Content classification for multimedia processing
A multimedia data, part of the technology, applied in the field of multimedia data processing, can solve problems such as performance changes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example -M
[0045] Encoding example - MPEG
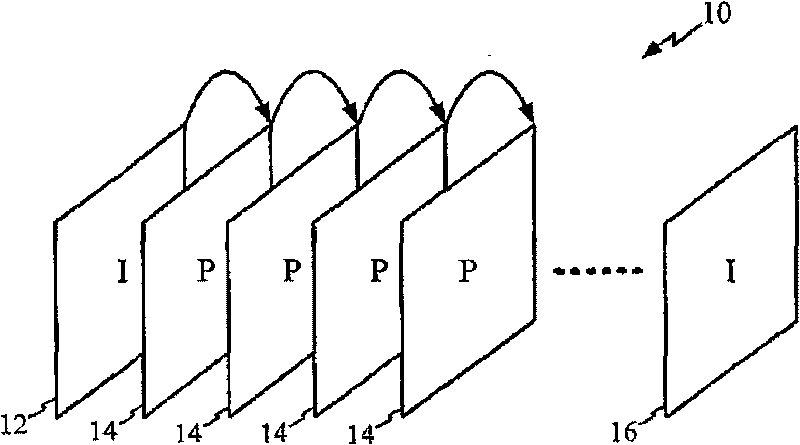
[0046] In a typical MPEG decoder, a block of pixels (e.g., a block including one or more motion vectors and a residual error component) is predictively coded with reference to a reference frame (where an intra frame or another predicted frame can serve as a reference frame) Implement decoding. figure 2 is a diagram illustrating the traditional MPEG-4 Simple Specification data flow, which depicts the frame dependencies of a Group of Pictures (GOP). A GOP 10 consists of an initial I-frame 12 followed by several forward-predicted P-frames 14 . Due to the P-frame's dependency on the previous I or P-frame, the loss of any P-frame 14 may result in the loss of information that may be critical to decoding other P-frames. Loss or elimination of P-frames may result in, for example, video jitter or the decoder not being able to continue decoding until the next I-frame 16 marking the start of the next GOP.
[0047] A P-frame (or any intermediate code...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com