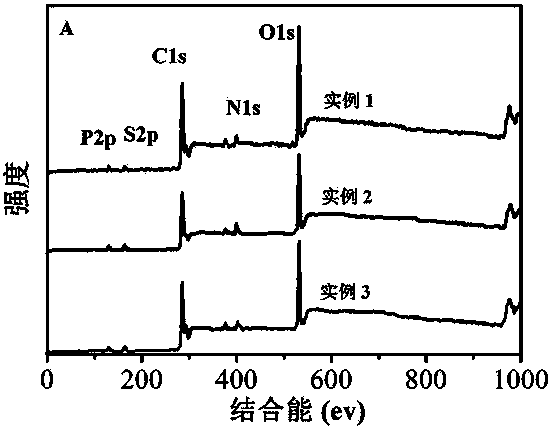
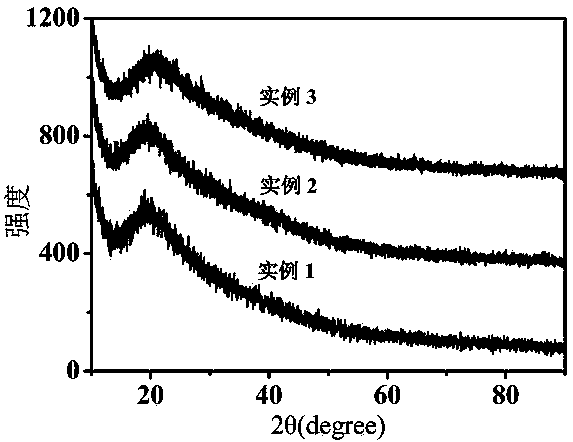
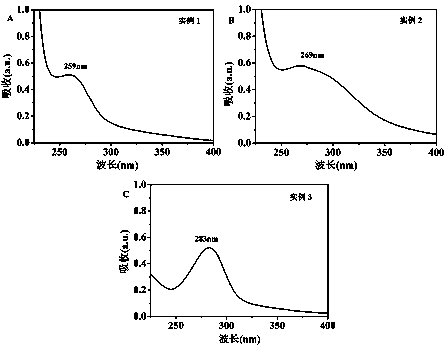
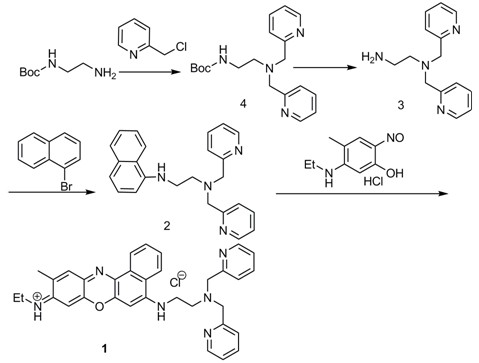
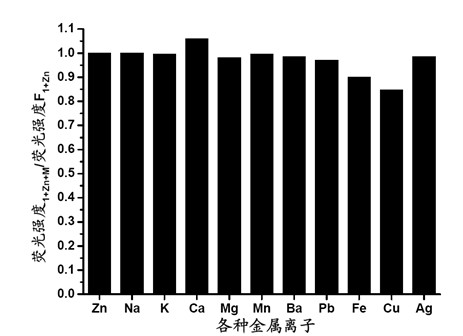
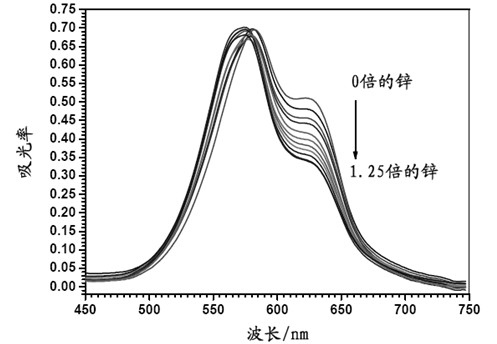
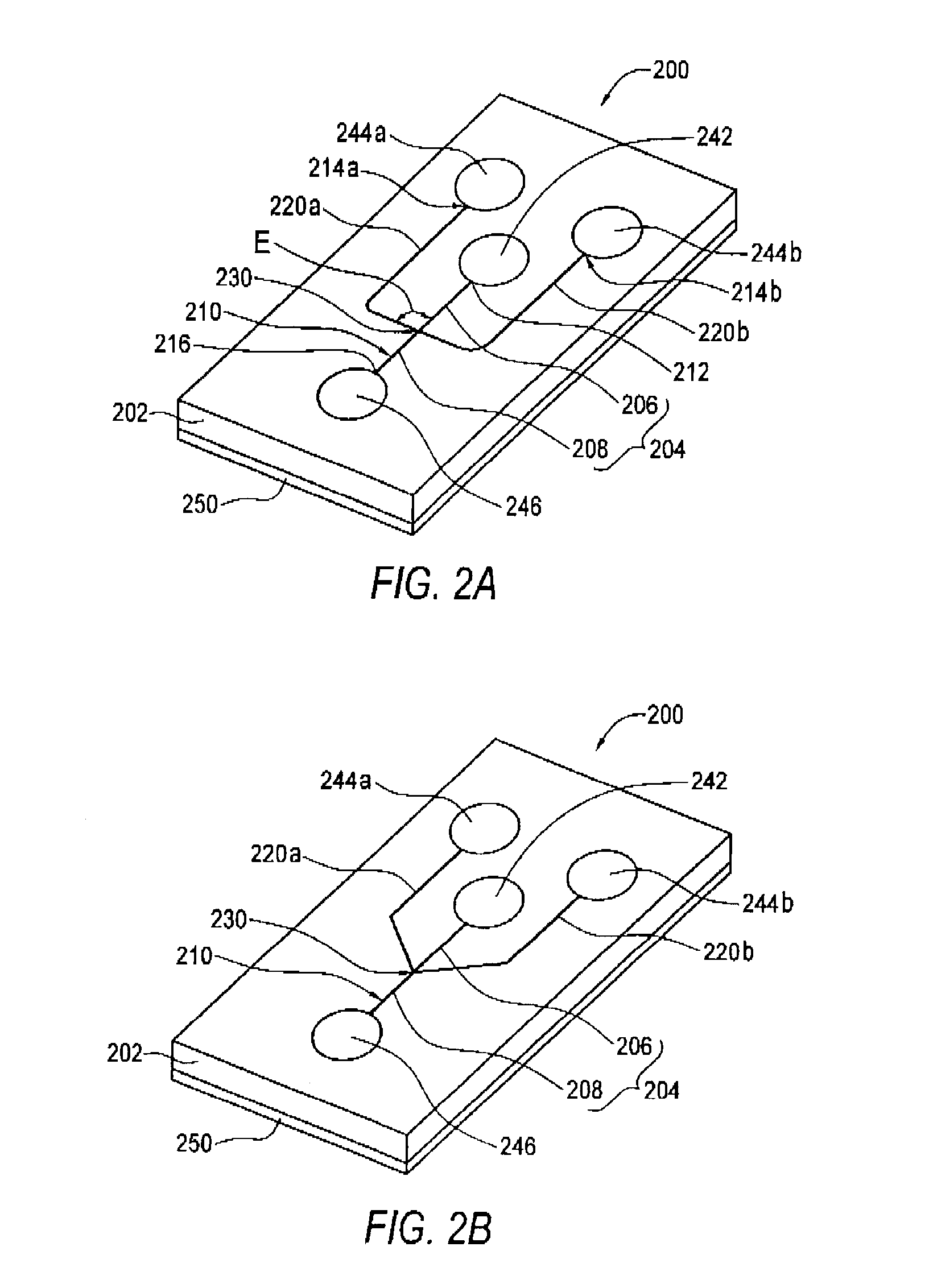
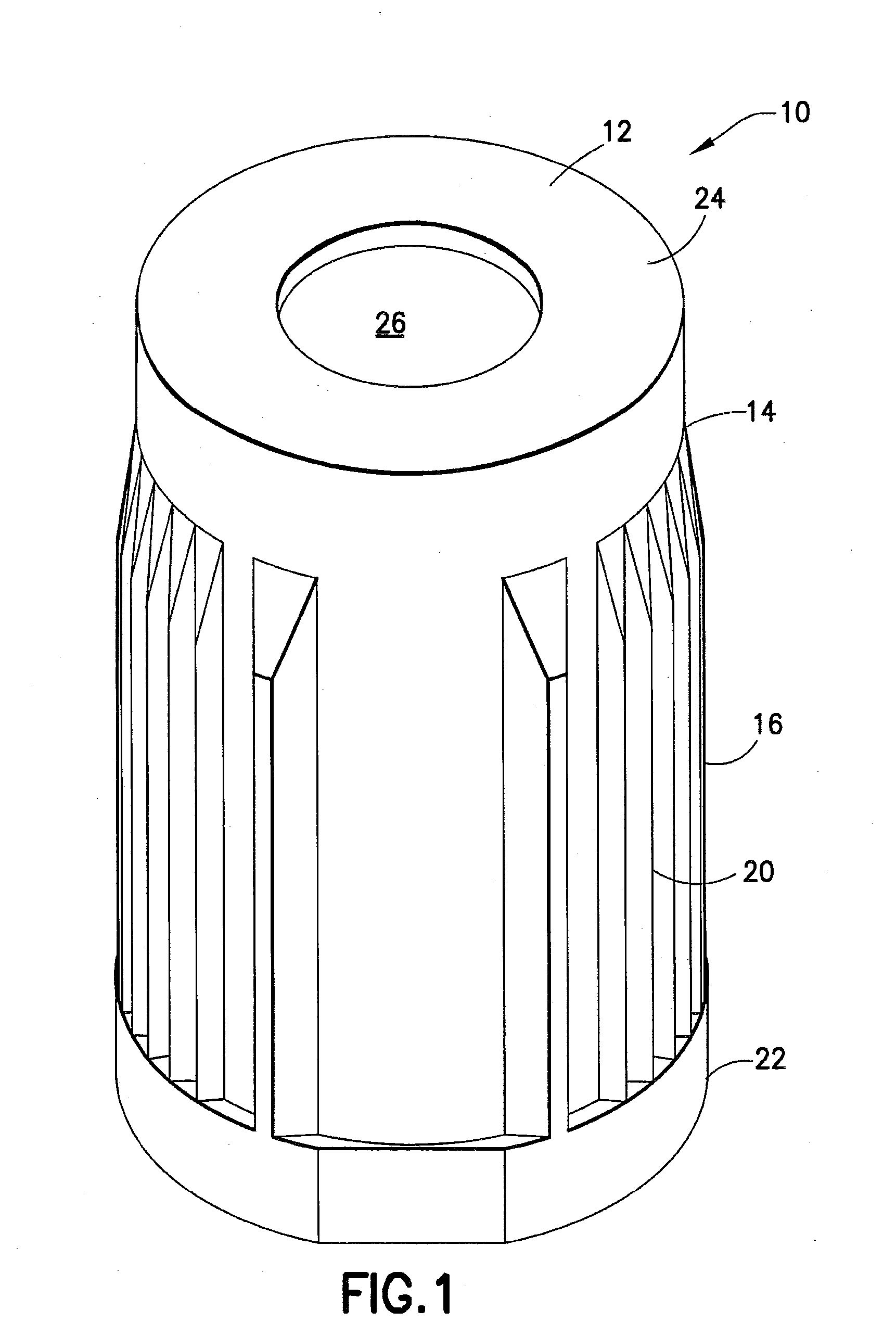
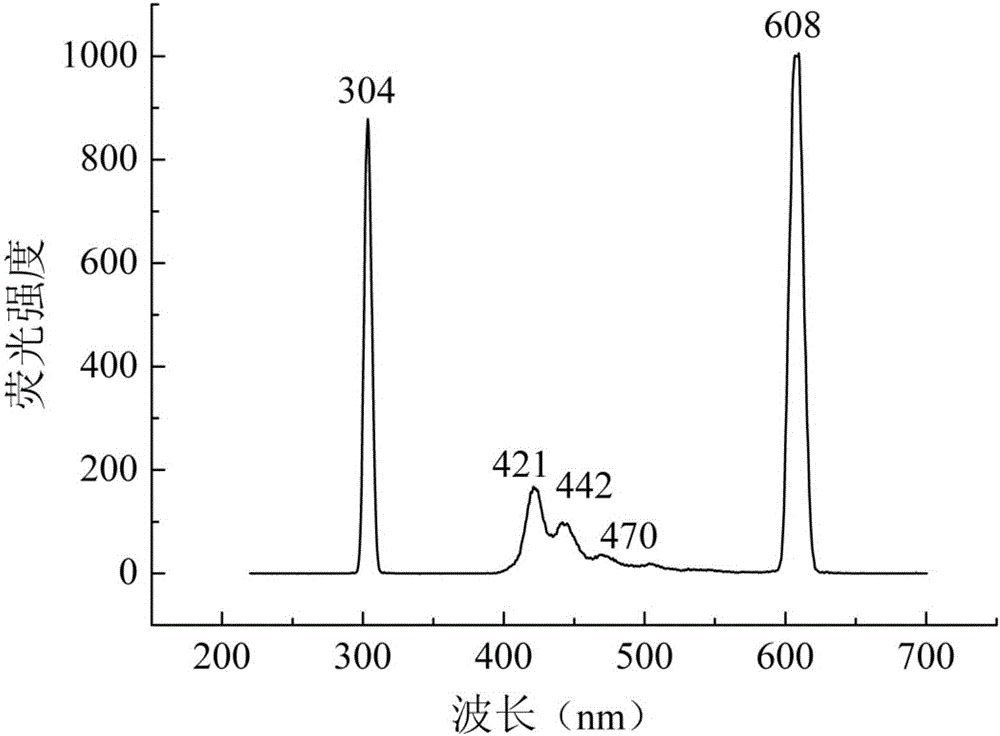
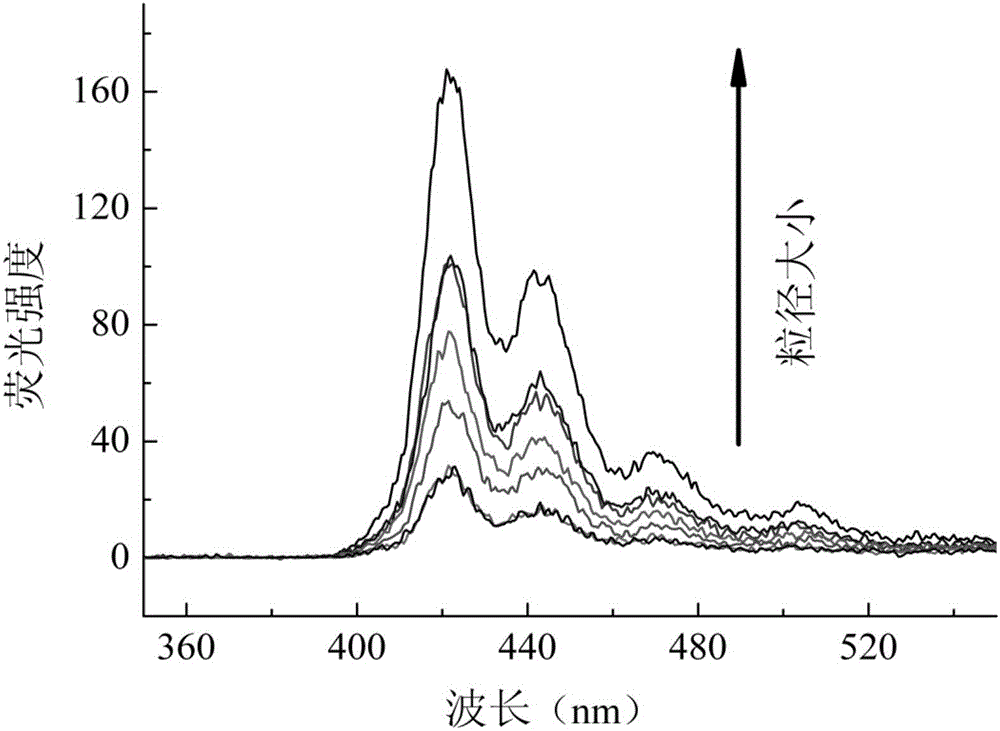
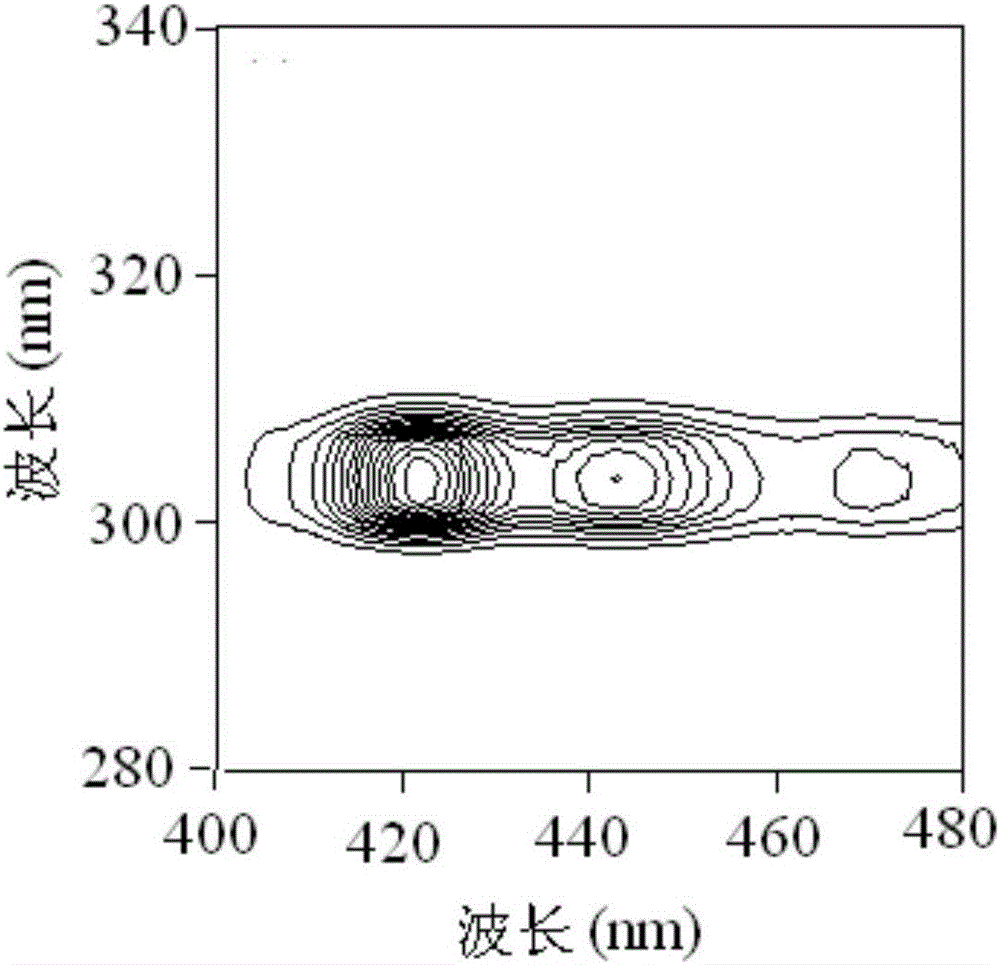
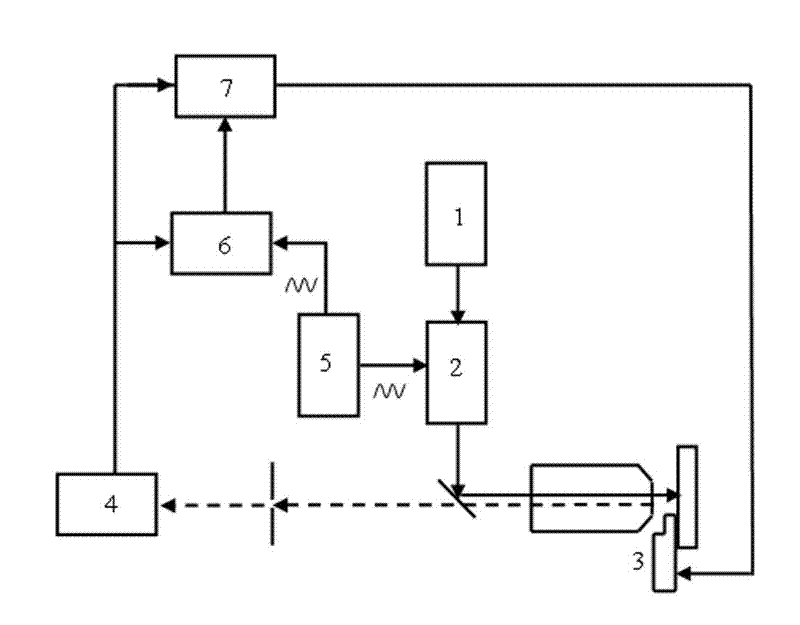
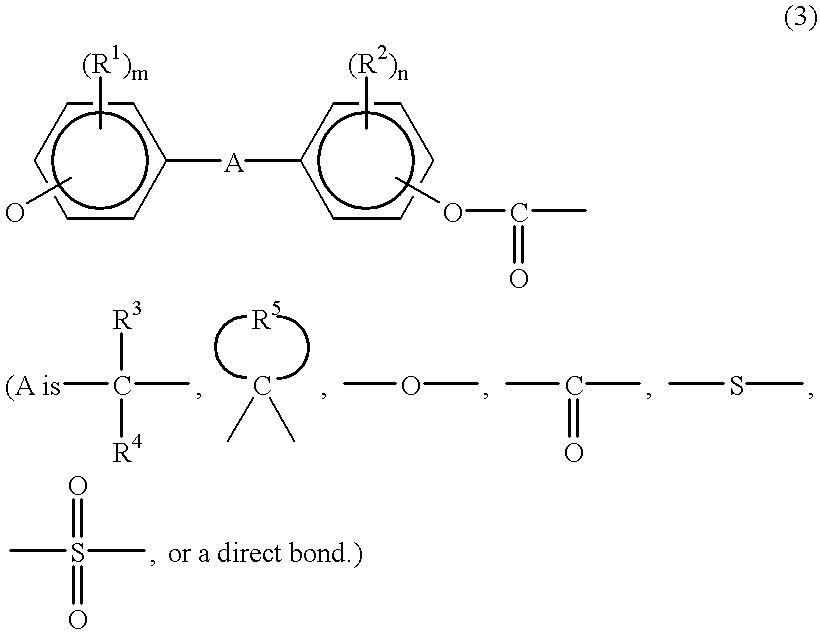Patents
Literature
156 results about "Fluorescent spectra" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
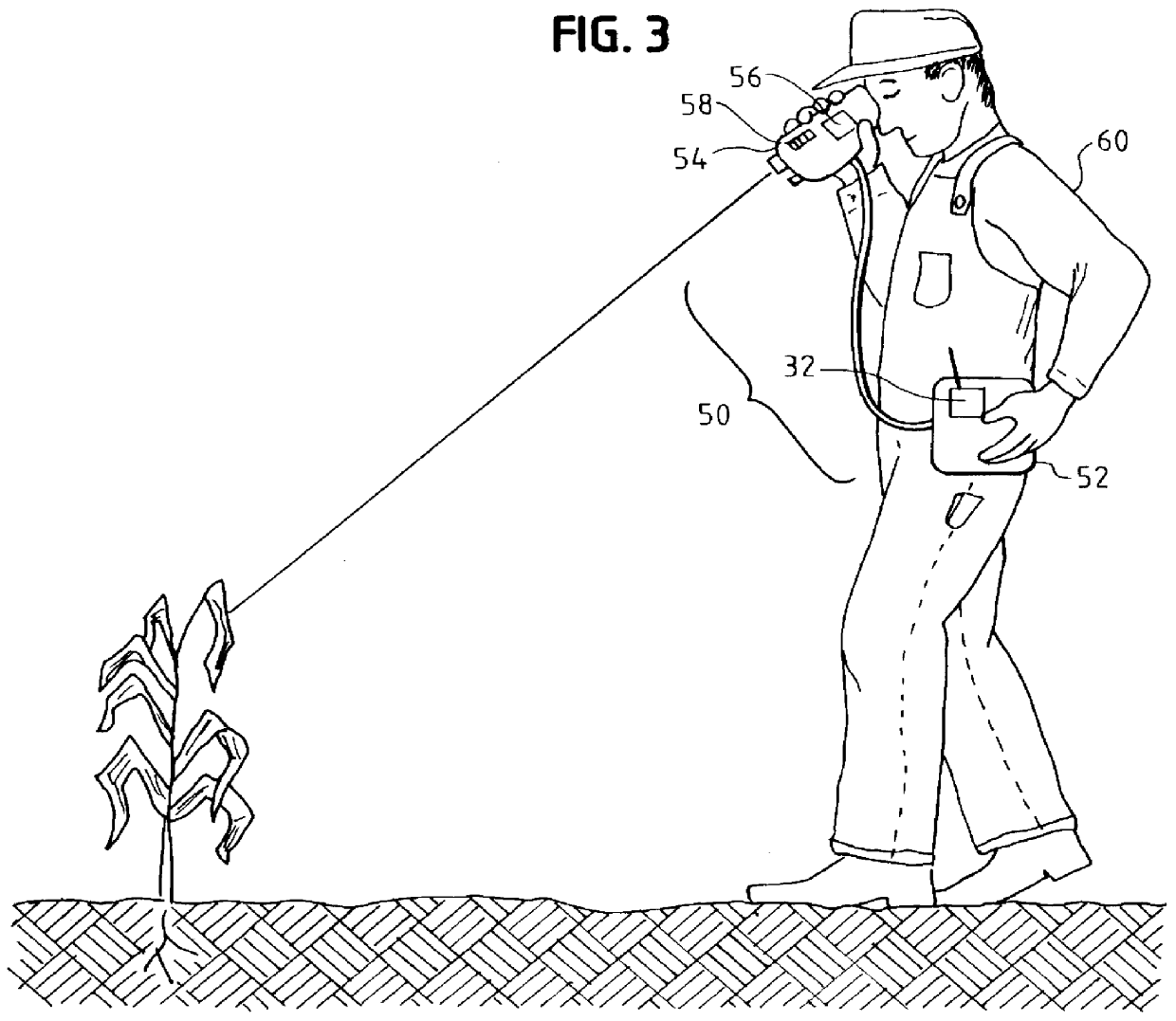
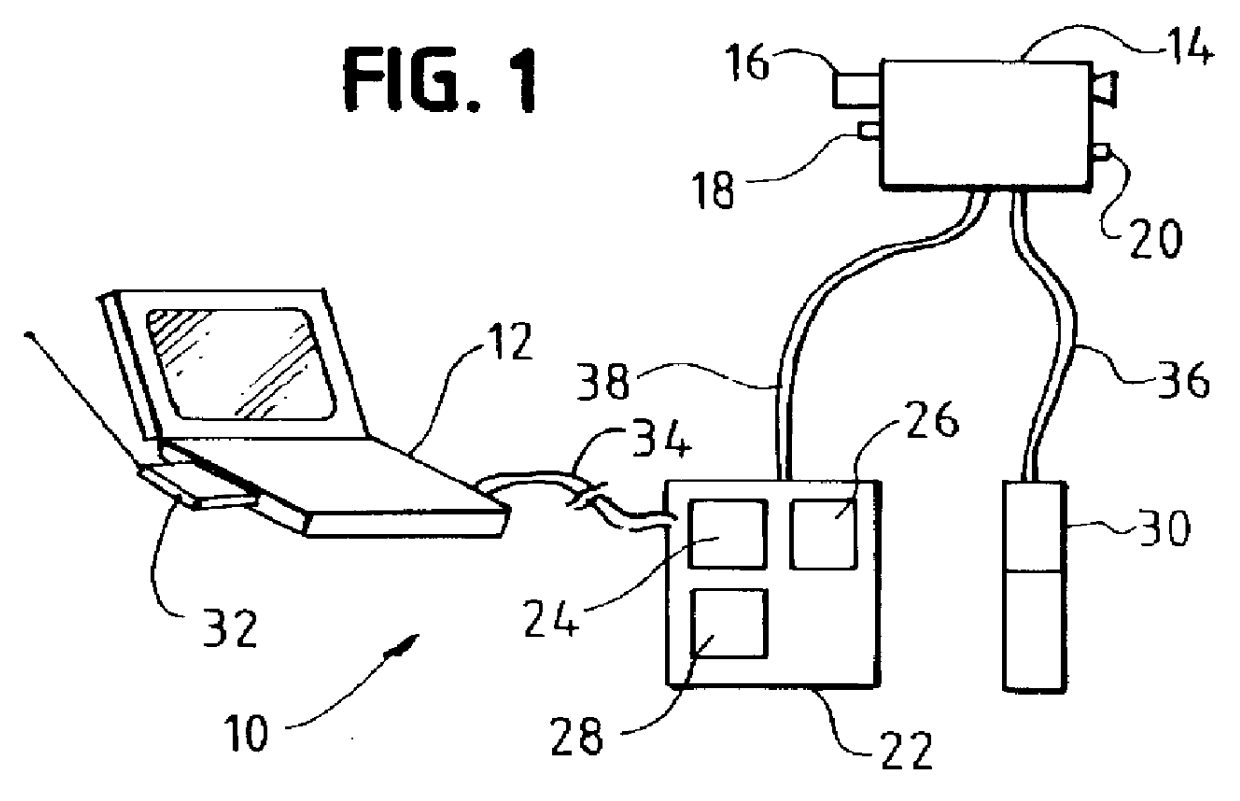
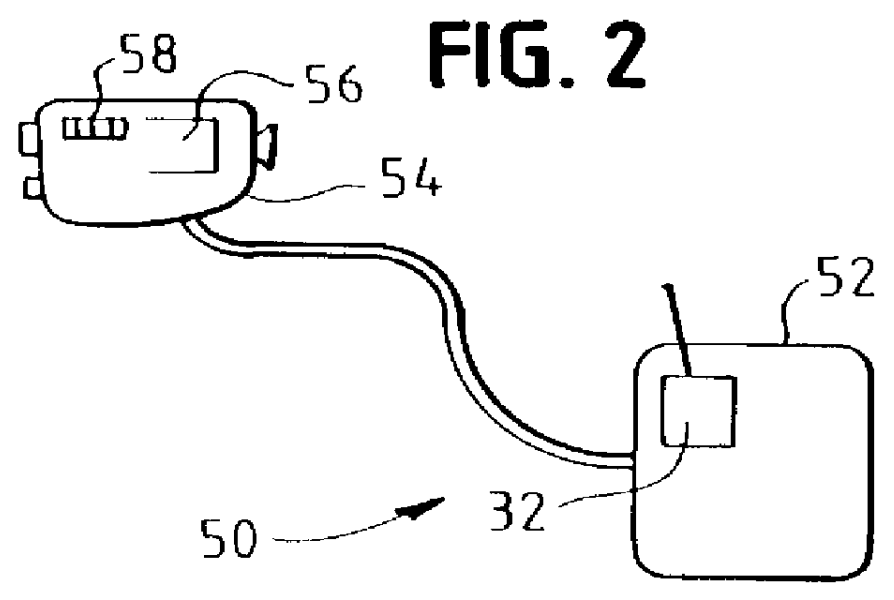
Hyperspectral polarization profiler for remote sensing
InactiveUS6052187AMinimize healthMinimize problemsRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyFluorescenceLarge range
A device to provide hyperspectral reflection spectrum, hyperspectral depolarization, and hyperspectral fluorescence spectrum data in a portable, remote sensing instrument. The device can provide a large range of remotely-sensed optical property data, presently only obtainable in laboratories, in a low-cost field instrument. Among its many uses, the present invention can be used by farmers as a tool for determining the nitrogen content of crops to optimize fertilizer laydown.
Owner:CONTAINERLESS RES
Stabilized aromatic polycarbonate
The relative intensity of fluorescent light of a melt-polycondensed aromatic polycarbonate produced by the transesterification process (melt polymerization process) of an aromatic dihydroxy compound and a carbonic acid diester in the presence of a catalyst comprising a basic nitrogen compound and / or a basic phosphorus compound in combination with an alkali metal compound is suppressed to 4.0x10-3 or below at a wavelength of 465 nm based on a standard substance in a fluorescent light spectrum obtained by the excitation wavelength of 320 nm. An aromatic polycarbonate having good color stability, especially good stability to the deterioration of the chip color during storage of the chip in air at room temperature can be produced by the present invention.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
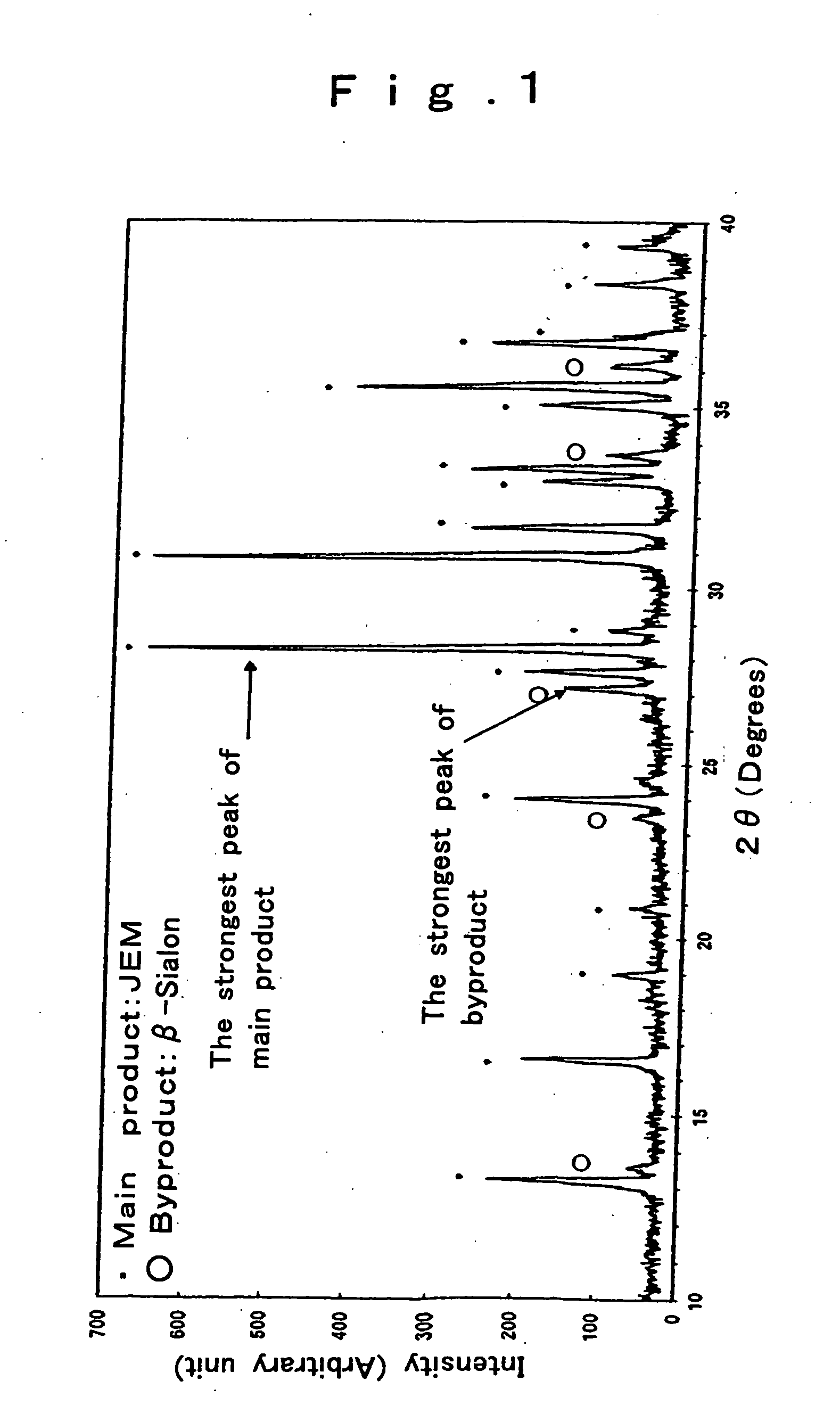
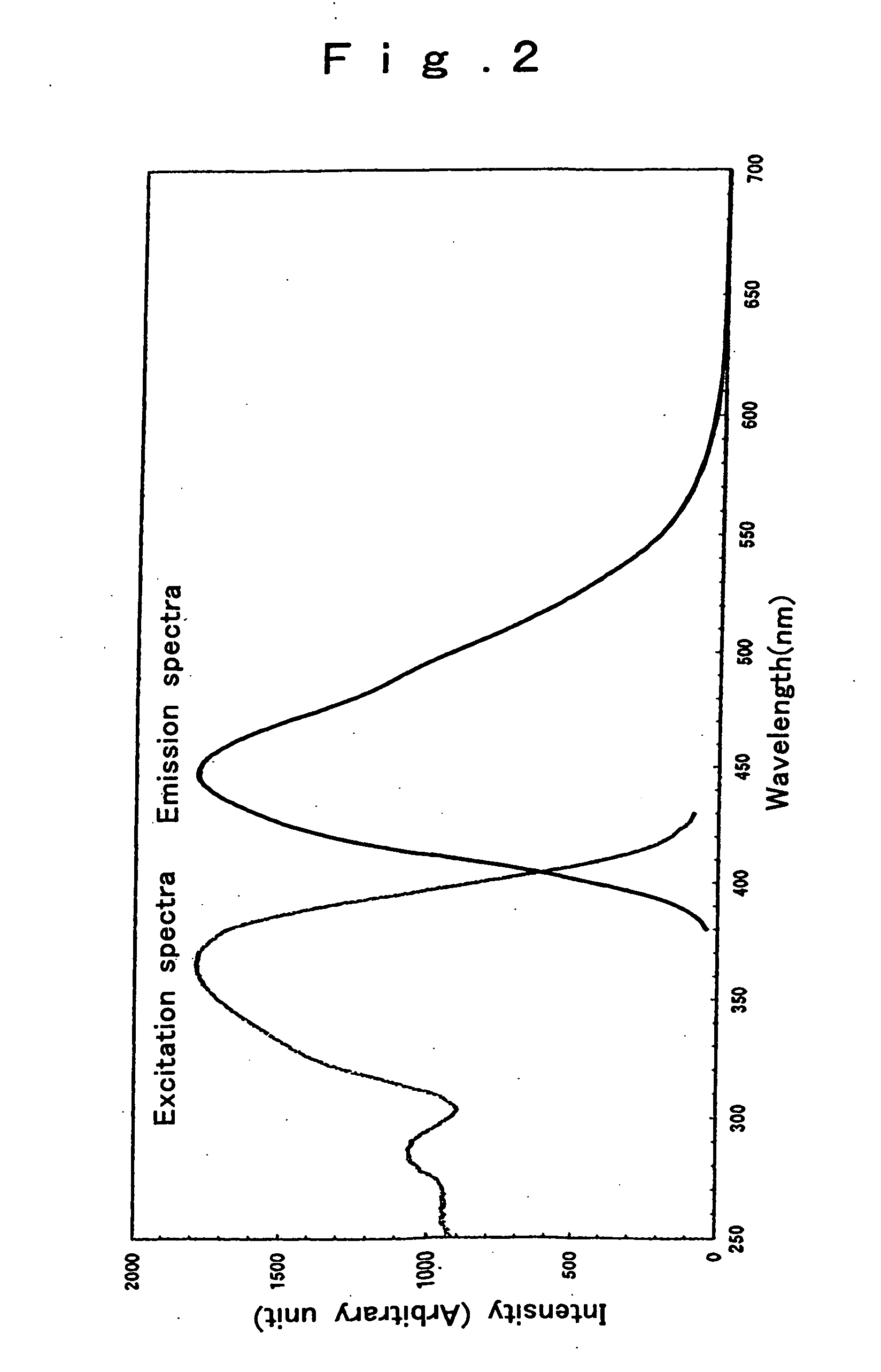
Oxynitride phosphor and light-emitting instrument
InactiveUS20070018567A1Increase brightnessReduced in material deterioration and luminance dropAddress electrodesSustain/scan electrodesRare-earth elementPhosphor
The invention has for its object the provision of an oxynitride fluorescent material has higher emission luminance than conventional rare earth element-activated sialon fluorescent materials. To this end, an oxynitride fluorescent material is designed in such a way as to contain as the primary constituent a JEM phase represented by a general formula MA1(Si6−zAlz)N10−zOz wherein M is one or two or more elements selected from the group consisting of La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb and Lu. For instance, this fluorescent material has a fluorescent spectrum maximum emission wavelength of 420 nm to 500 nm inclusive and an excitation spectrum maximum emission excitation wavelength of 250 nm to 400 nm inclusive.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
Method for separating fluorescence spectra of dyes present in a sample
ActiveUS20050046836A1Raman/scattering spectroscopyLuminescent dosimetersFluorescence spectrometryData acquisition
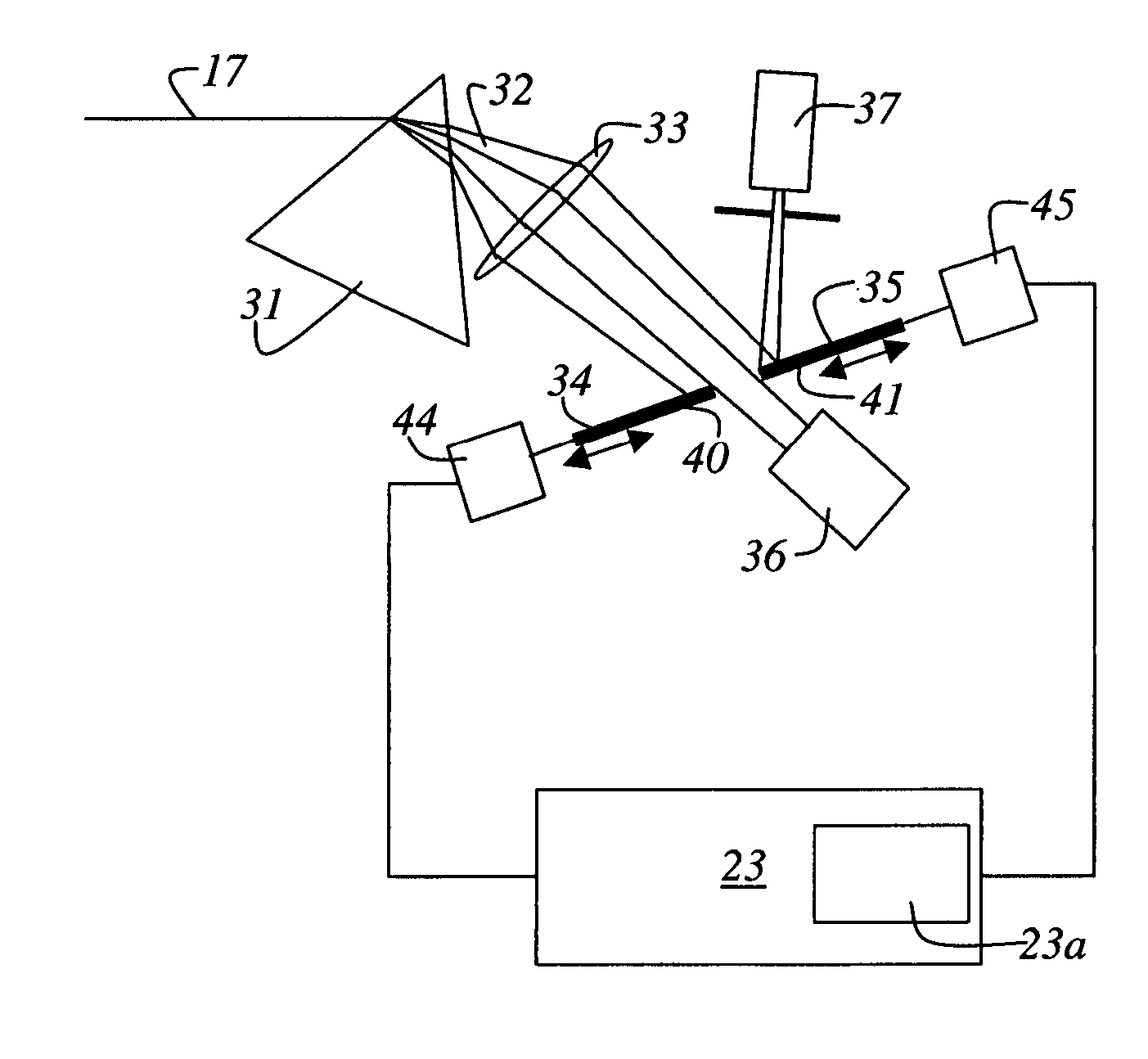
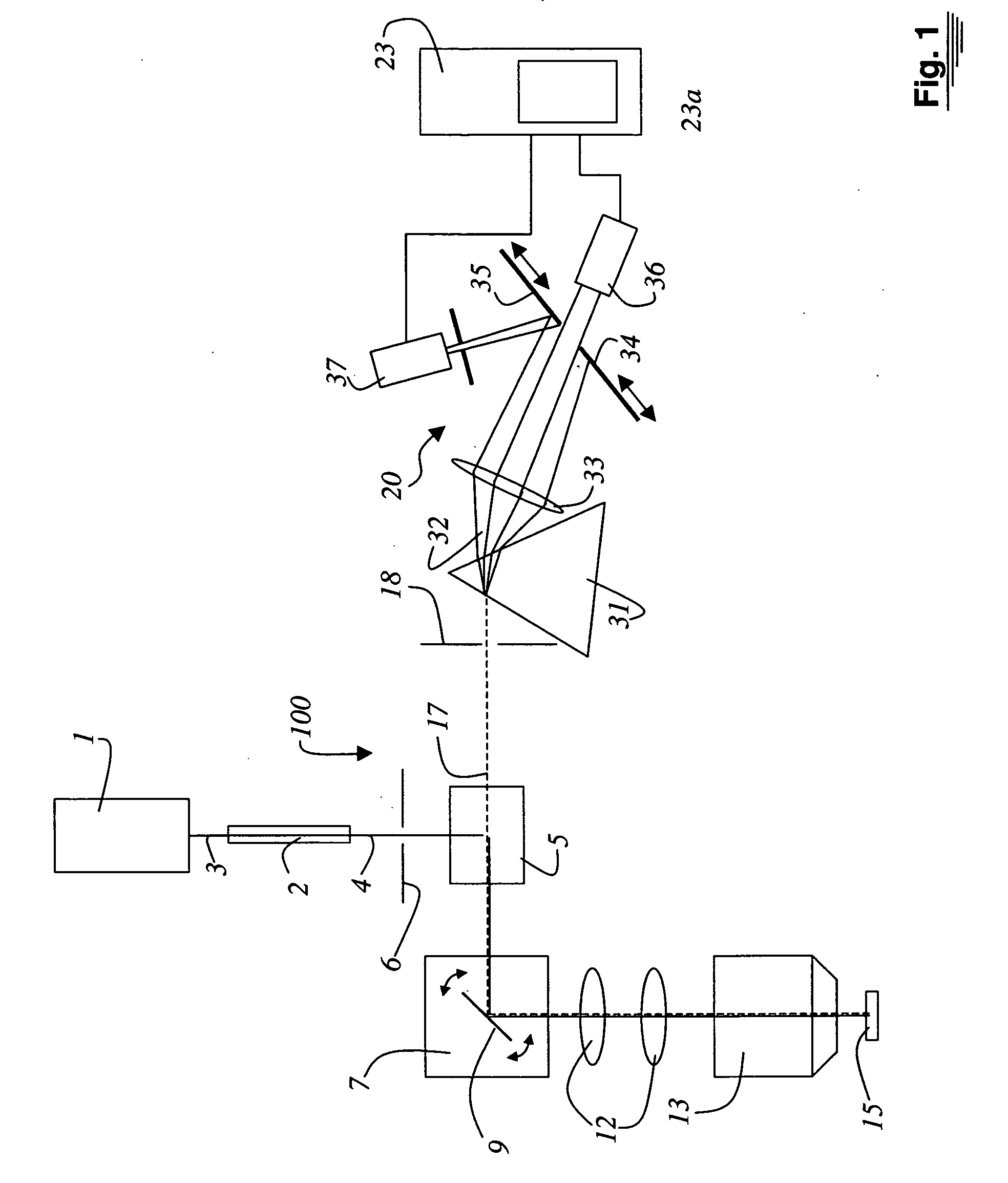
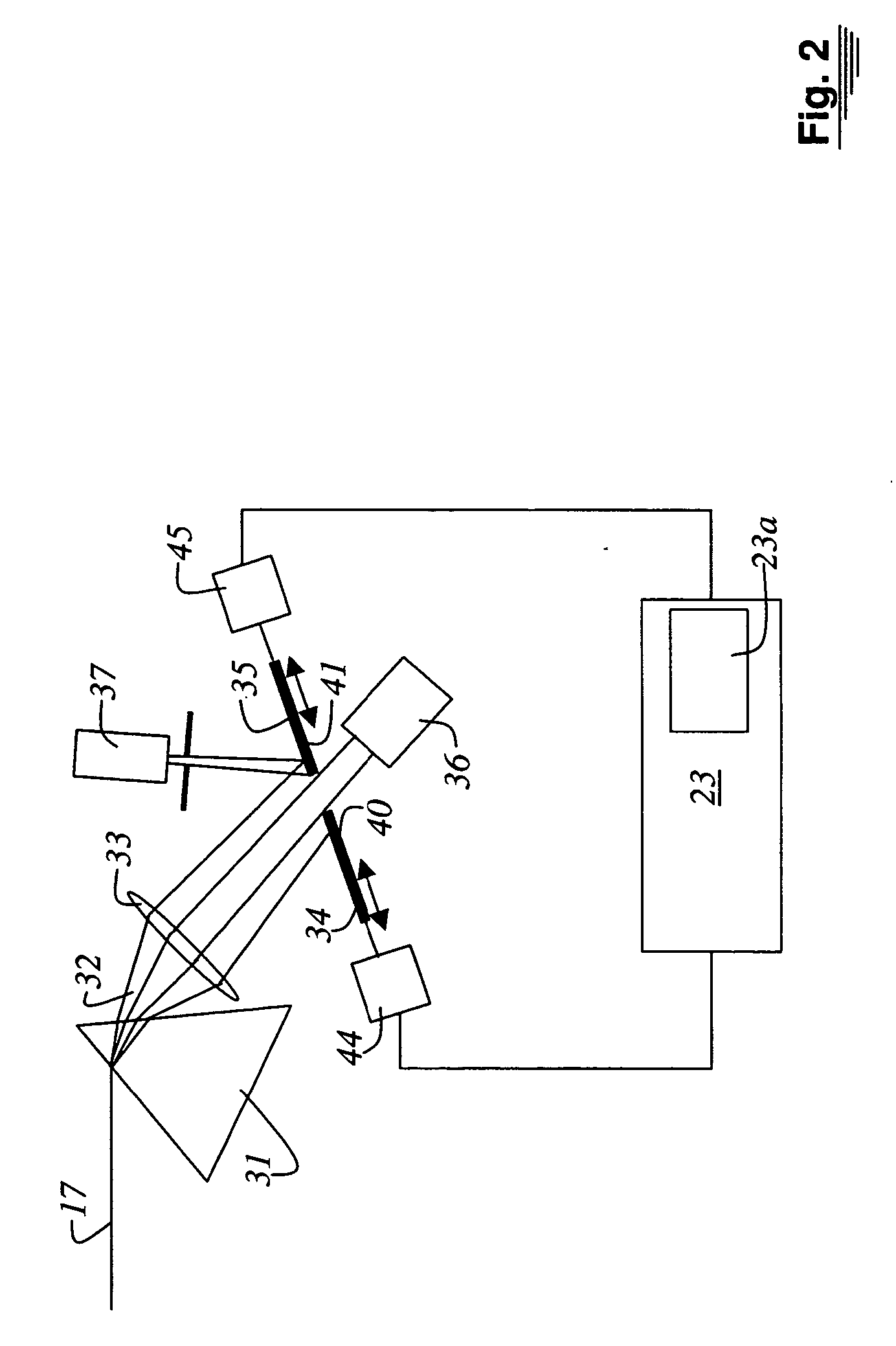
A system and a method for setting a fluorescence spectrum measurement system for microscopy is disclosed. Using illuminating light (3) from at least one laser that emits light of one wavelength, a continuous wavelength region is generated. Dyes are stored, with the pertinent excitation and emission spectra, in a database of a computer system (23). For each dye present in the specimen (15), a band of the illuminating light (3) and a band of the detected light (17) are calculated, the excitation and emission spectra read out from the database being employed. Setting of the calculated band in the illuminating light and in the detected band [sic] is performed on the basis of the calculation. Lastly, data acquisition is accomplished with the spectral microscope (100).
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
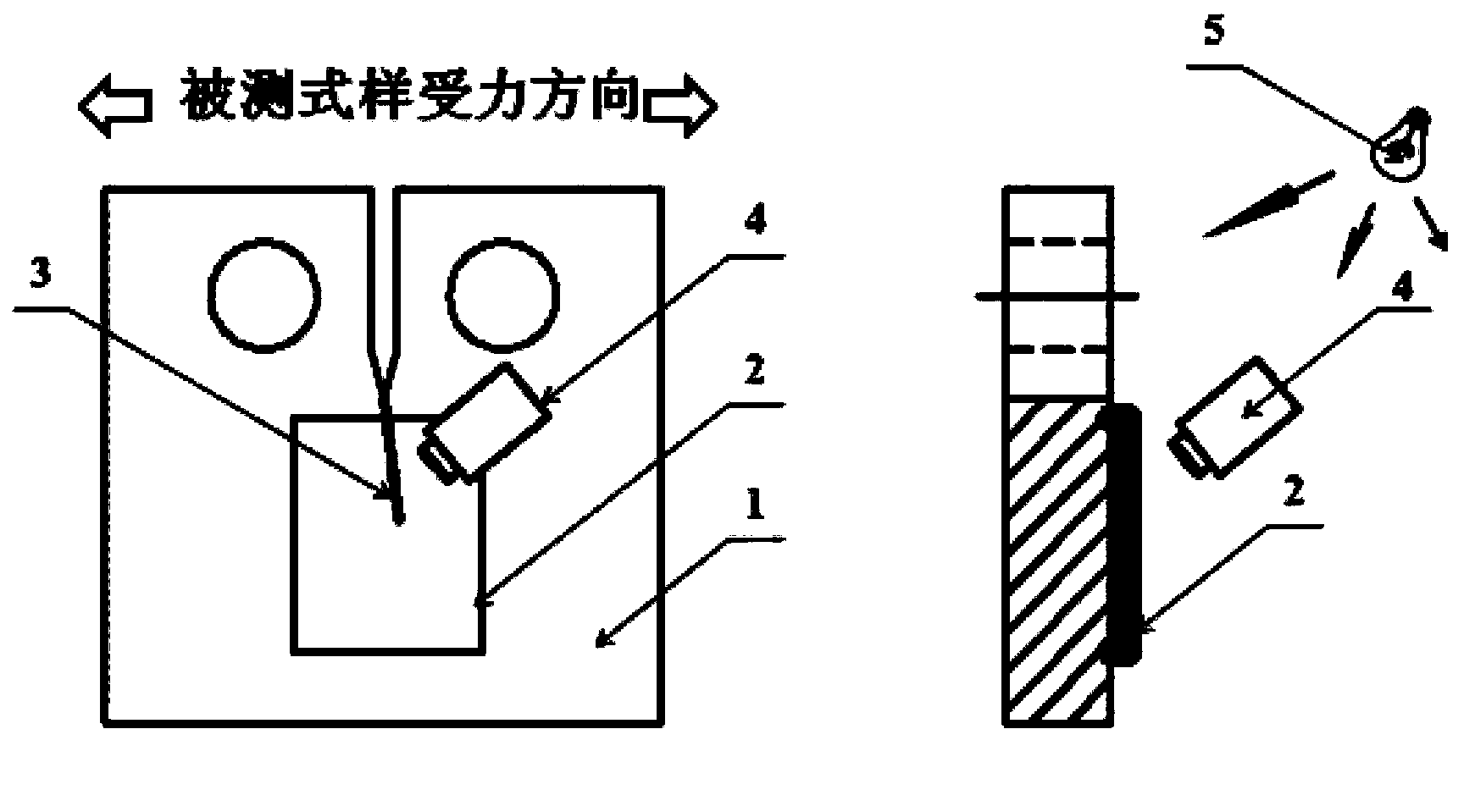
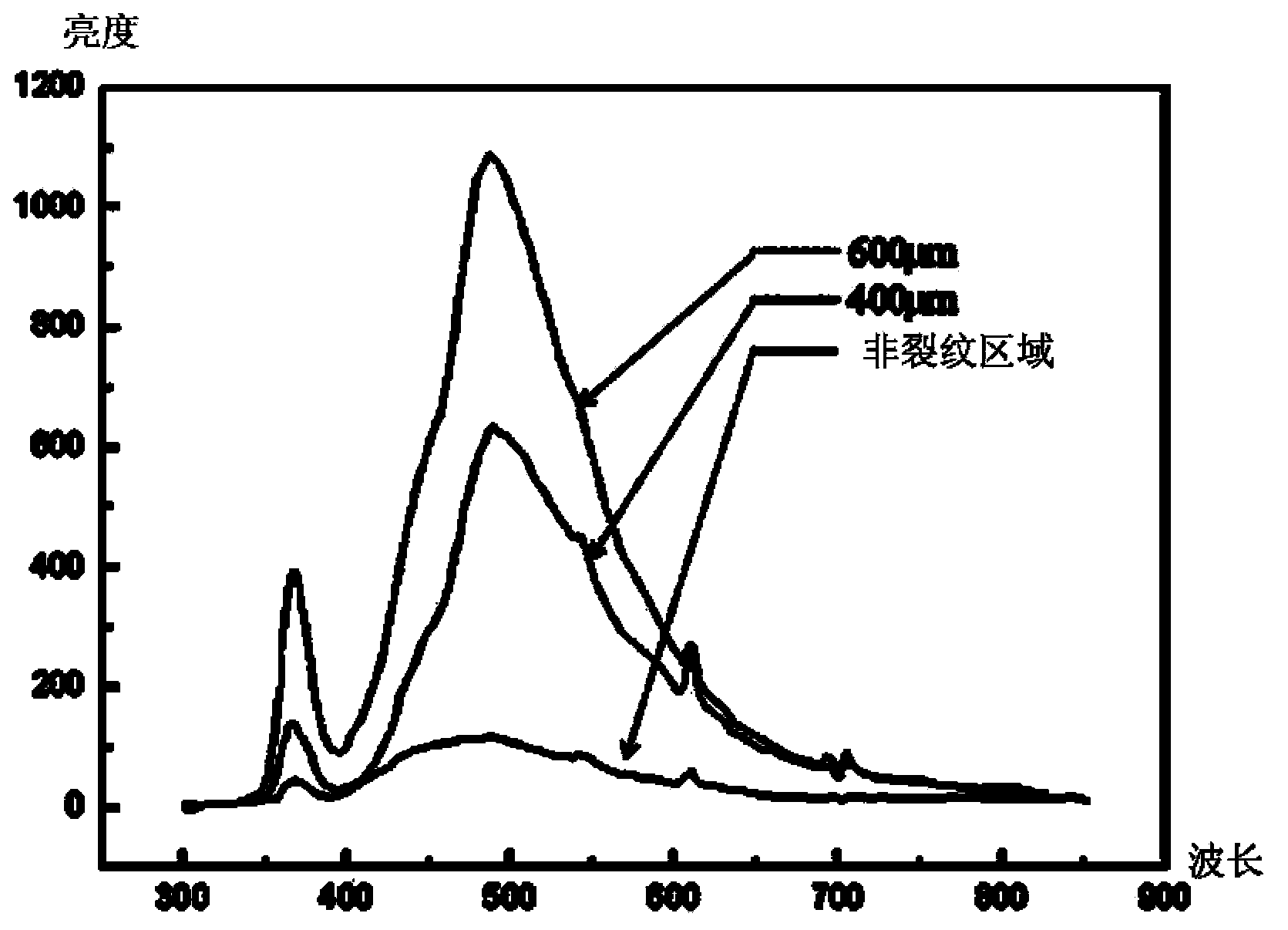
Method for detecting and monitoring cracks of mechanical parts by utilizing fluorescent quantum dots
InactiveCN103901003ACracks are detected in timeSimple methodFluorescence/phosphorescenceQuantum dotFluorescence spectrometry
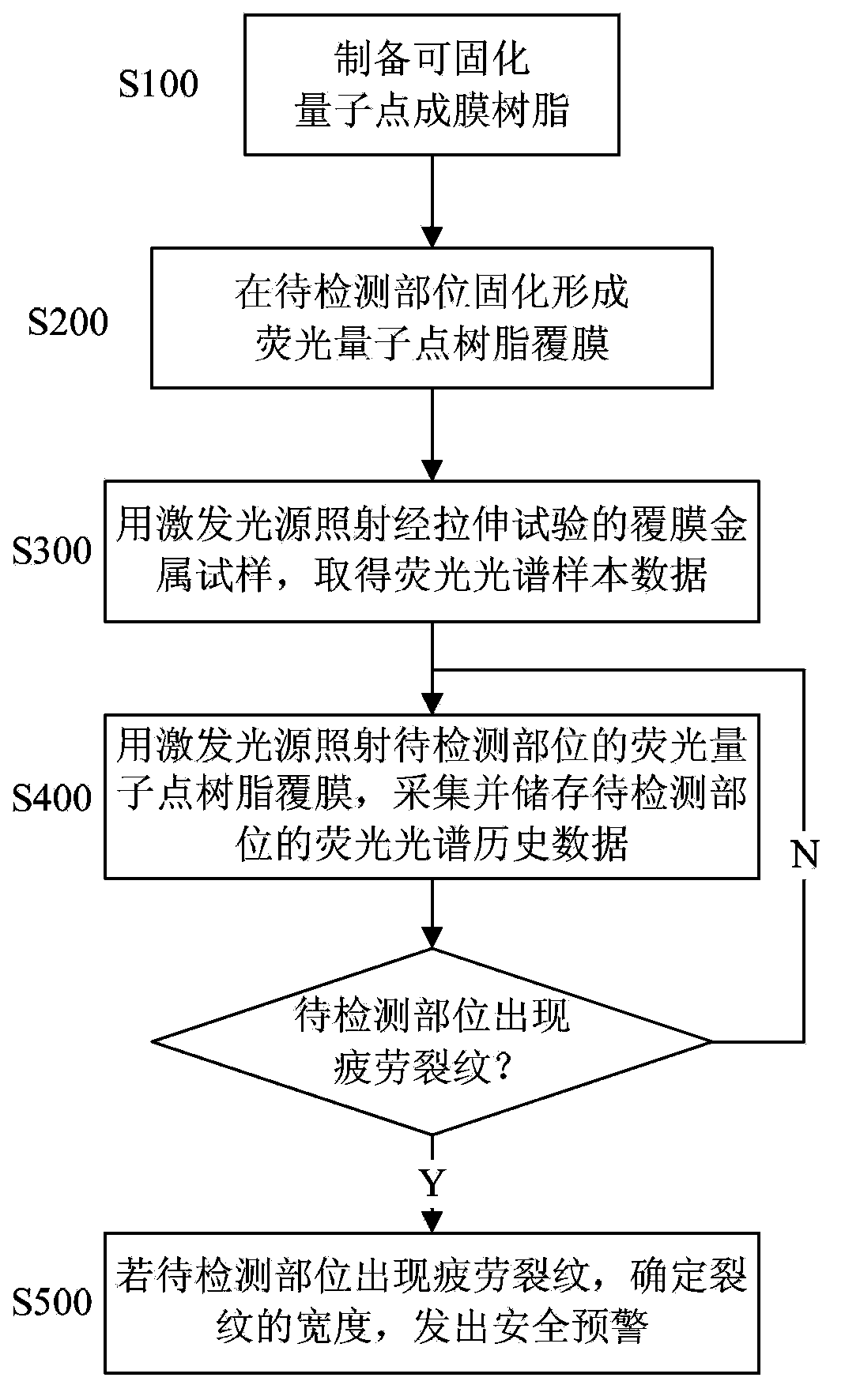
The invention discloses a method for detecting and monitoring cracks of mechanical parts by utilizing fluorescent quantum dots, and relates to material detection and analysis by utilizing optical methods. The method comprises the following steps: preparing solidifiable quantum dot film forming resin; solidifying at a part to be detected to form a fluorescent quantum dot resin coated film; carrying out a tensile test on a metal CT (Compact Tensile) specimen coated with quantum dot resin coated film to obtain fluorescence spectrum sample data; irradiating the fluorescent quantum dot resin coated film at the part to be detected by using an excitation light source, monitoring whether fatigue cracks occur at the part to be detected or not, and collecting and storing fluorescence spectrum historical data; if the fatigue cracks occur at the part to be detected, determining the width of cracks, and sending safety pre-warning. By detecting the quantum dot resin coated film solidified on a monitored mechanical part, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that tiny fatigue cracks on the mechanical part in an early stage can be discovered, the detection precision is high, the cost is low, influence caused by the appearance of a detected component can be avoided, dangerous parts of important mechanical parts can be subjected to real-time safety monitoring, and the application range is wide.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
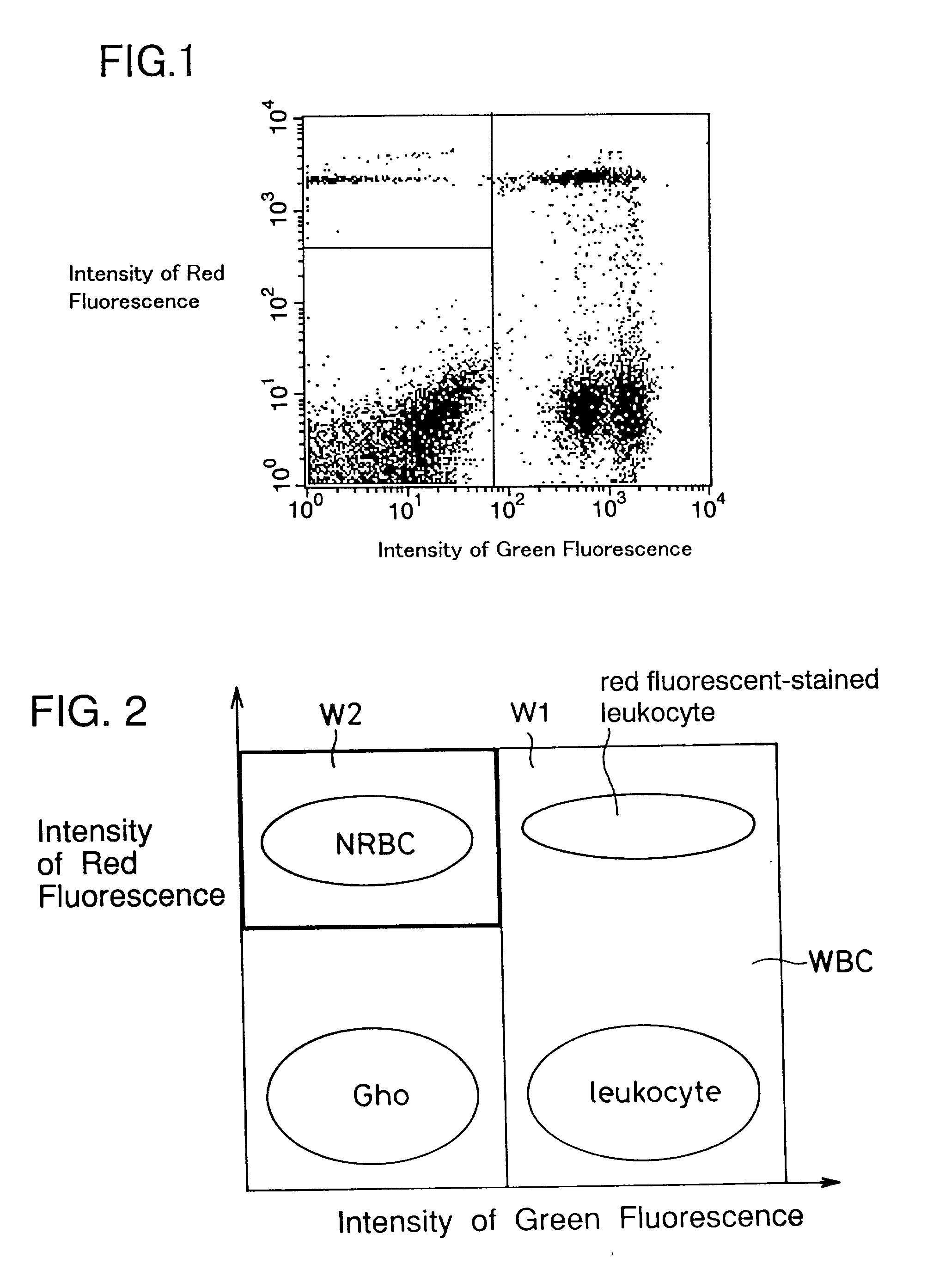
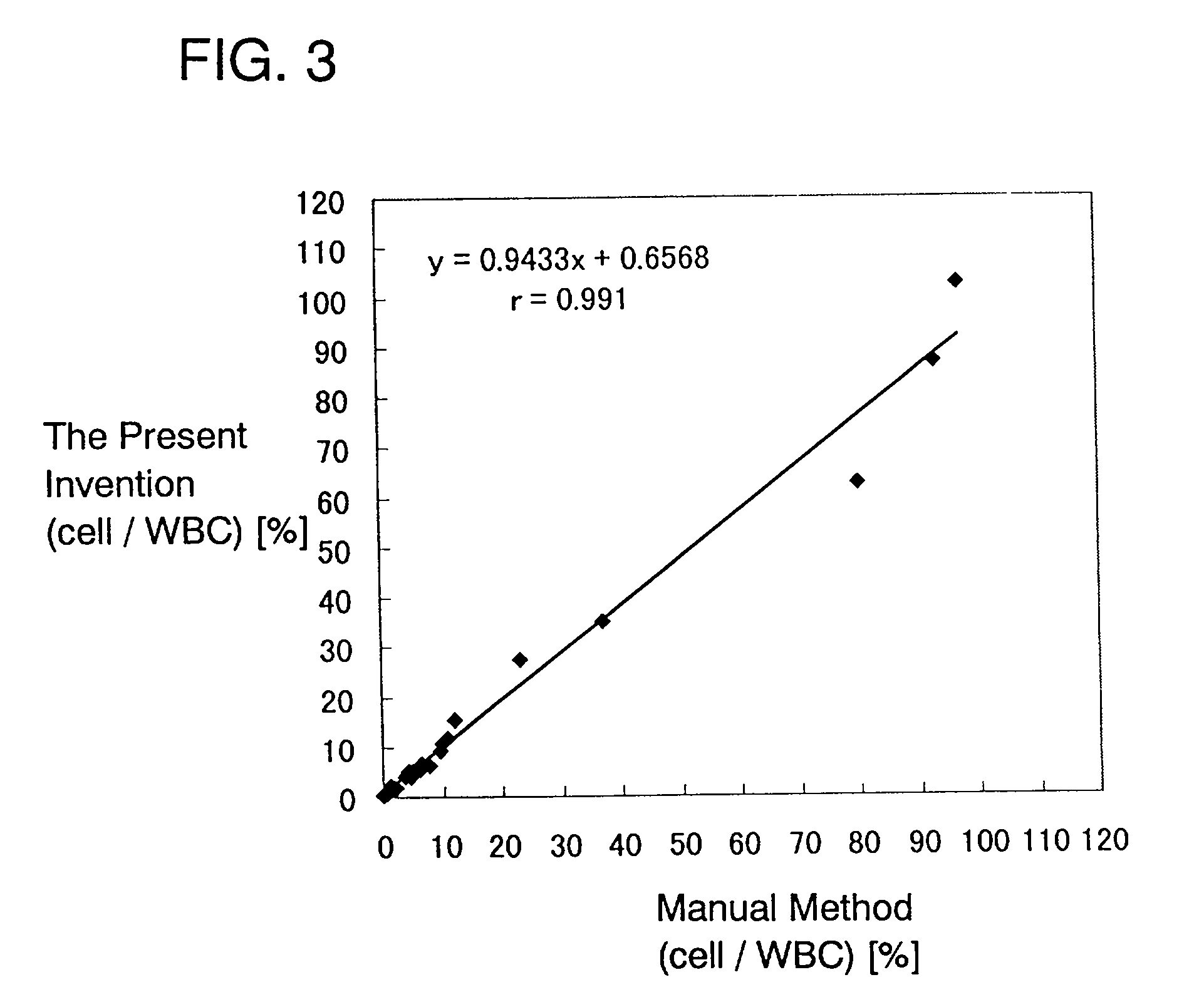
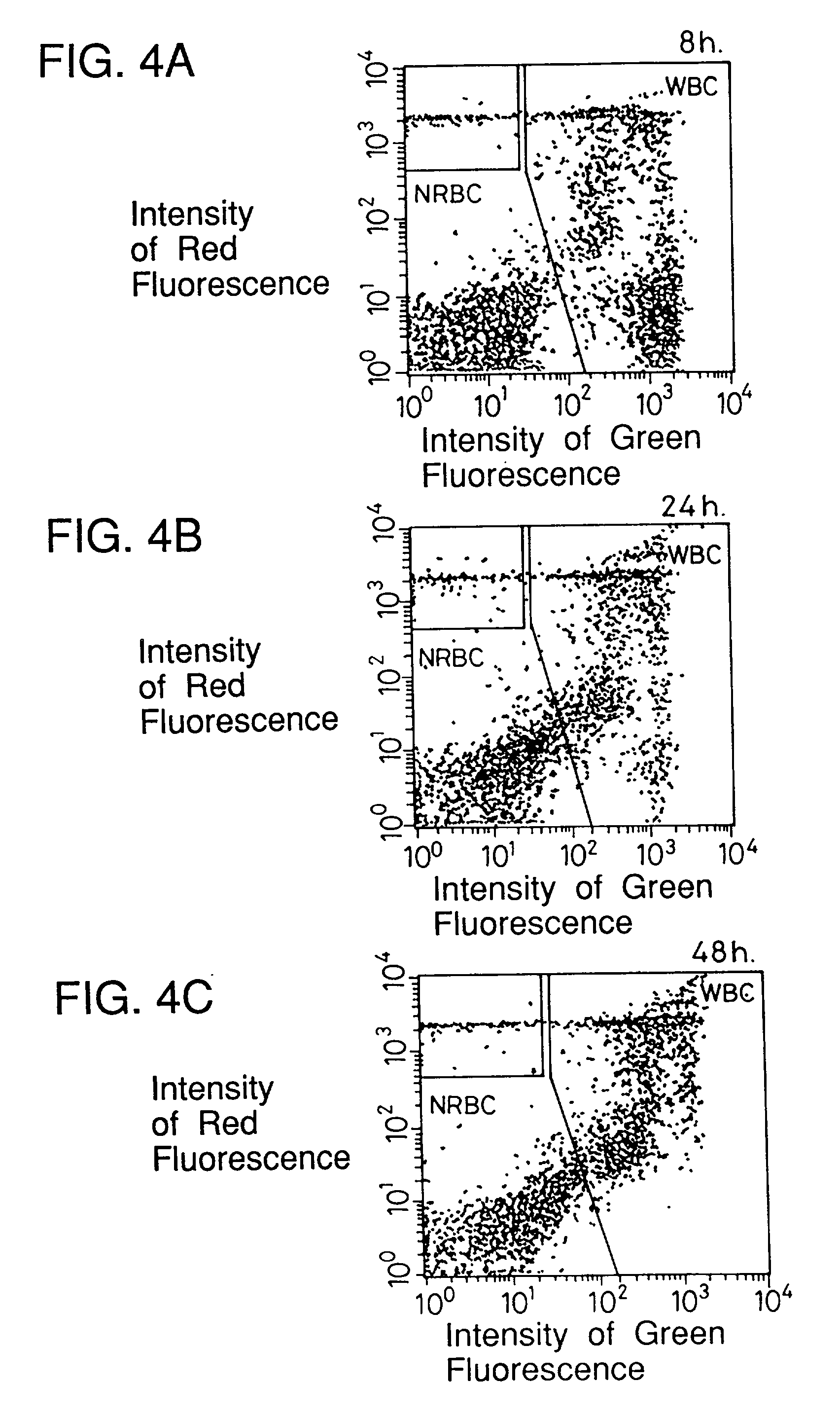
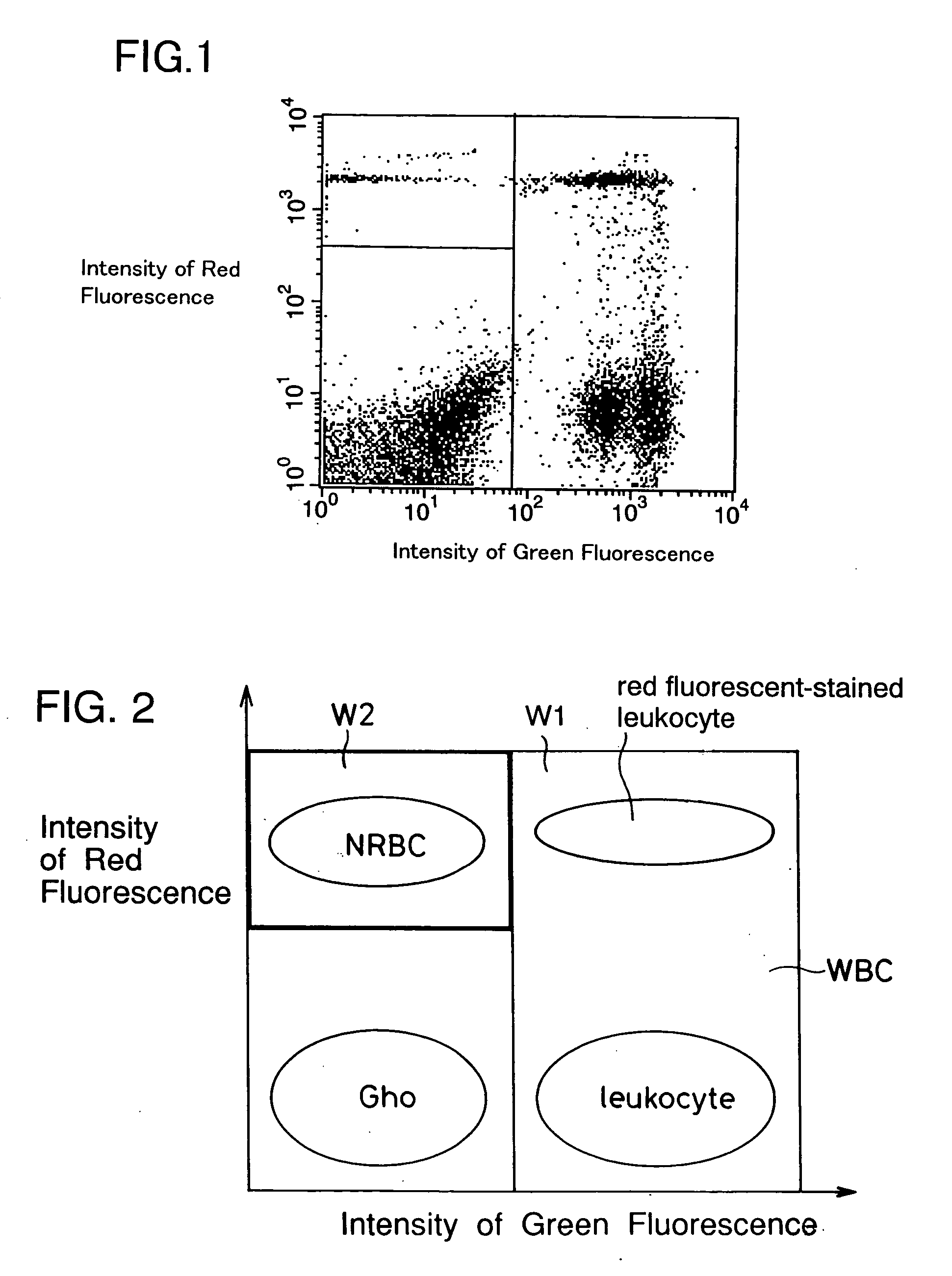
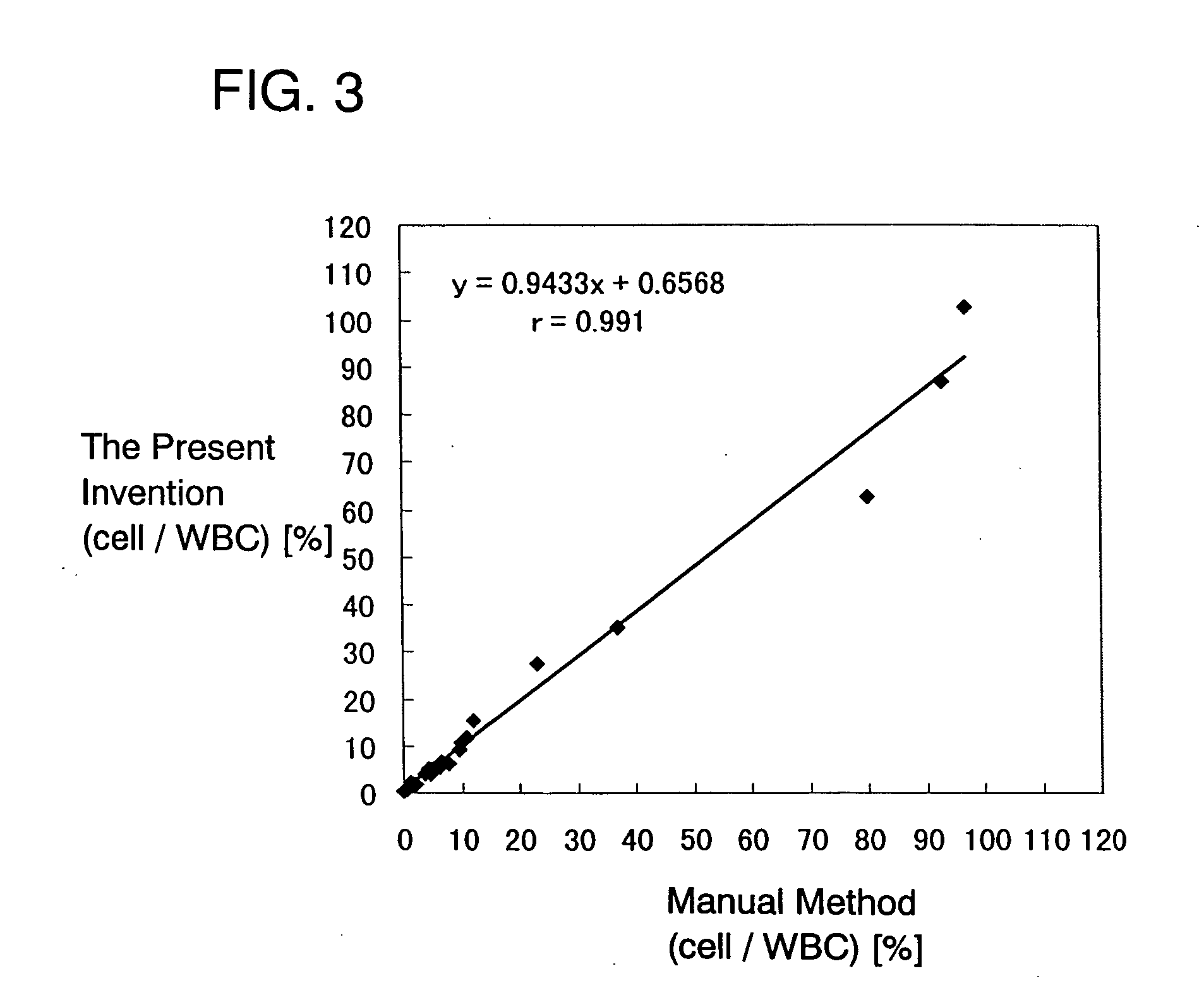
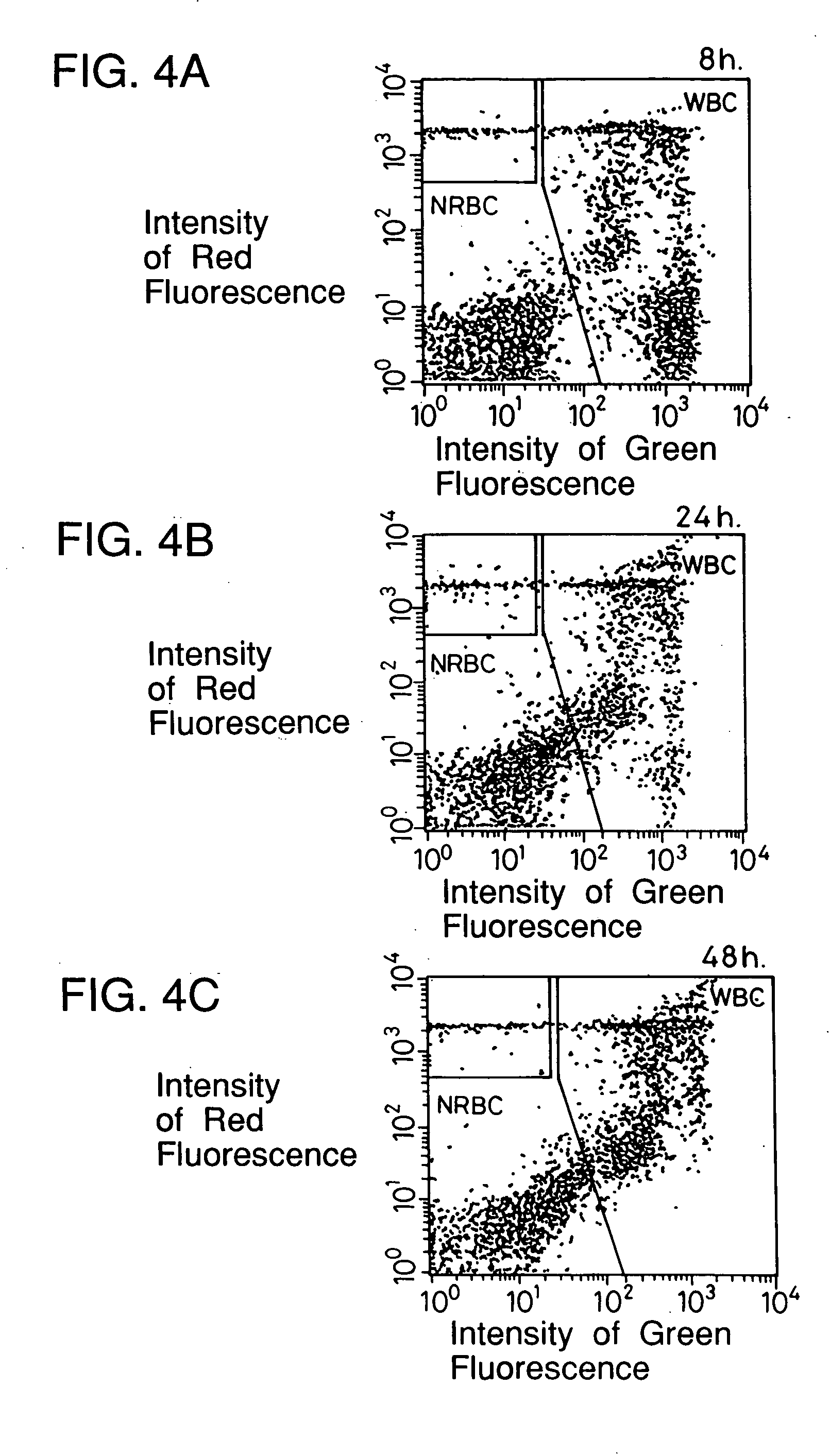
Process for discriminating and counting erythroblasts
InactiveUS20020006631A1Microbiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceRed blood cellWhite blood cell
A method for discriminating and counting erythroblasts comprises the steps of: (i) staining leukocytes in a hematologic sample by adding a fluorescent labeled antibody capable of binding specifically with leukocytes to the hematologic sample; (ii) raising the permeability only of cell membranes of erythroblasts in the hematologic sample to a nucleotide fluorescent dye which does not permeate a cell membrane usually, the nucleotide fluorescent dye having a fluorescent spectrum capable of being distinguished from that of a fluorescent labeling compound of the fluorescent labeled antibody in step (i); (iii) staining nuclei of the erythroblasts in the hematologic sample with the nucleotide fluorescent dye; (iv) subjecting the hematologic sample to flowcytometry to detect at least two fluorescent signals from each cell; and (v) discriminating and counting the erythroblasts from difference in intensity between the at least two fluorescent signals.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
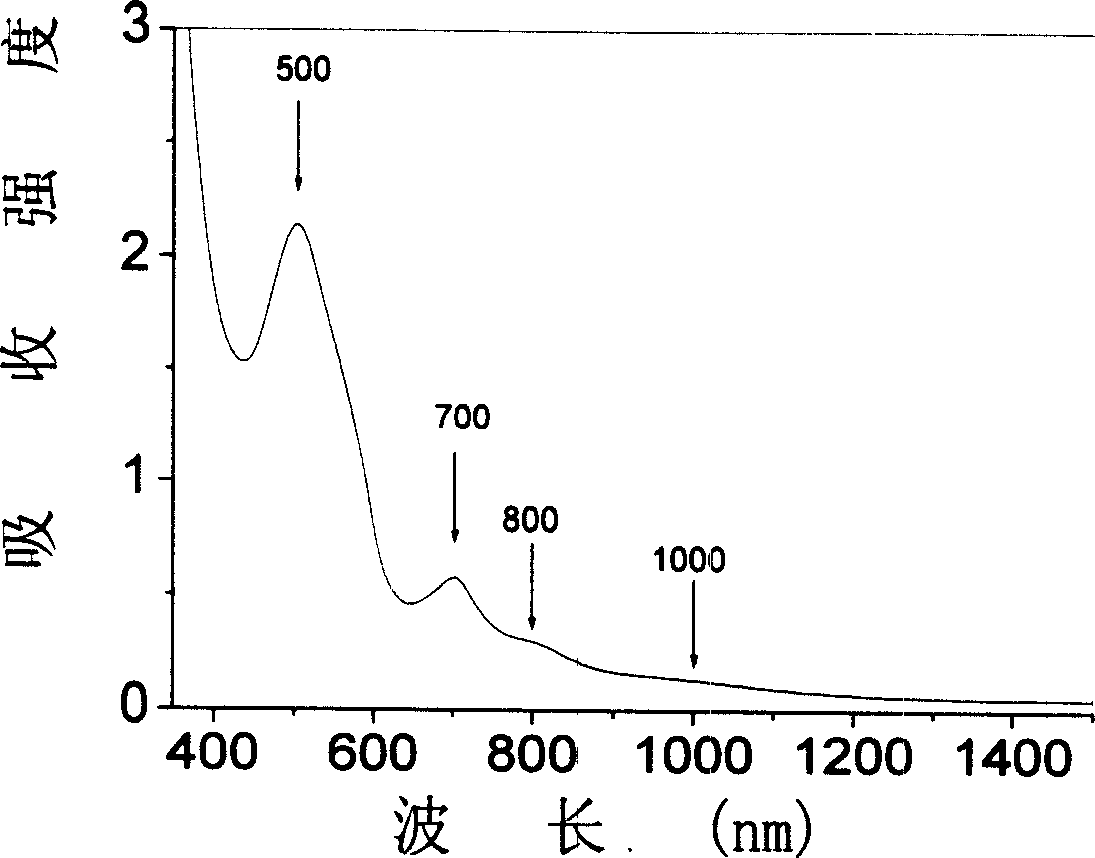
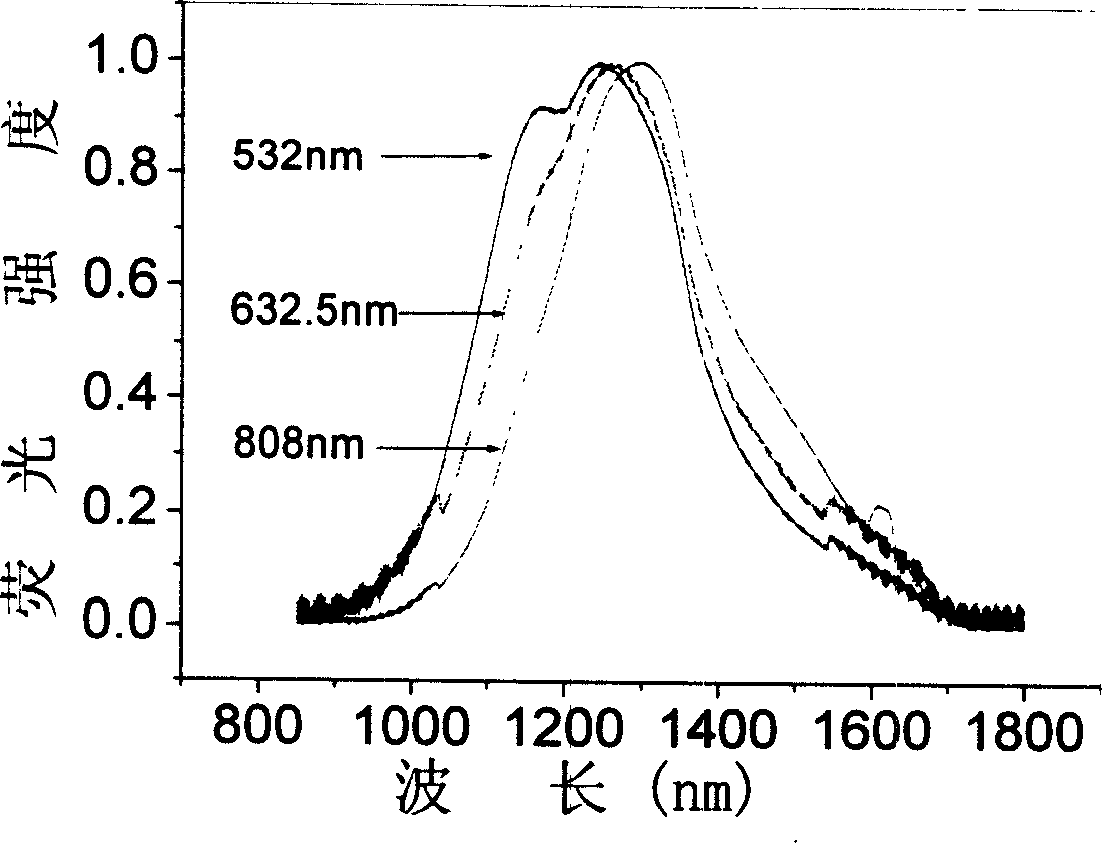
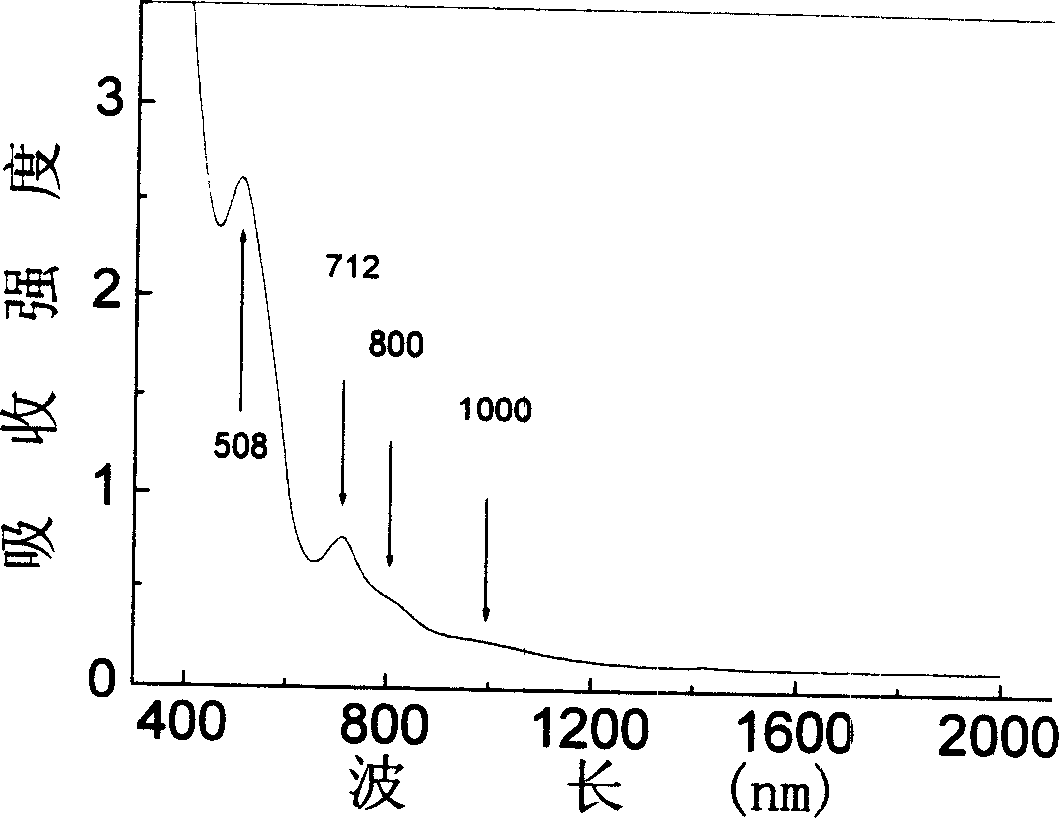
Bismuth blended germanium base optical glass
InactiveCN1587142AOvercome the disadvantage of higher melting temperatureEliminate the effects ofHigh power lasersFluorescence
The Bi doped germanium base optical glass has the molar composition of: GeO2 90-99.98 mol%, M 0.01-9 mol%, Bi2O3 0.01-5 mol%, where M is Al2O3, Ta2O5, Ga2O3 or B2O3. The glass has absorption spectrum covering the area from visible light to near infrared, central fluorescent spectrum wavelength in 1300 nm, fluorescent life greater than 0.2 ms and fluorescent full width at half maximum greater than 200 nm, and may be pumped with laser of 532 nm, 632.5 nm and 808 nm wavelength. These kinds of optical glass are expected to find the use in ultra wide band amplifier, high power laser, tunable laser and other technological fields.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Sulfur phosphorus nitrogen co-doped carbon point with adjustable fluorescence property and preparation method of sulfur phosphorus nitrogen co-doped carbon point
InactiveCN103911151AGood reproducibilityMaterial nanotechnologyNano-carbonFluorescent spectraCucumber juice
The invention discloses a sulfur phosphorus nitrogen co-doped carbon point with adjustable fluorescence property and a preparation method of the of sulfur phosphorus nitrogen co-doped carbon point. According to the technical scheme, the carbon point is prepared by processing cucumber juice as a precursor by virtue of a hydrothermal method in one step, has the particle size of 2-8nm, and is an amorphous fluorescent carbon point with the average particle sizes of 5.6nm, 3.5nm and 2.7nm respectively; the wavelengths of corresponding fluorescent spectrums are 450nm, 505nm and 571nm respectively. According to the preparation method, no chemical reagent is added, only the cucumber juice is taken as a unique raw material, a reaction is carried out in a hydrothermal reaction kettle, so that the preparation method is environmental friendly and is convenient, quick and good in repeatability.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
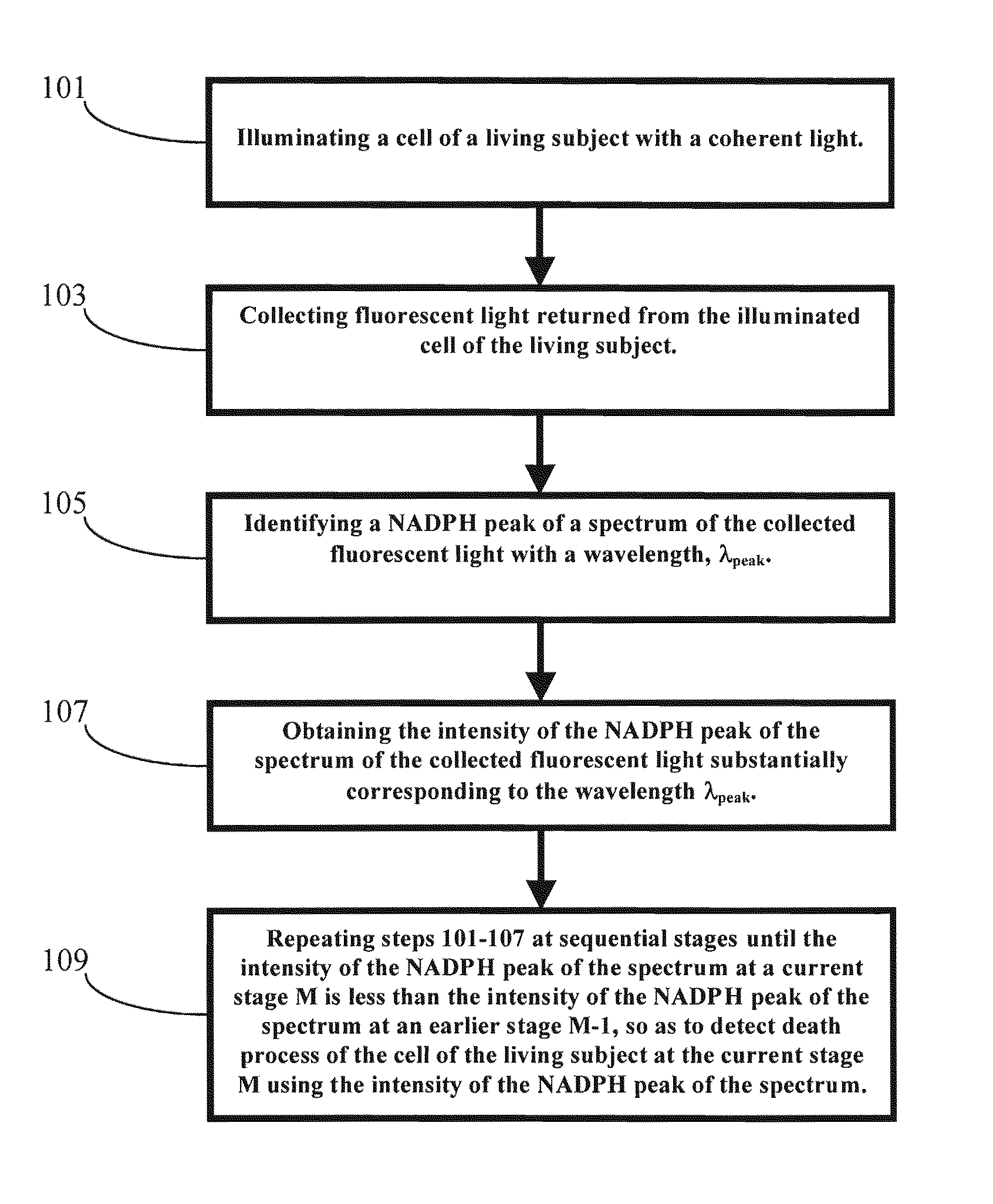
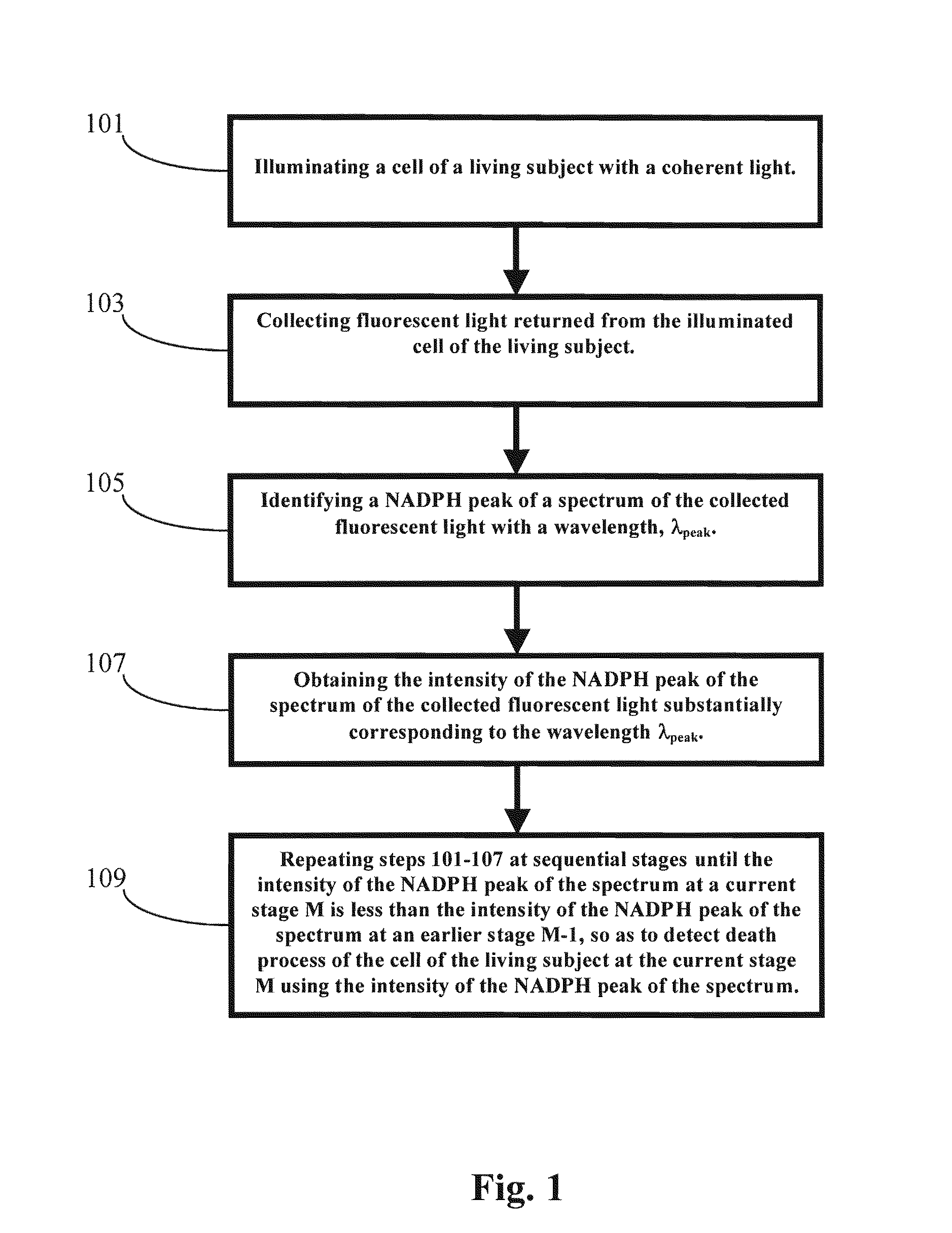
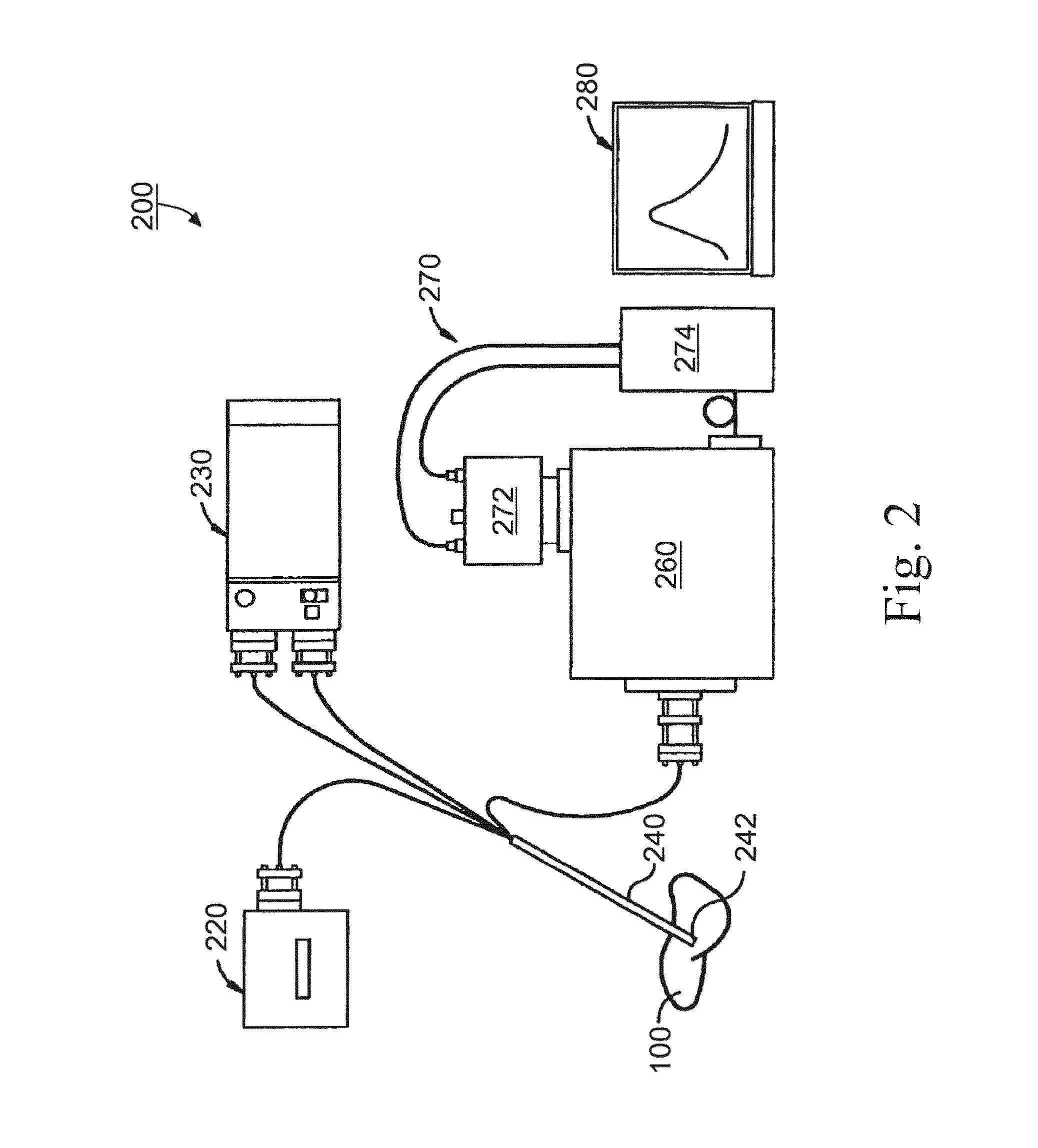
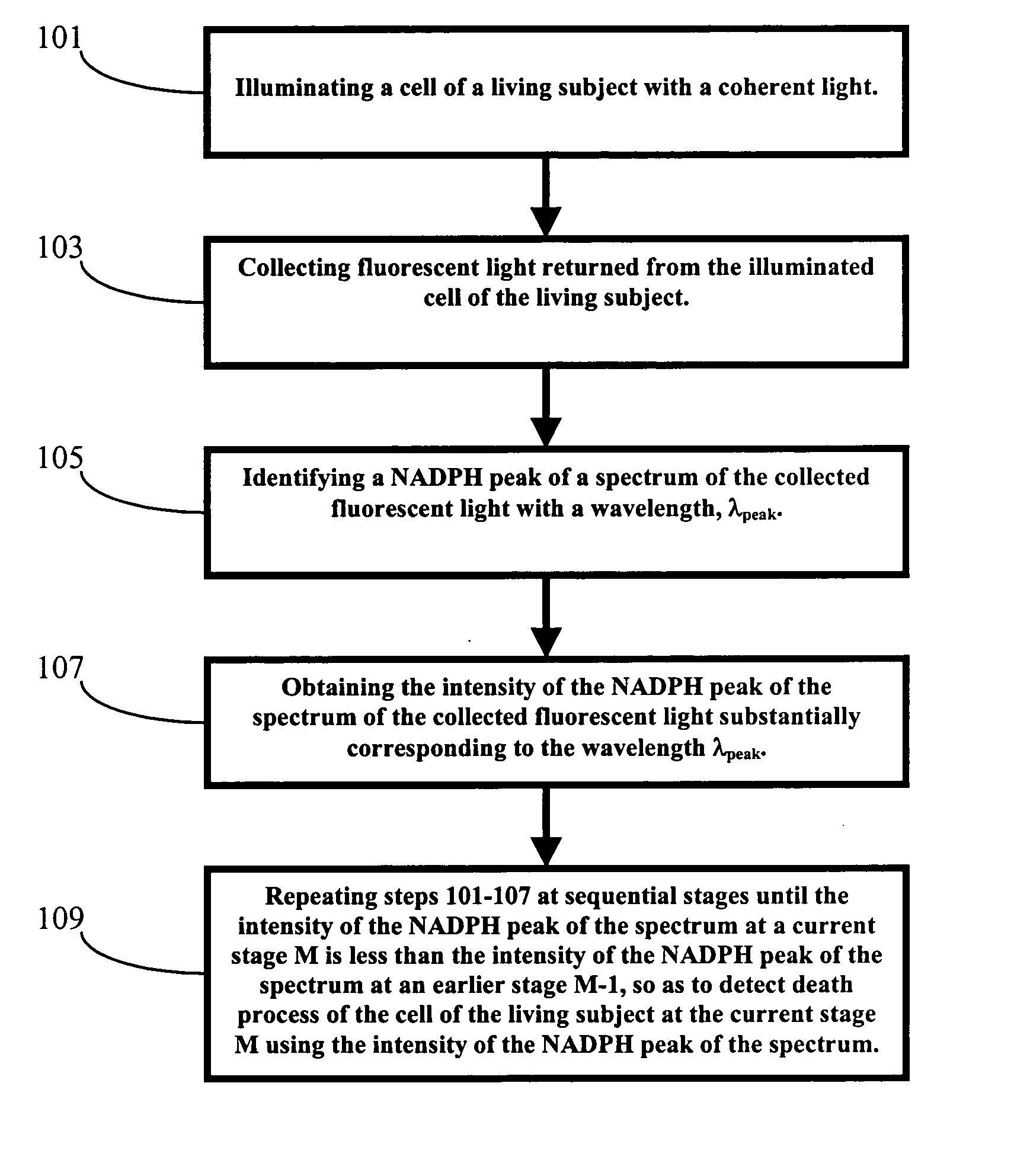
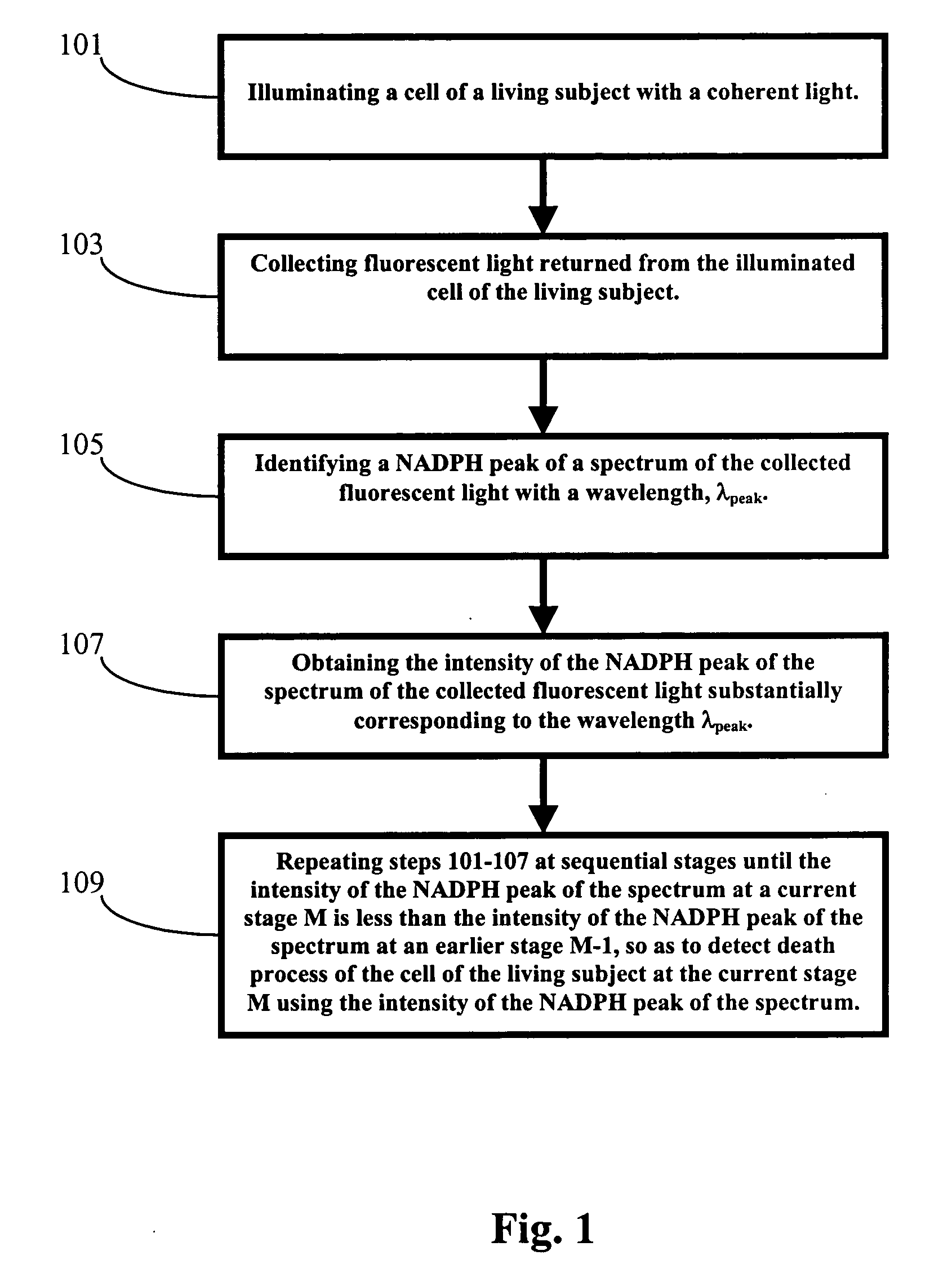
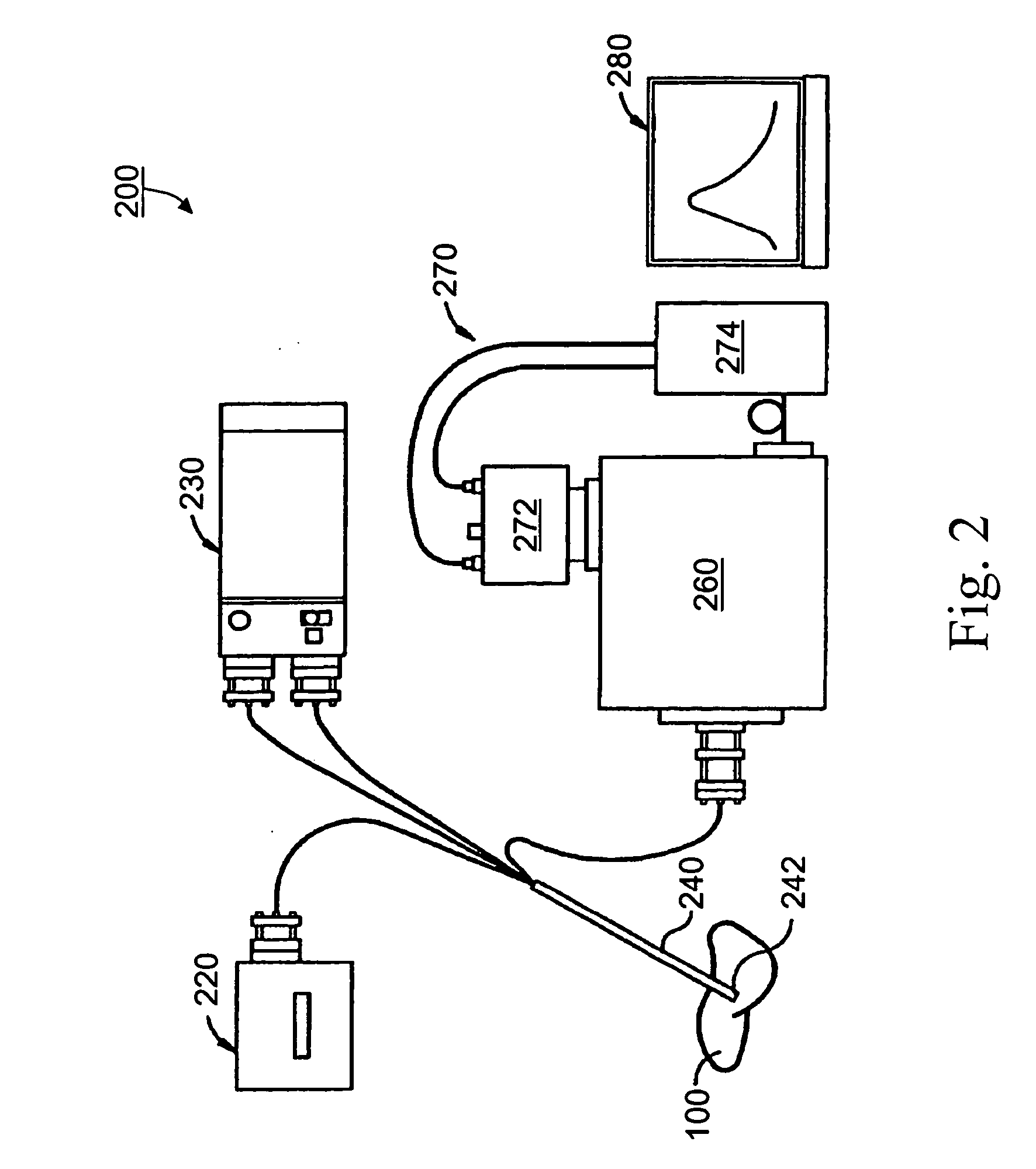
Methods and Apparatus for Optical Spectroscopic Detection of Cell and Tissue Death
A method for detecting death process of a cell or tissue of a living subject. In one embodiment, the method includes the steps of illuminating the cell or tissue of the living subject with a coherent light, collecting fluorescent light returned from the illuminated cell or tissue of the living subject, identifying a NAD(P)H peak of a spectrum of the collected fluorescent light with a wavelength, λpeak, and obtaining the intensity of the NAD(P)H peak of the spectrum of the collected fluorescent light substantially corresponding to the wavelength λpeak. These steps are repeated at sequential stages until the intensity of the NAD(P)H peak of the spectrum at a current stage is less than the intensity of the NAD(P)H peak of the spectrum at an earlier stage immediately prior to the current stage so as to detect death process of the cell of the living subject at the current stage using the intensity of the NAD(P)H peak of the spectrum.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV +1
Multimodal detection of tissue abnormalities based on raman and background fluorescence spectroscopy
Owner:BRITISH COLUMBIA CANCER AGENCY BRANCH
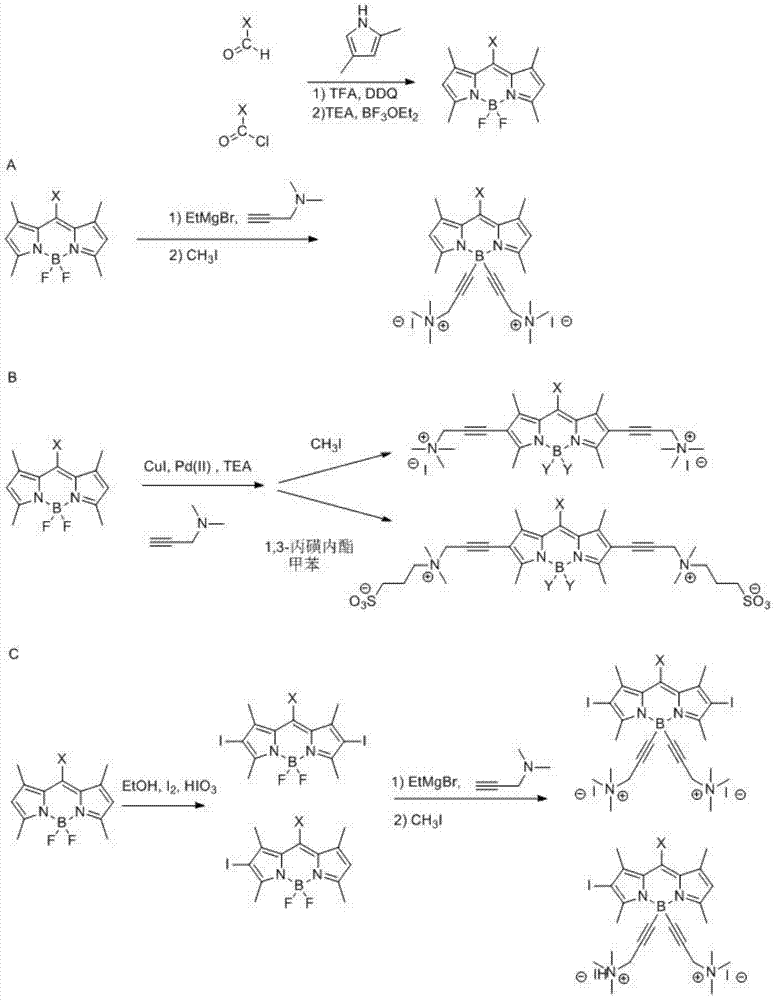
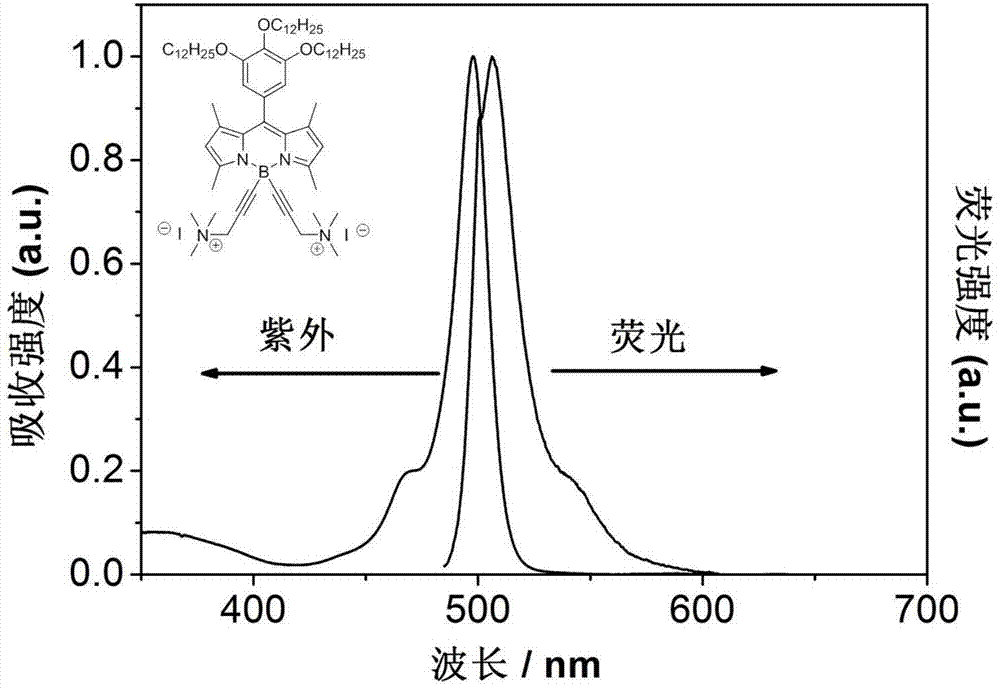
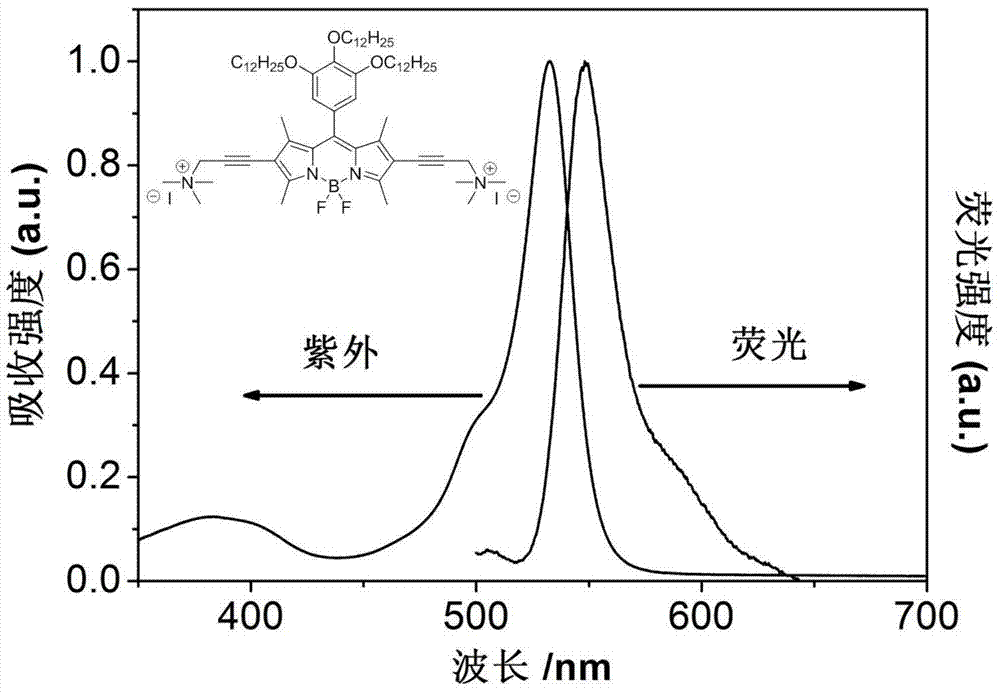
Boron fluoride dipyrrole fluorescent dye containing hydrophilic groups and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103865289ASimple reaction conditionsHigh yieldMethine/polymethine dyesLuminescent compositionsFluorescent spectraQuinone
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Near infrared fluorescent probe for detecting zinc ions in water phase and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102241970AHigh selectivityHigh sensitivityOrganic chemistryBiological testingFluorescent spectraFluoProbes
The invention belongs to the field of small molecular fluorescent probes and particularly relates to a near infrared fluorescent probe for detecting zinc ions in a water phase and a preparation method thereof. The near infrared fluorescent probe for detecting the zinc ions in the water phase is structured in the specification. The fluorescent probe has the advantages of high selectivity and high sensitivity, as well as an emission peak of fluorescence spectrum in a near infrared area, low cytotoxicity, good membrane permeability and good water solubility. The fluorescent probe has a capability of detection of the zinc ions and fluorescence imaging in cells.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
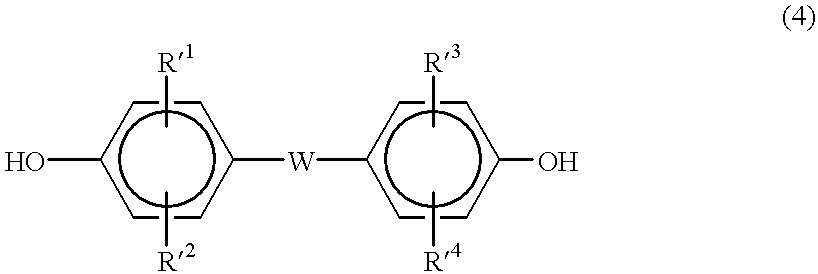
Beta-sialon, method for producing same and light-emitting device using same
ActiveUS20120228551A1Raise ratioLong wavelength luminescenceElectroluminescent light sourcesLuminescent compositionsSilicon nitrideOxide
β-Sialon comprising Eu2+ that is present in a solid solution form in P-sialon represented by Si6-zAlzOzN μm [wherein z is 0.3-1.5], which shows, when excited with light of 450 nm in wavelength, a peak wavelength of fluorescent spectrum of 545-560 nm, a half-value breadth of 55 nm or greater, and an external quantum efficiency of 45% or greater. The p-sialon can be produced by blending at least one kind of oxide selected from aluminum oxide and silicon oxide with silicon nitride and aluminum nitride in such a manner as to give z of 0.3-1.5, further adding thereto a europium compound and a β-sialon powder having an average particle diameter of 5 μm or greater and an average degree of circularity of 0.7 or greater, each in a definite amount, and baking the mixture.
Owner:DENKA CO LTD
Microfluid system and method to test for target molecules in a biological sample
ActiveUS20100151443A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsSludge treatmentFluorescent spectraTest sample
A system and method to test for the presence of target molecules in a biological test sample includes test molecules, a microfluidic chip, and irradiating and detection devices. The test molecules include bio-recognition molecules conjugable with the target molecules, and the corresponding conjugates. The microfluidic chip includes sample channels and flow focusing channels adjoining the sample channels. A buffer exiting from the focusing channels directs a single-file stream of the test molecules through one of the sample channels. The irradiating device delivers radiation for absorption by the test molecules in the single-file stream. After absorption, the test molecules emit fluorescence of a distinct fluorescent spectrum for each of the conjugates. The detection device monitors identifies the presence of the conjugates by monitoring for the distinct fluorescent spectrum. Thus, the test system and method identifies the presence of the target molecules in the test sample.
Owner:FIO CORP
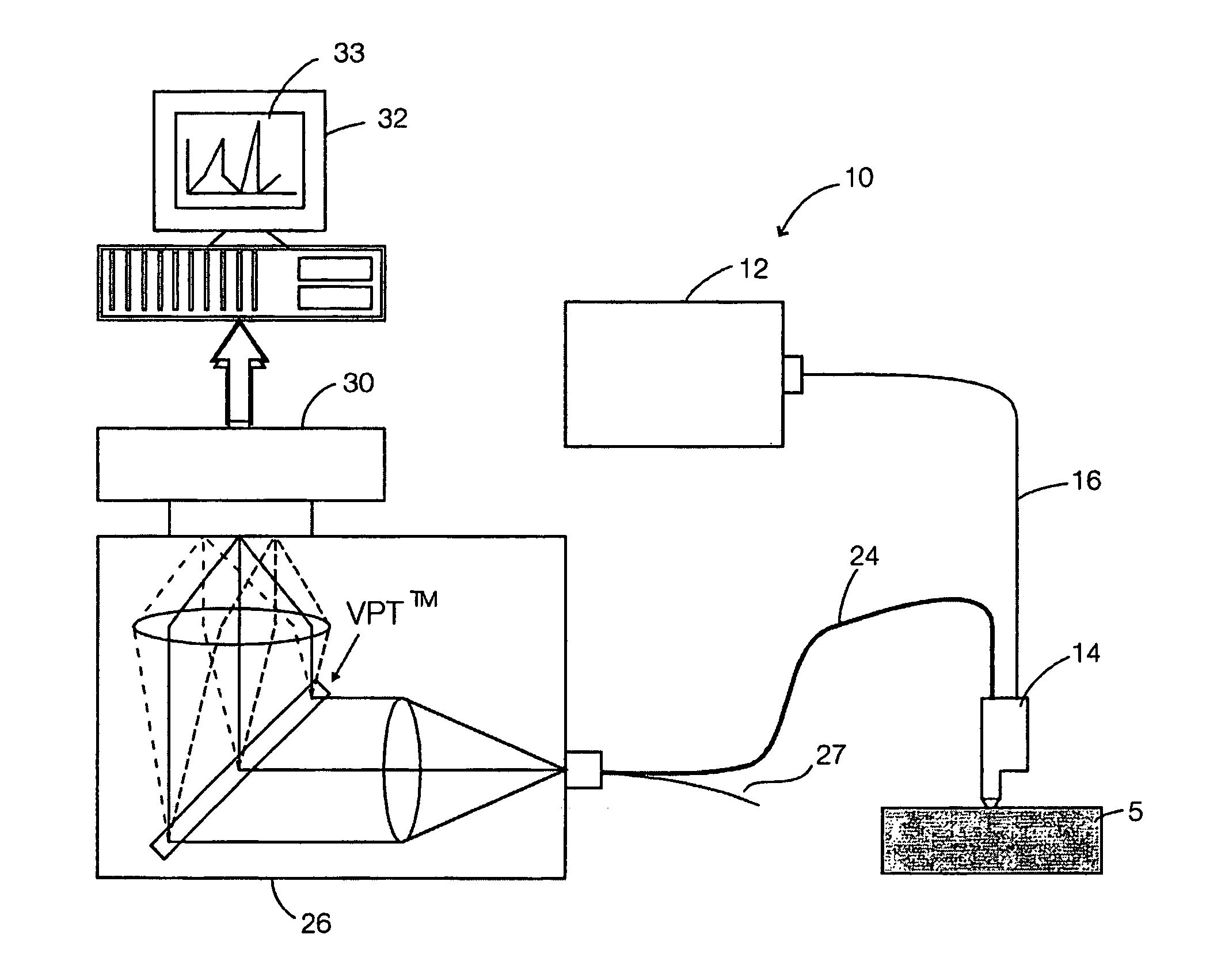
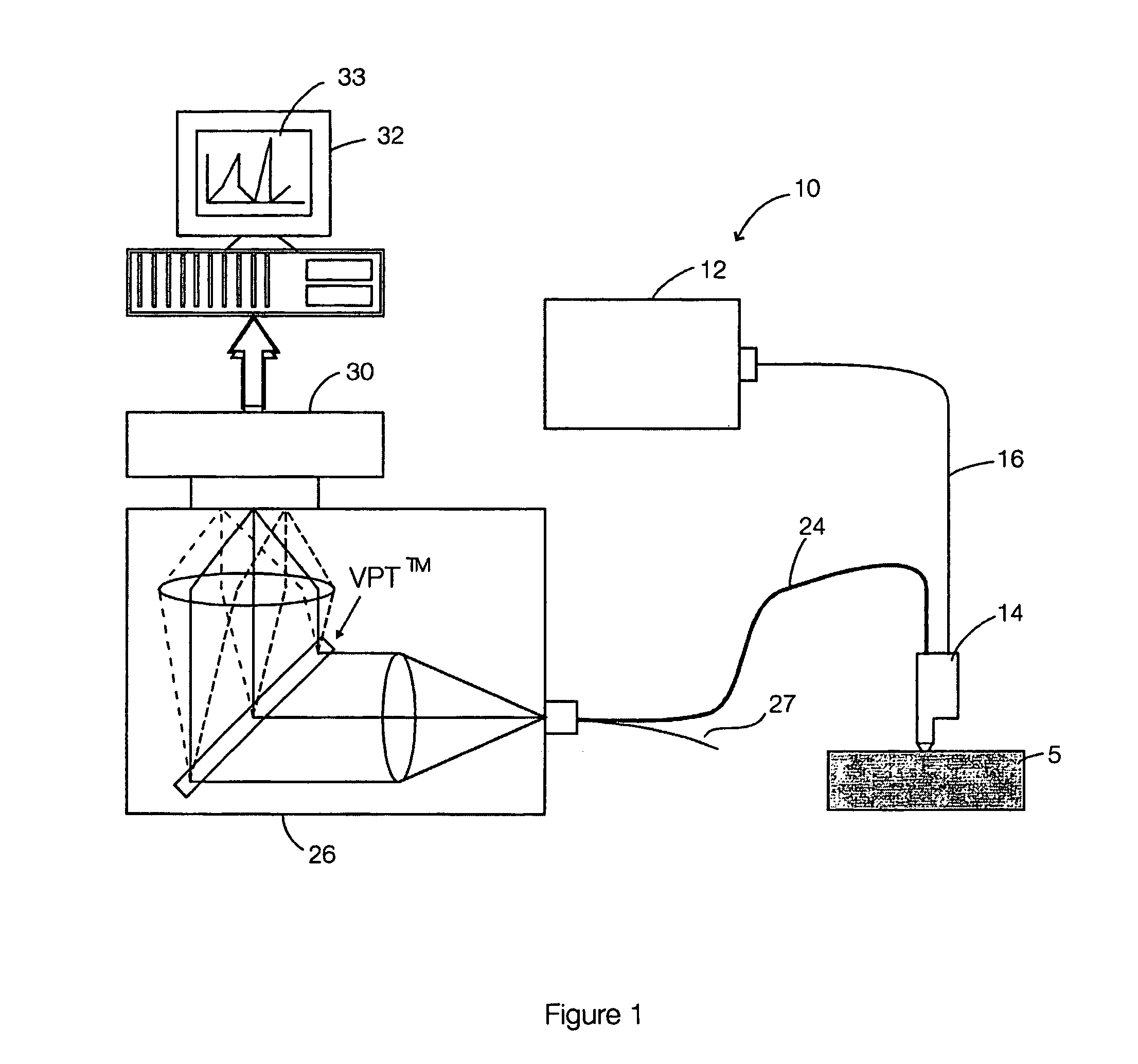
Method and apparatus for optical spectroscopic detection of cell and tissue death
A method for detecting death process of a cell or tissue of a living subject. In one embodiment, the method includes the steps of illuminating the cell or tissue of the living subject with a coherent light, collecting fluorescent light returned from the illuminated cell or tissue of the living subject, identifying a NAD(P)H peak of a spectrum of the collected fluorescent light with a wavelength, λpeak, and obtaining the intensity of the NAD(P)H peak of the spectrum of the collected fluorescent light substantially corresponding to the wavelength λpeak. These steps are repeated at sequential stages until the intensity of the NAD(P)H peak of the spectrum at a current stage is less than the intensity of the NAD(P)H peak of the spectrum at an earlier stage immediately prior to the current stage so as to detect death process of the cell of the living subject at the current stage using the intensity of the NAD(P)H peak of the spectrum.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV +1
Schiff base sensor molecule, its synthesis, and its application in fluorescent colorimetric detection of CN<-> in water
InactiveCN103992292AShort response timeOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorFluorescent spectraPotable water
The invention relates to a synthesis method of a Schiff base sensor molecule, and belongs to the technical field of anion detection. The sensor molecule has the advantages of highly selective colorimetric fluorescent binary channel identification of CN<-> in water, short response time, and no influences of anions on the detection process. Determination results show that the naked eye detection limit and the fluorescent spectrum detection limit of the sensor molecule to CN<-> in water are 2.0*10<-6>mol / L and 3.42*10<-8>mol / L respectively, and are far lower than the content standard (below 1.8muM) of normal drinking water, prescribed by World Health Organization.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Container Assembly and System for Detection Thereof
ActiveUS20110311416A1Improve automationAnalysis material containersVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsFluorescent spectraVisual perception
A closure and a container assembly are disclosed. The closure includes a first visual identifier and a second visual identifier, wherein the second visual identifier is different from the first visual identifier. The first visual identifier may be a first color, and the second visual identifier may be a second color. At least one of the first and / or second visual identifier may include a fluorescent compound having a characteristic fluorescent spectra. The first visual identifier and the second visual identifier may be provided on the annular skirt of the closure. The fluorescent compound may be provided on at least one of the closure and the container assembly and can be used to facilitate automated visualization of the fluorescent compound under fluorescence excitation light.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Optical excitation fluorescent spectra system having no requirement of stability of excitation light source
InactiveCN101581667AImprove signal-to-noise ratioFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescent spectraLuminous intensity
The invention relates to an optical excitation fluorescent spectra system having no requirement of stability of excitation light source, which comprises a light source, a spectrometer, an exciting light converging element, a beam splitter, a light intensity meter, a sample, an emitted light collecting element, an emission spectrometer, a detector and a computer, wherein the spectrometer is arranged behind the light source and used for dispersing a broad-spectrum optical signal sent by the light source into a narrowband light source or monochromatic source, the exciting light converging element is arranged behind the spectrometer and used for converging exciting light emitted by the spectrometer on a sample to be tested, the beam splitter is arranged behind the exciting light converging element and used for reflecting part of the exciting light emitted by the spectrometer to another direction to enter a light intensity meter, the light intensity meter is arranged at one side of the light path of the beam splitter and used for detecting the intensity of the exciting light reflected by the beam splitter and using the intensity as a reference light intensity, the sample is arranged behind the beam splitter, the emitted light collecting element is arranged behind the sample and used for converging the signal light emitted by the sample to an inlet of the emission spectrometer, the emission spectrometer is arranged behind the emitted light collecting element and used for dispersing the signal light to a the detector, the detector is arranged behind the emission spectrometer and used for detecting the intensity of a spectral signal dispersed by the emission spectrometer, and the computer is respectively connected with the spectrometer, the light intensity meter, the emission spectrometer and the detector and used for controlling the running of the whole system.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
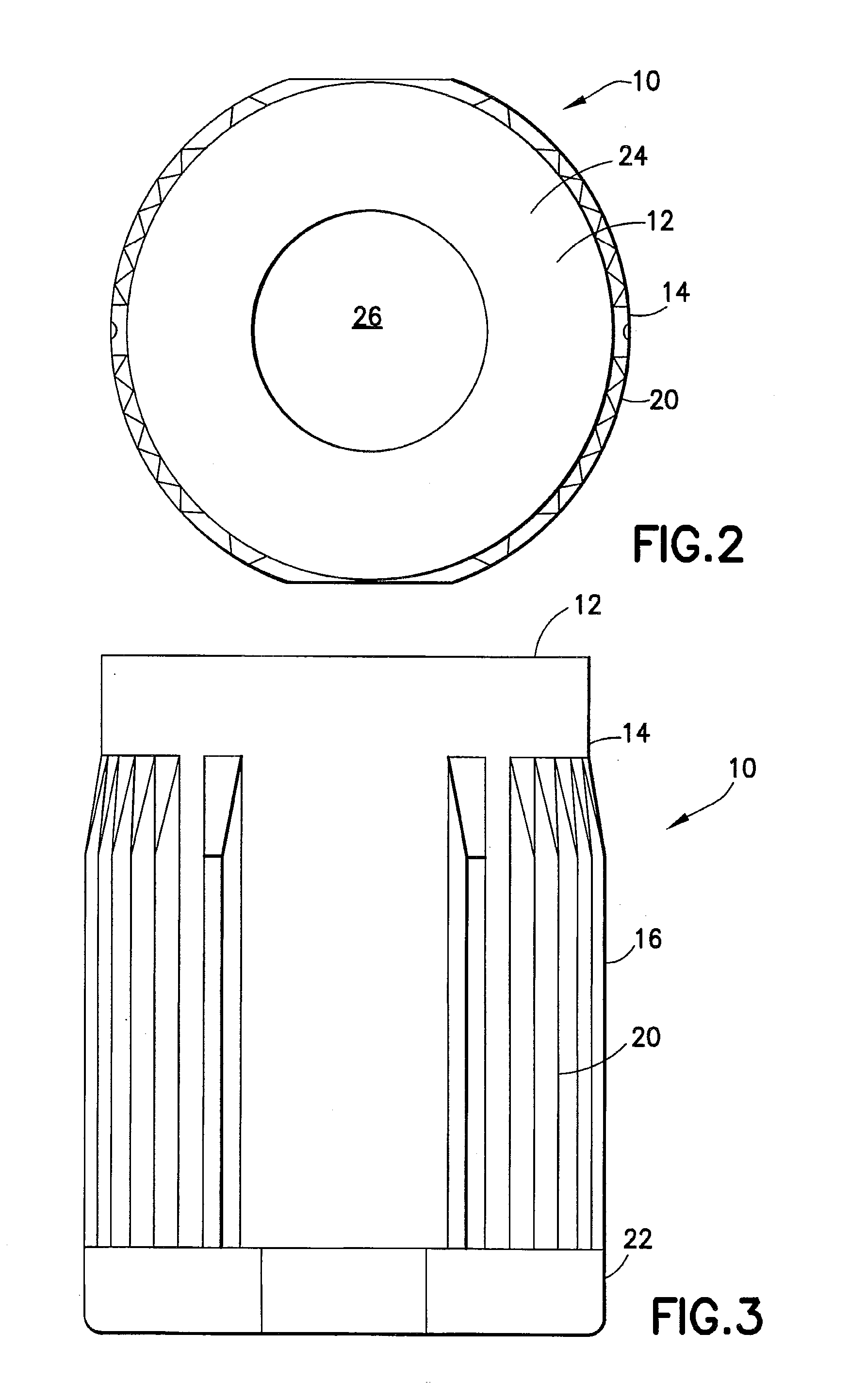
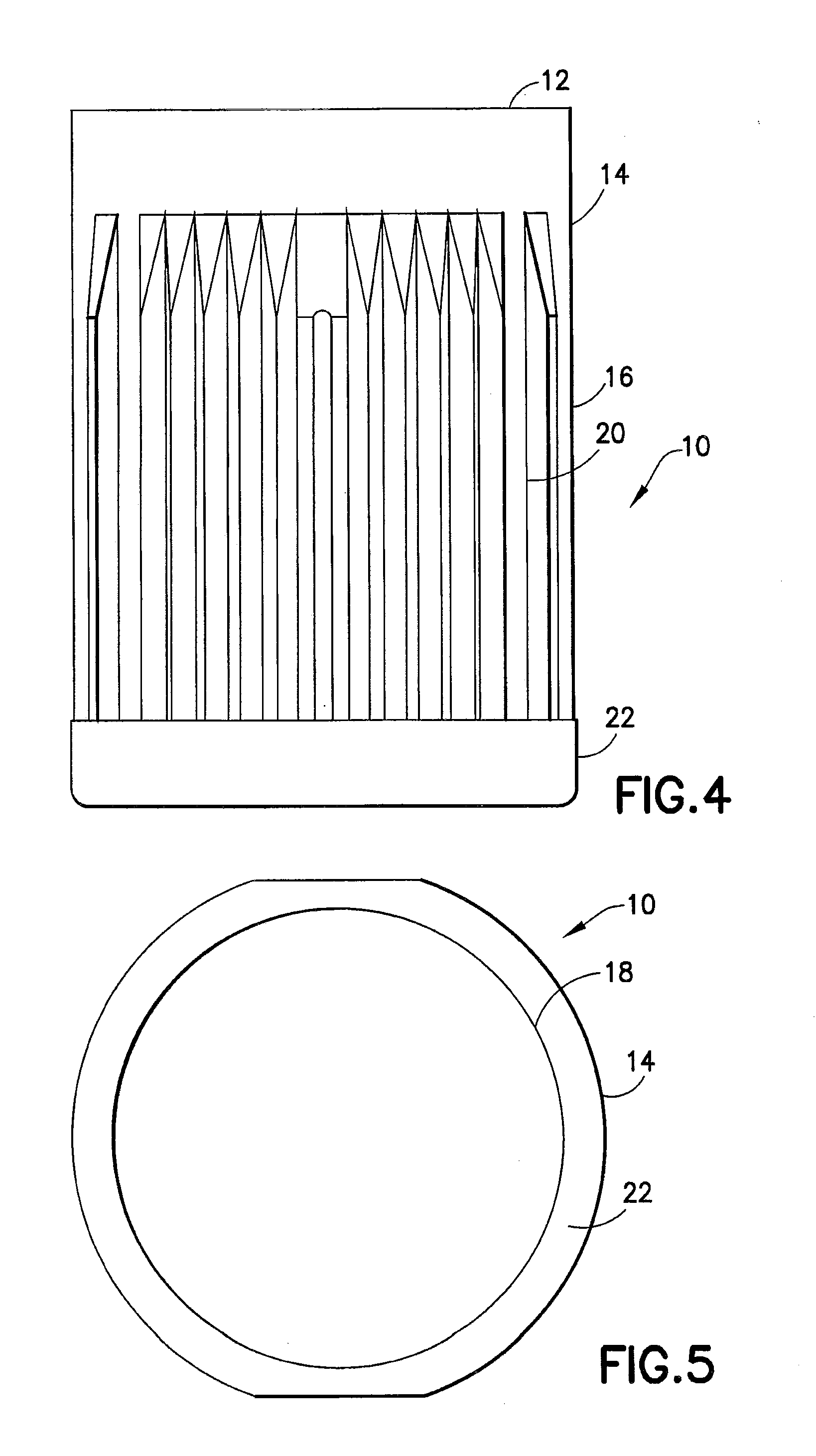
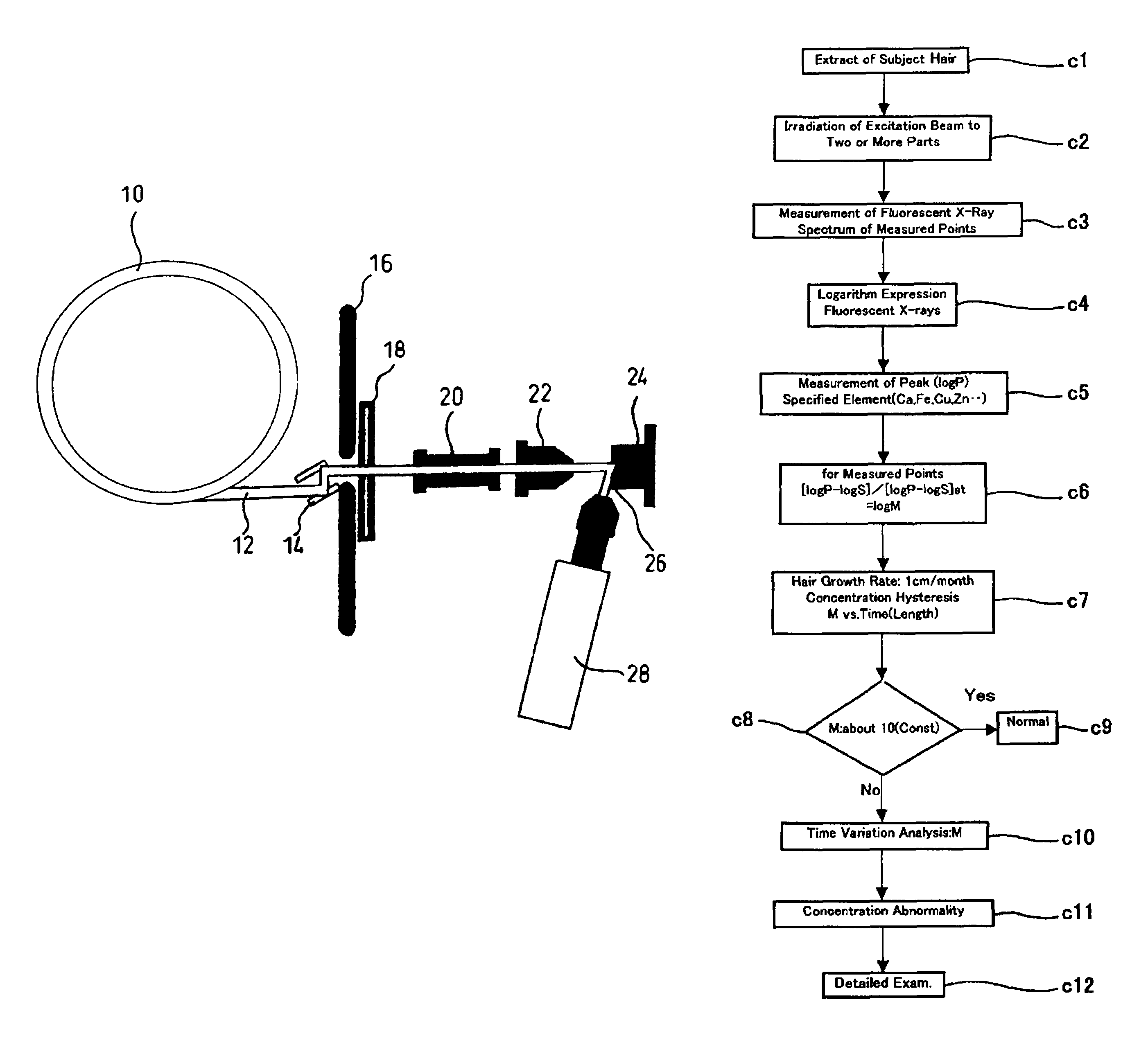
Method for evaluating physical conditions using head hair or body hair
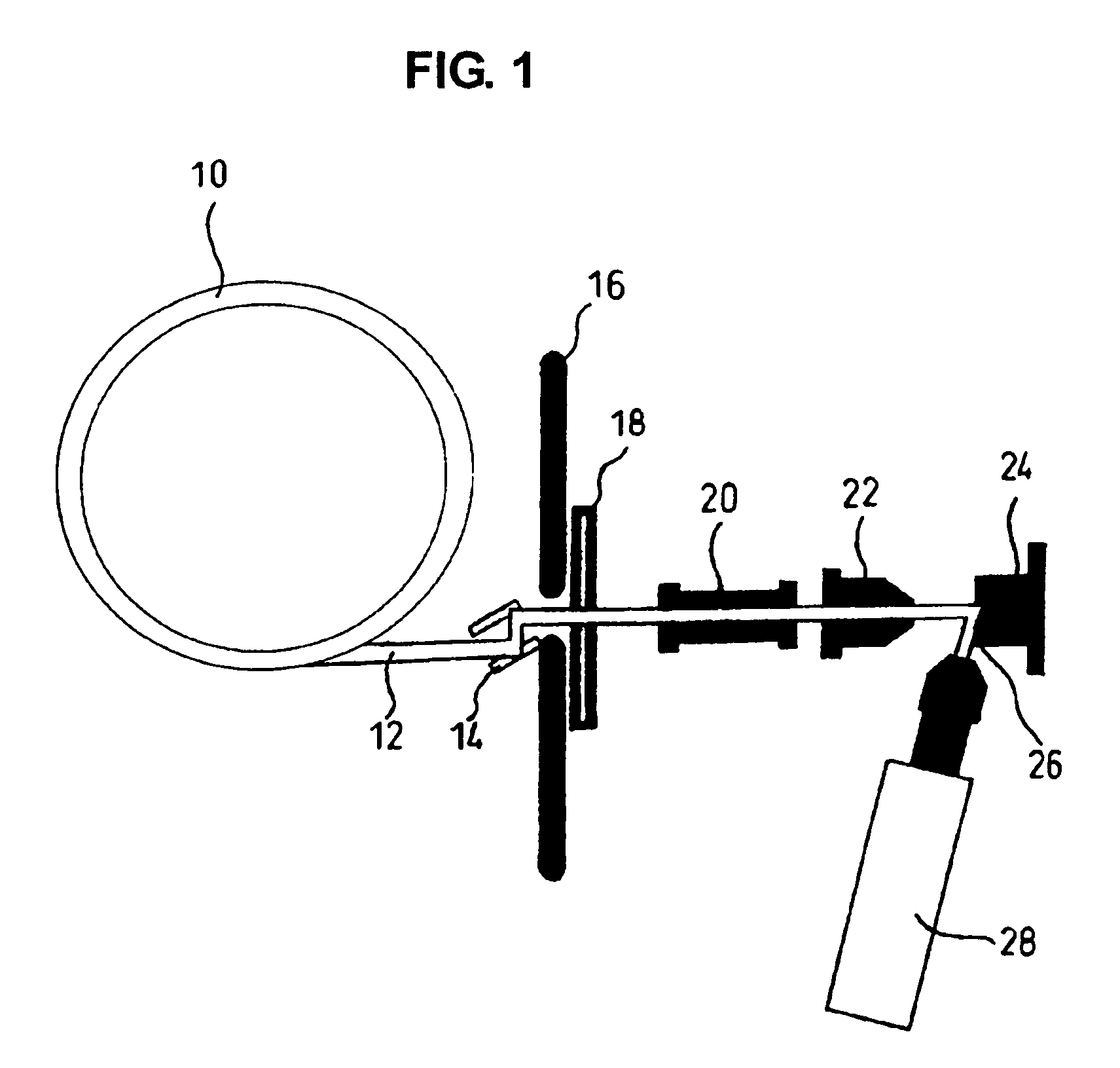
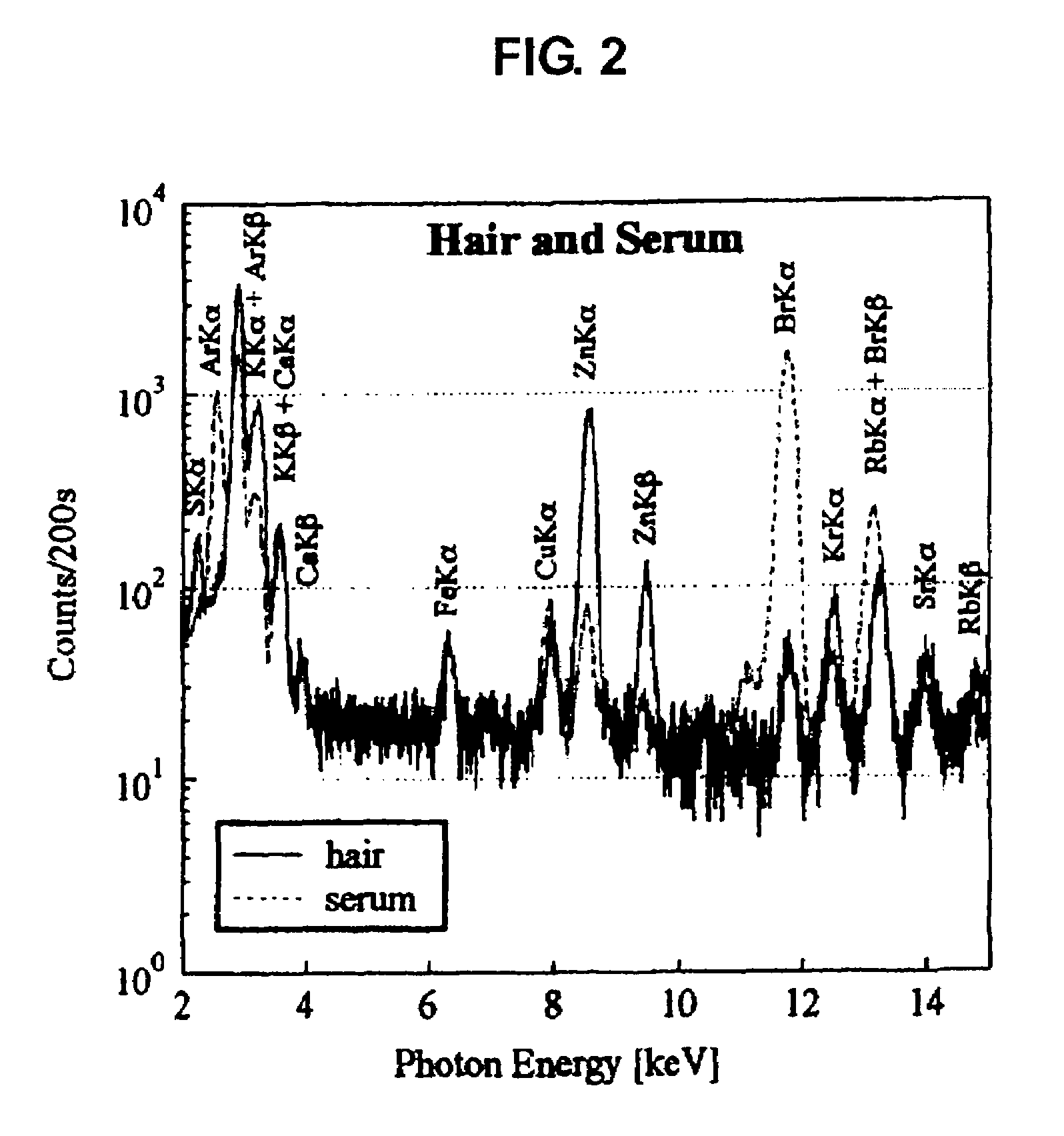
InactiveUS7688943B2Easy to handleEasy to implementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray spectral distribution measurementFluorescent spectraSerum protein
Elemental concentrations in hair (head and body hair) and dried serum have been measured by x-ray fluorescence analysis using synchrotron radiation. The relative concentration defined by log P−log S are obtained from the fluorescent spectra, where P is the peak height for the element and S is the background height. The observation shows that hair has two separate [Ca] concentration levels, the upper level and lower level. Since the content in hair growing at a steady state must be equal to the supply from serum, the upper and the lower level of hair [Ca] are attributed to open and close Ca ion channels of the hair matrix cells and can be derived from the serum concentrations of Ca ion and Ca atoms included in serum protein, respectively. The hair analysis is useful for cancer detection and protection as well as for diagnosing the Ca metabolism.
Owner:CHIKAWA JUN ICHI
N-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)-rhodamine B hydrazide and preparation method and application thereof
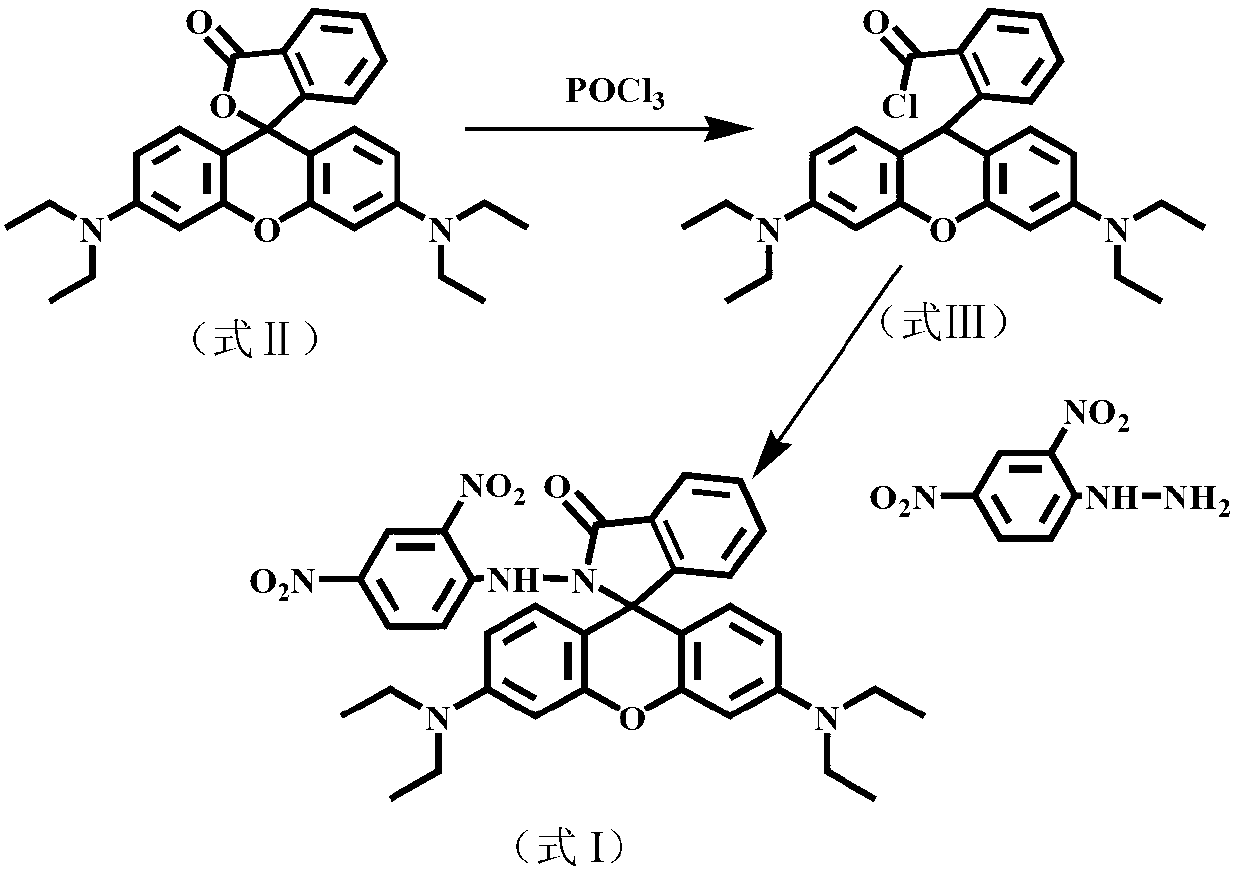
InactiveCN102827175ANo distractionEliminate distractionsOrganic chemistryColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescent spectraDinitrophenyl
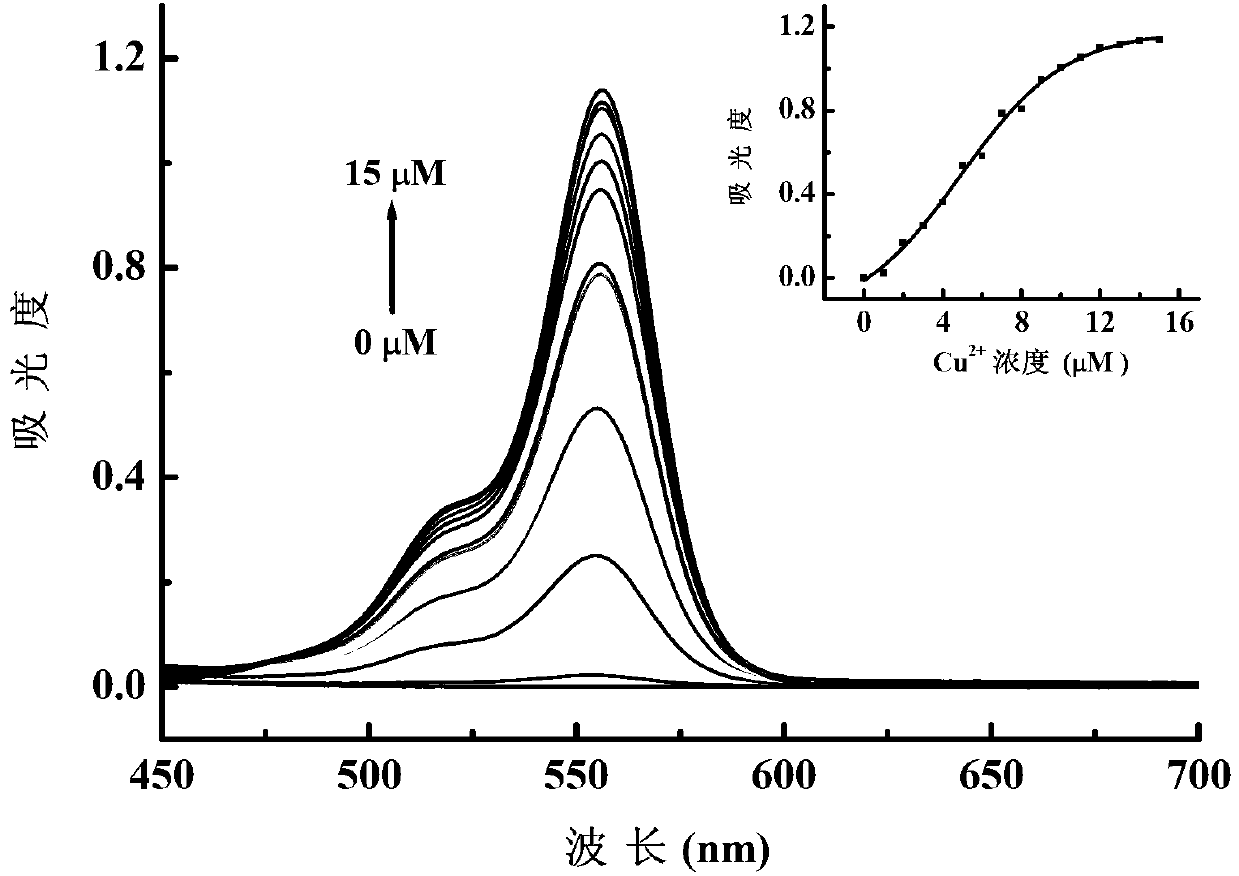
The invention discloses N-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)-rhodamine B hydrazide and a preparation method and an application of the N-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)-rhodamine B hydrazide. The rhodamine B derivative provided by the invention is N-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)-rhodamine B hydrazide, the structural formula of which is I. The N-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)-rhodamine B hydrazide, is colorless and free from fluorescence, but can selectively react with Cu<2+> ions in chromogenic and fluorescent opening reaction. The colorless substance generates a system with excellent optical performance, so that the detection sensitivity and selectivity of Cu<2+> ions are greatly improved. Therefore, the N-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)-rhodamine B hydrazide is appropriate for high selectivity and high sensitivity detection for the Cu<2+> ions. Detection can be carried out by a light absorption spectrum and a fluorescence spectrum. (FORMULA I).
Owner:NAT RESERACH CENT OF GEOANALYSIS +1
Process for discriminating and counting erythroblasts
InactiveUS20040241770A1Preparing sample for investigationBiological testingFluorescent spectraStaining
A method for discriminating and counting erythroblasts comprises the steps of: (i) staining leukocytes in a hematologic sample by adding a fluorescent labeled antibody capable of binding specifically with leukocytes to the hematologic sample; (ii) raising the permeability only of cell membranes of erythroblasts in the hematologic sample to a nucleotide fluorescent dye which does not permeate a cell membrane usually, the nucleotide fluorescent dye having a fluorescent spectrum capable of being distinguished from that of a fluorescent labeling compound of the fluorescent labeled antibody in step (i); (iii) staining nuclei of the erythroblasts in the hematologic sample with the nucleotide fluorescent dye; (iv) subjecting the hematologic sample to flowcytometry to detect at least two fluorescent signals from each cell; and (v) discriminating and counting the erythroblasts from difference in intensity between the at least two fluorescent signals.
Owner:HOUWEN BEREND +4
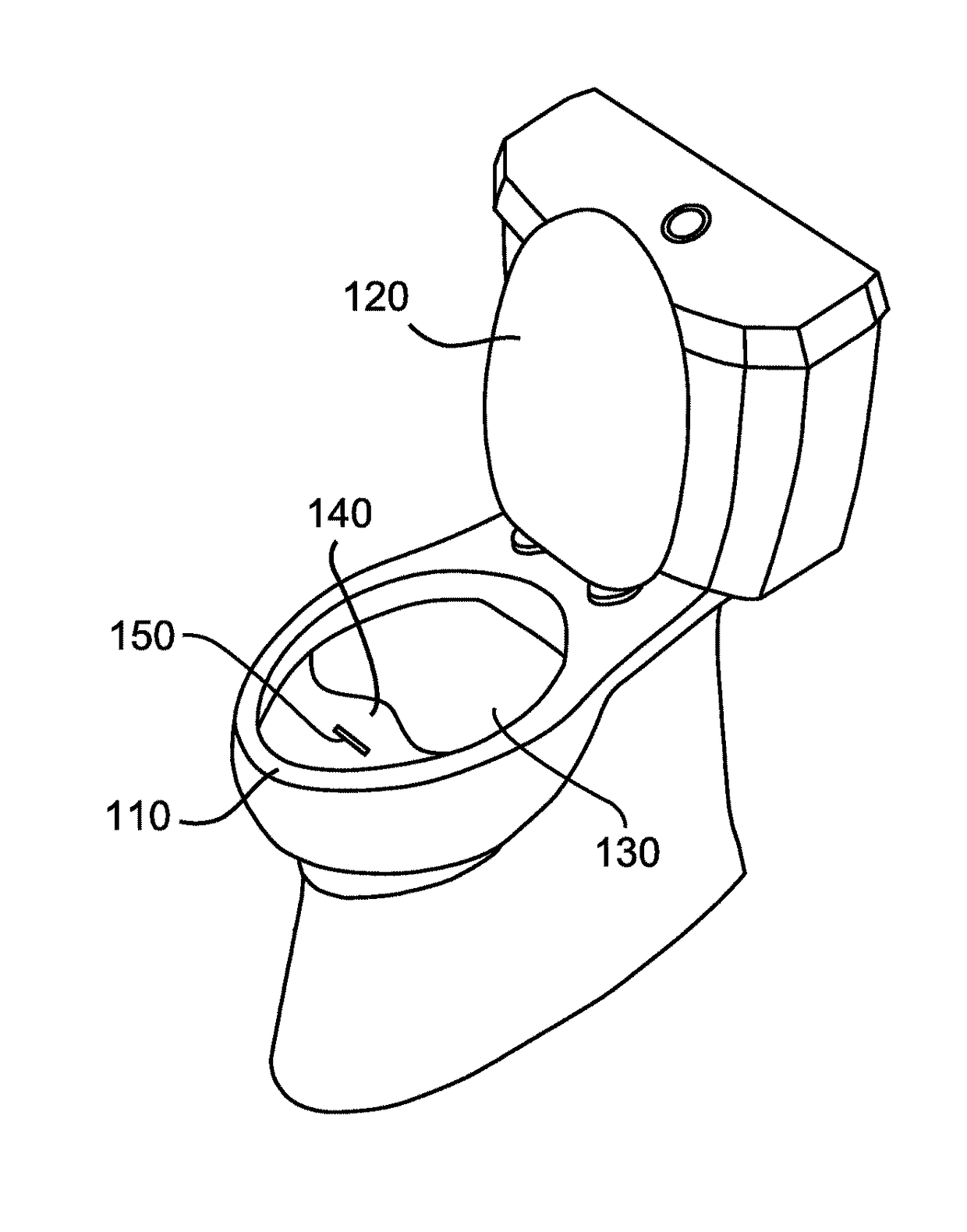
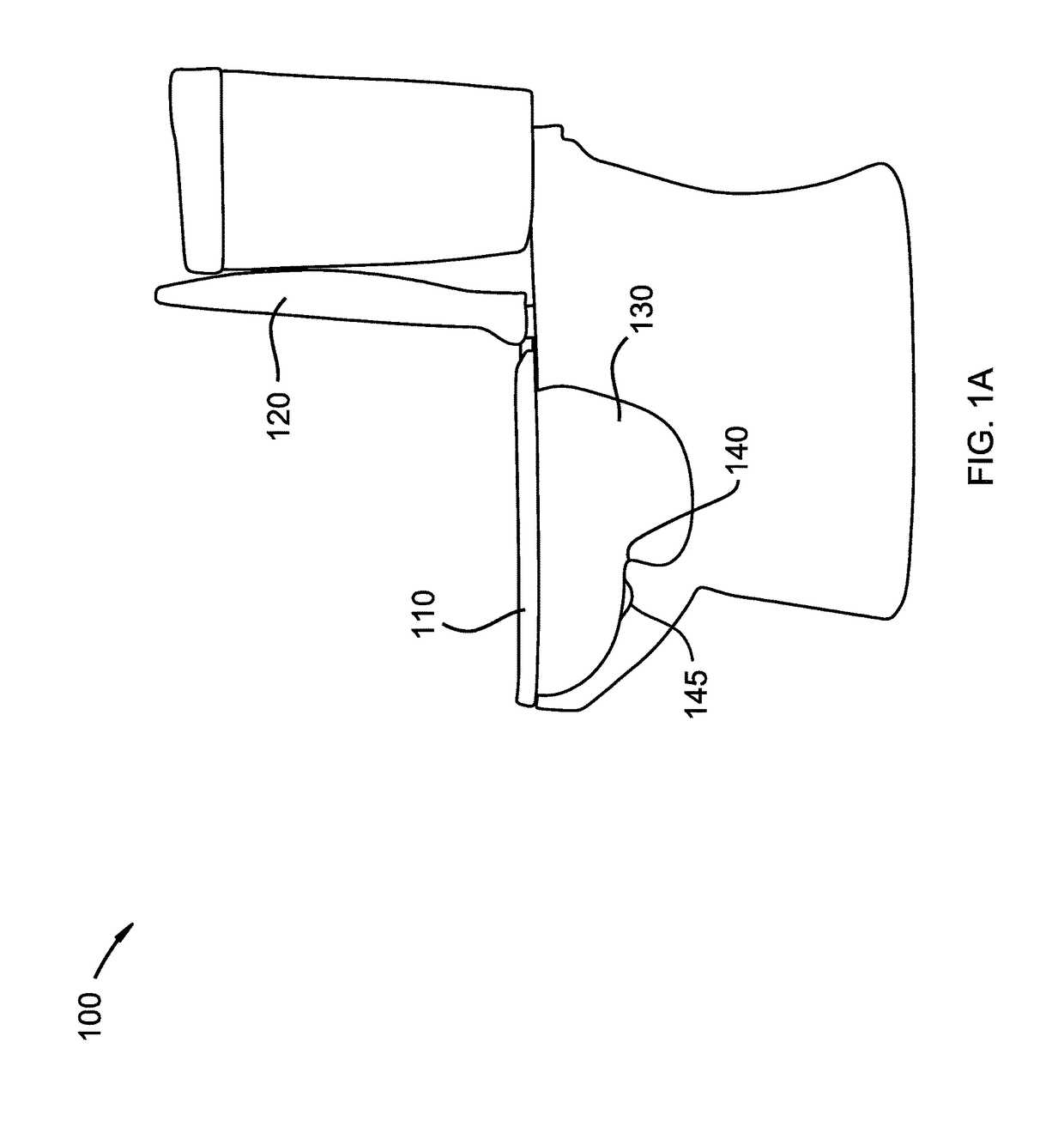
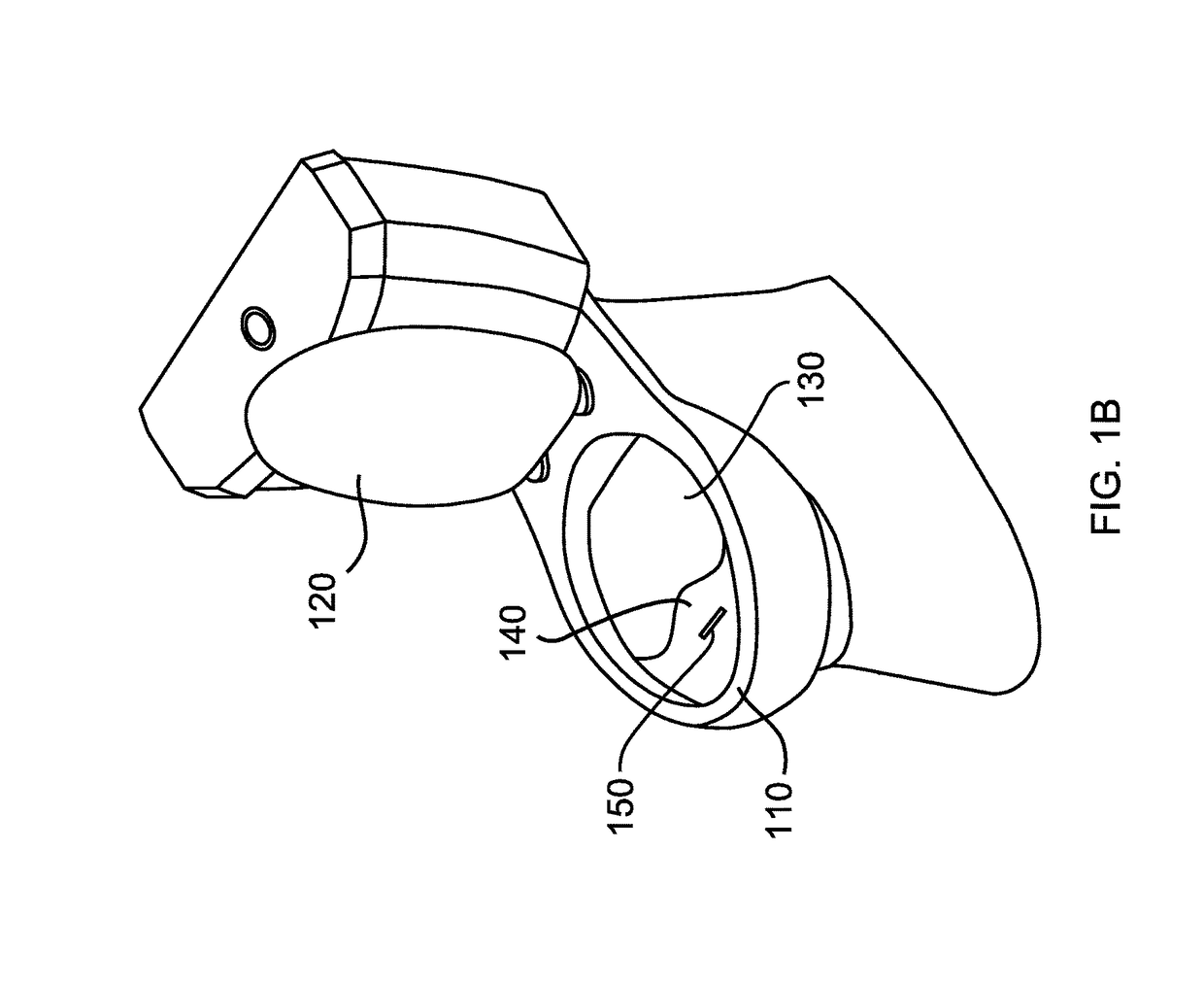
Toilet that detects fluorescent drug markers and methods of use thereof
The present disclosure describes a method of detecting a drug marker in urine a urine sample using a toilet. The drug markers are fluorophores each of which emits a unique fluorescence spectra. Accordingly, the method does not detect the drug but rather, the drug marker. The drug marker may include quantum dots which may be functionalized by connecting the quantum dot to a biomolecule. The biomolecule may be cleavable by a peptidase, a protease, or a nuclease to release the drug. Alternatively, the composition may include a liposome carrier. A user who has consumed the drug composition urinates into the toilet and a urine sample is captured. The toilet includes a mechanism for fluid handling which diverts urine into a fluorescence spectrometer. The fluorescence spectrometer screens the urine for drug markers based on their unique fluorescent spectra.
Owner:MEDIC INC
Projection display system and control method thereof
ActiveCN106353956AProjectorsPicture reproducers using projection devicesColor imageFluorescent spectra
The invention discloses a control method of a projection display system. The projection display system comprises a liquid crystal light modulation device and a light emitting device capable of emitting time sequence light laser and fluorescent light which have spectrum overlapping. The control method includes: acquiring basic-color image signals in a source image signal after being decoded; converting each basic color image signal in the decoded source image signal into a corresponding basic color modulation control signal, controlling the liquid crystal light modulation device to modulate time sequence light through the basic color modulation control signals; in the process when a first basic color modulates the control signals, modulating laser of time sequence and at least part of fluorescent light by the liquid crystal light modulation device, wherein brightness after spectrum overlapped laser is mixed with fluorescent light is identical with that of corresponding basic color image signals in source image signals after being decoded, and color coordinates after the laser is mixed with the fluorescent light are identical with those of the corresponding basic color image signals in the source image signals after being decoded. In this way, basic-color light which is good in both brightness and color coordinates is acquired.
Owner:APPOTRONICS CORP LTD
Water quality monitoring probe and method based on ultraviolet visible absorption spectrum and fluorescence spectrum
PendingCN107179285AReduce the impactReduce distractionsColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescent spectraUltraviolet
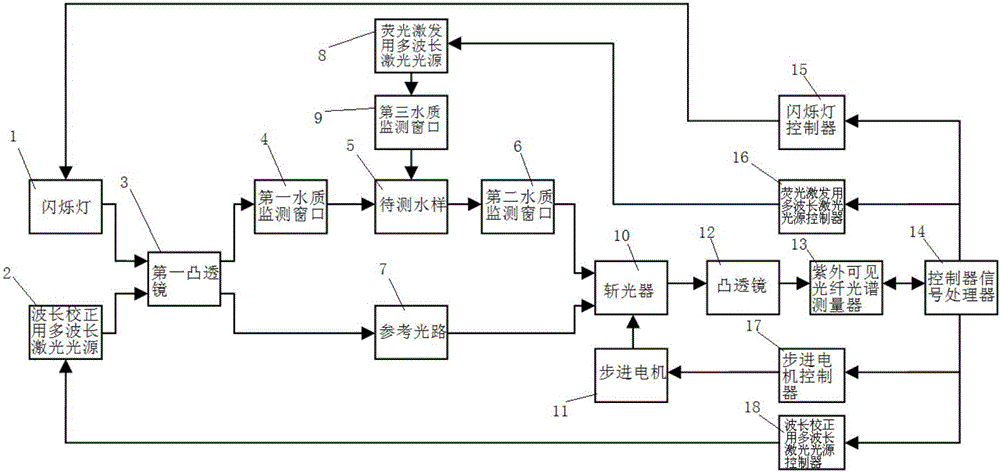
The invention relates to a water quality monitoring probe based on an ultraviolet visible absorption spectrum and a fluorescence spectrum. The water quality monitoring probe comprises a flash lamp, a first convex lens, a first water quality monitoring window, a second water quality monitoring window, a multi-wavelength laser source for exciting fluorescent light, a third water quality monitoring window, a chopper, a convex lens, an ultraviolet visible fiber spectrum measurer, a controller signal processor, a flash lamp controller, a multi-wavelength laser source controller for exciting fluorescent light and a stepping motor. A water sample can be scanned by a continuous ultraviolet visible spectral region, continuous absorbancy information in water quality is acquired, various parameters in the water quality are acquired by a diversified analyzing means, water characteristic information in the various data is calculated, a correcting model between spectrum data and the water quality parameters is established according to the data, and the model is used as a tool to realize water quality parameter analysis.
Owner:北京汇智精信科技有限公司
Correcting method for reducing influence of soil particle size upon polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon working curve
ActiveCN106442447AAchieve correctionScattering properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescent spectraPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
The invention discloses a correcting method for reducing influence of soil particle size upon a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon working curve, comprising the steps of screening soil with a screening device, dividing into N parts after screening, adding a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon into each part of soil, and mixing well to obtain N polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon soils having different concentrations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon; exciting polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon soils with an excitation light source to obtain fluorescent spectra of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon soils, and determining quantitative absorption bands A and Rayleigh scattering absorption bands B; extracting fluorescent intensities of the quantitative absorption bands A of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon soils to obtain quantitative absorption intensities; extracting scattering intensities of the Rayleigh scattering absorption bands B of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon soils to obtain Rayleigh scattering intensities; correcting the quantitative absorption intensities to obtain corrected fluorescent intensities Fs; establishing a corrected working curve according to Fs and concentration C. The correcting method can provide quick and effective correction for the influence of soil particle size upon polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon working curves.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
Method and device for improving definition of single-molecule fluorescence imaging
InactiveCN102507521AEliminate quantum fluctuationsImprove signal-to-noise ratioFluorescence/phosphorescenceSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Spectral imaging
The invention relates to a fluorescence spectrum imaging technique, aiming at solving the problem of fuzzy single-molecule fluorescence imaging arising from the fluctuation in molecular fluorescent radiation and lower signal-to-noise ratio. The invention provides a method and device for improving the definition of single-molecule fluorescence imaging. The method comprises the following steps of: scanning and irradiating a single-molecule sample by using laser which is subjected to intensity modulation by an acousto-optic modulator; receiving fluorescent photons emitted by the single-molecule sample and converting the fluorescent photons into a standard logic electrical pulse output signal by using a single-photon detector; inputting the logic electrical pulse output signal to a lock-in amplifier, meanwhile, inputting a synchronous sine waveform modulated voltage signal to the lock-in amplifier; and demodulating the logic electrical pulse output signal to obtain a detected fluorescence spectrum signal and imaging the fluorescence spectrum signal. According to the invention, the intensity modulation to the single-molecule fluorescent photons is achieved by using an intensity modulated excitation light field, the quantum fluctuation in photon counting is eliminated by using analog signals demodulated by the lock-in amplifier, the signal-to-noise ratio is increased, and therefore, the high-definition single-molecule fluorescence imaging is achieved.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Method for determining infiltration depth and infiltration capacity of protection agent on surface of cement-based material through fluorescent dye
ActiveCN105043955AHigh precisionSimple methodSurface/boundary effectPermeability/surface area analysisFluorescent spectraEnvironmental engineering
The invention provides a method for determining the infiltration depth and infiltration capacity of a protection agent on the surface of a cement-based material through a fluorescent dye. The method comprises the following steps: mixing the protective agent with the fluorescent dye reaching up to the amount of testing, making a mixture of the fluorescent dye and the protective agent act on the surface of the cement-based material at a certain age, sampling at different depths of the cement-based material, and performing fluorescence spectrum detection on samples, thereby obtaining the infiltration depth and concentration distribution of the fluorescent dye according to a ratio of fluorescence strength, the fluorescent dye and the protective agent, and further obtaining the content of the protective agent in different depth ranges of the samples. The method is simple and feasible, is short in measurement period, low in cost and wide in application range, can be applied to quantitative analysis on the concentration and mass distribution of the protective agent at different infiltration depth parts, and can be used for precisely evaluating the infiltration performance of the protective agent on the surface of the cement-based material and further effectively controlling the exertion of effect of the protective agent in the cement-based material.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Fluorescent probe and detection method for detection of methamphetamine or/and ketamine
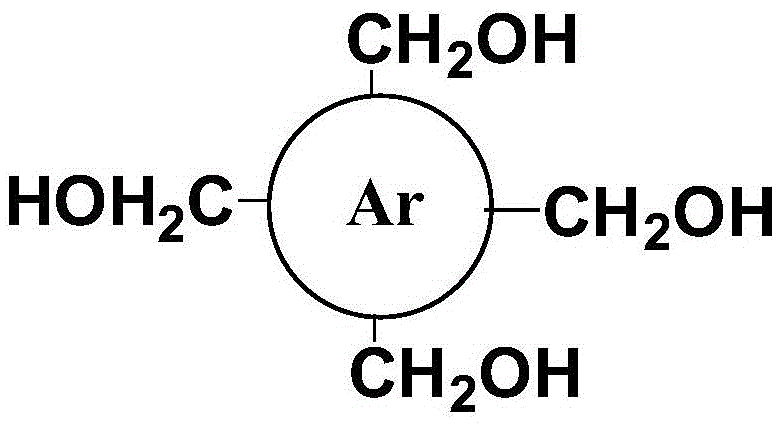
ActiveCN105548098AEasy to prepare in large quantitiesOptimal Control StructureOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorArylAlcohol
The invention relates to a fluorescent probe and detection method for detection of methamphetamine or / and ketamine. The fluorescent probe is characterized in that it is a substance composed of an aryl methyl alcohol structure and can emit fluorescence. The detection method consists of: preparing a solution of the probe, coating a substrate surface with the solution, and performing volatilization to remove the solvent so as to obtain a sensing film; and dropping a to-be-detected methamphetamine or ketamine solution to the sensing film surface directly, contrasting the fluorescence color and brightness change before and after dropwise adding, thus realizing detection of methamphetamine or ketamine. Specifically, Ar is a group selected from A1-A20. The detection method provided by the invention has the advantages of quick and sensitive detection reaction, the whole detection process can be realized within a few seconds, and the detection process has no need of adding any auxiliary reagent, thus avoiding background interference and reagent pollution. The probe can react with drugs to cause the change of the absorption and fluorescence spectrum of the material, and whether drugs exist can be determined according to the spectral signal change, also the drug concentration can also be determined according to the change degree, thereby realizing qualitative and quantitative detection of drugs.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
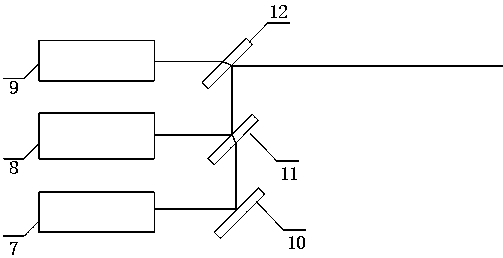
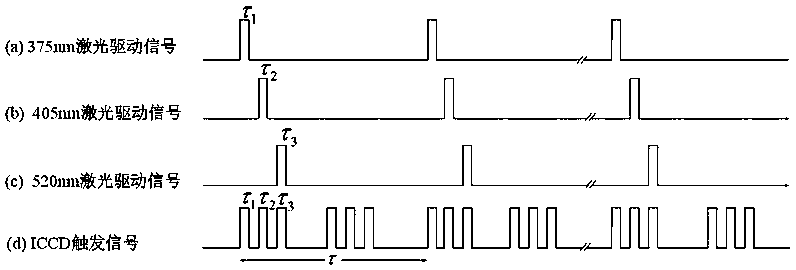
Remote sensing detection device with multi-wavelength time division excitation for fluorescent substances in water and detection method of remote sensing detection device
PendingCN107831155ASimple structureEasy Assembly SchedulingFluorescence/phosphorescenceSpectroscopyTime-sharing
The invention provides a remote sensing detection device with multi-wavelength time division excitation for fluorescent substances in water, comprising a data processing system connected with a lasercontroller that is also connected with a multi-wavelength laser emission system. The multi-wavelength laser emission system emits laser of different wavelengths to a target on the sea, and fluorescentsubstances in sea water are excited to irradiate with fluorescence. The remote sensing detection device also comprises a telescope for receiving fluorescence, a light splitting system for chromatically dispersing an optical signal from the telescope into optical signals having sequentially arranged wavelengths, and an ICCD (intensified charge coupled device) camera for acquiring the optical signals formed by the light splitting system; the ICCD camera is connected with the data processing system. In conjunction with a laser detection process, the remote sensing detection device can make fulluse of fluorescence spectrum division and fusion analytical capacities of exciting light sources having different wavelengths, qualitative and quantitative analytical capacities are effectively enhanced, and the remote sensing detection device is particularly applicable to rapid measurement of the composition and contents of fluorescent substances in water.
Owner:WEIHAI VOCATIONAL COLLEGE +1
Method and device for real-time online monitoring of sewage treatment plant
PendingCN108287140ASimple structureReduce installation, operation and maintenance costsColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescent spectraUltraviolet lights
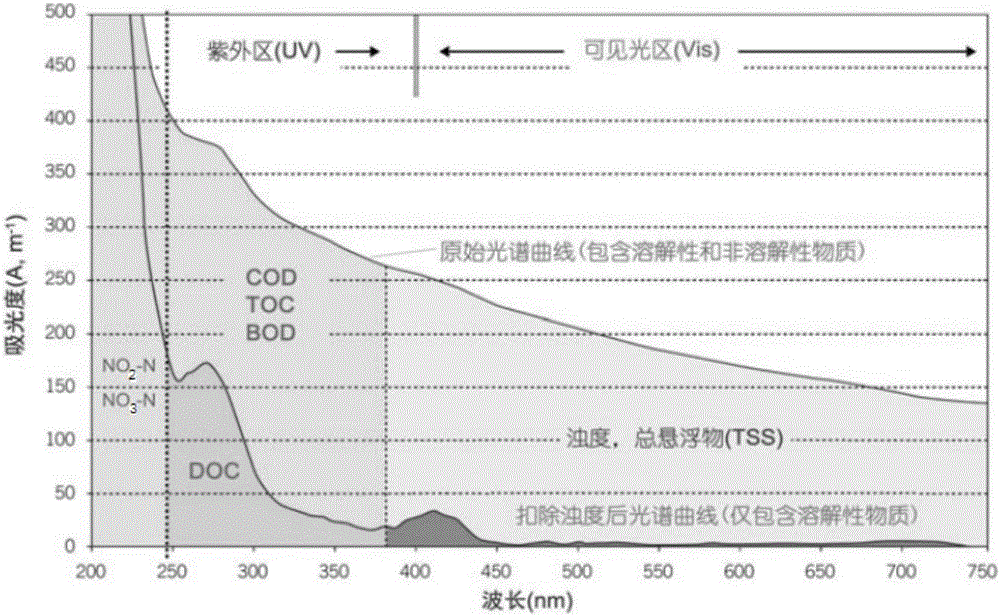
The invention provides a method and device for real-time online monitoring of a sewage treatment plant. Dual-mode detection of an ultraviolet spectrum method and a three-dimensional fluorescent spectrum method is involved. The ultraviolet spectrum method involves a multi-wavelength ultraviolet irradiation device, a water sample container and an absorption spectrum, the multi-wavelength ultravioletirradiation device can emit ultraviolet light of various wavelengths, the water sample container has a certain thickness b, and the absorption spectrum includes feature points and feature vectors ofthe full-wave-band absorption spectrum; the three-dimensional fluorescent spectrum method involves a multi-wavelength emission device, a water sample container and a fluorescence emission spectrum, the multi-wavelength emission device can constantly change the excitation wavelength, the fluorescence emission spectrum comprises emission spectra under different emission wavelengths, the ultravioletspectra and the fluorescent spectra have the high complementarity and can be combined for monitoring the sewage water quality change condition, and analytic measurement of various parameters of NO2, NO3, COD, DOC, BOD, TOC, TSS and the like can be performed.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com