Method for preclinical testing of immunomodulatory drugs
An immunomodulatory drug and drug technology, applied in biological testing, drug combination, immunoglobulin, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Example 1: Comparative Example
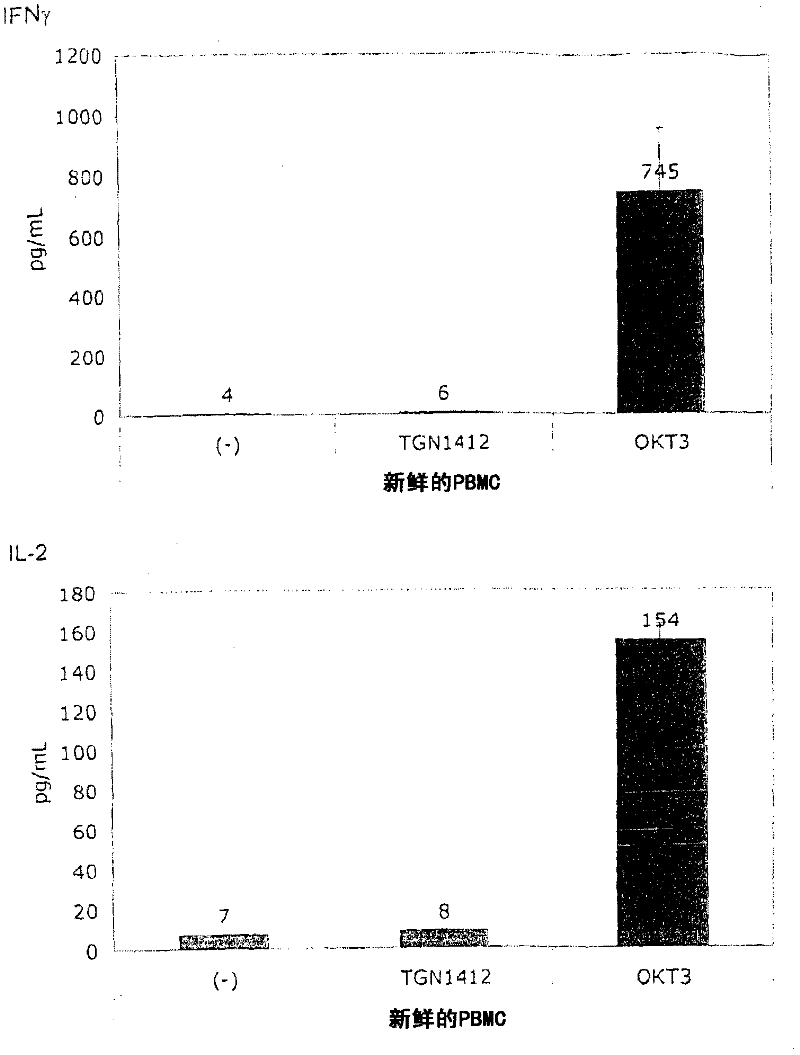
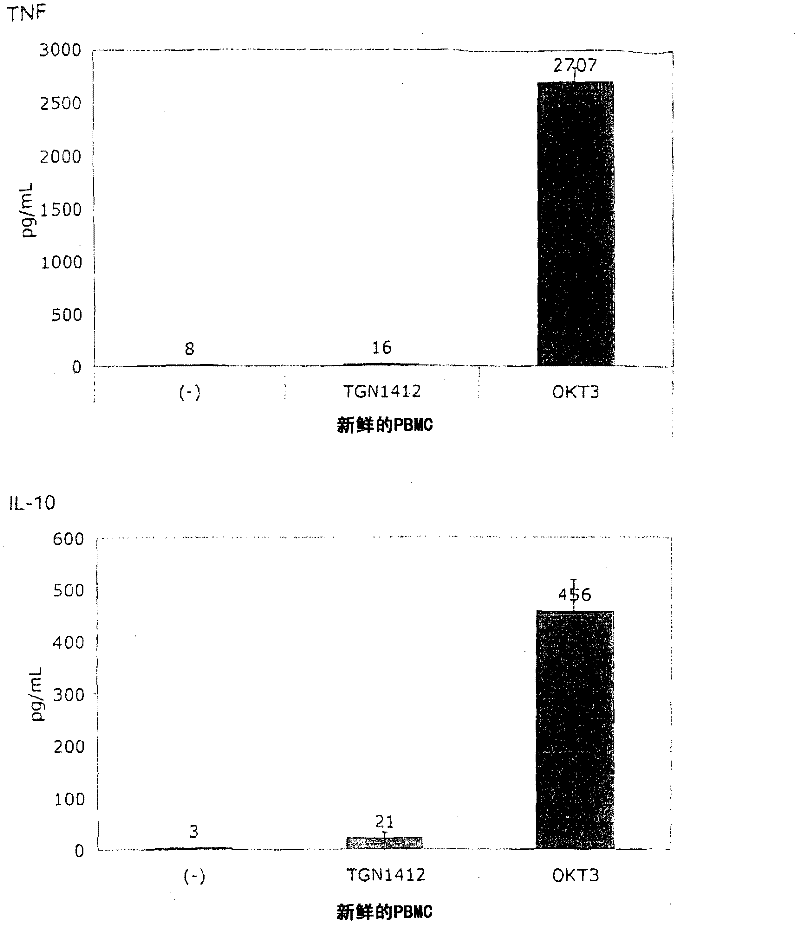
[0060] In order to induce the release of cytokines, the present invention and this comparative example use the standard system of PBMC stimulation because this system is used by researchers all over the world to study the response of human PBMC to immunomodulatory agents. The system uses freshly prepared PBMC, which is separated from heparinized venous blood by centrifugation on a density gradient (Lymphocyte Separation Medium LSM 1077, PAA Laboratories, Pasching, Germany) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Or, using fresh white blood cell concentrate as the raw material for sucrose purification, basically the same result is obtained, where the fresh white blood cell concentrate is used as a by-product in the preparation of platelet concentrate from the leukopenia system (Caridian Gambro BCT) , Lakewood, CO, USA) (Dietz et al., 2006). PBMC were cultured in 96-well tissue culture plates (Greiner bio-one, Frickenhausen, Germany), ...
Embodiment 2
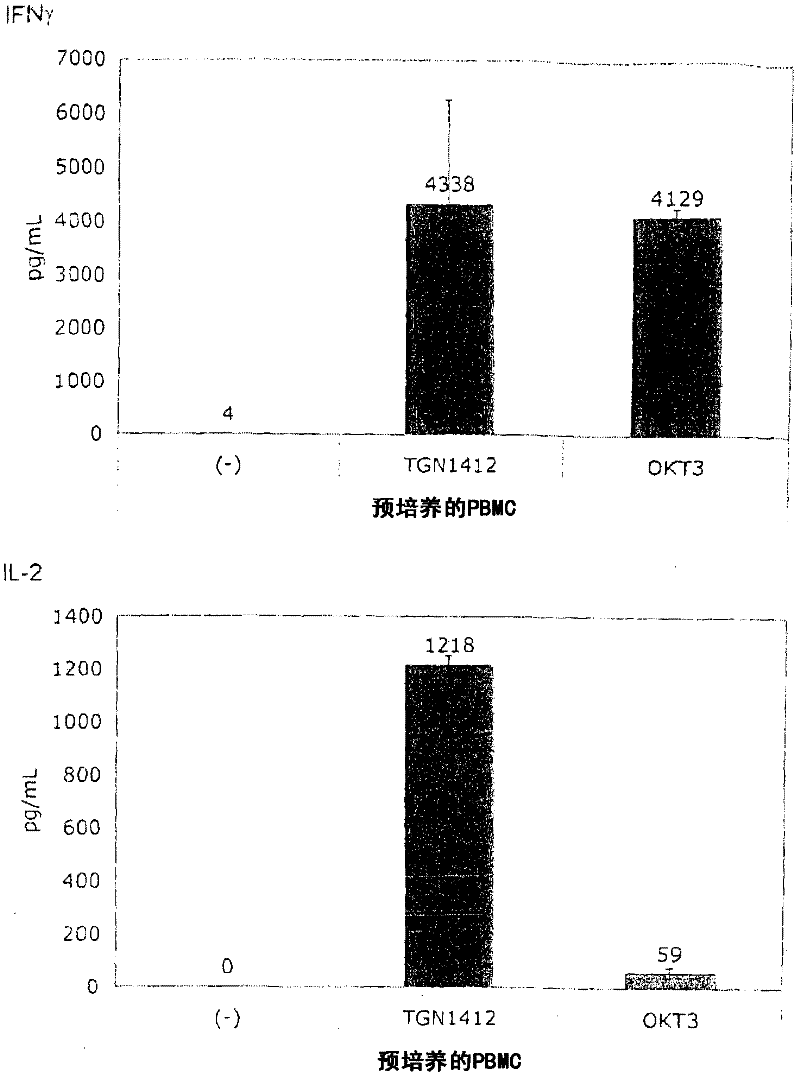
[0065] Example 2: Response by TGN1412 after pre-culture
[0066] for Figure 1B In the test, the PBMC obtained from healthy donors was mixed with 10% in 1.5ml medium in a 24-well flat-bottomed tissue culture plate. 7 / ml culture for 2 days, then rinse and readjust to 10 6 / ml. The same test as described in Example 1 was performed using these cells.
[0067] Figure 1B It is shown that, surprisingly, in the absence of obvious stimulation, the responsiveness to TGN1412 can be restored by simply pre-culturing PBMC for 2 days. When the cells were prepared on December 4, 2008, the number of PBMCs obtained exceeded the number required for this experiment, and the excess cells were stored in culture medium at 37°C for two days. When using these stored cells to perform the same test as previously using fresh cells ( Figure 1A ), something completely unexpected happened: now TGN1412 induces a comparable level of cytokine release such as OKT3. Figure 1B Examples of such tests are provided...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Example 3: Reproducibility of key observations
[0070] figure 2 Summarized the effect of pre-culture on the responsiveness to TGN1412 for 7 individual healthy donors. Data from 7 individual healthy donors are shown, each represented by a symbol. The conditions of antibody stimulation and pre-culture are shown in Figure 1. When there are donor-specific changes in both OKT3 response and TGN1412 response, it is clear that in all cases, fresh donor cells cannot respond to TGN1412 stimulation with cytokine release, and after 2 days of pre-culture This state of refusal disappeared. As illustrated by the huge difference in the level of the cytokine storm experienced by volunteers in the London TGN1412 trial (Suntharalingam et al., 2006), donor-specific changes can be expected.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com