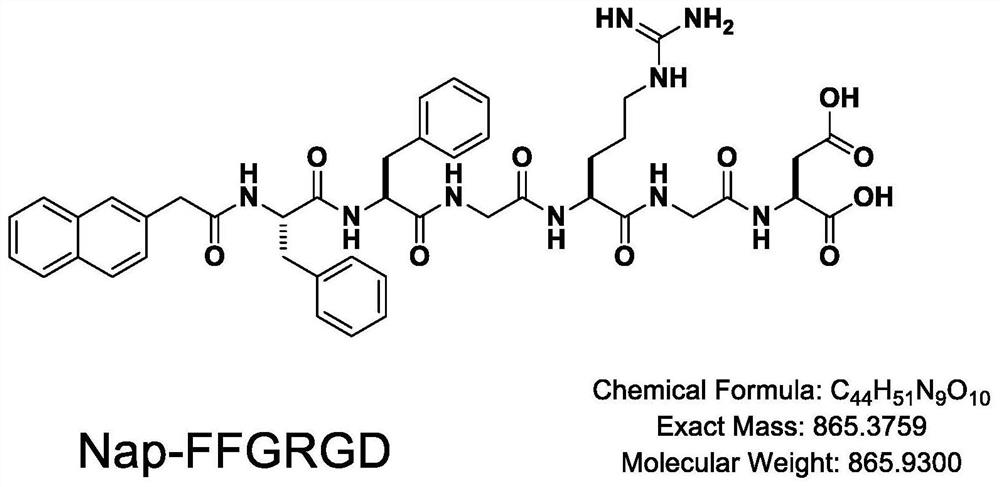
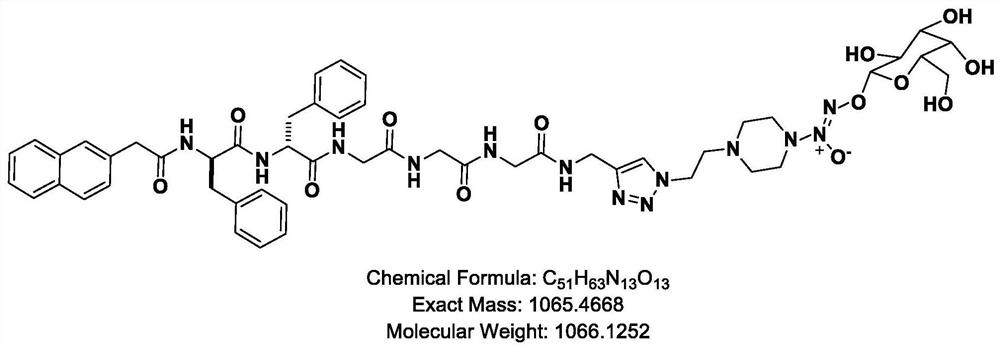
Patents
Literature
105 results about "Secreting cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Secretions in humans can be produced by a single cell or by a group of cells commonly called a gland. Some secretions perform special functions in the body (true secretions); others are eliminated as waste products (excretions). Digestive secretions include saliva, gastric juice, intestinal juice, pancreatic juice, and bile.
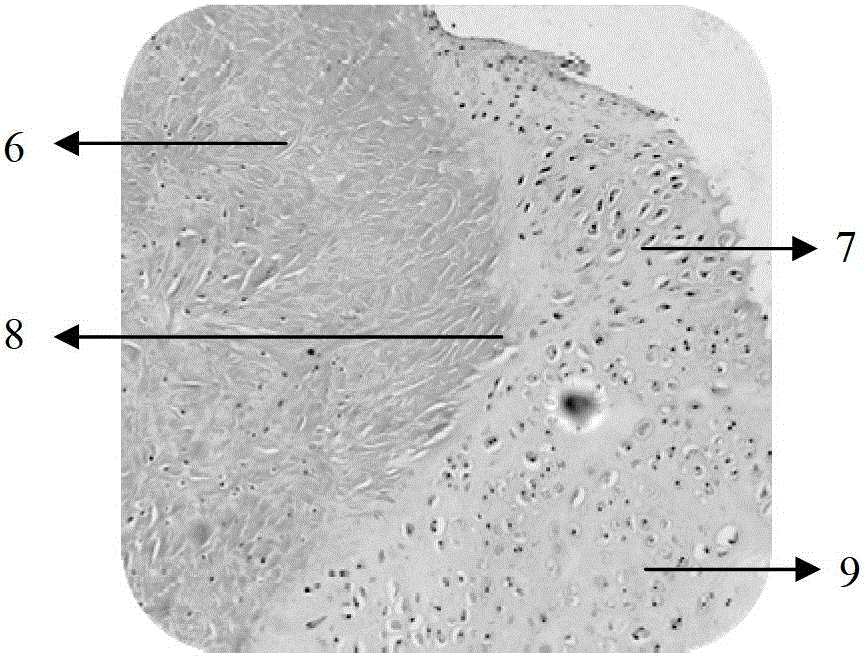
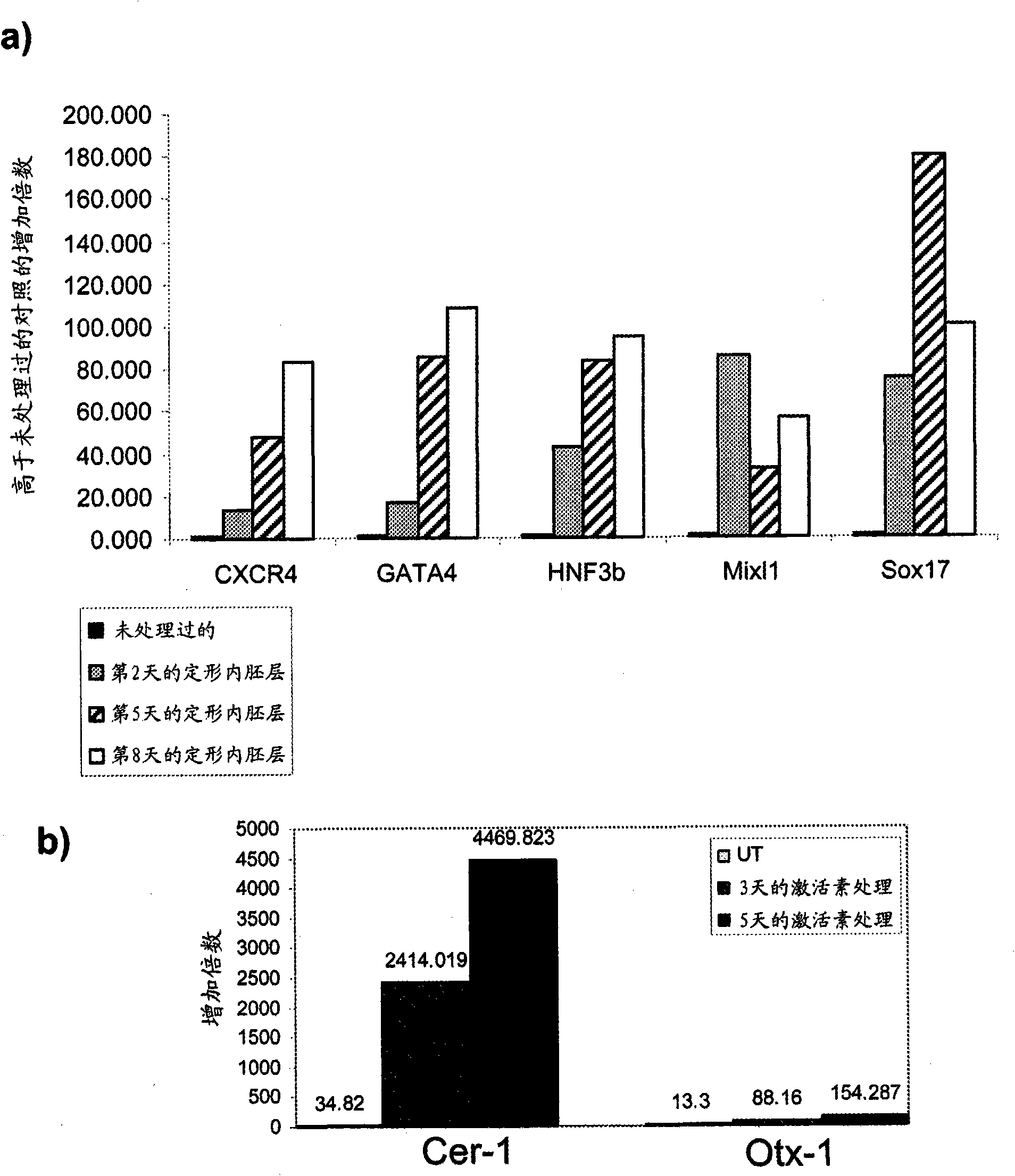
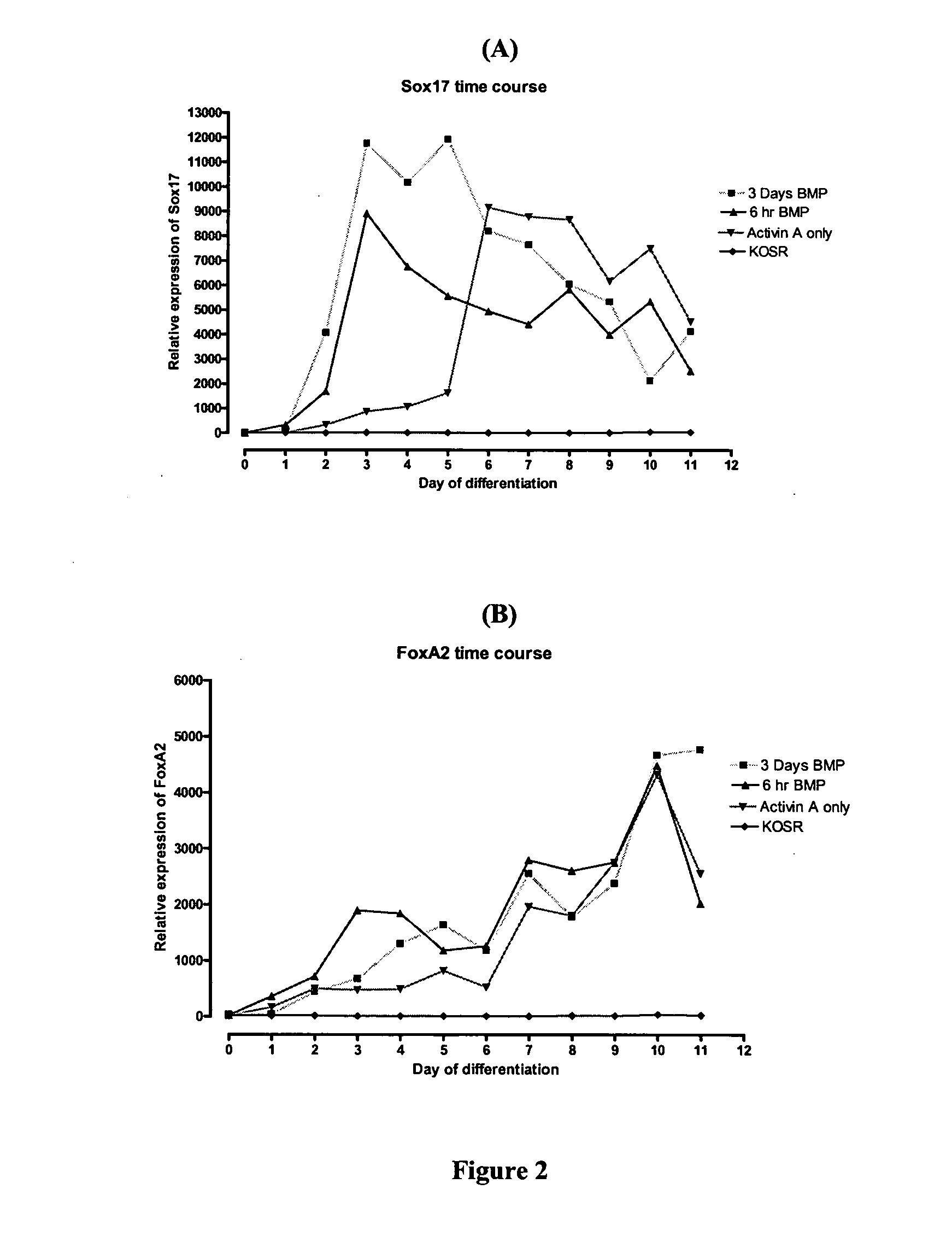
Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells
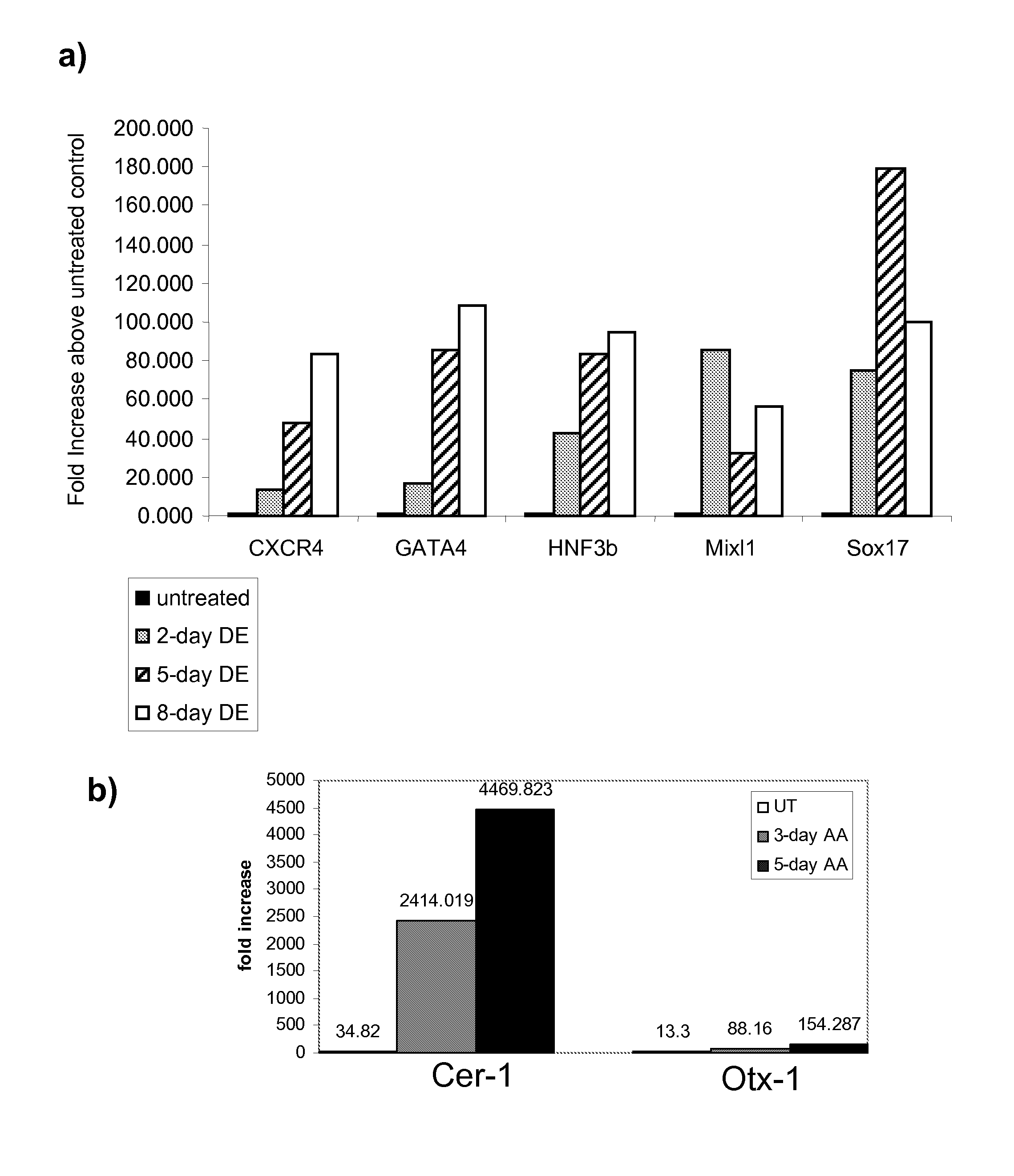
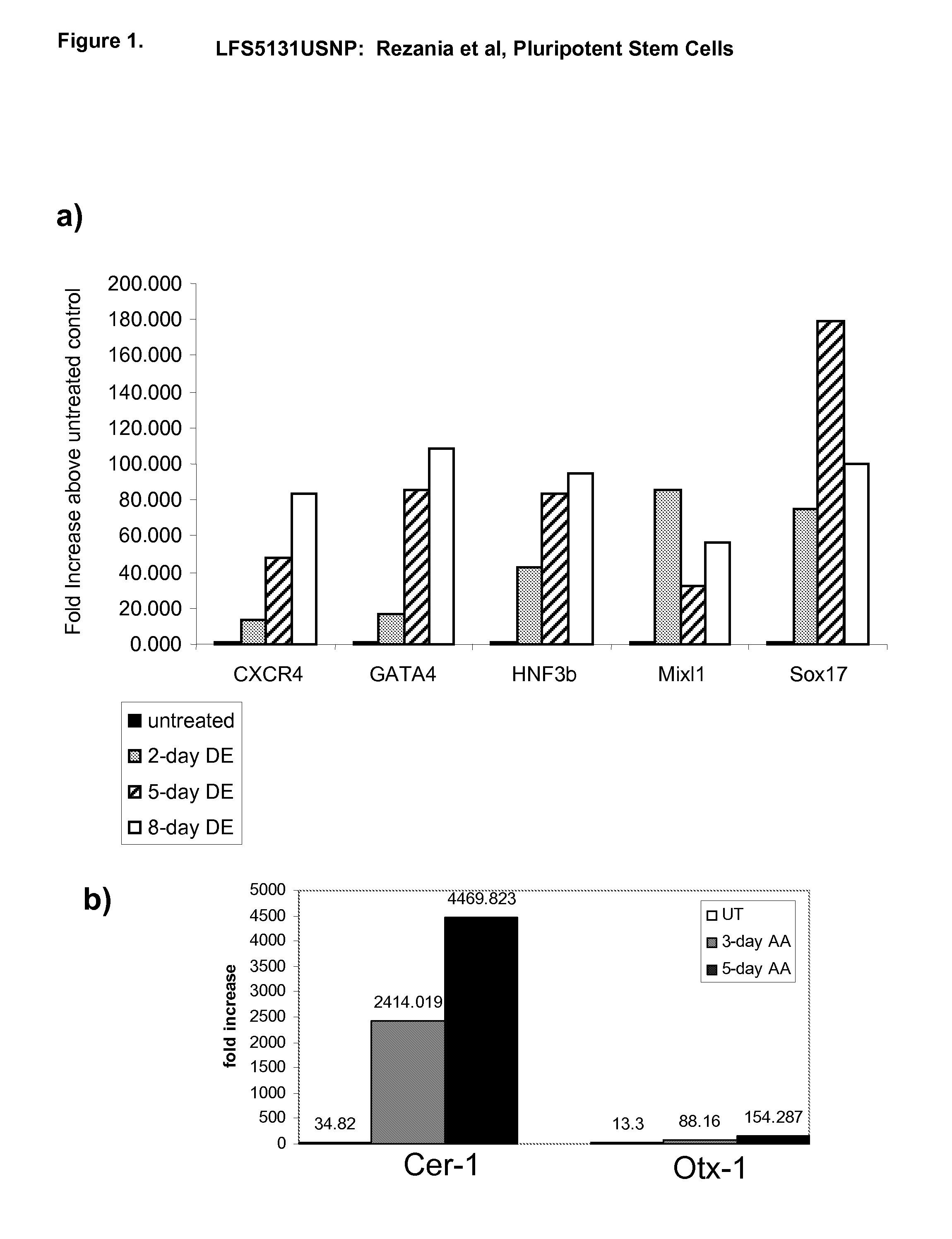
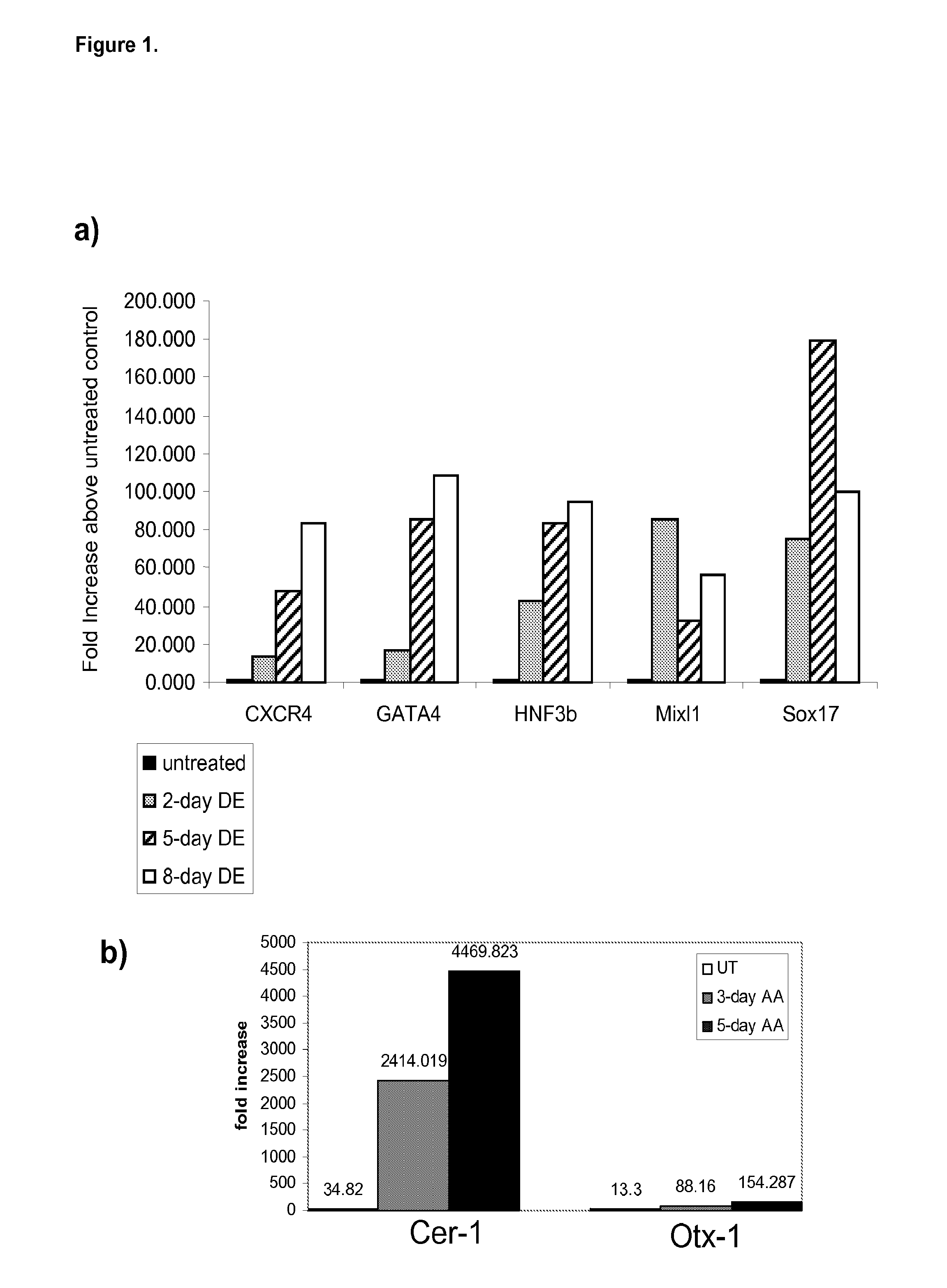
ActiveUS20070254359A1Inhibits Notch signalingPancreatic cellsArtificial cell constructsGerm layerPluripotential stem cell
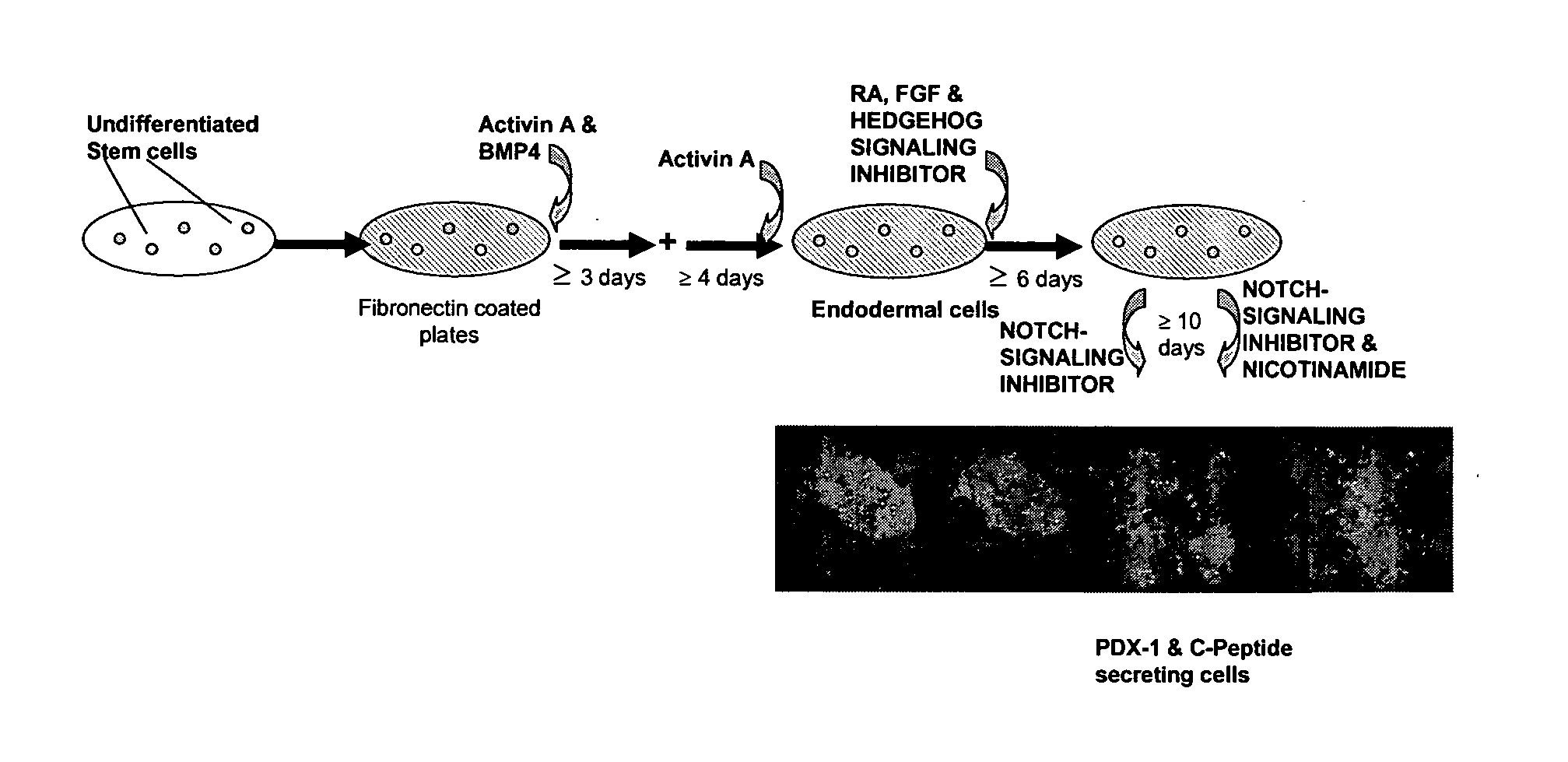
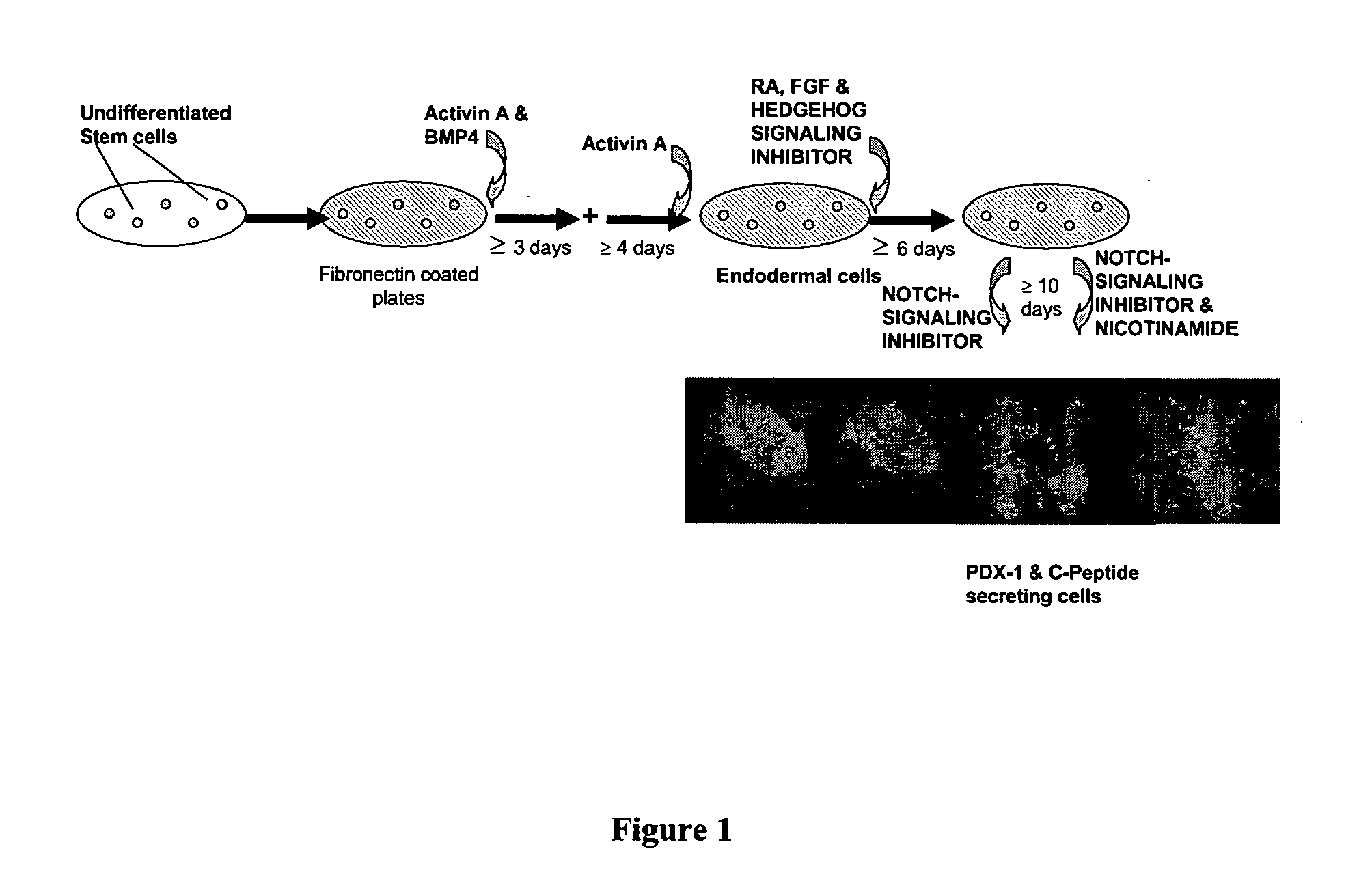
The present invention provides methods to promote the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells. In particular, the present invention provides an improved method for the formation of pancreatic endoderm, pancreatic hormone expressing cells and pancreatic hormone secreting cells. The present invention also provides methods to promote the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells without the use of a feeder cell layer.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells
The present invention provides methods to promote the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells. In particular, the present invention provides an improved method for the formation of pancreatic endoderm, pancreatic hormone expressing cells and pancreatic hormone secreting cells. The present invention also provides methods to promote the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells without the use of a feeder cell layer.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
Method for producing immortalised antibodies-secreting cells
A method for producing immortalized antibody-secreting cells, comprising: (a) providing a transgenic animal having antibody-secreting cells capable of expressing one or more transgenes, wherein the antibody-secreting cells are in a non-immortalized state in the absence of a stimulus and are capable of changing to an immortalized state by means of the transgenes or transgenes upon exposure of the cells to the stimulus; (b) extracting the antibody-secreting cells from the animal; and (c) exposing the antibody-secreting cells to the stimulus, thereby immortalizing the antibody secreting cells by means of the transgene or transgenes.
Owner:GRANTA BIOTECH
Cancer immunotherapy with a viral antigen-defined, immunomodulator-secreting cell vaccine
A human cell line, which lacks major histocompatibility class I (MHC-I) antigens and major histocompatibility class II (MHC-II) antigens and which has been modified to comprise and express (i) a nucleotide sequence encoding an immunomodulator and (ii) a nucleotide sequence encoding a viral antigen, and a method of inducing or stimulating an immune response in a human to a viral-associated disease or cancer comprising administering to the human (i) the aforementioned human cell line in an amount sufficient to induce or stimulate an immune response to the viral associated disease or cancer, (ii) a human cell line, which lacks MHC-I and MHC-11 antigens and which has been modified to comprise and express a nucleotide sequence encoding an immunomodulator, and a human cell line, which lacks MHC-I and MHC-II antigens and which has been modified to comprise and express a nucleotide sequence encoding an antigen of EBV, simultaneously or sequentially in either order, by the same or different routes, in amounts sufficient to induce or stimulate an immune response to the viral-associated disease or cancer, or (iii) an immunomodulator and a human cell line, which lacks MHC-I and MHC-II antigens and which has been modified to comprise and express a nucleotide sequence encoding an antigen of EBV, simultaneously or sequentially in either order, by the same or different routes, in amounts sufficient to induce or stimulate an immune response to the viral associated disease or cancer.
Owner:JOHNS HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Pd-1 antibodies in combination with a cytokine-secreting cell and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20100285013A1Good curative effectBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsTumor responseSecreting cell
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC +1
Biological material for repairing meniscus tear and preparation method for biological material
ActiveCN102716515APromote proliferationPromote wound healingProsthesisCartilage cellsAutologous tissue
The invention relates to a biological material for repairing meniscus tear and a preparation method for the biological material. The material consists of an acellular matrix membrane on the inner layer, a porous structure collagen matrix membrane on the middle layer, a cell layer formed by cartilage cells on the outer layer and a cell sheet. The repair material has certain elasticity and toughness and is high in biological activity; the cartilage cells can secrete cell factors per se, and nutritional ingredients can be directly obtained through articular cavity synovia, and thus, the establishment of communication link between tissue cells at both ends of the tear during the meniscus tear process is accelerated; the immigration and the infusion of the cells in the material and autologous tissue cells are promoted; the tissue regeneration and functional reconstruction time is shortened; and the ideal novel material and the preparation method for the material are provided for clinically repairing the damage of the meniscus tear (including blood supply zones), especially the tissue regeneration and the functional reconstruction of no-blood zones and low-blood zones.
Owner:西安博鸿生物技术有限公司
Methods of treating spinal cord injury and minimizing scarring
ActiveUS20090136457A1Promote functional recoveryPromote healingBiocideNervous disorderProgenitorSecreting cell
The invention is directed to methods of promoting the healing of spinal cord injury. The invention is further directed to methods of minimizing the extent of scarring following spinal cord injury. Such methods utilize novel compositions, including but not limited to extraembryonic cytokine secreting cells (herein referred to as ECS cells), including, but not limited to, amnion-derived multipotent progenitor cells (herein referred to as AMP cells) and conditioned media derived therefrom (herein referred to as amnion-derived cellular cytokine solution or ACCS), each alone or in combination with each other and / or other agents.
Owner:STEMNION
Methods for generating insulin-secreting cells suitable for transplantation
InactiveUS20030082810A1High degreeConvenient introductionBiocideGenetic material ingredientsGlucose sensitivityInsulin Secreting Cell
The invention relates to methods for generating insulin secreting cells from precursor stem cells or from adult pancreatic exocrine cells. The methods of the invention are useful, for example, for generation of glucose sensitive insulin-secreting beta-cells suitable for transplantation, as well as for in situ development of insulin-secreting cells in a patient in need thereof. Further, the method of the invention relates to methods for preventing premature differentiation of precursor stem cells into insulin-secreting beta-cells. Still further, the invention relates to assay methods for identification of compounds that prevent or activate beta-cell differentiation.
Owner:SERUP PALLE +2
Methods for promoting hair growth
The invention is directed to methods for promoting hair growth. Such methods utilize novel compositions, including but not limited to extraembryonic cytokine secreting cells (herein referred to as ECS cells), including, but not limited to, amnion-derived multipotent progenitor cells (herein referred to as AMP cells), conditioned media derived therefrom (herein referred to as amnion-derived cellular cytokine solution or ACCS), cell lysates derived therefrom, and cell products derived therefrom, each alone or in combination.
Owner:STEMNION
Method of transplanting in a mammal and treating diabetes mellitus by administering a pseudo-islet like aggregate differentiated from a nestin-positive pancreatic stem cell
InactiveUS20050244386A1Avoid immune responseReduce intensityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideInsulin dependent diabetesDuctal cells
Methods and compositions are described for the treatment of type I insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and other conditions using newly identified stem cells that are capable of differentiation into a variety of pancreatic islet cells, including insulin-producing beta cells, as well as hepatocytes. Nestin has been identified as a molecular marker for pancreatic stem cells, while cytokeratin-19 serves as a marker for a distinct class of islet ductal cells. Methods are described whereby nestin-positive stem cells can be isolated from pancreatic islets and cultured to obtain further stem cells or pseudo-islet like structures. Methods for ex vivo differentiation of the pancreatic stem cells are disclosed. Methods are described whereby pancreatic stem cells can be isolated, expanded, and transplanted into a patient in need thereof, either allogeneically, isogeneically or xenogenically, to provide replacement for lost or damaged insulin-secreting cells or other cells.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
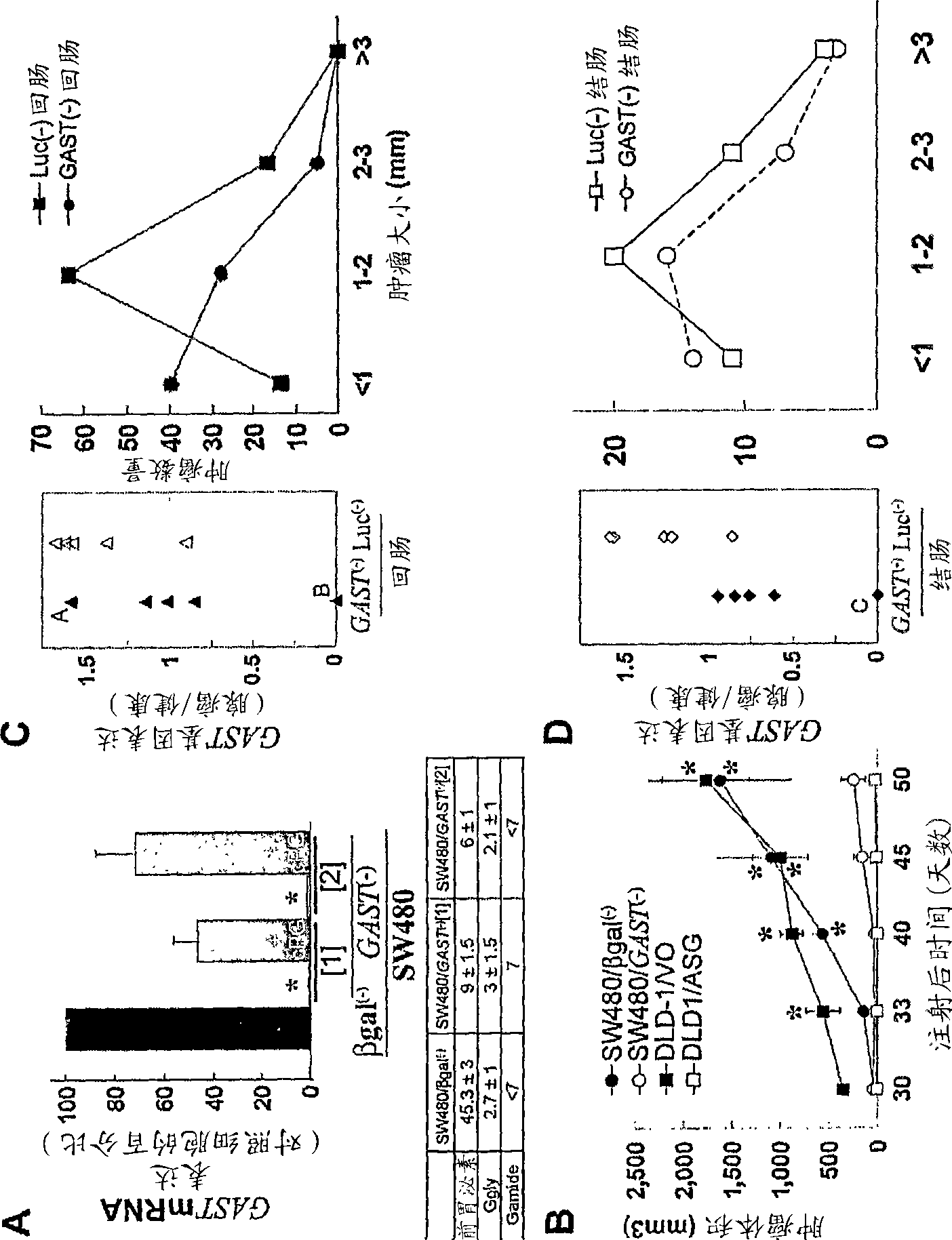
Progastrin inhibitors in the treatment of colon cancer
InactiveCN101460196ADigestive systemImmunoglobulins against hormonesConstitutively activeLymphatic Spread
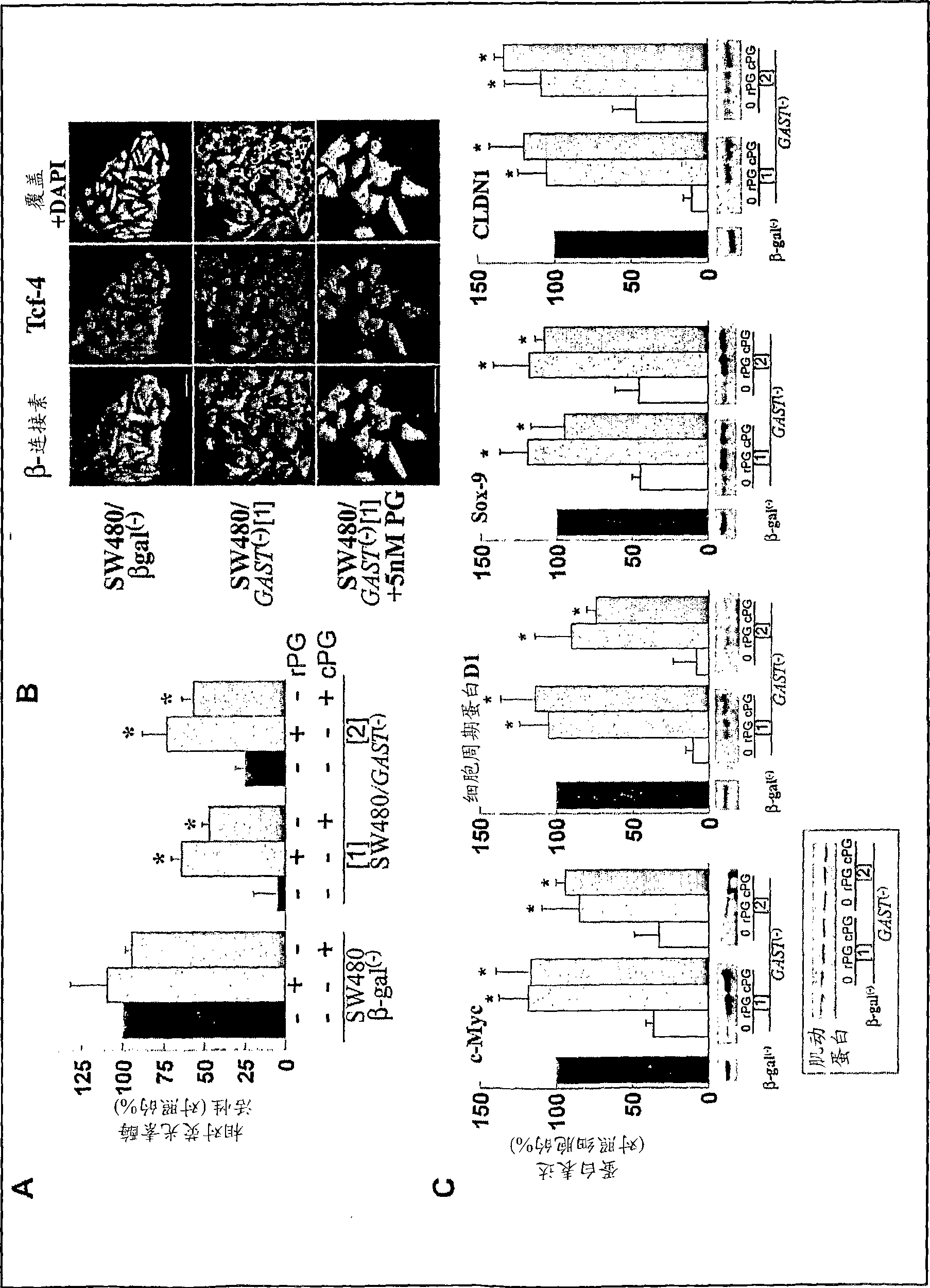
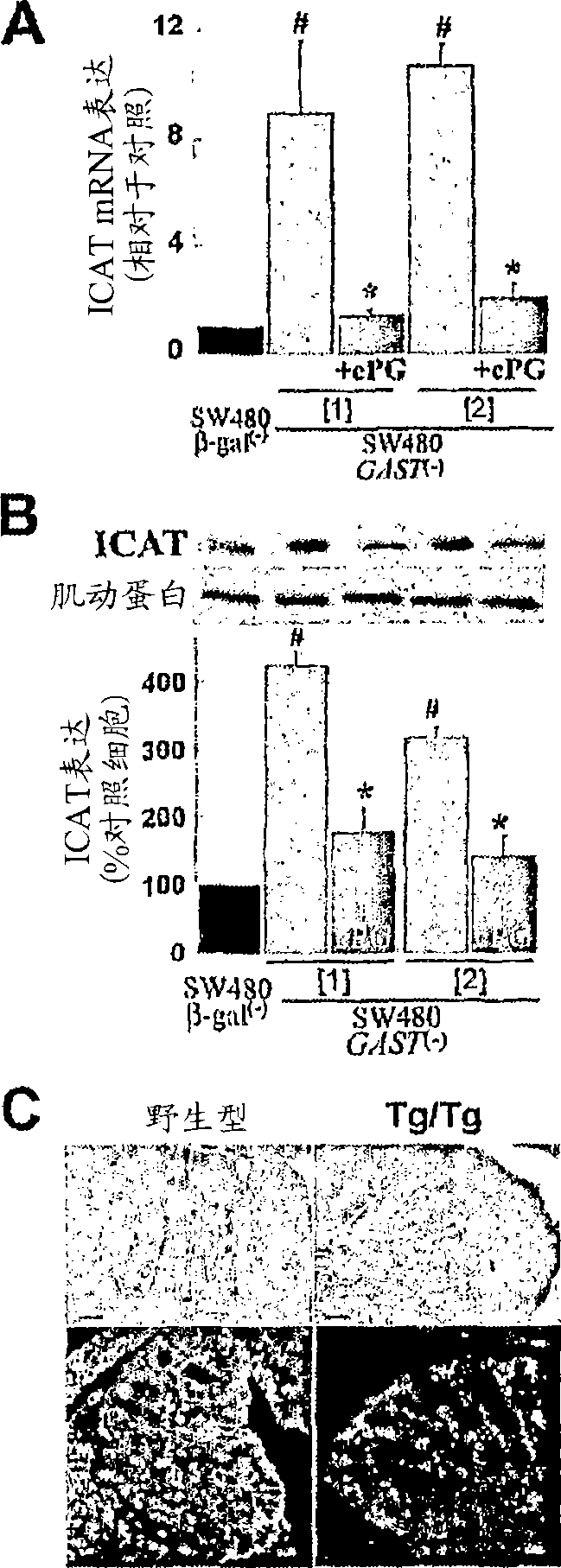
The present invention relates to inhibitors of progastrin induced repression of ICAT for treating and / or preventing colorectal cancer, adenomatous polyposis or metastasis displaying progastrin-secreting cells and cells in which the beta-catenin / Tcf-4-mediated transcriptional pathway is constitutively active.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +2
Methods related to surgery
ActiveUS20090010899A1Promote healingImproved and accelerated healingBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsProgenitorFistula
The invention is directed to methods related to surgery, for example gastrointestinal surgery. In particular, the invention is methods of treating fistulae, promoting accelerated healing of anastomoses and preventing failure of anastomoses. Such methods utilize novel compositions, including but not limited to extraembryonic cytokine secreting cells (herein referred to as ECS cells), including, but not limited to, amnion-derived multipotent progenitor cells (herein referred to as AMP cells), conditioned media derived therefrom (herein referred to as amnion-derived cellular cytokine solution or ACCS), cell lysates derived therefrom, and cell products derived therefrom, each alone or in combination.
Owner:STEMNION
Methods of treating spinal cord injury and minimizing scarring
ActiveUS8475788B2Promote healingMinimize the extent of scarringBiocideNervous disorderProgenitorSecreting cell
Owner:STEMNION
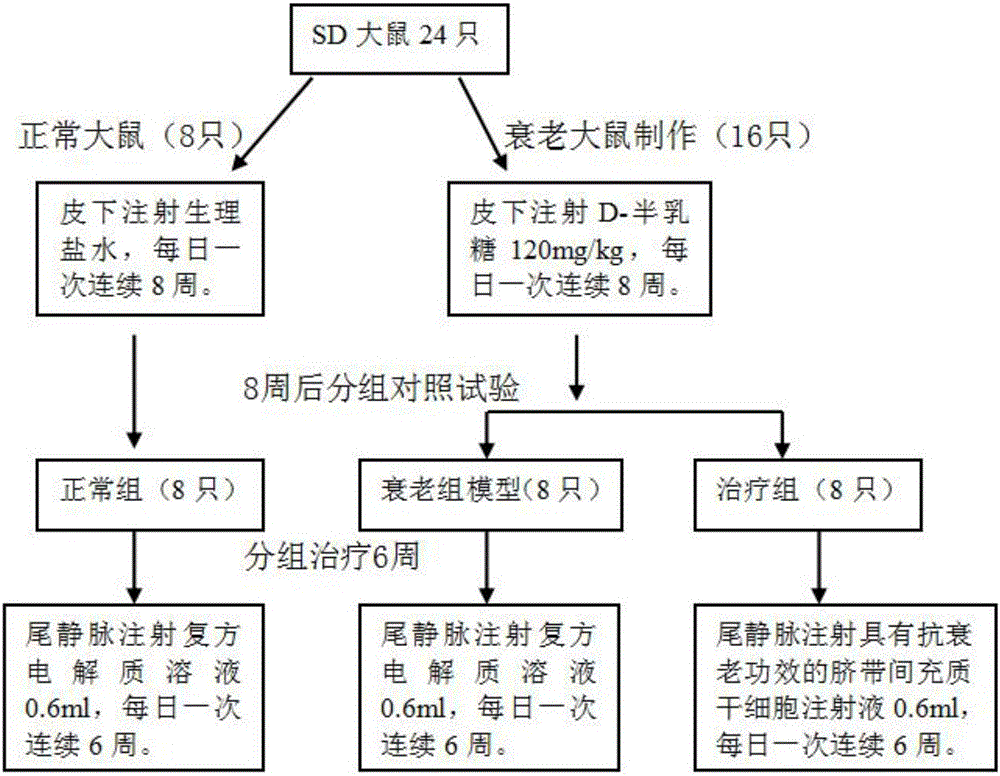
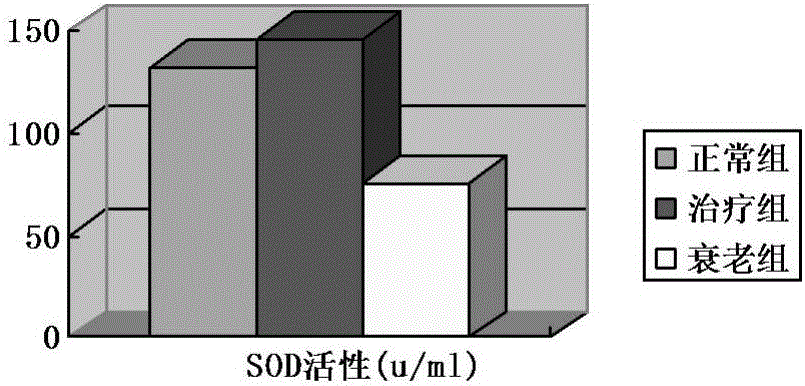
Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell injection with anti-aging function and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105920042AWith amplificationDirected differentiationCell dissociation methodsCulture processTissue repairSelf recovery
The invention provides an umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell injection with an anti-aging function and a preparation method thereof. The injection comprises the following components: umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell (5*10<5> to 10*10<5> / mL), 2 wt% of human albumin, and 98 wt% of compound electrolyte solution. The produced umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells can rapidly repair and replace damaged cells and tissues, and have the characteristics of amplification and directional cell differentiation; and after the stem cells receive the signals from damaged parts, the stem cells will move to the damage parts, amplify in the damage parts, carry out induced differentiation, promote the self recovery function of stem cells, rapidly repair and replace damaged cells and tissues, rapidly secrete cell factors, growth factors, and tissue related factors in time, thus improve the blood circulation, enhance the metabolism functions, improve the tissue repairing function and immunity, and finally achieve the anti-aging goal.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAYAN MEDICINE TECH CO LTD
In-vitro induced pancreas-islet-like structure forming method
InactiveCN102517248AEfficient removalFunction increaseVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
The invention discloses an in-vitro induced pancreas-islet-like structure forming method. Pancreas-islet endocrine cells prepared by committed induction of adult stem cells or induced pluripotent stem cell (iPS cells) or pancreas-islet endocrine cells from a pancreas-islet source are subjected to suspension culture in a culture medium which is added with similar components of natural i pancreas-islet extracellular matrix in a high-oxygen culture environment with 50% of O2, so that the in-vitro induced pancreas-islet-like structure is formed quickly and efficiently. The method has the advantages of high speed (4-24 hours) and high efficiency (the formation rate of the pancreas-islet-like structure is 90%), and the pancreas-islet-like structures formed by the method are uniform in size (like the natural pancreas-islet) and fine in function (the insulin secretion function thereof is superior to that of the non-islet-like structure). In addition, the in-vitro induced pancreas-islet-like structure forming method is a key technical method for preparing the pancreas islet according to the dry cell technology.
Owner:CHINA JAPAN FRIENDSHIP HOSPITAL
Methods for treating pustular conditions of the skin
InactiveUS20090004161A1Promote wound healingLess scarringCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsProgenitorPustulosis
The invention is directed to methods for treating pustular conditions of the skin, for example, acne. Such methods utilize novel compositions, including but not limited to extraembryonic cytokine secreting cells (herein referred to as ECS cells), including, but not limited to, amnion-derived multipotent progenitor cells (herein referred to as AMP cells), conditioned media derived therefrom (herein referred to as amnion-derived cellular cytokine solution or ACCS), cell lysates derived therefrom, and cell products derived therefrom, each alone or in combination.
Owner:STEMNION
Novel assay for detecting immune responses involving antigen specific cytokine and/or antigen specific cytokine secreting T-cells
InactiveUS20030143641A1Less laborAddressing slow performanceBiological material analysisBiological testingGamma interferonBiological activation
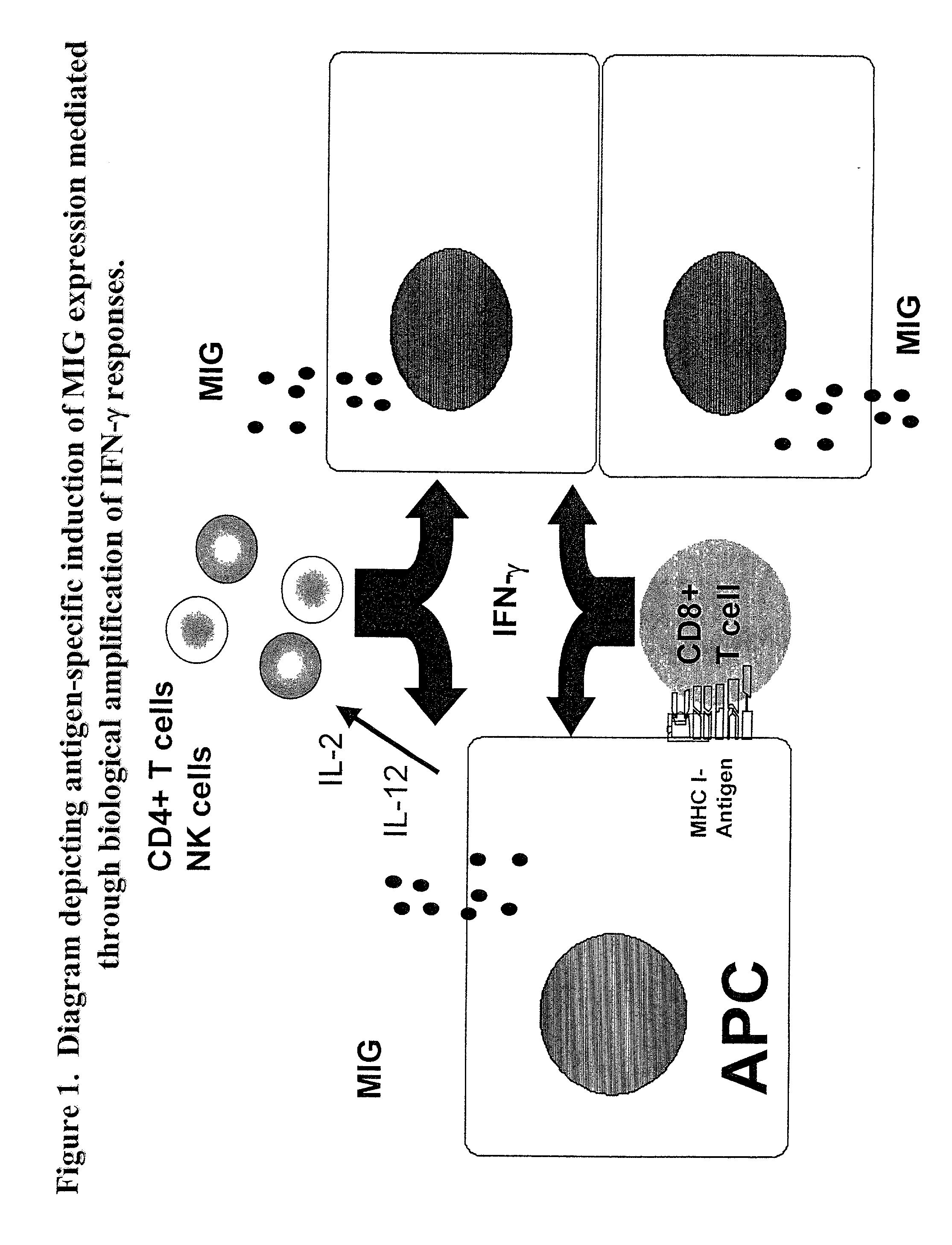
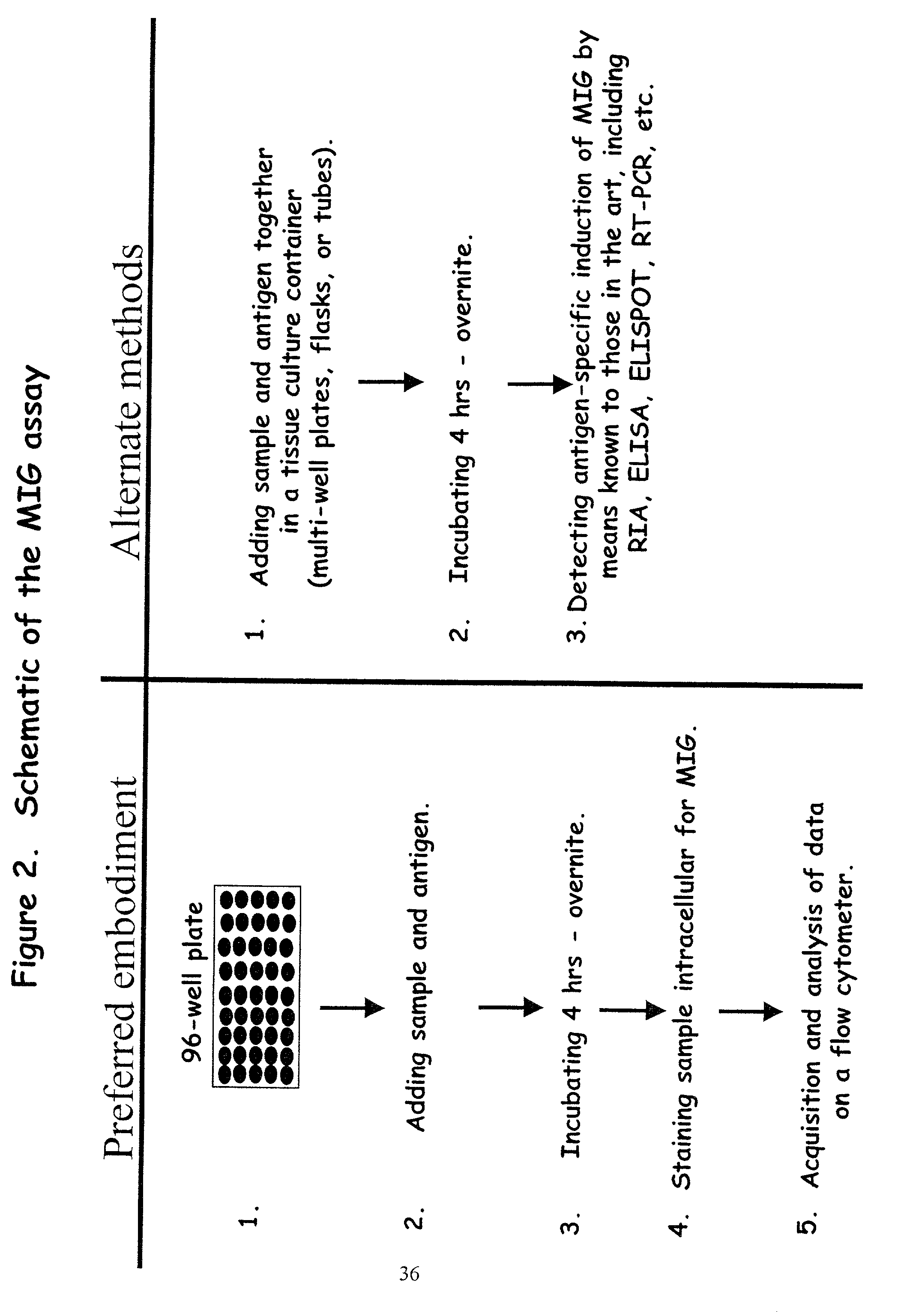
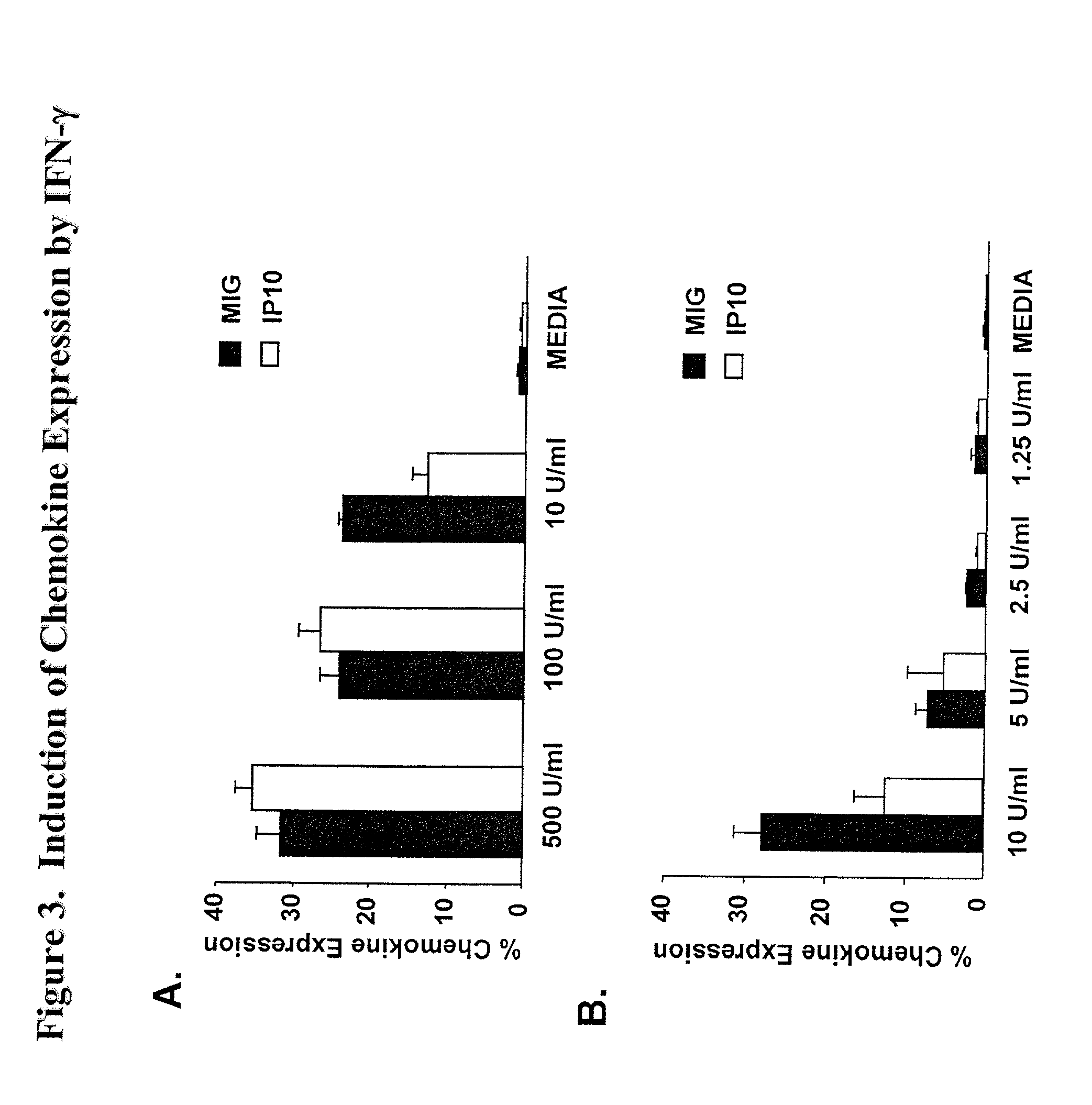
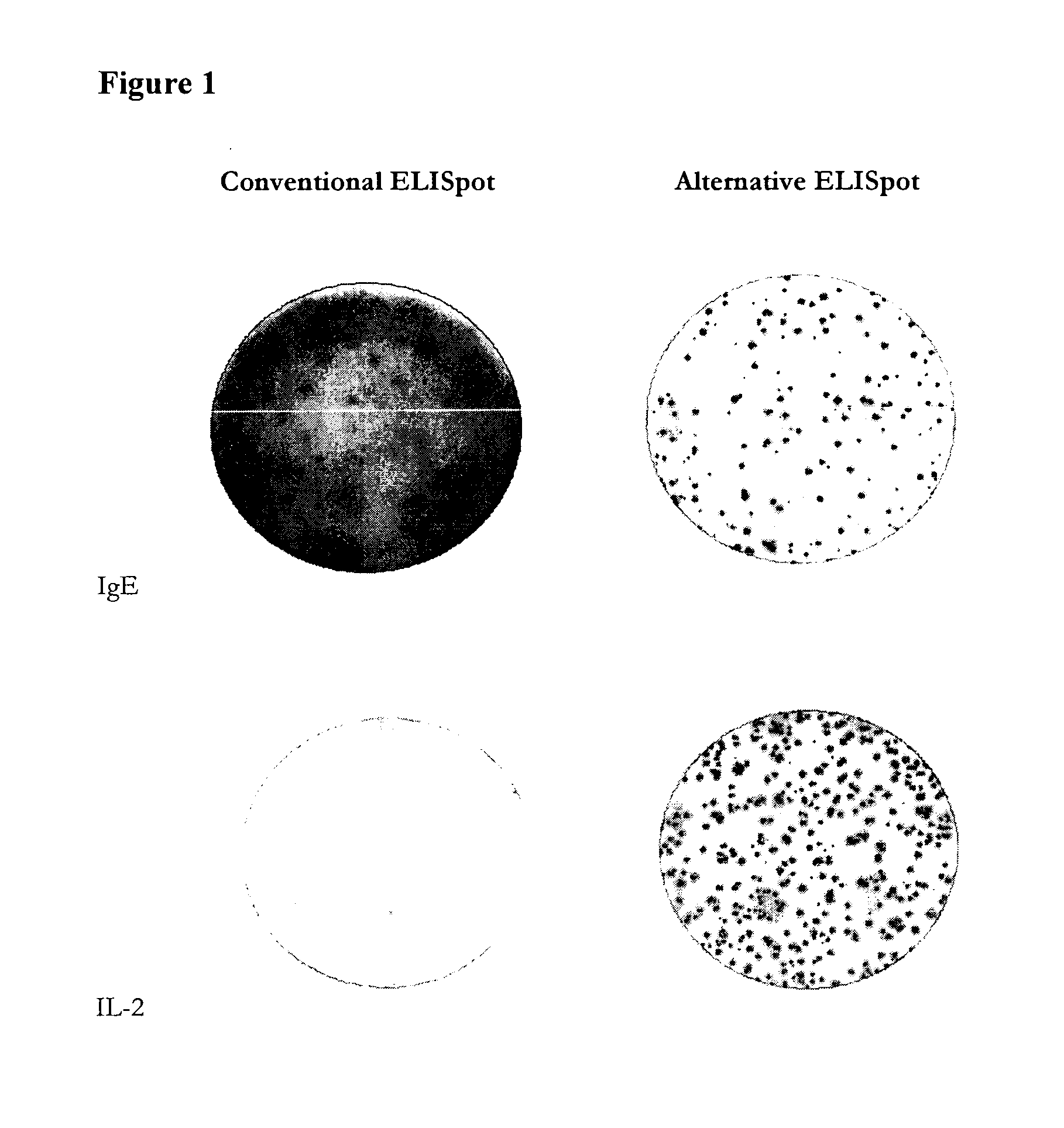
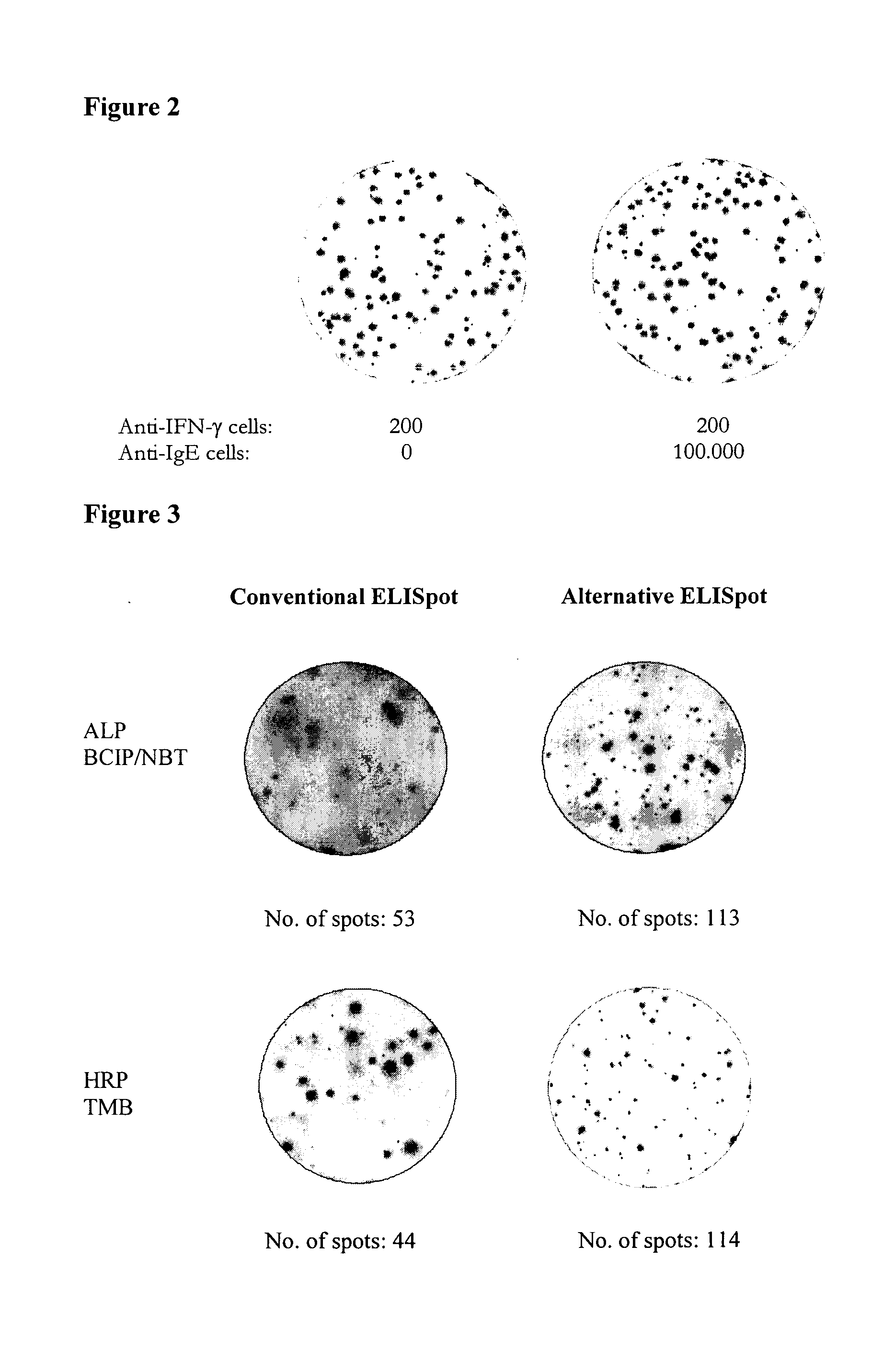
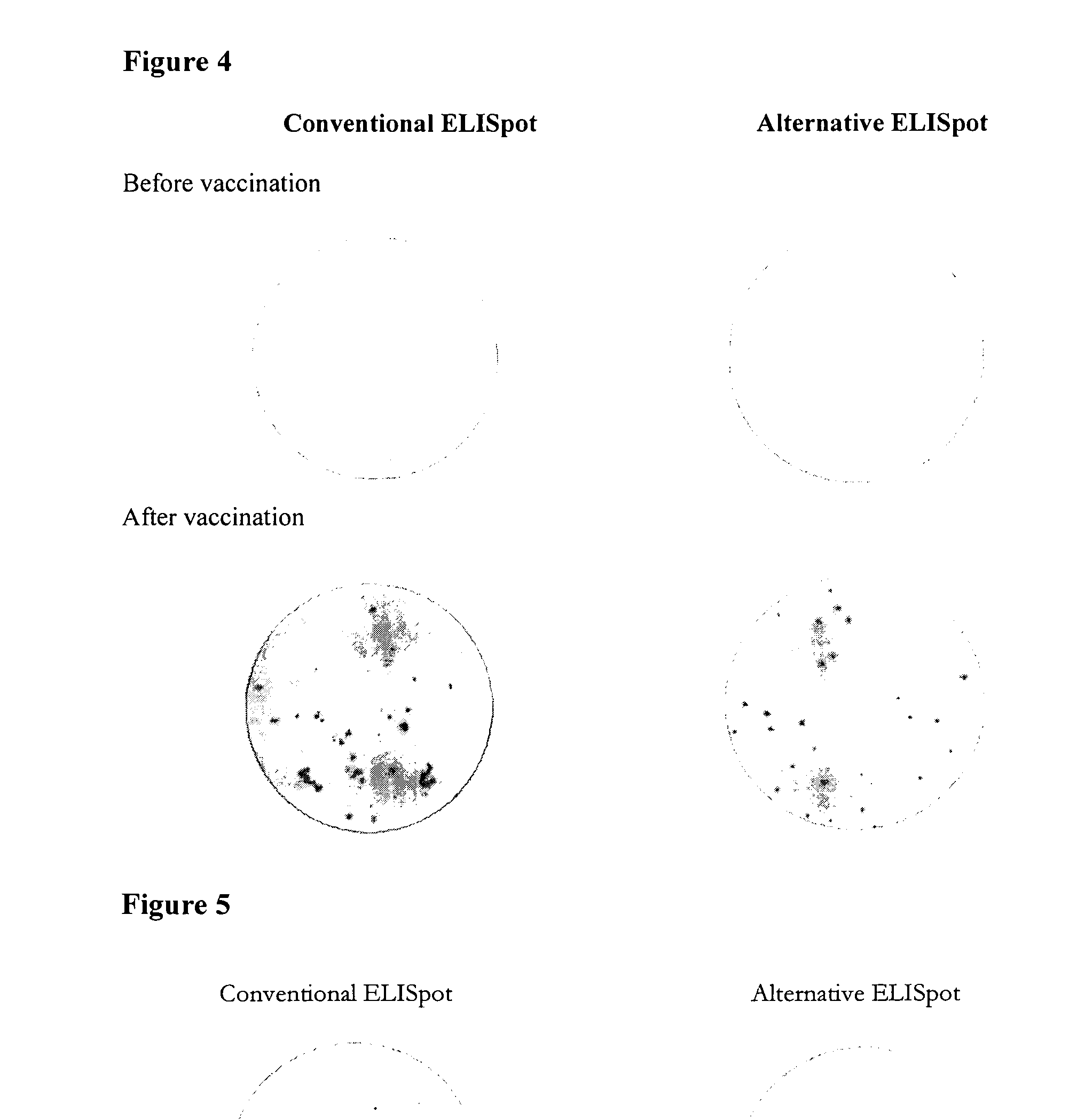
Here, we describe a sensitive and specific assay and kit for the detection of chemokines having activity that is upregulated by Th-1 cytokines (such IFN-gamma) and chemokines that upregulate the activity of Th-1 cytokines (such as IFN-gamma). In a typical embodiment, detection of the chemokine monokine induced by gamma interferon (MIG) provides a measure of the biological effect of IFN-gamma rather than direct quantitation of IFN-gamma or IFN-gamma secreting cells per se. Upregulation of MIG expression was observed following in vitro activation of PBMC with defined CD8+ T cell epitopes derived from influenza virus, CMV, or EBV, and in all cases this was antigen-specific, genetically restricted and dependent on both CD8+ T cells and IFN-gamma. Responses as assessed by the MIG assay paralleled those detected by conventional IFN-gamma ELISPOT, but the magnitude of response and sensitivity of the MIG assay were superior. Our data validate this novel method for the detection of high as well as low levels of antigen-specific and genetically restricted IFN-gamma activity or MIG.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY NAVAL RES LAB WASHINGTON
Treatment of mucus hypersecretion
InactiveUS20080249019A1Effective treatmentPrevent hypersecretionPeptide/protein ingredientsFusions for specific cell targetingAdjuvantObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
A polypeptide and a nucleic acid encoding the polypeptide are described. The polypeptide includes a cytotoxic toxin, a targeting domain that selectively binds to a target cell that is a mucus-secreting cell and a translocating domain that translocates the cytotoxic toxin into the target cell. A nucleic acid encoding the polypeptide is also described. Also described is a pharmaceutical composition for topical administration to a patient suffering from mucus hypersecretion which includes the polypeptide and a formulation component selected from the group consisting of an excipient, an adjuvant and a propellant. Methods of treating hypersecretion of mucus, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or asthma are also described. These methods include administering to a patient in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of the polypeptide.
Owner:HEALTH PROTECTION AGENCY
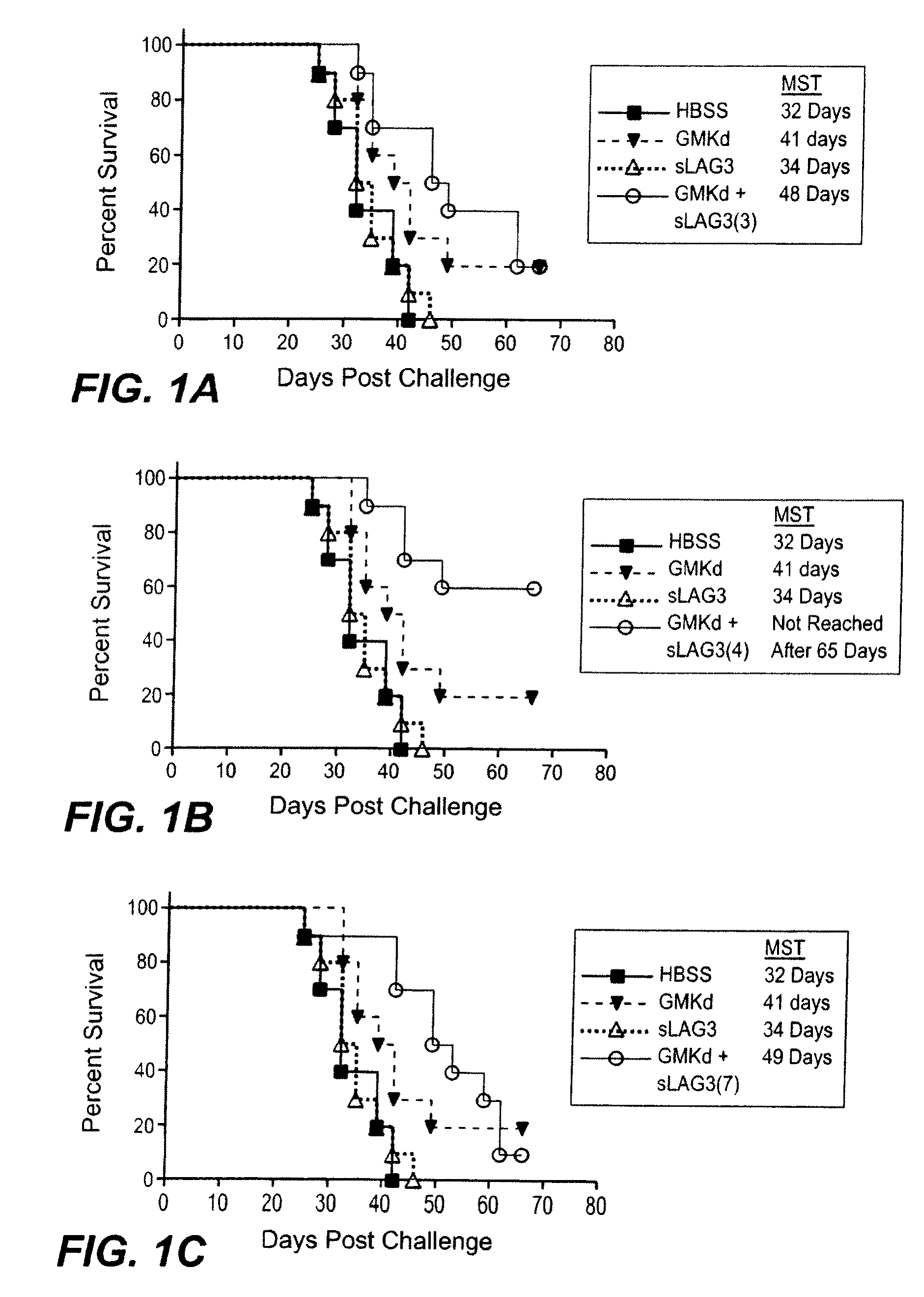
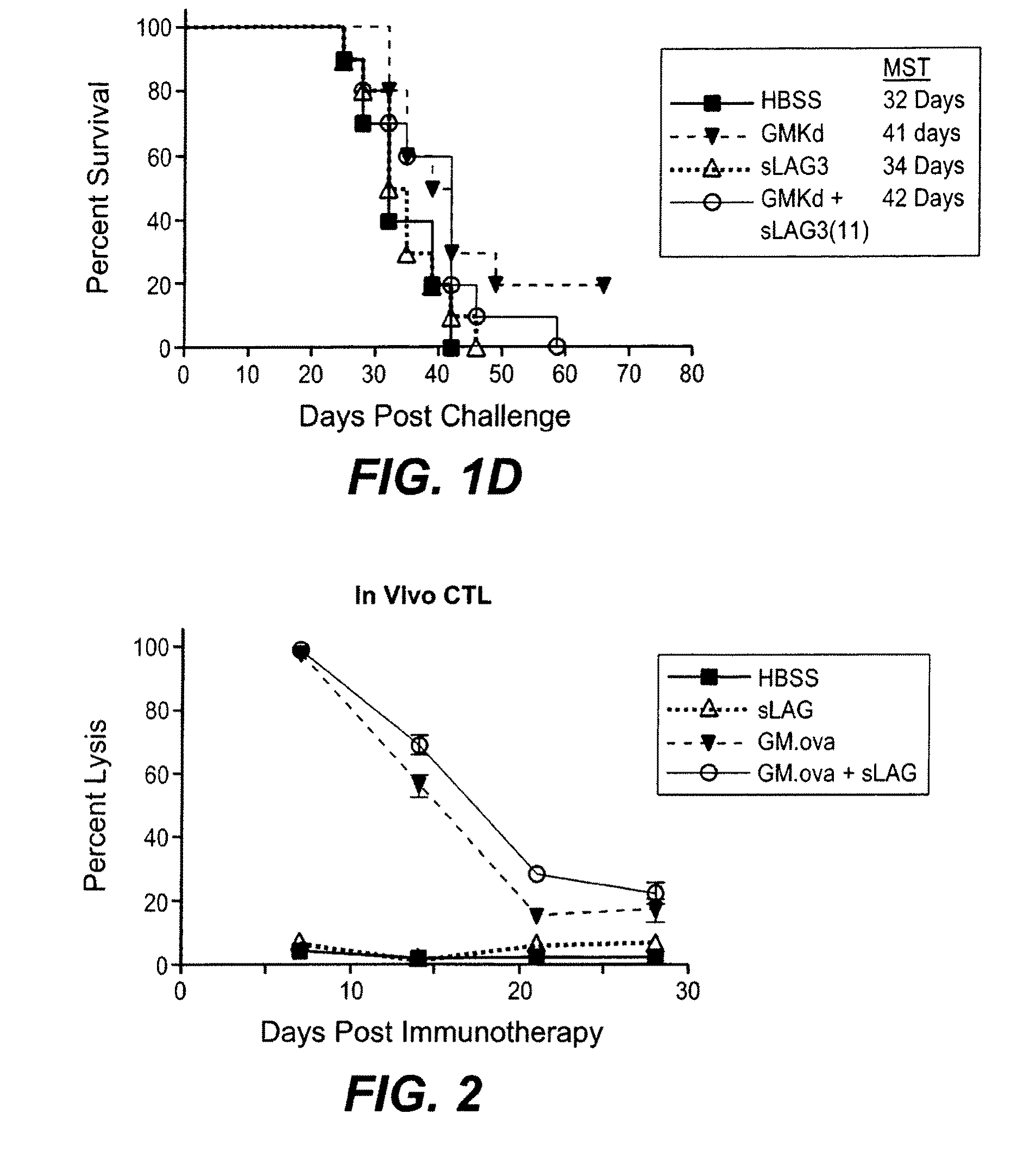
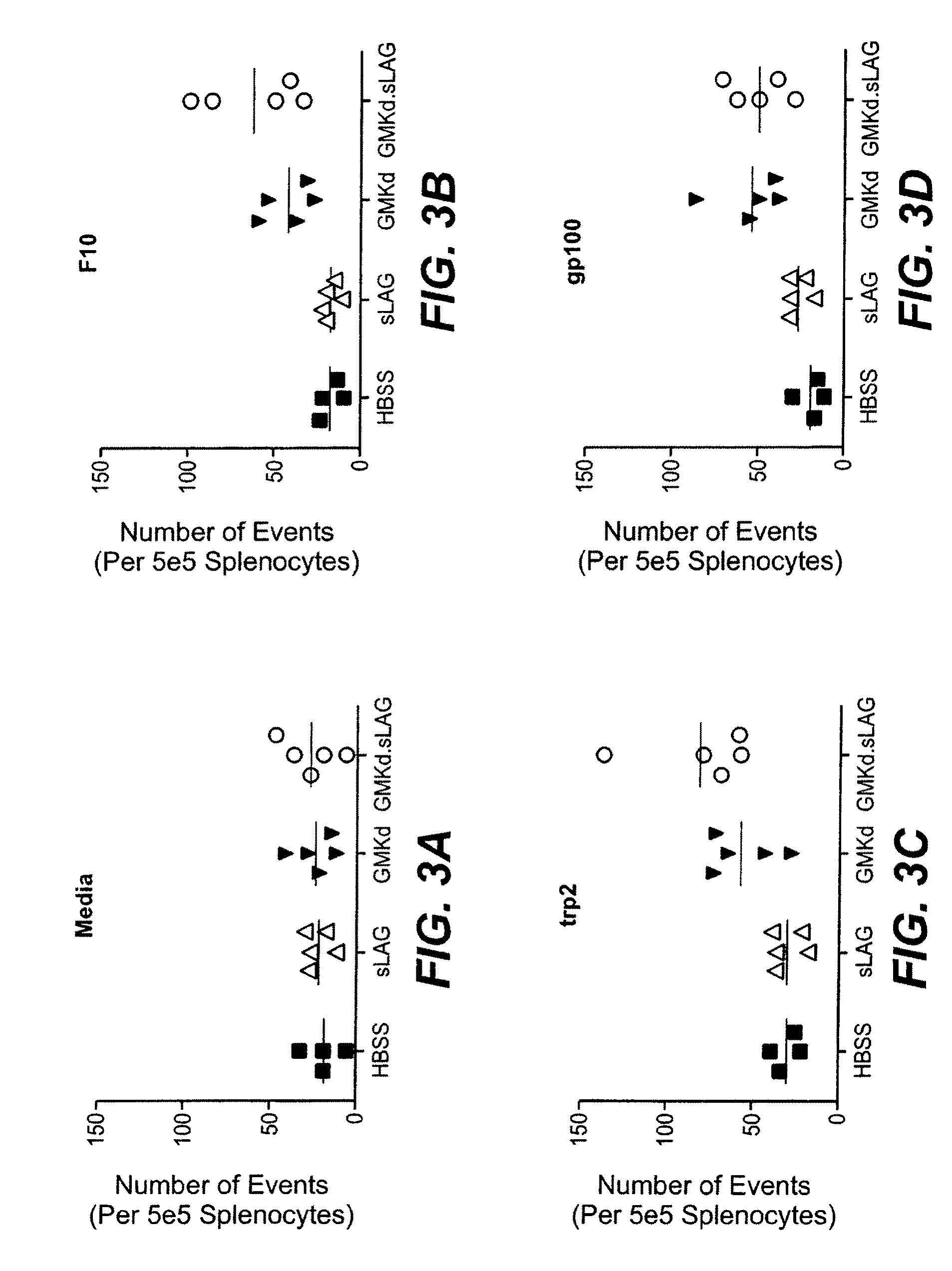
Apc activators in combination with a cytokine-secreting cell and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20090130054A1Good curative effectBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsSecreting cellTumor cells
The present invention relates to a method of enhancing anti-tumor protection in a mammal. More particularly, the invention is concerned with combinations comprising antigen presenting cell (APC) activators and a cytokine-secreting cell and methods of administering the combination for enhanced immune response to tumor cells in a patient with a cancer.
Owner:IMMUTEP
Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells
The present invention provides methods to promote the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells. In particular, the present invention provides an improved method for the formation of pancreatic endoderm, pancreatic hormone expressing cells and pancreatic hormone secreting cells. The present invention also provides methods to promote the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells without the use of a feeder cell layer.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
Method of Differentiating Stem Cells
InactiveUS20110008819A1Effectively lead to differentiationPancreatic cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementGerm layerScreening method
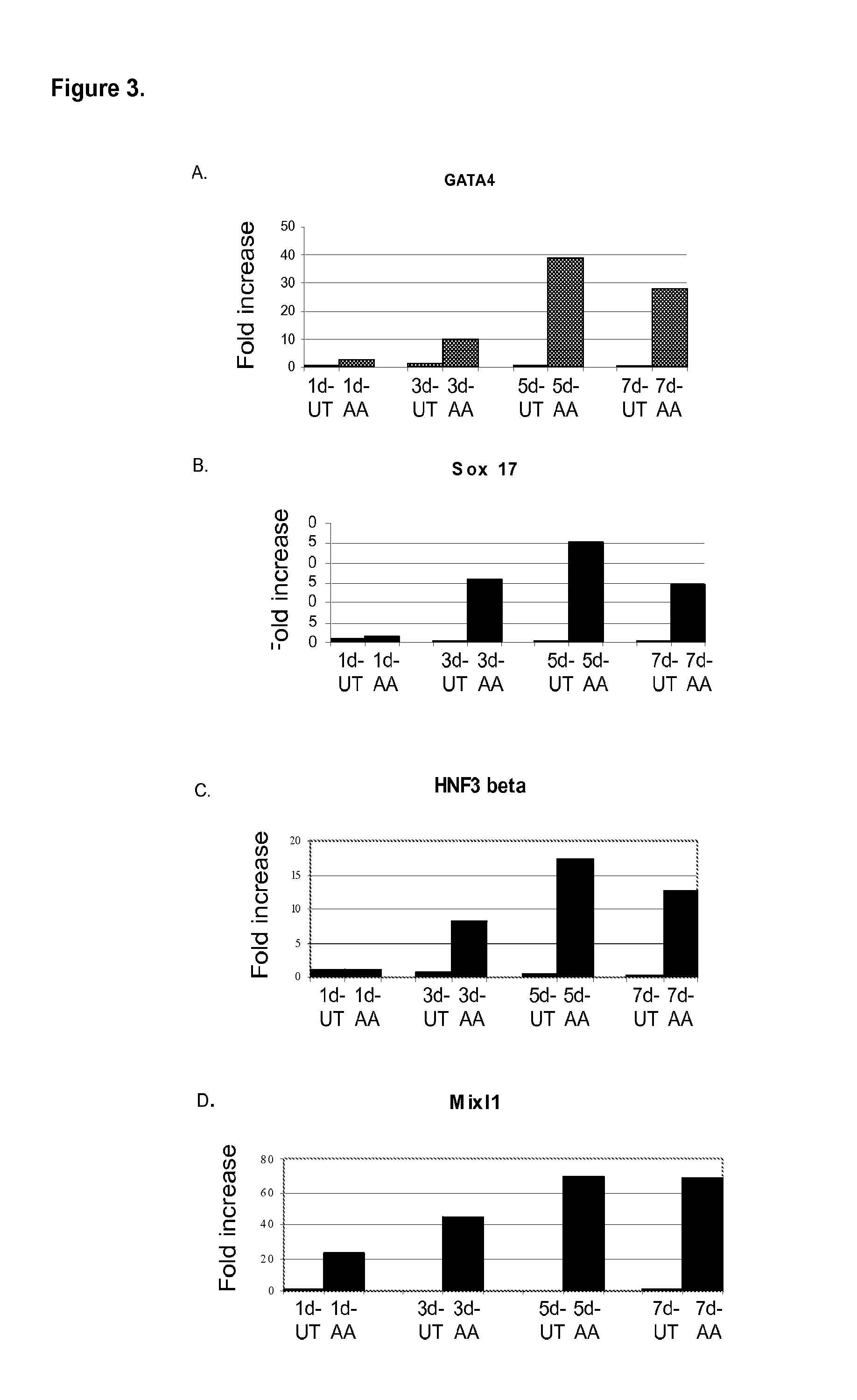
There is provided an improved efficient method for differentiating stem cells into pancreatic endoderm cells and pancreatic hormone expressing and secreting cells which express Pdx-1 and C-peptide. The invention further provides screening methods for detecting factors of interest that will affect the differentiation of the stem cells into pancreatic endoderm cells.
Owner:ES CELL INT
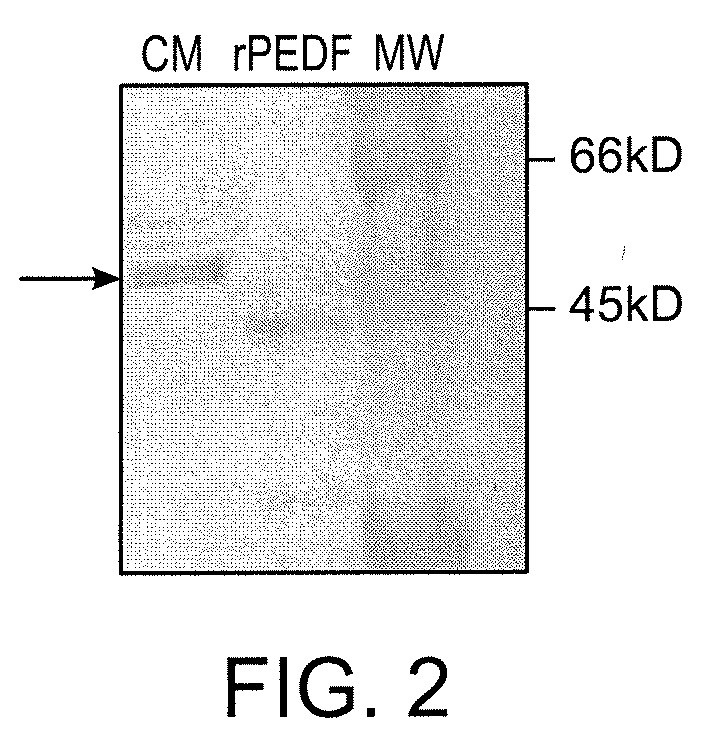
Use of PEDF in an Encapsulated Cell-Based Delivery System
InactiveUS20110111008A1Inhibiting neuralInhibiting retinal degradationBiocideSenses disorderDiseasePIGMENT EPITHELIUM-DERIVED FACTOR
The invention relates to a device for delivery of pigment epithelium derived factor (PEDF) to the eye utilizing encapsulated PEDF-secreting cells and related methods for the treatment and prevention of ophthalmic diseases and disorders.
Owner:NEUROTECH USA
Antibody-secreting cell assay
ActiveUS20110244477A1Less antigenLimited valueDisease diagnosisBiological testingEpitopeAntigen binding
An improved assay is described where a surface is provided with immobilized anti-Ig antibodies rather than antigen and where specific antibody-secreting cells (ASC) are detected using soluble antigen probes containing one of several possible labels. The method gives improved sensitivity with less background and is also more representative because antigen binding does not employ immobilized antigen. The assay is particularly effective for measuring antibody secreting cells against HIV, for determining whether an infection is acute as opposed to old or latent, for mapping epitopes and for measuring for ASCs against different antigens in the same reaction.
Owner:MABTECH
Vascular stent capable of promoting vascular cell proliferation and secreting extracellular matrix, preparation method of vascular stent and active artificial blood vessel
ActiveCN111714706AHigh activityImplement refactoringSurgeryTissue regenerationCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
The invention belongs to the technical field of tissue engineering, and particularly relates to a vascular stent capable of promoting vascular cell proliferation and secreting extracellular matrix. The vascular stent is characterized by comprising a tubular polymer fiber stent added with active factors, wherein the active factors comprise at least one of IGF-1, VEGF, PDGF and bFGF growth factors,and / or at least one of polypeptides corresponding to IGF-1, VEGF, PDGF and bFGF growth factors, and / or at least one of RGD short peptides and NO donor molecules; and the tubular polymer fiber stent ismade of degradable polymer materials. The vascular stent has the beneficial effects that according to the vascular stent modified by active and functions, in the process of constructing an extracellular matrix artificial blood vessel in vitro tissue engineering, the proliferation rate of cells and the rate of secreting the extracellular matrix can be remarkably increased, and the in vitro cell culture time is greatly shortened; and in addition, the tissue regeneration activity of the vascular material is also remarkably improved, and the requirement of clinical treatment is met.
Owner:领博生物科技(杭州)有限公司
A chamber for encapsulating secreting cells
ActiveCN105813630APeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderSemipermeable membraneSecreting cell
Owner:DEFYMED
Preparation process for insulin-secreting cells and special medium composition used therein
InactiveCN103184186ANo importEasy to operateArtificial cell constructsArtificially induced pluripotent cellsINSULIN USEInsulin Secreting Cell
The invention discloses a medium composition for inducing mesenchymal stem cells into insulin-secreting cells. The medium composition comprises a medium A, a medium B and a medium C. The medium A comprises the following solutes: a fetal calf serum with a concentration of 4.75 to 5.25 ml / L and activin A with a concentration of 4.75 to 5.25ng / mL. The medium B comprises the following solutes: retinoic acid with a concentration of 0.95 * 10<-5> to 1.05 * 10<-5> mol / L, EGF with a concentration of 19 to 21ng / ml, bFGF with a concentration of 19 to 21ng / ml, glutamine with a concentration of 1.9 to 2.1 mmol / L, 0.95 to 1.05% of non-essential amino acids and 1.9 to 2.1% of B27. The medium C comprises the following solutes: a fetal bovine serum with a concentration of 4.5 to 5.5 ml / L, exendin-4 with a concentration of 19 to 21 ng / ml, activin A with a concentration of 9.5 to 10.5 ng / ml, nicotinamide with a concentration of 9.5 to 10.5 mmol / L, 1.9 to 2.1% of B27 and 0.95 to 1.05% of N2. An induction culture method provided by the invention is applicable to a variety of tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells and has the advantages of no introduction of viruses, easy operation and high efficiency.
Owner:THE INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
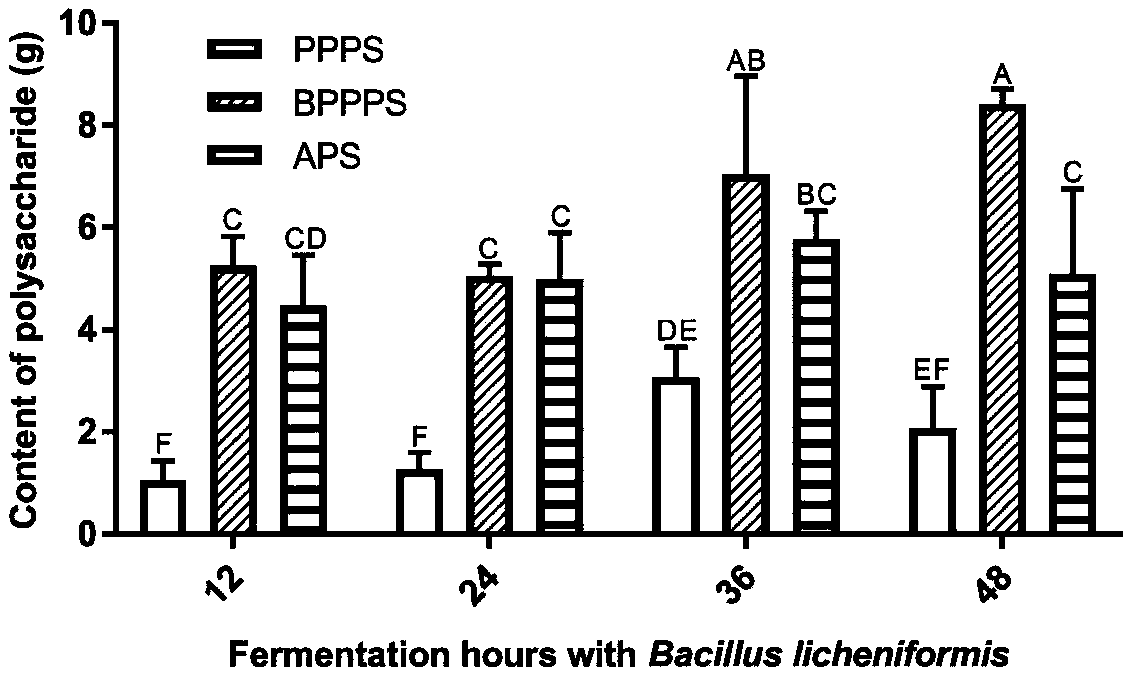
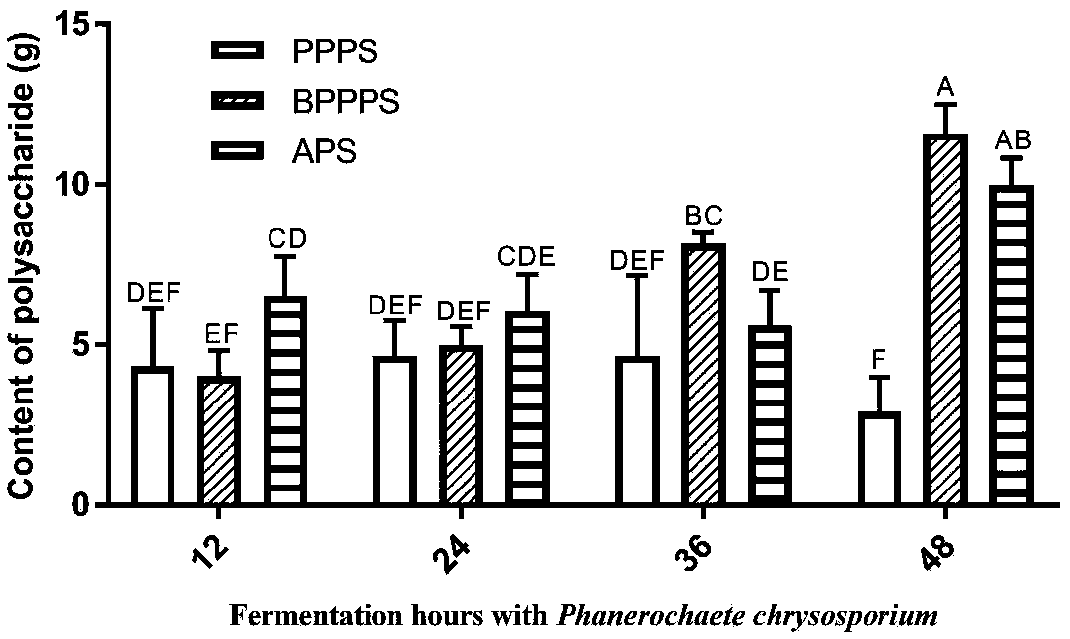
Extraction method of natural plant polysaccharide
The invention provides an extraction method of natural plant polysaccharide and belongs to the field of natural product preparation. The extraction method comprises the steps of inoculating enzyme-producing bacteria capable of secreting cell wall degrading enzyme to an enzyme-producing fermentation culture medium, then adding natural plant powder for incubating and fermenting, mixing an obtained fermentation liquid with an alcohol solution, and conducting precipitation. The extraction method greatly simplifies the extraction steps of the natural plant polysaccharide, reduces the extraction cost, improves the efficiency of extracting the natural plant polysaccharide, avoids the use of toxic and harmful reagents including ether, chloroform and the like, and is beneficial to mass applicationof the natural plant polysaccharide in animal husbandry.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Methods for the production of biologically active agents contained in an extracellular matrix
InactiveUS6232121B1Extended half-lifeImprove effectivenessCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell-Extracellular MatrixActive agent
The present invention relates to methods for the production in vitro of cell growth supportive surfaces comprising naturally secreted human extracellular matrix material comprising biologically active agents such as growth factors ideally produced and elaborated by the extracellular matrix-secreting cells. The present invention provides an efficient method for improving growth factor potency and extending half-life in order to promote cell attachment, growth and / or differentiation. The surfaces of the present invention enable propagation of difficult cells in culture.
Owner:KEEPING HUGH S
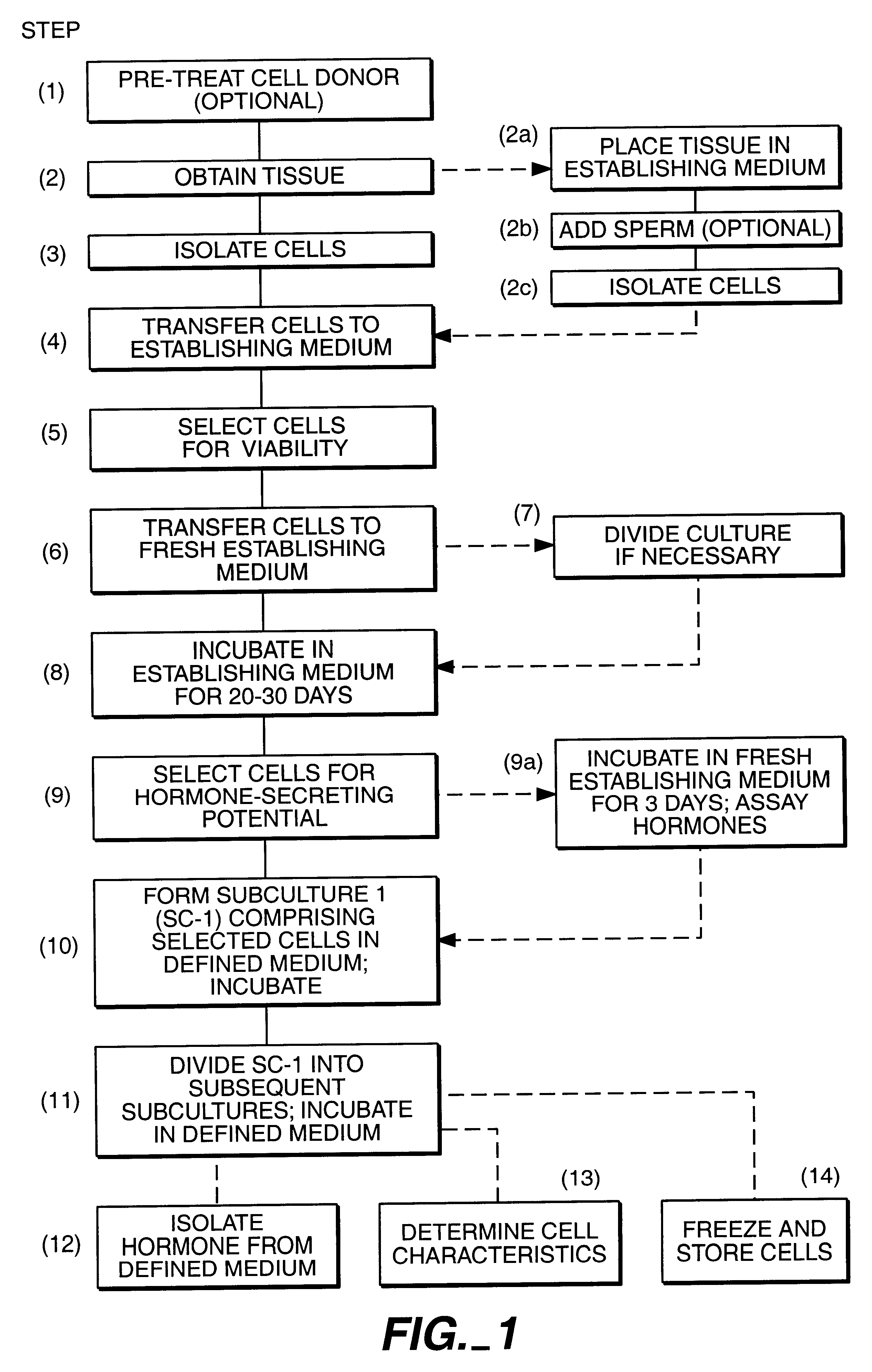
Hormone-secreting cells maintained in long-term culture
InactiveUS6372493B1Increased insulin secretionHigh glucose concentrationPeptide/protein ingredientsDiagnosticsCulture mediumsHuman chorionic gonadotropin
Methods are provided for the establishment and maintenance in long term culture of hormone secreting cells. Cells are derived from tumorous or non-tumorous animal or human tissues, including ovary, endometrium, trophoblast, pituitary, thyroid, and pancreas. The cells secrete into the culture medium hormones such as estrogens, progestins, follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, human chorionic gonadotrophin, thyroxin, glucagon, and insulin, depending on the tissue of origin of individual cell cultures. Contact with an appropriate secretogogue causes the cells to respond with increased hormone secretion. For instance, ovarian follicular cells respond to follicle-stimulating hormone with increased estrogen and progesterone secretion. Pancreatic cells respond to elevated glucose with increased insulin secretion. The cells proliferate in in vitro for up to one year or longer, during which time they retain their hormone-secretion profile. The cells may be frozen for storage, and retain their hormone-secretion profile after thawing. The cell cultures are useful for the production of human hormones, for the bio-assay of drugs such as therapeutic gonadotrophin, for the testing of drug efficacy and design, and for toxicity testing of drugs and chemicals. The cells may also be implanted in an individual to replace deficient hormone secretion. For instance, insulin secreting pancreatic cells may be implanted in a diabetic individual as an adjunct or replacement therapy for exogenously administered insulin.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOMEDICAL RES INC
Application of L.p (lactobacillus paracasei) R3-10 in preparation of medicines for preventing or treating oral inflammatory diseases
ActiveCN111904985AInhibition of secretionInhibit aggregationCosmetic preparationsAntipyreticInflammatory factorsNeutrophil granulocyte
The invention discloses an application of L.p R3-10 in preparation of medicines for preventing or treating oral inflammatory diseases, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. Inactivatedand non-inactivated fermentation supernatant and bacterial suspension of the L.p R3-10 disclosed by the invention have the effect of inhibiting LPS from stimulating human gingival fibroblasts to secrete cell inflammatory factors IL6, TNF-alpha and PGE2 in vitro; in an in-vivo inflammation model, neutrophils and macrophages can be remarkably inhibited from being gathered to the inflammation position of the tail fin of a zebra fish, and clearing of the neutrophils and the macrophages at the inflammation position of the tail fin of the zebra fish is remarkably promoted; and meanwhile, damage repair of the tail fin of the zebra fish can be remarkably promoted. The L.p R3-10 disclosed by the invention has a huge potential application prospect in the aspect of treating and / or preventing the oral inflammatory diseases.
Owner:广东南芯医疗科技有限公司 +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com