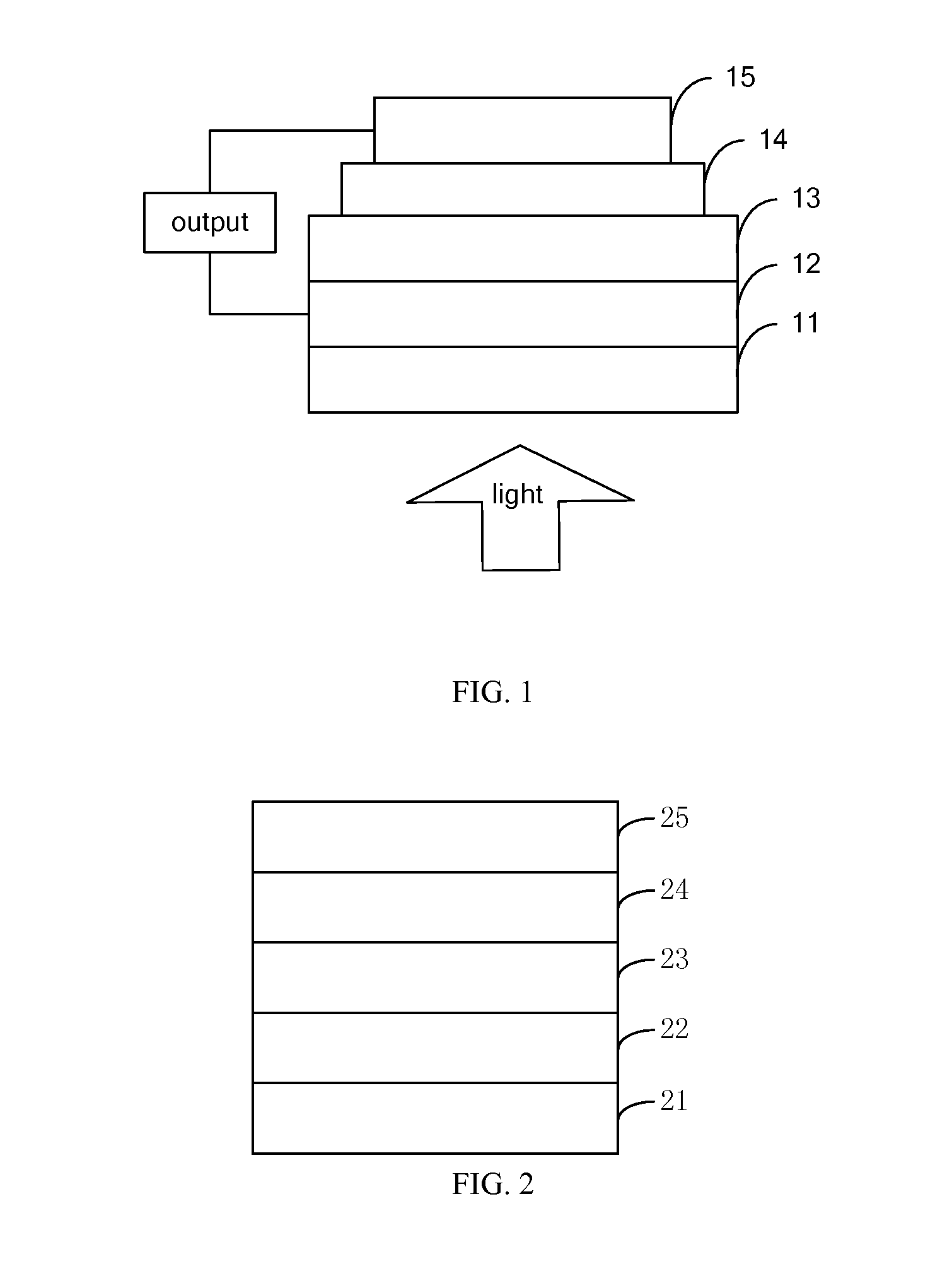
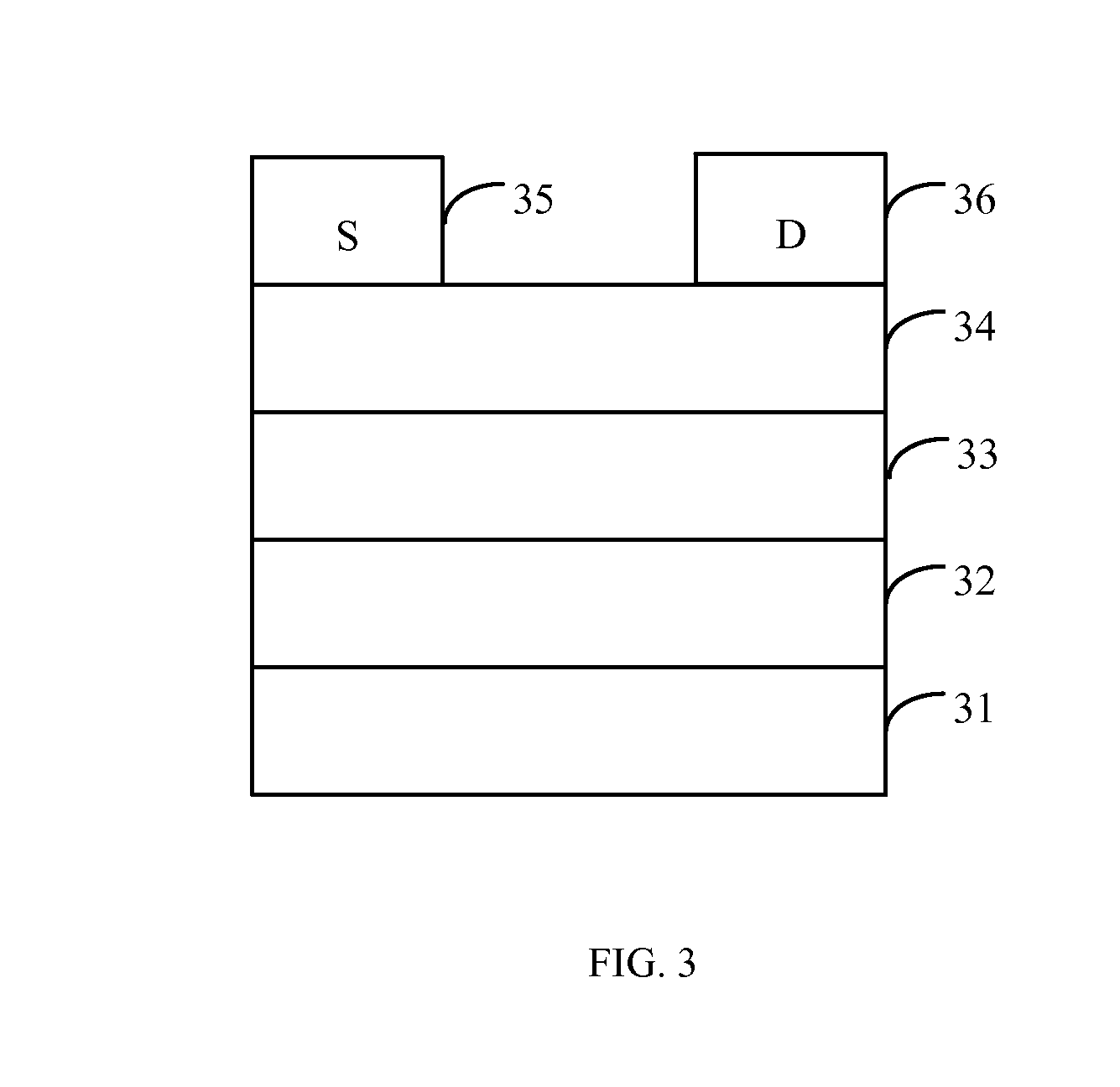
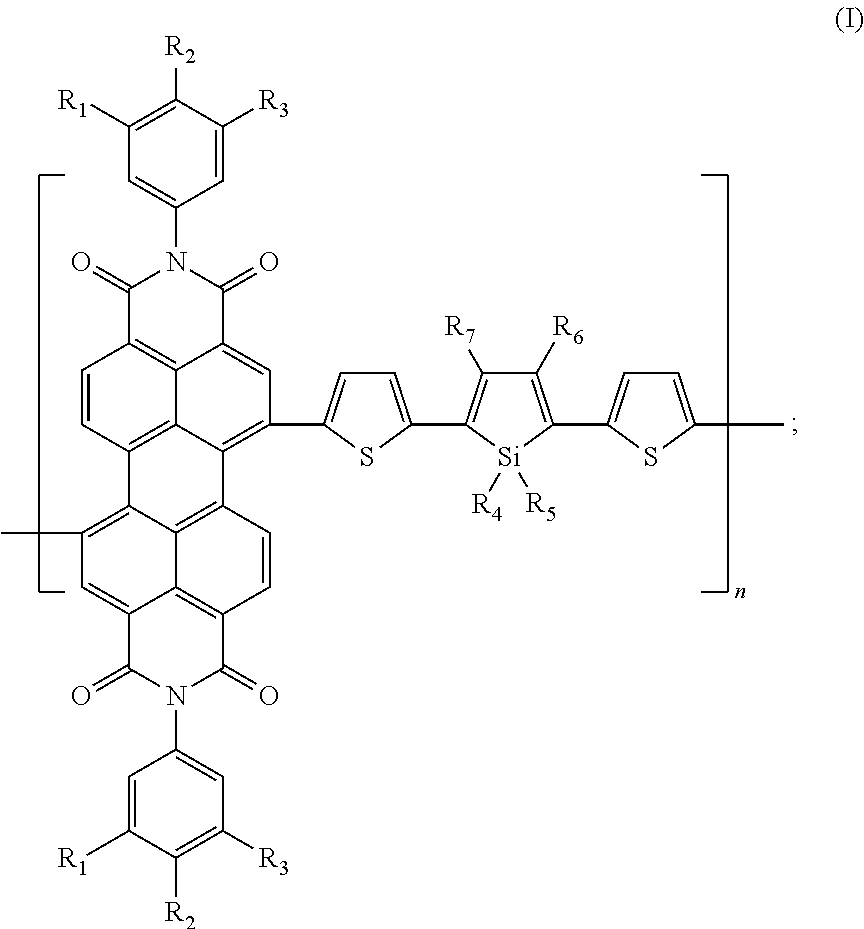
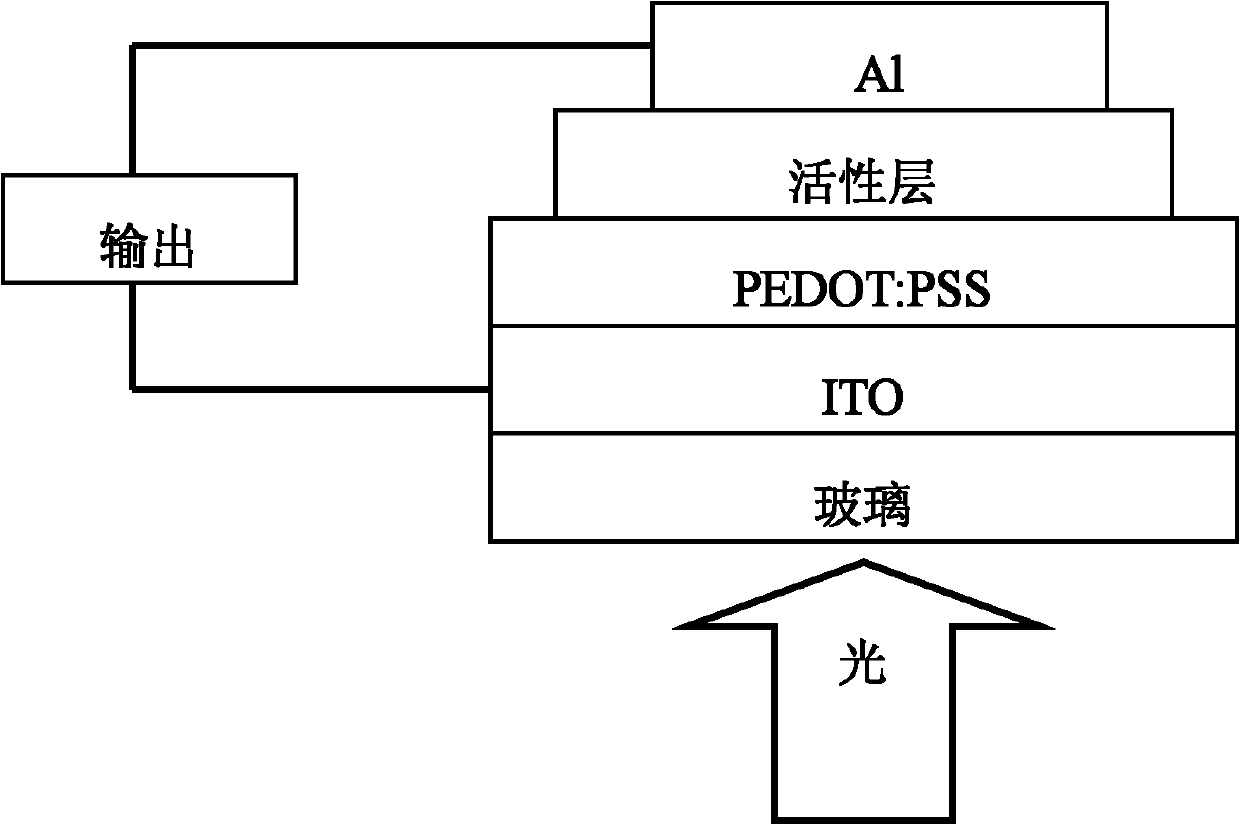
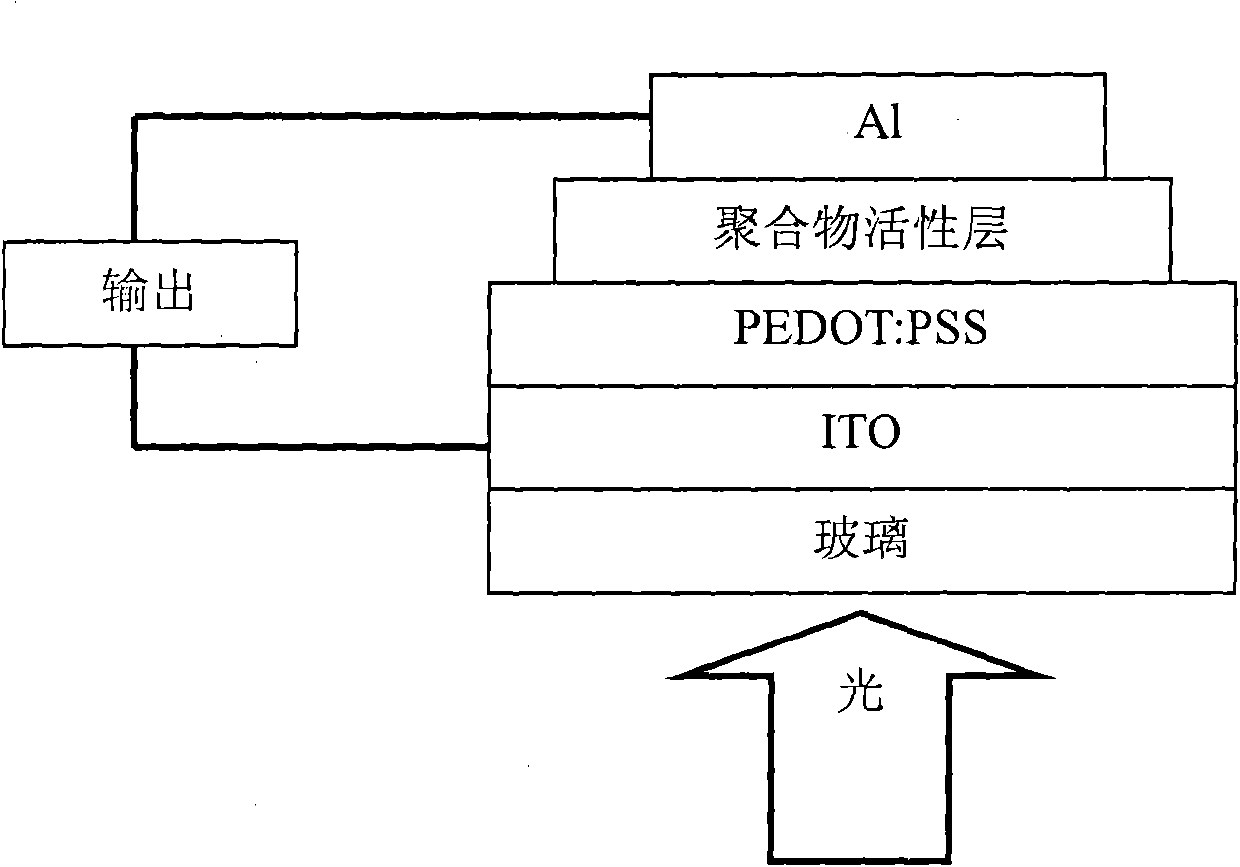
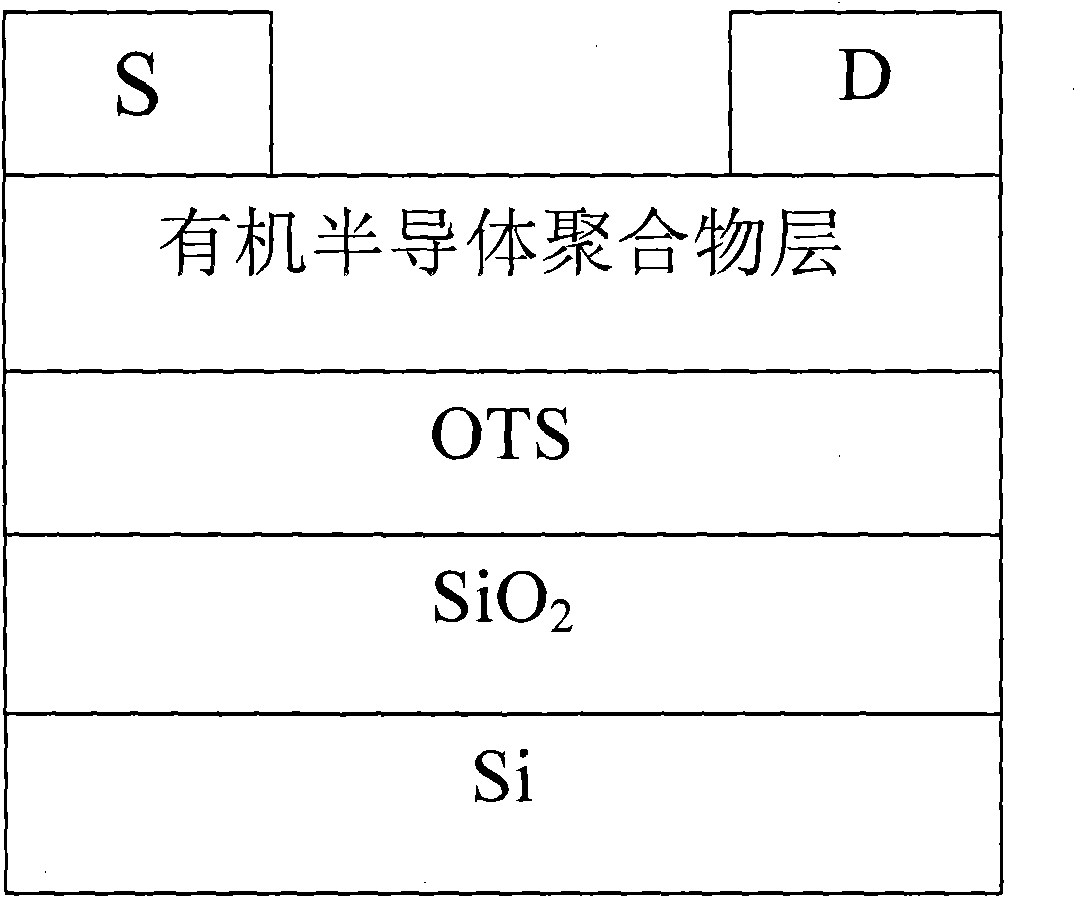
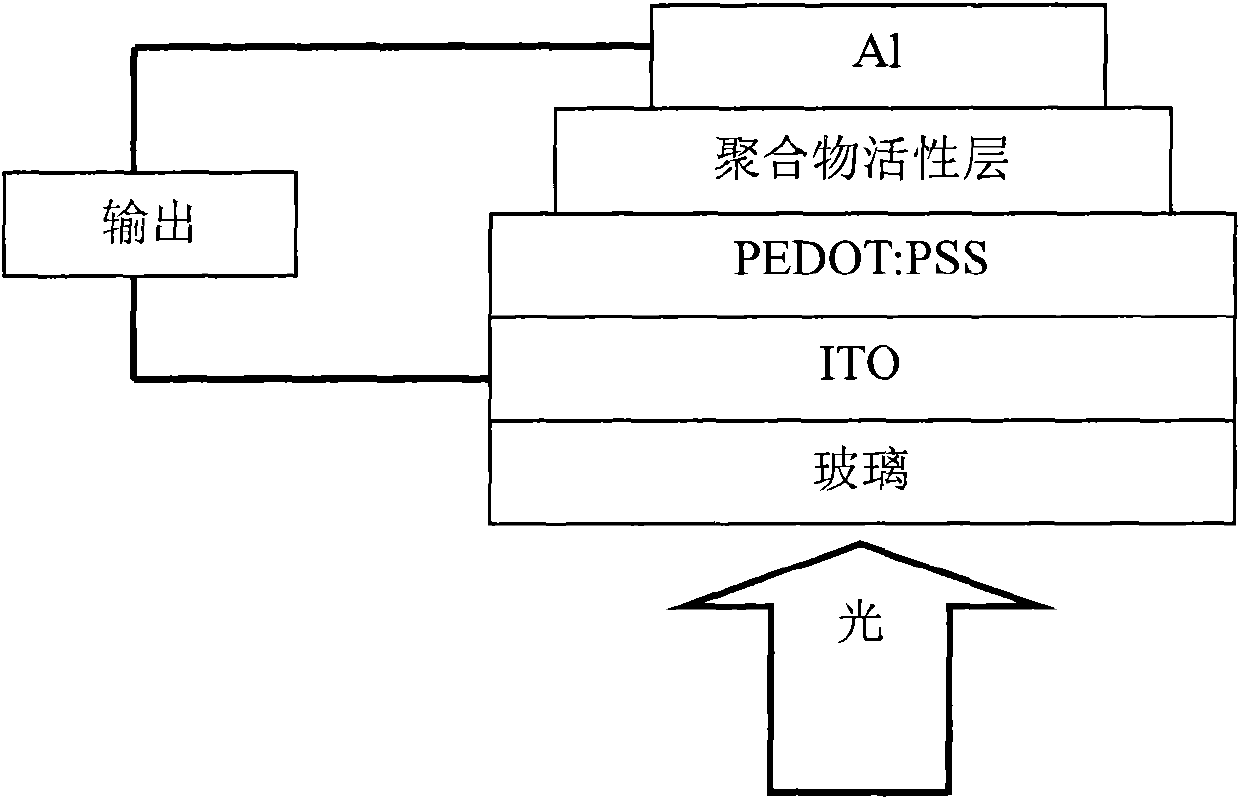
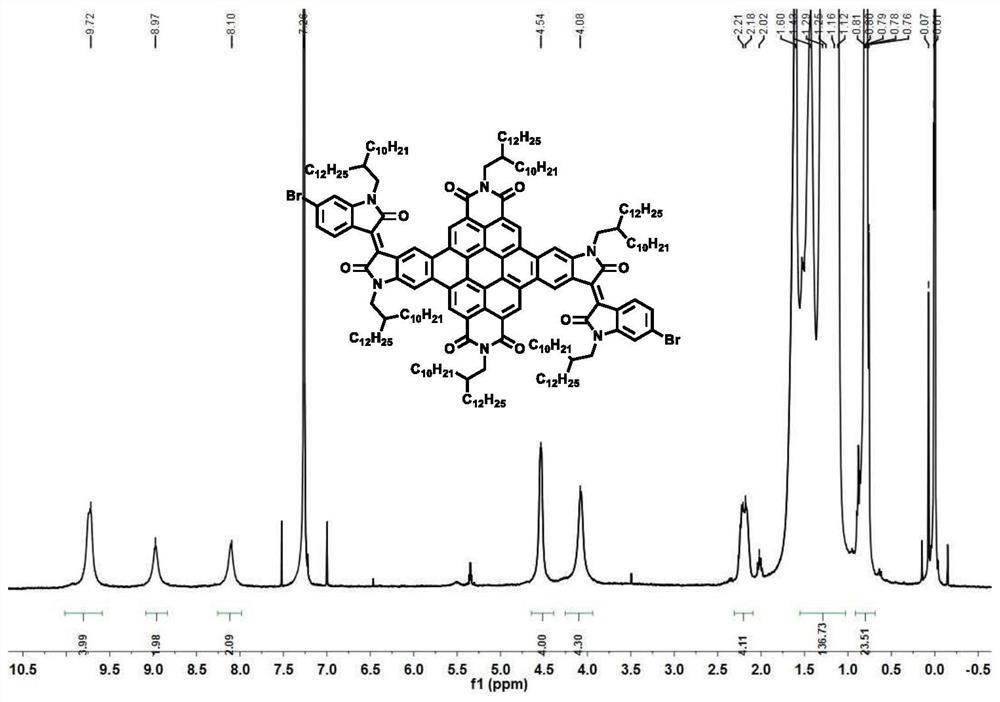
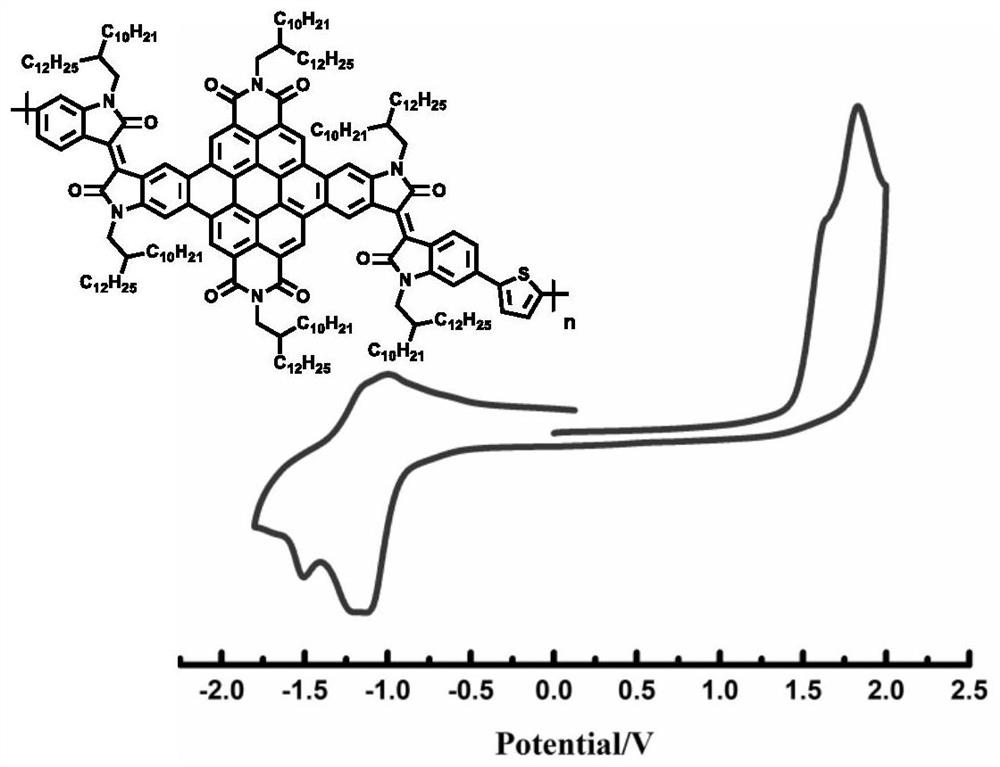
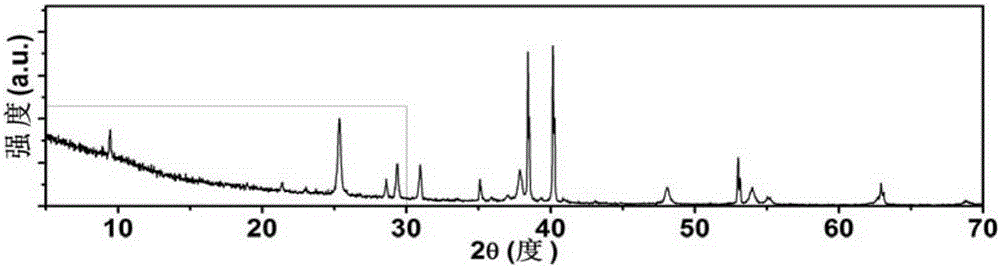
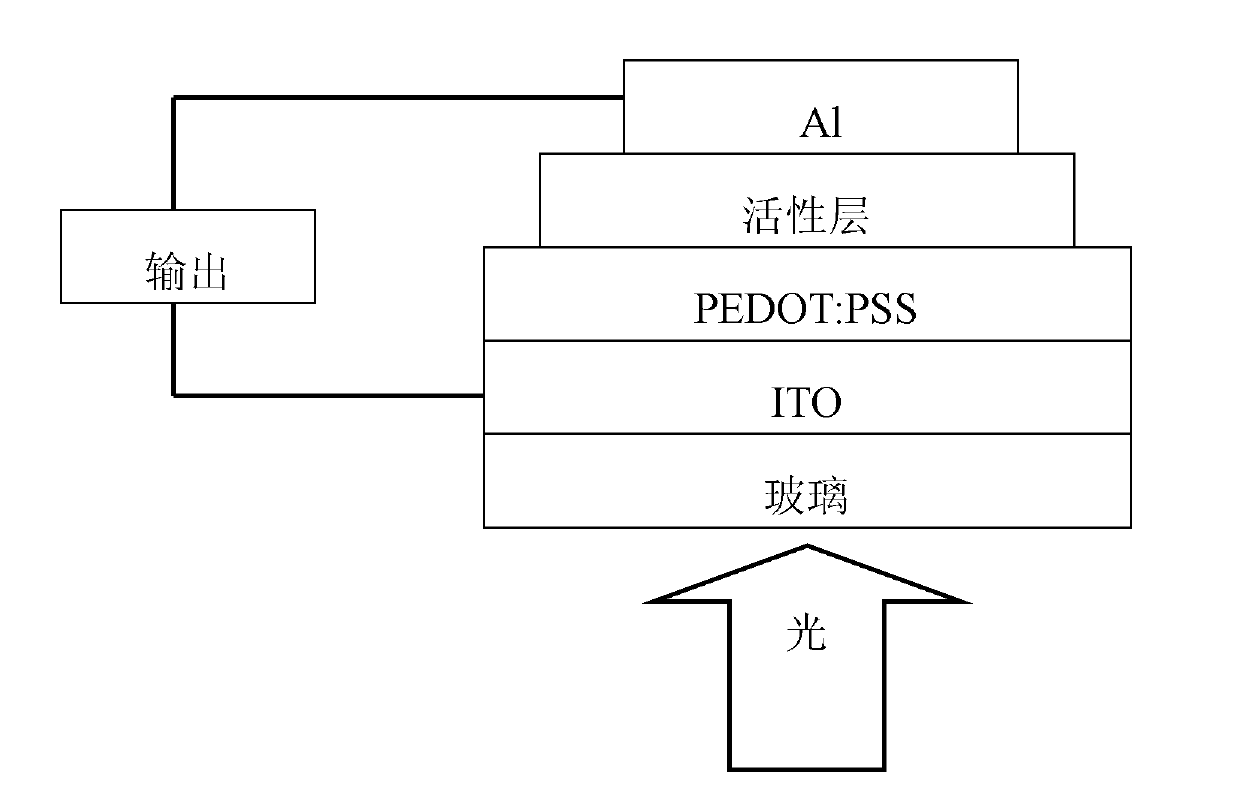
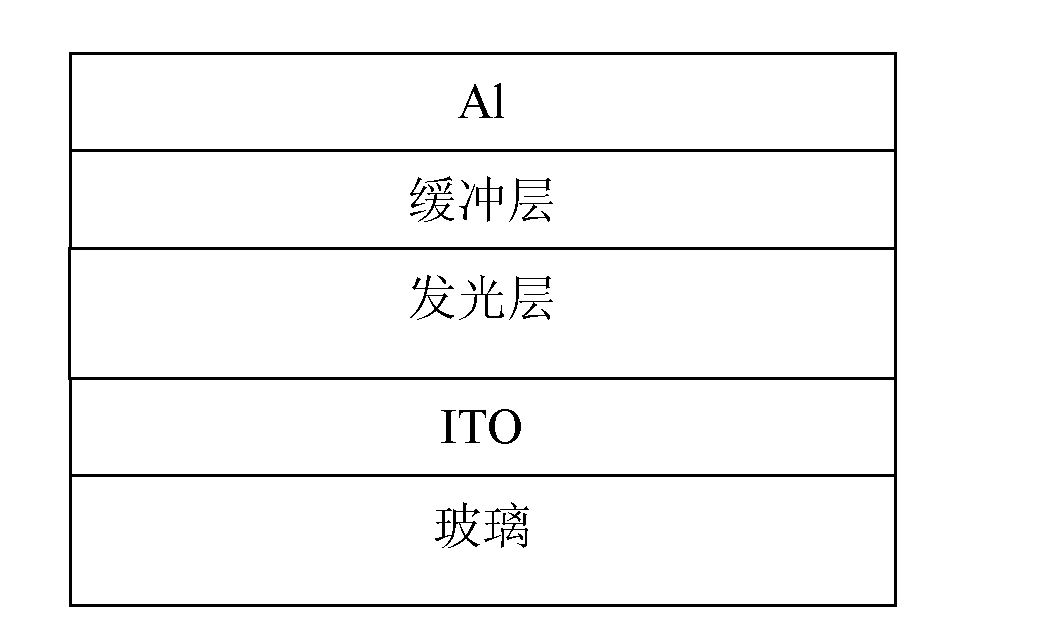
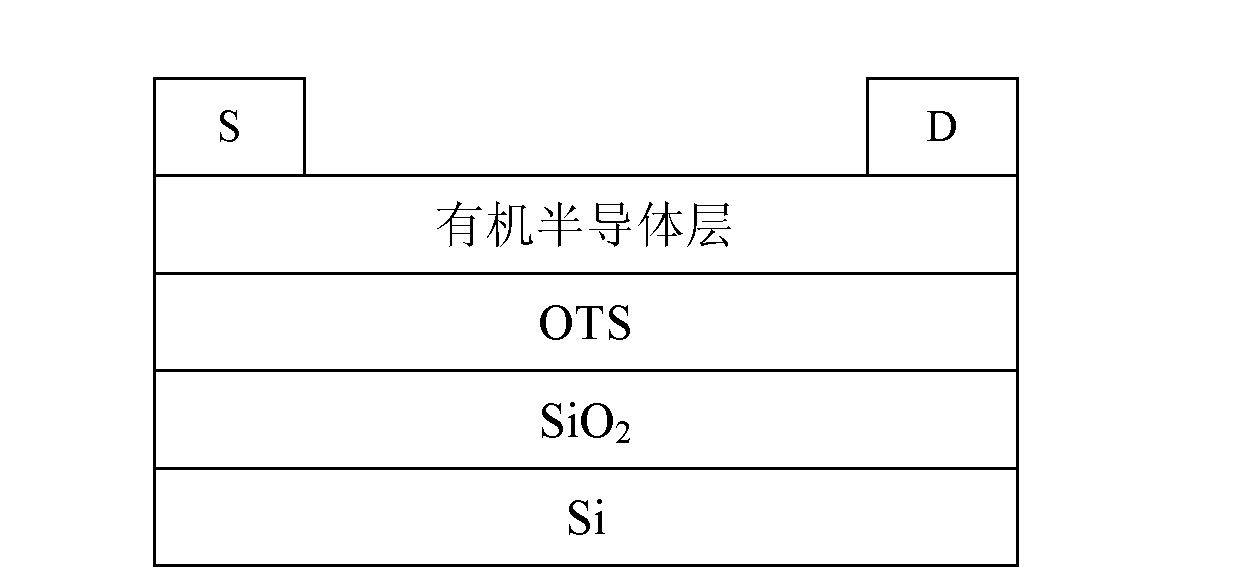
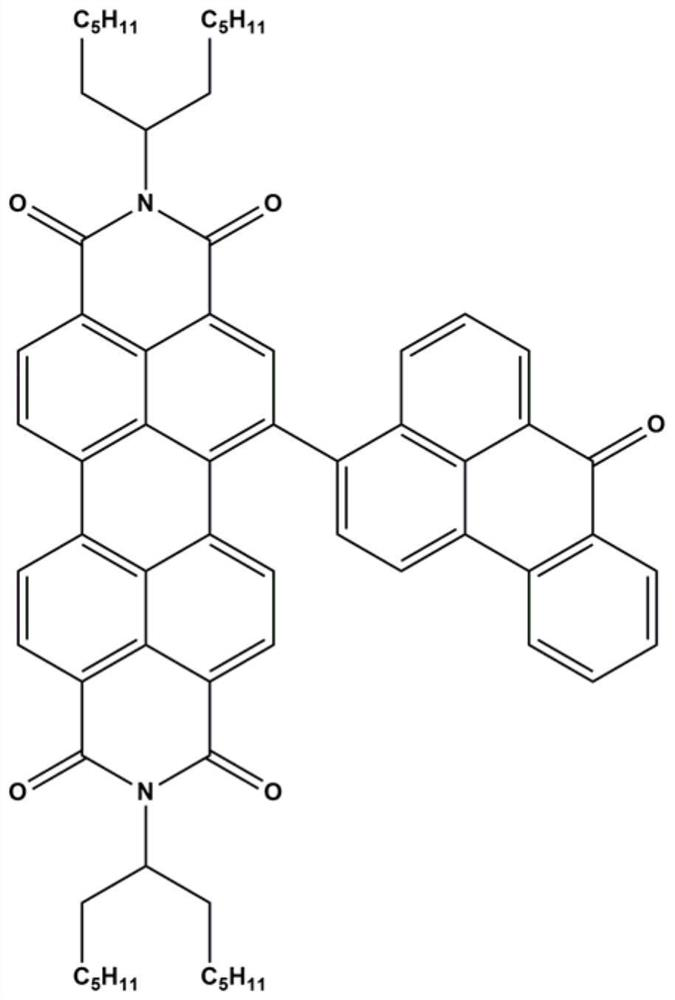
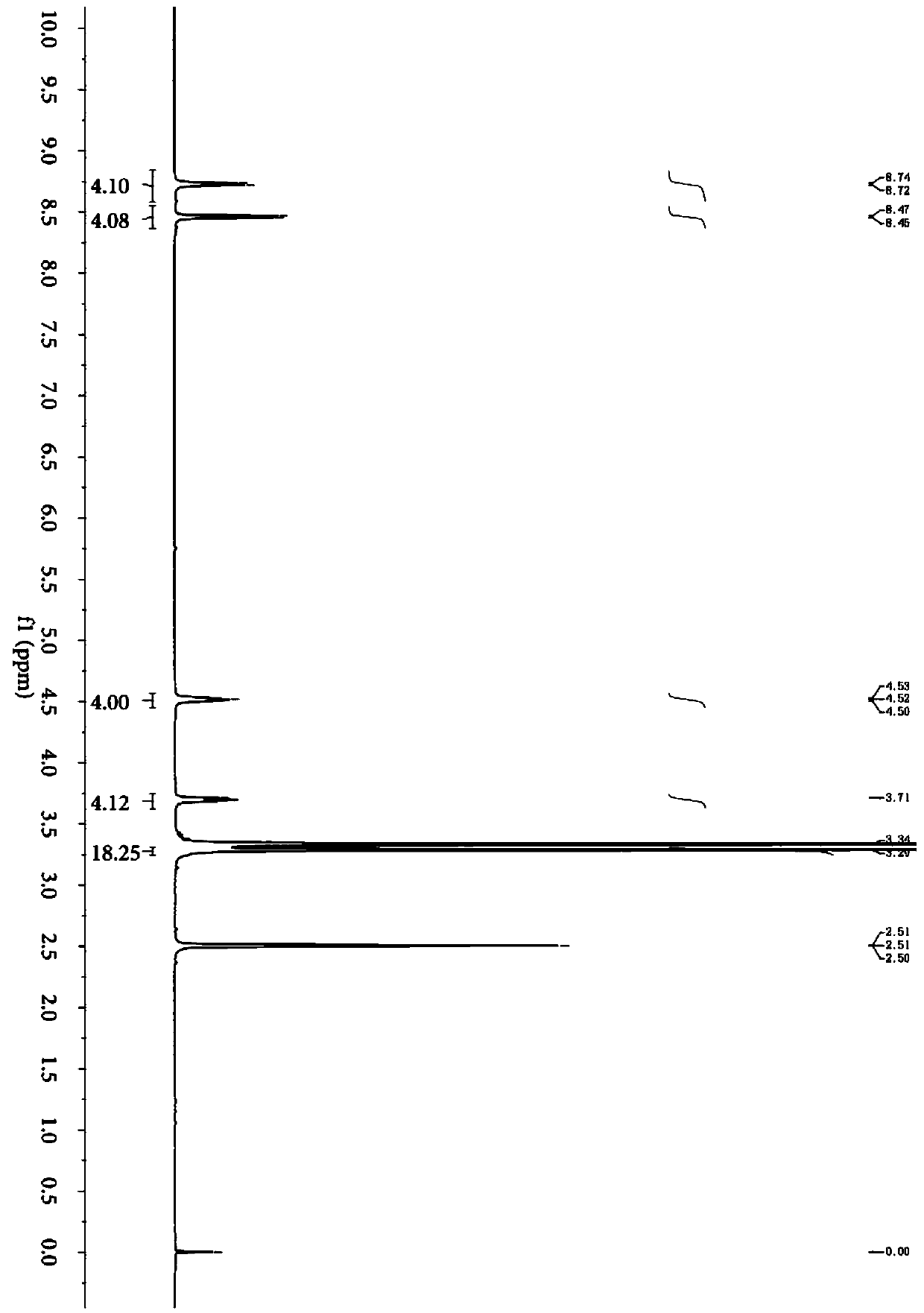
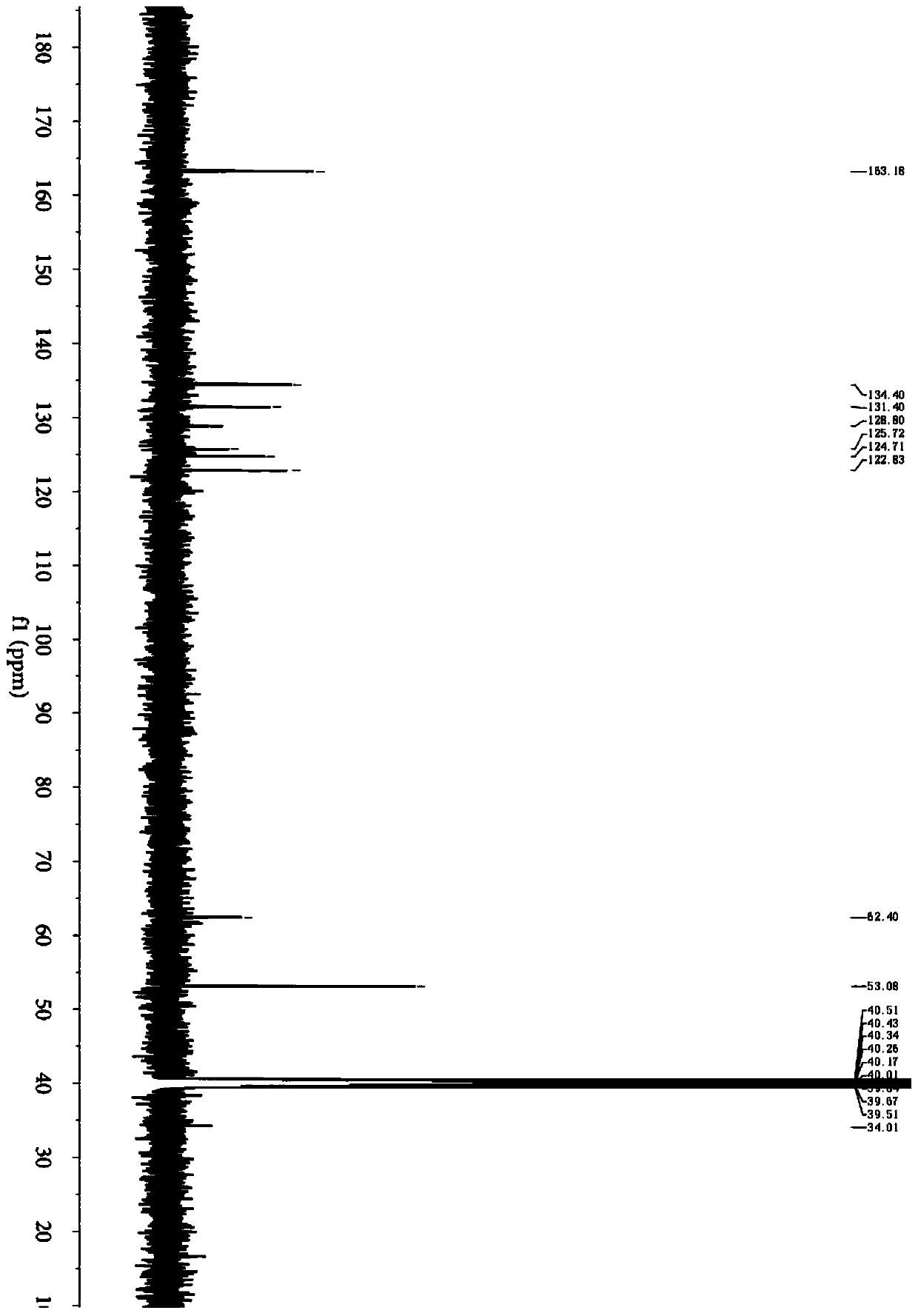
Patents
Literature
45 results about "Perylenetetracarboxylic diimide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
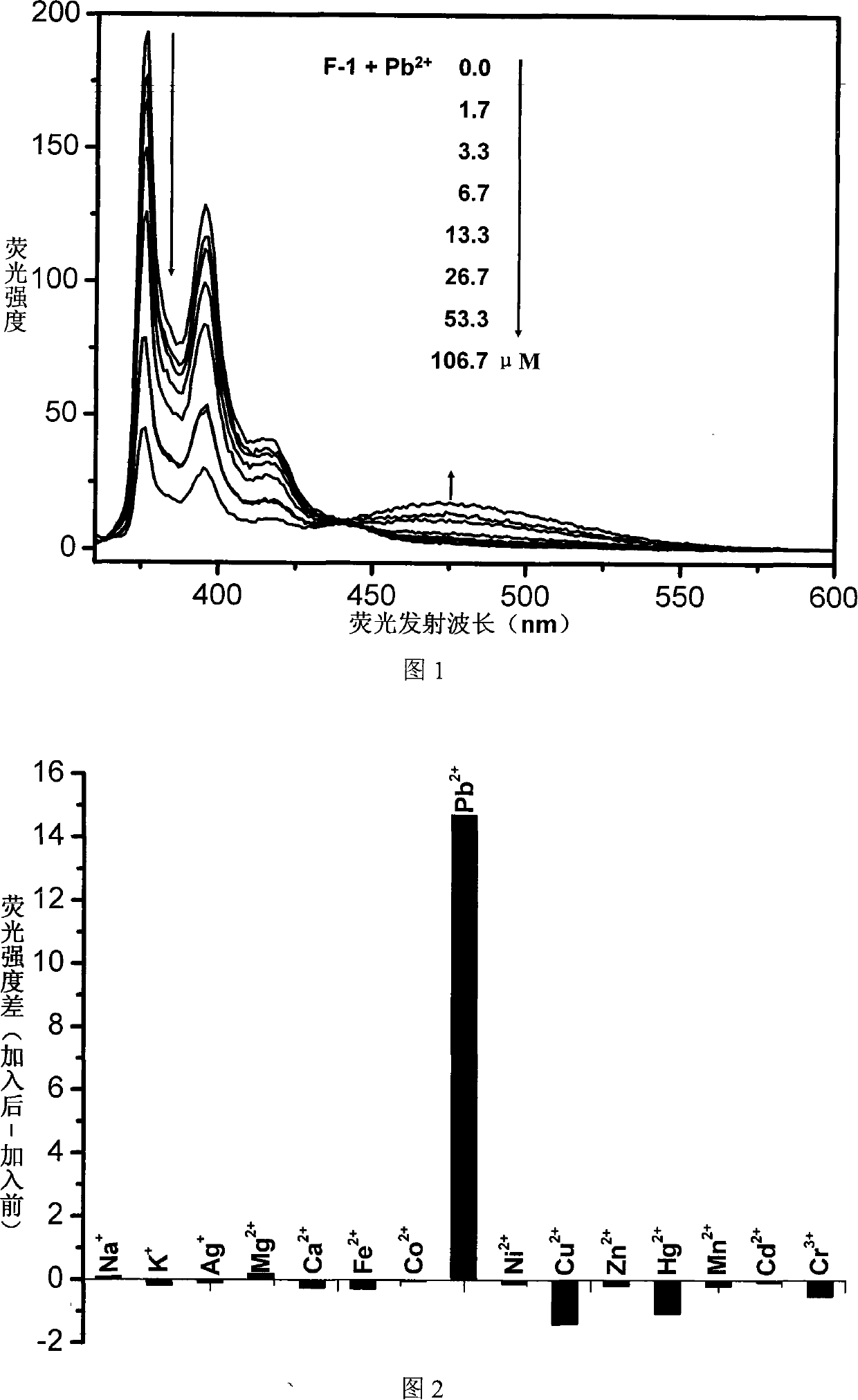
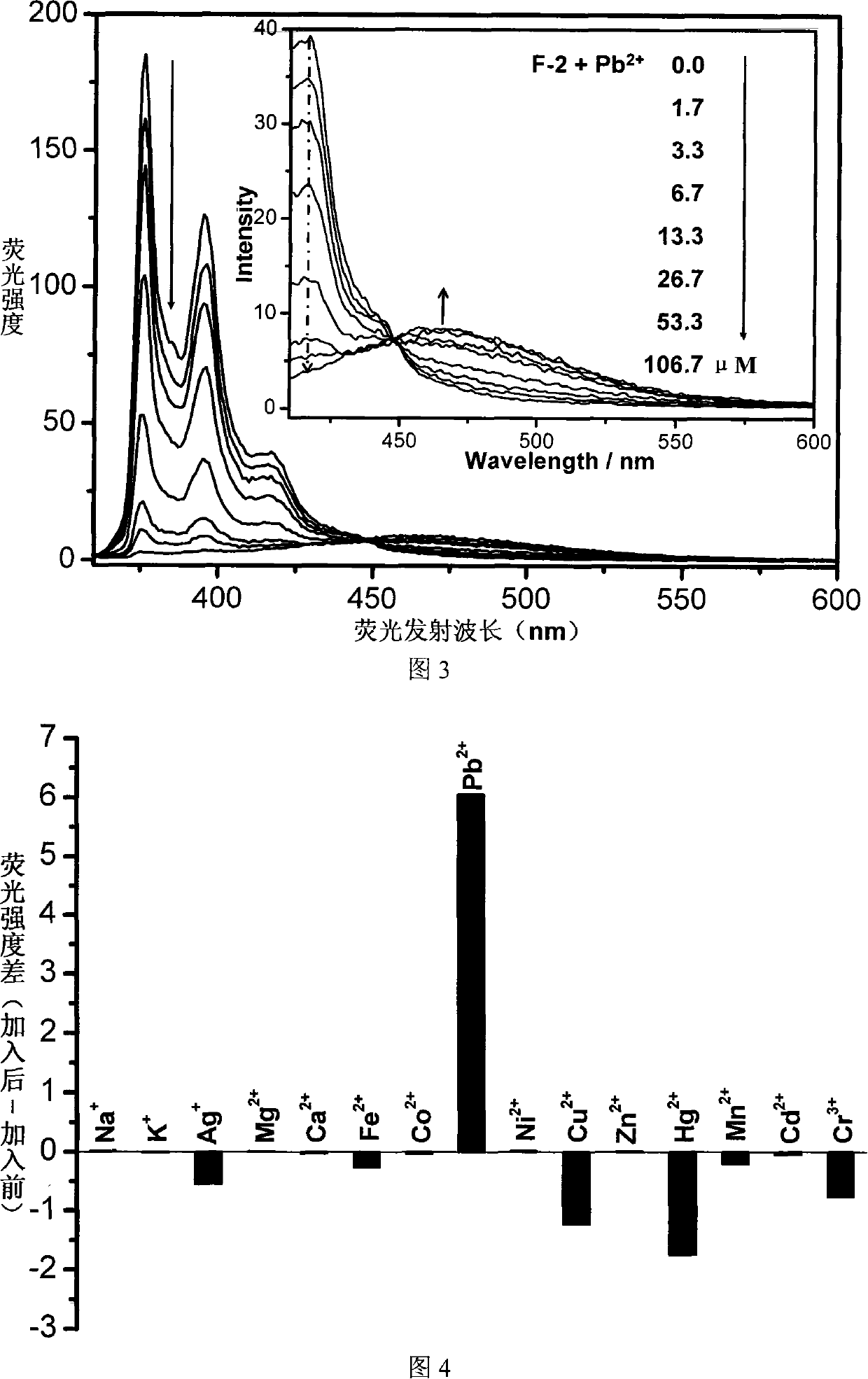
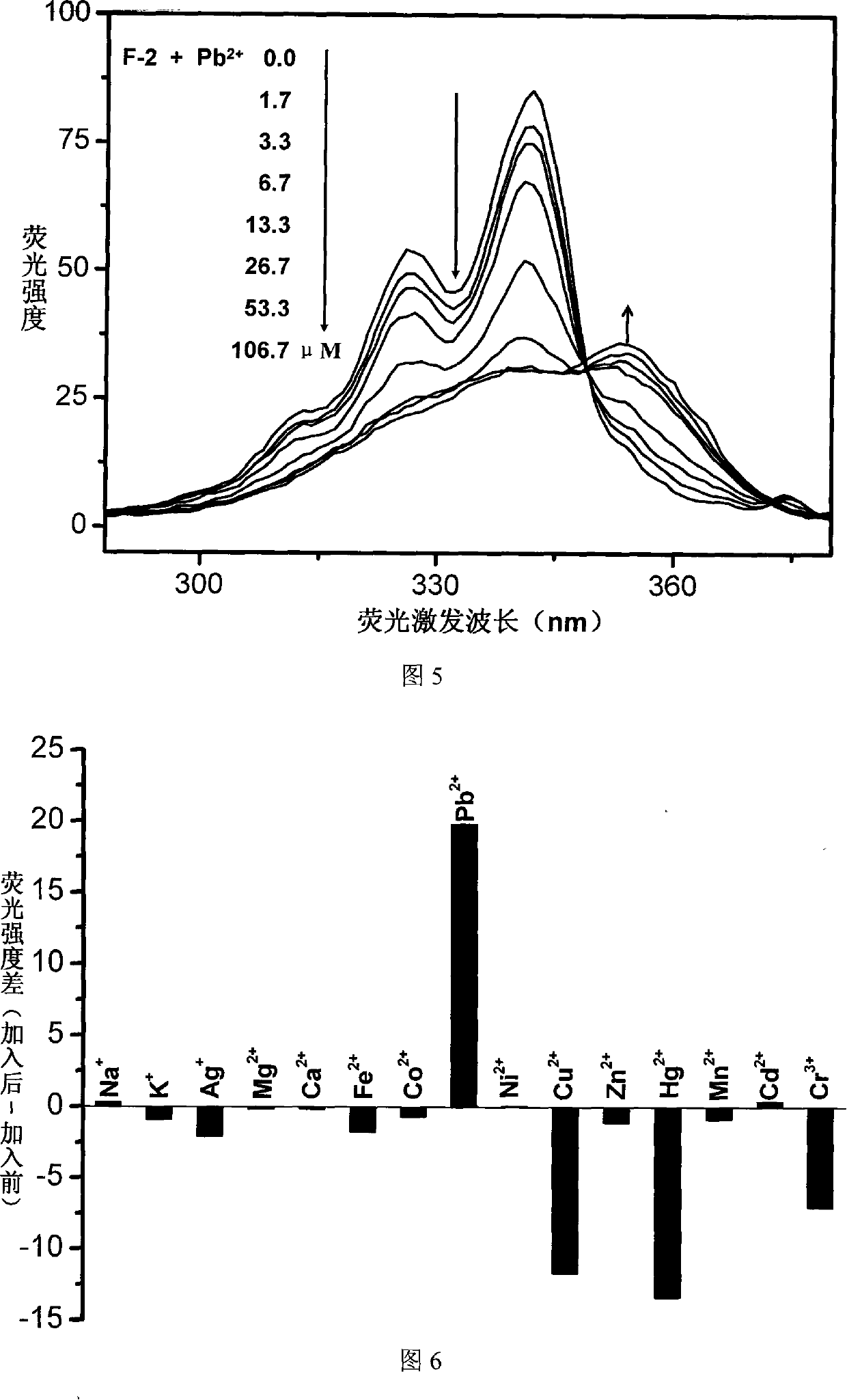
Fluorescent ion probe and its application in ion detecting
InactiveCN101153848AEasy to synthesizeSimple structureChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceLuminescent compositionsBenzoxazoleFluorophore
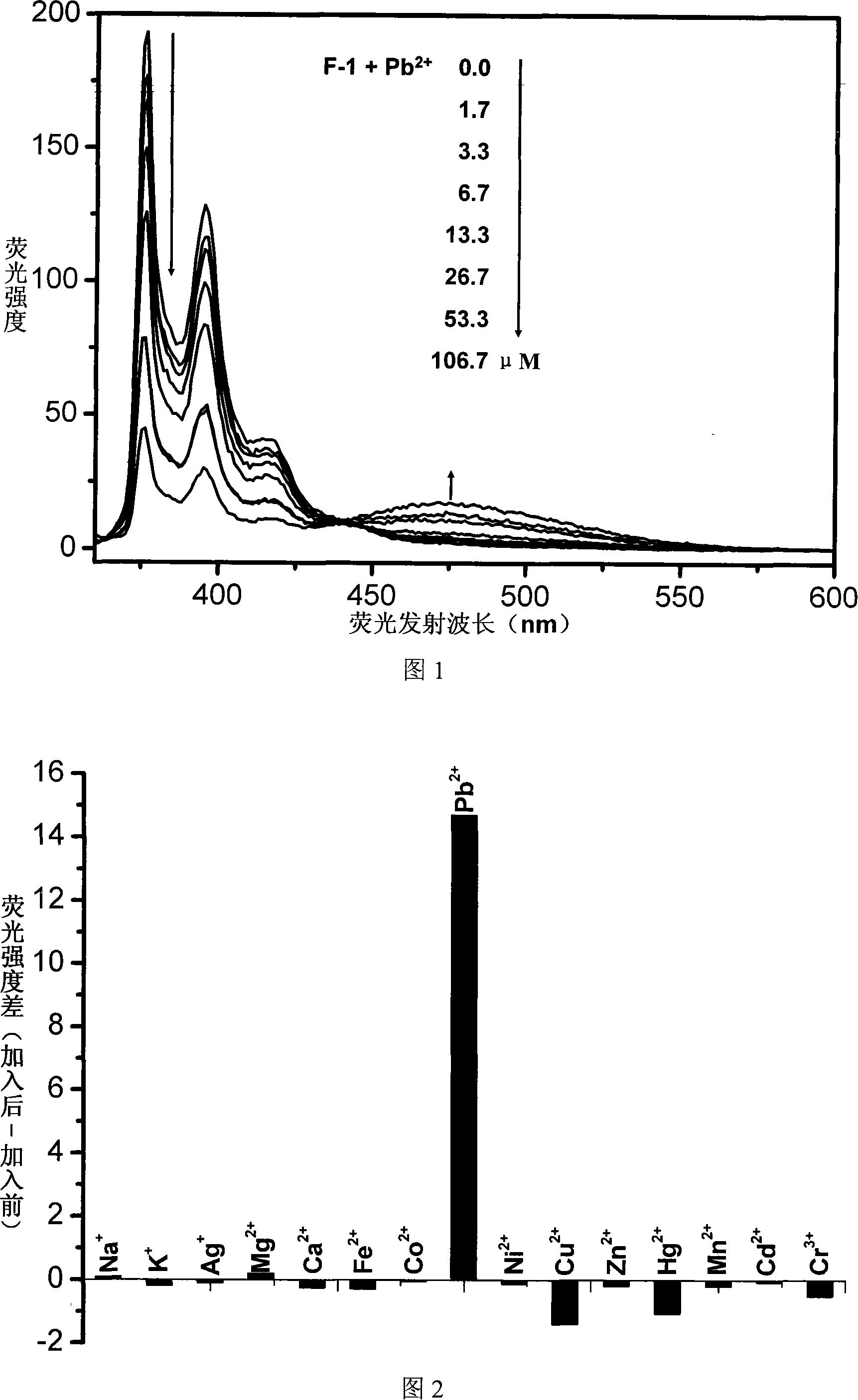
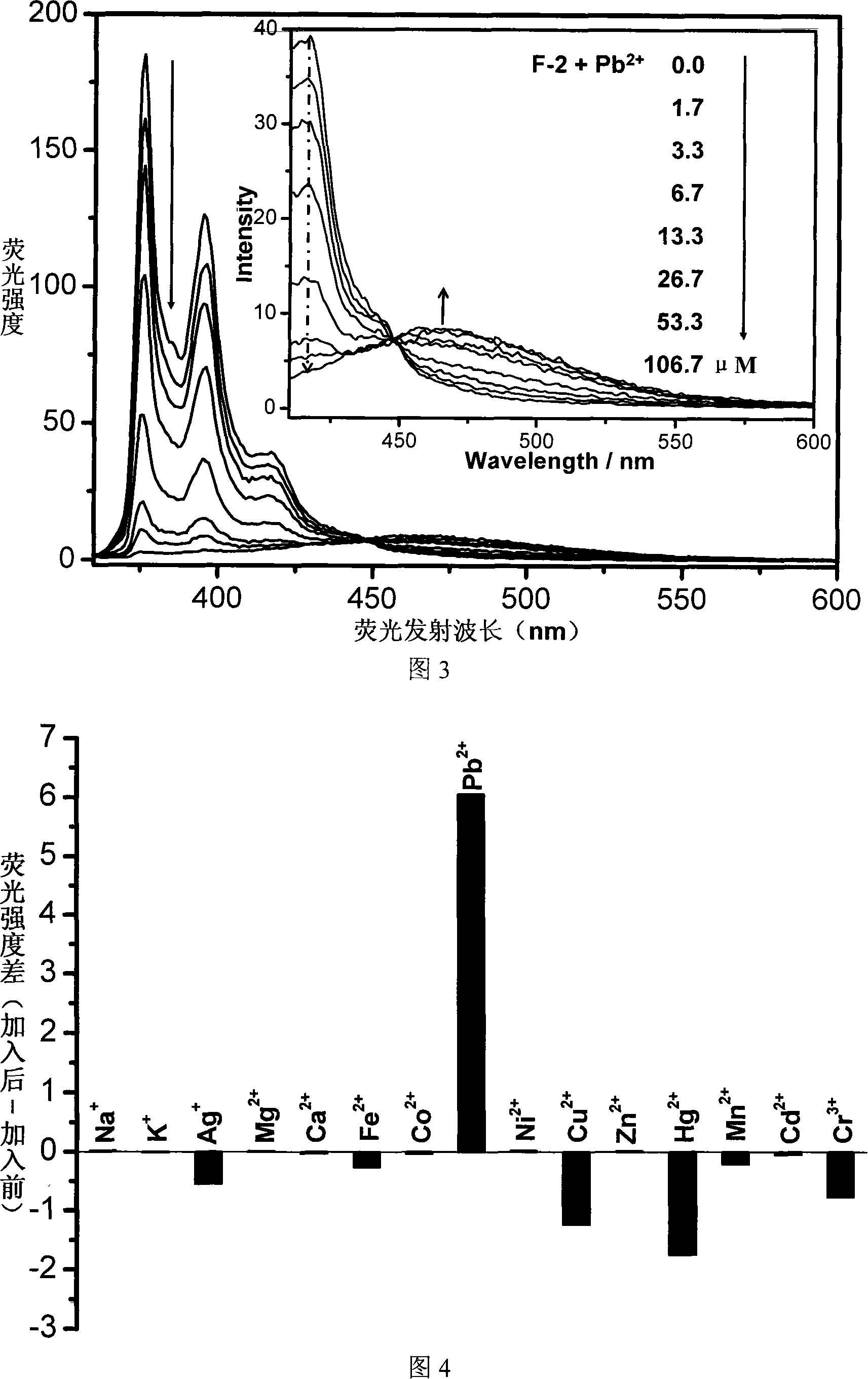
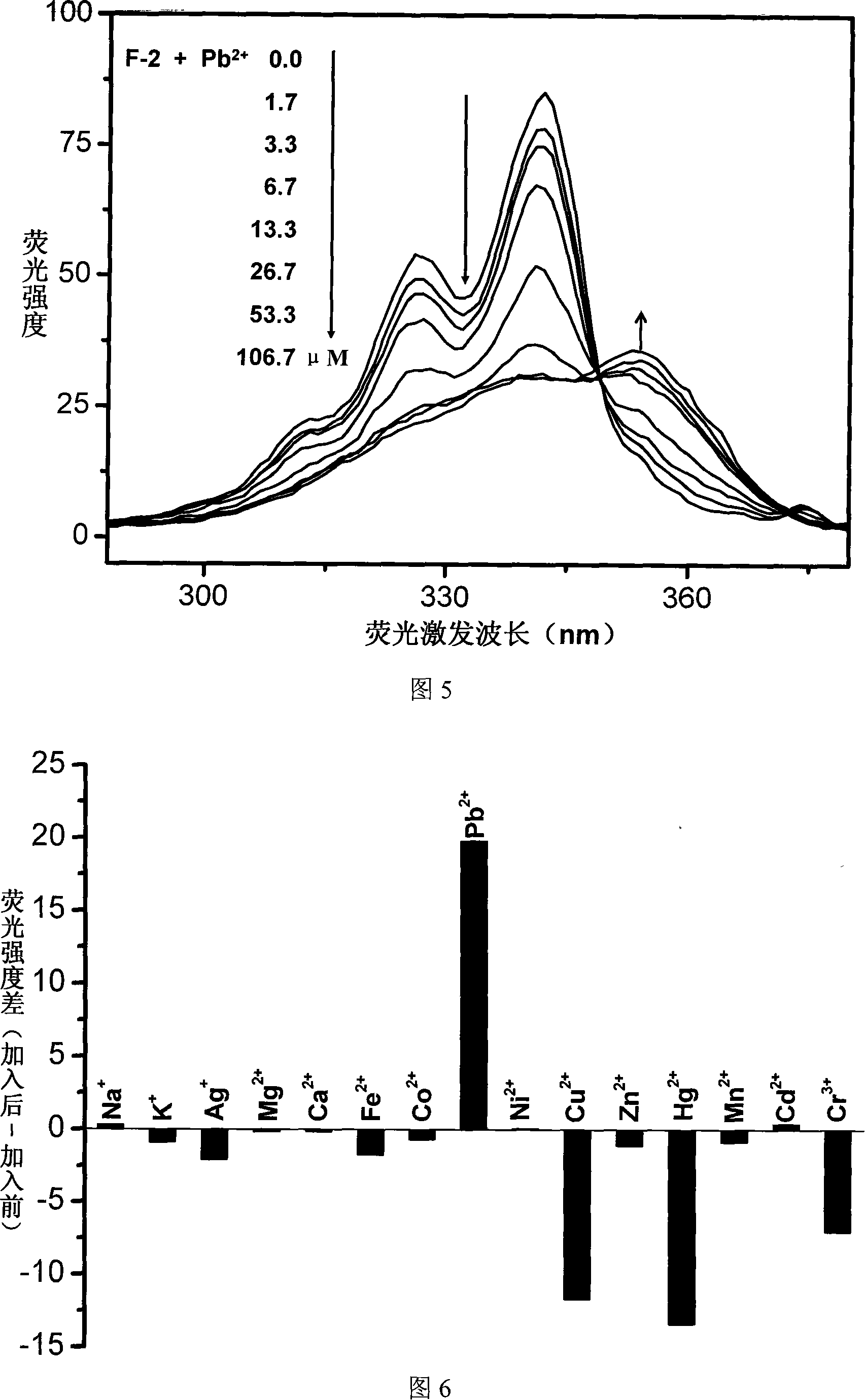
The invention relates to a fluorescent ion probe (I) with high selectivity and high sensitivity in detection and the application of the fluorescent ion probe in identifying and detecting heavy metal ion and transition metal ion, wherein, the Y is an organic conjugate group with fluorescence transmitting function such as pyrene, naphthalene, 4-amidogen-1, 8-naphthyl imide, Dan sulfonamide, anthracene, carbazole, benzimidazoins, benzoxazoles, boron fluoride bipyrrole (BODIPY), fluorescein, 3, 4, 9, 10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide or rhodamine B; the X is acylamino group, sulfoamino group or ester group. The fluorescent ion probe uses the fluorescence peak of fluorescence chromophore aggregate as the response signal to identify metal ion, thereby effectively avoiding the quenching effect of transition metal ion and heavy metal ion on fluorophore; moreover, the fluorescent ion probe realizes selective identification of heavy metal ion and transition metal ion in various solvents and aqueous solution in particular.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Synthesis of new 3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide cyclometalated iridium complex and application to regulate fluorescence-phosphorescence dual emission through utilization of solution concentration of complex
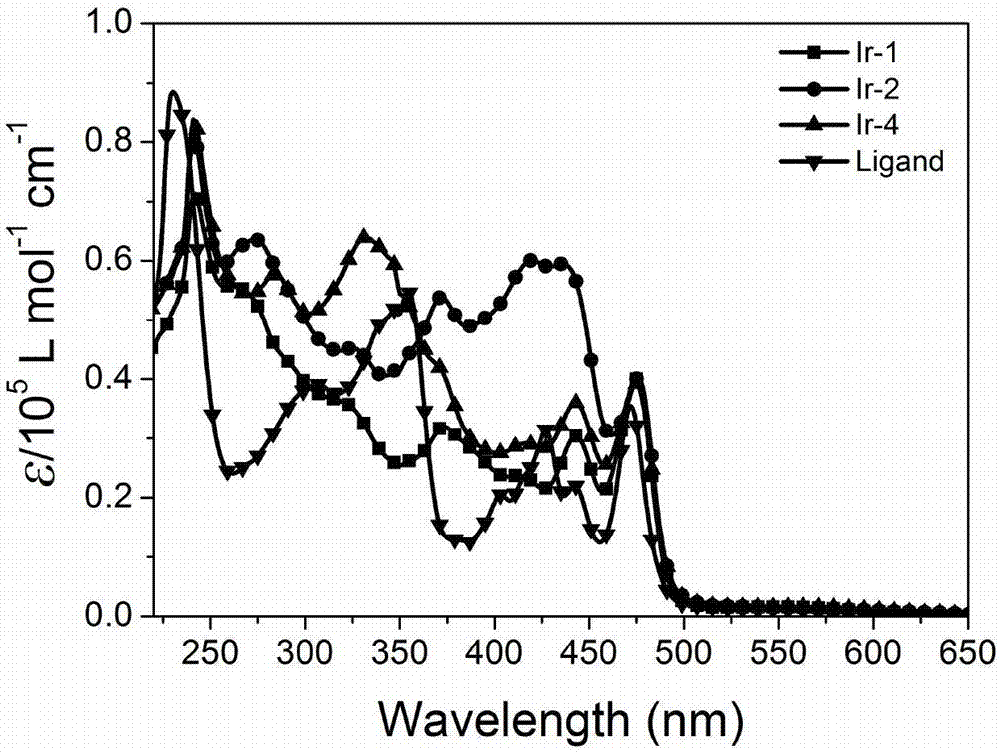
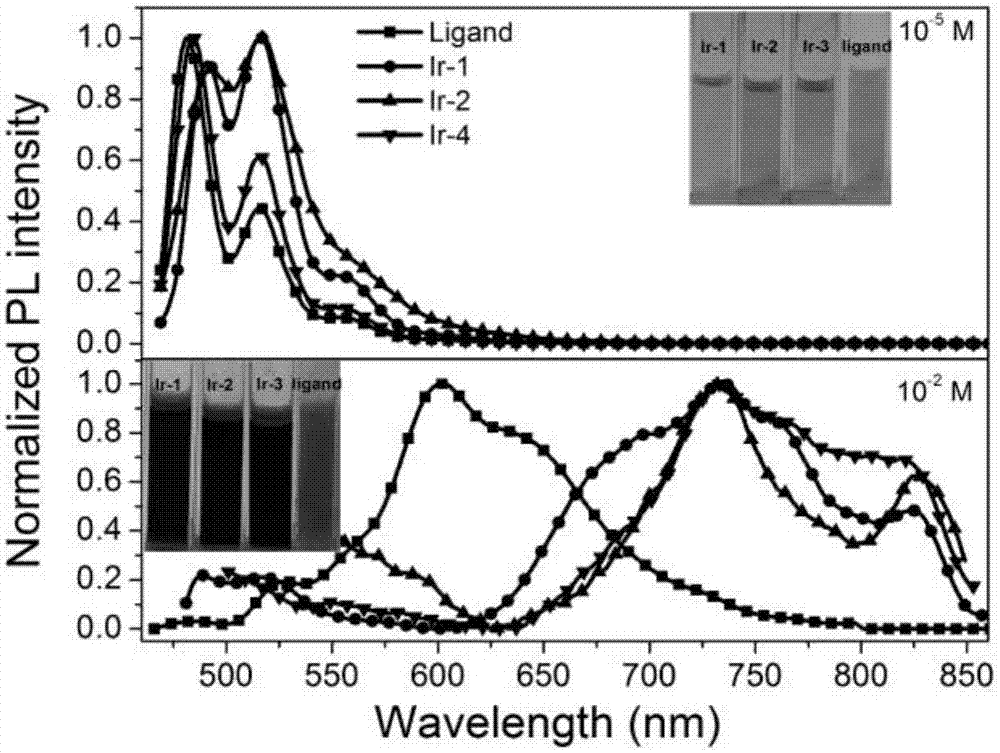
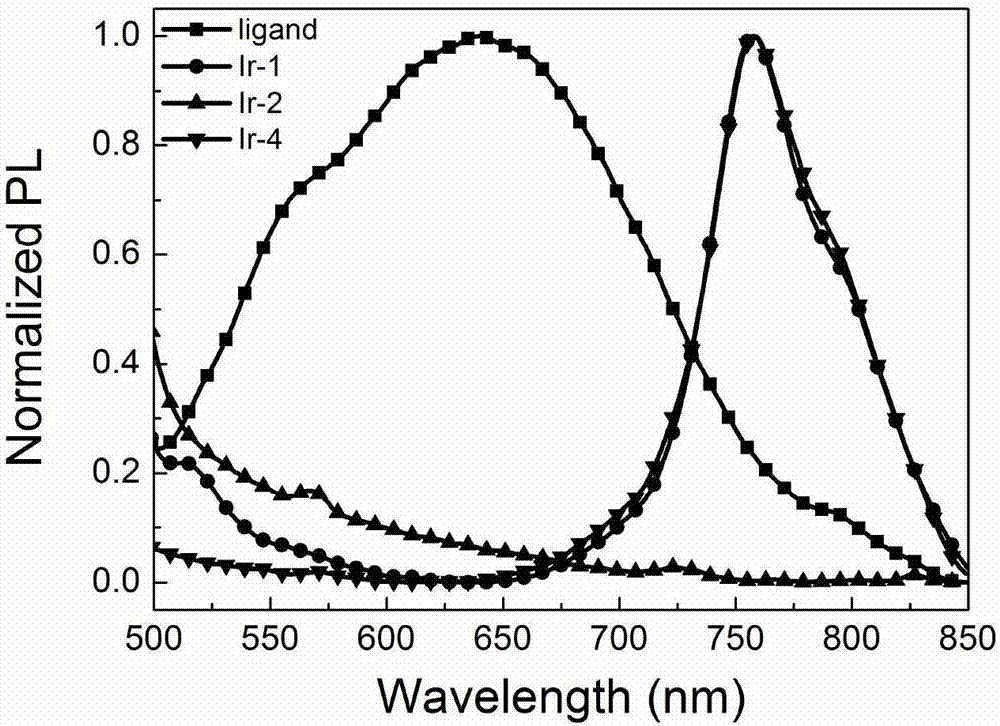
The invention discloses a 3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic-diimide-based cyclometalated iridium complex fluorescence-phosphorescence dual emission material and an application to regulate excited state luminescence through utilization of the solution concentration of the material. The cyclometalated iridium complex takes a 3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide derivative as an auxiliary ligand and takes a phenyl pyridine derivative as a main ligand unit. Through introduction of triphenylamine, carbazole and Mi borane electron-donating / electron-withdrawing groups to phenyl pyridine, energy levels of the ligand and complex are regulated. The material in a low-concentration solution (10<-5>M) emits yellow fluorescence, and has a maximum emission peak of 520 nm. The material in a high-concentration solution (10<-2>M) emits near-infrared phosphorescence, and has a maximum emission peak of 740 nm. As far as we know, it is reported for the first time, the excited state luminescence of the cyclometalated iridium complex is regulated through utilization of the solution concentration.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Perylenetetracarboxylic diimide copolymer containing thiophenepyrrole dione unit, preparation method thereof and application thereof
InactiveCN102344550AEffective bandgap adjustmentImprove solubilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenCharge carrier mobility
The invention discloses a perylenetetracarboxylic diimide copolymer containing a thiophenepyrrole dione unit, a preparation method thereof and an application thereof. The molecular structure of the copolymer is represented by general formula (I); and in the formula (I), n is an integer between 1 and 200, R1, R2, and R3 are selected from hydrogen, C1-C20 alkyl, C1-C20 alkyloxyphenyl, or phenyl, R4and R5 are selected from C1-C20 alkyl, and R6 is selected from C1-C20 alkyl or alkyloxy. The perylenetetracarboxylic diimide copolymer containing the thiophenepyrrole dione unit of the invention has the advantages of good solvability, high carrier mobility, strong absorbance, wide light absorption range, and improvement of the sunlight utilization rate; and the preparation method has the advantages of simple process, high yield, and easy operation and control.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +1
Degradable photoelectric material and preparing method for degradable photoelectric material
InactiveCN104377305AReduce pollutionHas double conductivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVinyl carbazolePhthalocyanine
The invention discloses a degradable photoelectric material and a preparing method for the degradable photoelectric material. The degradable photoelectric material comprises, by mass, 10 parts to 20 parts of manganese phthalocyanine, 8 parts to 15 parts of silicon dioxide, 1 part to 6 parts of dimethyl sulfoxide, 2 parts to 8 parts of polyaniline, 20 parts to 40 parts of polylactic acid, 1 part to 8 parts of zinc stearate, 2 parts to 8 parts of vinylcarbazole, 5 parts to 15 parts of PTC, 1.2 parts to 3.7 parts of methylamine, 0.18 part to 1.25 parts of light stabilizers and 1.8 parts to 3.5 parts of ultraviolet absorbents, and further comprises, by mass, 0.31 part to 1.92 parts of N,N'-dimethyl-3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide. The degradable photoelectric material has the dual-conduction performance and is small in toxicity, small in environment pollution, degradable, high in photoelectric conversion efficiency, light in weight, simple and practicable in preparing method and low in production cost.
Owner:WUXI SUNOCEAN
Lyotropic chromophoric compounds, liquid crystal systems and optically anisotropic films
Lyotropic chromophoric compounds comprised of a naphthalimide derivative, a perylene-3,4-dicarboxylic imide derivative, or a perylenetetracarboxylic diimide derivative are described. The compounds can be used to form liquid crystal systems possessing high quality optical properties. The resulting liquid crystal systems are readily applied onto a substrate to obtain optically isotropic or anisotropic, at least partially crystalline films applicable in various fields.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
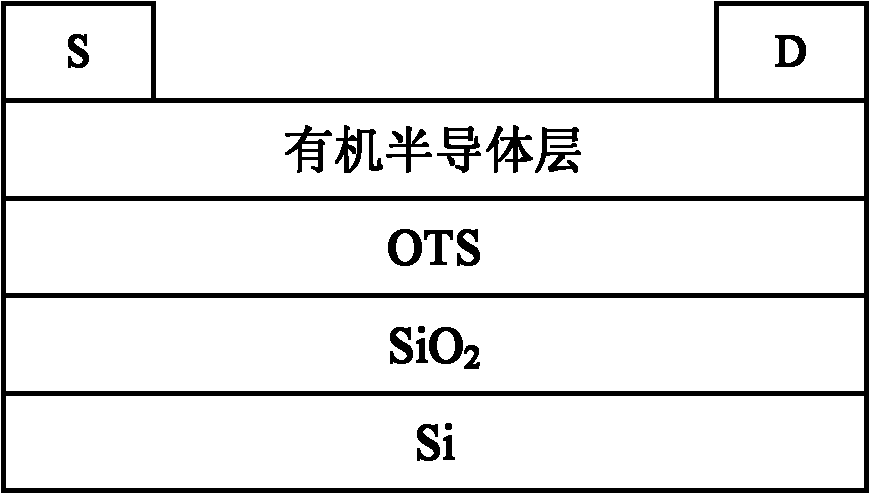
Perylenetetracarboxylic diimide organic semiconductor material and the preparation method and application thereof
ActiveUS20130165616A1Improve propertiesAttenuation bandwidthElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesHydrogenSemiconductor materials
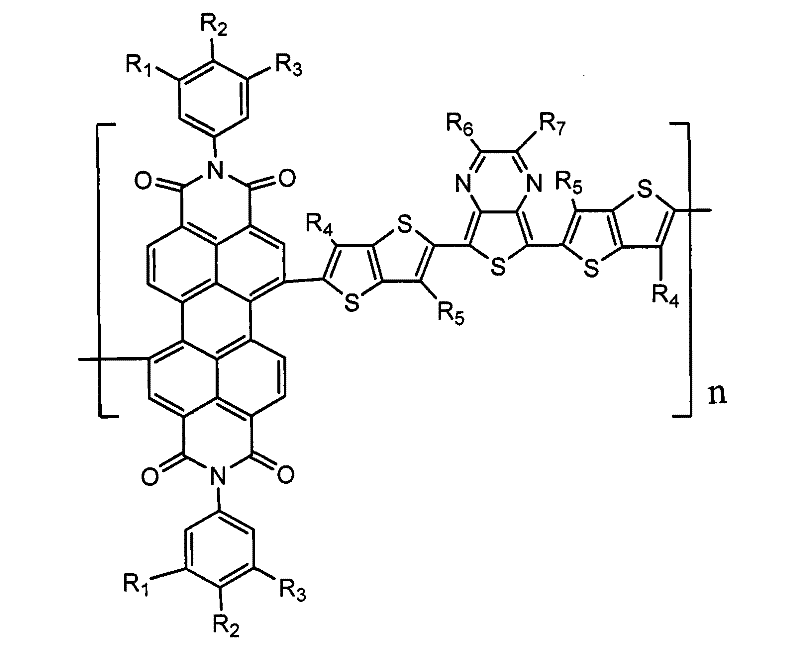
Disclosed is a perylenetetracarboxylic acid diimide organic semiconductive material represented by the following formula (I), which belongs to the field of photoelectric material. In formula (I), n is an integer of 1-100, R1, R2 or R3 is hydrogen, C1-C20 alkyl, C1-C20 alkoxyl, phenyl or alkoxyphenyl, R4 or R5 is C1-C20 alkyl, R6 or R7 is hydrogen, C1-C20 alkyl, C1-C20 alkoxyl or phenyl. The preparation method of said perylenetetracarboxylic acid diimide organic semiconductive material and the use thereof are also disclosed.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD
Perylene tetracarboxylic acid diimide copolymer containing dithienoquinoxaline unit, preparation method and application
InactiveCN102286140AImprove solubilityStrong absorbanceFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesQuinoxalineSolubility
The invention discloses a perylene tetracarboxylic diimide copolymer containing a dithieno quinoxaline unit as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The copolymer is shown in the specification. The preparation method comprises adding a perylene tetracarboxylic diimide dibromide and a 6,9-bis(tributyl tin)-dithieno[3,2-f:2',3'-h]quinoxaline derivative in an organic solvent, adding a catalyst, carrying out Stille coupling reaction at the temperature of 50-120 DEG C for 24-72 hours, and refining to obtain the copolymer. The copolymer disclosed by the invention can be applied to manufacture of polymer solar cell devices, organic field effect transistors, organic electroluminescent devices, organic light storage devices, organic nonlinear materials or organic laser devices. Thecopolymer disclosed by the invention has the advantages of good solubility, strong light absorbency and excellent charge transfer performance, the absorption range of the copolymer can extend to a near infrared region, and the sunlight utilization rate can be increased; and the preparation method has a simple synthesis route and a low process requirement.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +1
Synthetic method and micrometer wire preparation method of perylene bisimide derivative
The invention relates to a synthetic method and a micrometer wire preparation method of a perylene bisimide derivative. The synthetic method of the perylene bisimide derivative comprises the step of dissolving 1-NO2-3,4 and 9,10-perylene tetracarboxylic acid imidodicarbonic diamide into a polarity organic solvent, stirring and reacting for 4 to 6h at the temperature of 150 to 180 DEG C, dropping a solution after reacting into diluted hydrochloric acid, separating out precipitation, filtering, washing, drying and purifying to obtain a product. Dissolving the perylene bisimide derivative into a chloroformic solution, and preparing into 2x10<-3>mol / L of concentrated solution, taking 2mL of the to-be-used concentrated solution into a test tube, injecting 3 to 5mL of methanol solution into the test tube, and standing for one day, so as to obtain the micrometer wire corresponding to the perylene bisimide derivative. The synthetic method of the compound is simple, the cost is relatively low, the reaction is finished by one step, and the product purity is relatively high. An oxygen atom five-membered ring is introduced in a bay position, so that the conjugate pi system of the plane part of a perylene molecule is increased, and the acting force among the perylene molecules is changed, so that the preparation of the micrometer wire is realized.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
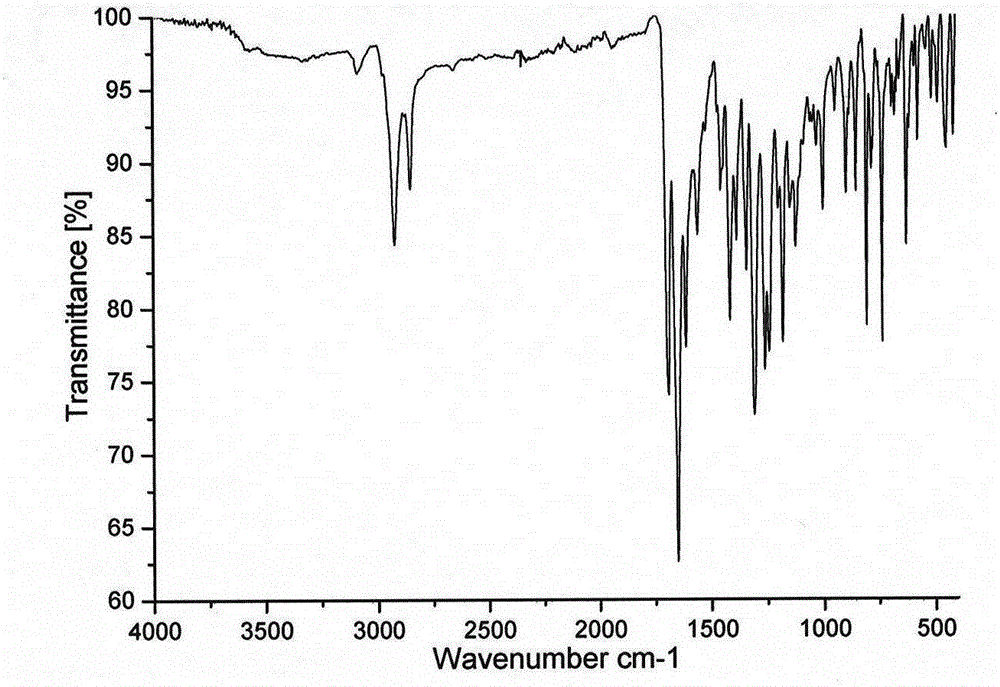
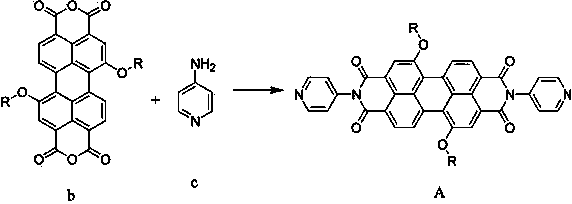
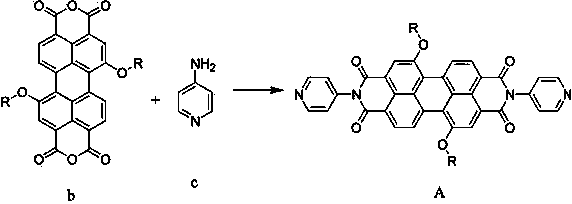
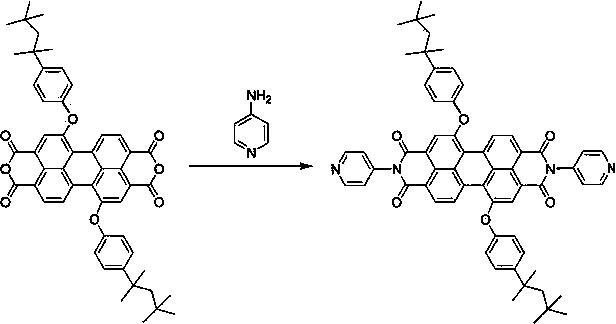
Preparation and photocatalytic hydrogen generation performance of N-pyridyl perylenetetracarboxylic diimide
InactiveCN104557931AOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPolymer chemistryPhotochemistry
The invention relates to N-pyridyl perylenetetracarboxylic diimide with a formula shown in specification, a preparation method and application thereof. The compound is prepared from substitutional perylenetetracarboxylic anhydride and 4-aminopyridine under a high temperature condition; the process is simple and easy to be carried out; N-pyridyl perylenetetracarboxylic diimide and a dimethylglyoxime complex are combined to be used as a photocatalyst for hydrogen generation through solar visible photocatalytic water decomposing; N-pyridyl perylenetetracarboxylic diimide can absorb the visible light, generate electrons and then transmit to cobalt through a coordinate bond, so as to catalyze the water decomposing for hydrogen generation.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
A 3, 4, 9, 10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide flexible organic electrode prepared based on a phase transition method
InactiveCN109004180AHigh mechanical strengthImprove flexibilitySecondary cellsPositive electrodesLithium-ion batteryInorganic materials
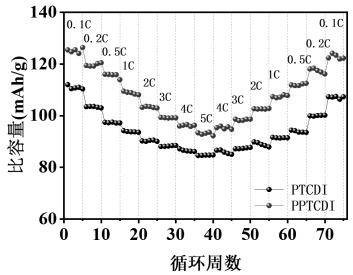
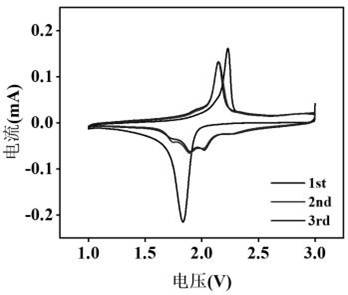
The invention discloses a 3, 4, 9, 10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide flexible organic electrode prepared based on a phase transition method, and relates to the field of composite materials of flexible lithium ion batteries. The flexible organic electrode uses 3, 4, 9, 10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide as an organic active material, polyurethane as a framework substrate, and carbon black as a conductive agent, and is a flexible self-supporting electrode formed by compounding through a phase transition preparation method. The 3, 4, 9, 10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide flexible organic electrode of the invention improves the capacity and cycle stability of a battery, and avoids the environmental pollution problem caused by inorganic material.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Perylenetetracarboxylic diimide copolymers, preparation method thereof and application thereof
ActiveCN102372837AEffective bandgap adjustmentImprove solubilityLaser active region structureFinal product manufactureHydrogenCharge carrier mobility
The invention which belongs to the optoelectronic material field discloses perylenetetracarboxylic diimide copolymers. The perylenetetracarboxylic diimide copolymers have a structural formula represented by formula (I). In the formula (I), n is an integer between 1 and 100; R1, R2 and R3 are hydrogen, C1-C20 alkyl, C1-C20 alkoxy, phenyl, or alkoxybenzene; R4 is C1-C20 alkyl; and R5 is hydrogen, C1-C20 alkyl, C1-C20 alkoxy, or phenyl. The invention also provides a preparation method and an application of the perylenetetracarboxylic diimide copolymers. The diphenyl silole unit-contained perylenetetracarboxylic diimide copolymers have the advantages of good dissolving performance, high carrier mobility, strong absorbance, wide light absorption range, and sunlight utilization rate improvement; and the preparation method which has the advantages of simple process and high yield is easy to operate and control.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +1
Perylene diimide-fluorene-thiophene and (3, 4-b) pyrazine conjugated polymer and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102134307AWide light absorption rangeIncrease profitOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesSolubilitySuccinchlorimide
The invention discloses a perylene diimide-fluorene-thiophene and (3, 4-b) pyrazine conjugated polymer shown in a general formula (I) and a preparation method and application thereof. The invention comprising the following steps: causing 1, 7-dibromo-3, 4, 9, 10-perylene tetracid anhydride to react with 3, 4, 5-trialkyl (tri-oxygroup)-1-anline to obtain a monomer; then causing a 3', 4'-diamido-2,2': 5', 2''-terthienyl compound to react with a benzil compound to obtain a midbody; and then causing the midbody to react with N-bromosuccinimide to obtain another monomer; and under the oxygen-freecondition, causing the two monomers and the bi-boric acid ester to conduct polymerization to obtain a target product. The preparation method is simple, easy to operate and control, and suitable for industrialized production; the target product prepared by the method has good dissolubility, has strong absorbance and wide absorption range when being used in the field of organic solar cell, and can be extended to a near infrared region, thus improving the utilization rate of the sunlight.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +1
Perylene tetracarboxylic acid bisimide derivative, n-type semiconductor, a method for producing n-type semiconductor, and electronic device
InactiveUS20140024171A1High carrier mobilityImprove solubilitySilicon organic compoundsFinal product manufactureHalogenChemistry
The present invention provides a perylene tetracarboxylic acid bisimide derivative which enables the formation of an n-type semiconductor having high carrier mobility and has superior solubility. The perylene tetracarboxylic acid bisimide derivative is a perylene tetracarboxylic acid bisimide derivative represented by the following chemical formula (I), a tautomer or stereoisomer of the perylene tetracarboxylic acid bisimide derivative, or a salt of the perylene tetracarboxylic acid bisimide derivative or the tautomer or stereoisomer,In the chemical formula (I), R1 to R6 each represents a hydrogen atom, organooligosiloxane, or any substituent, at least one of R1 to R6 represents a monovalent substituent derived from organooligosiloxane, L1 and L2 each represents a single bond or a linking group, R7 to R10 each represents a lower alkyl group or a halogen, and o, p, q, and r each represents an integer from 0 to 2.
Owner:KAGAWA UNIVERSITY
Thiophene-containing perylene tetracarboxylic diimide copolymer, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102234366AEnhanced flatness and conjugationHigh carrier mobilityOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesPhenyl groupBenzene
The invention discloses a thiophene-containing perylene tetracarboxylic diimide copolymer, and a preparation method and application thereof. The thiophene-containing perylene tetracarboxylic diimide copolymer has a general molecular structural formula shown in (I), wherein n is an integer ranging from 1 to 200; R1, R2 and R3, the same or different, are selected from -H, C1-C15 alkyl, and C1-C15 alkoxy benzene or phenyl; R4 and R5, the same or different, are selected from C1-C15 alkyl, C1-C15 alkoxy, and C1-C15 alkoxy benzene or phenyl; and R6 and R7, the same or different, are selected from C1- C15 alkyl, C1-C15 alkyloxy, and C1-C15 alkoxy benzene or phenyl. The thiophene-containing perylene tetracarboxylic diimide copolymer disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high solubility, high carrier mobility, strong absorbance and wide light absorption range, and improves the utilization rate of sunlight. The preparation method of the thiophene-containing perylene tetracarboxylic diimide copolymer is simple in process, high in produce yield, and easy to operate and control.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +1
Mitochondrion 3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic dianhydride targeting fluorescent probe and application thereof
InactiveCN106518925AReduced responseGood water solubilityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceCytotoxicity
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
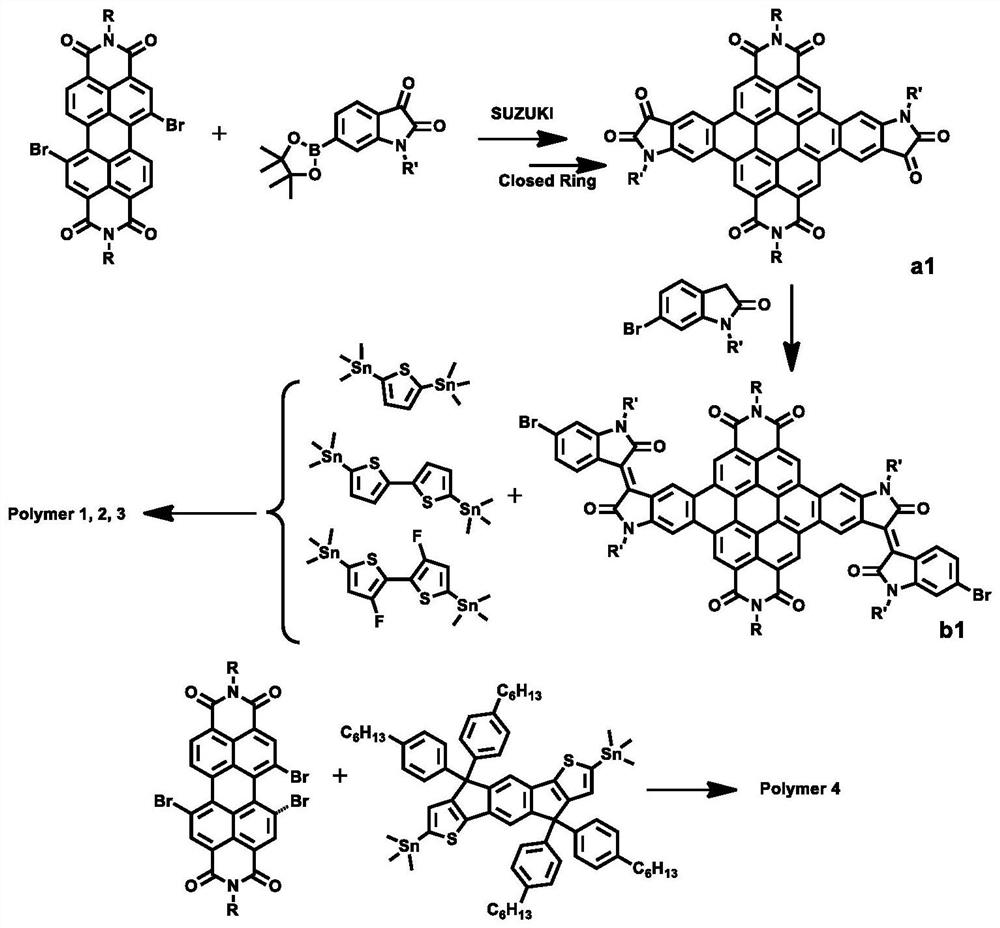
D-A polymer based on conjugate plane expansion of 3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111944127ALow unoccupied molecular orbitalHigh electron affinitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingImidePerylenemonoimide
The invention discloses a novel, stable and good-solubility D-A polymer based on conjugate plane expansion of 3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide and a preparation method of the D-A polymer. Thepolymer effectively improves the device performance of an organic semiconductor. The structural general formulas of the D-A polymer based on the conjugate plane expansion of 3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide are shown as formulas (I) and (II). In the formulas, R and R'are C5-C18 fork chains or straight chains, and n is a positive integer in a range of 1 to 100.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Inorganic/organic semiconductor nano-composite structure and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105152122AArranged in orderIncrease profitDecorative surface effectsCoupling light guidesOrganic filmTio2 nanotube
The invention discloses an inorganic / organic semiconductor nano-composite structure and a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: etching and cleaning a titanium foil serving as a substrate to obtain a titanium substrate, obtaining an inorganic semiconductor TiO<2> nanotube array on the surface of the titanium substrate by means of a positive electrode oxidation method; and depositing a layer of perylenetetracarboxylic diimide organic semiconductor film on the surface of the TiO2 nanotube array serving as a growing substrate through a physical vapor deposition method to obtain the inorganic / organic semiconductor nano-composite structure. Meanwhile, nano-composite structures with different organic film deposition amounts can be realized by changing the substrate position of the TiO<2> nanotube array. The method is simple and feasible, and an experimental basis is laid for a hierarchical assembly of inorganic and organic semiconductor materials. As proved by a result of research on the application of the obtained nano-composite structure in the field of photocatalytic hydrogen production by water decomposition of photo-electrochemical cells, the structure has efficient photocatalytic performance.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method for preparing C.I. pigment red 179
The invention relates to a method for preparing N,N'-dimethyl-3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide (C.I. pigment red 179). A reaction is conducted on N-methyl-1,8-naphthalimide in a system composed of a mixed base composed of caesium hydroxide or hydrate thereof and DBU and polar aryl halide at 140 DEG C-190 DEG C, and N,N'-dimethyl-3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide can be obtained. After pigment-based processing is conducted on N,N'-dimethyl-3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide, the crystal form of N,N'-dimethyl-3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide is the same as that of a C.I. pigment red 179 product.
Owner:LIAONING LIANGANG PIGMENT & DYESTUFF CHEM +2
Copolymer containing diketopyrrolopyrrole and perylene diimide, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103865043AImprove stabilityLower bandgapOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesPyrroleBand gap
The invention relates to a copolymer containing diketopyrrolopyrrole and perylene diimide, and the compolymer comprises the structural formula shown in the specification. In the structural formula, n is a natural number between 1 to 100, R1 is C1-C20 alkyl or a structure shown in the specification, and in the R1 structure, R2, R3 and R4 are H, C1-C20 alkyl or C1-C20 alkyloxy, and R5, R6 and R7 are H or C1-C20 alkyl. The copolymer consisting of diketopyrrolopyrrole and perylene diimide can form an extremely strong donor-acceptor structure, thereby helping to improving the material stability on the one hand, and helping to reduce the material band gap on the other hand, so that the light absorption scope of the material is enlarged, and the photoelectric converting efficiency is improved. Additionally, the invention also relates to a preparation method and application of the copolymer.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +2
Copolymer containing perylenetetracarboxylic diimide-s-indacenobithiophene, preparation method thereof and applications thereof
InactiveCN103626969AStrong absorbanceWide absorption rangeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenElectron donor
The invention belongs to the field of organic semiconductor materials, and discloses a copolymer containing perylenetetracarboxylic diimide-s-indacenobithiophene, a preparation method thereof and applications thereof. The copolymer has a general structure formula as follows, wherein n is an integer between 1 and 100; R1, R2 and R3 are the same or different and are selected from hydrogen, C1-C20 alkyl or C1-C20 alkoxy; and R4 is C1-C20 alkyl or C1-C20 alkylbenzene. According to the copolymer, the s-indacenobithiophene unit and the perylenetetracarboxylic diimide are subjected to copolymerization to form an electron donor-receptor structure so as to adjust the bad gap of the polymer and to push the absorption band edge of the polymer to infrared and near infrared zones, thus increasing the sunlight utilization rate and further increasing the light conversion rate.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +2
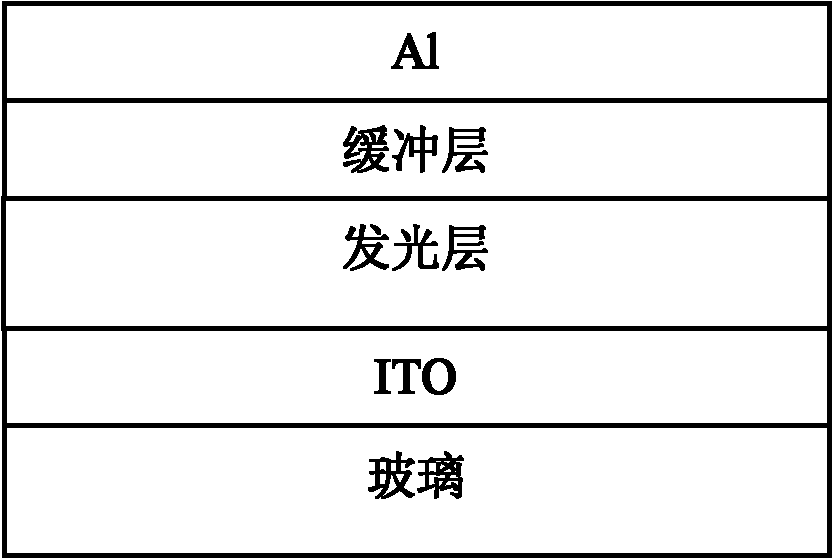
Organic light-emitting superlattice film as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112510166AQuality improvementImprove luminous brightnessMaterial nanotechnologySolid-state devicesSource materialCarboxylic acid
The invention discloses an organic light-emitting superlattice film and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of organic semiconductor photoelectric materials. The organic light-emitting superlattice film is an organic light-emitting film formed by alternate epitaxial growth of two two-dimensional organic molecules on the surface of a substrate, and the two-dimensional organic molecules are selected from 3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic dianhydride, N,N'-dimethyl-3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide, N,N'-dioctyl-3,4,9,10-perylenedicarboximide and 3,4,9,10-Perylenetetracarboxylic diimide. The preparation method comprises the following steps: placing a growth source material of a first two-dimensional organic molecule and a substrate at different positions of a tube furnace, and epitaxially growing a first layer of organic light-emitting film on the surface of the substrate; replacing a growth source material with a second two-dimensional organic molecule, and growing a second layer of organic light-emitting film; and repeatedly replacing the growth source material, and alternately growing multiple layers of organic light-emitting films to obtainthe organic light-emitting superlattice film. The organic light-emitting superlattice thin film has high quality and high light-emitting intensity, and can be used as a light-emitting layer of an organic light-emitting field effect transistor.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Perylene tetracarboxylic acid diimide copolymer containing naphthodithiophene unit, preparation method and application
InactiveCN102295746AImprove solubilityStrong absorbanceLaser active region structureFinal product manufactureSolubilityOrganic laser
The invention discloses thiophanthrene unit-containing perylene tetracarboxylic diimide copolymer and a preparation method as well as application thereof. The preparation method of the copolymer comprises the following steps of: putting perylene tetracarboxylic diimide dibromide and a 2,6-bis(tributyl tin)-naphtho [2,1-b:3, 4-b'] dithiophene derivative serving as raw materials in an organic solvent; adding a catalyst to perform Stille coupling reaction at the temperature of 50-120 DEG C for 24-72 hours; and refining to obtain the copolymer. The copolymer is applied to manufacturing of a polymer solar cell device, manufacturing of an organic field effect transistor, manufacturing of an organic electroluminescent device, manufacturing of an organic light storage device, manufacturing of an organic nonlinear material and manufacturing of an organic laser device. The copolymer has the advantages of high dissolubility, strong absorbency, superior charge transfer performance, capability of extending an absorption range to a near infrared region, capability of increasing utilization rate of sunlight, simple synthetic route and low technological requirements.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +1
Chemical self-doping of one-dimensional organic nanomaterials for high conductivity application in chemiresistive sensing gas or vapor
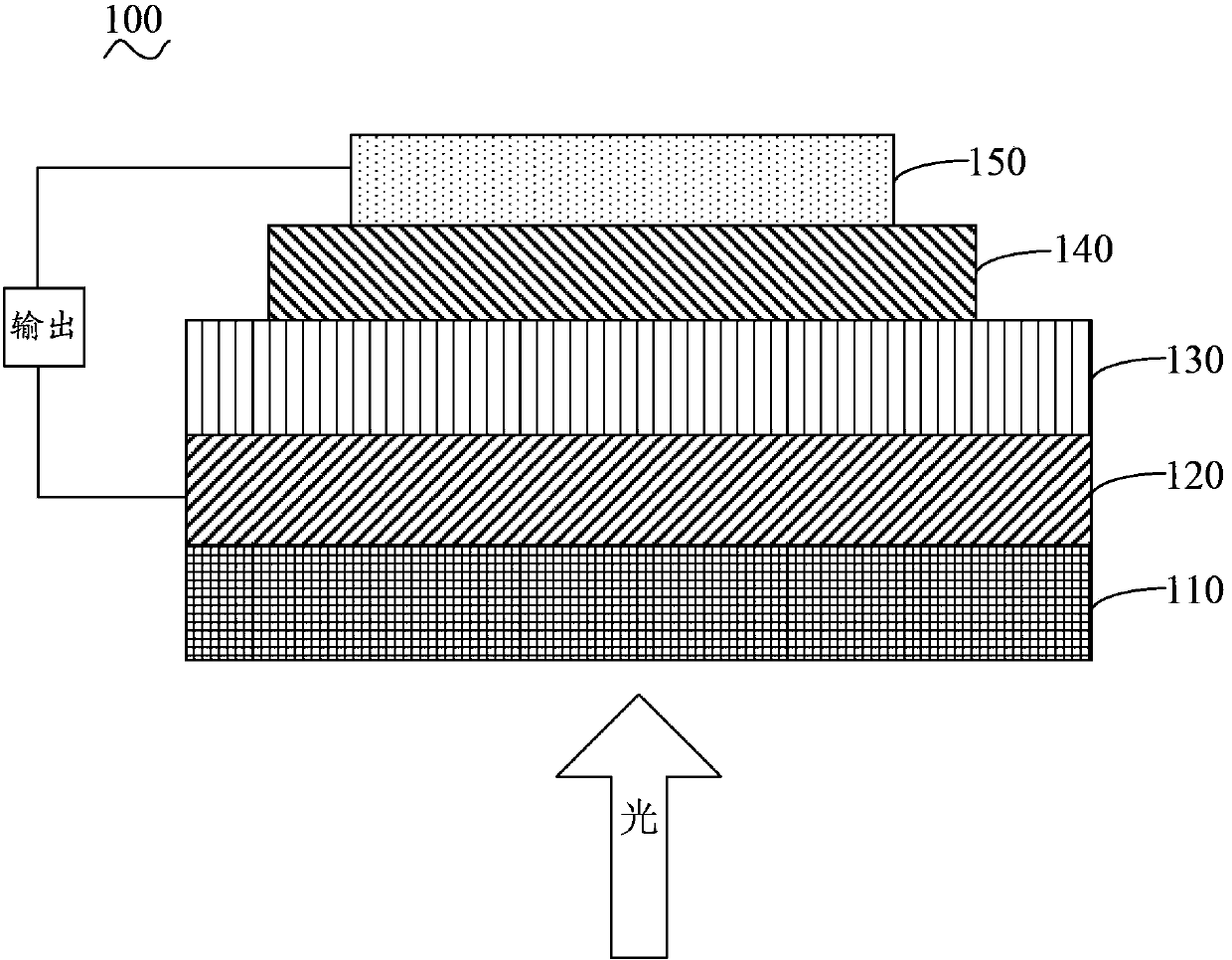
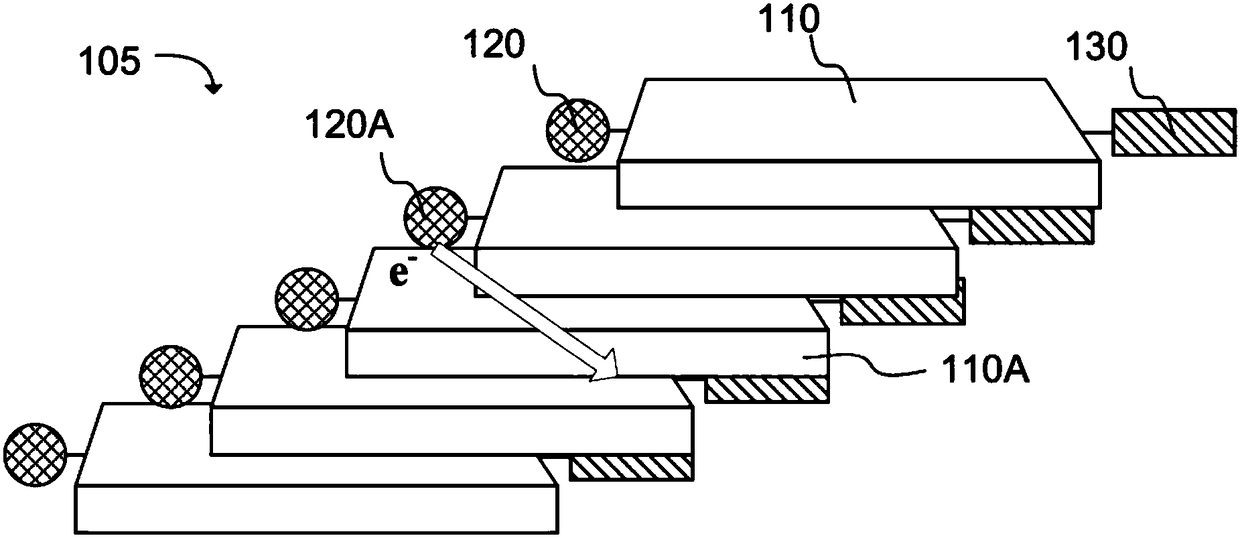
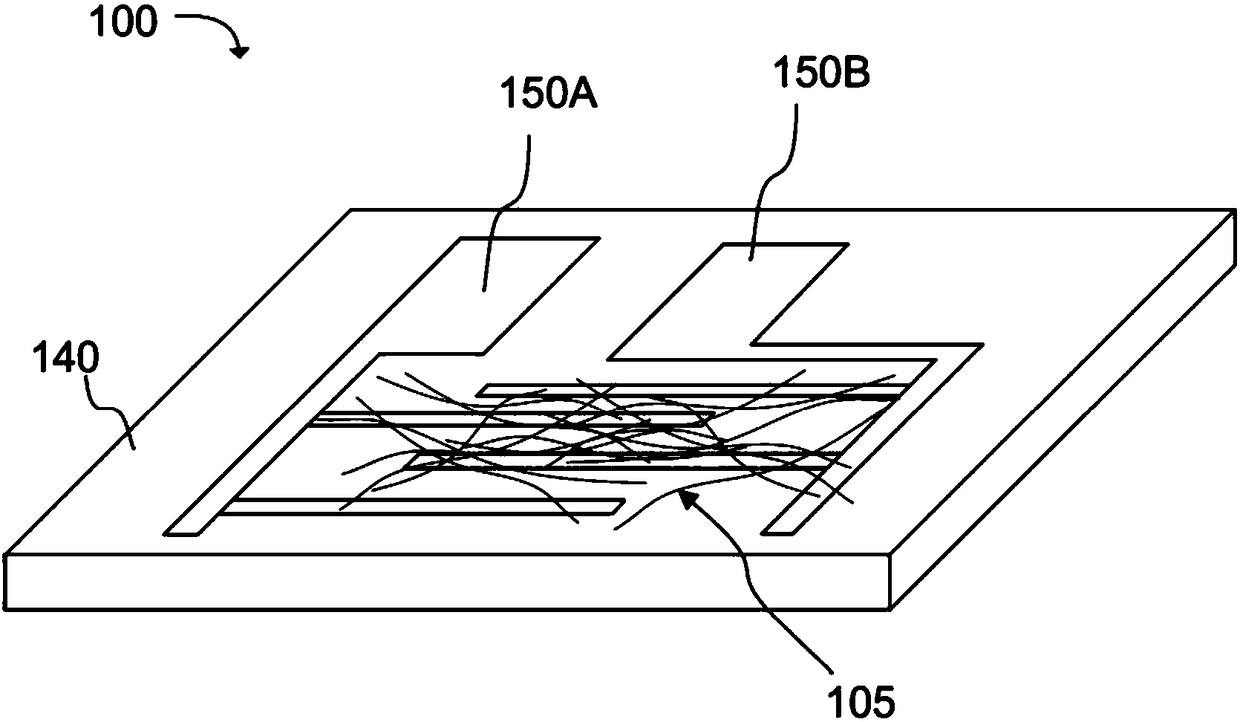
A chemiresistive vapor sensor compound for detecting target vapors can comprise a perylene-tetracarboxylic diimide (PTCDI) core according to structure (I), where R can be a morphology control group or-A'-D', A and A' can be independently a linking group, D and D' can be independently a strong electron donor which transfers electrons to the PTCDI core sufficient to form an anionic PTCDI radical ofthe PTCDI core, and Rl to R8 can be independently a side group. A chemiresi stive vapor sensor (100) for detection of a target compound can comprise an assembly of nanofibers (105) formed of the chemiresi stive sensor compound and a pair of electrodes (150A, 150B) operatively oriented about the assembly of nanofibers (105) to allow electrical current to pass from a first electrode in the pair ofelectrodes (150A, 150B) through the assembly of nanofibers (105) and to a second electrode in the pair of electrodes.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Perylene diimide fluorescent dye with ortho-substituted benzanthrone, and preparation ,method and application thereof
ActiveCN113321653AGreat application potentialLarge two-photon absorption cross-sectionOrganic chemistryPhotodynamic therapyBenzanthreneTwo-photon absorption
The invention relates to a perylene diimide fluorescent dye with ortho-substituted benzanthrone. 3, 4, 9, 10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide is used as a core group, imide nitrogen atoms at two ends of the core group are connected with 7-tridecyl, and the ortho-position of the core group is connected with benzanthrone. The 7-tridecyl group is introduced to the perylene diimide group, and the benzanthrone group is introduced to the ortho position, so that the obtained perylene diimide fluorescent dye of ortho-substituted benzanthrone has a large two-photon absorption cross section value, the third-order nonlinear optical activity is greatly improved, and the perylene diimide fluorescent dye can be applied to a third-order nonlinear optical material. Meanwhile, no matter whether single photons or two photons are used for exciting the aggregation states of the two photons, the perylene diimide fluorescent dye with ortho-substituted benzanthrone shows AIE properties, and has great application potential in the aspects of two-photon fluorescence imaging and two-photon dynamic therapy.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV
Process for preparing c.i. Pigment Red 179
The invention relates to a method for preparing N,N'-dimethyl-3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide (C.I. pigment red 179). A reaction is conducted on N-methyl-1,8-naphthalimide in a system composed of a mixed base composed of caesium hydroxide or hydrate thereof and DBU and polar aryl halide at 140 DEG C-190 DEG C, and N,N'-dimethyl-3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide can be obtained. After pigment-based processing is conducted on N,N'-dimethyl-3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide, the crystal form of N,N'-dimethyl-3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide is the same as that of a C.I. pigment red 179 product.
Owner:LIAONING LIANGANG PIGMENT & DYESTUFF CHEM +2
Fluorescent probe for detecting activity of acetylcholin esterase as well as synthesis method and application of fluorescent probe
ActiveCN111072657AImprove featuresHigh sensitivityMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic chemistryFluorescent spectraFluoProbes
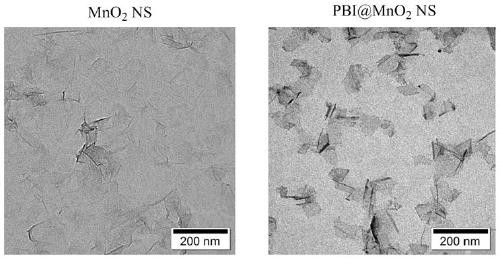
The invention discloses a fluorescent probe for detecting activity of acetylcholin esterase as well as a synthesis method and an application of the fluorescent probe. Based on the electrostatic interaction between MnO2 nanosheets and cationic derivatives (PBI-DM) of perylenetetracarboxylic diimide and the fluorescence spectrum characteristics of PBI-DM in the aggregation and dispersion process, the detection of the AChE activity is realized. The synthesized fluorescent probe PBI-DM-coated MnO2NS disclosed by the invention has a low detection limit of 0.24 mU / mL on the detection of AChE, has the advantages that the PBI-DM-coated MnO2NS is high in selectivity, interference of other low-concentration sulfhydryl compounds can be avoided, the PBI-DM-coated MnO2NS can be used for screening AChEinhibitors, and has great potential in the field of clinical diagnosis.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Polyperylene tetracarboxylic diimide, preparation method thereof and application of polyperylene tetracarboxylic diimide in lithium/sodium battery
The invention discloses polyperylene tetracarboxylic diimide, a preparation method of the polyperylene tetracarboxylic diimide and application of the polyperylene tetracarboxylic diimide in a lithium / sodium battery, and belongs to the technical field of lithium / sodium ion battery positive electrode materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing 3, 4, 9, 10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide and ferric trichloride in a ball milling tank, carrying out ball milling reaction for 20-30 minutes by using a ball mill, washing the obtained product with methanol, and drying to obtain poly-3, 4, 9, 10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide, and the mass ratio of 3, 4, 9, 10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide to ferric trichloride is 1: (2-3). Detection on a lithium ion battery or a sodium ion battery assembled by the battery material shows that compared with an unpolymerized perylene tetracarboxylic diimide positive electrode material, the polyperylene tetracarboxylic diimide positive electrode material disclosed by the invention shows better thermal stability and more excellent cycling stability and rate capability.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Perylene tetracarboxylic dianiline conjugated polymer and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102146151BStrong absorbanceWide absorption rangeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic solar cellImide
The invention relates to a perylene tetracarboxylic dianiline conjugated polymer which has high solubility and high film forming processing performance and can effectively utilize sunlight and a preparation method and application thereof. The perylene tetracarboxylic dianiline conjugated polymer utilizes high carrier mobility of thiophene [3,2-b] bithiophene and has the advantage of solution processibility. The thiophene [3,2-b] bithiophene is copolymerized with a narrow-band system monomer diazosulfide unit and perylene tetracarboxylic dianiline so as to regulate a band gap of the polymer. An absorption edge of the perylene tetracarboxylic dianiline conjugated polymer is pushed to an infrared and near-infrared region. Decorated perylene tetracarboxylic dianiline have high solubility, strong absorbance and wide adsorption range and can be extended to the near-infrared region. The sunlight utilization rate of the perylene tetracarboxylic dianiline conjugated polymer is improved. The perylene tetracarboxylic dianiline conjugated polymer has excellent charge transfer performance and has wide application prospect in the fields of an organic solar cell and the like.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +1
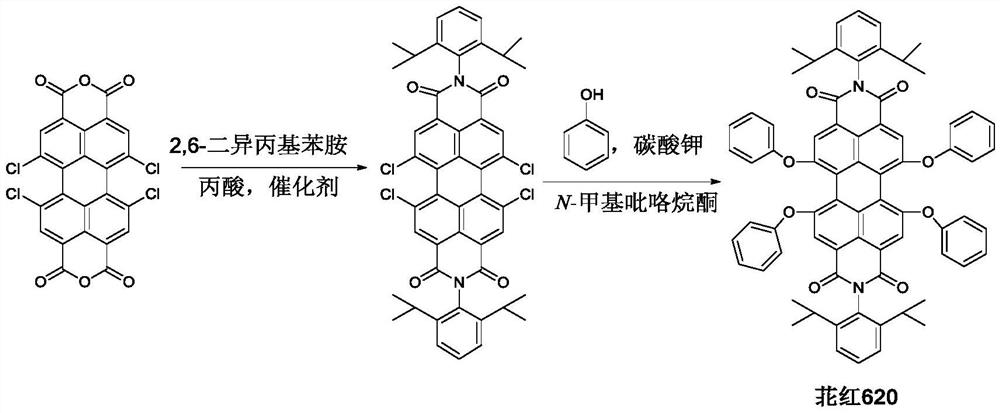
A kind of synthetic method of perylene red dye perylene red 620
ActiveCN109096790BReduce the synthesis reaction temperatureHigh purityAnthracene dyesLuminescent compositionsImidePtru catalyst
The invention discloses a synthetic method of perylene red 620 as perylene red dye. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1,6,7,12-tetrachloro-3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylicdianhydride is taken as a raw material and subjected to a reaction with 2,6-diisopropylanilineby catalysis of a catalyst under protection of inert gas, and the intermediate N,N'-bis(2,6-diisopropyl)phenyl-1,6,7,12-tetrachloro-3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide is obtained; the intermediate is subjected to a reaction with phenol, and a crude perylene red 620 product is obtained; the crude product is washed and subjected to other processing, and perylene red 620 with higher purity is obtained. After introduction of the catalyst, synthetic reaction temperature of the intermediate is reduced, and reaction time is shortened by 2 / 3; the original column chromatographic process is replaced with a cooling, standing and suction filtration method, and accordingly, purity of the intermediate isimproved; the method has the characteristics of safe and reasonable process, simple processing steps, high yield, low cost, high product purity and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fluorescent ion probe and its application in ion detecting
InactiveCN101153848BEasy to synthesizeSimple structureChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceLuminescent compositionsBenzoxazoleFluorophore
The invention relates to a fluorescent ion probe (I) with high selectivity and high sensitivity in detection and the application of the fluorescent ion probe in identifying and detecting heavy metal ion and transition metal ion, wherein, the Y is an organic conjugate group with fluorescence transmitting function such as pyrene, naphthalene, 4-amidogen-1, 8-naphthyl imide, Dan sulfonamide, anthracene, carbazole, benzimidazoins, benzoxazoles, boron fluoride bipyrrole (BODIPY), fluorescein, 3, 4, 9, 10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide or rhodamine B; the X is acylamino group, sulfoamino group orester group. The fluorescent ion probe uses the fluorescence peak of fluorescence chromophore aggregate as the response signal to identify metal ion, thereby effectively avoiding the quenching effectof transition metal ion and heavy metal ion on fluorophore; moreover, the fluorescent ion probe realizes selective identification of heavy metal ion and transition metal ion in various solvents and aqueous solution in particular.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com