Optical excitation fluorescent spectra system having no requirement of stability of excitation light source
A technology of excitation light source and stability, applied in the field of spectral analysis, which can solve the problems such as the influence of the response curve, the influence of the test results, and the questioning of the repeatability, stability and reliability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
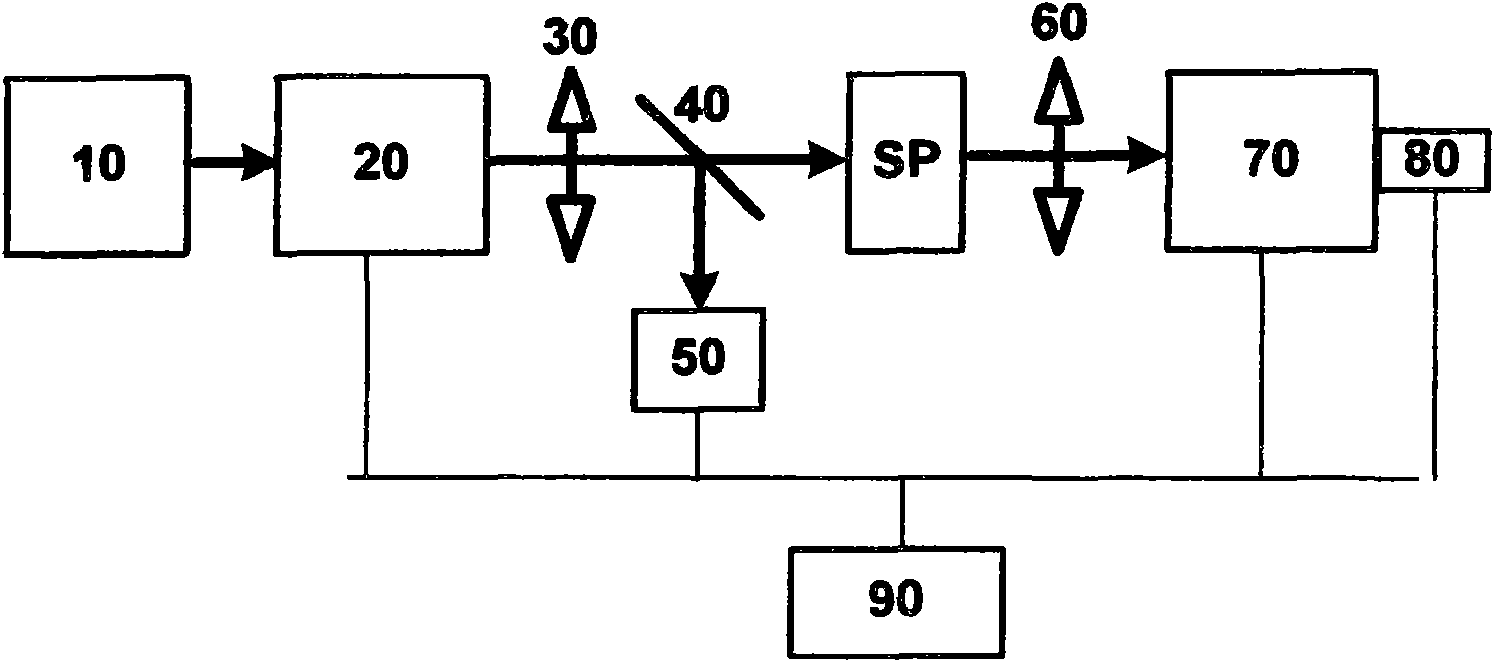
[0025] see figure 1 As shown, a set of photoexcited fluorescence spectrum system of the present invention has no stability requirement to the excitation light source, and the system includes:
[0026] A light source 10, the light source 10 is selected according to the excitation light wavelength range required by the sample, and the light source 10 is a xenon lamp or a halogen tungsten lamp in a broad-spectrum light source;
[0027] A spectrometer 20, the spectrometer 20 is located behind the light source 10, and is used to disperse the broad-spectrum optical signal emitted by the light source into a narrow-band light source or a monochromatic light source, and the selection of the grating of the spectrometer 20 is determined by the spectral wavelength range of the excitation light;
[0028] An excitation light converging element 30, the excitation light converging element 30 is located behind the spectrometer 20, and is used for converging the excitation light split by the sp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com