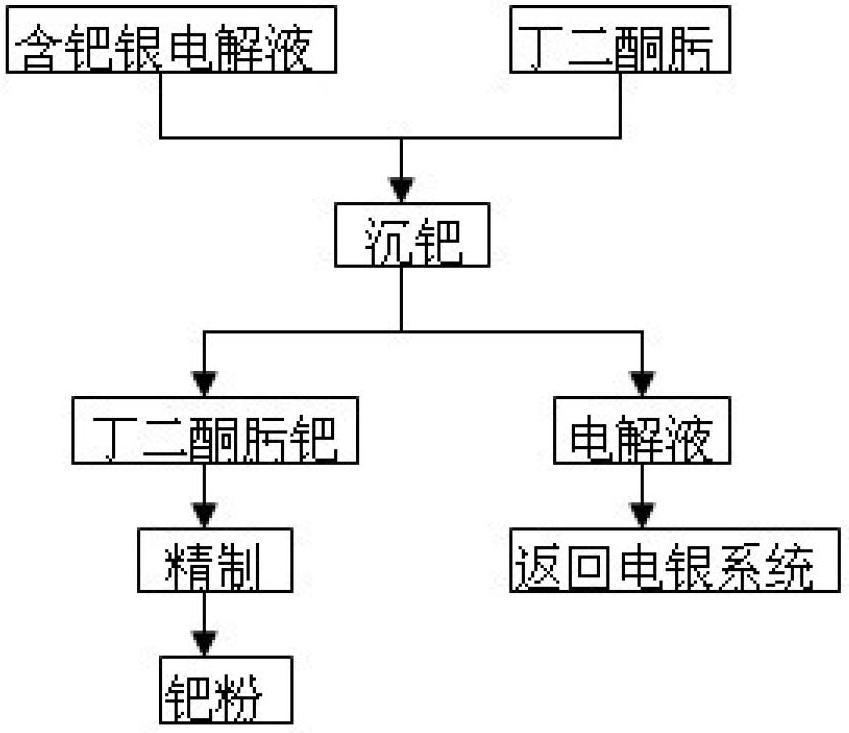
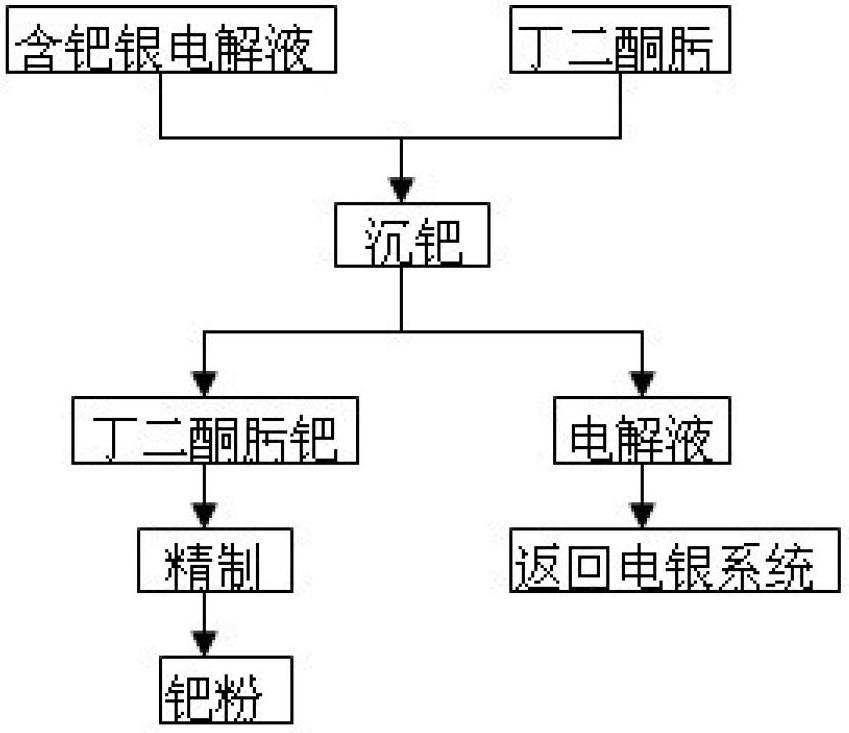
Method for recycling palladium from silver electrolyte by using dimethylglyoxime
A technology of dimethylglyoxime and electrolyte, which is applied in the field of recovering palladium in silver electrolyte by using dimethylglyoxime, can solve the problems of increasing difficulty in purifying palladium, affecting reuse, poor selectivity, etc., and achieves easy purification and simple operation procedures , the effect of small dosage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0013] Silver electrolyte 3000L, its composition is: silver 86g / L, palladium 0.43g / L, copper 23g / L.
[0014] (1) Transfer the palladium-containing silver electrolyte to a palladium-immersed stirring tank, weigh out the diacetyl oxime according to the mass ratio of palladium: diacetyl oxime = 1:2.5, and dissolve it in ethanol, then stir while Add dimethylglyoxime ethanol solution to the silver electrolyte, and finally the palladium precipitation end point is that the dropwise addition of dimethylglyoxime does not produce orange-yellow precipitation;
[0015] (2) After the palladium precipitation is over, press filtration is used for solid-liquid separation. The filtrate contains 86g / L silver, 23g / L copper, and 0.005g / L palladium. The filtrate is returned as electrolyte. The filter residue is washed with nitric acid acidified water with pH=1.0, and washed until the washing water is colorless to obtain crude palladium diacetyl oxime;
[0016] (3) Dissolve the crude product of diacetyl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com