Method for in-vitro directional differentiation inducing of mesenchymal stem cell towards melanocyte
A technology of mesenchymal stem cells and directed differentiation, applied in the direction of artificial cell constructs, animal cells, vertebrate cells, etc., can solve the problems of low immunogenicity and difficult acquisition, and achieve low immunogenicity, easy acquisition, and difficulty in individual differences Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0041] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with specific implementation examples.
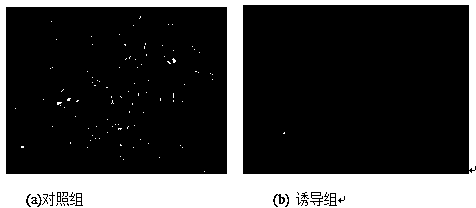
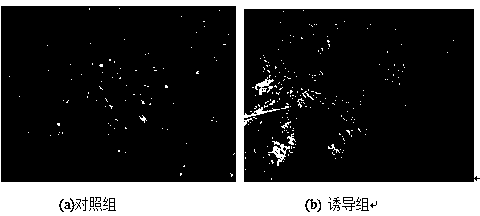
[0042] The method for inducing directional differentiation of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells to melanocytes in vitro is completed according to the following steps:
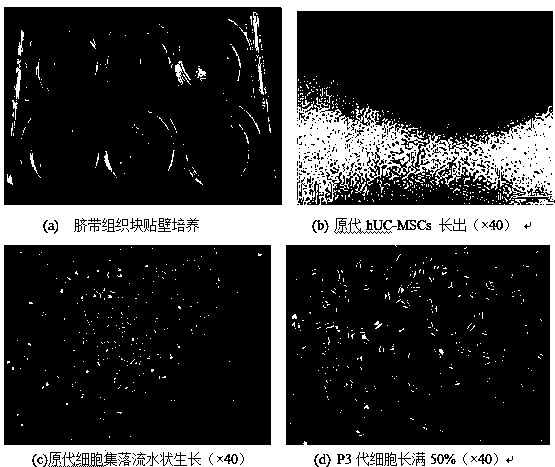
[0043] (1) Cultivation of primary hUC-MSCs by explant method (subculture and morphological observation)
[0044] A. After the human umbilical cord is obtained from the operating table, it is immersed in 0.9% sterile saline and transported aseptically to the laboratory.
[0045] laboratory.
[0046] B. Take it out in the ultra-clean bench, wash 3 times with PBS buffer containing 1% double antibody (penicillin and streptomycin),
[0047] To remove blood stains and fully clean the lumen of the umbilical vein, peel off the arteries and veins, take the connective tissue of the umbilical cord, and cut it into 4-5mm3 tissue pieces.
[0048] C. Inoculate the tissue block into a 6-well ce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com