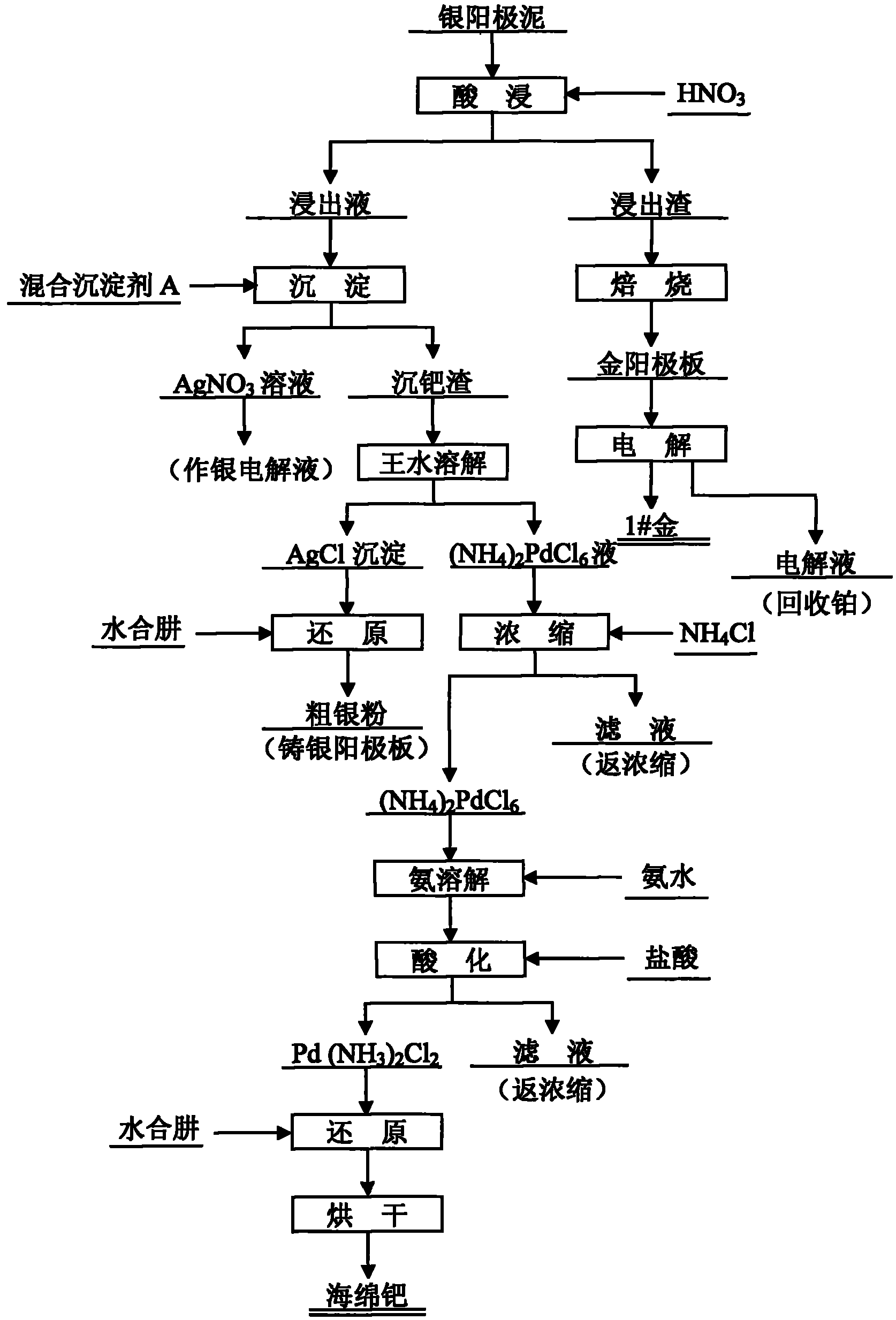
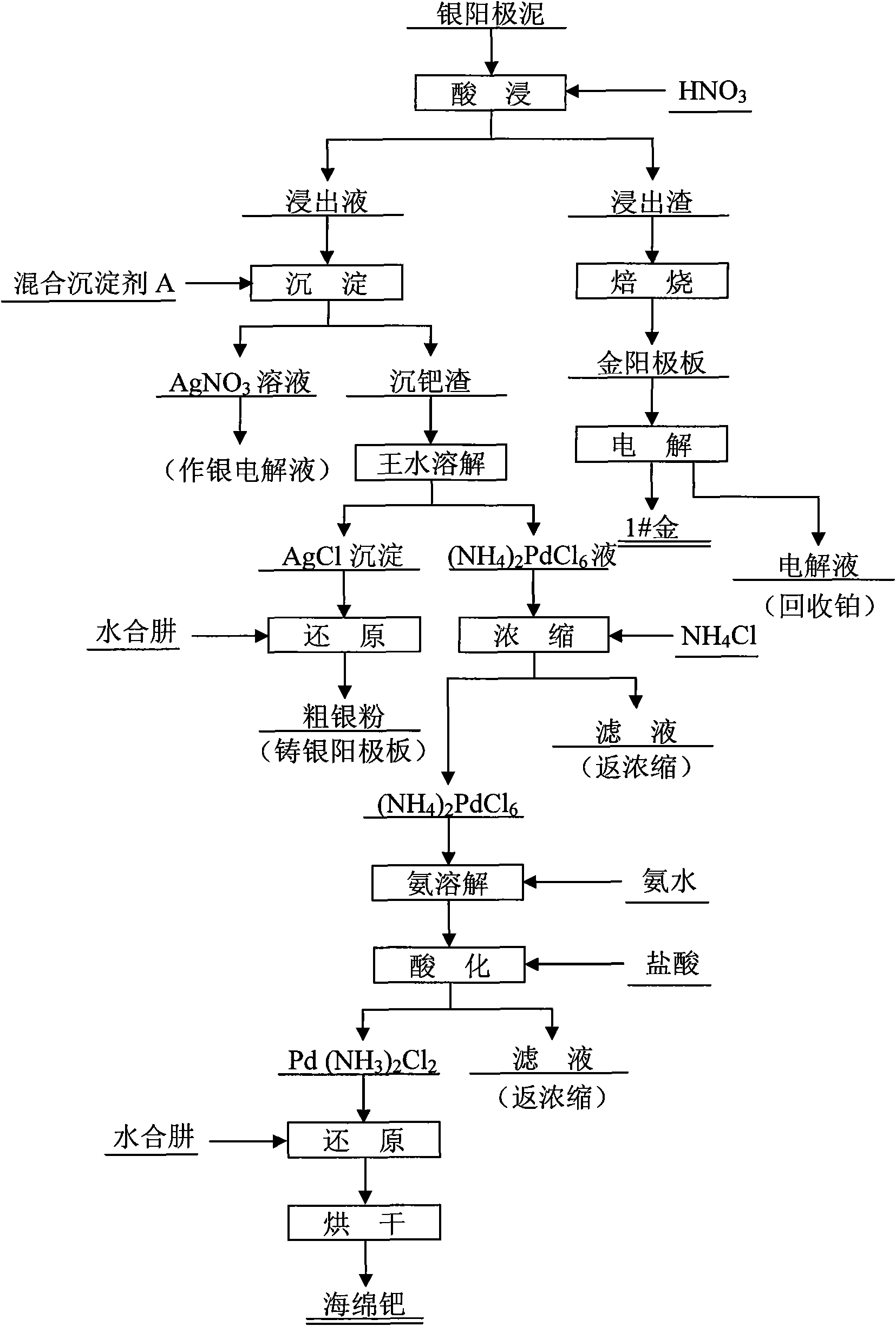
Silver anode mud treatment process
A silver anode slime and treatment process technology, which is applied in the field of silver anode slime treatment process, can solve the problems of economic loss, difficulty in miniaturization, low recovery rate, etc., achieve high comprehensive recovery degree, obvious economic benefits, and realize open-circuit recovery Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0013] A treatment process for silver anode slime, leaching silver anode slime with 20% nitric acid solution (liquid-solid ratio 2:1) with mechanical stirring at 50°C, silver, palladium and base metals enter the solution, while gold and platinum remain in the slag middle. After the leaching slag is roasted to remove impurities, the gold anode plate is cast for electrolysis to obtain 1# gold, and the electrolyte can recover platinum. Adjust the pH of the leaching solution to 0.5, add a mixed precipitant A solution of 1 times the theoretical amount to selectively precipitate palladium at 70°C, and obtain a precipitated palladium residue; the liquid after the palladium precipitation is mainly AgNO 3 solution, back to silver electrolysis. The precipitated palladium residue is completely dissolved in aqua regia and then filtered. The filter residue is mainly AgCl precipitate, which is reduced with hydrazine hydrate to obtain coarse silver powder, which is then cast back into the s...
Embodiment 2
[0015] A treatment process for silver anode slime, leaching silver anode slime with 25% nitric acid solution (liquid-solid ratio 3:1) at 60°C with mechanical stirring, silver, palladium and base metals enter the solution, while gold and platinum remain in the slag middle. After the leaching slag is roasted to remove impurities, the gold anode plate is cast for electrolysis to obtain 1# gold, and the electrolyte can recover platinum. Adjust the pH of the leaching solution to 1.5, add a mixed precipitant A solution 1.2 times the theoretical amount to selectively precipitate palladium at 80°C, and obtain a precipitated palladium residue; the solution after the precipitated palladium is mainly AgNO 3 solution, back to silver electrolysis. The precipitated palladium residue is completely dissolved in aqua regia and then filtered. The filter residue is mainly AgCl precipitate, which is reduced with hydrazine hydrate to obtain coarse silver powder, which is then cast back into the s...
Embodiment 3
[0017] A treatment process for silver anode slime, leaching silver anode slime with 30% nitric acid solution (liquid-solid ratio 4:1) with mechanical stirring at 70°C, silver, palladium and base metals enter the solution, while gold and platinum remain in the slag middle. After the leaching slag is roasted to remove impurities, the gold anode plate is cast for electrolysis to obtain 1# gold, and the electrolyte can recover platinum. Adjust the pH of the leaching solution to 2.5, add a mixed precipitant A solution 1.4 times the theoretical amount to selectively precipitate palladium at 90°C, and obtain a precipitated palladium residue; the solution after the precipitated palladium is mainly AgNO 3 solution, back to silver electrolysis. The precipitated palladium residue is completely dissolved in aqua regia and then filtered. The filter residue is mainly AgCl precipitate, which is reduced with hydrazine hydrate to obtain coarse silver powder, which is then cast back into the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com