Patents
Literature
2028 results about "Operation room" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
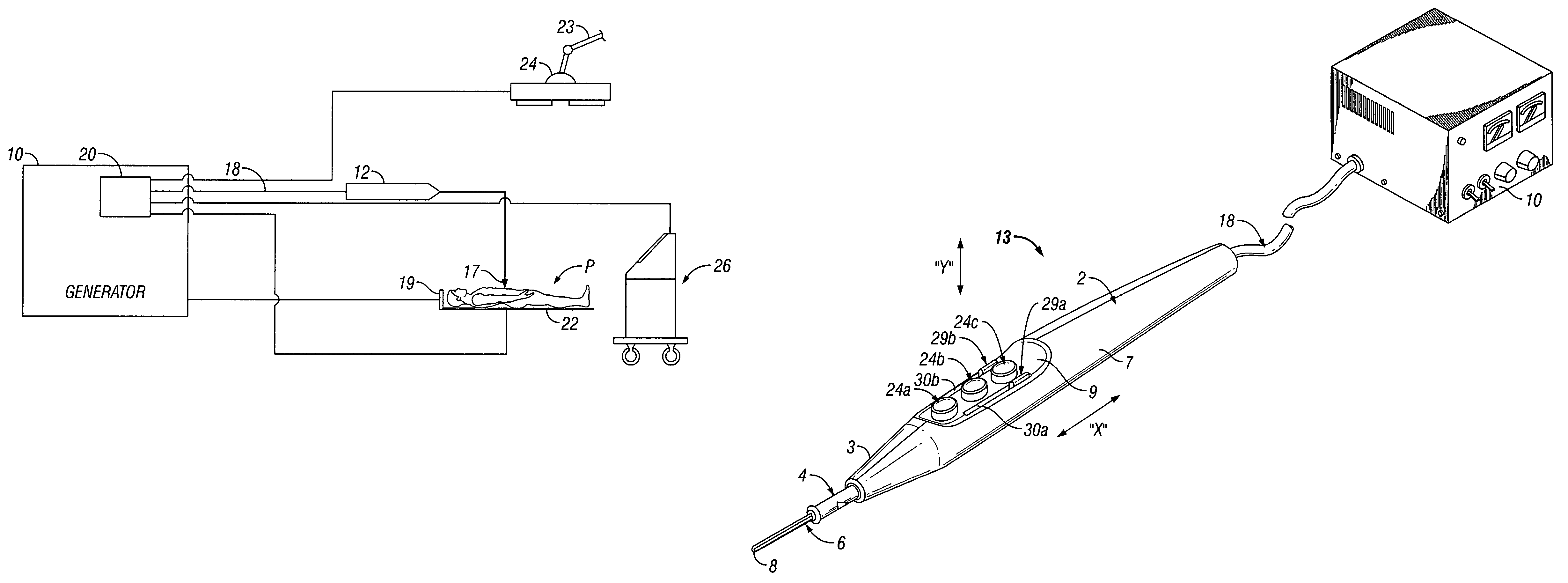
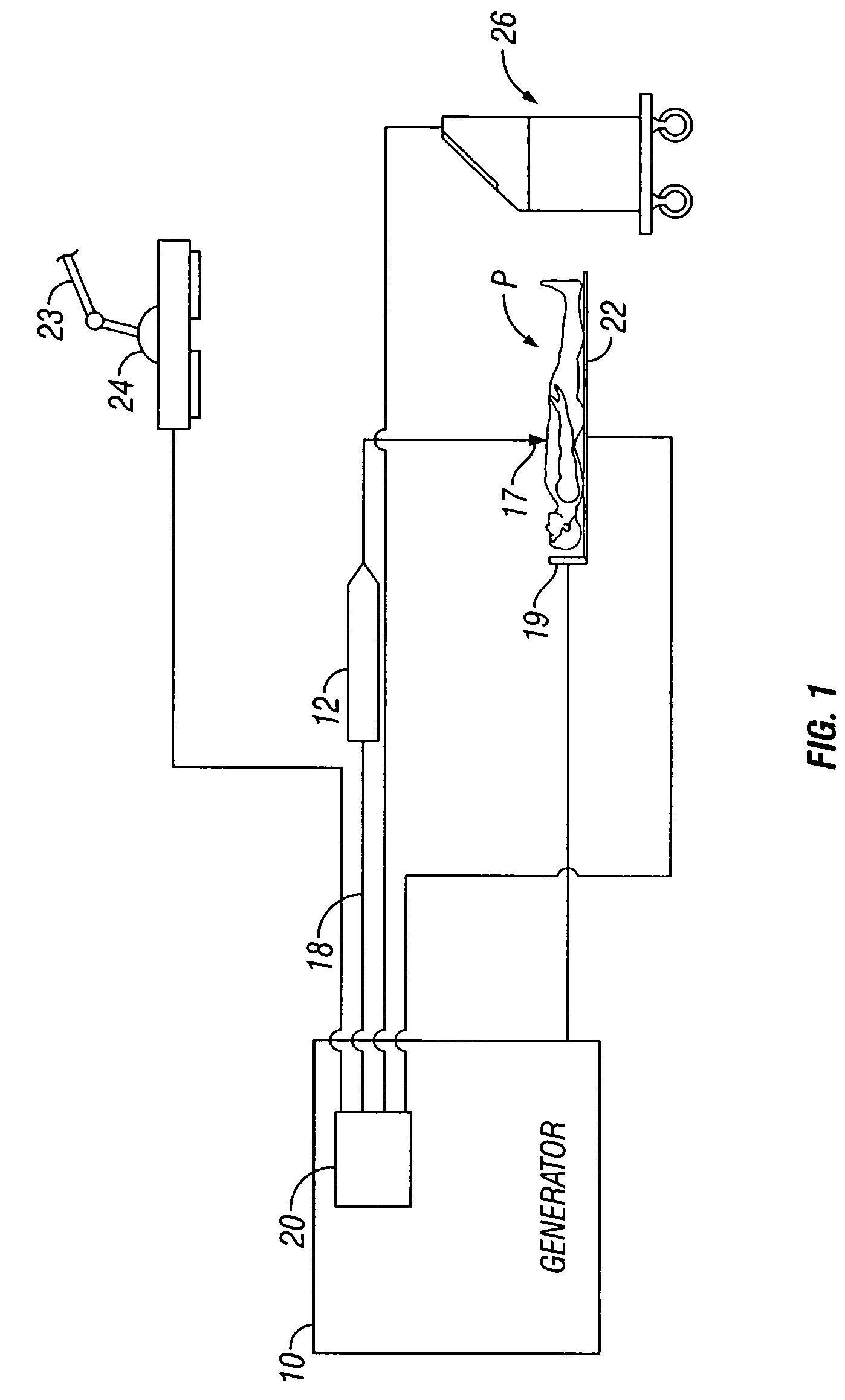
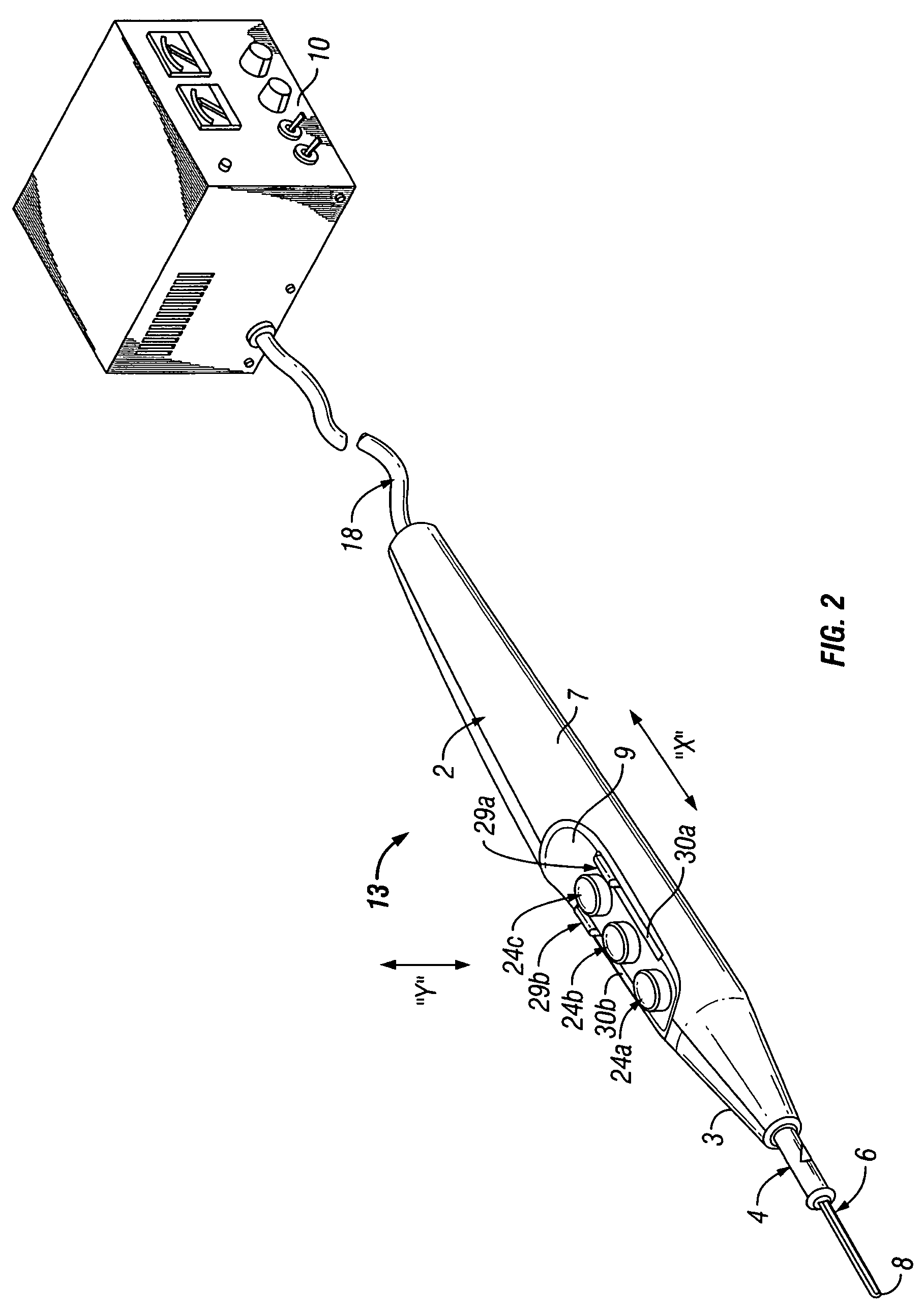
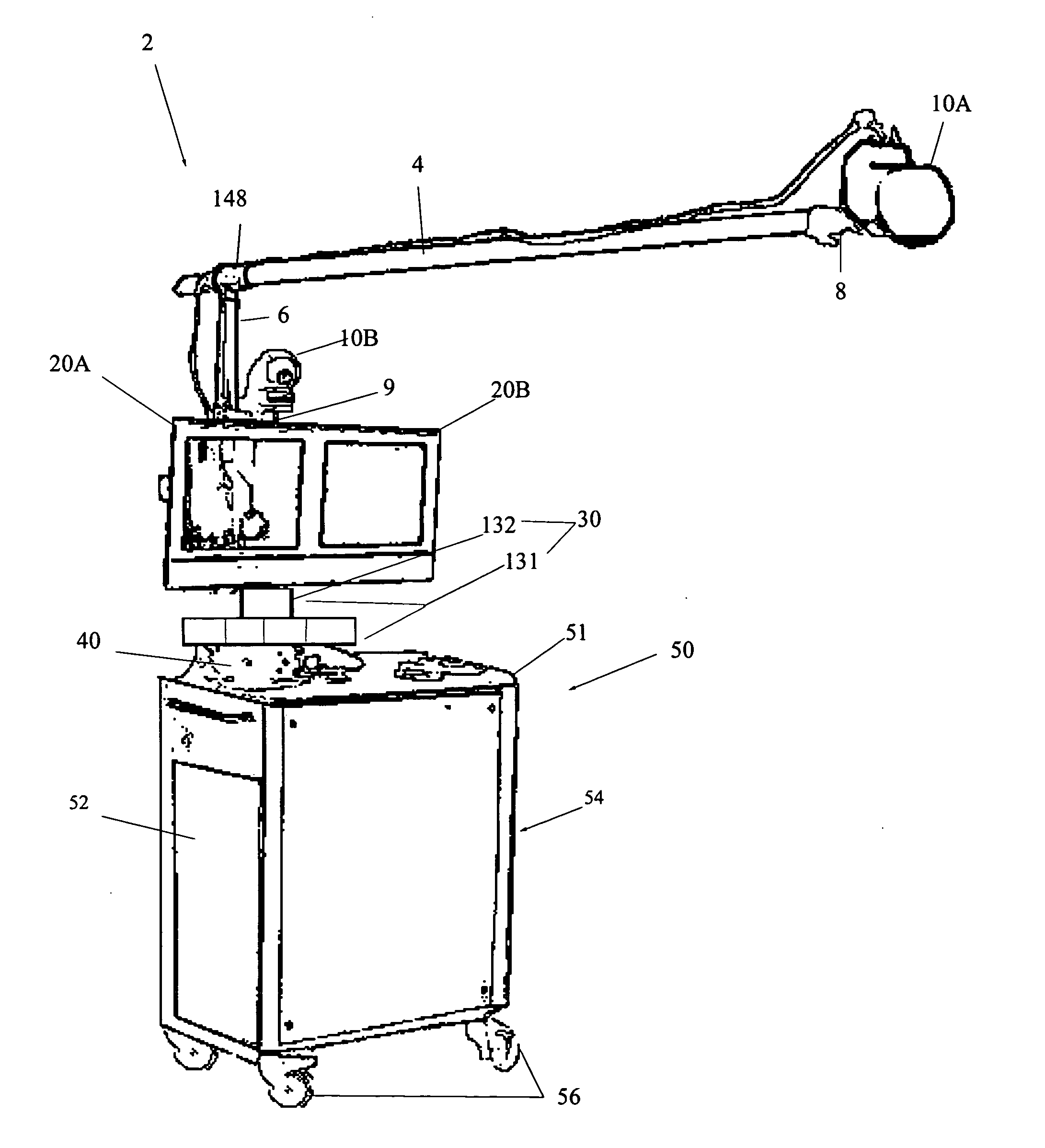
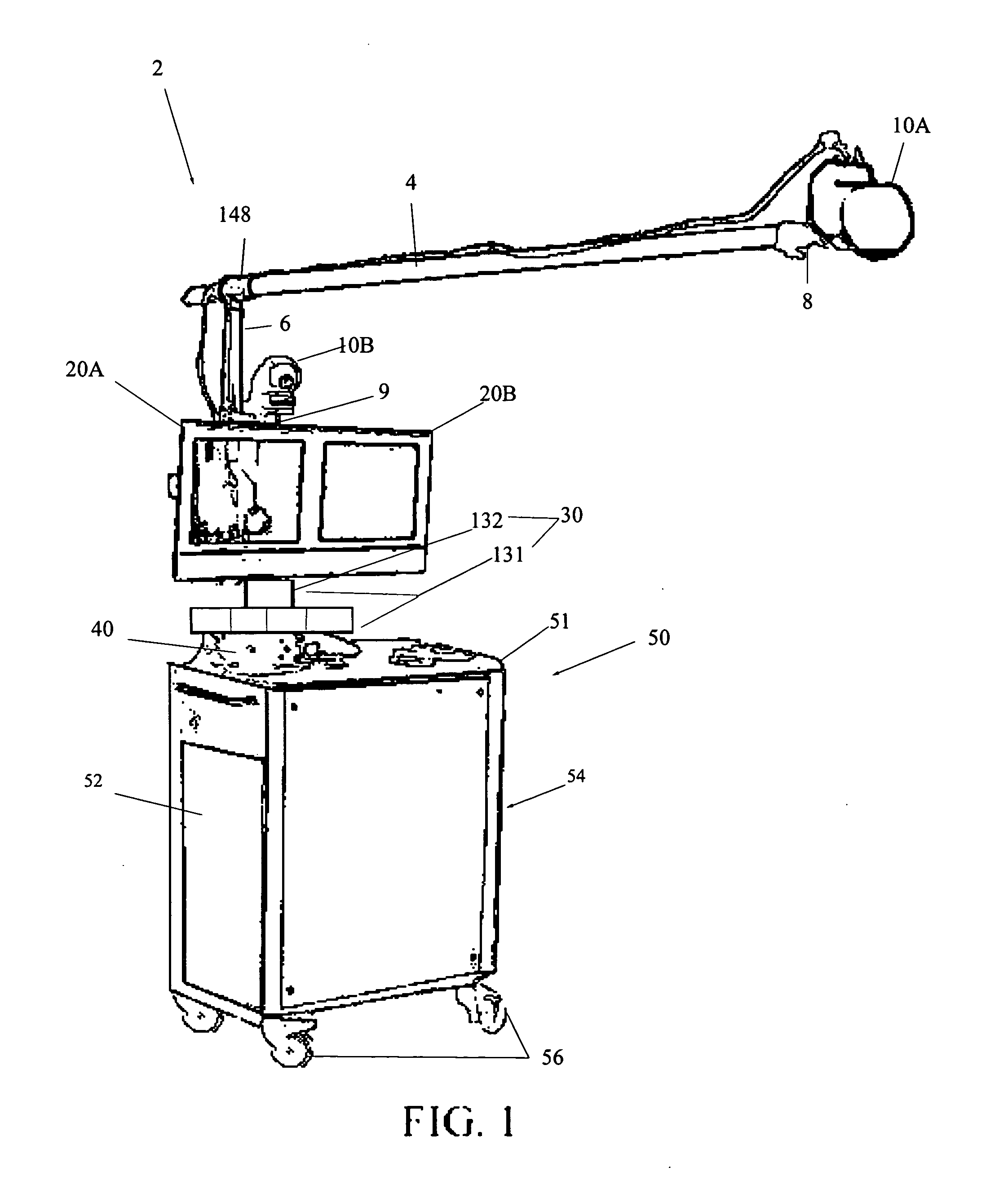
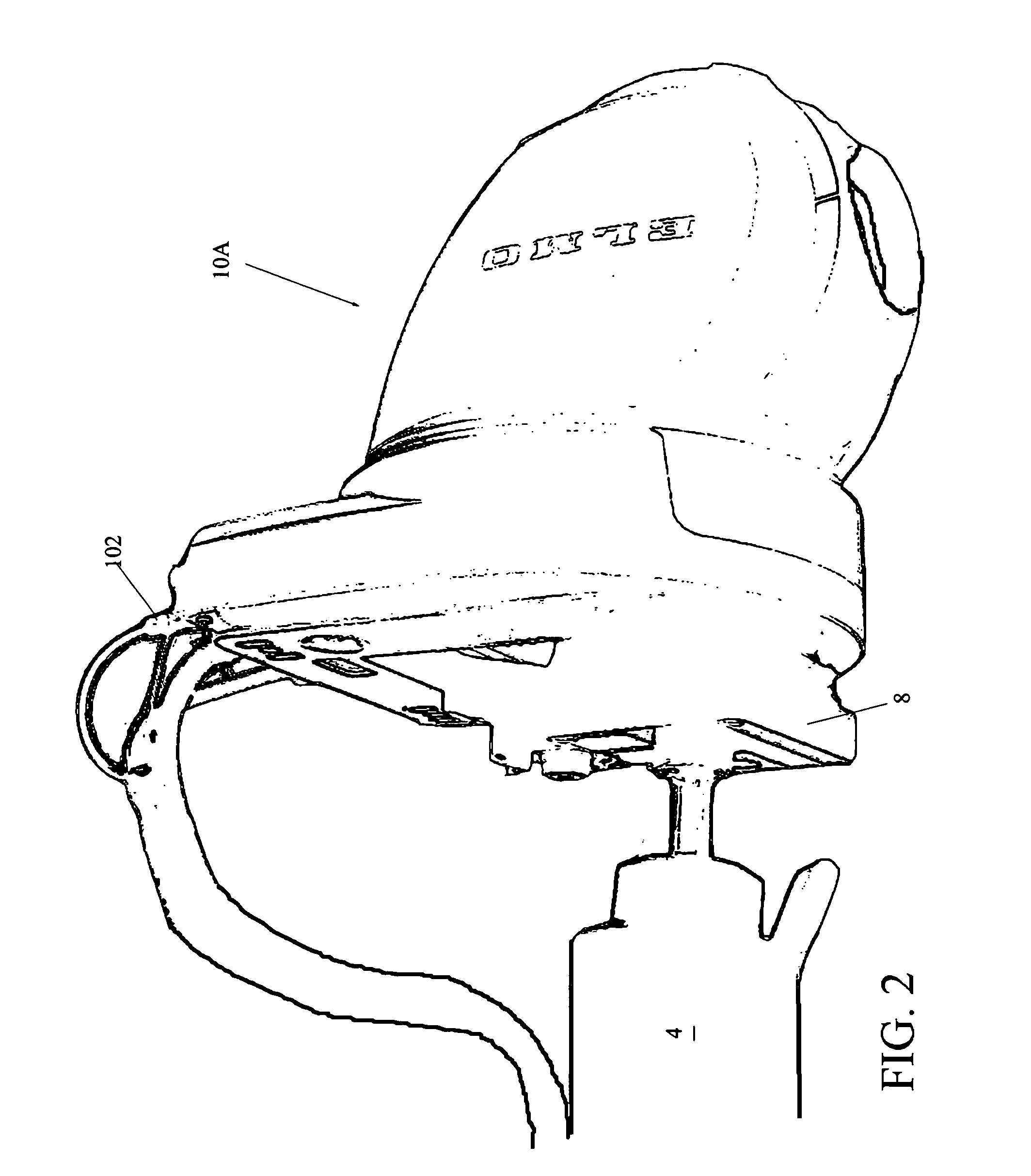
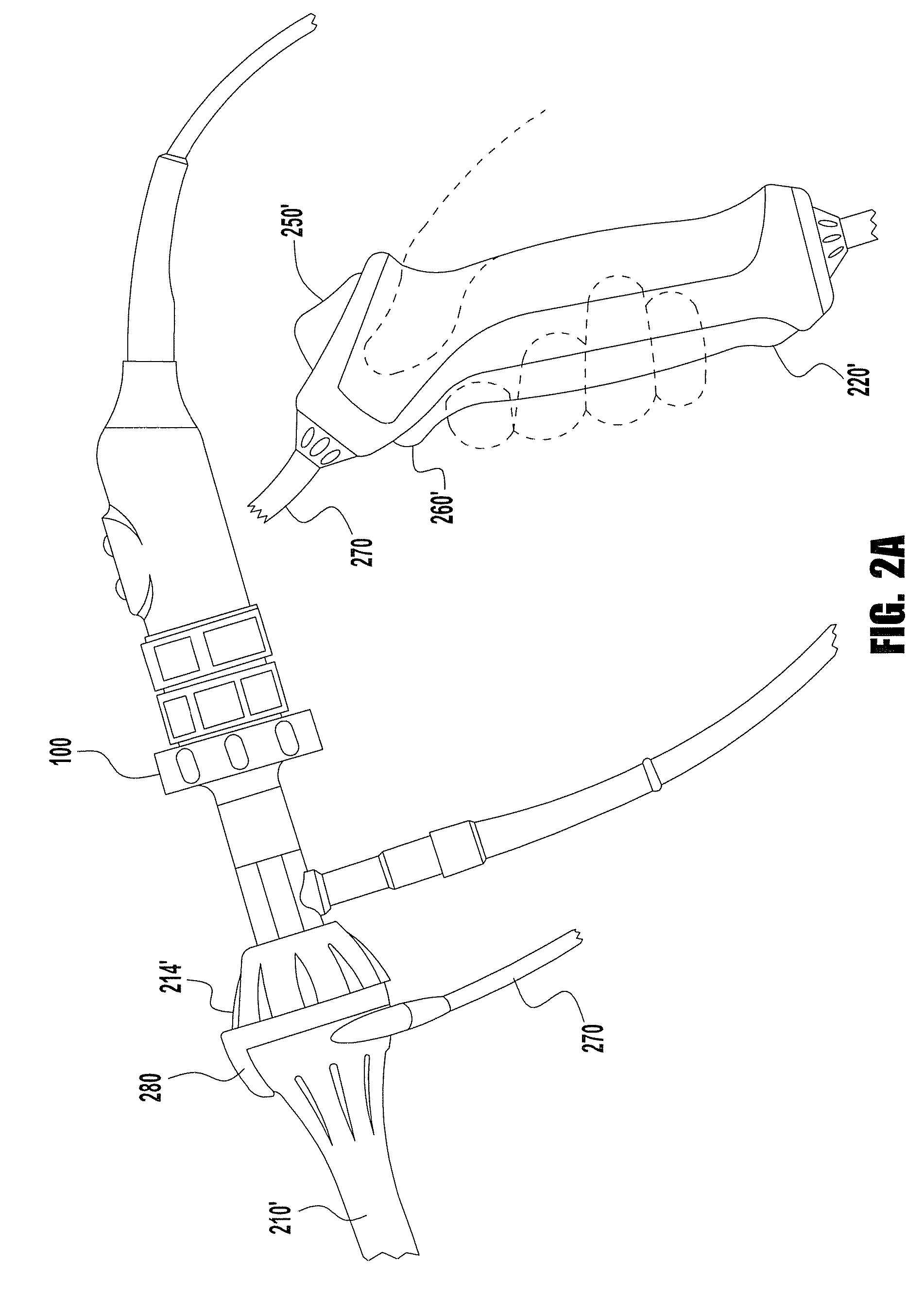
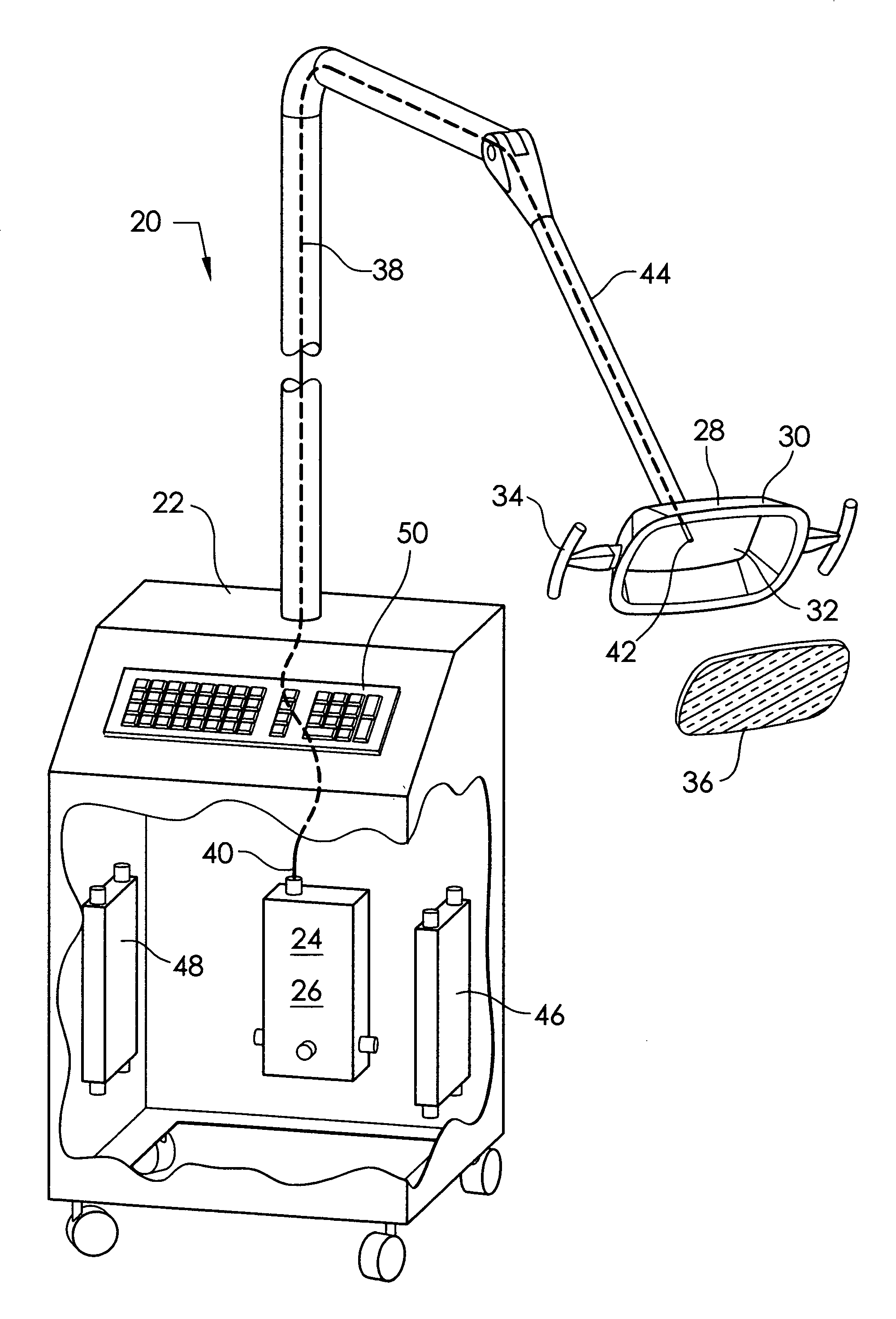
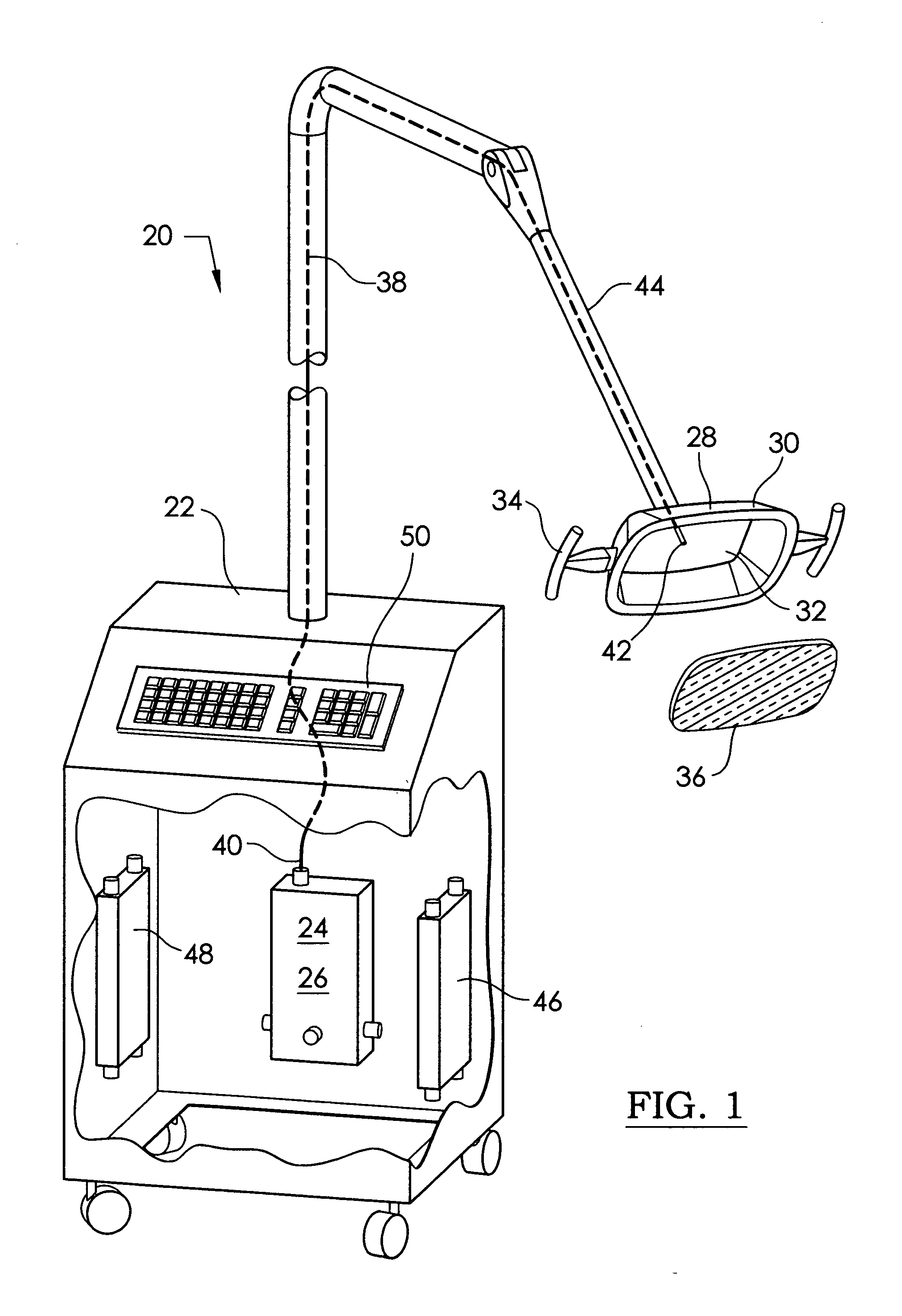
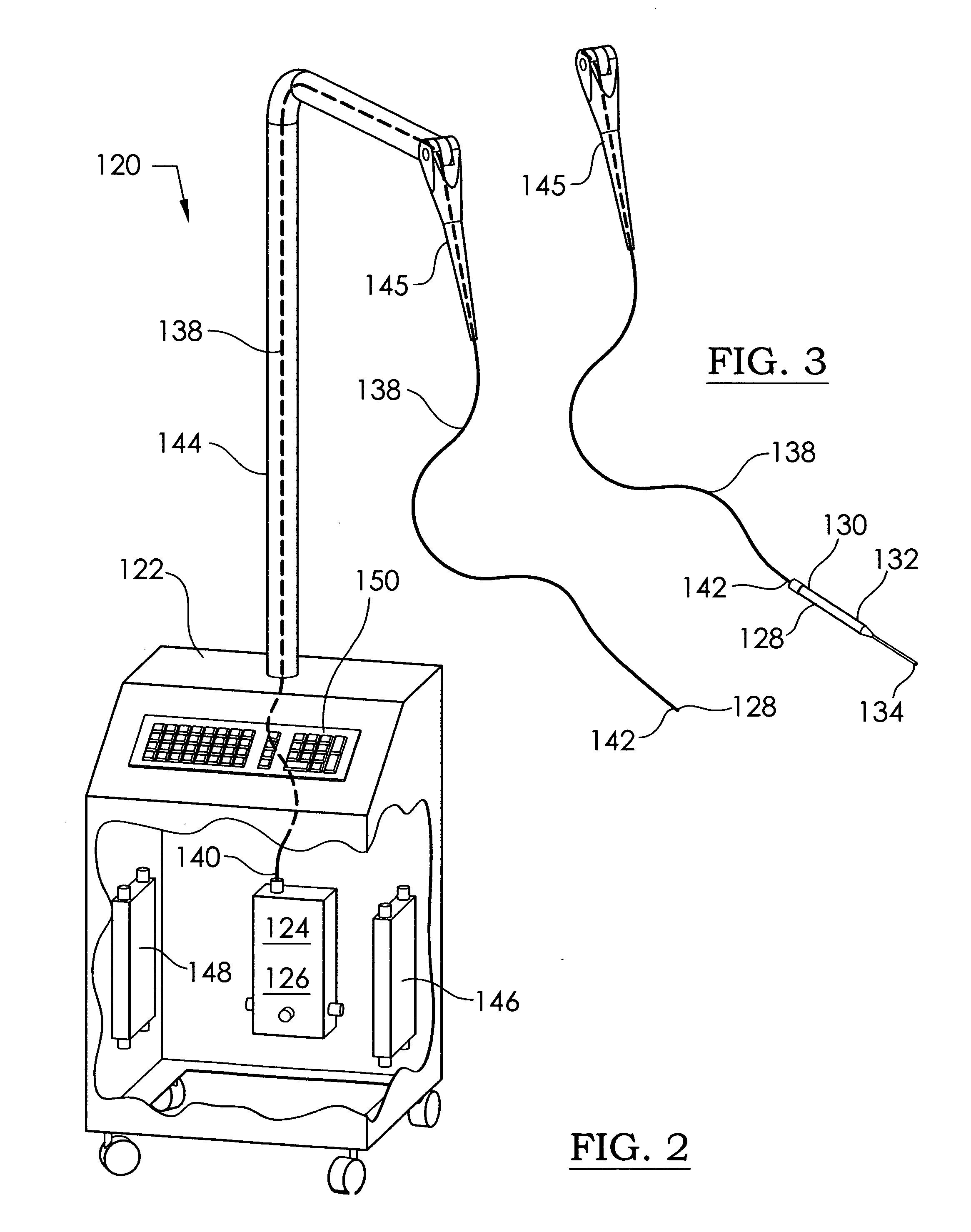
Handheld electrosurgical apparatus for controlling operating room equipment
A system and apparatus for controlling operating room equipment during an electrosurgical procedure is disclosed. The system includes an electrosurgical generator, a controller in electrical communication with and configured to control the electrosurgical generator and at least one operating room device, and a handpiece having a housing and a cable extending proximally from the housing providing electrical connection to the controller, the handpiece further includes first controls for controlling the generator and second controls for controlling at least one operating room device.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
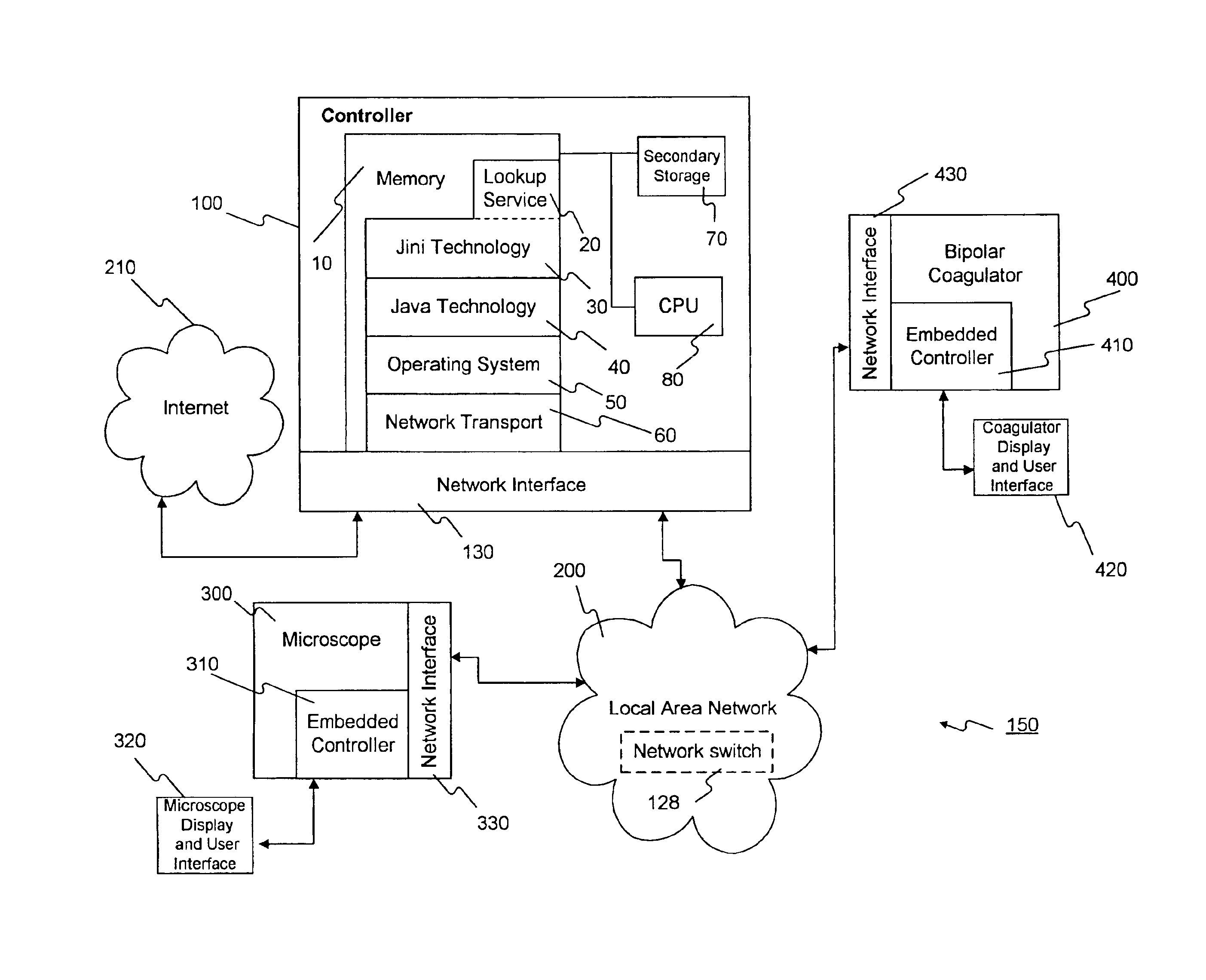
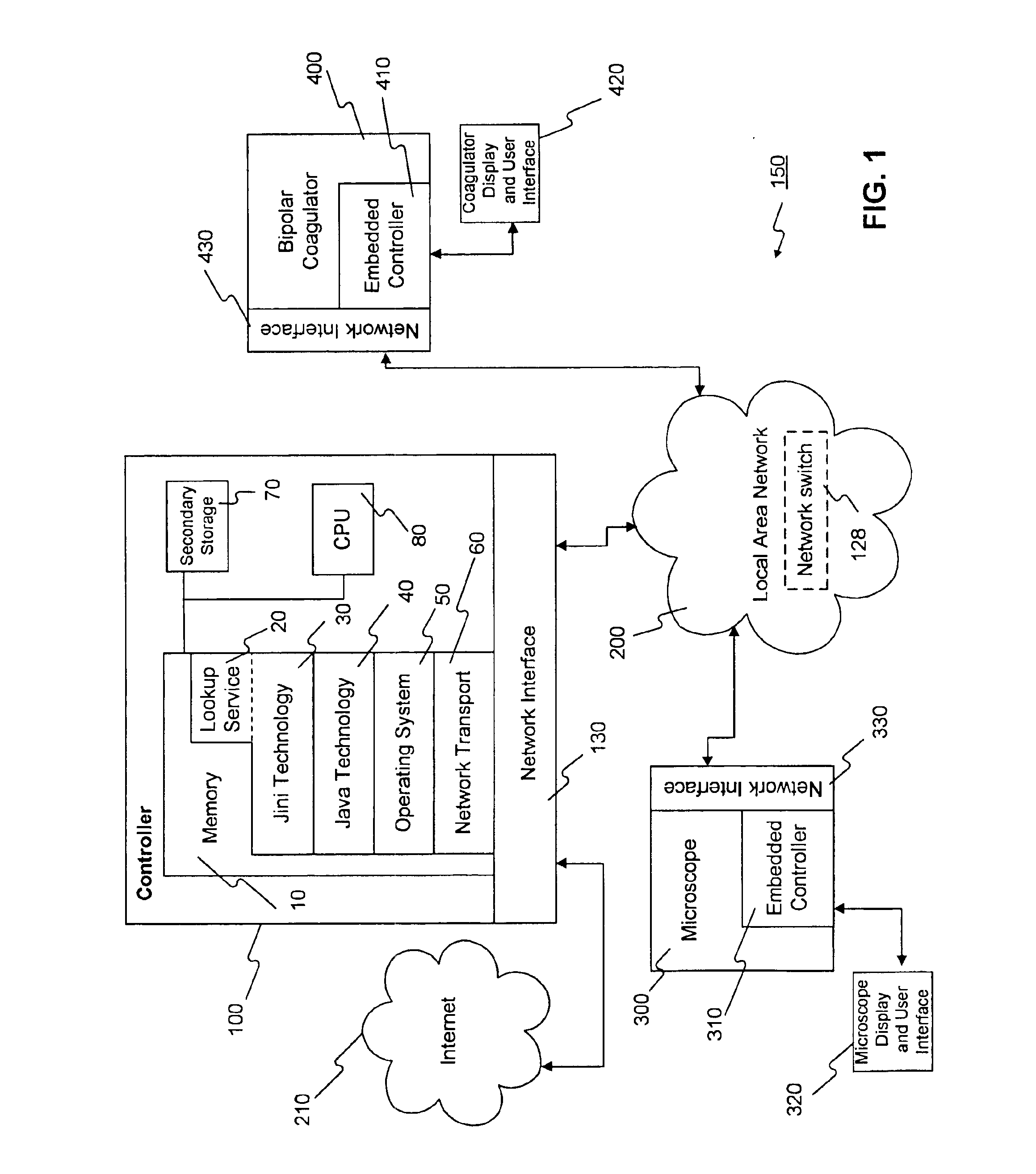
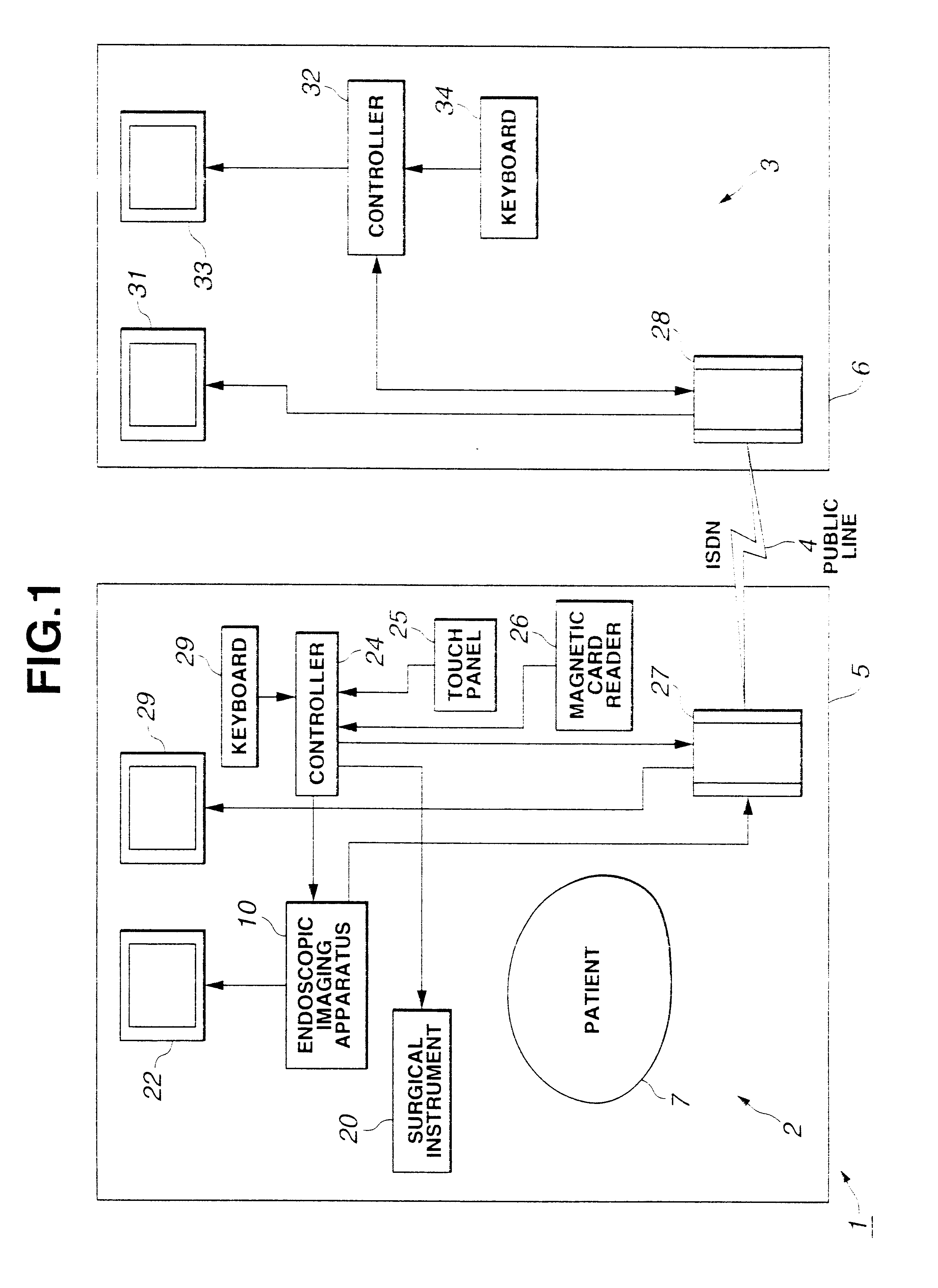
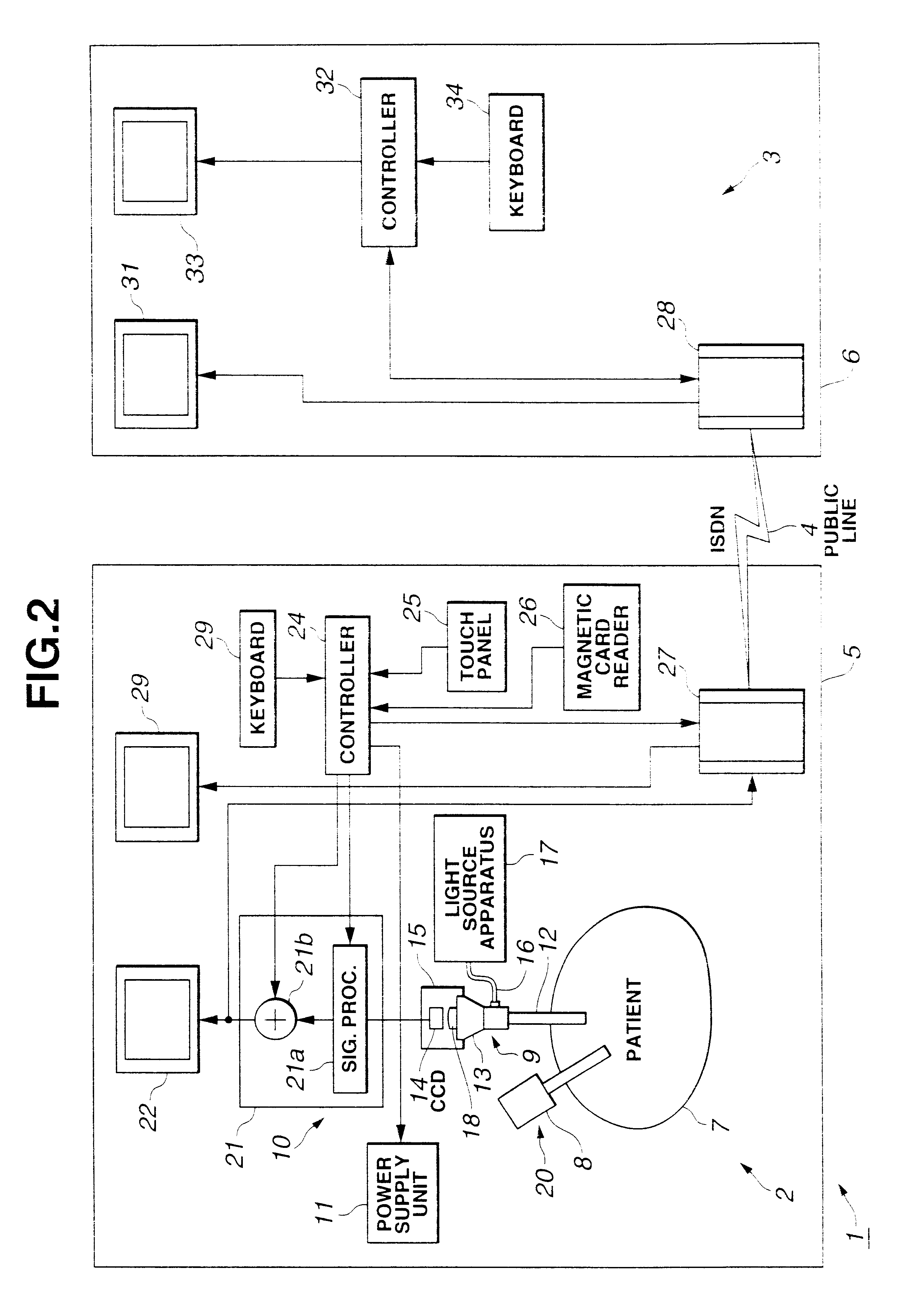
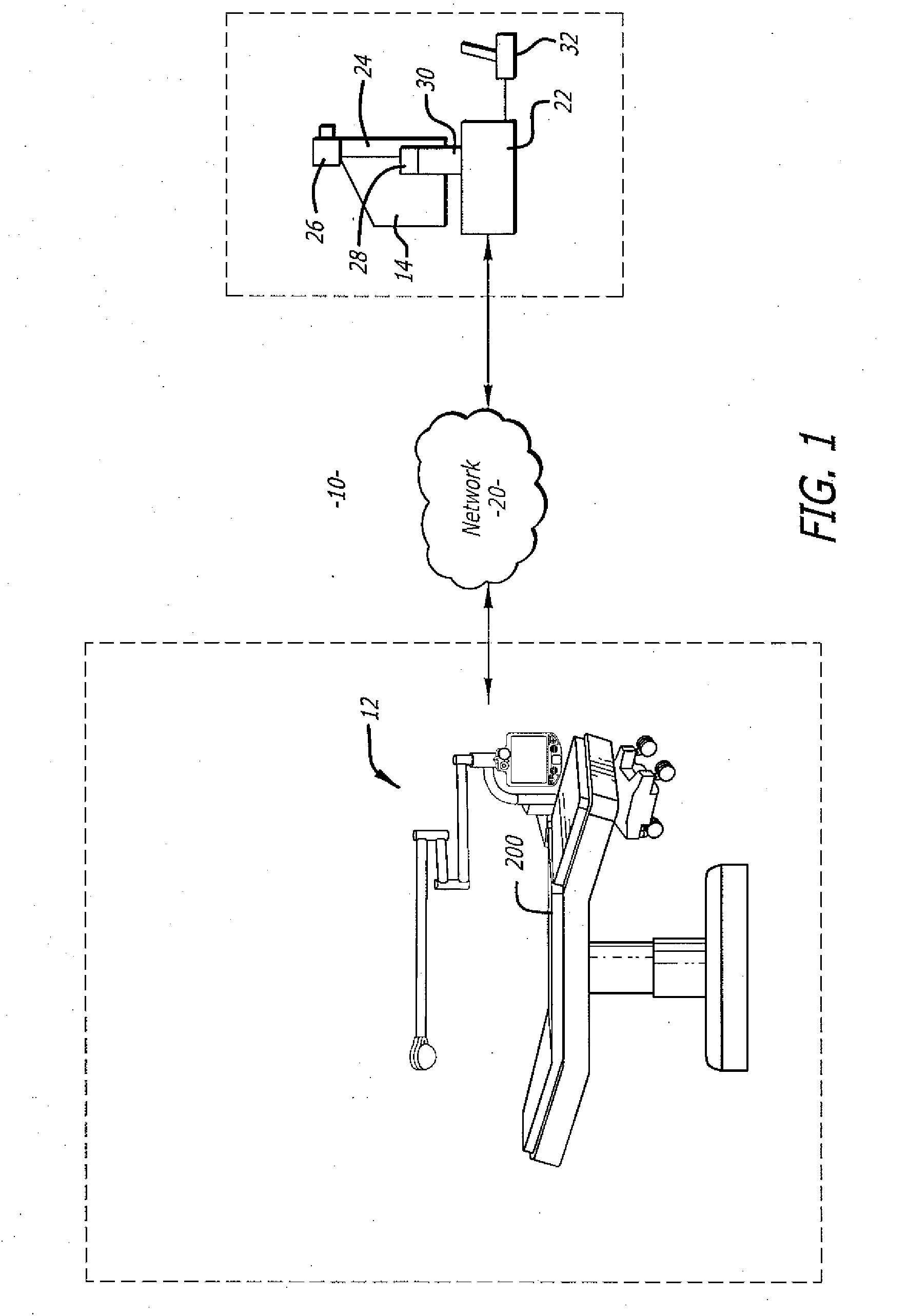
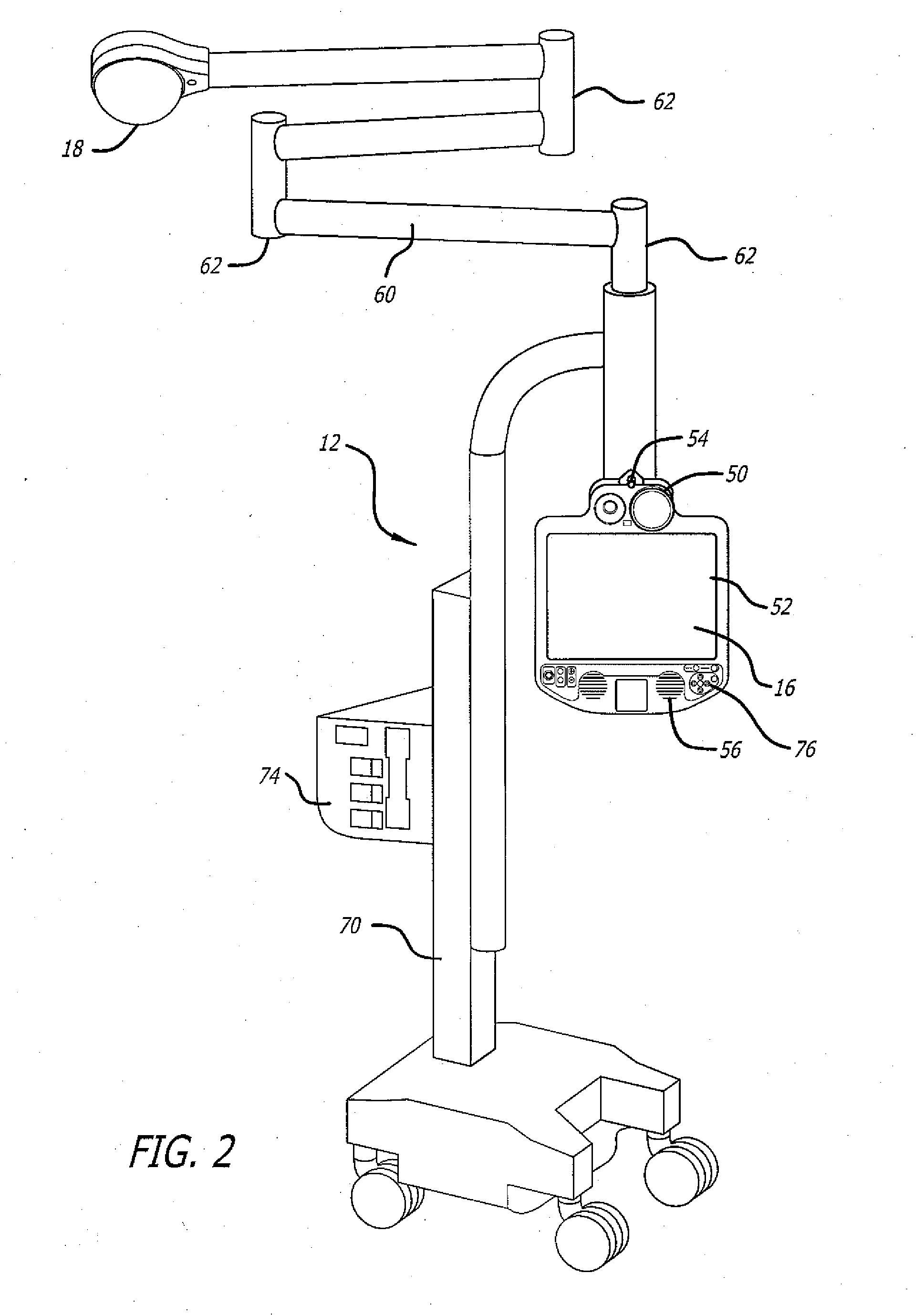
Method and apparatus for accessing medical data over a network
A method and apparatus for retrieving, accessing, and storing medical data relating to a patient during a medical procedure. The invention provides a single interface to many disparate forms of medical data, which is accessible over a local area network, wide area network, direct connection, or combinations thereof. In one embodiment, an operating room control system for use during a medical procedure on a patient includes an input device, a display device, and a controller that is coupled to the input device and the display device. The controller receives one or more user inputs, transmits a command to a server located outside of the operating room to retrieve medical data, receives the medical data from the server, and displays the medical data on the display device.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC +1
Telepresence robot with a camera boom
A remote controlled robot with a head that supports a monitor and is coupled to a mobile platform. The mobile robot also includes an auxiliary camera coupled to the mobile platform by a boom. The mobile robot is controlled by a remote control station. By way of example, the robot can be remotely moved about an operating room. The auxiliary camera extends from the boom so that it provides a relatively close view of a patient or other item in the room. An assistant in the operating room may move the boom and the camera. The boom may be connected to a robot head that can be remotely moved by the remote control station.
Owner:TELADOC HEALTH INC +1
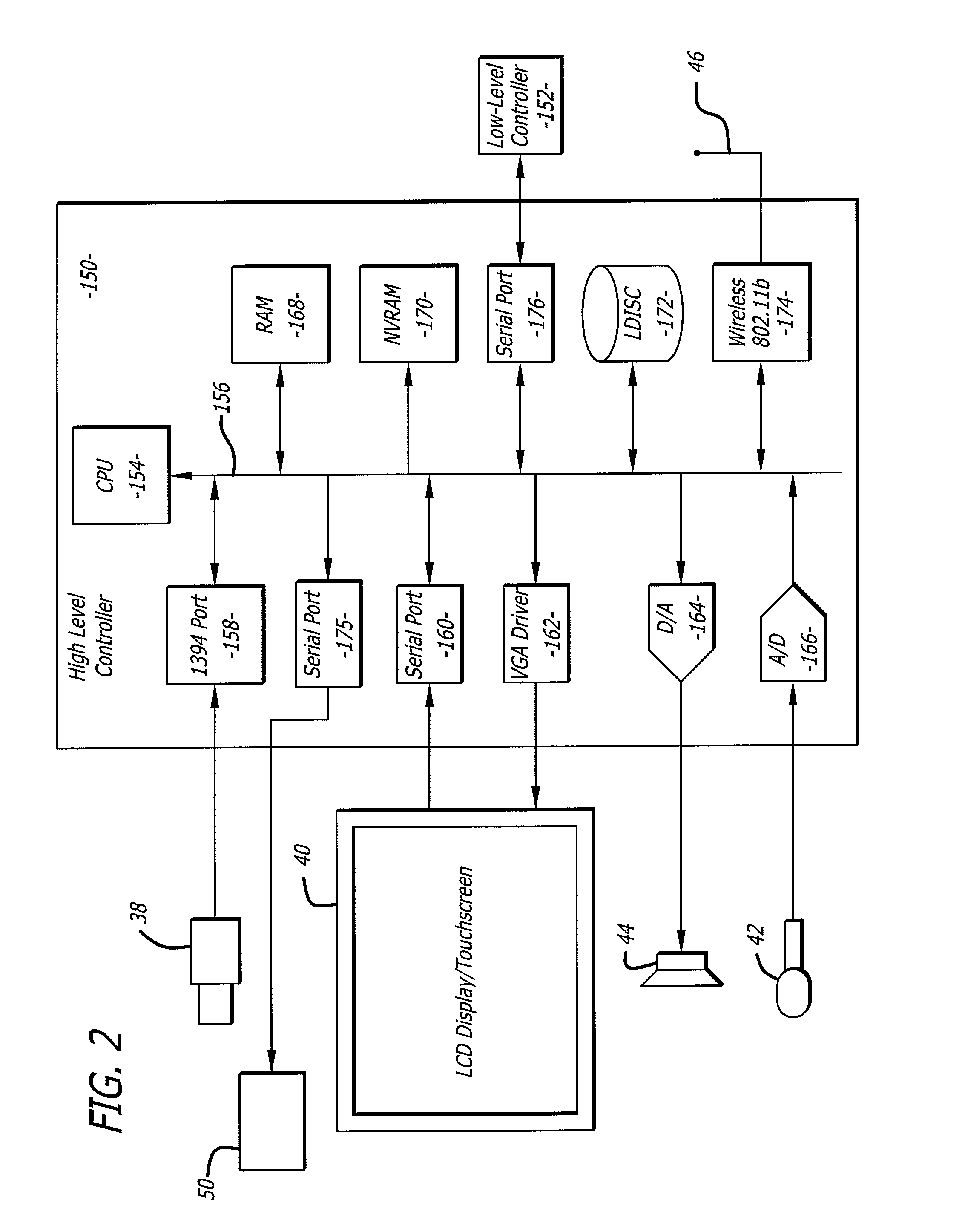
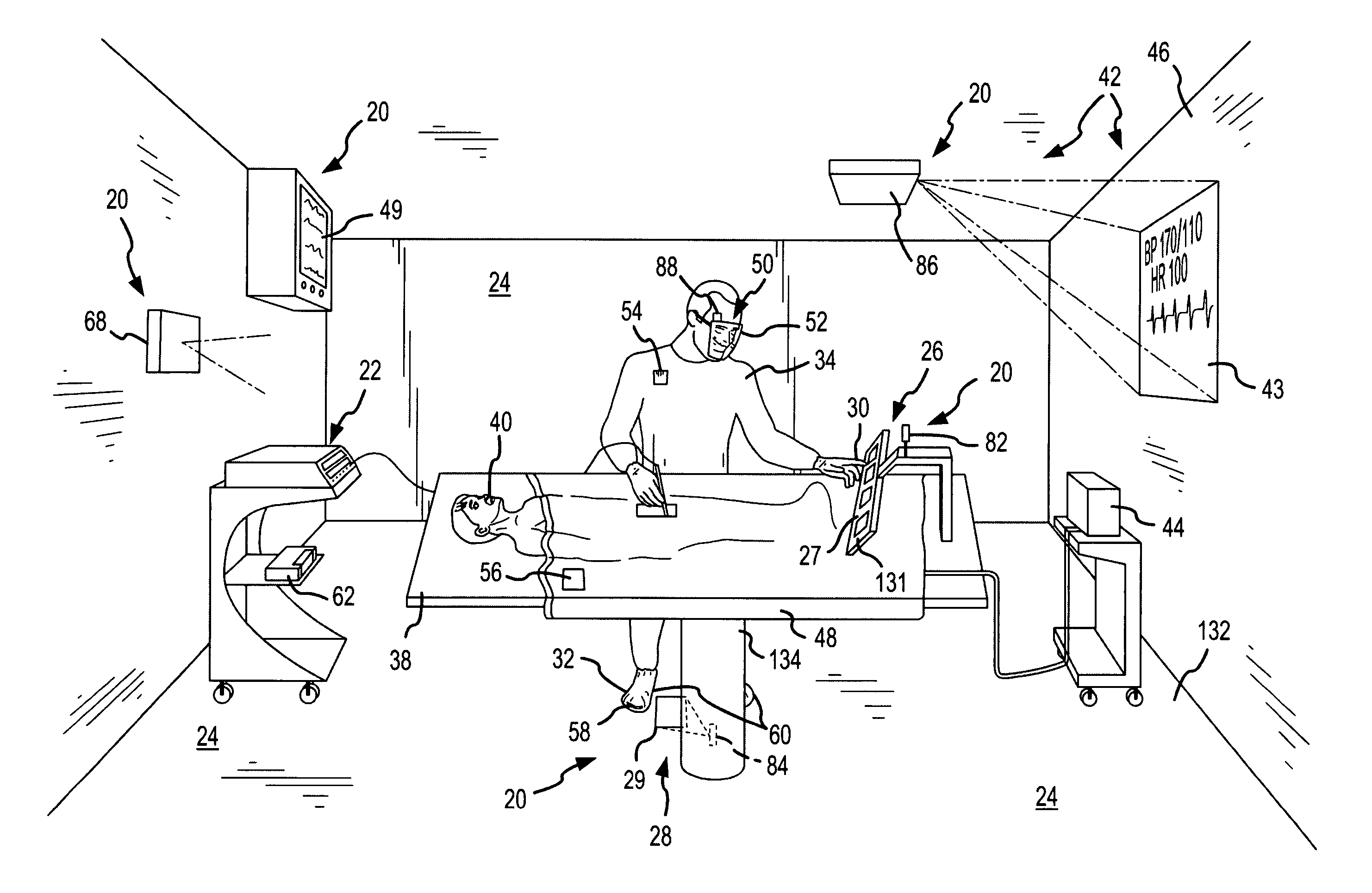
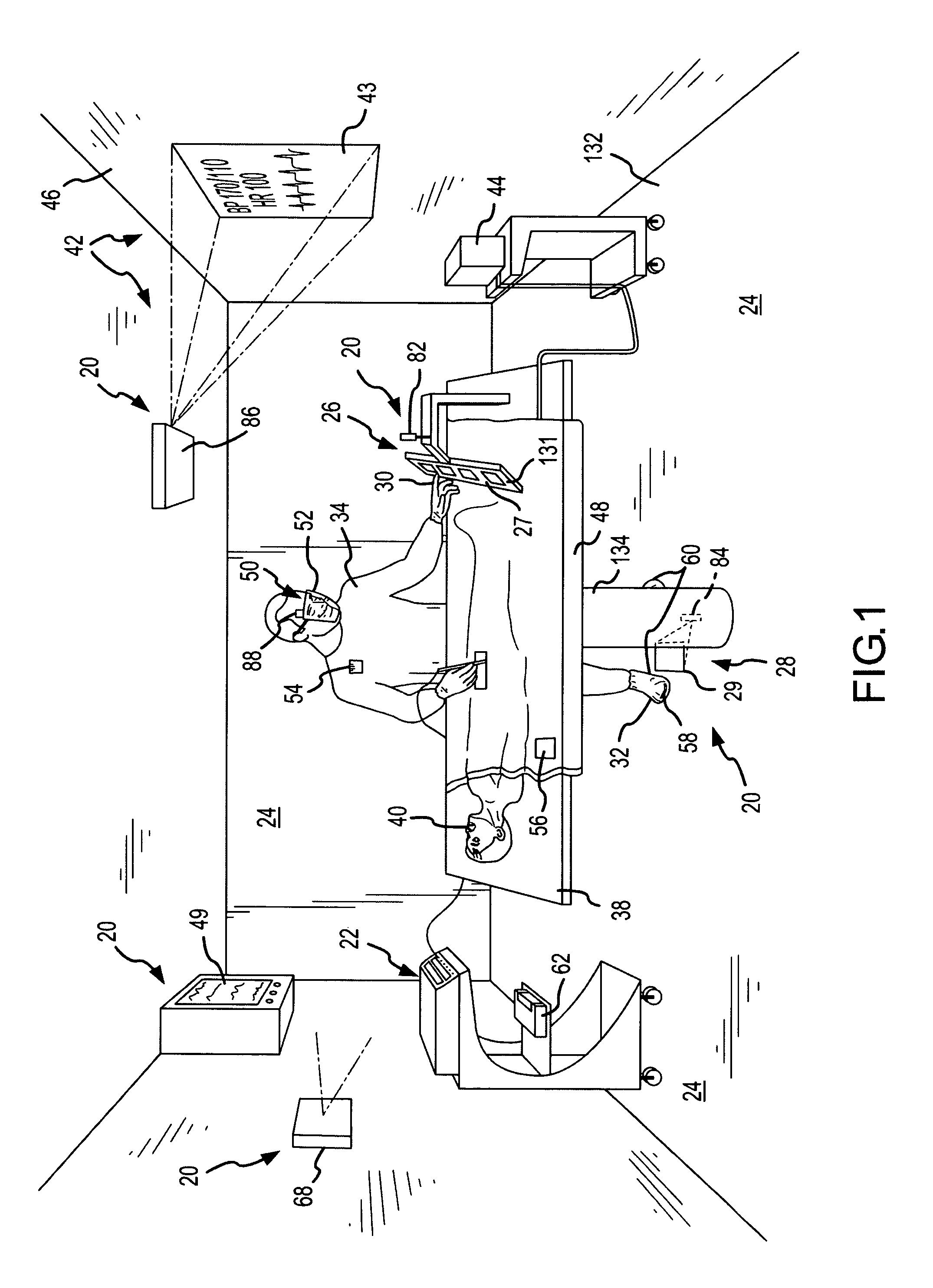
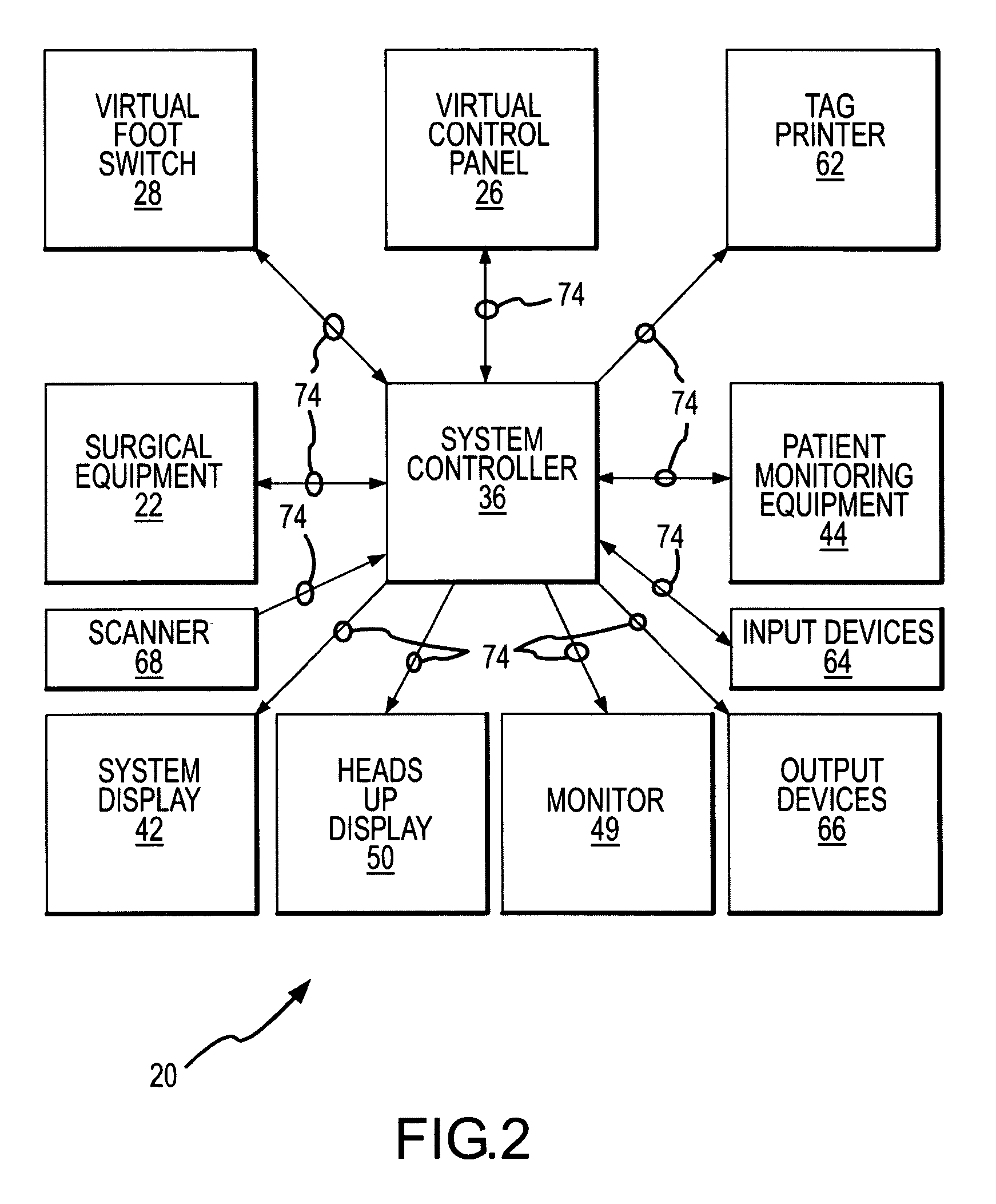
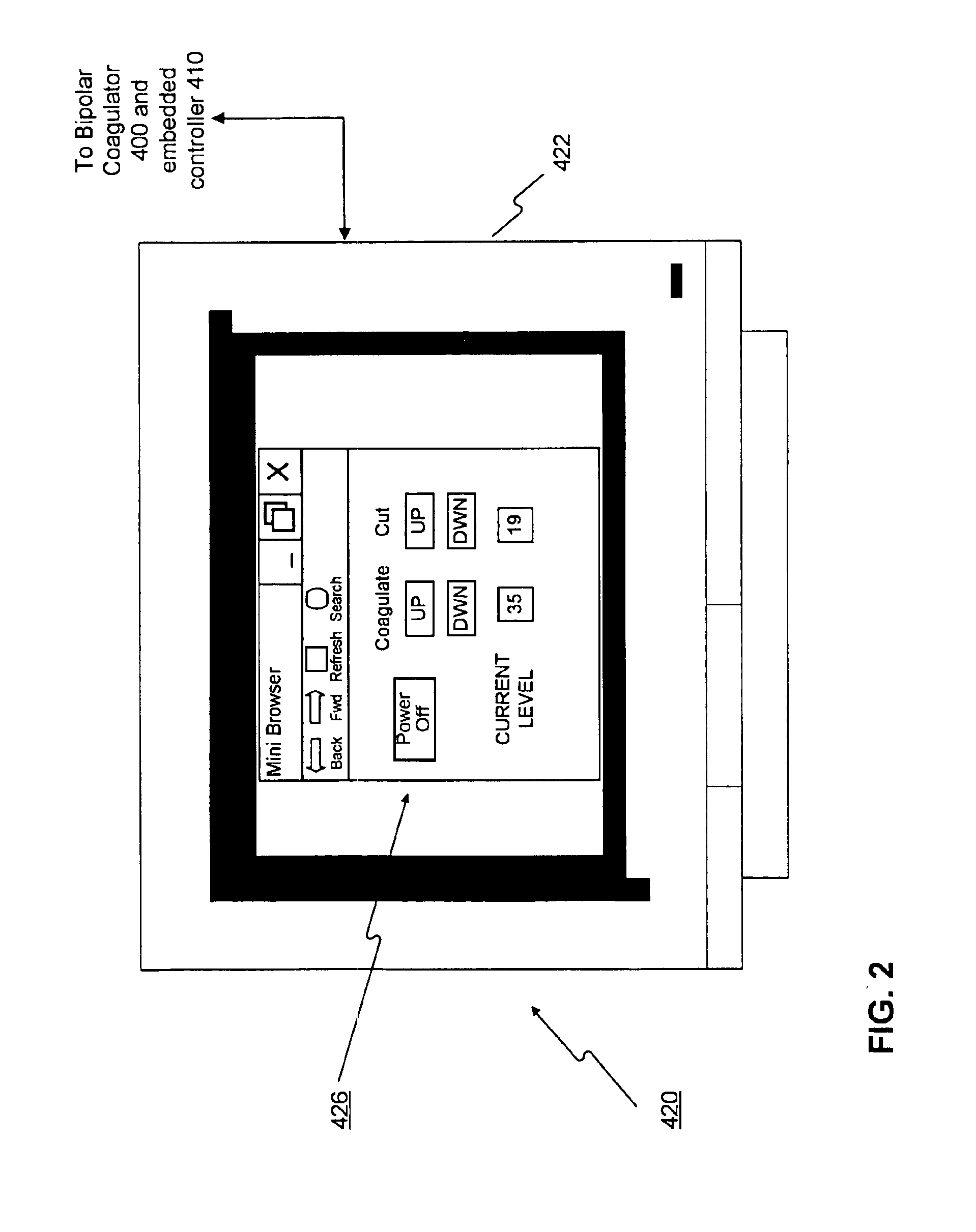
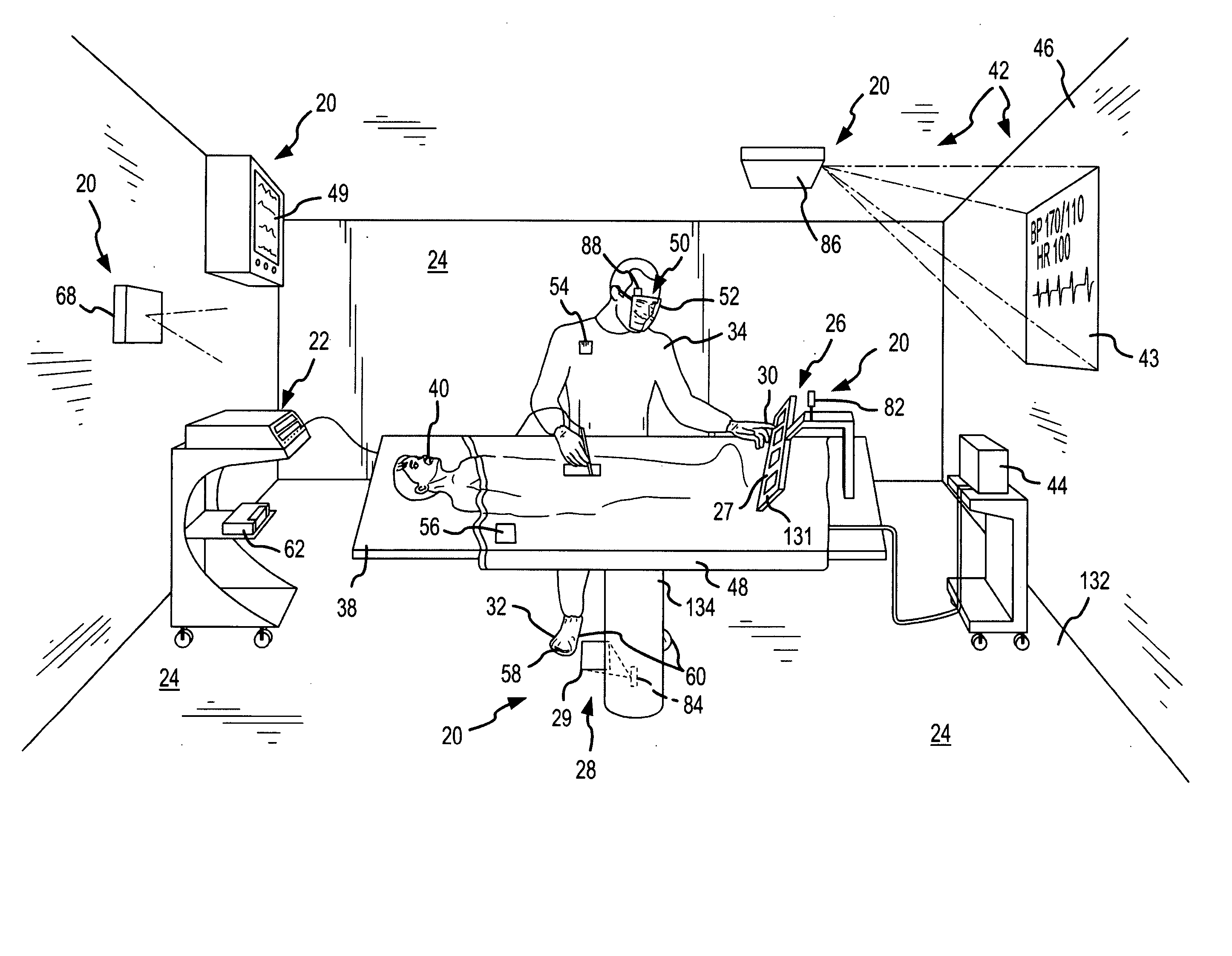
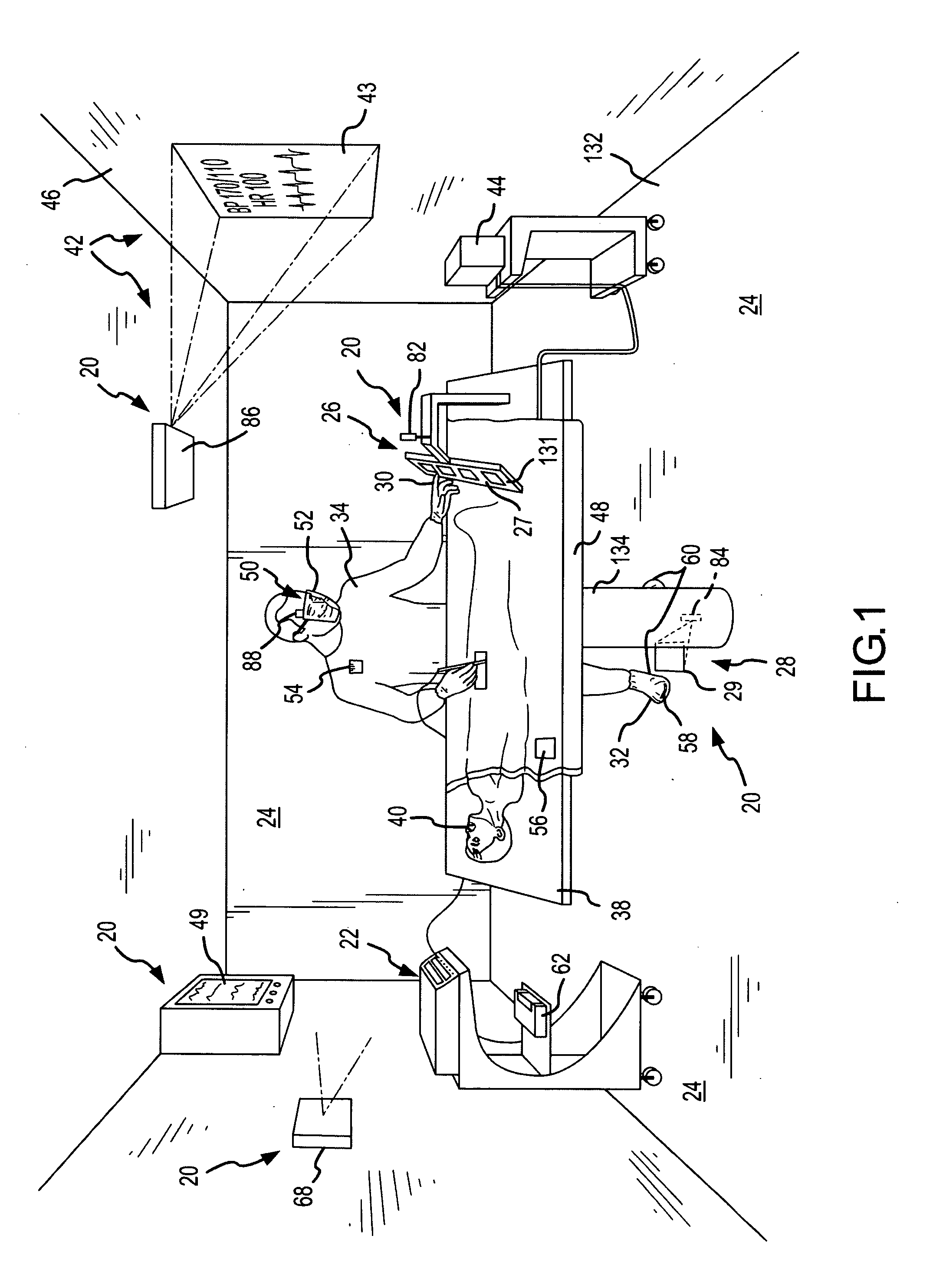
Virtual operating room integration
InactiveUS7317955B2Direct and accurate controlEliminating clutter and risk of trippingElectrotherapyMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesSurgical operationSTERILE FIELD
A virtual control system for an operating room establishes virtual control devices to control surgical equipment and patient monitoring equipment and to display control, status and functionality information concerning the surgical equipment and condition information of the patient. The virtual control devices permit direct interaction by the surgeon while maintaining a sterile field, and avoid the use of actual physical devices and electrical cables connecting them to the surgical equipment.
Owner:CONMED CORP
Module for acquiring electroencephalograph signals from a patient
InactiveUS6430437B1Good techniqueEliminate artifactsElectroencephalographyPloughsAudio power amplifierMultiplexer
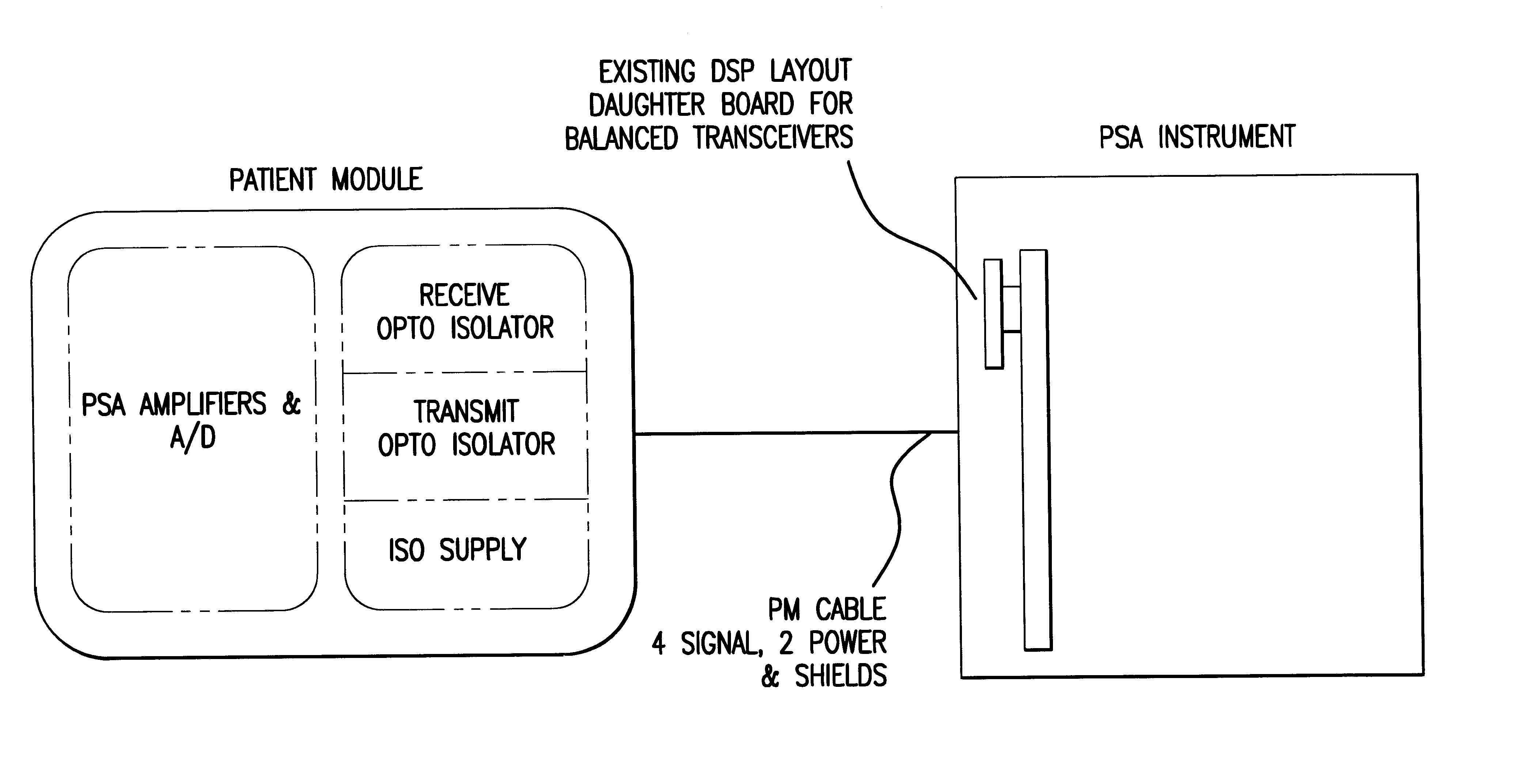
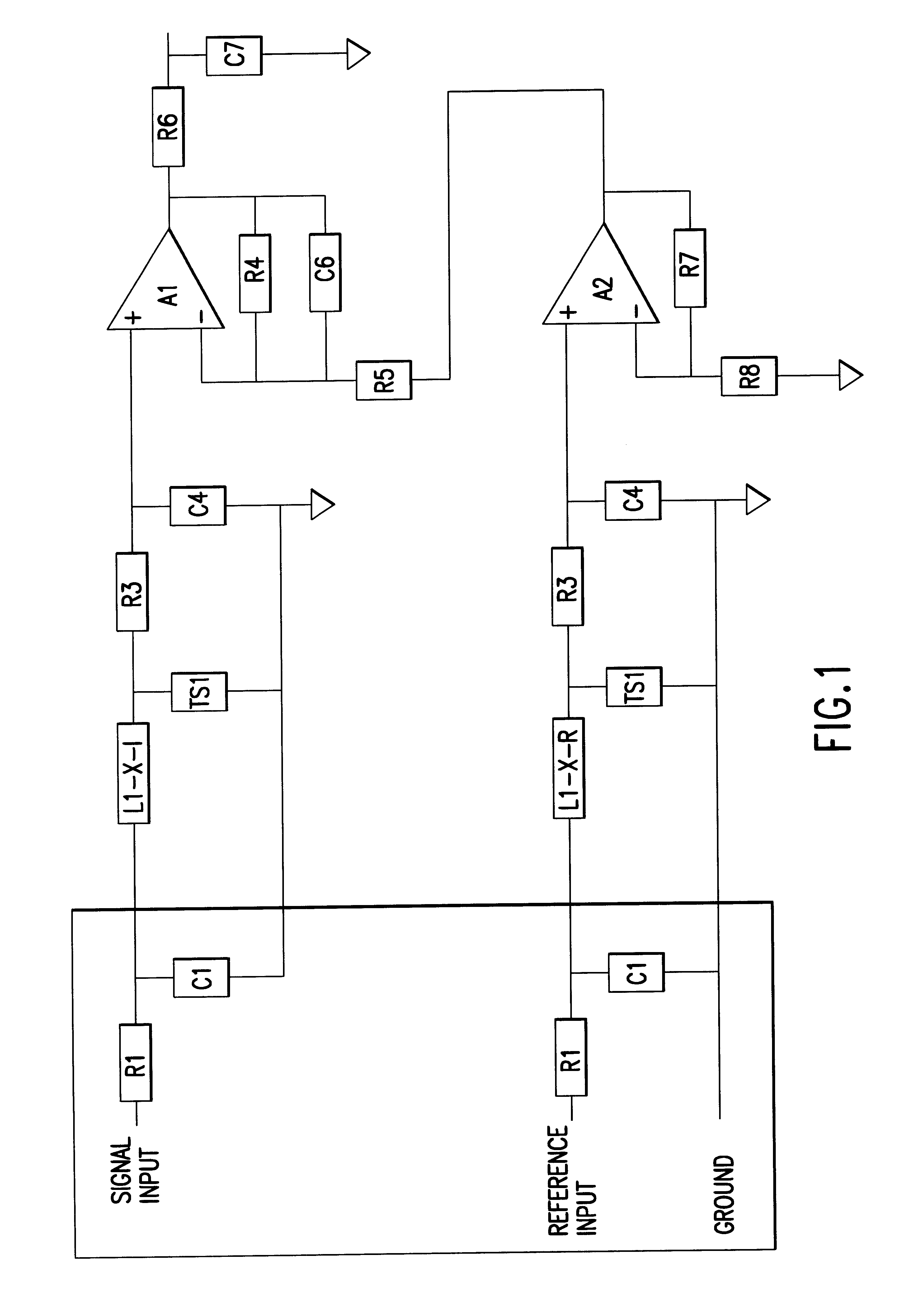
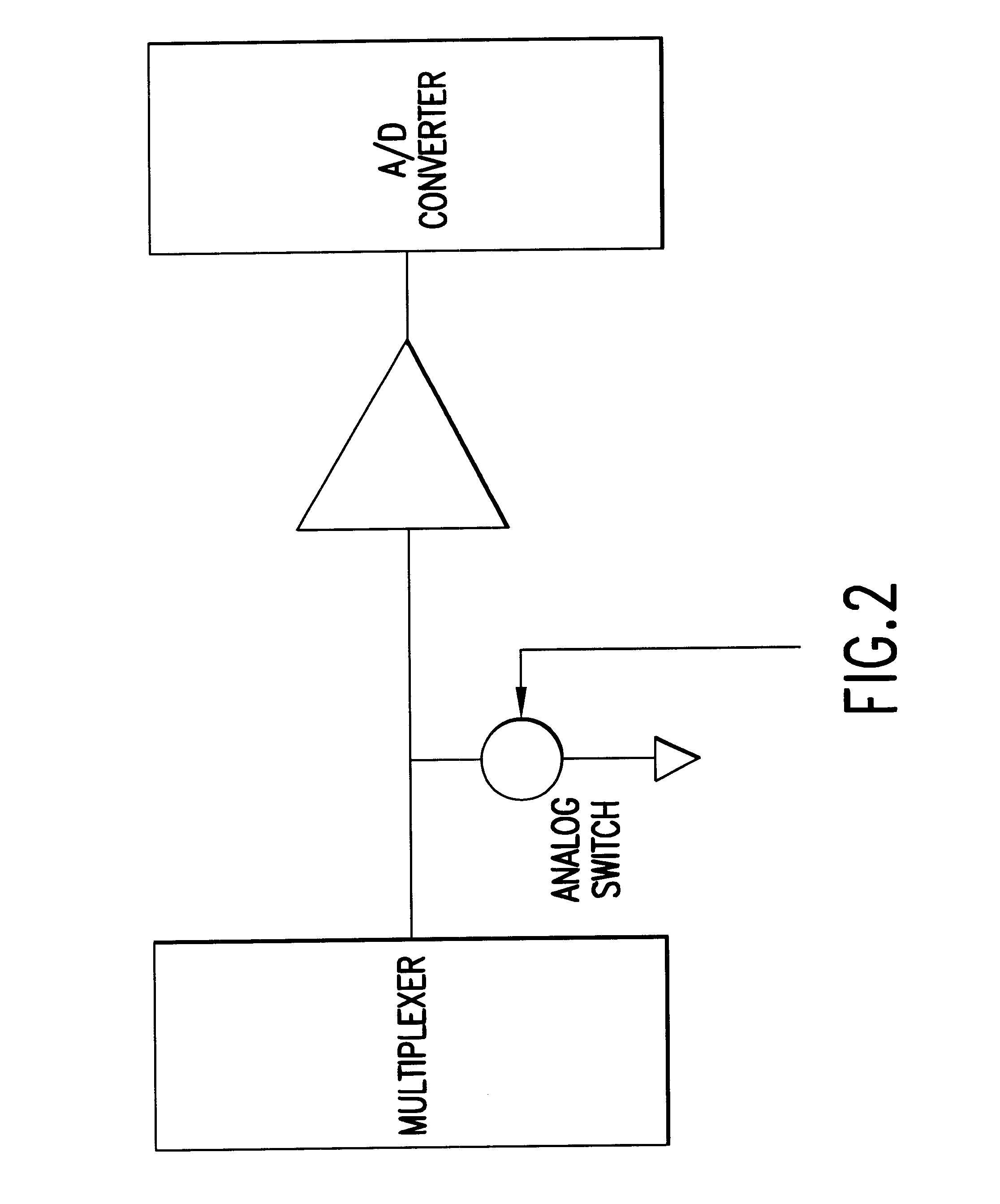
A patient module comprising an 8 channel EEG pre-amplifier whose signal acquisition and processing characteristics are optimized for use in the operating room and intensive care unit. This patient module comprises at least an optimized multistage input filter, an optimized input stage circuit topography, ultra-isolation, oversampling, a multiplexer inter-sample charge dump, and high performance low-frequency-enhanced shielding.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
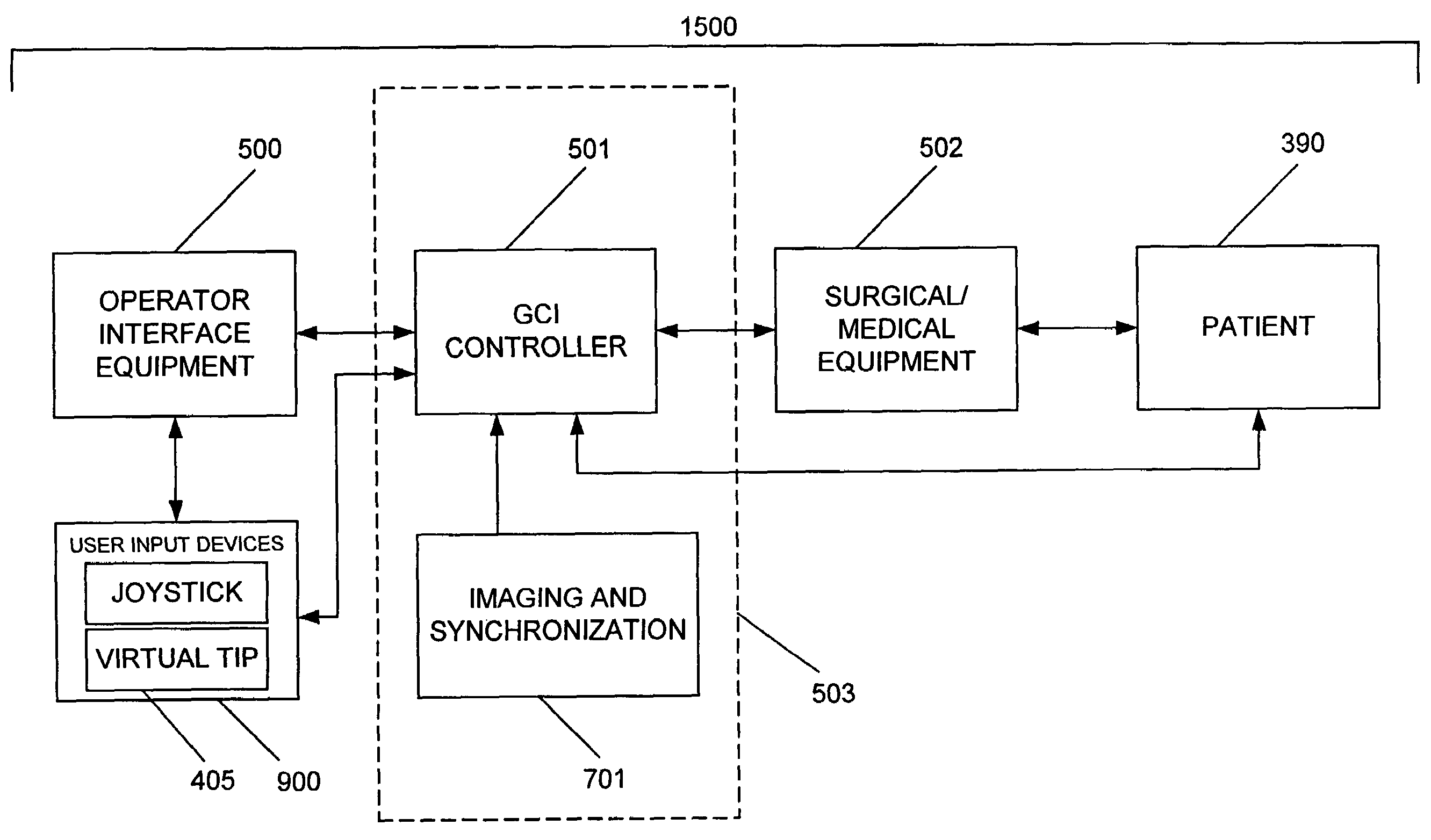
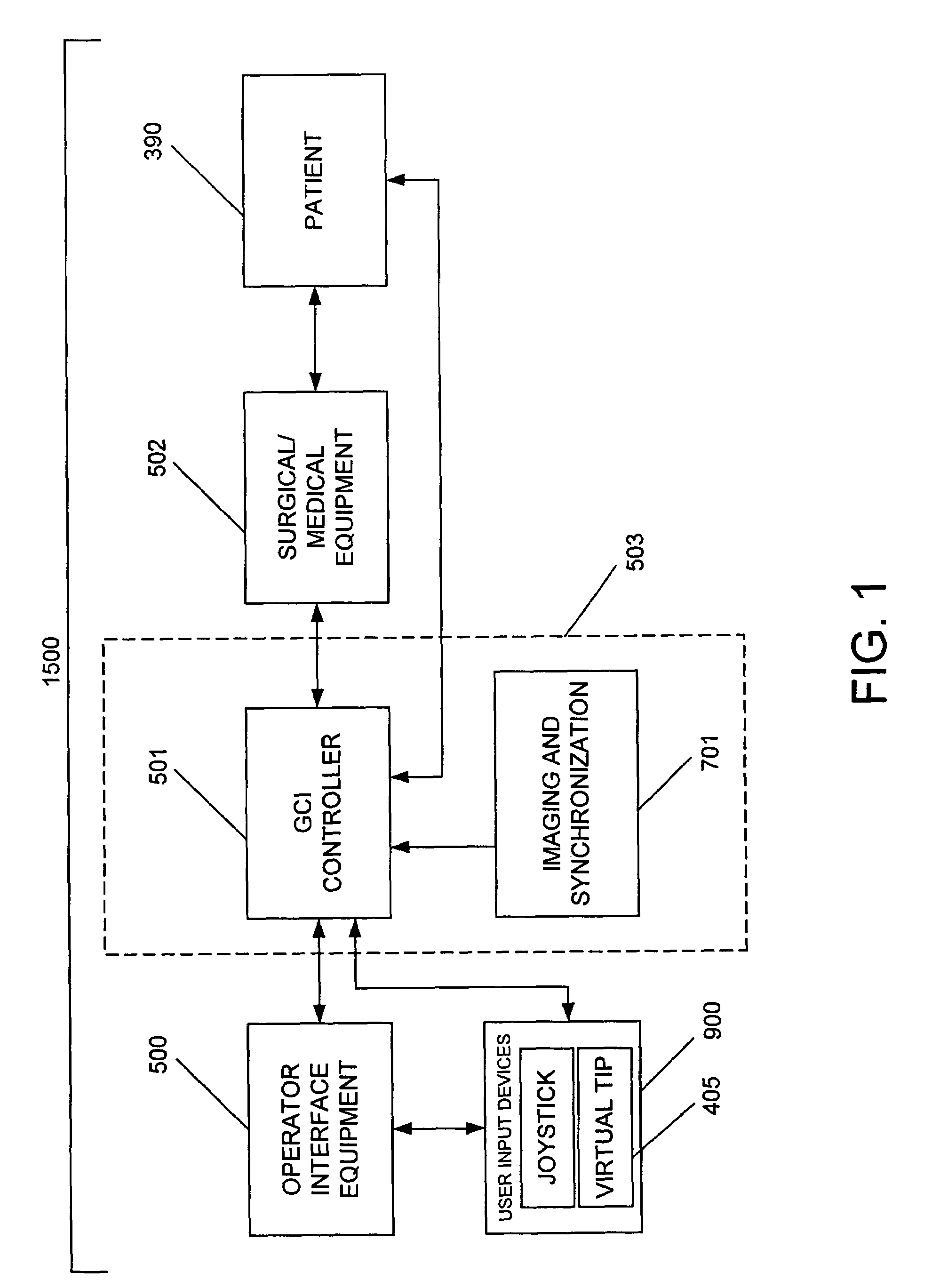
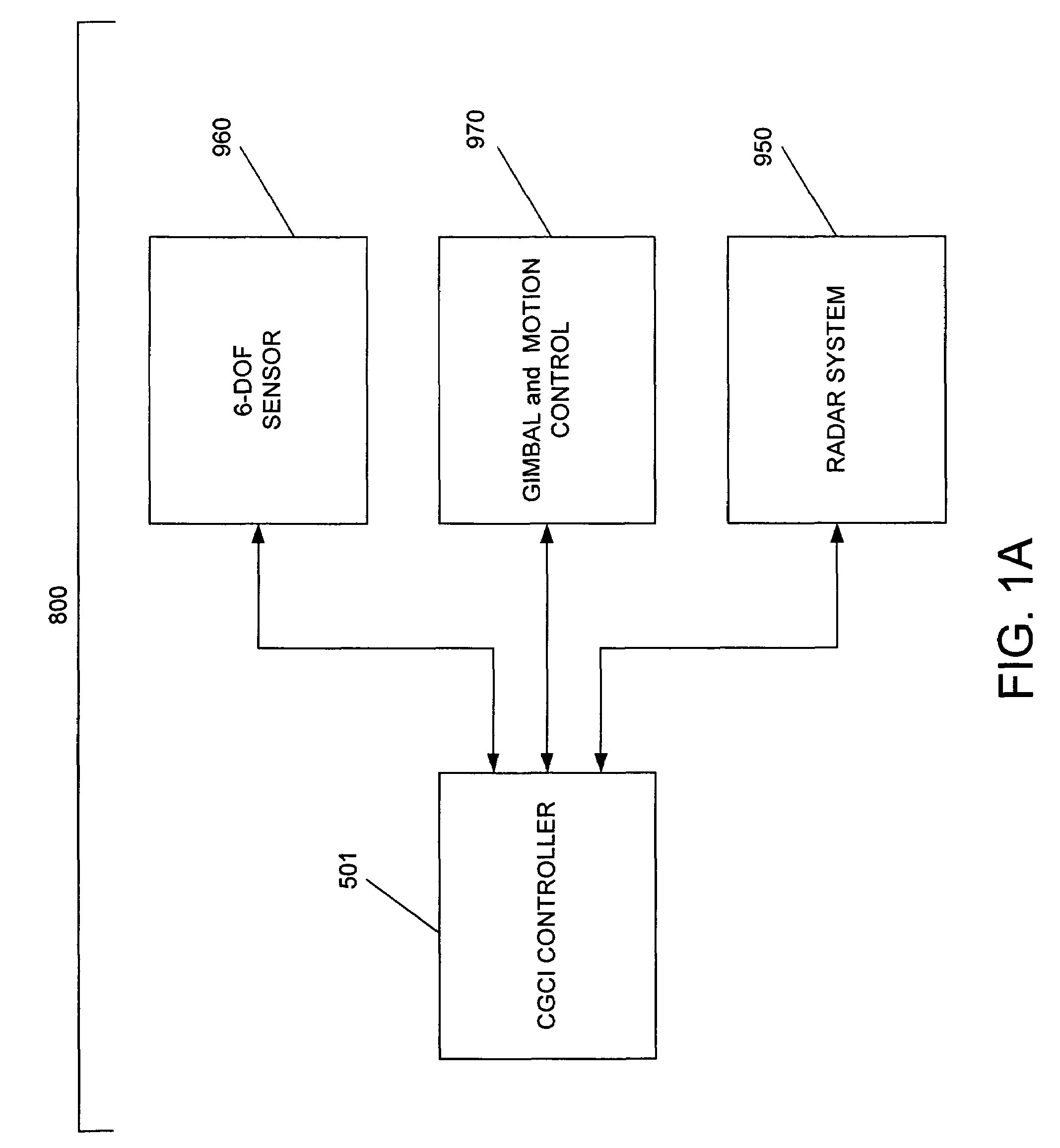
System and method for radar-assisted catheter guidance and control
InactiveUS20050096589A1Less trainingMinimizing and eliminating useEndoscopesMedical devicesRadar systemsGuidance control
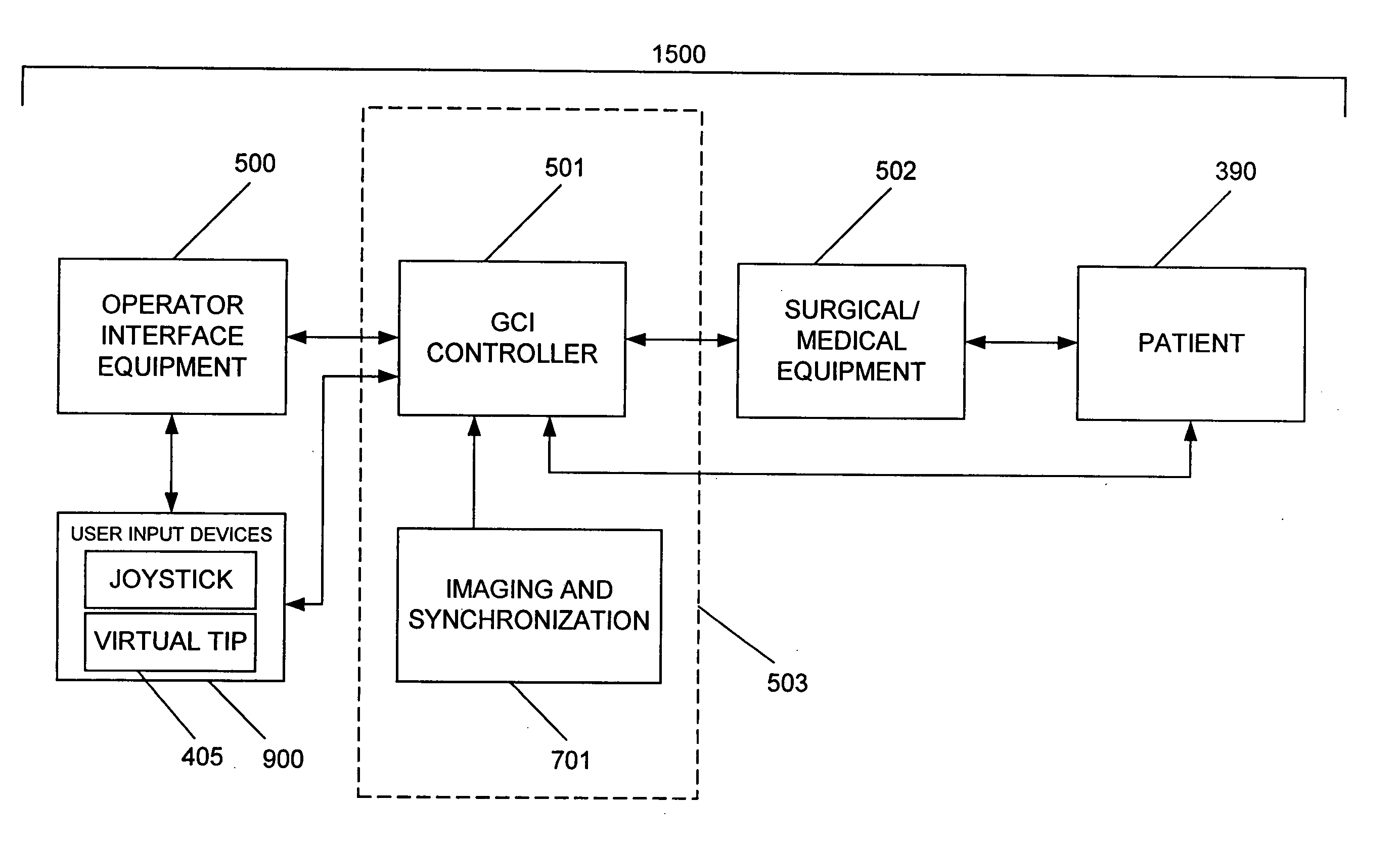
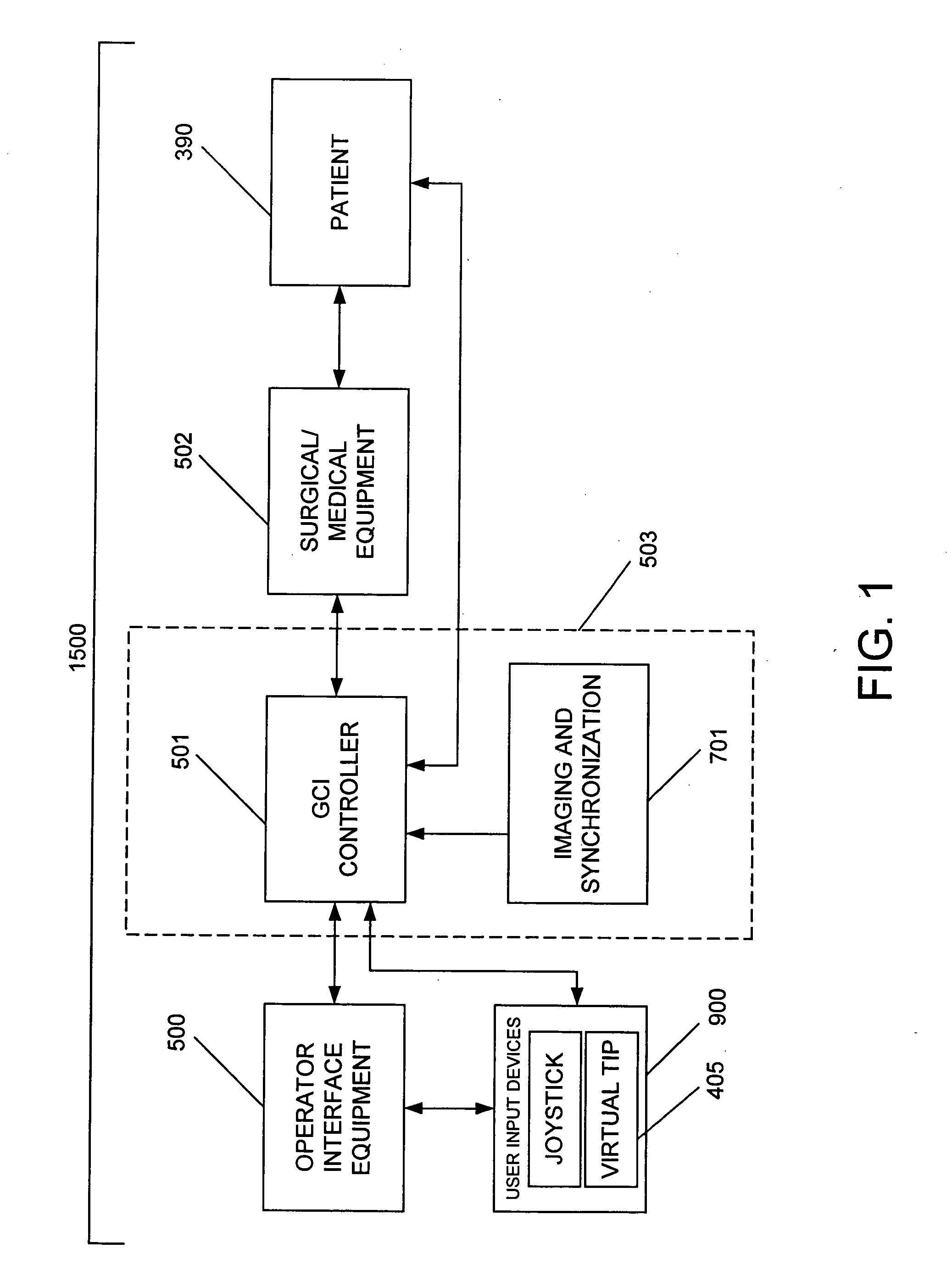
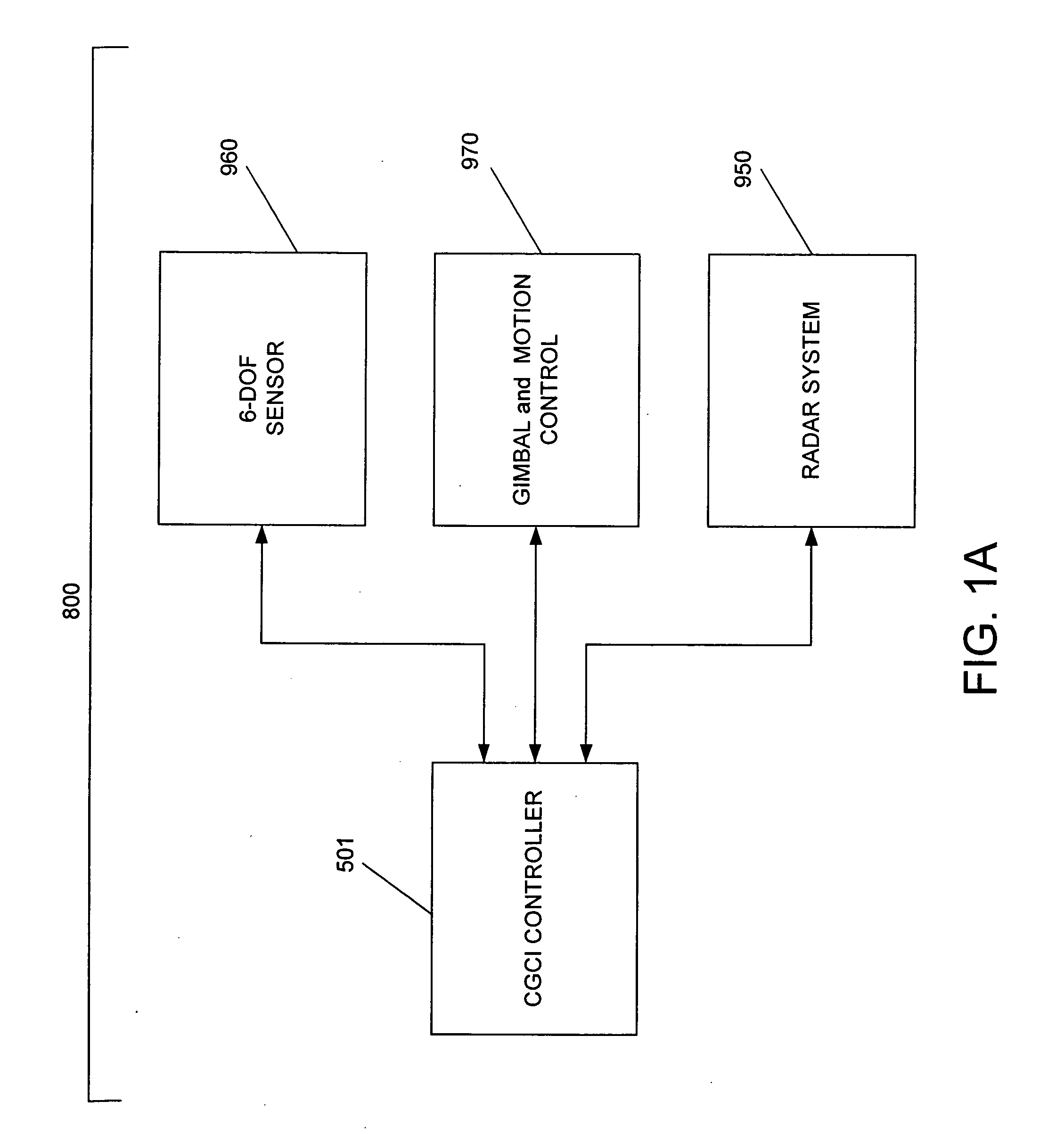
A Catheter Guidance Control and Imaging (CGCI) system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and influenced positionally so as to allow diagnostic and therapeutic procedures to be performed is described. The tools that can be so equipped include catheters, guidewires, and secondary tools such as lasers and balloons. The magnetic tip performs two functions. First, it allows the position and orientation of the tip to be determined by using a radar system such as, for example, a radar range finder or radar imaging system. Incorporating the radar system allows the CGCI apparatus to detect accurately the position, orientation and rotation of the surgical tool embedded in a patient during surgery. In one embodiment, the image generated by the radar is displayed with the operating room imagery equipment such as, for example, X-ray, Fluoroscopy, Ultrasound, MRI, CAT-Scan, PET-Scan, etc. In one embodiment, the image is synchronized with the aid of fiduciary markers located by a 6-Degrees of Freedom (6-DOF) sensor. The CGCI apparatus combined with the radar and the 6-DOF sensor allows the tool tip to be pulled, pushed, turned, and forcefully held in the desired position by applying an appropriate magnetic field external to the patient's body. A virtual representation of the magnetic tip serves as an operator control. This control possesses a one-to-one positional relationship with the magnetic tip inside the patient's body. Additionally, this control provides tactile feedback to the operator's hands in the appropriate axis or axes if the magnetic tip encounters an obstacle. The output of this control combined with the magnetic tip position and orientation feedback allows a servo system to control the external magnetic field.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
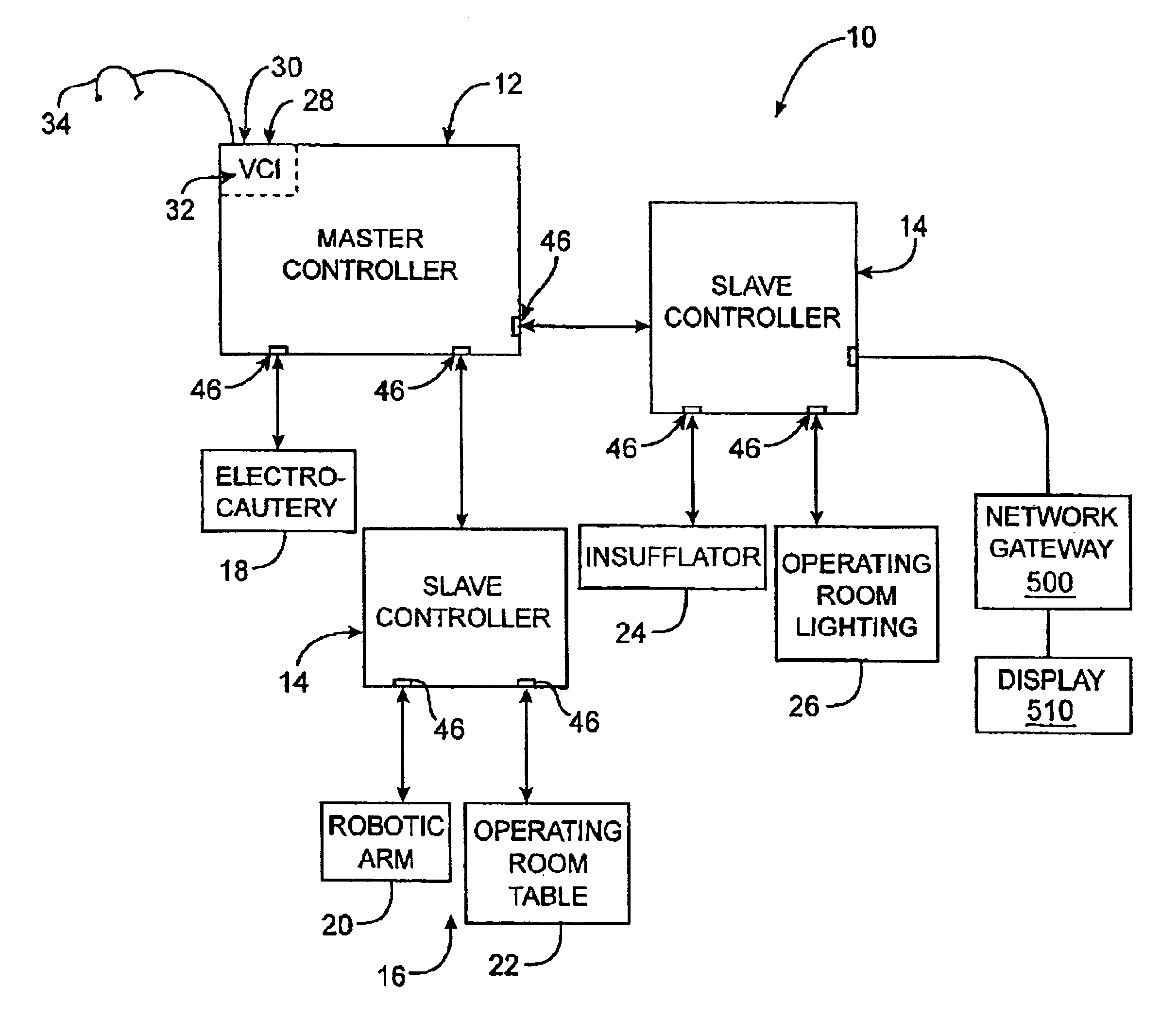
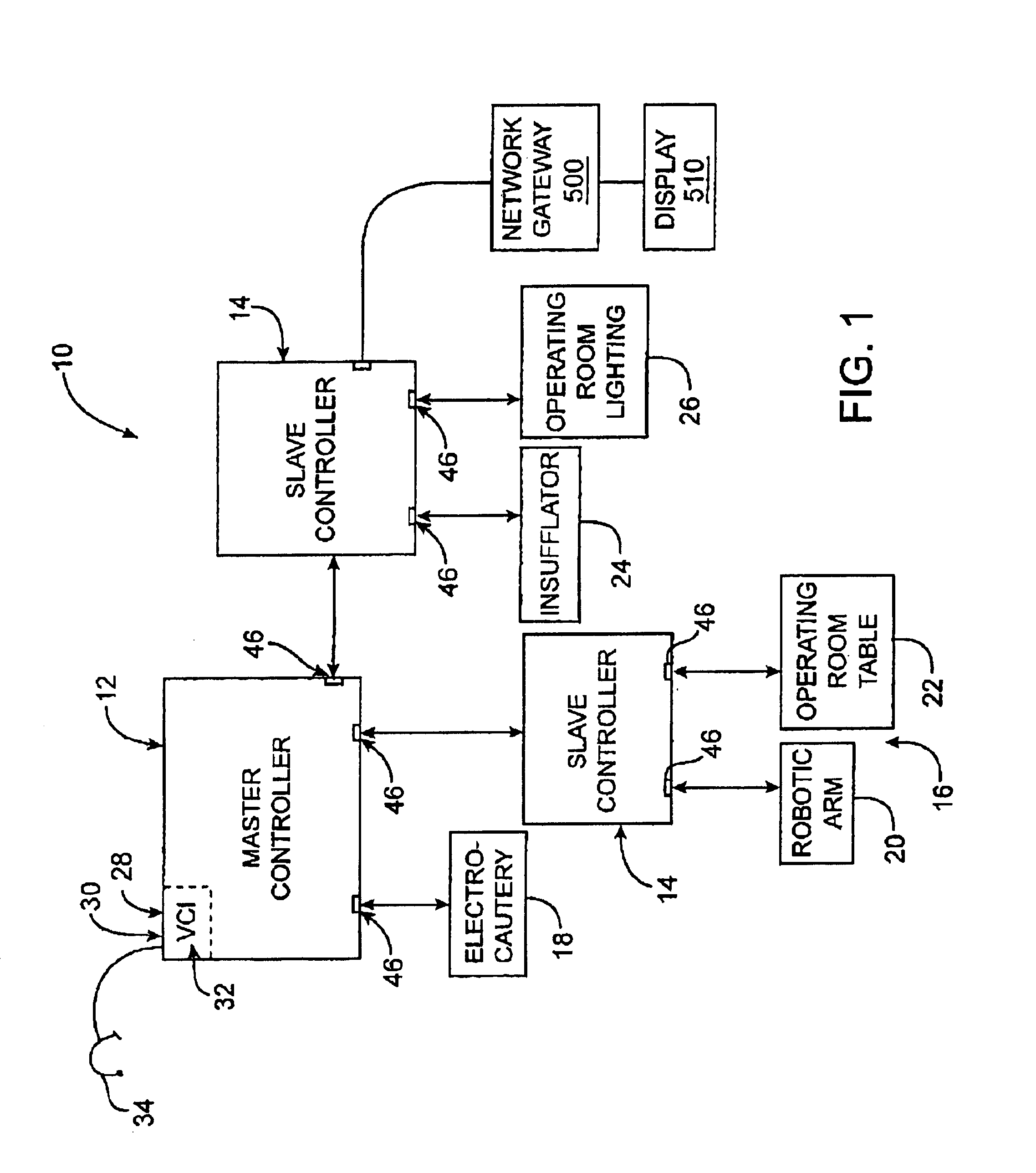
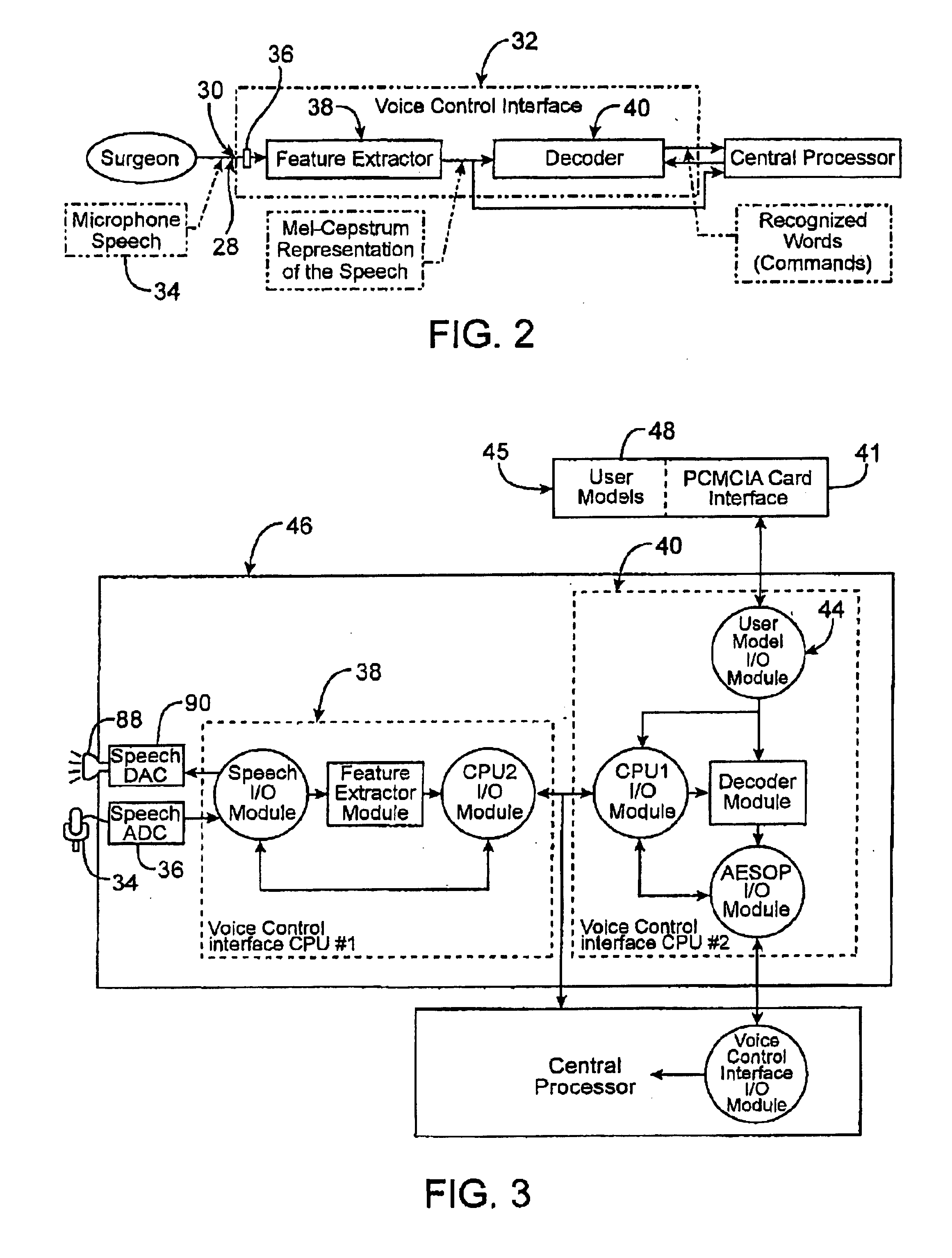
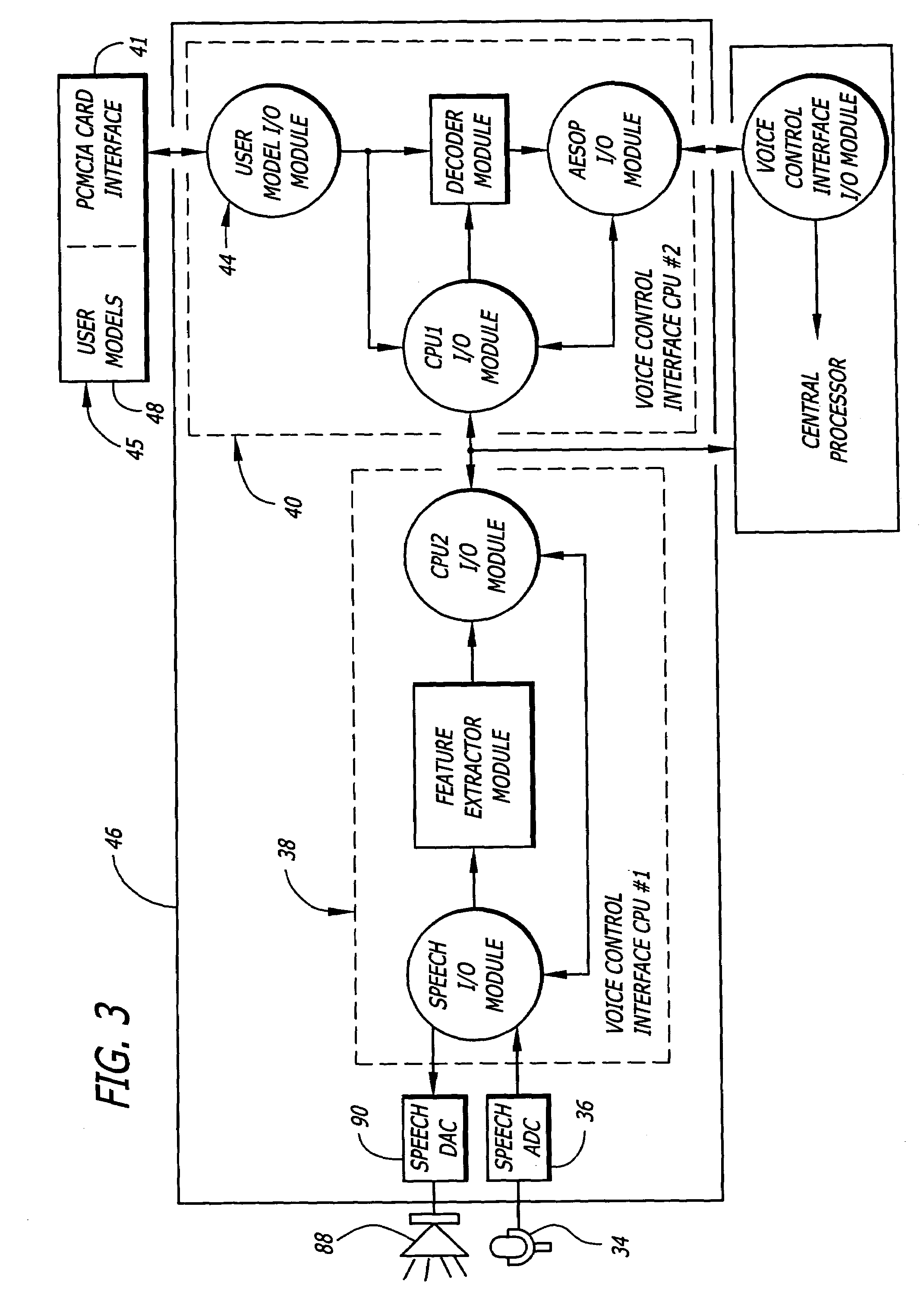
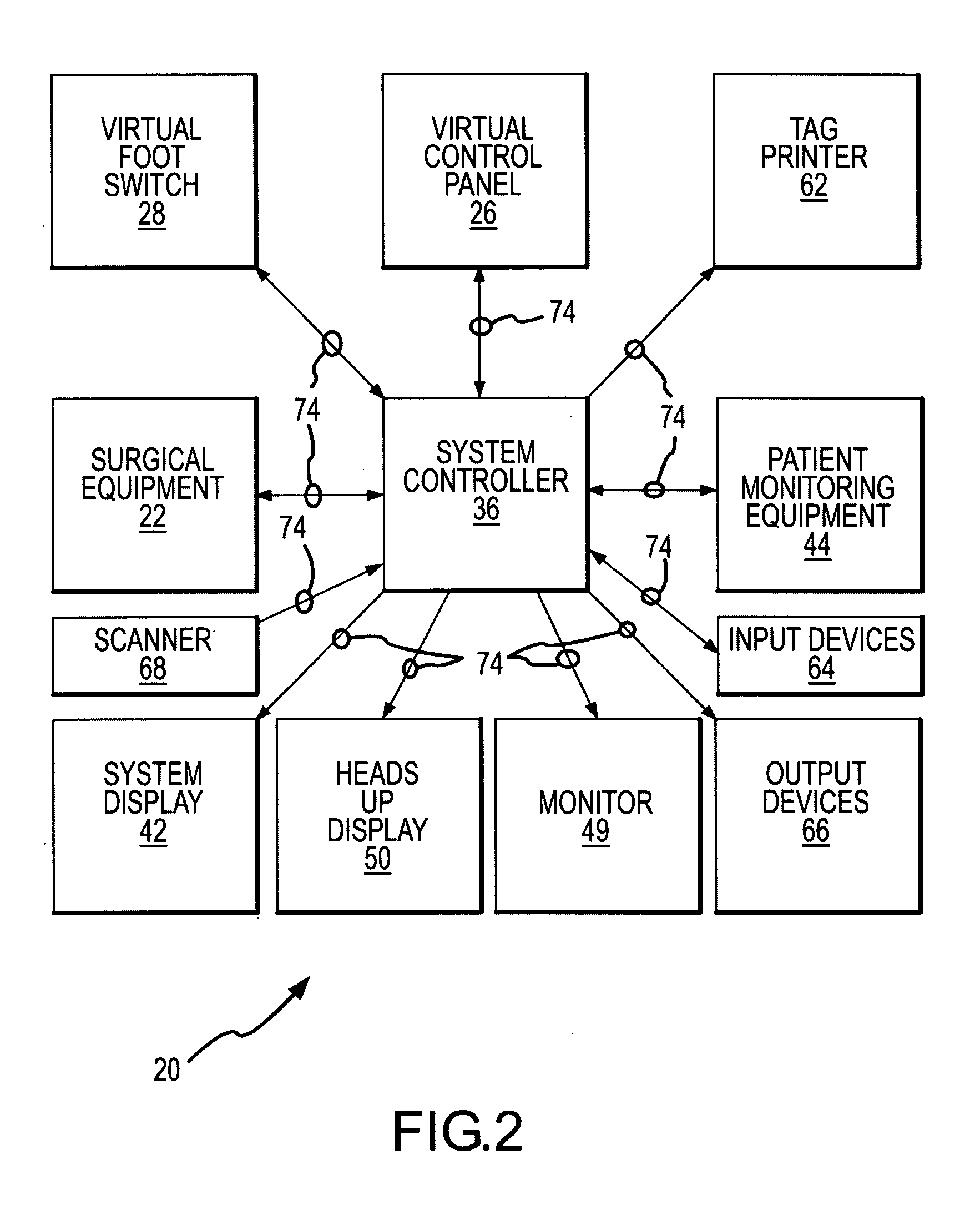
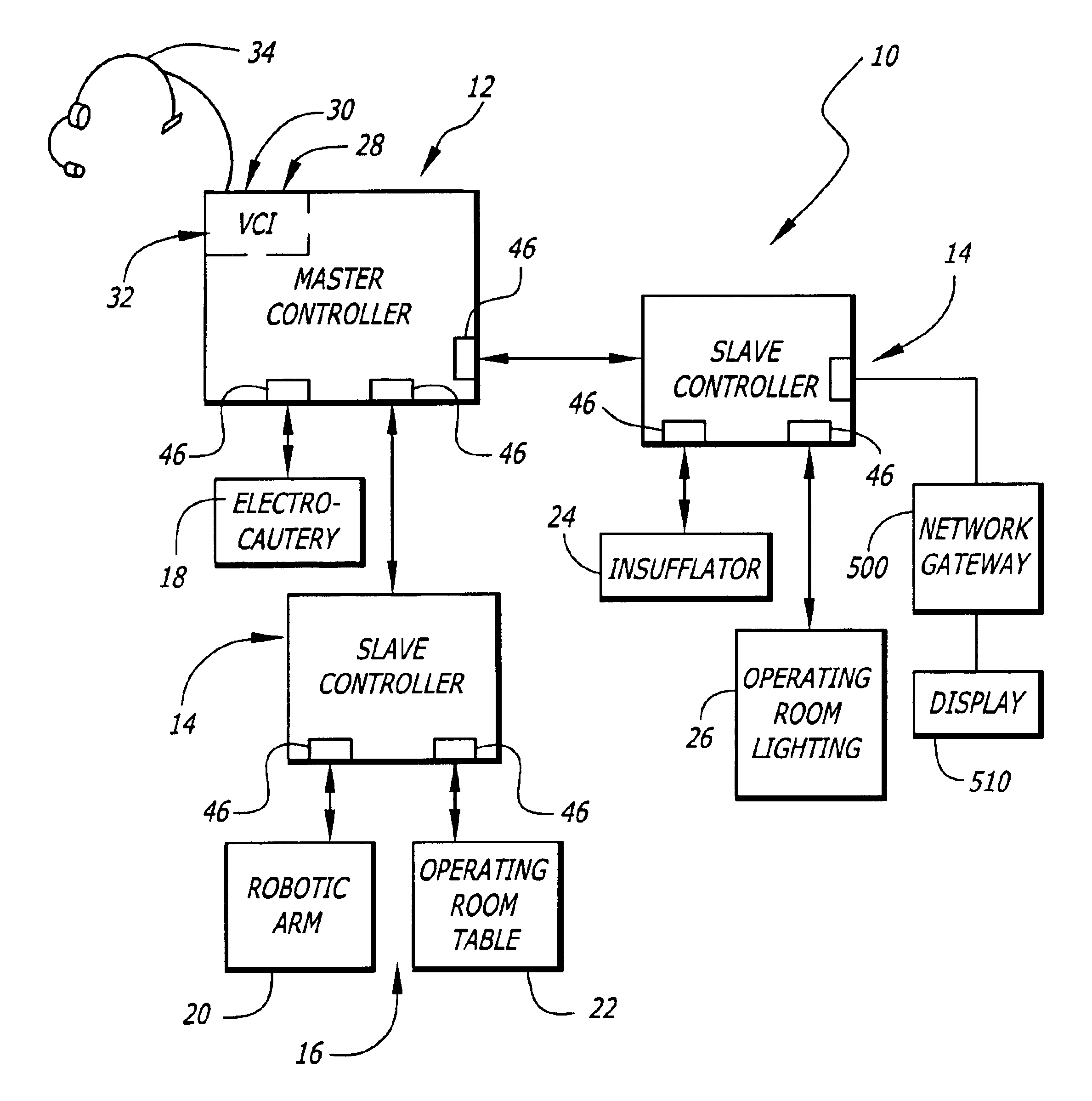
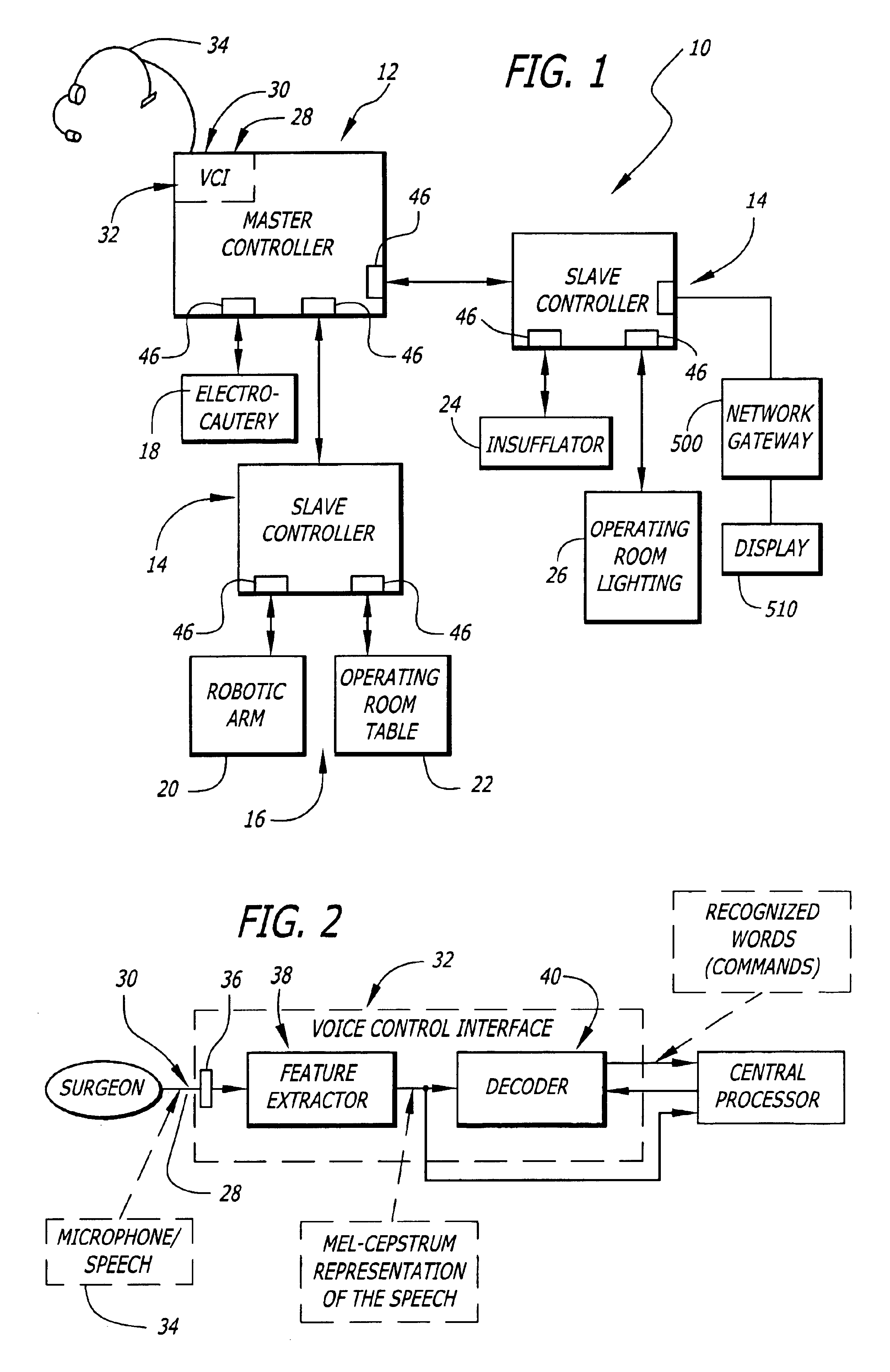
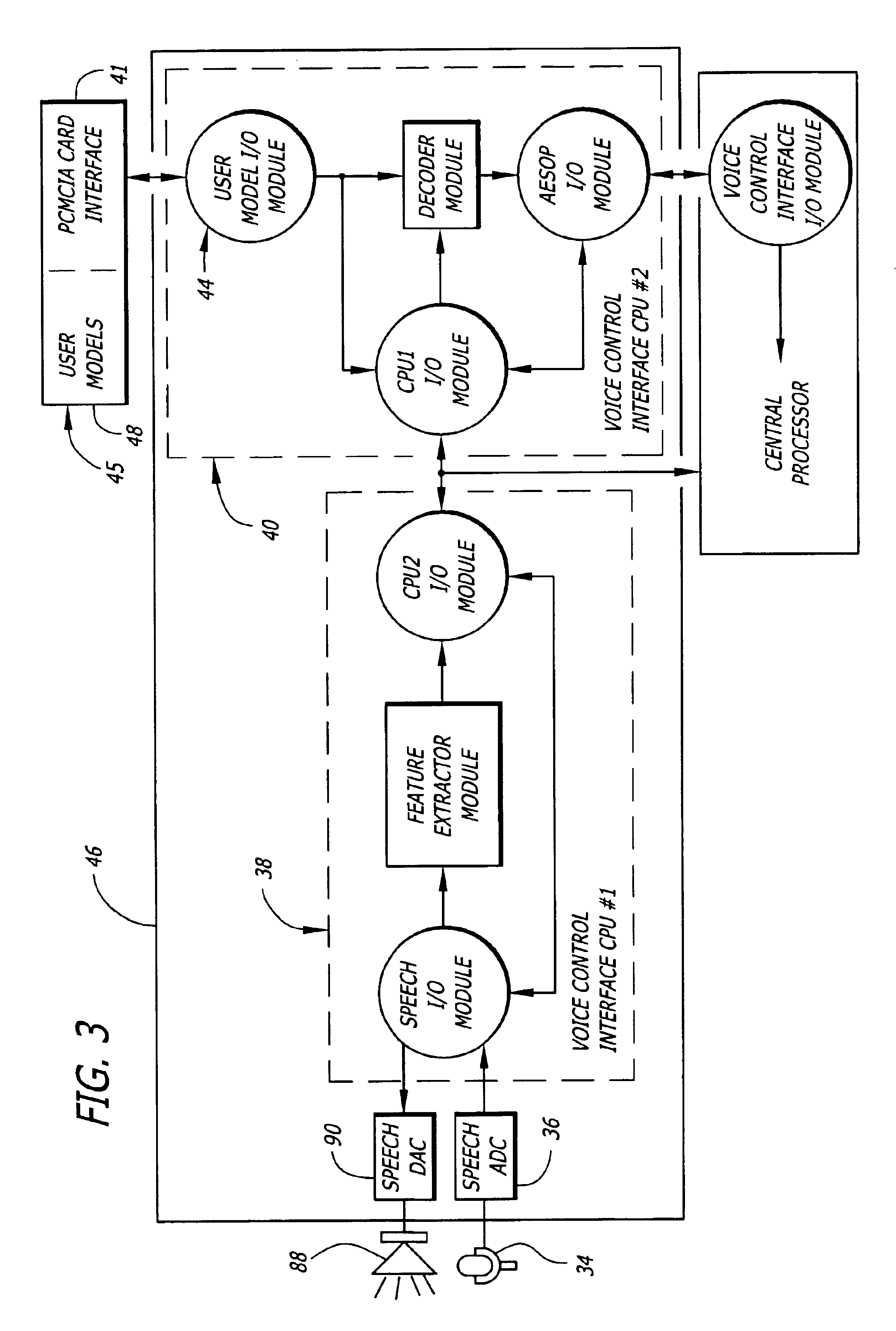
General purpose distributed operating room control system
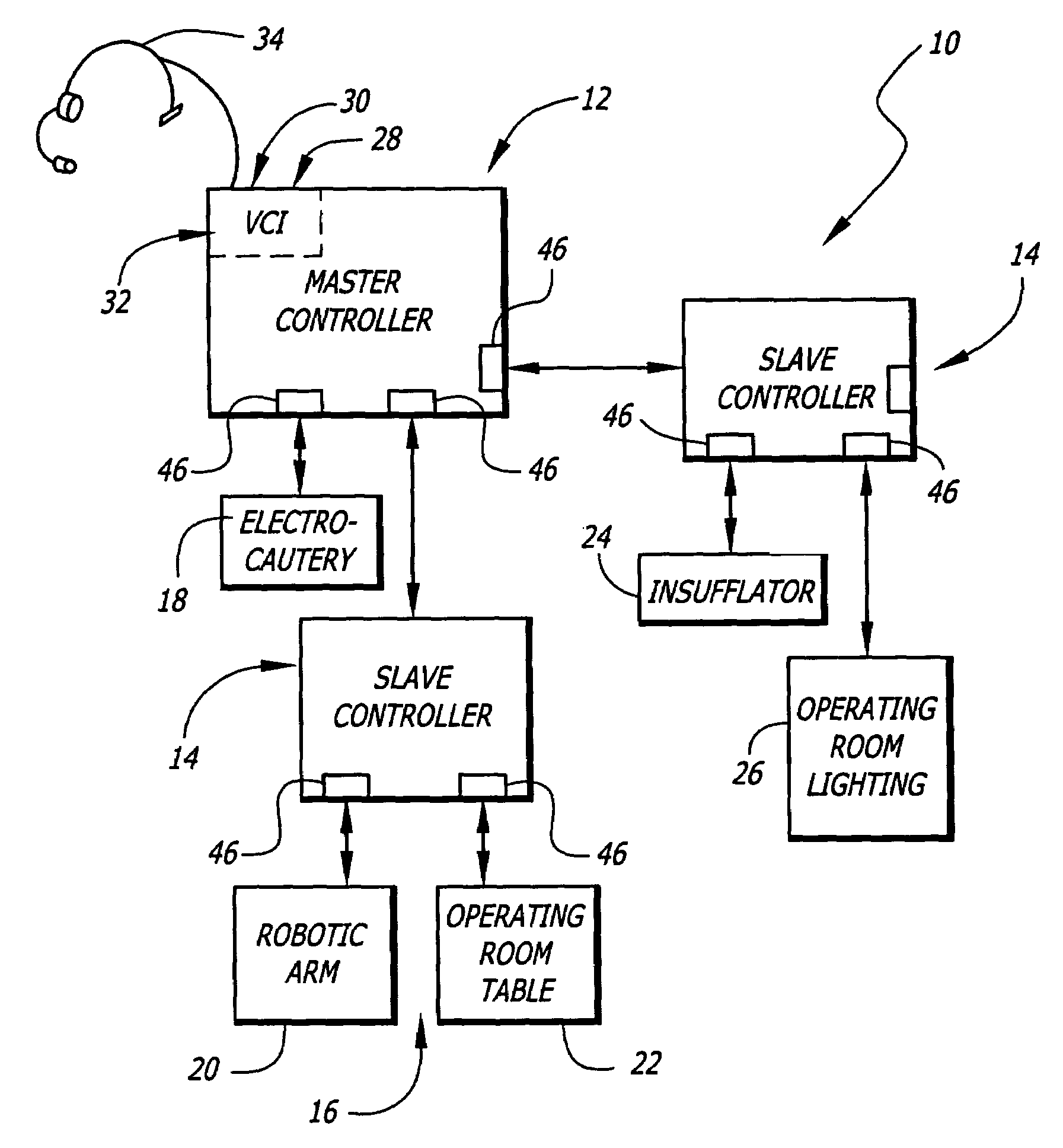
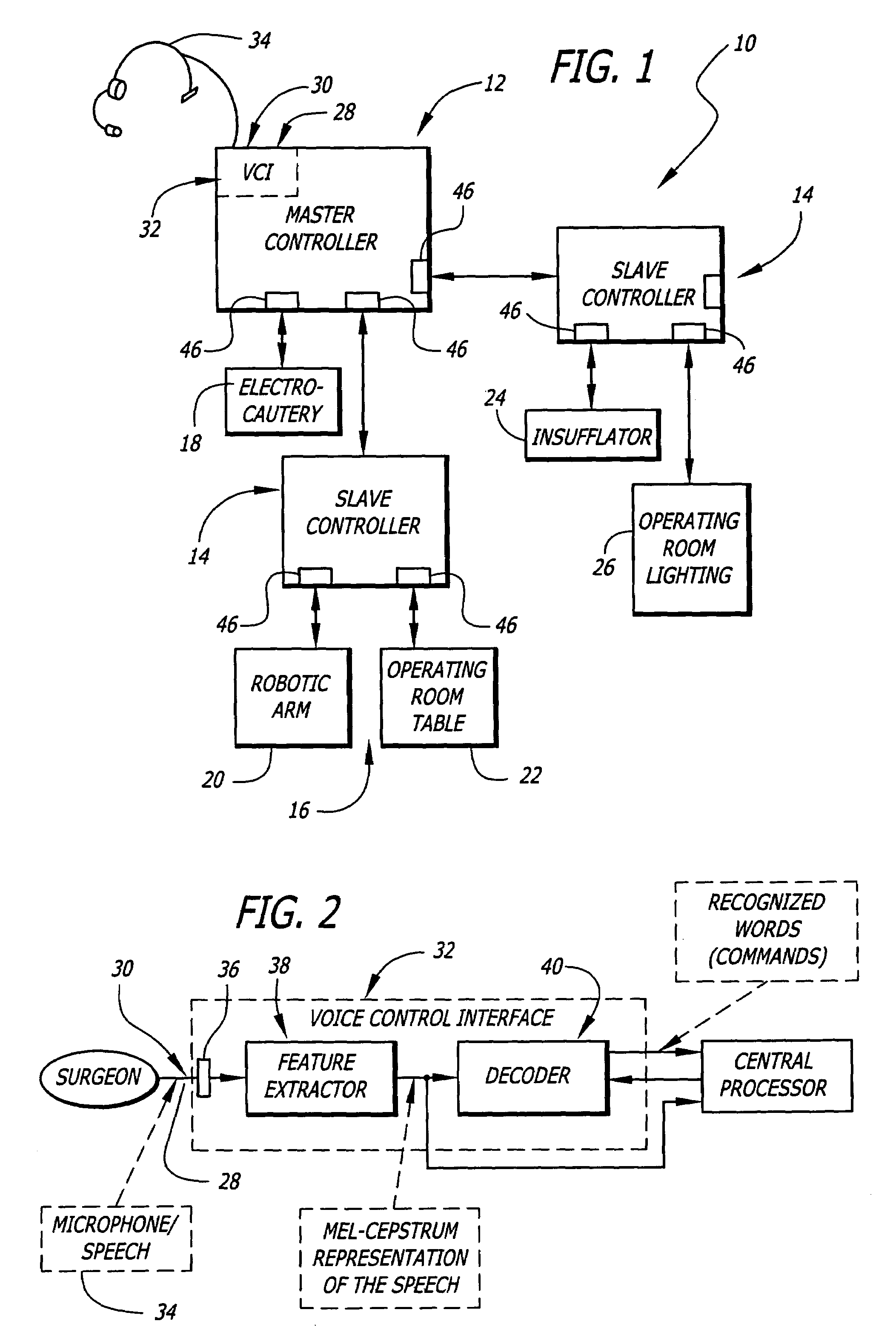
The present invention pertains to control systems and provides a run time configurable control system for selecting and operating one of a plurality of operating room devices from a single input source, the system comprising a master controller having a voice control interface and means for routing control signals. The system additionally may include a plurality of slave controllers to provide expandability of the system. Also, the system includes output means for generating messages to the user relating to the status of the control system in general and to the status of devices connected thereto.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
System and method for radar-assisted catheter guidance and control
InactiveUS7280863B2Less trainingMinimizing and eliminating useMedical devicesEndoscopesRadar systemsTip position
A Catheter Guidance Control and Imaging (CGCI) system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and influenced positionally so as to allow diagnostic and therapeutic procedures to be performed is described. The tools that can be so equipped include catheters, guidewires, and secondary tools such as lasers and balloons. The magnetic tip performs two functions. First, it allows the position and orientation of the tip to be determined by using a radar system such as, for example, a radar range finder or radar imaging system. Incorporating the radar system allows the CGCI apparatus to detect accurately the position, orientation and rotation of the surgical tool embedded in a patient during surgery. In one embodiment, the image generated by the radar is displayed with the operating room imagery equipment such as, for example, X-ray, Fluoroscopy, Ultrasound, MRI, CAT-Scan, PET-Scan, etc. In one embodiment, the image is synchronized with the aid of fiduciary markers located by a 6-Degrees of Freedom (6-DOF) sensor. The CGCI apparatus combined with the radar and the 6-DOF sensor allows the tool tip to be pulled, pushed, turned, and forcefully held in the desired position by applying an appropriate magnetic field external to the patient's body. A virtual representation of the magnetic tip serves as an operator control. This control possesses a one-to-one positional relationship with the magnetic tip inside the patient's body. Additionally, this control provides tactile feedback to the operator's hands in the appropriate axis or axes if the magnetic tip encounters an obstacle. The output of this control combined with the magnetic tip position and orientation feedback allows a servo system to control the external magnetic field.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
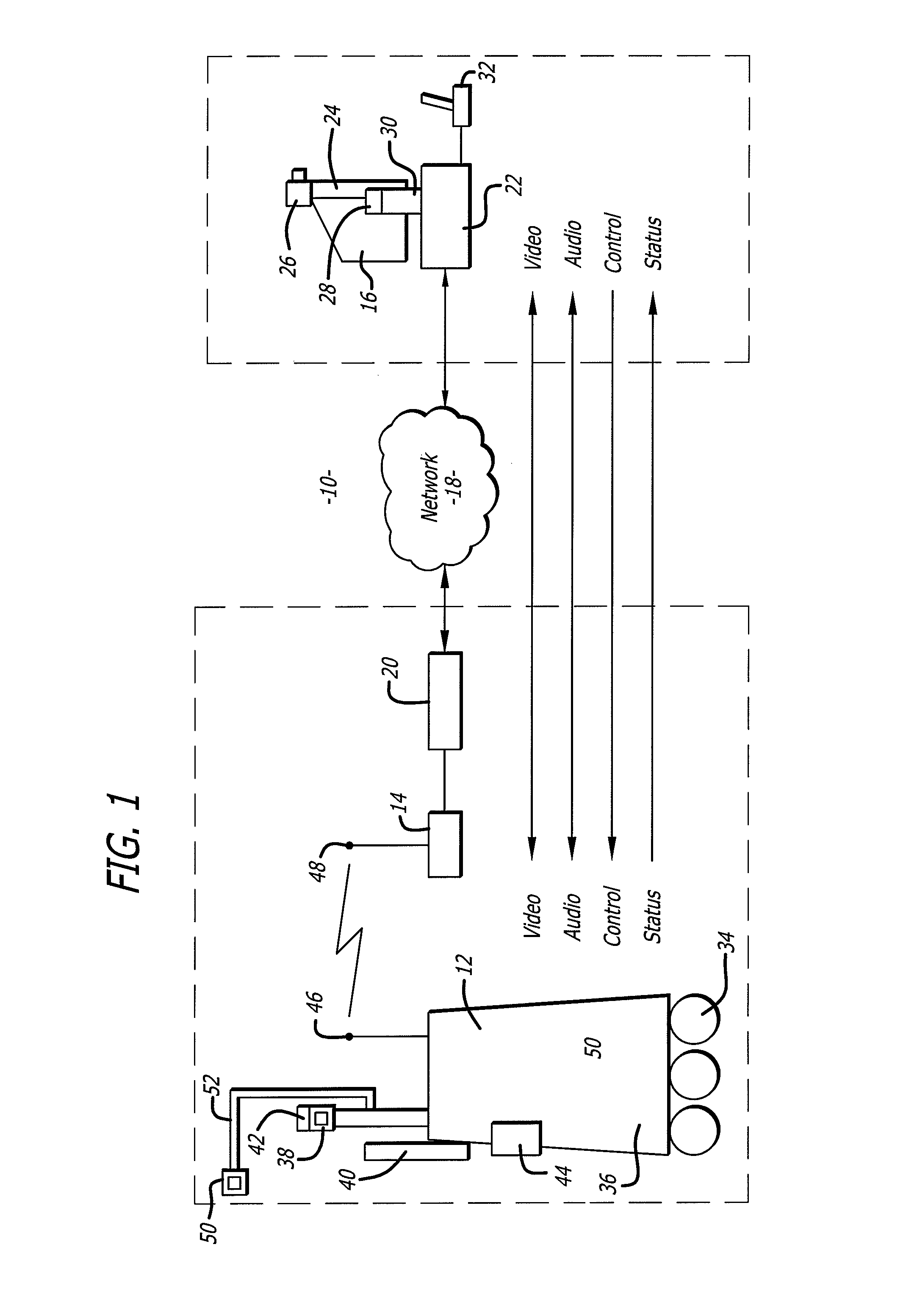
Mobile videoimaging, videocommunication, video production (VCVP) system
A mobile self-powered videoimaging, video communication, video production (VCVP) system designed specifically for health care industry that provides high-resolution audio, video and data communications, production and recording capabilities at hospital operating room / procedure room or field environments for transmission to other remote locations. The VCVP system generally comprises a mobile platform with a plurality of cameras, at least one being mounted on an extensible boom for overhead imaging of surgical procedures. An array of video production equipment is rack-mounted inside the platform, as is an array of network teleconferencing equipment. The mobile imaging system may be parked at a convenient location in an operating room or other environment and controlled by a single operator. As the surgery proceeds, the operator can multiplex the camera signals into a live high resolution video / audio feed that is networked in real time for teleconferencing, and / or recorded to a hard drive or in any known format such as Mini-DV, S-VHS, VHS and DVD as desired.
Owner:REMY CHRISTOPHE +1
Networking infrastructure for an operating room
InactiveUS6928490B1Electric signal transmission systemsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesComputer networkMedical device
A networking infrastructure for an operating room, comprising a plurality of medical devices, each device of which is connected through a single communication channel to the network, wherein each device may be controlled through a local interface, or through a remote interface available through the network. Furthermore, the networking infrastructure operates in robust manner with respect to the removal of a communication channel to the network associated with the removal of medical device from the network, or with respect to the addition of a communication channel to the network associated with the addition of a medical device to the network.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
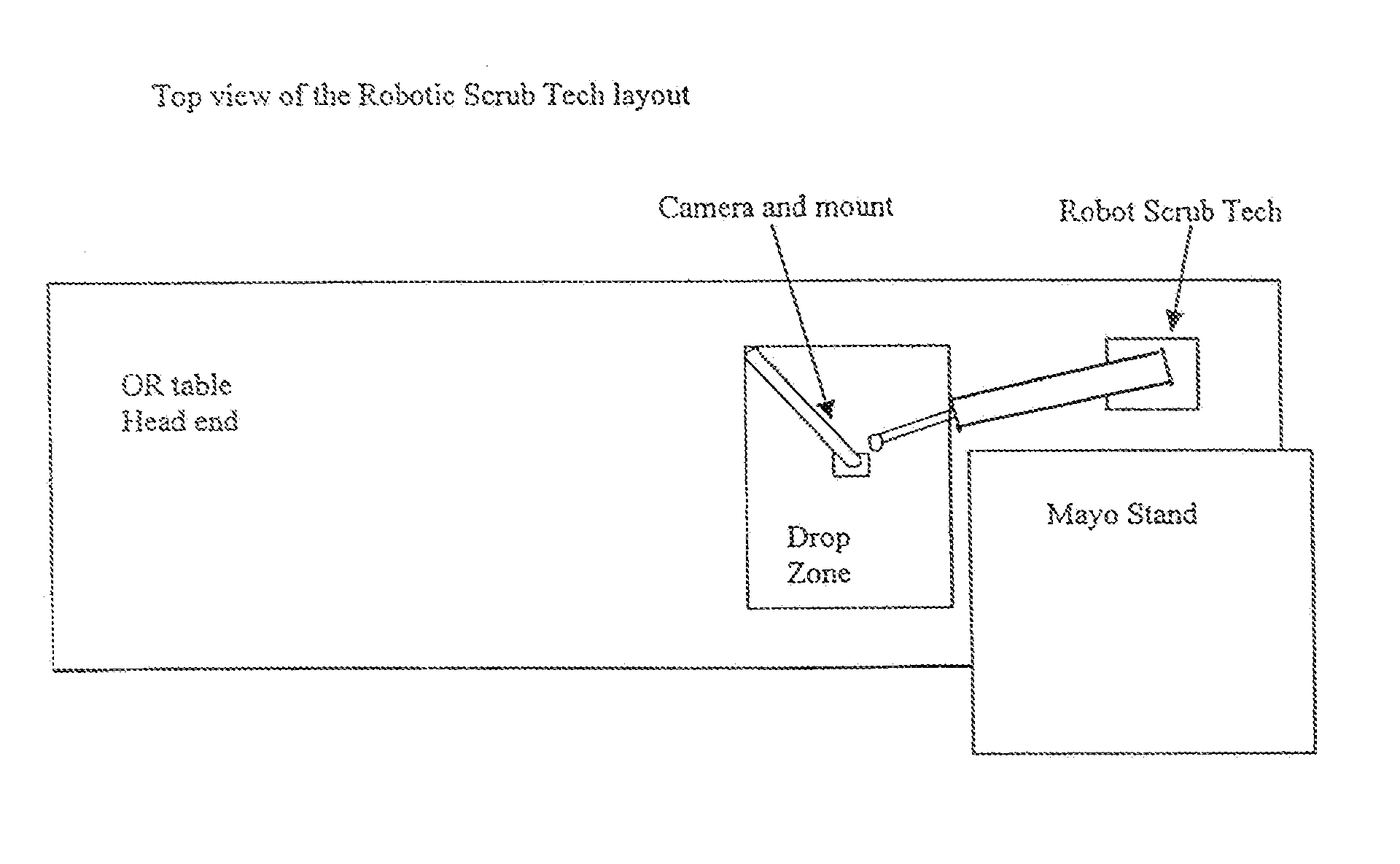
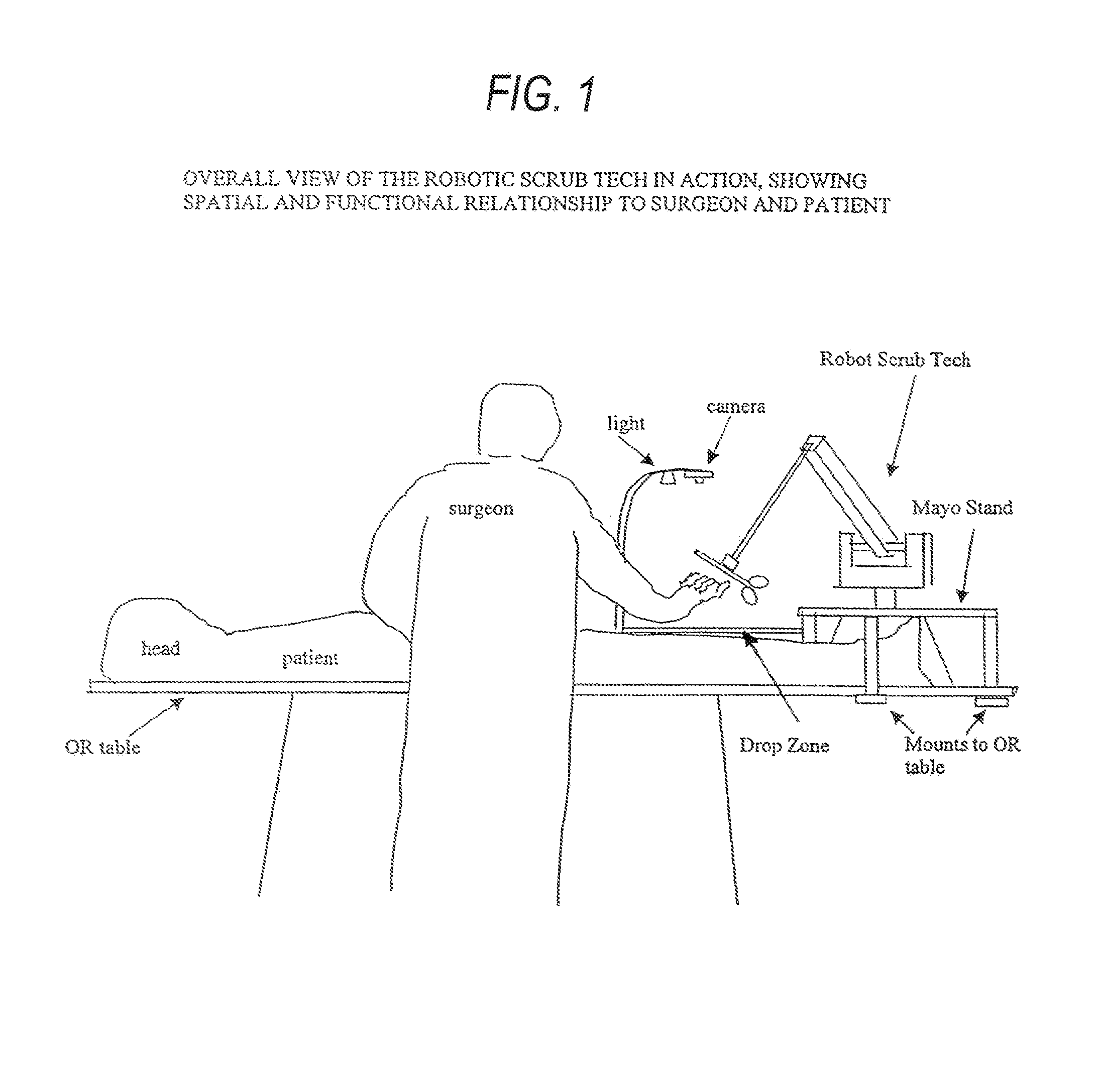
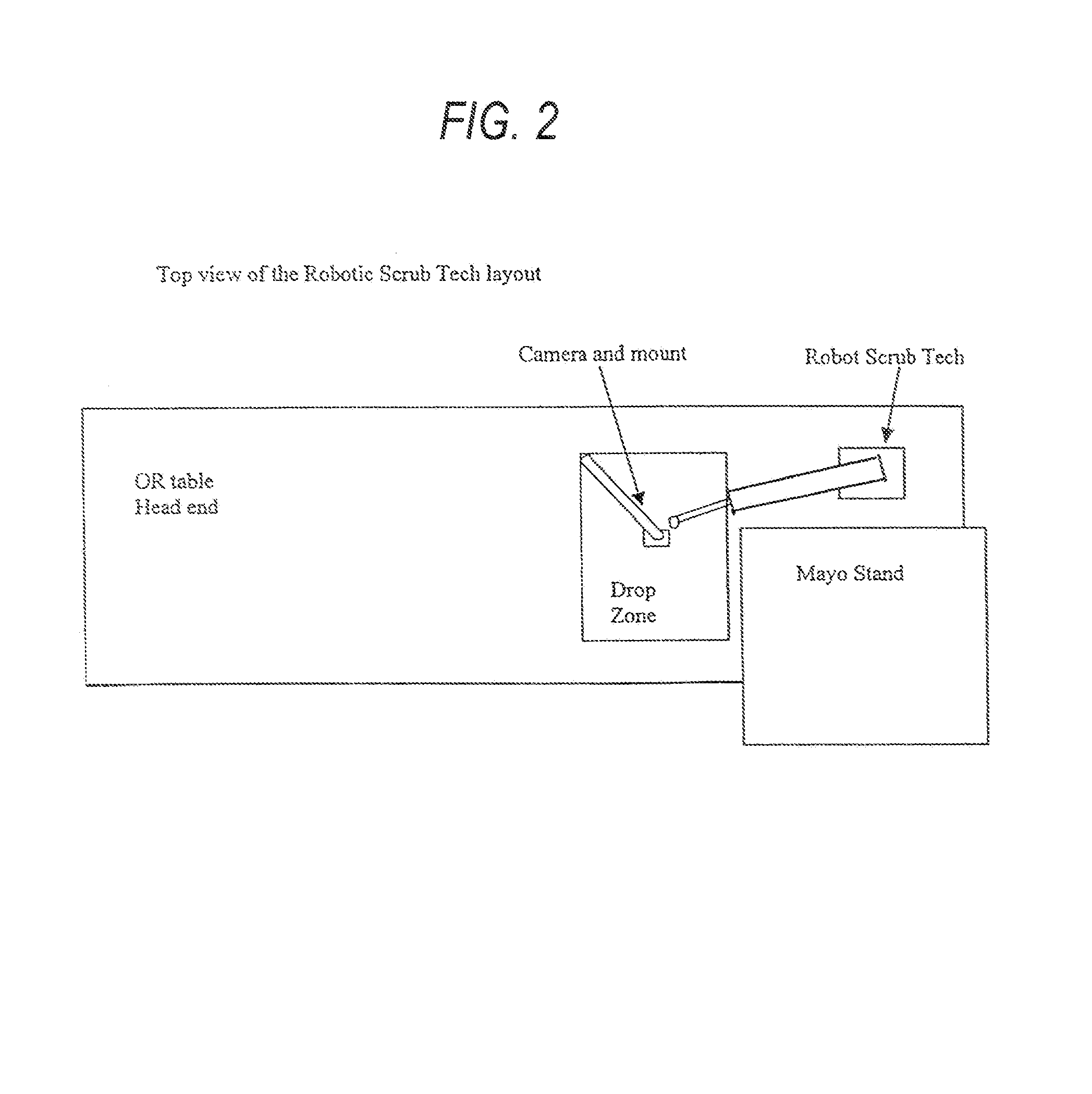
Robotic scrub nurse
A robotic system, and corresponding method, performs the function of a human scrub technician in an operating room. A device, and associated method for using the device, performs one, or more, of the following functions: instrument identification, instrument localization, instrument handling, interaction with a human, and integration of functions through a cognitive system. A method for movement of the device comprises the steps of modeling the arm of the robot to create a model comprising elements of finite mass joined by junctions, using an algorithm to calculate results of the effect of applying force to the elements of the model, using attractive, replusive and postural forces in the algorithm, and using the results of the model to direct motion of the device.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
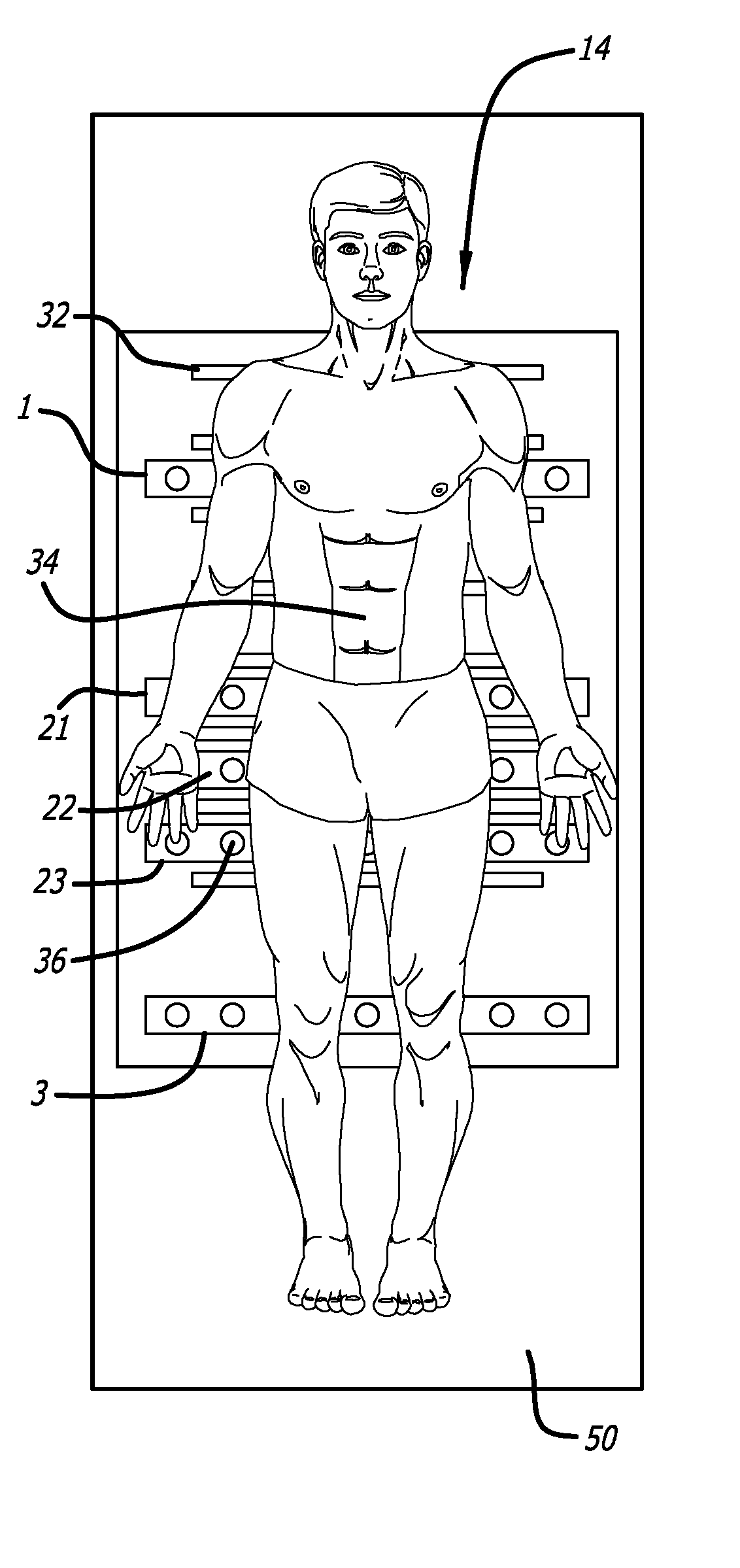
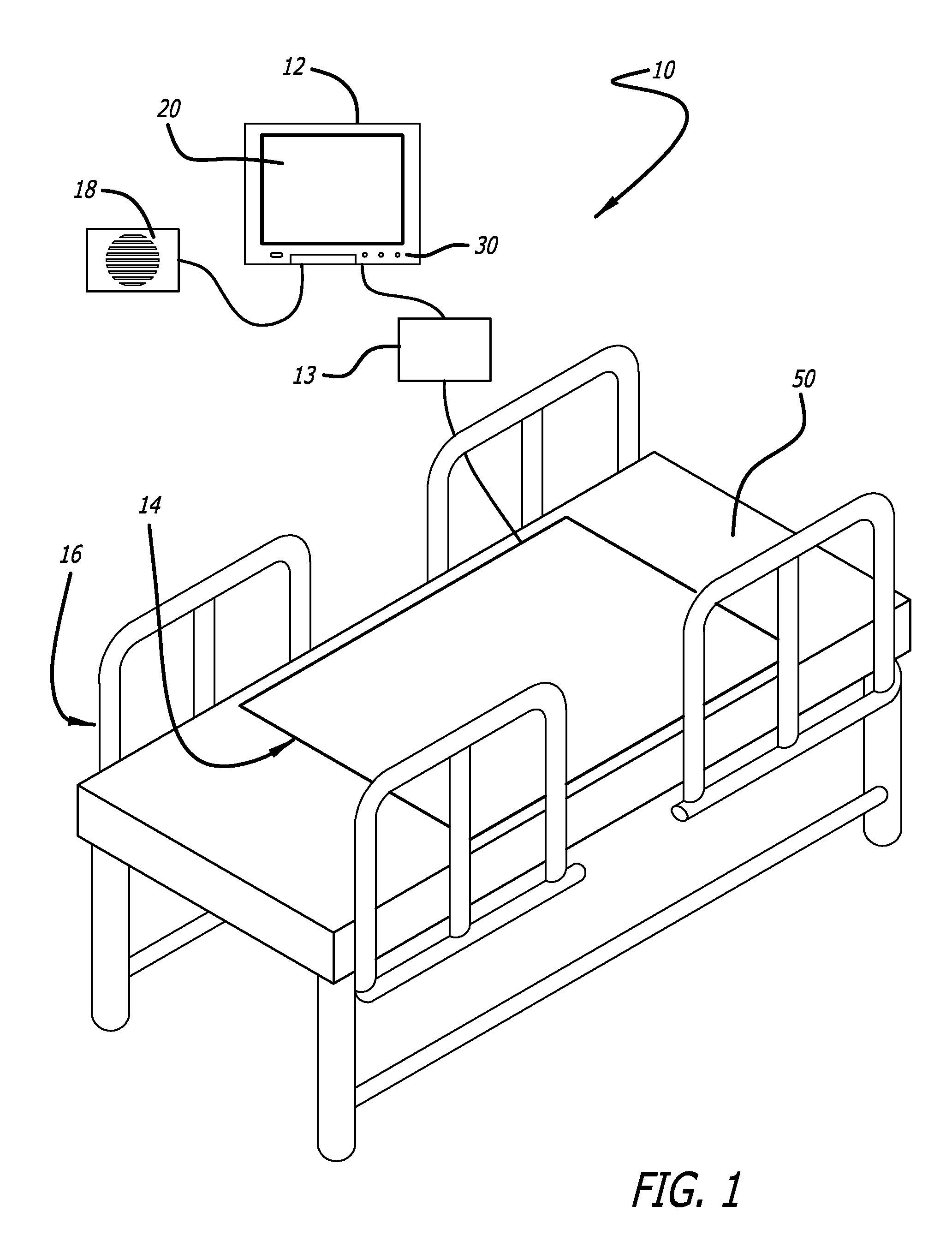
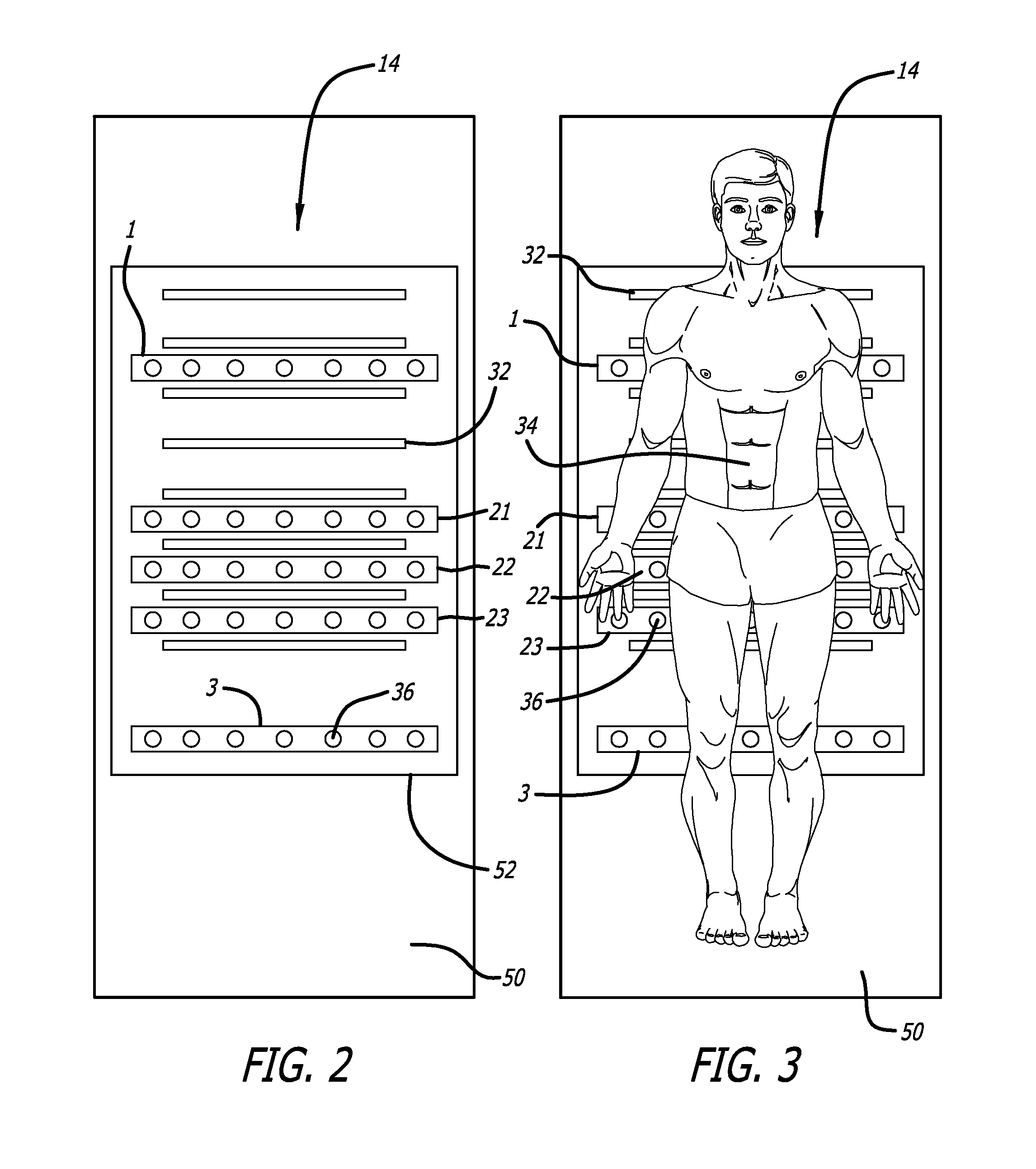
Bed exit and patient detection system
InactiveUS20080169931A1Accurate and reliable positioningEasy to useBedsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateMultiple inputSpeech sound
A bed exit and patient detection system especially adapted for use in the general medical or surgical floor area of a hospital or other healthcare facility as part of a vital signs monitoring and remote warning system includes a plurality of pressure sensors disposed in the patient's bed in a series of rectangular strips or zones that run laterally across the bed in the area of the patient's mid-back, hips and mid-legs, respectively. Each zone contains a plurality of sensors, arranged symmetrically about the centerline of the bed, with the corresponding sensors on opposite sides of the centerline in each zone being connected in parallel. The sensors are connected to a processor with multiple input channels that continuously monitors the sensor states to determine, from the pattern of sensor states observed, whether the patient is in bed, out of bed or is actively attempting to ext the bed at the sides or foot of the bed. At least three different sets of bed exit logic rules are available for user selection to configure the system for high, medium or low sensitivity, or bed exit privileges, for any particular patient. In some embodiments, the system also is capable of detecting when a patient is attempting to assume certain prohibited in-bed positions, such as sitting positions or slumping positions. An alarm in the form of a pre-recorded voice announcement or an alarm over a pre-existing nurse call system is provided when the sensor states are indicative of an out-of-bed or an exiting bed condition, or other prohibited in-bed positions, for a predetermined minimum period of time.
Owner:HOANA MEDICAL
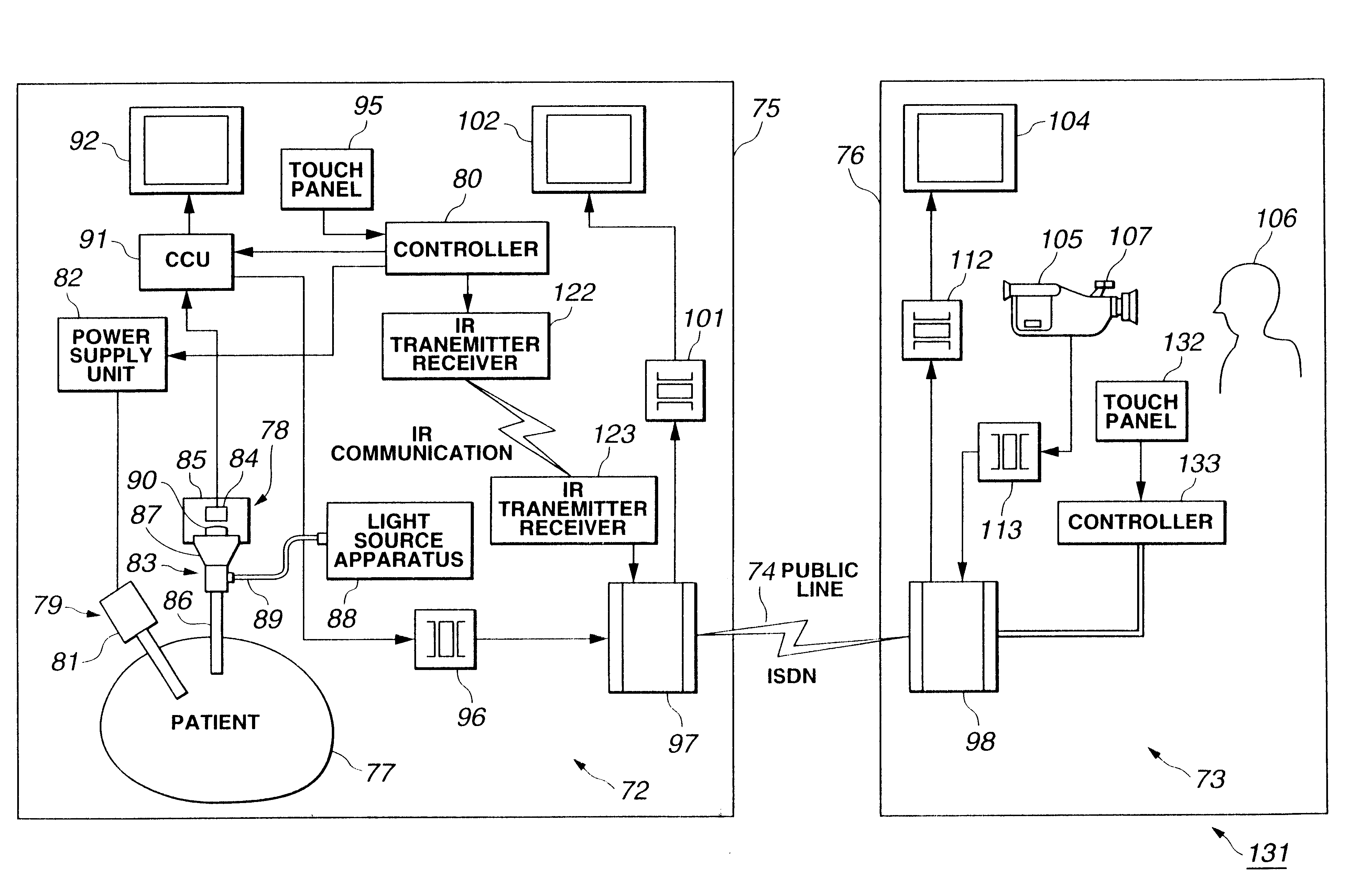
Remote surgery support system
InactiveUS6602185B1Easy to checkReadily of informationSurgeryEndoscopesSupporting systemRemote surgery
A first signal transmission apparatus installed in an operating room and a second signal transmission apparatus installed in a remote control room in a remote place are linked by a public line. Assuming that surgery is performed on a patient using a surgical instrument in the operating room while endoscopic images are viewed, the surgical instrument can be controlled using a first controller. The control and patient data are displayed on a display device via a second controller connected to the second signal transmission apparatus. The state of the surgical instrument and the patient data can always be checked in the remote control room. Surgical instructions or any other surgical support can be given easily.
Owner:OLYMPUS OPTICAL CO LTD
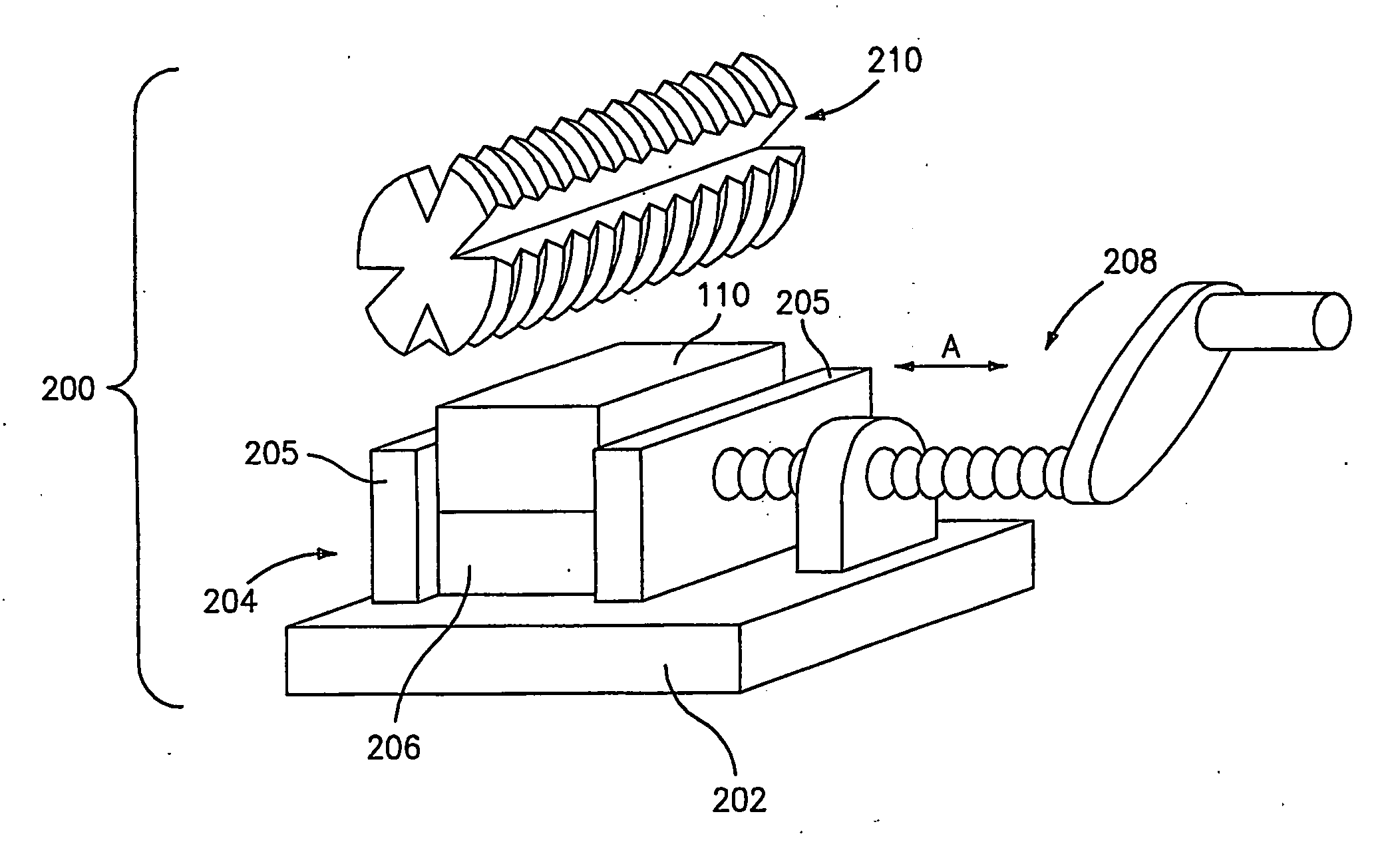
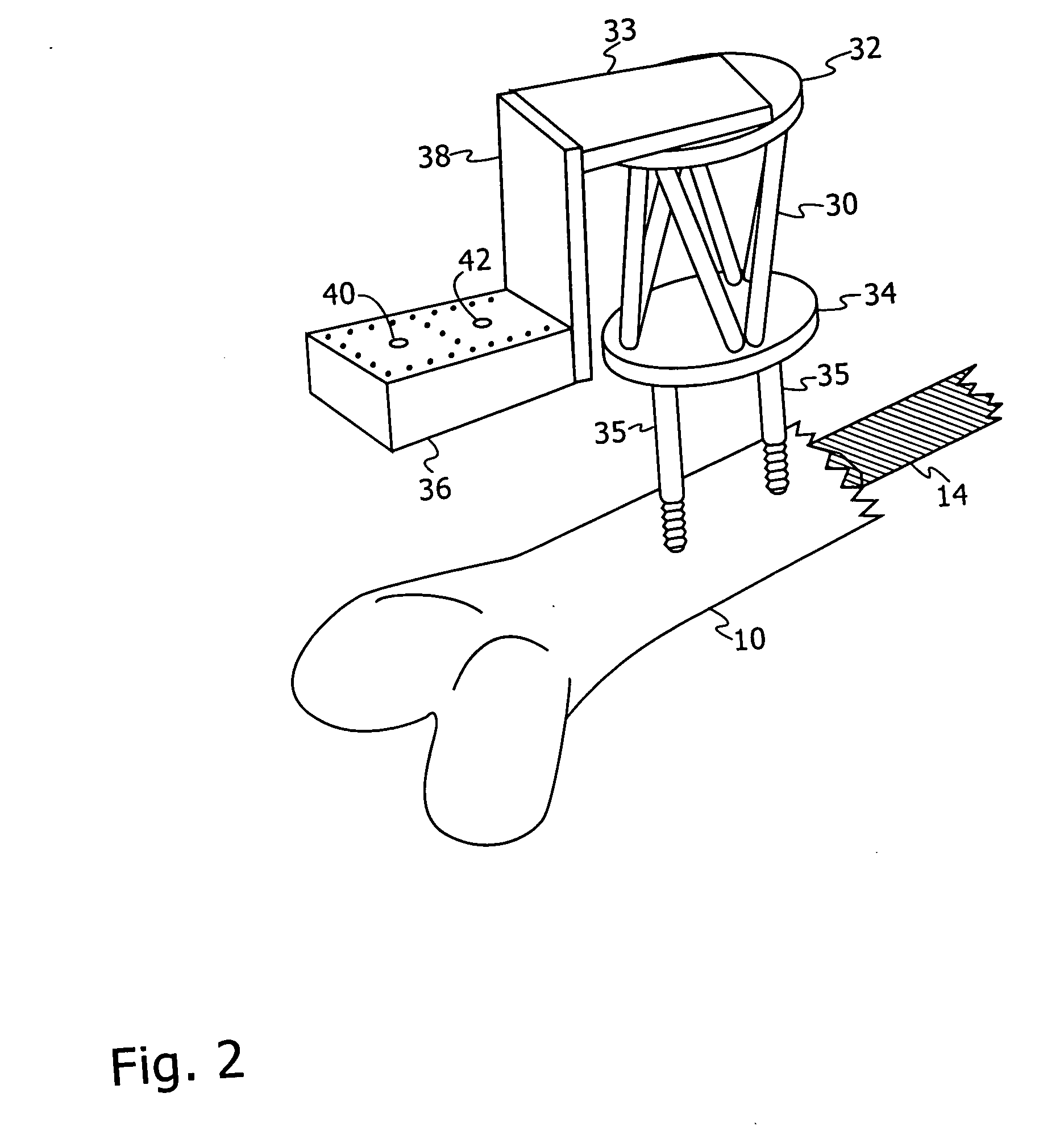
Method and apparatus for machining a surgical implant
InactiveUS20050244239A1Permit adjustment of overall mechanical propertyReduced strengthBone implantMilling cuttersEngineeringBiomedical engineering
A method is provided for machining a customized surgical implant in the operating room provided. Apparatus and a kit for carrying out the method are also provided.
Owner:OSTEOTECH
Robot for use with orthopaedic inserts
ActiveUS20060098851A1Simple and safe processReduce the possibilityProgramme controlInternal osteosythesisX-rayTrial and error
A robot-guided system to assist orthopaedic surgeons in performing orthopaedic surgical procedures on pre-positioned inserts, including for the fixation of bone fractures, and especially for use in long bone distal intramedullary locking procedures. The system provides a mechanical guide for drilling the holes for distal screws in intramedullary nailing surgery. The drill guide is automatically positioned by the robot relative to the distal locking nail holes, using data derived from only a small number of X-ray fluoroscopic images. The system allows the performance of the locking procedure without trial and error, thus enabling the procedure to be successfully performed by less experienced surgeons, reduces exposure of patient and operating room personnel to radiation, shortens the intra-operative time, and thus reduces post-operative complications.
Owner:MAZOR ROBOTICS
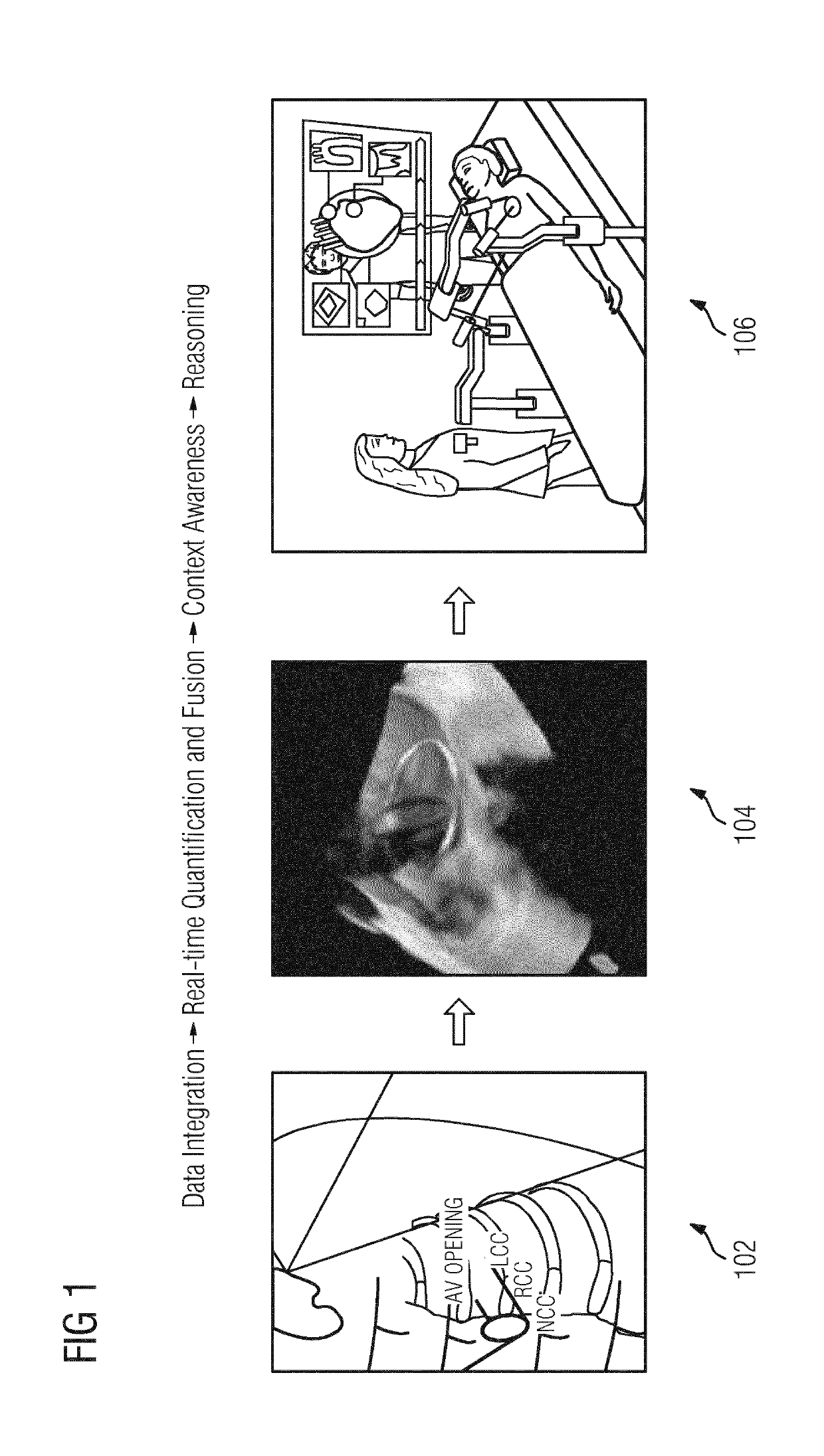
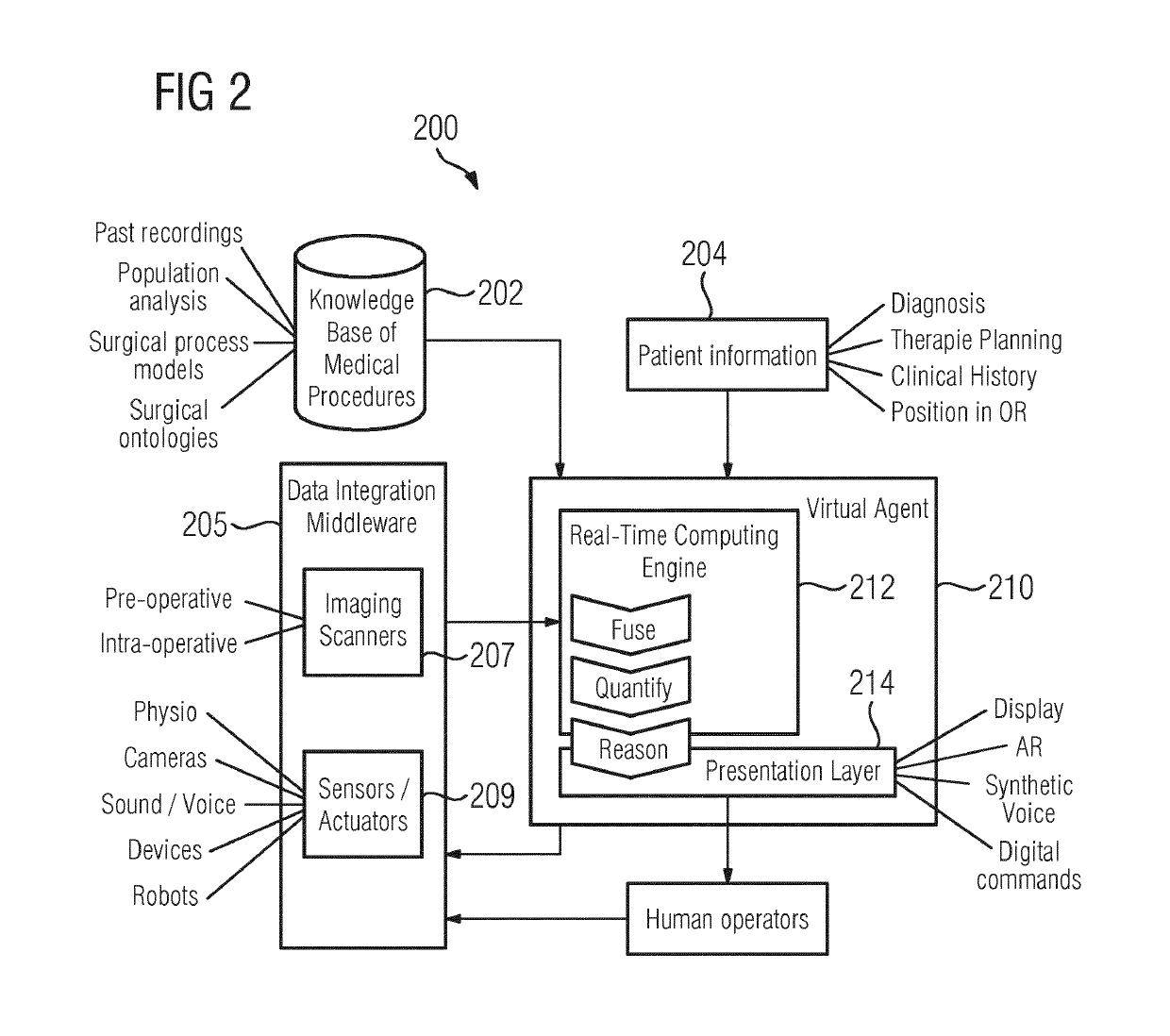
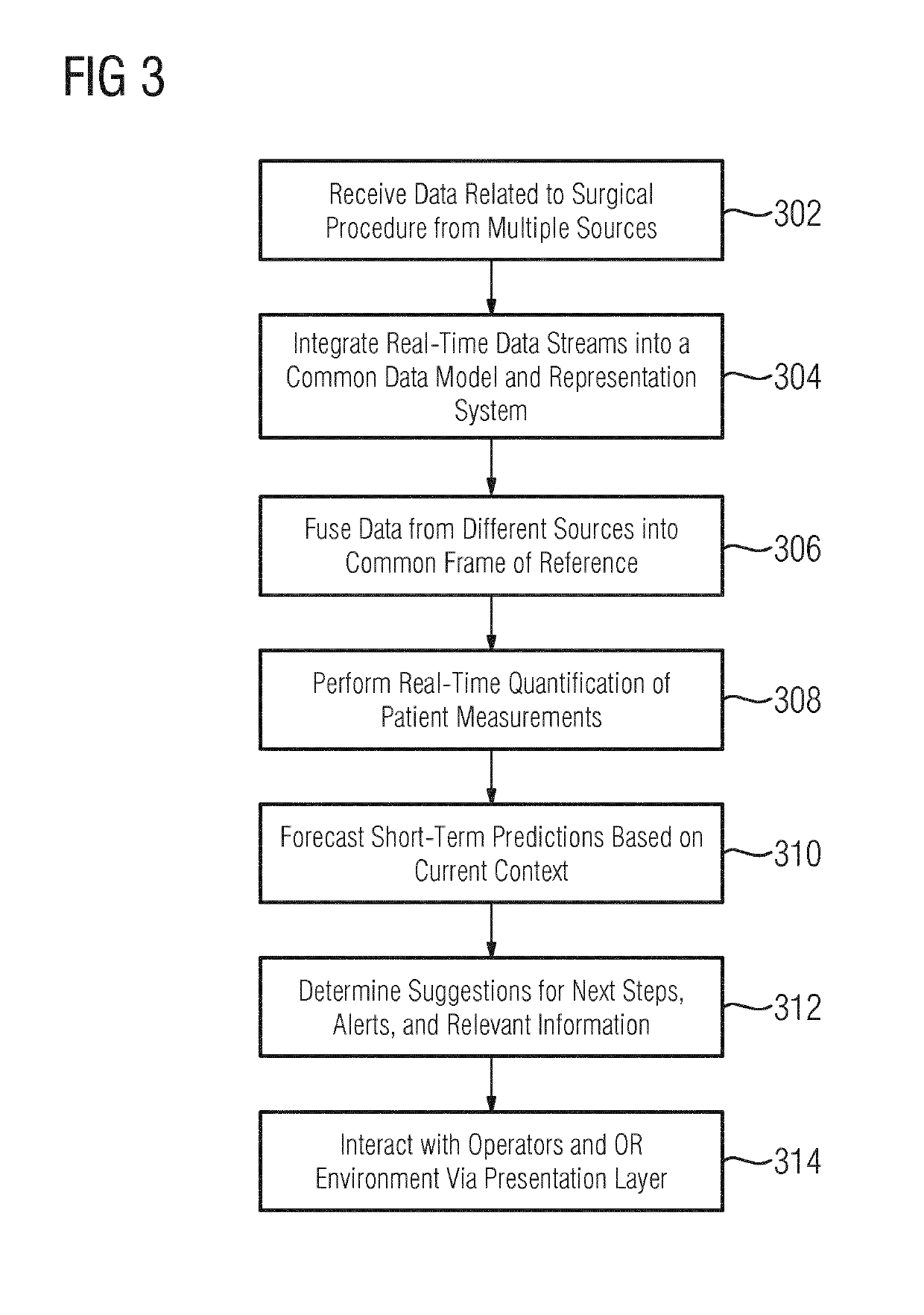
System and method for artificial agent based cognitive operating rooms
ActiveUS20190333626A1Improve efficacyImprove securityImage enhancementMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDiagnostic Radiology ModalityRelevant information
An artificial agent based cognitive operating room system and a method thereof providing automated assistance for a surgical procedure are disclosed. Data related to the surgical procedure from multiple data sources is fused based on a current context. The data includes medical images of a patient acquired using one or more medical imaging modalities. Real-time quantification of patient measurements based on the data from the multiple data sources is performed based on the current context. Short-term predictions in the surgical procedure are forecasted based on the current context, the fused data, and the real-time quantification of the patient measurements. Suggestions for next steps in the surgical procedure and relevant information in the fused data are determined based on the current context and the short-term predictions. The suggestions for the next steps and the relevant information in the fused data are presented to an operator.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
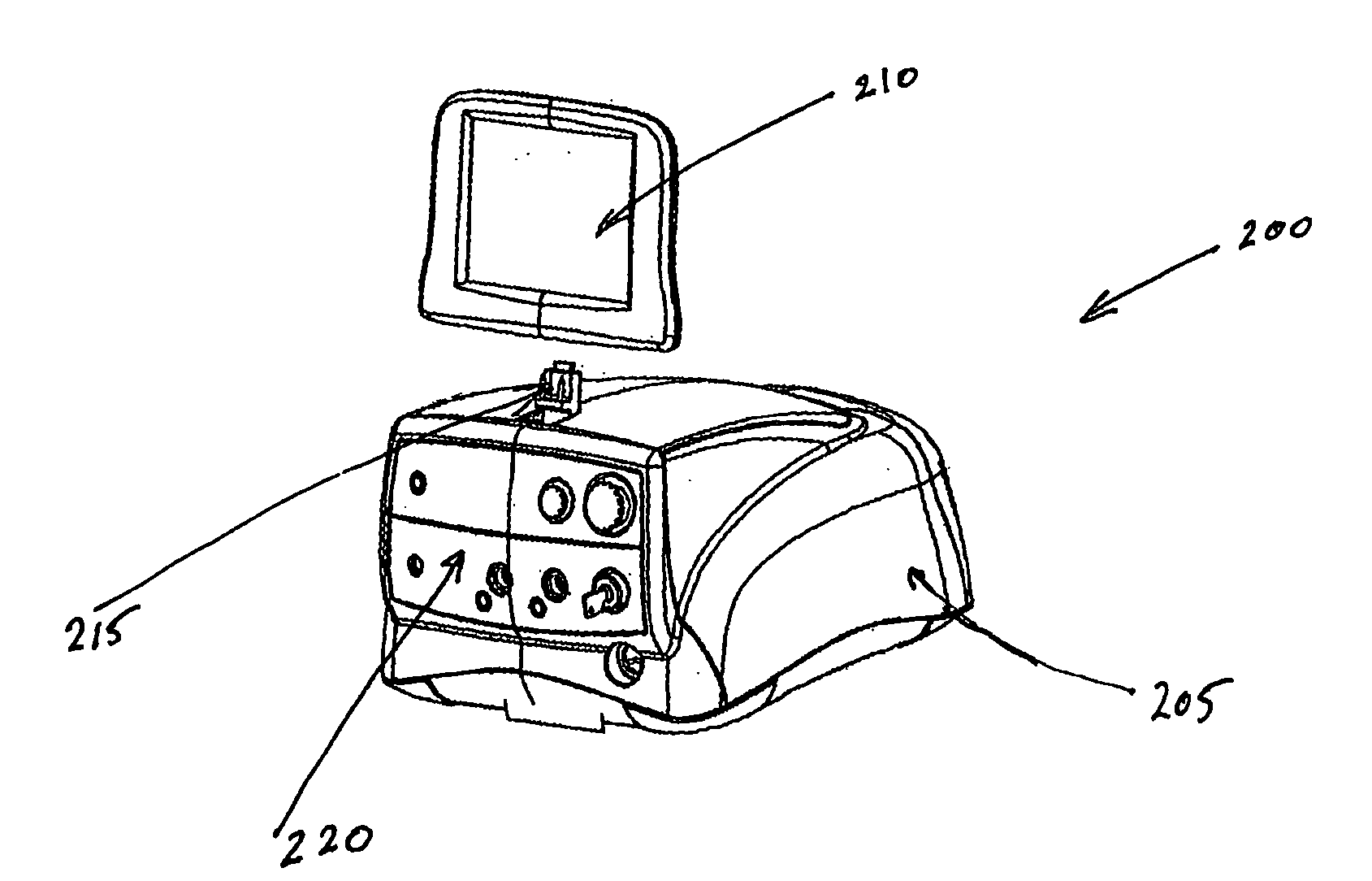
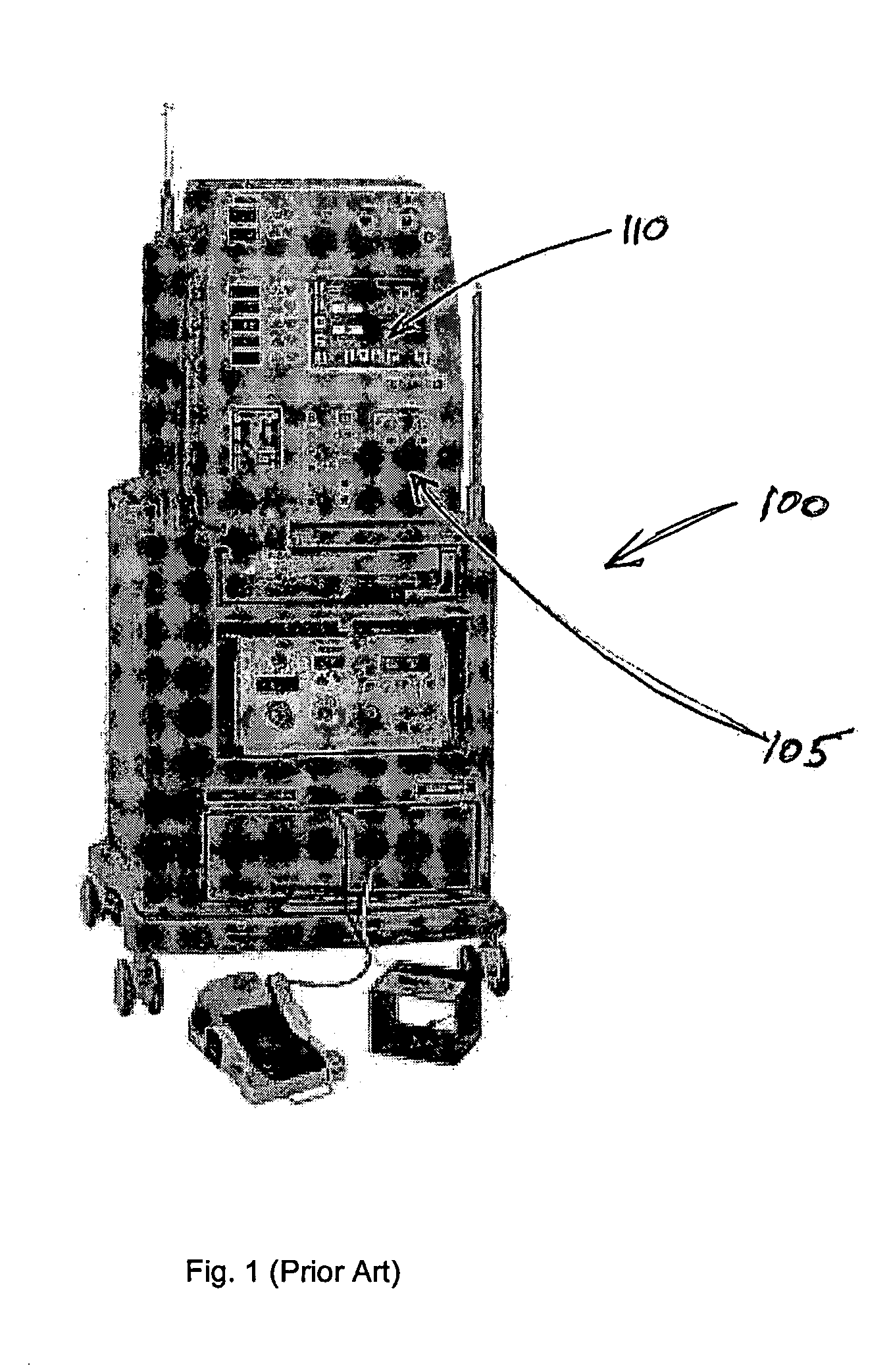
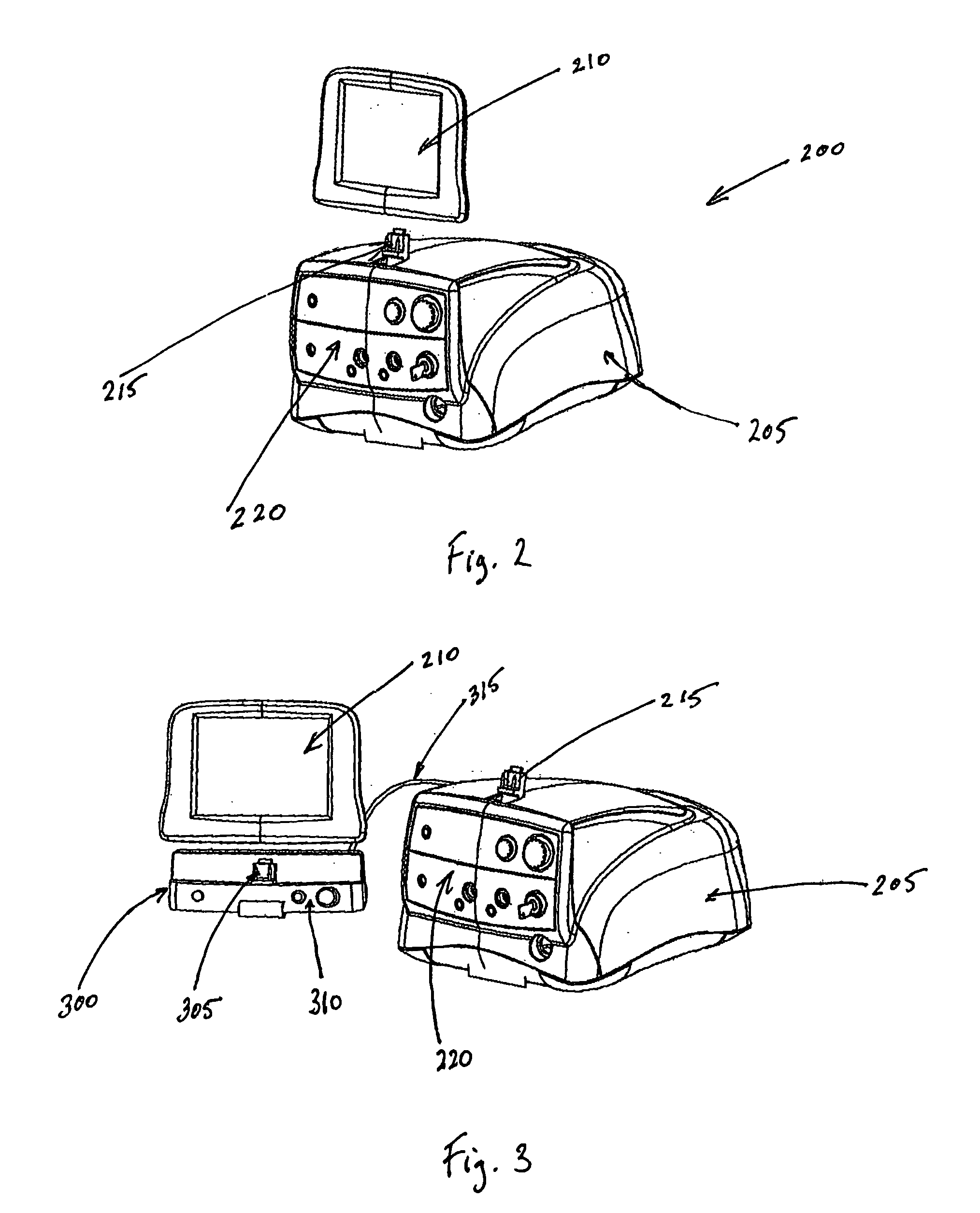
Surgical machine with removable display
A surgical system includes a main surgical unit, a display in communication with the main surgical unit, and a cradle for receiving the display when the display is removed from the main surgical unit. The display is removable from the main surgical unit so that the display can be located inside a sterile field of an operating room and the main surgical unit can be located outside the sterile field of the operating room.
Owner:ALCON INC
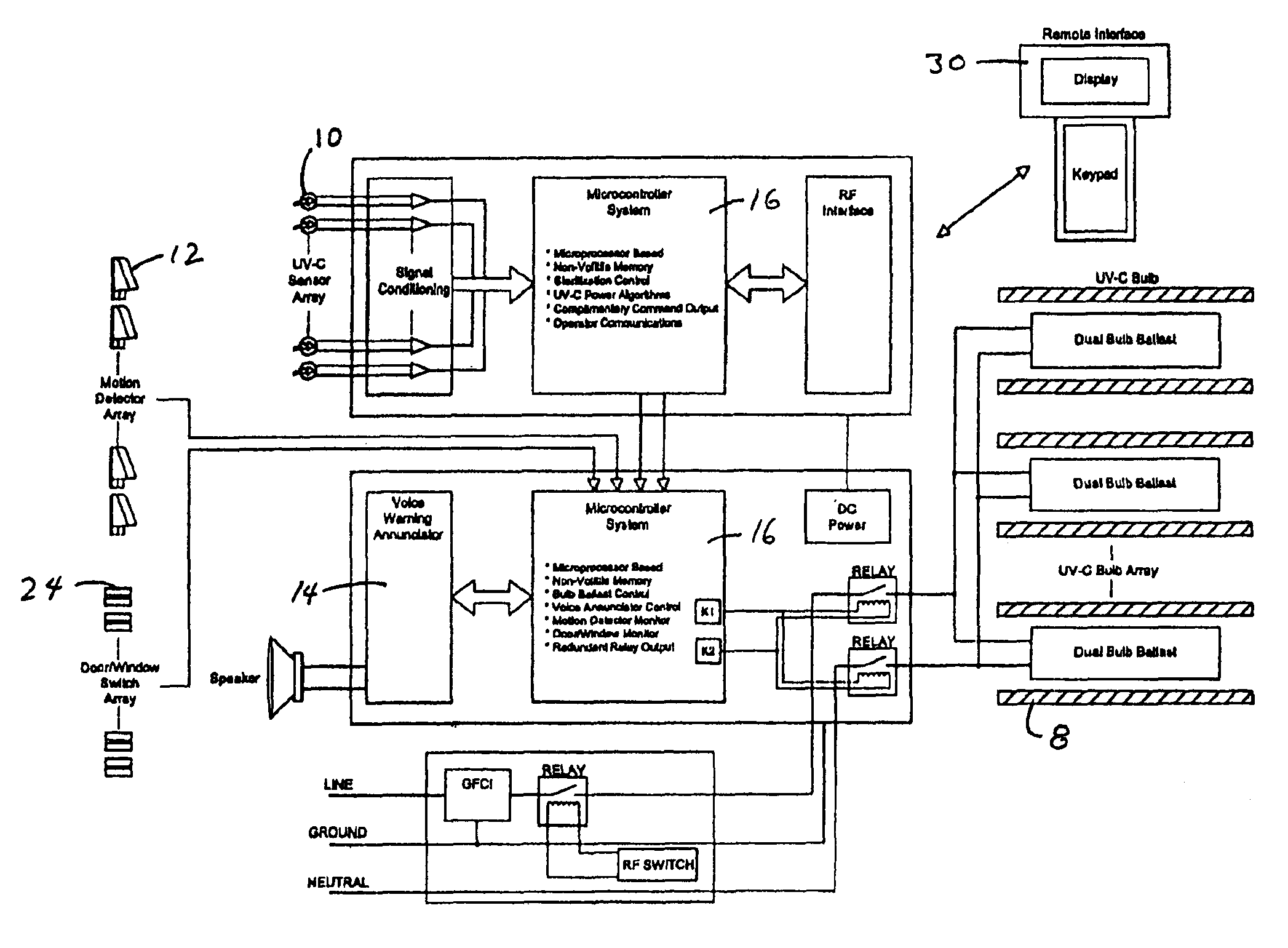
Ultraviolet area sterilizer and method of area sterilization using ultraviolet radiation
An ultraviolet area sterilizer (UVAS) is mobile or stationary. The UVAS is positioned in a room, such an operating room or intensive care unit. Motion detectors sense movement, to assure that personnel have evacuated the space to be sterilized. Subsequently, UV-C generators, such mercury bulbs, generate UV-C from multiple locations within the room or other enclosed space. Multiple UV-C sensors scan the room, and determine the area reflecting the lowest level of UV-C back to the sensors. The device calculates the time required to obtain a bactericidal dose of UV-C reflected back to the sensors. Once an effective bactericidal dose has been reflected to all the sensors, the unit notifies the operator and shuts down.
Owner:UVAS
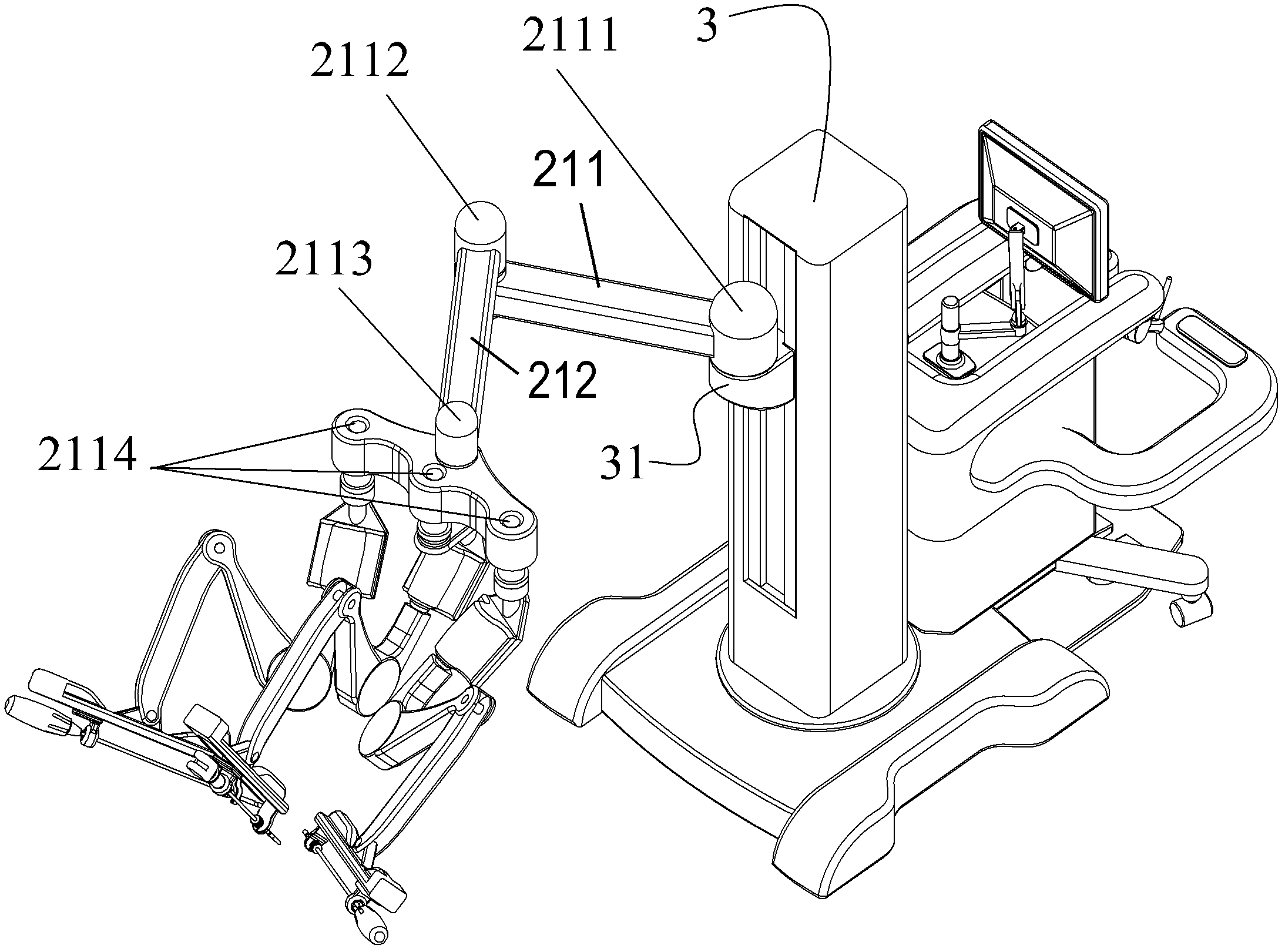
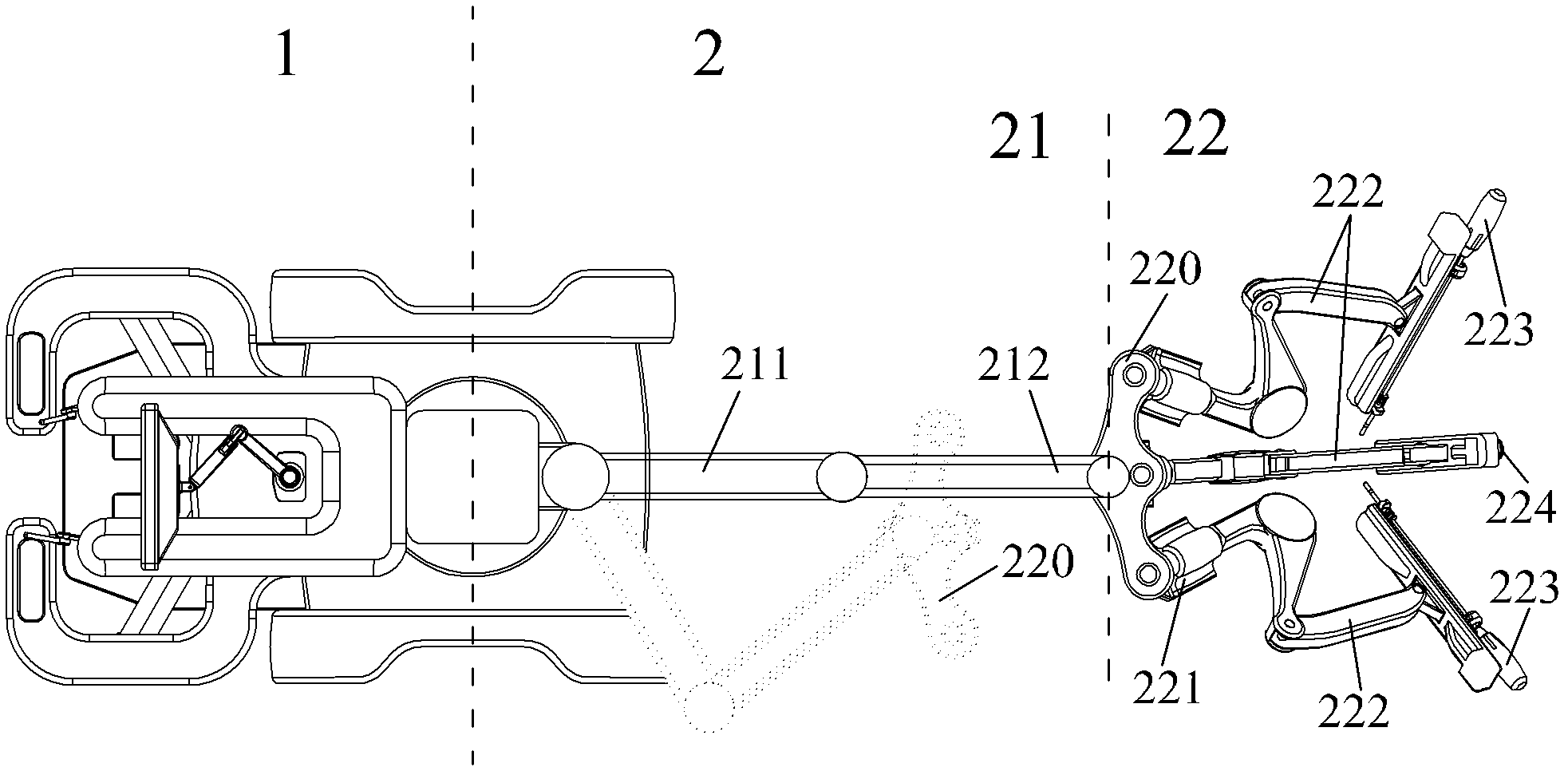
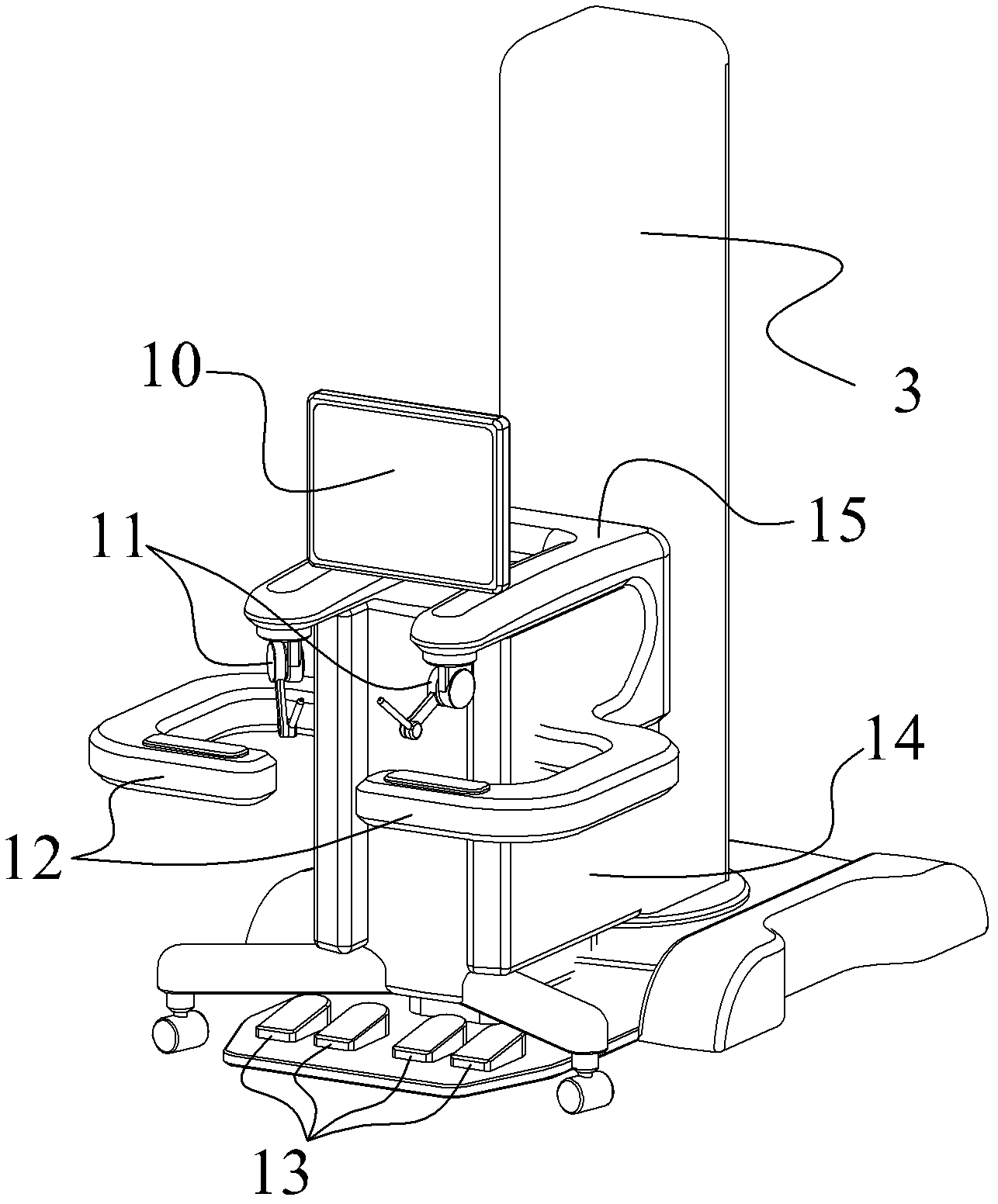
Arrangement structure for mechanical arm of minimally invasive surgery robot
InactiveCN102973317AEasy transferReduce in quantityDiagnosticsSurgical robotsLess invasive surgeryControl theory
An arrangement structure for a mechanical arm of a minimally invasive surgery robot comprises a main operation end part, an auxiliary operation end part, a driven adjusting arm and a driving operation arm combination. The main operation end part and the auxiliary operation end part are connected in a front and back mode through a vertical column to form a whole, and a sliding block vertically sliding is arranged on the front end face of the vertical column. The driven adjusting arm comprises a first connection rod and a second connection rod, the driving operation arm combination comprises a driving arm support platform, at least three driving arm seats and at least three driving operation arms, and at least three same driving arms are respectively in rotating connection with at least three driving arm seats. The arrangement structure for the mechanical arm of the minimally invasive surgery robot has the advantages that a main operation end is integrated with a driven operating end to enable the robot to be conveniently shifted, the arrangement structure for the mechanical arm of the minimally invasive surgery robot achieves support and adjustment of a plurality of driving operation arms, reduces total volume of the robot, and improves utilization rate of a space in a surgery room, and the arrangement structure for the mechanical arm of the minimally invasive surgery robot not only saves the space of the surgery room, but also has the advantage of being capable of fast moving, and does not need a special surgery room.
Owner:周宁新 +1
Virtual operating room integration
InactiveUS20050128184A1Direct and accurate controlEliminate clutterElectrotherapyMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesControl systemSTERILE FIELD
A virtual control system for an operating room establishes virtual control devices to control surgical equipment and patient monitoring equipment and to display control, status and functionality information concerning the surgical equipment and condition information of the patient. The virtual control devices permit direct interaction by the surgeon while maintaining a sterile field, and avoid the use of actual physical devices and electrical cables connecting them to the surgical equipment.
Owner:CONMED CORP
Point of care diagnostic systems
InactiveUS6936476B1Accurate concentrationAccurately presenceScattering properties measurementsComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionPoint of careDiagnostic test
Systems and methods for medical diagnosis or risk assessment for a patient are provided. These systems and methods are designed to be employed at the point of care, such as in emergency rooms and operating rooms, or in any situation in which a rapid and accurate result is desired. The systems and methods process patient data, particularly data from point of care diagnostic tests or assays, including immunoassays, electrocardiograms, X-rays and other such tests, and provide an indication of a medical condition or risk or absence thereof. The systems include an instrument for reading or evaluating the test data and software for converting the data into diagnostic or risk assessment information.
Owner:CYTYC CORP
Remote presence system including a cart that supports a robot face and an overhead camera
A tele-presence system that includes a cart. The cart includes a robot face that has a robot monitor, a robot camera, a robot speaker, a robot microphone, and an overhead camera. The system also includes a remote station that is coupled to the robot face and the overhead camera. The remote station includes a station monitor, a station camera, a station speaker and a station microphone. The remote station can display video images captured by the robot camera and / or overhead camera. By way of example, the cart can be used in an operating room, wherein the overhead camera can be placed in a sterile field and the robot face can be used in a non-sterile field. The user at the remote station can conduct a teleconference through the robot face and also obtain a view of a medical procedure through the overhead camera.
Owner:JONATA SUB TWO INC +1
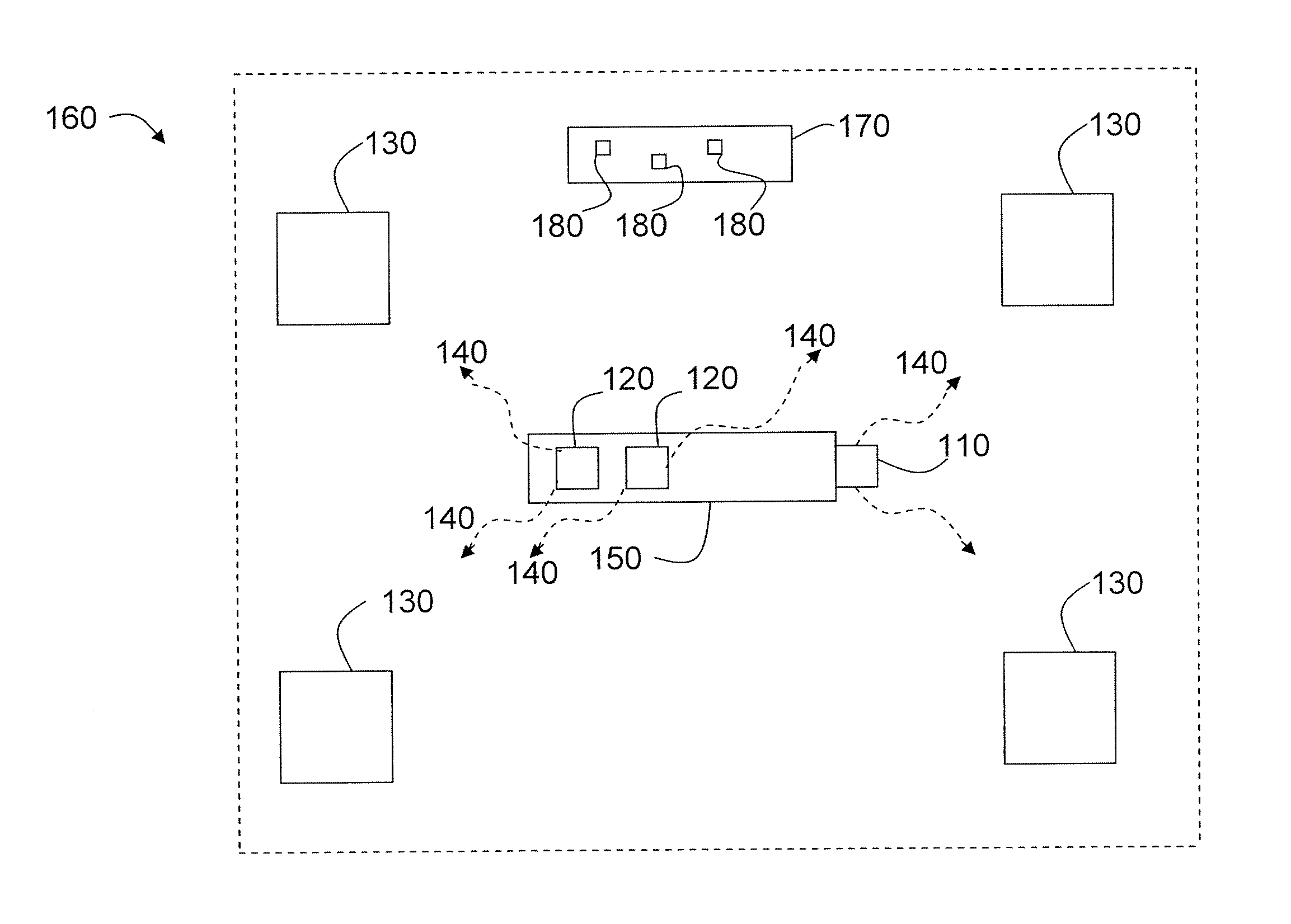
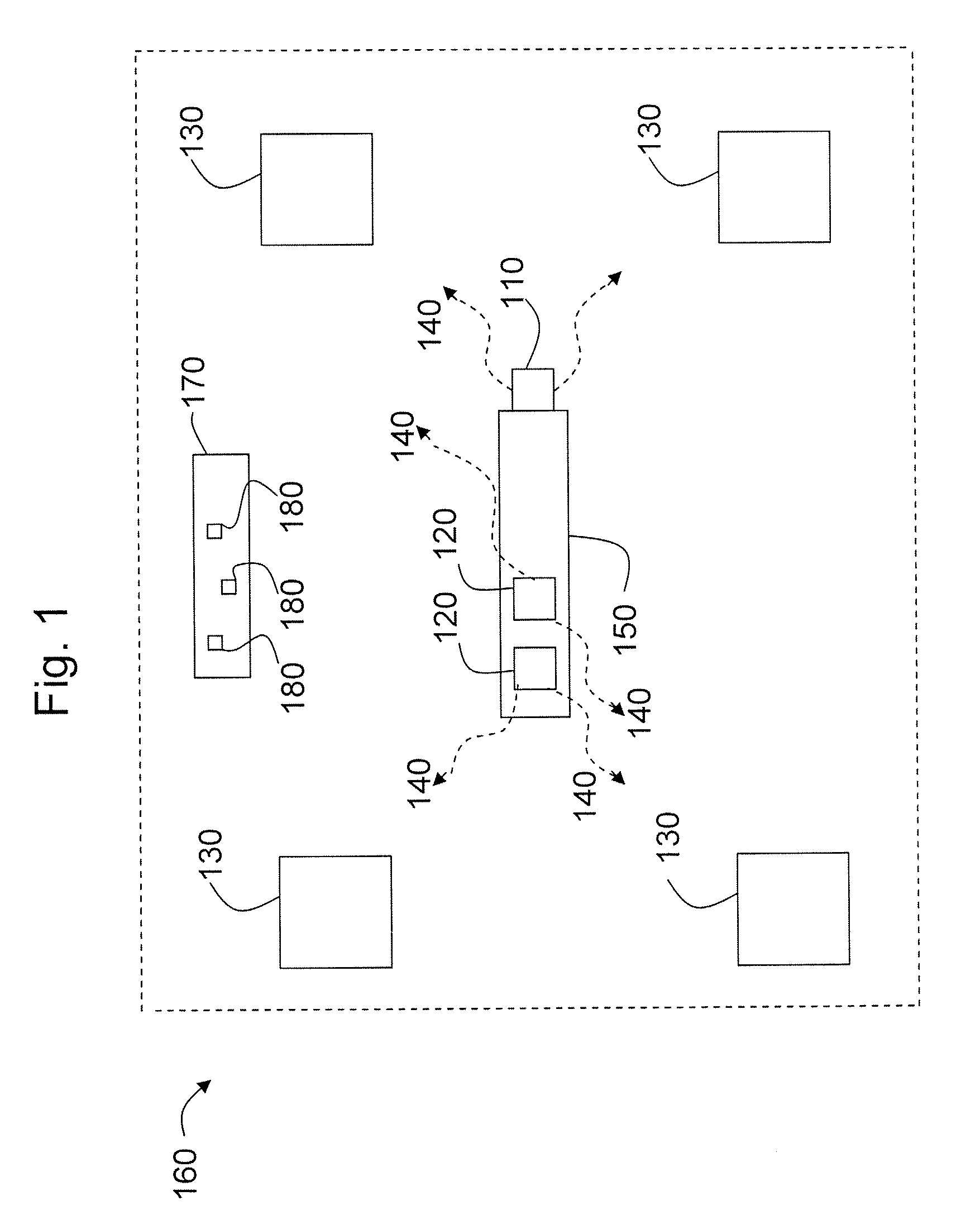
System utilizing radio frequency signals for tracking and improving navigation of slender instruments during insertion in the body
ActiveUS20070238985A1Easy to navigateShorten the timeSurgical needlesSurgical navigation systemsSignal onRobotic arm
The present invention concerns a system for utilizing radio frequency signals to dynamically determine the location of a medical device throughout a procedure and to improve navigation of the medical device. For these purposes, a plurality of RF receivers are mounted at operative locations in the operating room and operate on the same clock signal. The system also utilizes a diagnostic medical image such as an MRI, and overlays the position feedback signal on the image. This allows, for example, a surgeon to pick a desired spot on the diagnostic image, and then cause a robotic arm driven device to be moved to that particular spot inside the human body.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC +2
Remote presence system mounted to operating room hardware
ActiveUS20090240371A1Medical communicationPhysical therapies and activitiesRobotic systemsEngineering
A robot system that includes a remote station and a robot face. The robot face includes a camera that is coupled to a monitor of the remote station and a monitor that is coupled to a camera of the remote station. The robot face and remote station also have speakers and microphones that are coupled together. The robot face may be coupled to a boom. The boom can extend from the ceiling of a medical facility. Alternatively, the robot face may be attached to a medical table with an attachment mechanism. The robot face and remote station allows medical personnel to provide medical consultation through the system.
Owner:TELADOC HEALTH INC +1
Mobile videoimaging, videocommunication, video production (VCVP) system
A mobile self-powered videoimaging, video communication, video production (VCVP) system designed specifically for health care industry that provides high-resolution audio, video and data communications, production and recording capabilities at hospital operating room / procedure room or field environments for transmission to other remote locations. The VCVP system generally comprises a mobile platform with a plurality of cameras, at least one being mounted on an extensible boom for overhead imaging of surgical procedures. An array of video production equipment is rack-mounted inside the platform, as is an array of network teleconferencing equipment. The mobile imaging system may be parked at a convenient location in an operating room or other environment and controlled by a single operator. As the surgery proceeds, the operator can multiplex the camera signals into a live high resolution video / audio feed that is networked in real time for teleconferencing, and / or recorded to a hard drive or in any known format such as Mini-DV, S-VHS, VHS and DVD as desired.
Owner:REMY CHRISTOPHE +1
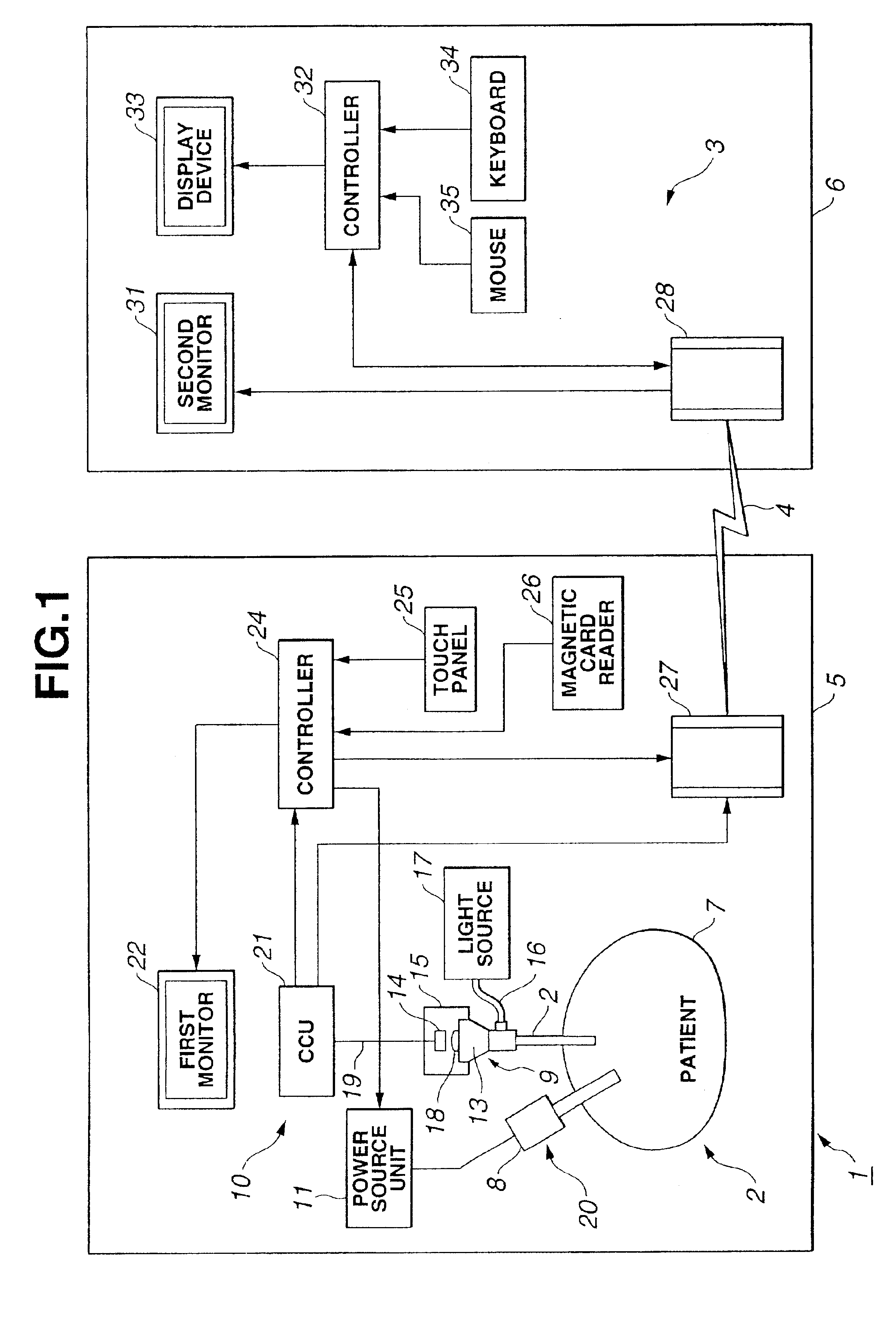
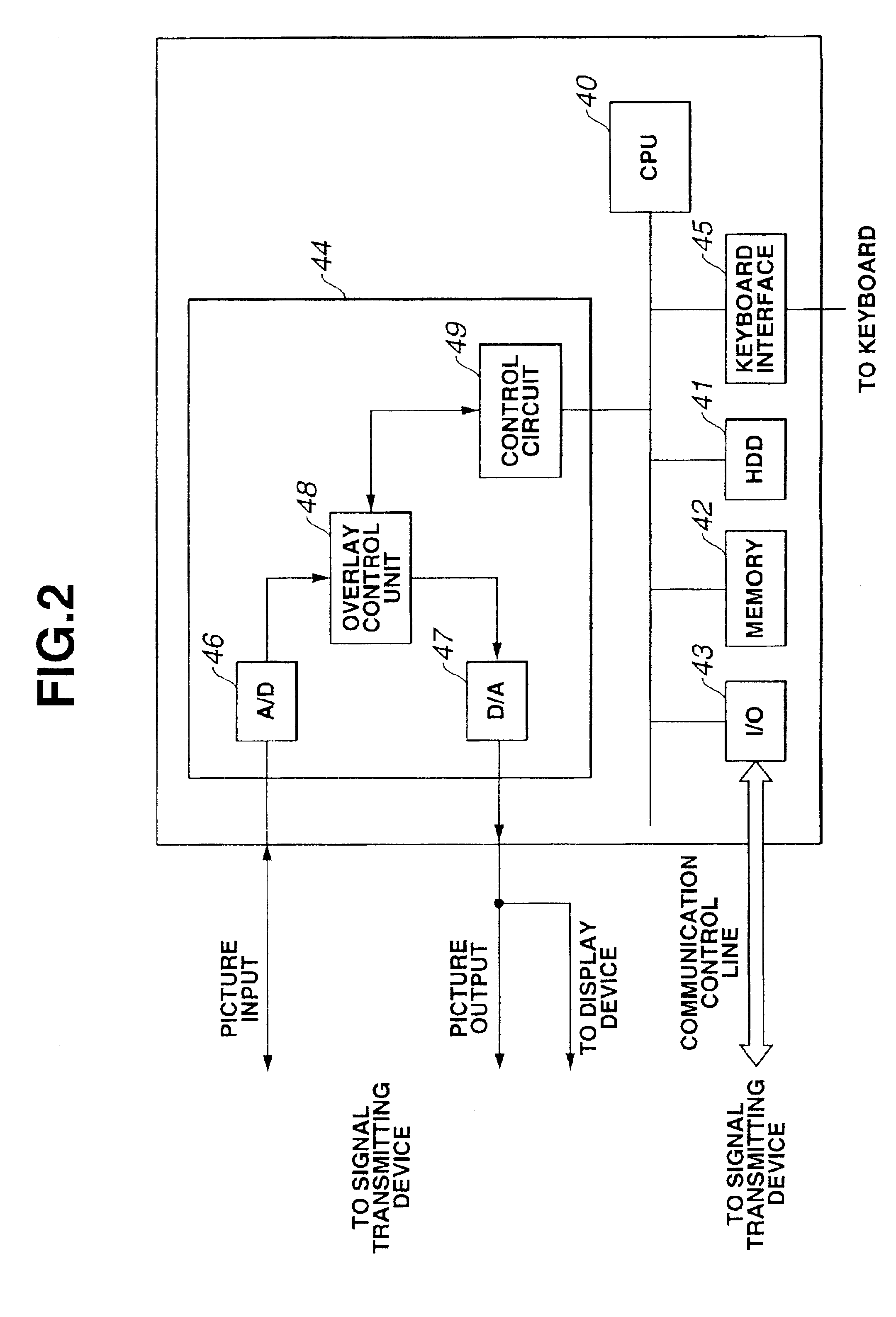
Surgery support system and surgery support method
A first controller synthesizes image output of a CCU and a cursor created based on trigger information from a second controller, following location information. The synthesized image is displayed on a first monitor, so an endoscope image and a cursor image which moves synchronously with the cursor image on a display device can be simultaneously viewed at the surgery room side on a single monitor, and accordingly, the problem of the working space inside the surgery room becoming crowded due to providing multiple observation monitors in the surgery room does not occur.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Device for maintaining visualization with surgical scopes
The present application discloses several embodiments of a devices for maintaining visualization with a surgical scope. The embodiments of the device are adapted to shield, defog or clean the lens of the surgical scope while the surgical scope is being used to perform a surgical procedure within a patient's body. In one embodiment, a view optimizer is provided that is adapted to deliver at least one fluid to the objective lens of the laparoscope to clean and / or defog the objective lens of the laparoscope without the need to remove the laparoscope from the surgical field. In additional embodiments, a view optimizer is provided that is adapted to create leakage or venting of gas from the body cavity so as to ensure continuous gas flow from an insufflator.
Owner:FLOSHIELD INC
General purpose distributed operating room control system
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Ultraviolet sterilizer for surgery
InactiveUS20110054574A1Prevent moistureAvoid burnsLight therapyRadioactive sourcesUv disinfectionArthroscopy
An ultraviolet sterilizer for use during surgery is mounted in a base cabinet. The UV light source can be a laser, or an LED. An optical frequency multiplier can be used that outputs UV of less than 280 nm, or greater than 320 nm, to avoid burning the patient. A visible LED aiming light directs the UV light toward the surgery. A crosshair image can be projected to position the light.One lamp has a housing, a cavity, a handle, and an ocular plate to pass the UV and the aiming light. An articulated arm allows selective positioning of the lamp. Another lamp has a stylus, a handle, and a tip small enough for easy insertion into a small incision for arthroscopy. A fiber optic cable connects the UV and the aiming light to the lamp. Lenses or filters can be used with the fiber optic cable.An electronic power supply and a CPU connect to the UV and the aiming light sources. A keyboard inputs commands to the CPU. A sensor provides feedback.Another UV sterilizer is mounted on a ceiling of the operating room. A lamp has a housing with a cavity. Either a curved or a flat substrate is mounted in the cavity. Solid state UV elements are arrayed on the substrate, along with visible LEDs for aiming. Either a curved or a flat mirror is disposed behind the substrate. An ocular plate passes the UV and the aiming light, and protects the elements from damage. The ocular plate is a diffuser, a filter, or a fresnel lens.
Owner:FELIX PERRY
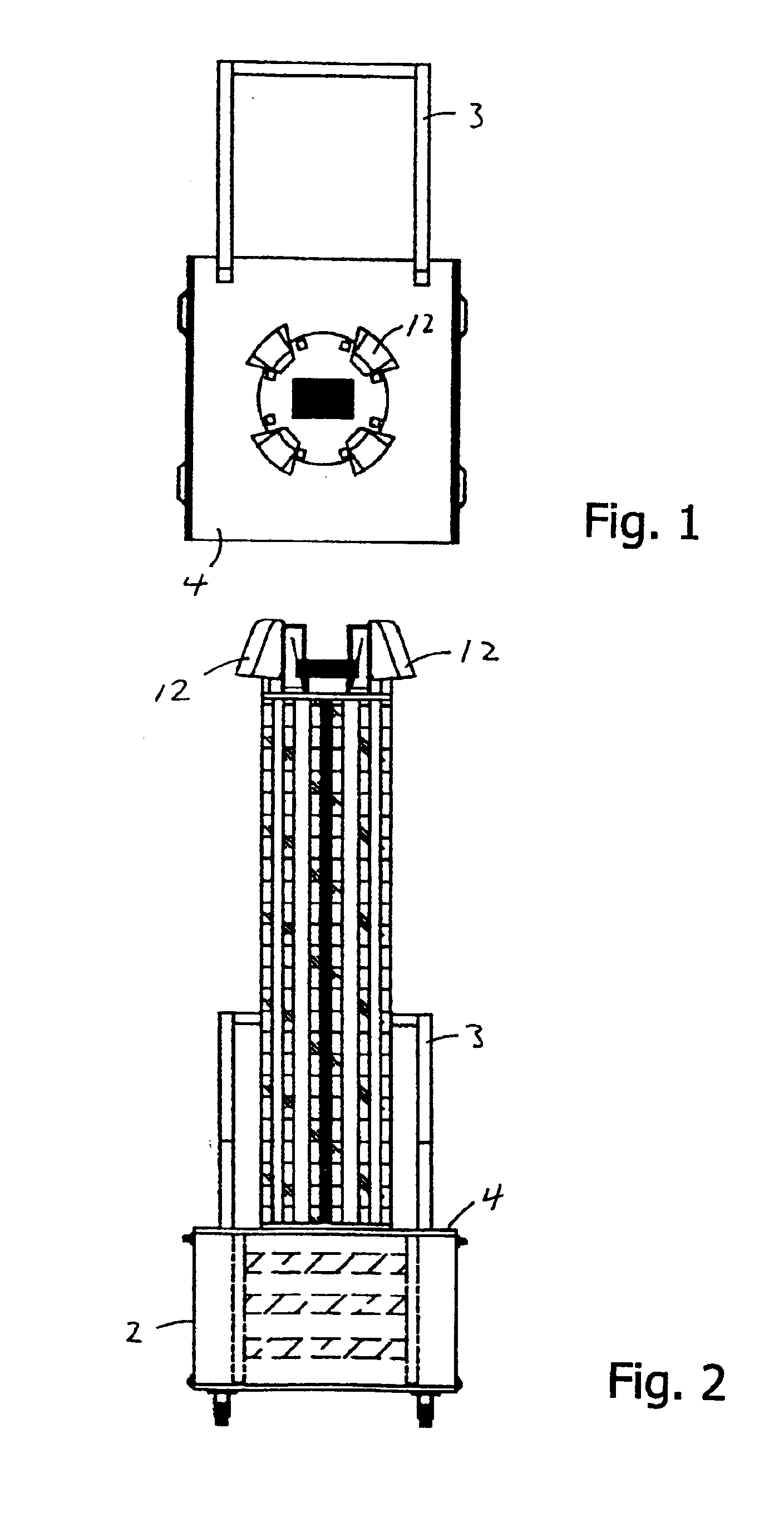
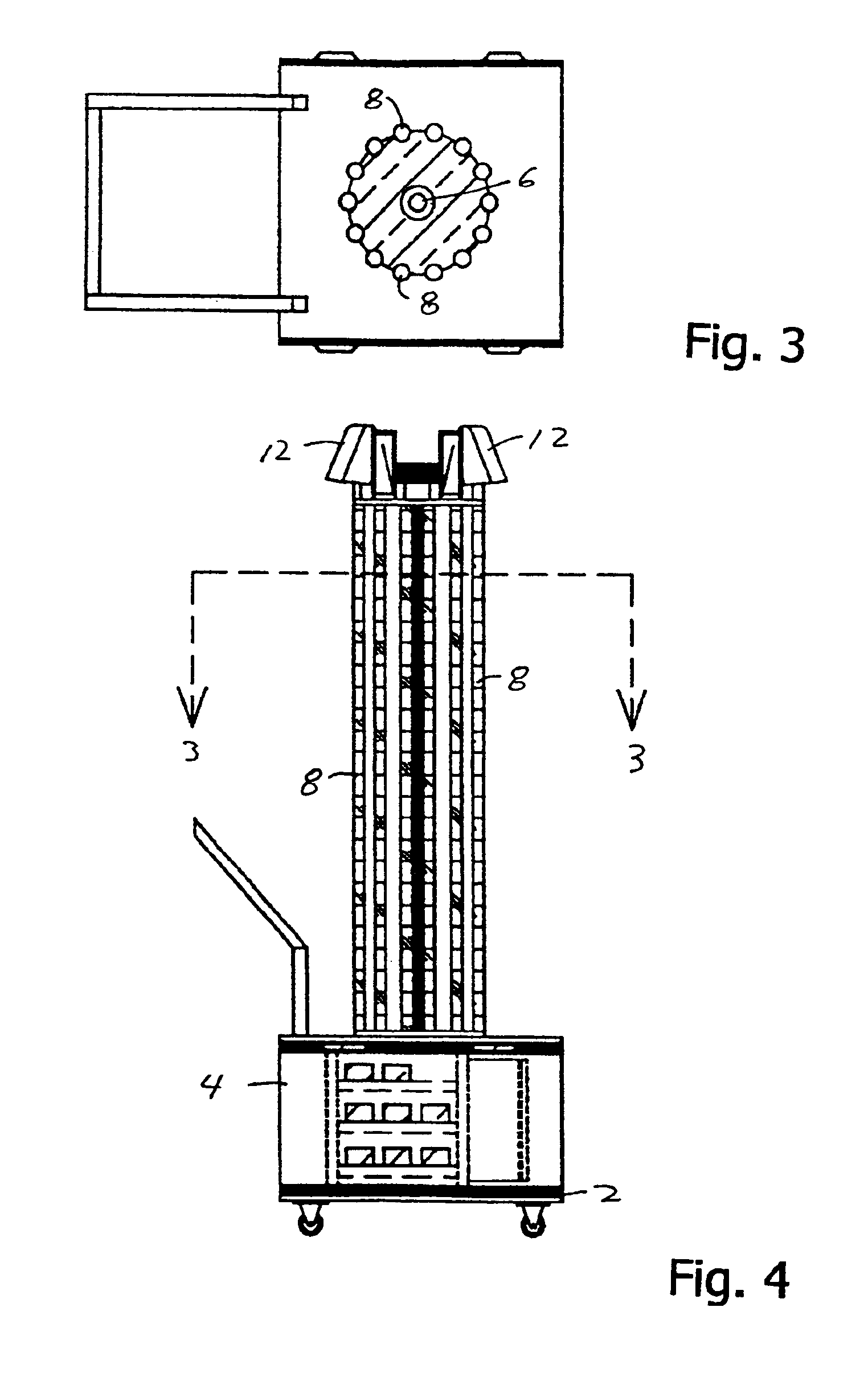
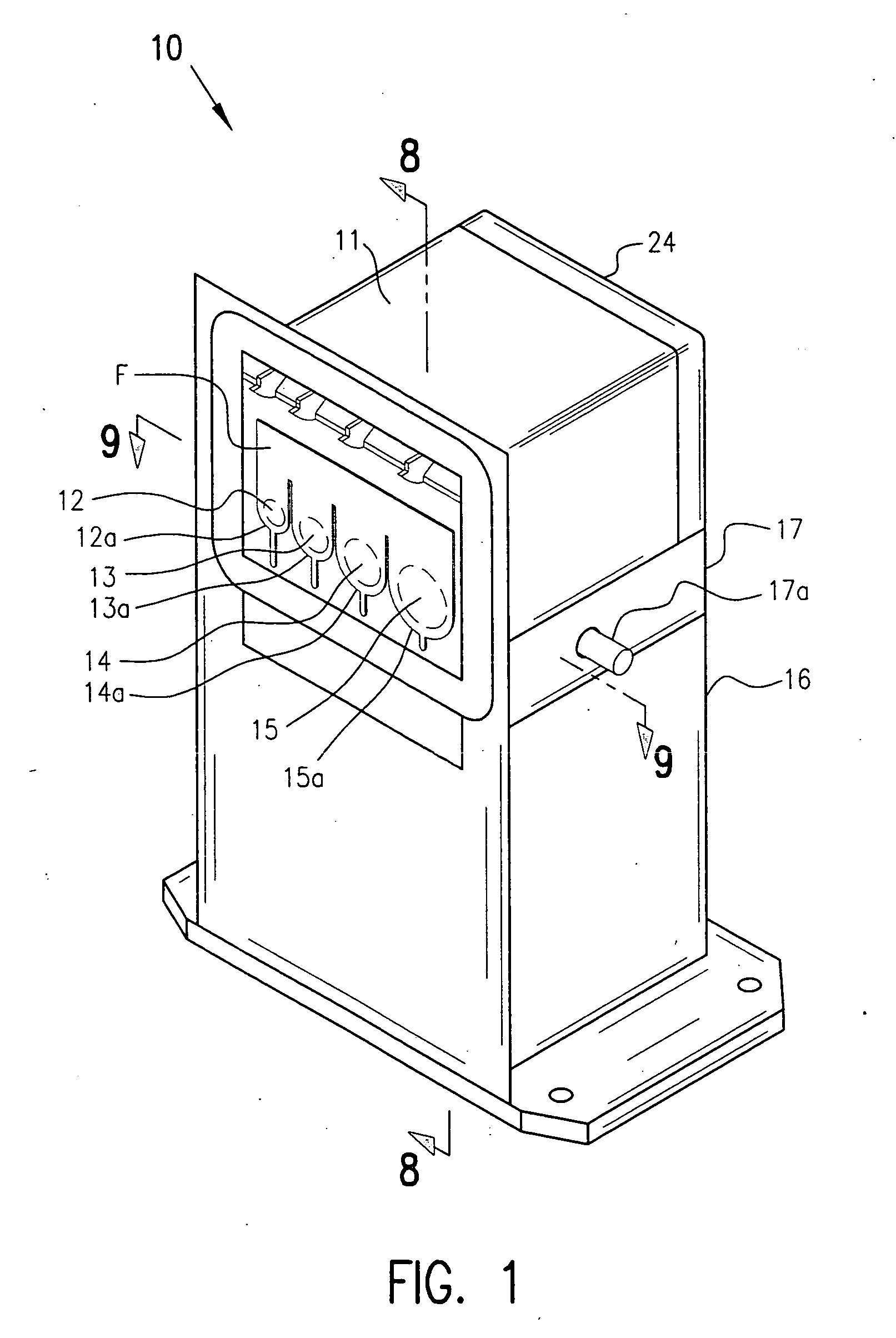
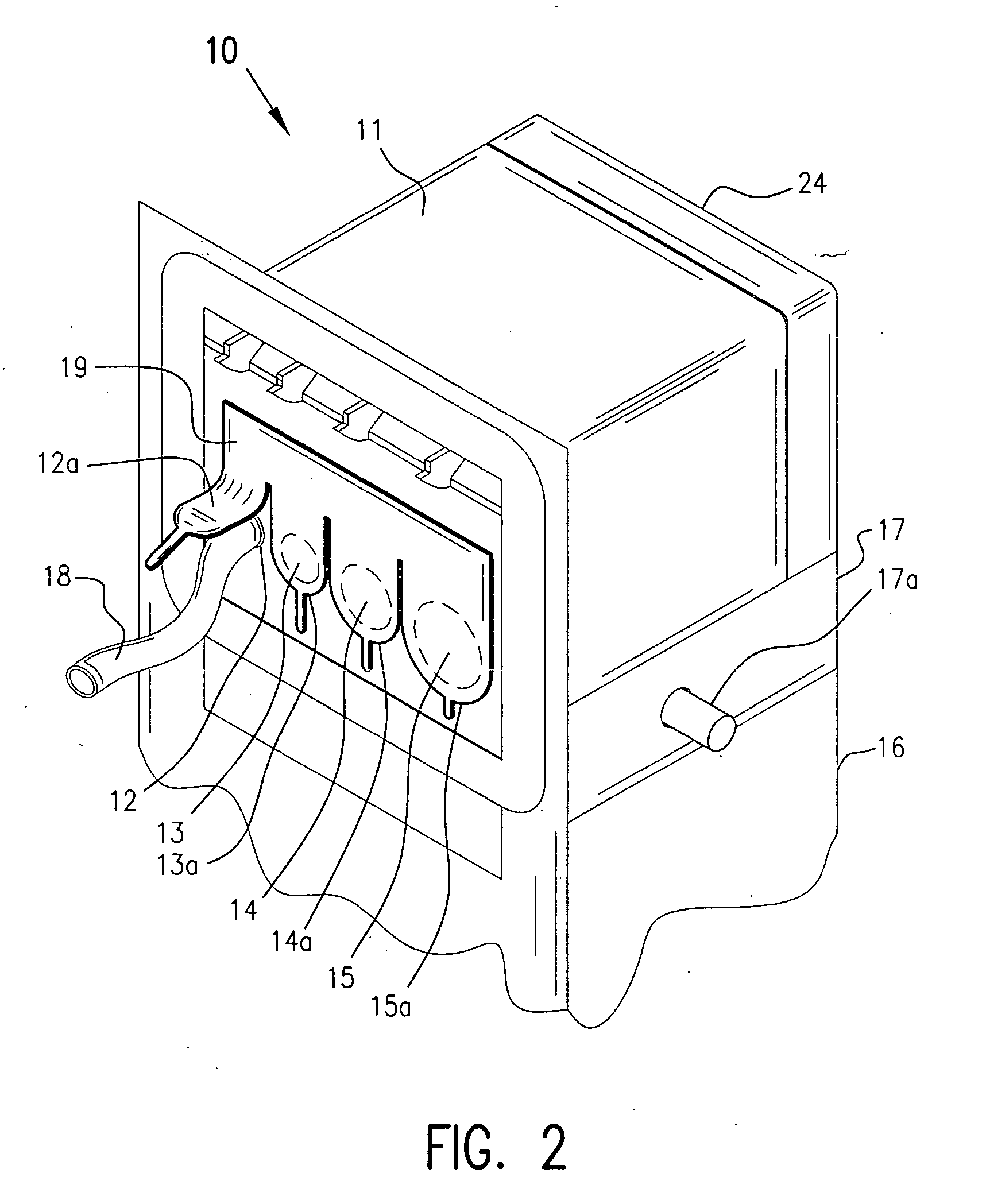
Operating room smoke evacuator with integrated vacuum motor and filter
The present invention broadly comprises a multiport filter having at least three intake ports and at least two layers—a first layer for containing particles 3 microns or greater and a second layer that contains particles 3 microns or less in size. In alternate embodiments, the filter includes a third layer for trapping odors and gases and a fourth layer for trapping fines. The second layer may be comprised of ULPA material and may have antimicrobial material. The invention also includes a contaminant removal system for the filtering and recirculation of air contaminated with smoke from cautery-type surgical procedures. The invention also broadly comprises a surgical assemblies control service head designed to house powered surgical devices and a vacuum-filtering system for the treatment of air contamination caused by surgical procedures.
Owner:BUFFALO FILTER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com