Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells
A cell differentiation and pluripotent stem cell technology, applied in the field of promoting pluripotent stem cell differentiation, can solve the problem of not completely simulating the developmental program of higher mammals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0320] Human embryonic stem cell culture
[0321] Human embryonic stem cell lines H1, H7, and H9 were obtained from WiCell Research Institute, Inc., (Madison, WI) and cultured according to instructions provided by the source company. Briefly, cells were cultured on mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) feeder cells in ES cell medium supplemented with 20% knockout serum replacer, 100 nM MEM non-essential amino acids, 0.5 mM Beta-mercaptoethanol, DMEM / F12 (Invitrogen / GIBCO) composition with 4 ng / ml human basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) in 2 mM L-glutamine (all from Invitrogen / GIBCO). MEF cells derived from E13 to 13.5 mouse embryos were purchased from Charles River. MEF cells were expanded in DMEM medium supplemented with 10% FBS (Hyclone), 2 mM glutamine and 100 mM MEM non-essential amino acids. Subconfluent MEF cells were treated with 10 μg / ml mitomycin C (Sigma, St. Louis, MO) for 3 hours to arrest cell division, then treated with trypsin and incubated with 2 × 10 4 / cm...
example 2
[0323] Formation of definitive endoderm cells
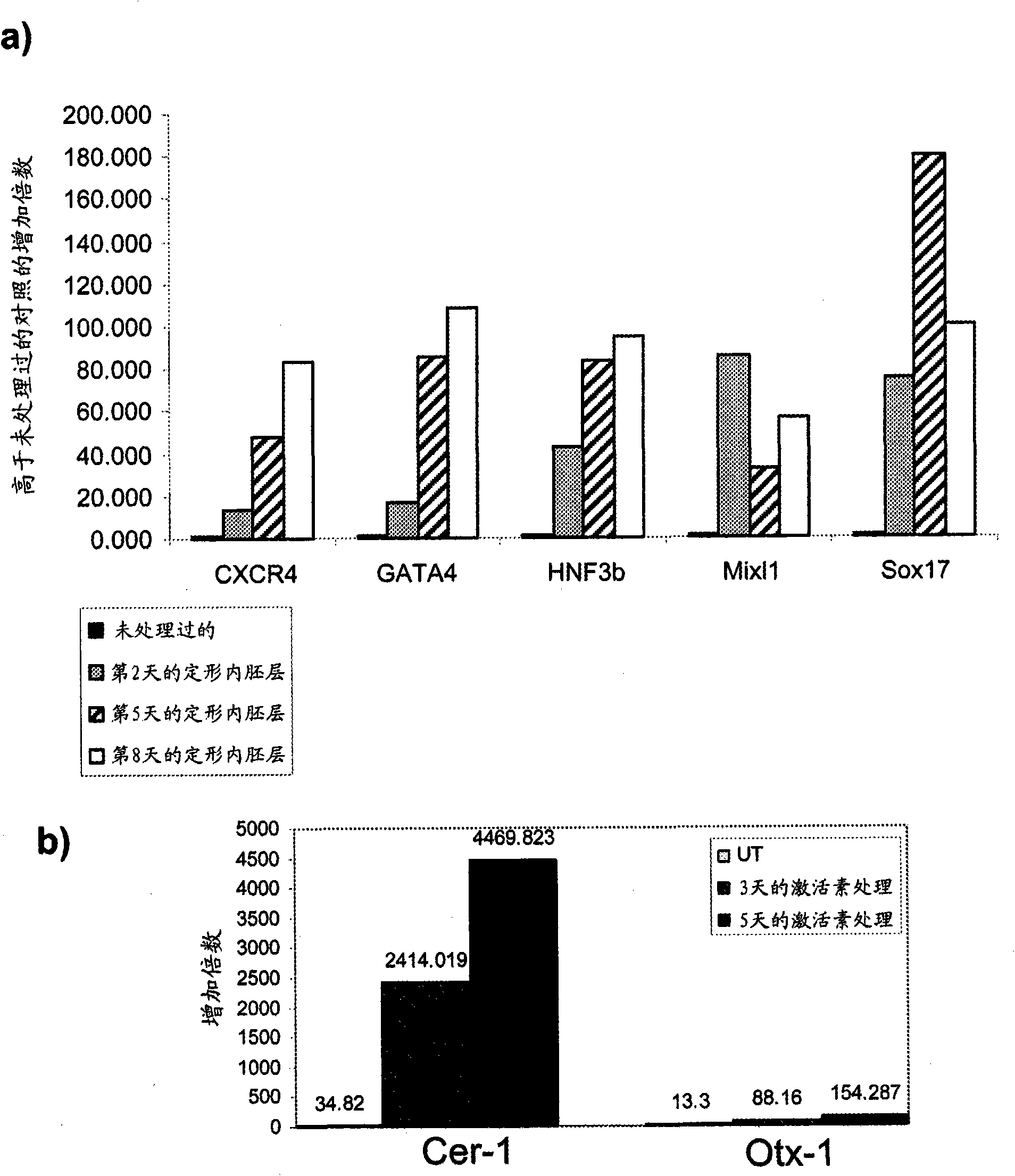
[0324] The effect of activin A on markers of definitive endoderm was examined. Activin A (100 ng / ml) was added to human embryonic stem cell populations cultured on mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Cells were continuously cultured in the presence of Activin A and harvested at the indicated times. By PCR ( figure 1 ), FACS (results are summarized in Table II) and immunohistochemistry ( figure 2 ) to test the expression levels of definitive endoderm markers.
[0325] Activin A caused a time-dependent increase in the mRNA expression of CXCR4, GATA4, HNF-3β, Mixl1 and Sox-17 in the H9 line ( figure 1 , sub-figure a). Significant upregulation of the anterior endoderm markers Cerberus, Otx-1, and Hex genes was also observed ( figure 1 , sub-figure b). Increased CXCR4 protein was observed by FACS after treatment with Activin A. Expression of E-cadherin and N-cadherin was not altered after treatment with activin A (Table IIA). CXC...
example 3
[0327] Pancreatic endoderm cell formation
[0328] Growth factors known to induce differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into pancreatic endoderm are added to the cell culture. Specifically, activin A, bFGF and retinoic acid, known to induce pancreatic endoderm formation, were added to the cultures.
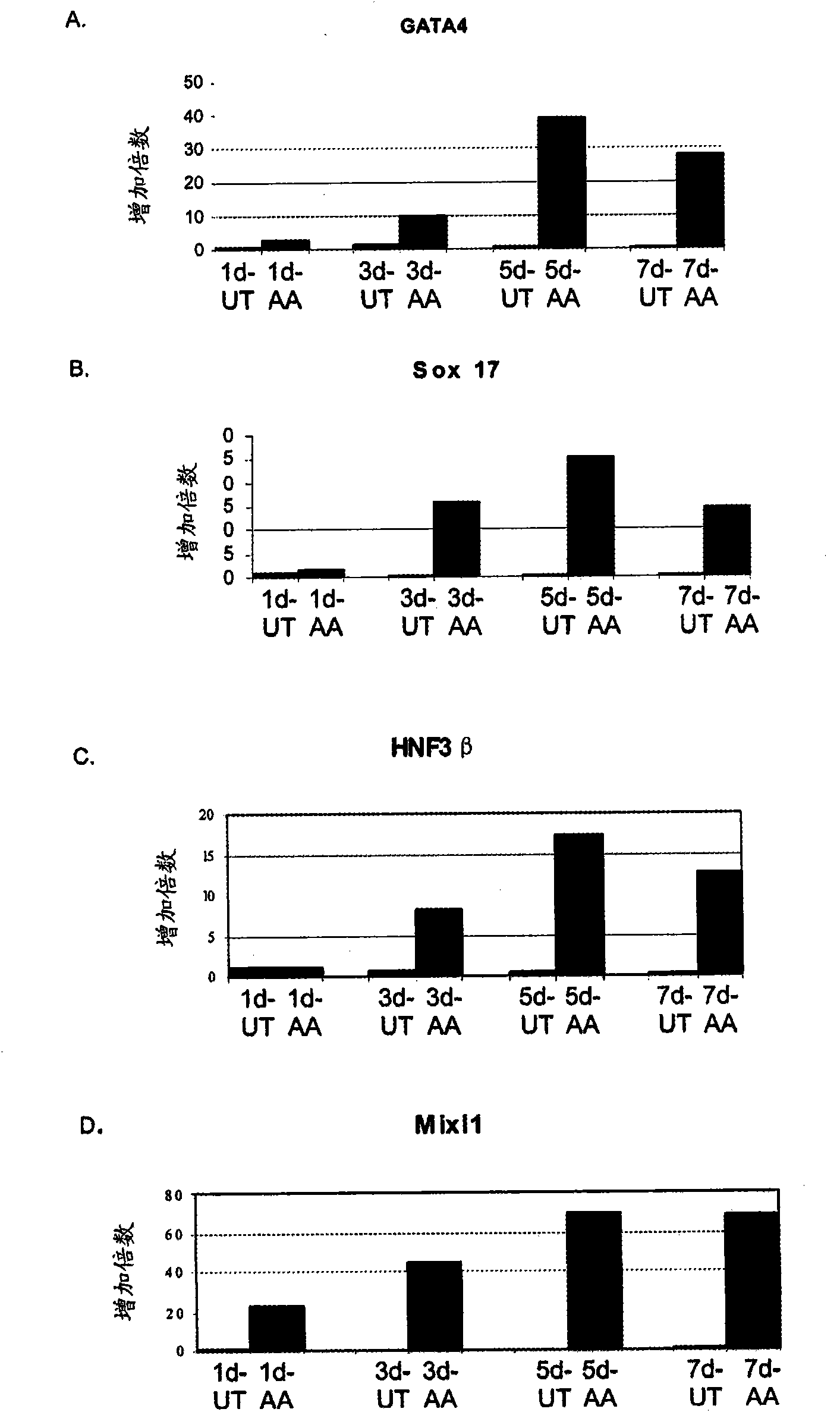
[0329] In an initial series of experiments, activin A was added to human embryonic fibroblasts cultured for up to seven days in DMEM / F12 supplemented with 0% to 2% serum and activin A (100 ng / ml). in embryonic stem cell populations. exist image 3 Cells were harvested at the time points indicated in and the expression of the indicated genes was determined by PCR ( image 3 , 4 and 5). exist image 3 Among them, PCR analysis showed that activin-treated cells expressed a broad spectrum of genes related to endoderm development, including GATA4( image 3 , sub-figure a), Sox-17 ( image 3 , sub-figure b), HNF-3β ( image 3 , sub-figure c) and Mixl-1( image 3 , sub...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com