Strain identification method based on dunaliella core genome sequence
A genome sequence, Dunaliella technology, applied in the field of plant molecular identification, can solve the problems of lack of, long result output cycle, long calculation time, etc., to achieve broad application prospects, easy computer operation, and a wide range of software effects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] A method for de novo assembly of Dunaliella D.quartolecta whole genome sequencing and its core genome sequence fragments, comprising the following steps:
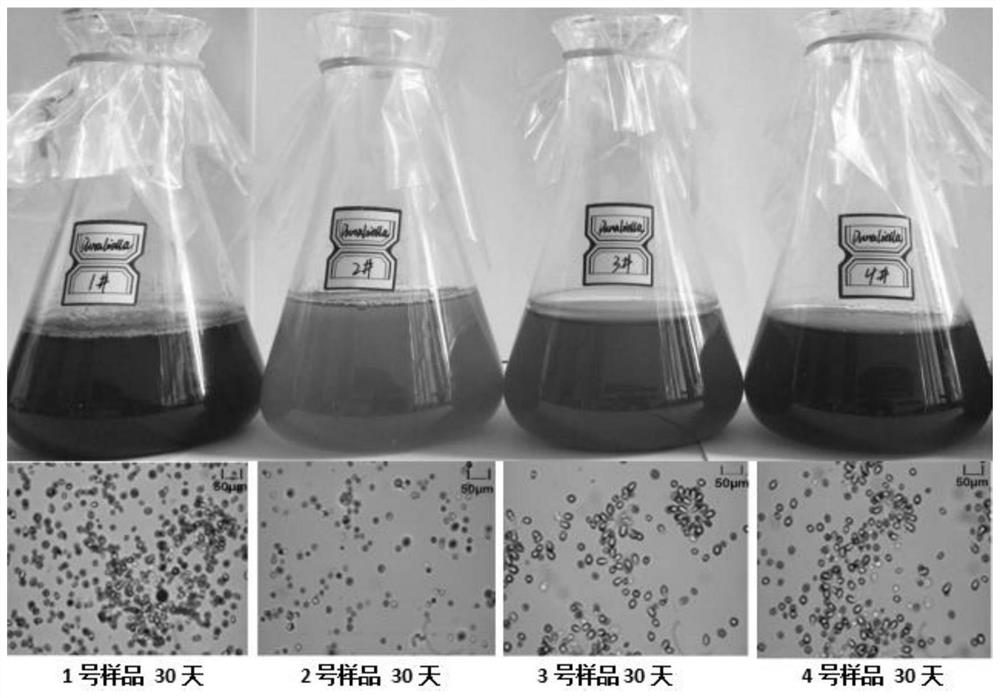
[0051] Step 1: Pick a single clone of the algal cells of a strain of Dunaliella D.quartolecta under sterile conditions, and carry out indoor expansion culture under sterile conditions after the microscopic examination is qualified. The indoor expansion culture conditions are as follows: the photoperiod is 18h: 6h, light intensity 19000lx, temperature: 23±3°C, maintain a sterile and ventilated environment, shake the culture dish every 5 days to prevent algae cells from adhering to the wall, and take 0.5-1mL algae liquid for microscopic examination, and the culture period is After 28±7 days, prepare the following medium solution for indoor expansion of the algae strains to be tested. The medium formula is as follows:
[0052] 30g / L NaCl, 1.5g / L NaNO 3 , 1.4g / L K 2 HPO 4 , 1.75g / L MgSO4 7H 2 O, 1.36g / LCaCl 2 ·7H 2...
Embodiment 2
[0123] A method for strain identification using the Dunaliella D.quartolecta core genome sequence, comprising the following steps:
[0124]Step 1, sample collection, purification and cultivation: collect the algae strain to be tested (tentatively named Dunaliella sp.), purify the algae strain to be tested and carry out indoor expansion culture, the specific steps are: aseptic Picking of single clones under the conditions, after the microscopic examination is qualified, carry out indoor expansion culture under sterile conditions, the indoor expansion culture conditions are: photoperiod 18h: 6h, light intensity 19000lx, temperature: 23±3℃, keep sterile In a ventilated environment, shake the culture dish every 5 days to prevent algae cells from adhering to the wall, and take 0.5~1mL algae liquid for microscopic examination. The culture period is 28±7 days. For expanded culture, the formula of the culture medium is as follows:
[0125] 30g / L NaCl, 1.5g / L NaNO 3 , 1.4g / L K 2 HPO...
Embodiment 3
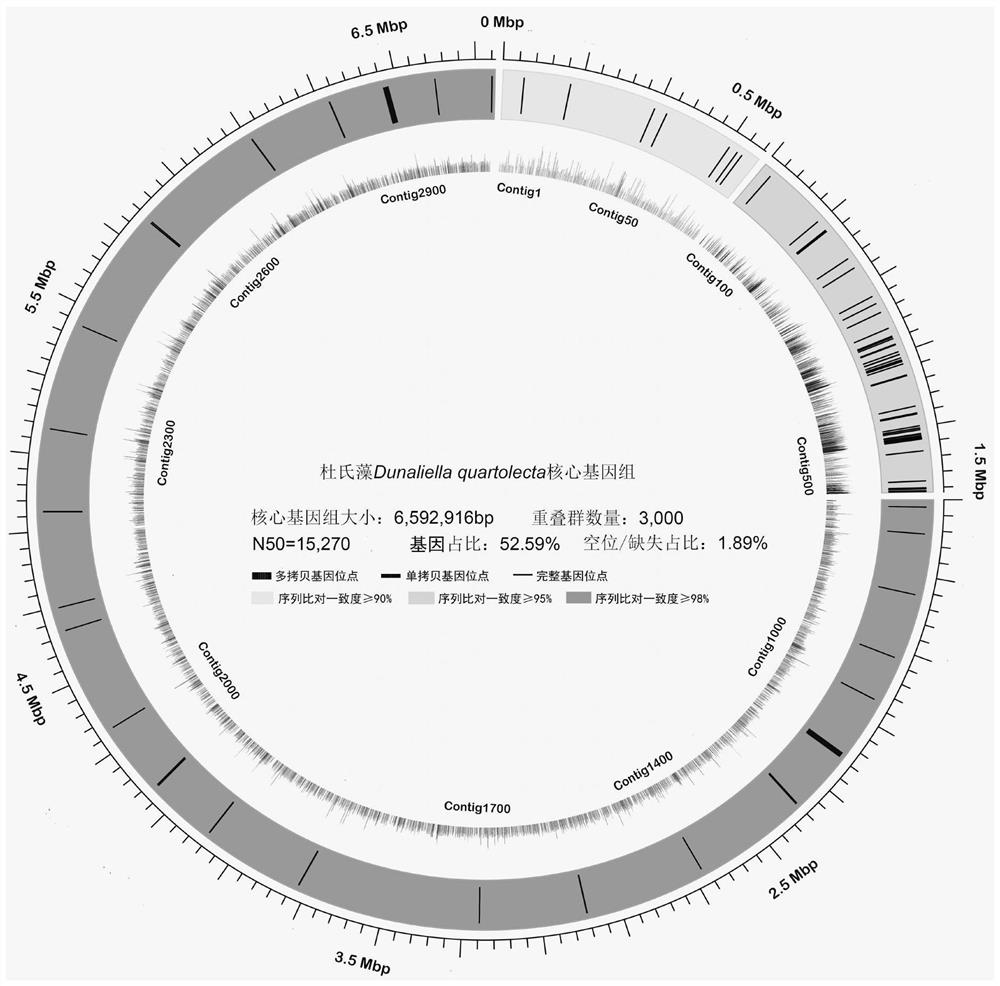
[0170] Using the core genome data of Dunaliella D.quartolecta as a reference, the genetic variation and evolution characteristics of an identified strain Dq_SX genome were analyzed, including the following steps:
[0171] Step 1, referring to the method for screening and assembling Dunaliella D.quartolecta core genome sequencing data constructed in the present invention (see Example 1), use SOAPde novo 2.04 software to analyze the whole genome of an identified Dunaliella strain (tentatively named Dq_SX). The core fragment screening and de novo assembly were performed on the genome sequencing data (see Examples 1 and 2 for the method). The main indicators of the screened and assembled core genome sequence of the algae strain are shown in Table 4.
[0172] Step 2, use the LASTZ 1.02.00 software to perform collinearity analysis on the Dunaliella Dq_SX core genome assembly data constructed in step 1, and obtain the repeated fragments of the duplication events between different regi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com