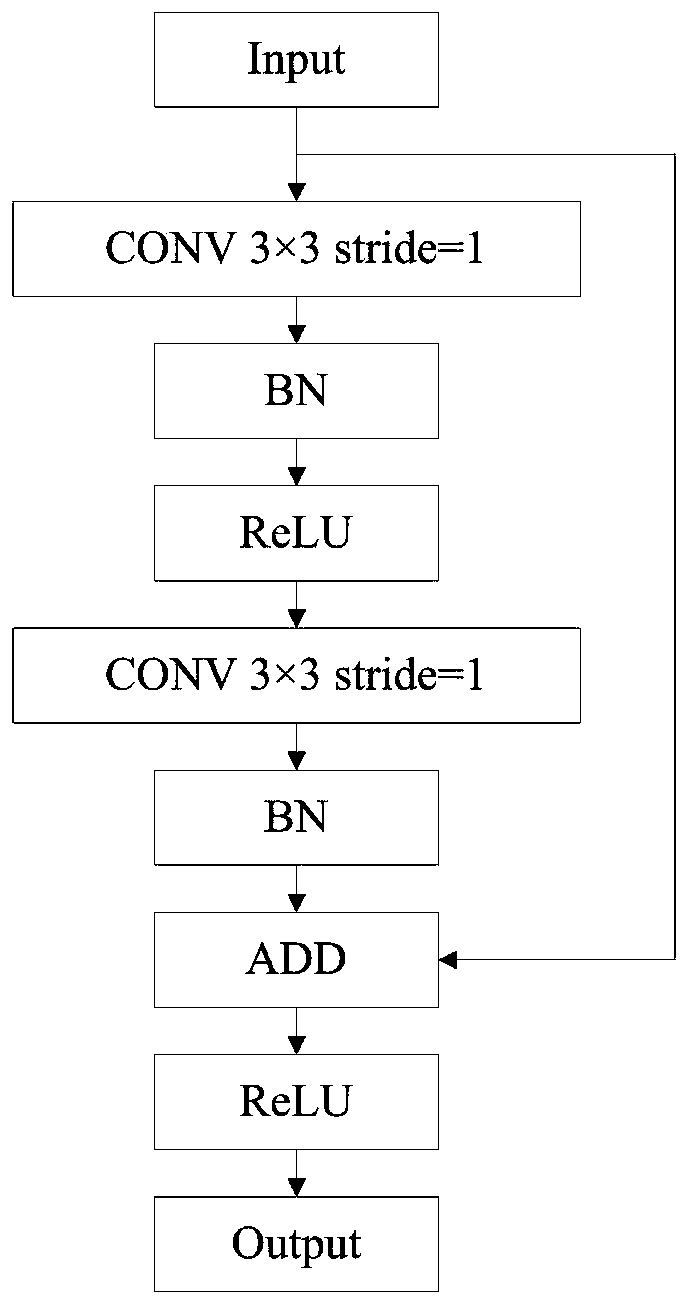
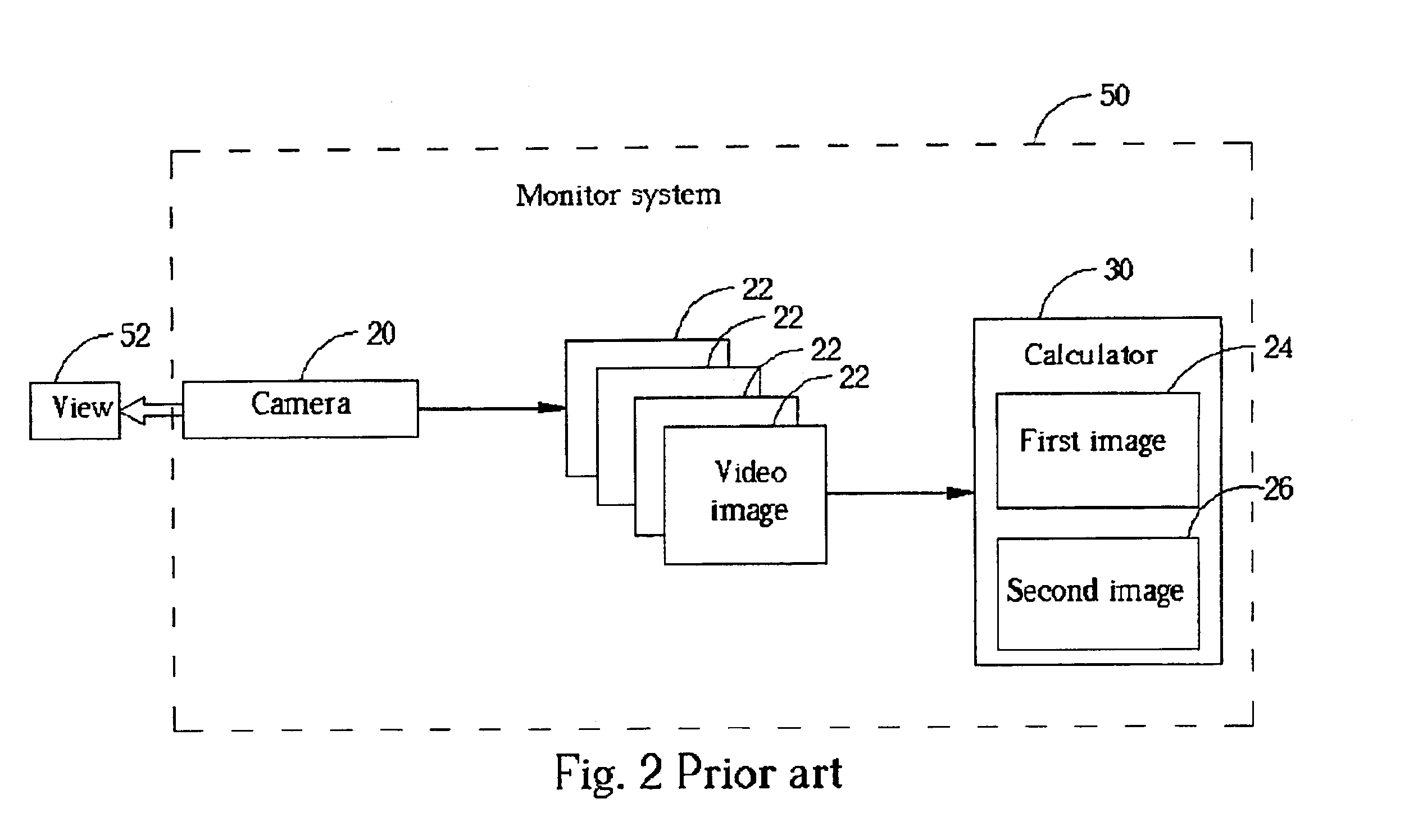
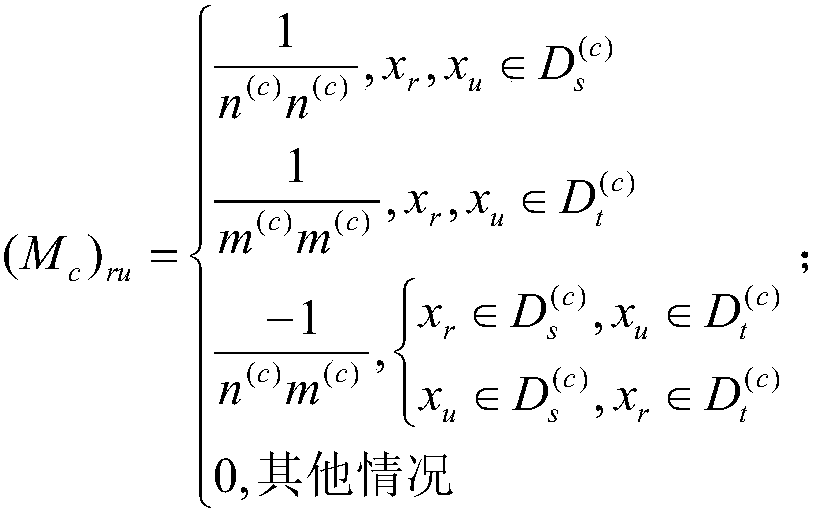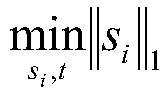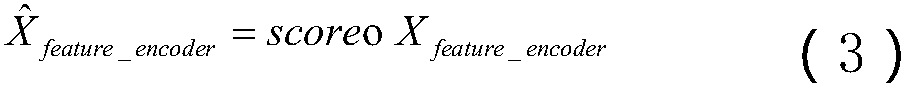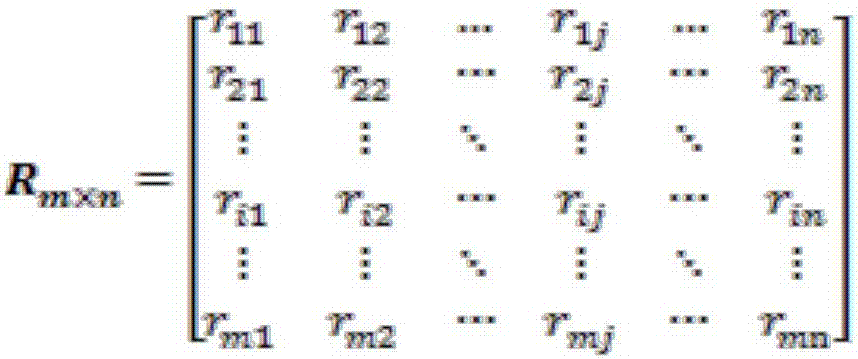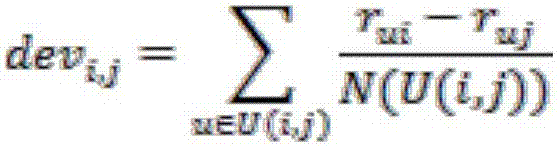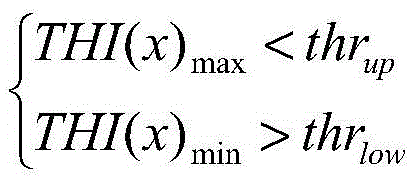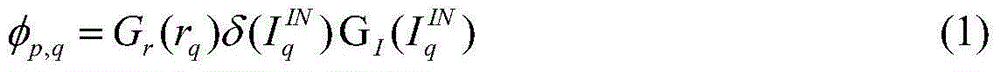Patents
Literature
94 results about "Mean difference" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The mean absolute difference (univariate) is a measure of statistical dispersion equal to the average absolute difference of two independent values drawn from a probability distribution. A related statistic is the relative mean absolute difference, which is the mean absolute difference divided by the arithmetic mean, and equal to twice the Gini coefficient. The mean absolute difference is also known as the absolute mean difference (not to be confused with the absolute value of the mean signed difference) and the Gini mean difference (GMD). The mean absolute difference is sometimes denoted by Δ or as MD.
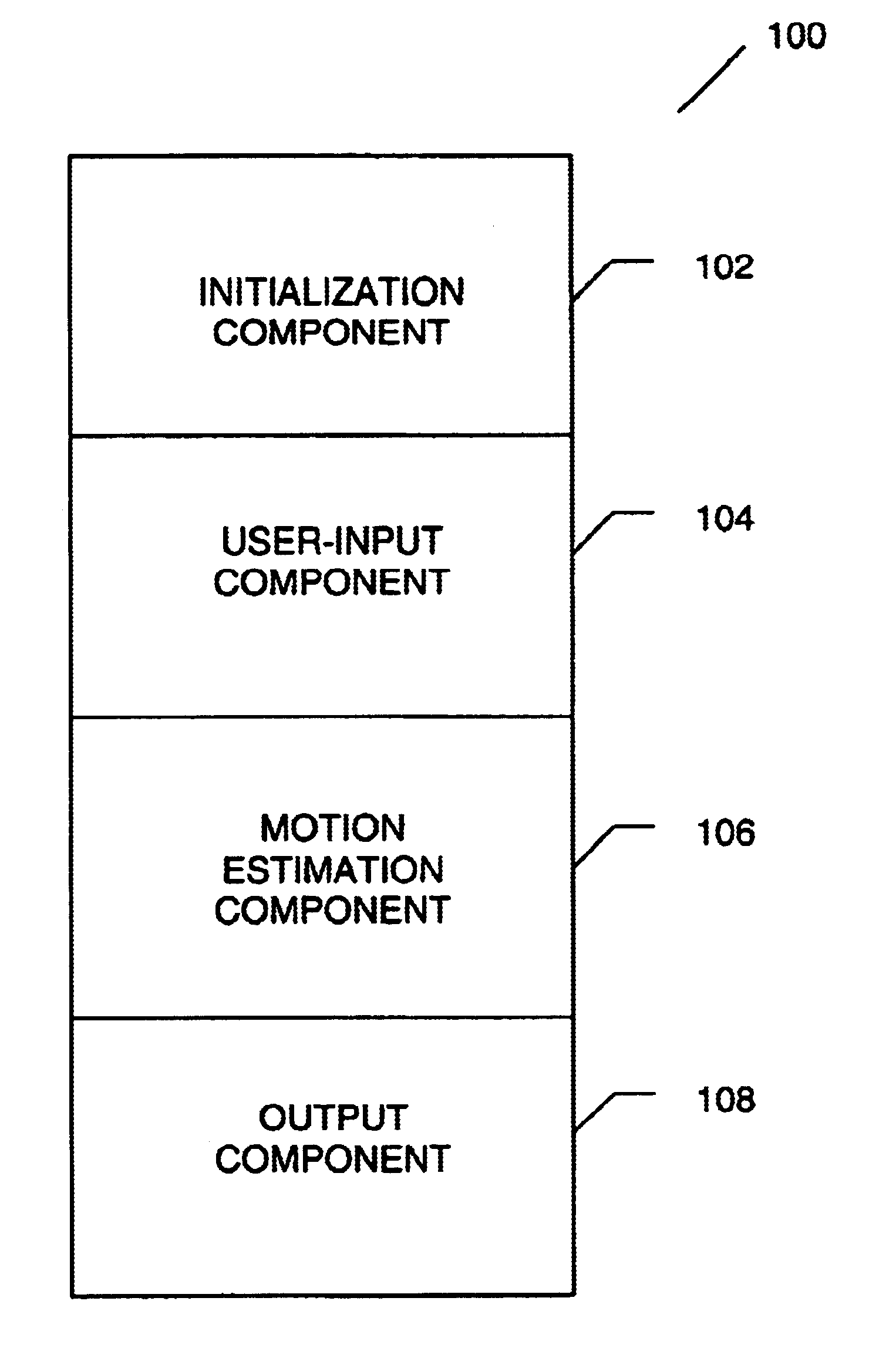
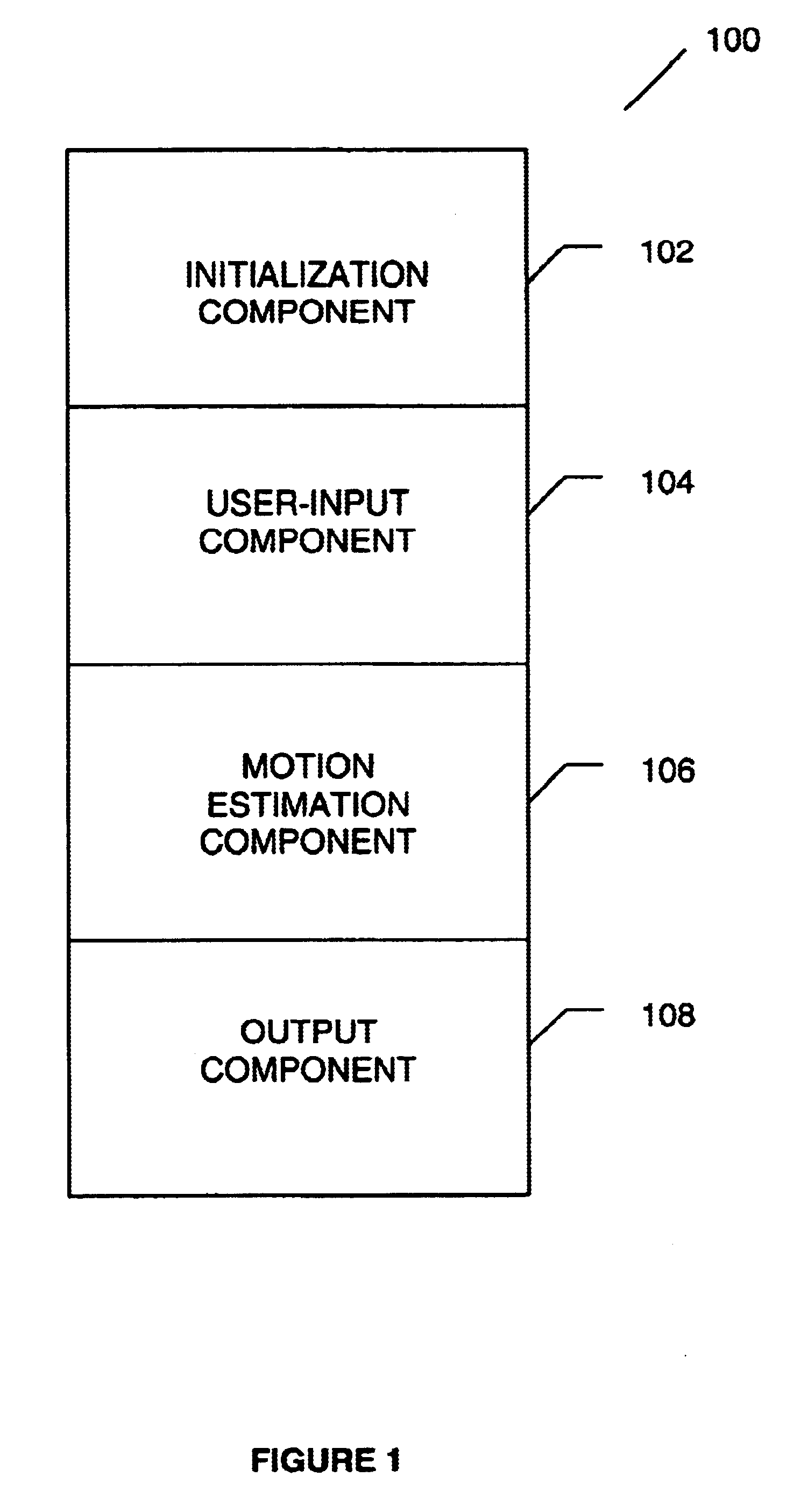
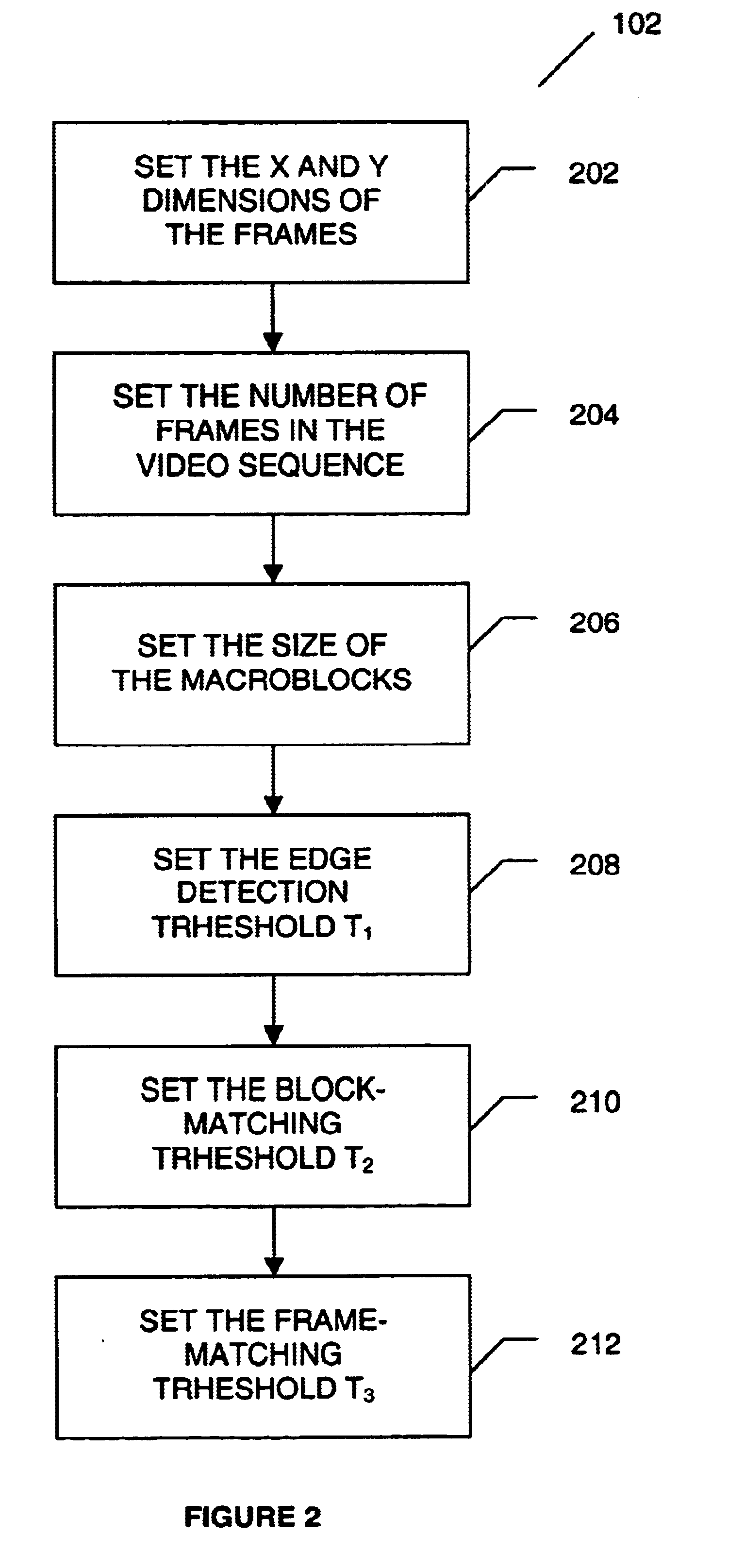
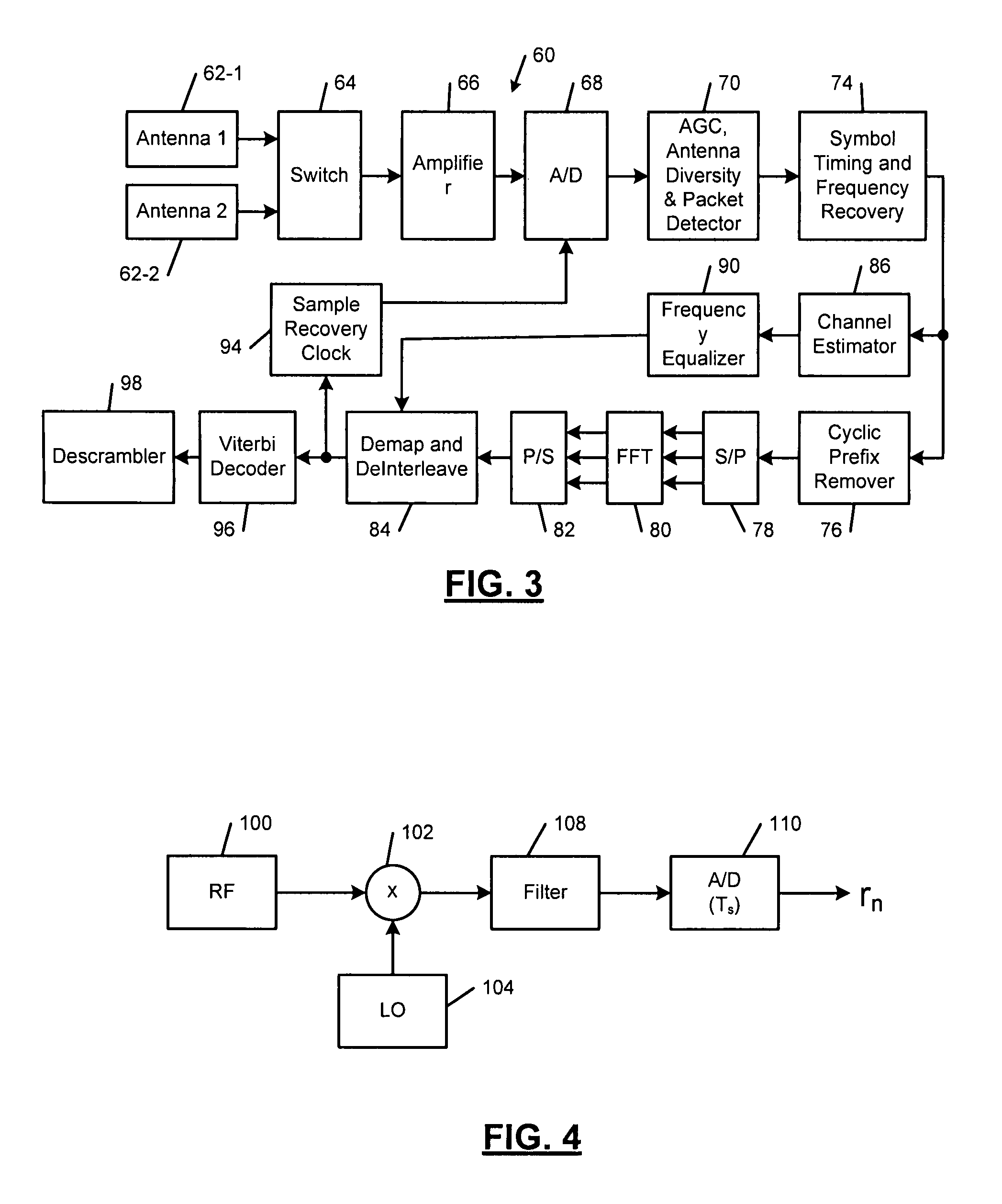
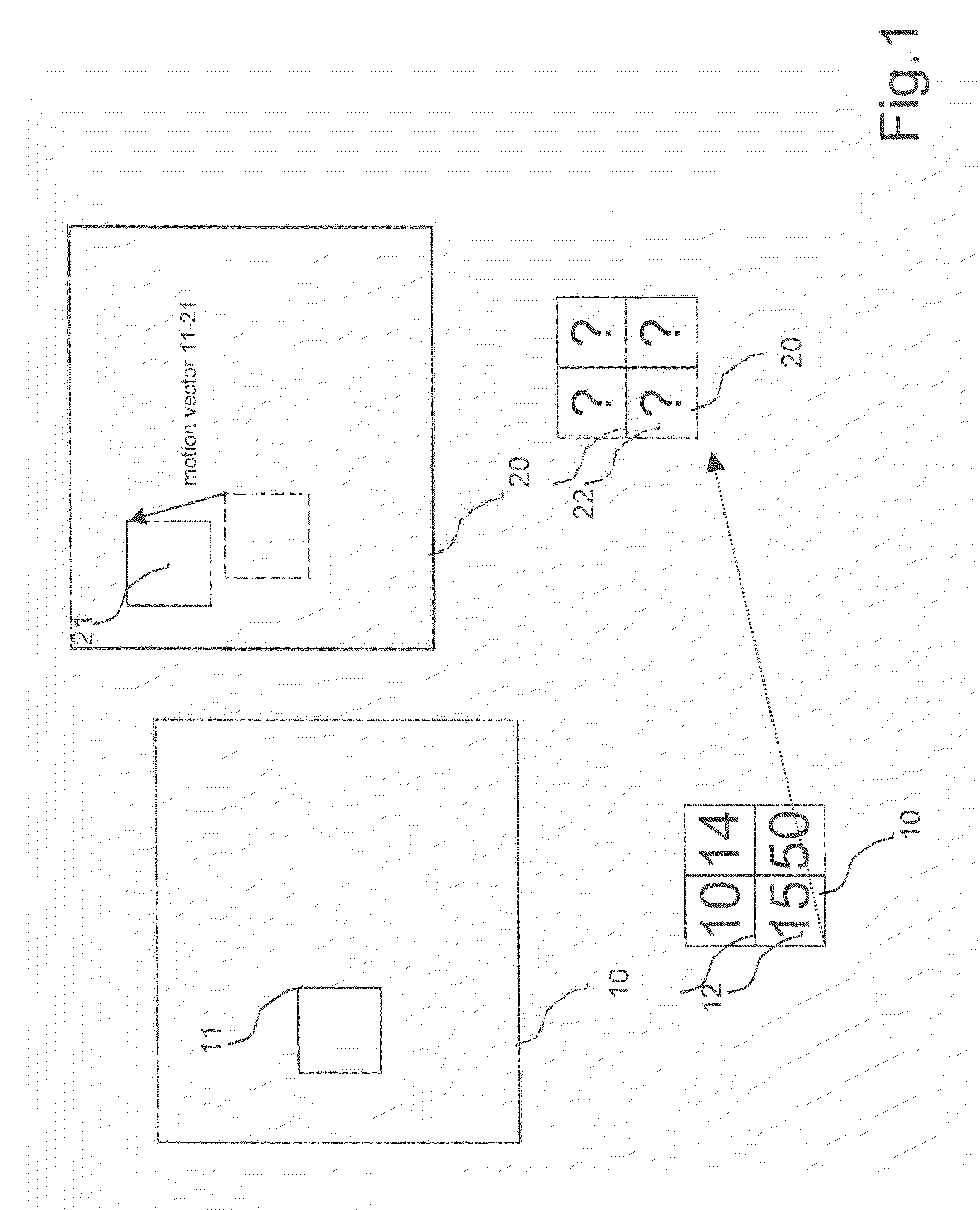
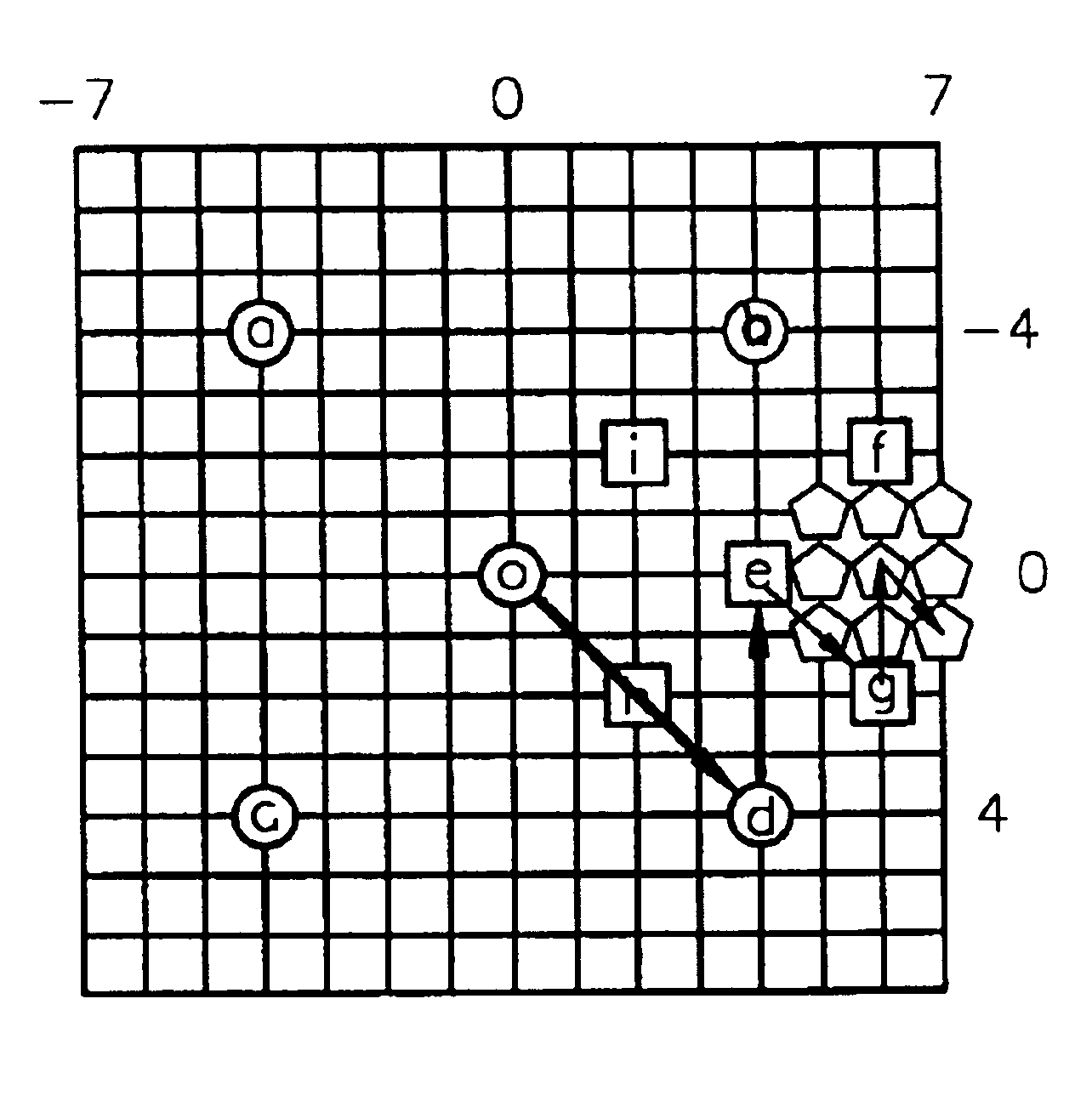
Systems and methods for tracking objects in video sequences
InactiveUS6901110B1Reduce computational overheadPrevent steppingImage enhancementTelevision system detailsMotion vectorMean difference
A method for tracking one or multiple objects from an input video sequence allows a user to select one or more regions that contain the object(s) of interest in the first and the last frame of their choice. An initialization component selects the current and the search frame and divides the selected region into equal sized macroblocks. An edge detection component computes the gradient of the current frame for each macroblock and a threshold component decides then which of the macroblocks contain sufficient information for tracking the desired object. A motion estimation component computes for each macroblock in the current frame its position in the search frame. The motion estimation component utilizes a search component that executes a novel search algorithm to find the best match. The mean absolute difference between two macroblocks is used as the matching criterion. The motion estimation component returns the estimated displacement vector for each block. An output component collects the motion vectors of all the predicted blocks and calculates the new position of the object in the next frame.
Owner:SONY CORP
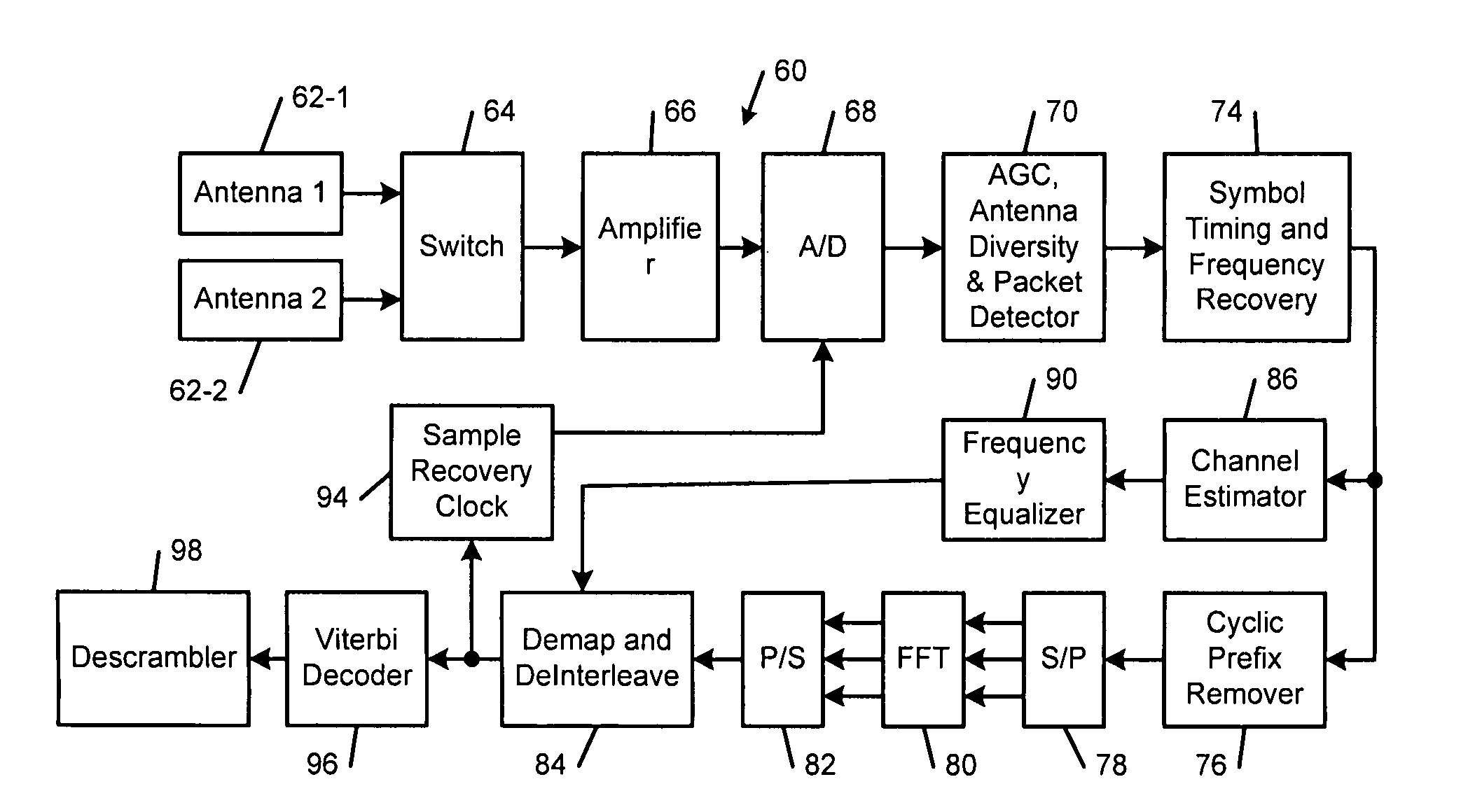
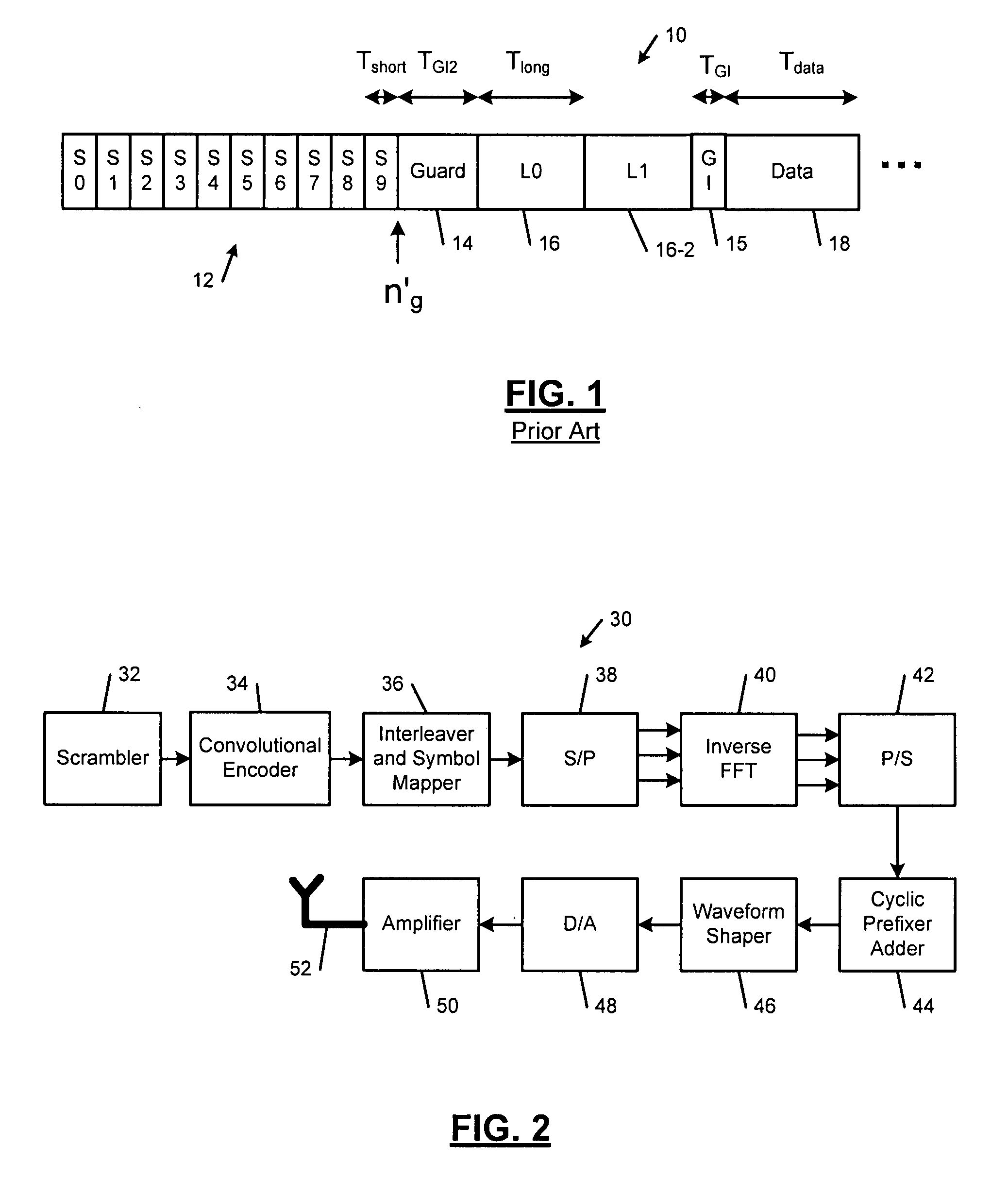
Method and apparatus for acquistion and tracking of orthogonal frequency division multiplexing symbol timing, carrier frequency offset and phase noise
InactiveUS7532693B1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsOrthogonal multiplexPhase noiseCarrier frequency offset
A method for estimating symbol timing of a guard interval in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing receiver of a wireless local area network comprises receiving a preamble including a plurality of short training symbols; sampling said short training symbols of said preamble at a first rate; correlating a first short training symbol with a second short training symbol that is adjacent to said first short training symbol and generating a correlation signal; normalizing said correlation signal to generate a normalized correlation signal; and calculating a mean absolute difference of said normalized correlation signal.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
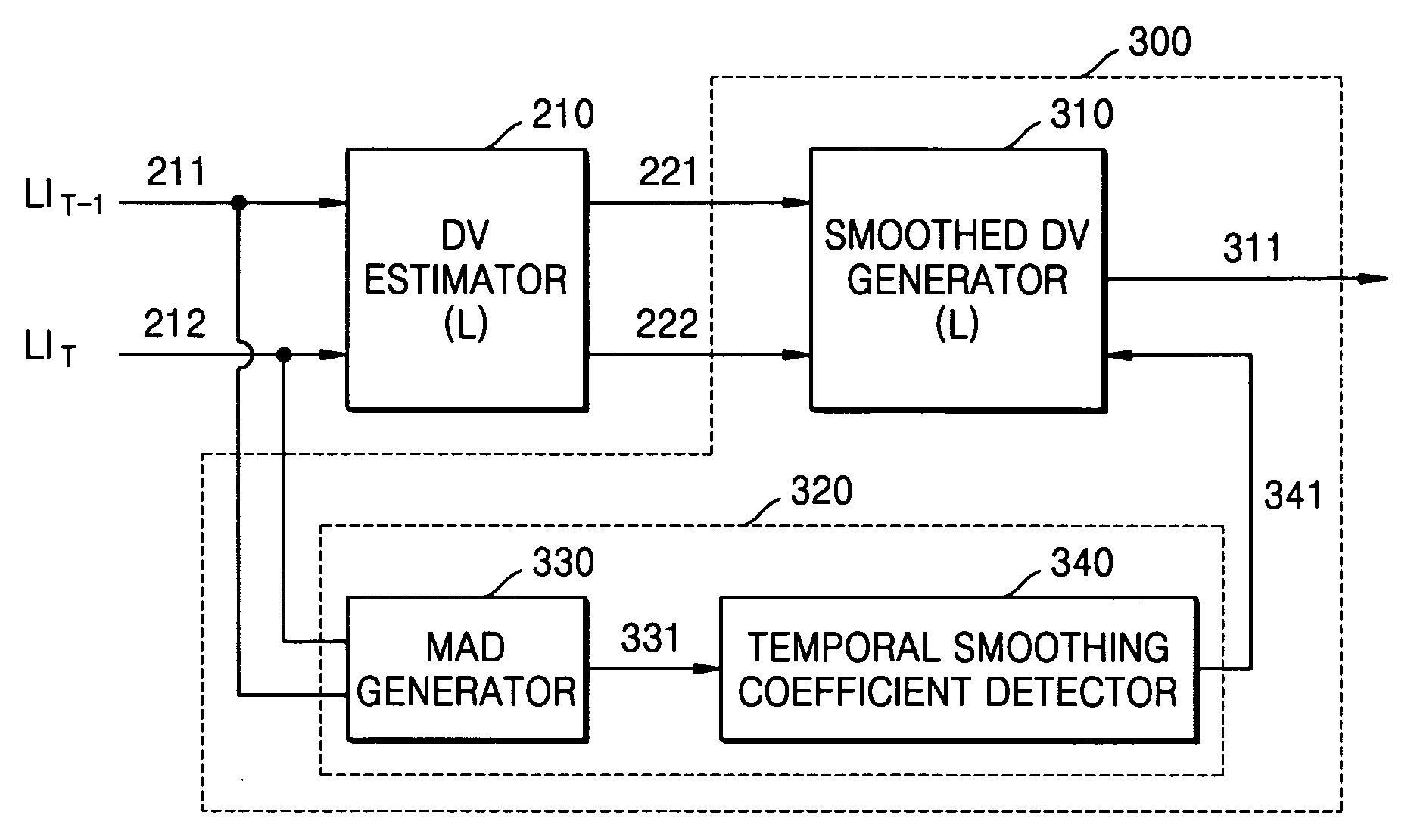
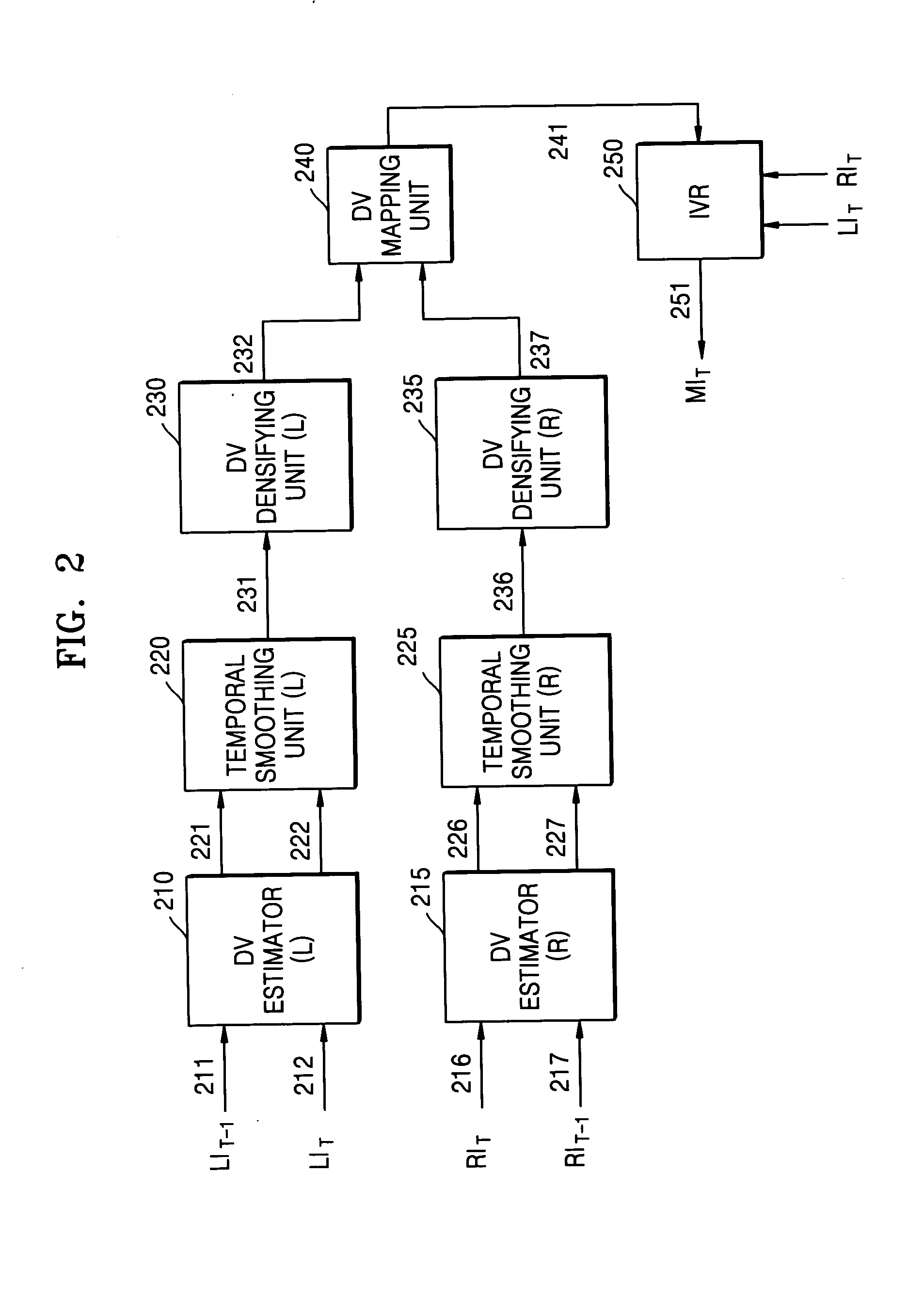
Temporal smoothing apparatus and method for synthesizing intermediate image
InactiveUS20050105610A1Quality improvementTelevision system detailsImage enhancementParallaxIntermediate image
A temporal smoothing apparatus and method for synthesizing an intermediate image, the apparatus including a disparity vector estimator which receives a previous image and a present images and generates a previous disparity vector and a present disparity vector for every image block of a predetermined size, and a temporal smoothing unit which receives the previous and present images and the previous and present disparity vectors and generates a temporally-smoothed disparity vector. The temporal smoothing unit generates a distinct temporally-smoothed disparity vector for each frame on the basis of a mean absolute difference (MAD) between the previous image and the present image, so that a flickering phenomenon of an intermediate image can be removed without deterioration of image quality by adaptively performing a temporal smoothing process in accordance with types of an image.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
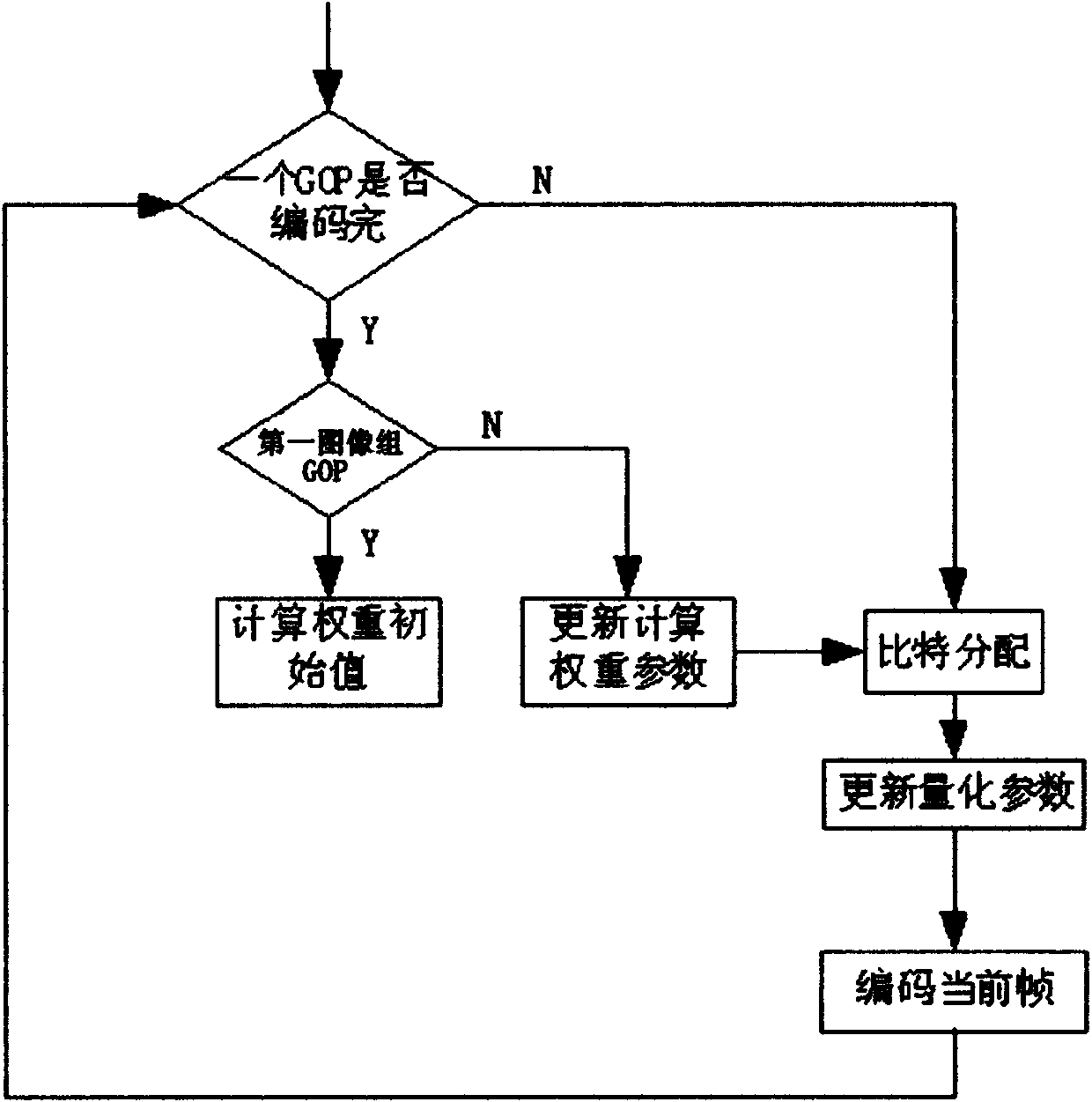
H.264 code rate control method
InactiveCN101895759AImprove smoothnessReduce occupancyTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationImaging qualityVideo image
The invention discloses an H.264 code rate control method which belongs to the technical field of video coding. The prior method is realized in a way that: the weighted sum of the mean difference of image gray histograms and the mean absolute error rate of image brightness components is used as a frame complexity factor, and the target bit number of the current coded frame is determined according to the complexity factor. On the basis of the prior method, the method of the invention considers the effects of the characteristics of the coded frames on the control on the code rate of the current frame, introduces an adjustment factor, and dynamically adjusts quantization parameters and optimizes the rate distortion by using the adjustment factor. The method can accurately control the code rate and obtain better image quality at the same time. The method also well inhibits the interframe quality fluctuations, thereby enhancing the smoothness of video images and keeping a lower occupancy rate of an encoder buffer area.
Owner:常熟市广播电视总台
Migration classification learning method for maintaining sparse structure of image classification
ActiveCN107895177ASolve unsatisfactory defectsImprove performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionSparse learningStructural risk minimization
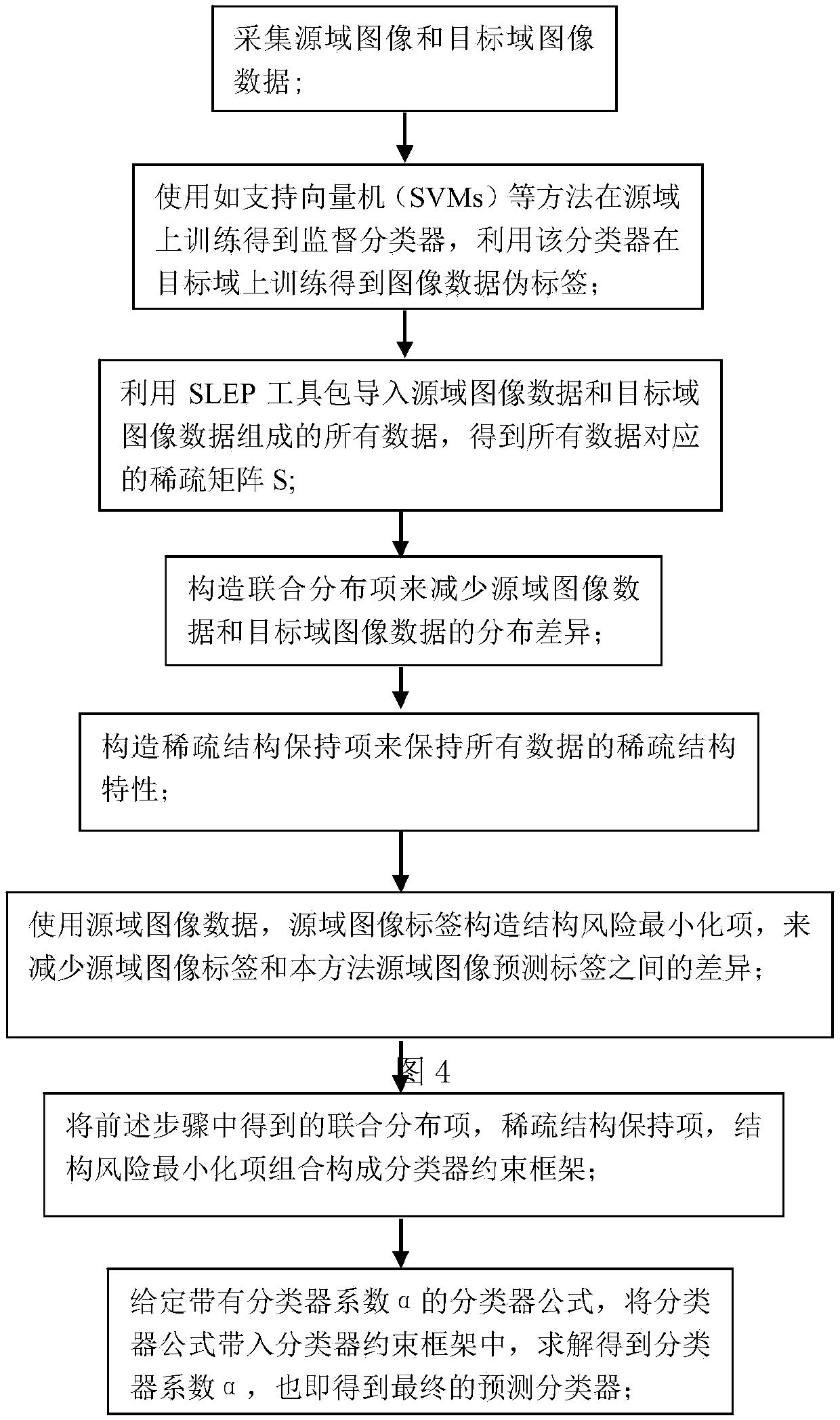
The invention discloses a migration classification learning method for maintaining a sparse structure of image classification. The method includes the steps of finding two different source and targetdomains with similar distribution, the source domain containing label data, firstly, training a classification classifier on the source domain by using a supervised classification method, and predicting a pseudo label of target domain data by using the classifier; secondly, constructing edge distribution and conditional distribution terms of the source and target domain data respectively by usingthe maximum mean difference, and combining the both to form a joint distribution term; thirdly, constructing a sparse representation matrix S on all the data by using an effective projection sparse learning toolkit, to construct a sparse structure preserving term; fourthly, constructing a structural risk minimization term by using the structural risk minimization principle; and fifthly, combiningthe structural risk minimization term, the joint distribution term, and the sparse structure preserving term to construct a uniform migration classification learning framework, and substituting into the framework using a classification function representation theorem including a kernel function to obtain a classifier that can be finally used to predict the target domain category.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Inter-frame module selecting method based on three-dimensional wavelet video code
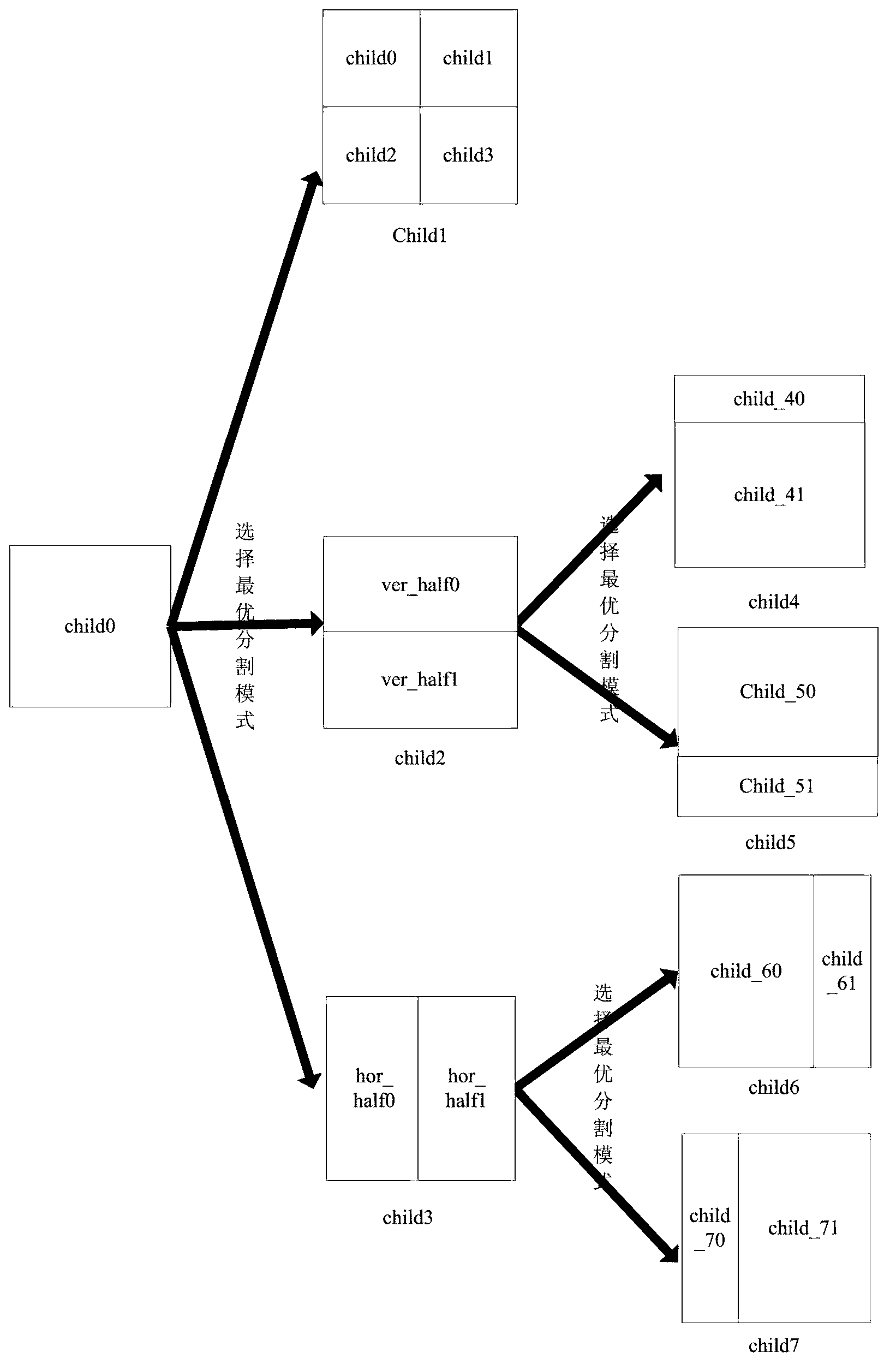
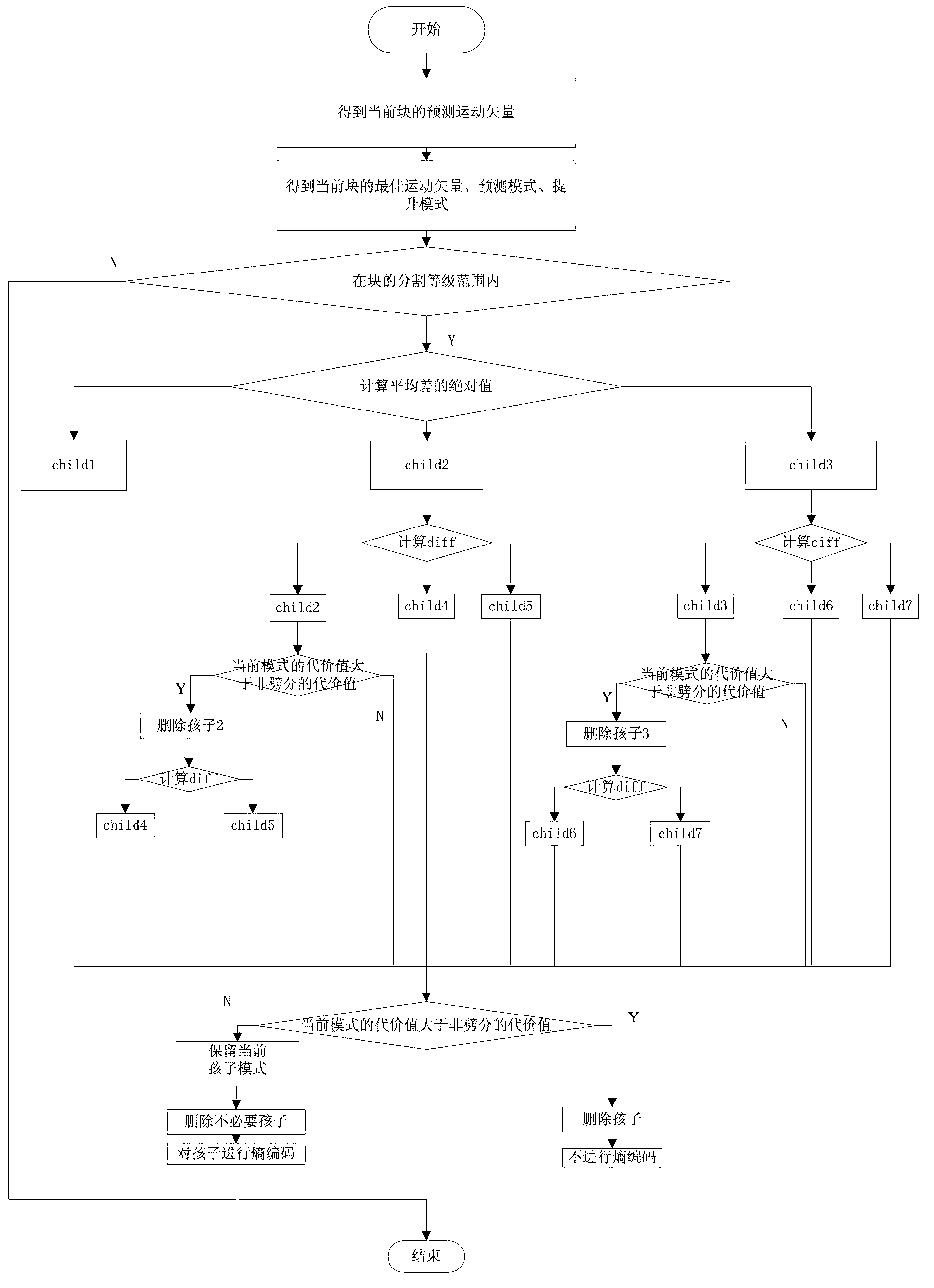
InactiveCN102801976AImprove matching accuracyNo added time complexityTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationRound complexityRelationship - Father
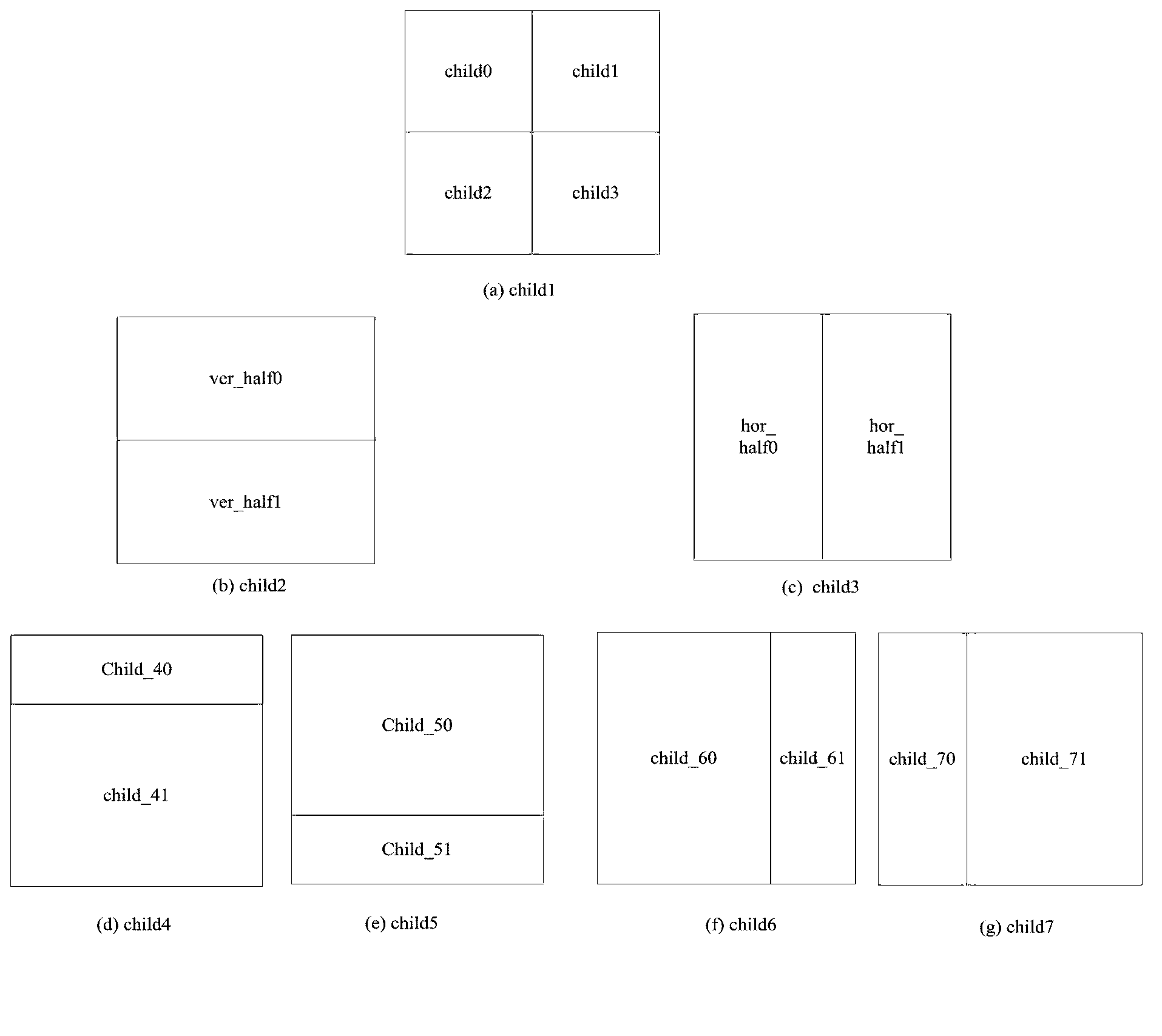
The invention discloses an inter-frame module selecting method based on a three-dimensional wavelet video code, comprising the following steps of: step 1), utilizing mean absolute difference values MAD (Mean Absolute Difference), MADV (Vertical Mean Absolute Difference) and MADH (Horizontal Mean Absolute Difference) of a father block pixel as references of texture complexity; selecting one from child types including child1, child2 and child3; if selecting the child type child1, executing step 4); otherwise, executing step 2); step 2), calculating respective mean values of two sub-blocks of the corresponding child type and calculating the difference of the two mean values; step 3), selecting a specific binary tree dividing module according to the mean value differences; and step 4), finally, comparing a father block movement compensation value with the sum of child movement compensation values; if the father movement compensation value is small, not carrying out block division; and if the child movement compensation values are small, keeping the corresponding child type and carrying out the block division. According to the inter-frame module selecting method disclosed by the invention, a mixed quartic tree and binary tree dividing method is adopted, the flexibility of the block division is improved; and texture threshold value information is adopted so that an amount of time complexity of an algorithm can not be increased.
Owner:INFORMATION RES INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
Method for monitoring and diagnosing indoor air quality (IAQ) sensor on line
ActiveCN102393882ATimely maintenanceTimely calibrationSpecial data processing applicationsIndoor air qualityMean difference
The invention discloses a method for monitoring and diagnosing an indoor air quality (IAQ) sensor on line. In the invention, on the base of the virtual model of an IAQ sensor, the IAQ sensor is monitored and diagnosed on line through a control graph, wherein the control graph can monitor the mean difference and variance between an IAQ parameter value predicted by the virtual model of the IAQ sensor and an IAQ parameter value measured by the sensor. By the model, according to the invention, as the accurate, stable and reliable virtual model of the IAQ has the functions of monitoring the IAQ sensor on line, initiatively finding potential faults, timely maintaining and calibrating the sensor, the invention has the advantages that the cost is low, the initiative is good, and the pertinence is strong.
Owner:JIZHONG ENERGY SAVING TECH SUZHOU
Face deception detection method based on domain adaptive learning and domain generalization
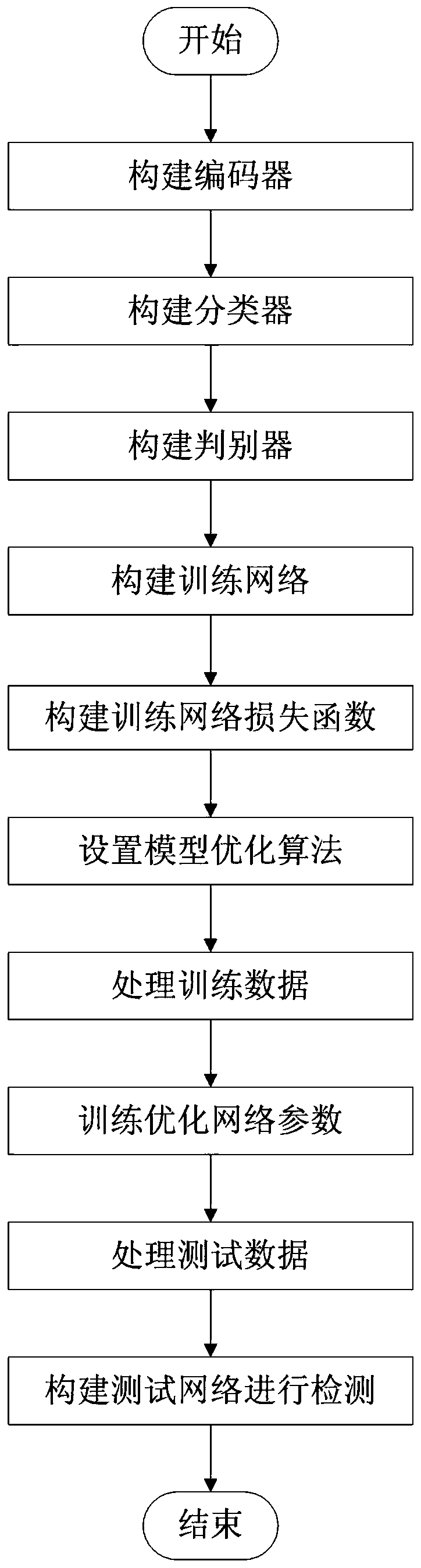
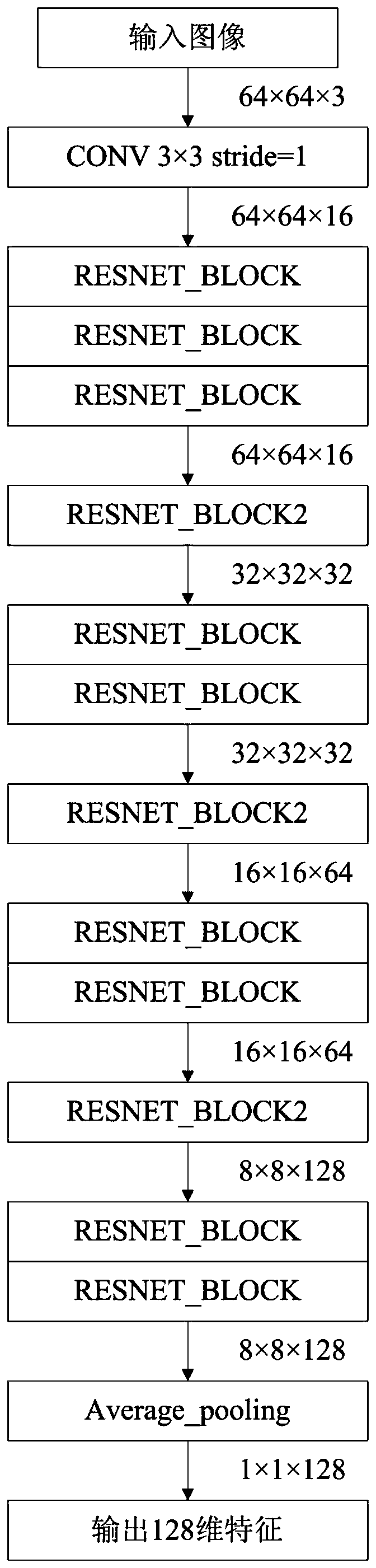
ActiveCN110309798AImprove generalization abilityEasy to detectCharacter and pattern recognitionDiscriminatorPattern recognition
The invention discloses a face cheating detection method based on domain adaptive learning and domain generalization. The face cheating detection method mainly comprises the following steps: constructing an encoder based on a deep residual network; constructing a classifier for detecting face cheating; constructing a discriminator which is used for guiding characteristics to accord with Laplace distribution; forming a training network by using the three parts; constructing a loss function of network training; setting a model optimization algorithm; processing the training data set sample imageto change the size; training and optimizing network parameters; processing the test image to change the size; and carrying out face cheating detection by using the trained encoder and classifier. According to the invention, common features of source domain training data are extracted through a maximum mean difference MMD training encoder; and meanwhile, by combining AAE technology of an anti-autoencoder. The characteristics conform to Laplace distribution, the generalization performance of the detection method is further improved, and the detection performance of the method on face spoofing attacks under complex conditions in practical application is effectively improved.
Owner:CHINA-SINGAPORE INT JOINT RES INST
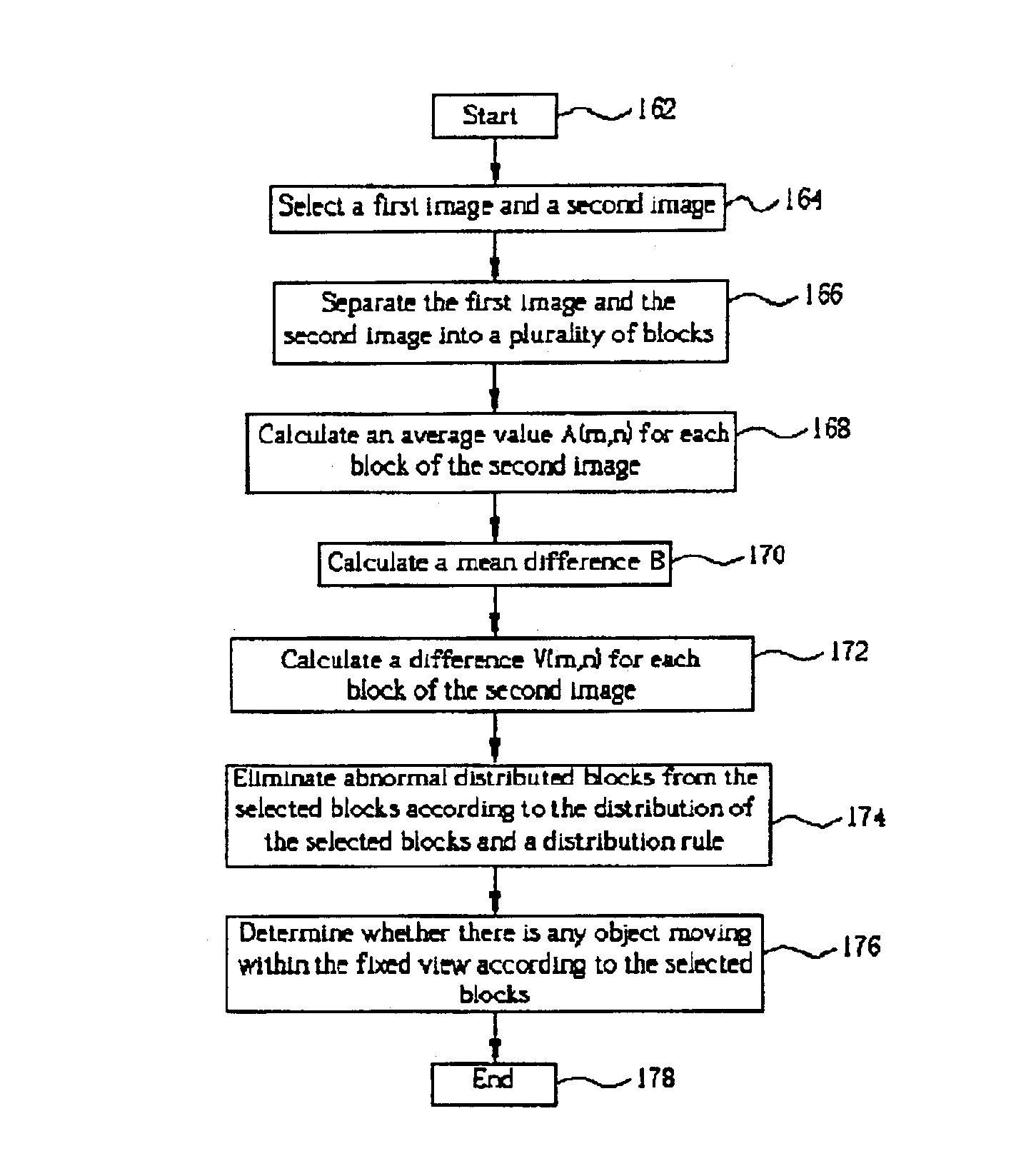
Method for detecting moving objects by comparing video images
A method detects activity within a fixed view by comparing first and second images. The first and second images respectively include a plurality of blocks, and each of the blocks having a plurality of pixels. The method including: calculating an average value A for each block of the second image, each of the average values A is equal to an average of differences between pixels of one of the blocks of the second image and pixels of a corresponding block of the first image; calculating a mean difference B between average pixel values of the first and second images; calculating a difference V between average value A and mean difference B for each block of the second image, and selecting blocks of the second image that have corresponding differences V greater than a threshold value; and determining whether there is any object moving within the fixed view according to the selected blocks.
Owner:HUPER LAB
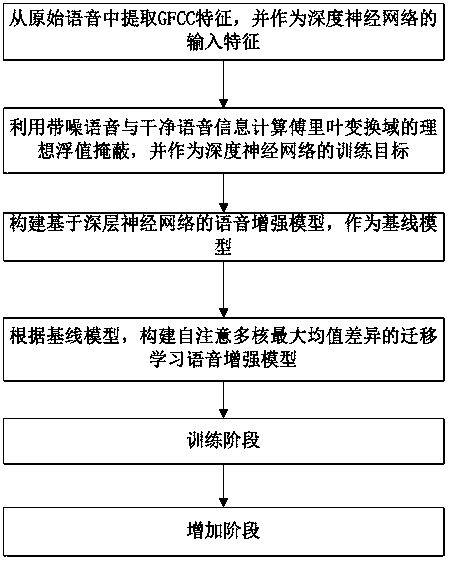
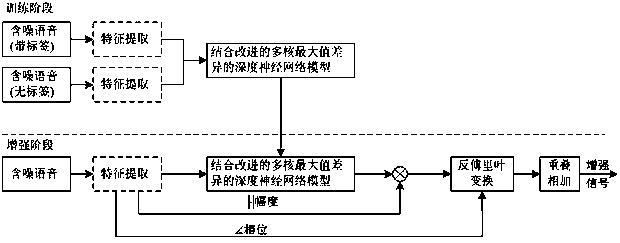
Self-attention multi-core maximum mean difference-based transfer learning speech enhancement method
ActiveCN110111803AImprove feature effectivenessImprove robustnessSpeech analysisFloat ValueSelf attention
The invention discloses a self-attention multi-core maximum mean difference-based transfer learning speech enhancement method, which comprises the following steps: extracting GFCC features from original speech and using the GFCC features as input features of a deep neural network; calculating ideal floating value masking of Fourier transform domain by using noisy speech and clean speech information, and using the ideal floating value masking as the training target of the deep neural network; building a speech enhancement model based on deep neural network; building a self-attention multi-coremaximum mean difference-based transfer learning speech enhancement model; training the self-attention multi-core maximum mean difference-based transfer learning speech enhancement model; inputting frame-level features of the noisy speech in the target domain, and rebuilding enhanced speech waveform. By adding a self-attention algorithm to the front end of the multi-core maximum mean difference andby minimizing the multi-core maximum mean difference between features noticed by the source field and features noticed by the target domain, transfer learning of the unlabeled target domain is realized, and the speech enhancement performance is improved. The method of the invention has a good application prospect.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
Block based codec friendly edge detection and transform selection
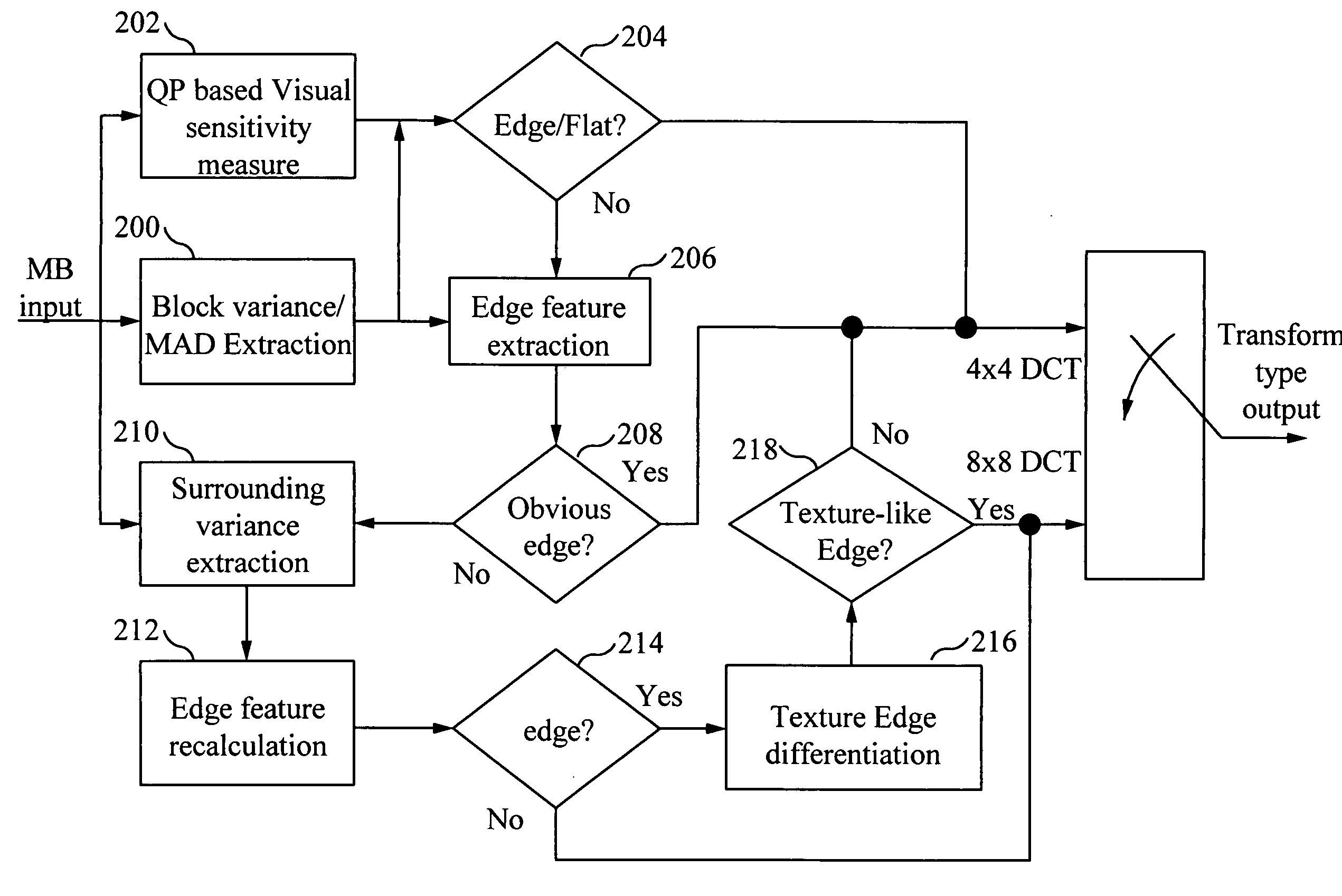
ActiveUS20090262800A1Improve visual qualityEfficient and accurate edge detectionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMean differenceRound complexity
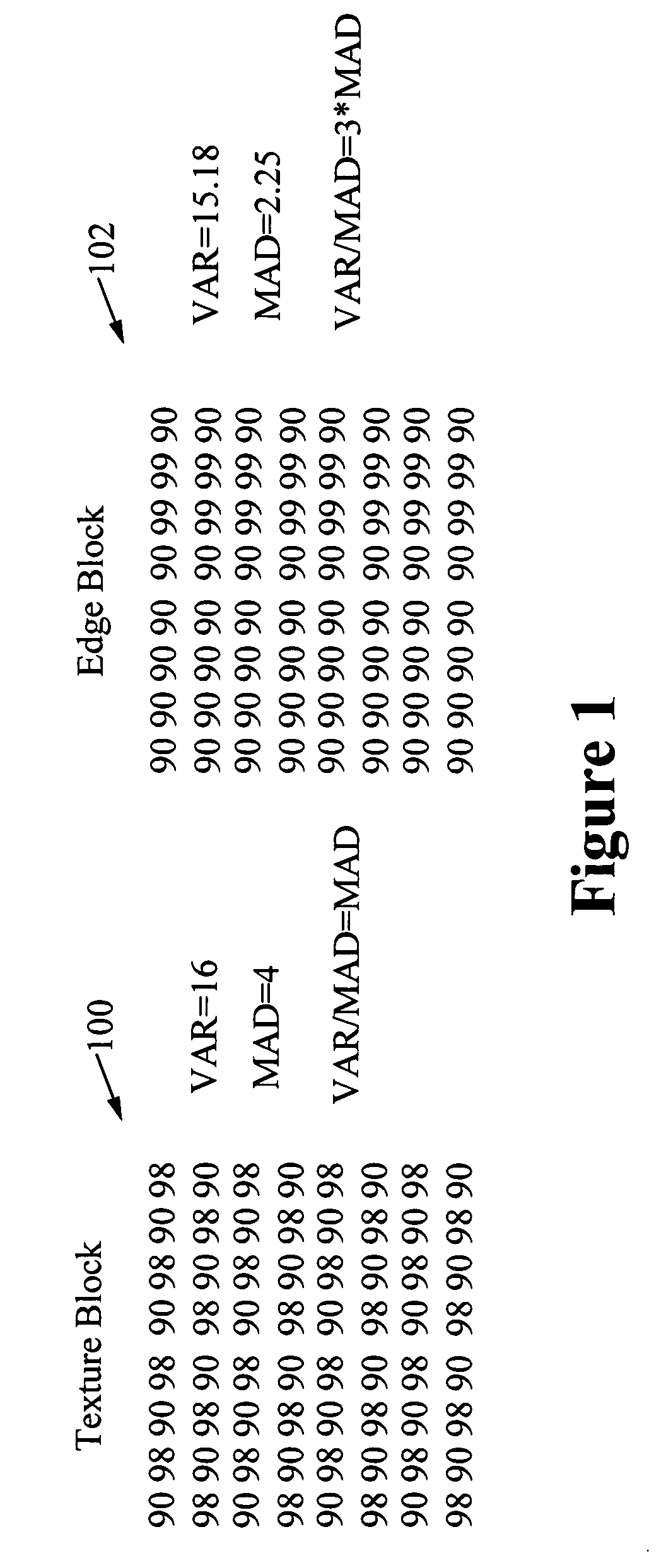
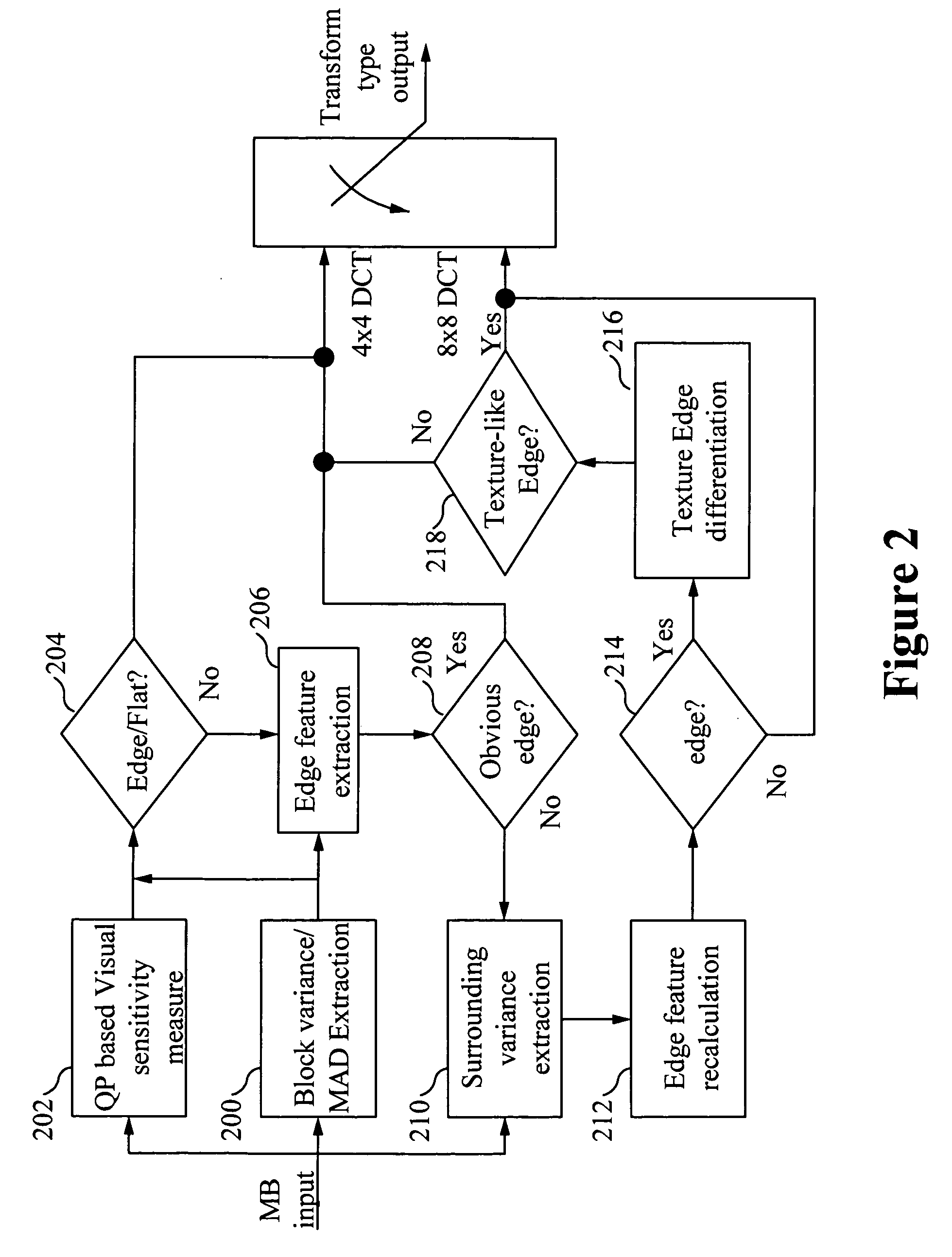
Low complexity edge detection and DCT type selection method to improve the visual quality of H.264 / AVC encoded video sequence is described. Encoding-generated information is reused to detect an edge macroblock. Variance and Mean Absolute Difference (MAD) of one macroblock shows a certain relationship that is able to be used to differentiate the edge macroblock and the non-edge macroblock. Also, the variance difference of neighbor macroblocks provides a hint for edge existence. Then, a block-based edge detection method uses this information. To determine the DCT type for each block, the detected edges are differentiated as visual obvious edge, texture-like edge, soft edge and strong edge. 8×8 DCT is used for texture-like edges and the 4×4 DCT is used for all the other edges. The result is an efficient and accurate edge detection and transform selection method.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Spatial enhancement layer code rate control realization method for scalable video coding
InactiveCN102186084ATelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationTime domainComputer architecture
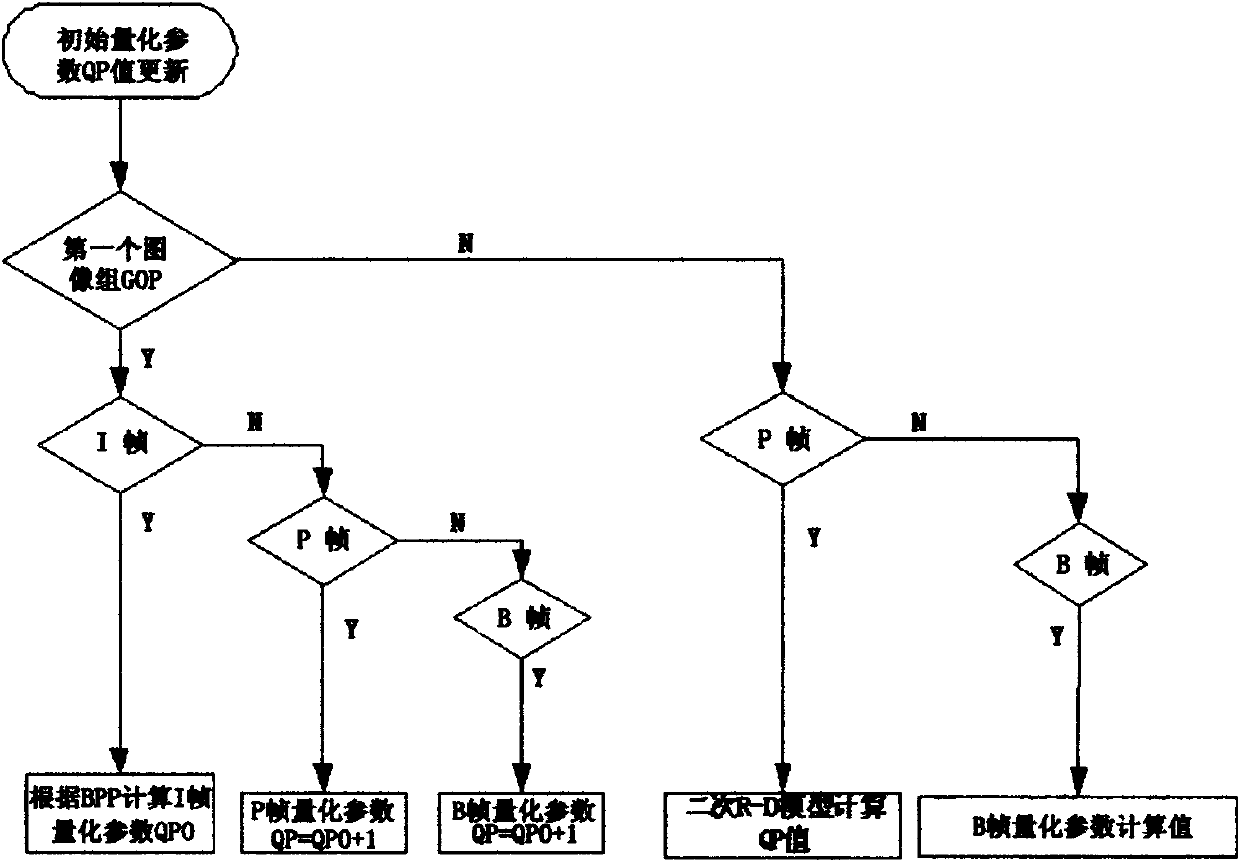
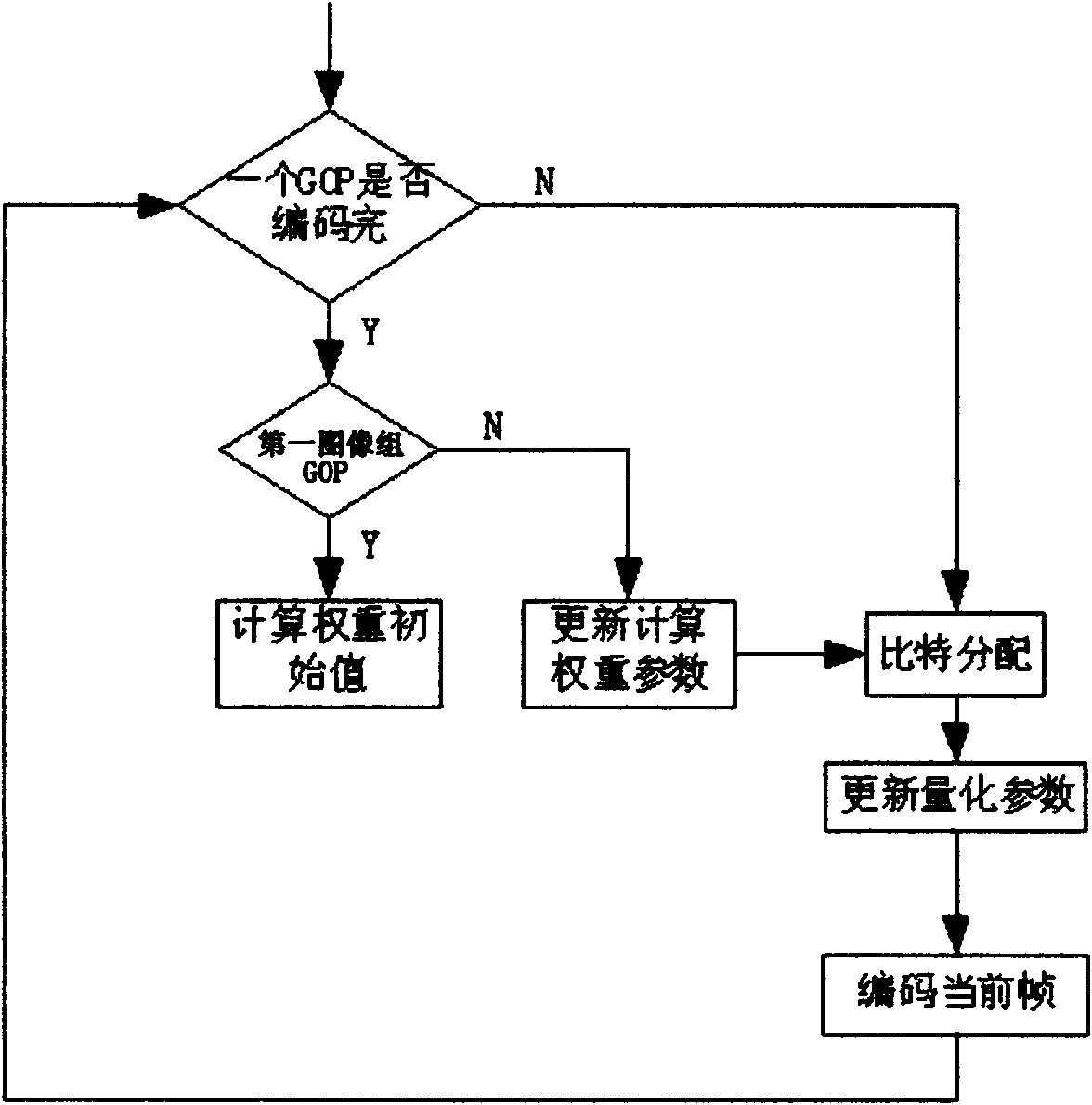
The invention discloses a spatial enhancement layer code rate control realization method for scalable video coding. The method comprises the following steps of: adaptively setting initial quantization parameter (QP) values of I, P and B frames of a first code; calculating the coding complexity and a mean absolute difference (MAD) value of each frame according to an actual coded bit number; after the coding of a group of pictures (GOP) is finished, calculating the weight of the image frame on temporal and spatial levels according to the actual coded bit number of the whole GOP, the coding complexity of each frame, and the temporal and spatial levels of each frame; and for a key frame, calculating quantization parameters and performing coding by utilizing an allocated bit number and a secondary rate-distortion (R-D) model, and for a non-key frame, determining the QP of the non-key frame by utilizing the QPs of the two key frames closest to the non-key frame and a time domain to which the two key frames closest to the non-key frame belong. By the spatial enhancement layer code rate control realization method for the scalable video coding, spatial enhancement layer code rate control for the scalable video coding can be realized, and the shortcoming of only basic layer code rate control of the scalable video coding is overcome.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS & INFORMATION ENG IN
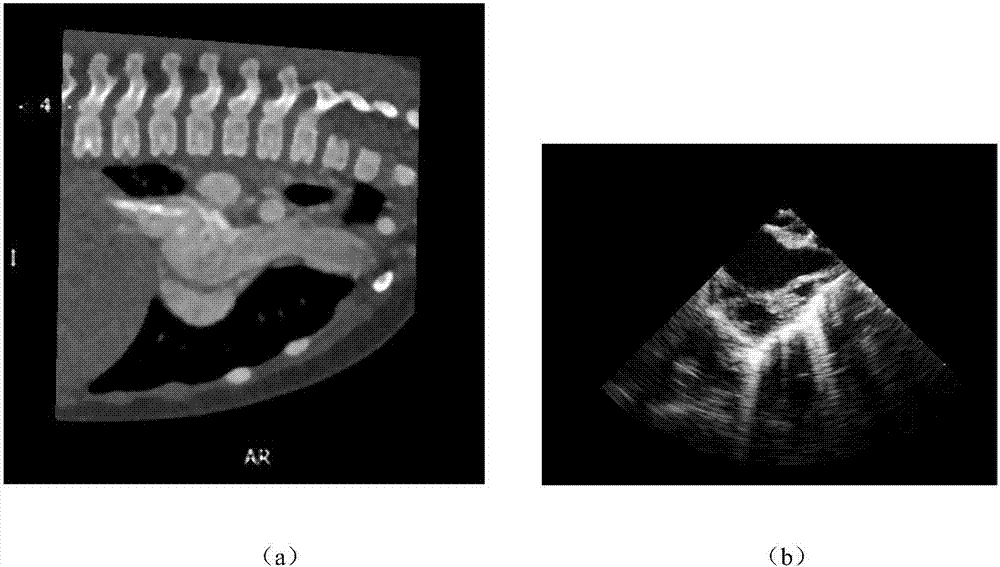
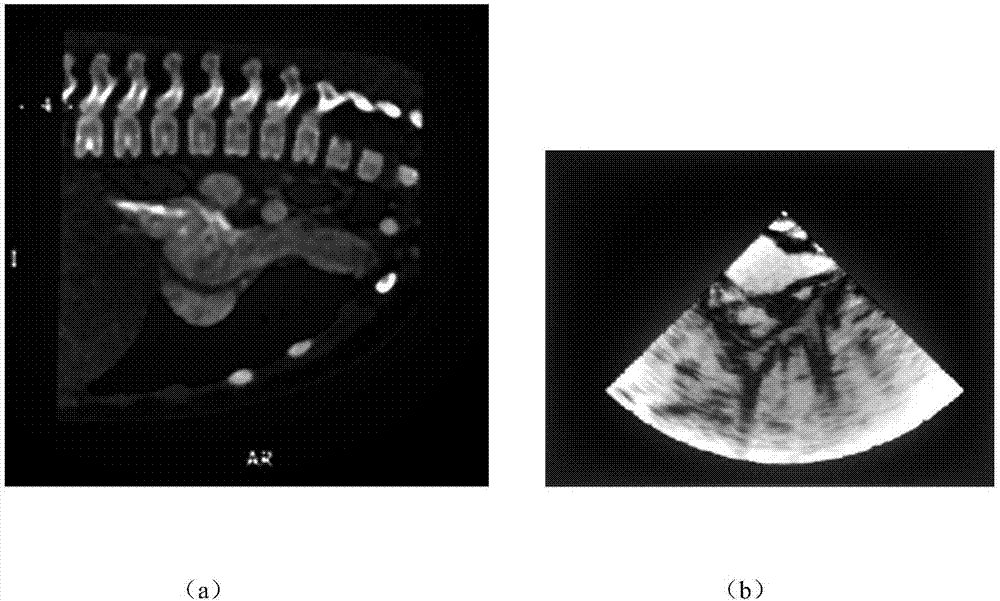
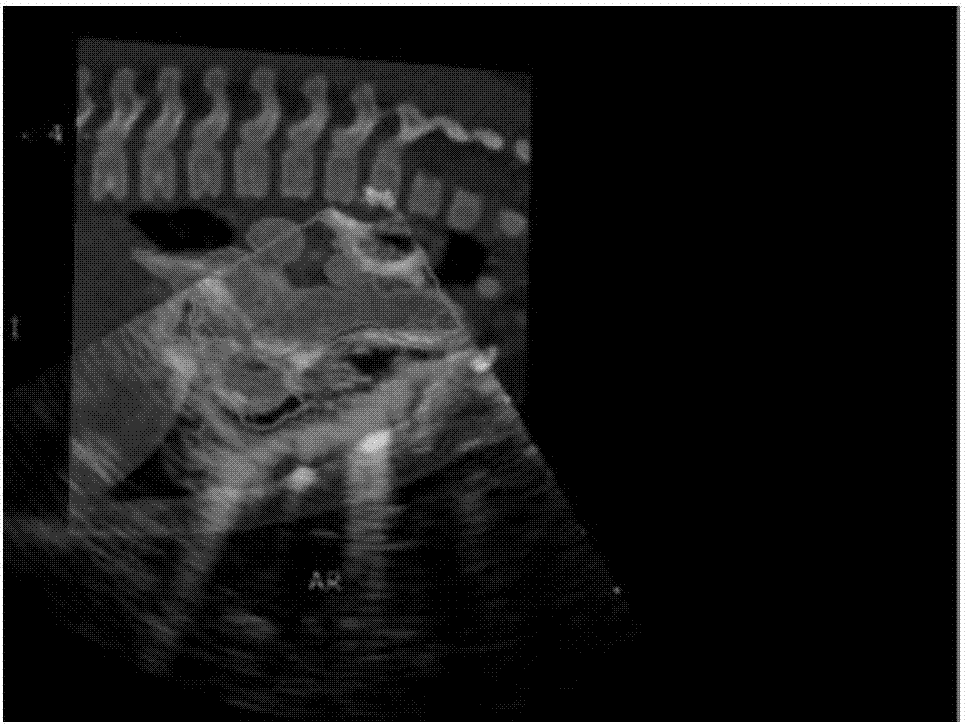
Cardiac CT and ultrasound image registration method based on salient region area matching
The invention discloses a cardiac CT and ultrasound image registration method based on salient region area matching, and the method mainly solves a problem of low registration precision and low speed in the prior art. The method comprises the steps: 1) pre-processed CT and ultrasound images respectively serves as a reference image and a floating image, and a gray-scale feature pyramid model and a neighbourhood mean difference feature pyramid model of the two images are respectively established; 2) saliency maps of the reference image and the floating image are respectively generated based on above two pyramid models, and the saliency maps are binarized; 3) for the binarized results, regions of interest are extracted according to region area features, coarse registration based on region centroid distance and precise registration based on ICP algorithm are performed on the regions of interest, and registration parameters are obtained; 5) according to the registration parameters, rotation and translation transformation is performed on the floating image, and a registration result is obtained. According to the invention, the method has high registration precision and fast speed and can be used for real-time registration of preoperative CT image and intraoperative ultrasound image.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
Estimation method for quick video motion
InactiveCN101009841ASmall amount of calculationImprove match rateTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationEstimation methodsMean difference
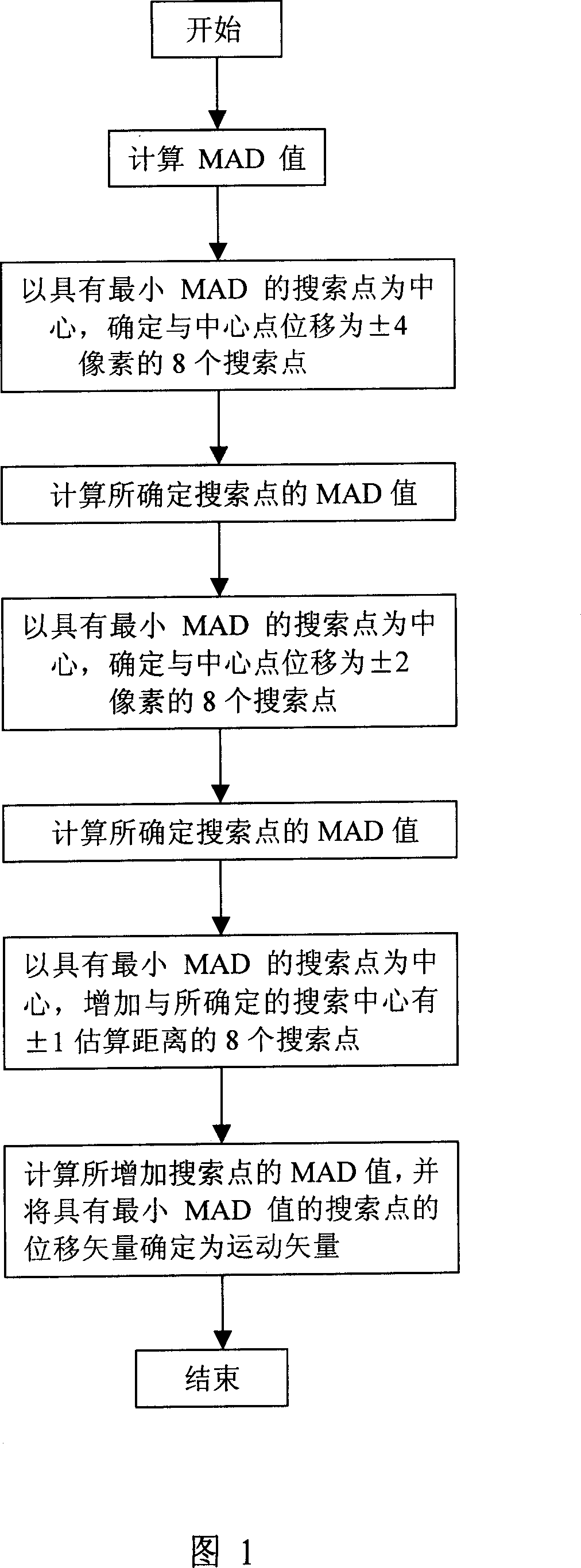
The disclosed estimation method for video fast motion comprises: (a) calculating the search block center point and the MAD of every vertex of large and small diamonds with the center point as center; and (b) according to the position of minimal MAD point, gradual reducing search area for fine search. This invention reduces calculation amount on matching block greatly, special fit to hardware implementation, and can be used widely to H.264, H.261, H.263, MPEG-2 and MPEG-4 standard, etc.
Owner:无锡翔劲计算机科技有限公司
Quick point cloud registration method based on curved surface fitting coefficient features
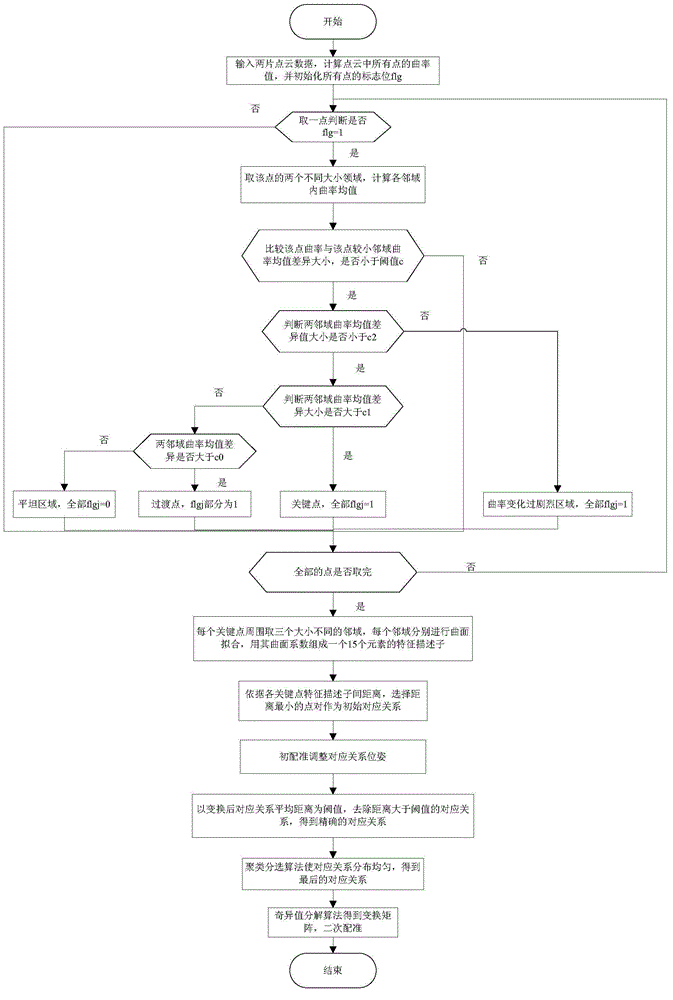
ActiveCN105046694AReduce extraction timeEvenly distributedImage analysisDetails involving 3D image dataSingular value decompositionPoint cloud
The invention discloses a quick point cloud registration method based on curved surface fitting coefficient features. Curvature mean differences of neighborhoods of different sizes are compared, points whose differences exceed a set threshold are selected to serve as key points, and key point candidate points are adaptively selected according to the differences. Multiple neighborhoods are selected at the key point for curved surface fitting, and a curved surface coefficient serves as a feature descriptor for the key point. Through comparing distances between key point feature descriptors, a key point pair with the smallest distance is selected to serve as an initial corresponding relation. A transformation matrix obtained through the initial corresponding relation is used for adjusting positions and orientations of the corresponding relation for basic coincidence, a distance threshold is set, and corresponding relations whose distances are larger than the threshold are removed. Then, a clustering method is used for enabling the corresponding relations to be uniformly distributed, a covariance matrix for the corresponding relations after optimization is calculated, and singular value decomposition is then carried out on the covariance matrix to obtain a final transformation matrix. The method of the invention has the advantages of quick registration, high precision and good anti-noise ability.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
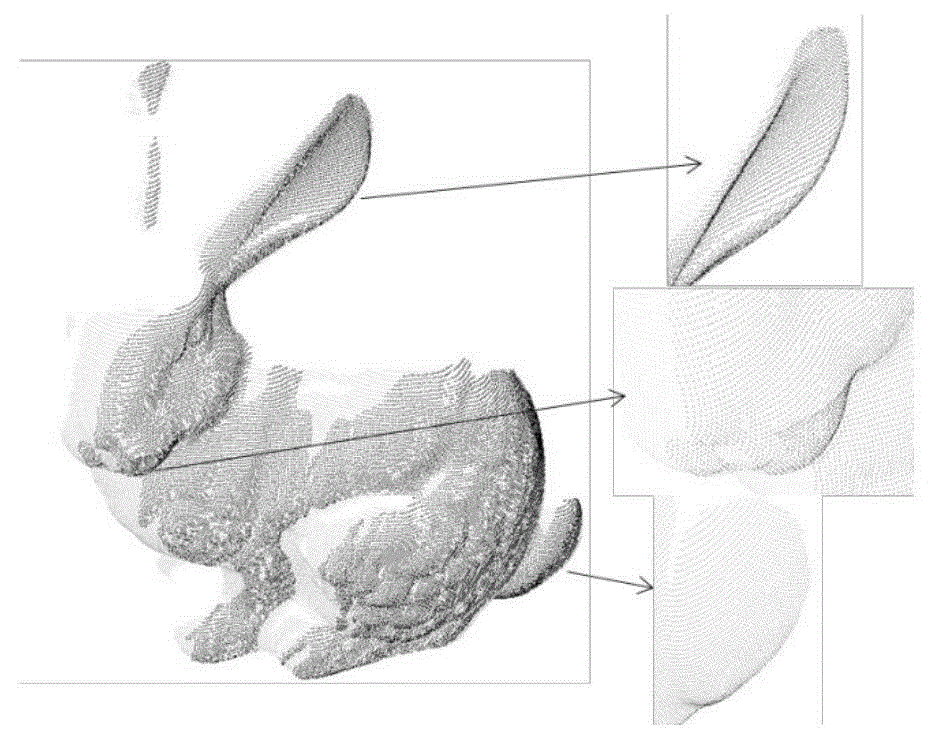
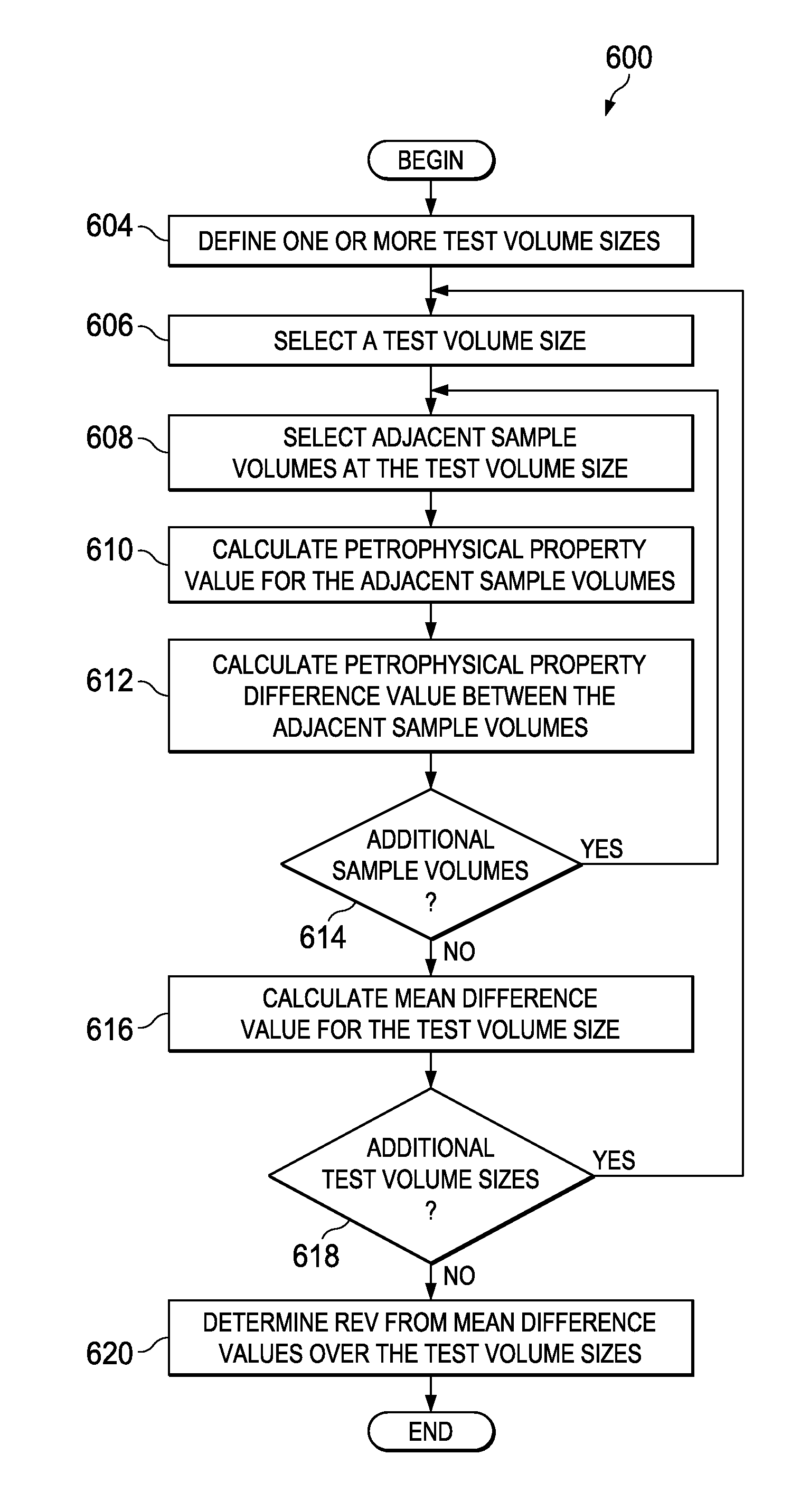
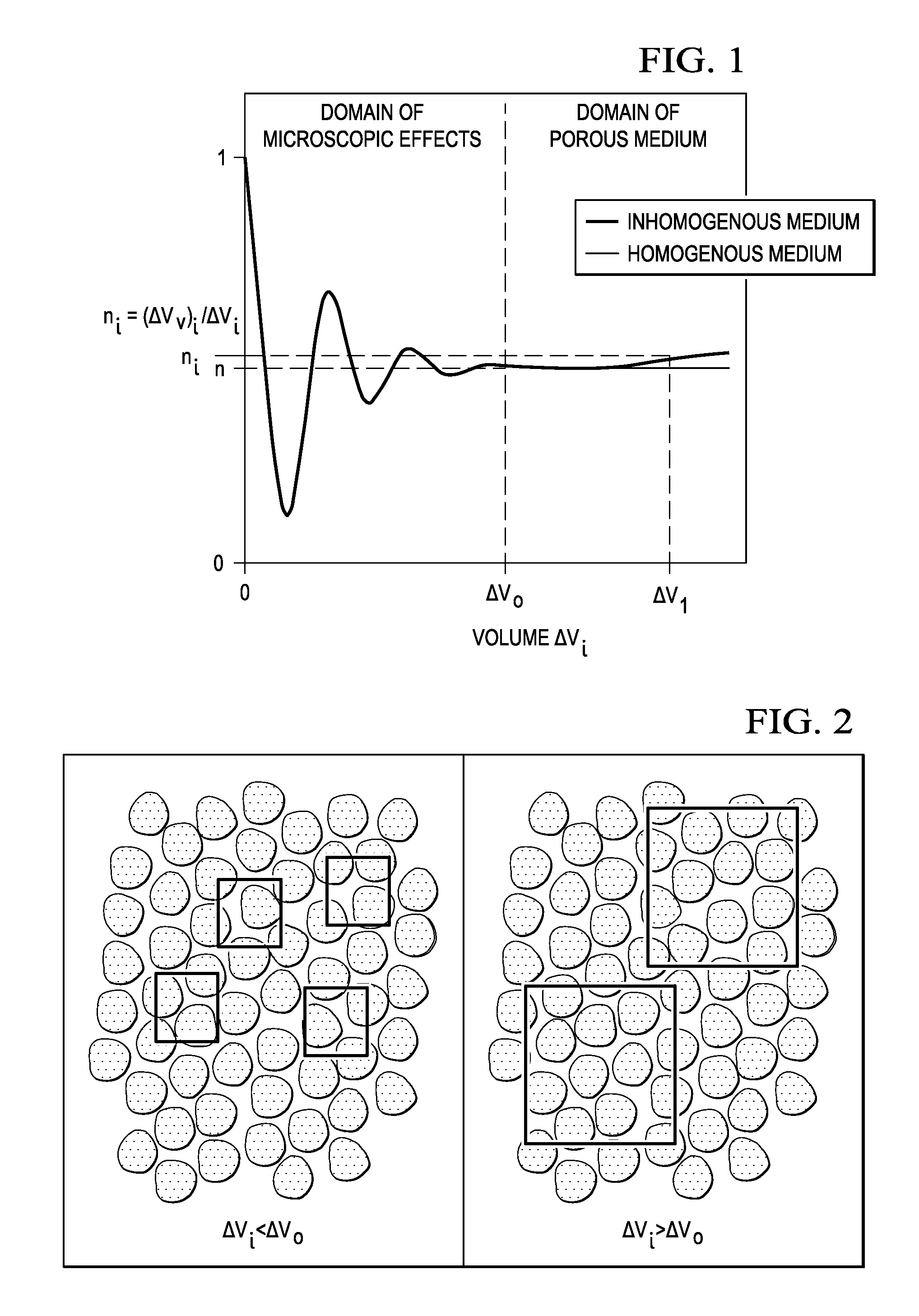
Systems and Methods for Improving Direct Numerical Simulation of Material Properties from Rock Samples and Determining Uncertainty in the Material Properties
A testing system for analyzing a 3D digital volume of a material sample. The testing system defines several test volume sizes with each test volume size including a different numbers of voxels, defining the size of portions of the 3D digital volume to analyze. For each test volume size, the testing system acquires two adjacent portions of 3D digital volume at the test volume size currently being analyzed. The testing system calculates a material property value for the two adjacent portions of the 3D digital volume, and a difference value between the two adjacent portions of the 3D digital volume. The process is repeated over the different test volume sizes. The testing system calculates mean difference values for the different test volume sizes, from which it determines a representative elementary volume.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
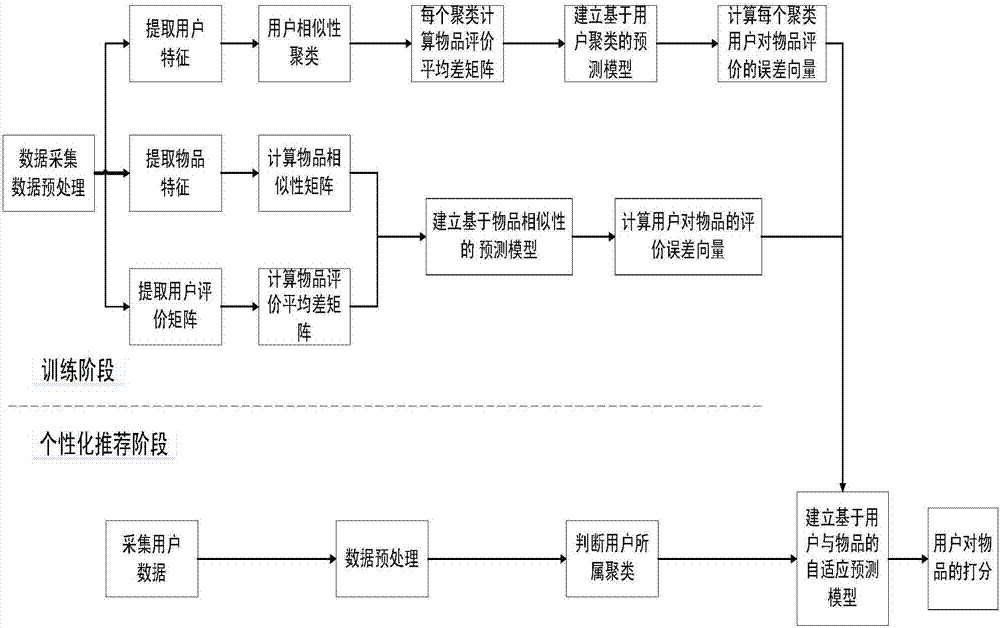
Adaptive customized recommendation method based on users and articles
InactiveCN106897911AHigh precisionImprove performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionBuying/selling/leasing transactionsPersonalizationMean difference
The invention discloses an adaptive customized recommendation method based on users and articles. The method comprises two stages of training and customized recommendation. For the training stage, firstly, data including the user personal information, user behavior characteristics and object evaluation of the users is acquired through a platform; similar users are clustered according to the user data, a mean difference matrix of the object evaluation of the users is calculated, a prediction model based on user clustering is established, and an evaluation prediction error of the model for all the objects is calculated; similarities among objects are calculated according to attributes of the objects, mean object evaluation difference of the users is calculated, a prediction model is established, an adaptive prediction model based on the users and the objects is formed. For the customized recommendation stage, firstly, user attribute clustering is determined, the adaptive prediction model integrated with the users and the objects is utilized, evaluation of the users for the objects is predicted, and the objects with high prediction evaluation are recommended to the users. The method is advantaged in that the method has adaptive capability and higher accuracy compared with a traditional customized recommendation method.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
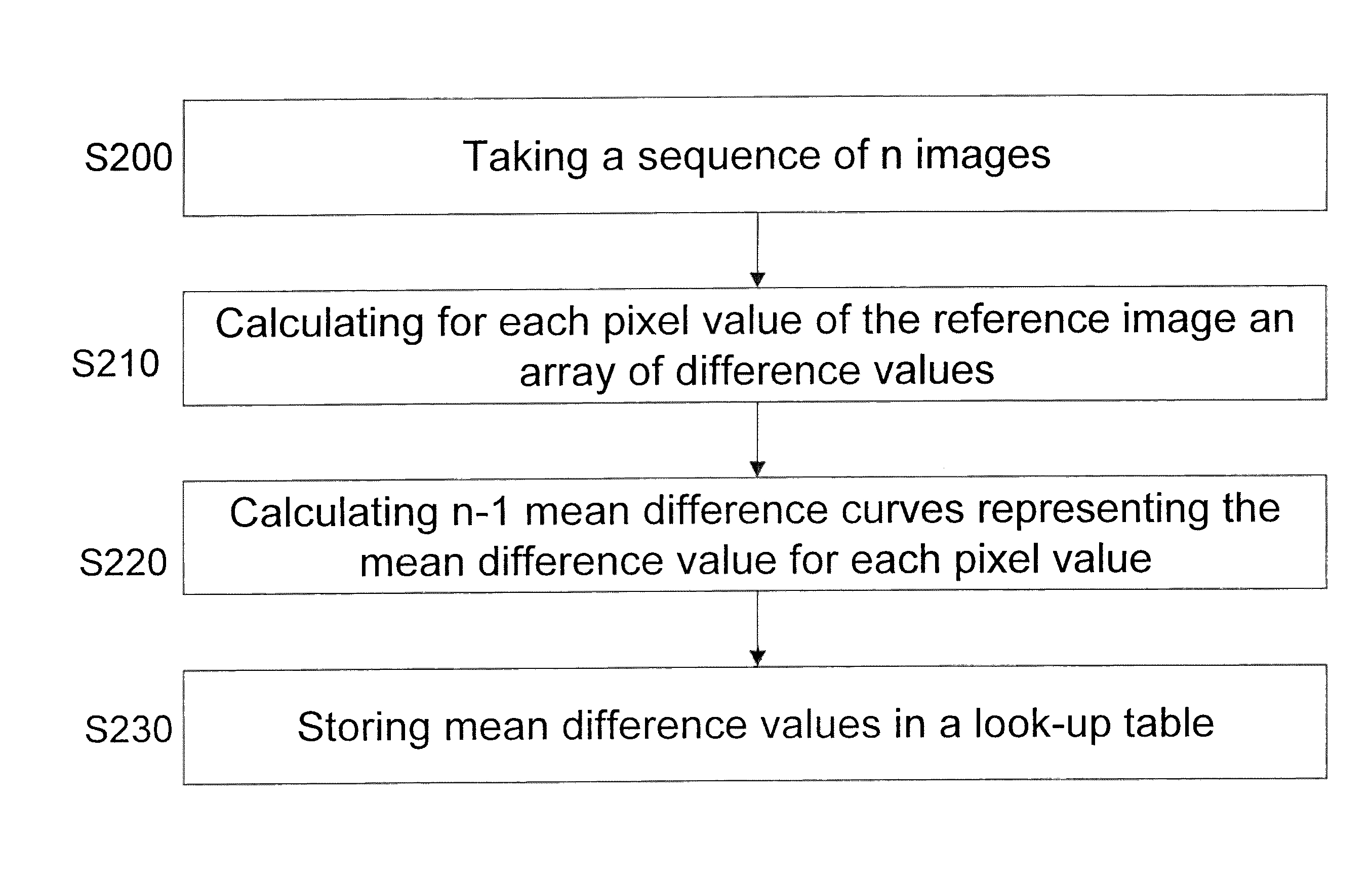
Method and unit for generating high dynamic range image and video frame
An embodiment of the invention relates to a method for High Dynamic Range (HDR) image creation by generating a mean difference curve for use in aligning the images of a sequence of images taken with different exposures, wherein the difference in exposure might derive from a difference in exposure time or a difference in aperture size. A further embodiment of the invention relates to a method for HDR image creation by generating images with different exposures from a single image. A further embodiment of the invention relates to a method for HDR video creation by generating frames with different exposures from a single frame.
Owner:SONY CORP
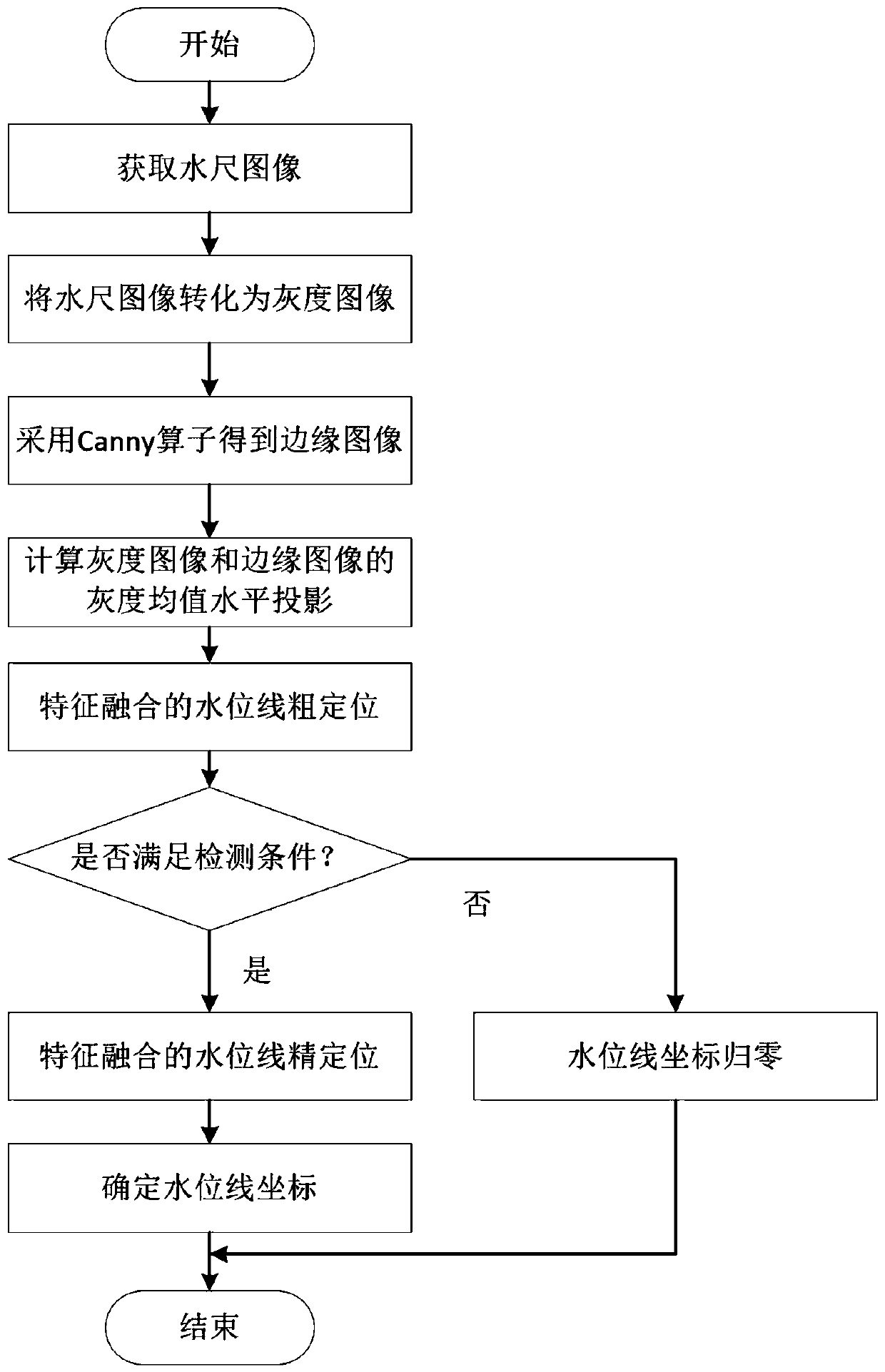
Water gauge waterline visual detection method suitable for complex illumination conditions
ActiveCN109764930AImprove robustnessImprove detection accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisMean differenceWater level
The invention discloses a water gauge water level line visual detection method suitable for complex illumination conditions. By utilizing a difference between a water gauge image and a water surface image, a gray scale mean difference of a gray image and an edge image is calculated, the maximum value of the two features is taken as an index for measuring the image difference, then a water level line detection method combining coarse positioning and fine positioning is adopted, and high robustness is achieved for water gauge water level line detection under the complex lighting conditions. According to the water gauge water level line visual detection method suitable for the complex illumination conditions, detailed information of a water gauge is provided under the condition that the images are blurred, water level line detection is performed with a single pixel as a step during the fine positioning, and the detection precision can reach a single pixel. The water gauge water level linevisual detection method is suitable for the conditions of natural illumination (daytime) and infrared illumination (nighttime), and false detections due to uneven distribution of image gray scales caused by the natural illumination and nighttime fill light can be effectively avoided.
Owner:安徽金海迪尔信息技术有限责任公司
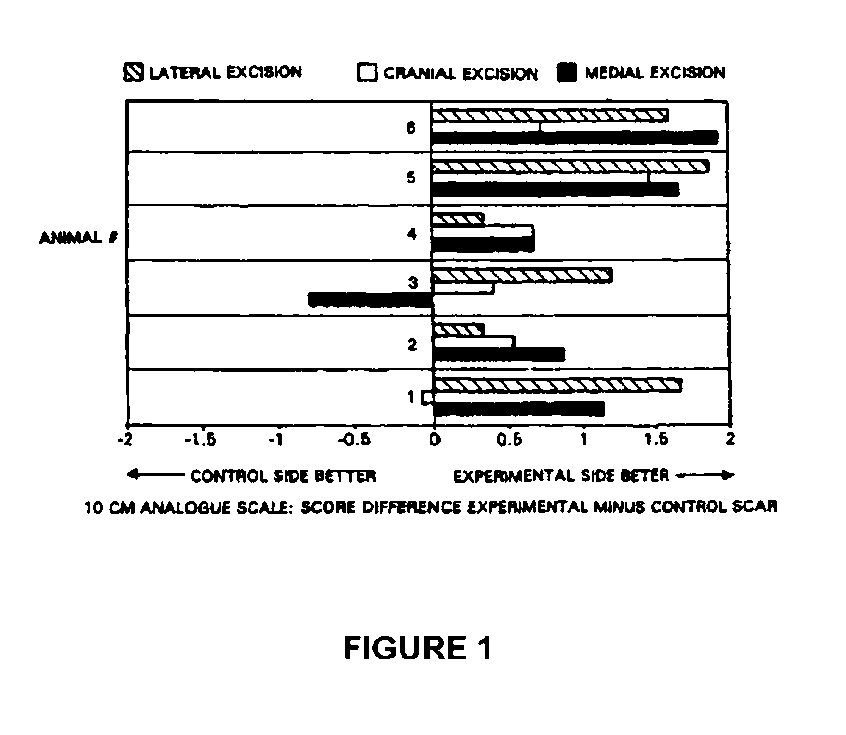
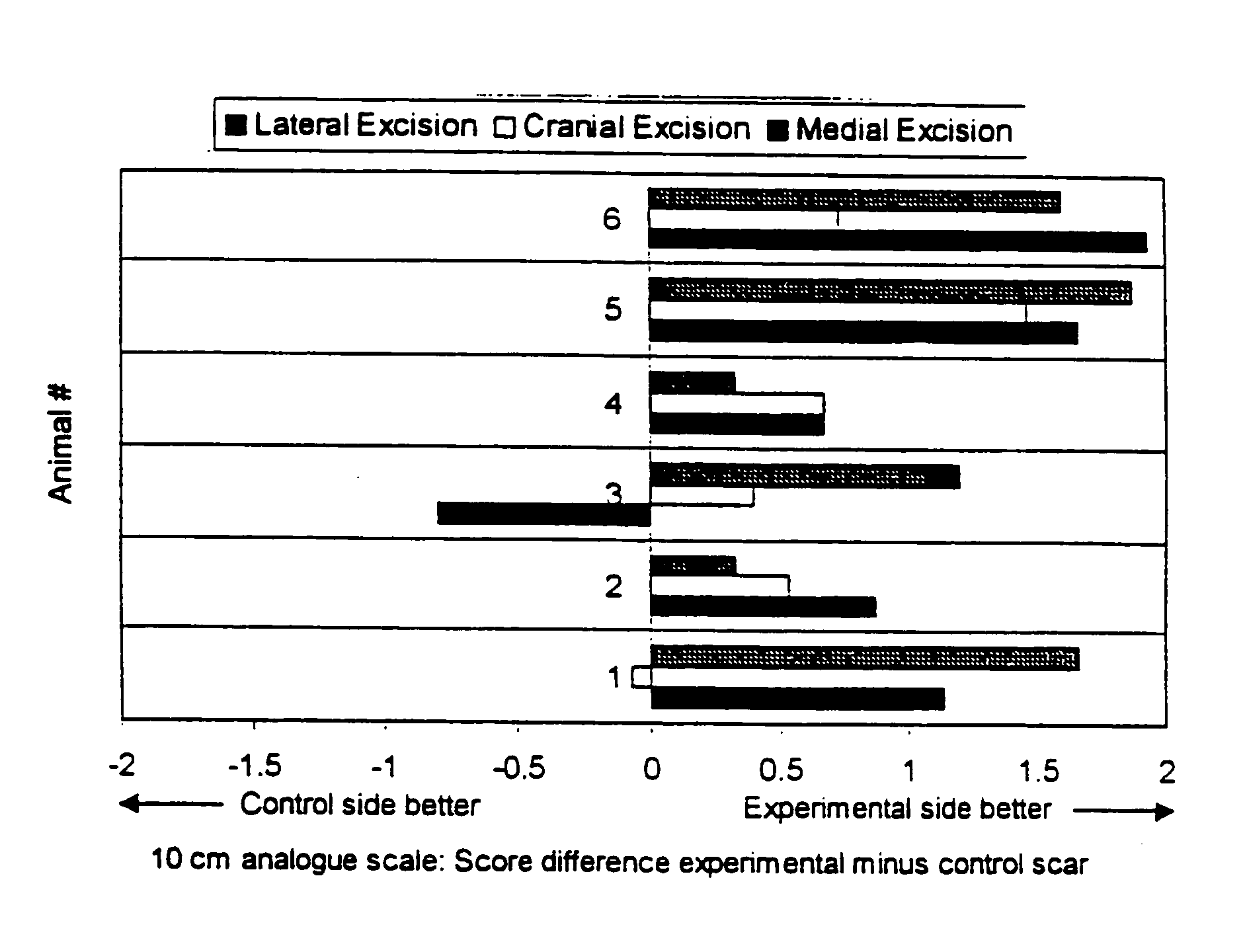
Methods for enhancing wound healing
InactiveUS20060039930A2Reduce tensionPromote wound healingBiocideBacterial antigen ingredientsWound healingMean difference
Abstract of the DisclosureA method for treating a patient having a wound is described. The method includes administering an amount of a chemodenervating agent such that healing of the wound is enhanced. The method is illustrated by detailing the mean differences of the scores of the paired experimental and control scars across three observers.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Wide operating temperature range electrophoretic device
ActiveUS20160246154A1Aromatic content is minimized and avoidedIncreasing solubility and toxicityLight protection screensNon-linear opticsElectrophoresisMean difference
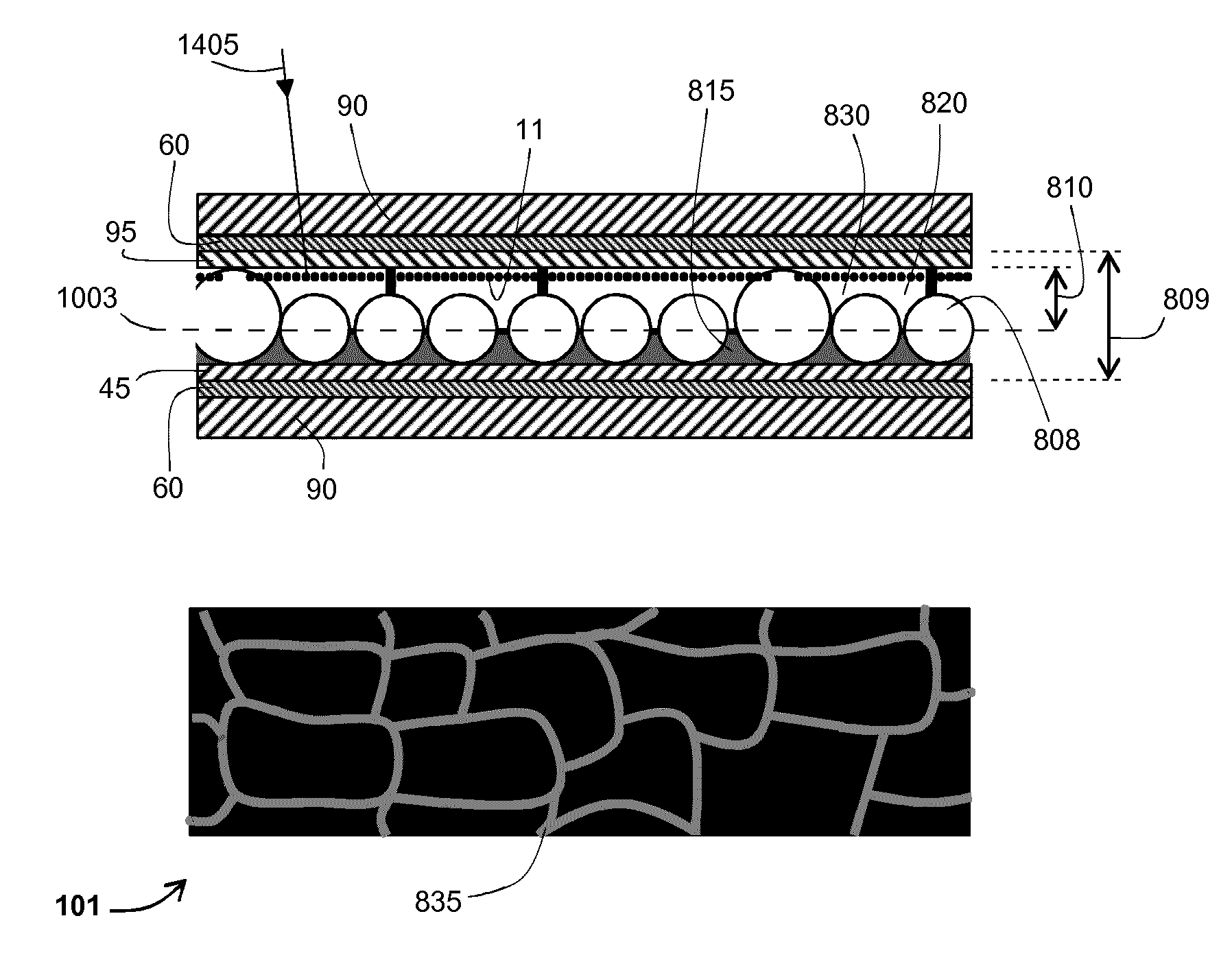
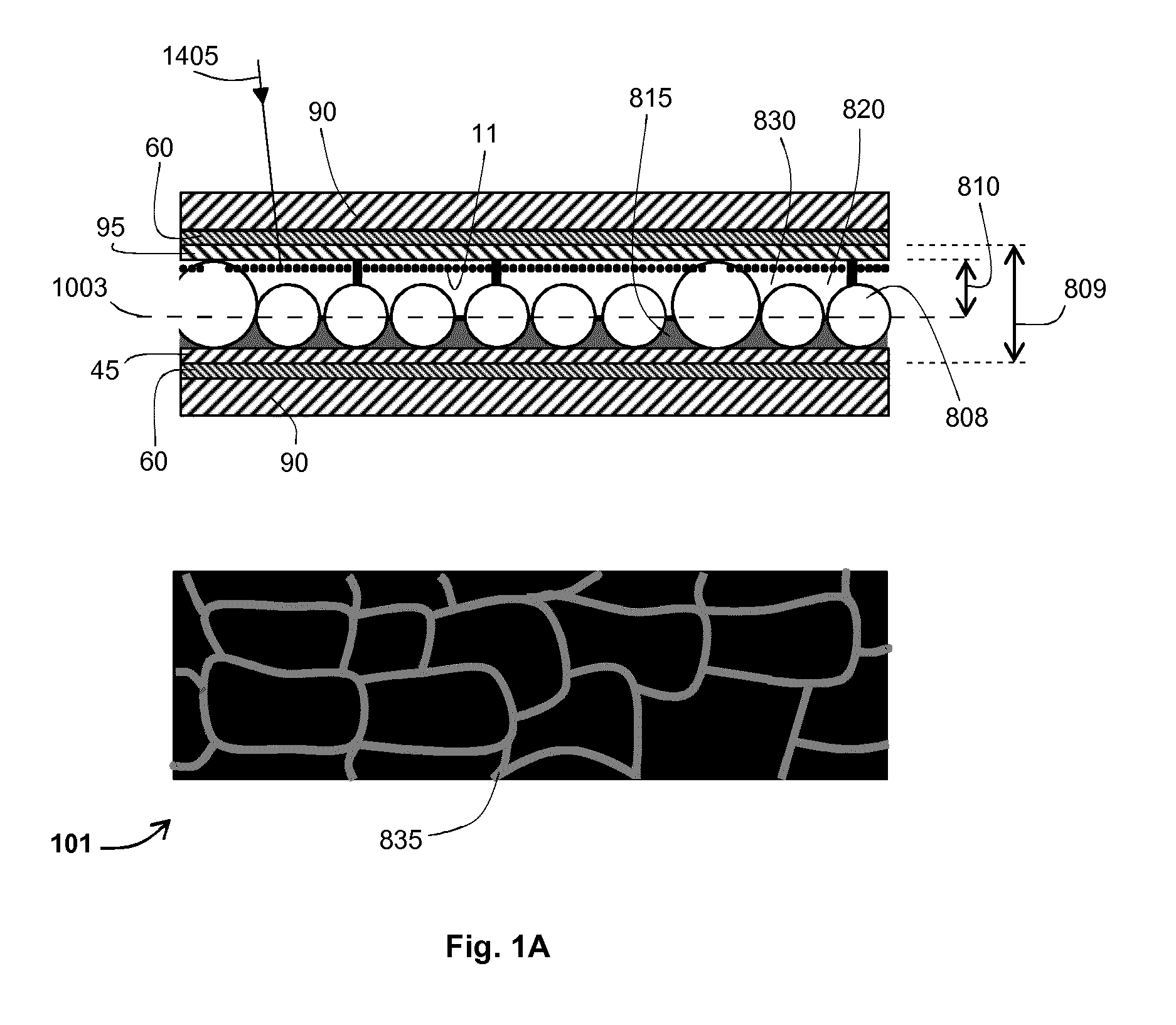
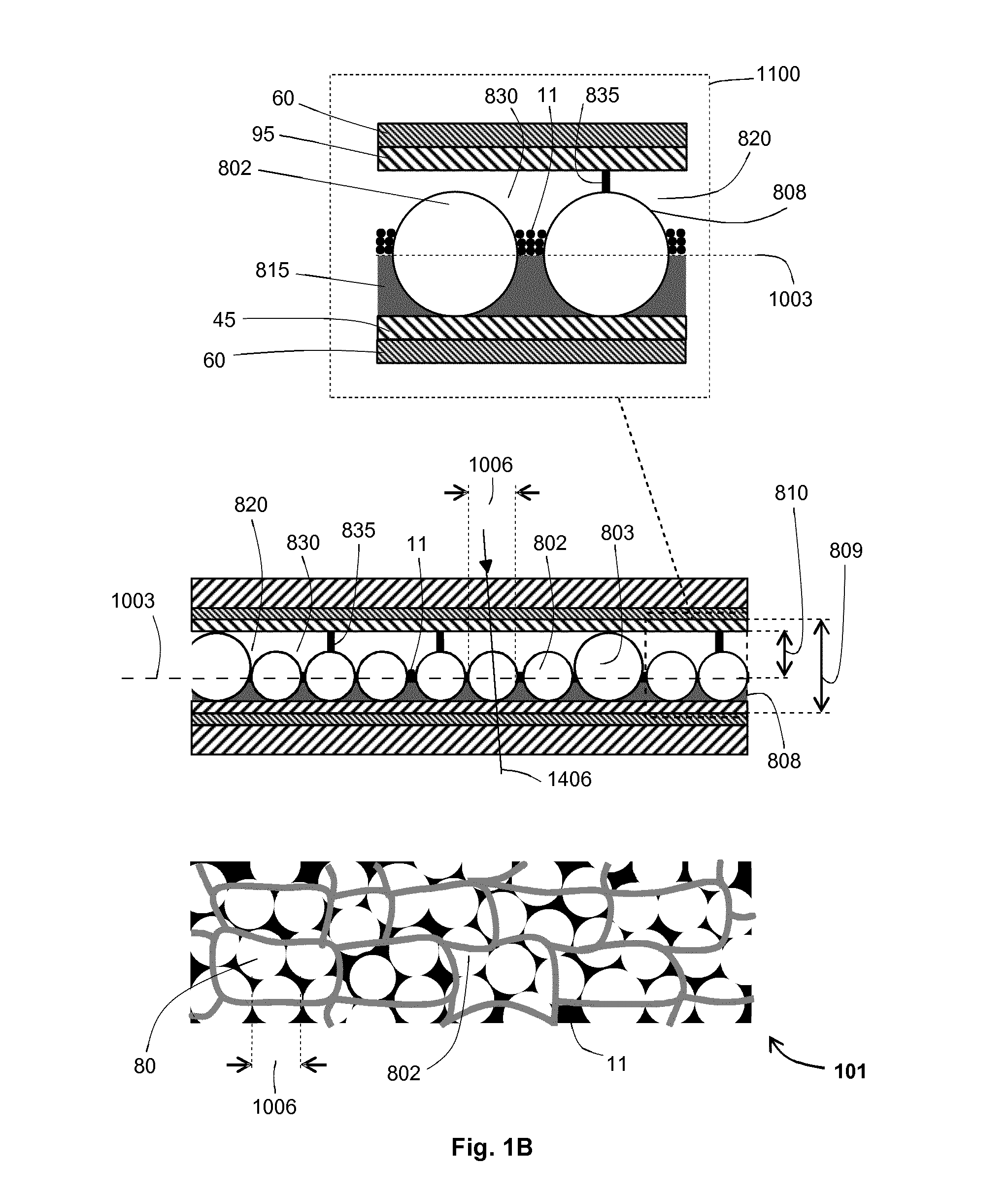
An electrophoretic device (101) comprises a first electrode (60) and a second electrode (60) spaced apart from the first electrode (60). An electrophoretic cell (809) containing an electrophoretic ink (830) and one or more optically-transparent, non-planar, solid polymer elements (808) is located between the electrodes (60). The ink (830) includes charged particles (11) of at least one type suspended in an optically-transparent suspending fluid (820). The refractive indices of the solid polymer elements (808) and the suspending fluid (820) are matched to have a difference of less than 0.0075, and for half or more of the operating temperature range of the device (0° C.-70° C.), the thermo-optic coefficients (temperature coefficient of refractive index per Kelvin) of the solid polymer elements (808) and the suspending fluid (820) are matched to have an arithmetic-mean difference of less than 0.0002 / K in magnitude.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Testing method and system of thickness sensor
InactiveCN105574985AFully automatedImprove test efficiencyPaper-money testing devicesMean differenceTest efficiency
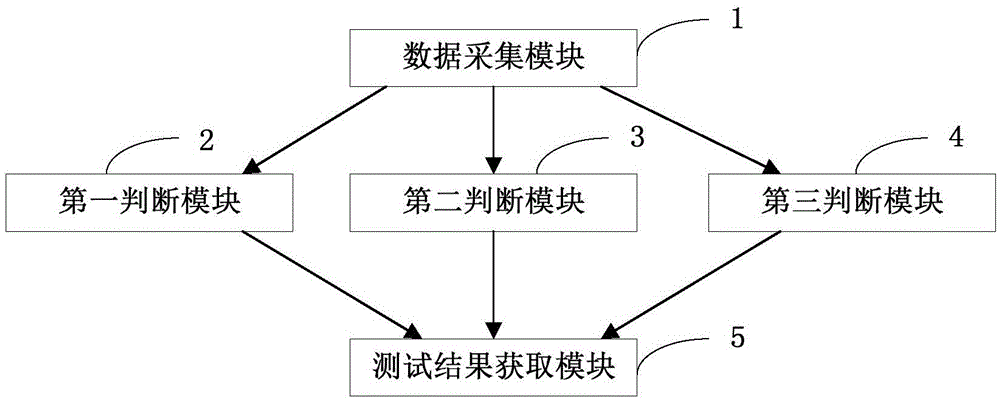
The invention provides a testing method and system of a thickness sensor and relates to the technical field of electronic testing. The method comprises the steps of: utilizing the thickness sensor to collect thickness data of a plurality of pieces of standard tested bank notes; according to thickness data collected by each channel of the thickness sensor, obtaining the fluctuation range of the data collected by each channel, and judging whether the fluctuation range of the data collected by each channel is in a preset fluctuation range; according to the thickness data collected by each channel of the thickness sensor, calculating a difference parameter of each channel, and judging whether the difference parameter of each channel is smaller than a preset difference parameter threshold; according to the thickness data collected by each channel of the thickness sensor, calculating a mean difference parameter of each channel, and judging whether the mean difference parameter of each channel is smaller than a preset mean difference parameter threshold; and according to the above three judging results, determining whether the sensor is normal. According to the invention, automatic detection of the thickness sensor is realized, manpower and time consumed by the testing are reduced, and the testing efficiency and the reliability of the testing result are improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN YIHUA COMP +2
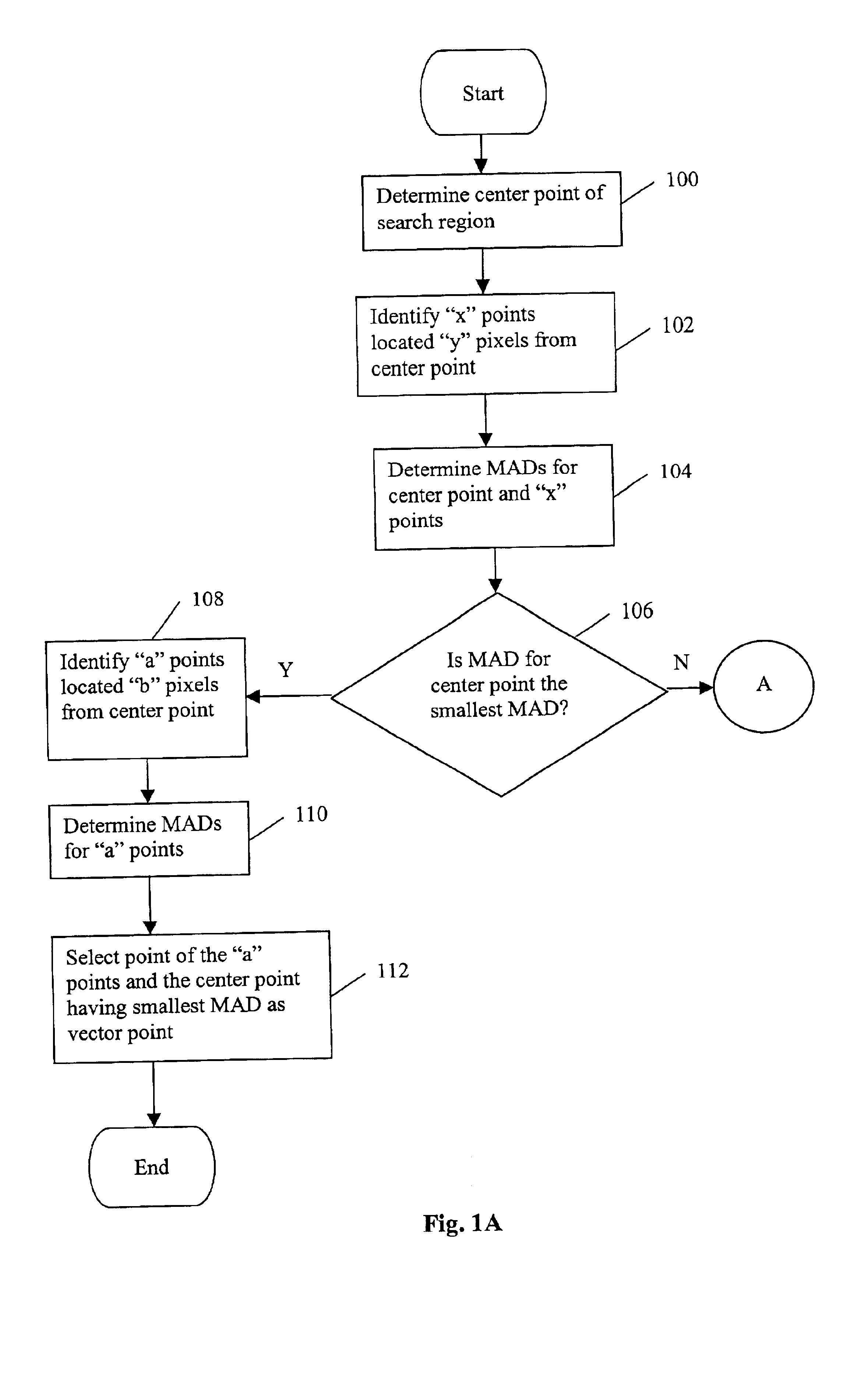
Methods for enhancing wound healing
InactiveUS20050175637A1Reduce tensionPromote wound healingBiocideBacterial antigen ingredientsMean differenceAnesthesia
A method for treating a patient having a wound is described. The method includes administering an amount of a chemodenervating agent such that healing of the wound is enhanced. The method is illustrated by detailing the mean differences of the scores of the paired experimental and control scars across three observers.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
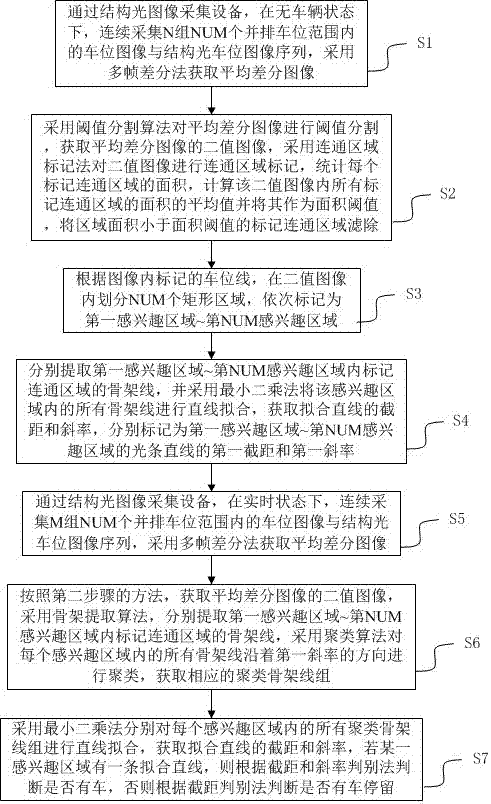
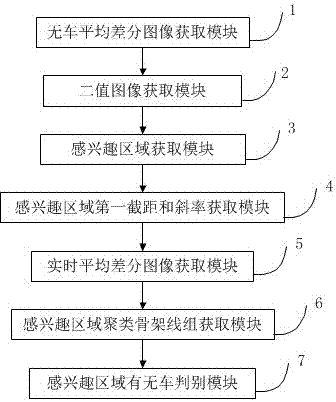
Parking space method and device based on structured light
ActiveCN107133591AEasy to implementImprove robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisMultiple frameMean difference
The invention provides a parking space method based on structured light, and the method comprises the steps: collecting a parking space image and a structured light parking space image when there is no vehicle, and obtaining a mean difference image through a multi-frame difference method; obtaining a binary image of a marked communication area; obtaining an AOI (area-of-interest) according to a marked parking space line; extracting a skeleton line in the AOI, carrying out the linear fitting, and obtaining a first intercept and slope of the AOI; collecting the parking space image and the structured light parking space image in real time, and obtaining the mean difference image through the multi-frame difference method; extracting the skeleton lines, carrying out the clustering of the skeleton lines of all AOIs, and obtaining a cluster skeleton line group; carrying out the linear fitting of the cluster skeleton line group, obtaining the intercept and slope, and carrying out the judgment whether there is a vehicle or not. Compared with the prior art, the method can achieve the quick detection of the current states of a plurality of parking spaces, and is better in robustness for a low-brightness scene.
Owner:SHENZHEN QIANHAI INTELLIDATA TECH CO LTD
Heat image detail enhancement method based on normal distribution adjustment
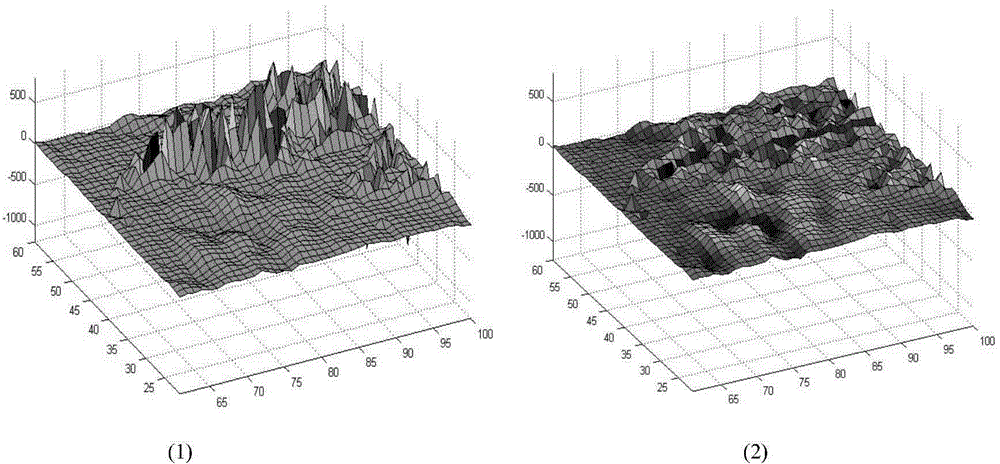
ActiveCN104157003AOvercome two major flawsImprove noise characteristicsSpecial data processing applications3D-image renderingGray levelAbsolute difference
The invention relates to a heat image detail enhancement method based on normal distribution adjustment, and belongs to the technical field of infrared thermography. The method comprises the following steps: further adjustment is conducted on detail image gray level distribution separated by bilateral filter through a normal distribution function of average absolute difference; pseudomorphism is restricted; noise characteristics of the detail image are improved to obtain a new detail image; meanwhile, a platform histogram is utilized to compress an original image to obtain a basic image; scene detail information is retained; the detail image and the basic image are combined to form an output image. The processed noise characteristics of the detail image are improved remarkably; meanwhile, the processing retains the pseudomorphism; gray scale layer sense of the final output image is improved; the method can be used for various infrared focal plane imaging systems, provides effective infrared image detail enhancement technique means, and improves target detection, search and identification capacity.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
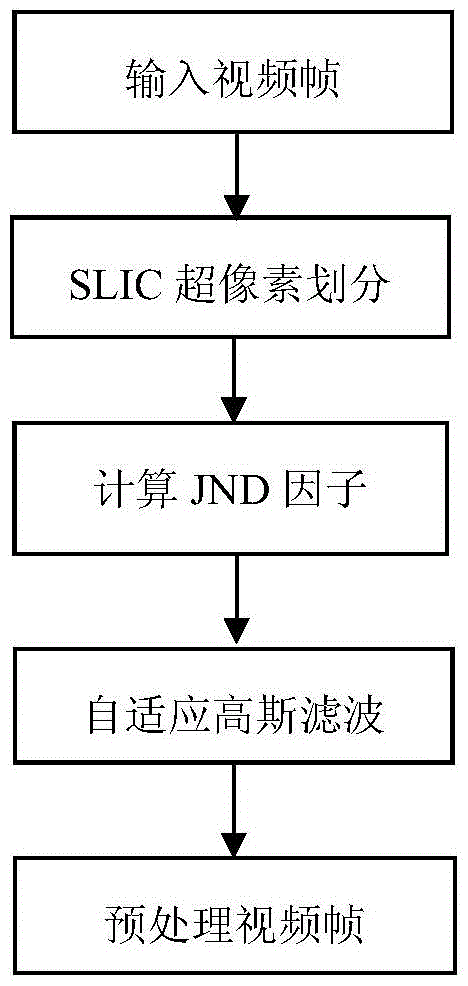
Super pixel Gaussian filtering pre-processing method based on JND factor
InactiveCN104992419AReduce bit rateNo lossImage enhancementDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionPretreatment method
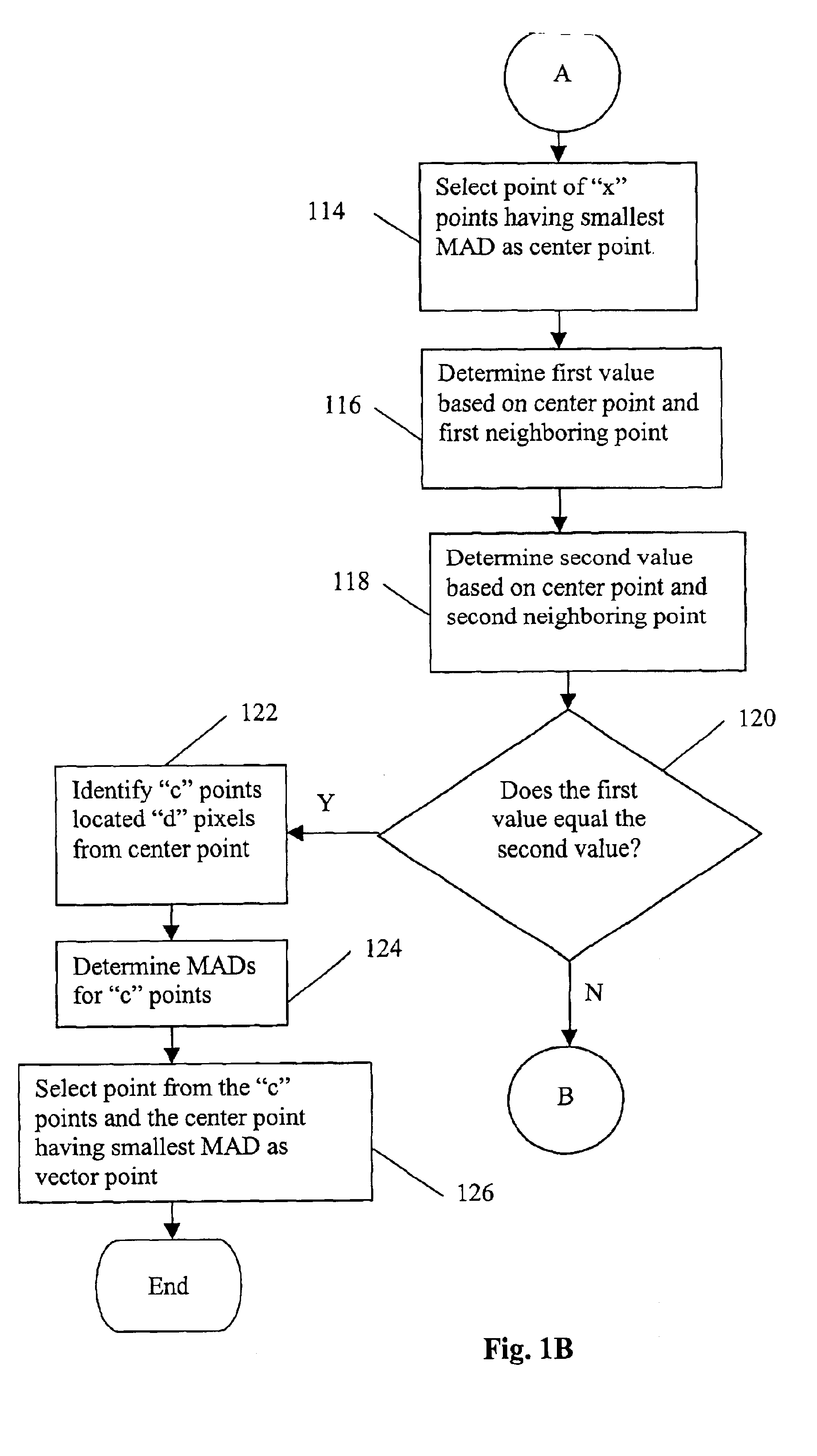
The invention discloses a super pixel Gaussian filtering pre-processing method based on a JND factor, comprising the following steps: video image data reading-in; super pixel classification: segmenting an image into super pixels which are of a predetermined size and are composed of similar pixels based on an SLIC super pixel method; JND factor calculation: calculating the visual-information-based JND factor of each pixel point in the super pixels, obtaining the average value of the JND factor, and obtaining the association between the average value and image texture and smoothness, wherein the calculated JND factor is the weighted brightness mean difference; and adaptive Gaussian filtering of the super pixels: determining the Gaussian filtering parameters of the super pixels according to the average value of the JND factor of the super pixels, and adopting the Gaussian filtering parameters to perform Gaussian filtering on the corresponding super pixels, thus obtaining a pre-processed video frame. According to the invention, a video can be adaptively filtered based on the sensitivity of the human eye to the image region, and obvious rate decline can be achieved without causing loss to subjective quality.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
On-satellite infrared image stripe noise removal method based on similar line window mean value compensation
ActiveCN108830808AReduce computational complexityMeet the real-time processing requirements on the starImage enhancementImage analysisRobustificationNoise removal
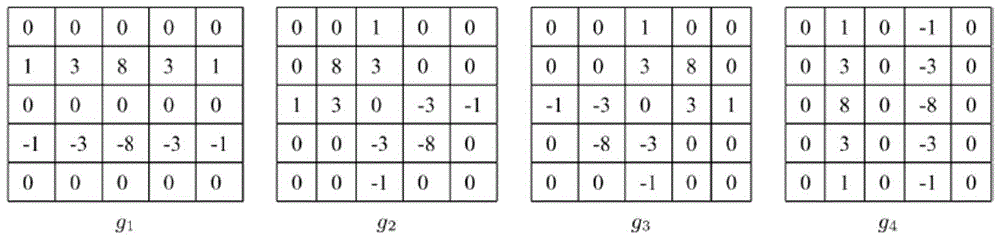
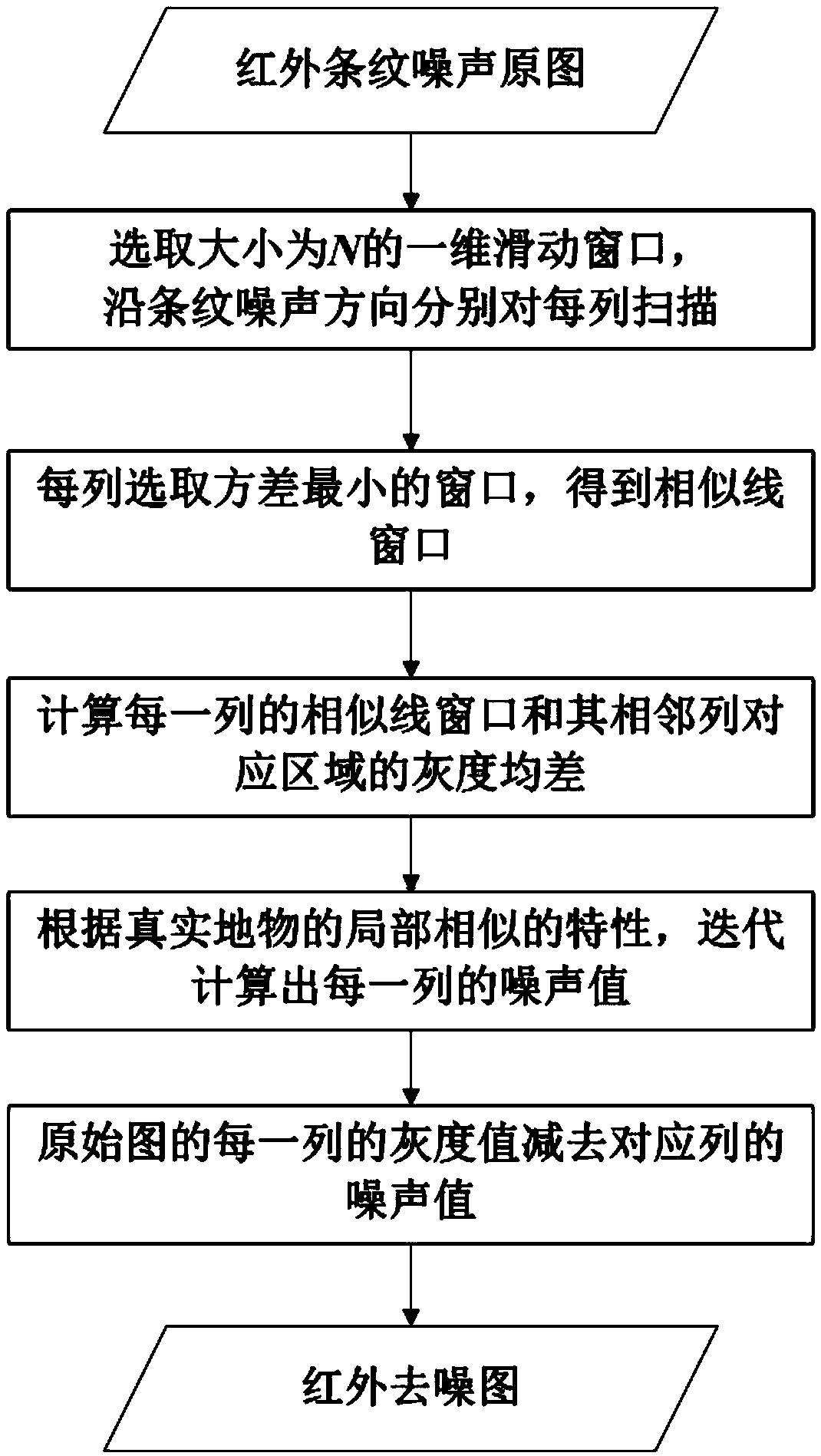
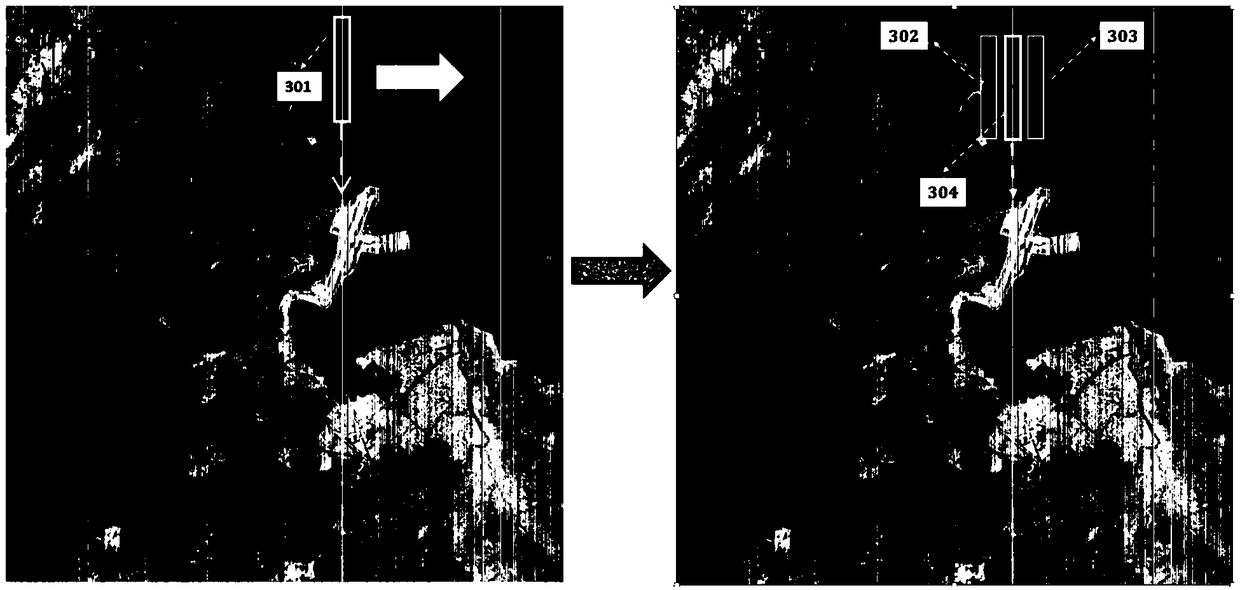
The invention discloses an on-satellite infrared image stripe noise removal method based on similar line window mean compensation. According to the method, firstly, a one-dimensional sliding window with a size N is selected according to an image size to be used as a sliding line window. The sliding line window carries out scanning from an uppermost end to a lowermost end of each column along a stripe noise direction, and a line window with smallest variance, namely, a similar line window of each column, is selected; then gray level mean difference of the similar line window and adjacent areasthereof is calculated to obtain stripe noise difference values of adjacent columns; and finally, a stripe noise value of a first column is set to zero, a noise value of each column is iteratively calculated according to the stripe noise difference values of the adjacent columns, and ideal gray level values of a real ground object can be obtained by subtracting the noise values from original gray level values. Compared with the prior art, the method is low in computational complexity, good in robustness, and high in fidelity on texture details.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
Video constant quality control method in the mode of pyramid type bidirectional estimation
ActiveCN101110957ALimit volatilityQuality improvementTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Absolute difference
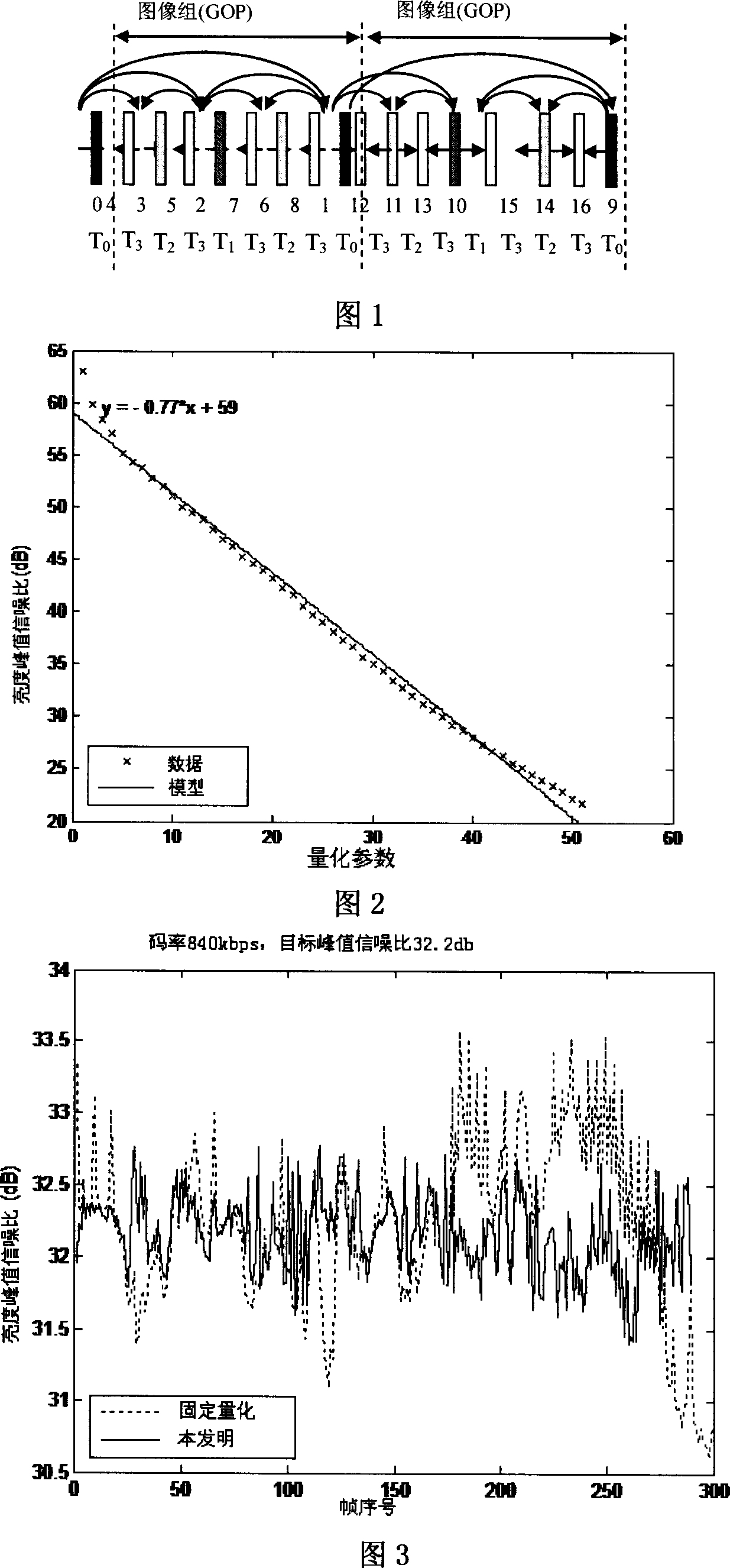
The present invention relates to a control method for the video constant quality in a pyramid type double-way prediction mode, which belongs to the video technical field. The present invention comprises the following procedures: the first step, an initial quantization parameter to the whole video sequence is set according to the linear relationship between the peak value speech noise ratio and the quantization parameter; the second step, the quantization parameter of the time basic layer is adjusted according to the changing information of the average absolute difference among the peak value speech noise ratio of the decoded image, the decoded frame, and the reference frame; the third step, the quantization parameter of the time enhance layer is adjusted according to the changing information of the time basic layer parameter and the average absolute difference of the previous and current reference frame, to realize the control to the video constant quality in the pyramid type double-way prediction mode. The present invention can improve the consistency of the decode quality of the scalable video in a time zone, and efficiently decreases the volatility among the video frames.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT OF DIGITAL TELEVISION
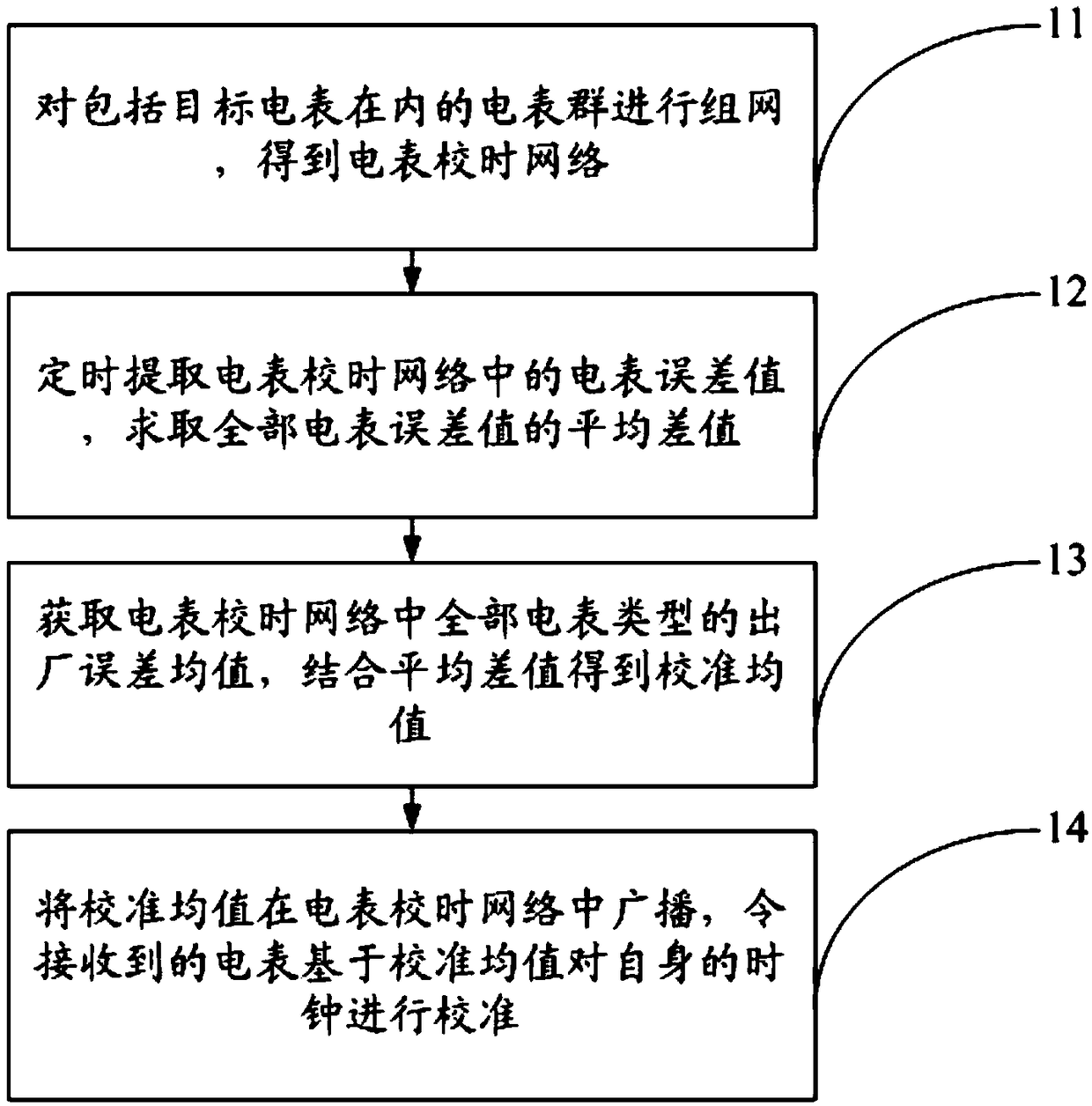
Electricity meter clock correction method based on mean difference value
ActiveCN109239640AReduce mistakesCommission accuracyRadio-controlled time-piecesElectrical measurementsMean differenceElectricity meter
The invention provides an electricity meter clock correction method based on a mean difference value, belonging to the field of time calibration. The method comprises the following steps: networking for an electricity meter group containing a target electricity meter, thereby obtaining an electricity meter timing network; periodically extracting an electricity meter error value in the electricitymeter timing network, and solving the mean difference value of all the electricity meter error values; acquiring a factory error mean of all electricity meter types in the electricity meter timing network, and obtaining a calibration mean in combination with the mean difference value; and broadcasting the calibration mean in the electricity meter timing network. In the method, the mean is solved based on the current errors of all the electricity meters in the network, and by taking the solved mean as calibration quantity, the electricity meters in the whole network are calibrated. Since a stepof extracting the electricity meter error values is triggered periodically, errors of the electricity meters in the whole network can be reduced effectively through multiple iterative operations, andthe electricity meters of the whole network are calibrated based on the reduced errors, thus, the electricity meters in the whole network can be in a state of having relatively less error, and accuracy of clocks in the electricity meters is improved effectively.
Owner:STATE GRID ZHEJIANG NINGBO FENGHUA POWER SUPPLY CO LTD +1
Motion estimation method
InactiveUS6912296B2Avoid matching problemsReduce complexityTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputation complexityRound complexity
A motion estimation method is provided. In the method, respective mean difference values for a current search point within a search block and neighboring search points within the search block are calculated. Then, motion estimation is performed around the current search point if the mean difference value of the current search point is smaller than the mean difference values of the neighboring search points. On the other hand, motion estimation is performed based on the mean difference values of at least some of the neighboring search points if the mean difference value of the current search point is not smaller than the mean difference values of at least one the neighboring search points. The motion estimation method of the present invention does not deteriorate the quality of pictures during image compression in contrast to conventional motion estimation methods and enhances image compression speed by reducing remarkably computational complexity.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com