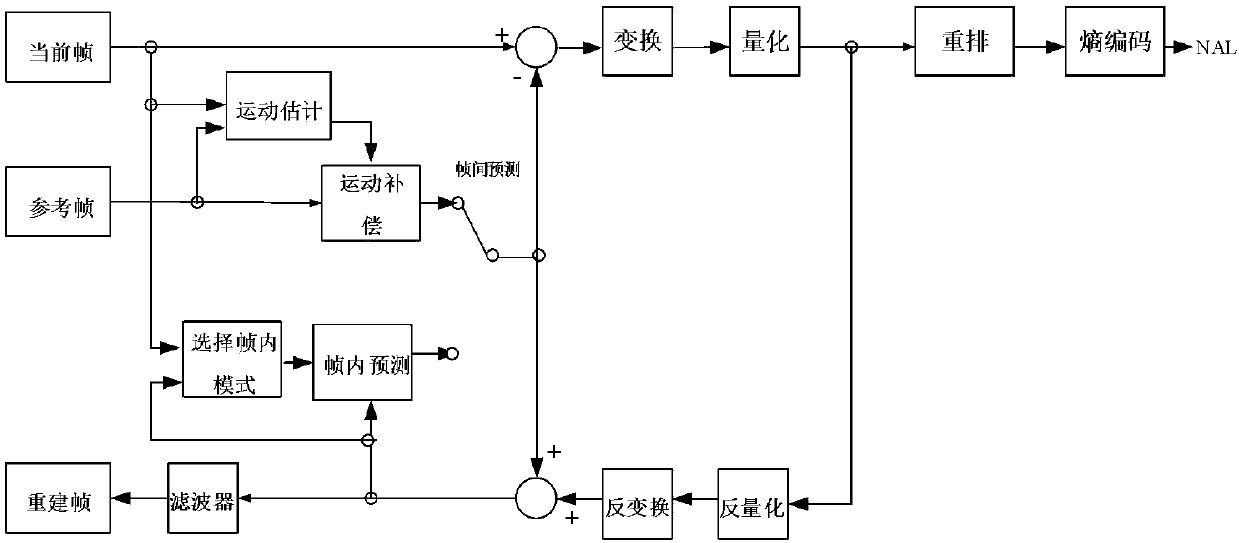
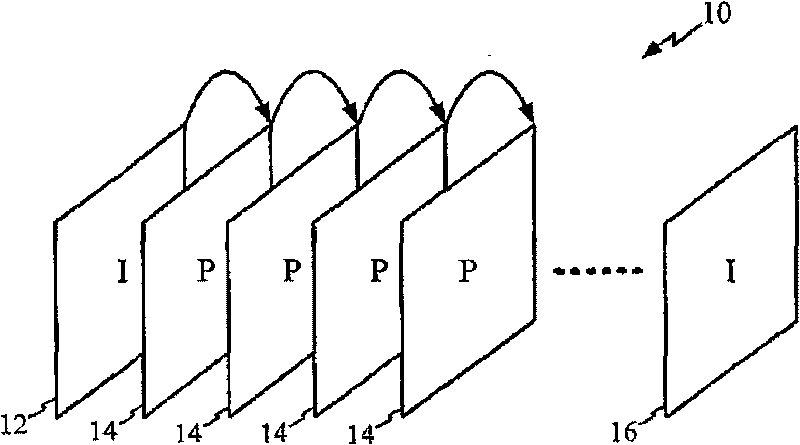
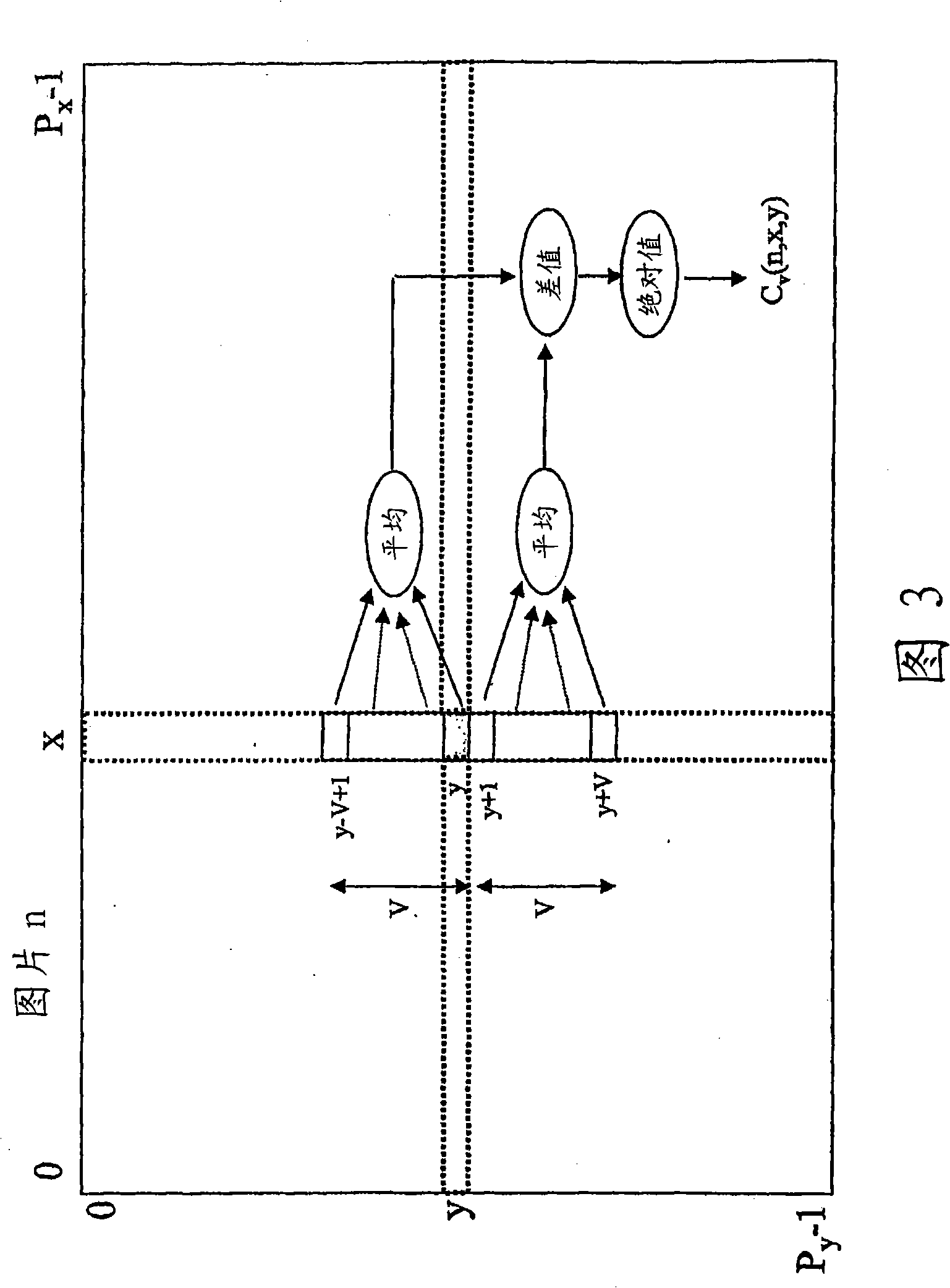
Target bitrate estimator, picture activity and buffer management in rate control for video coder
InactiveUS7453938B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPolicy decisionRound complexity
A rate control system is disclosed for video coding applications. The rate controller assigns a quantization parameter for video data in a picture in response to complexity indicators indicative of spatial complexity, motion complexity and / or bits per pel of the picture. A virtual buffer based quantizer parameter is proposed based on a virtual buffer fullness analysis and a target rate estimate, which is derived from the complexity indicators. A second quantizer parameter is proposed from a linear regression analysis of quantizer parameters used to code previously coded pictures of similar type (e.g., I pictures, P pictures or B pictures). A coding policy decision unit defines a final quantizer parameter from a comparison of the two proposed quantizer parameters.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
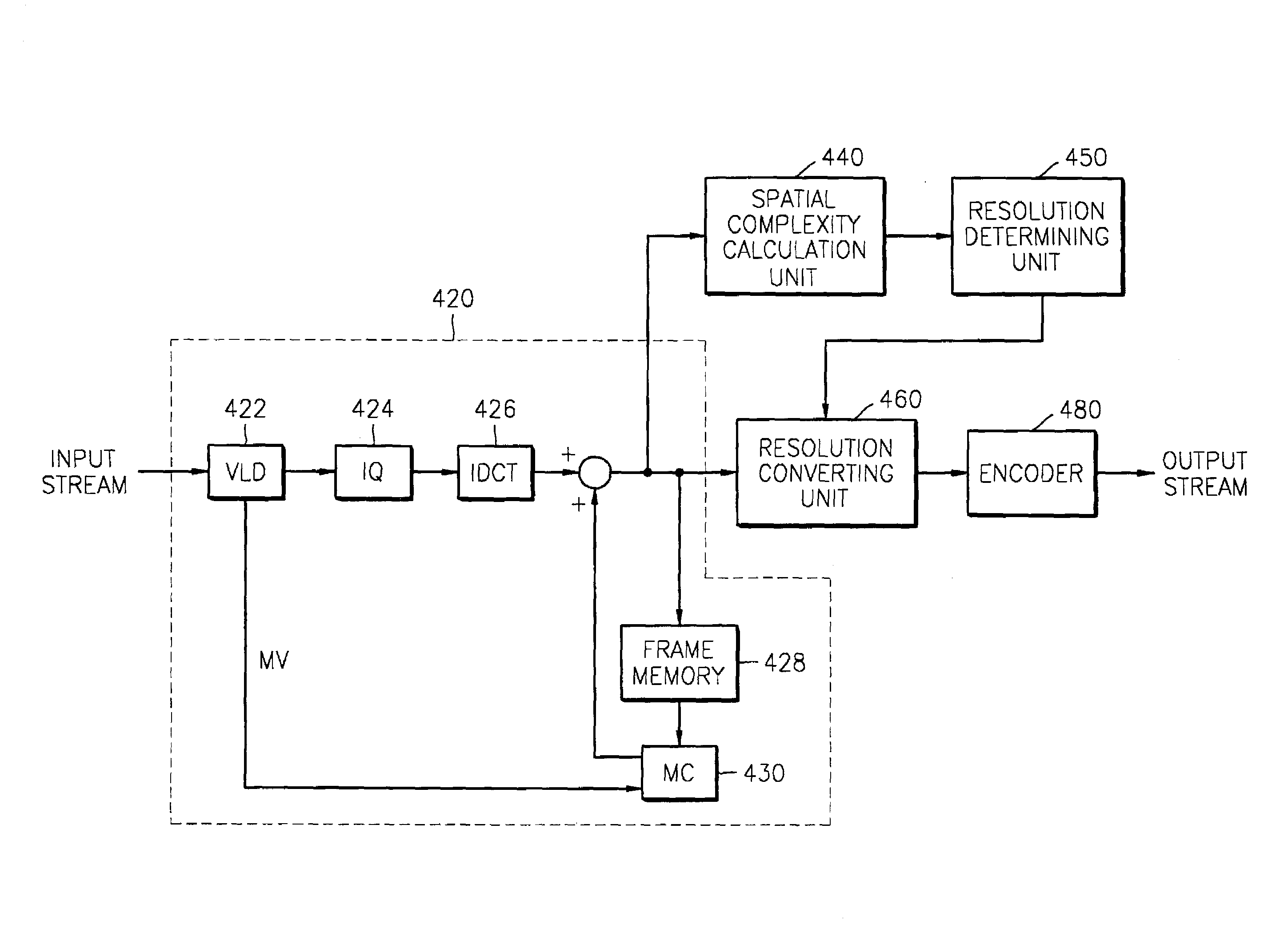
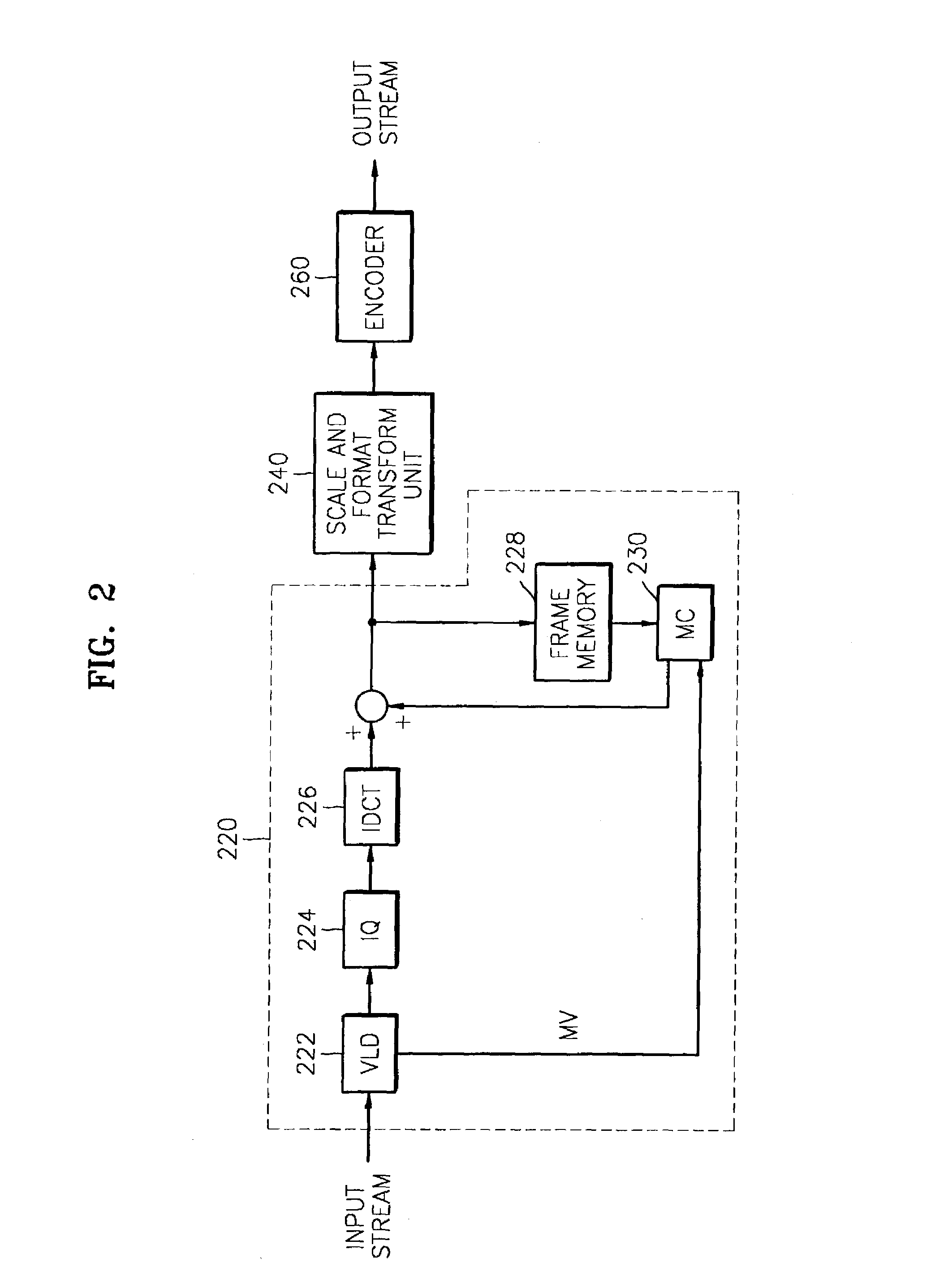
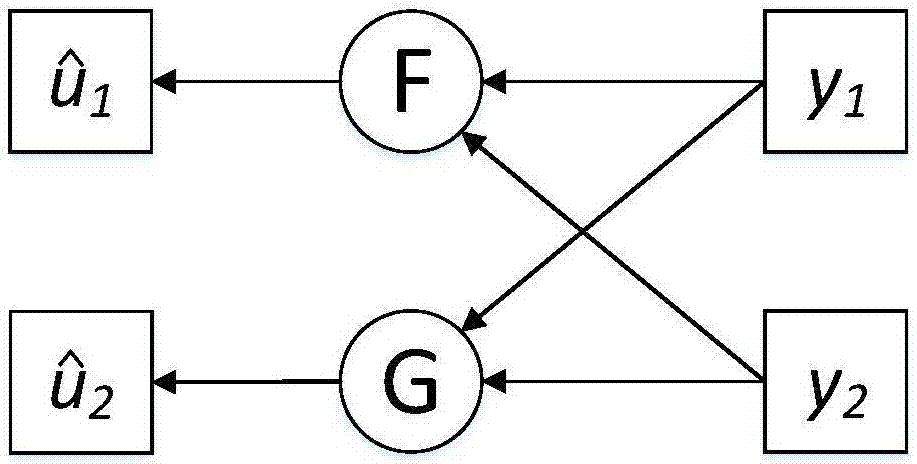
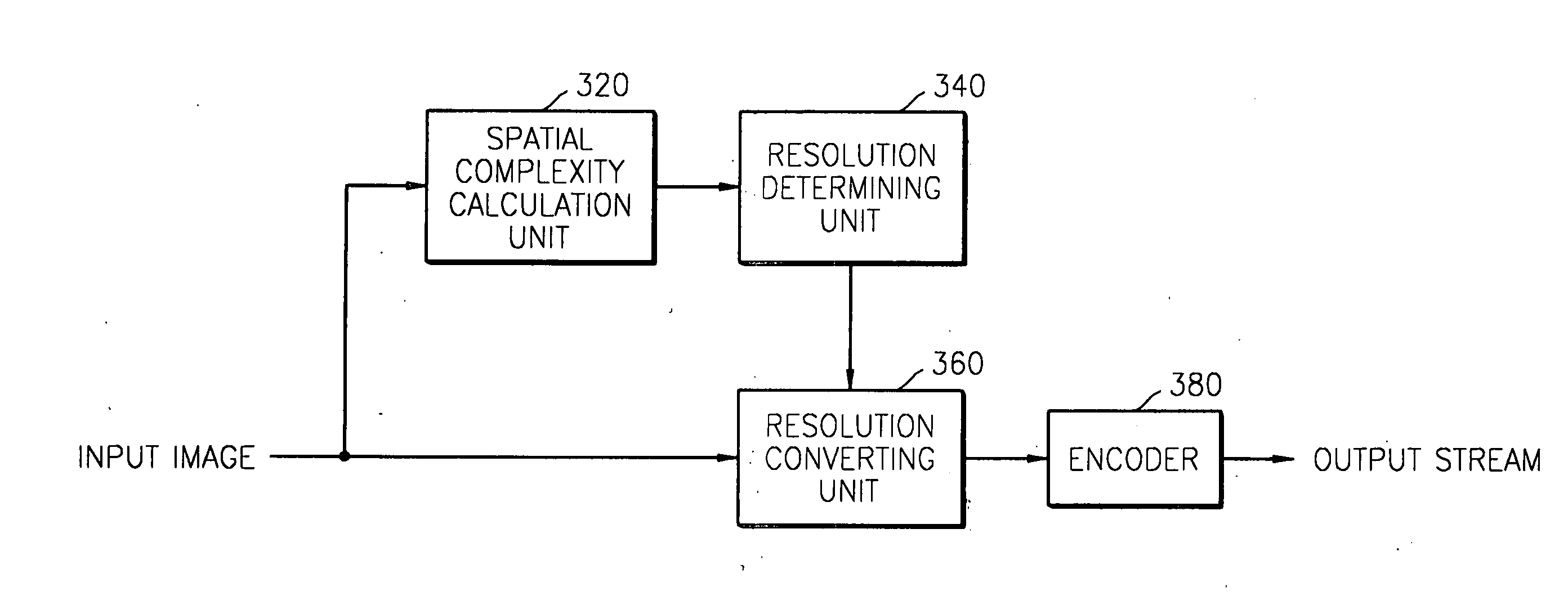
Method for adaptively encoding motion image based on temporal and spatial complexity and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS7280708B2Improve efficiencyMaximize efficiencyPulse modulation television signal transmissionCode conversionImage resolutionSelf adaptive
A method and an apparatus adaptively encode a motion image based on temporal and / or spatial complexity. In the method, encoding is performed with different temporal and spatial resolutions at frame rates based on the temporal and / or spatial complexity of an input image so that image data is stored with high efficiency. The method includes calculating a spatial complexity of input image data, determining a resolution by comparing the calculated spatial complexity with a predetermined threshold, and converting the resolution of the input image data based on the resolution.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
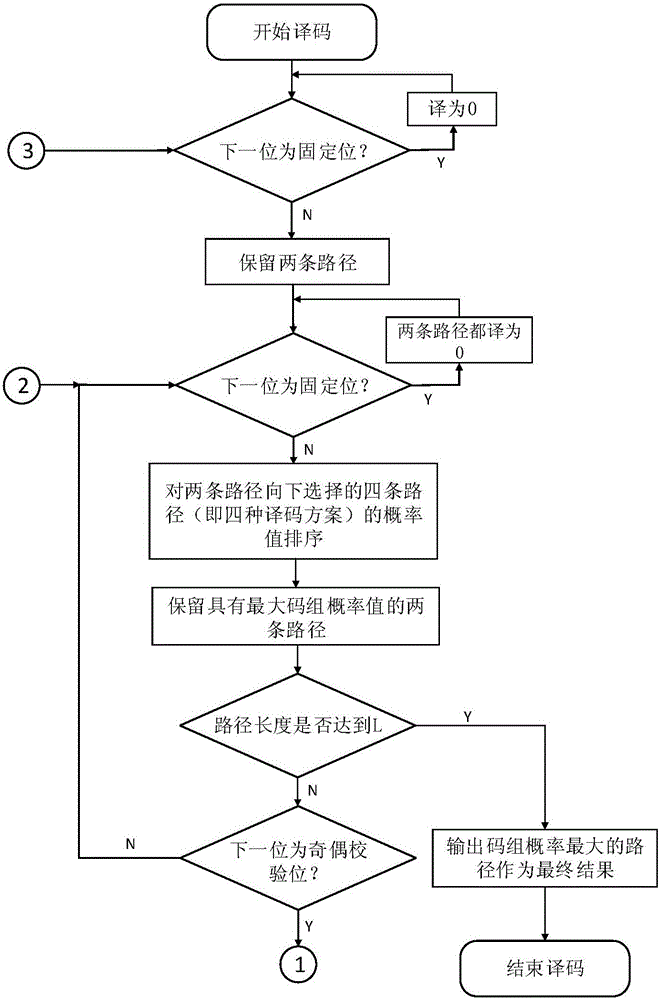
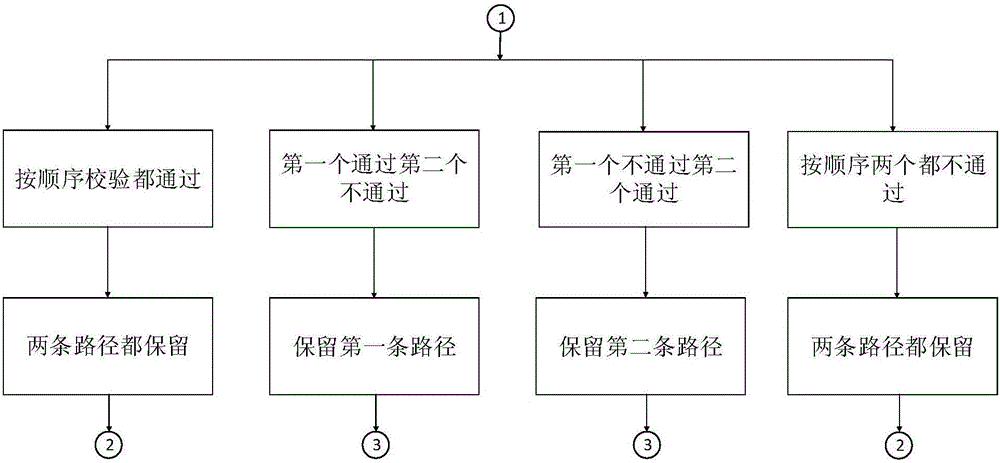
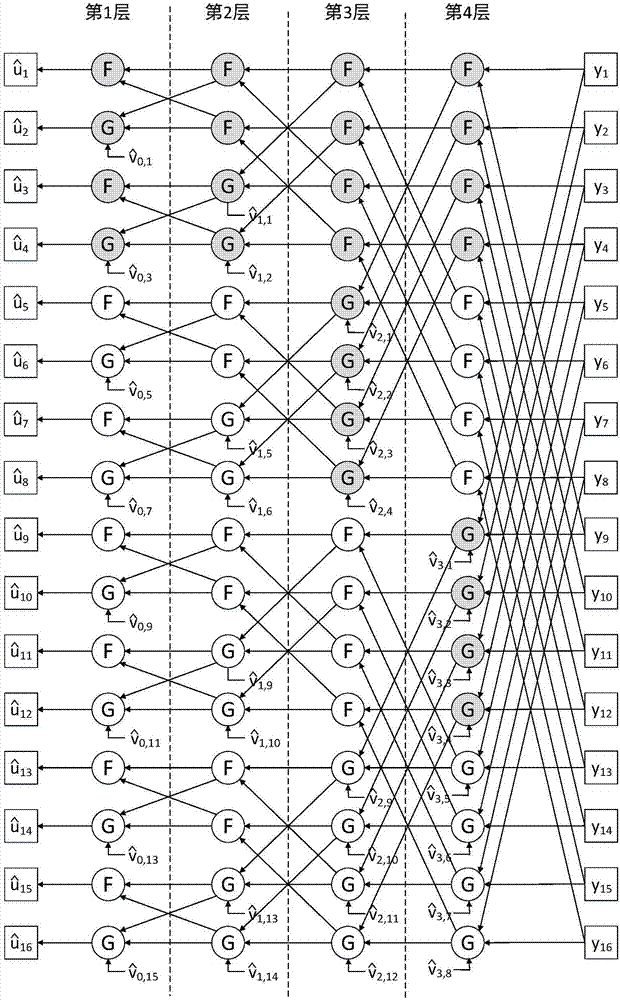
Low-complexity polarization code decryption SCL algorithm based on segmented verification assistance
InactiveCN105933010AReduce time complexityPrevent error propagationError correction/detection using linear codesError detection onlyRound complexitySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a low-complexity polarization code decryption SCL algorithm based on segmented verification assistance, and the algorithm selects a parity check code, repeatedly uses the parity check code in a decryption process, and achieves the performances of SCL-CRC24. Moreover, compared with a conventional scheme, the algorithm is better in low signal to noise ratio anti-noise performance and error rate. In addition, the spatial complexity of the algorithm is lower than that of the SCL-CRC24, the time complexity is greatly reduced, and the decoding speed is greatly improved. Compared with a CRC-24 verification algorithm sacrificing multiple information bits, the algorithm employs a parity check method, enables verification elements to be distributed in the information bits, is repeatedly used in the decoding process, and is lower in time complexity than the prior art.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
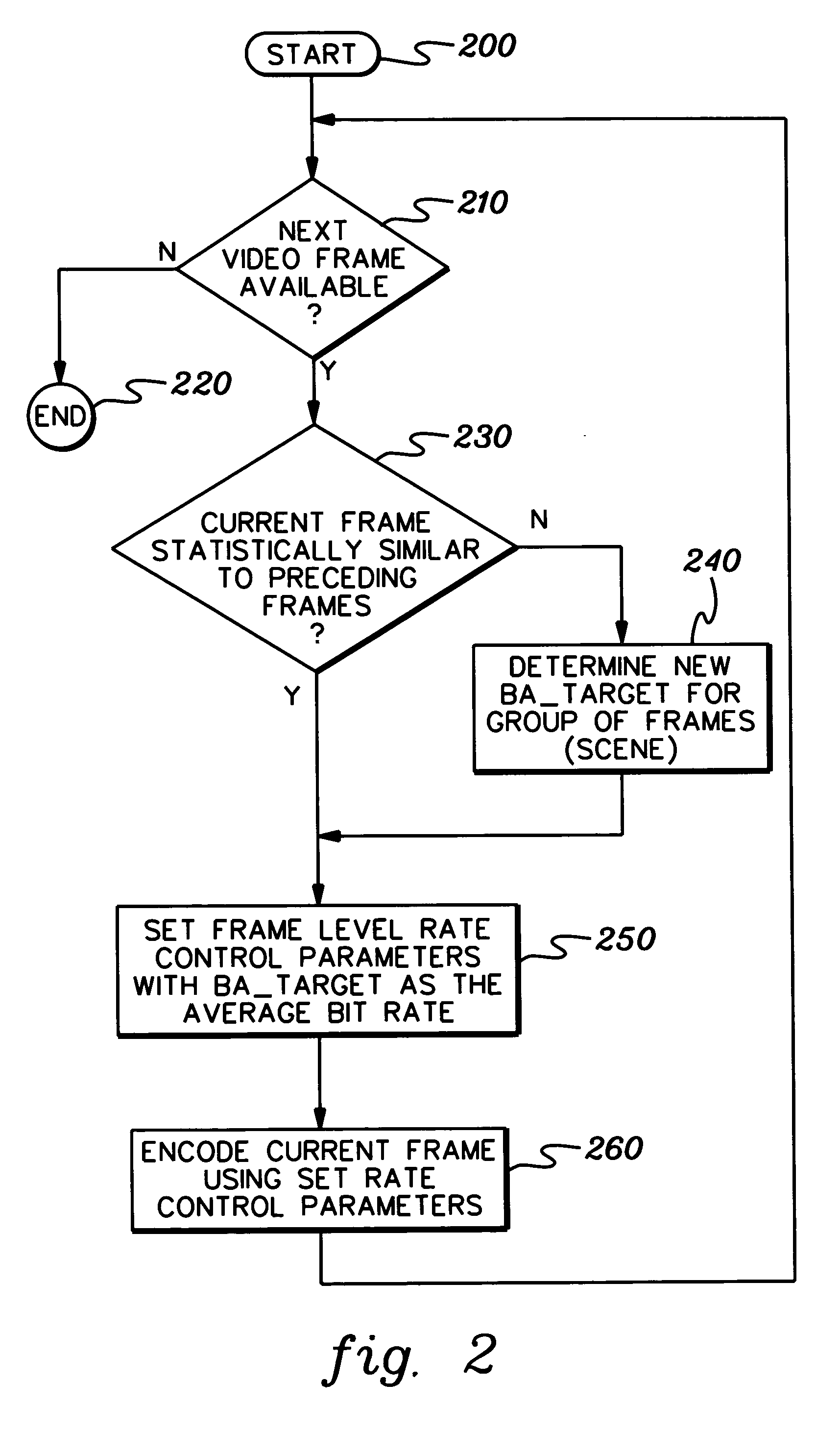
Single pass variable bit rate control strategy and encoder for processing a video frame of a sequence of video frames
InactiveUS20060062292A1Easy to compressQuality improvementColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionVariable bit rate vbr
An encode control strategy is provided for variable bit rate encoding of a sequence of video frames in a single pass. The control strategy includes determining whether a video frame has a complexity level statistically outside a defined range from a complexity level of at least one preceding frame of the sequence of video frames, and if so, determining a new average bit rate target for the video frame. The new average bit rate for the video frame is determined employing at least one of spatial complexity and temporal complexity of the video frame. The new average bit rate target for the video frame is used to set frame level bit rate control parameter(s), and the video frame is encoded using the set frame level bit rate control parameter(s).
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Perceptual optimization for model-based video encoding
Perceptual statistics may be used to compute importance maps that indicate which regions of a video frame are important to the human visual system. Importance maps may be applied to the video encoding process to enhance the quality of encoded bitstreams. The temporal contrast sensitivity function (TCSF) may be computed from the encoder's motion vectors. Motion vector quality metrics may be used to construct a true motion vector map (TMVM) that can be used to refine the TCSF. Spatial complexity maps (SCMs) can be calculated from metrics such as block variance, block luminance, SSIM, and edge strength, and the SCMs can be combined with the TCSF to obtain a unified importance map. Importance maps may be used to improve encoding by modifying the criterion for selecting optimum encoding solutions or by modifying the quantization for each target block to be encoded.
Owner:EUCLID DISCOVERIES LLC
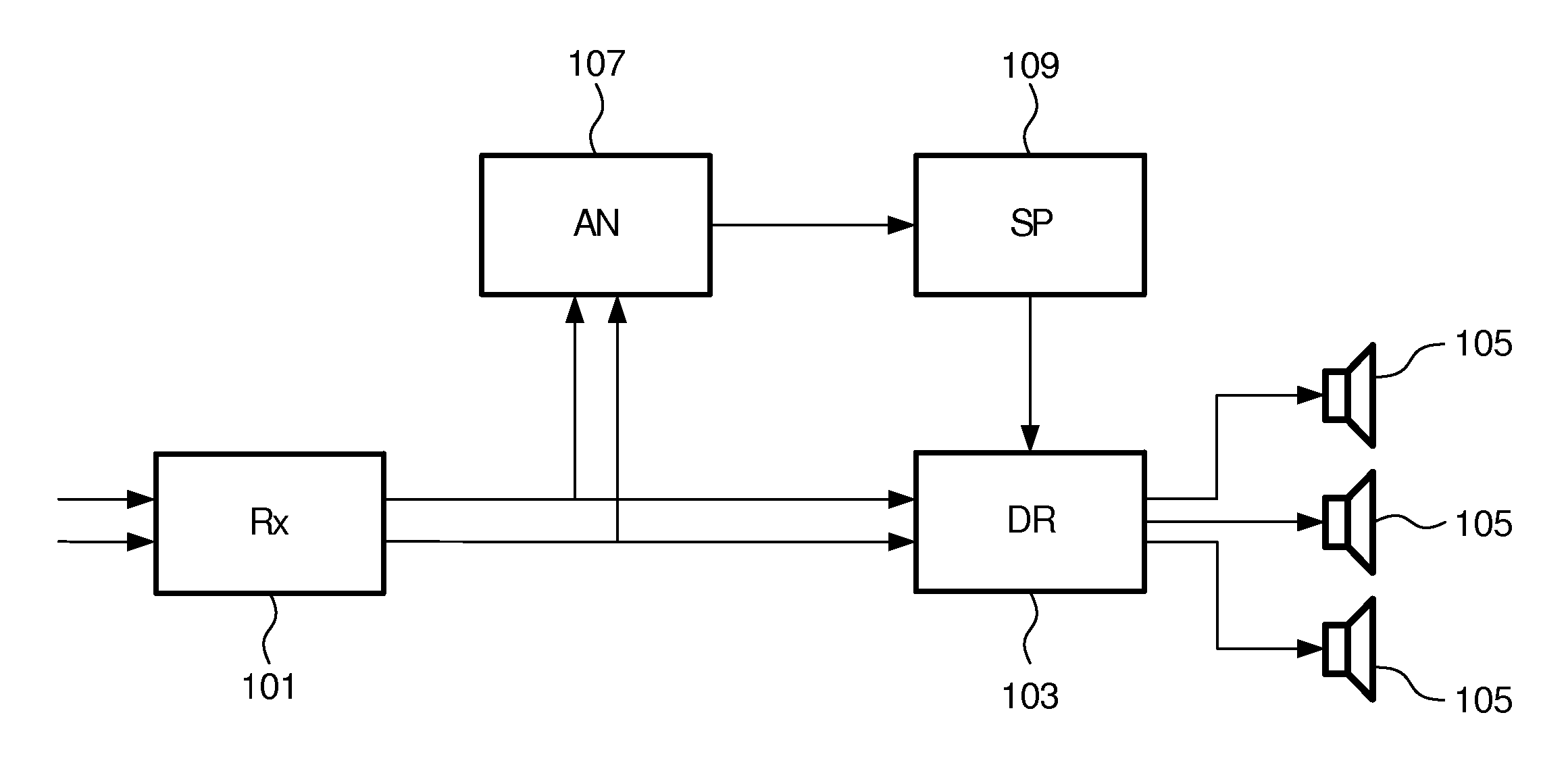
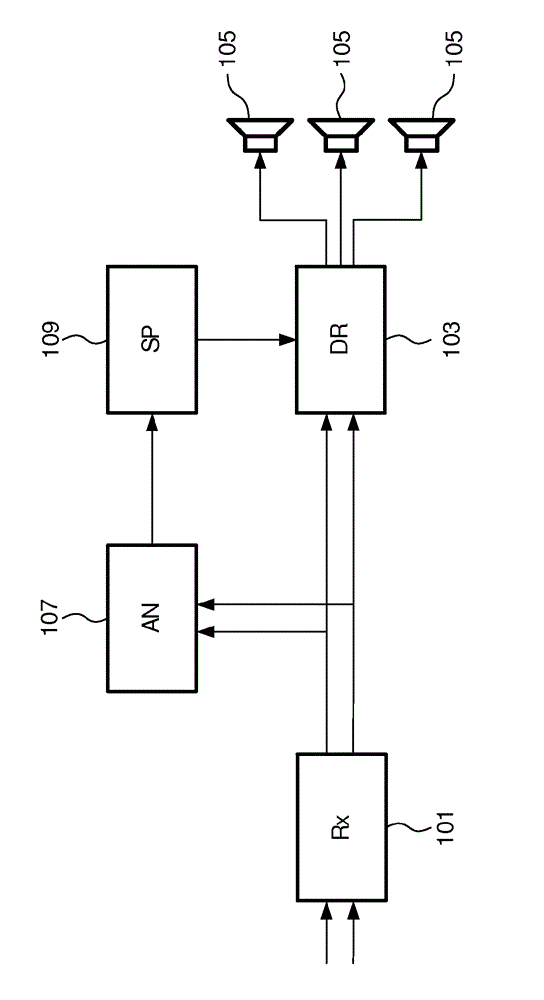
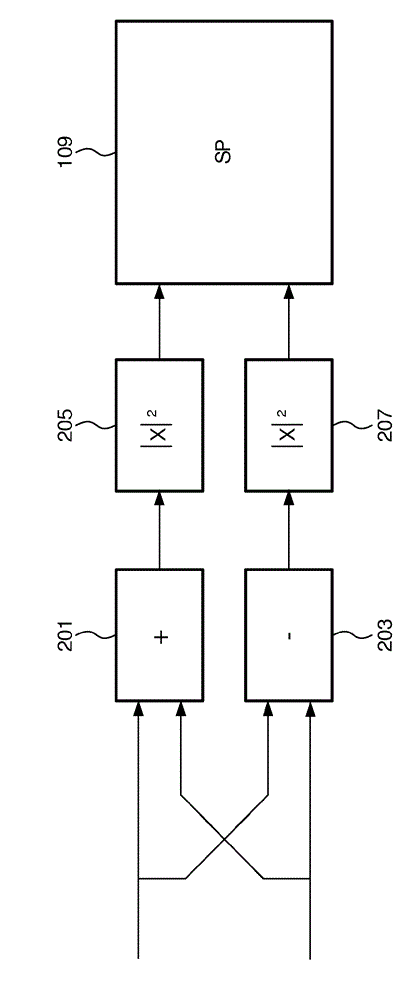
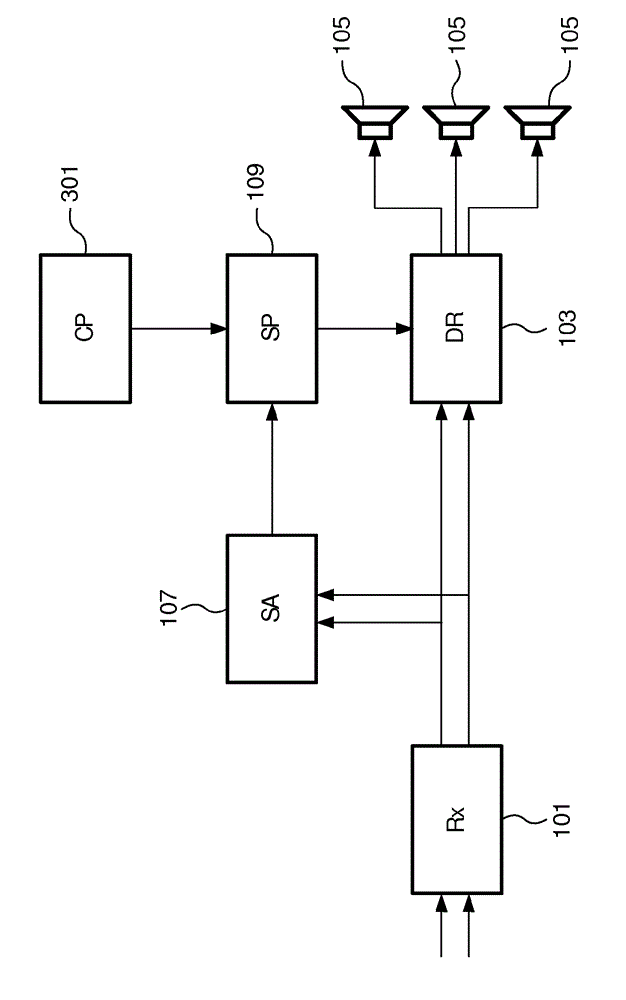
Spatial sound reproduction
InactiveUS20120328109A1Enhance listening experienceImprove performancePseudo-stereo systemsStereophonic arrangmentsVocal tractShort terms
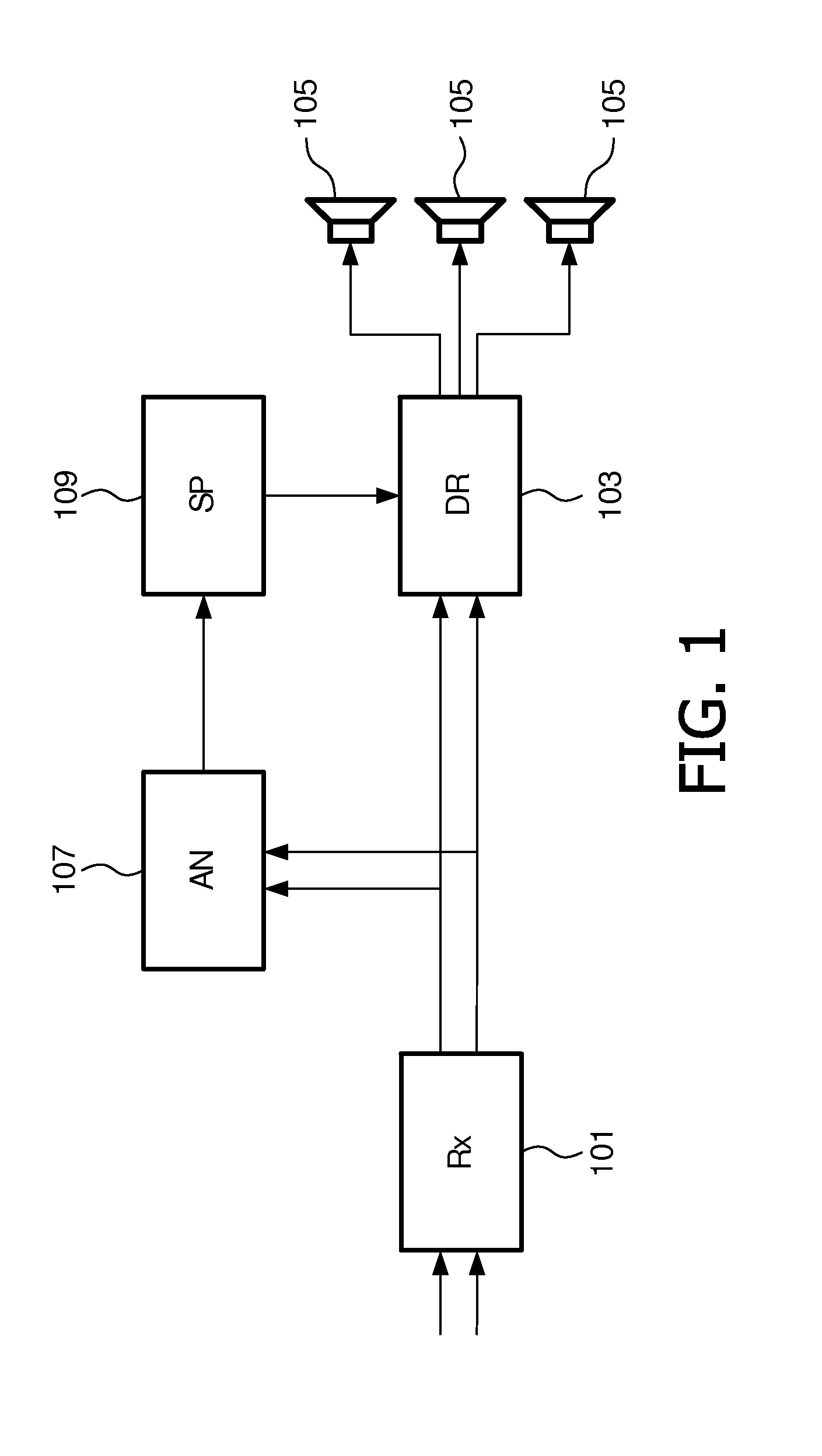
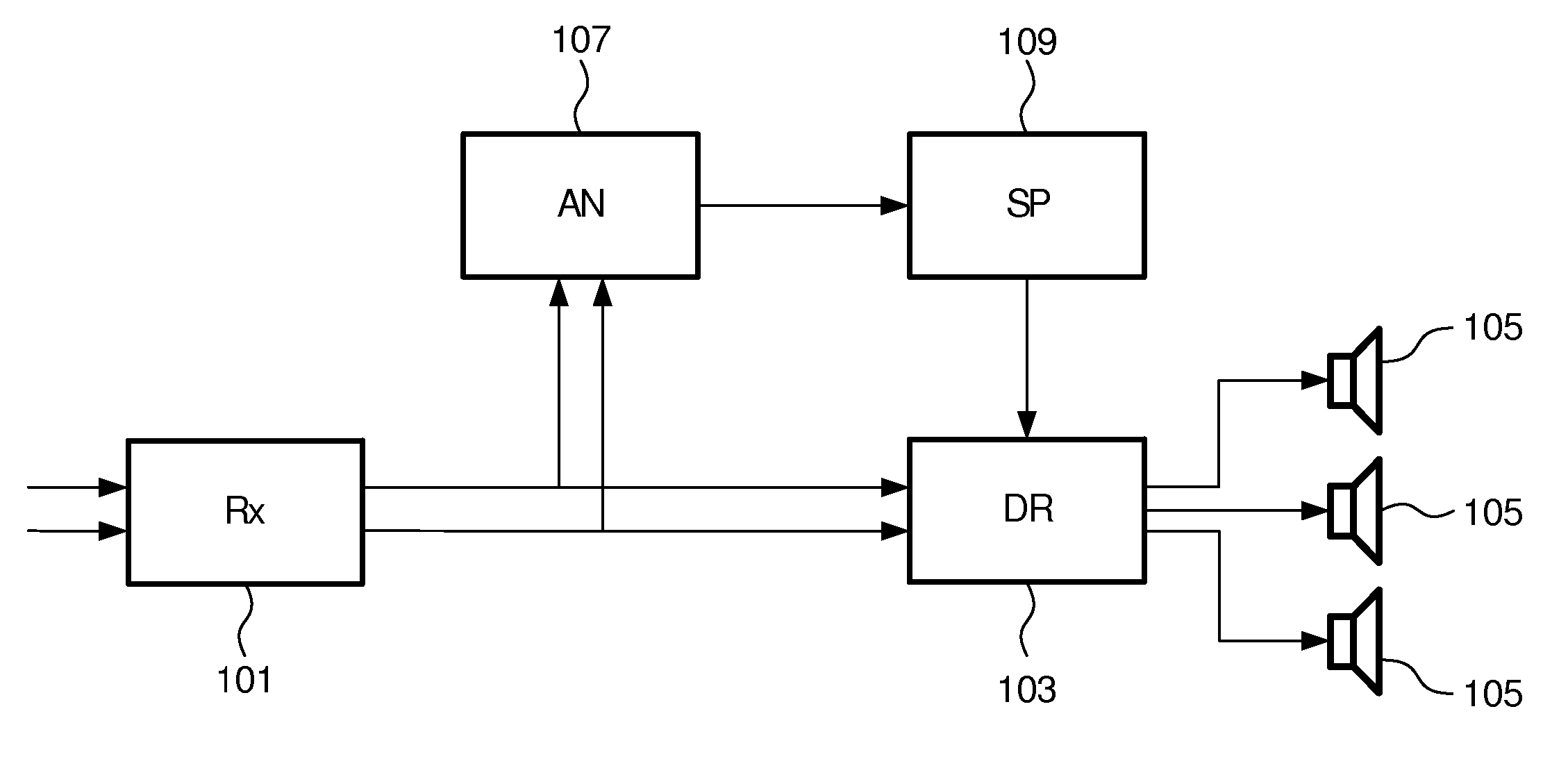
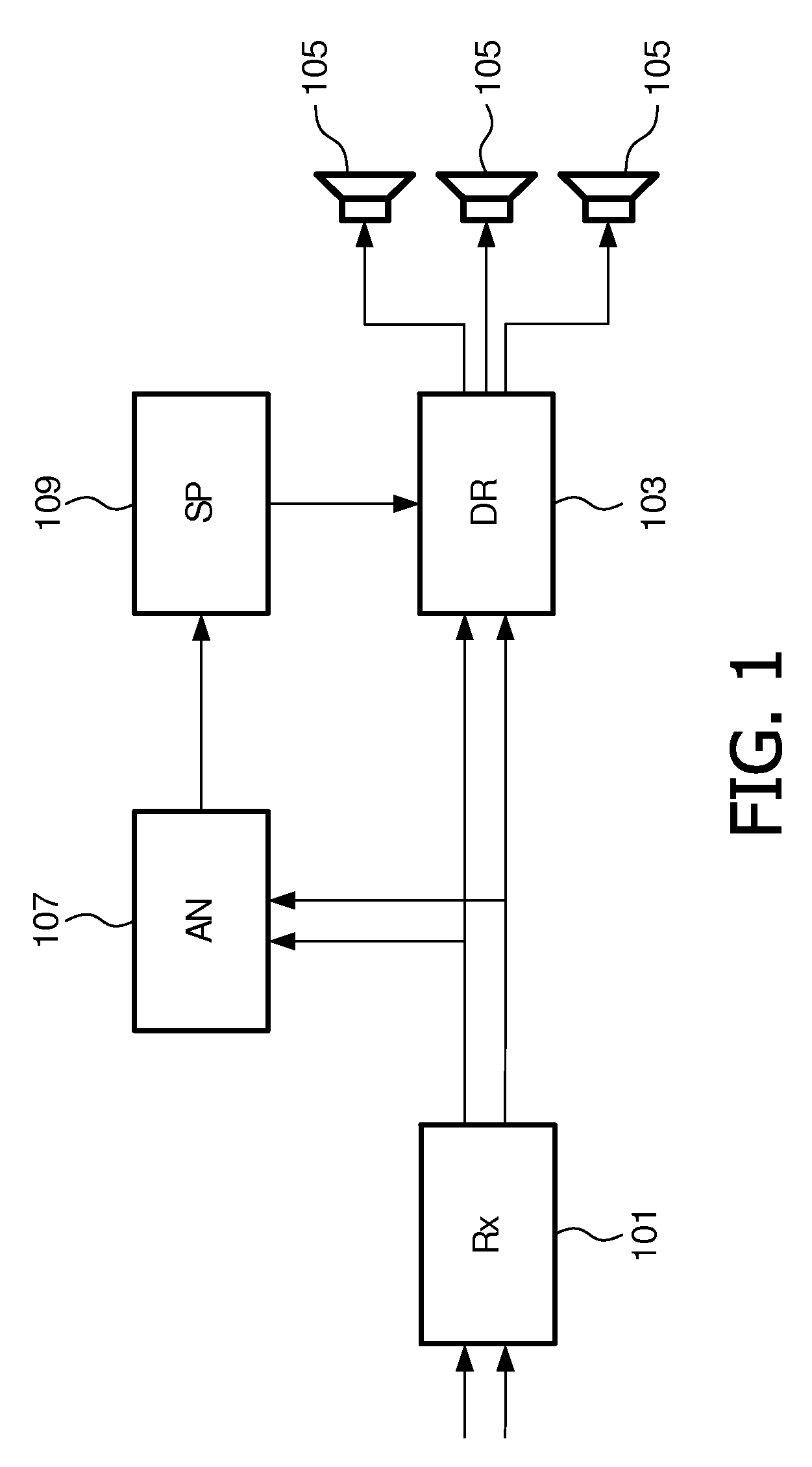
An apparatus for spatial sound reproduction comprises a receiver (101) for receiving a multi-channel audio signal. An analyzer (107) determines a spatial property of the multi-channel audio signal, such as a spatial complexity or organization. A selection processor (109) then selects a reproduction mode from a plurality of sound reproduction modes where the multi-channel sound reproduction modes employ different spatial rendering techniques. A reproduction circuit (103) then drives a set of loud-speakers (105) to reproduce the multi-channel audio signal using the selected reproduction mode. The switching between the reproduction modes may be fast (e.g. in the order of 100 ms to 10 secs) thereby allowing a short term adaptation of the reproduction mode to the signal characteristics. The approach may in particular provide an improved spatial experience to a listener.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
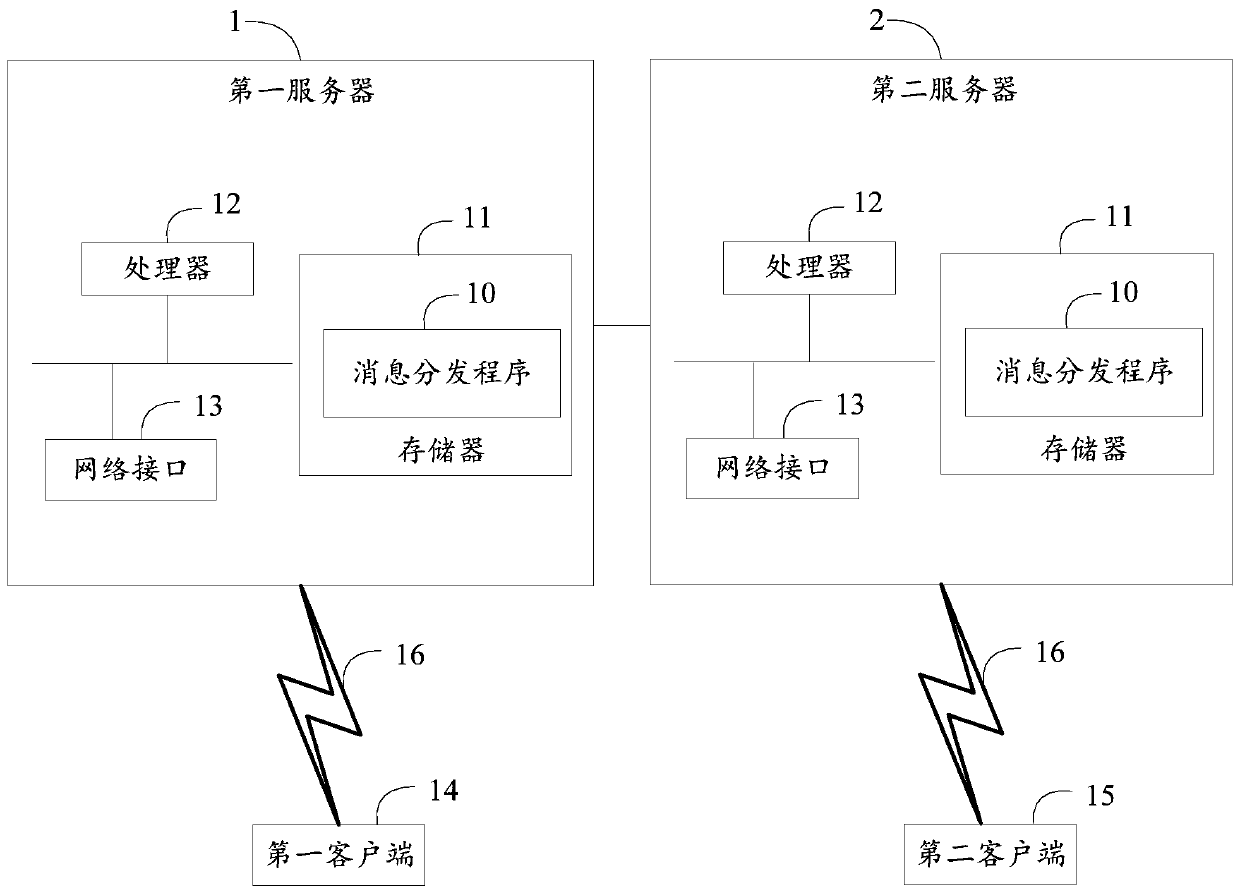
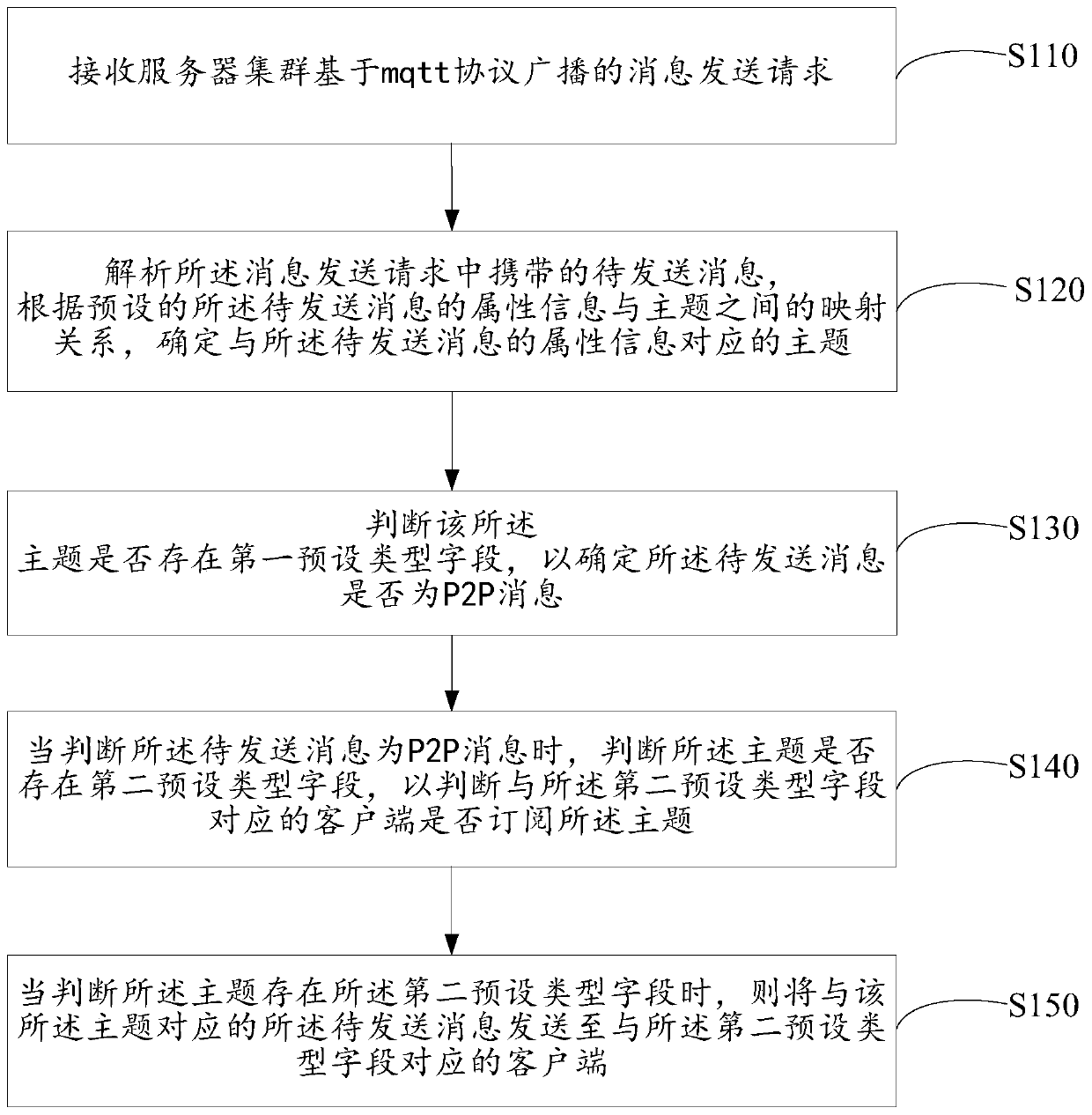
Message distribution method based on mqtt, server and storage medium
ActiveCN110086636AImprove distribution efficiencyReduce space complexitySpecial service provision for substationDistribution methodTime complexity
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Method and apparatus for determining encoding mode based on temporal and spatial complexity
ActiveCN101926178AProcessing speedReduce computational complexityTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationComputation complexityRound complexity
The present invention relates to a method and an apparatus for determining an encoding mode based on temporal and spatial complexity. The encoding-mode-determining apparatus based on temporal complexity is characterized in that it comprises: a temporal complexity calculation unit which calculates the temporal complexity of a macro block; and a mode determining unit which determines the encoding mode based on temporal complexity. The temporal complexity and the spatial complexity of a macroblock can be calculated with higher accuracy, and additionally the optimal encoding mode can be selected based on the calculated complexity. Accordingly, the complexity of the calculation involved in rate-distortion optimization can be reduced and the processing speed can be increased.
Owner:SK PLANET CO LTD
Low-decoding complexity rate matching polarization code transmission method based on QUP method
ActiveCN107395324AOvercoming technical defects with high complexityReduce space complexityError preventionCoding decodingTime complexity
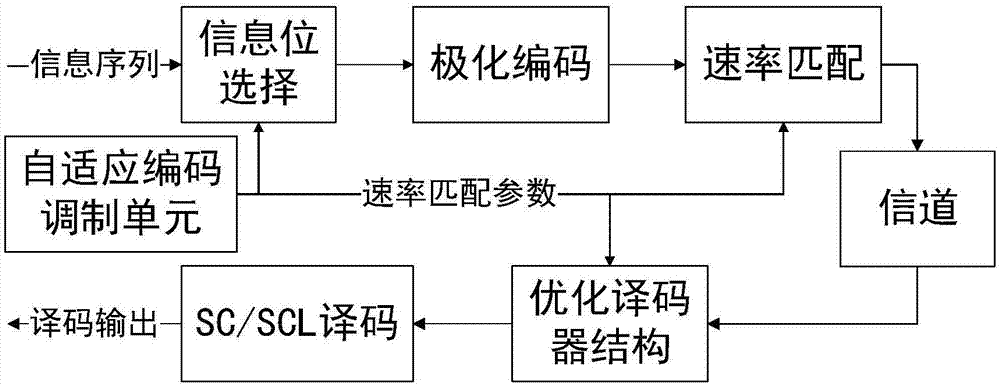
The invention discloses a low-decoding complexity rate matching polarization code transmission method based on a QUP method, and belongs to the technical field of the channel coding / decoding. The method comprises the following steps: step one, determining a punch position and a punch parameter; step two, constructing an information sequence; step three, performing polarization coding, and outputting a coding sequence; step four, outputting the punched coding sequence according to the punch parameter determined in the step one; step five, sending the coding sequence punched in the step four one bit by one bit by a sending end; step six, receiving the coding sequence sent in the step five through channel transmission by a receiving end; step seven, optimizing a decoder structure according to the punch parameter determined in the step one, and outputting the optimized SC decoder; and step eight, performing polarization code decoding by using the SC decoder optimized in the step seven. By using the method disclosed by the invention, the spatial complexity and the time complexity of the polarization code decoding are effectively lowered, and the saved time and time source is increased along the increasing of the punch number.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for adaptively encoding motion image based on temporal and spatial complexity and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20060210184A1Improve efficiencyMaximize efficiencyPulse modulation television signal transmissionCode conversionImage resolutionSpacetime
A method and an apparatus adaptively encode a motion image based on temporal and / or spatial complexity. In the method, encoding is performed with different temporal and spatial resolutions at frame rates based on the temporal and / or spatial complexity of an input image so that image data is stored with high efficiency. The method includes calculating a spatial complexity of input image data, determining a resolution by comparing the calculated spatial complexity with a predetermined threshold, and converting the resolution of the input image data based on the resolution.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Spatial sound reproduction
An apparatus for spatial sound reproduction comprises a receiver (101) for receiving a multi-channel audio signal. An analyzer (107) determines a spatial property of the multi-channel audio signal, such as a spatial complexity or organization. A selection processor (109) then selects a reproduction mode from a plurality of sound reproduction modes where the multi-channel sound reproduction modes employ different spatial rendering techniques. A reproduction circuit (103) then drives a set of loudspeakers (105) to reproduce the multi-channel audio signal using the selected reproduction mode. The switching between the reproduction modes may be fast (e.g. in the order of 100 ms to 10 secs) thereby allowing a short term adaptation of the reproduction mode to the signal characteristics. The approach may in particular provide an improved spatial experience to a listener.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
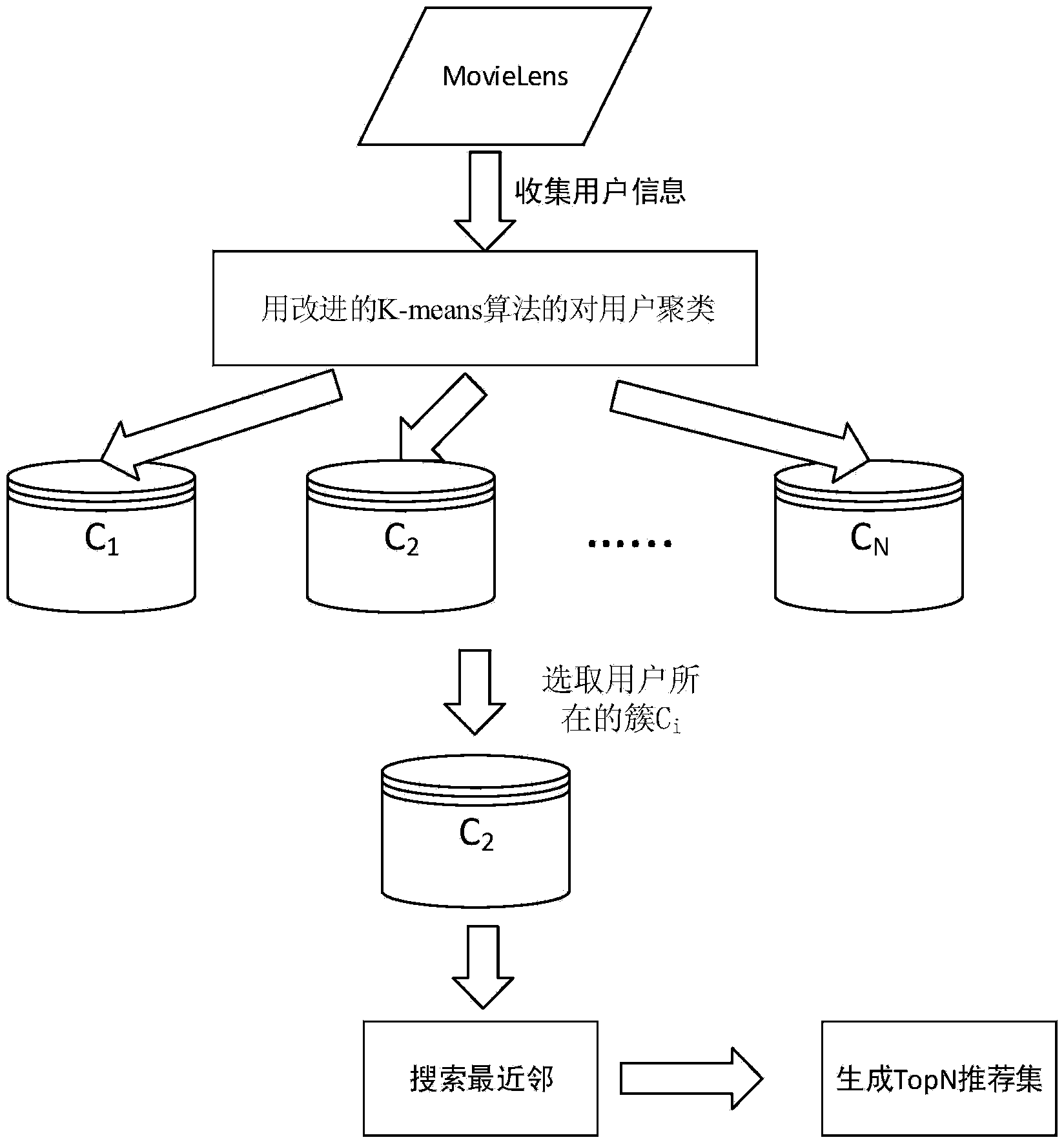
Collaborative filtering processor
InactiveCN103886003ARun fastReduce the scope of calculationSpecial data processing applicationsMatrix decompositionMachine learning
The invention discloses a collaborative filtering processor. A method includes the following steps: adopting an improved K-means algorithm to perform clustering on users; selecting a cluster formed by the users similar to a target user in attribute; acquiring a nearest neighbour set of the target user; generating a recommendation set. The main idea includes that the users identical in feature are clustered into a class through clustering to lower dimensionality of a matrix and reduce spatial complexity, sparse matrices are filled through matrix decomposition, and then collaborative filtering is performed on the filled matrices.
Owner:TIANJIN SIBOKE TECH DEV
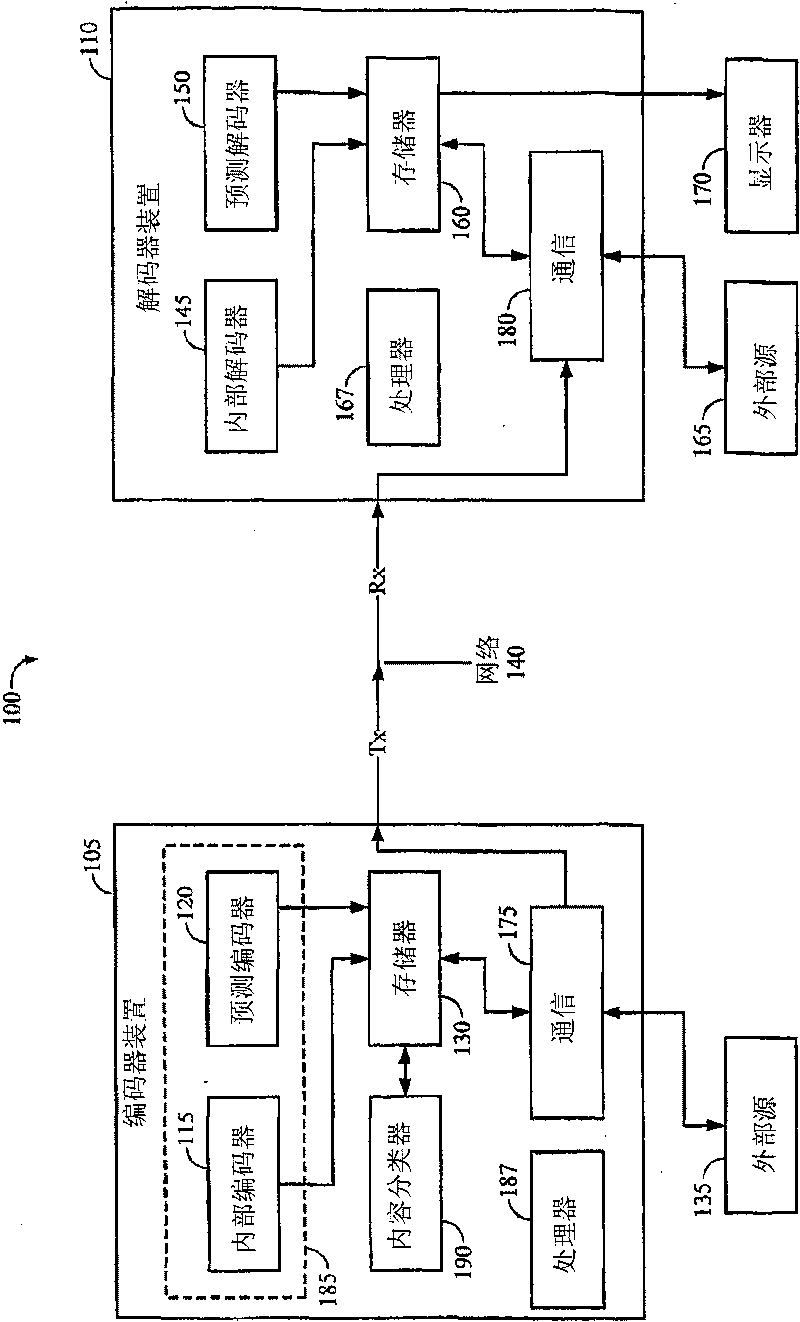
Content classification for multimedia processing
ActiveCN101171843APulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital video signal modificationSample complexityAudio frequency
An apparatus and method for processing multimedia data, such as, for example, video data, audio data, or both video and audio data for encoding utilizing a determined content classification is claimed. Processing the multimedia data includes determining complexity of multimedia data, classifying the multimedia data based on the determined complexity, and, determining a bit rate for encoding the multimedia data based on its classification. The complexity can include a spatial complexity component and a temporal complexity component of the multimedia data. The multimedia data is classified using content classifications, which are based on a visual quality value for viewing multimedia data, using the spatial complexity, the temporal complexity, or both the spatial complexity and temporal complexity.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
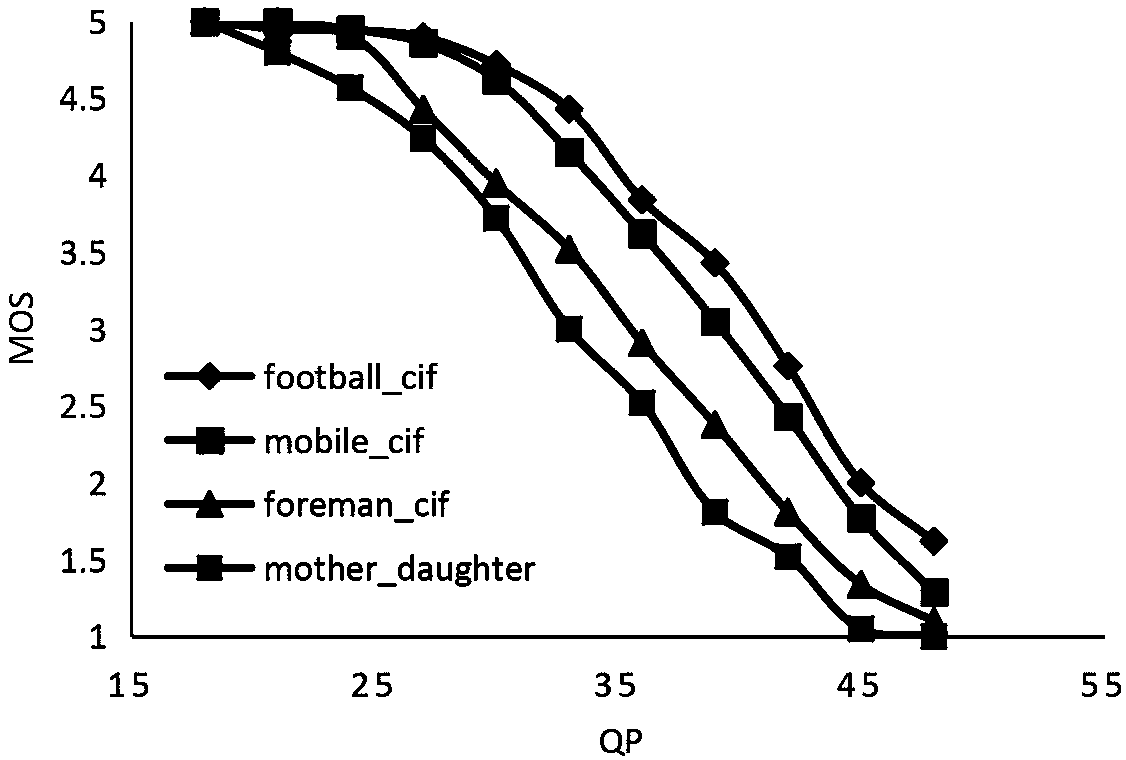
Content-based bit stream layer video quality assessment model
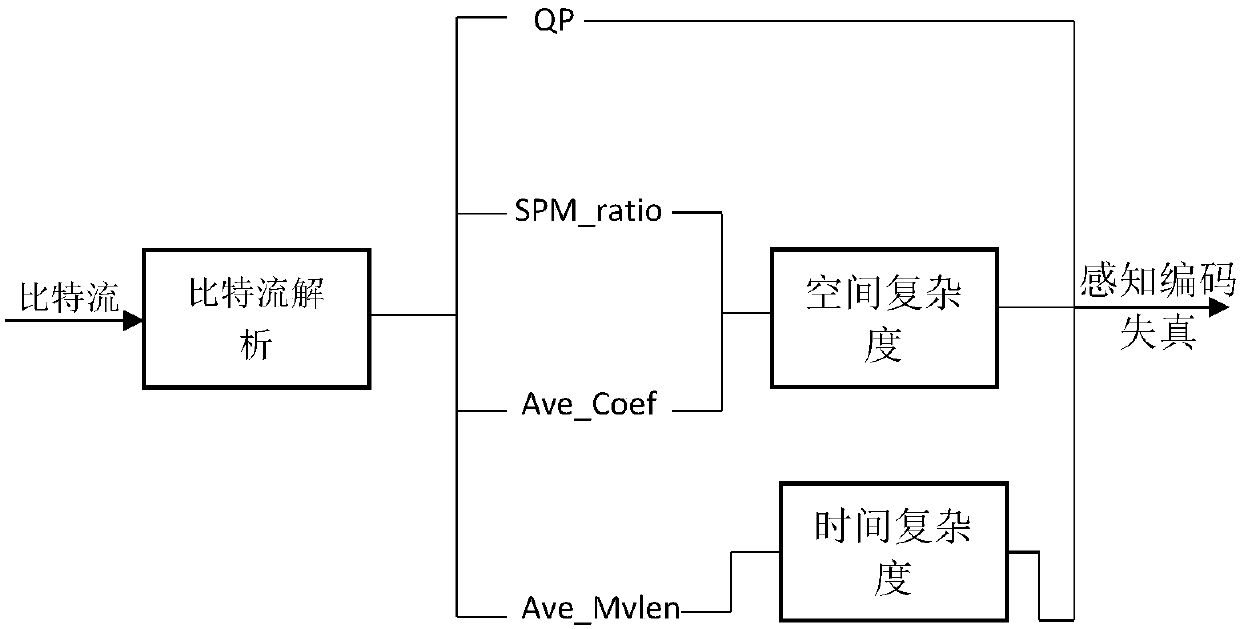
The invention discloses a content-based bit stream layer video quality assessment model, and belongs to the technical field of multi-media. A compressed domain model can directly extract a video parameter from a code stream, for performing non-invasive quality monitoring in real time. The model mainly aims at an H.264 video coding standard, for assessing the quality of coding distortion. A basic relation is built between sensed quality and a quantization parameter (QP). In view of significant dependence of the sensed quality on video content, the video content is defined to be combinations with different time complexity and spatial complexity. According to the model provided by the invention, the occupied ratio (SPM_Ratio) of a small prediction bock and a proportion (Ave_Coef) of an average DCT nonzero number in each 4*4 block in an I frame are used for synchronously describing the spatial complexity of the video. An average normalization parameter (Ave_Mvlen) of a suffix length of motion vector information in the code stream is used for describing the spatial complexity of the video. All information can be directly extracted from the code stream, with no need to perform decoding operation.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Parallel mechanism with four degrees of freedom
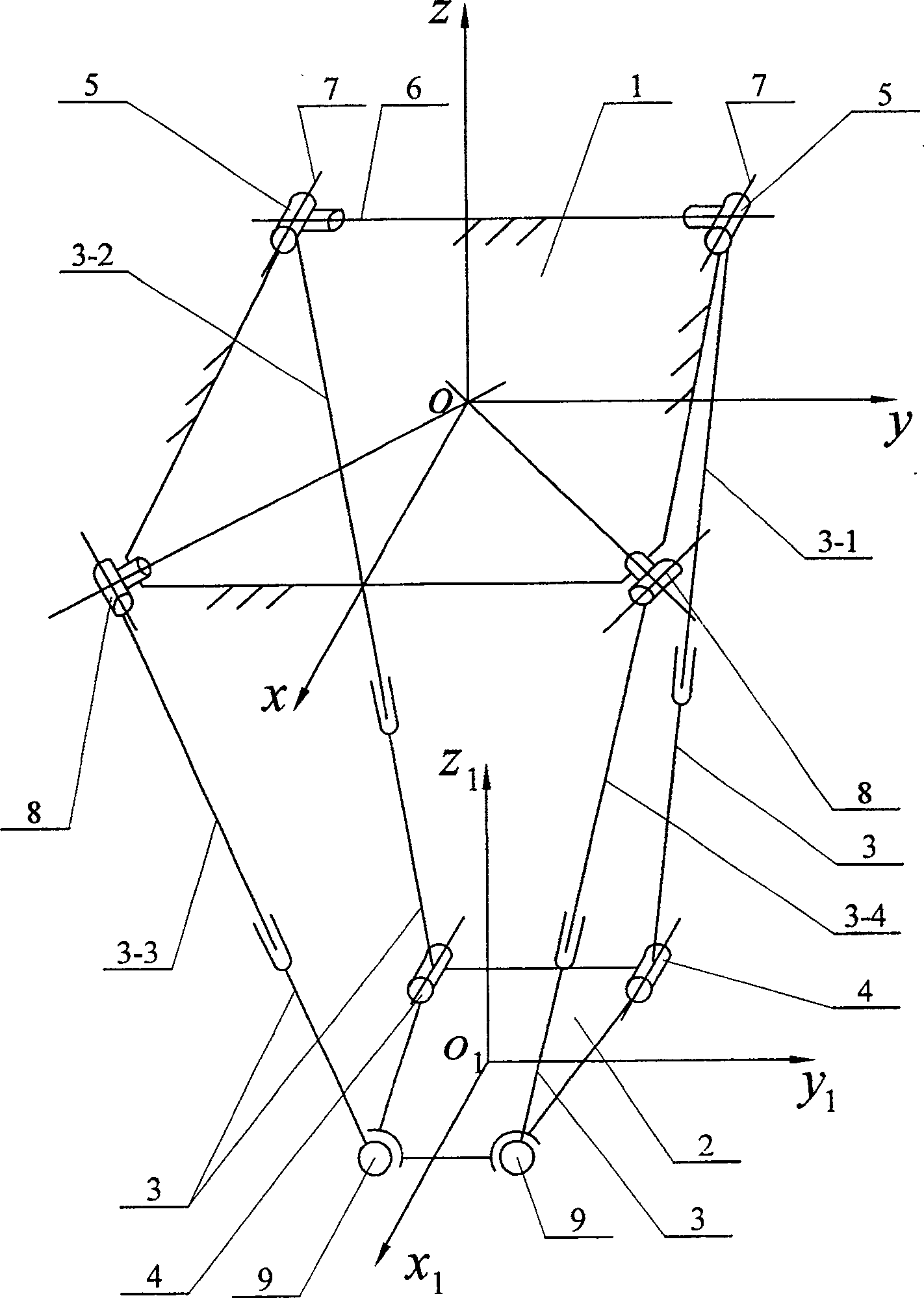
InactiveCN100513062CSimple structureReduce manufacturing costProgramme-controlled manipulatorLarge fixed membersEngineeringRotational degrees of freedom
A four-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism relates to a four-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism for a parallel machine tool. Aiming at the problems that the current six-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism has a complex structure, the volume of the working space and the mechanism is relatively small, and the manufacturing cost is high. The upper ends of the first and second telescopic links of the present invention are hinged to the fixed platform (1) through the first Hooke hinge (5), the lower ends are connected to the moving platform (2) through the rotating pair (4), and the third and fourth telescopic links The upper end of the rod is hinged to the fixed platform (1) through the second Hooke hinge (8), and the lower end is hinged to the moving platform (2) through the spherical hinge (9). The motion platform of the present invention can realize three-dimensional movement and one-dimensional rotation in space, and a rotation degree of freedom can be connected in series on the motion platform or a workbench to realize five-degree-of-freedom motion of three-dimensional movement and two-dimensional rotation in space, which can completely replace the traditional The tandem multi-axis machine tool and six-degree-of-freedom parallel machine tool are used to realize the processing of space-complex curved surface parts.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
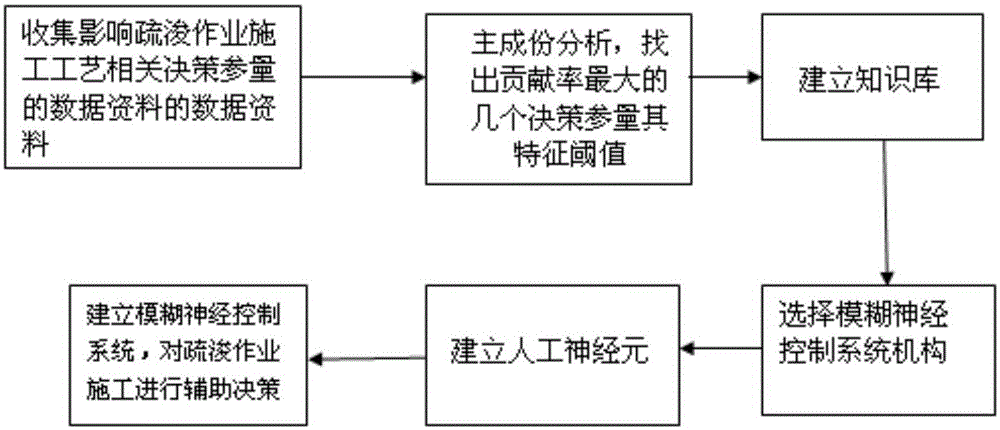
Dredging process intelligent decision analysis method based on fuzzy neural control system
InactiveCN105045091AHigh degree of automationAdaptableAdaptive controlNerve networkPrincipal component analysis
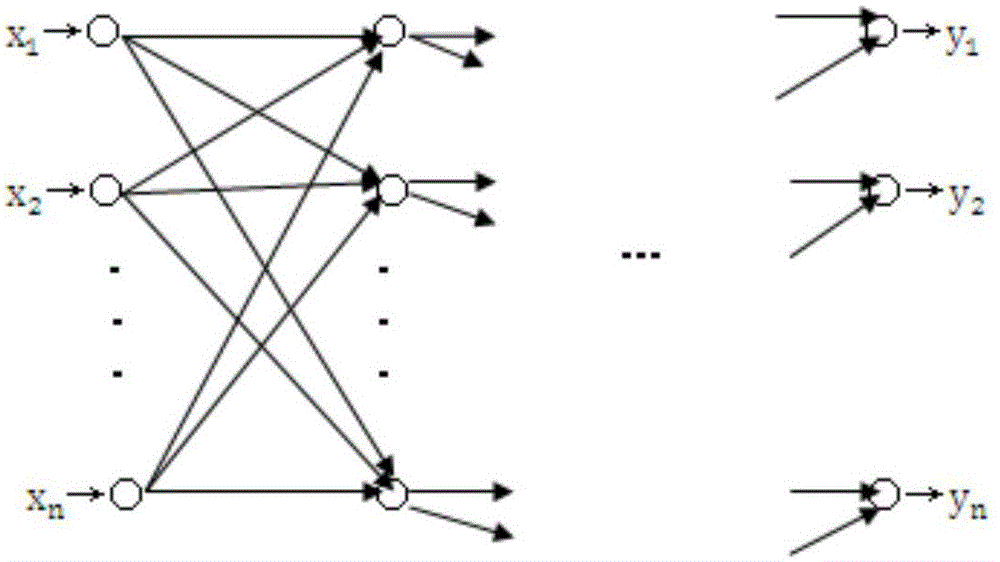
The invention discloses a dredging process intelligent decision analysis method based on a fuzzy neural control system. The method comprises the steps that 1, data influencing related decision parameters of a dredging construction technology are collected; 2, a matlab principal component analysis method is used to find out the feature thresholds of several decision parameters with the maximum contribution rate; 3, a knowledge base is established; 4, a fuzzy neural control system mechanism is selected and artificial neurons are established, and the number of hidden layers of a neural network is determined according to the dredging complexity; and 5, the fuzzy neural control system is established to carry out assisted decision on dredging construction. According to the invention, the space complexity of the neural network and fuzzy control time complexity are fused, so that the degree of dredging automation is high.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
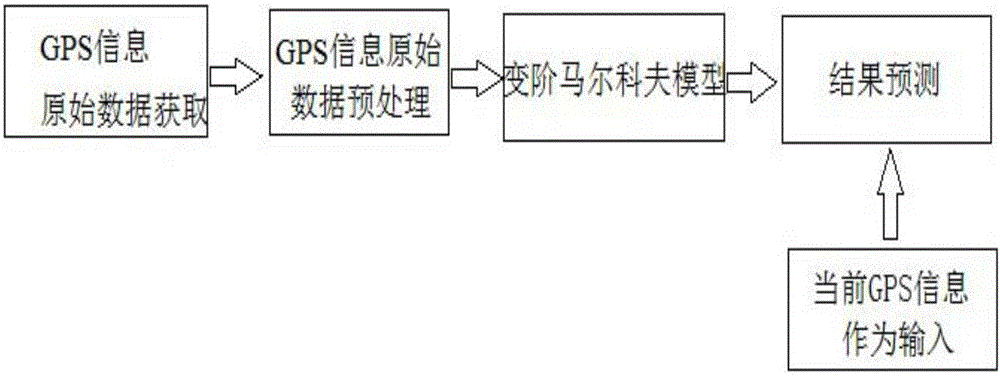
Destination identification method for plug-in type hybrid vehicle
The invention discloses a destination identification method for a plug-in type hybrid vehicle, comprising the steps of obtaining vehicle running state data; and identifying a destination based on a variable-order Markov model. When a destination is not set, the method effectively abstracts the driving habits and rules of a driver according to GPS historic traveling track data, forecasts a destination greater than a confidence coefficient threshold and a path node sequence to the destination, and further estimates the whole vehicle energy consumption of each path node; the method lays the foundation for energy management strategy global optimization, is conductive to increasing automobile dynamic property and economical efficiency, and accords with the energy saving and environmental protection themes of current automobile development. The method uses a PMM algorithm to reduce the space complexity and calculated quantity of a prediction model and a zero frequency problem, utilizes the variable-order Markov model to match automobile historic and current multi-source data, can more flexibly and more accurately predict a destination node and journey sequence, and is of great significance for the intelligent vehicle technology.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Content classification for multimedia processing
InactiveCN101697591APulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital video signal modificationSample complexityAudio frequency
The invention relates to an content classification for multimedia processing. An apparatus and method for processing multimedia data, such as, for example, video data, audio data, or both video and audio data for encoding utilizing a determined content classification is claimed. Processing the multimedia data includes determining complexity of multimedia data, classifying the multimedia data based on the determined complexity, and, determining a bit rate for encoding the multimedia data based on its classification. The complexity can include a spatial complexity component and a temporal complexity component of the multimedia data. The multimedia data is classified using content classifications, which are based on a visual quality value for viewing multimedia data, using the spatial complexity, the temporal complexity, or both the spatial complexity and temporal complexity.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
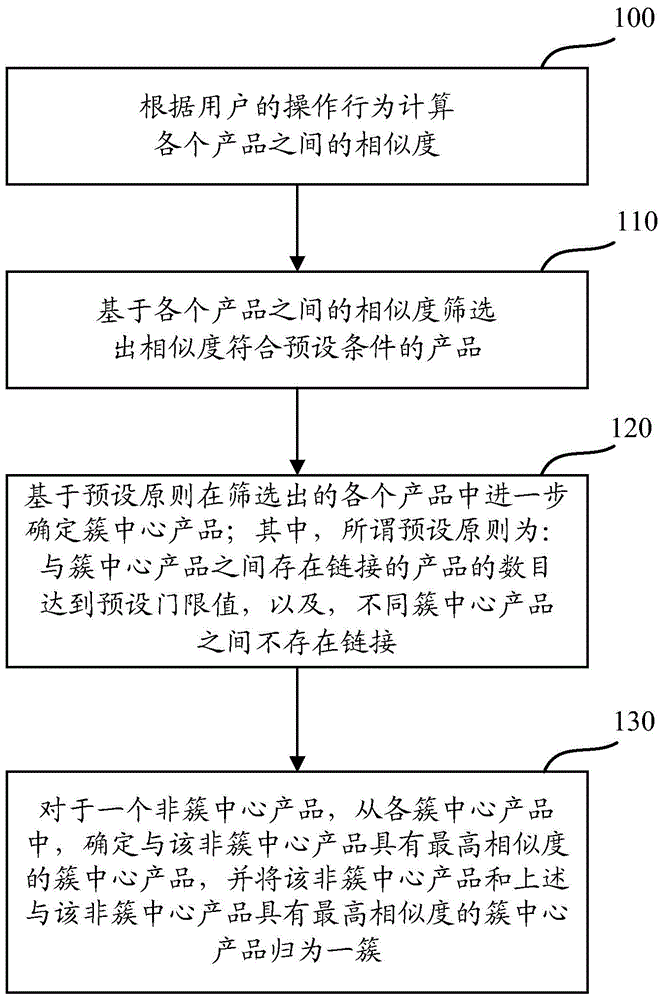
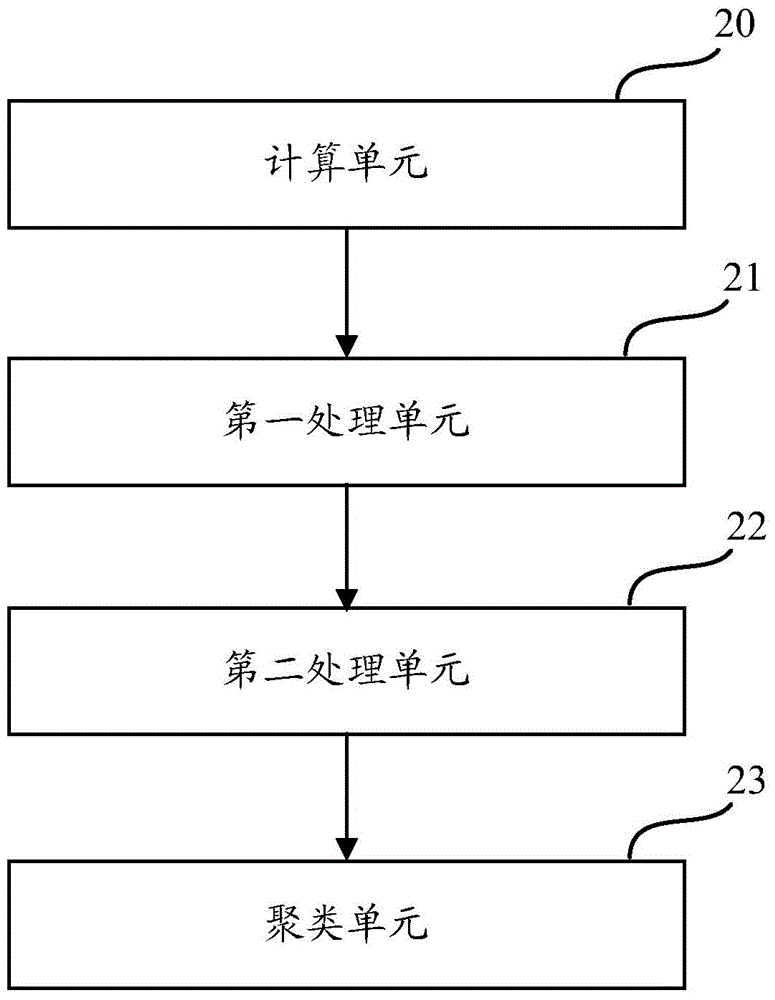
Product clustering method and apparatus
ActiveCN105335368AImprove accuracyReduce time complexityCommerceSpecial data processing applicationsProduct baseE-commerce
The present application relates to electronic commerce technology, and particularly relates to a product clustering method and apparatus. The method comprises: based on similarity between products, sorting out products with similarity meeting a preset condition; determining cluster center products among the sorted out products based on a preset principle; and based on each cluster center product, classifying each non-cluster center product to a same cluster as a cluster center product with highest similarity to the non-cluster center product. The above method is not limited by the number of clusters, the product similarity needs to be calculated only once to construct a similarity network and achieve product clustering progressively based on a heuristic algorithm. In this way, not only the accuracy of the clustering result can be significantly improved, but also time complexity and spatial complexity of the product clustering can be greatly reduced, thus preventing a heavy operation load from being caused to a system and controlling the implementation cost within an ideal range. The method and apparatus are particularly applicable to large-scale product clustering.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
Method for propylea japonica indoor raising
The invention relates to a method for large-quantity propylea japonica indoor raising. Wheat aphids, melanaphis sacchari and corn leaf aphids are used as aphids for feeding propylea japonica, and through specific technical measures such as host young aphid cultivating, aphid expanding propagation and propylea japonica artificial feeding, a large quantity of field-preventing and indoor-theory-study propylea japonica is obtained by expanding propagation. According to the method, wheat aphid feeding is carried out at a larval phase, and wheat aphid, melanaphis sacchari and corn leaf aphid feeding is carried out at an adult spawning period. The nutritional requirements of propylea japonica are improved, and the fecundity of propylea japonica is greatly improved. During raising, corn seedlings are placed, the habitat of propylea japonica is enlarged, space complexity is improved, propylea japonica autotomy and competition are lowered, and raising density can be greatly improved. The method is summarized according to the habit of propylea japonica and is easy to operate, economical and practical. Propylea japonica obtained by expanding propagation is high in survival rate and high in fecundity, and large-scale artificial breeding of propylea japonica can be achieved.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Automatic discovery method of complex system oriented MAXQ task graph structure
ActiveCN102521202ATroubleshoot auto-tiering issuesAutomatic layering implementationDigital computer detailsElectric digital data processingCluster algorithmAlgorithm
The invention provides an automatic discovery method of a complex system oriented MAXQ task graph structure. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly searching state variables influencing actions by adopting a Q-learning exploration environment; then scheduling a clustering algorithm based on the action execution effect, wherein the policy uses a data object as one atomic class, and the atomic classes are aggregated; gradually aggregating the atomic classes to a crescent class until the end condition is met; the process of an aggregation algorithm is as follows: forming a single cluster by each member in the beginning, and combining the adjacent clusters into one cluster in the later iterative process until all the members form one cluster, wherein the time and space complexities are O (n2); combining two clusters through a clustering method, which cannot be separated to the prior state; and (3) obtaining a hierarchical task graph. The method establishes a clustering model by using all learned and perceived information, and automatically constructs the MAXQ task graph through clustering and finally realizes automatic hierarchy of the MAXQ.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Rule-based stream data processing method and unified monitoring platform
InactiveCN107943482ASolve technical problems with narrow adaptabilityImprove scalabilityHardware monitoringSpecial data processing applicationsStreaming dataTime complexity
The invention provides a rule-based stream data processing method and a rule-based stream data unified monitoring platform. A distributed stream processing framework can be adapted; and rules are dynamically identified, loaded, compiled and sent to a distributed environment, so that matching data is dynamically generated. For complex data and varied business demands, a data generation mode of one-time deployment and flexible rule addition is proposed, and a one-stop data processing platform integrating distributed processing, stream processing, regularization and monitoring is provided, so that the development cost is reduced, the learning difficulty is lowered, and the spatial complexity and the time complexity of data processing are greatly lowered.
Owner:QIANXUN SPATIAL INTELLIGENCE INC
Spatial sound reproduction
InactiveUS9282417B2Promote reproductionImprove experiencePseudo-stereo systemsStereophonic broadcast receivingVocal tractLoudspeaker
An apparatus for spatial sound reproduction comprises a receiver (101) for receiving a multi-channel audio signal. An analyzer (107) determines a spatial property of the multi-channel audio signal, such as a spatial complexity or organization. A selection processor (109) then selects a reproduction mode from a plurality of sound reproduction modes where the multi-channel sound reproduction modes employ different spatial rendering techniques. A reproduction circuit (103) then drives a set of loudspeakers (105) to reproduce the multi-channel audio signal using the selected reproduction mode. The switching between the reproduction modes may be fast (e.g. in the order of 100 ms to 10 secs) thereby allowing a short term adaptation of the reproduction mode to the signal characteristics. The approach may in particular provide an improved spatial experience to a listener.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
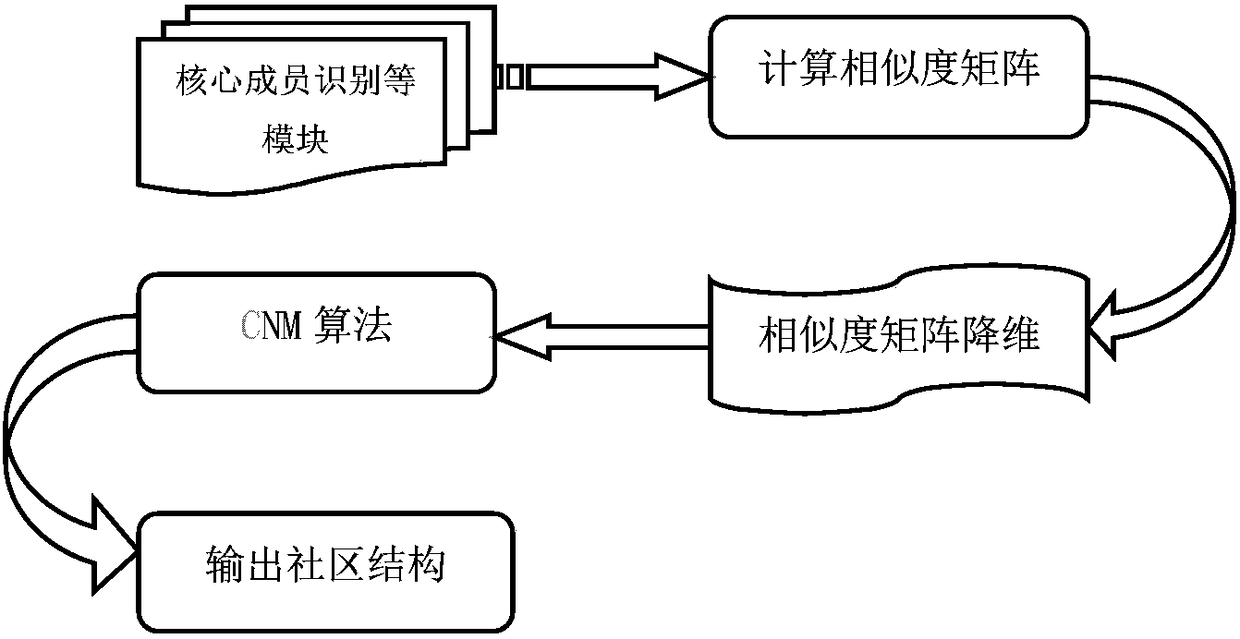
Core member identification-based community discovery method
InactiveCN108268603AReduce wasted timeReduce space complexityData miningWebsite content managementNODALAlgorithm
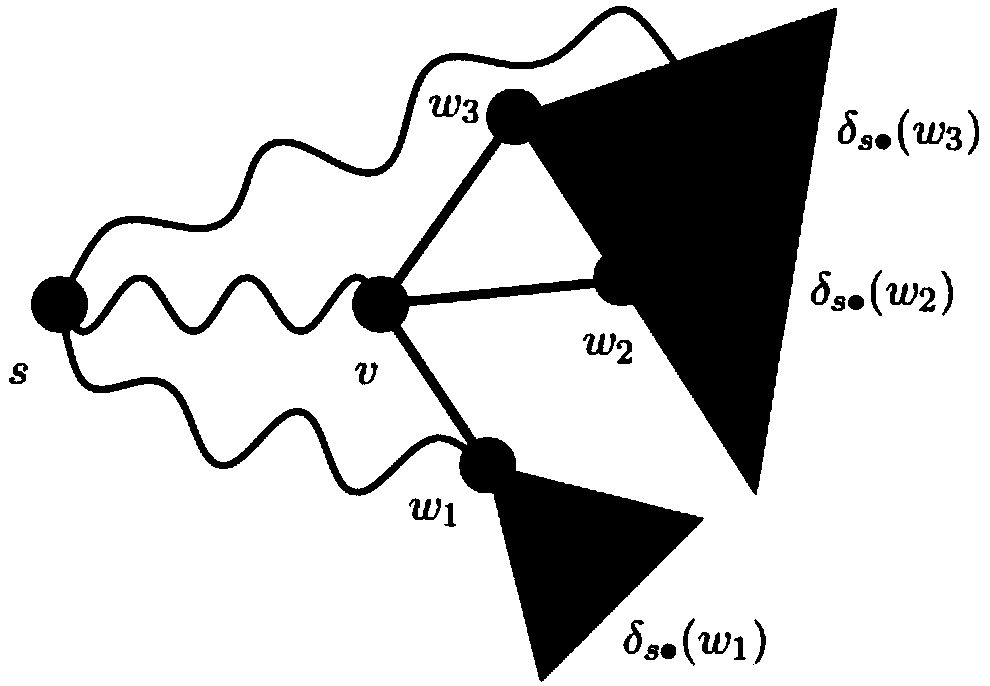
The invention discloses a core member identification-based community discovery method. The method comprises the following steps of firstly performing node betweenness center value-based core member identification on nodes in a network, then performing initial clustering, and forming an initial social network structure according to the effects of the nodes in the network; and secondly regarding aninitially clustered node as a node, performing dimension reduction on a similarity matrix M among the nodes to form a new similarity matrix M', and replacing a modularity increment matrix to serve asan input of a CNM algorithm. The core member identification provides a condition for the initial clustering; and the matrix scale can be reduced through the dimension reduction when the similarity among the nodes is calculated, so that the algorithm loss time is shortened. The core member identification algorithm adopts a breadth-first search-based quick betweenness centrality calculation method,and the spatial complexity and the practical complexity of the core member identification algorithm are both lower than those of a conventional algorithm, so that important members in a community network can be quickly located and reasonable division of a social network structure is facilitated.
Owner:NO 30 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP
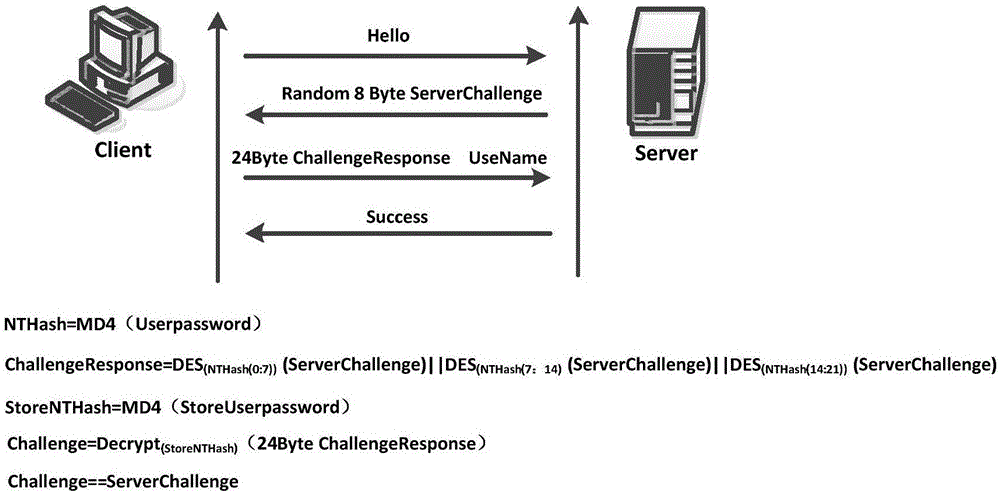
High-speed analysis and recovering method for VPN encrypted channel
InactiveCN106789524AAuthentication aggressivenessVerify validityNetworks interconnectionDecoding methodsData link layer
The invention discloses a high-speed analysis and recovering method for a VPN encrypted channel. The method comprises the steps of high-speed analysis and recovering of a PPTP encrypted channel; high-speed analysis and recovering of an L2TP encrypted channel; and high-speed analysis and recovering of an IPSec active mode channel.The method starts from the bottom-layer protocol of the VPN channel, data link layer and network layer protocols of the VPN are emphatically studied, the security mechanism of the protocol is analyzed, unsafe points during an authentication interaction process and an encrypted transmission process are found, then an analysis and decoding method for the VPN encrypted channel is provided, and sensitive information on the VPN encrypted channel is further recovered in real time. The high performance computation technology in the method can effectively improve the decoding speed, reduces attack time and spatial complexity of encryption algorithms such as RC4 and DES in the VON, and enlarges categories of cracking algorithms by integrating Hashcat source codes.
Owner:NO 30 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP
Non-instructive video quality measurement
This invention is concerned with a video quality measurement method, in particular where the video signal having: an original form; encoded form in which video signal has been encoded using a compression algorithm utilising a variable quantiser step size such that the encoded signal includes a quantiser step size parameter; and, a decoded form in which the encoded video signal has been at least in part reconverted to the original form. The method comprises the steps of: a) generating a first quality measure which is a function of said quantiser step size parameter; b) generating a second quality measure which is a function of the spatial complexity of the frames represented by the video signal in the decoded form; and, c) combining the first and second measures.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Distributed Qos multicast routing method based on information entropy in Ad Hoc network
InactiveCN1731763AReduce overheadImprove transmission performanceData switching networksRound complexityTime complexity
This invention relates to a distributing Qos multi-case route method based on information entropy in Ad Hoc net, which comprises the following steps: a, determining net model of QoS constraint multi-case method; b, determining information of net state; c, determining the metric of information entropy; d, determining circuit-testing method; f, analyzing space and time complexity. The invention is based on the space and time complexity of information entropy and choosing route in distribution way, which makes the route have better Expandable ability, stability, long life, and be applied in larger scale Ad Hoc net.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for acquiring a plurality of reliable communication paths based on field intensity in multi-layer wireless network
ActiveCN104093182AReduce the number of timesReduce computationHigh level techniquesWireless communicationShort path algorithmRadio frequency signal
The invention relates to a method for acquiring a plurality of reliable communication paths based on the field intensity in a multi-layer wireless network, and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication. First, each node of a wireless network receives radio frequency signals sent by other nodes and acquires neighbor field intensity information; a forward optimal path set and a forward optimal path from a source node to a destination node are acquired through calculation by use of a multi-point shortest path algorithm; a reverse optimal path set and a reverse optimal path from the destination node to the source node are acquired through calculation by use of a multi-point optimal path algorithm; sub-optimal paths are worked out based on a forward optimal path weight and a reverse optimal path weight; and a plurality of optimal paths of the wireless network are determined by testing the optimal paths and the sub-optimal paths. The amount of calculation and the spatial complexity in the process of optimal path acquiring are reduced, the energy consumption of a system is reduced, and the communication reliability of the wireless network is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN NEOWAY TECH
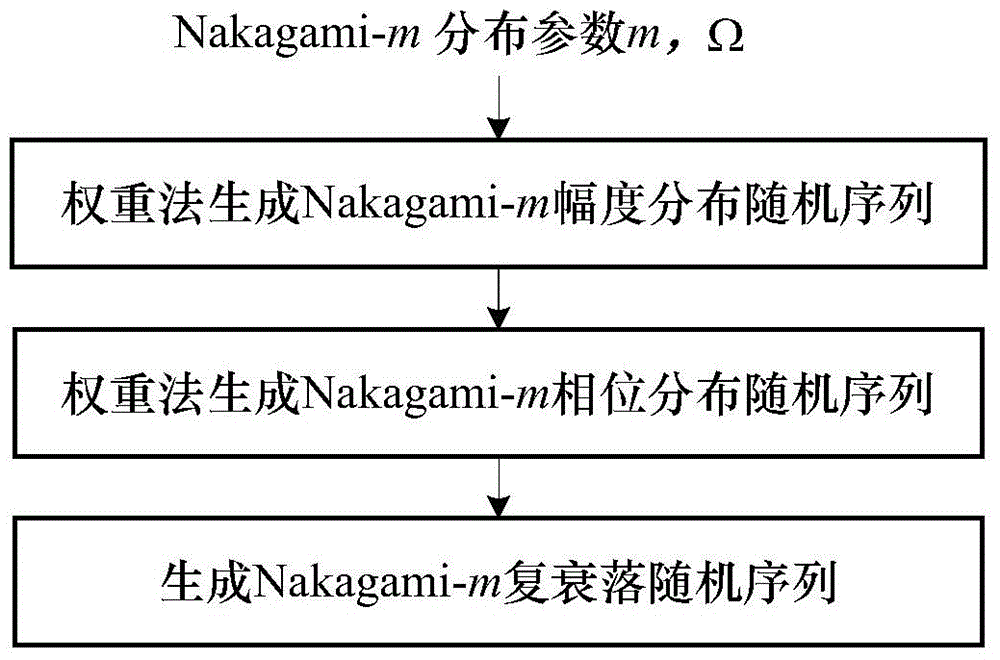
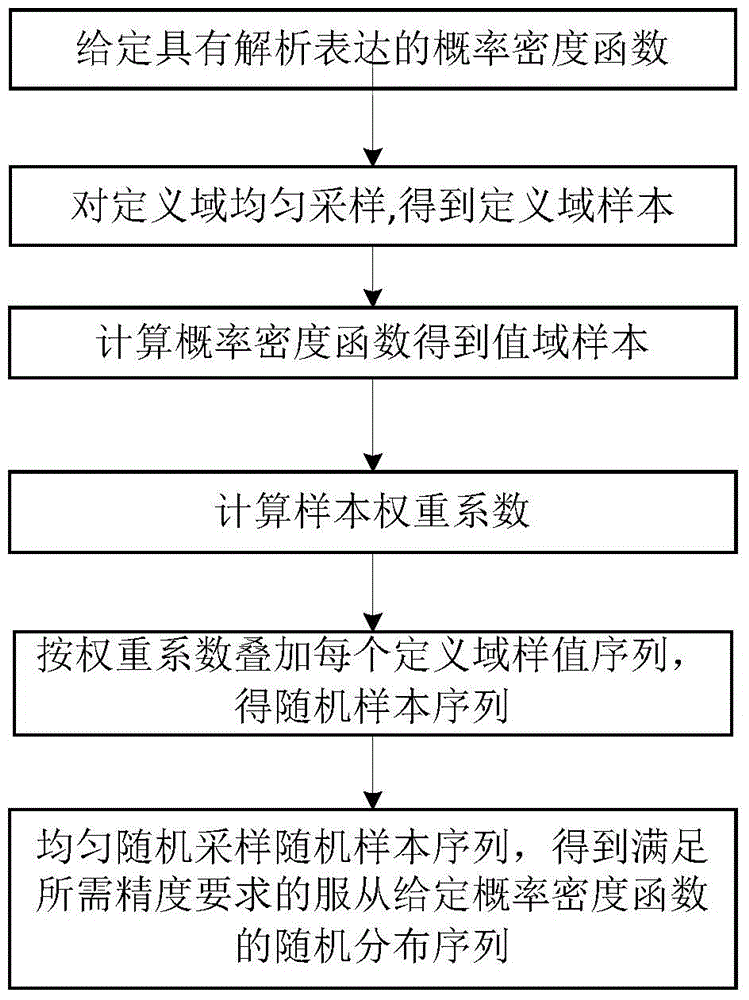
Weight method-based generation method of complex Nakagami-m fading random sequences
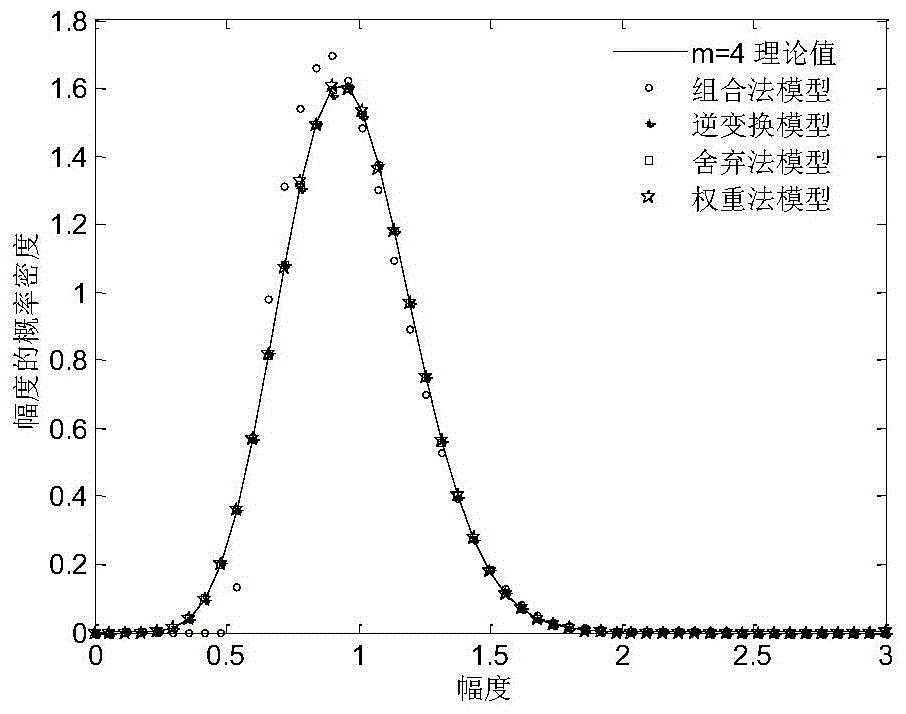
InactiveCN104881267AAvoid errorsImprove versatilityRandom number generatorsSequence pointAnalytical expressions
A weight method-based generation method of complex Nakagami-m fading random sequences includes: according to Nakagami-m fading amplitude and a phase fading distribution function, generating an amplitude random sequence and a phase random sequence by the weight method, and generating a complex random sequence via the amplitude random sequence and the phase random sequence. The method has the advantages that time efficiency and simulation precision are gained via low spatial complexity, generation is achieved by adjusting the number of sample value sampling points and the number of target sequence points according to the need for actual simulation, errors caused by interpolation by the other methods having high precision demands can be avoided, the method is available for the actual simulation of generation of random sequences of any distribution functions having analytical expressions, and the method is of high universality.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Cyclic update mode-based decision tree construction method
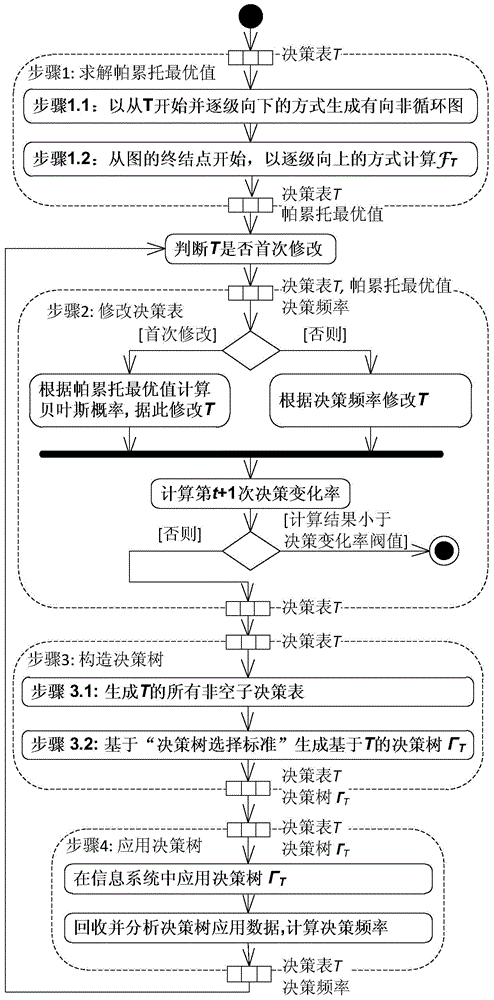
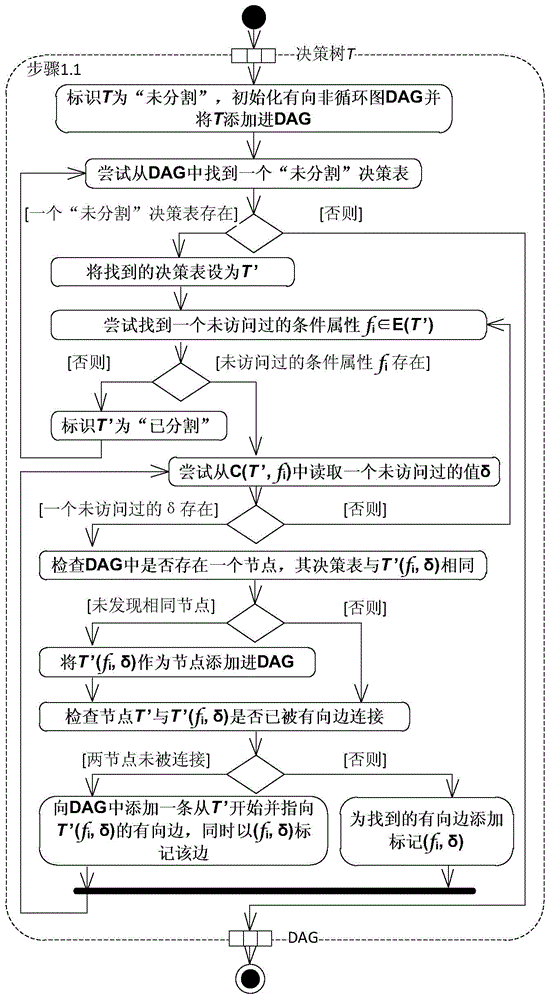
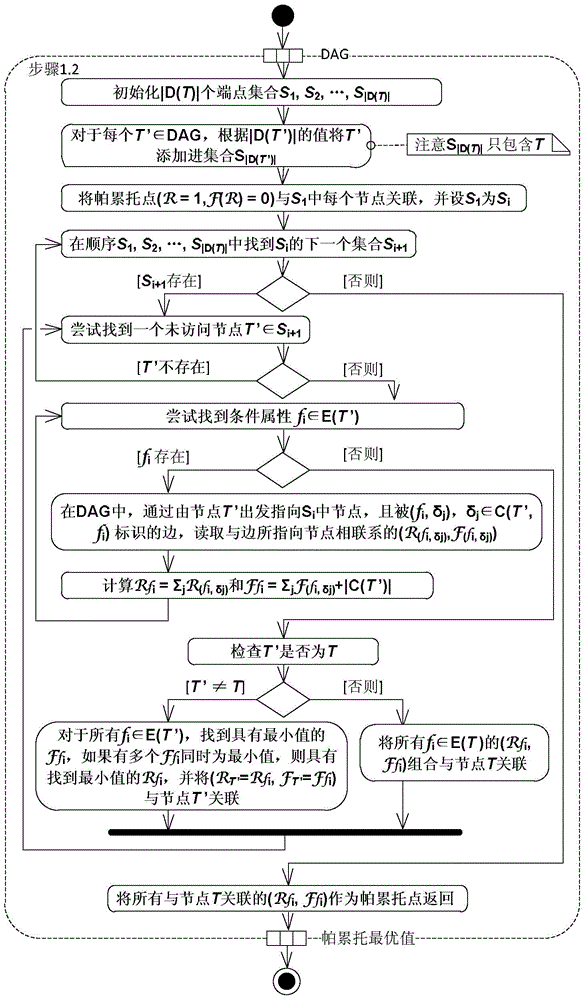
InactiveCN104866314AEfficient automatic decision-making functionSpecific program execution arrangementsDecision tableBayesian probability
The present invention relates to a cyclic update mode-based decision tree construction method. The method comprises: calculating a Bayesian probability by using a target function Pareto optimal value based on time and spatial complexity of the decision tree and the Bayesian theory; modifying a given decision table according to the Bayesian probability; constructing, by using a decision tree selection standard-based calculation method, a decision tree in which a decision table is modified; and applying the decision tree in an information system for automatic decision making, and recording the decision making process. After the system runs for a period of time, a ratio of the automatic decision times of each row in a corresponding decision table to the total decision times of all the rows in the decision table is calculated according to the data of the recorded decision making process, the decision table is modified according to the ratio, a new decision tree of the modified decision table is constructed by using the decision tree selection standard-based calculation method, and the new decision tree is re-applied to the information system. such steps are repeatedly performed until the calculated ratio of each row is less than a decision change probability threshold. The information system employing the technical solution according to the present invention has high-efficiency automatic decision function.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com