Diagnostic imaging hepatic tissue-specific contrast medium comprising manganese silicate nanoparticle
A nanoparticle, liver tissue technology, applied in MRI/MRI contrast agent, nanomedicine, nanotechnology, etc., can solve the problems of unresearched differential diagnosis, slow speed of Mn2+, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0109] Example 1. Material preparation and steps
[0110] 1-1. Experimental materials
[0111] Use purchased MnCl without any purification 2 4H 2 O(kanto), sodium oleate (TCI), 1-octadecene (Aldrich), CO-520 (Aldrich), tetraethyl silicate (Acros), NH 4 OH(Samchun Chem.), Ni(NO 3 )6H 2 O(Strem), Cu(NO 3 ) 2 ·3H 2 O(Strem), NaBH 4 (Samchun Chem.), 2-[methoxy(polyethyleneoxy)-propyl]9-12-trimethoxysilane (MPEOPS, Gelest, Inc.), fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC, Aldrich) and 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES, Aldrich).
[0112] 1-2. Preparation of HMS (hollow manganese silicate)
[0113] According to previously reported techniques, by making MnO@SiO 2 / Cu 2+ Annealing followed by selective etching of the outer silica shell of Cu@HSNPs (hollow-structured NPs) (Kim, J.G., Kim, S.M. & Lee, I.S. Mechanistic insight into the yolk@shell transformation of MnO@silica nanospheres incorporating Ni 2+ ionstoward a colloidal hollow nanoreactor.Small 11, 1930-1938(2015)) ...
example 2
[0128] Example 2. Mn Relaxation Properties and T1 Contrast Enhancement Properties of Hollow Manganese Silicate (HMS) Nanoparticles
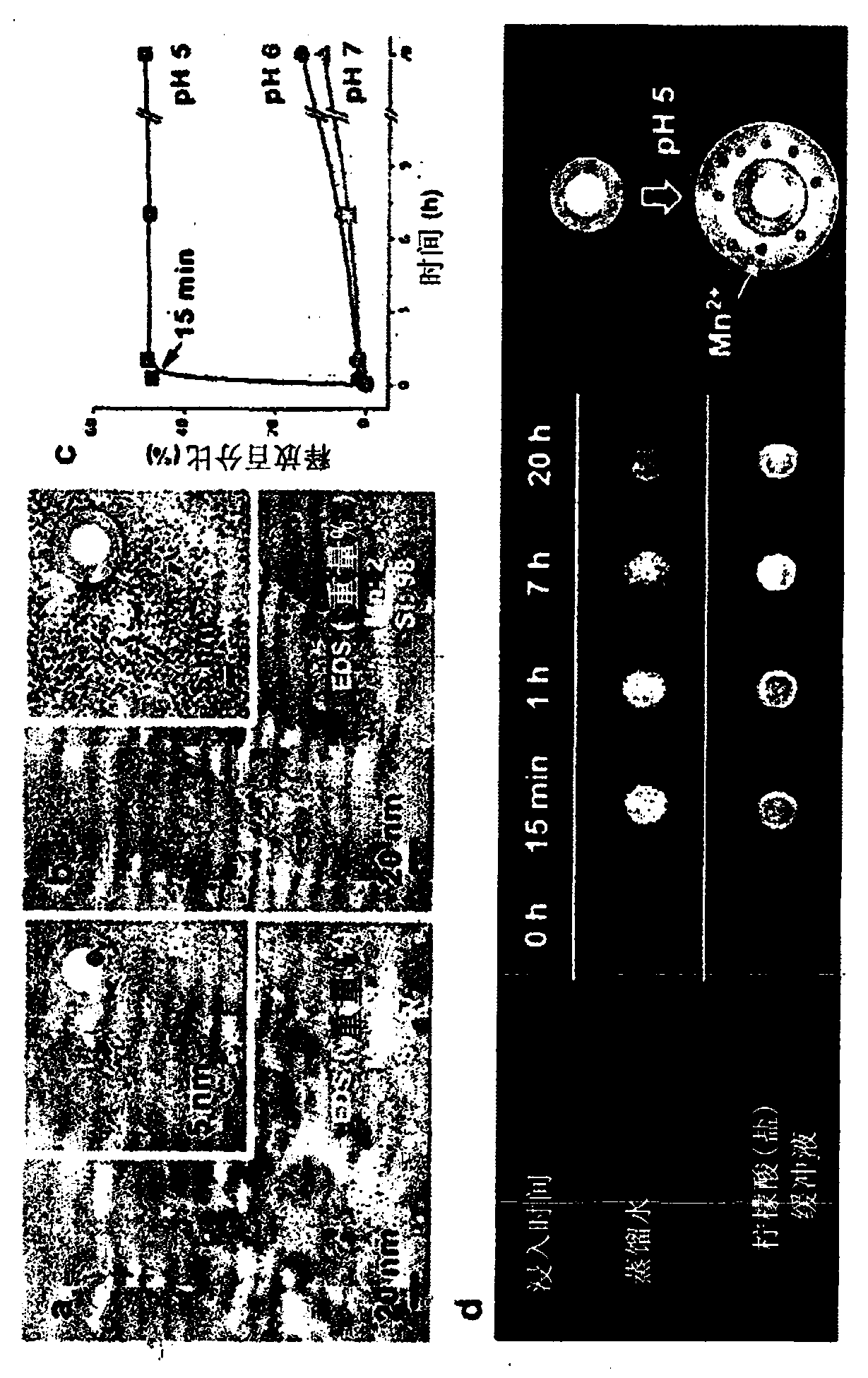
[0129] The Mn relaxation properties and T1 contrast enhancement properties of the HMS prepared in Examples 1-2 were tested according to Examples 1-3. TEM was used to observe the synthesized nanoparticles and the nanoparticles isolated from the pH 5.0 buffer solution ( figure 1 a and figure 1 b).
[0130] like figure 1 c and figure 1 The result of d, when the PEG-modified HMS containing 19.3wt% Mn was immersed in the buffer solution of pH 5.0, all the Mn that could be released 2+ Immediate release and increase to free Mn within 15 minutes 2+ the maximum concentration of ions. On the contrary, when the PEG-modified HMS was immersed in a pH 6.0 buffer solution or distilled water, Mn 2+ Ions are released very slowly ( figure 1 c). Additionally, T1-weighted images in distilled water were not affected by HMS. However, when HMS was added to th...
example 3
[0132] Example 3. Evaluation of contrast-enhancing patterns of HMS in HCC
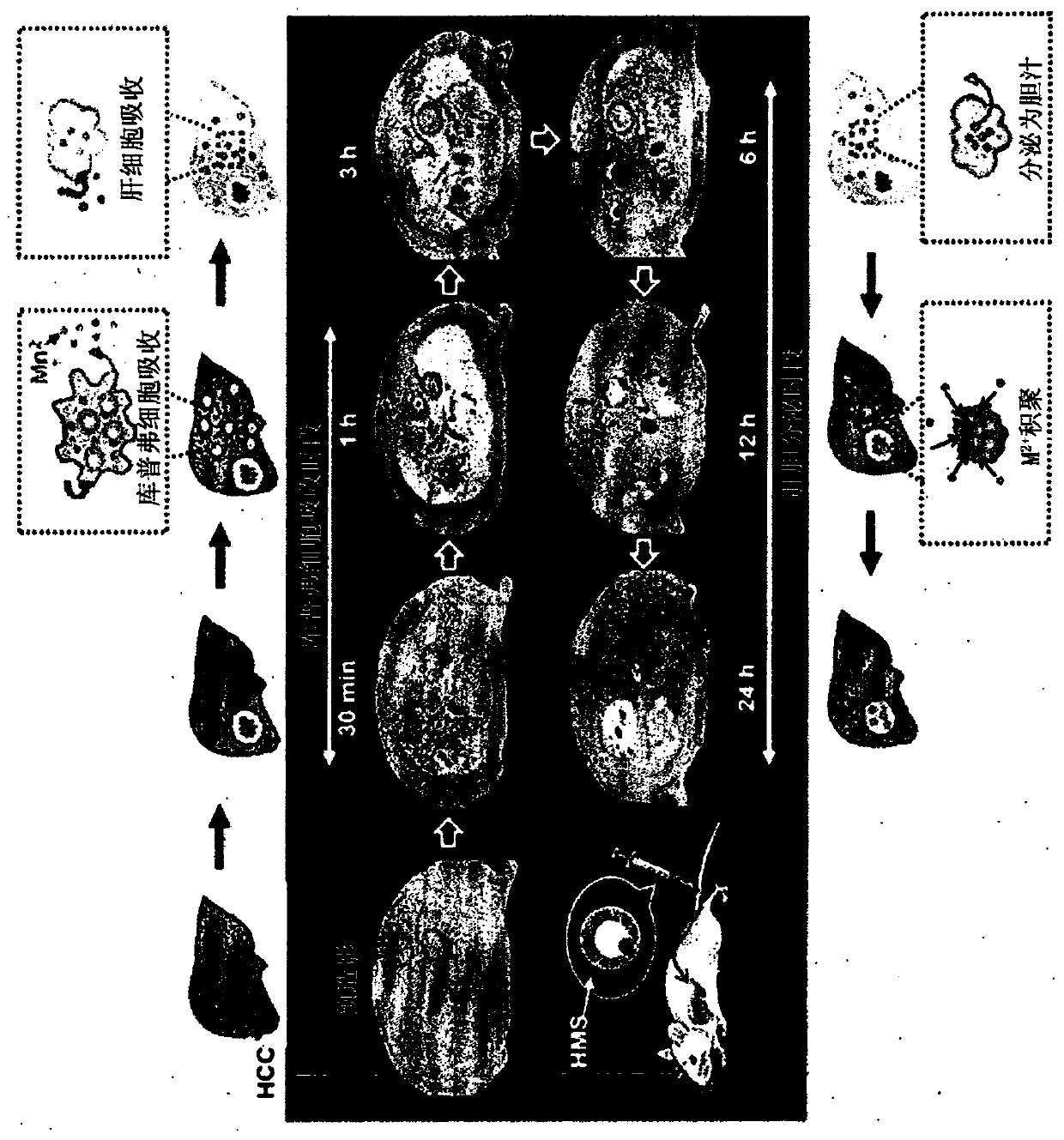
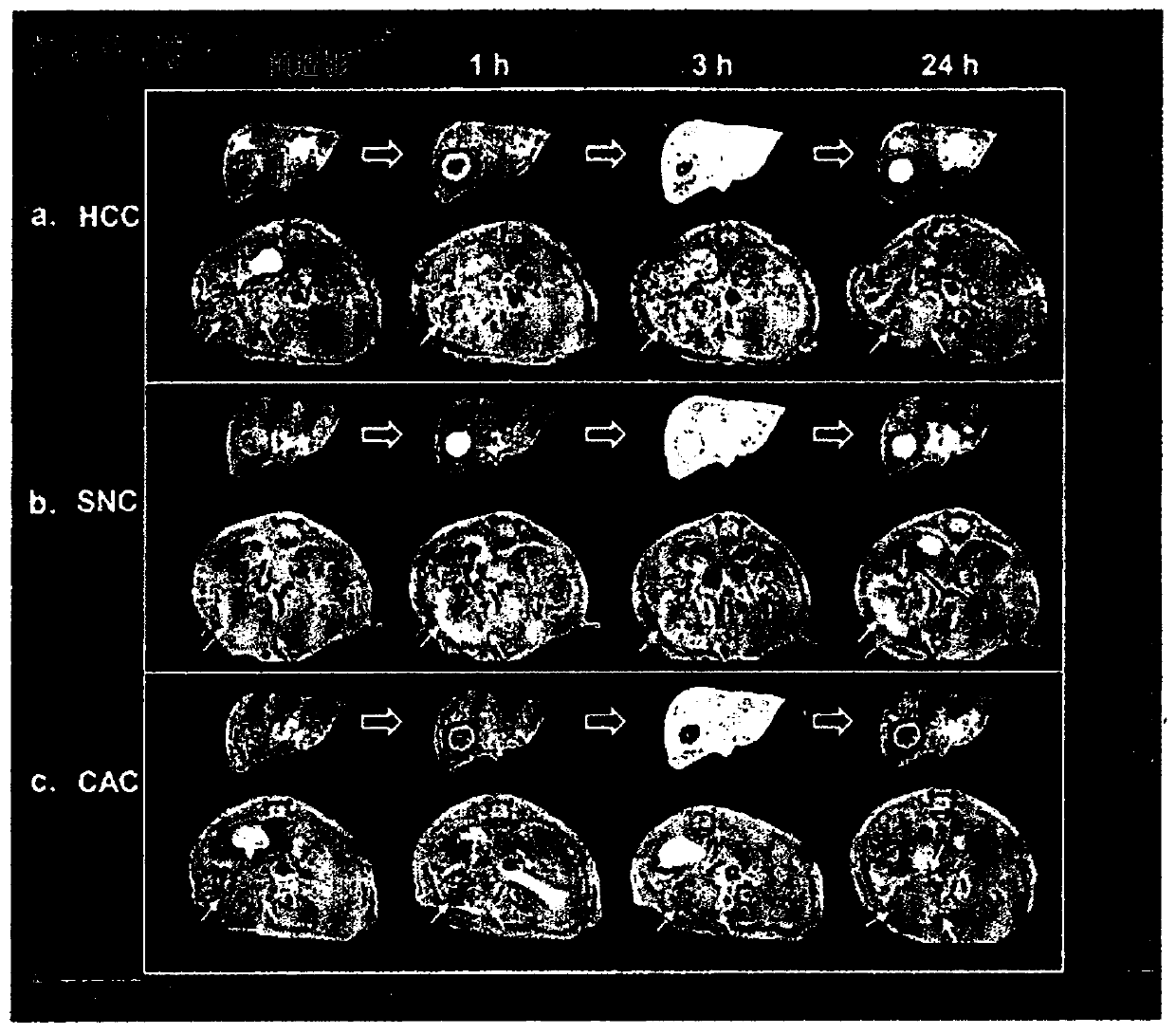
[0133] First, HMS was injected (3 mg / kg body weight) into a human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) model and observed within 0.5 hours to 24 hours after HMS injection to evaluate the potential of HMS as a contrast agent for distinguishing liver tumors sex.
[0134] like figure 2 As a result, obvious contrast enhancement was observed within 0.5 hours to 6 hours after HMS injection, and then slowly began to brighten from the peripheral area to the central area within 6 hours to 24 hours, and the necrotic area was not enhanced.
[0135] It can be interpreted that these results show that during the initial 0.5 h to 6 h period (Cooper cell (Coopercell) uptake phase), Mn 2+ Ions are released from nanoparticles absorbed in Kupffer cells and then released to Mn in liver tissue within 6 hours to 24 hours (biliary release period) 2+ Ions are taken up by hepatocytes and released into bile, ie, ions are taken up...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com