Patents
Literature
30 results about "Platinum silicide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Platinum silicide, also known as platinum monosilicide, is the inorganic compound with the formula PtSi and forms an orthorhombic crystalline structure when synthesized.
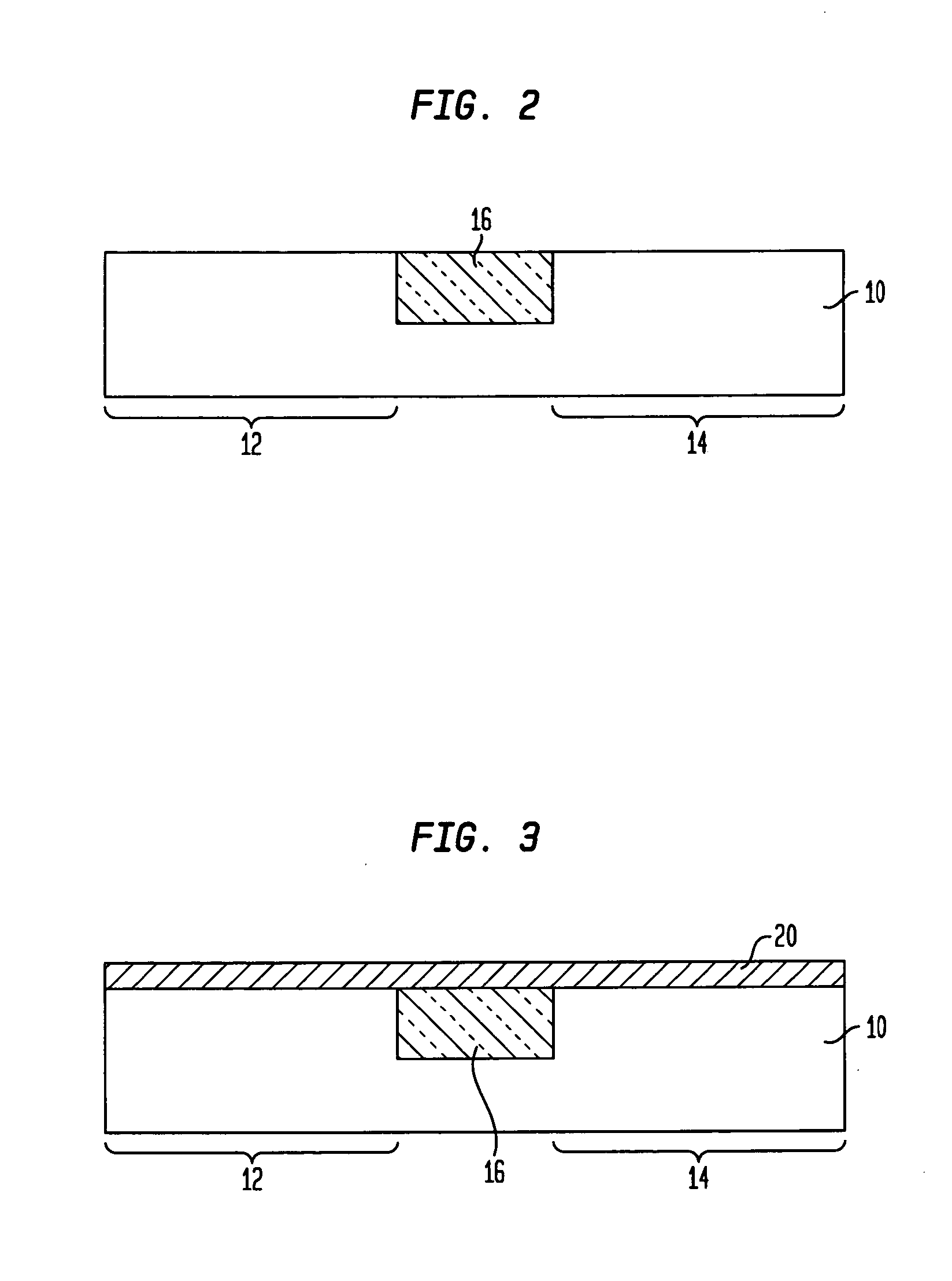
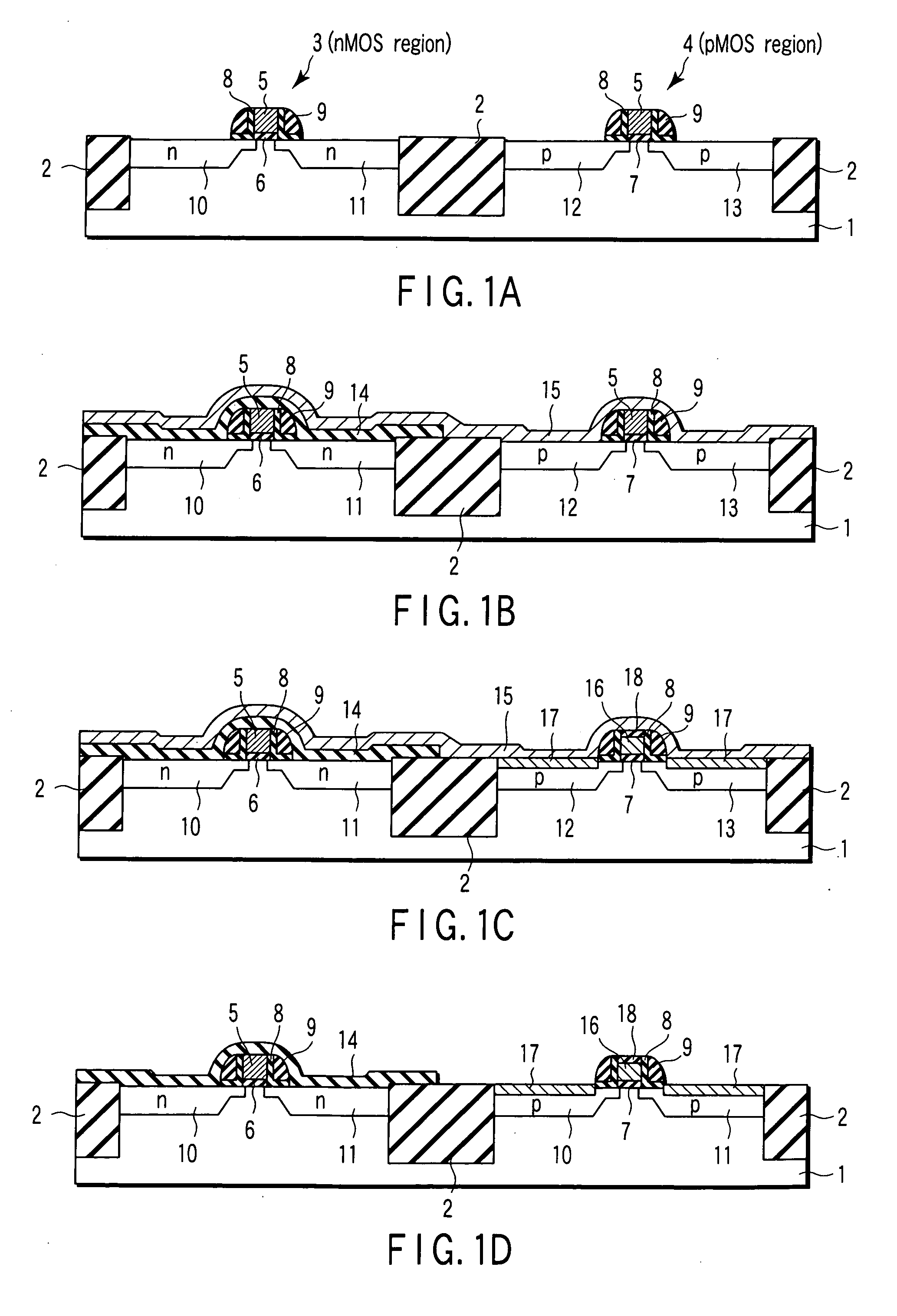
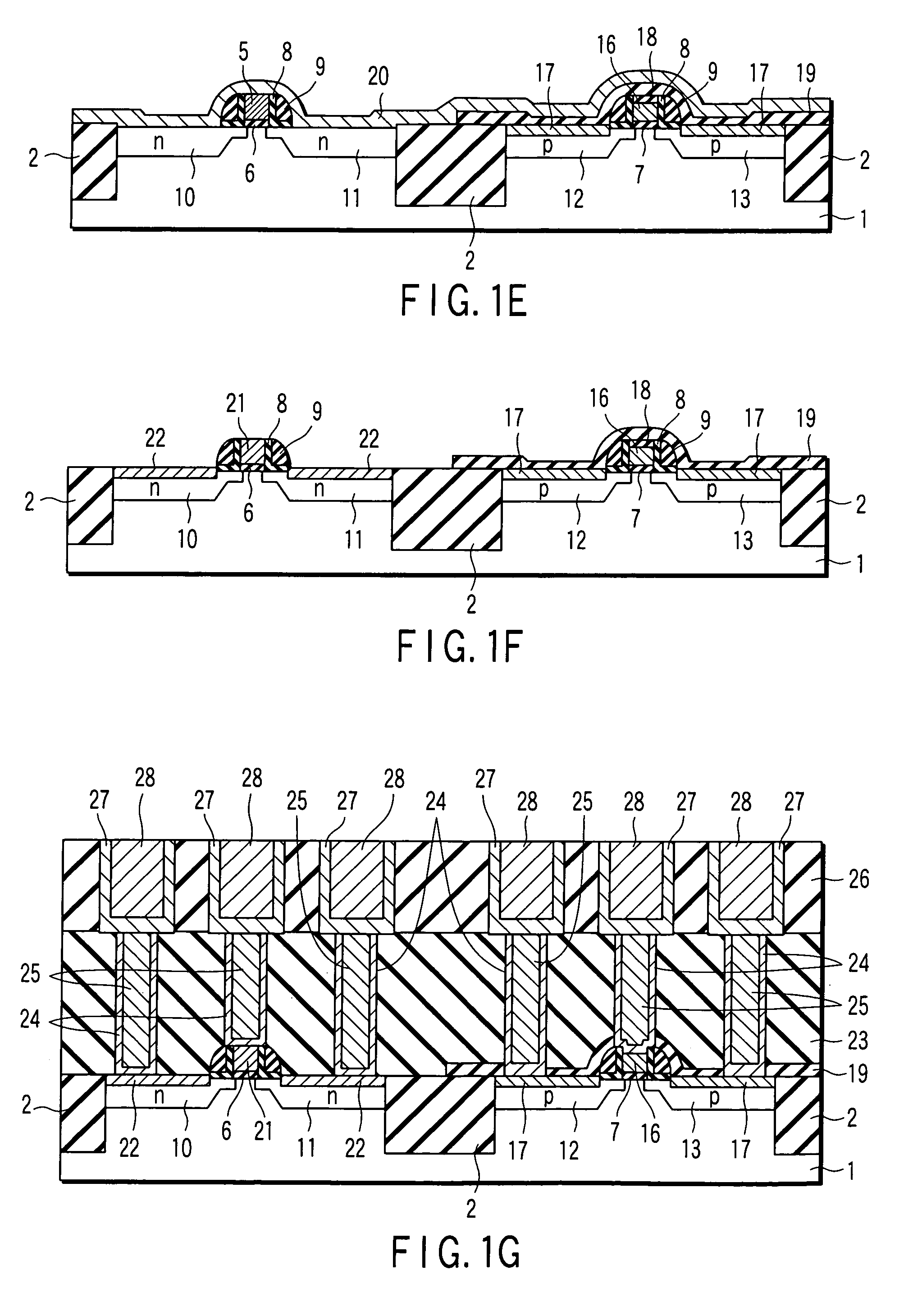
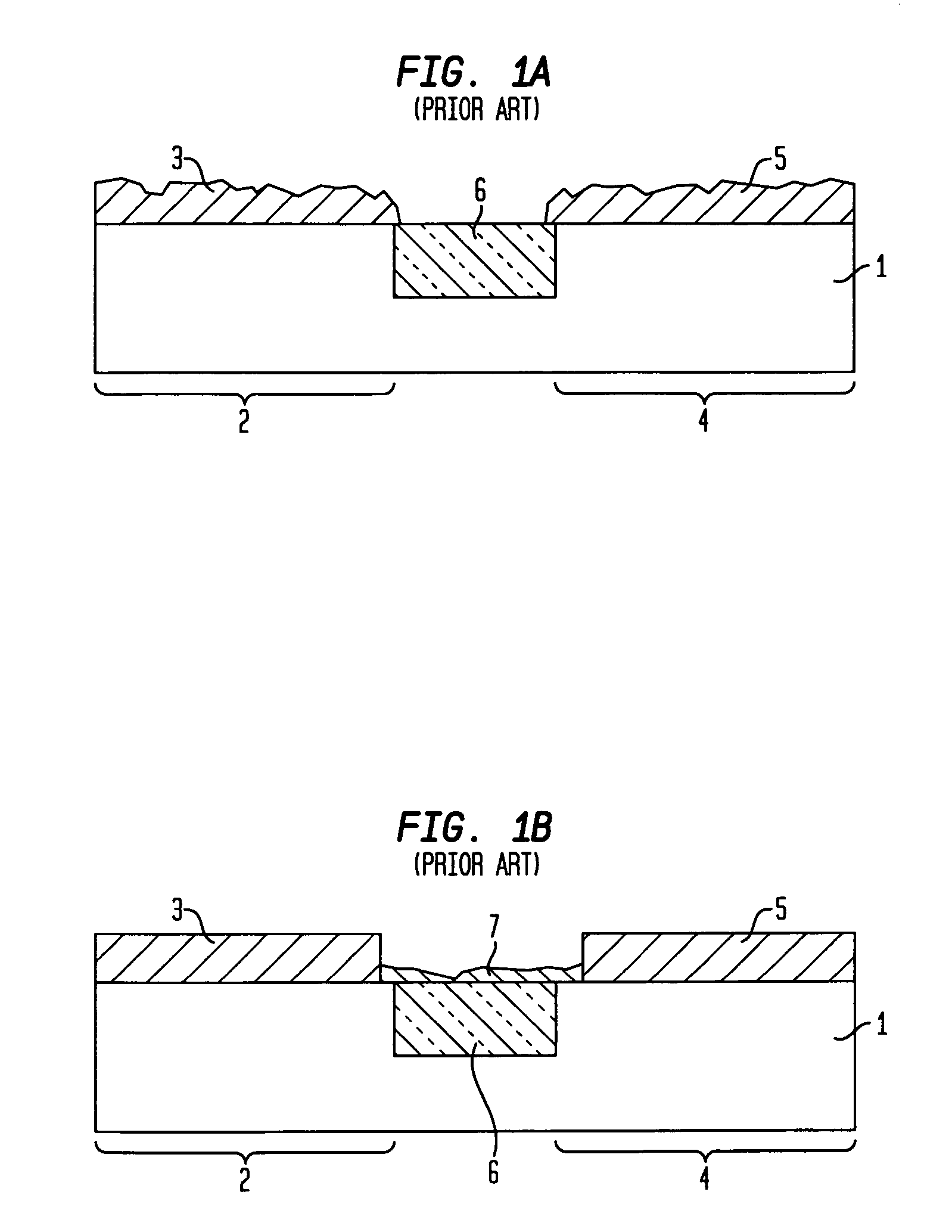
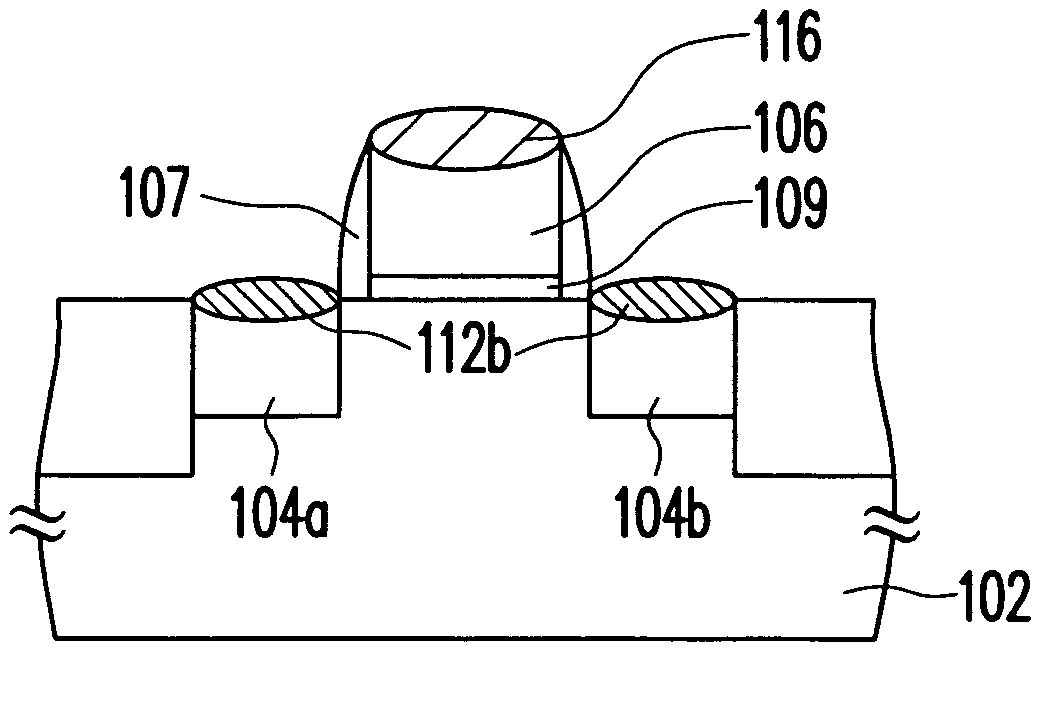
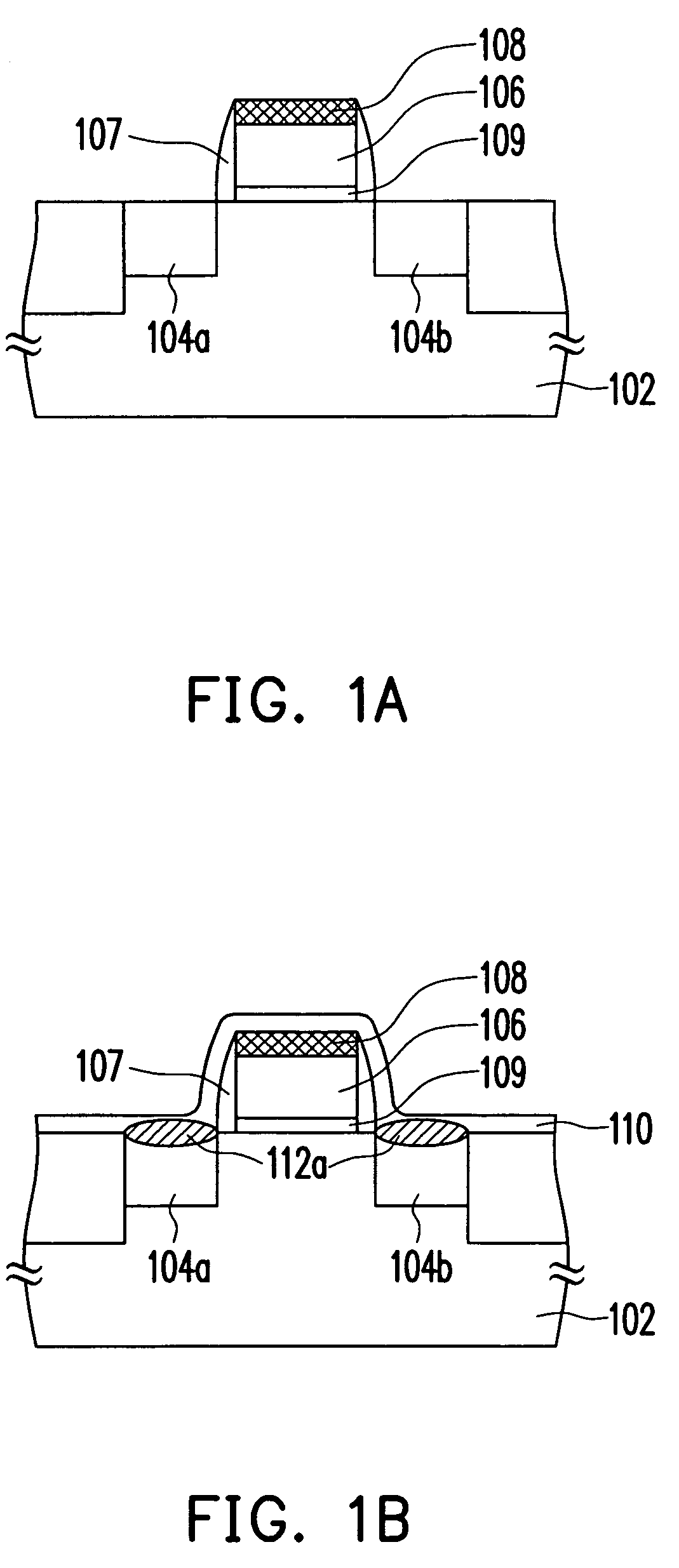
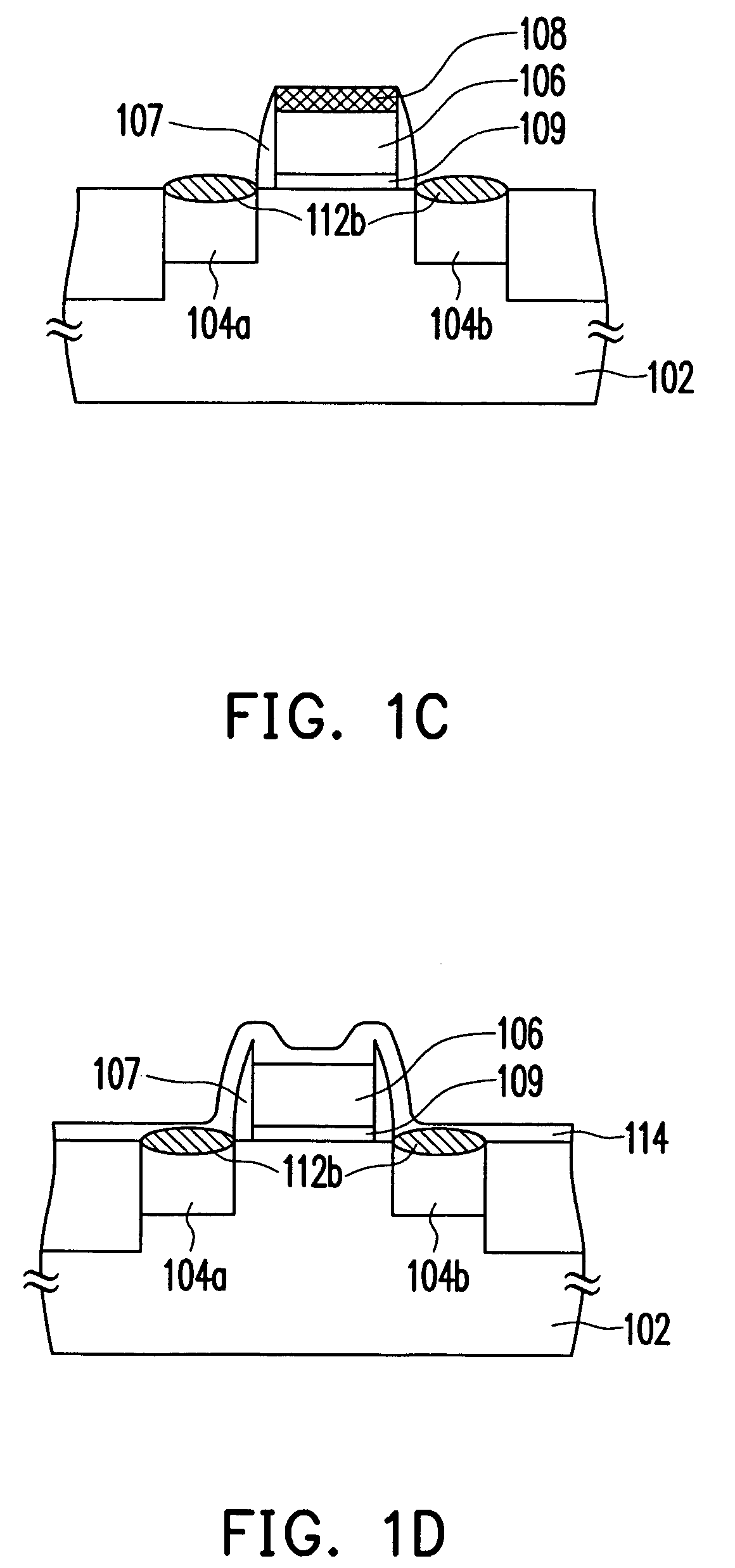
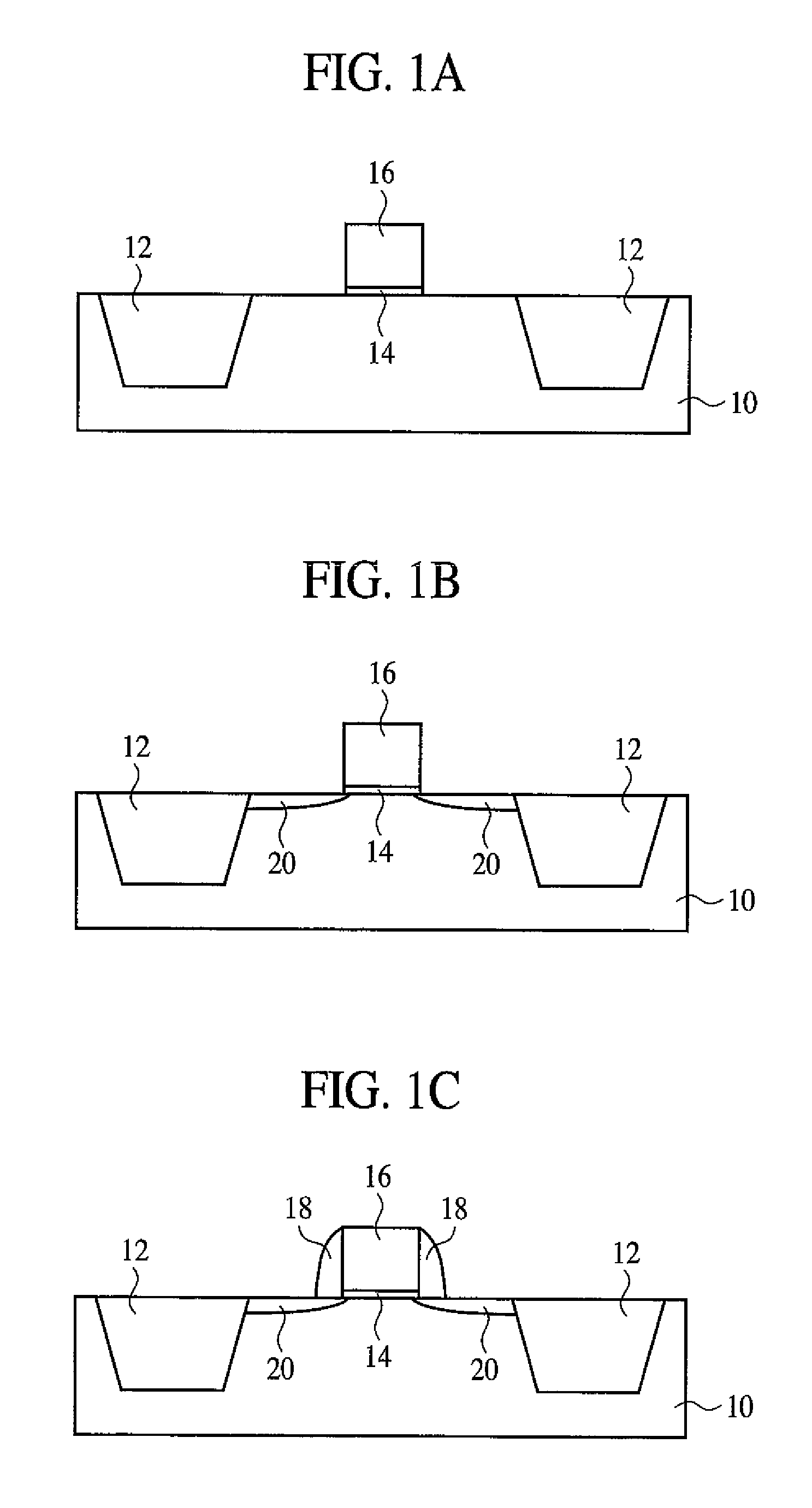
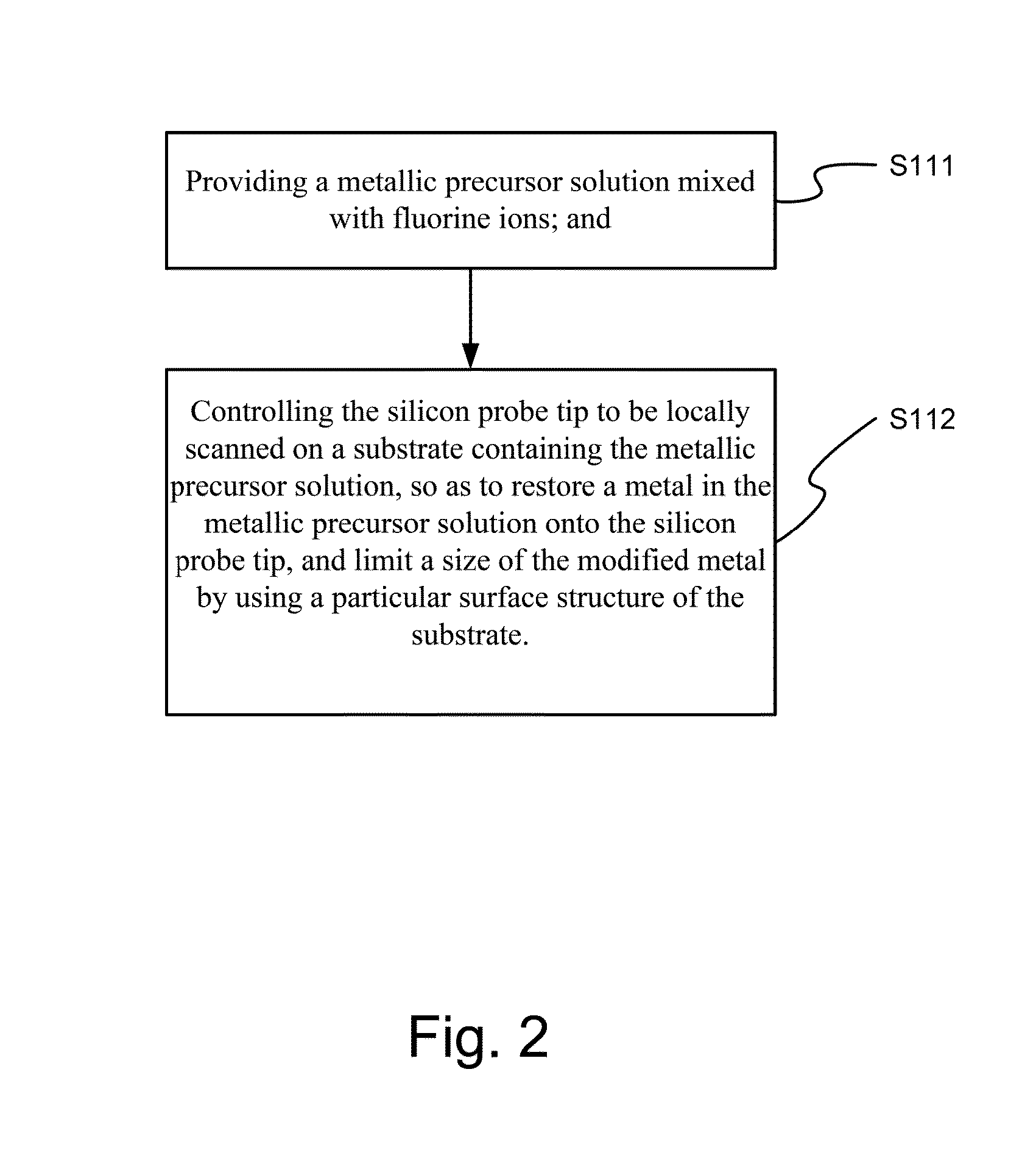
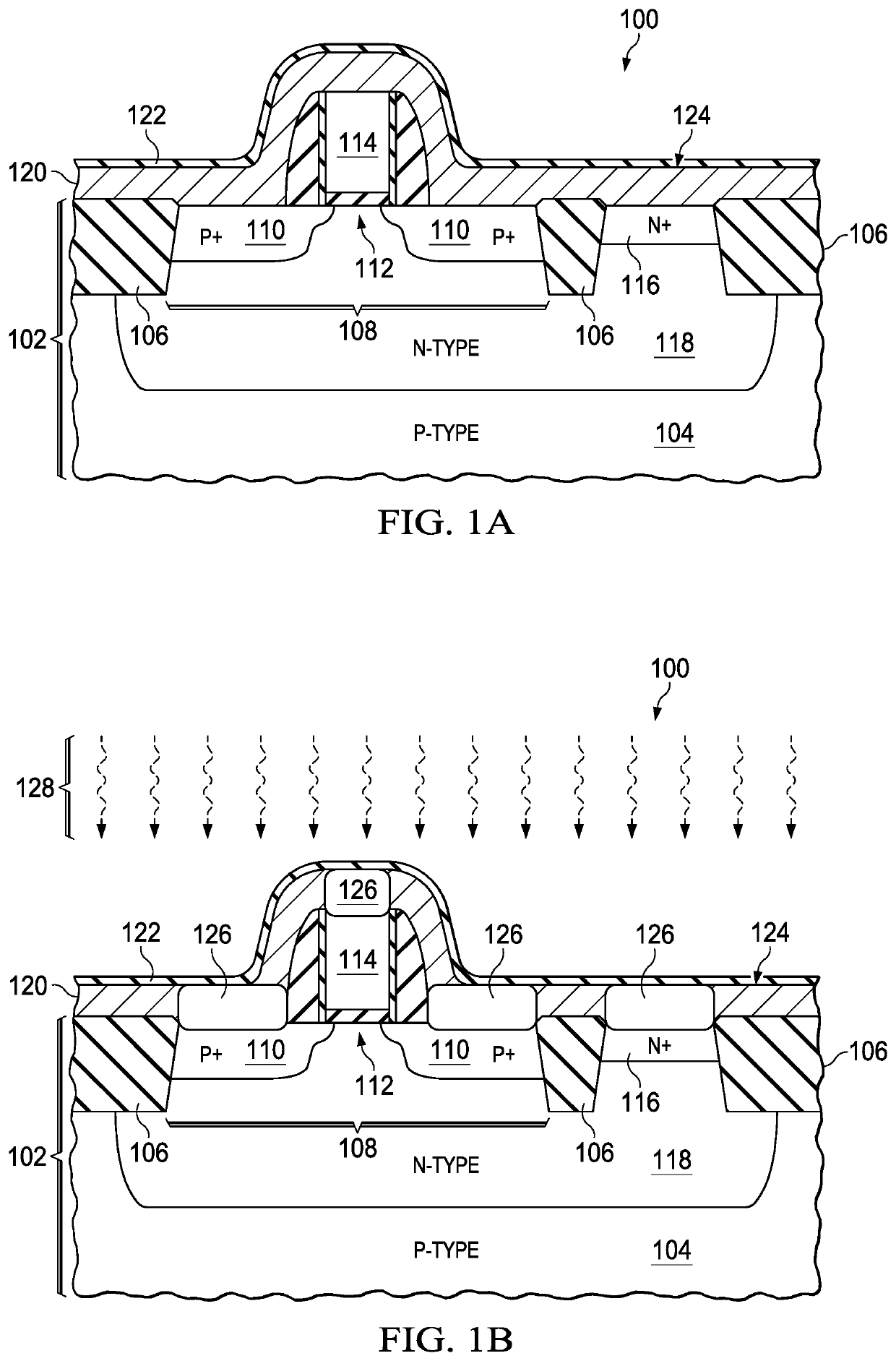
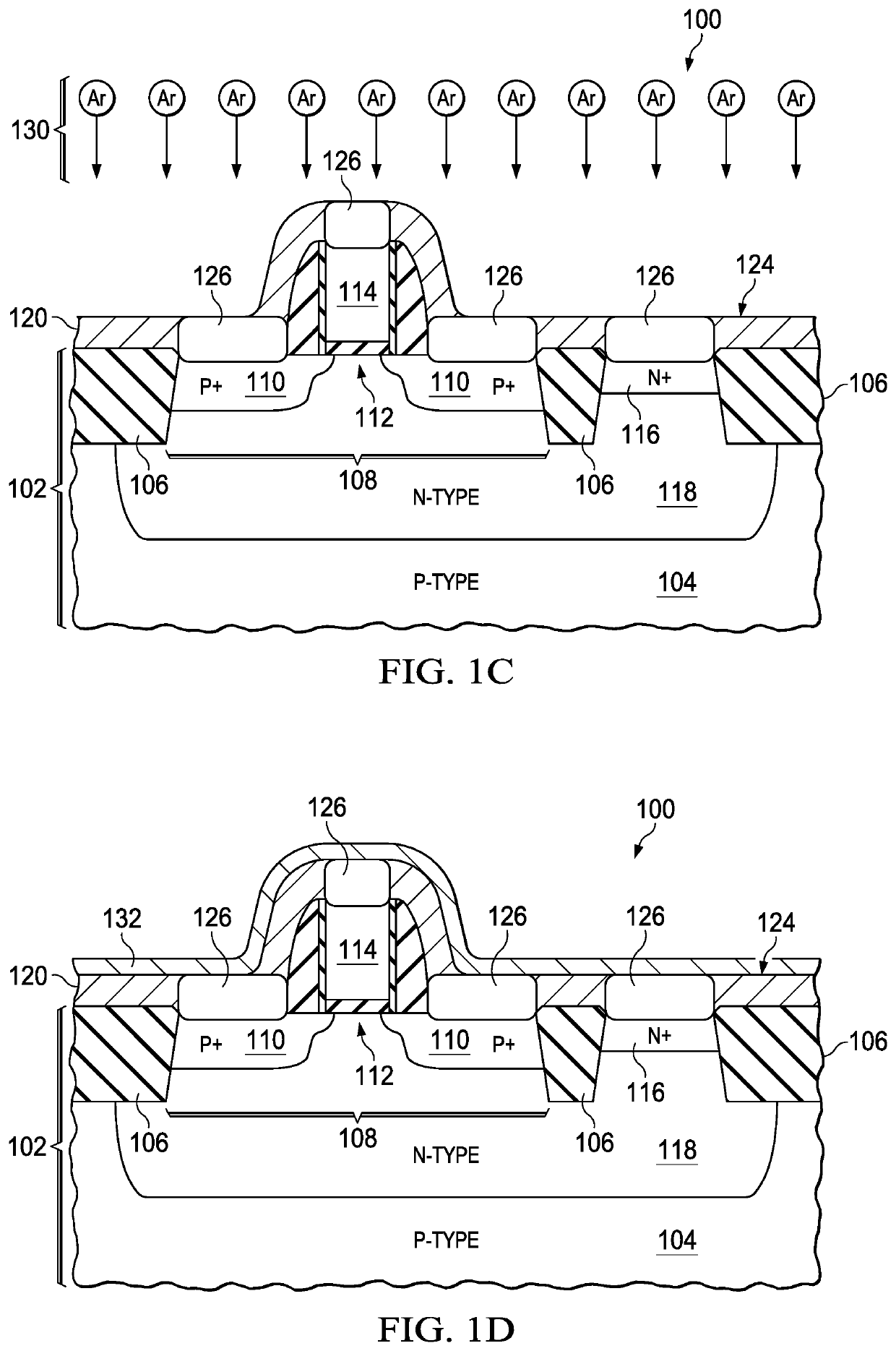
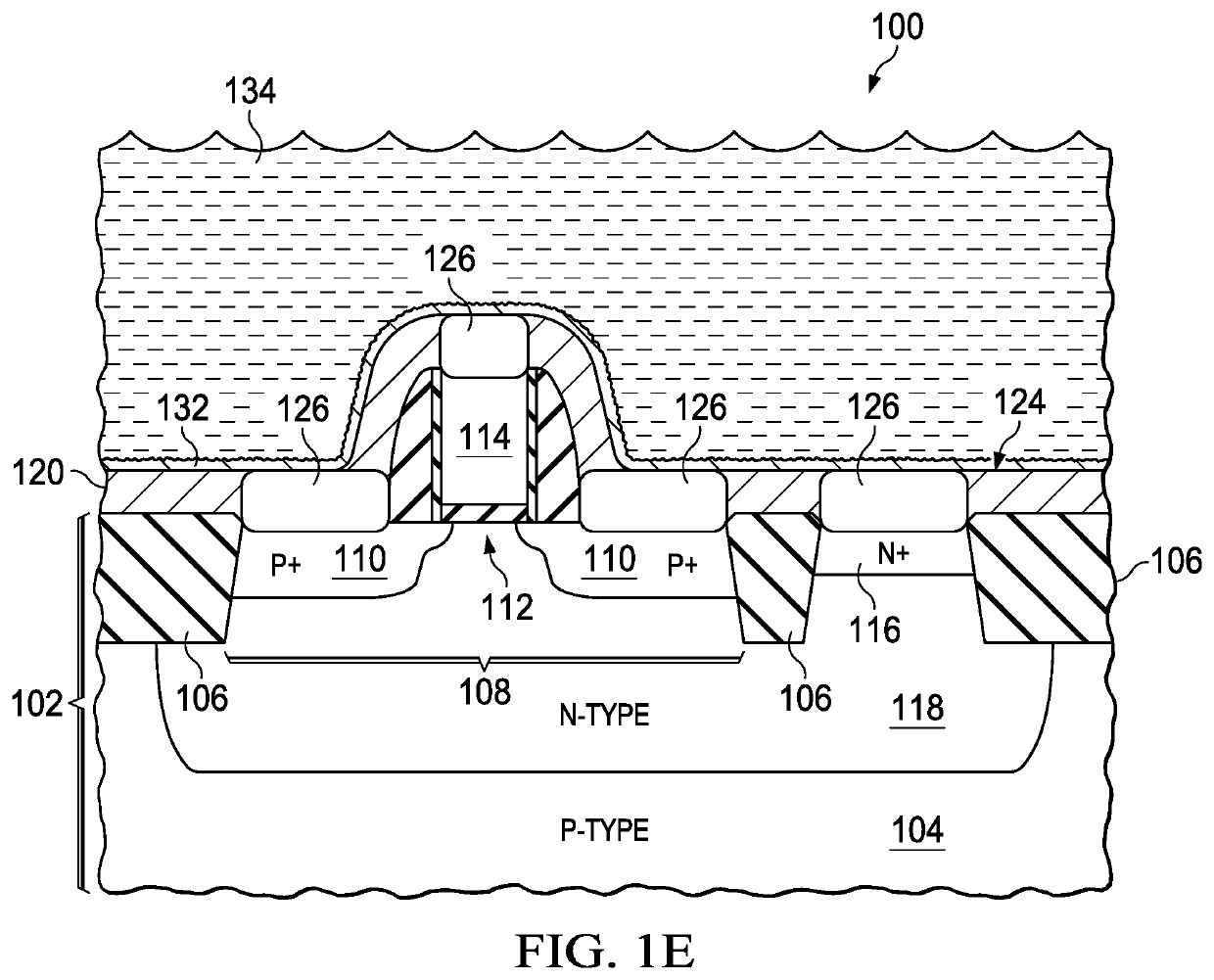
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20080090369A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlatinum silicideDevice material
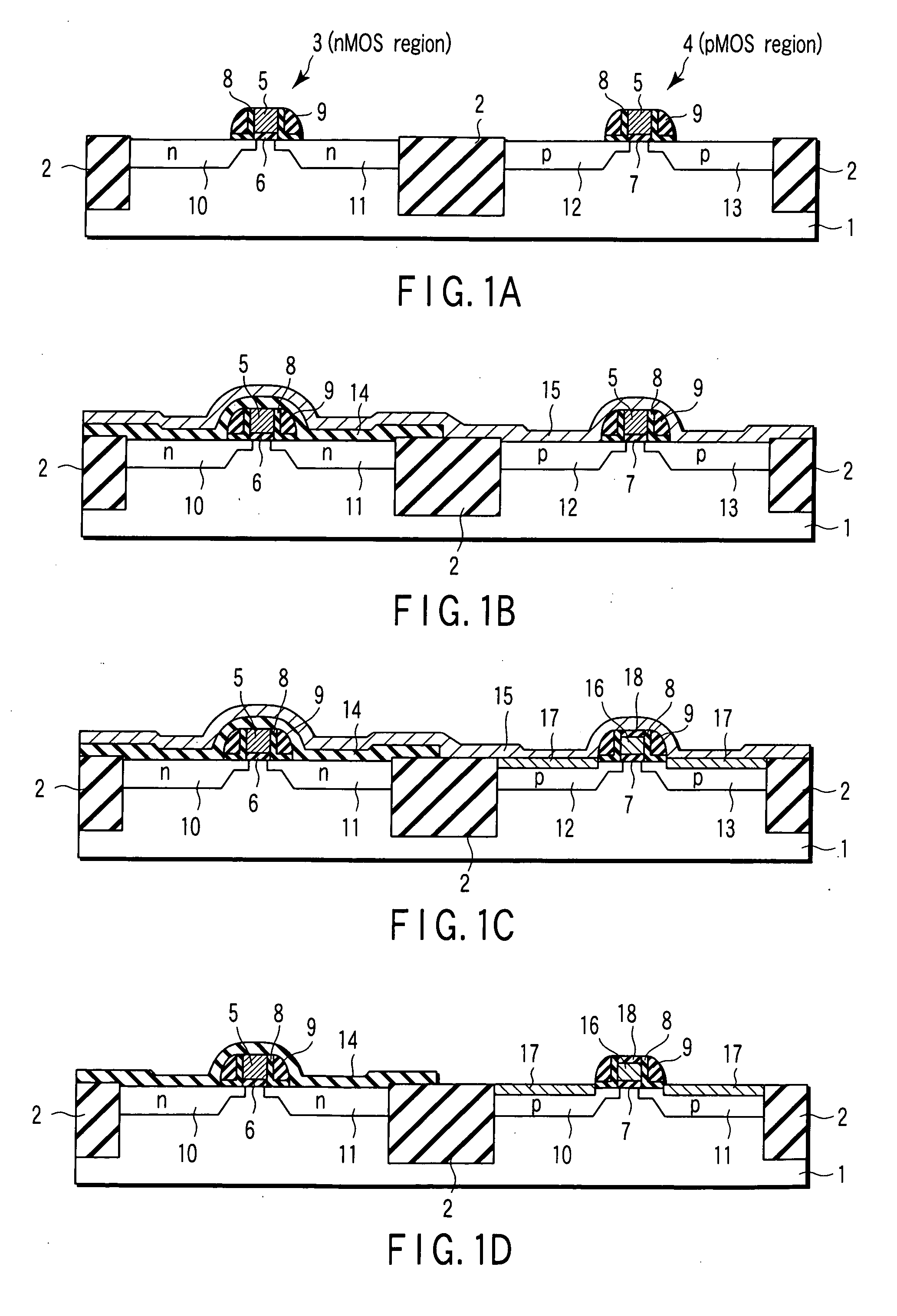
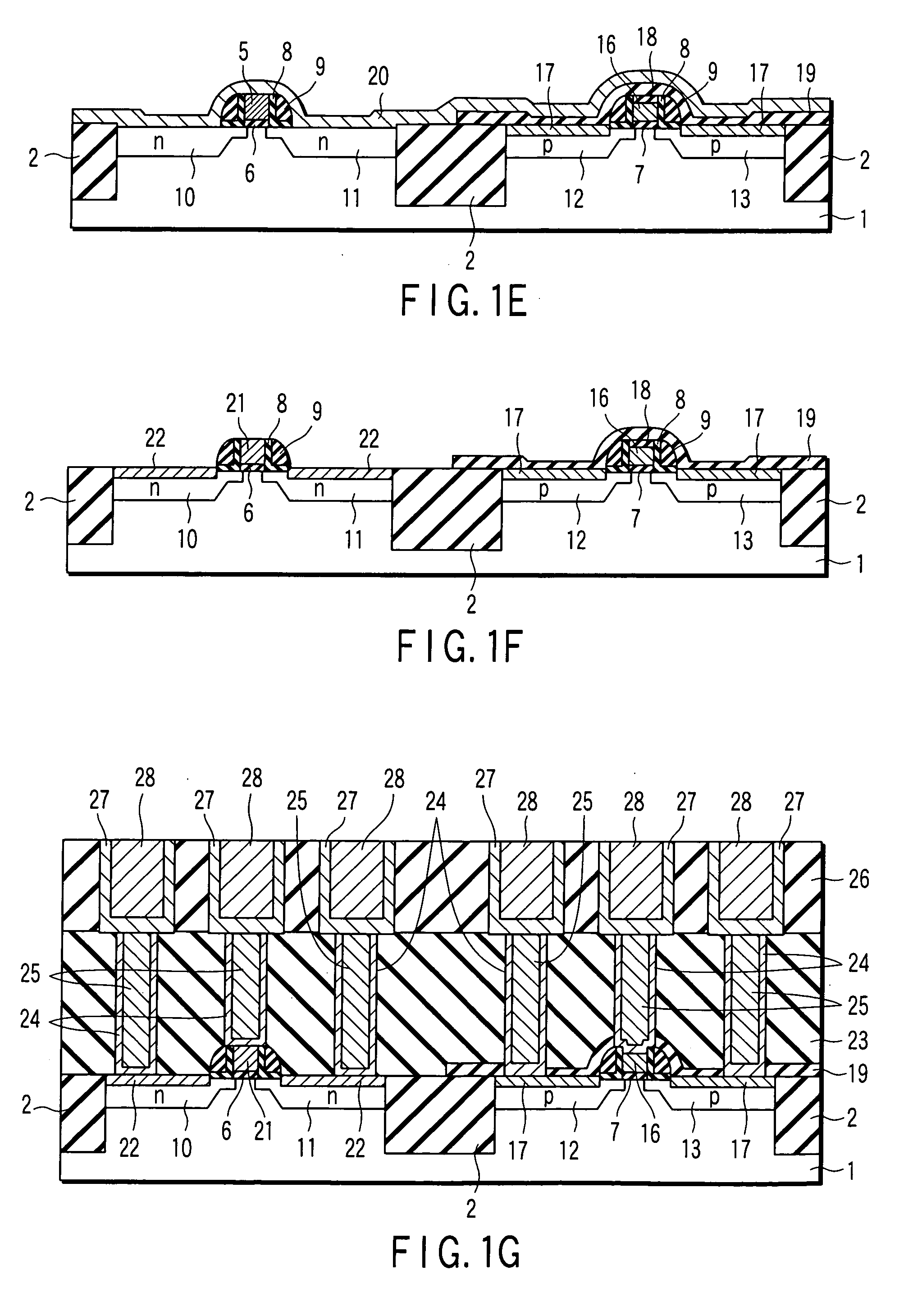
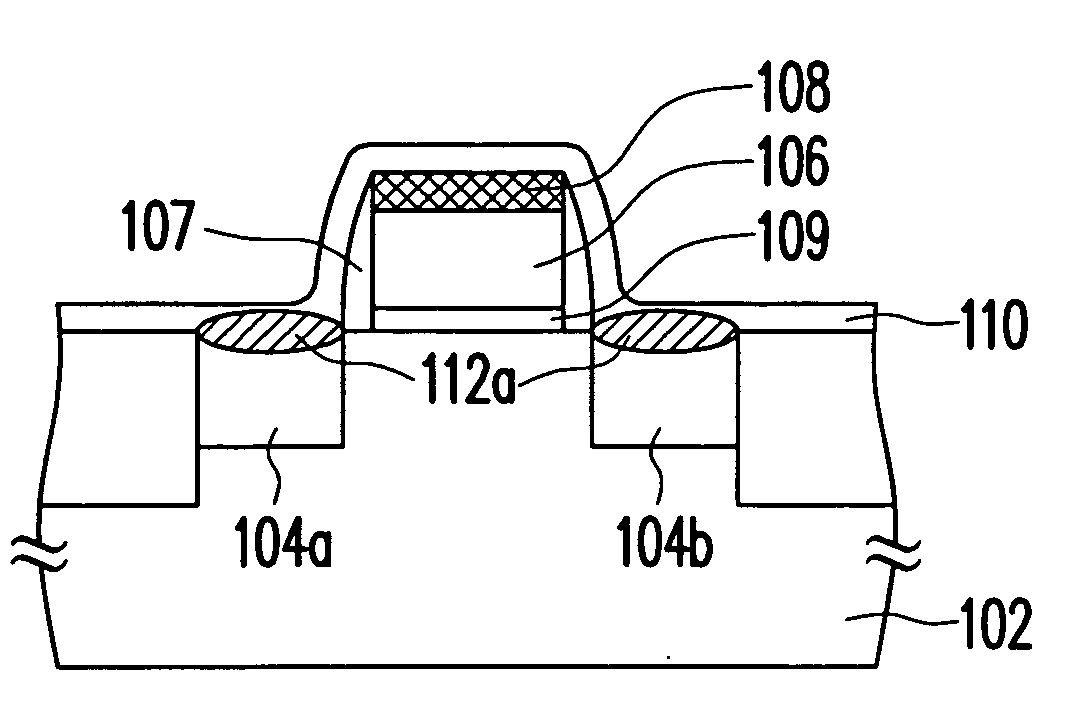
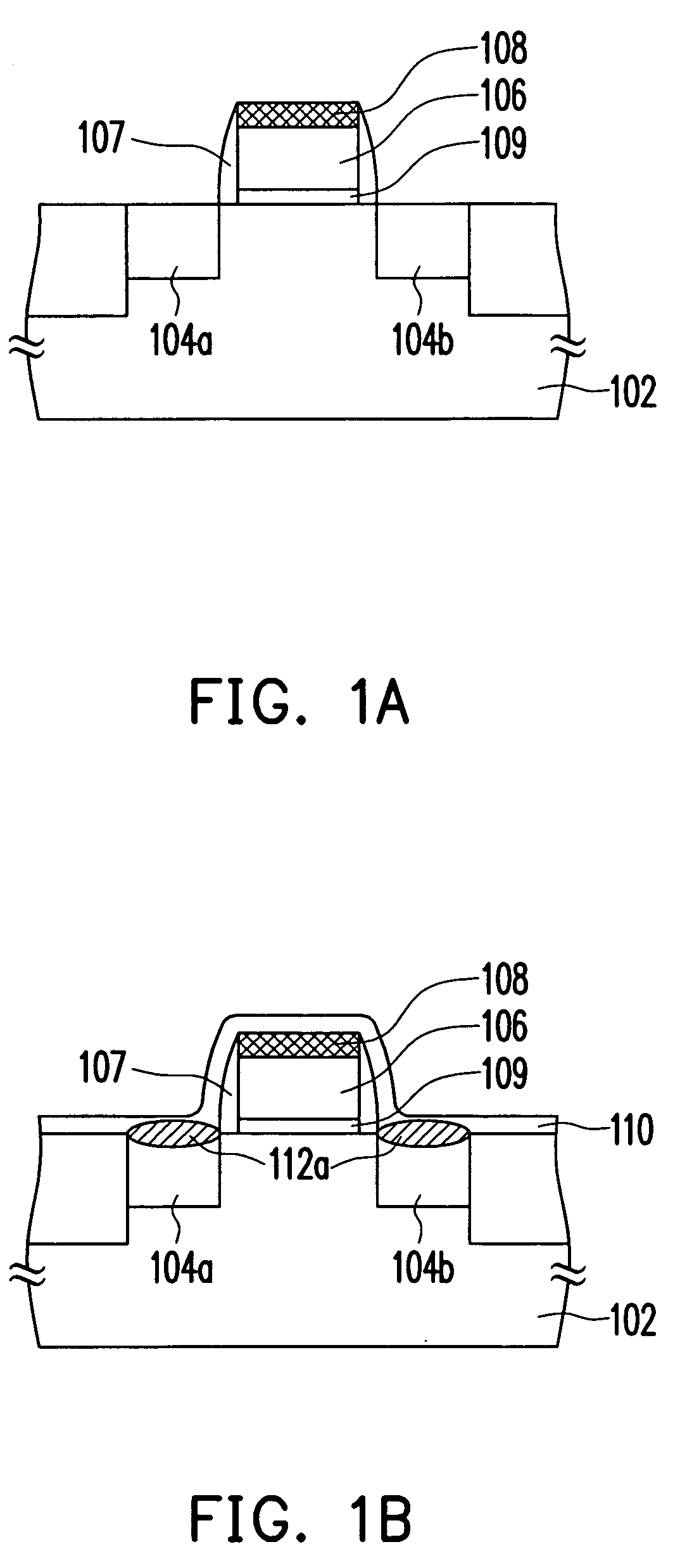
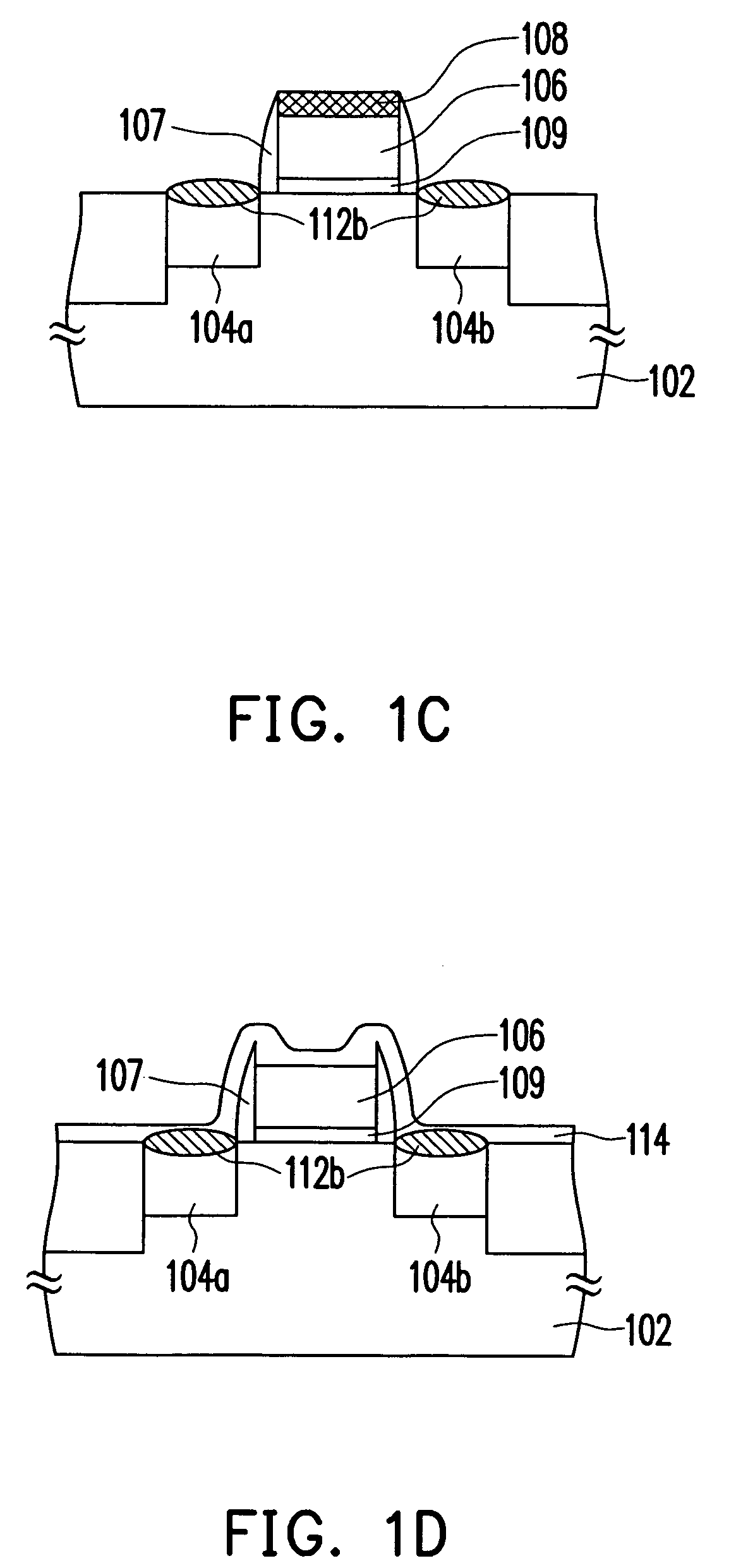
The method of manufacturing the semiconductor device comprises forming a transistor including a gate electrode and a source / drain diffused layer over a semiconductor substrate, forming a nickel platinum film over the semiconductor substrate, covering the gate electrode and the source / drain diffused layer, making a first thermal processing to react the nickel platinum film with the source / drain diffused layer to form a nickel platinum silicide film, and removing an unreacted part of the nickel platinum film using a chemical liquid of 71° C. or more containing hydrogen peroxide.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
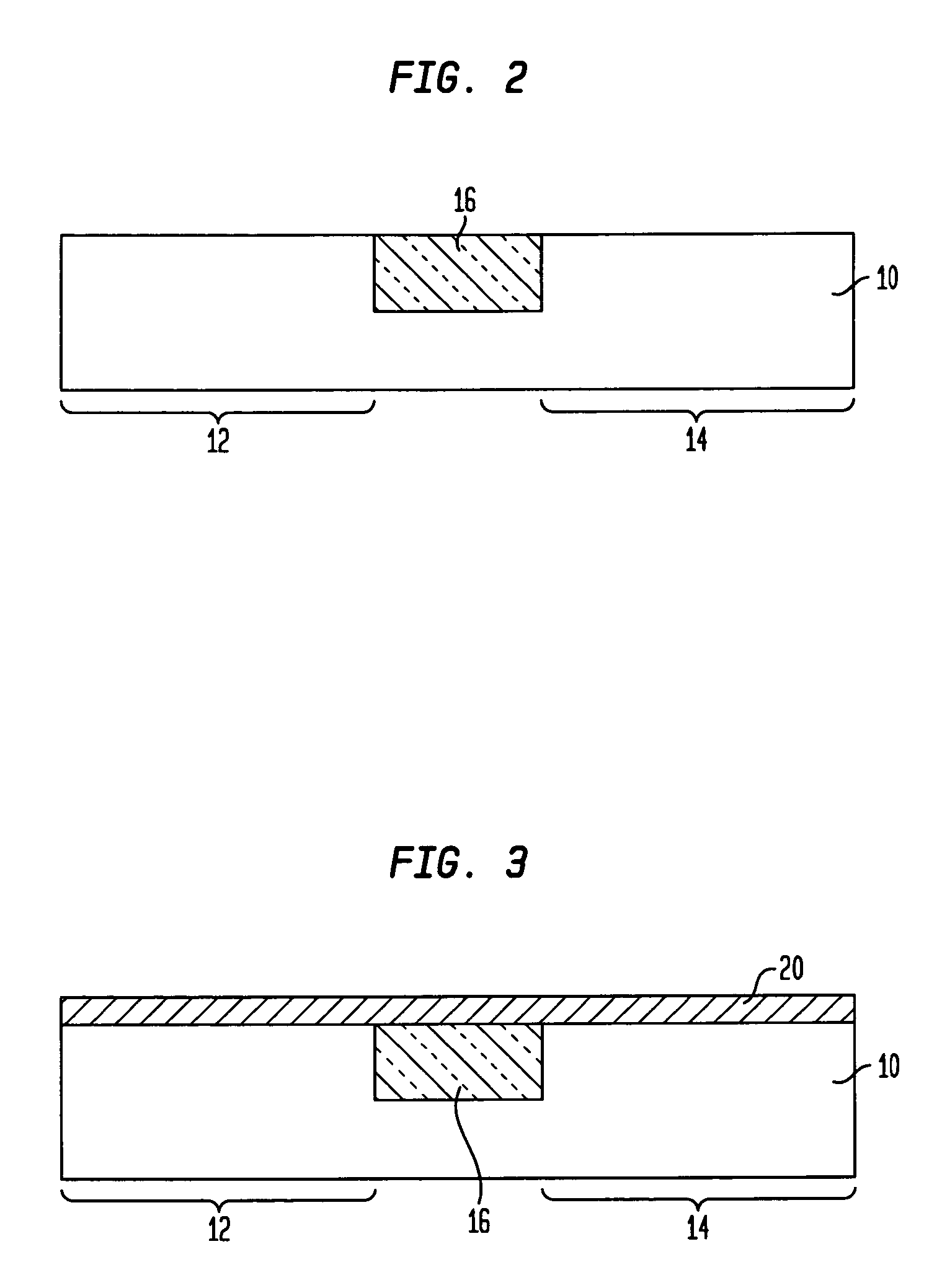
Method of fabricating a nickel/platinum monsilicide film
InactiveUS6531396B1Improve solubilityDiffusion fastSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPlatinum silicideSemiconductor structure
A method of fabricating a silicide layer on a silicon region of a semiconductor structure, the method comprising the steps of: providing a semiconductor structure having at least one silicon region on a surface thereof; depositing a layer comprising nickel and platinum on the at least one silicon layer; annealing the semiconductor structure and the nickel / platinum layer to react the nickel and the platinum with underlying silicon to form a nickel-platinum silicide, wherein annealing step takes place at temperature of between 680° C. and 720° C.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Method for forming self-aligned metal silicide contacts
InactiveUS20070254479A1Minimizes deleterious formation of residual materialReduce riskSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingPlatinum silicide
The present invention relates to a method for forming self-aligned metal silicide contacts over at least two silicon-containing semiconductor regions that are spaced apart from each other by an exposed dielectric region. Preferably, each of the self-aligned metal silicide contacts so formed comprises at least nickel silicide and platinum silicide with a substantially smooth surface, and the exposed dielectric region is essentially free of metal and metal silicide. More preferably, the method comprises the steps of nickel or nickel alloy deposition, low-temperature annealing, nickel etching, high-temperature annealing, and aqua regia etching.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
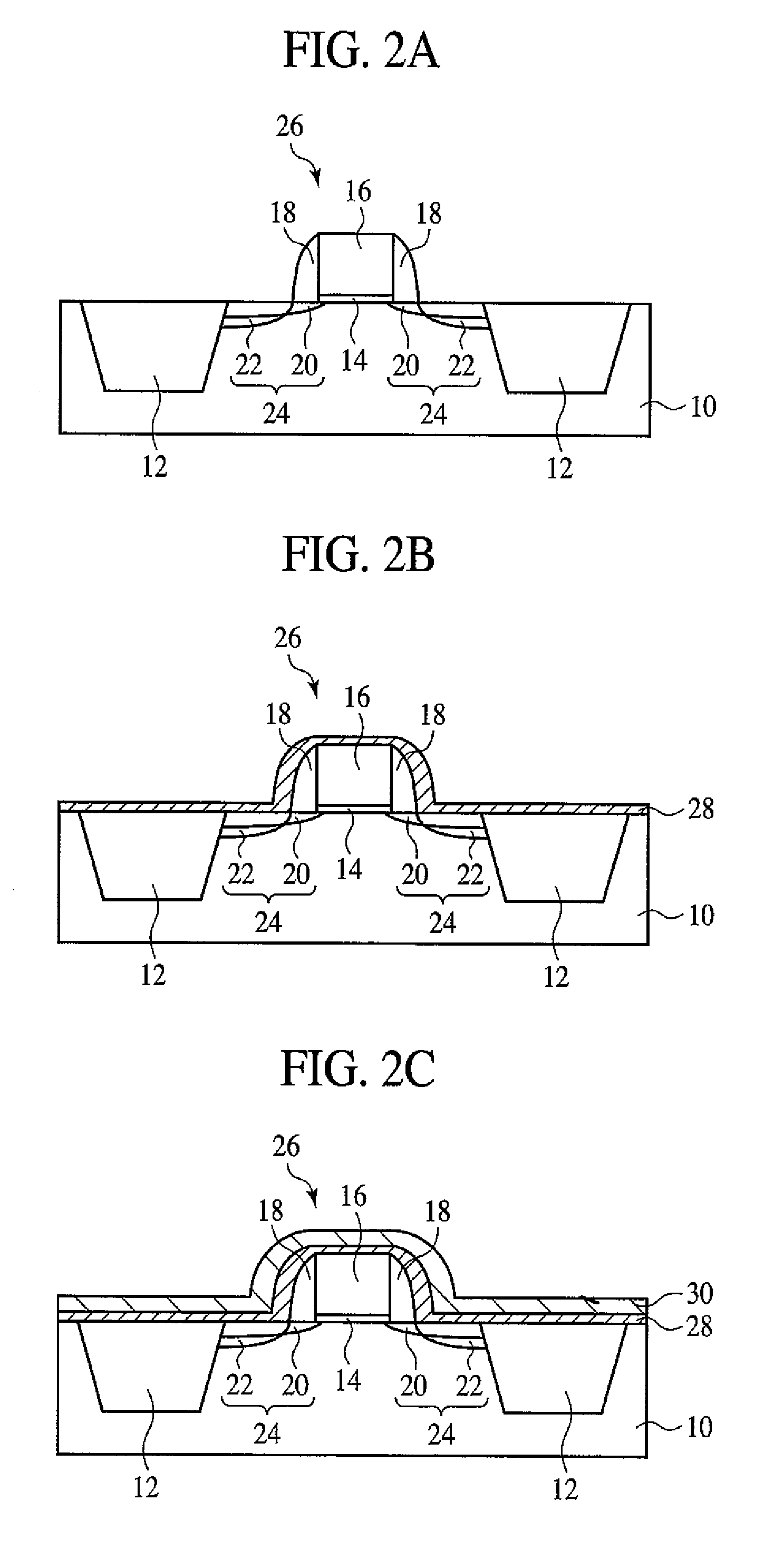
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
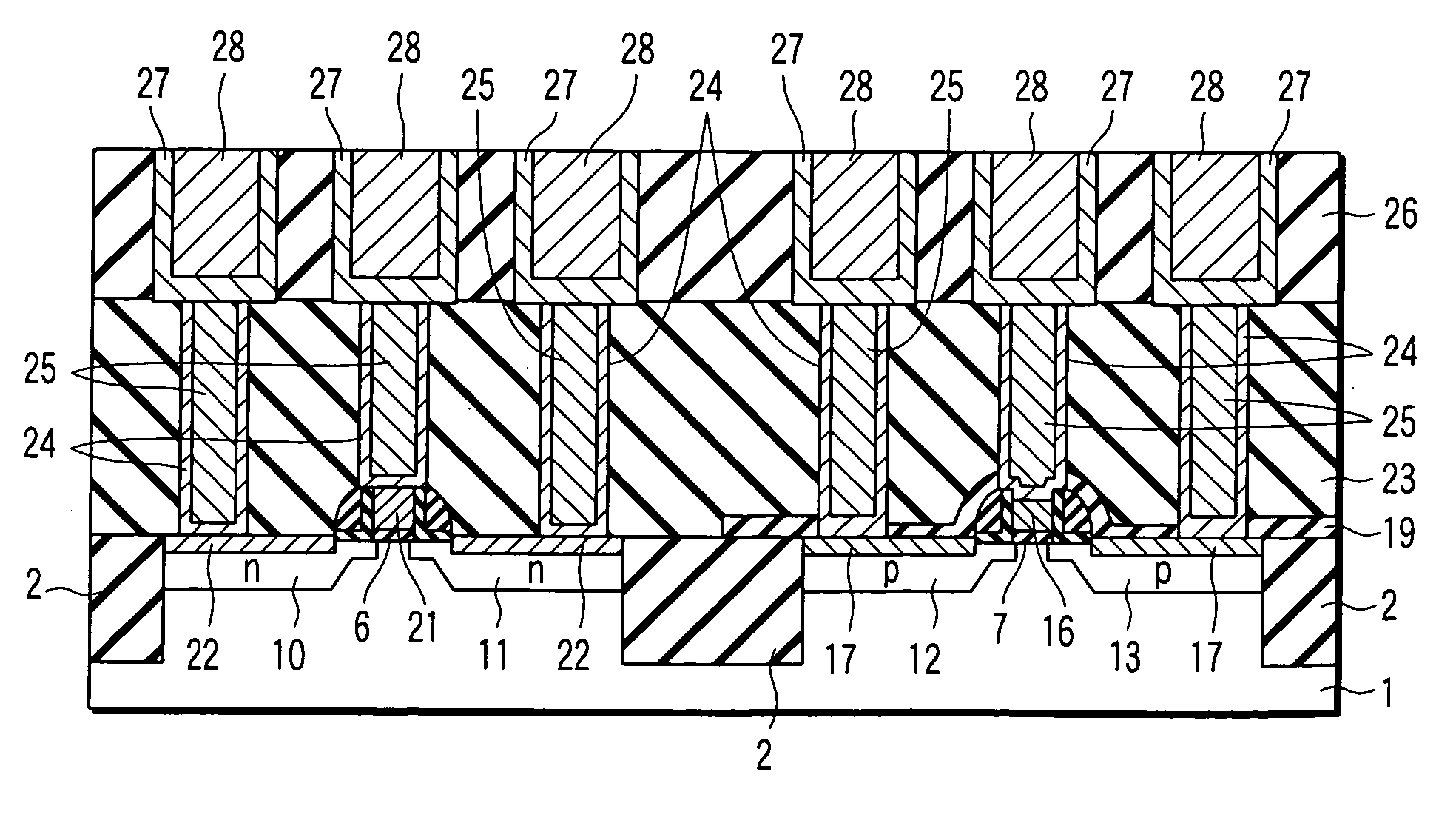
A technique capable of reducing threshold voltage and reducing high-temperature heat treatment after forming a gate electrode is provided. An n-type MIS transistor or a p-type MIS transistor is formed on an active region isolated by an element isolation region of a semiconductor substrate. In the n-type MIS transistor, a gate electrode is formed through a gate insulating film, and the gate electrode is composed of a hafnium silicide film. On the other hand, in the p-type MIS transistor, a gate electrode is formed through a gate insulating film, and the gate electrode is composed of a platinum silicide film. Also, the gate electrodes are formed after the activation annealing (heat treatment) for activating impurities implanted into a source region and a drain region.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP +2
Method of forming a nickel platinum silicide
A substrate having at least one silicon device is provided. A nickel platinum alloy layer is formed on the substrate. A rapid thermal process is performed to react the nickel platinum alloy layer with the silicon device to produce a nickel platinum silicide. A passivation layer is formed on the nickel platinum silicide followed by using a solution consisting of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid to remove unreacted portions of the nickel platinum alloy layer.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
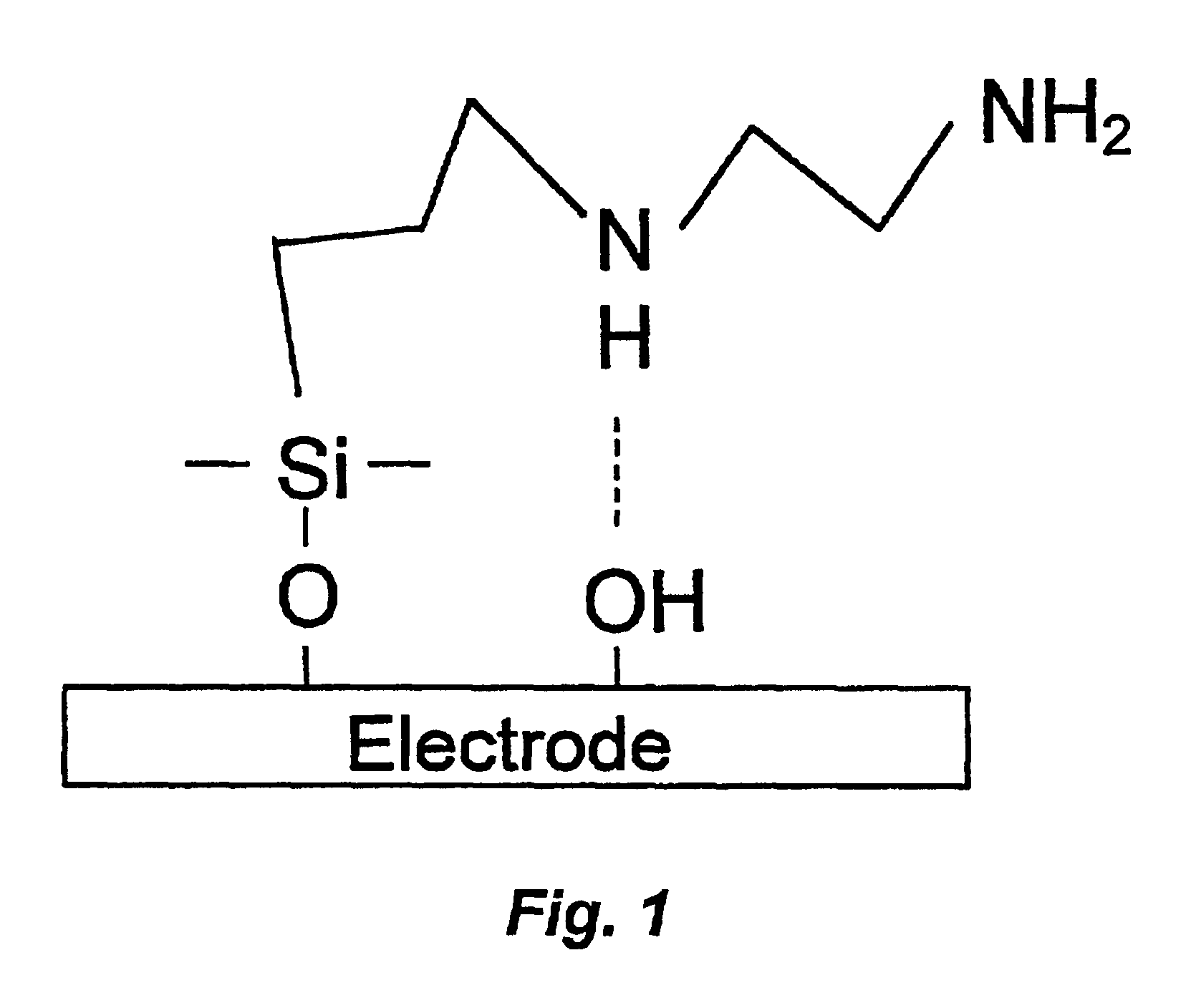
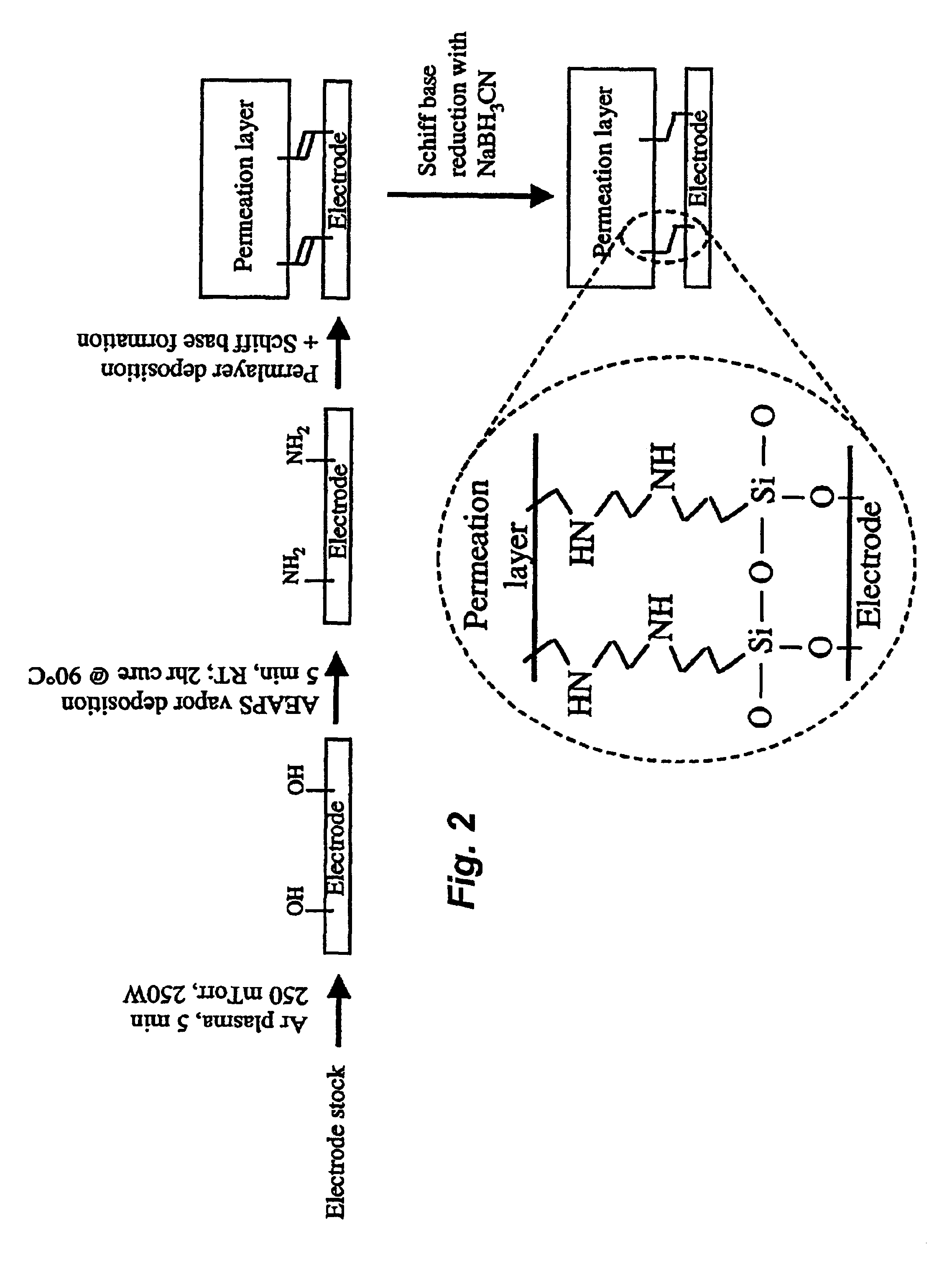
Platinum silicide permeation layer device with microlocations
InactiveUS6838053B2Robust permeation layerEasy to transportBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPeptide librariesPlatinum silicideSilanes
Owner:ADOR DIAGNOSTICS SRL
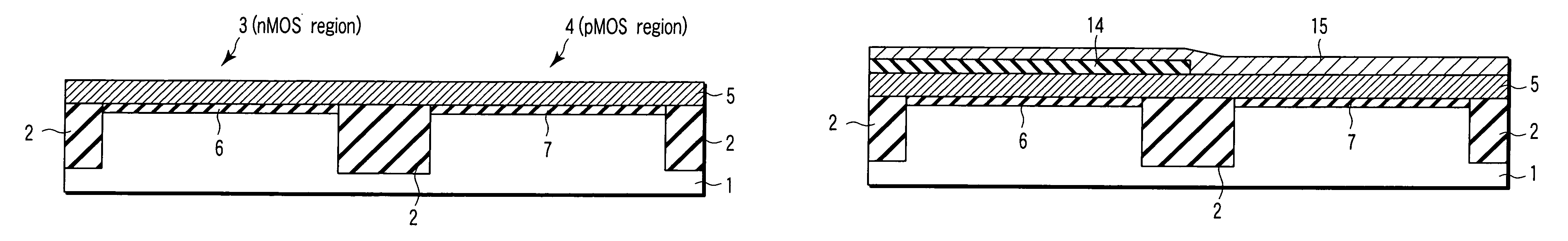
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS7465624B2TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlatinum silicideSilicon oxide
The present invention provides a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device, comprising forming an electrode pattern made of silicon on a gate insulating film in an n-MOS region and a p-MOS region of a semiconductor substrate, masking the n-MOS region including the first electrode pattern with a first insulating film pattern, forming a first metal film made of platinum all over the surface, forming a gate electrode consisting of a platinum silicide in the p-MOS region, forming an silicon oxide film on the surface of the gate electrode by oxidation, dissolving away a non-reacting Pt film, removing the first insulating film pattern, masking the p-MOS region including the electrode pattern with a second insulating film pattern, forming a second metal film made of europium all over the surface, and forming a gate electrode consisting of a europium silicide in the n-MOS region.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
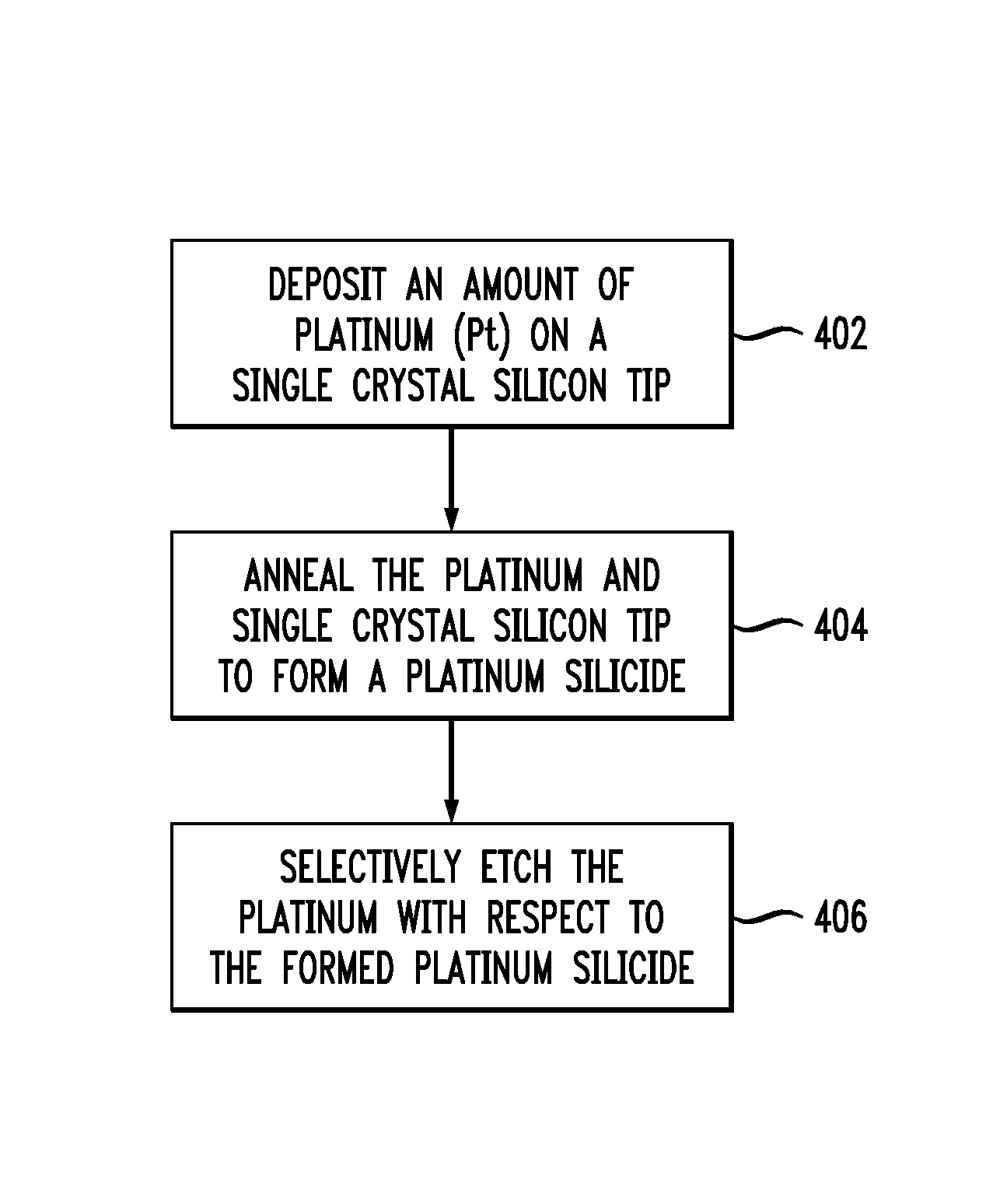
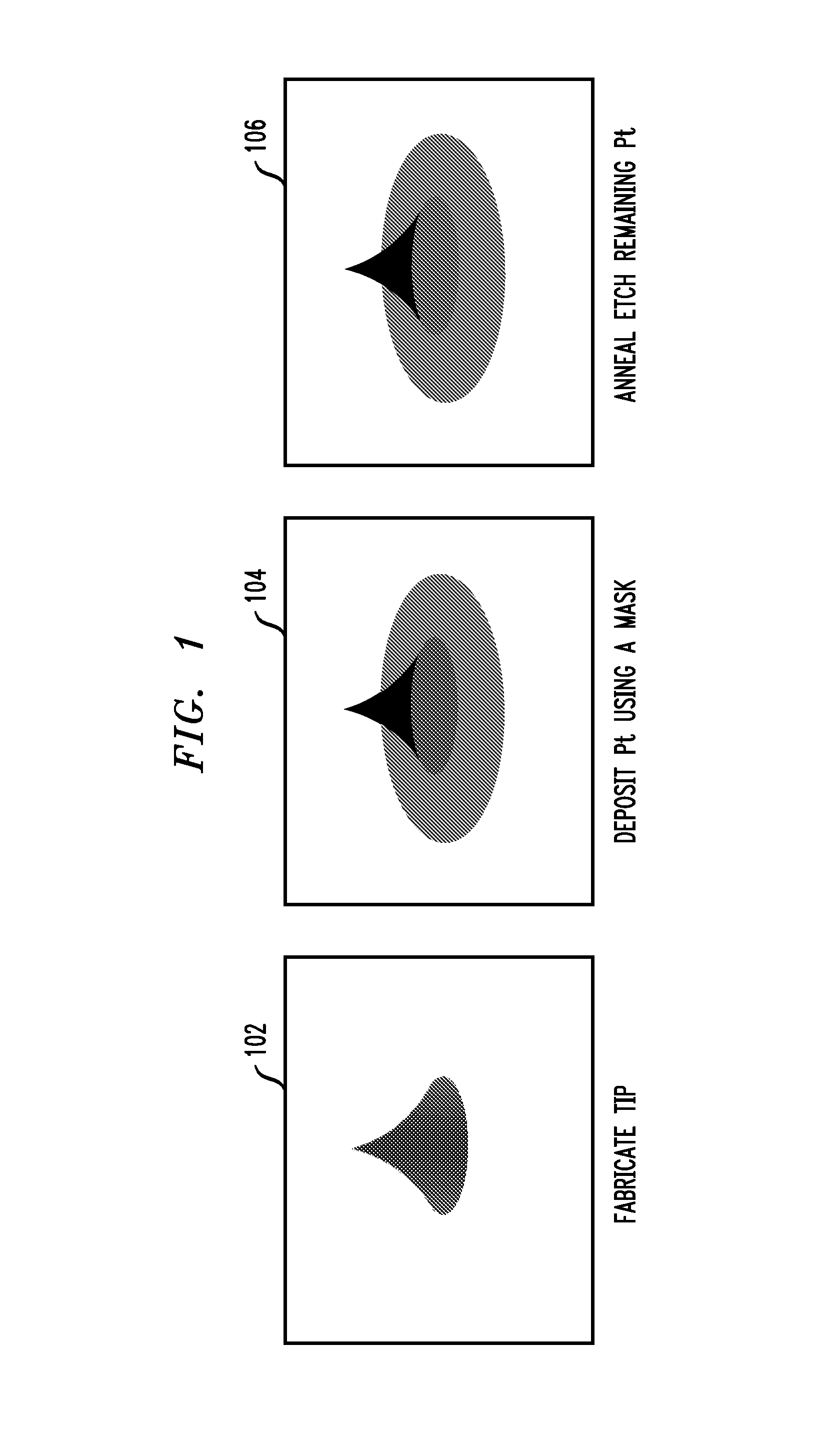
Platinum silicide tip apices for probe-based technologies
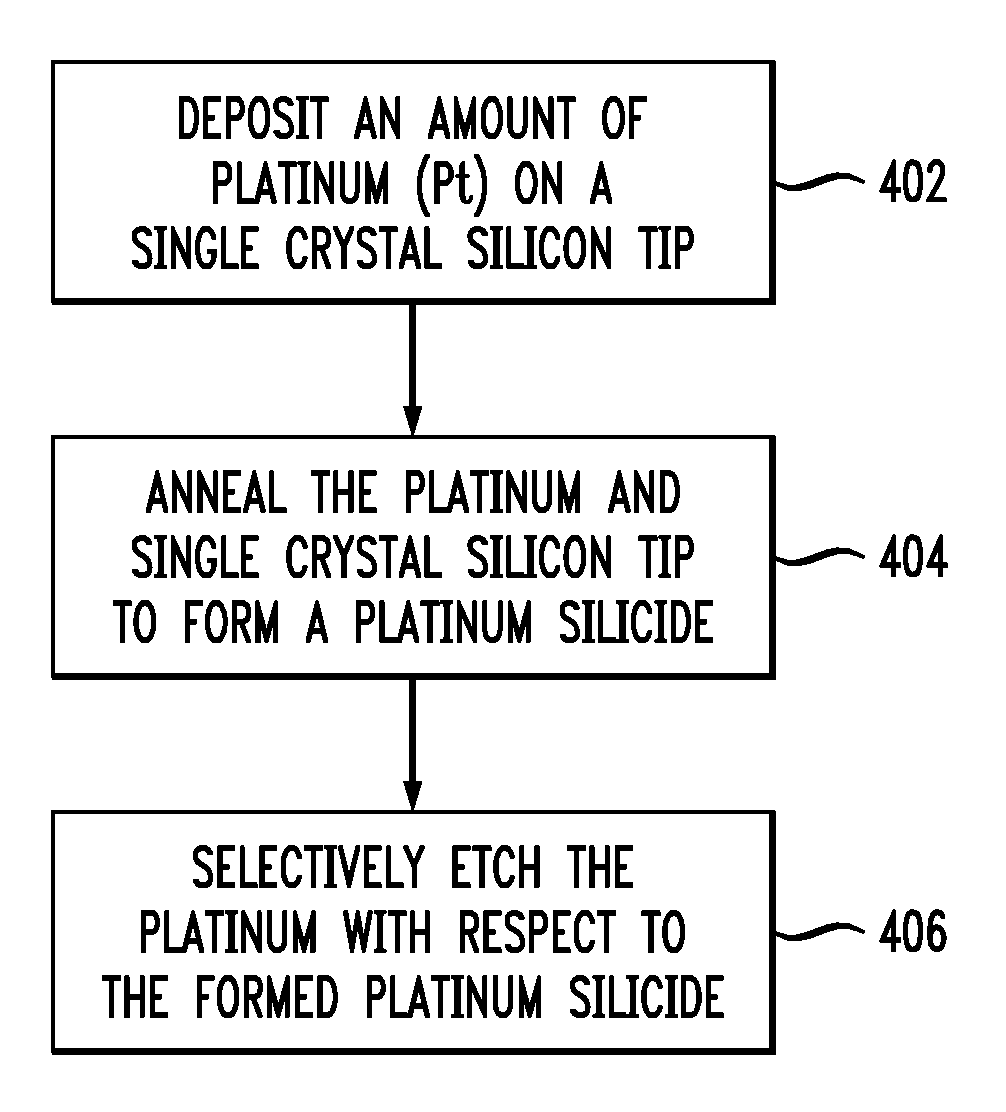
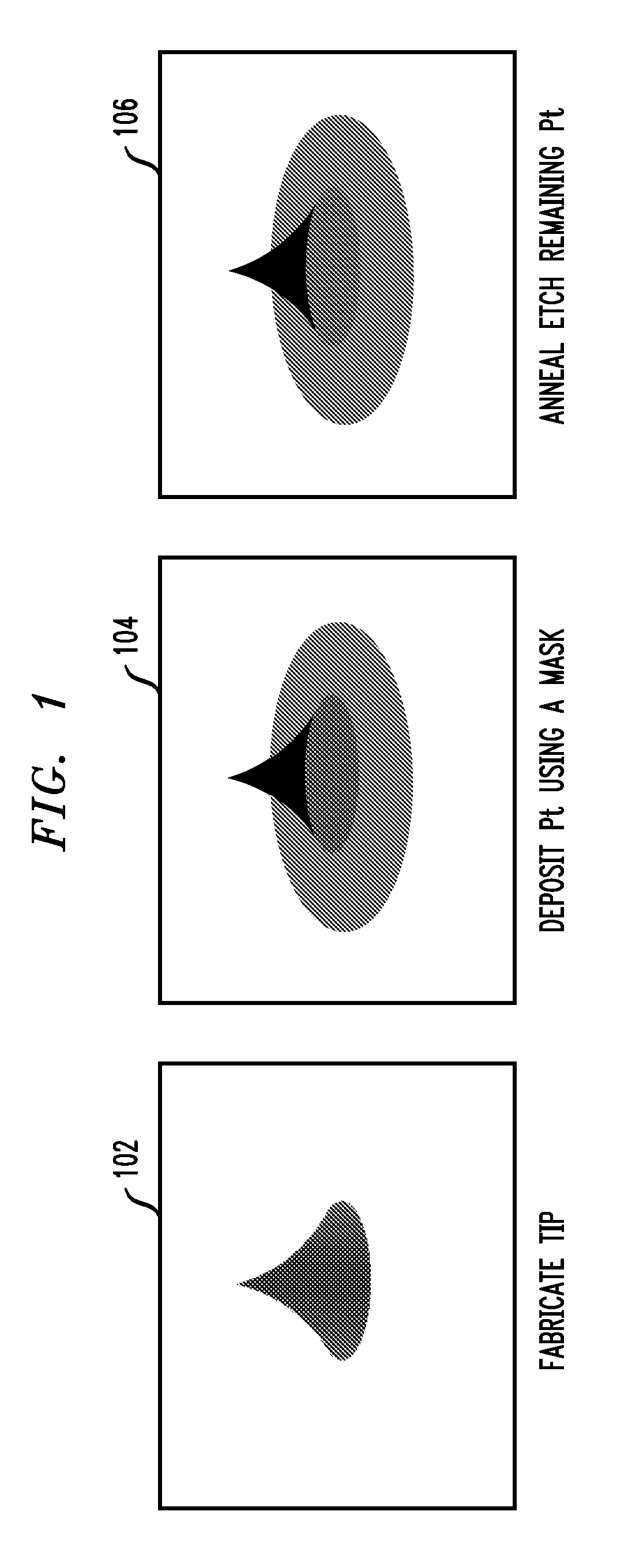
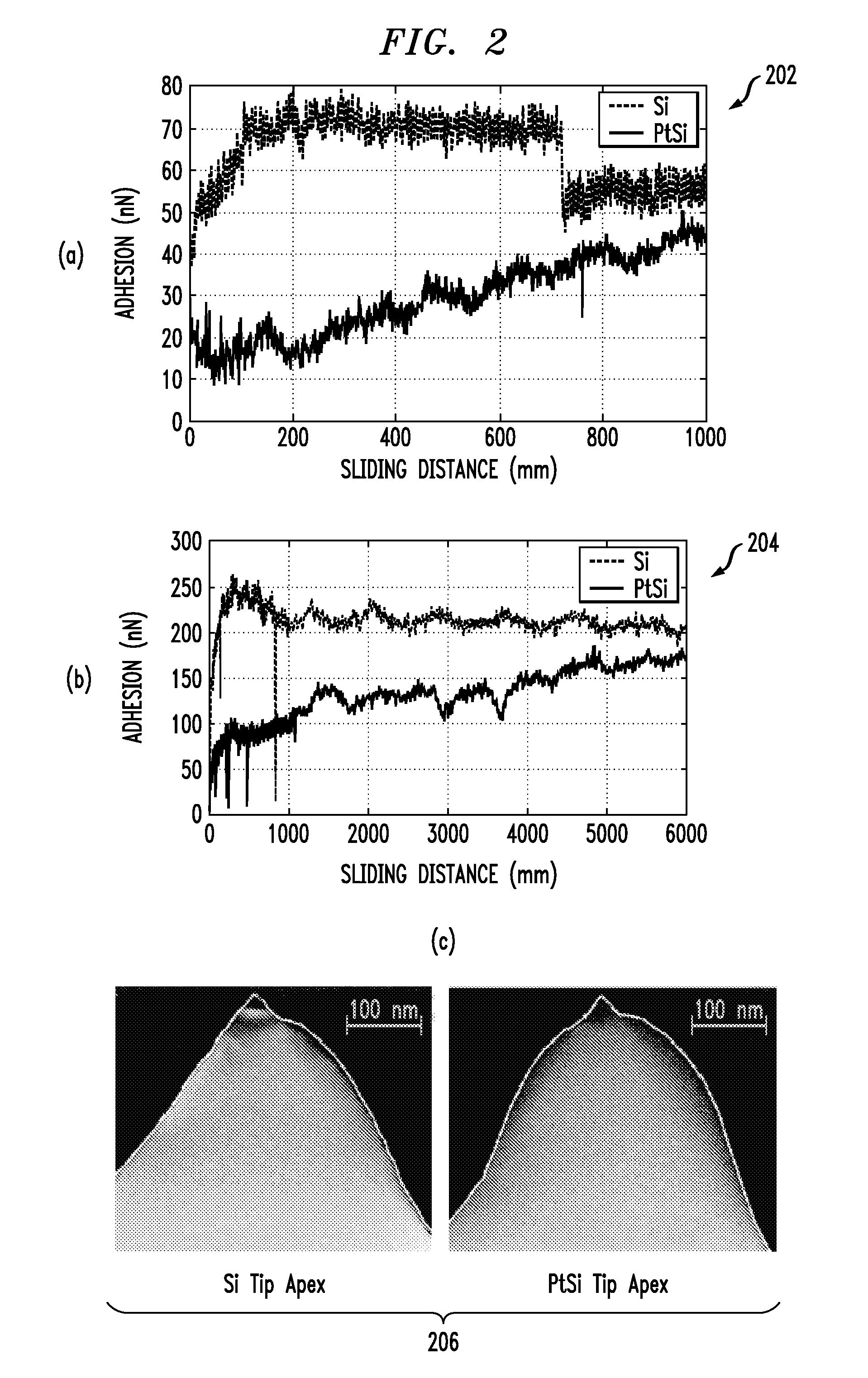
Tips including a platinum silicide at an apex of a single crystal silicon tip are provided herein. Also, techniques for creating a tip are provided. The techniques include depositing an amount of platinum (Pt) on a single crystal silicon tip, annealing the platinum and single crystal silicon tip to form a platinum silicide, and selectively etching the platinum with respect to the formed platinum silicide.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Platinum silicide tip apices for probe-based technologies
Tips including a platinum silicide at an apex of a single crystal silicon tip are provided herein. Also, techniques for creating a tip are provided. The techniques include depositing an amount of platinum (Pt) on a single crystal silicon tip, annealing the platinum and single crystal silicon tip to form a platinum silicide, and selectively etching the platinum with respect to the formed platinum silicide.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for forming self-aligned metal silicide contacts
InactiveUS7618891B2Minimizes deleterious formation of residual materialReduce riskSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSalicideEtching
The present invention relates to a method for forming self-aligned metal silicide contacts over at least two silicon-containing semiconductor regions that are spaced apart from each other by an exposed dielectric region. Preferably, each of the self-aligned metal silicide contacts so formed comprises at least nickel silicide and platinum silicide with a substantially smooth surface, and the exposed dielectric region is essentially free of metal and metal silicide. More preferably, the method comprises the steps of nickel or nickel alloy deposition, low-temperature annealing, nickel etching, high-temperature annealing, and aqua regia etching.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
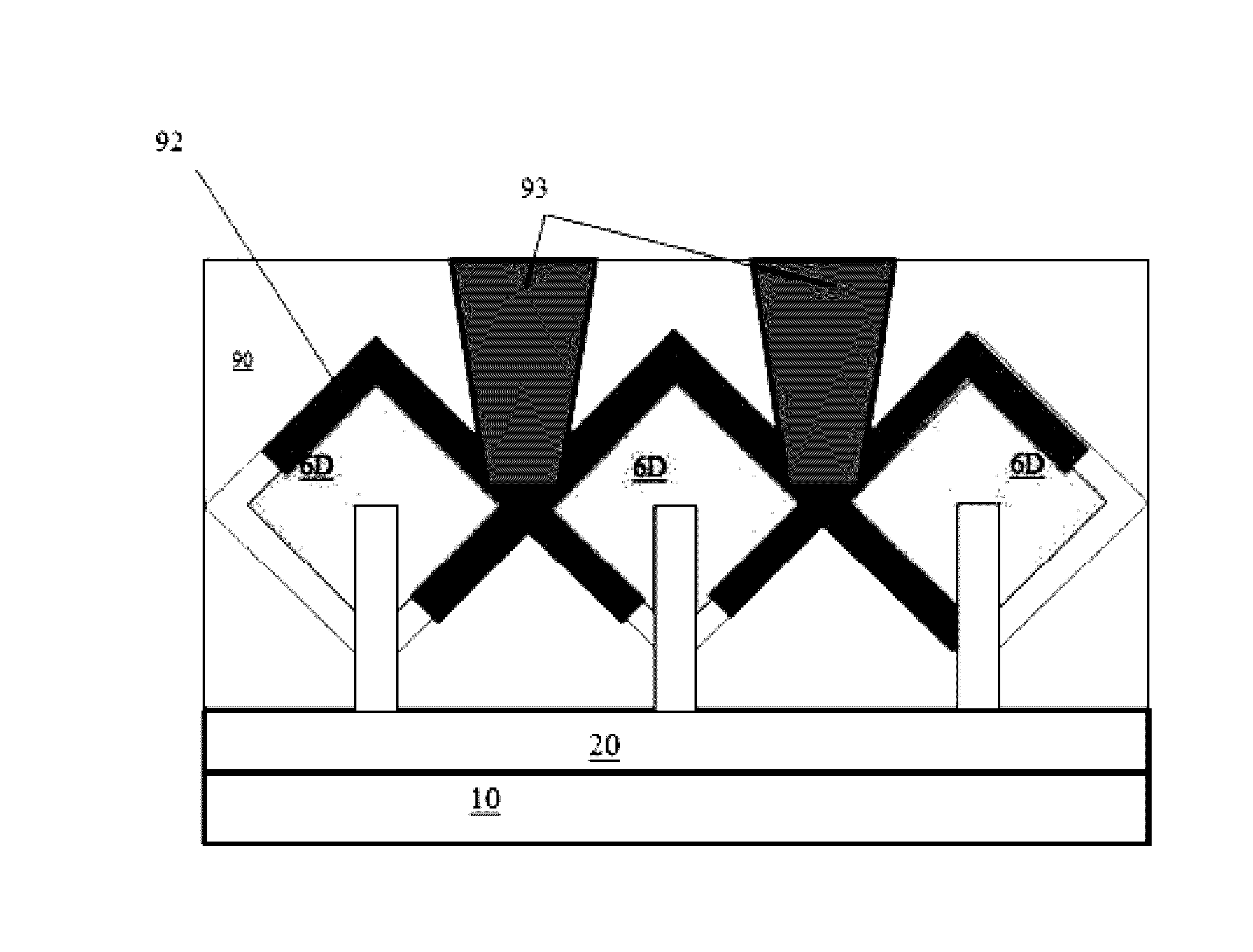
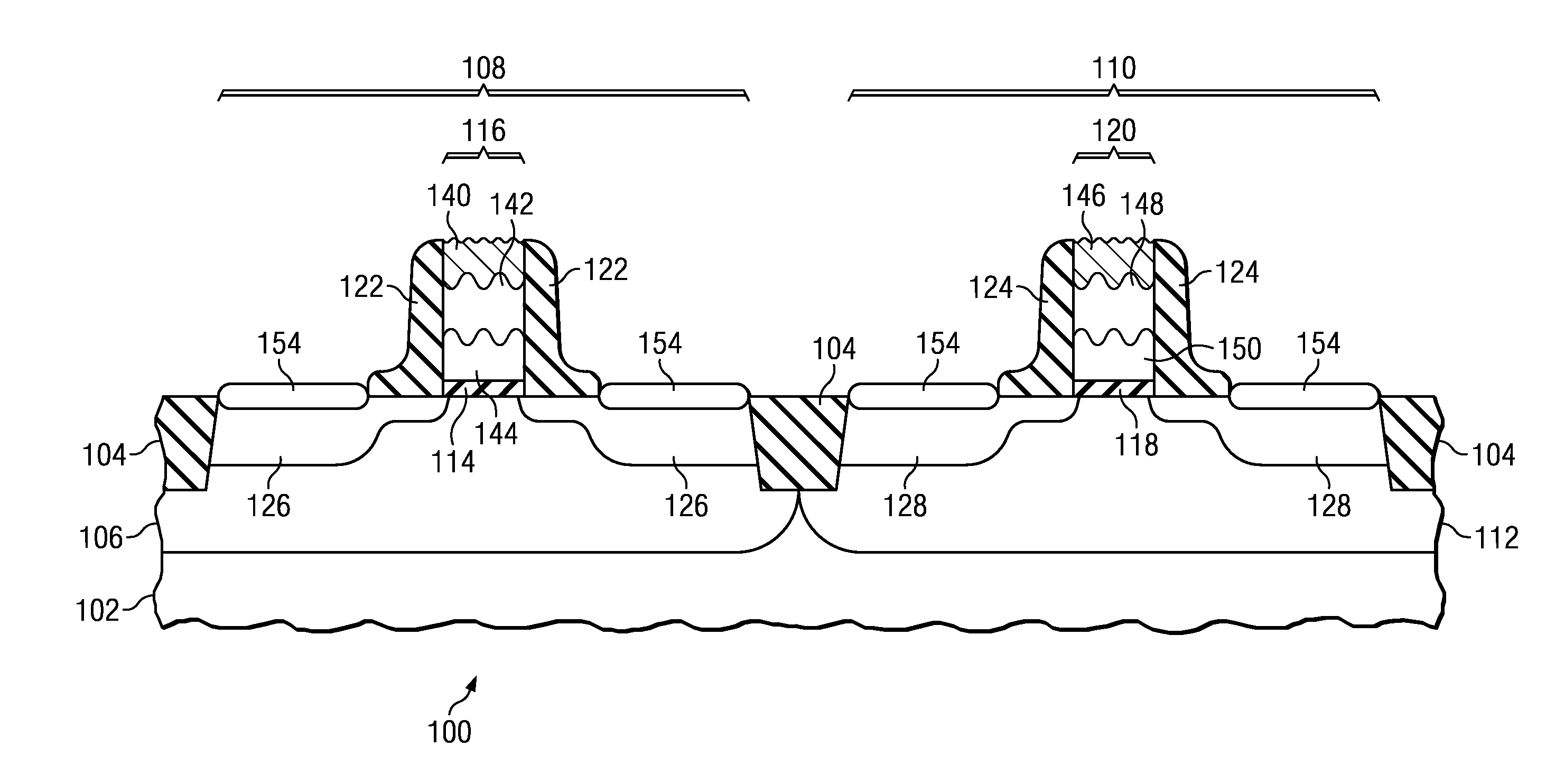
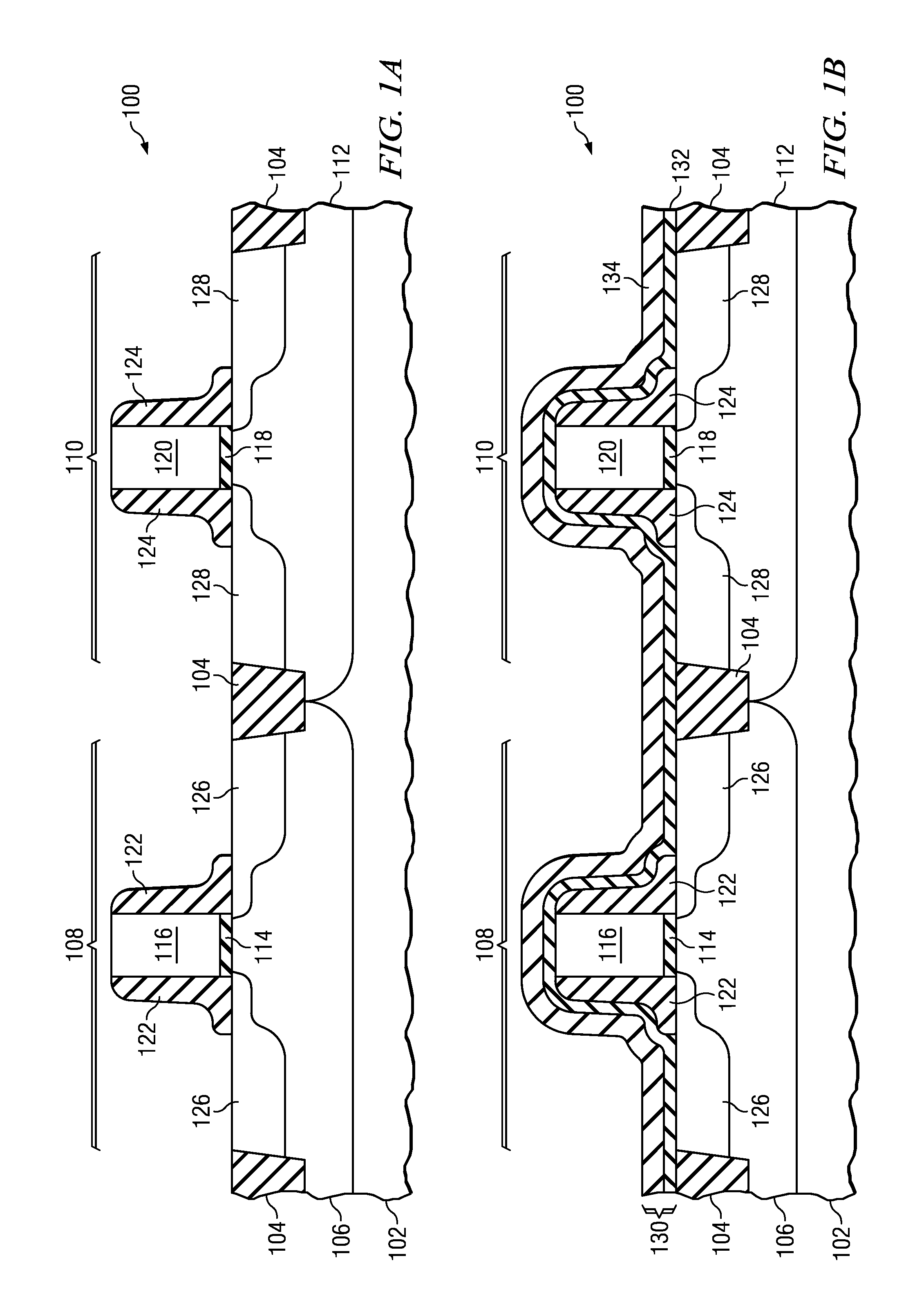
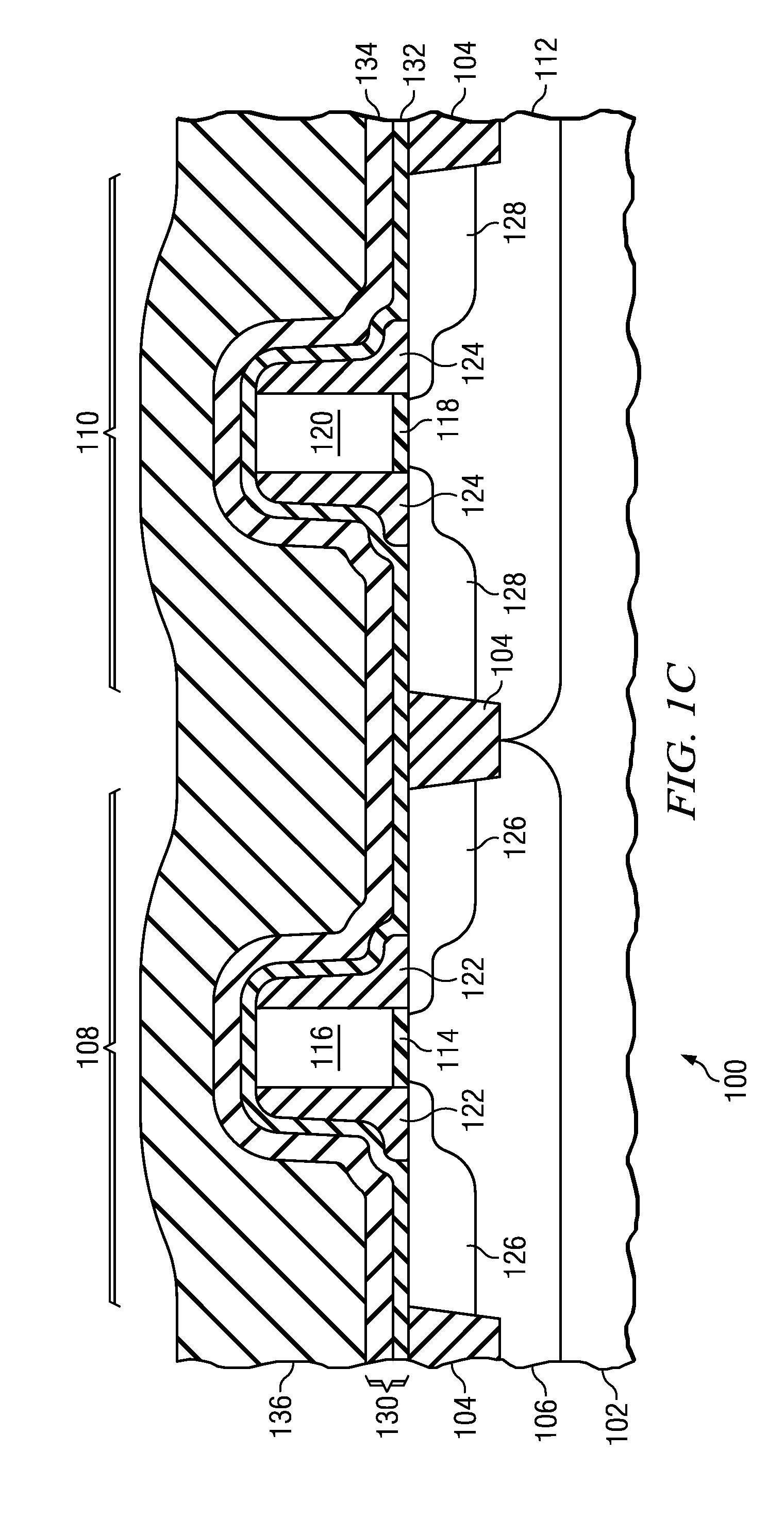
LOW PARASITIC CAPACITANCE AND RESISTANCE finFET DEVICE
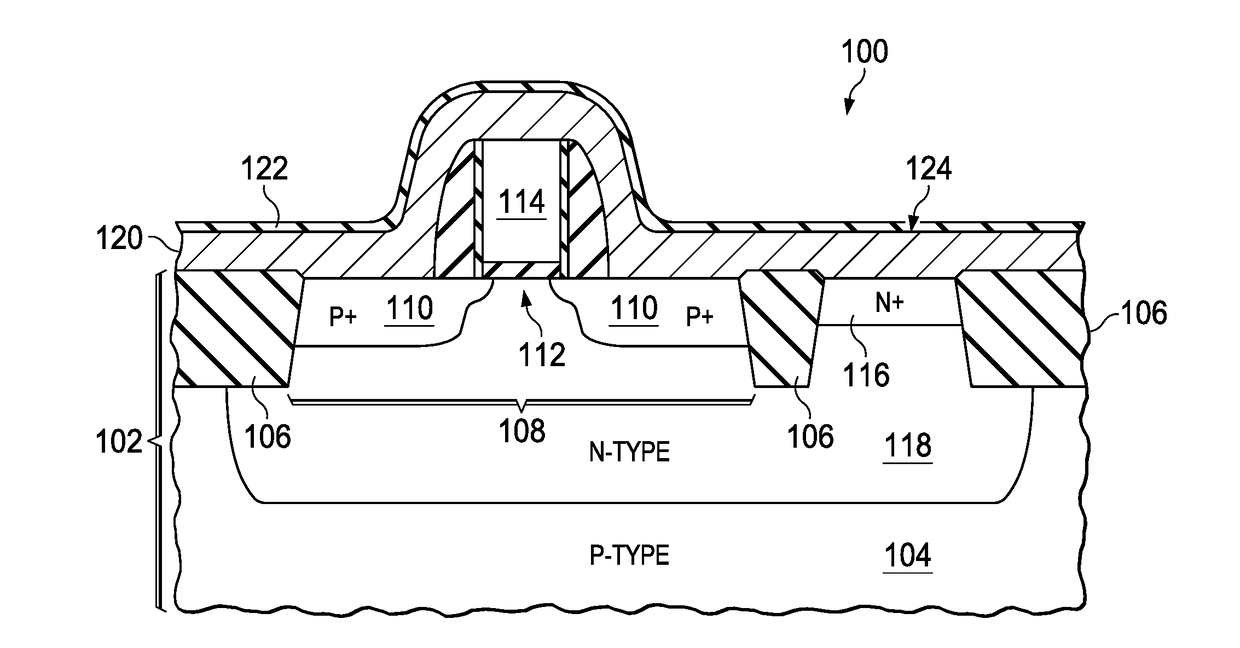
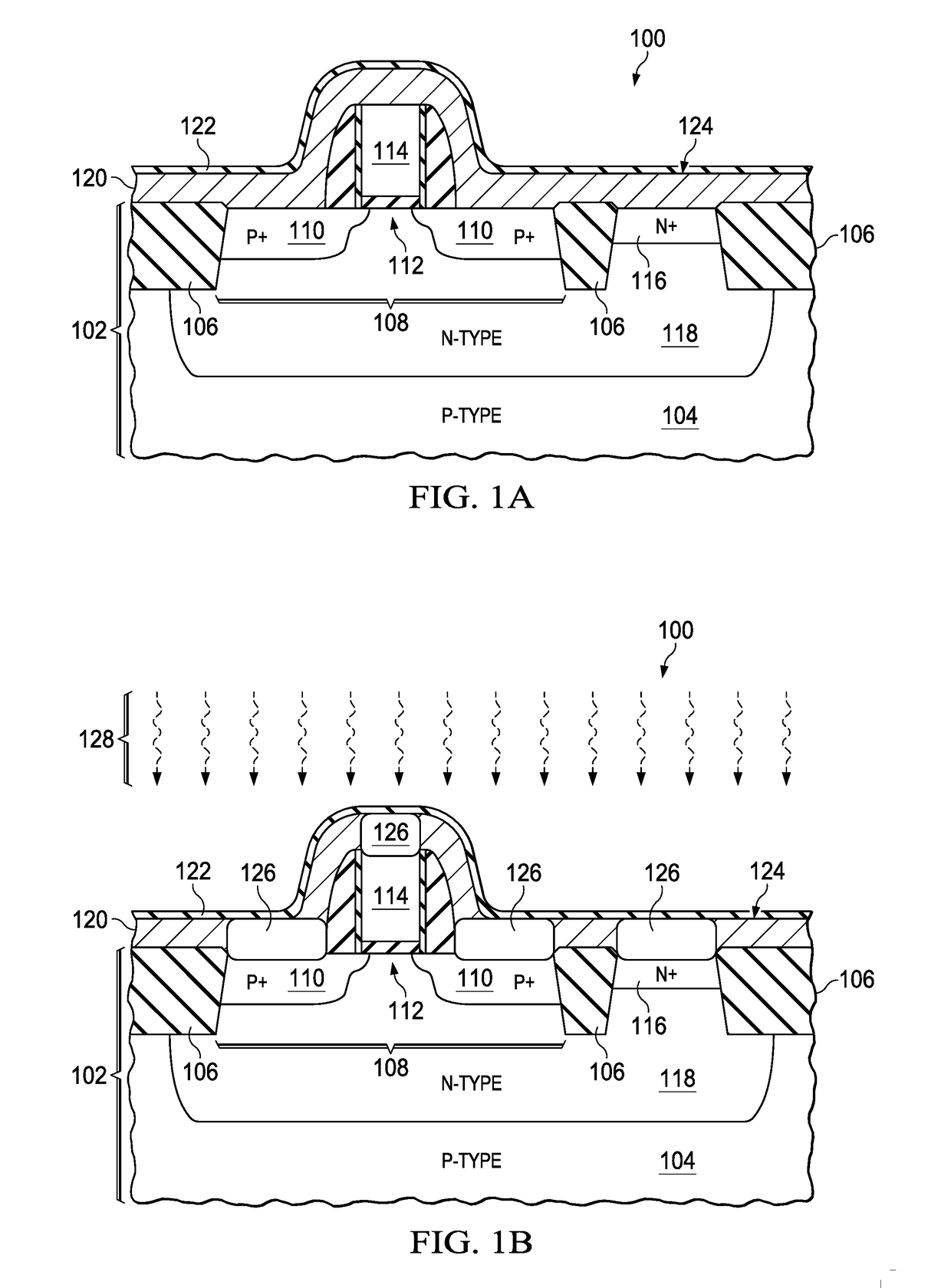
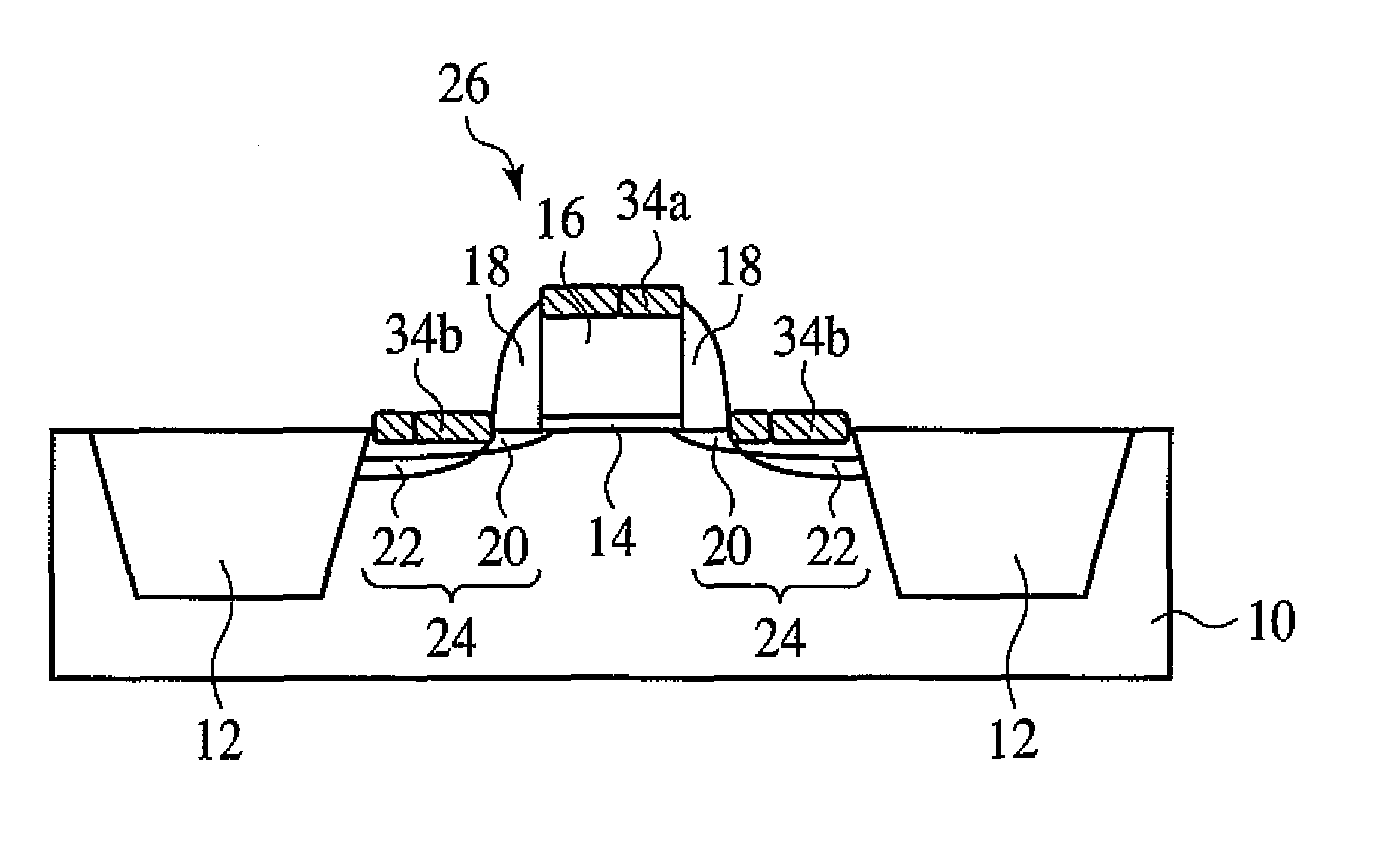
Described herein is a semiconductor structure and method of manufacture. The semiconductor structure includes a plurality of semiconductor fins on a substrate and a plurality of raised active regions, wherein each raised active region is located on sidewalls of a corresponding semiconductor fin among said plurality of semiconductor fins. The raised active regions are laterally spaced from any other of the raised active regions. Each raised active region comprises angled sidewall surfaces that are not parallel or perpendicular to a topmost horizontal surface of said substrate. The raised active regions are silicon germanium (SiGe). The semiconductor structure includes a metal semiconductor alloy region contacting at least said angled sidewall surfaces of at least two adjacent raised active regions. The semiconductor alloy region includes a material selected from the group consisting of nickel silicide, nickel-platinum silicide and cobalt silicide.
Owner:IBM CORP
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS7429770B2Lower threshold voltageImprove suppression propertiesTransistorSolid-state devicesPlatinum silicideEngineering
A technique capable of reducing threshold voltage and reducing high-temperature heat treatment after forming a gate electrode is provided. An n-type MIS transistor or a p-type MIS transistor is formed on an active region isolated by an element isolation region of a semiconductor substrate. In the n-type MIS transistor, a gate electrode is formed through a gate insulating film, and the gate electrode is composed of a hafnium silicide film. On the other hand, in the p-type MIS transistor, a gate electrode is formed through a gate insulating film, and the gate electrode is composed of a platinum silicide film. Also, the gate electrodes are formed after the activation annealing (heat treatment) for activating impurities implanted into a source region and a drain region.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP +2
Method of fabricating metal silicide layer
ActiveUS7229920B2Minimizing increase in resistanceReduce line widthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh resistanceSalicide
A method of fabricating a metal silicide layer over a substrate is provided. First, a hard mask layer is formed over a gate formed on a substrate and a portion of the substrate is exposed. Thereafter, a first metal silicide layer, which is a cobalt silicide or a titanium silicide layer, is formed on the exposed substrate. After that, the hard mask layer is removed and a second metal silicide layer is formed over the gate, wherein a material of the second metal silicide layer is selected from a group consisting of nickel silicide, platinum silicide, palladium silicide and nickel alloy. Since different metal silicide layers are formed on the substrate and the gate, the problem of having a high resistance in lines with a narrow line width and the problem of nickel silicide forming spikes and pipelines in the source region and the drain region are improved.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20070099385A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlatinum silicideDevice material
The present invention provides a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device, comprising forming an electrode pattern made of silicon on a gate insulating film in an n-MOS region and a p-MOS region of a semiconductor substrate, masking the n-MOS region including the first electrode pattern with a first insulating film pattern, forming a first metal film made of platinum all over the surface, forming a gate electrode consisting of a platinum silicide in the p-MOS region, forming an silicon oxide film on the surface of the gate electrode by oxidation, dissolving away a non-reacting Pt film, removing the first insulating film pattern, masking the p-MOS region including the electrode pattern with a second insulating film pattern, forming a second metal film made of europium all over the surface, and forming a gate electrode consisting of a europium silicide in the n-MOS region.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Etching platinum-containing thin film using protective cap layer
ActiveUS20180204734A1Well formedTransistorRuthenium/rhodium/palladium/osmium/iridium/platinum oxides/hydroxidesPlatinum silicidePlatinum oxide
A microelectronic device is formed by forming a platinum-containing layer on a substrate of the microelectronic device. A cap layer is formed on the platinum-containing layer so that an interface between the cap layer and the platinum-containing layer is free of platinum oxide. The cap layer is etchable in an etch solution which also etches the platinum-containing layer. The cap layer may be formed on the platinum-containing layer before platinum oxide forms on the platinum-containing layer. Alternatively, platinum oxide on the platinum-containing layer may be removed before forming the cap layer. The platinum-containing layer may be used to form platinum silicide. The platinum-containing layer may be patterned by forming a hard mask or masking platinum oxide on a portion of the top surface of the platinum-containing layer to block the wet etchant.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
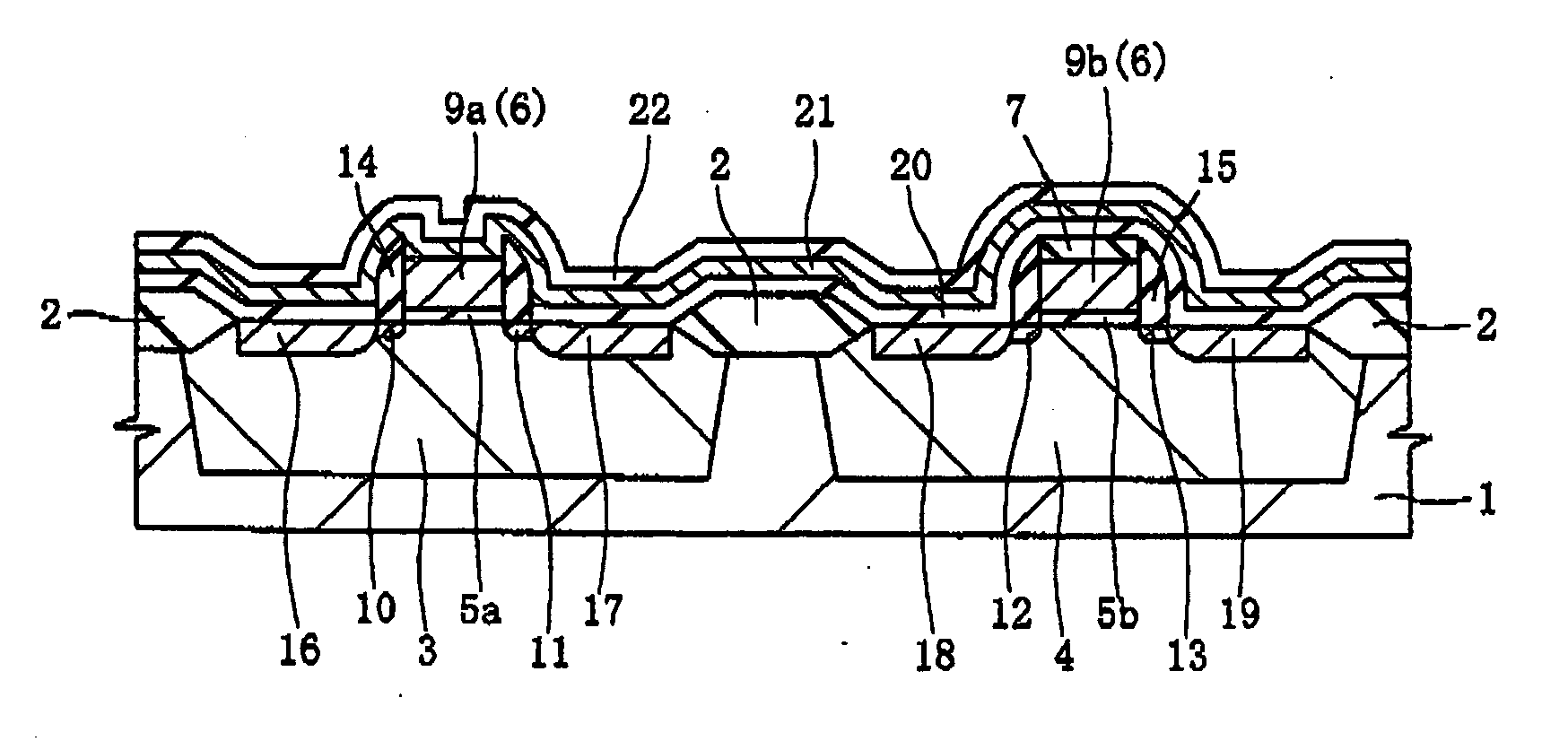
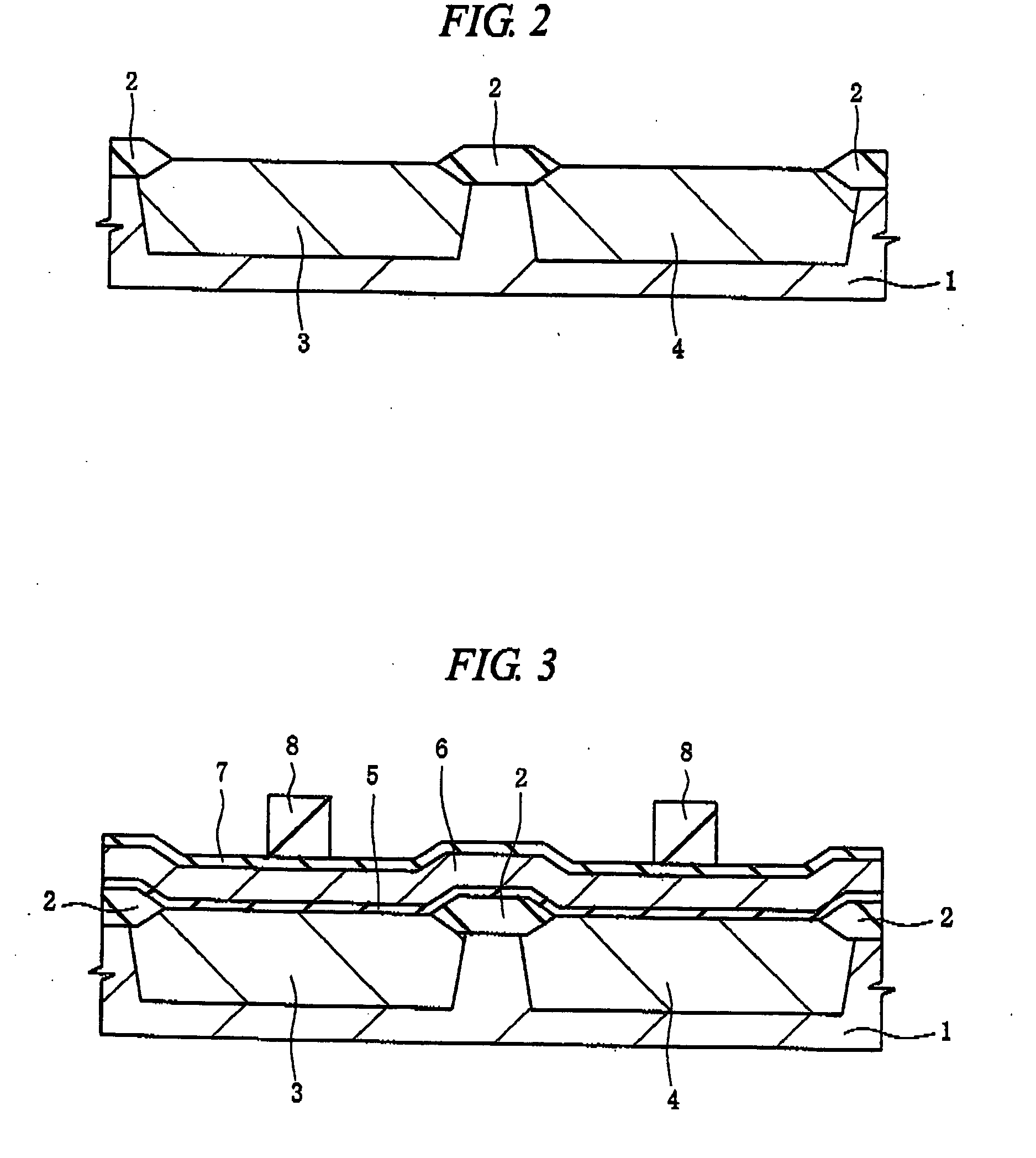
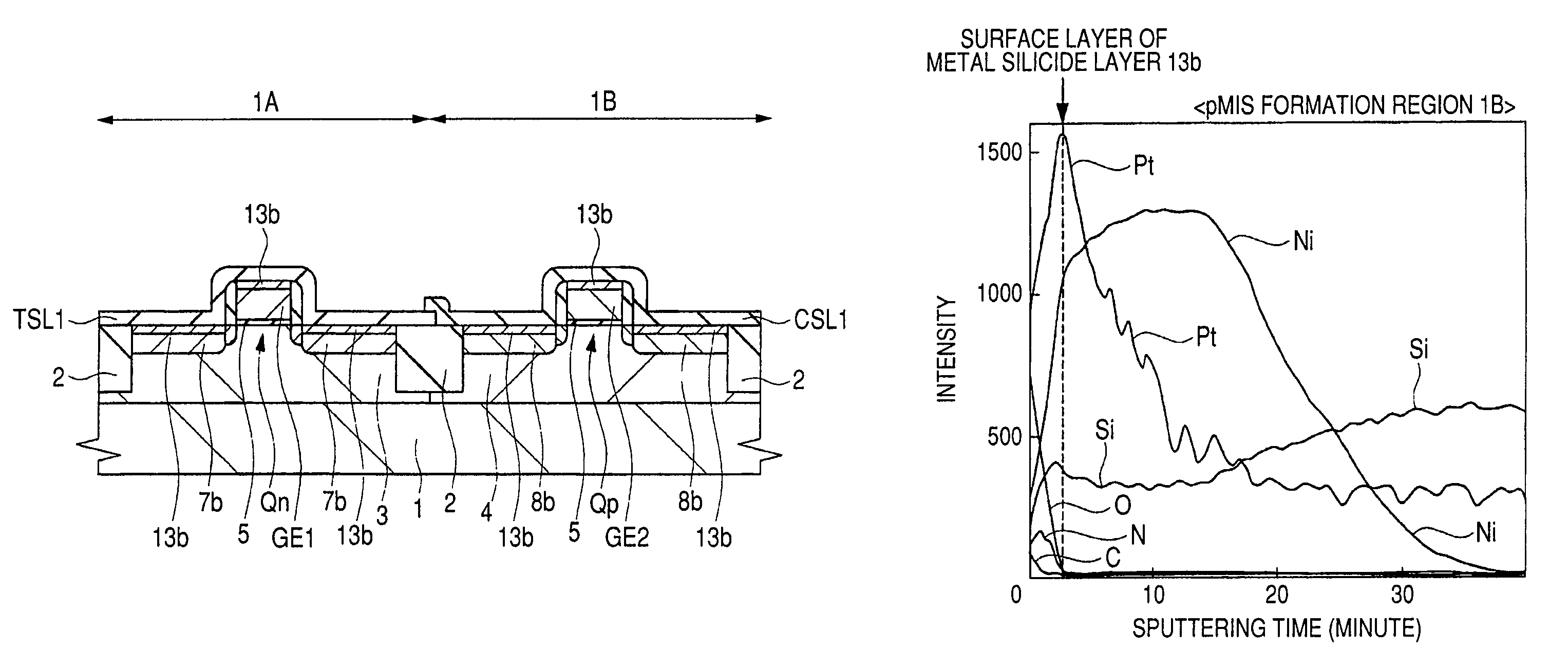
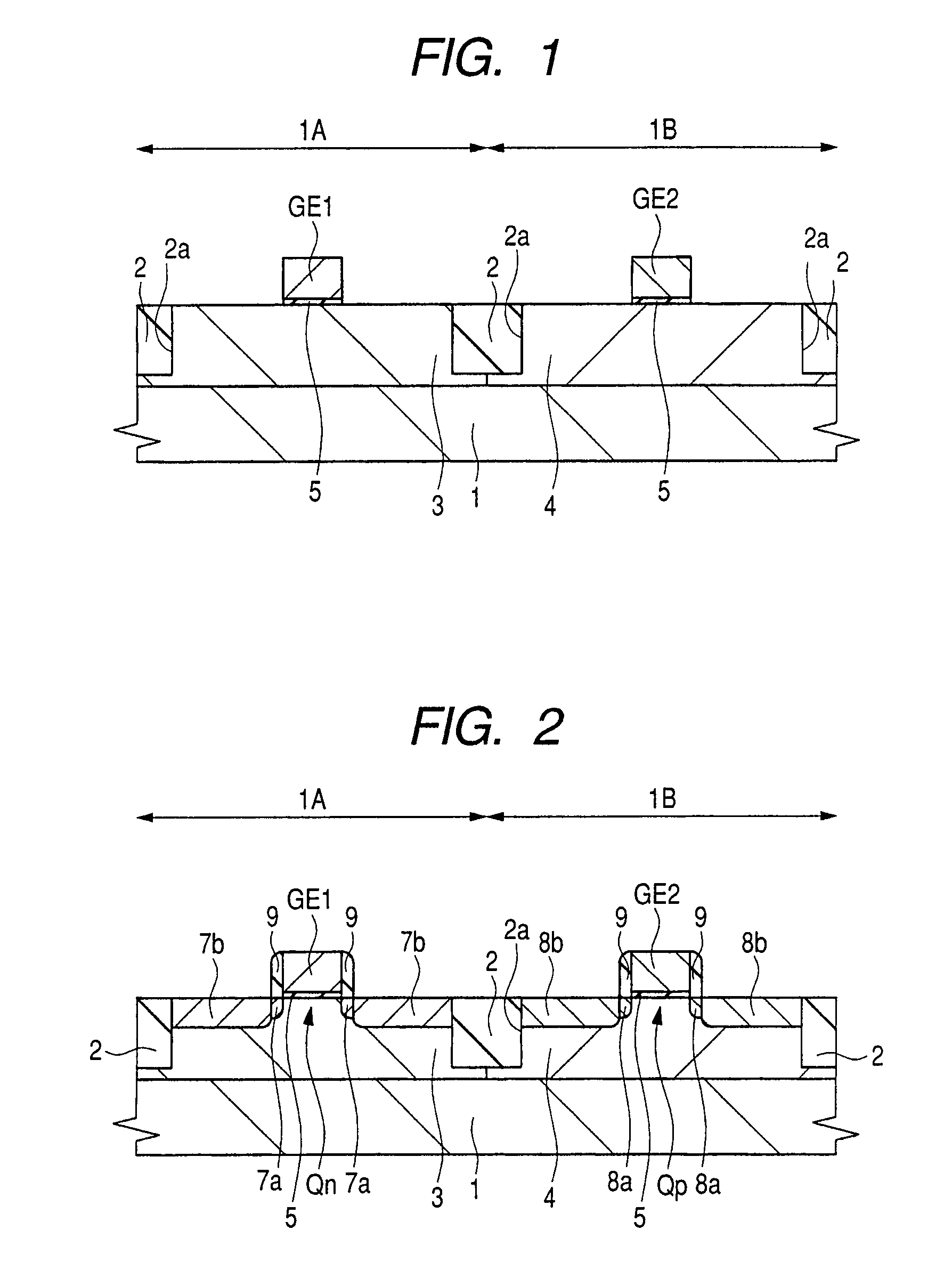
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing same
InactiveUS20100230761A1Improve semiconductor device performanceImprove performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSalicidePlatinum silicide
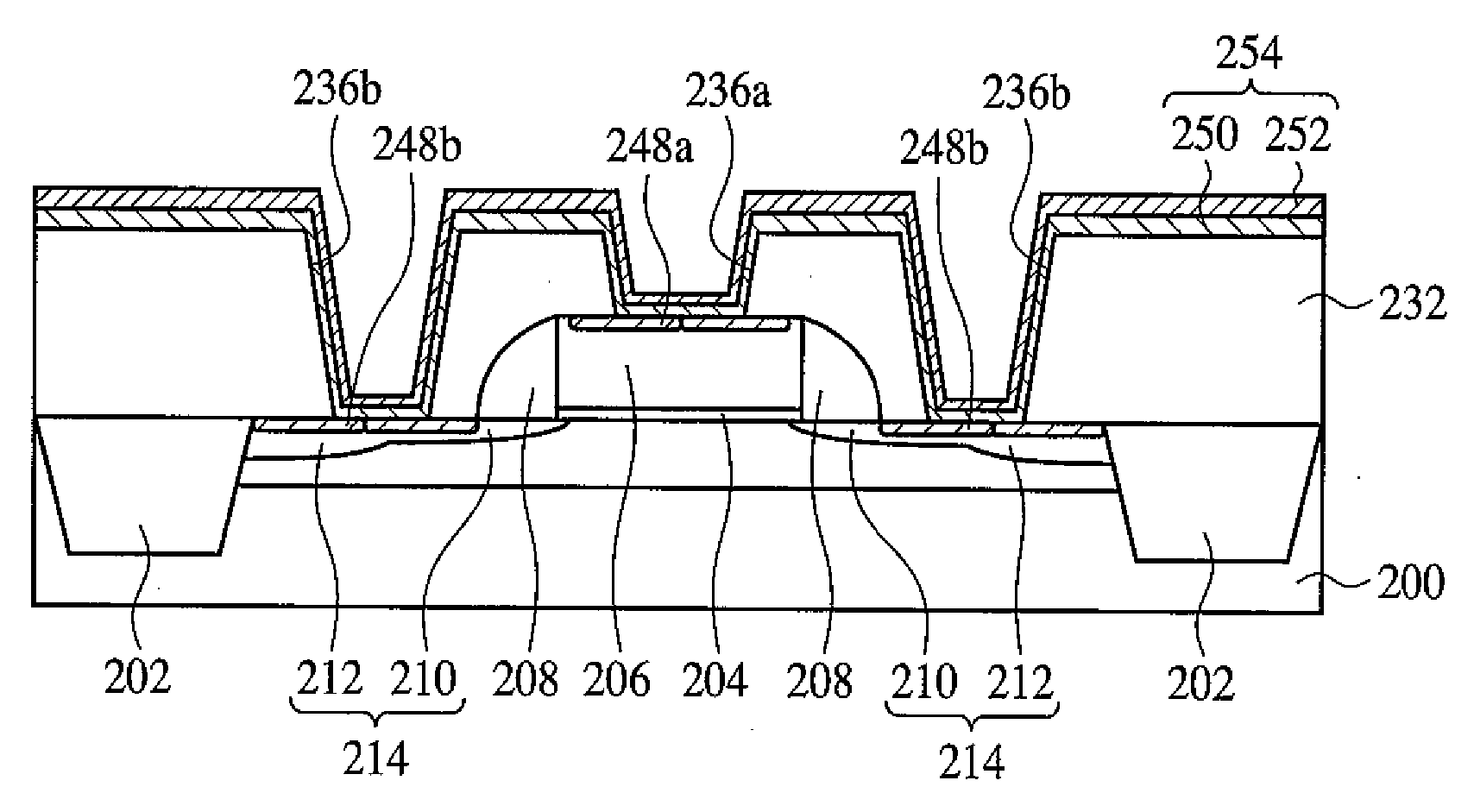
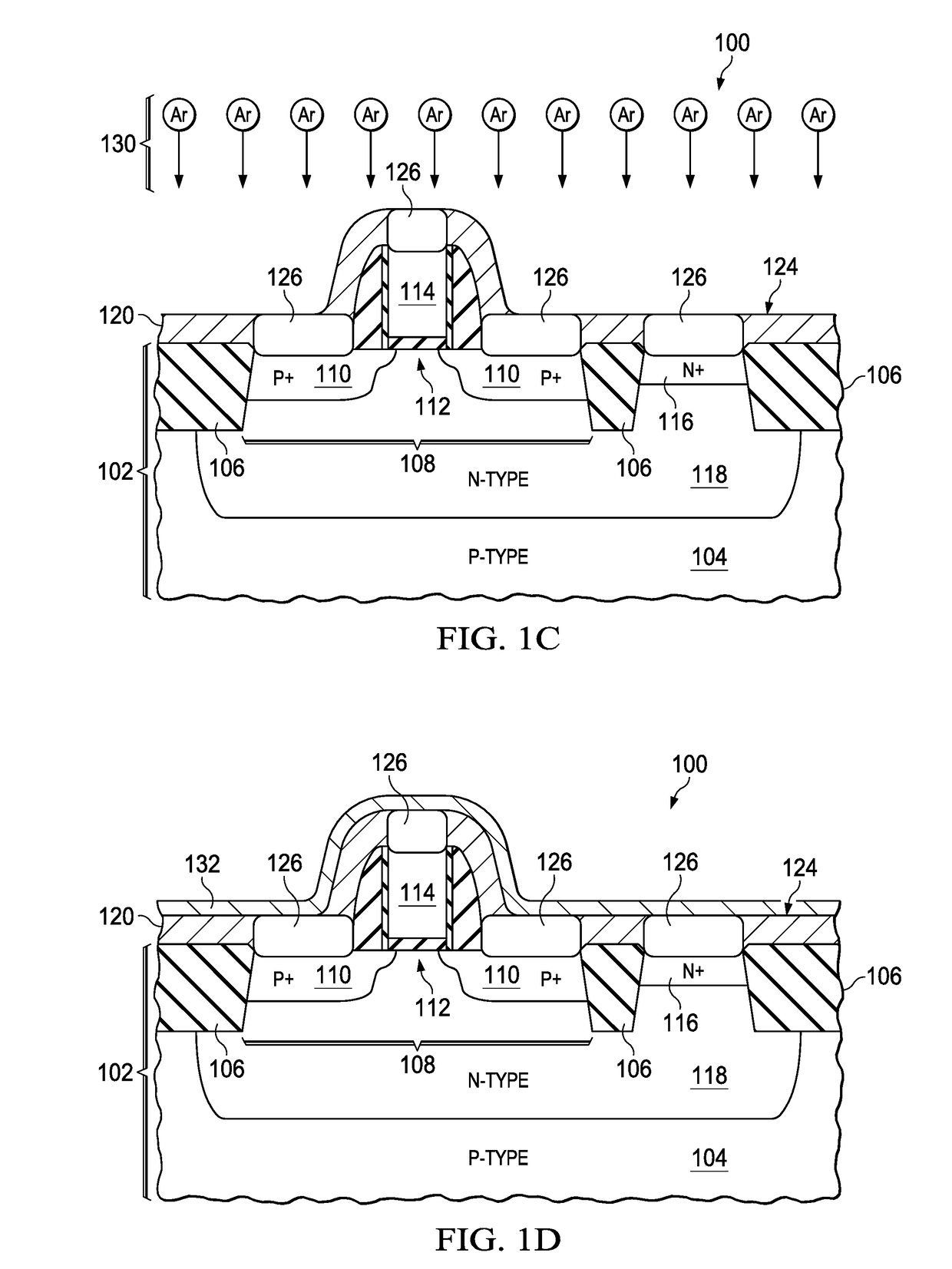
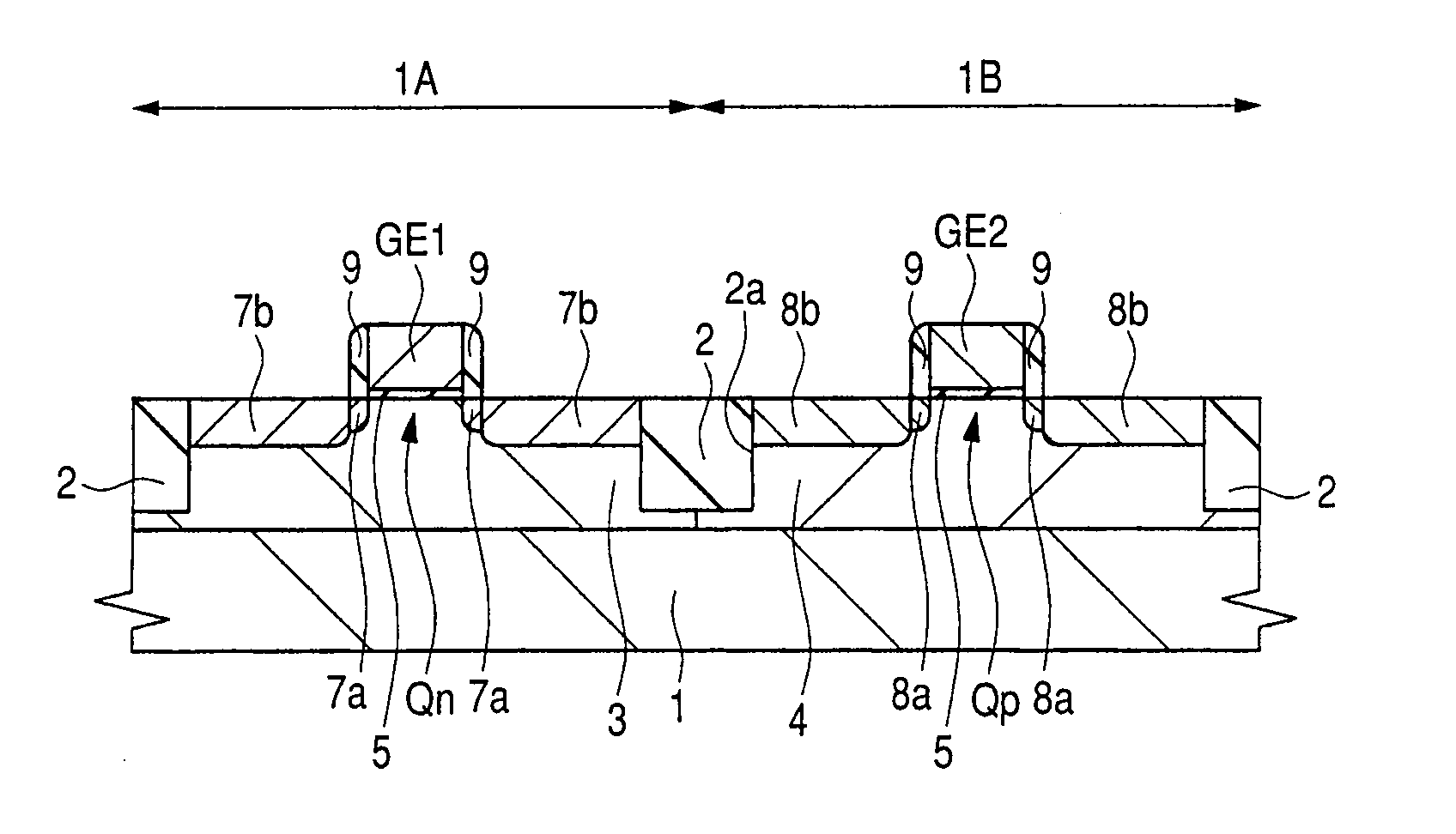
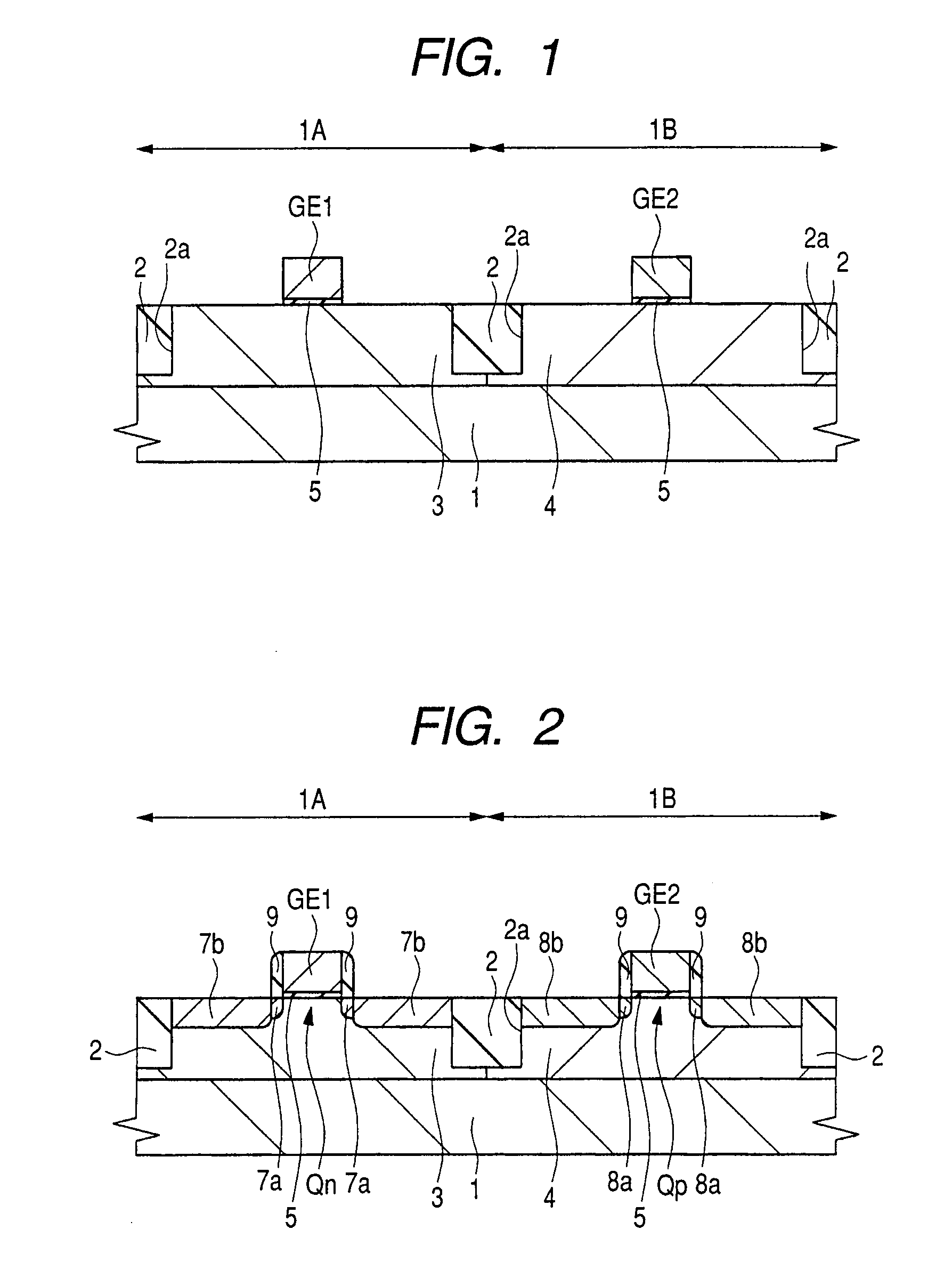
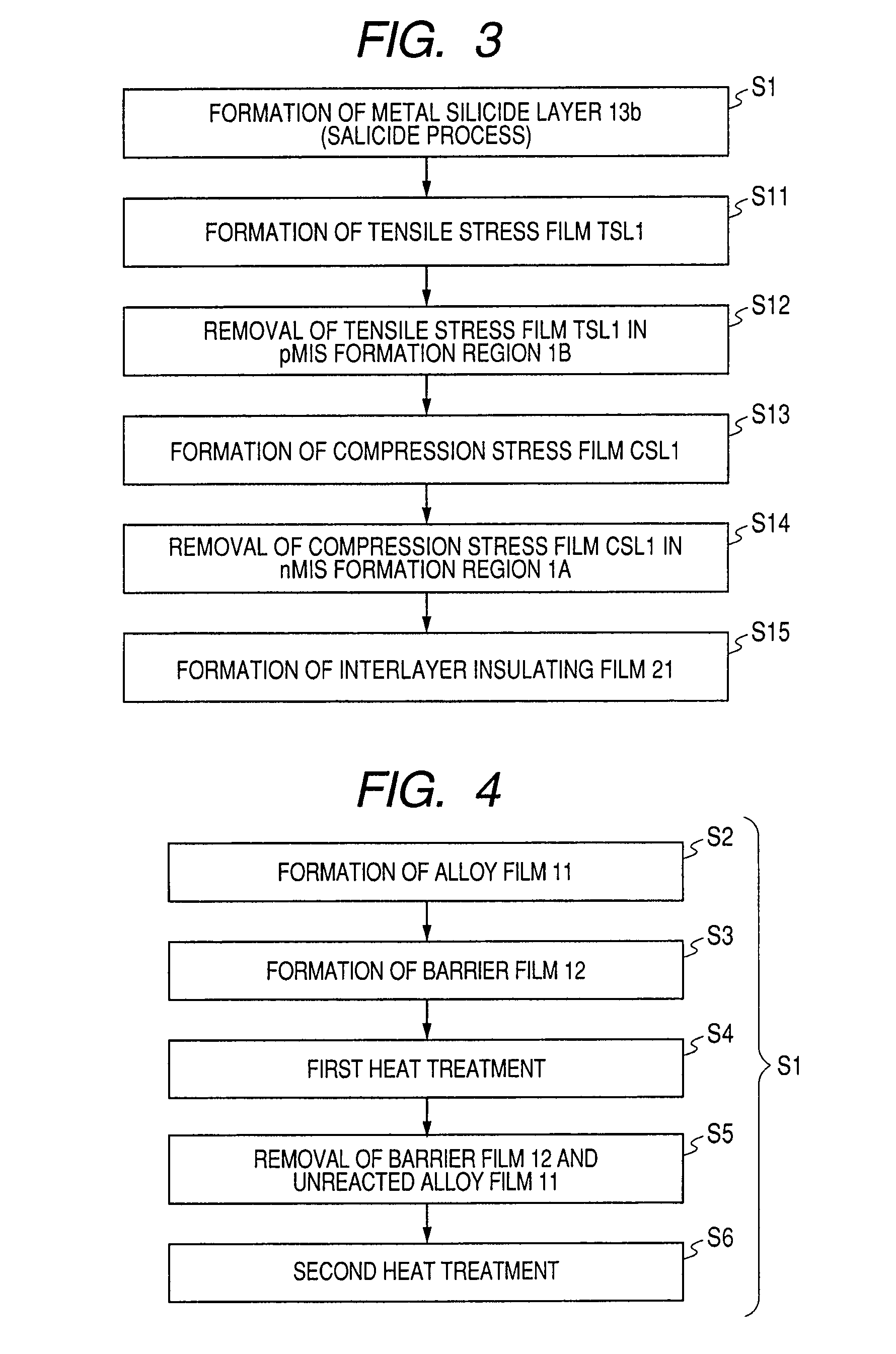
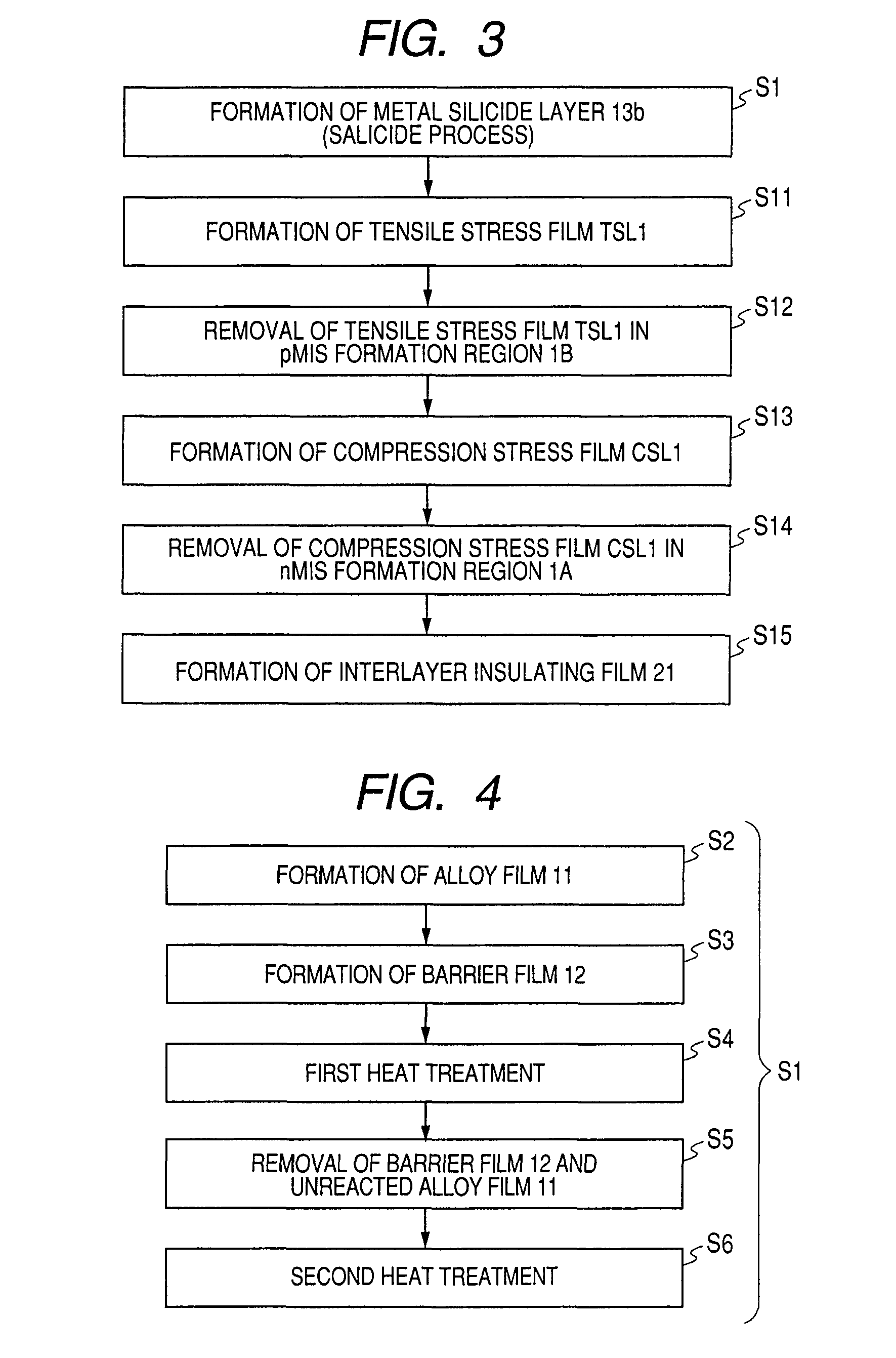
To improve the performance of semiconductor devices. Over an n+-type semiconductor region for source / drain of an n-channel type MISFET and a first gate electrode, and over a p+-type semiconductor region for source / drain of a p-channel type MISFET and a second gate electrode, which are formed over a semiconductor substrate, a metal silicide layer including nickel platinum silicide is formed by a salicide process. After that, a tensile stress film is formed over the whole face of the semiconductor substrate, and then the tensile stress film over the p-channel type MISFET is removed by dry-etching, and, after a compression stress film is formed over the whole face of the semiconductor substrate, the compression stress film over the n-channel type MISFET is removed by dry-etching. The Pt concentration in the metal silicide layer is highest at the surface, and becomes lower as the depth from the surface increases.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Method Of Preparing An Organohalosilane
InactiveUS20120289730A1Silicon organic compoundsOrganic chemistry methodsPlatinumMedicinal chemistry
A method of preparing organohalosilanes comprising combining an organohalide having the formula RX (I), wherein R is a hydrocarbyl group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms and X is fluoro, chloro, bromo, or iodo, with a contact mass comprising at least 2% (w / w) of a palladium suicide of the formula PdxSiy (II), wherein x is an integer from 1 to 5 and y is 1 to 8, or a platinum suicide of formula Pt2Si (III), wherein z is 1 or 2, in a reactor at a temperature from 250 to 700° C. to form an organohalosilane.
Owner:DOW CORNING CORP
Method of fabricating metal silicide layer
ActiveUS20060154474A1Increase resistanceReduce line widthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh resistancePlatinum silicide
A method of fabricating a metal silicide layer over a substrate is provided. First, a hard mask layer is formed over a gate formed on a substrate and a portion of the substrate is exposed. Thereafter, a first metal silicide layer, which is a cobalt silicide or a titanium silicide layer, is formed on the exposed substrate. After that, the hard mask layer is removed and a second metal silicide layer is formed over the gate, wherein a material of the second metal silicide layer is selected from a group consisting of nickel silicide, platinum silicide, palladium silicide and nickel alloy. Since different metal silicide layers are formed on the substrate and the gate, the problem of having a high resistance in lines with a narrow line width and the problem of nickel silicide forming spikes and pipelines in the source region and the drain region are improved.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS8679973B2TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor devicePlatinum silicide
The method of manufacturing the semiconductor device comprises forming a transistor including a gate electrode and a source / drain diffused layer over a semiconductor substrate, forming a nickel platinum film over the semiconductor substrate, covering the gate electrode and the source / drain diffused layer, making a first thermal processing to react the nickel platinum film with the source / drain diffused layer to form a nickel platinum silicide film, and removing an unreacted part of the nickel platinum film using a chemical liquid of 71° C. or more containing hydrogen peroxide.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
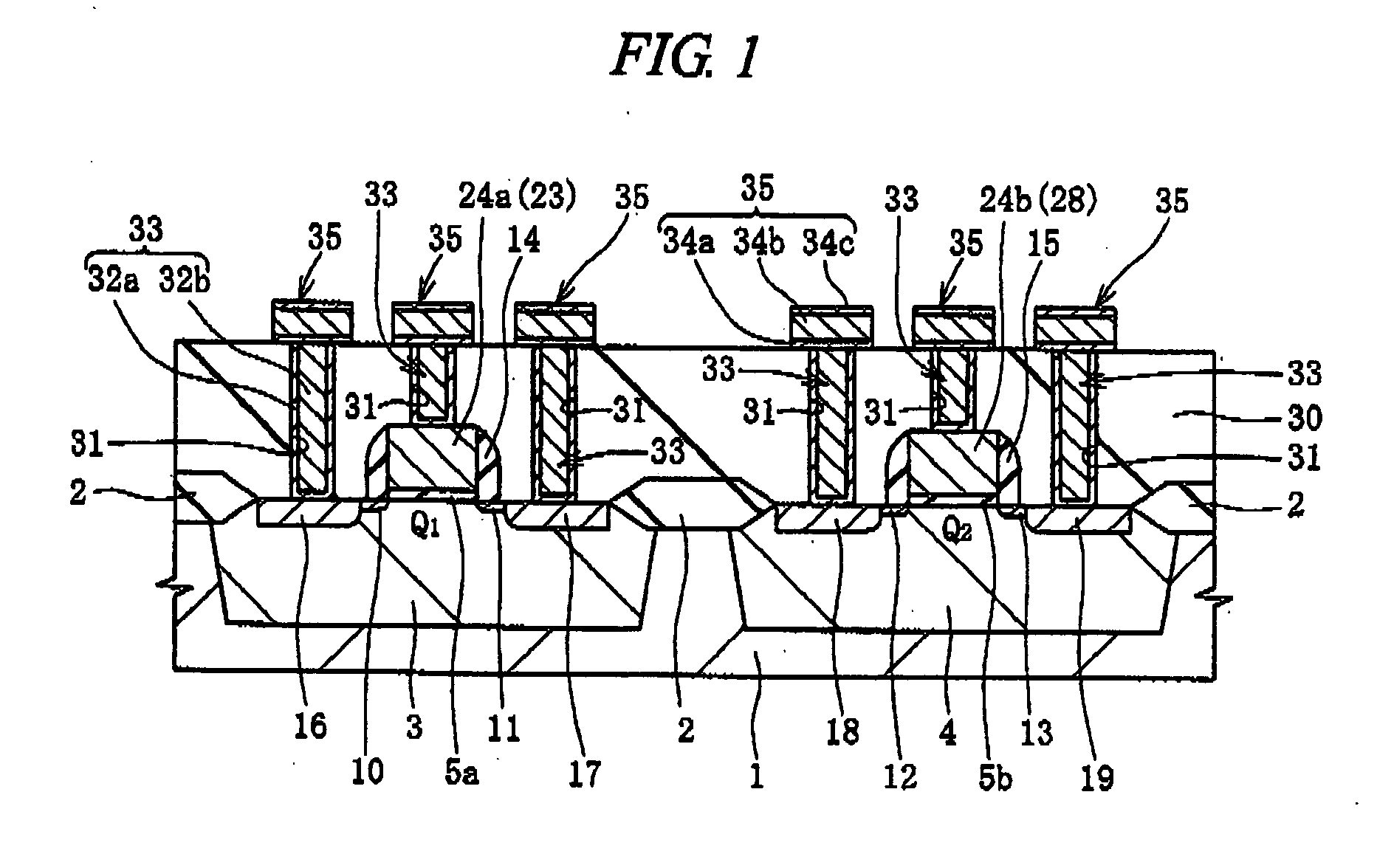
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing same
InactiveUS8338247B2Improve mobilityReduce resistanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSalicidePlatinum silicide
To improve the performance of semiconductor devices. Over an n+-type semiconductor region for source / drain of an n-channel type MISFET and a first gate electrode, and over a p+-type semiconductor region for source / drain of a p-channel type MISFET and a second gate electrode, which are formed over a semiconductor substrate, a metal silicide layer including nickel platinum silicide is formed by a salicide process. After that, a tensile stress film is formed over the whole face of the semiconductor substrate, and then the tensile stress film over the p-channel type MISFET is removed by dry-etching, and, after a compression stress film is formed over the whole face of the semiconductor substrate, the compression stress film over the n-channel type MISFET is removed by dry-etching. The Pt concentration in the metal silicide layer is highest at the surface, and becomes lower as the depth from the surface increases.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Etching platinum-containing thin film using protective cap layer
ActiveUS10504733B2TransistorRuthenium/rhodium/palladium/osmium/iridium/platinum oxides/hydroxidesPlatinum silicidePlatinum oxide
A microelectronic device is formed by forming a platinum-containing layer on a substrate of the microelectronic device. A cap layer is formed on the platinum-containing layer so that an interface between the cap layer and the platinum-containing layer is free of platinum oxide. The cap layer is etchable in an etch solution which also etches the platinum-containing layer. The cap layer may be formed on the platinum-containing layer before platinum oxide forms on the platinum-containing layer. Alternatively, platinum oxide on the platinum-containing layer may be removed before forming the cap layer. The platinum-containing layer may be used to form platinum silicide. The platinum-containing layer may be patterned by forming a hard mask or masking platinum oxide on a portion of the top surface of the platinum-containing layer to block the wet etchant.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Low parasitic capacitance and resistance finFET device
Described herein is a semiconductor structure and method of manufacture. The semiconductor structure includes a plurality of semiconductor fins on a substrate and a plurality of raised active regions, wherein each raised active region is located on sidewalls of a corresponding semiconductor fin among said plurality of semiconductor fins. The raised active regions are laterally spaced from any other of the raised active regions. Each raised active region comprises angled sidewall surfaces that are not parallel or perpendicular to a topmost horizontal surface of said substrate. The raised active regions are silicon germanium (SiGe). The semiconductor structure includes a metal semiconductor alloy region contacting at least said angled sidewall surfaces of at least two adjacent raised active regions. The semiconductor alloy region includes a material selected from the group consisting of nickel silicide, nickel-platinum silicide and cobalt silicide.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Technical window method for removing unreacted nickel-platinum silicide in increased wet method
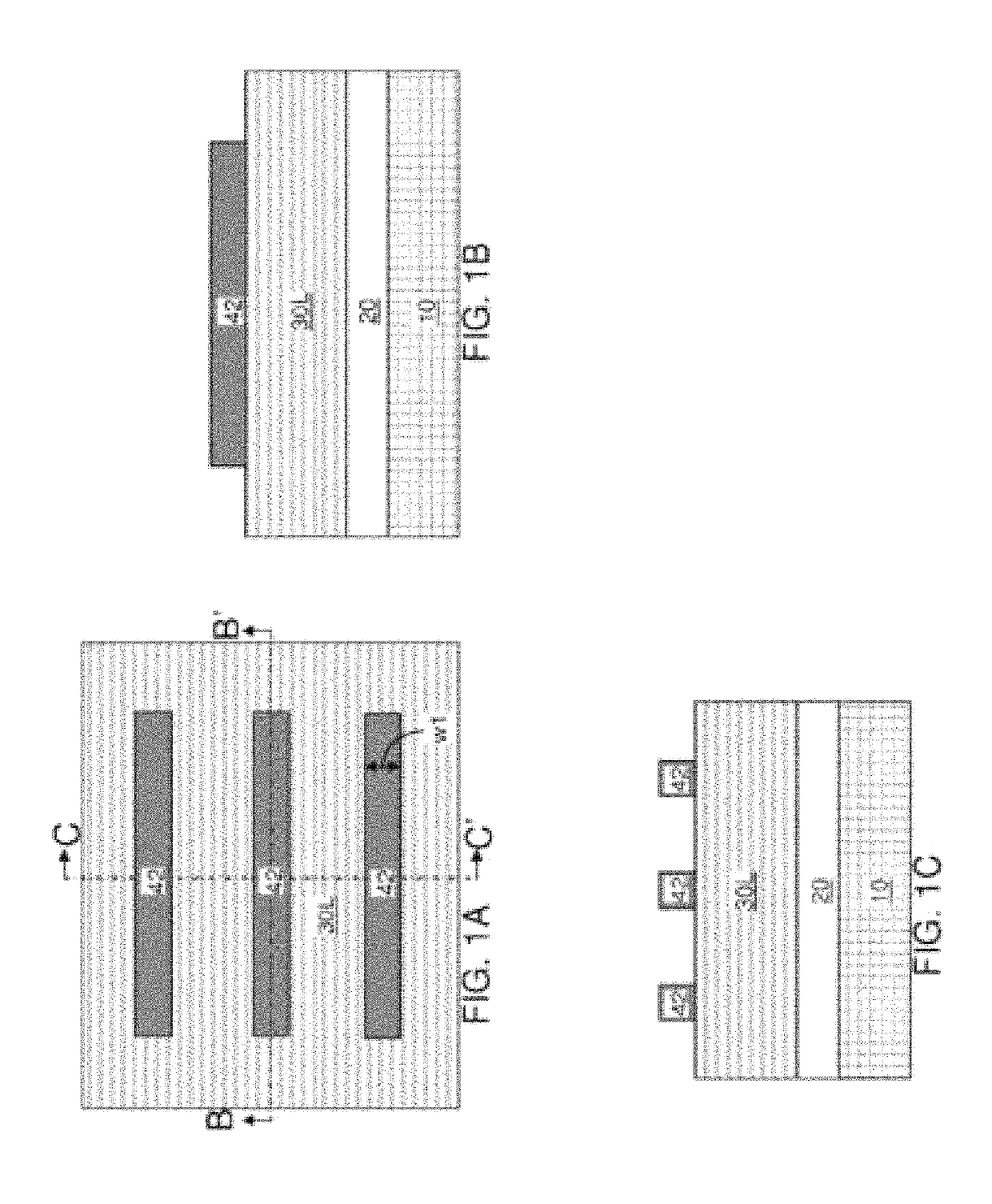
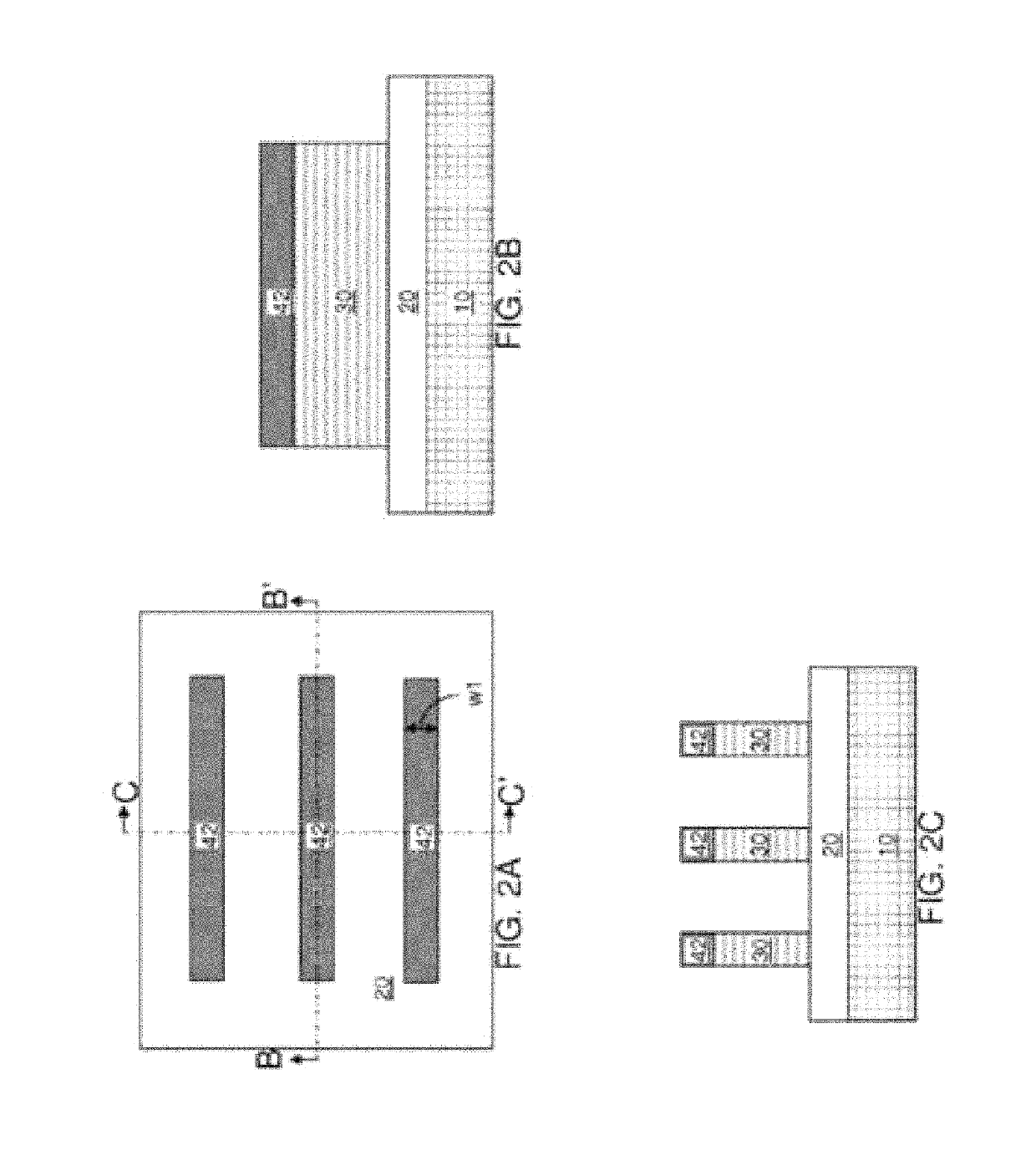
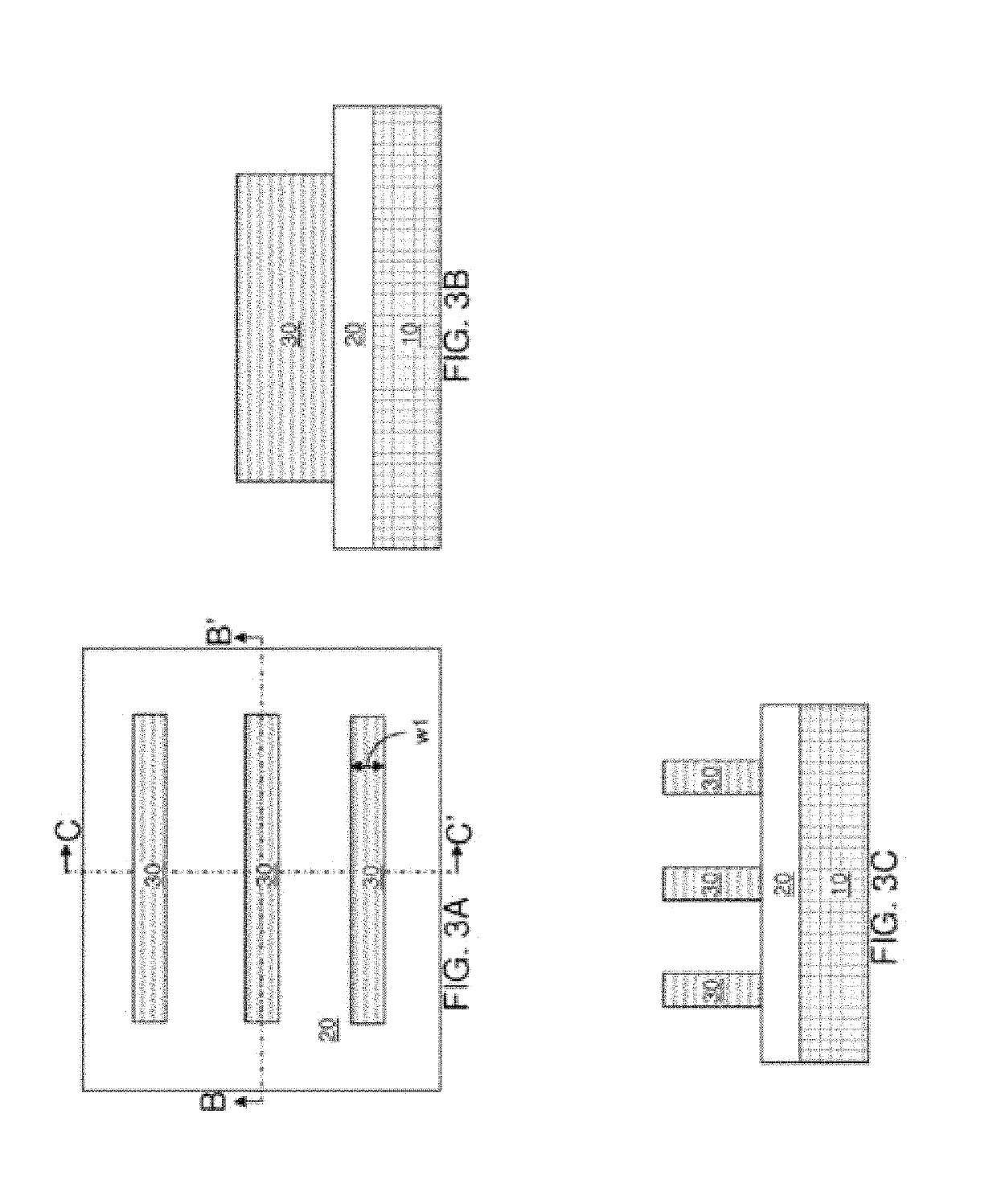
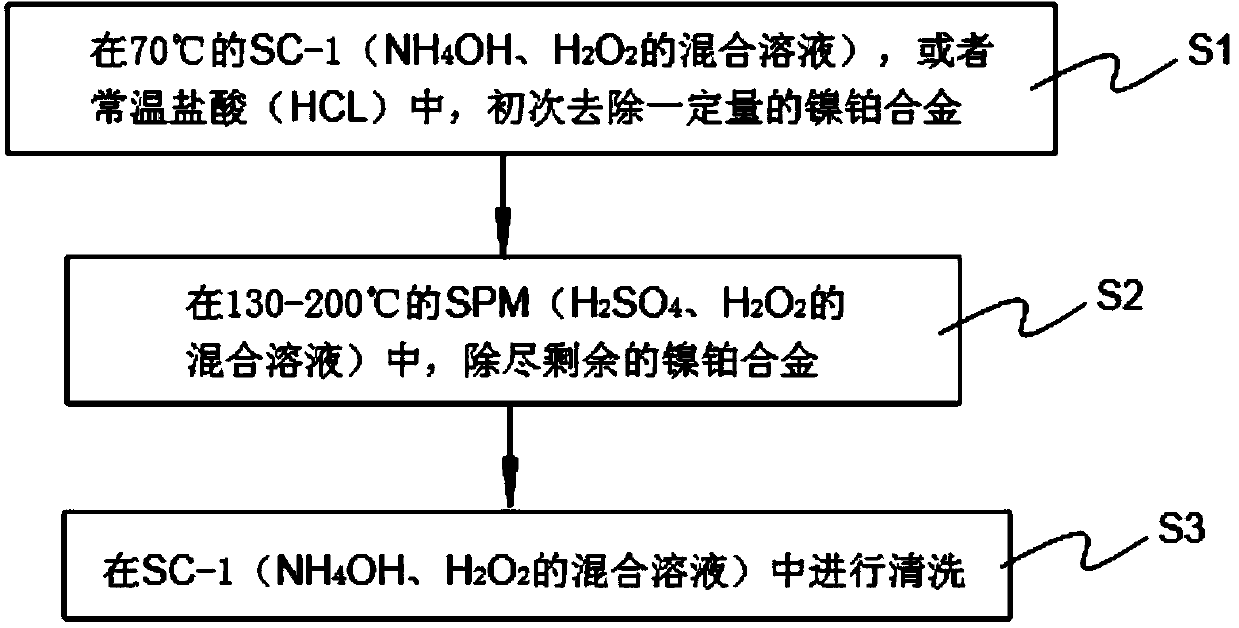
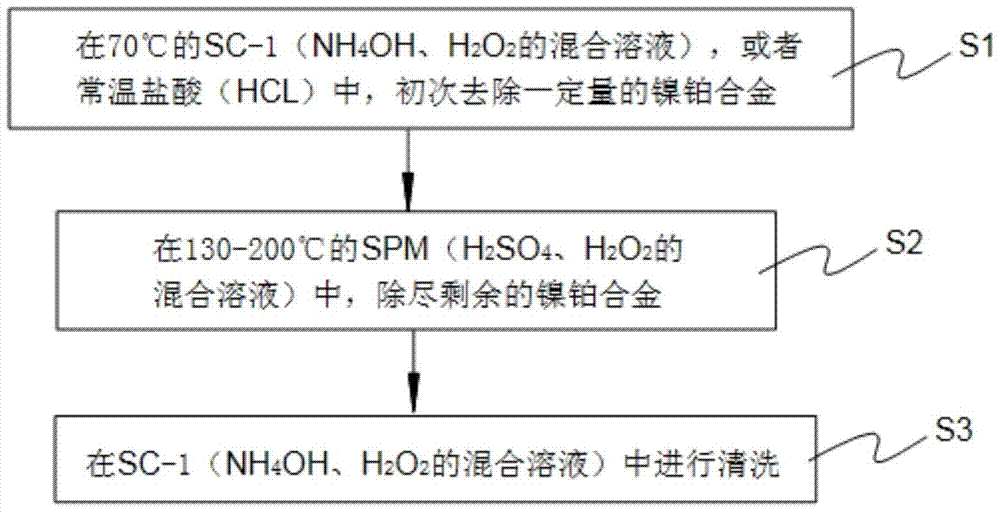
Provided is a technical window method for removing unreacted nickel-platinum silicide in an increased wet method. The method comprises the steps that S1) certain amount of nickel and platinum alloy is removed from an NH4OH and H2O2 mixed solution SC-1 at 70 DEG C or hydrochloric acid (HCL) at normal temperature for the first time; S2) residual nickel and platinum alloy is completely removed from an NH4OH and H2O2 mixed solution SPM at 130 to 200 DEG C; and S3) cleaning is carried out in the NH4OH and H2O2 mixed solution SC-1. According to the method, certain amount of nickel and platinum alloy is removed from the NH4OH and H2O2 mixed solution SC-1 at 70 DEG C or hydrochloric acid (HCL) at normal temperature for the first time; the residual nickel and platinum alloy is completely removed from the NH4OH and H2O2 mixed solution SPM at 130 to 200 DEG C due to the fact that proper excessive etching is carried out due to the excellent selectivity ratio of SPM to the nickel-platinum alloy; and thus, a technical window can be etched in the increased wet method.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Method for Enlarging the Process Window of Wet Removal of Unreacted Nickel-Platinum Silicide
Provided is a technical window method for removing unreacted nickel-platinum silicide in an increased wet method. The method comprises the steps that S1) certain amount of nickel and platinum alloy is removed from an NH4OH and H2O2 mixed solution SC-1 at 70 DEG C or hydrochloric acid (HCL) at normal temperature for the first time; S2) residual nickel and platinum alloy is completely removed from an NH4OH and H2O2 mixed solution SPM at 130 to 200 DEG C; and S3) cleaning is carried out in the NH4OH and H2O2 mixed solution SC-1. According to the method, certain amount of nickel and platinum alloy is removed from the NH4OH and H2O2 mixed solution SC-1 at 70 DEG C or hydrochloric acid (HCL) at normal temperature for the first time; the residual nickel and platinum alloy is completely removed from the NH4OH and H2O2 mixed solution SPM at 130 to 200 DEG C due to the fact that proper excessive etching is carried out due to the excellent selectivity ratio of SPM to the nickel-platinum alloy; and thus, a technical window can be etched in the increased wet method.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI MICROELECTRONICS CORP
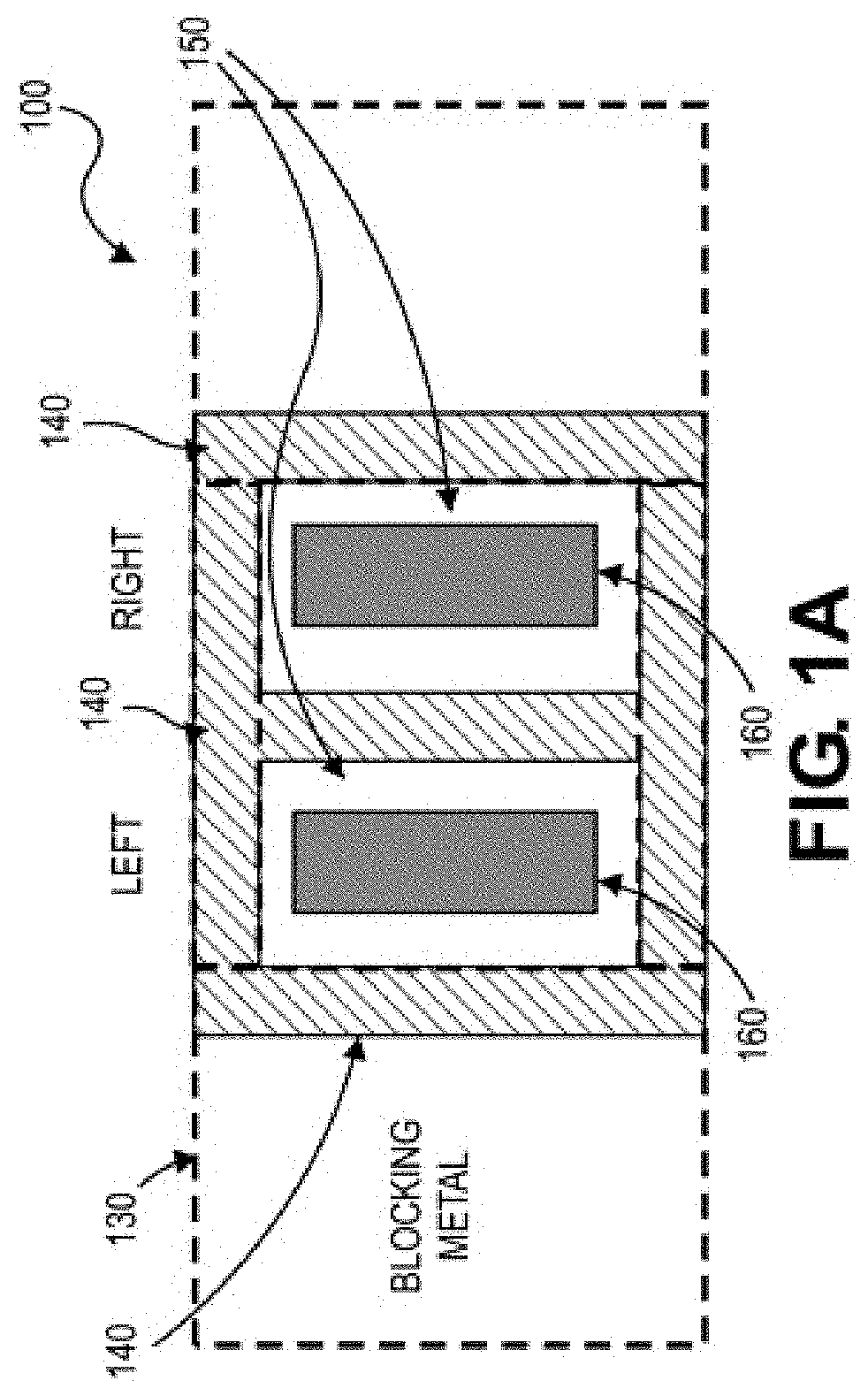
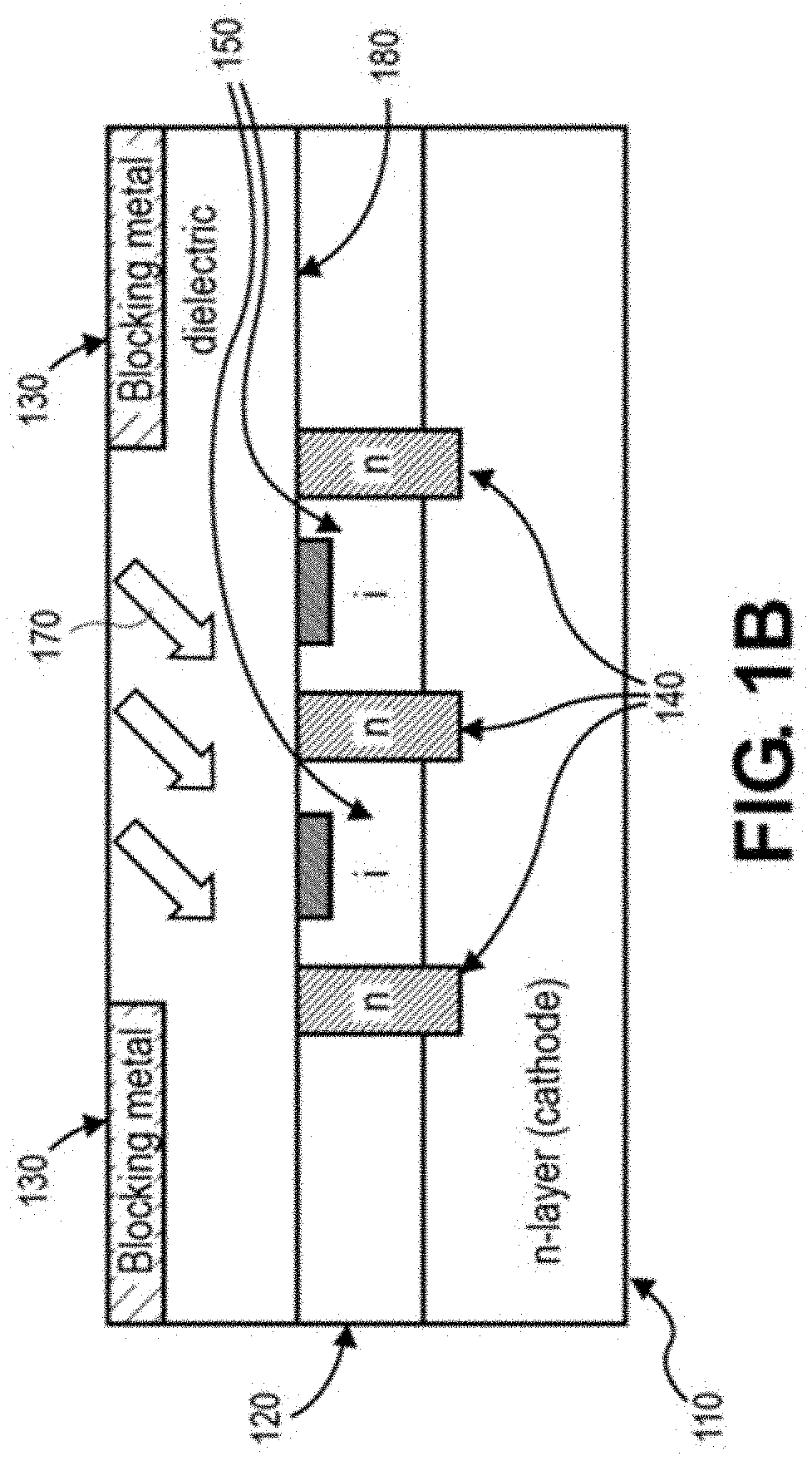
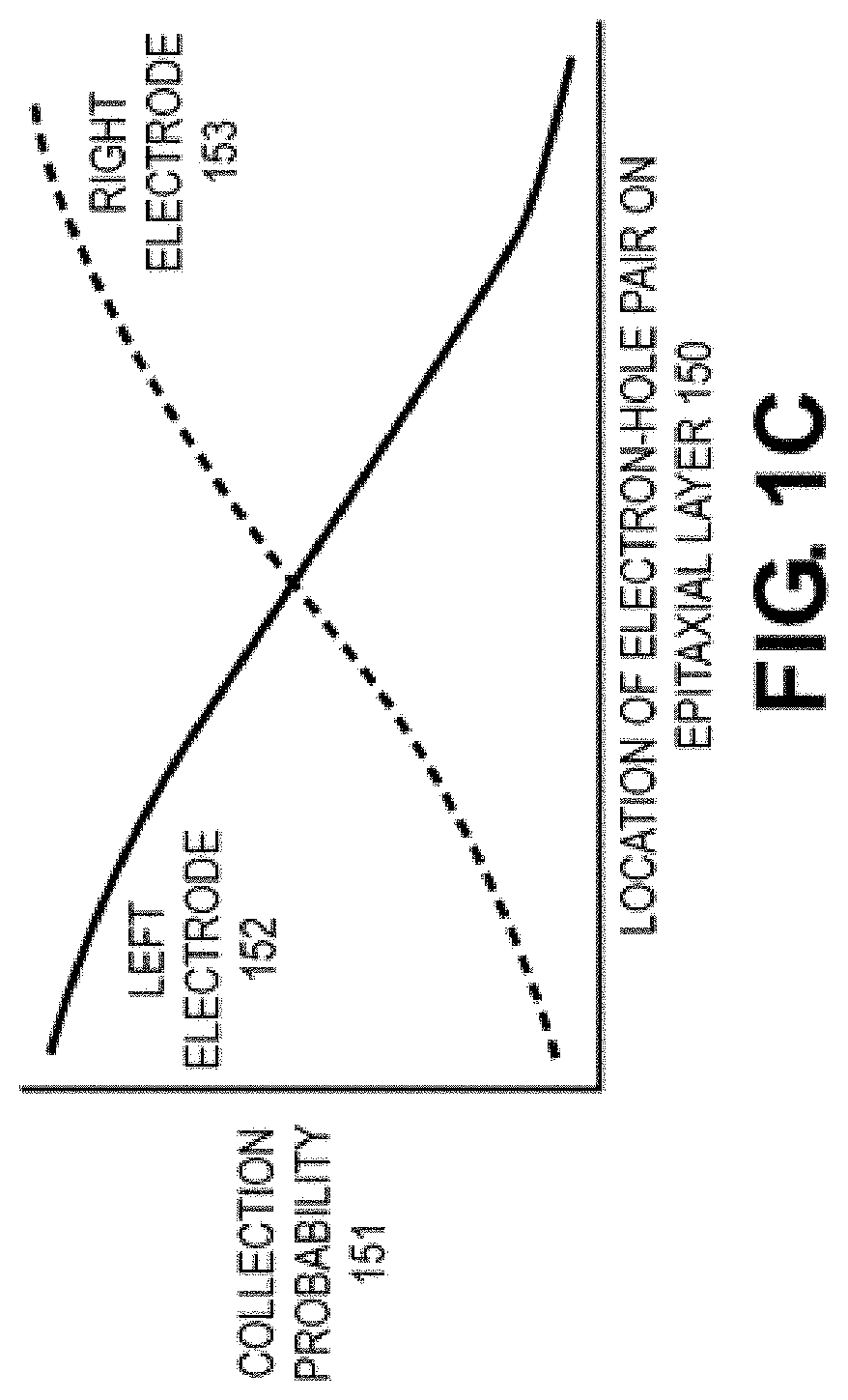
Self-aligned light angle sensor using thin metal silicide anodes
PendingCN113494894AChange positionExemplary stableFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesThin metalPlatinum silicide
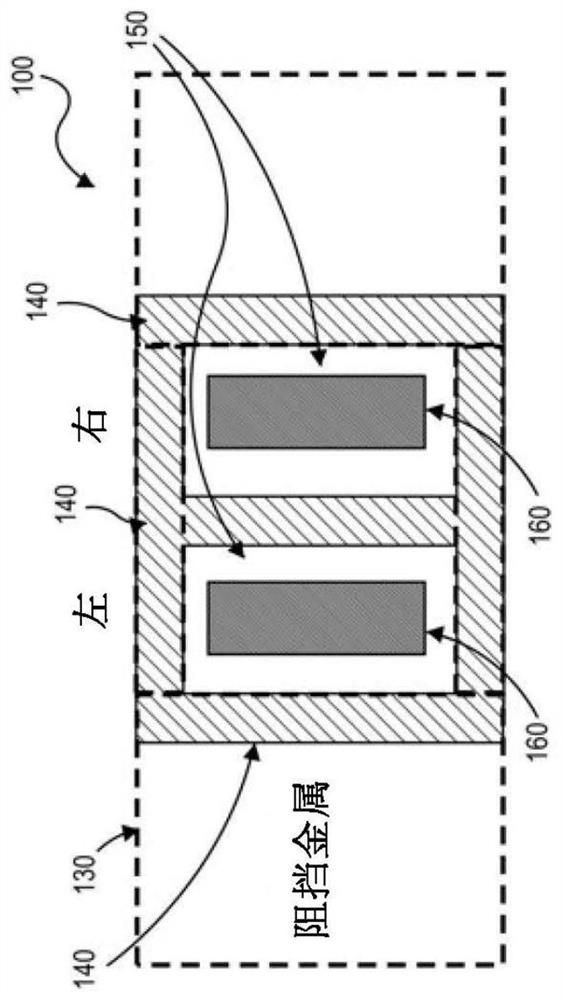
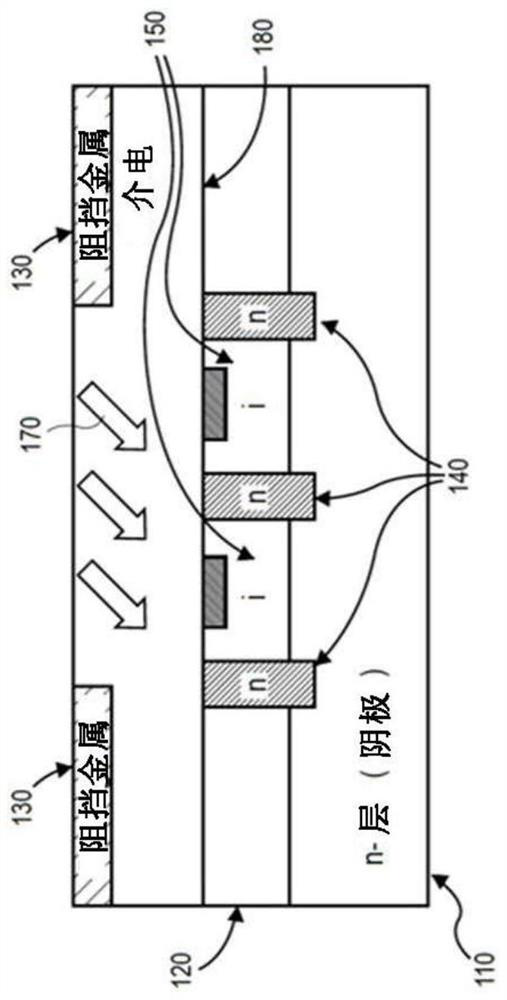
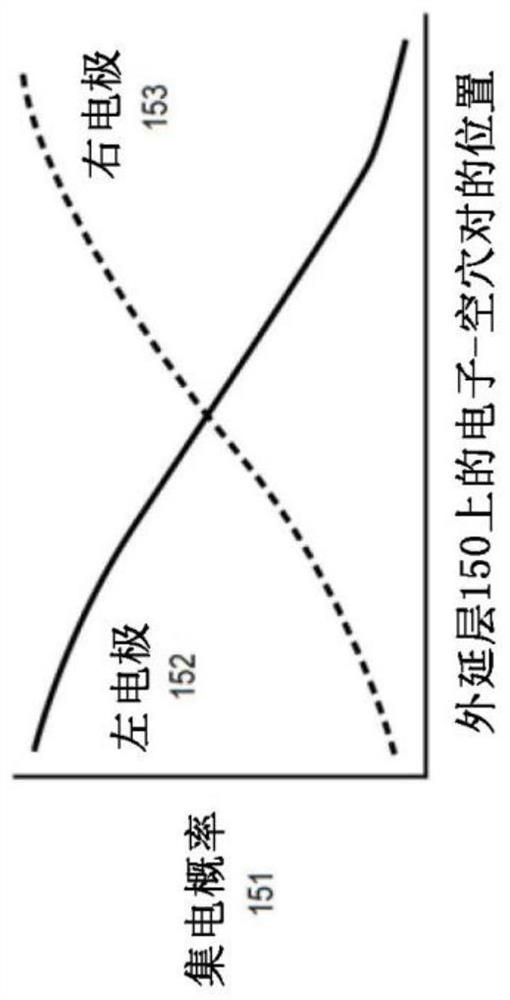
The invention relates to a self-aligned light angle sensor using thin metal silicide anodes. Aspects of the embodiments are directed to non-contact systems, methods and devices for optical detection of objects in space at precise angles. This method involves the design and fabrication of photodiode arrays for measuring angular response using self-aligned Schottky platinum silicide (PtSi) PIN photodiodes (PN-diodes with an intrinsic layer sandwiched in between) that provide linear angular measurements from incident light in multiple dimensions. A self-aligned device is defined as one in which is not sensitive to photomask layer registrations. This design eliminates device offset between "left" and right" channels for normal incident light as compared to more conventional PIN diode constructions.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Self-aligned light angle sensor using thin metal silicide anodes
ActiveUS20210293535A1Improve flowSolid-state devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringThin metalPlatinum silicide
Aspects of the embodiments are directed to non-contact systems, methods and devices for optical detection of objects in space at precise angles. This method involves the design and fabrication of photodiode arrays for measuring angular response using self-aligned Schottky platinum silicide (PtSi) PIN photodiodes (PN-diodes with an intrinsic layer sandwiched in between) that provide linear angular measurements from incident light in multiple dimensions. A self-aligned device is defined as one in which is not sensitive to photomask layer registrations. This design eliminates device offset between “left” and right” channels for normal incident light as compared to more conventional PIN diode constructions.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
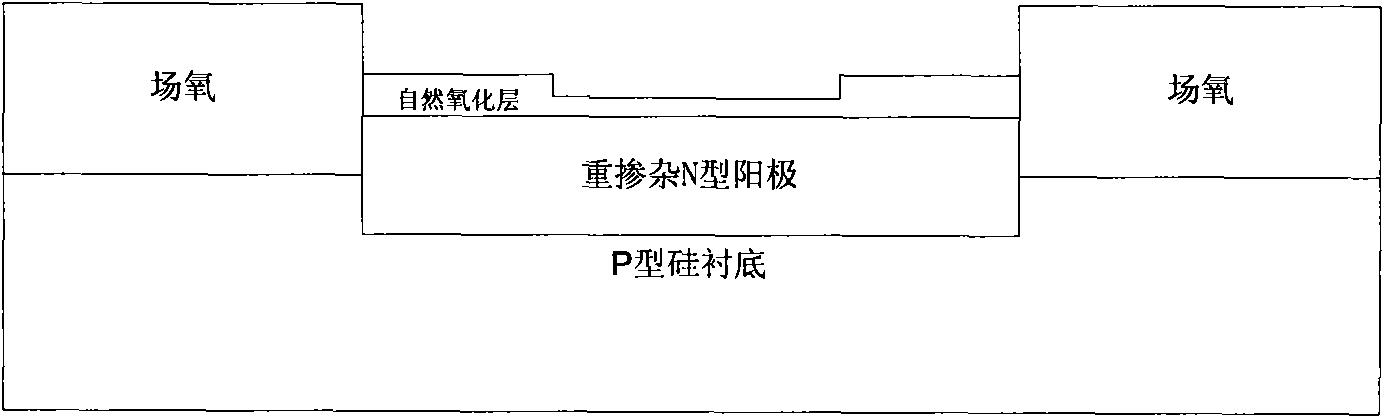
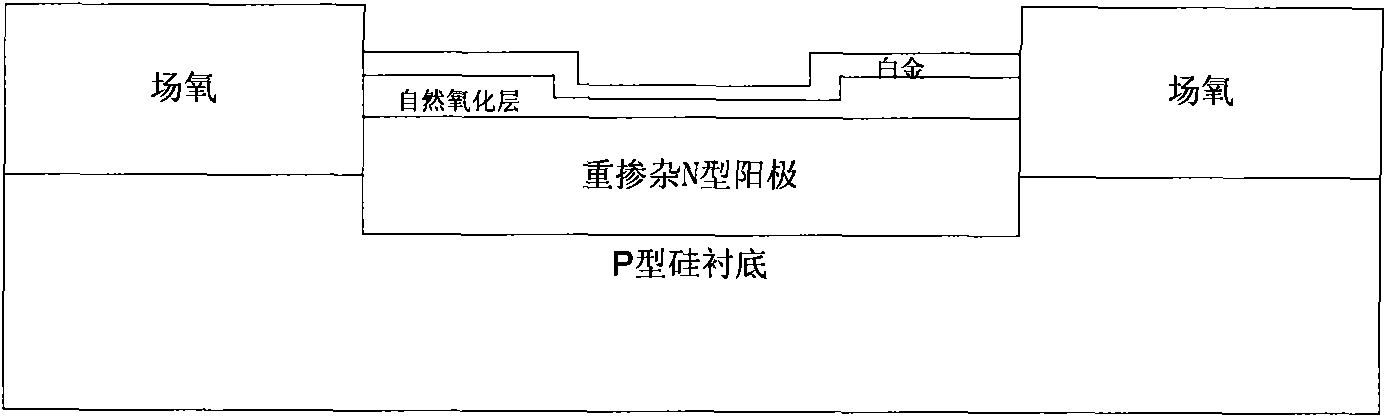
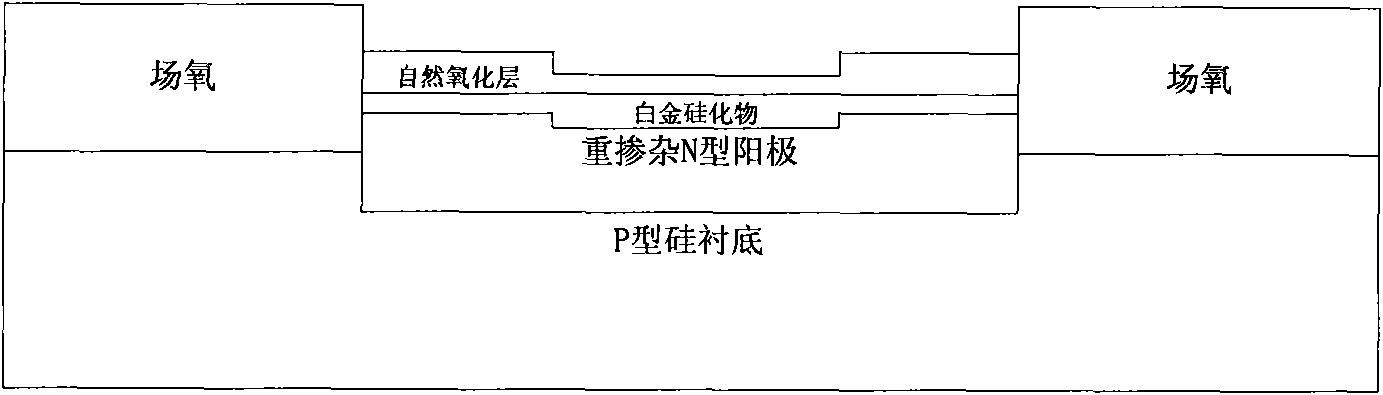
Fast recovery diode and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101882631AGuaranteed uniformitySolving Velocity Uniformity IssuesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSalicidePlatinum silicide
The invention discloses a fast recovery diode and a manufacturing method thereof, relating to the field of micro-electronics, and solving the problem of speed uniformity of switching DIE to DIE and WAFER to WAFER of the fast recovery diode manufactured by the traditional technology. The fast recovery diode of the invention comprises a silicon substrate, a heavy doping anode, field oxide, a platinum silicide layer and an even silicon dioxide layer, wherein the heavy doping anode is deposited on the silicon substrate, the field oxide is deposited on the silicon substrate and is arranged on two sides of the heavy doping anode, the platinum silicide layer is formed on the heavy doping anode, and the even silicon dioxide layer is formed on the platinum silicide layer. The method comprises the following steps: forming the even silicide dioxide layer on the silicon substrate on which the heavy doping anode and the field oxide are deposited after the cleaning; depositing a metal layer with the sputtering or evaporating method; and by using the alloy technology, forming even silicide nodes. The invention is applied to manufacture of the fast recovery diode.
Owner:商海涵
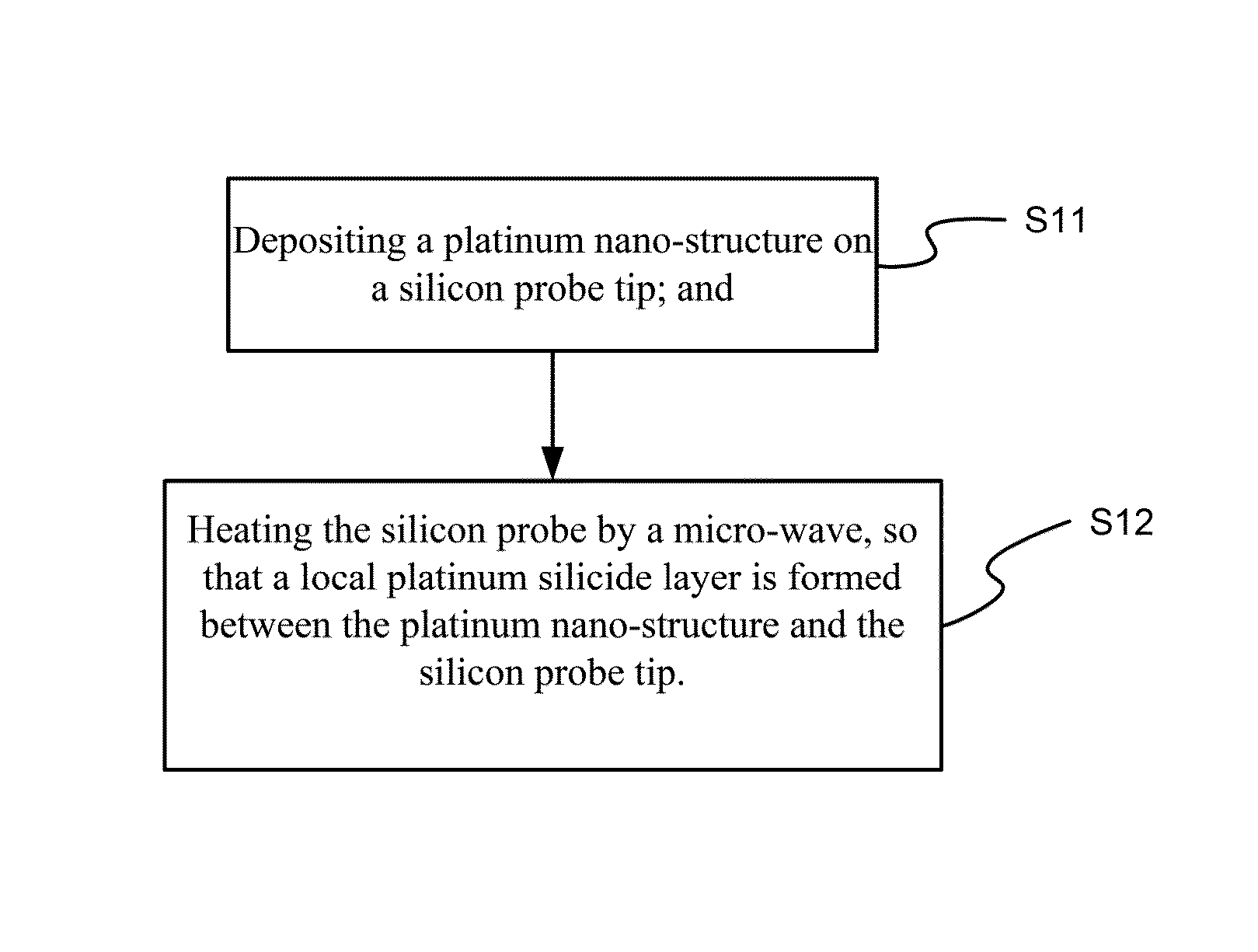
Tip structure of platinum-platinum silicide-silicon composite field sensor probe and method for forming MSTA strucutre on the probe
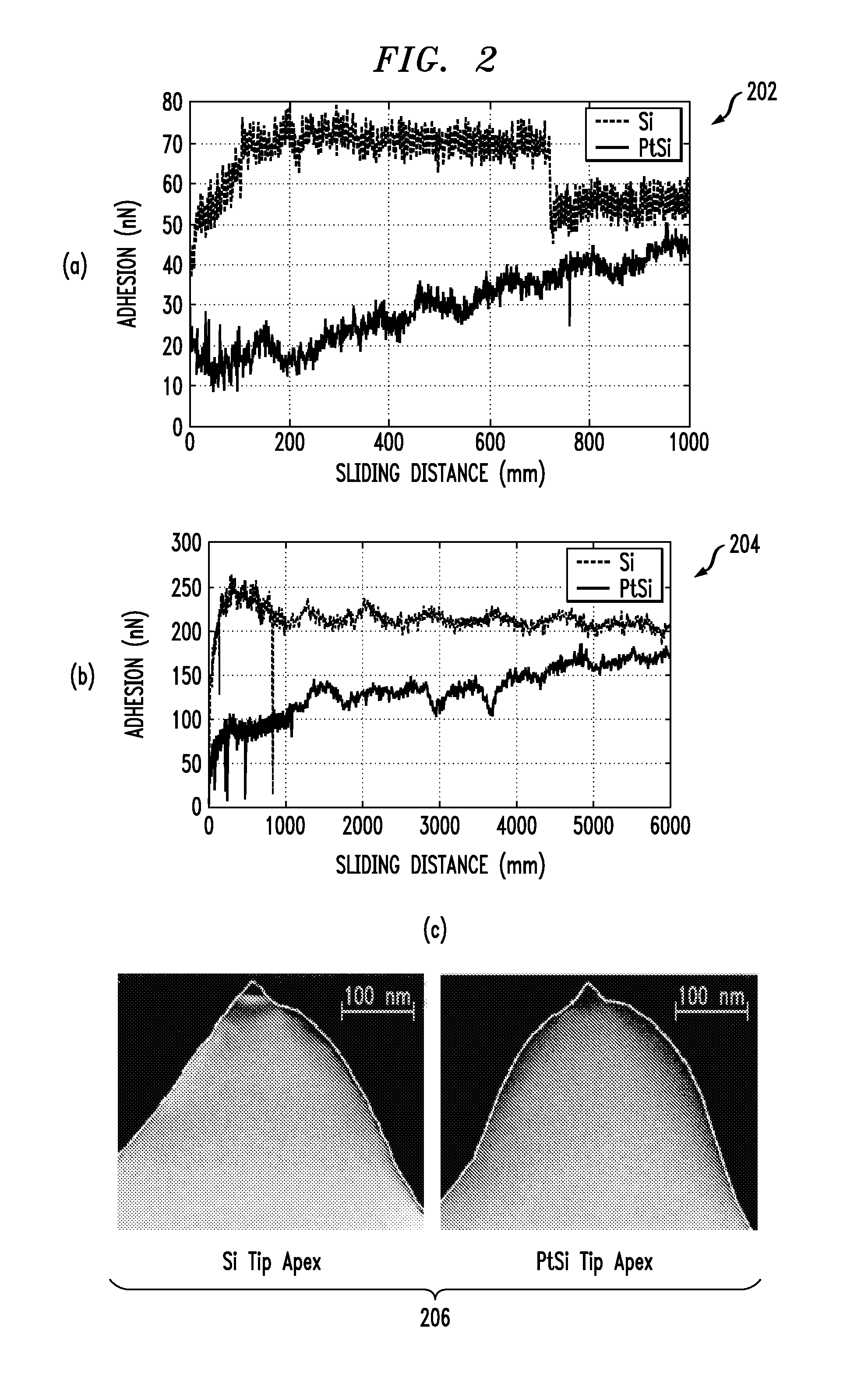
ActiveUS9255944B1Good spatial resolution and sensitivityImprove conductivityScanning probe microscopyNano structuringImaging quality
A platinum-platinum silicide modified silicon composite tip apex, and a method for forming the aforesaid tip apex are disclosed, where a metallic precursor solution and a silicon probe are reacted to form a local platinum nano-structure, which could be precisely controlled with local selectivity, and a local platinum silicide layer is formed between the platinum nano-structure and the silicon probe with an atmospheric microwave annealing (a-MWA) process conducted as well, largely enhancing the conductivity of the tip and spatial resolution of the field detection in field sensitive scanning probe microscopy. In addition to exemption from a stray-field effect and thus having better image quality, the platinum silicide-containing probe could more efficiently enhance the interfacial electron transfer efficiency as compared to the probe tip having only a platinum nano-structure, so that the probe could be applicable to a controlled conductive probe having high spatial resolution.
Owner:NAT APPLIED RES LAB
Method to attain low defectivity fully silicided gates
ActiveUS8273645B2High yieldIncreased complexityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSalicidePlatinum silicide
A method of forming fully silicided (FUSI) gates in MOS transistors which is compatible with wet etch processes used in source / drain silicide formation is disclosed. The gate silicide formation step produces a top layer of metal rich silicide which is resistant to removal in wet etch processes. A blocking layer over active areas prevents source / drain silicide formation during gate silicide formation. Wet etches during removal of the blocking layer and source / drain metal strip do not remove the metal rich gate silicide layer. Anneal of the gate silicide to produce a FUSI gate with a desired stoichiometry is delayed until after formation of the source / drain silicide. The disclosed method is compatible with nickel and nickel-platinum silicide processes.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Etching platinum-containing thin film using protective cap layer
ActiveUS20200083050A1TransistorRuthenium/rhodium/palladium/osmium/iridium/platinum oxides/hydroxidesPlatinum silicidePhysical chemistry
A microelectronic device is formed by forming a platinum-containing layer on a substrate of the microelectronic device. A cap layer is formed on the platinum-containing layer so that an interface between the cap layer and the platinum-containing layer is free of platinum oxide. The cap layer is etchable in an etch solution which also etches the platinum-containing layer. The cap layer may be formed on the platinum-containing layer before platinum oxide forms on the platinum-containing layer. Alternatively, platinum oxide on the platinum-containing layer may be removed before forming the cap layer. The platinum-containing layer may be used to form platinum silicide. The platinum-containing layer may be patterned by forming a hard mask or masking platinum oxide on a portion of the top surface of the platinum-containing layer to block the wet etchant.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com