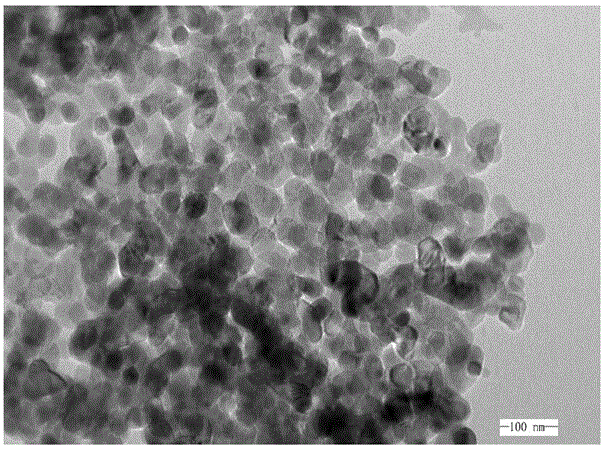
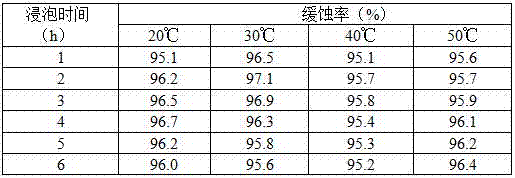
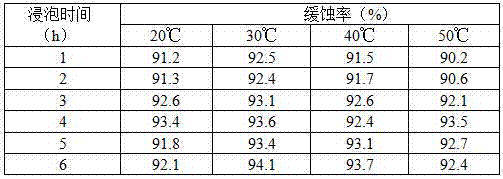
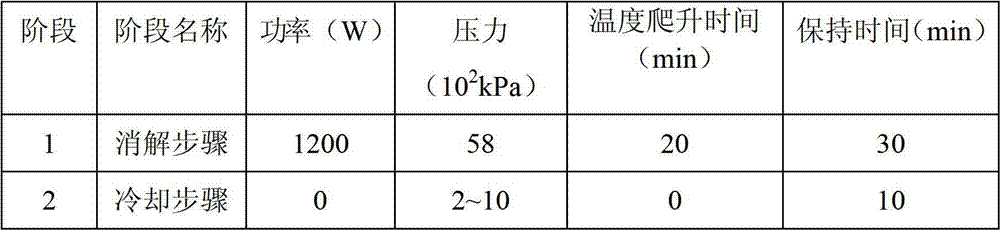
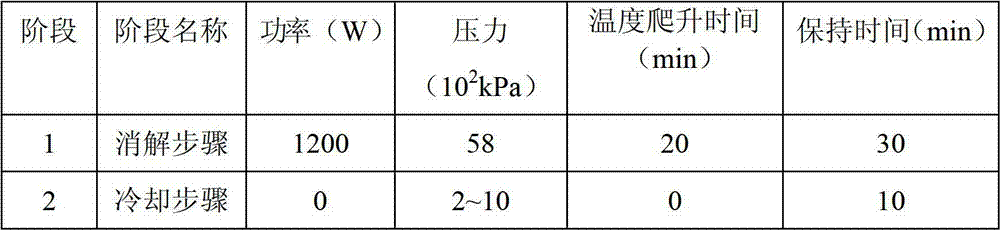
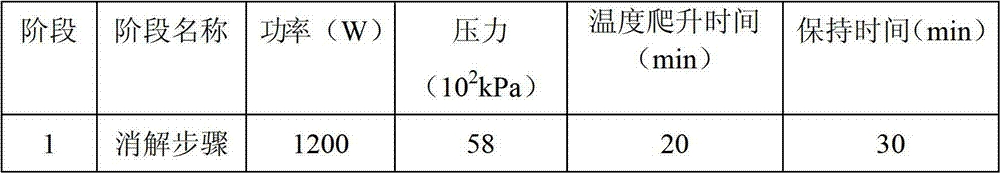
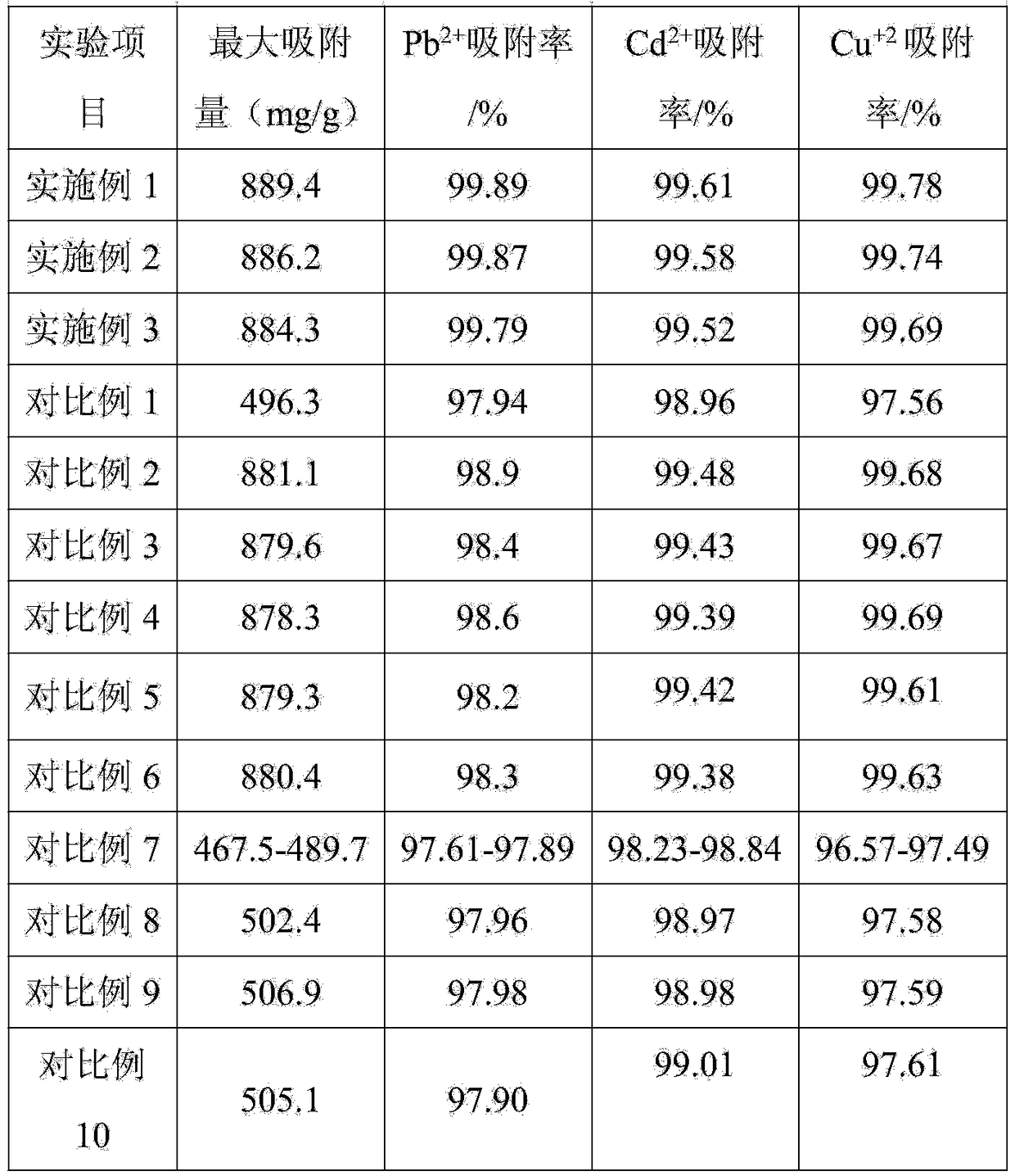
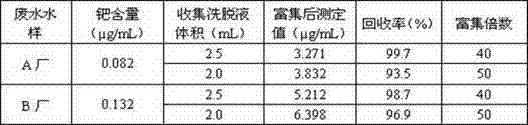
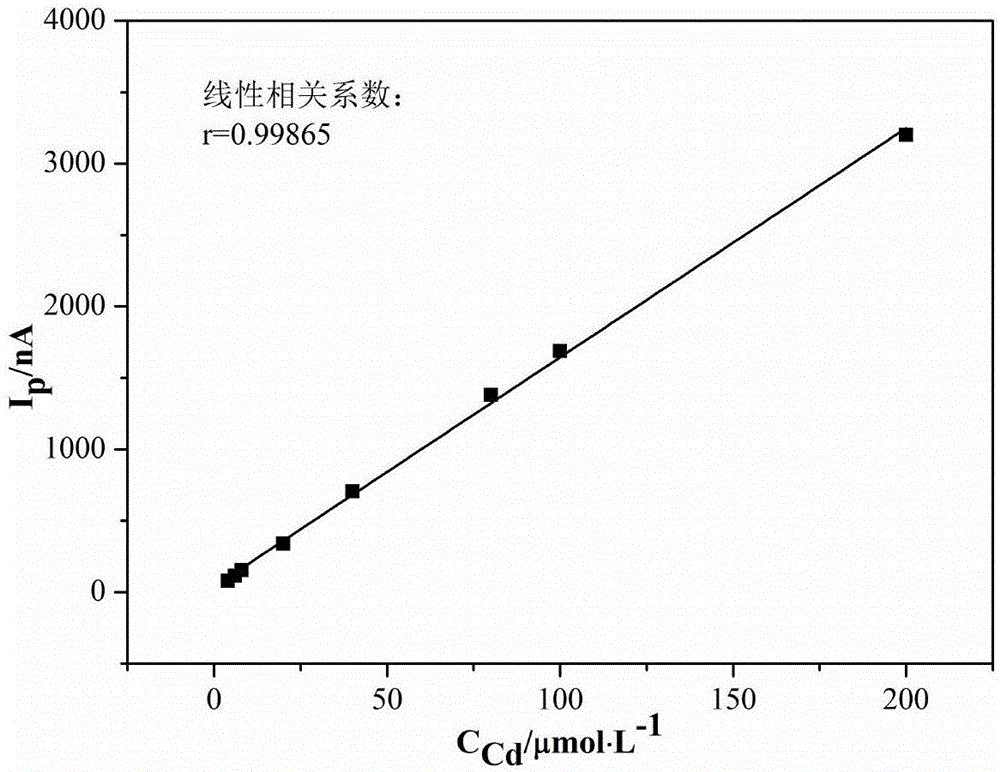
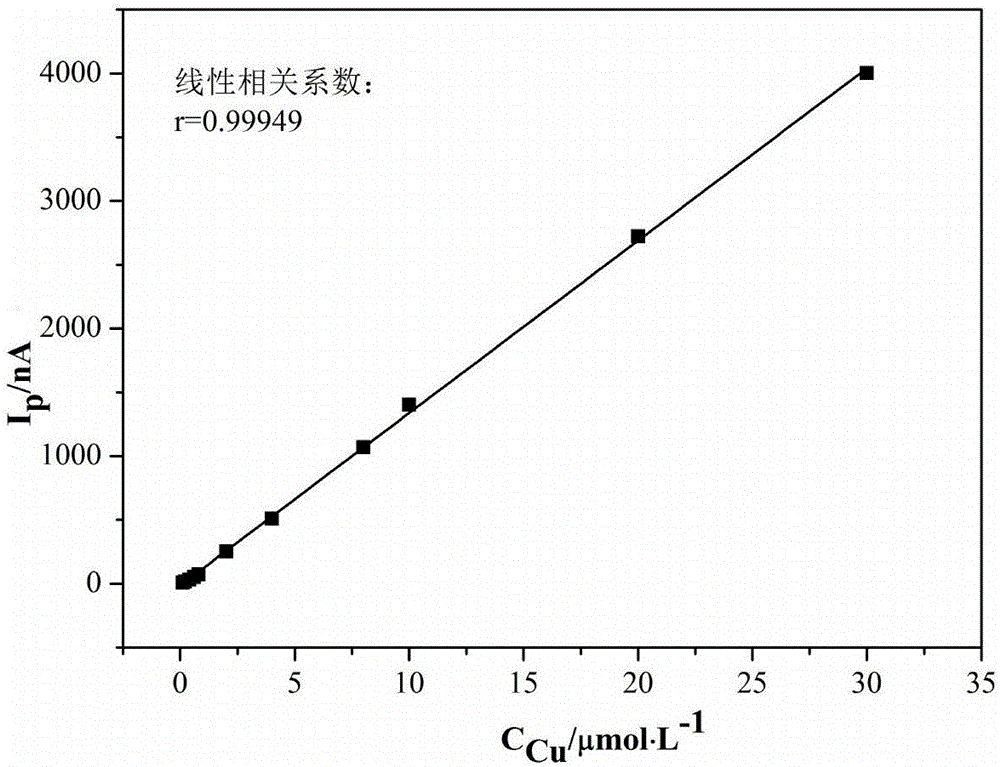
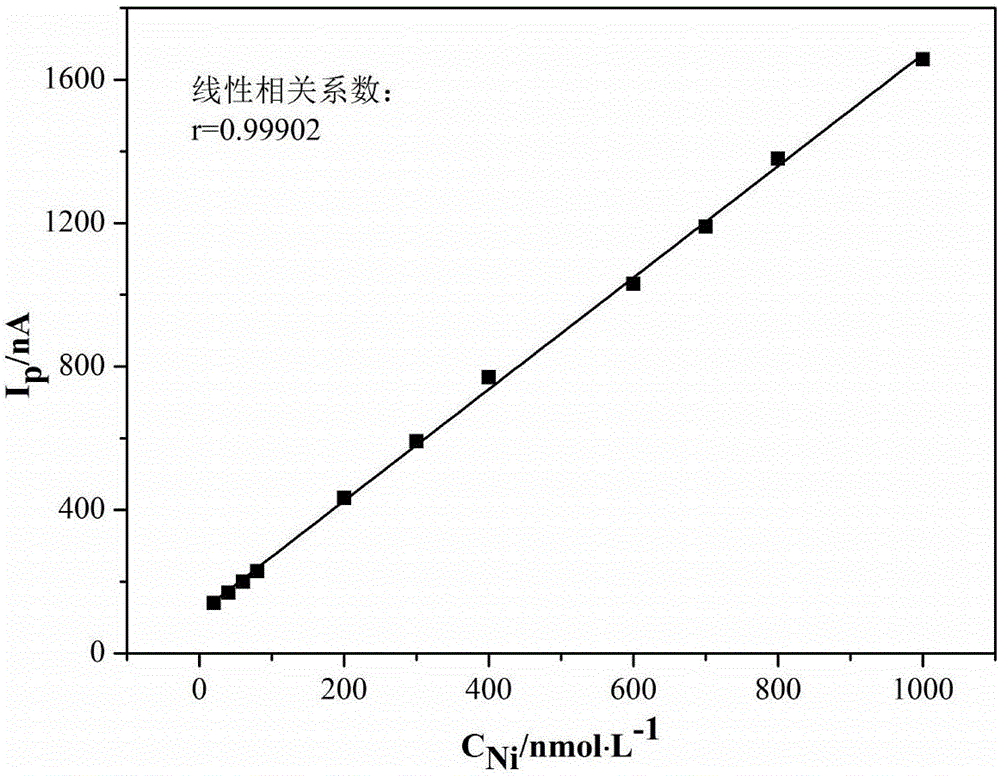
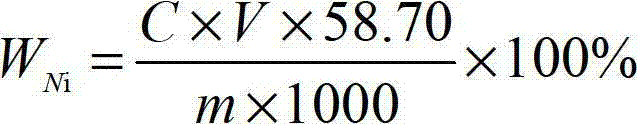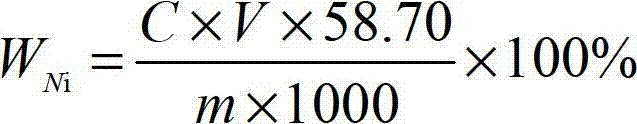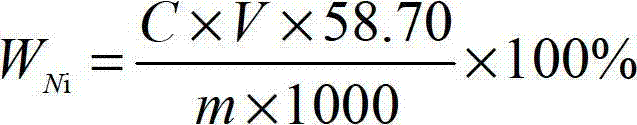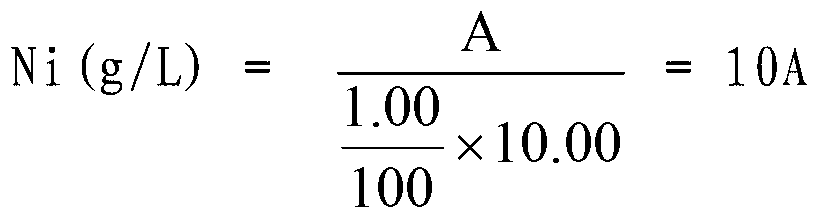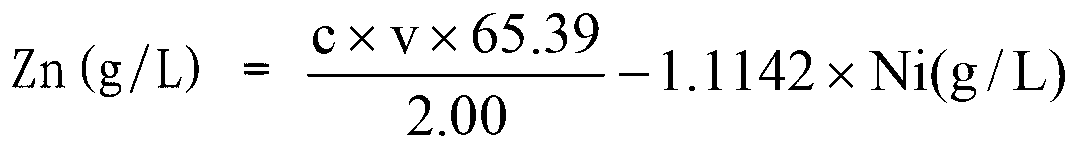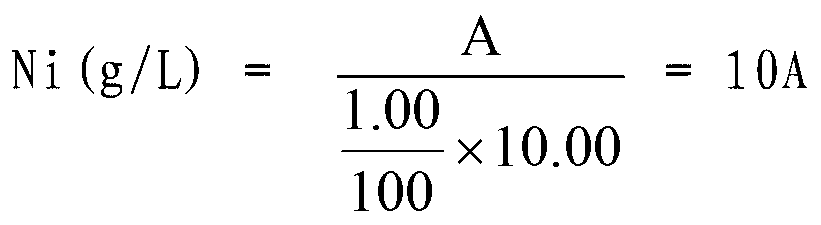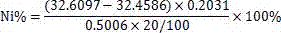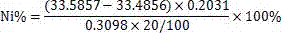Patents
Literature
129 results about "Dimethylglyoxime" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
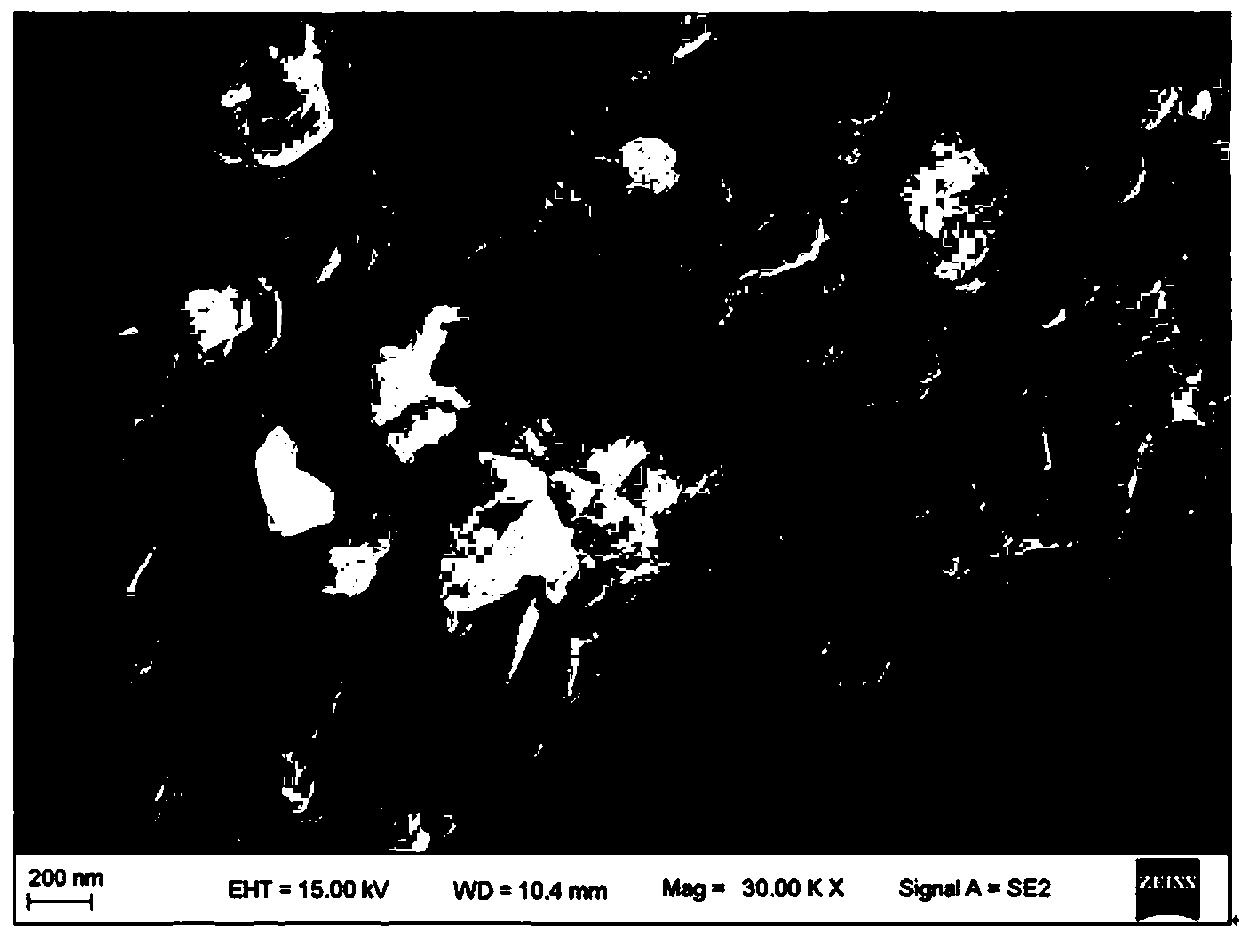
Dimethylglyoxime is a chemical compound described by the formula CH₃C(NOH)C(NOH)CH₃. Its abbreviation is dmgH₂ for neutral form, and dmgH for anionic form, where H stands for hydrogen. This colourless solid is the dioxime derivative of the diketone butane-2,3-dione (also known as diacetyl). DmgH₂ is used in the analysis of palladium or nickel. Its coordination complexes are of theoretical interest as models for enzymes and as catalysts. Many related ligands can be prepared from other diketones, e.g. benzil.
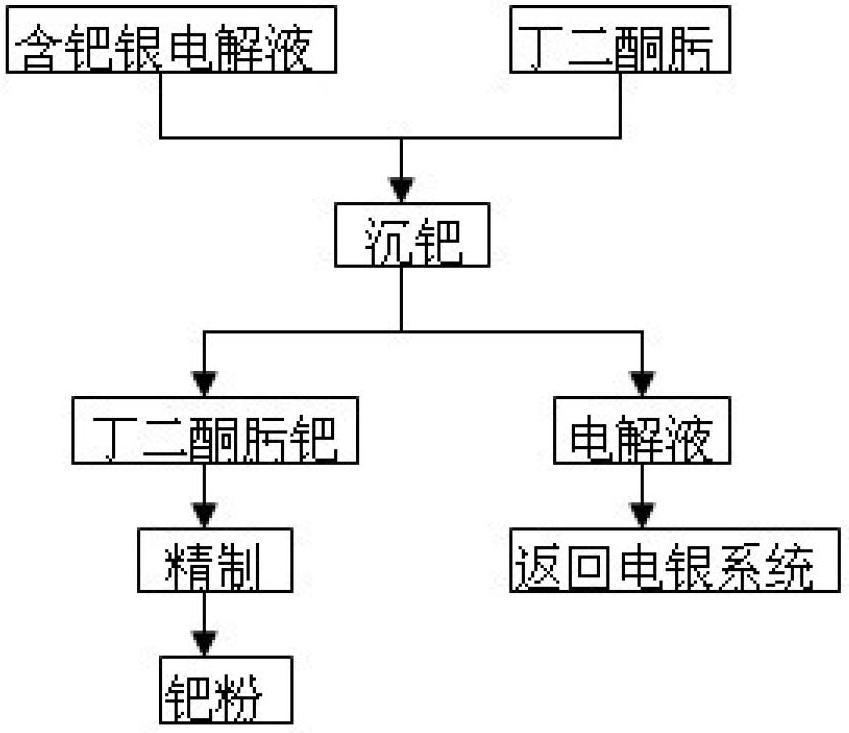
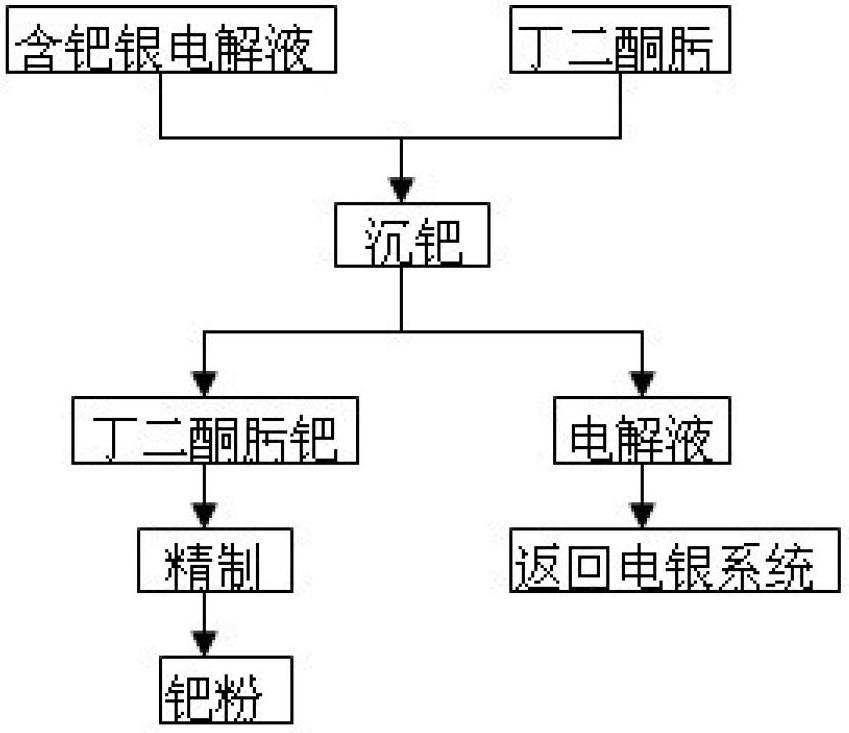
Method for recycling palladium from silver electrolyte by using dimethylglyoxime
InactiveCN102676837ANo heating requiredSimplify operating proceduresProcess efficiency improvementElectrolyteEthanol
The invention discloses a method for recycling palladium from a silver electrolyte by using dimethylglyoxime. The method comprises the following steps: adding dimethylglyoxime into a palladium-containing electrolyte for precipitating palladium; performing solid-liquid separation, returning filtrate as an electrolyte, and eluting filter residue with nitric acid acidification water to obtain a dimethylglyoxime palladium crude product; dissolving the dimethylglyoxime palladium crude product with aqua regia, and then precipitating palladium with ammonium chloride; eluting an obtained ammonium chloropalladate precipitate with an ammonium chloride solution until filtrate is colorless; and adding water, heating, and dissolving; filtering, and cooling filtrate; adding ammonia water, complexing and dissolving; cooling, filtering, and eluting the filter residue with ammonia water; adding hydrochloric acid for acidifying filtrate; filtering to obtain a diammonium dichloropalladite precipitate; and reducing the precipitate by hydrazine hydrate to obtain palladium sponge with the grade of 99.99%. Heating and pH regulation are not required, and only quantitative precipitation of palladium is required; the selectivity is good; and the precipitated dimethylglyoxime palladium can achieve a very high purity after simple eluting, so that the palladium purifying process is greatly shortened and the palladium recycling rate is improved; the using amount of dimethylglyoxime is low; and except a small amount of ethanol, other ions are not brought, so that the reuse of the electrolyte is not affected.
Owner:SIHUI CITY HONGMING PRECIOUS METALS
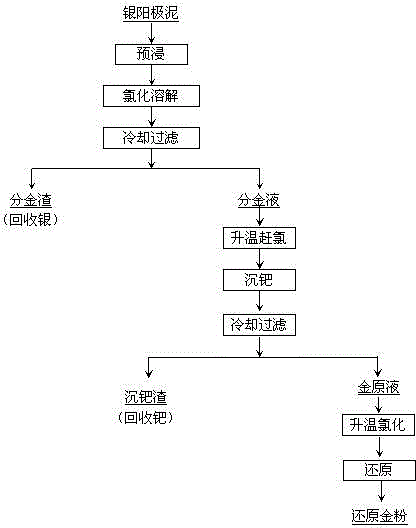
Method for extracting refined gold from palladium-silver-containing anode mud
InactiveCN104451186AEfficient separationShort process structureProcess efficiency improvementSodium bisulfateImpurity
The invention provides a method for extracting refined gold from palladium-silver-containing anode mud, relates to the field of noble metal wet metallurgy, and particularly relates to a method for purifying the gold from the palladium-silver-containing anode mud. The method mainly comprises the following steps: adding the palladium-silver-containing anode mud into hydrochloric acid and carrying out chlorination dissolving; carrying out temperature rising type chlorine removing on filtered parting liquid; then adding dimethylglyoxime to carry out palladium sedimentation and impurity removal; after reaction is finished, carrying out precision filtering, wherein filtrate is gold raw liquid; introducing choline into the gold raw liquid and increasing electric potential; when the electric potential is up to more than 1000mV, stopping the introducing of the choline; adding a saturated sodium hydrogen sulfite solution into the gold raw liquid and reducing; when the electric potential is up to 620mV-630mV, stopping the reducing; and filtering after cooling, and further recycling valuable metal from the filtrate, wherein a filter cake is reduced gold powder. According to the process, the impurity palladium removing rate is high, the valuable metal can be comprehensively recycled, a flow structure is simple and the cost is low. When dimethylglyoxime is used for carrying out palladium sedimentation operation, the reaction is environmentally-friendly; and toxic and harmful gas is not generated and the reaction is rapid and efficient.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Method for measuring content of nickel in ferronickel
InactiveCN102879388AEliminate distractionsEasy to measureMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationMurexideStandard samples
Owner:PANGANG GROUP JIANGYOU CHANGCHENG SPECIAL STEEL
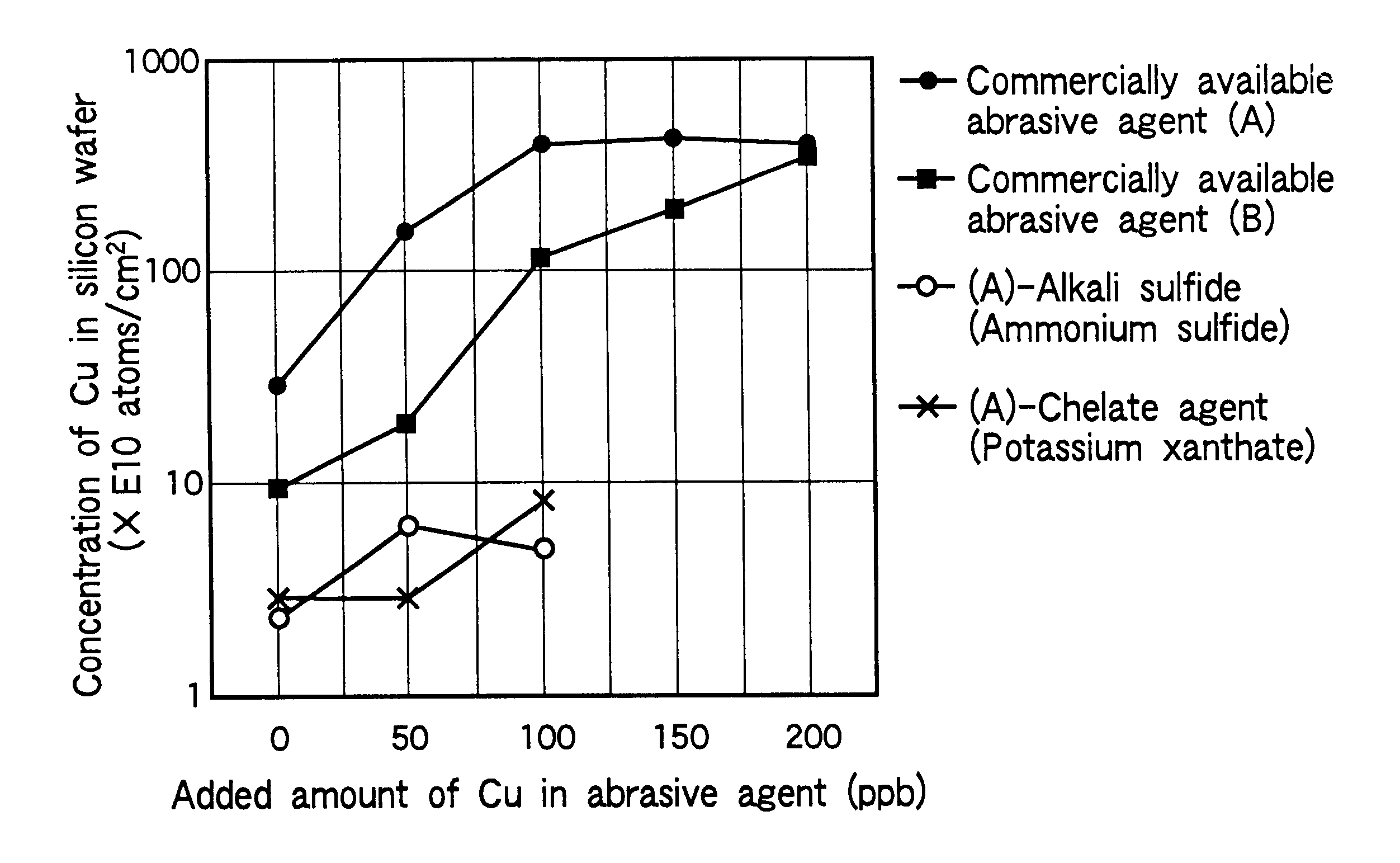
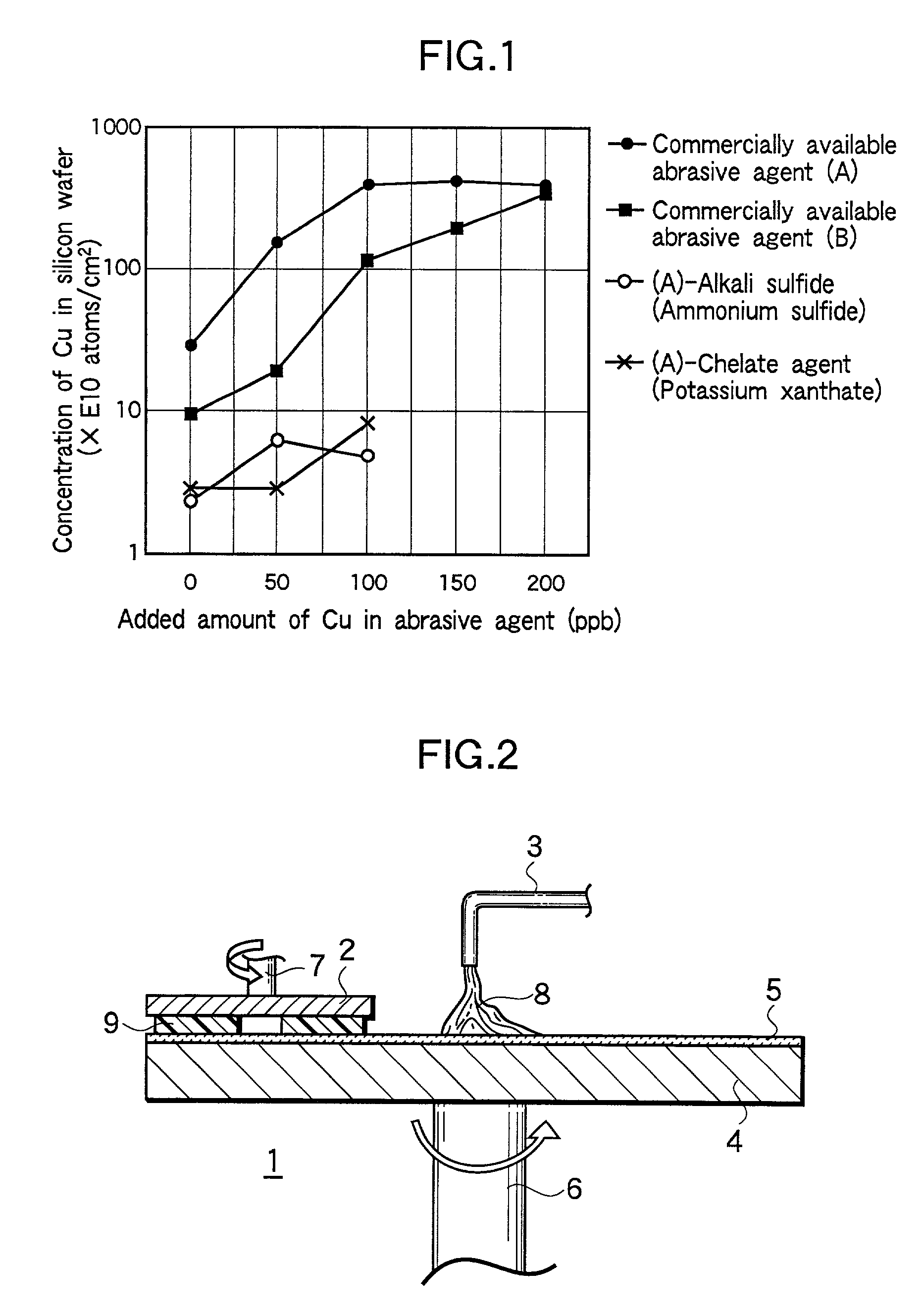
Method of polishing silicon wafer
InactiveUS6383060B2Polishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesAdditive ingredient2-Naphthol
Mirror-polishing of a silicon wafer is conducted using an abrasive agent which contains silica as a principal ingredient, and either one of the ingredients set forth at (1) and (2):(1) an ingredient which is selected from alkali sulfide, alkali hydrogensulfide, and the mixture thereof; and(2) a chelate agent which contains at least alpha-benzoinoxime, diethyldithiocarbamic acid, cupferron, xanthogenic acid, neocupferron, beryllon II, beta-quinolinol, 1,1,1-trifluoro-3(2-thenoyl)acetone, dimethylglyoxime, and 1-(2-pyridylazo)-2-naphthol.
Owner:SUMITOMO MITSUBISHI SILICON CORP
Method for analyzing component content of zinc-nickel alloy electroplating solution
InactiveCN104237221AQuality improvementImprove corrosion resistanceMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsAbsorbanceSodium hydroxide
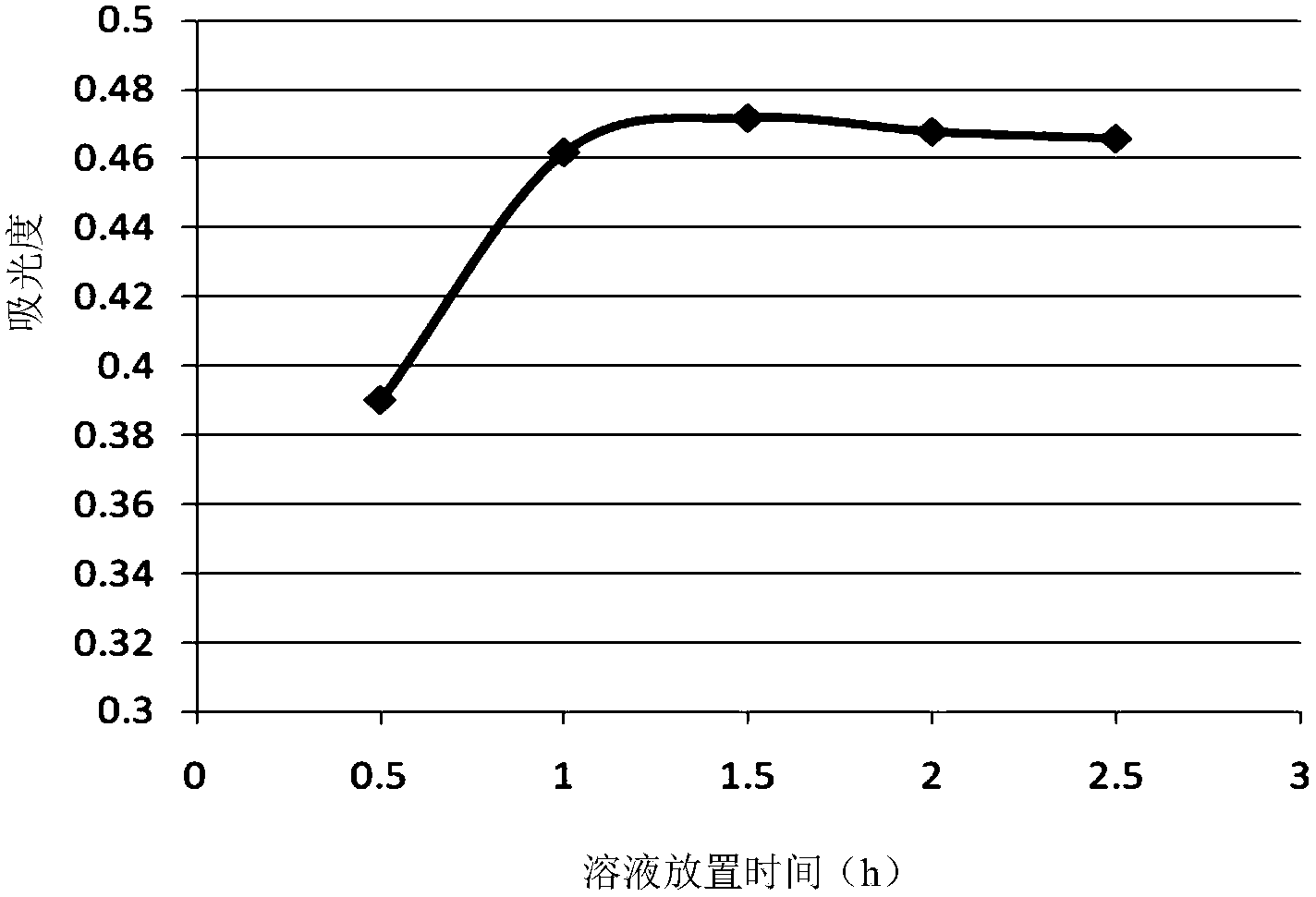
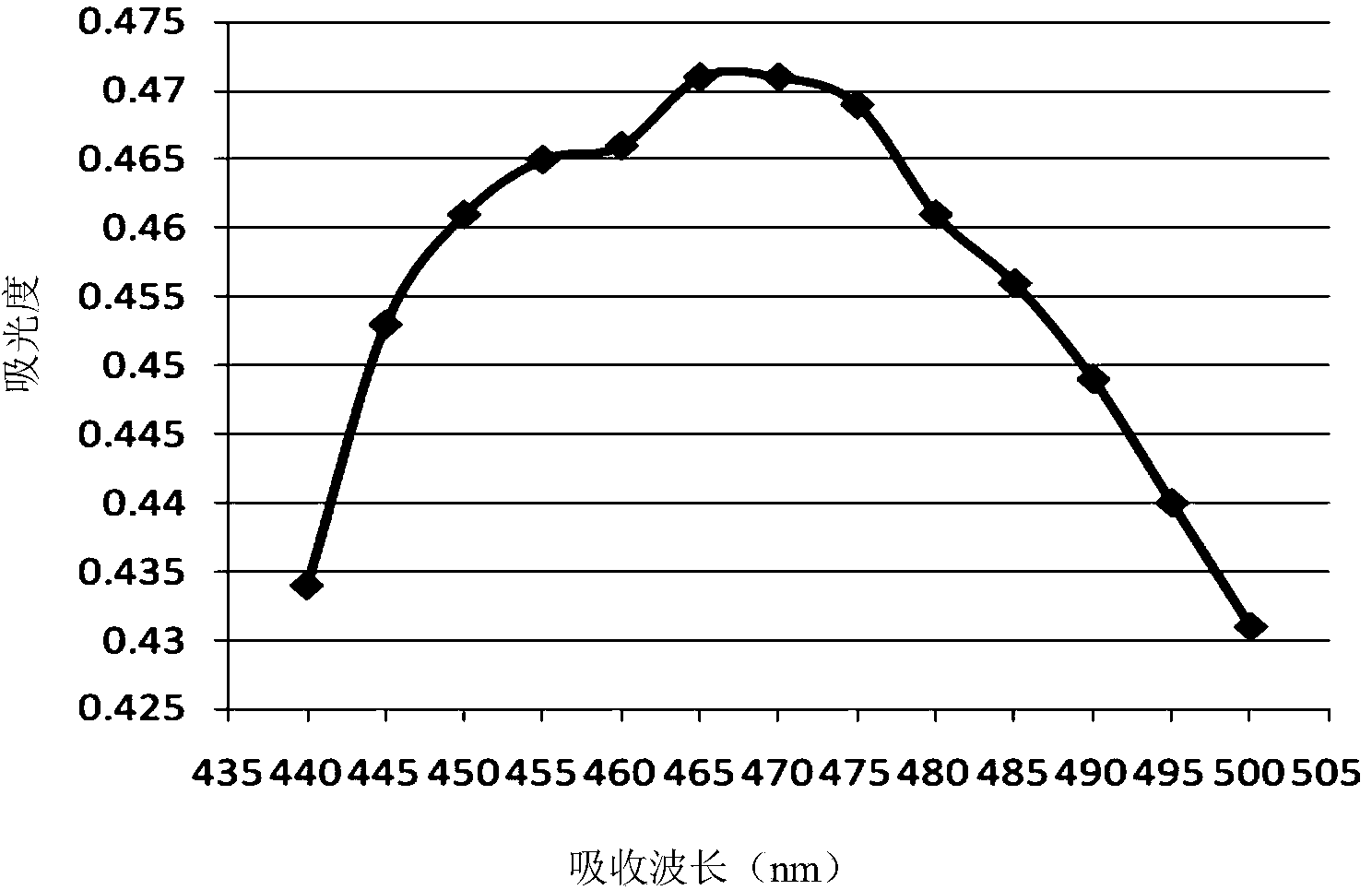
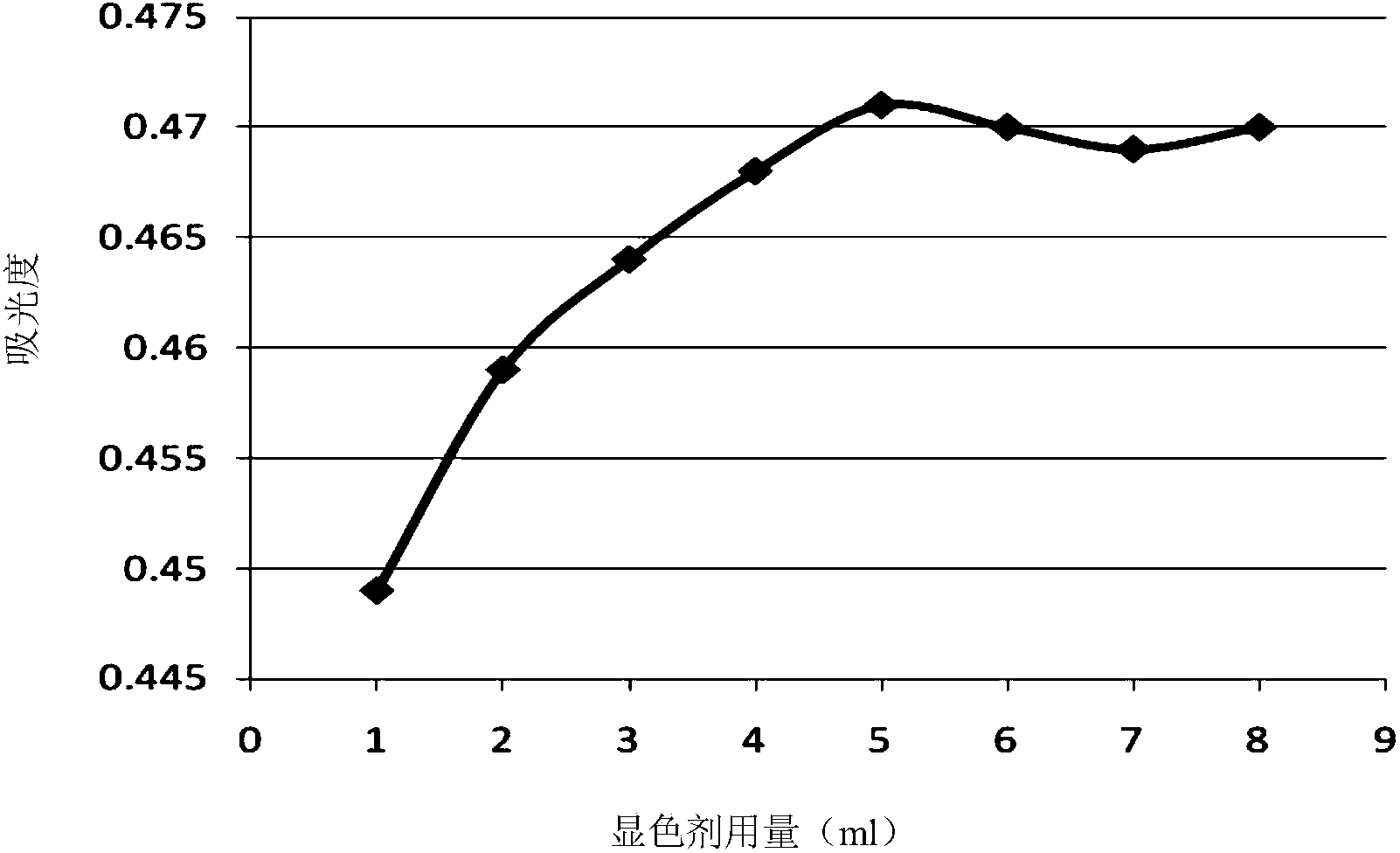
The invention provides a method for analyzing the component content of a zinc-nickel alloy electroplating solution. The method comprises a step of measuring nickel ion content, wherein the step comprises the sub-steps of adding a tartaric acid solution, a sodium hydroxide solution, an ammonium persulfate solution and a mixed solution of dimethylglyoxime and sodium hydroxide in the zinc-nickel alloy electroplating solution and measuring the absorbance of the obtained mixture under the wavelength range of 460 to 475nm. The method can further comprises steps of measuring zinc oxide content and sodium hydroxide content. In the step of measuring the nickel ion content, the proper standing time of the mixed solution, of which the absorbance is measured, and a proper absorption wavelength for the measurement of the absorbance are selected, so that the measurement accuracy of nickel ions is improved. In the step of measuring the zinc oxide content, ammonium fluoride and triethanolamide are added, so that the operability and accuracy in measurement of zinc oxide are improved. In addition, the method comprises a few steps, and is high in accuracy, low in cost and suitable for industrial application.
Owner:SICHUAN JIUZHOU ELECTRIC GROUP
Method for preparing nano nickel oxide from nickeliferous waste materials
InactiveCN105460985ASmall and uniform particle sizeHigh crystallinityMaterial nanotechnologySolid waste disposalCrystallinityMuffle furnace
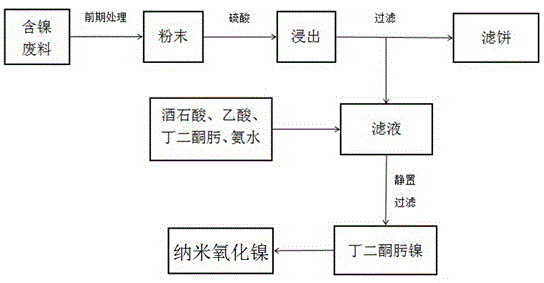
The invention discloses a method for preparing nano nickel oxide from nickeliferous waste materials, and belongs to the technical field of nickeliferous waste material recycling. The method comprises the steps that powder nickeliferous waste materials are leached through sulfuric acid, a tartaric acid solution is added to a nickeliferous sulfuric acid solution to serve as a screening agent, ammonia water is added, the solution is always kept clear, acetic acid is slowly added to enable pH of the solution to be controlled to range from 3 to 6, and the solution is heated to 50-65 DEG C; a dimethylglyoxime ethanol solution is added, an enough amount of ammonia water is added to make pH of the solution be 10, filtering and washing are conducted after standing is conducted, nickel dimethylglyoxime is obtained and calcined through a muffle furnace, and the nano nickel oxide is obtained. The nano nickel oxide prepared through the method has the advantages of being small and uniform in particle size and the like, the heat preservation time in the calcining process is short, and the advantages of being complete in particle and high in crystallinity are guaranteed.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for measuring zinc and nickel contents in zinc-nickel alloy electroplating solution
ActiveCN103344641AAvoid serious harmGuaranteed sensitive to color changeMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSodium acetateImpurity
The invention relates to a method for measuring zinc and nickel contents in a zinc-nickel alloy electroplating solution and belongs to the technical field of methods for analyzing the electroplating solution. The method is mainly and technically characterized by comprising the following steps of: reacting dimethylglyoxime and Ni4+ to form a red soluble complex in the presence of an oxidant ammonium persulfate, adding sodium tartrate to eliminate iron and other impurity interference, and measuring the content of nickel in the zinc-nickel alloy electroplating solution by employing a colorimetric method; adding tartaric acid to mask iron and other impurities, with CuY-PAN as an indicator, titrating in an acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution with the PH being 5.5 by using an ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) standard titration solution by utilizing a replacement titration principle, calculating the total contents of zinc and nickel in the zinc-nickel alloy electroplating solution, and subtracting the nickel content from the total contents of zinc and nickel to solve the zinc content in the zinc-nickel alloy electroplating solution. The measurement method has the characteristics of simpleness in detection, convenient, rapid and environment-friendly detection process, low cost, accurate and consistent detection result and the like.
Owner:江南工业集团有限公司
Polishing process for stainless steel base tape for coated conductor
InactiveCN102703937AChange ingredientsImprove adsorption capacityElectrical conductorPhosphoric acid
The invention relates to a polishing process for a stainless steel base tape for a coated conductor, which belongs to the technical field of surface polishing for base tapes of high-temperature coated superconductors and mainly provides a stainless steel polishing process integrating acid cleaning, chemical polishing and electrochemical polishing. According to the invention, toxic chromic acid and hydroflouric acid and volatile hydrochloric acid solution in the traditional polishing solution are removed, pollution to environmental, harm to human body and corrosion to equipment of the used materials are reduced, the raw materials of the polishing solution, including common phosphoric acid and sulfuric acid solutions, hydrogen peroxide used as an oxidant, dimethylglyoxime used as a complexing agent and ZP-1 corrosion inhibitor, are easily obtained, the cost is low, the operability of the preparation process is strong, the prepared solution can be used at normal temperature, the energy consumption of equipment is reduced, the electricity is saved, the production cost is saved by the optimized polishing process, and the polishing finish is enhanced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Nickel-containing wastewater treatment technology
InactiveCN101580317AReduce processing costsMultistage water/sewage treatmentNickel saltNickel deposition
The invention discloses nickel-containing wastewater treatment technology, which comprises the following steps: using sodium hydroxide or ammonia water to adjust the pH value of nickel-containing wastewater to between 5.5 and 9.5; adding dimethylglyoxime into the nickel-containing wastewater under the stirring at normal temperature for a nickel deposition reaction, wherein the molar ratio of the dimethylglyoxime to Ni in a filtrate is 2.2:1-2.4: 1; filtering after the reaction is performed for 20 to 60 minutes; washing a filter cake by hot water with a temperature between 40 and 90 DEG C, and then obtaining a pure nickel chelate through the filtration; using hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid or nitric acid to dissolve the nickel chelate according to product requirements; and obtaining corresponding nickel salt solution and the dimethylglyoxime after the filtration; recovering the dimethylglyoxime from an acid-dissolved filtrate; removing residual Fe through neutralization; heating hydrolysis and filtration, and then evaporating, washing, crystallizing the filtrate and drying the crystal to obtain a product; merging the filtrates in step two and recovering the dimethylglyoxime; and using the recovered dimethylglyoxime for the nickel deposition reaction. The nickel-containing wastewater treatment technology can ensure that the nickel-containing wastewater reaches the standard after the treatment and the content of the residual Ni is less than 1mg / L, can also completely recover nickel, and has low treatment cost and less equipment investment.
Owner:邱致忠
Metallic nickel-nitrogen doped porous carbon materials, preparation method and application of metallic nickel-nitrogen doped porous carbon materials
The invention discloses metallic nickel-nitrogen doped porous carbon materials, a preparation method and application of the metallic nickel-nitrogen doped porous carbon materials, and belongs to the technical field of nano materials. Nickel dimethylglyoxime as a micromolecule coordination compound is compounded under a mild condition, then under the protective atmosphere, metallic nickel-nitrogen doped porous carbon materials with different contents of metallic nickel are prepared through pyrolysis at the temperature of 400-1000 DEG C and then are soaked in an HC1 solution with certain solubility, and N-doped porous carbon materials with different contents of the metallic nickel are obtained; when the concentration of HC1 is 12 M, all the metallic nickel can be washed out, so that nitrogen-doped porous carbon materials are prepared; and when the nickel dimethylglyoxime serves as a template, under dry air, nano metallic nickel materials can be prepared through pyrolysis at the temperature of 350-550 DEG C. The compounded metallic nickel-nitrogen doped porous carbon materials serve as catalysts for catalyzing and reducing p-nitrophenol, high catalytic activity is shown, and nano metallic oxide and nitrogen doped porous carbon materials serve as electrode materials and have certain specific capacitance.
Owner:KEY LAB OF INORGANIC SYNTHESIS & PEPARATIVE CHEM AT JILIN UNIV IN ZHUHAI
Method for purification and impurity removal of nickel liquid
InactiveCN101603125AAvoid pollutionReduce solubilityProcess efficiency improvementNickel saltEvaporation
The invention relates to a method for the purification and impurity removal of nickel liquid. In the invention, environmental pollution caused by introducing toxic fluoride can be avoided, the technique steps also can be simplified, the yield of nickel, copper and cobalt is enhanced, and waste water generated in the production process does not need to be processed again. In the method, a soluble carbonate solution is added into nickel liquid after iron removal, and Ca and Mg are removed in a carbonate precipitation form; the solution after being filtered is controlled at 40 to 90 DEG C, dimethylglyoxime is added by stirring to carry out a nickel precipitation reaction, a filter cake after being filtered is washed by hot water of 40 to 95 DEG C, and a pure nickel chelate complex is obtained; Cu and Co are extracted and recovered after nickel precipitation filter liquor and filter liquor after being filtered and washed by the hot water are merged and the dimethylglyoxime is recovered; the nickel chelate complex is dissolved by hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid or nitric acid and is filtered to obtain a corresponding nickel salt solution and the dimethylglyoxime; after the dimethylglyoxime dissolved in acid soluble filter liquor is recovered, residual Fe is removed by neutralization, condensation and filtration, and a nickel salt product is obtained after evaporation, crystallization, washing and drying; and the recovered dimethylglyoxime is recycled for a nickel precipitation reaction.
Owner:邱致忠
Novel method for measuring content of zinc in alkaline zinc-nickel alloy plating solution
ActiveCN104849400ANon-toxicChemical analysis using titrationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPotassium cyanidePrecipitation
The invention discloses a method for analyzing zinc in an alkaline zinc-nickel alloy plating solution. The method comprises the steps of enabling Ni<2+> ions in the alkaline zinc-nickel alloy plating solution and dimethylglyoxime to generate precipitate under the condition the pH is equal to 4-6; filtering and separating the precipitate; then, measuring the content of the zinc in the filtrate; under the condition that the pH is equal to 10, taking chrome black T as an indicator, and titrating the zinc by ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) standard solution. According to the method, nickel is separated by a precipitation separation method, zinc is measured by titration, and the used reagents are non-toxic and harmless. The existing method adopts potassium cyanide to screen nickel, so that potential safety hazard is brought to laboratory management, and the environment is polluted.
Owner:江苏大春电力器材有限公司
Detection agent for determining content of nickel in water
InactiveCN103278457ALow priceEasy to carryColor/spectral properties measurementsEthylenediaminePolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to a detection agent for determining the content of nickel in water. According to the detection agent, firstly, sodium citrate, potassium hydroxide and ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid disodium are weighed according to the mass ratio of 12: 6: 1, are mixed uniformly and are then ground so as to obtain powder I; then, ammonium citrate, potassium iodide, iodine and dimethyl glyoxime are weighed according to the mass ratio of 16: 2: 1: 1, are mixed uniformly and are then ground so as to obtain powder II; and finally, the powder I, the powder II and polyethylene glycol are weighed according to the mass ratio of 5: 1: 1 and are mixed uniformly, thereby obtaining the detection agent for determining the content of nickel in water. During use, 0.7g of the detection agent is poured into 10ml of a water sample to be determined, shaking is carried out for 1 min so as to dissolve the detection agent, and a colorimeter or spectrophotometer is utilized for measuring. According to the detection agent disclosed by the invention, the carrying is convenient, the storage is easy, any reagent is not required for being added during use, and the determination results are accurate, so that the detection agent is applicable to the on-site detection on the content of nickel in surface water, seawater and industrial wastewater.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
A method for measuring nickel in raw gold
InactiveCN107478765AAccurate measurementEasy to recycleChemical analysis using titrationHexamethylenetetramineFiltration
The invention relates to a method for measuring nickel in raw gold, and belongs to methods for measuring the nickel content in raw gold. The method includes dissolving a specimen with nitrohydrochloric acid; precipitating and separating gold by utilizing hydrazine hydrate; performing filtration with the filter residue being used for recovering the gold; adding ammonium chloride and ammonia water into the filtrate to form an alkaline buffer system; precipitating and separating nickel by adding dimethylglyoxime into the system; adding an excessive amount of EDTA and reacting the EDTA with the nickel by adopting hexamethylenetetramine as a buffer solution; titrating the excess EDTA until an end point of a color conversion from yellow to purplish red of the solution by adopting xylenol orange as an indicator and adopting zinc chloride as a titrant; and calculating the nickel content of the raw gold. The method can accurately measure the nickel content of the raw gold, is suitable for large-scale analysis, and fills the gap of nickel content measurement methods for raw gold.
Owner:CHANGCHUN GOLD RES INST
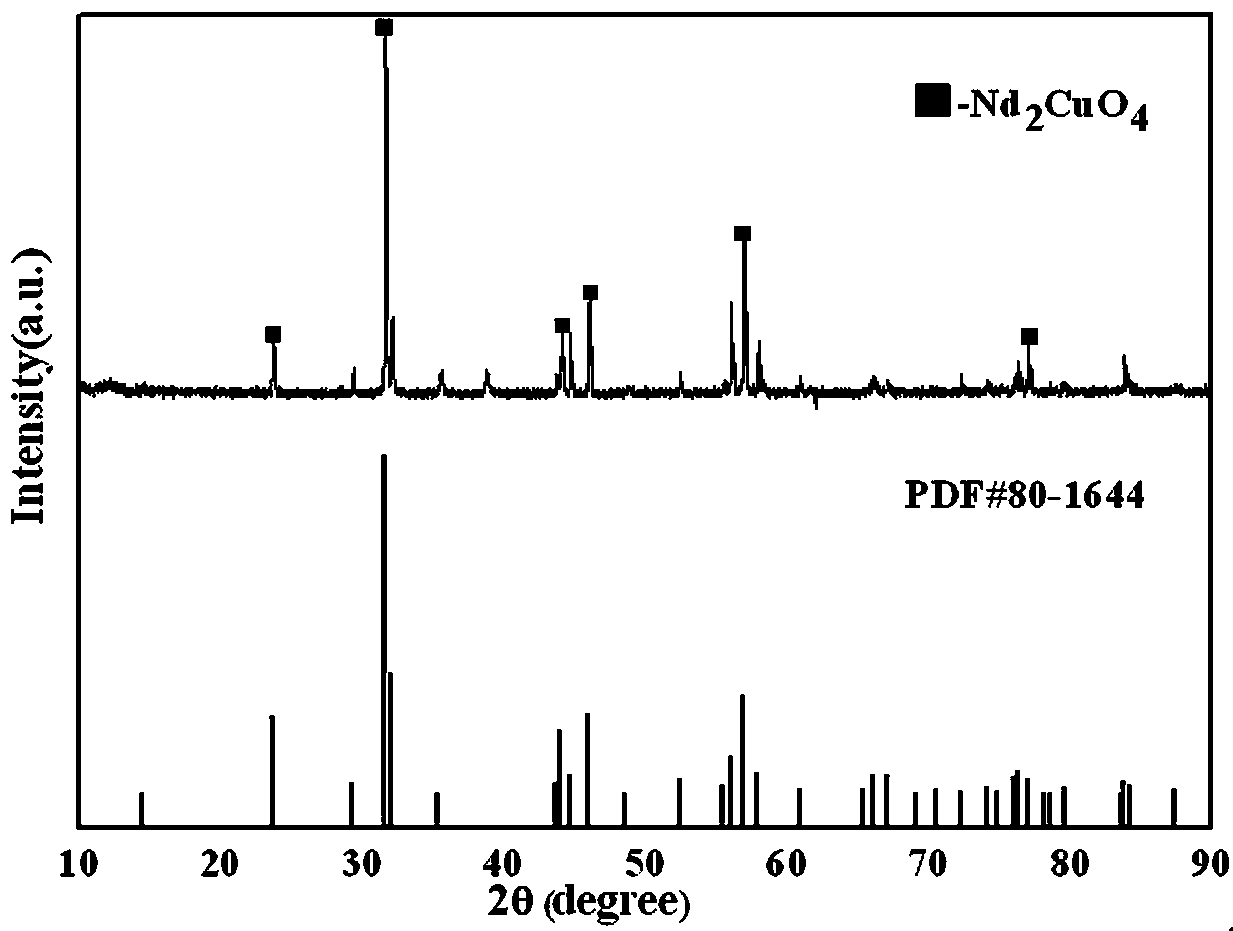
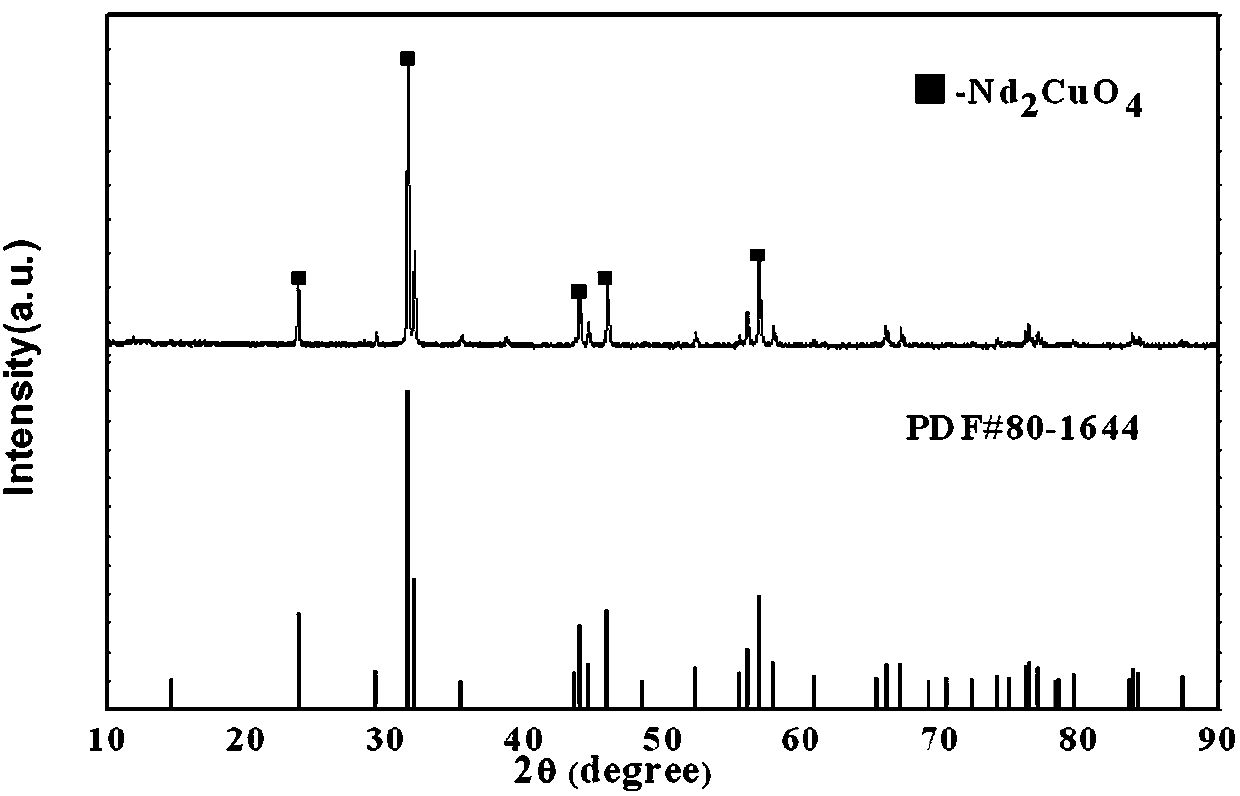
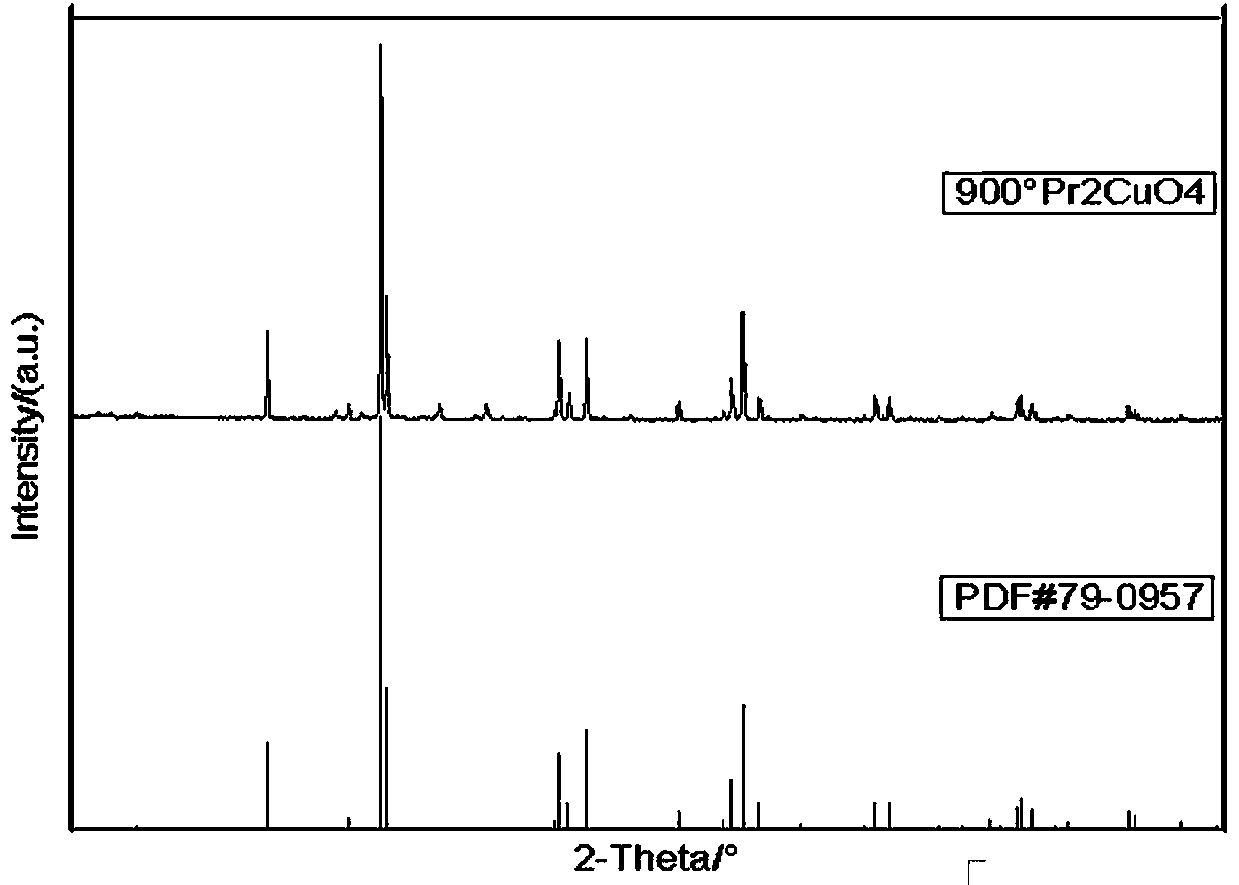
Preparation method and application of neodymium cuprate nano-powder
ActiveCN107673392AImprove performanceImprove the coordination effectMaterial nanotechnologyCopper compoundsMalachite greenMalachite green stain
The invention relates to the technical field of photocatalysis of nano-materials and in particular relates to a preparation method and application of neodymium cuprate nano-powder. The preparation method comprises the following steps: weighing soluble salt of copper and neodymium according to the mol ratio of Cu to Nd in Nd2CuO4; dissolving the soluble salt into de-ionized water and stirring untilthe soluble salt is dissolved to obtain a solution A; weighing dimethylglyoxime and putting the dimethylglyoxime into a beaker; adding de-ionized water and stirring until the dimethylglyoxime is dissolved to obtain a solution B; slowly pouring the solution B into the solution A and stirring until the solution A and the solution B are uniformly mixed to obtain a solution C; heating the solution Cunder the condition that the temperature is 60 DEG C to 80 DEG C; stirring until the solution is viscous and drying to obtain a substance D; taking out the substance D and putting the substance D intoa crucible; calcining in a low-temperature furnace; then putting the substance D into a high-temperature nitrogen furnace and calcining to obtain a calcined product; crushing and grinding to obtain the neodymium cuprate Nd2CuO4 nano-powder. The preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages that a preparation technology is simple and feasible and the obtained Nd2CuO4 nano-powderhas excellent performance and has an obvious photocatalytic effect on malachite green; the photocatalytic effect is not reported at present.
Owner:东北大学秦皇岛分校
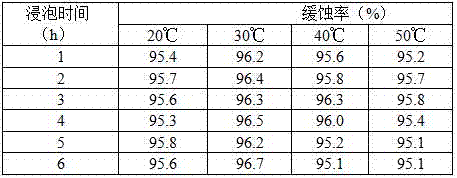
Efficient compound corrosion inhibitor as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses an efficient compound corrosion inhibitor as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The efficient compound corrosion inhibitor comprises the following components: 0.1-1.0g / L of lauryl sodium sulfate, 0.05-0.5g / L of polyvinyl alcohol, 0.05-0.1g / L of dimethylglyoxime, 0.01-0.05g / L of protocatechualdehyde and the balance of pickling solution. The efficient compound corrosion inhibitor has the advantages of being high in corrosion inhibition efficiency, remarkable in mutual synergistic effect, high in adaptability, excellent in after effectiveness and high-temperature resistant, obviously restrains the corrosive action of hydrochloric acid to aluminum, is suitable for cleaning aluminum in hydrochloric acid, can be used for cleaning petrochemical equipment, a boiler, an aluminium product, a pipeline and other equipment, and is convenient and safe to use, and simple to operate, and takes effect quickly.
Owner:SOUTHWEST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for determining nickel content in nickel-chromium-aluminum coated diatomite
InactiveCN102735794AImprove accuracyDetermination is accurate and reliableChemical analysis using titrationPreparing sample for investigationElement analysisMaterial resources
The invention belongs to a nickel-chromium-aluminum coated diatomite element analysis technology, and relates to a method for determining nickel content in nickel-chromium-aluminum coated diatomite. According to the method, 5-10 mL of hydrochloric acid, 1-5 mL of nitric acid and 5-10 drops of hydrofluoric acid are adopted to treat (metal-inorganic non-metal powder) nickel-chromium-aluminum coated diatomite, such that problems of large use amounts of reagents for dissolving the sample, difficult dissolving of the sample, incomplete dissolving of the sample, and the like in the prior art are solved. With the present invention, a classical chemical method-dimethylglyoxime-EDTA volumetric method is adopted to determine the nickel content in the nickel-chromium-aluminum coated diatomite, and an appropriate standard substance is adopted as a control so as to improve accuracy of analytical measurement; the study results show that the established method for determining the nickel content in the nickel-chromium-aluminum coated diatomite is accurate and reliable, and can meet requirements of research and production; and the method of the present invention has characteristics of rapidness, easy operation, manpower saving and material resource saving.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Adsorption composite material used for water quality detection, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108371947AImprove adsorption capacityReduce adverse effectsOther chemical processesWater contaminantsPhosphateSulfite salt
The invention discloses an adsorption composite material used for water quality detection, and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of adsorption material preparation. Theadsorption composite material used for water quality detection comprises following raw materials: a modified adsorbent, a modified filling material, chitosan, a polyhydroxyalkanoate, silane coupling agent KH-570, ferrous sulphate, sodium polyacrylate, sodium citrate, anhydrous sodium sulfate, disodium ethylene diamine tetraacetate, sodium sulfite, polyethylene glycol, potassium iodide, nanometer ceramic powder, ammonium citrate, sodium carbonate, propylene glycol, dimethylglyoxime, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, sodium tetraborate, and sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate. The adsorption composite material used for water quality detection is prepared via following steps: preparation of a base material and modified materials, mixing of the base material and the modified materials, and moulding, and calcining. The adsorption composite material used for water quality detection is capable of improving the adsorption performance on water body pollution factors and heavy metal effectively.
Owner:CHANGSHA XIAORU INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Testing method of content of nickel in cathode material for lithium ion battery
PendingCN107300510AAccurate contentThe content is accurately obtainedWeighing by removing componentElectrical batteryEvaporation
The invention discloses a testing method of the content of nickel in a cathode material for a lithium ion battery. The testing method comprises the following steps: S01: weighing a cathode material for a to-be-tested lithium ion battery, adding acid for dissolution and heating for evaporation and realizing constant volume; S02: adding concentrated nitric acid into test fluid prepared in S01, then fractionally adding an excessive amount of potassium chlorate or sodium chlorate and filtering after a reaction is completed, so as to obtain filtrate and manganese dioxide sediment; S03: quantitatively measuring the filtrate in S02, adding water, ammonium chloride solution and tartaric acid solution, uniformly stirring the mixture and performing a complete reaction; S04: filtering the mixed solution to obtain filtrate and nickel dimethylglyoxime sediment, drying to constant weight and weighing; S05: calculating the content of a nickel element. The invention provides the testing method, so that the problem of an error existing in a process of testing the content of nickel in the cathode material for the lithium ion battery by using a spectrophotometric method and a chemical titration method can be solved, and the accurate numerical value of the content of nickel in the cathode material can be obtained.
Owner:SHENZHEN BAK POWER BATTERY CO LTD
Wooden furniture surface coating material
The invention relates to the technical field of furniture surface treatment, in particular to a wooden furniture surface coating material. The wooden furniture surface coating material is prepared from a main agent and a curing agent, wherein the main agent is prepared from, by weight, 50-60 parts of saturated polyester resin, 5-10 parts of dimethylglyoxime, 3-5 parts of phosphoric acid triallyl ester, 2-4 parts of white corundum, 1-6 parts of attapulgite, 0.5-1.0 part of copper naphthenate, 0.2-0.4 part of cobalt iso-octoate and 2-6 parts of titanium dioxide, the curing agent is prepared from, by weight, 10-20 parts of methyl ethyl ketone peroxide, 5-8 parts of gas phase SiO2, 15-25 parts of dibutyl terephthalate and 0.1-0.3 part of polyvinylpyrrolidone. According to the wooden furniture surface coating material, no deformation or contraction of a base material will be caused in the base material treatment process, and therefore the decorative coating is not broken.
Owner:桐乡市美意家具有限公司
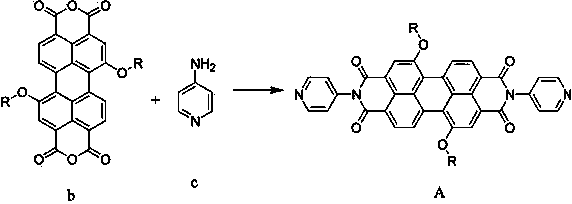
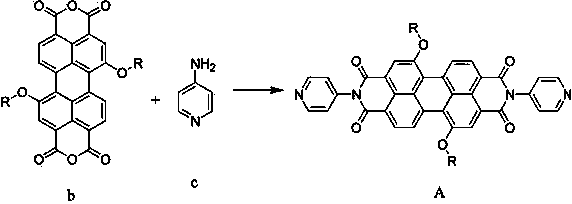
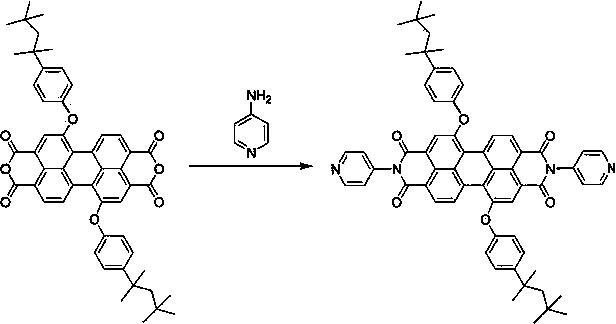
Preparation and photocatalytic hydrogen generation performance of N-pyridyl perylenetetracarboxylic diimide
InactiveCN104557931AOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPolymer chemistryPhotochemistry
The invention relates to N-pyridyl perylenetetracarboxylic diimide with a formula shown in specification, a preparation method and application thereof. The compound is prepared from substitutional perylenetetracarboxylic anhydride and 4-aminopyridine under a high temperature condition; the process is simple and easy to be carried out; N-pyridyl perylenetetracarboxylic diimide and a dimethylglyoxime complex are combined to be used as a photocatalyst for hydrogen generation through solar visible photocatalytic water decomposing; N-pyridyl perylenetetracarboxylic diimide can absorb the visible light, generate electrons and then transmit to cobalt through a coordinate bond, so as to catalyze the water decomposing for hydrogen generation.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Method of polishing silicon wafer
InactiveUS20010036799A1Polishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesAdditive ingredientSulfide
Mirror-polishing of a silicon wafer is conducted using an abrasive agent which contains silica as a principal ingredient, and either one of the ingredients set forth at (1) and (2): (1) an ingredient which is selected from alkali sulfide, alkali hydrogensulfide, and the mixture thereof; and (2) a chelate agent which contains at least alpha-benzoinoxime, diethyldithiocarbamic acid, cupferron, xanthogenic acid, neocupferron, beryllon II, beta-quinolinol, 1,1,1-trifluoro-3(2-thenoyl)acetone, dimethylglyoxime, and 1-(2-pyridylazo)-2-naphthol.
Owner:SUMITOMO MITSUBISHI SILICON CORP
Catalyst for processing azo dyes in printing and dyeing waste water and preparation method
InactiveCN102463108ALow component contentLow costWater/sewage treatment by irradiationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystPlasticizer
The invention discloses a catalyst for processing azo dyes in printing and dyeing waste water and a preparation method. The catalyst disclosed by the invention contains an active metal component, a rare-earth metal oxide, a plasticizer, an organic foaming agent, a curing agent and the like. The specific preparation method of the catalyst comprises the following steps of: (1) weighing a proper amount of curing agent according to the mass percentage of a formula, drying, grinding and sieving the curing agent, adding the plasticizer and the organic foaming agent and mixing uniformly, and sintering at 500-800 DEG C for 4-6 h to obtain a honeycomb type solid; (2) weighing a certain amount of rare-earth oxide, dissolving the rare-earth oxide in a nitric acid solution with the concentration of 20-40%, filtering, and adding dimethylglyoxime and the active metal component into the filtrate to obtain a metal dispersion system; and (3), immersing the obtained honeycomb type solid in the dispersion system for 5-45 min, and drying to obtain a honeycomb type solid catalyst. The catalyst prepared by using the preparation method has the characteristics of long service life, higher activity, better catalytic property on the azo dyes in the printing and dyeing waste water and the like.
Owner:CHANGZHOU YAHUAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Preparation method and application of praseodymium cuprate nano absorbing material
ActiveCN107777719APromote NanoizationUniform particlesMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesCuprateControllability
The invention belongs to the technical field of nano absorbing materials and particularly relates to a preparation method and application of a praseodymium cuprate nano absorbing material. The preparation method is implemented through impressed voltage, and through control over an applied electric field, can change morphology and related characters of prepared PrCuO4 nano powder, thereby achievinghigh controllability. The preparation method of the praseodymium cuprate nano absorbing material improves common electric field operation, combines the electric field with solution, and control overthe added amount of dispersing agent of dimethylglyoxime with change in the pH of the solution to prepare the nano powder with a large specific surface area and uniform particles; the nano powder hassingle absorbing effects, provides a new material and a new idea for existing water pollution treatment and develops new properties.
Owner:东北大学秦皇岛分校
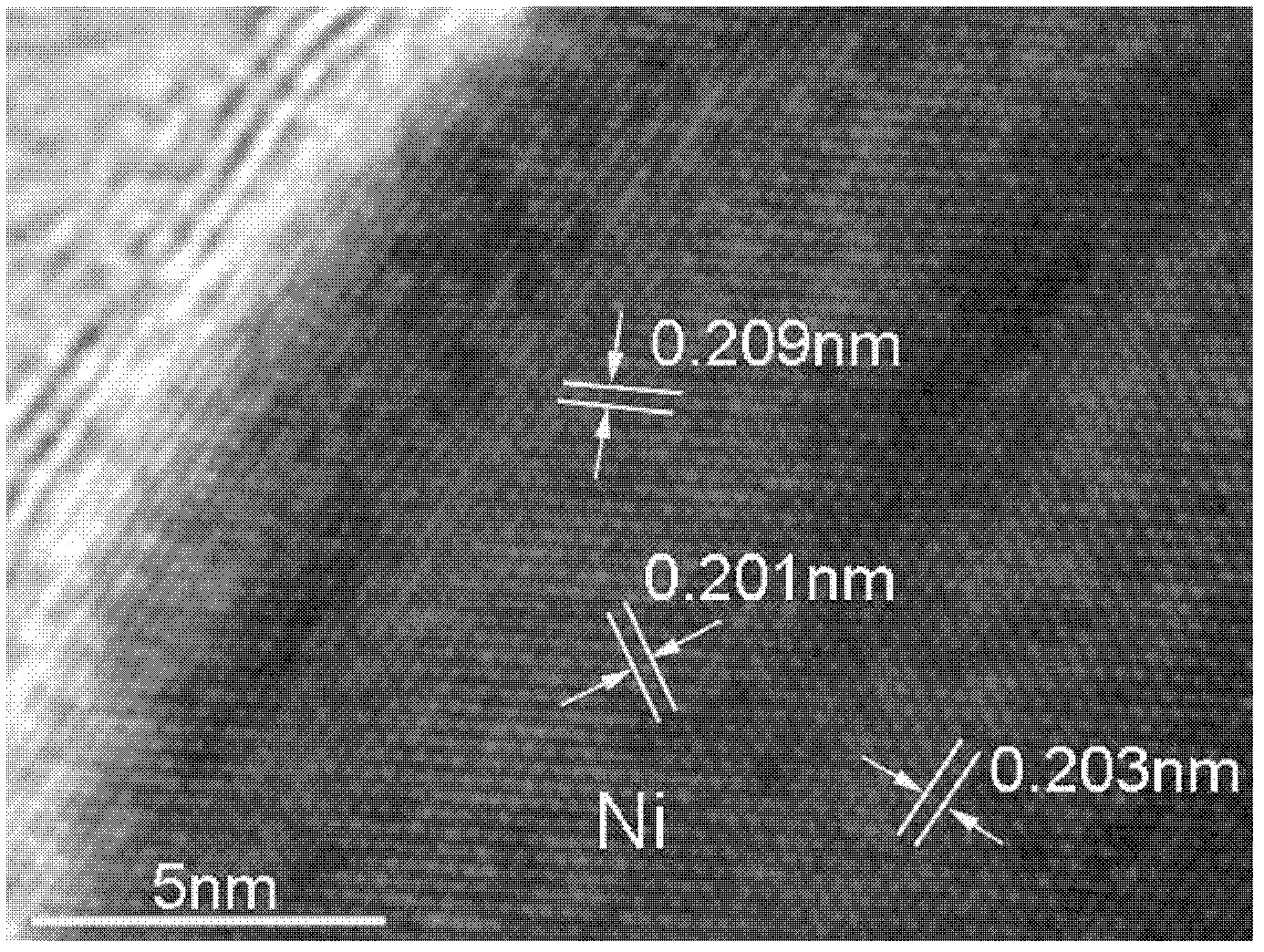
Preparation method for nickel/graphene nanometer compound material
InactiveCN102350505AAvoid the defect of uneven dispersionSimple preparation processMaterial nanotechnologyNickel saltGraphene nanocomposites
The invention aims to provide a preparation method for a nickel / graphene nanometer compound material, which is simple in operation, high in yield and uniform in dispersion of metallic nanometer particles on a graphene surface. According to the preparation method, dimethylglyoxime and nickel salt are taken as raw materials for preparing nickel dimethylglyoxime, and the decomposition reaction is performed on the nickel dimethylglyoxime at high temperature, thereby acquiring the nickel / graphene nanometer compound material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: weighting the dimethylglyoxime and the nickel salt; placing the nickel salt into deionized water, and placing the dimethylglyoxime into absolute ethyl alcohol and then adding aqueous ammonia; filtering the nickel dimethylglyoxime acquired by uniformly mixing the two solutions, washing the nickel dimethylglyoxime with the deionized water and drying; and performing the decomposition reaction on the dried nickel dimethylglyoxime at high temperature, thereby acquiring the nickel / graphene nanometer compound material.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing mass wormlike palladium nanotubes
InactiveCN103272590AHigh catalytic activityImprove stabilityCell electrodesNanotechnologyPolymer scienceCentrifugation
The invention discloses a method for preparing mass wormlike palladium nanotubes. According to the method, precipitates are obtained through reacting PdCl2 with dimethylglyoxime, the mole ratio of PdCl2 to dimethylglyoxime is 1: (1-2), the produced precipitates are subjected to centrifugation, are thoroughly cleaned with water, are dried at the temperature of 60 DEG C and are then calcined for 2 hours in a muffle furnace at the temperature of 450 DEG C so as to obtain PdO WNTs, and the PdO WNTs is subjected to reduction by using NaBH4 so as to obtain a final product Pd WNTs. The Pd WNTs prepared by the method has great catalytic activity and high stability to the electrocatalytic oxidation of ethylene glycol (EG).
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Palladium solid phase extraction column with color rendering and indicating functions
InactiveCN102949863AWith color indication functionWith qualitative analysis functionOther chemical processesSolid sorbent liquid separationPre enrichmentSolid phase extraction
The invention discloses a palladium solid phase extraction column and a using method thereof. According to the palladium solid phase extraction column disclosed by the invention, magnesium titanate is used as a matrix; dimethylglyoxime with a color rendering function is modified and loaded on the matrix; and a prepared palladium solid phase extracting agent with the adsorbing, color rendering and indicating functions is filled in a colorless and transparent column pipe to obtain the solid phase extraction column with the color rendering and indicating functions; and the solid phase extraction column is used for qualitative analysis and pre-enrichment and separation of palladium ions in a water sample in the analyzed and monitored field and can also be used for separation, enrichment and recovery of palladium in the metallurgy field. The palladium solid phase extraction column with the color rendering and indicating functions, which is disclosed by the invention, can be used for conveniently and qualitatively judging the palladium in solution directly by color change; in the process of separating, enriching and recovering the palladium, the extraction state and the use condition of the column can be judged by color; and the column has good selectivity, is stable, has strong enrichment and separation capacity and is convenient to use.
Owner:SHENYANG LIGONG UNIV
Method for measuring nickel content in copper alloy by use of dimethylglyoxime spectrophotometric method
InactiveCN102980867AGuaranteed accuracyEnsure precisionColor/spectral properties measurementsAbsorbent cottonCopper alloy
The invention discloses a method for measuring nickel content in a copper alloy by use of a dimethylglyoxime spectrophotometric method. The method comprises the following steps of: dissolving a copper alloy sample with acid; separating nickel from the sample solution by use of a dimethylglyoxime complex in a pH range from 6.5 to 7.2 of the solution; extracting the complex by use of trichloromethane; and measuring the nickel content by use of the spectrophotometric method. The measured nickel content is less than or equal to 0.50%m / m. According to the invention, by adopting a method of adjusting the consistency of matrix copper content in the sample solution, separating nickel by use of dimethylglyoxime-ethanol and filtering the color development liquid with absorbent cotton, the shortcomings of the GB / T5121.5-2008 method IV are overcome, and the measurement accuracy is guaranteed. The method disclosed by the invention is suitable for measuring nickel content which is not greater than 0.50%m / m in the copper alloy.
Owner:GUIZHOU AEROSPACE PRECISION PRODS
Environmentally friendly putty
The invention discloses environmentally friendly putty. The putty comprises a main body and a curing agent, wherein the main body comprises the following components, by weight, 56-60 parts of an air-dried aqueous unsaturated polyester resin, 2-5 parts of styrene, 0.5-0.8 parts of triethylenetetramine, 0.8-1.2 parts of dimethylaniline, 1.2-1.5 parts of polymethyl methacrylate, 1.2-1.6 parts of BYK-980, 0.01-0.02 parts of dimethylglyoxime, 0.015-0.025 parts of polyamide wax, 0.2-0.3 parts of methylparaben, 4-8 parts of hollow glass bead, 1-3 parts of bentonite, 5-7 parts of calcium carbonate, 10-15 parts of titanium dioxide, 1-2 parts of a glass fiber, and 3-5 parts of barium sulfate; and the curing agent comprises, by weight, 60-64 parts of benzoyl peroxide, 20-24 parts of dibutyl phthalate, and 4-8 parts of silica.
Owner:上海苏中建设工程有限公司
Method for measuring content of copper, cadmium, nickel and cobalt in zinc electrolyte simultaneously
ActiveCN107179339AMask interferenceReduce the impactMaterial electrochemical variablesCadmium CationPrecipitation
The invention discloses a method for measuring the content of copper, cadmium, nickel and cobalt in zinc electrolyte simultaneously. The method comprises the steps as follows: a to-be-measured zinc electrolyte is reacted with a detection system composed of sodium borate, sodium citrate and dimethylglyoxime, adsorption polarographic waves of copper, cadmium, nickel and cobalt complexes are determined, and the content of copper, cadmium, nickel and cobalt is calculated based on an obtained second derivative wave crest current. According to the method, sodium borate, sodium citrate and dimethylglyoxime are adopted as the detection system, and the content of copper, cadmium, nickel and cobalt is measured simultaneously by adjustment of the pH value; the detection system can completely shelter interference of zinc ions, and pretreatment of the measured zinc electrolyte is not needed; through a standard addition method, an influence of other coexisting ions in the to-be-measured zinc electrolyte is weakened, the selectivity is high, and measurement results are accurate; adopted instruments are cheap and easy to operate; few types of reagents are used, the stability is good, price is low, no sediment is produced in a detection process, analysis speed is high, automation is easy to realize, and the method is applicable to online detection.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com