Analytical method for determining aromatic constituents in tea
An analysis method and quantitative analysis technology, applied in the direction of analyzing materials, measuring devices, and material separation, can solve problems such as poor selectivity, limited coating types, and large differences in enrichment capabilities, and achieve mild conditions, eliminate pollution, and operate simple effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1 Aroma Analysis of Longjing Tea
[0026] After a large number of experiments by the inventor, the optimization conditions and parameters are as follows:
[0027] In order to obtain the parameters of headspace-solid phase microextraction, the inventors found that the weighted amount of tea leaves was 10g, water was added 30ml, and the water bath temperature was 60°C, which was the optimum after the comparative experiment analysis by the inventor. Under this condition, the instrument response value of the main aroma components in tea leaves was the highest. Peak shapes work best.
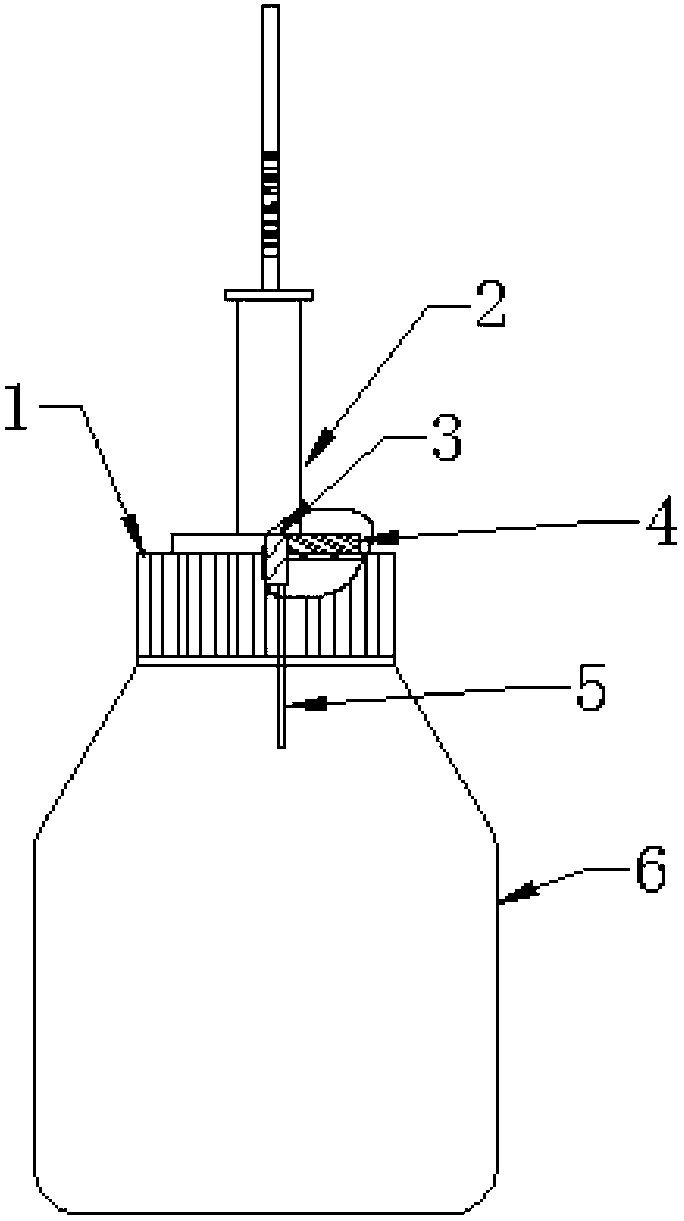
[0028] Headspace-SPME conditions: Weigh 10g of Longjing tea sample, add 30ml of boiling water, shake gently to infiltrate the tea sample, place in a water bath at 60°C, equilibrate for 5min, insert the extraction head into a 500ml sampling bottle (see figure 1 ) static headspace solid phase microextraction for 60min. The sampling bottle is composed of a bottle cap 1; an extraction ne...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment 2 Tieguanyin aroma analysis
[0041] As described in Example 1, headspace-SPME conditions: Weigh 15g of Tieguanyin tea sample, add 40ml of boiling water, shake gently to infiltrate the tea sample, place in a water bath at 70°C, equilibrate for 5 minutes, and place the extraction head Insert a 500ml sampling bottle for static headspace solid-phase microextraction for 50min.
[0042] Extraction head screening: 50 / 30μm DVB / CAR / PDMS type solid phase microextraction head was used, and the GC-MS injection time was 3min. Gas chromatography mass spectrometry conditions and mass spectrometry conditions and analysis methods are also as described in Example 1.
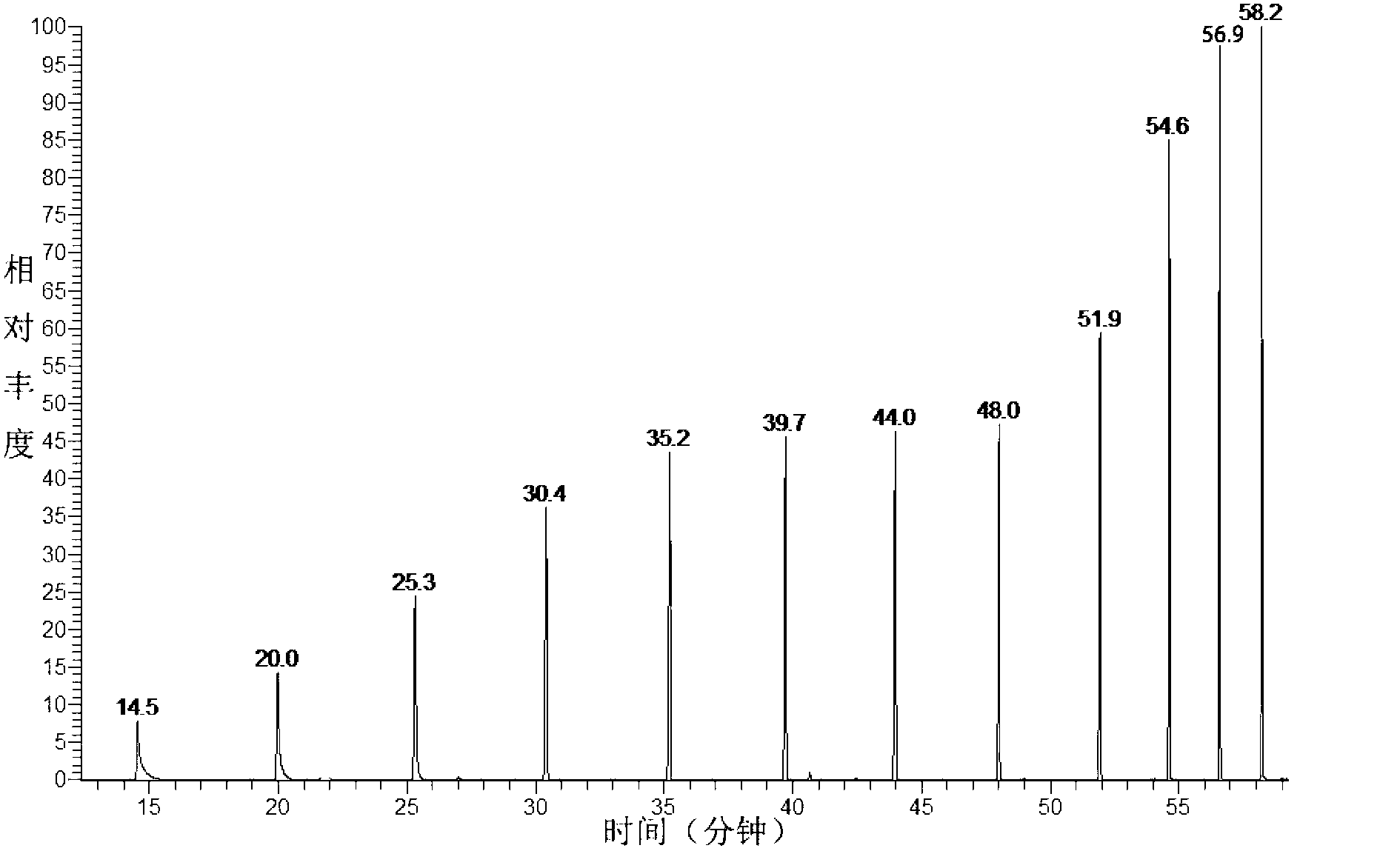
[0043] Results The main components of 40 different aromas were identified, see Table 2, see the qualitative results Figure 4 .
[0044] Table 2: Names and relative contents of aroma components of Tieguanyin
[0045]
[0046]
Embodiment 3
[0047] Embodiment 3 Aroma analysis of black tea
[0048] As described in Example 1, headspace-SPME conditions: Weigh 5g of Tieguanyin tea sample, add 10ml of boiling water, shake gently to infiltrate the tea sample, place in a water bath at 40°C, equilibrate for 5 minutes, and place the extraction head Insert a 500ml sampling bottle for static headspace solid-phase microextraction for 40min.
[0049] Extraction head screening: 50 / 30μm DVB / CAR / PDMS type solid phase microextraction head was used, and the GC-MS injection time was 3min. Gas chromatography mass spectrometry conditions and mass spectrometry conditions and analysis methods are also as described in Example 1.
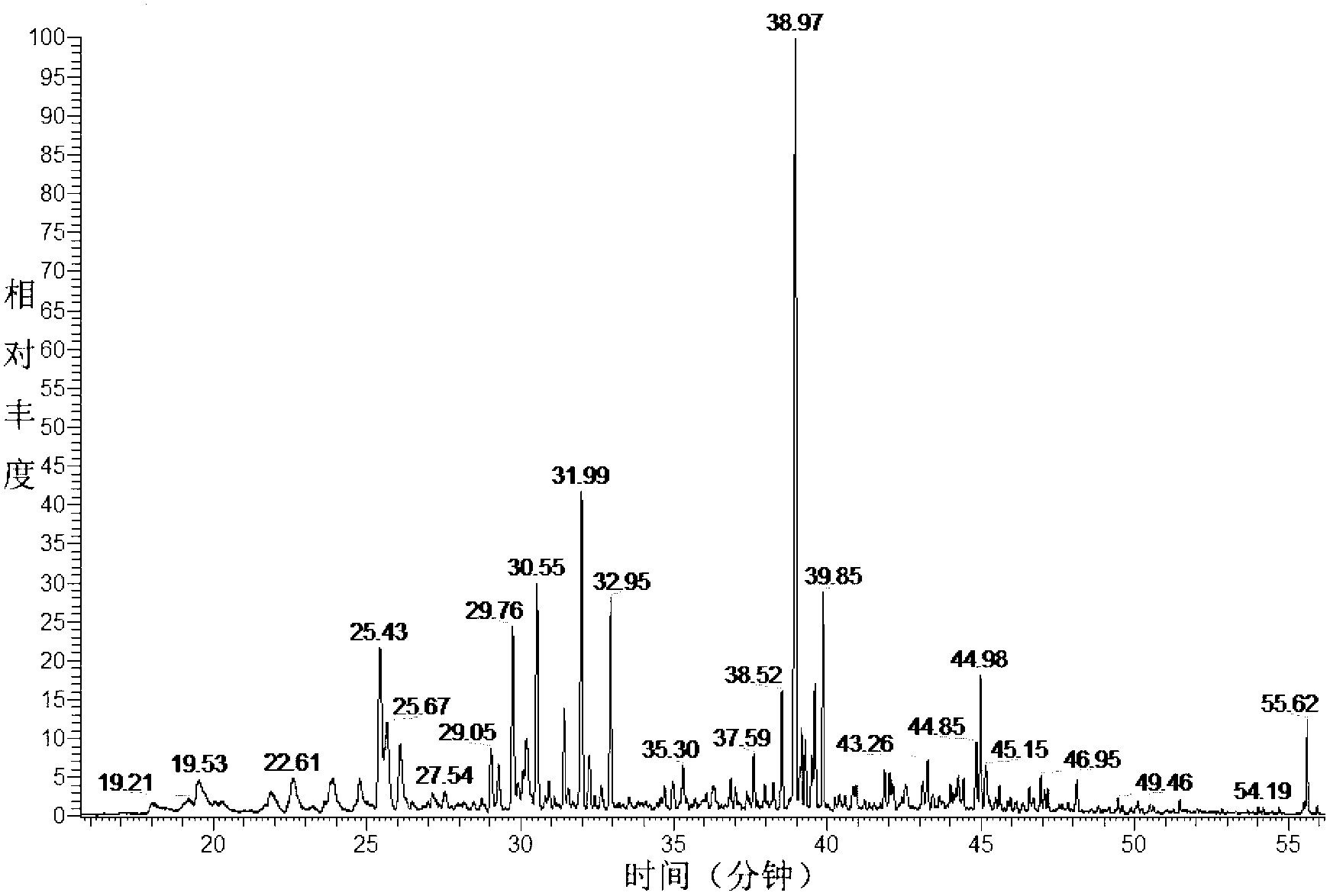
[0050] Results The main components of 40 different aromas were identified, see Table 3, see the qualitative results Figure 5 .
[0051] Table 3: Names and relative contents of aroma components in black tea
[0052]
[0053]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com