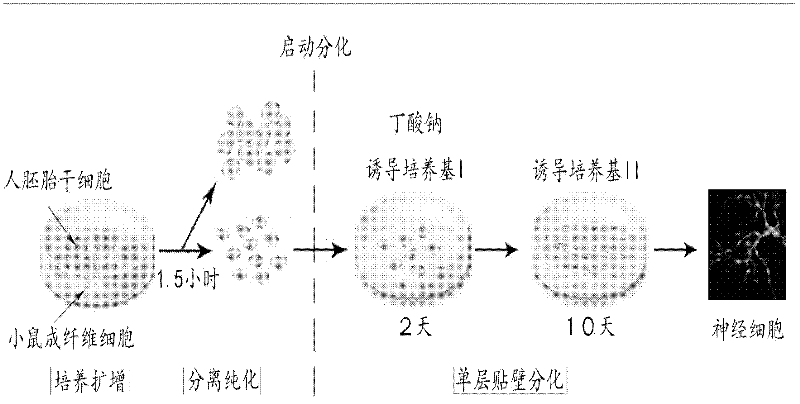
Method for differentiating human embryonic stem cell into nerve cells
A technology of human embryonic stem cells and nerve cells, which is applied in the fields of developmental biology, cell biology and cell therapy, can solve problems such as uneven distribution, complicated operating procedures, and many types of cells, and achieve a short induction cycle and uniform cell differentiation High, easy-to-operate effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Example 1: Induction of neural cell differentiation
[0050] (1) Separation and purification of human embryonic stem cells;
[0051] Inoculate human embryonic stem cells onto mouse fibroblast feeder cells in 0.1% gelatin-coated culture well plates, in human embryonic stem cell culture medium, 37°C, 5% CO 2 , cultured under 100% humidity for 6 days to obtain a cell mixture of mouse fibroblasts and expanded human embryonic stem cells; the obtained cell mixture was digested in the digestion solution for 5 minutes at 37°C, and the suspension was obtained and placed in a human In culture flasks coated with 1% gelatin in embryonic stem cell culture medium, culture at 37°C for 1.5 hours, the mouse fibroblast feeder layer cells will adhere to the wall, while most of the human embryonic stem cells are still suspended in the culture medium, collect the culture medium Centrifuge, and discard the supernatant to obtain amplified human embryonic stem cell monomers; the digestion sol...
Embodiment 2
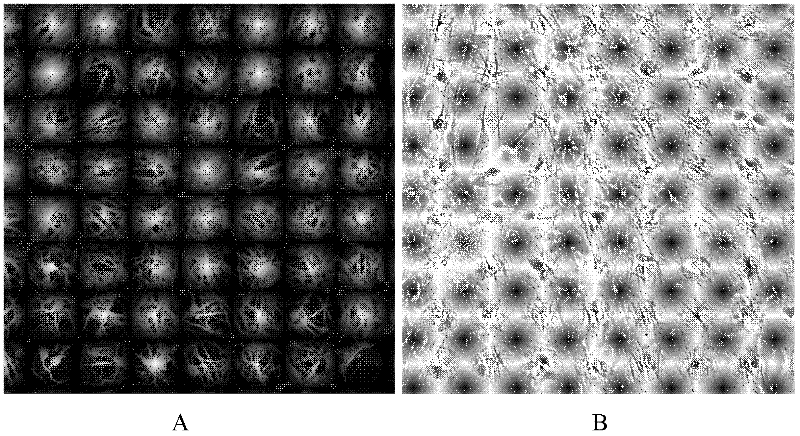
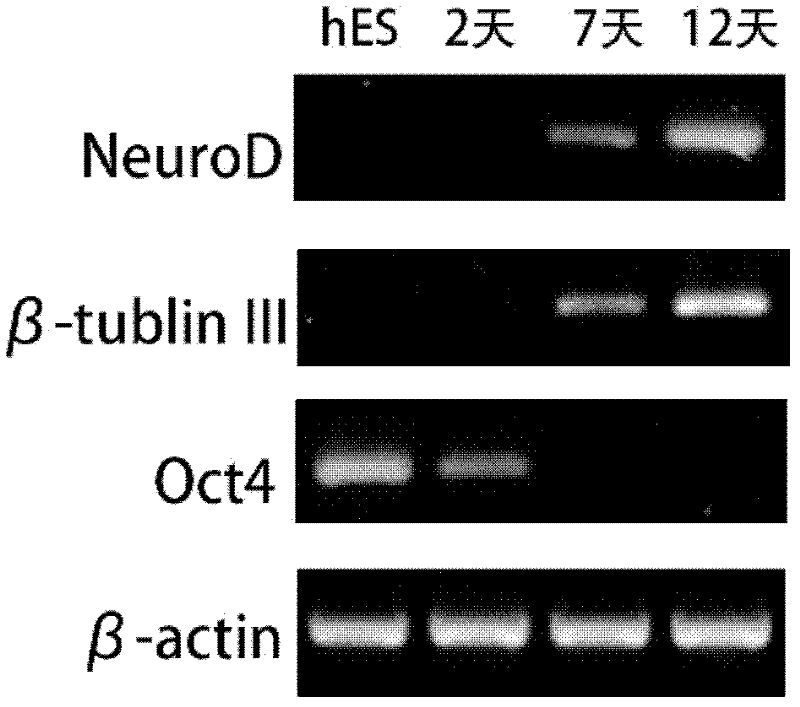
[0056] Example 2: Detection of nerve cells
[0057] 1. Immunohistochemistry
[0058] step
[0059] (1) Add 3 ml of nerve cells obtained by the method in Example 1 to preheat to 35° C., and rinse the cells with Duchenne’s phosphate buffered solution (DPBS) twice, each time for 3 minutes;
[0060] (2) Add 3ml of 4% paraformaldehyde fixative, fix at room temperature for 30min;
[0061] (3) Rinse with DPBS 3 times, 3 minutes each time. Incubate with DPBS containing 1% detergent (Triton X-100) at 37°C for 30 minutes.
[0062] (4) Add 3ml of DPBS (blocking solution) containing 5% goat serum, and act for 30min at room temperature.
[0063] (5) After aspirating and discarding the blocking solution with a pipette tip, add 1:500 diluted mouse anti-human β-tublin III monoclonal antibody (Millipore Company). 4°C overnight (more than 18h).
[0064] (6) Discard the primary antibody reaction solution with a pipette tip, rinse with DPBS 3 times, 5 min each time.
[0065] (7) Add goat a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com