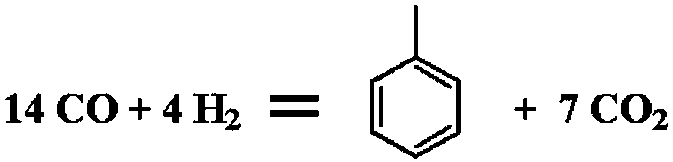
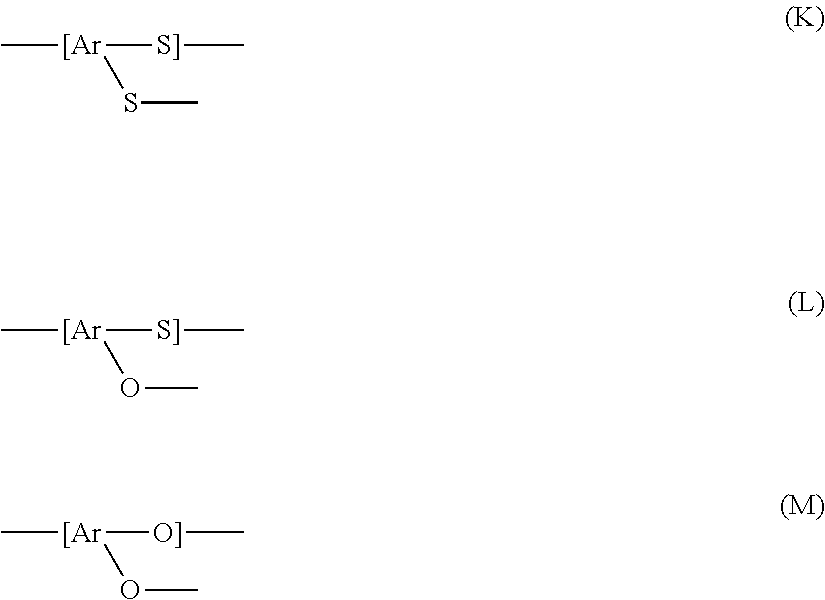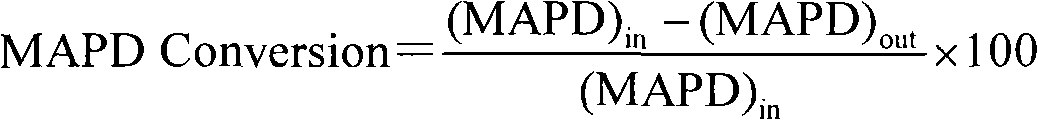Patents
Literature
84results about How to "Low component content" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aqueous Polymer Compositions Obtained From Epoxidized Natural Oils
ActiveUS20100330375A1Quickly self-crosslinkImproved color stabilitySynthetic resin layered productsPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPolyurethane dispersionCarbamate
Aqueous polyurethane dispersions are made from urethane prepolymers comprising one or more polyhydroxy compounds from ketone functional molecules derived from an epoxidized natural oil. Addition of a hydrazine functional moiety to the prepolymer dispersion can further provide a crosslinking mechanism resulting in the formation of azomethine linkages in the resulting polyurethane during drying. When the ketone functional molecule is derived from levulinic acid and epoxidized vegetable oil, the resulting urethane dispersion can also be converted into a hybrid polyurethane-vinyl dispersion by adding and polymerizing one or more vinyl monomers in the polyurethane prepolymer or polyurethane dispersion.
Owner:LUBRIZOL ADVANCED MATERIALS INC
Petroleum hydrocarbon cracking carbon nine cut fraction hydrogenation technology
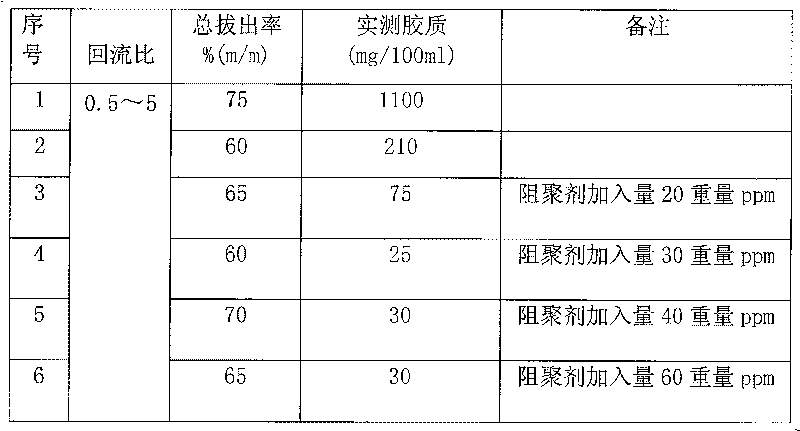
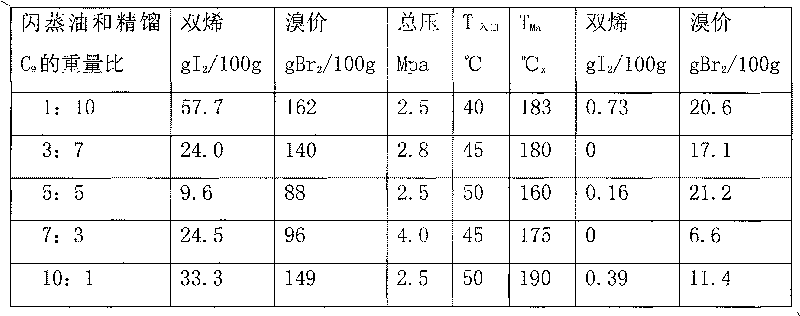
ActiveCN1948441ALow component contentReduces pungent odorsTreatment with hydrotreatment processesColloidPetroleum
This invention relates to a craft of hydrogenation of petroleum alkanes schizolysis carbon nine fraction of distillate, and it applies the craft of the combination of pressure thermal polymerization and finestill. Some of the carbon nine is conducted pressure thermal polymerization, while the other is conducted negative pressure finestill. The hydrogenation is conducted on flash evaporation oil which is from pressure thermal polymerization and finestill carbon nine which is from negative pressure finestill. This craft can inprove the carbon nine distill proportion and cut down the amount of colloid of schizolysis carbon nine, which make the schizolysis carbon nine product after hydrogenation colorless and none stimulant smell.
Owner:广东省茂名华粤集团有限公司 +2
Gasoline desulfurization method
InactiveCN104673376ARealize deep desulfurizationLow component contentTreatment with hydrotreatment processesGasolineRaw material
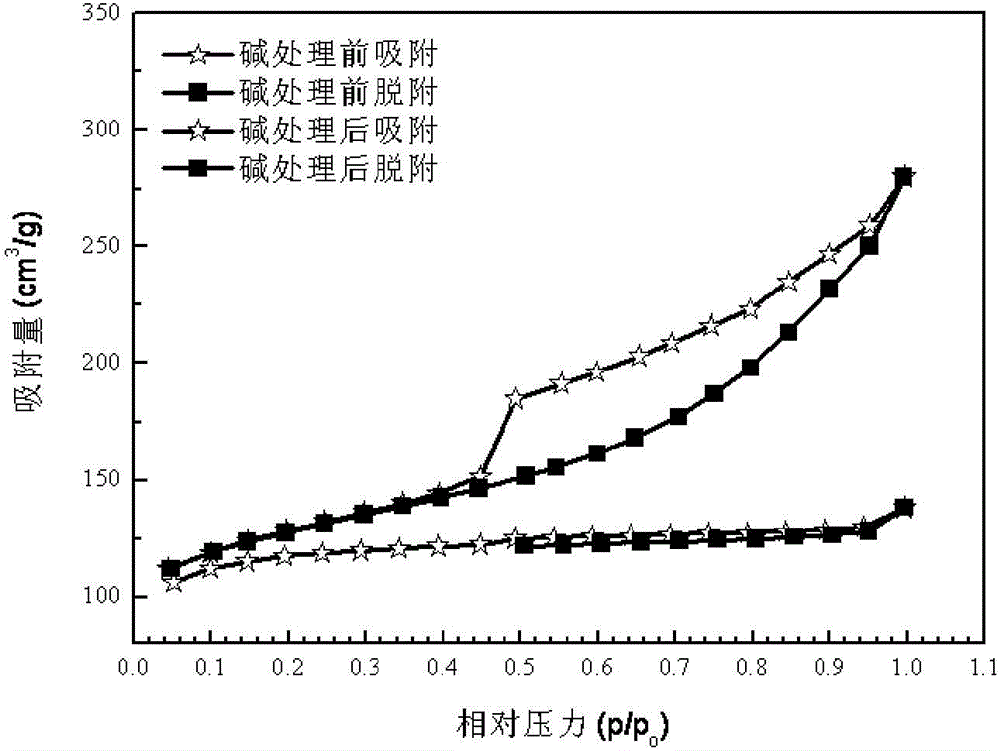
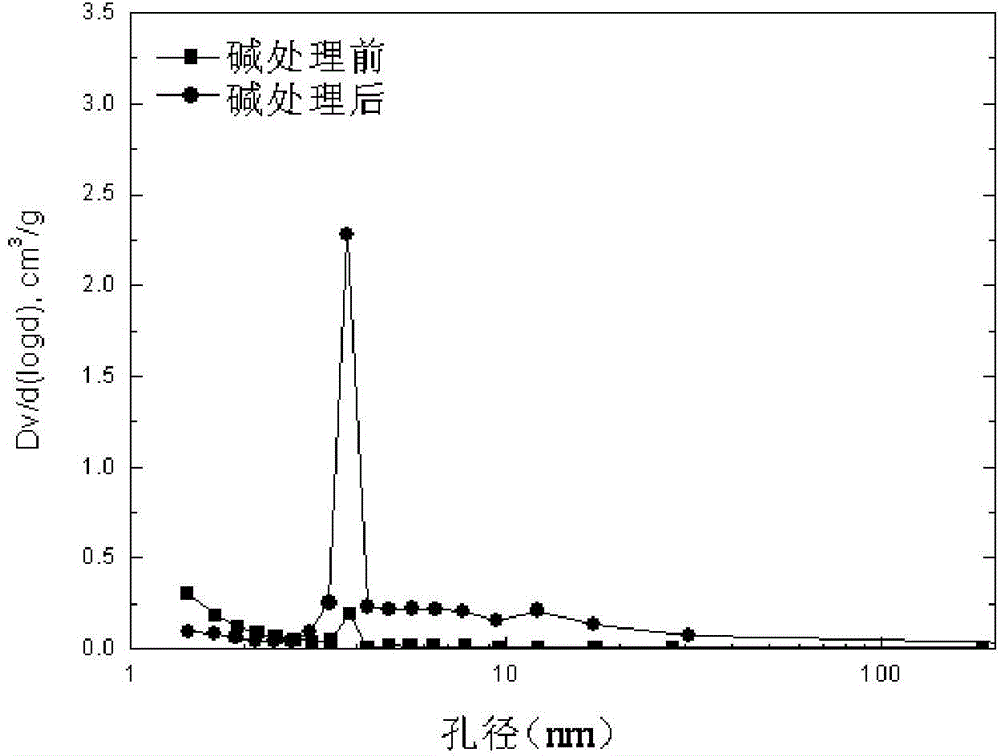
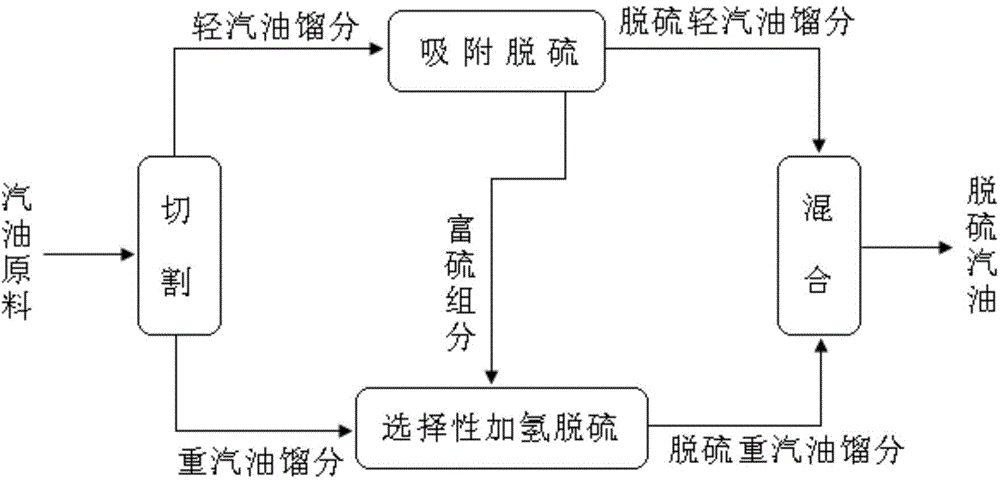
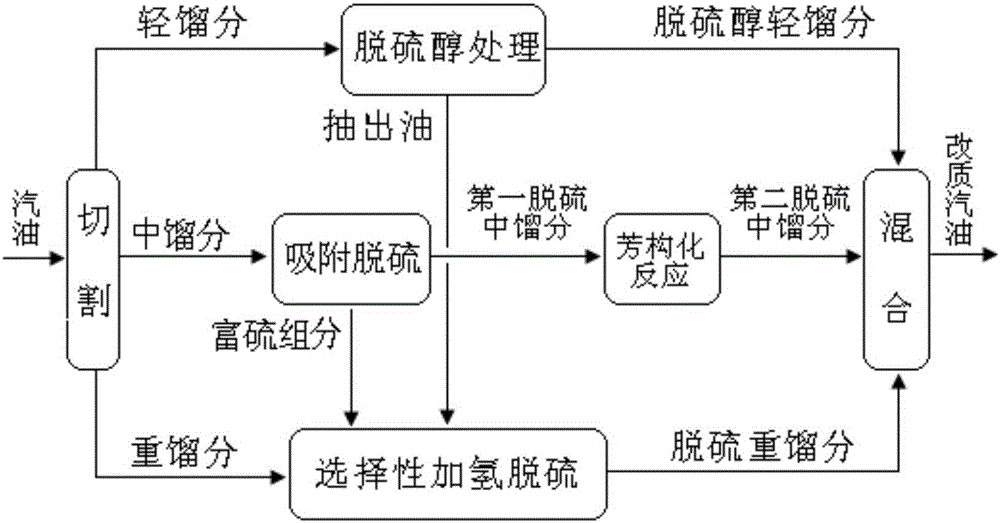
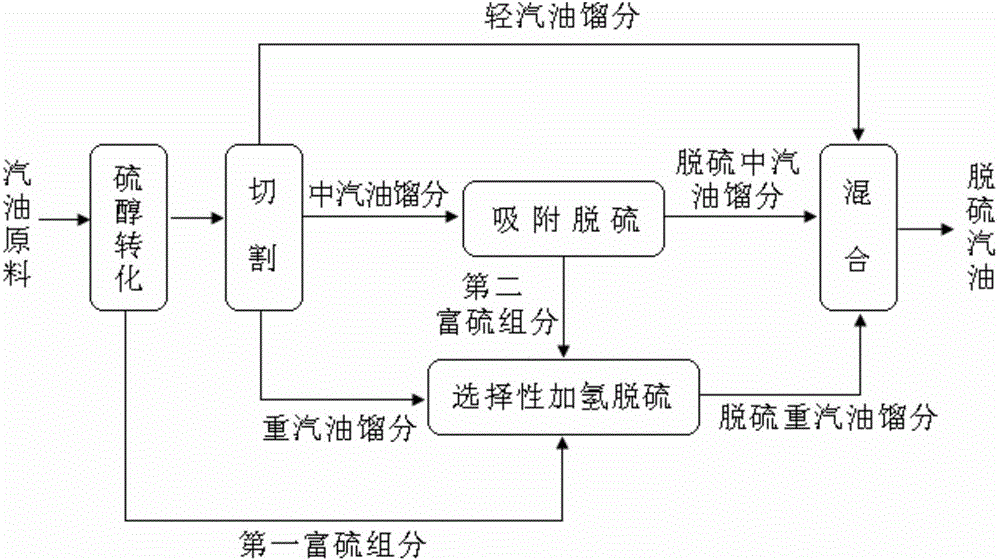
The invention provides a gasoline desulfurization method. The gasoline desulfurization comprises the following steps: cutting a gasoline raw material into a light gasoline fraction and a heavy gasoline fraction; performing adsorption desulfurization on the light gasoline fraction to obtain desulfurized light gasoline fraction; and performing selective hydrogenation desulfurization on the heavy gasoline fraction to obtain desulfurized heavy gasoline fraction, wherein the cutting temperature of the light gasoline fraction and the heavy gasoline fraction is 70-110 DEG C. By adopting the gasoline desulfurization method, not only can deep desulfurization of gasoline be realized, but also the octane loss is low.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING) +1
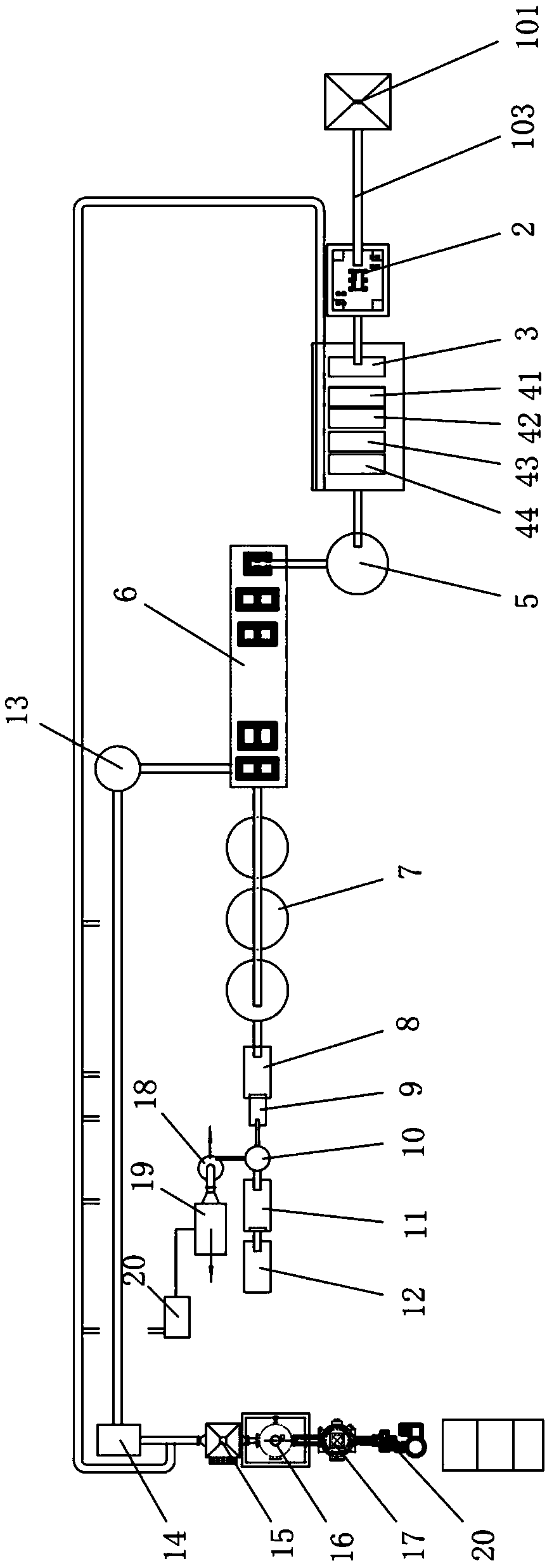
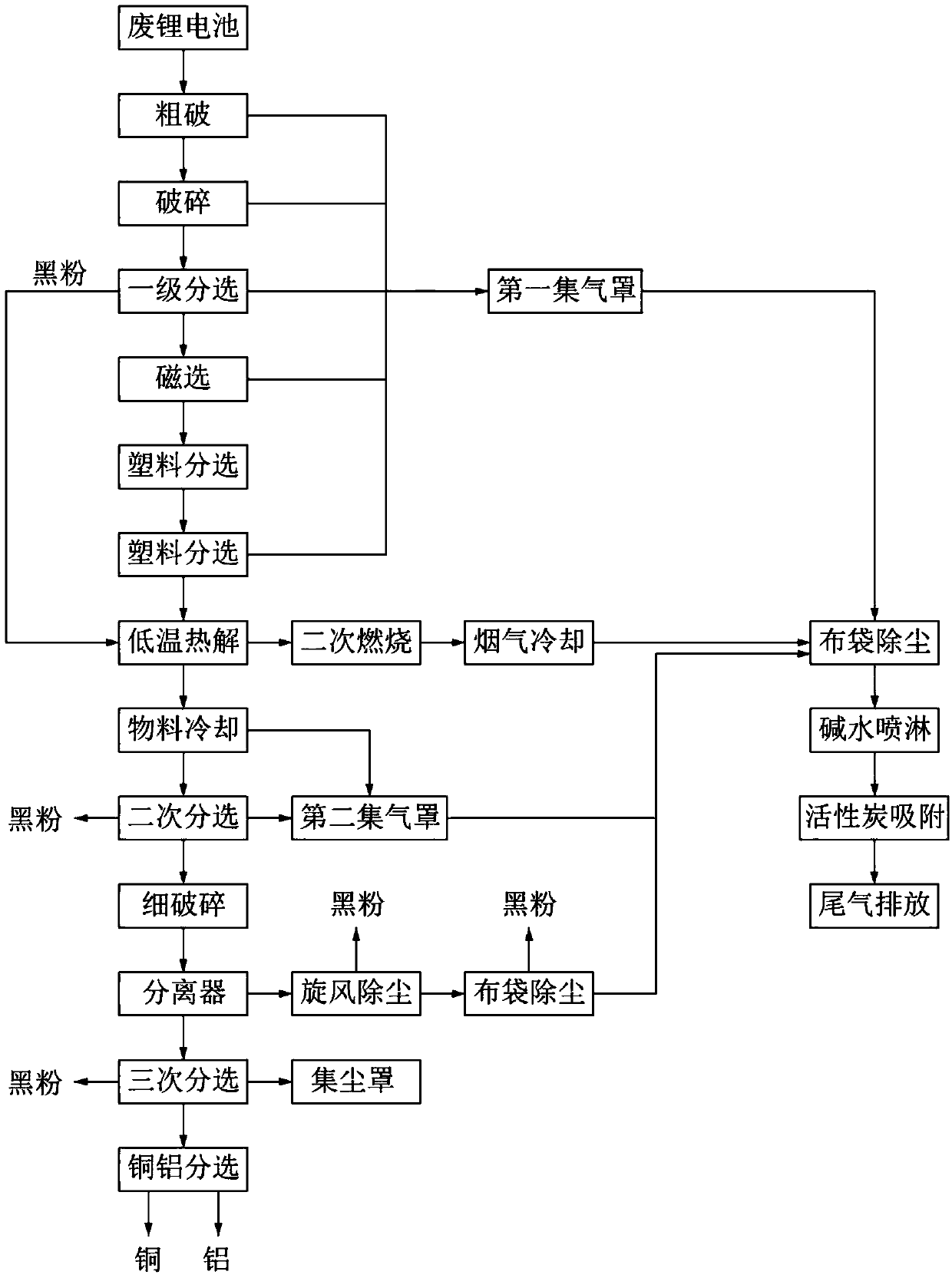
Waste lithium ion battery crushing and sorting device and method
PendingCN109604024AFull play to recycling valueImprove sorting effectWaste accumulators reclaimingGrain treatmentsElectrical batteryEngineering
The invention discloses a waste lithium ion battery crushing and sorting device and method. The crushing and sorting device comprises a feeding device; a rough crushing machine of which the feeding end is connected with the discharging end of the feeding device; a crushing machine of which the feeding end is connected with the discharging end of the rough crushing machine; a multistage sorting device of which the feeding end is connected with the discharging end of the crushing machine; a pyrolyzing furnace of which the feeding end is connected with the discharging end of the multistage sorting device; a material cooling bin of which the feeding end is connected with the discharging end of the pyrolyzing furnace; a second vibrating screen of which the feeding end is connected with the discharging end of the material cooling bin; a fine crushing machine of the feeding end is connected with the discharging end of the second vibrating screen; a third vibrating screen of which the feedingend is connected with the discharging end of a separator; and a jigging machine of which the feeding end is connected with the discharging end of the third vibrating screen. According to the waste lithium ion battery crushing and sorting device and method, high-efficiency recovery of valuable components in a lithium ion battery can be achieved; and the sorting effect is good, and the recovery rateof black powder is high.
Owner:ZHUZHOU DINGDUAN EQUIP CO LTD
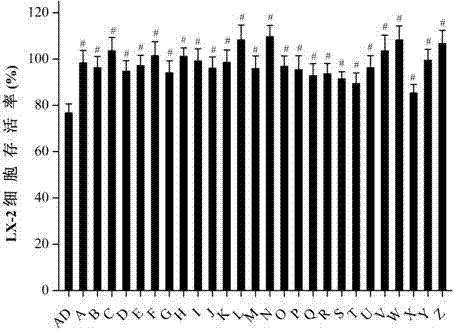
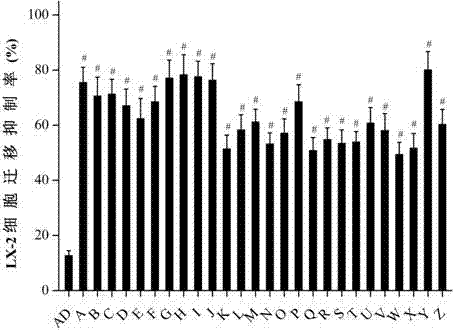
Applications of andrographolide derivatives and 3,19 esterified compounds thereof in preparation of anti-hepatic fibrosis medicines
ActiveCN106946821ADefinitive anti-hepatic fibrosis activityInhibit migrationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCell-Extracellular MatrixHepatic stellate cell activation
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, discloses applications of andrographolide derivatives in preparation of medicines preventing and treating hepatic fibrosis, and relates to 15-benzylidene-14-deoxy-11,12-dehydroandrographolide derivatives and 3,19 esterified compounds thereof. Experiments prove that the compounds significantly inhibit human hepatic stellate cell LX-2 metastasis and activation, significantly reduce the fibrosis level of hepatic tissues of rats affected with hepatic fibrosis, reduce contents of extracellular matrix protein (ECM) related components, significantly reduce the level of immune inflammation correlation factors of rats affected with hepatic fibrosis, effectively inhibit immuno-inflammatory responses, inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation in hepatic tissues, and promote collagen degradation. The compounds are used as active components for preparing the anti-hepatic fibrosis medicines, and are efficient and low in toxicity, thus providing a novel medicine route for hepatic fibrosis treatment and prevention, and expanding the optional range of clinical medicine application. The compounds and the applications have good development prospects.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Quality improvement method of catalytic cracking gasoline
InactiveCN104673377ARealize deep desulfurizationFlexible operationTreatment with hydrotreatment processesHydrocarbon oils treatment productsHydrodesulfurizationAromatization
The invention provides a quality improvement method of catalytic cracking gasoline. The quality improvement method comprises the following steps of: cutting a gasoline raw material into light, medium and heavy gasoline fractions; desulfurizing the medium gasoline fraction to obtain first desulfurized medium gasoline fraction; carrying out aromatization / hydroisomerization reaction on the first desulfurized medium gasoline fraction in the presence of a catalyst to obtain second desulfurized medium gasoline fraction; carrying out selective hydrodesulfurization on the heavy gasoline fraction to obtain desulfurized heavy gasoline fraction; mixing the light gasoline fraction, the second desulfurized medium gasoline fraction and the desulfurized heavy gasoline fraction to obtain quality improved gasoline, wherein the cutting temperature of the light and medium gasoline fractions is 35-60 DEG C, and the cutting temperature of the medium and heavy gasoline fraction is 70-130 DEG C. The quality improvement method provided by the invention can not only realize the deep desulfurization of the catalytic cracking gasoline, but also be used for outstandingly increasing the octane value.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
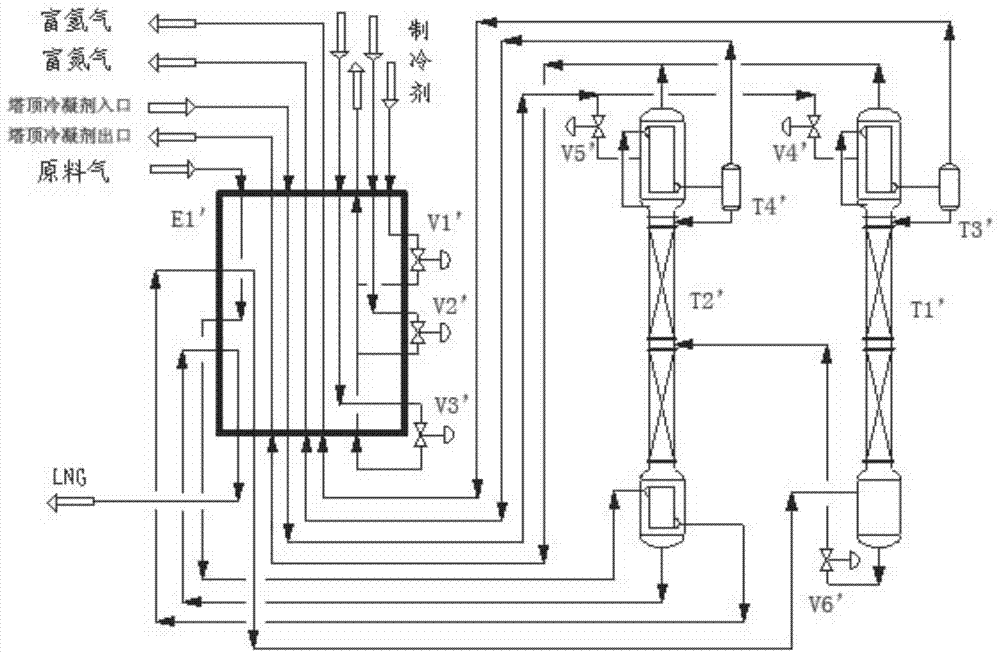
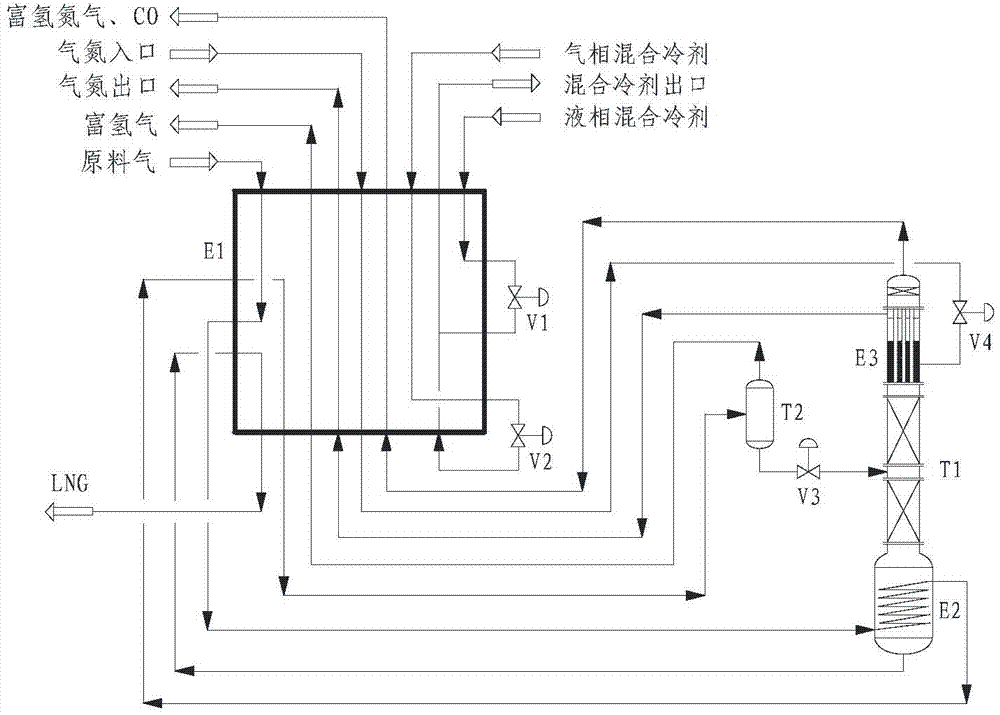
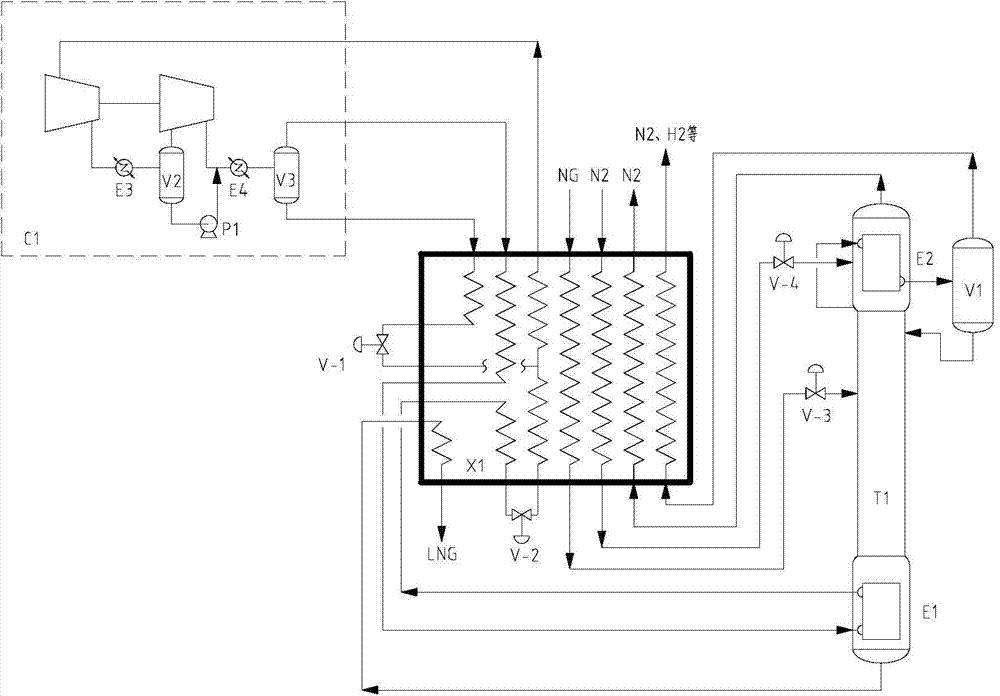
Technology and device for removing hydrogen and nitrogen from methane-rich gas through rectification and producing liquefied natural gas
ActiveCN104513680AReduced equipment investment and maintenance costsLow content of impurity componentsSolidificationLiquefactionChemistryRefrigerant
A technology and a device for removing hydrogen and nitrogen from methane-rich gas through rectification and producing liquefied natural gas. The technology comprises two parts: low-temperature liquefaction and rectification separation, wherein the low-temperature liquefaction includes following steps: firstly feeding the methane-rich gas containing hydrogen and nitrogen into a refrigerating box and liquefying a methane component in the refrigerating box with a mixed refrigerant for providing cooling capacity; and the rectification separation includes: directly feeding the liquefied methane-rich gas containing hydrogen and nitrogen into a single rectifying column to perform rectification for removing the hydrogen, the nitrogen and a less amount of carbon monoxide, wherein a gas mixture containing the hydrogen, the nitrogen and the less amount of the carbon monoxide is obtained at the top of the rectifying column; passing the gas mixture through the refrigerating box for recycling the cooling capacity and discharging the gas mixture out from the refrigerating box; and feeding back a liquid phase at the bottom of the rectifying column to the refrigerating box for being supercooled and then discharging the liquid phase out from the system to obtain a liquefied natural gas product which is not more than 500 ppm in the content of the hydrogen, is not more than 2% in the content of the nitrogen and is not more than 2% in the content of carbon monoxide. The invention provides a technology in which liquefied natural gas is produced by liquefying the methane-rich gas and meanwhile the hydrogen, the nitrogen and the carbon monoxide are removed. The technology is simple in processes and is low in equipment investment cost.
Owner:XINDI ENERGY ENG TECH
Polyarylene sulfide and method for producing the same
A method is provided for producing a polyarylene sulfide by reacting a sulfidizing agent with a dihalogenated aromatic compound in an organic polar solvent in the presence of an alkali metal hydroxide, the method includes <Step 1>: carrying out the reaction in such a manner that the polymerization time in a temperature range of 230° C. to less than 245° C. (T1a) is not less than 30 minutes and less than 3.5 hours and that the conversion ratio of the dihalogenated aromatic compound at the end of the step is 70 to 98 mol. % and <Step 2>: carrying out the reaction in such a manner that the polymerization time in a temperature range of 245° C. to less than 280° C. (T2) is not less than 5 minutes and less than 1 hour.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
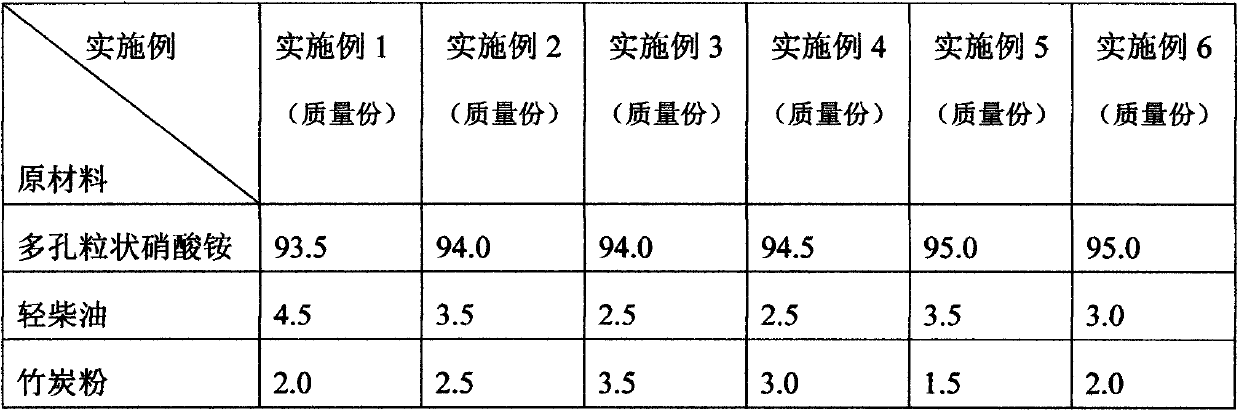
Improved type porous granular ammonium nitrate fuel oil explosive and preparing method thereof
The invention discloses an improved type porous granular ammonium nitrate fuel oil explosive and a preparing method thereof. The improved type porous granular ammonium nitrate fuel oil explosive is prepared by mixing the following three raw materials in percentage by weight: 93%-95% of porous granular ammonium nitrate, 2.5%-5.0% of light diesel oil and 1.5%-4.0% of bamboo charcoal powder. The preparing method comprises the following steps of adding the porous granular ammonium nitrate to a dispersator according to quantity, then slowly adding sufficient light diesel oil, sufficiently stirring for 5 minutes, and then stopping stirring; standing for 5 minutes, starting the dispersator again, slowly adding the residual bamboo charcoal powder, continuously stirring till color and luster are uniform, wherein the black bamboo charcoal powder is uniformly absorbed on the surface of the porous granular ammonium nitrate; finally filling and sealing to obtain the finished improved type porous granular ammonium nitrate fuel oil explosive product which has the advantages of uniform stirring, excellent property, low moisture absorption and agglomeration ratio, stability in storage, safety, environmental protection, energy conservation, low consumption and low cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ZHENKAI CHEM IND +1
C3 fraction selective hydrogenation catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101875009AReduce loadHigh activityHydrocarbon by hydrogenationCatalyst activation/preparationSingle substanceLow load
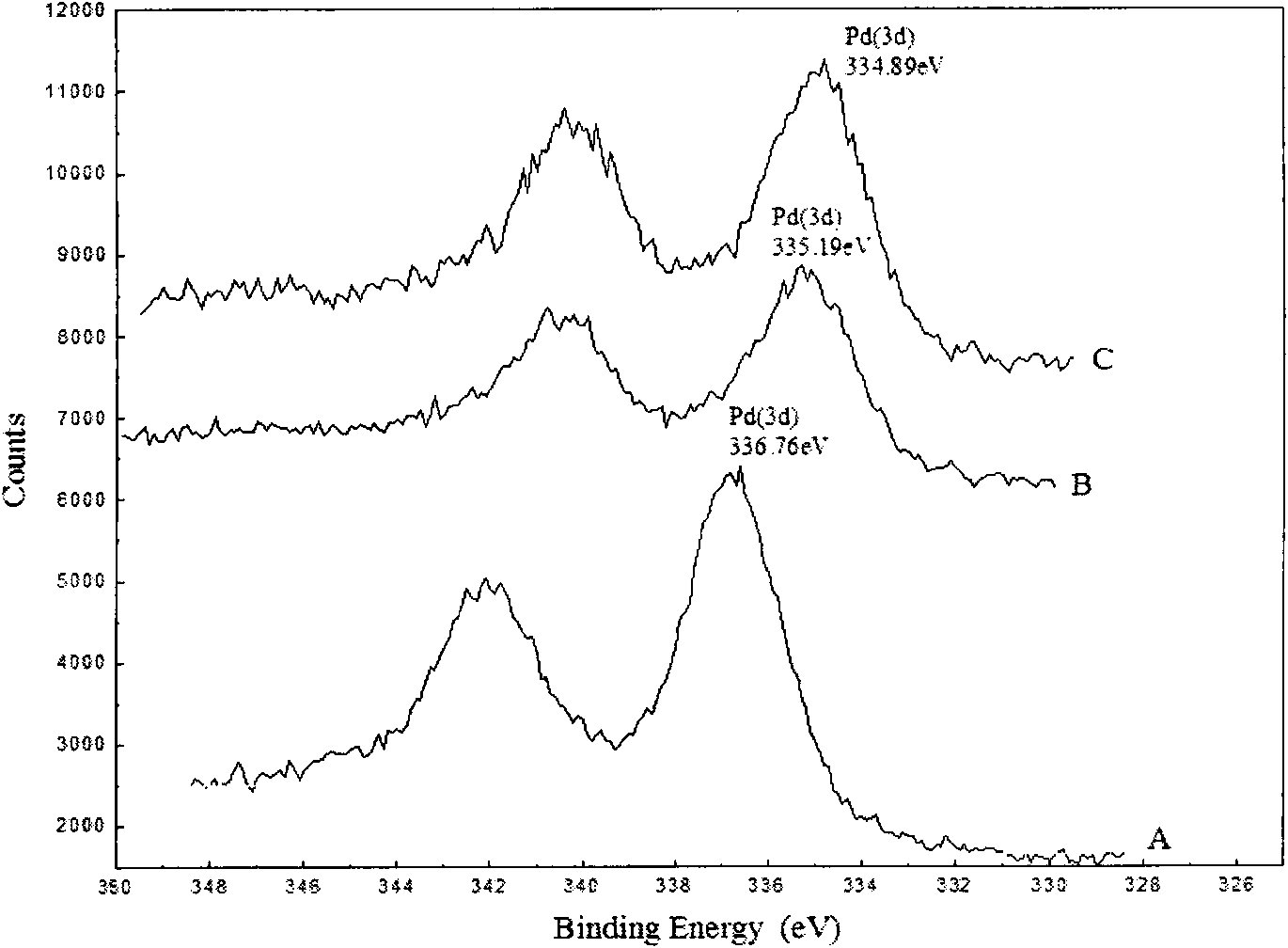
The invention discloses a propylene catalyst for allylene and propadiene selective hydrogenation in C3 fraction and a preparation method thereof; in the invention, after the catalyst passes through the load active metal component, ionization irradiation treatment is needed to be carried out, and the main active metal component Pd of the prepared catalyst is in a single-substance state under room temperature and air condition, and the mean grain size of the active metal component is less than 15nm. The catalyst has the advantages of low load capacity of active metal component Pd, simple preparation process, being applied to the production process of petrochemical industry propylene, and high activity and selectivity.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
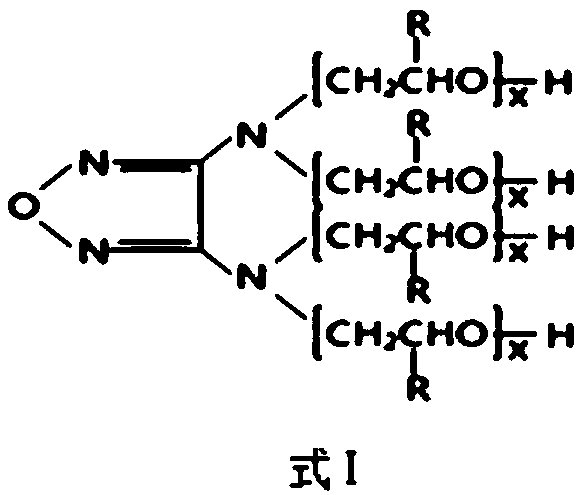
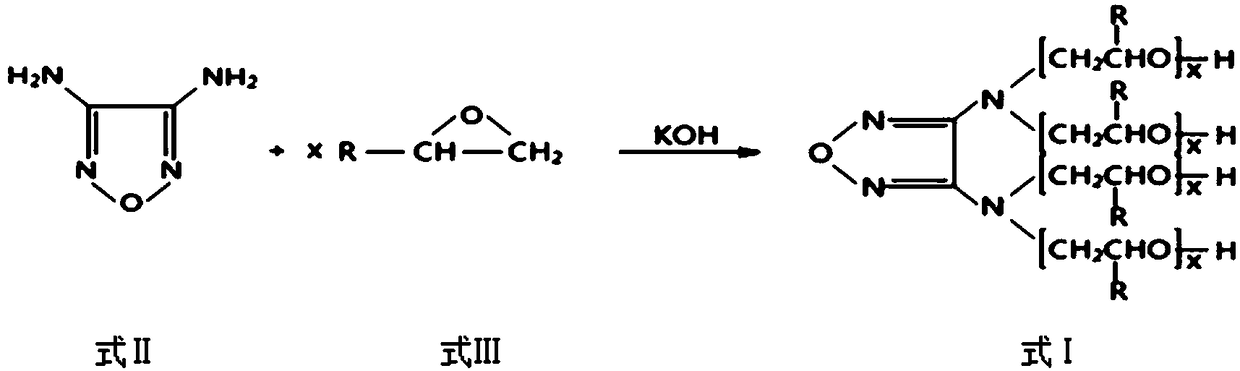
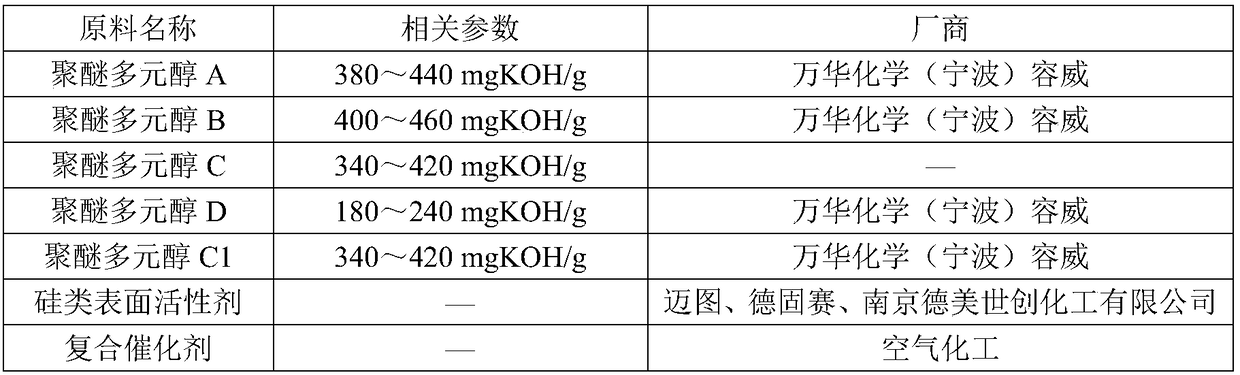
3,4-diaminofurazan polyether polyol, preparation method, rigid polyurethane foam prepared from 3,4-diaminofurazan polyether polyol and preparation method
The invention discloses 3,4-diaminofurazan polyether polyol, a preparation method, a rigid polyurethane foam prepared from the 3,4-diaminofurazan polyether polyol and a preparation method. The 3,4-diaminofurazan polyether polyol is prepared by taking 3,4-diaminofurazan as a starting material and carrying out addition reaction on the 3,4-diaminofurazan and olefin oxide to obtain the 3,4-diaminofurazan polyether polyol. The raw materials of the rigid polyurethane foam comprise compound polyether, a foaming agent and polyisocyanates according to the mass ratio of 100: 12-23: 130-160, the compoundpolyether contains 3,4-diaminofurazan polyether polyol, and the foaming agent contains HFC-134a. The 3,4-diaminofurazan is used as a novel polyether monomer of an initiator, and is compatible to HFC-134a well, and the prepared polyurethane foam has good dimensional stability and heat-insulation property when at low density.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM NINGBO RONGWEI POLYURETHANE
Petroleum hydrocarbon cracking carbon nine cut fraction hydrogenation technology
ActiveCN1948441BLow component contentReduces pungent odorsTreatment with hydrotreatment processesColloidPetroleum
This invention relates to a craft of hydrogenation of petroleum alkanes schizolysis carbon nine fraction of distillate, and it applies the craft of the combination of pressure thermal polymerization and finestill. Some of the carbon nine is conducted pressure thermal polymerization, while the other is conducted negative pressure finestill. The hydrogenation is conducted on flash evaporation oil which is from pressure thermal polymerization and finestill carbon nine which is from negative pressure finestill. This craft can inprove the carbon nine distill proportion and cut down the amount of colloid of schizolysis carbon nine, which make the schizolysis carbon nine product after hydrogenation colorless and none stimulant smell.
Owner:广东省茂名华粤集团有限公司 +2
A kind of upgrading method of catalytic cracking gasoline
InactiveCN104673377BRealize deep desulfurizationFlexible operationTreatment with hydrotreatment processesHydrocarbon oils treatment productsHydrodesulfurizationGasoline
The invention provides a quality improvement method of catalytic cracking gasoline. The quality improvement method comprises the following steps of: cutting a gasoline raw material into light, medium and heavy gasoline fractions; desulfurizing the medium gasoline fraction to obtain first desulfurized medium gasoline fraction; carrying out aromatization / hydroisomerization reaction on the first desulfurized medium gasoline fraction in the presence of a catalyst to obtain second desulfurized medium gasoline fraction; carrying out selective hydrodesulfurization on the heavy gasoline fraction to obtain desulfurized heavy gasoline fraction; mixing the light gasoline fraction, the second desulfurized medium gasoline fraction and the desulfurized heavy gasoline fraction to obtain quality improved gasoline, wherein the cutting temperature of the light and medium gasoline fractions is 35-60 DEG C, and the cutting temperature of the medium and heavy gasoline fraction is 70-130 DEG C. The quality improvement method provided by the invention can not only realize the deep desulfurization of the catalytic cracking gasoline, but also be used for outstandingly increasing the octane value.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Electric furnace phosphorus preparation method
InactiveCN105480958AIncrease profitTake advantage ofRaw phosphate material treatmentPhosphoritePre treatment
The invention discloses an electric furnace phosphorus preparation method, comprising phosphorite pretreatment and phosphorus preparation in a furnace, wherein the phosphorite pretreatment comprises steps of: mixing phosphorite powder with a binder to obtain mixed ore powder; pressing the mixed ore powder into pellets; performing first high temperature roasting and cementing on the pellets to obtain pretreatment pellets. The phosphorus preparation in the furnace comprises the steps of: feeding the pretreatment pellets into a yellow phosphorus electric furnace, and performing second high temperature roasting cementing by furnace gas; reacting in a melting zone to prepare the yellow phosphorus. The method can effectively use powdery phosphorite, obviously improve finished product quality and obviously reduce energy consumption.
Owner:罗宗恬
Catalyst for quickly degrading formaldehyde in air at room temperature and method for preparing catalyst
PendingCN109395741APromotes rapid oxidationCatalytic reaction temperature is lowGas treatmentHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsCatalytic oxidationReaction temperature
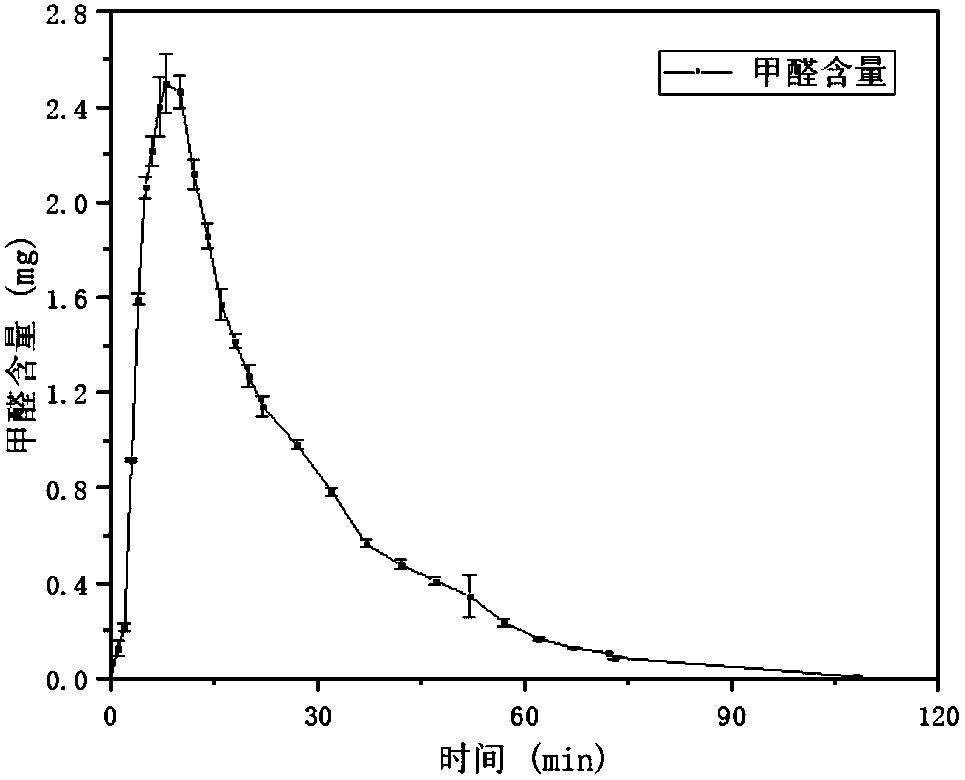
The invention discloses a catalyst for quickly degrading formaldehyde in air at the room temperature. The catalyst comprises metal compounds and adsorption carriers for loading the metal compounds. Precious metal components are loaded on the metal compounds. The catalyst has the advantages that metal oxide is loaded on inexpensive adsorption materials such as zeolite, effects of adsorbing and enriching gas can be sufficiently realized by the adsorption materials, effects of quickly catalytically oxidizing the formaldehyde can be realized by oxide groups in the presence of molecular electrostatic fields, and effects of reducing the catalytic reaction temperatures can be realized by precious metal; the precious metal components are low in content, accordingly, the problems of high cost and quick room-temperature degradation of precious metal catalysts in the prior art can be solved by the aid of the catalyst, and the formaldehyde can be quickly oxidized into carbon dioxide and water at the room temperature by the catalyst; the low content of the precious metal components can reach 0.019-0.031% and is far lower than the contents of precious metal components in existing catalysts.
Owner:北京艾驰凯环保科技有限公司
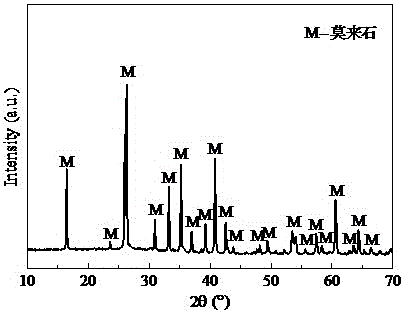
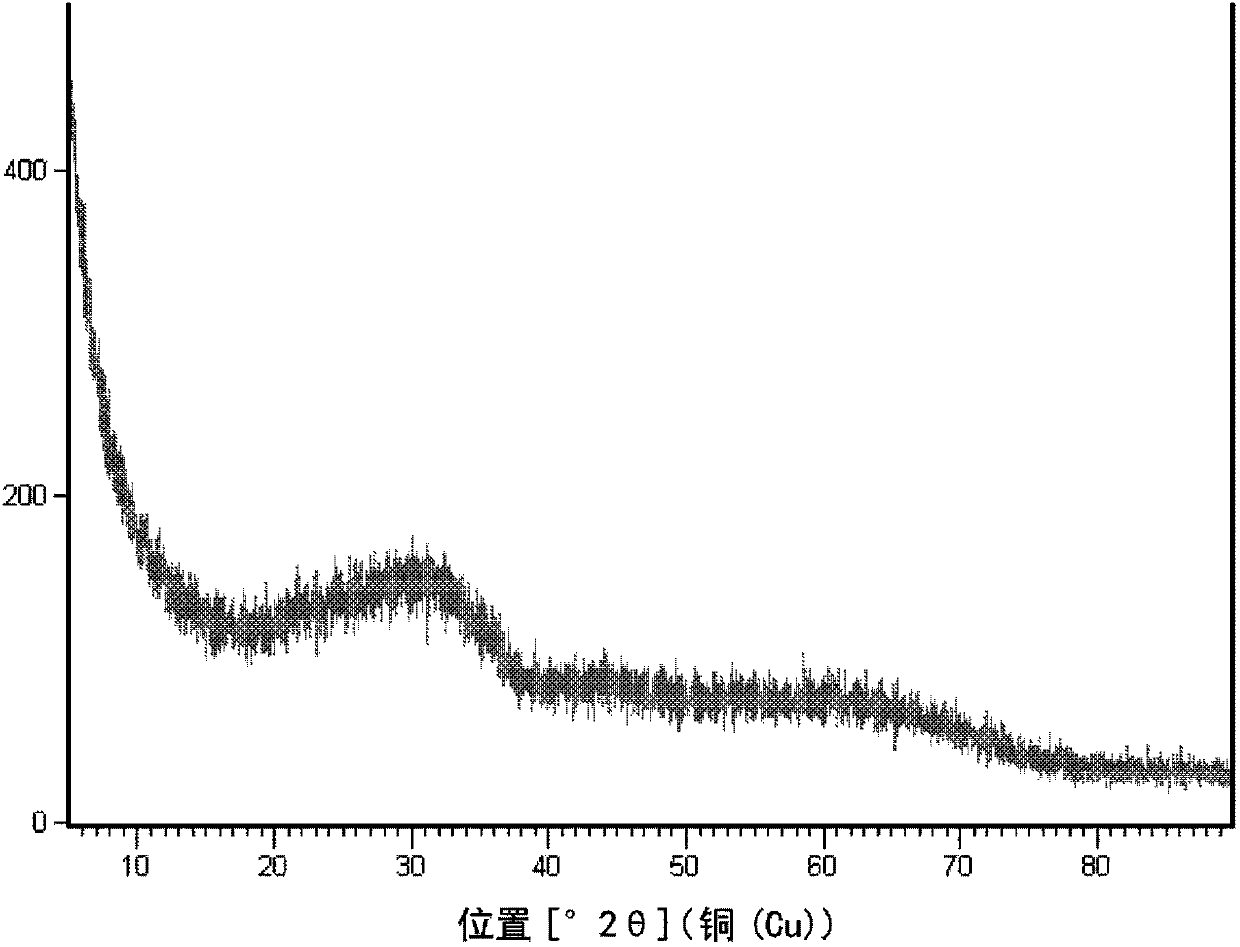
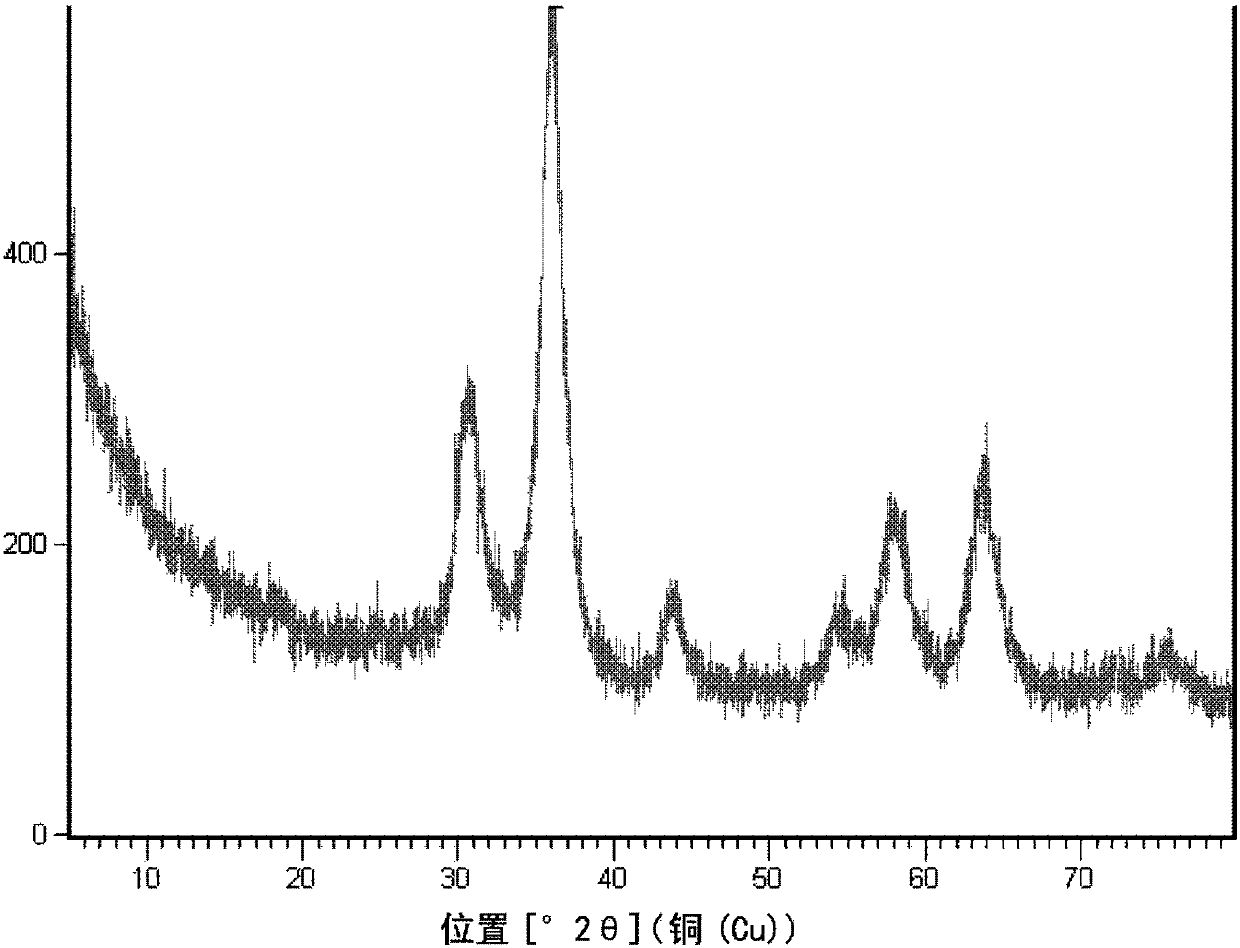
Method for preparing high-purity mullite powder through modified fly ash at high yield
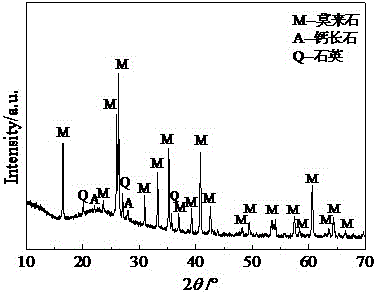
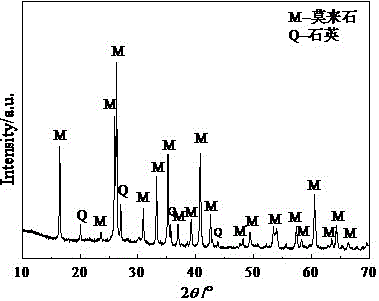
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-purity mullite powder through modified fly ash at the high yield, and belongs to the technical field of fine ceramics. The method comprises the following process steps that (1) 2-8% of alumina sol is added into fly ash powder, the alumina sol and the fly ash powder are mixed through ball milling, and coating modification of the surfaces of fly ash powder particles is achieved; (2) the modified fly ash is calcined at the certain temperature, so that the content of mullite in the fly ash reaches 60-70%, and mullitization of the fly ash powder is achieved; (3) the calcined fly ash is subjected to hydrothermal treatment in an alkaline aqueous solution and cleaned with an acid aqueous solution, glass phases and other oxide impurities such as CaO, MgO, Na2O, K2O and Fe2O3 in the fly ash are removed, and mullite powder is obtained; and (4) a reverse flotation technology is adopted, quartz impurities in the mullite powder is removed, and the high-purity mullite powder with the purity larger than 98% is prepared.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Method of directly preparing paraxylene from synthetic gas and aromatic hydrocarbon
ActiveCN109776249ASolution to short lifeLow component contentHydrocarbon by isomerisationHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMolecular sievePtru catalyst
The invention discloses a method of directly preparing paraxylene from synthetic gas and aromatic hydrocarbon. The method comprises the steps of allowing a raw material containing the synthetic gas and aromatic hydrocarbon except paraxylene to be contacted with a catalyst in a reaction area under a reaction condition sufficient to convert at least part of the raw material to form a reaction effluent containing paraxylene, and separating paraxylene from the reaction effluent, wherein the catalyst comprises an inert carrier confinement high dispersion metal oxide material, an acidic molecular sieve, and at least one of optional graphite powder and a dispersing agent; in the inert carrier confinement high dispersion metal oxide material, an inert carrier is at least one of silicon oxide and aluminum oxide; a content of metal oxide calculated as per a metal is less than or equal to 10wt% based on the weight of the inert carrier confinement high dispersion metal oxide material; and the acidic molecular sieve is selected from a modified acidic ZSM-5 molecular sieve, a modified acidic ZSM-11 molecular sieve and a mixture of the modified acidic ZSM-5 molecular sieve and the modified acidicZSM-11 molecular sieve.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
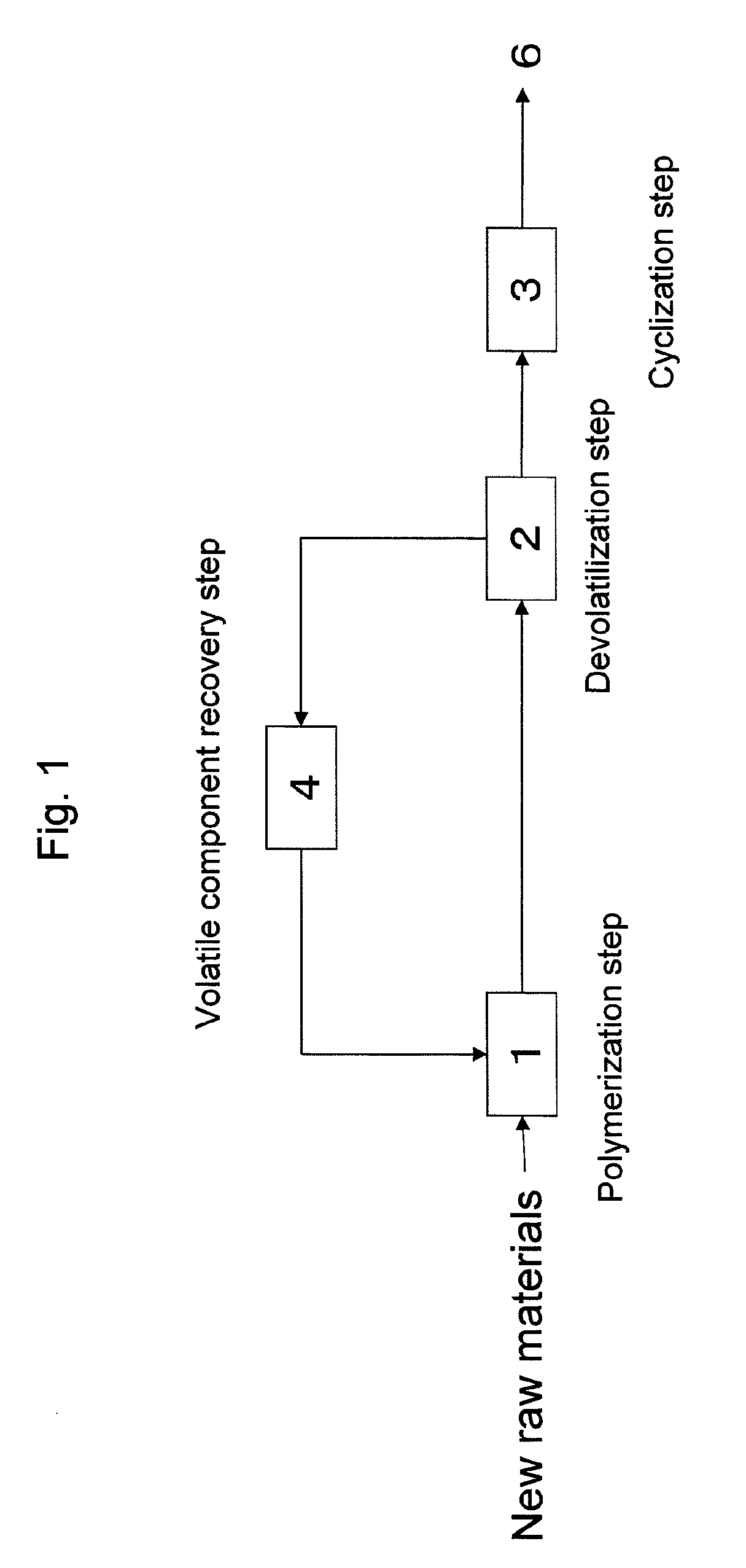
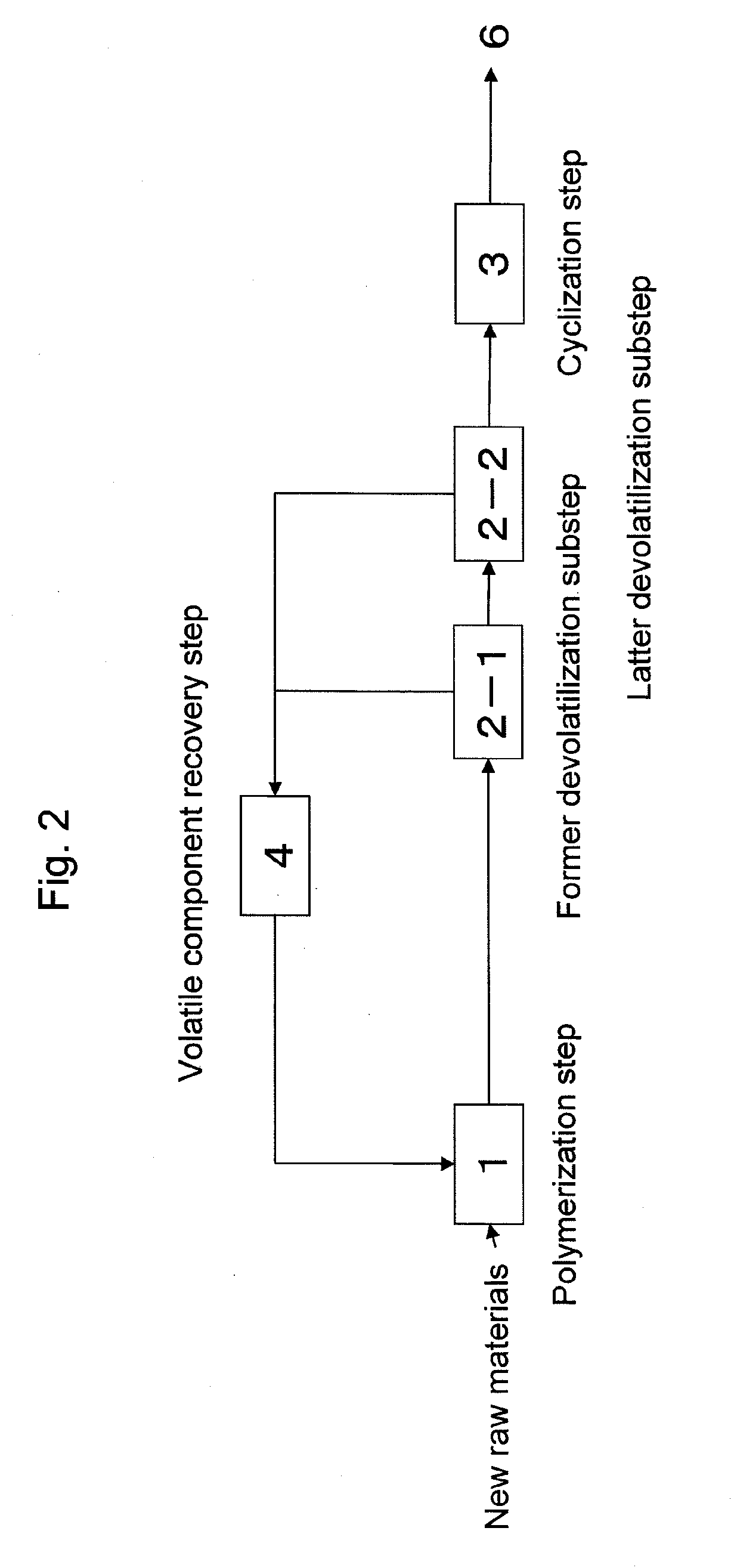
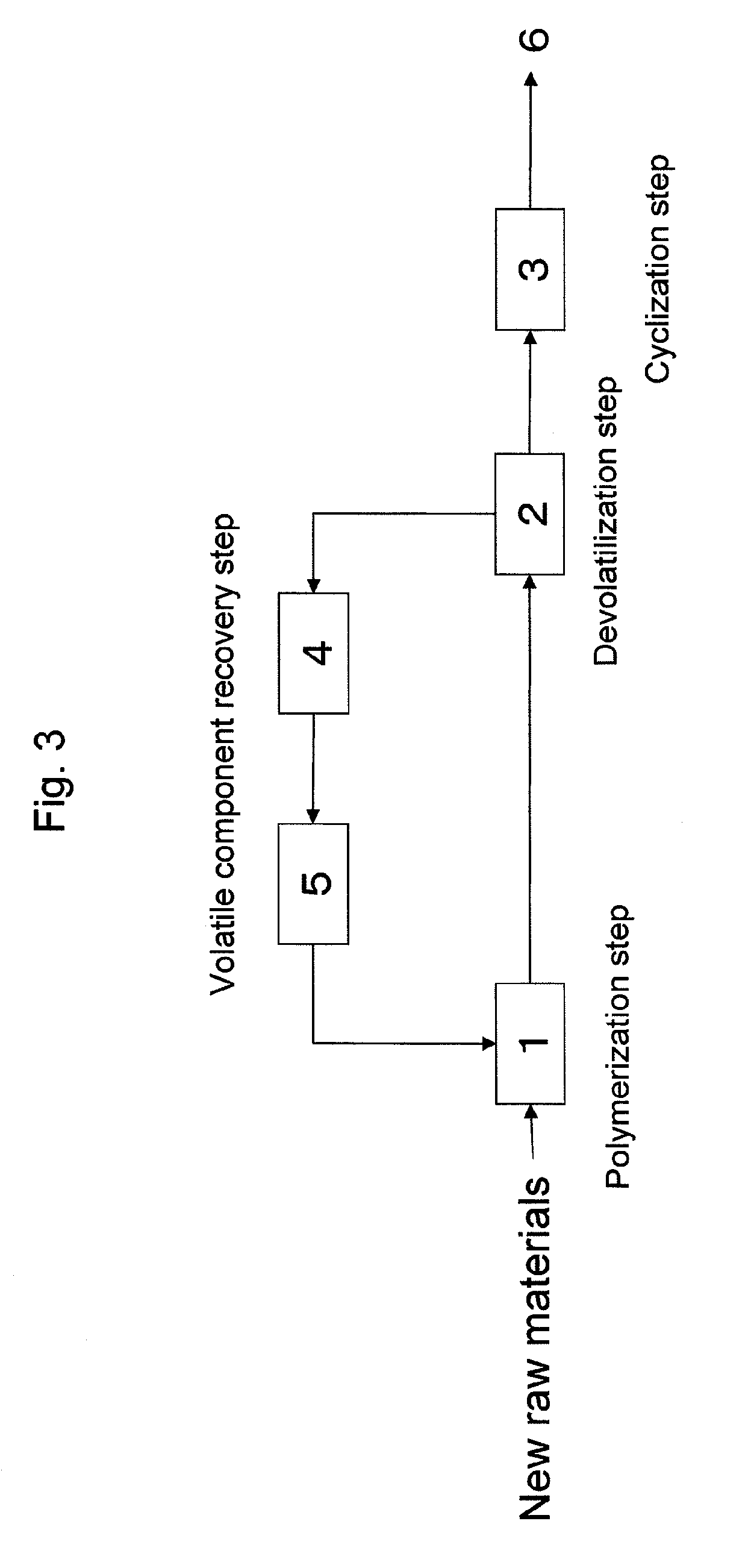
Process for production of thermoplastic copolymer
A process for continuously producing a thermoplastic copolymer, in which a copolymer (A) containing unsaturated carboxylic acid alkyl ester units and unsaturated carboxylic acid units is produced and in succession heat-treated to perform intramolecular cyclization reaction by dehydration and / or dealcoholization reaction, for producing a thermoplastic copolymer (B) containing glutaric anhydride units and the unsaturated carboxylic acid alkyl ester units. The obtained copolymer is excellent in heat resistance and colorless transparency and very small in foreign matter content.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Deep gasoline desulfurization method
InactiveCN104673379ARealization of deep desulfurizationReduce the number of regenerationsOther chemical processesTreatment with hydrotreatment processesHydrodesulfurizationGasoline
The invention provides a deep gasoline desulfurization method which comprises the following steps of: carrying out mercaptan removing treatment on a gasoline raw material; cutting the gasoline raw material subjected to the mercaptan removing treatment into light, medium and heavy gasoline fractions; carrying out adsorption desulfurization on the medium gasoline fraction to obtain a desulfurized medium gasoline fraction; carrying out selective hydrodesulfurization on the heavy gasoline fraction to obtain a desulfurized heavy gasoline fraction; mixing the light gasoline fraction, the desulfurized medium gasoline fraction and the desulfurized heavy gasoline fraction to obtain desulfurized gasoline, wherein the cutting temperature of the light and medium gasoline fractions is 35-60 DEG C, and the cutting temperature of the medium and heavy gasoline fractions is 70-130 DEG C. The deep gasoline desulfurization method provided by the invention can not only realize the deep desulfurization of gasoline, but also has low octane value loss.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Planting method for improving growth and development and fruit quality of tomatoes
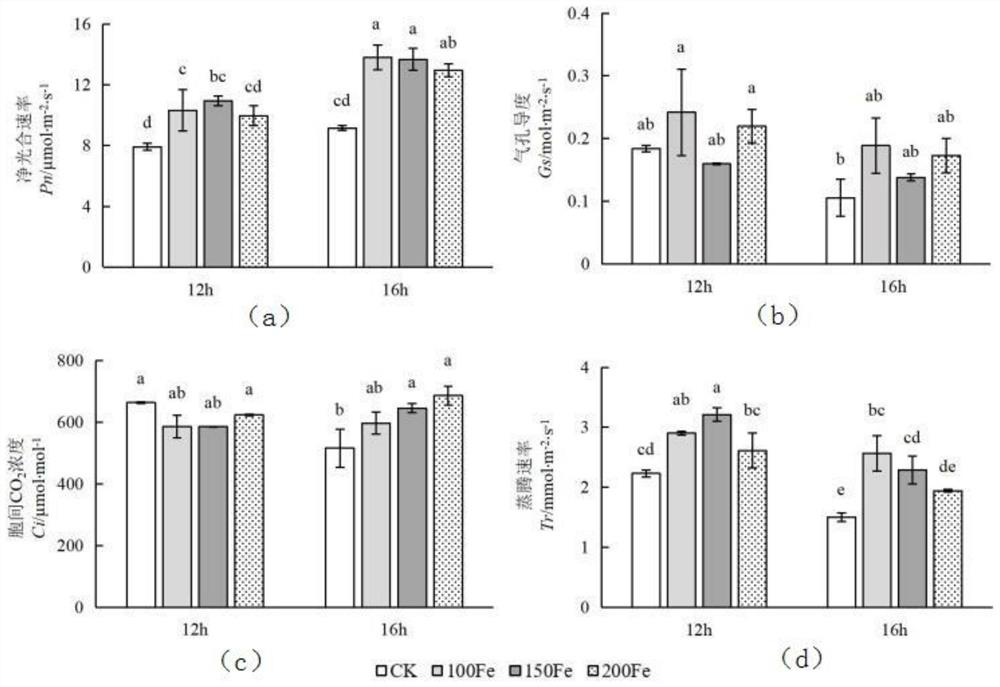
PendingCN112840973AShort internodeReduce plant heightSaving energy measuresFertilising methodsNutrient solutionPlant growth
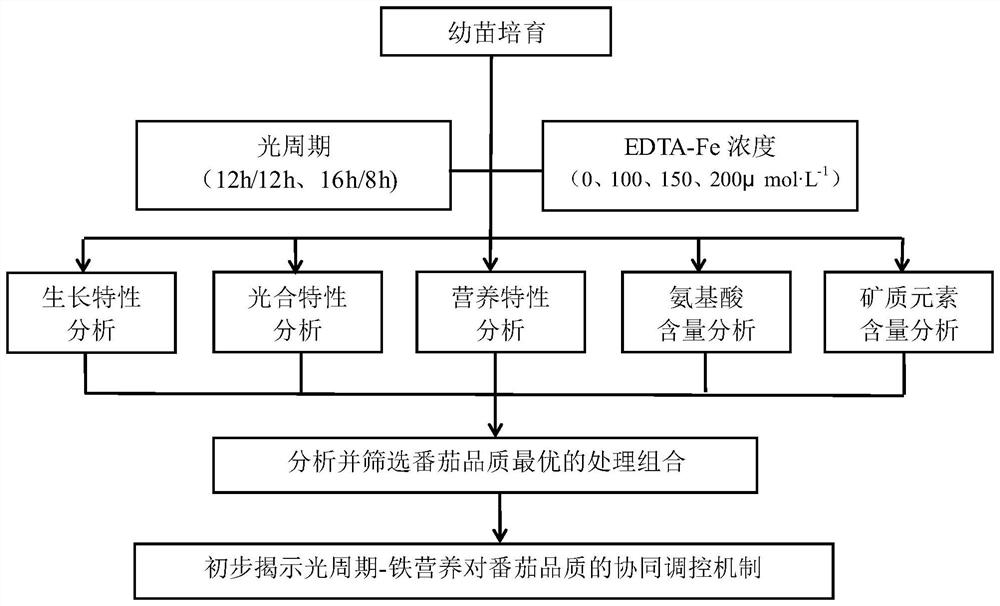
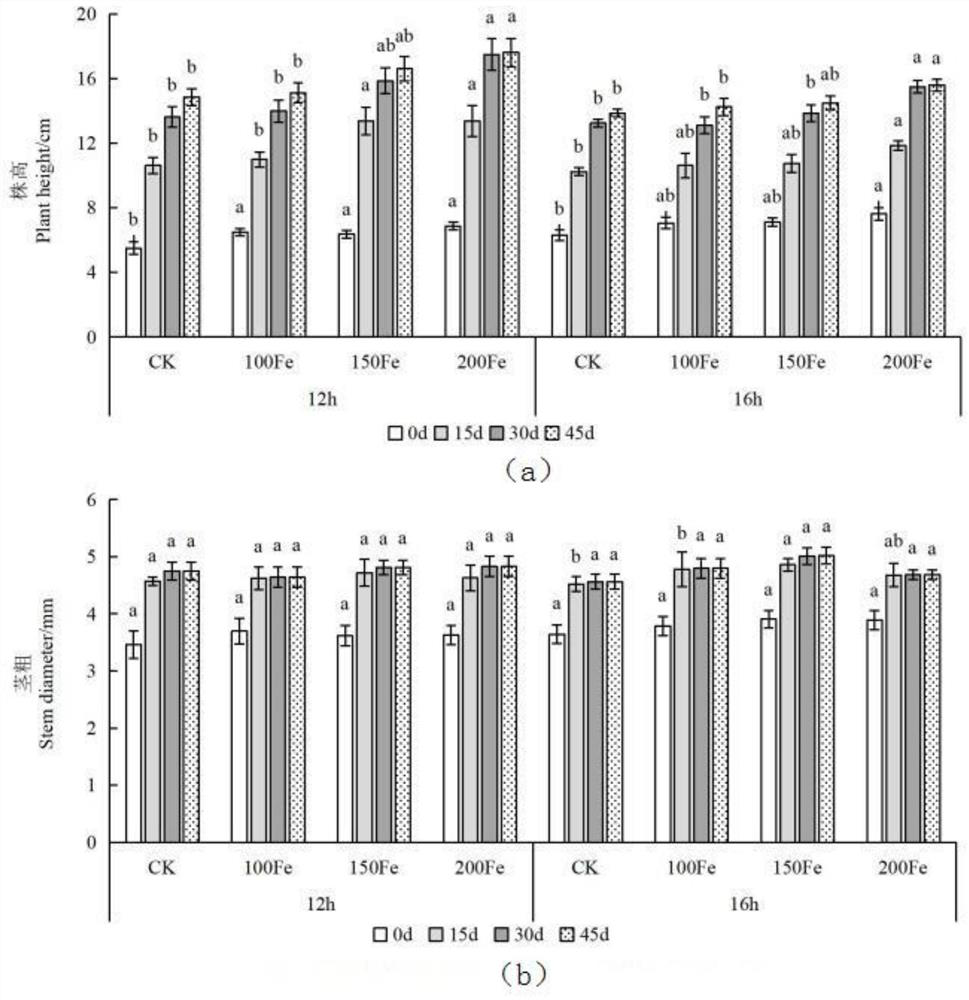
The invention discloses a planting method for improving growth and development and fruit quality of tomatoes. The planting method comprises the steps that tomato seedlings are cultivated; LED plant growth lamps are adopted as light sources to be arranged above the tomato seedlings for irradiation, and the light period every day is set to be 12 h illumination / 12 h non-illumination or 16 h illumination / 8 h non-illumination; when the tomatoes enter the flowering stage, an EDTA-Fe aqueous solution with the concentration of 100-200 [mu] mol.L <-1 > is sprayed to tomato plants, the EDTA-Fe aqueous solution is uniformly sprayed to the front and back surfaces of leaves once a week, and the tomato plants are irrigated with a nutrient solution containing no Fe element once every other month to ensure sufficient nutrients; and after the EDTA-Fe aqueous solution is sprayed for 55-65 days, when 80% of the tomatoes on the tomato plants turn red and peels are slightly soft, spraying of the EDTA-Fe aqueous solution is stopped. According to the planting method for improving growth and development and fruit quality of the tomatoes, the tomato quality improvement effect is optimal by spraying 100 to 150 [mu] mol.L <-1 > EDTA-Fe aqueous solution on the surfaces of the leaves in the photoperiod of 16 h illumination / 8 h non-illumination.
Owner:SHANXI AGRI UNIV +1
Road prime coat oil and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104356655ALow viscosityEasy to penetrateHydrocarbon oils refiningProcess engineeringEnvironmental geology
The invention provides road prime coat oil which comprises components in percentage by mass as follows: 50%-58% of mildoxidation slurry oil, 0.5%-2.5% of an emulsifier and the balance of water. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the road prime coat oil. The road prime coat oil can meet the technical requirements for emulsified asphalt prime coat oil for routine roads while the production cost can be lower than the emulsified asphalt prime coat oil by 20%.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
Method for directly preparing p-xylene from synthesis gas and methylbenzene
ActiveCN109776250ASolution to short lifeLow component contentMolecular sieve catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationChemistryOxide
The invention discloses a method for directly preparing p-xylene from synthesis gas and methylbenzene. The method comprises the following steps: enabling raw materials comprising the synthesis gas andmethylbenzene to be in contact with a catalyst in a reaction zone under a reaction condition that at least a part of raw materials is sufficiently converted, so as to obtain a reaction effluent containing p-xylene; and separating p-xylene from the reaction effluent, wherein the catalyst comprises a high dispersion metallic oxide material with the range limited by an inert carrier, an acid molecular sieve and at least one of graphite powder and a dispersing agent; in the high dispersion metallic oxide material with the range limited by the inert carrier, the inert carrier comprises at least one of silicon oxide and aluminum oxide; the metal content of metallic oxide is less than or equal to 10% by mass; and the high dispersion metallic oxide material with the range limited by the inert carrier is counted by weight, and the acid molecular sieve is selected from a modified acid ZSM-5 molecular sieve, a modified acid ZSM-11 molecular sieve and a mixture of the modified acid ZSM-5 molecular sieve and the modified acid ZSM-11 molecular sieve.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Stem cell extract and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a stem cell extract and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method includes the following steps that primary stem cells are inoculated in a culture medium, primary culturing is carried out, a solution is changed every other day, when the primary stem cells grow to 80-90%, the medium is removed, the remaining stem cells are rinsed and then mixed with physiological saline, and after the induced culture is carried out, centrifugal separation is carried out to obtain a supernatant; and then the supernatant is filtered to obtain the stem cell extract. According to the stem cell extract and the preparation method and application thereof, more safety is achieved due to non-exogenous animal components, and the obtained extract presents abundant cytokines and can be directly used as a pharmaceutical preparation or mixed with adjuvants after freezing to prepare a medicine.
Owner:博品(上海)生物医药科技有限公司
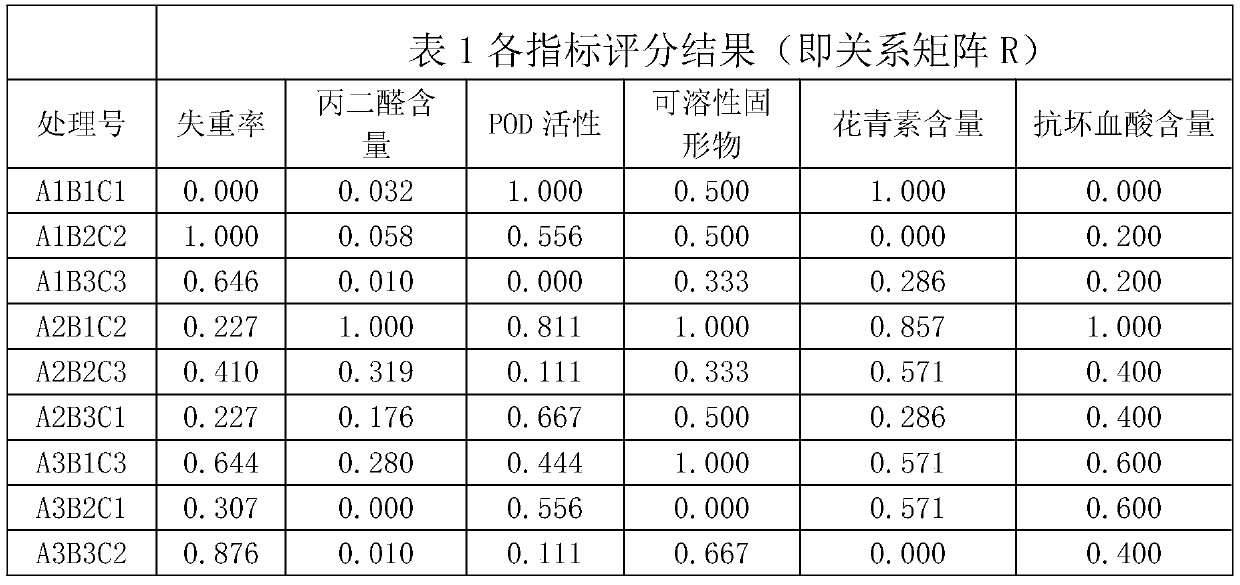
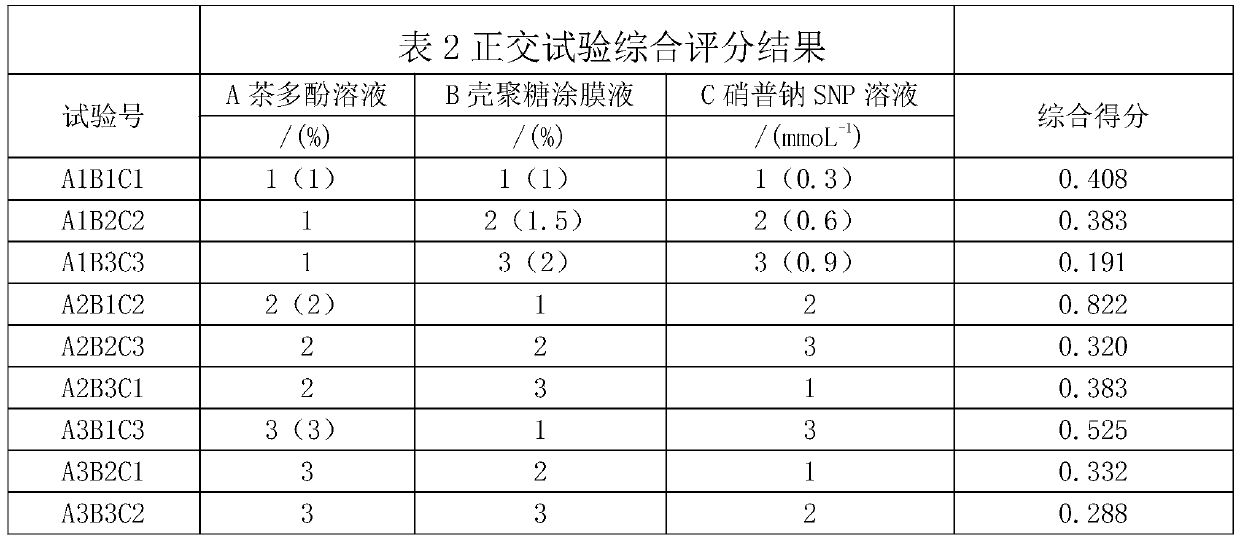
Technology for preserving grapes by using tea polyphenol composite preservative
InactiveCN110447711ALow component contentReduce processing costsFruit and vegetables preservationFood ingredient for microbe protectionVitis viniferaPreservative
The invention discloses a technology for preserving grapes by using a tea polyphenol composite preservative. According to the invention, a tea polyphenol solution, a chitosan solution and a sodium nitroprusside solution are used as preservatives, and the grapes are preserved after being soaked. The fresh-keeping technology of the present invention is environmentally friendly, has low cost, and hasgood fresh-keeping effect of grapes at normal temperature.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Preparation method for health cigarette and product
InactiveCN102090711AReduce harmImprove rabbit immunityTobacco treatmentPlant ingredientsBiotechnologyTaraxacum officinale leaf
The invention discloses a preparation method for a health cigarette, and a product. The preparation method for the health cigarette is characterized by comprising the following steps of: boiling mixed liquid of the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 2 to 4 percent of sliced dwarf lilyturf root, 2 to 4 percent of sliced asparagus, 5 to 10 percent of sliced liquoric root, 5 to 7 percent of unibract fritillary bulb and the balance of water, cooling to 40 to 50 DEG C, immersing tobacco leaves in the filtered clear liquid for 25 to 40 minutes, taking the tobacco leaves out, mixing the tobacco leaves, Mongolian dandelion herb leaves and fresh heartleaf houttuynia herb leaves according to the proportion of 1:1:2, drying, and coiling the leaves to prepare the cigarette. The cigarette prepared from traditional Chinese medicines reduces the tobacco content, and has the effects of preventing and treating pneumonia, phthisis, sore throat and constipation.
Owner:DALIAN FISHERIES UNIVERSITY
Antistatic finishing agent for textiles
InactiveCN106192378AGood antistatic functionLow component contentFibre treatmentVegetable oilPreservative
The invention discloses an antistatic finishing agent for textiles. The antistatic finishing agent comprises silicon dioxide, nano silicate, polyethylene glycol, chitosan, isopropanol, fatty alcohol-polyoxyethylene ether, vegetable oil, a thickening agent and a preservative. The invention has the benefits that the finishing agent has an excellent antistatic function, can be mixed with a cationic or non-ionic textile finishing agent or can serve as an alkali weight reduction accelerant, is small in content of each component, does not have any irritation or allergy to skin or any potential carcinogen effect and has excellent antibacterial finishing function, antistatic durability and washing resistance.
Owner:苏州极地实业有限公司
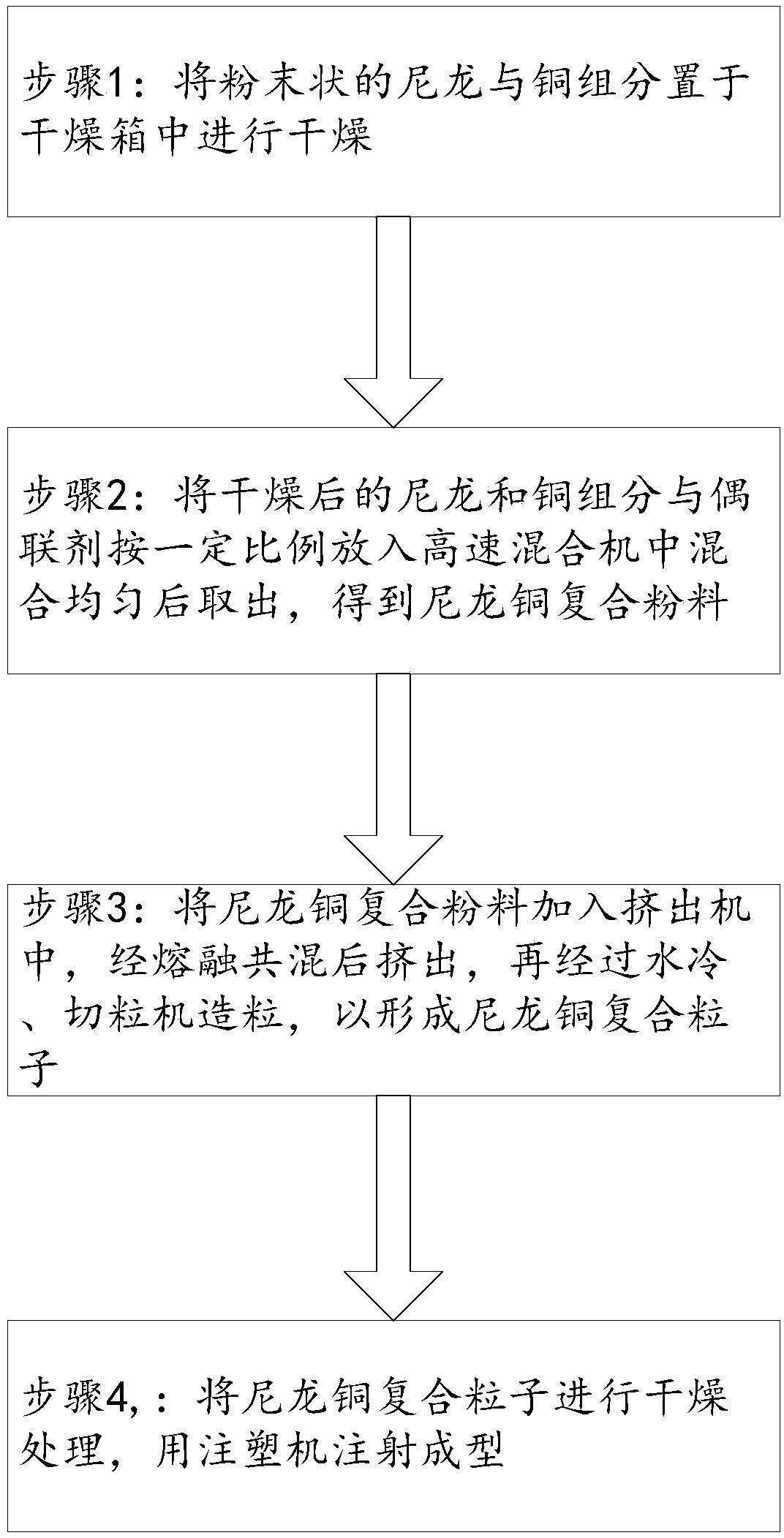
Biofouling-proof nylon copper composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a biofouling-proof nylon copper composite material and a preparation method thereof. The biofouling-proof nylon copper composite material comprises, in percent by mass, 0.5-10%of a copper component, 0.1-1% of a coupling agent and 89-99.4% of nylon. The biofouling-proof nylon copper composite material includes the copper component, coupling agent and nylon which are common,and has simple compositions, no toxic substances and no pollution to the environment; the content of the copper component in the material is low, so that the cost of the material is low; when the copper compound in the copper component is compared with metallic copper, the copper compound can be dissolved out in seawater easily, and a minimum seepage concentration of antifouling organisms can be ensured.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
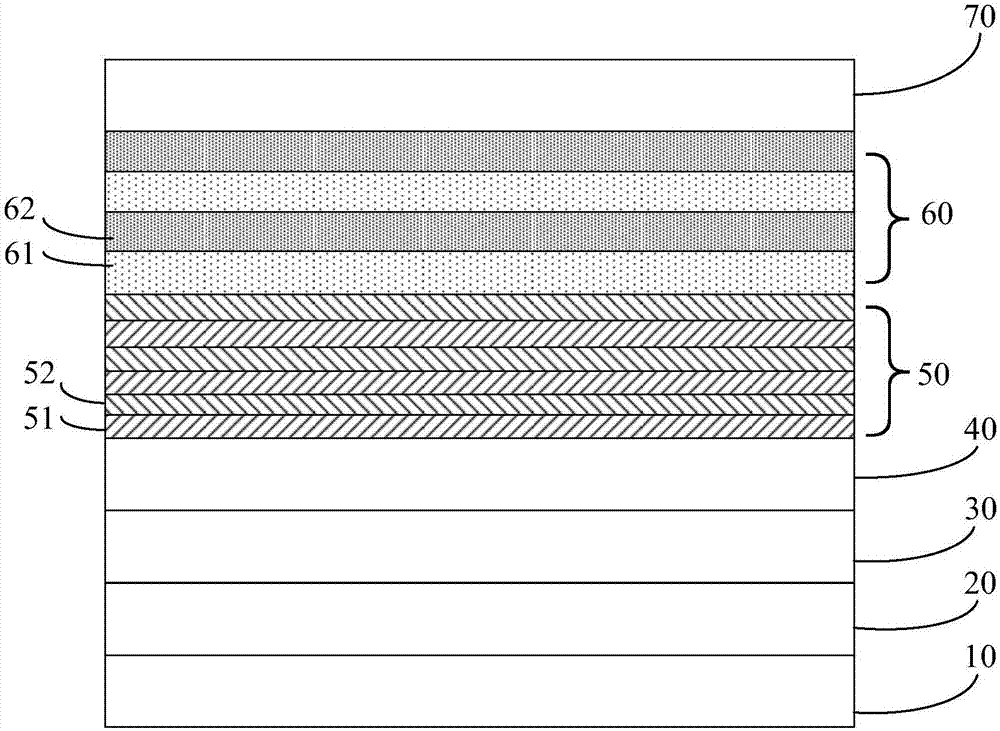
Epitaxial wafer of light-emitting diode and preparation method thereof
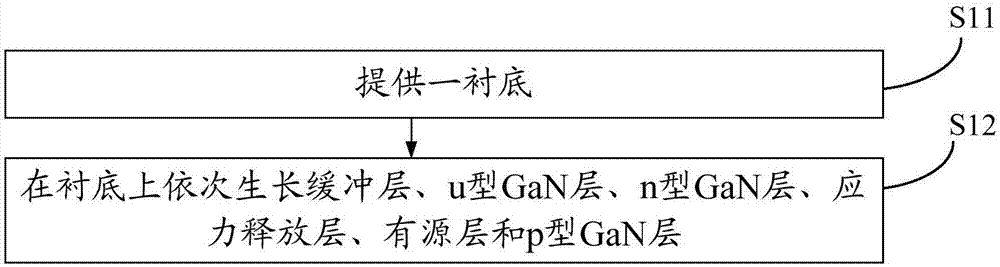
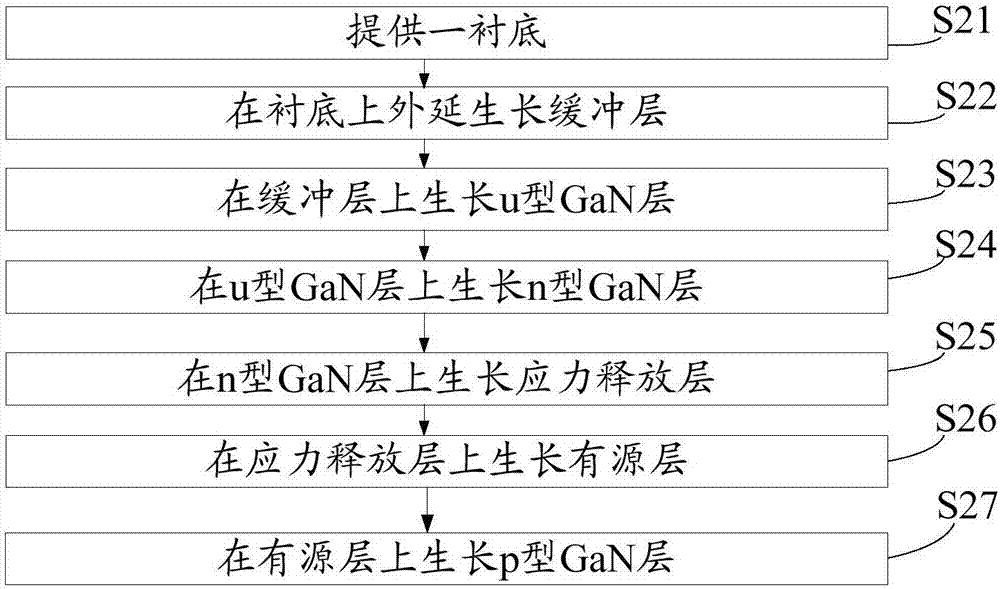
ActiveCN107359228ALow component contentSmall latticeSemiconductor devicesActive layerLight-emitting diode
The invention discloses an epitaxial wafer of a light-emitting diode and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of phoelectrons. The epitaxial wafer includes a substrate, a buffer layer, a u-shaped GaN layer, an n-shaped GaN layer, a stress release layer, an active layer and a p-shaped GaN layer. The stress release layer includes InxGa (1-x) N alyers and n-shaped AlyGa (1-y) N layers which are alternated. Since the constituent component of In in the InxGa (1-x) N layers which approach the n-shaped GaN layer is smaller than the constituent component of In in the InxGa (1-x) N layers which approach the active layer, the stress release layer reduces the recession of the epitaxial wafer and has smaller protrusion. The constituent component of In in the InmGa (1-m) N well layer is smaller than the constituent component in the InxGa (1-x) N layer. The active layer makes the epitaxial layer to recess towards one side of the substrate when the active layer grows, which offsets the protrusion which is formed upon growing the stress release layer and reduces warpage of the epitaxial wafer.
Owner:HC SEMITEK CORP
Method of manufacturing artificial fish reef with residence frame to be disassembled
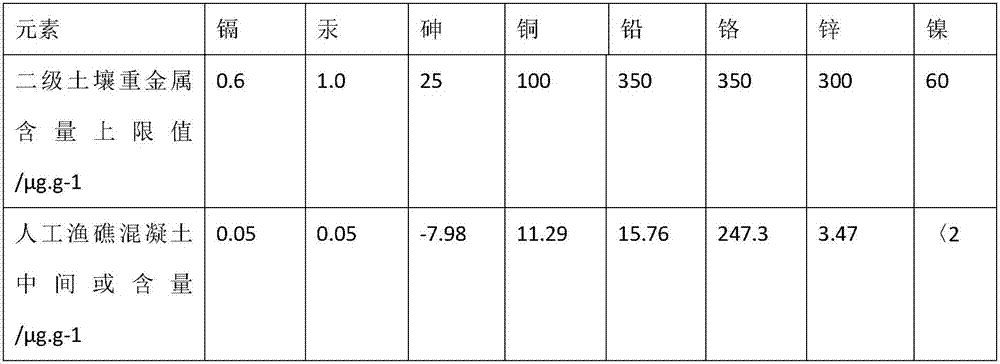
ActiveCN107125181AEfficient manufacturingReduce pollutionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaRebarPollution
The invention discloses a method of manufacturing an artificial fish reef with a residence frame to be disassembled. The method includes the preparing steps of cutting reinforced concrete of the residence frame to be disassembled, processing notches and processing the surface of the reinforced concrete. In the notch processing step, organosilicon emulsion is used as a waterproof coating for the fracture face of the reinforced concrete, surface coating is conducted, the coating permeates into the surface layer of the concrete by 2-3 mm to form a waterproof layer, and consequently sea water is prevented from entering; cured type fluorocarbon resin paint is used for forming a finishing coating, and then the finishing coating is dried. The method has the advantages of being low in manufacturing cost, capable of effectively using the residence frame to be disassembled and reducing environment pollution, low in heavy metal content and beneficial for fish shoal elusion or survival and achieving resource recycling.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
Catalyst for improving syngas converted product selectivity and preparation method and application thereof
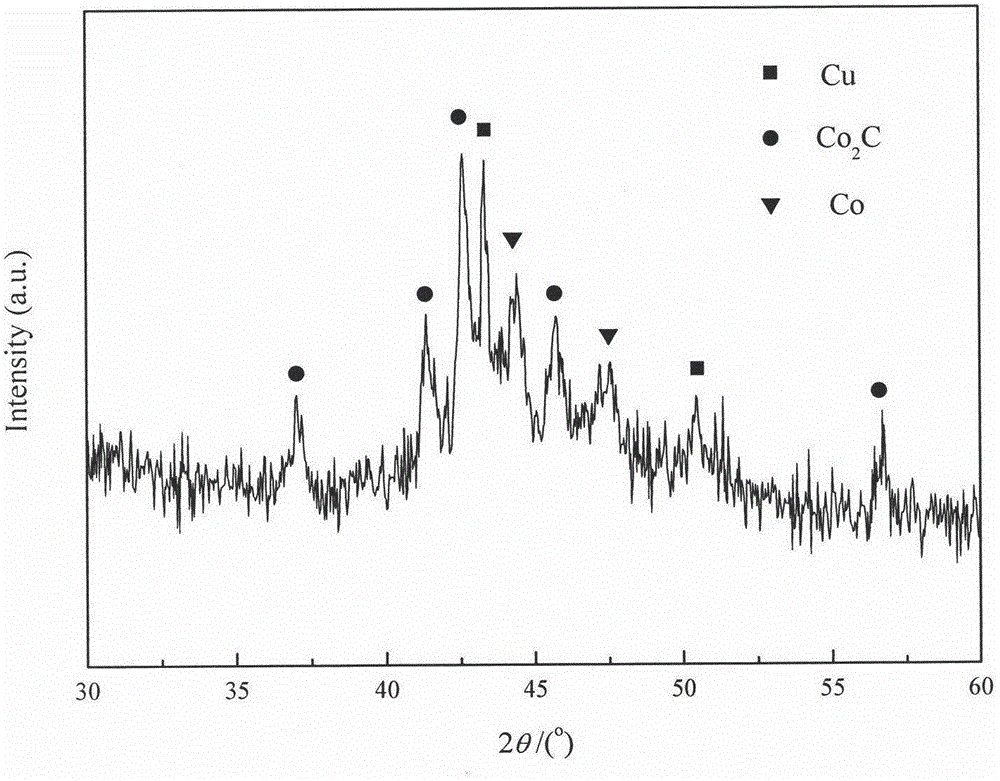
InactiveCN106140192AHigh selectivityIncrease component contentOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationSyngasManganese oxide
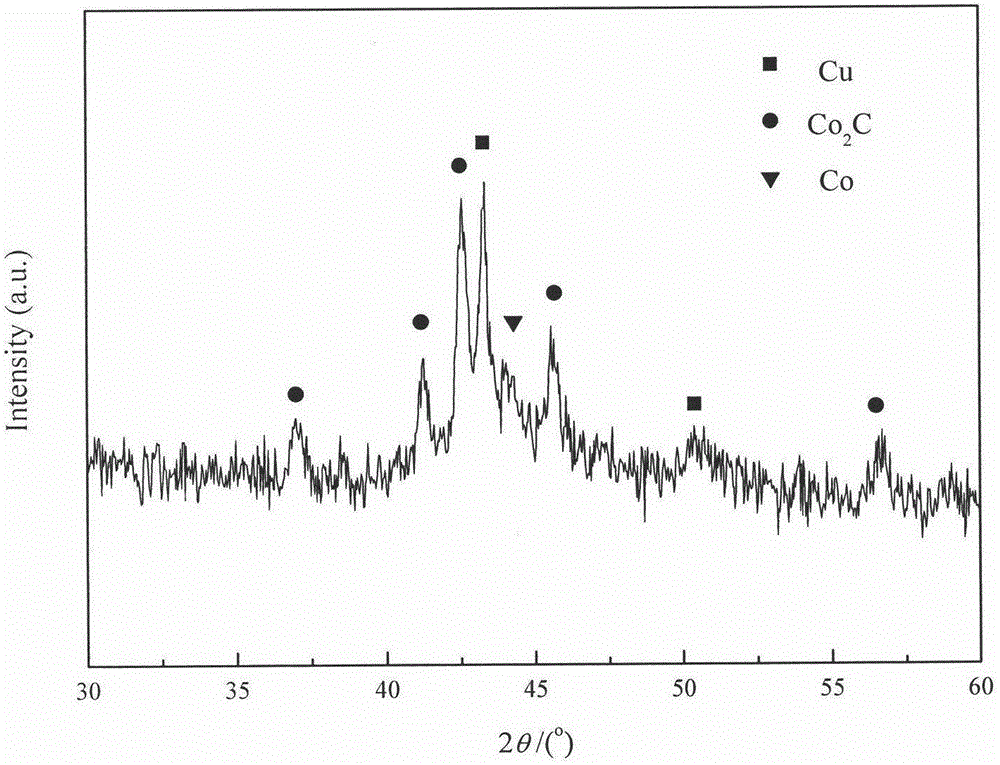
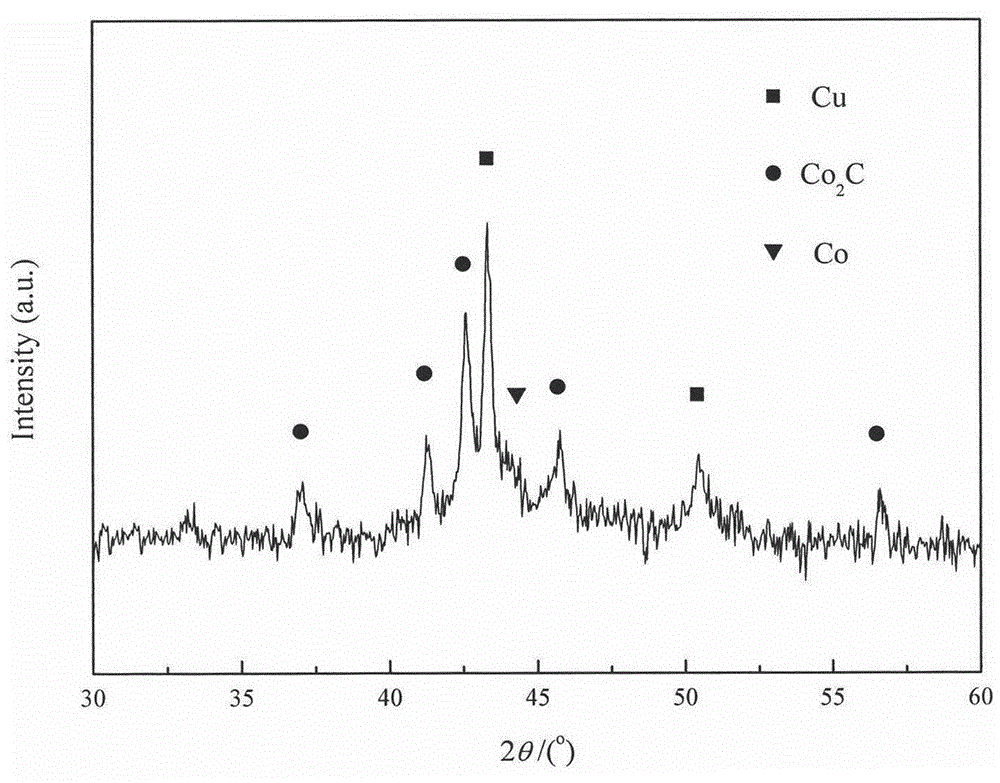
The invention provides a catalyst for improving syngas converted product selectivity and a preparation method and application thereof, relates to a cobalt-copper-manganese catalyst taking activated carbon as a carrier, and belongs to the technical field of chemical engineering. The catalyst is prepared through a co-impregnation method and is subjected to reduction activation before using. The catalyst is prepared from, by weight, 76%-83% of carrier activated carbon (AC), 6.3%-12.5% of active component metallic cobalt (Co), 3.3%-6.3% of active component metallic copper (Cu) and 1%-8.2% of auxiliary manganese oxide (MnO). The catalyst can enable syngas to generate a linear alcohol mixture which is low in methanol content and has alcohols distributed and concentrated between C2 to C5 under proper conditions. The catalyst for improving the syngas converted product selectivity and the preparation method and application thereof have the advantages of being simple in preparation, easy to operate and low in cost and have an obvious economical benefit.
Owner:裴彦鹏
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com