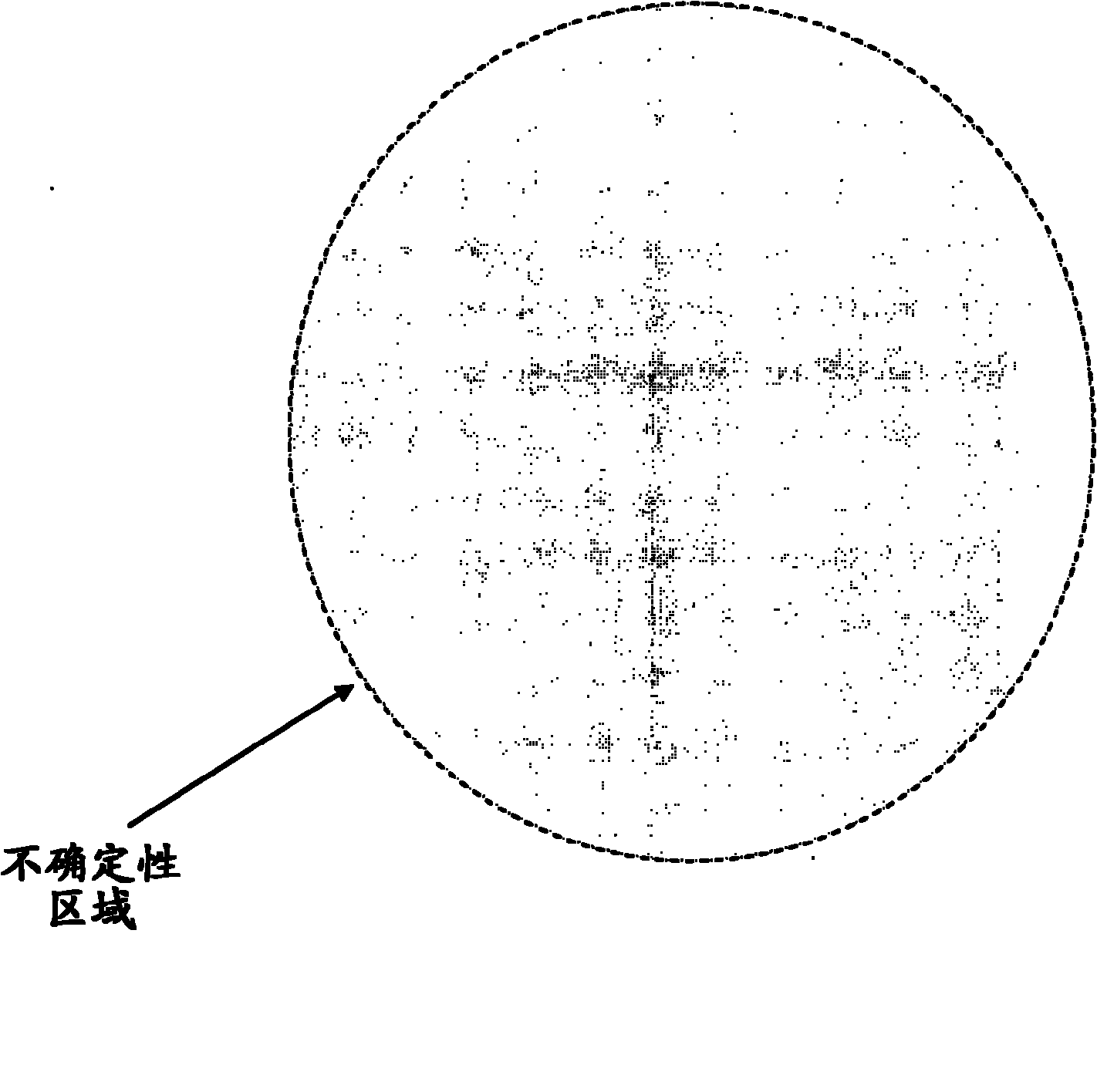
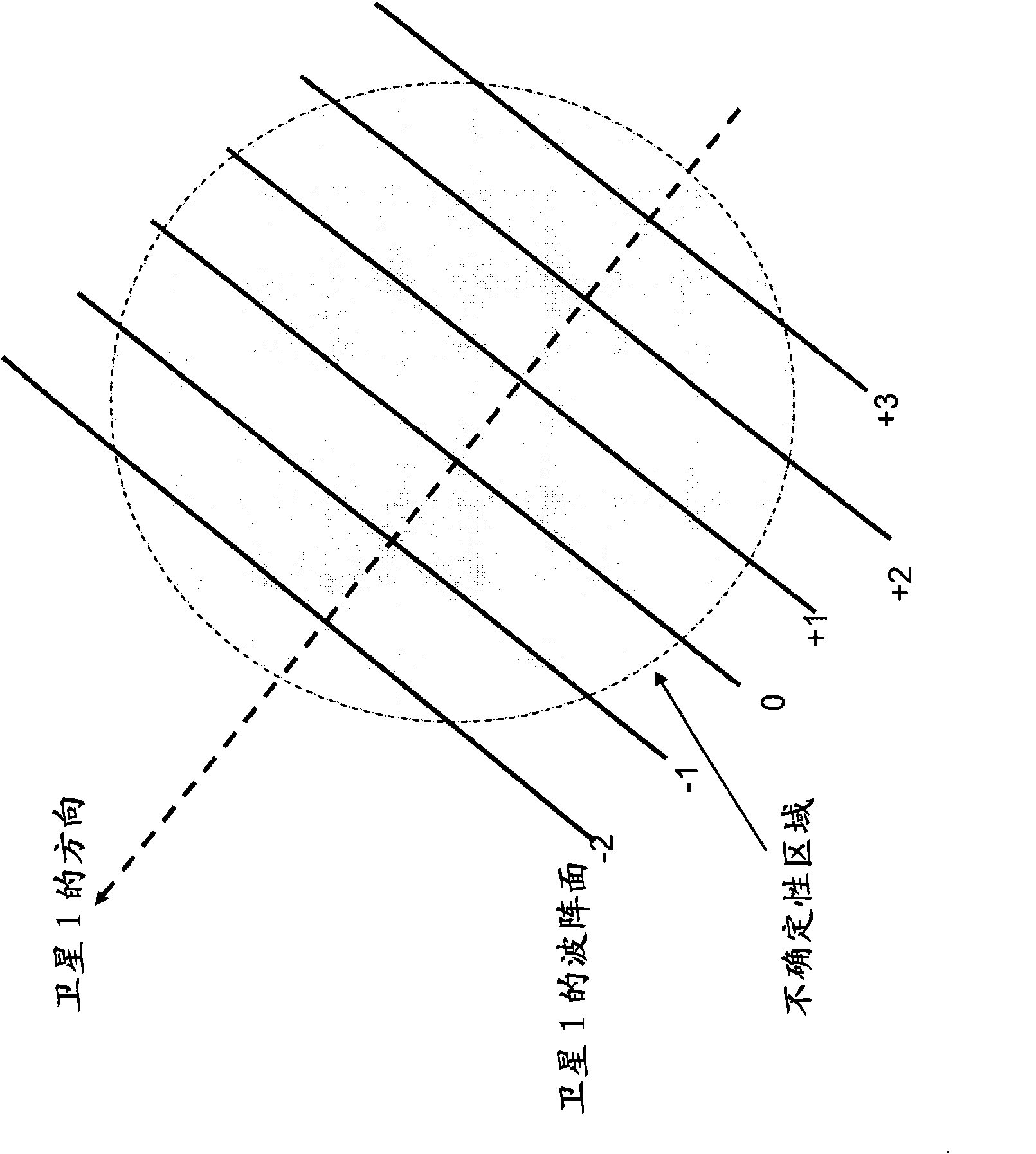
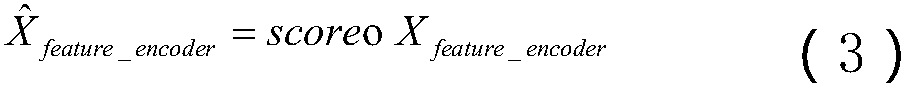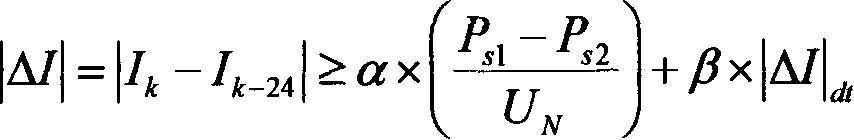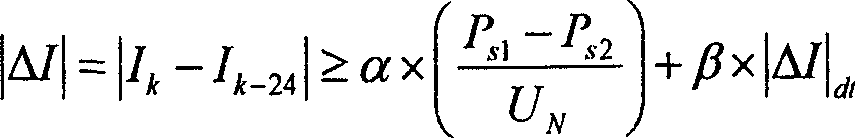Patents
Literature
41 results about "Float Value" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Float is a term is used in various programming languages to define a variable with a fractional value. Numbers created using a float variable declaration will have digits on both sides of a decimal point.
Macroscopic fundamental diagram-based road network key section identification method
ActiveCN105702031AImprove dynamic traffic characteristics requirementsImprove defects such as dynamic traffic characteristics requirementsDetection of traffic movementFloat ValueStructure recognition
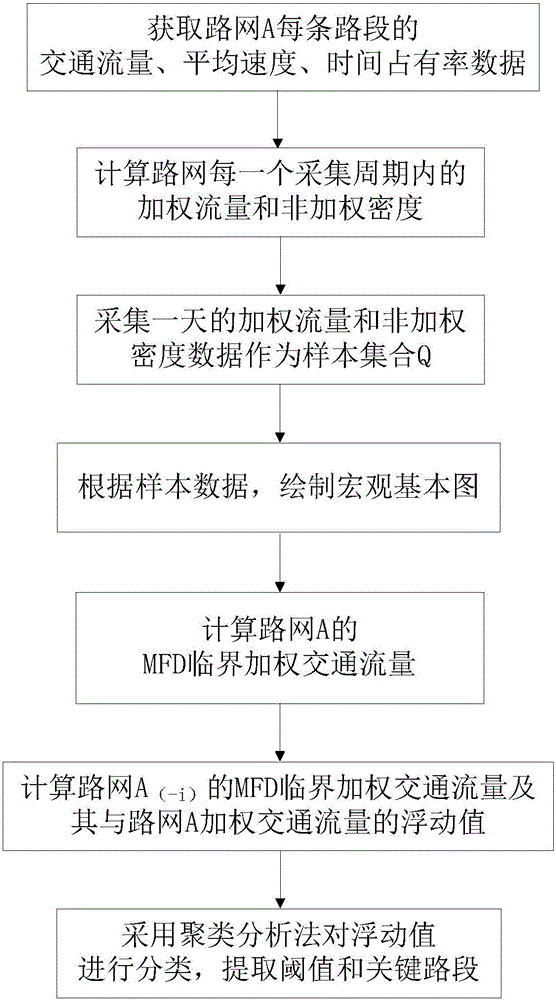
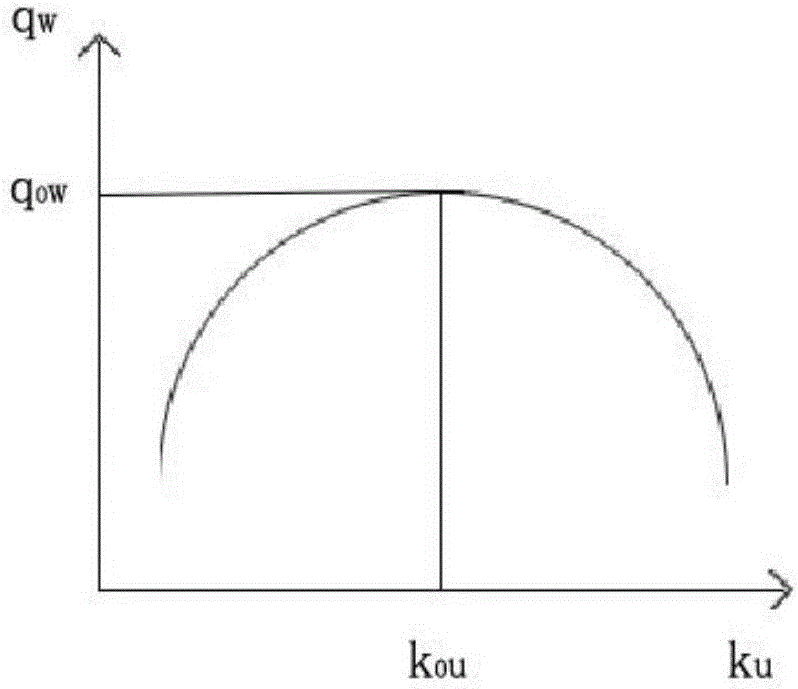
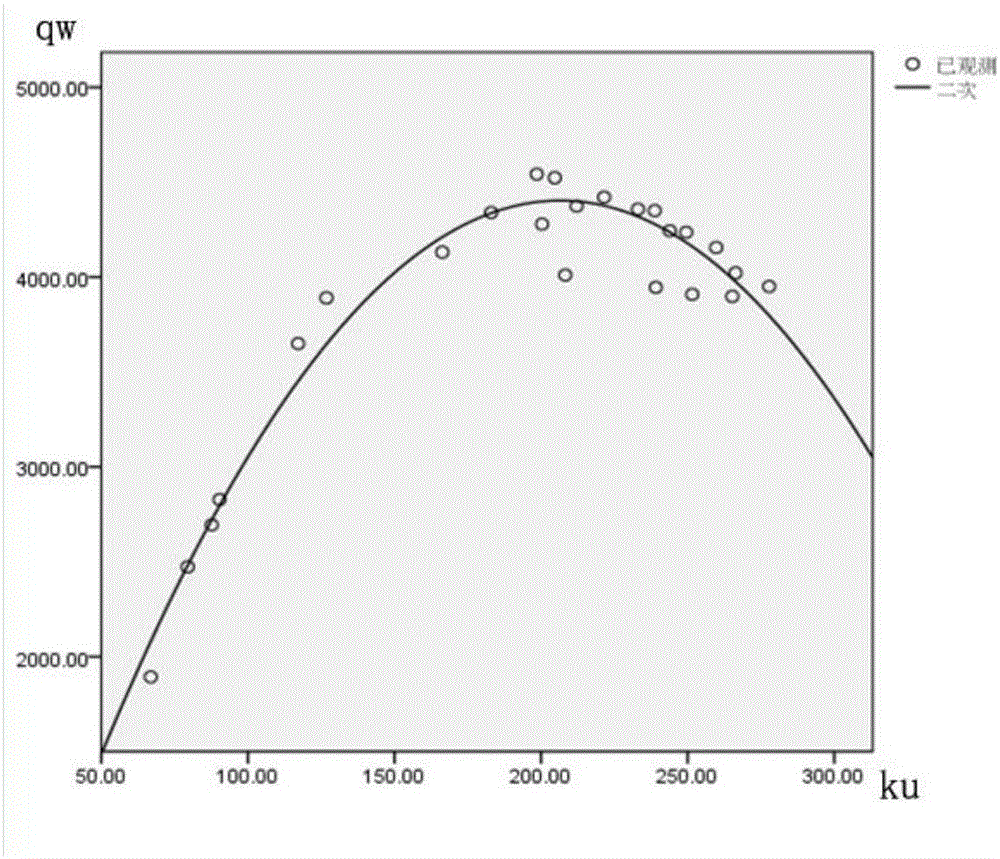
The invention discloses a macroscopic fundamental diagram-based road network key section identification method. The method comprises the steps of 1, acquiring the traffic flow, the average speed and the time occupancy data of each road section of an urban road network A; 2, calculating a weighted flow and a non-weighted density of the road network within each acquisition period; 3, getting a set of samples; 4, drawing a macroscopic fundamental scatter diagram; 5, calculating the critical weighted traffic flow of the road network MFD; 6, arbitrarily deleting one road section, and calculating the critical weighted traffic flow of the road network (-i)MFD without the above deleted road section and the floating value of the MFD critical weighted traffic flow of the road network A; 7, adopting the clustering analysis method for classification, and extracting a threshold r and a key road section. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the defect that the key section identification result based on the static topology structure of the road network is not consistent with the dynamic characteristics of the road network traffic flow can be overcome. Therefore, the method is more applicable to the change characteristics of the road network traffic flow. Therefore, the reliability of calculated data is ensured to be high.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
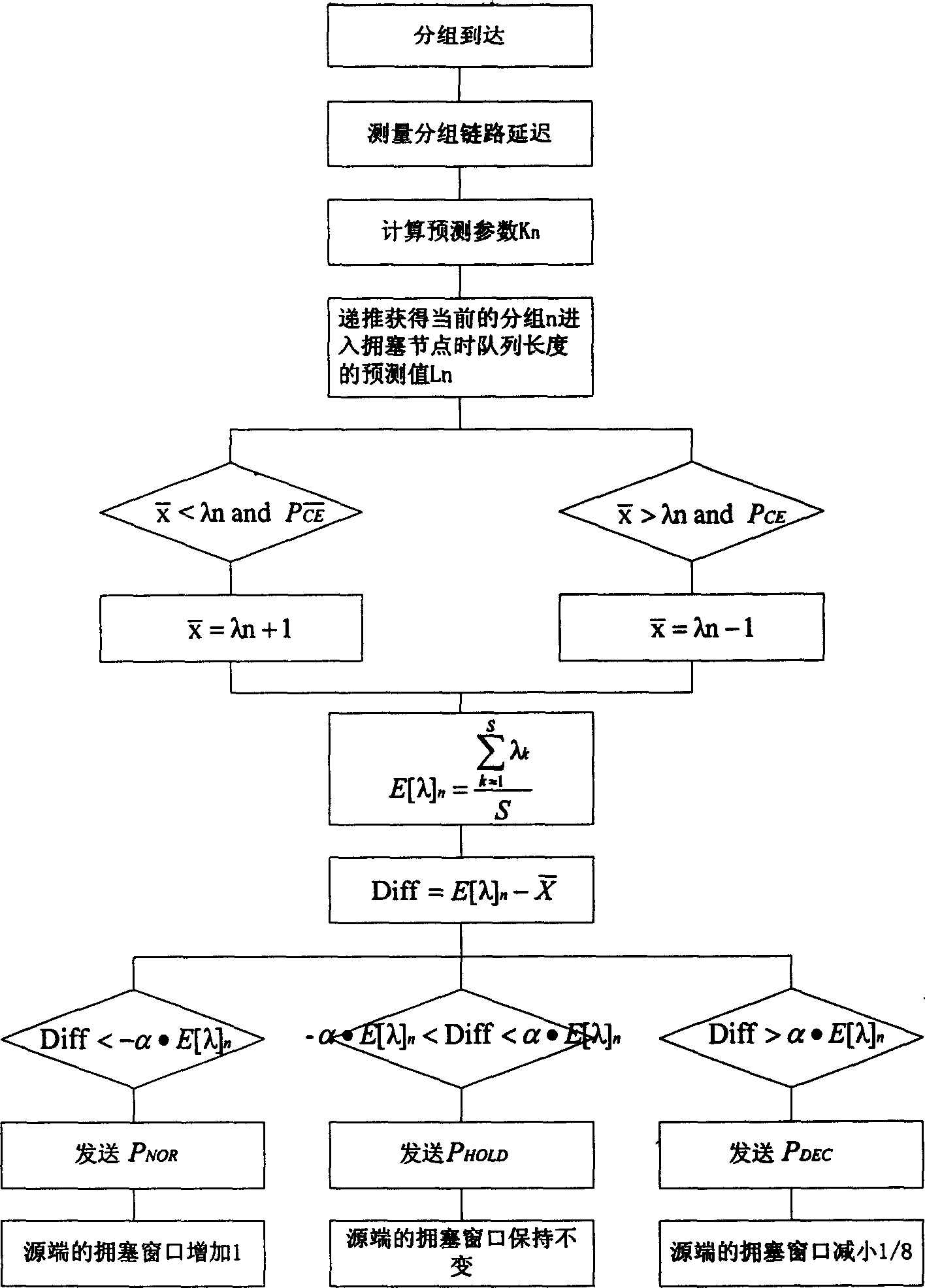
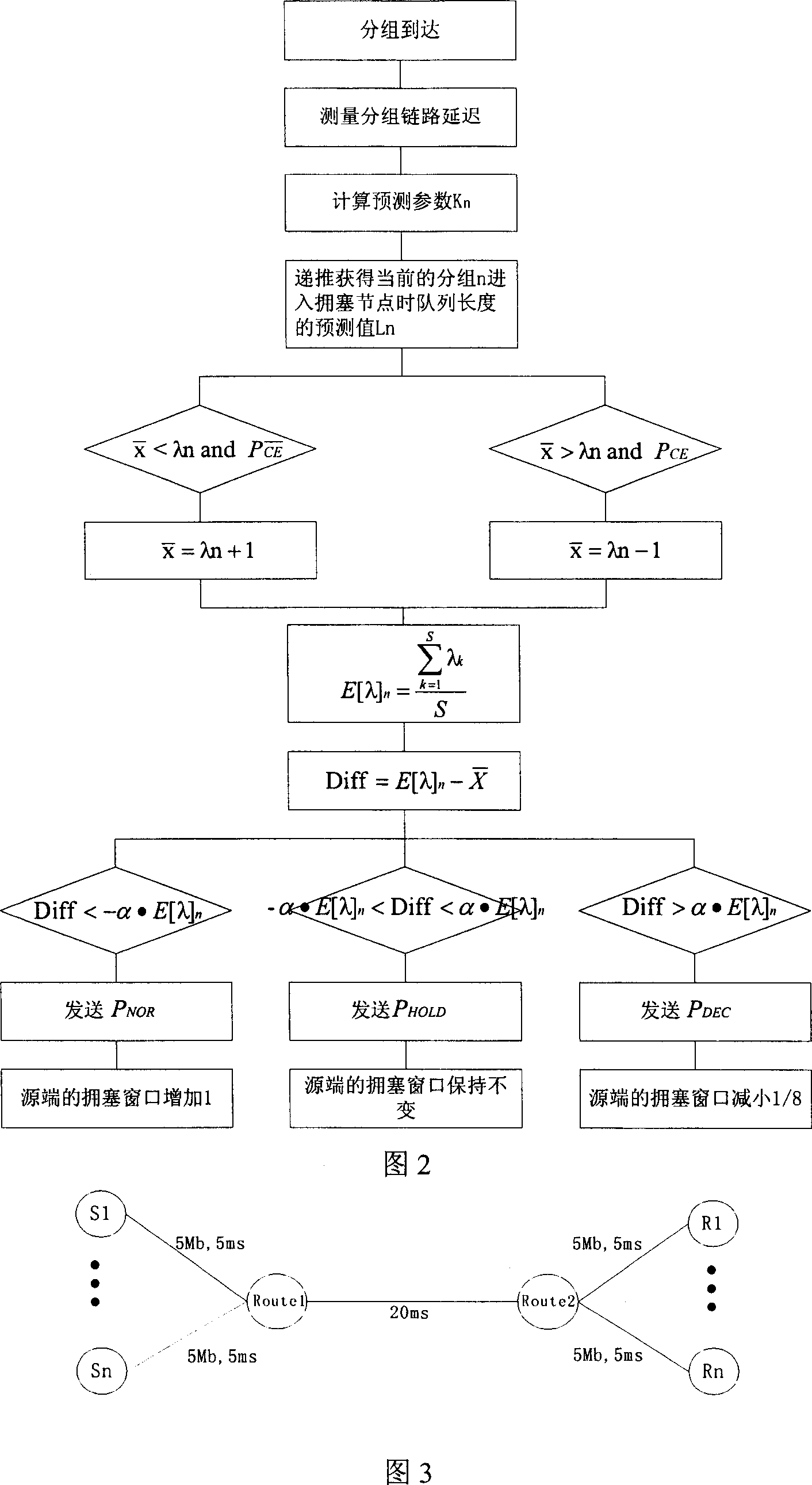
ECN based congestion control method with prediction verification
The invention is an ECN-based forecasting and verifying congestion control method, firstly using the difference between two adjacent packets to calculate forecast parameters of a current packet, by this recurring to the corresponding forecast queue length of, and able to refer to the congestion conditions of nodes to correct the forecast length as a common forecast threshold value for all the packets; taking 2 x the first packet delay as signal transmitting time and all the packets as forecast packets in order to find a forecast value of average queue length of all the packets, a receiving end compares the difference between the forecast value and the forecast threshold value with predicted floating value of the forecast value, so as to be able to send a confirm packet increasing, decreasing or keeping the length of congestion window to the source end, convenient for the source end to regulate the packet transmitting speed. This receiving end driving method has the advantage of reducing loss rate and average packet delay at the same time, has stale and higher network utilization ratio and can also forecast the network's congestion conditions.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
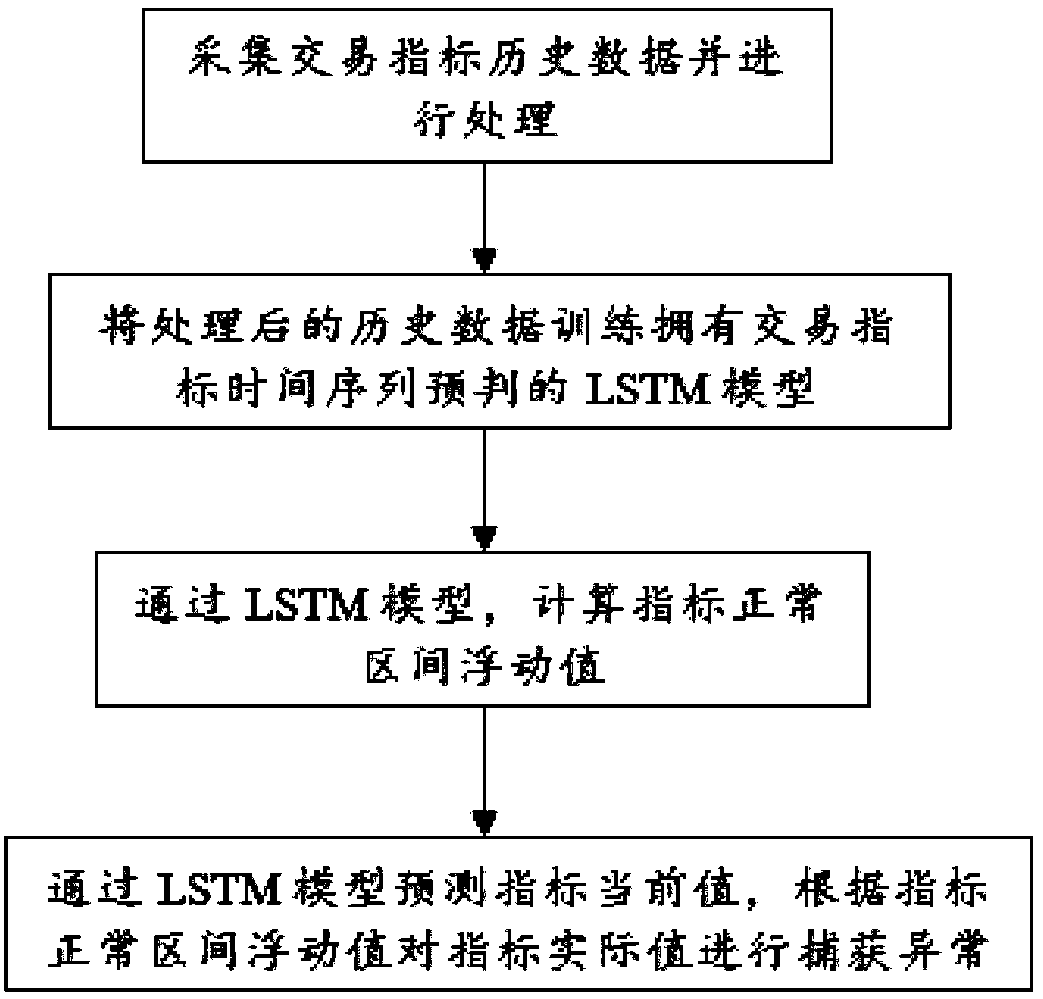
Transaction index abnormality monitoring method based on deep learning model LSTM
The invention discloses a transaction index abnormality monitoring method based on a deep learning model LSTM. The method comprises the steps that 1 transaction index historical data are collected and processed; 2 the LSTM model with transaction index time series pre-determining is trained for the historical data processed in the step 1; 3 through the LSTM model of the step 2, the normal index interval floating value is calculated; and 4 the current index value is predicted through the LSTM model of the step 2, and abnormality capturing is carried out on the actual index value according to the normal index interval floating value of the step 3. According to the invention, the time series index is predicted through the deep learning model LSTM; the predicted current index value is accurate; the pre-determining accuracy of irregular time series indexes is greatly improved; subsequent abnormality capture is accurate; the output result predicted by the LSTM model is combined, and a residual fitting formula and a logistic regression model algorithm are used to calculate the normal interval floating value; abnormality capture is accurate; and the efficiency is improved.
Owner:SICHUAN XW BANK CO LTD
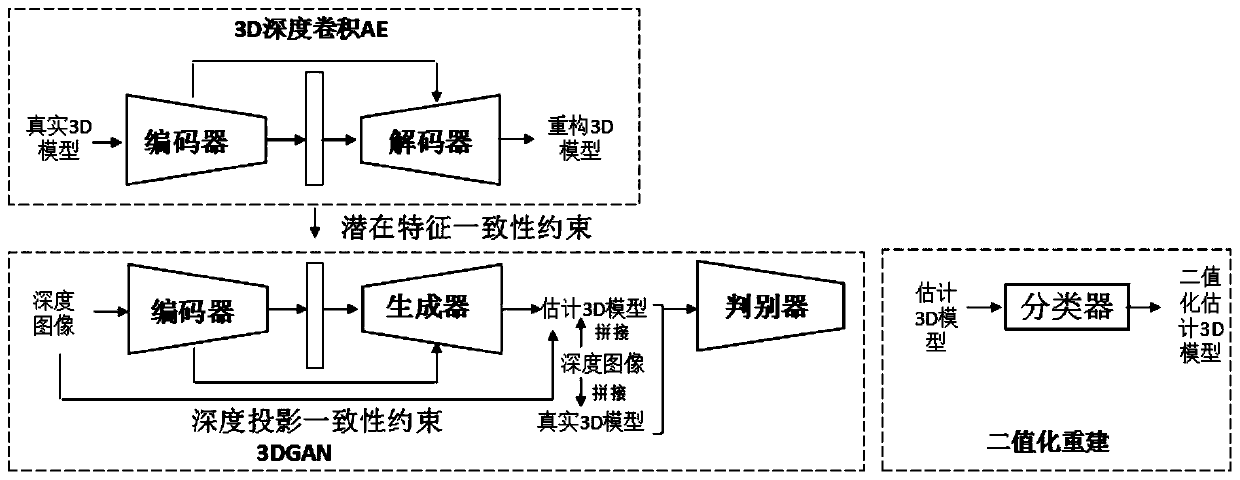
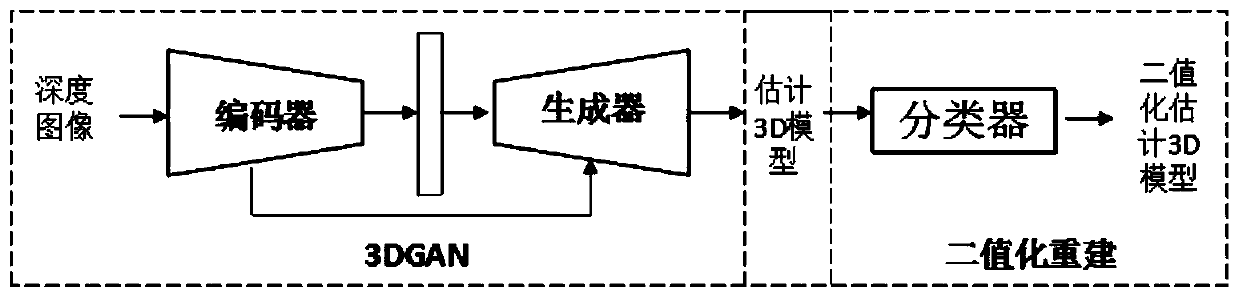
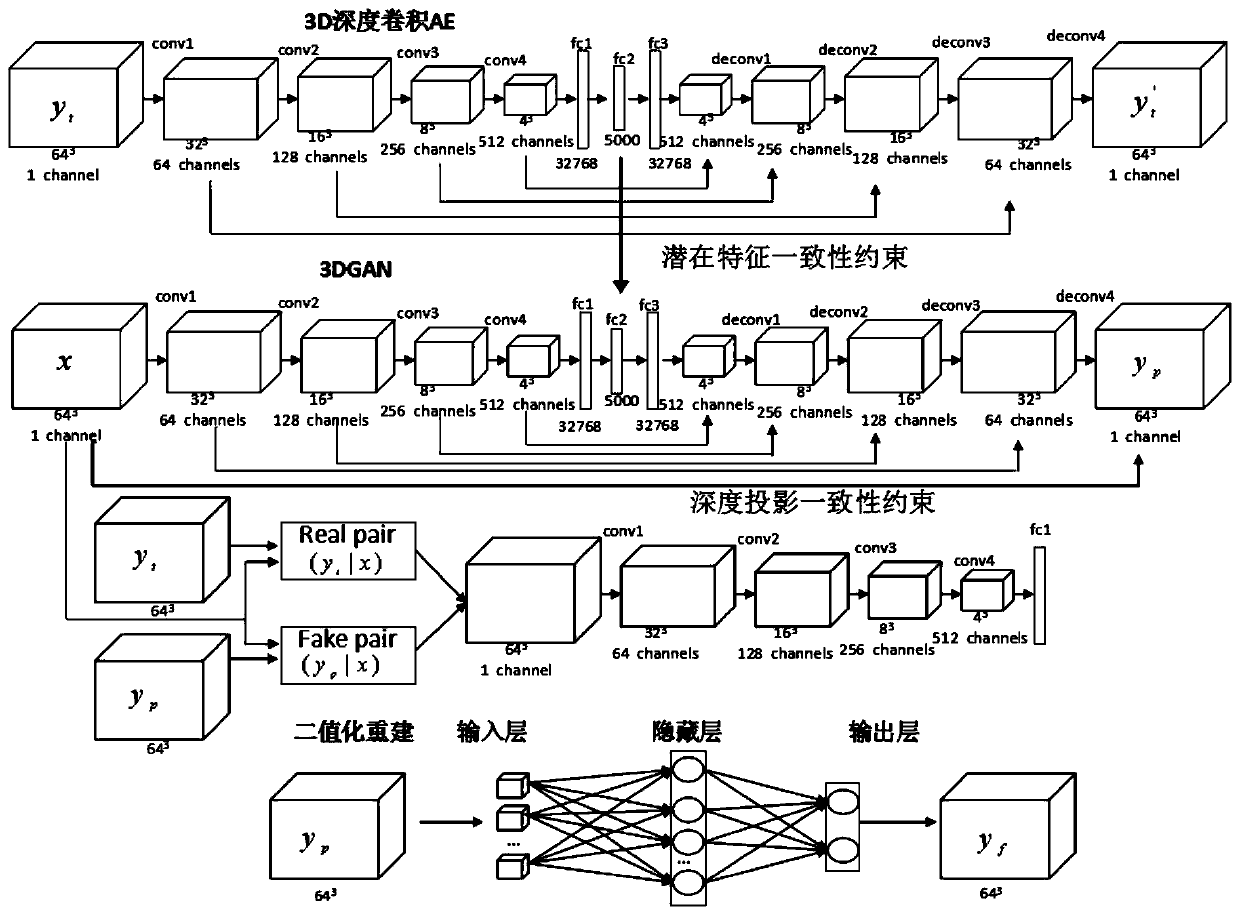
Three-dimensional reconstruction method based on deep learning
ActiveCN109993825AAvoid introducingAvoid multi-link error accumulationImage enhancementImage analysisLearning machineVoxel
The invention discloses a three-dimensional reconstruction method based on deep learning, and the method comprises the steps: (1), reconstructing a complete three-dimensional shape of a target througha constrained potential vector of an input image, carrying out the mapping between a learning part and the complete three-dimensional shape, and achieving the three-dimensional reconstruction of a single depth image; (2) learning intermediate feature representation between the three-dimensional real object and the reconstruction object so as to obtain a target potential variable in the step (1);and (3) converting the predicted voxel floating value in the step (1) into a binary value by using an extreme learning machine to complete high-precision reconstruction.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
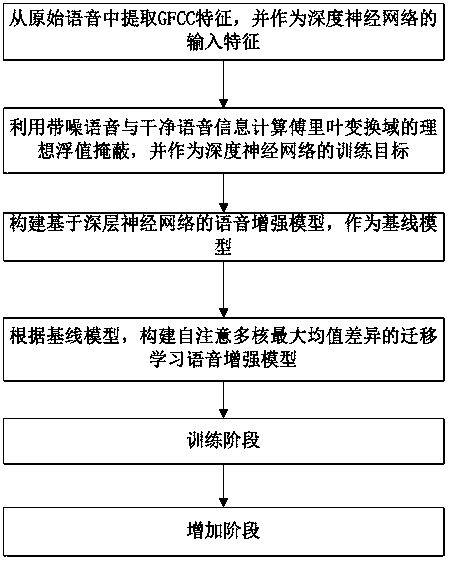
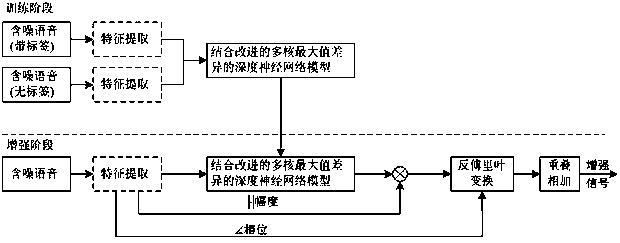
Self-attention multi-core maximum mean difference-based transfer learning speech enhancement method
ActiveCN110111803AImprove feature effectivenessImprove robustnessSpeech analysisFloat ValueSelf attention
The invention discloses a self-attention multi-core maximum mean difference-based transfer learning speech enhancement method, which comprises the following steps: extracting GFCC features from original speech and using the GFCC features as input features of a deep neural network; calculating ideal floating value masking of Fourier transform domain by using noisy speech and clean speech information, and using the ideal floating value masking as the training target of the deep neural network; building a speech enhancement model based on deep neural network; building a self-attention multi-coremaximum mean difference-based transfer learning speech enhancement model; training the self-attention multi-core maximum mean difference-based transfer learning speech enhancement model; inputting frame-level features of the noisy speech in the target domain, and rebuilding enhanced speech waveform. By adding a self-attention algorithm to the front end of the multi-core maximum mean difference andby minimizing the multi-core maximum mean difference between features noticed by the source field and features noticed by the target domain, transfer learning of the unlabeled target domain is realized, and the speech enhancement performance is improved. The method of the invention has a good application prospect.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
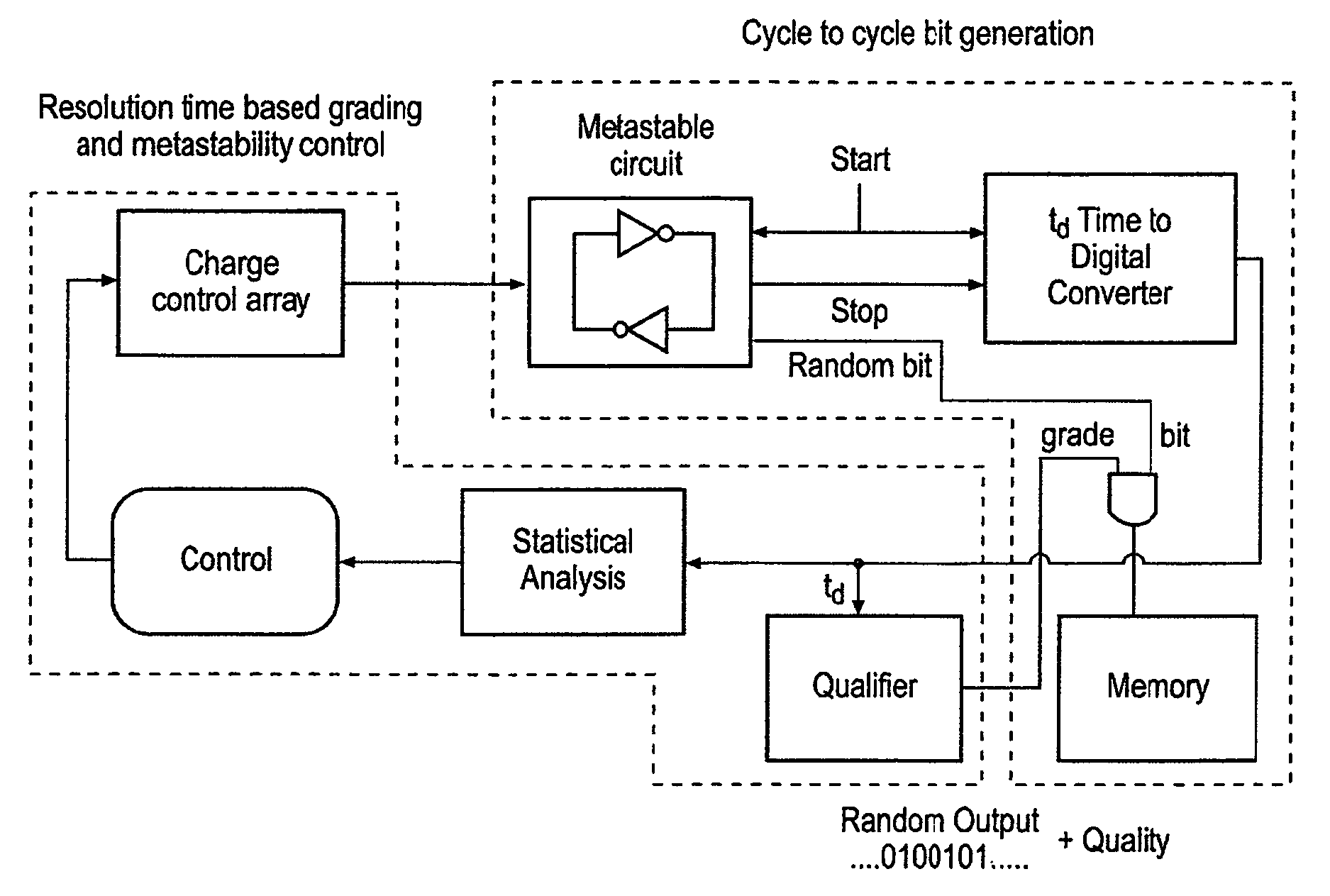
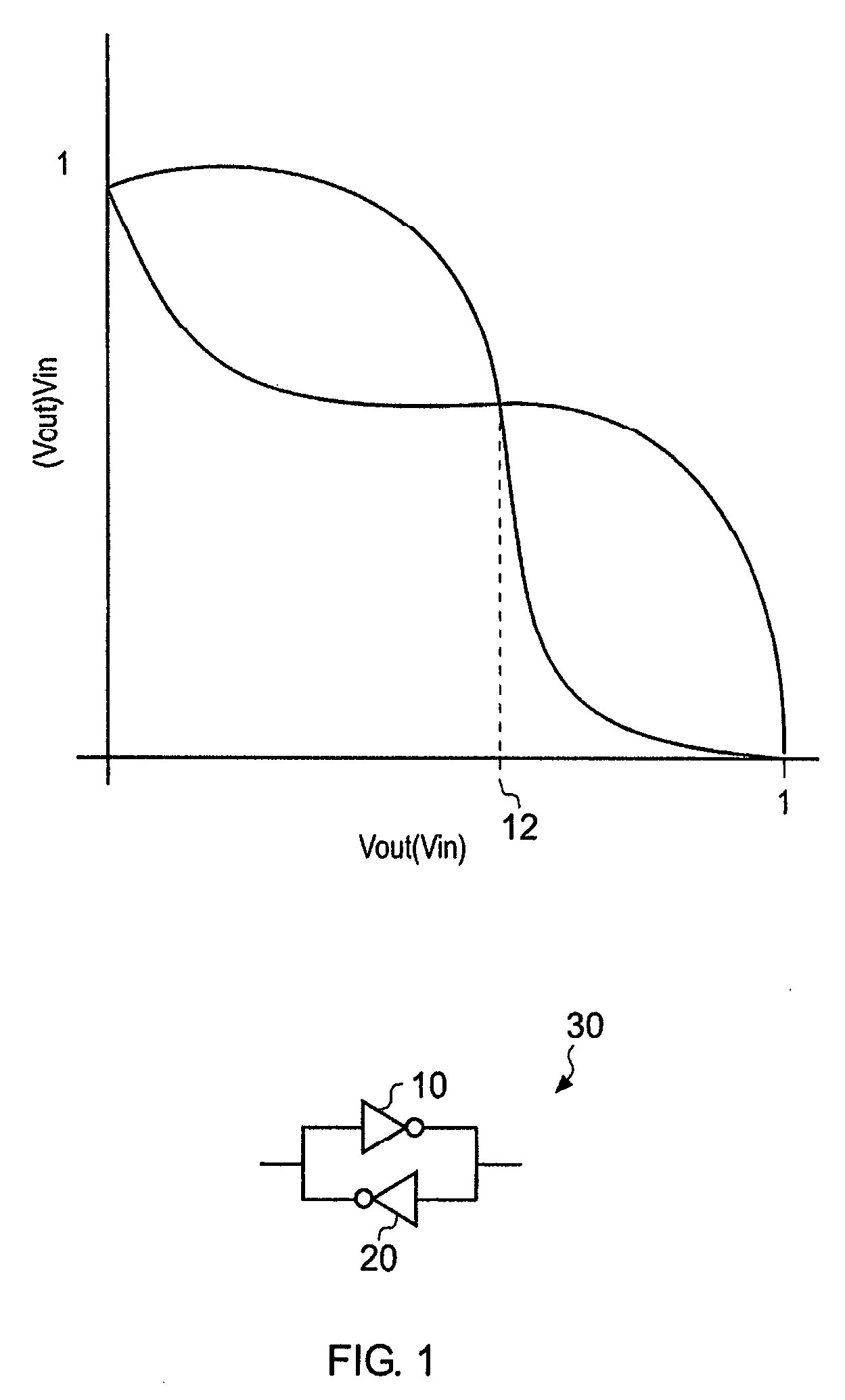
Random number generator
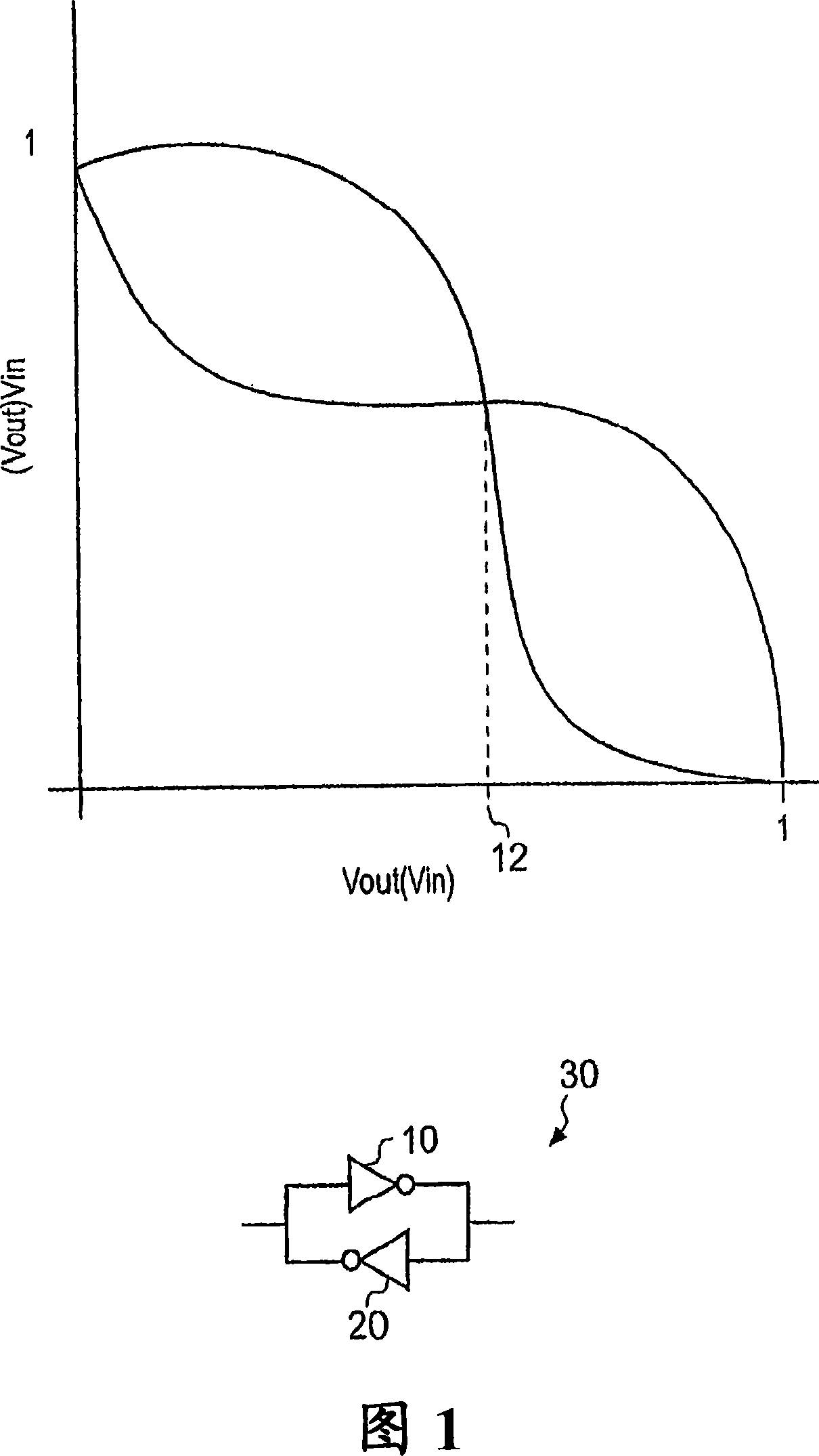
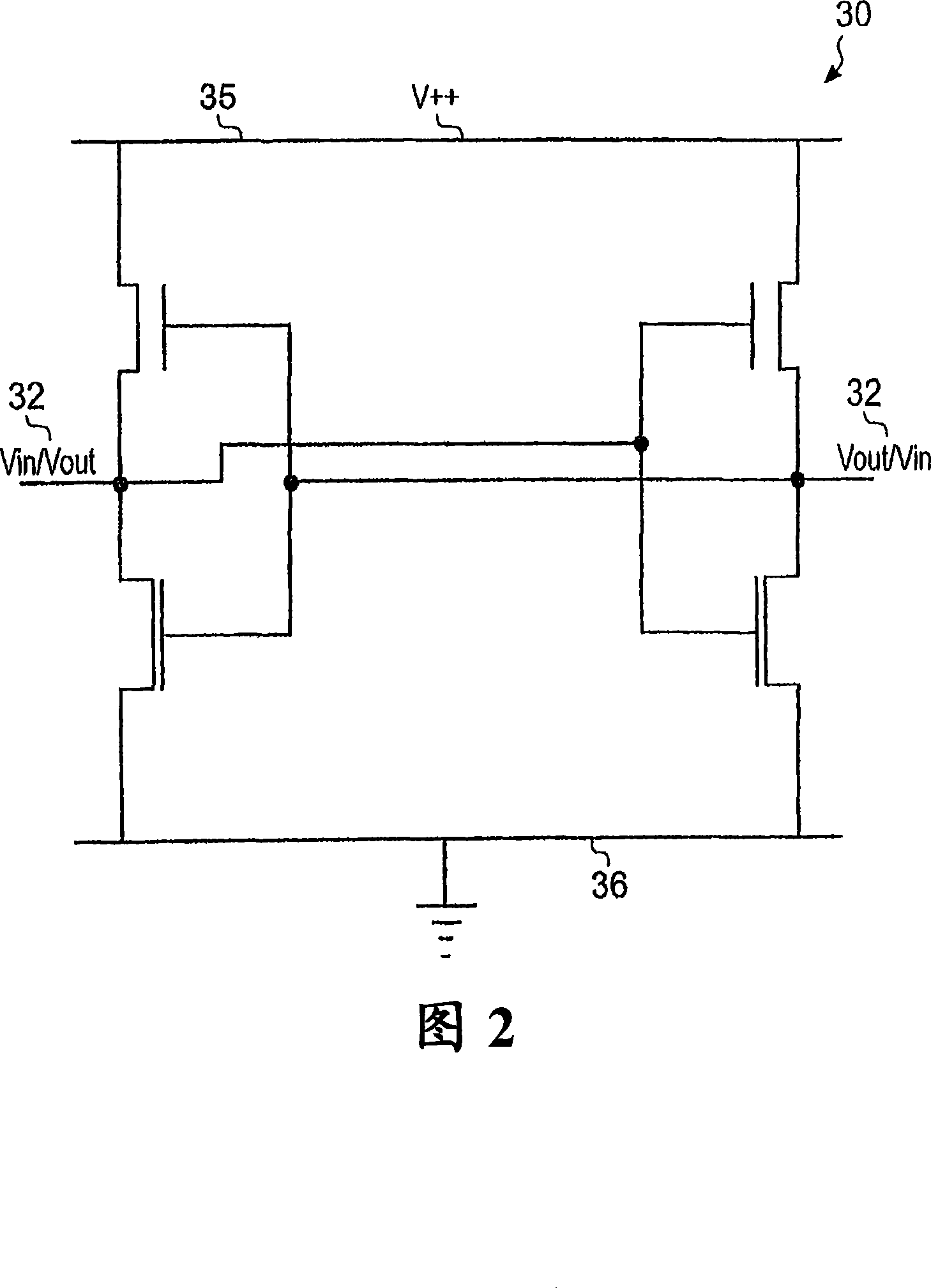
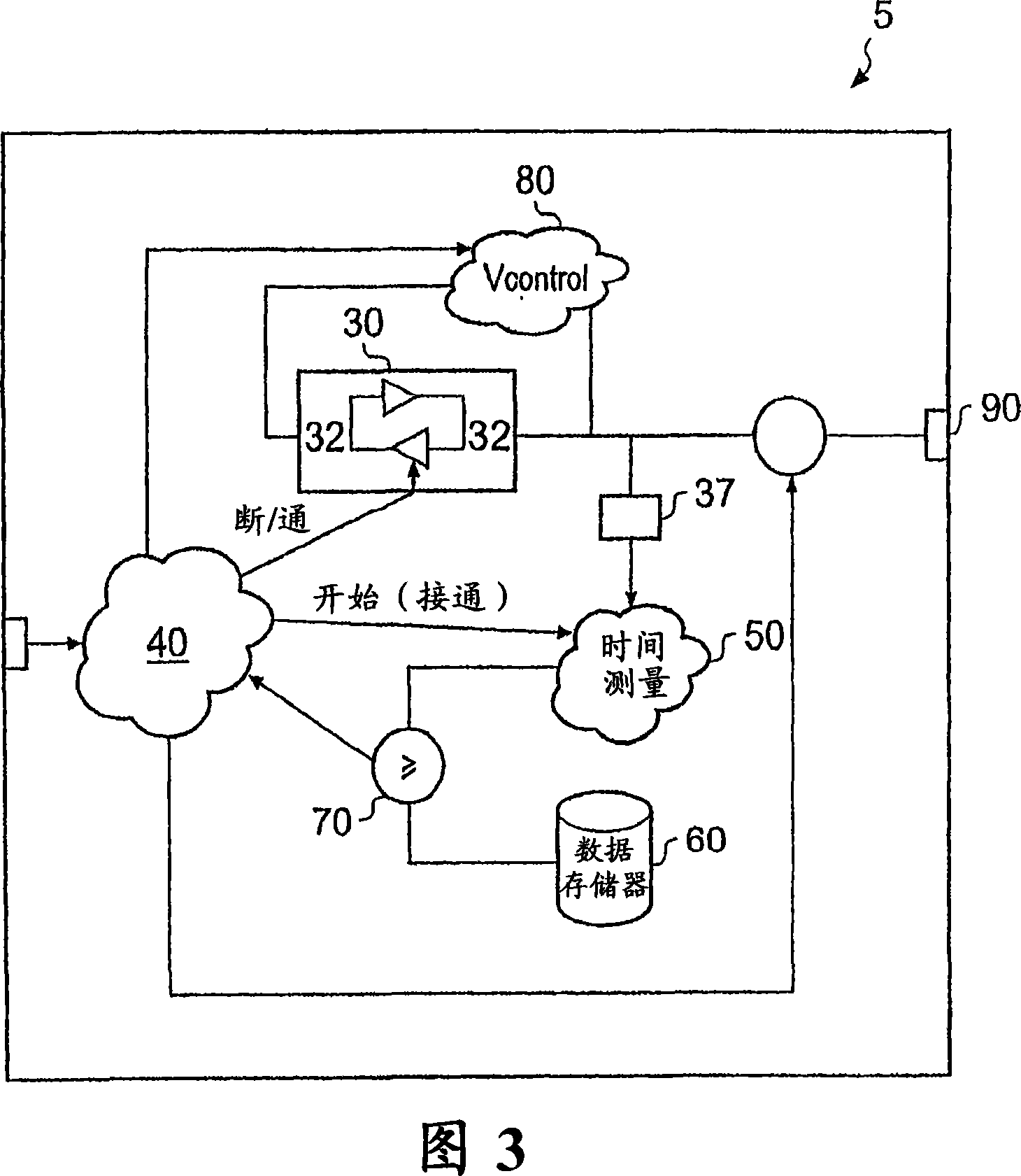
InactiveUS20080091755A1Avoid the needRandom number generatorsSecuring communicationStable stateBistable circuits
A circuit for generating a random output value is disclosed that comprises: a bistable circuit having two stable states in which a 0 or a 1 is output and having a balanced metastable state in which a floating value between 0 and 1 is output, said bistable circuit resolving from said metastable state to one of said stable states on being switched on, said state depending on a voltage level at a port on said bistable circuit; a voltage level control circuit for controlling a voltage level at said port on said bistable circuit; a time measuring circuit for measuring a switching time taken for said bistable circuit to switch from said metastable state to one of said stable states following switch on; and control logic for controlling said time measuring circuit, said voltage level control circuit and a switching off and on of said bistable circuit, said control logic being adapted to perform a following sequence: control said voltage level control circuit to set a predetermined voltage level at said port on said bistable circuit, switch said bistable circuit on, detect a measured switching time, and turn said bistable circuit off and if said measured switching time is longer than a predetermined value, output said resolved stable state of said bistable circuit as said random output value.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Air condition assist device electrical heating running method
ActiveCN104390312AAchieve securityImprove securityMechanical apparatusAir treatment detailsElectricityAutomatic control
The invention relates to the technical field of air conditioner devices, in particular to an air condition assist device electrical heating running method. The air condition assist device electrical heating running method uses a heat pump system and an auxiliary heating system. After the heat pump system is started, the auxiliary heating system is automatically started and stopped by constantly detecting indoor temperature. A default temperature range of single use of the heat pump system is set to range from -delta T to delta T, wherein T is given indoor temperature, delta T is upper and lower floating value of the given indoor temperature T, and when the indoor temperature is lower than or equal to the temperature -delta T, the auxiliary heating system is started for heating, and furthermore when the indoor temperature is larger than the temperature delta T, the auxiliary heating system stops the heating. The air condition assist device electrical heating running method can automatically control heating modes, preferentially uses a heat pump for the heating, saves energy resources, and simultaneously adjusts release heat of the auxiliary heating system according to the indoor temperature and the given temperature difference range, and thereby achieves optimal configuration of the heat, and is good in safety, stability and reliability.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES CHONGQING +2
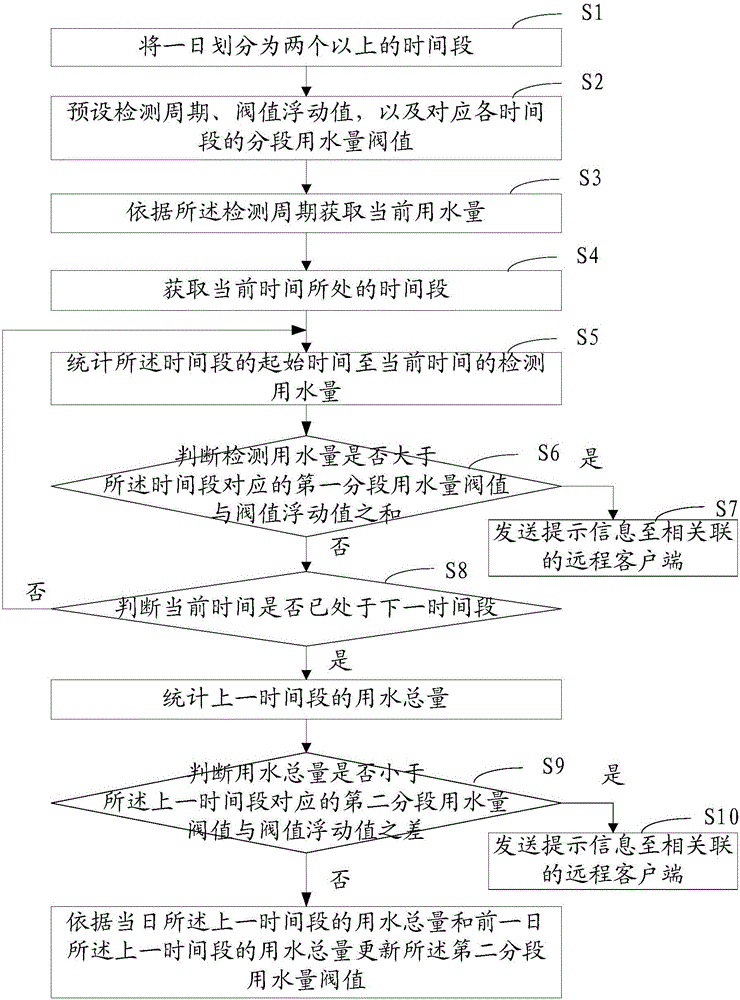
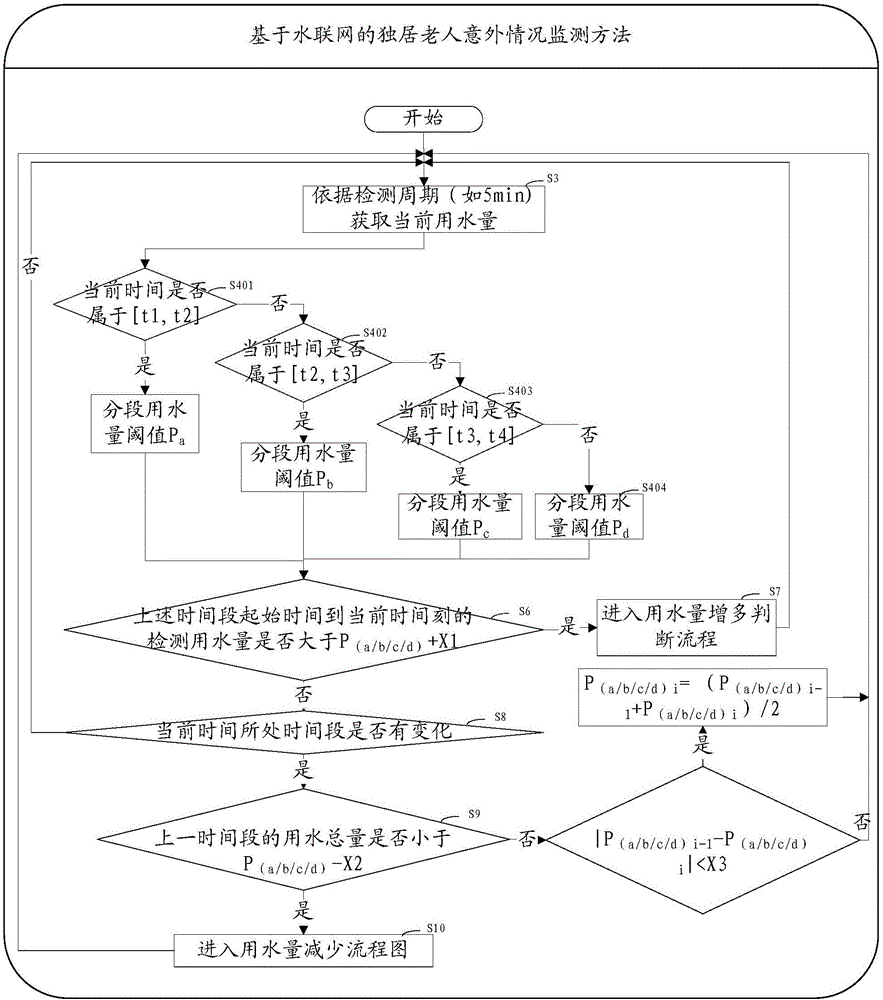
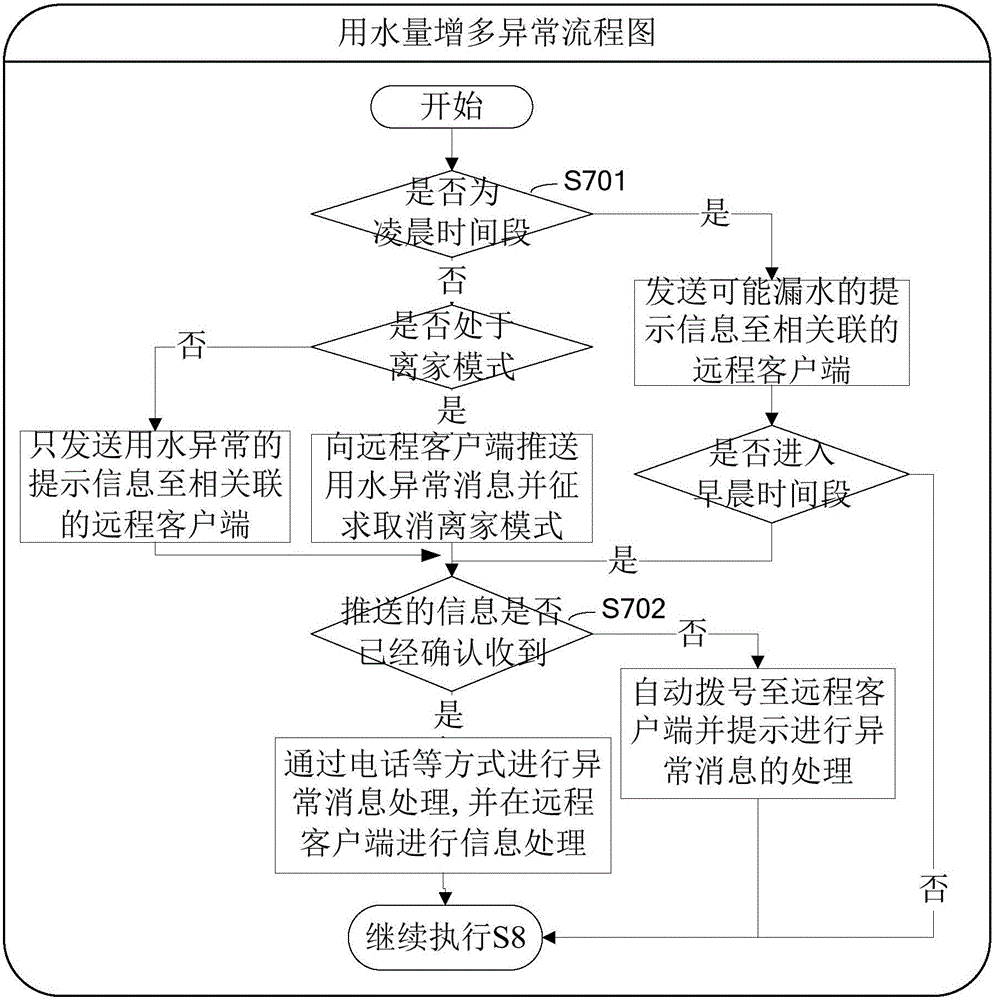
Internet of Water based remote monitoring method, system and client for elderly people living alone
InactiveCN105160616AMaster life status in real timeReal-time activityData processing applicationsWater basedFloat Value
The invention provides an Internet of Water based remote monitoring method, system and client for elderly people living alone. The method includes acquiring current water consumption volume; acquiring the time segment of the current time point; metering the detection water consumption volume from the start time point to the current time point of the time segment and calculating the difference value between a second time segment water consumption volume threshold and a threshold floating value; detecting whether the water consumption volume is greater than the sum of a first time segment water consumption threshold and the threshold floating value, sending prompt information to the connected remote client if water consumption volume is greater than the sum of the first time segment water consumption threshold and the threshold floating value the or judging whether the current time point is in the next time segment or not if the water consumption volume is not greater than the sum of a first time segment water consumption threshold and the threshold floating value; metering the water consumption total volume of the last time segment if the current time point is in the next time segment and judging whether the water consumption total volume is smaller than the difference value of the water consumption volume threshold of the second time segment corresponding to the last time segment and the threshold floating value; sending the prompt information to the client if the water consumption total volume is smaller than the difference value of the water consumption volume threshold of the second time segment corresponding to the last time segment and the threshold floating value or updating the time segment water consumption volume threshold of the corresponding time segment according to the water consumption total volume of the last time segment of the last day and the water consumption total volume of the last time segment of the day. Therefore, low-cost and high-accuracy remote monitoring of life state of the elderly people is realized and safety condition of the elderly people can be controlled.
Owner:FUJIAN UNIV OF TECH
Guide float valve tray
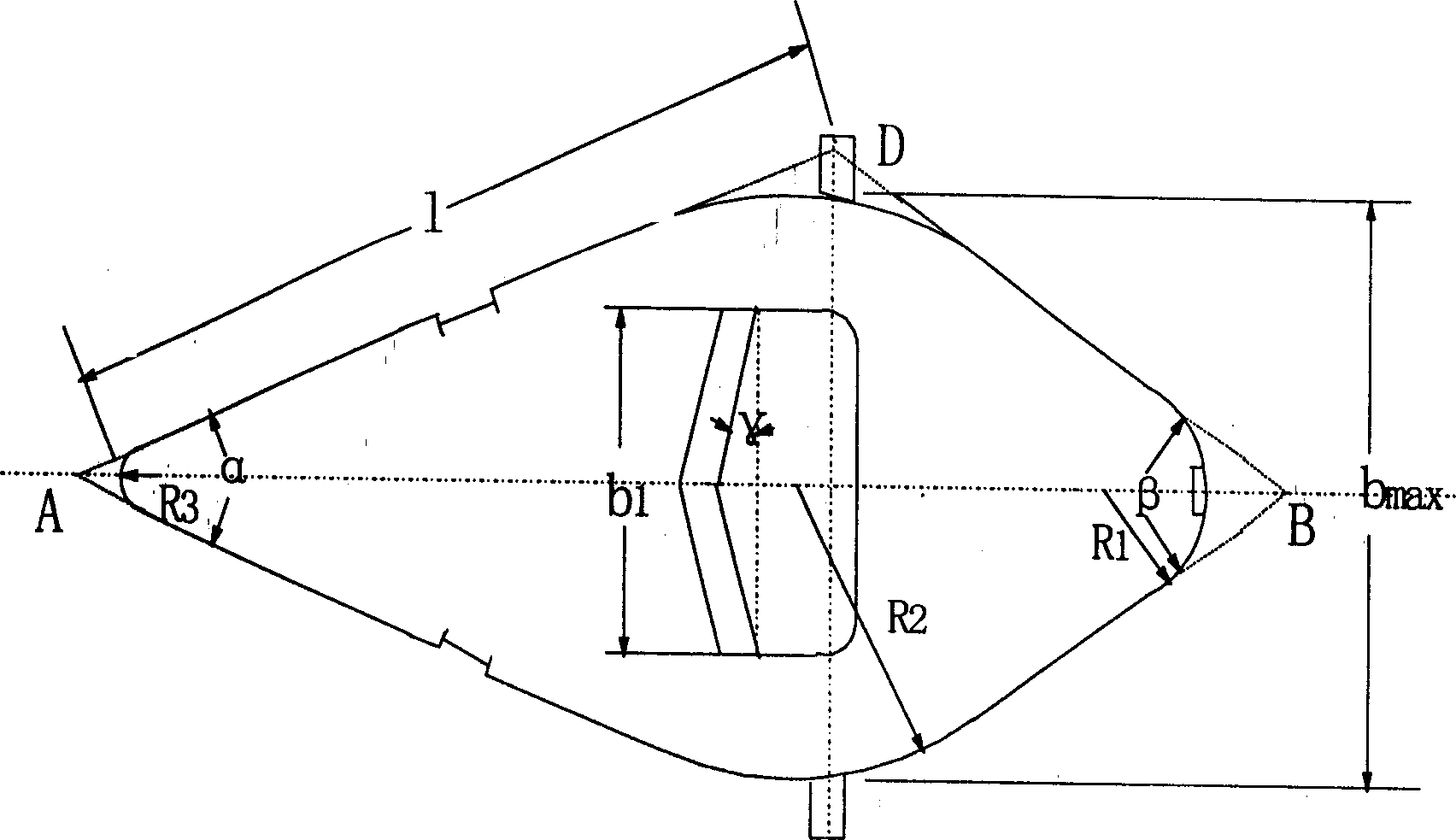
InactiveCN1389287AReduce resistanceLittle reverse propulsionFractional distillationFloat ValueLeg length
The present invention relates to a guide float valve plate which comprises a guide float valve which is a symmetrical quadrangular guide float valve, its valve cover is a quadrangular from with symmetrical diagonal liens, the included angle of long edges is directed against overflow weir, under the valve cover more than three valve legs are mouthed, front valve leg length is longer than rear valve leg length, so that when the float value is completely opened, between valve cover and valve hole plate an included angle toward overflow weir is opened, said included angle is 2-10 deg, and on the valve cover can be mounted the guide hole and guide plate. Said invention can effectively reduce liquid level gradient on the plate, raise plate flux, raise mass transfer efficiency and reduce resistance of plate.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
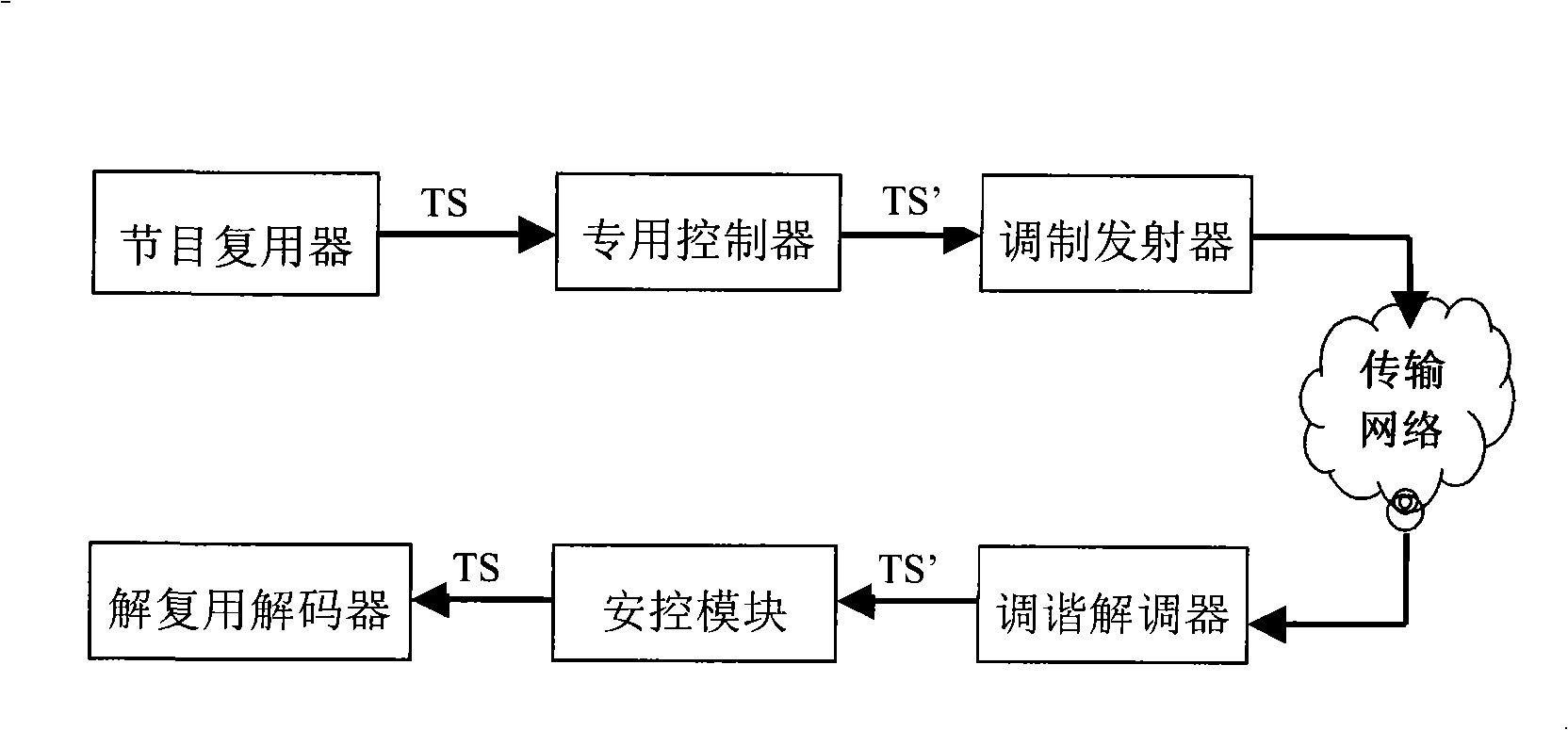
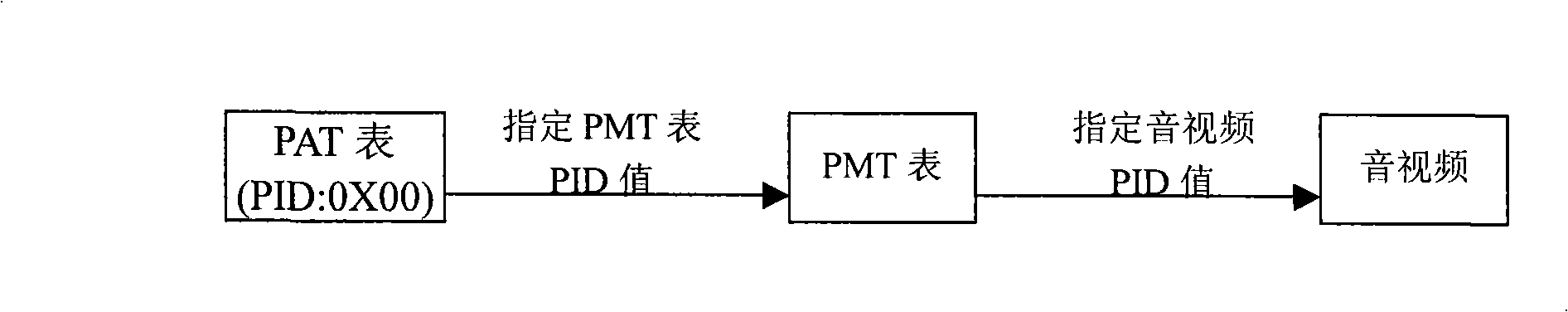
Transmission control method of digital television transmission stream and apparatus thereof
InactiveCN101360226ABlock receptionProtect interestsPulse modulation television signal transmissionFloat ValueDigital television
The invention relates to a transmission controlling method and a device for digital television transport stream, which make random floating to PID value of an appointed transport stream when an uplink port of a digital television system reuses a program and adopts the floated value as the actual PID value of transport stream; the uplink port transports the floating value of PID to a receiving equipment by an encryption mode; the receiving equipment analyzes random rules and obtains the actual PID value of the transport stream according to the appointed PID of the transport stream. The illegal receiving equipment cannot obtain the floating random number of the PID value and receive the program without knowing the encryption mode, a cryptographic key and transmission rules.
Owner:HUAYA MICROELECTRONICS (SHANGHAI) INC
GNSS signal processing methods and apparatus with ambiguity convergence indication
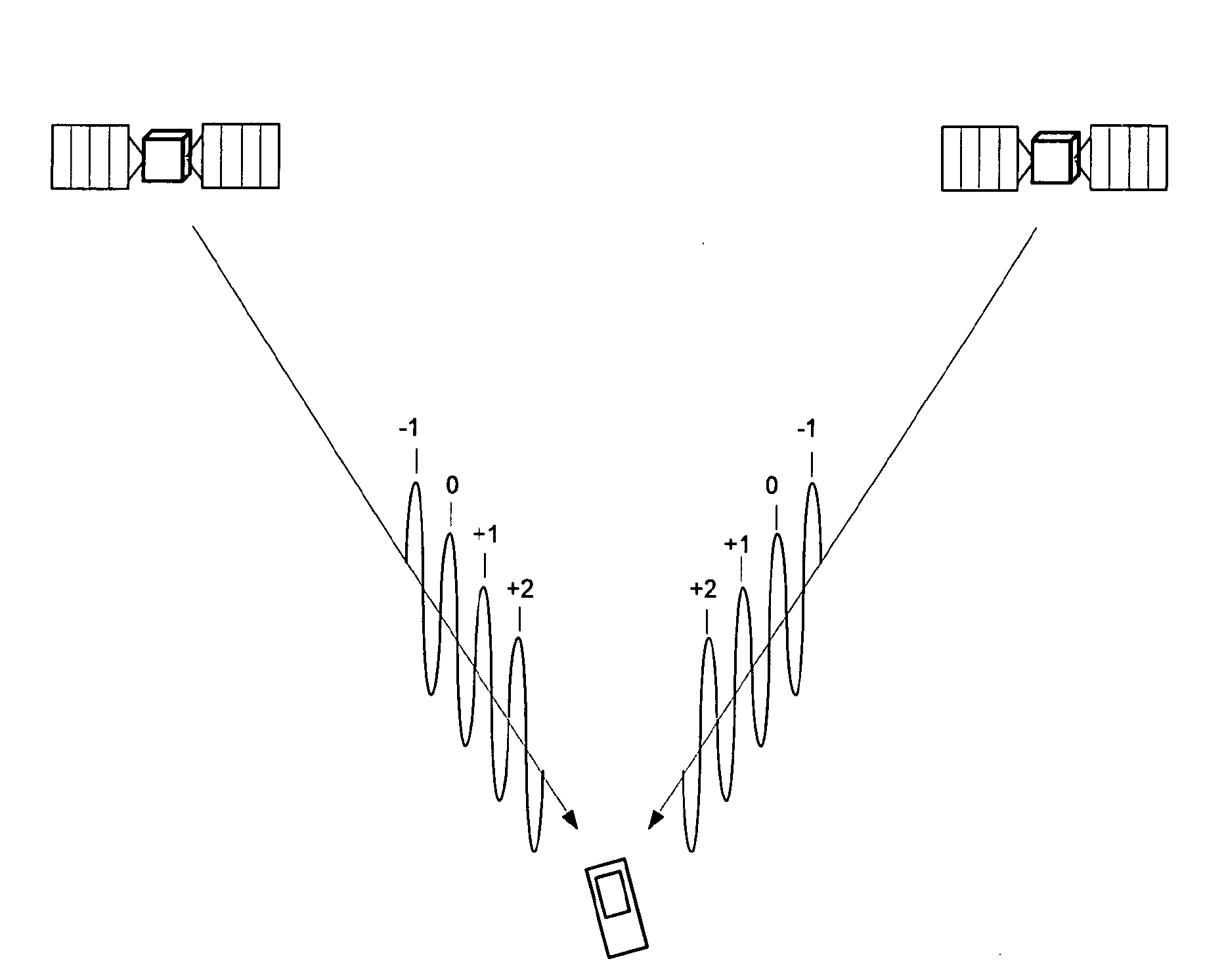
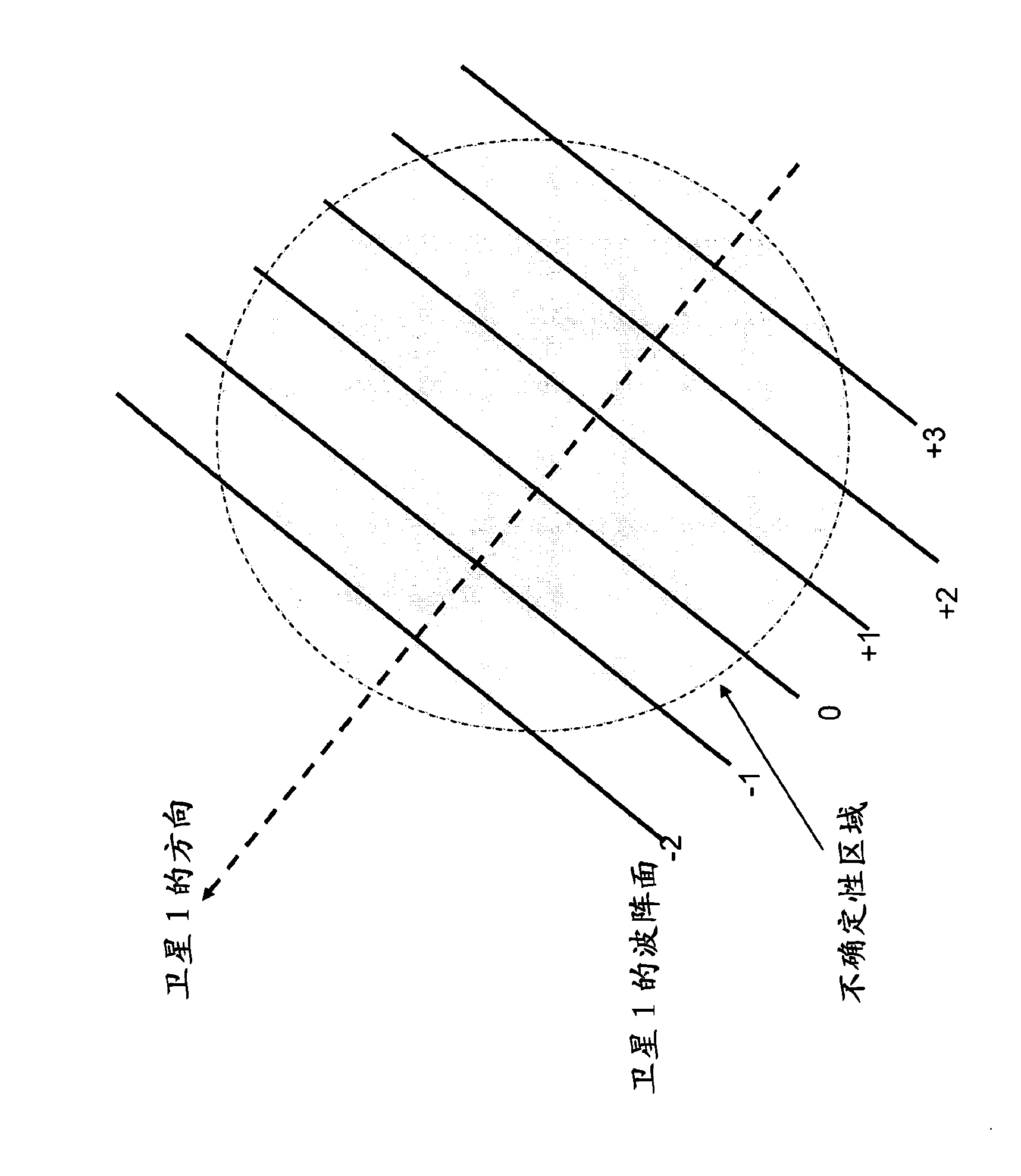
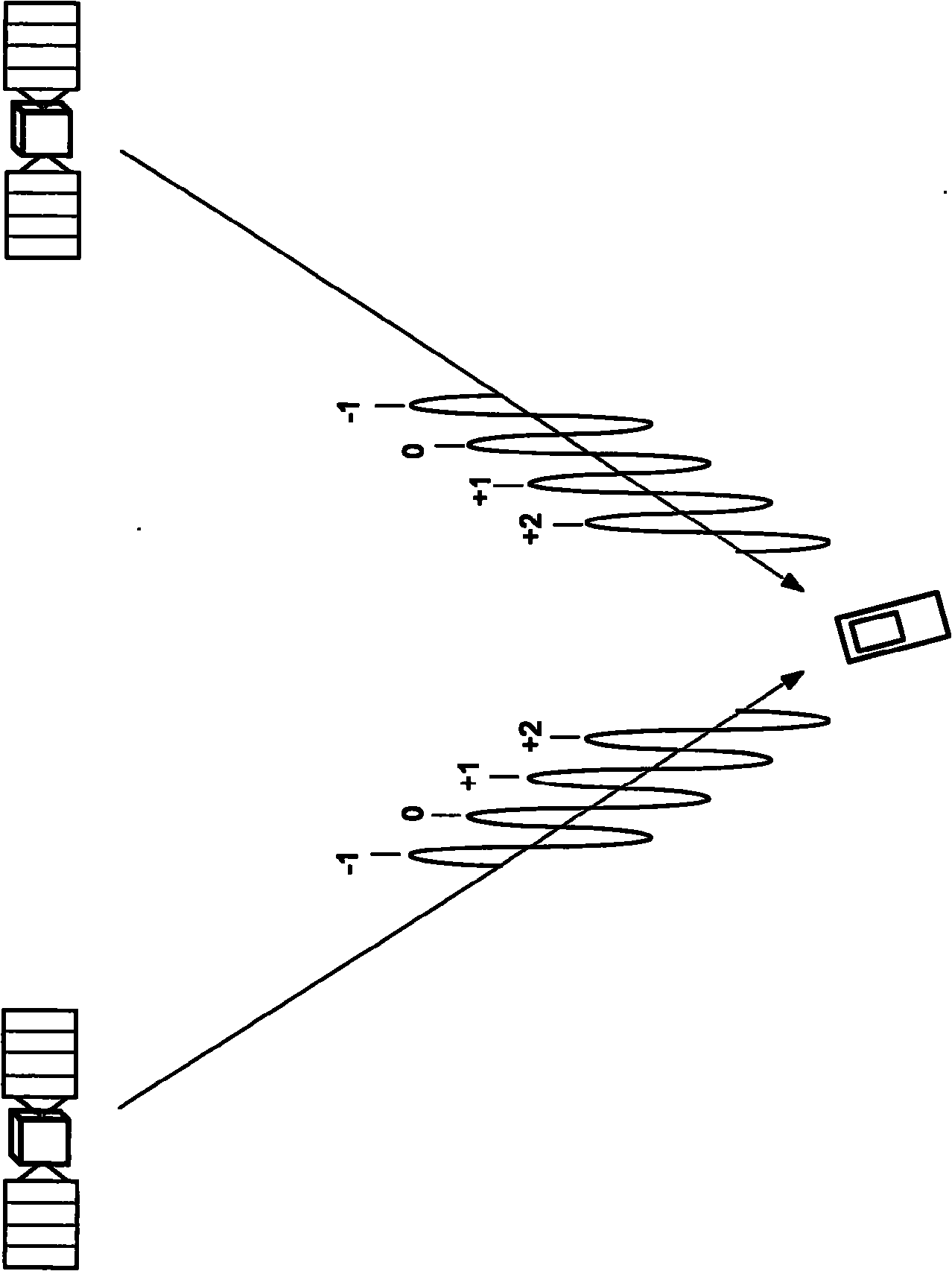
Methods and apparatus are provided for estimating parameters, i.e. ambiguities, derived from GNSS signals. Observations of a GNSS signal from each of a plurality of GNSS satellites are obtained (2120). The observations are fed to a filter having a state vector comprising a float ambiguity for each received frequency of the GNSS signals (2140). The filter estimates a float value for each float ambiguity of the state vector and covariance values associated with the state vector. Integer values are assigned to at least a subgroup of the estimated float values to define a plurality of integer ambiguity candidate sets (2160). A weighted average of the candidate sets is formed (2200). A formal precision value based on covariance values of the filter is determined (2205), the formal precision value being a measure for an achievable precision. An achieved precision value of the weighted average is determined (2210). The achieved precision value is compared with the formal precision value to obtain a convergence value (2215). A convergence of the determination of the state vector is indicated (2218). Ambiguities of the weighted average can be used in subsequent operations to aid in determining a position of the receiver or can be used to prepare data, e.g., in a network processor that can be used to augment position information of a rover.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Trip discrimination method for pure electric power system
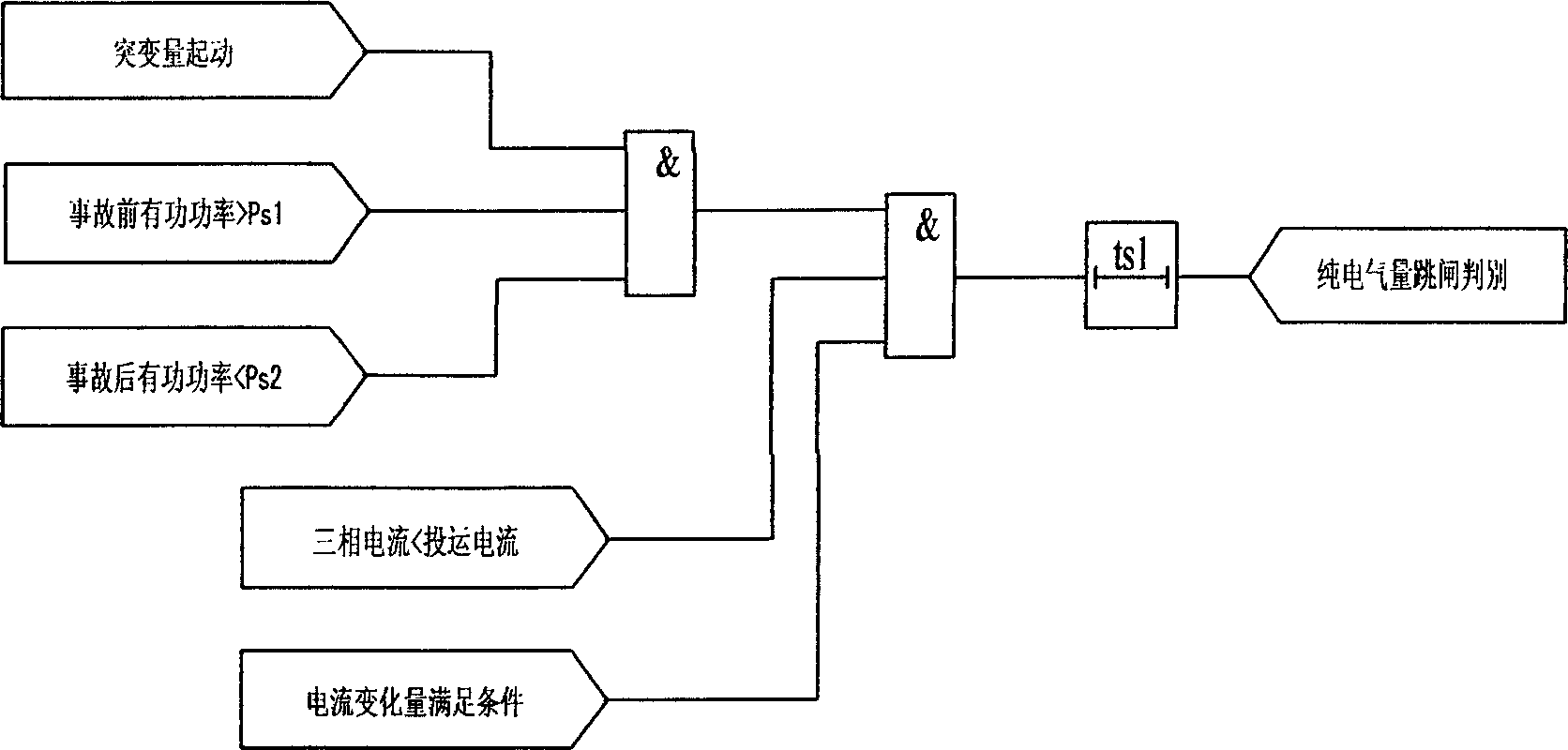
InactiveCN1808821AIncrease the total output valueTrip will notEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault locationElectricityFloat Value
This invention relates to electricity power system jump judging method, which adopts the following bases: A, protruding variables starting; b, )P-0.2Sí¦PS1 means front power larger than set value PSI; c, PtíœPS2, fault power smaller than set value PS2; d, three-phase current IíœIS1, current smaller than operation current; e, current variable satisfies the base larger than current float gate; f, tí¦tS1, determining the above data time lag, wherein the PSI smaller than transmission power value; PS2 is larger than zero and the maximum floating value with operation current IS1 larger than open circuit current; the UN is ratio voltage.
Owner:NR ELECTRIC CO LTD
Intelligent recognition system for optimal charging current and method thereof
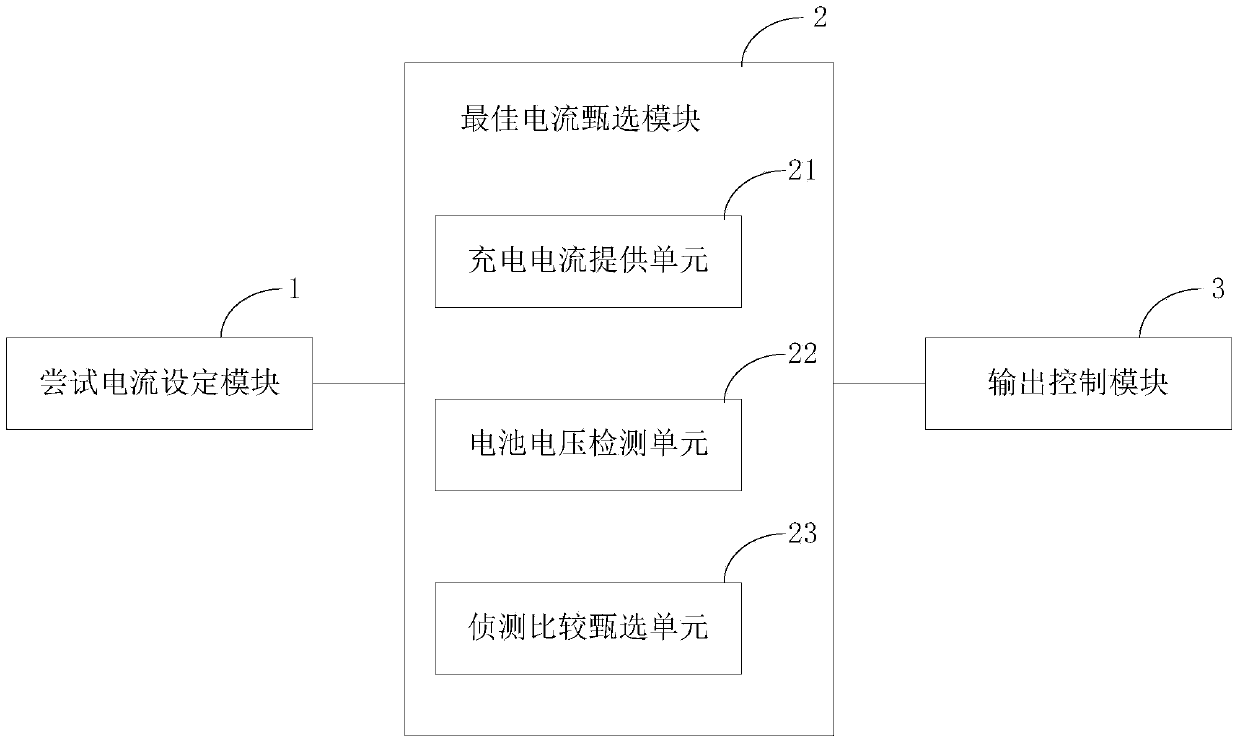
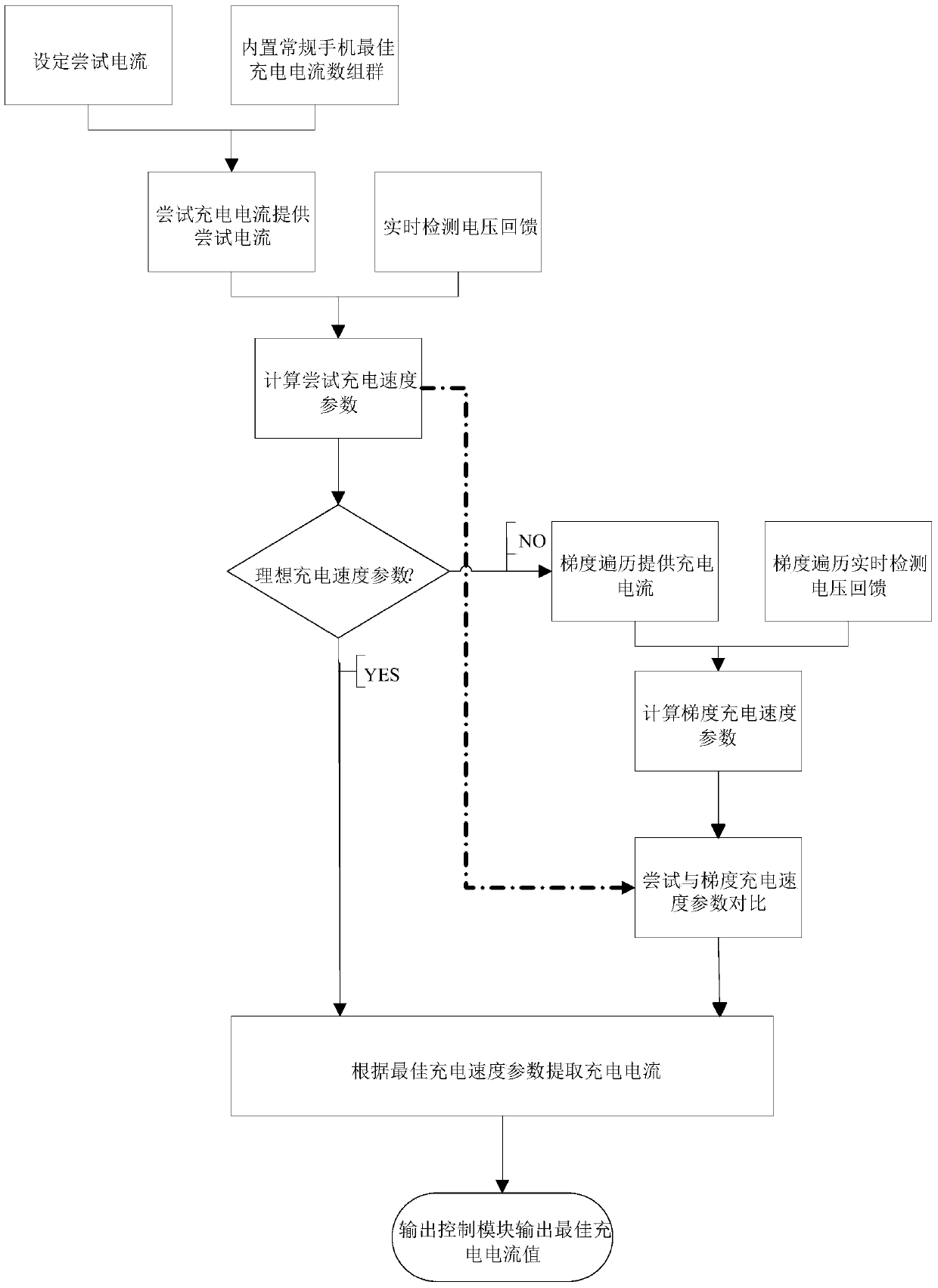
InactiveCN103746421AAvoid lossBest charging currentBatteries circuit arrangementsSecondary cells charging/dischargingFloat ValueCharge current
The invention discloses an intelligent recognition system for an optimal charging current and a method thereof. The intelligent recognition system comprises a trial current setting module, an optimal current selecting module and an output control module, wherein the trial current setting module is used for setting a charging current of a mobile phone, and the charging current of the mobile phone is tried by the optimal current selecting module; the optimal current selecting module is used for detecting the floating value of the current charging voltage at intervals of set time, if the floating value is greater than a set value, other charging currents are selected from the charging currents set by the trial current setting module, and if all the charging currents set by the trial current setting module are detected, the charging current of which the floating value of the charging voltage is minimum is selected as the optimal charging current; the output control module is used for charging batteries of the mobile phone according to the result selected by the optimal current selecting module. By using the intelligent recognition system and the method, the problems that the batteries can not be charged caused by insufficient charging current and the service life of the batteries is shortened by charging under the condition of overcurrent charging current can be solved effectively.
Owner:WINGTECH COMM
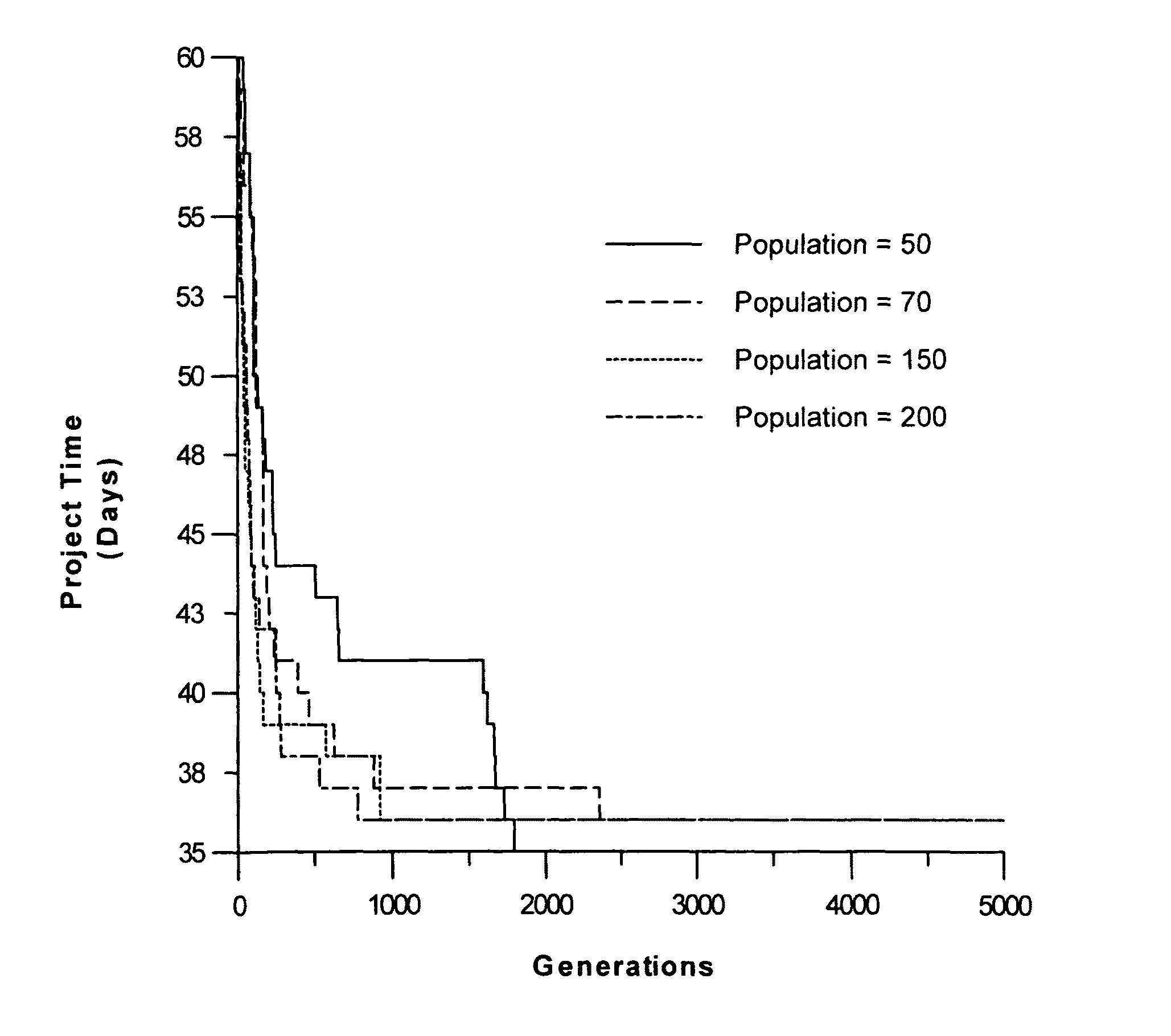
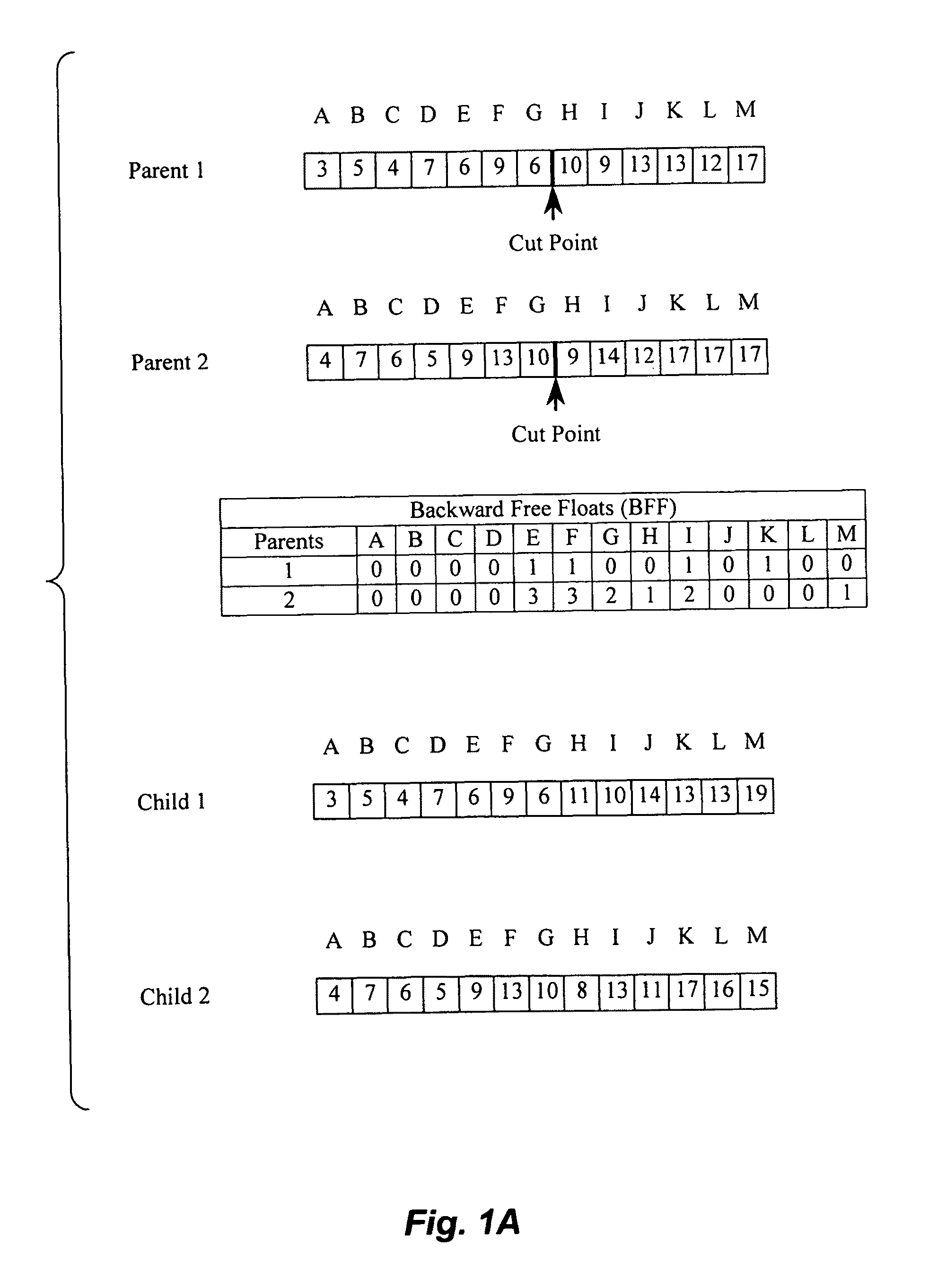
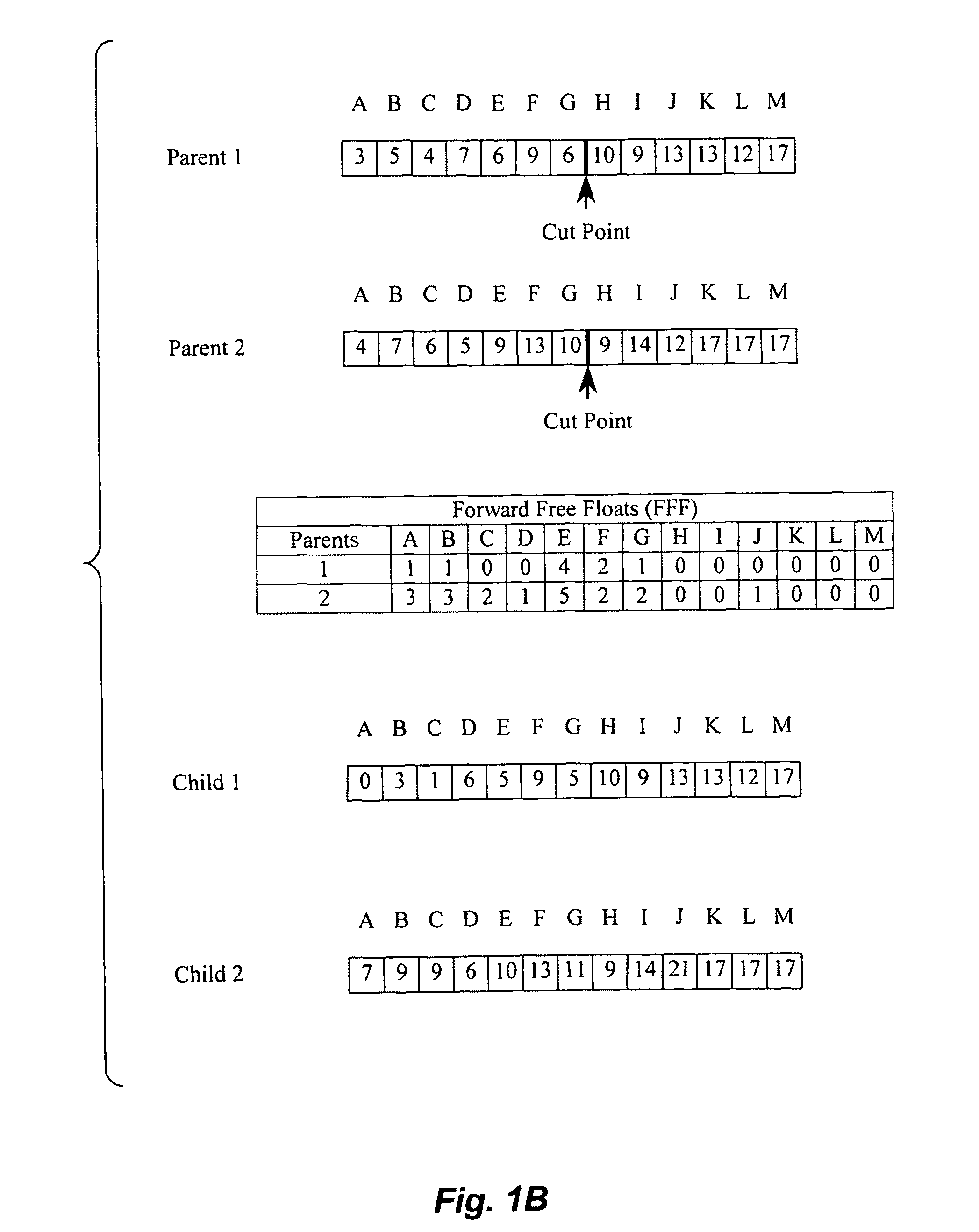
Method of generating precedence-preserving crossover and mutation operations in genetic algorithms
InactiveUS8250007B2Computing operations for optimisationDigital computer detailsStart timeFloat Value
A method for generating precedence-preserving crossover and mutations operations for genetic algorithms is provided. The method is based on the determination of activities' Forward Free Float (FFF) and Backward Free Float (BFF) values, utilizing these float values in randomly selected forward and backward paths, respectively. The method may be applied to the finance-based scheduling domain using large scale projects, with the chromosomes of the genetic algorithm encoding activities' start times in a resource-constrained scheduling problem.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
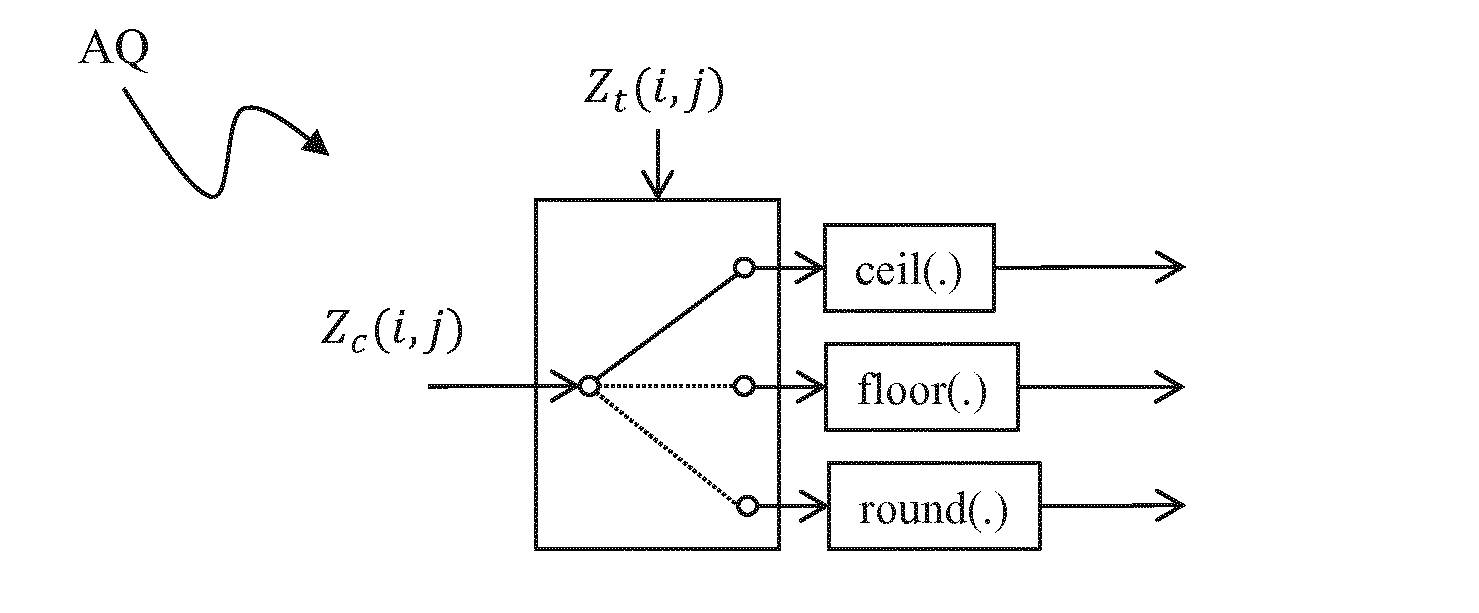
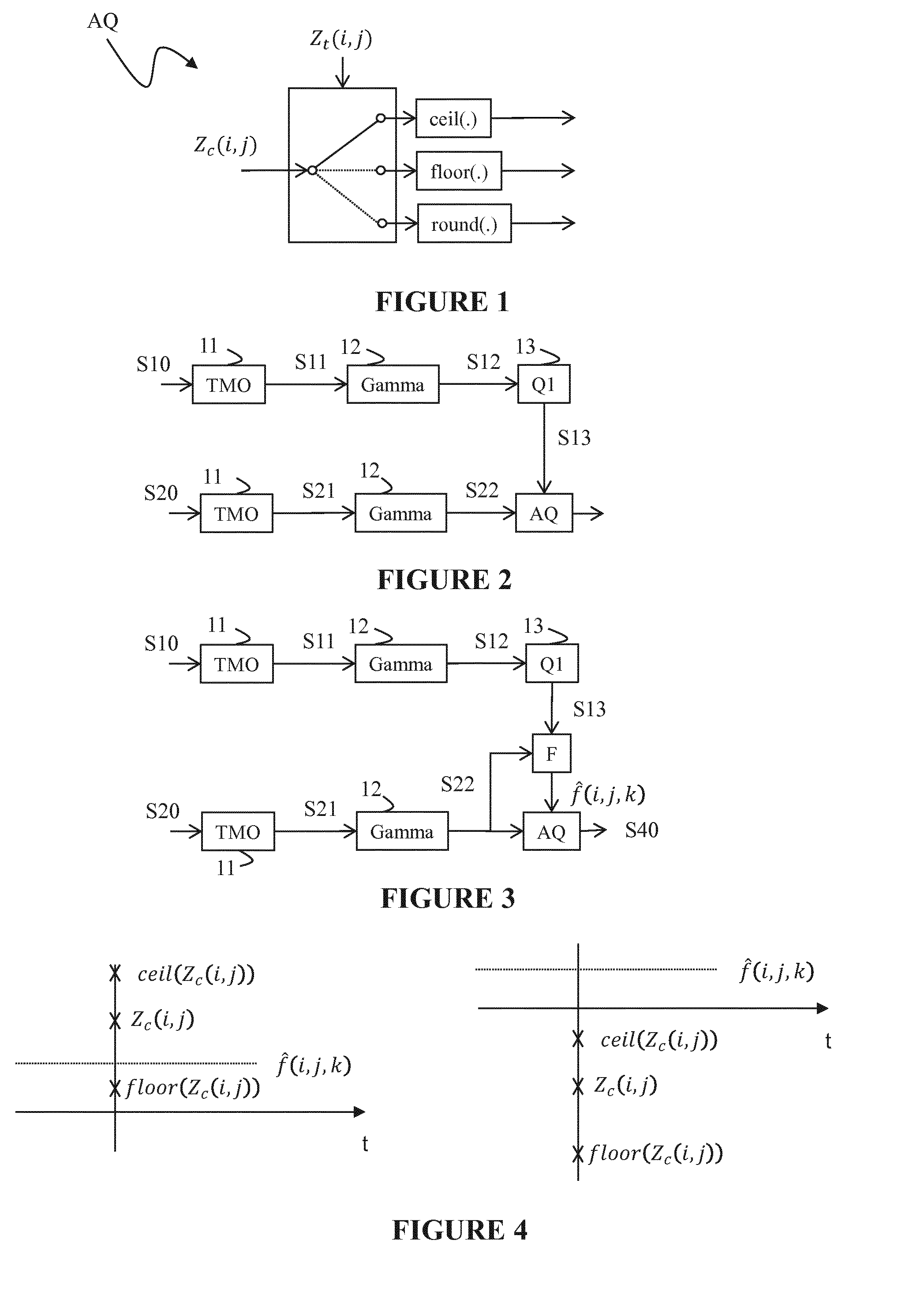
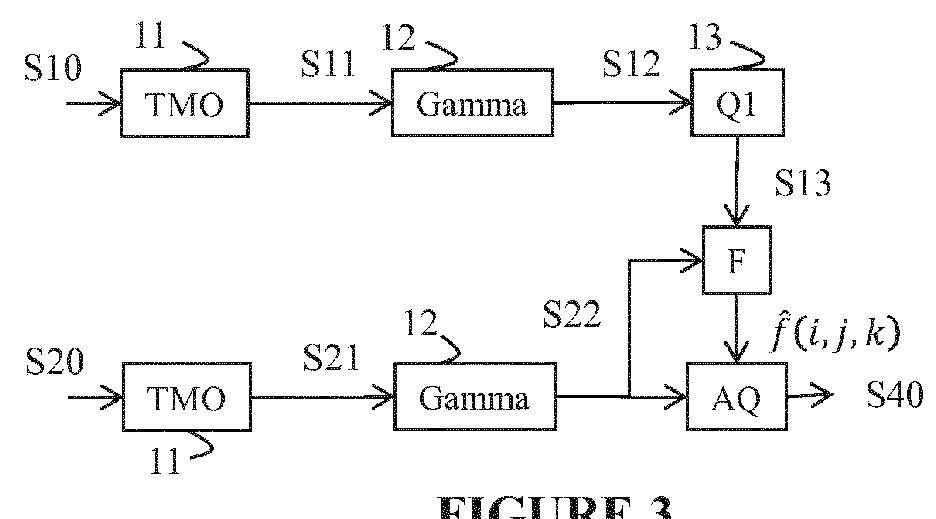
Method and device for quantising the floating value of a pixel in an image
ActiveUS20170006288A1Improve coding efficiencyImage enhancementDigital video signal modificationFloat ValueAlgorithm
The invention relates to a method and device for quantising the floating value of a pixel of an image by rounding either to a lesser whole number, to a greater whole number, or to the whole number closest to this floating value. The method is characterised in that the selection of rounding this floating value is determined based on a test value.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
Random value generator
InactiveCN101174201AAids in detectionRandom number generatorsSecuring communicationStable stateBistable circuits
The present invention discloses a circuit for generating a random output value which comprises: a bistable circuit having two stable states in which a 0 or a 1 is output and having a balanced metastable state in which a floating value between 0 and 1 is output, said bistable circuit resolving from said metastable state to one of said stable states on being switched on, said state depending on a voltage level at a port on said bistable circuit; a voltage level control circuit for controlling a voltage level at said port on said bistable circuit; a time measuring circuit for measuring a switching time taken for said bistable circuit to switch from said metastable state to one of said stable states following switch on; and control logic for controlling said time measuring circuit, said voltage level control circuit and a switching off and on of said bistable circuit, said control logic being adapted to perform a following sequence: control said voltage level control circuit to set a predetermined voltage level at said port on said bistable circuit, switch said bistable circuit on, detect a measured switching time, and turn said bistable circuit off and if said measured switching timeis longer than a predetermined value, output said resolved stable state of said bistable circuit as said random output value.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
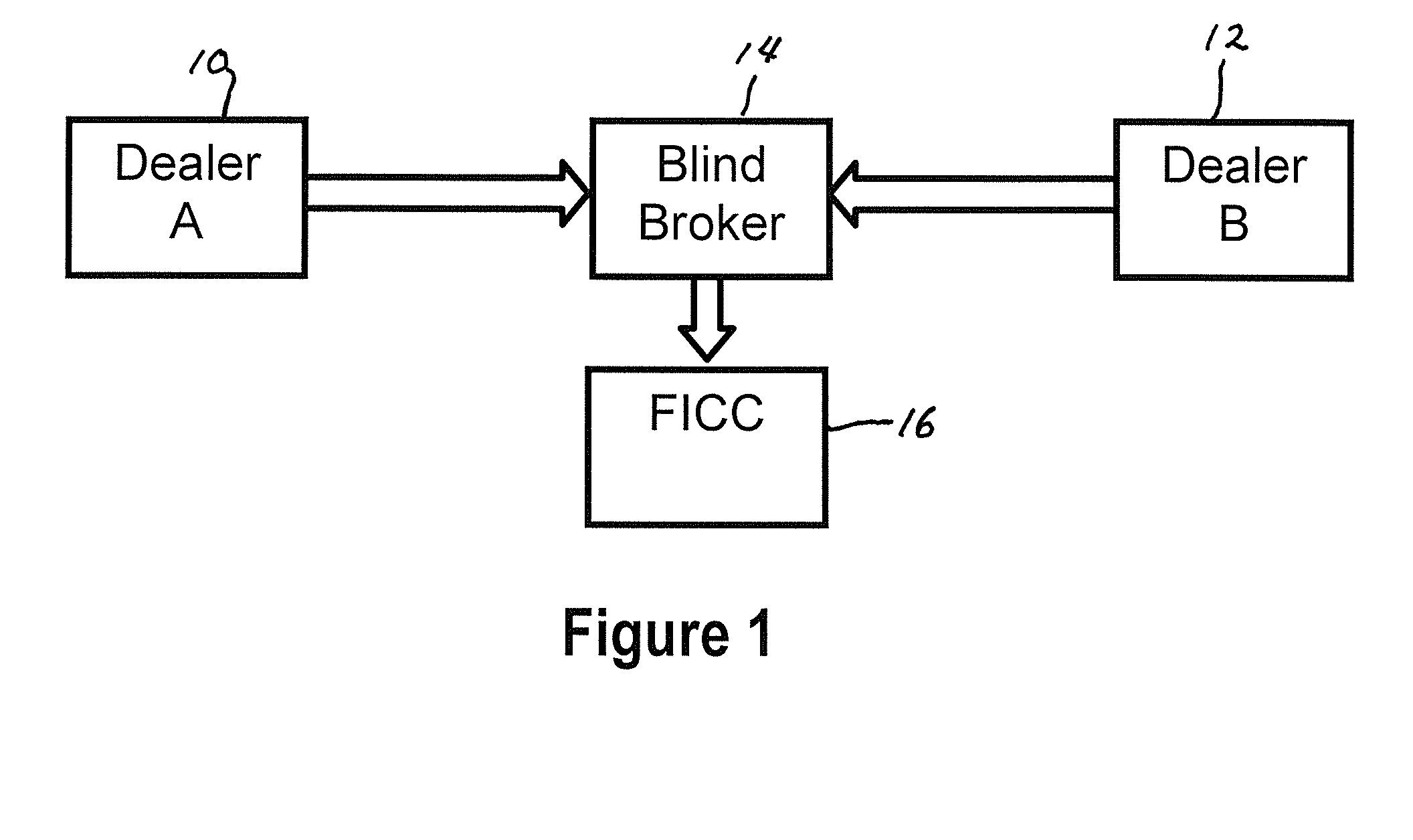
Method and apparatus for gcf repo index instrument
A method and system for a GCF repo swap transaction includes generating an index using a limited set of GCF contracts, and using the index value as a value in a GCF repo swap. The index value may be used as a variable or floating value in the swap, or may be used at the fixed value in the swap.
Owner:DEPOSITORY TRUST & CLEARING CORPORATION
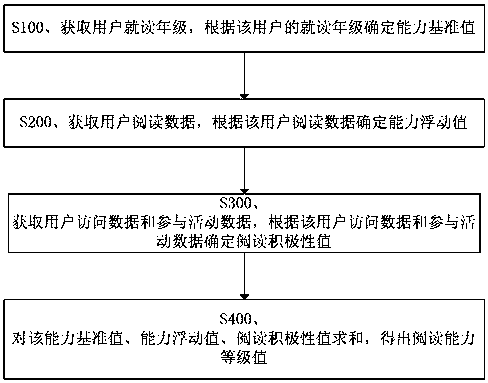
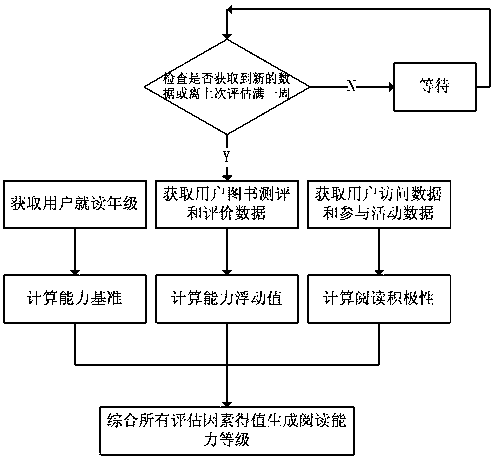
Reading ability level assessment method and system
The present invention provides a method for assessing reading ability grades, which at least includes the following steps: obtaining a user's grade, determining a benchmark value of ability according to the user's grade; obtaining user reading data, and determining a floating value of ability according to the user's reading data; obtaining user Access data and participation activity data, determine the reading enthusiasm value according to the user access data and participation activity data; sum the ability benchmark value, ability floating value, and reading enthusiasm value to obtain the reading ability level value. The invention also provides a reading ability grade evaluation system.
Owner:深圳悦好科技有限公司
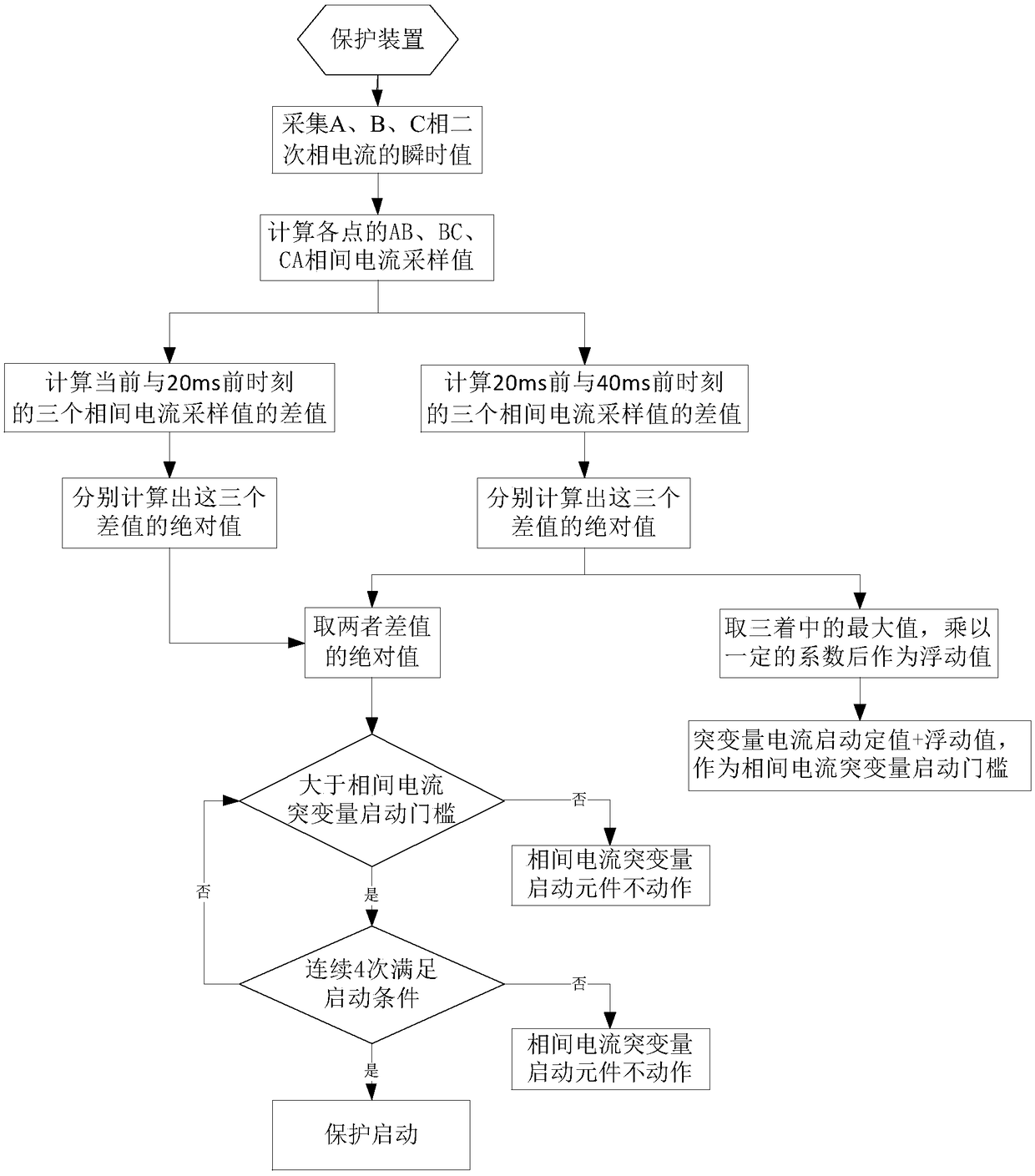
A method for judging the startup of an interphase current mutation amount through a floating threshold
ActiveCN109193591AAvoid frequent startupProtection frequently startsArrangements responsive to excess currentFloat ValueEngineering
The invention discloses a method for judging the startup of an interphase current mutation amount through a floating threshold. The realization method is that the floating value is increased on the basis of the fixed value of the starting current of the sudden change amount, and the starting threshold of the sudden change amount of the current between phases is taken as the starting threshold value. When the instantaneous value of the interphase current abrupt change is greater than the threshold of the interphase current abrupt change, the interphase current abrupt change element is allowed to start. Using the method of judging the sudden change of current between phases by floating threshold, the frequent start-up of the protection device can be prevented when the error of the system frequency relative to the power frequency exceeds + / - 2 Hz during operation.
Owner:BEIJING SIFANG JIBAO AUTOMATION +1
ECN based congestion control method with prediction verification
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
GNSS signal processing methods and apparatus with ambiguity selection
Methods and apparatus are provided for estimating parameters, i.e. ambiguities, derived from GNSS signals. Observations of a GNSS signal from each of a plurality of GNSS satellites are obtained (4120). The observations are fed to a filter having a state vector at least comprising a float ambiguity for each received frequency of the GNSS signals, each float ambiguity constituting a real number estimate associated with an integer number of wavelengths of the GNSS signal between a receiver of the GNSS signal and the GNSS satellite from which it is received, and the filter being for estimating a float value for each float ambiguity of the state vector (4140). A subset of float ambiguities of the state vector is selected (4150). Integer values are assigned to the estimated float values of the float ambiguities of the subset to define a plurality of integer ambiguity candidate sets (4160). A quality measure is determined for each of the candidate sets. A weighted average of the candidate sets is formed (4200). Ambiguities of the weighted average can be used in subsequent operations to aid in determining a position of the receiver or can be used to prepare data, e.g., in a network processor that can be used to augment position information of a rover.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Method and system for scheduling resource
InactiveCN101354763AImprove the speed of schedulingMeet the needs of resource schedulingRoad vehicles traffic controlResourcesTime informationFloat Value
The invention discloses a method and a system for resource scheduling, which are used to solve the problems that the prior method for resource scheduling requires an operator to make sure of resource scheduling each working day, and the implementation is more troublesome. The method comprises the following steps that: the system for resource scheduling captures information on operation of a resource unit in each period, information on the operating status of the resource unit in each period, information on operation time in each run of the resource unit, information on free time after each run, and information on floating value of the free time after each run of the resource unit in each period, information on maximum total time and minimum total time from the first run to the last run of the resource unit, information on maximum free time information and minimum free time of the resource unit; the resource scheduling system schedules the resource unit according to the information.
Owner:ZTE ITS CO LTD
Comprehensive cooling testing working method for vehicle silencing
ActiveCN108716427AIncrease volumeReduce noiseCoolant flow controlSilencing apparatusMicrocontrollerFloat Value
The invention provides a comprehensive cooling testing working method for vehicle silencing. The method comprises the steps of S1, after tail gas current enters a second chamber through an air inlet pipe, acquiring a sound wave signal of the air inlet pipe by a first standing wave tube; S2, after a single-chip microcomputer receives the sound wave signal of the first standing wave tube, performinganalysis and calculation on the signal of each standing wave tube; S3, mounting a temperature sensor in a silencing device for performing real-time acquisition on an inner air current temperature; S4, sampling the temperature value of a cylinder body by the temperature sensor; S5, determining a voltage floating value through comparing an input voltage change reference signal with a feedback output detecting signal; and S6, if cylinder body temperature reduction cannot be realized because of a fault of a circulating water pump, after the temperature value which is acquired by the temperature sensor exceeds a certain threshold, transmitting a signal to a processor through an overheat protecting circuit, and performing real-time monitoring on operation of the circulating water pipe through acorresponding protecting circuit. The comprehensive cooling testing working method has advantages of ensuring stable operation of a water pump, and prolonging service life of a circulating refrigerating system.
Owner:新昌县精锐机械有限公司
GNSS signal processing methods and apparatus with candidate set selection
Methods and apparatus are provided for estimating parameters, i.e. ambiguities, derived from GNSS signals. Observations of GNSS signals are obtained from each of a plurality of GNSS satellites (120). The observations are fed to a filter having a state vector at least comprising a float ambiguity for each received frequency of the GNSS signals (140). The filter estimates a float value for each float ambiguity of the state vector. Integer values are assigned to at least a subgroup of the estimated float values to define a plurality of integer ambiguity candidate sets (160). A first number of candidate sets is selected having a quality measure better than a first threshold, wherein the first threshold is determined based on a reference quality measure of a reference candidate set (180). A weighted average of the selected candidate sets is formed, each candidate set weighted in the weighted average based on its quality measure (200). Ambiguities of the weighted average can be used in subsequent operations to aid in determining a position of the receiver or can be used to prepare data, e.g., in a network processor that can be used to augment position information of a rover.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Gnss signal processing methods and apparatus with scaling of quality measure
ActiveCN102124365APosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingFloat ValueExpected value of sample information
Methods and apparatus are provided for estimating parameters, i.e. ambiguities, derived from GNSS signals. Observations of GNSS signals are obtained from each of a plurality of GNSS satellites (1120). The observations are fed to a filter (1140) having a state vector at least comprising a float ambiguity for each received frequency of the GNSS signals. The filter estimates a float value for each float ambiguity of the state vector. Integer values are assigned to at least a subgroup of the estimated float values to define a plurality of integer ambiguity candidate sets (1160). A quality measure is determined for each of the candidate sets. The best quality measure of the candidate sets is determined. An expectation value (1170) of the candidate set having the best quality measure is determined. An error measure as a ratio of the best quality measure to the expectation value is determined. The quality measures of the candidate sets (1180) is adapted as a function of the error measure. A weighted average of a subgroup of the candidate sets on the basis of the adapted quality measures is formed, wherein at least one of selecting the subgroup of the candidate sets and the weighting of each candidate set in the weighted average is based on the adapted quality measure (1200). Ambiguities of the weighted average can be used in subsequent operations to aid in determining a position of the receiver or can be used to prepare data, e.g., in a network processor that can be used to augment position information of a rover.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Gnss signal processing methods and apparatus with tracking interruption
Methods and apparatus are provided for estimating parameters, i.e. ambiguities, derived from GNSS signals. Observations of each of received frequencies of a GNSS signal from a plurality of GNSS satellites are obtained for a plurality of instances in time (3120). The time sequence of observations is fed to a filter to estimate a state vector comprising float ambiguities, wherein each float ambiguity constitutes a non integer estimate of an integer number of wavelengths for a received frequency of a GNSS signal between a receiver of the GNSS signal and the GNSS satellite from which it is received and wherein the float ambiguities of the state vector are updated over time on the basis of the observations (3140). The occurrence of an interruption in tracking of at least one signal of a satellite is determined (3121). The float ambiguity of the state vector for the at least one signal for which an interruption in tracking occurred is maintained at the value before the interruption in tracking occurred (3122). Integer values are assigned to at least a subgroup of the estimated float values to define a plurality of integer ambiguity candidate sets (3160). A quality measure is determined for each of the candidate sets. A weighted average of the candidate sets is formed (3200). Ambiguities of the weighted average can be used in subsequent operations to aid in determining a position of the receiver or can be used to prepare data, e.g., in a network processor that can be used to augment position information of a rover.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
GNSS signal processing methods and apparatus with ambiguity selection
Methods and apparatus are provided for estimating parameters, i.e. ambiguities, derived from GNSS signals. Observations of a GNSS signal from each of a plurality of GNSS satellites are obtained (2120). The observations are fed to a filter having a state vector comprising a float ambiguity for each received frequency of the GNSS signals (2140). The filter estimates a float value for each float ambiguity of the state vector and co-variance values associated with the state vector. Integer values are assigned to at least a subgroup of the estimated float values to define a plurality of integer ambiguity candidate sets (2160). A weighted average of the candidate sets is formed (2200). A formal precision value based on covariance values of the filter is determined (2205), the formal precision value being a measure for an achievable precision. An achieved precision value of the weighted average is determined (2210). The achieved precision value is compared with the formal precision value to obtain a convergence value (2215). A convergence of the determination of the state vector is indicated (2218). Ambiguities of the weighted average can be used in subsequent operations to aid in determining a position of the receiver or can be used to prepare data, e.g., in a network processor that can be used to augment position information of a rover.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
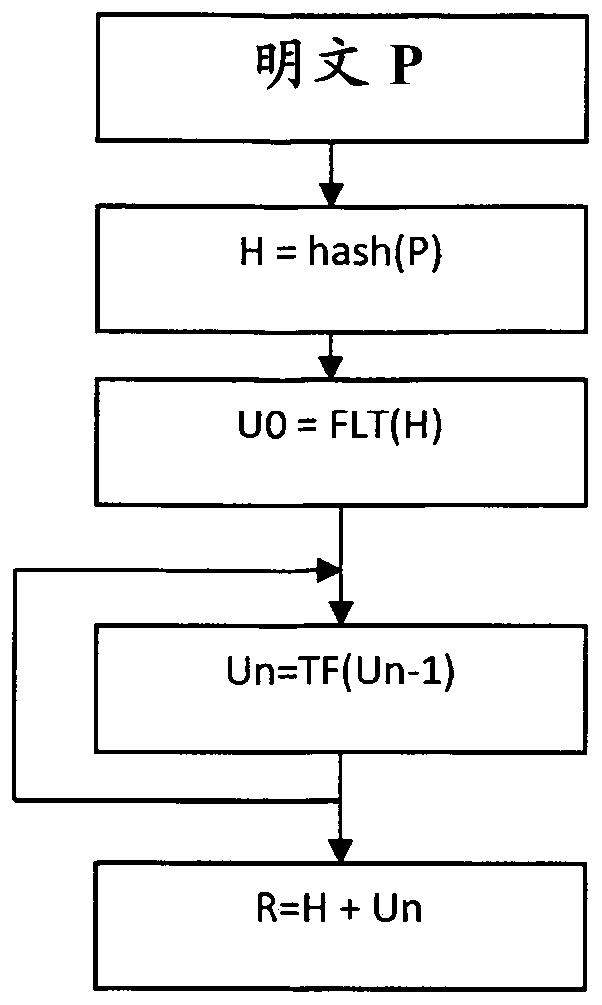
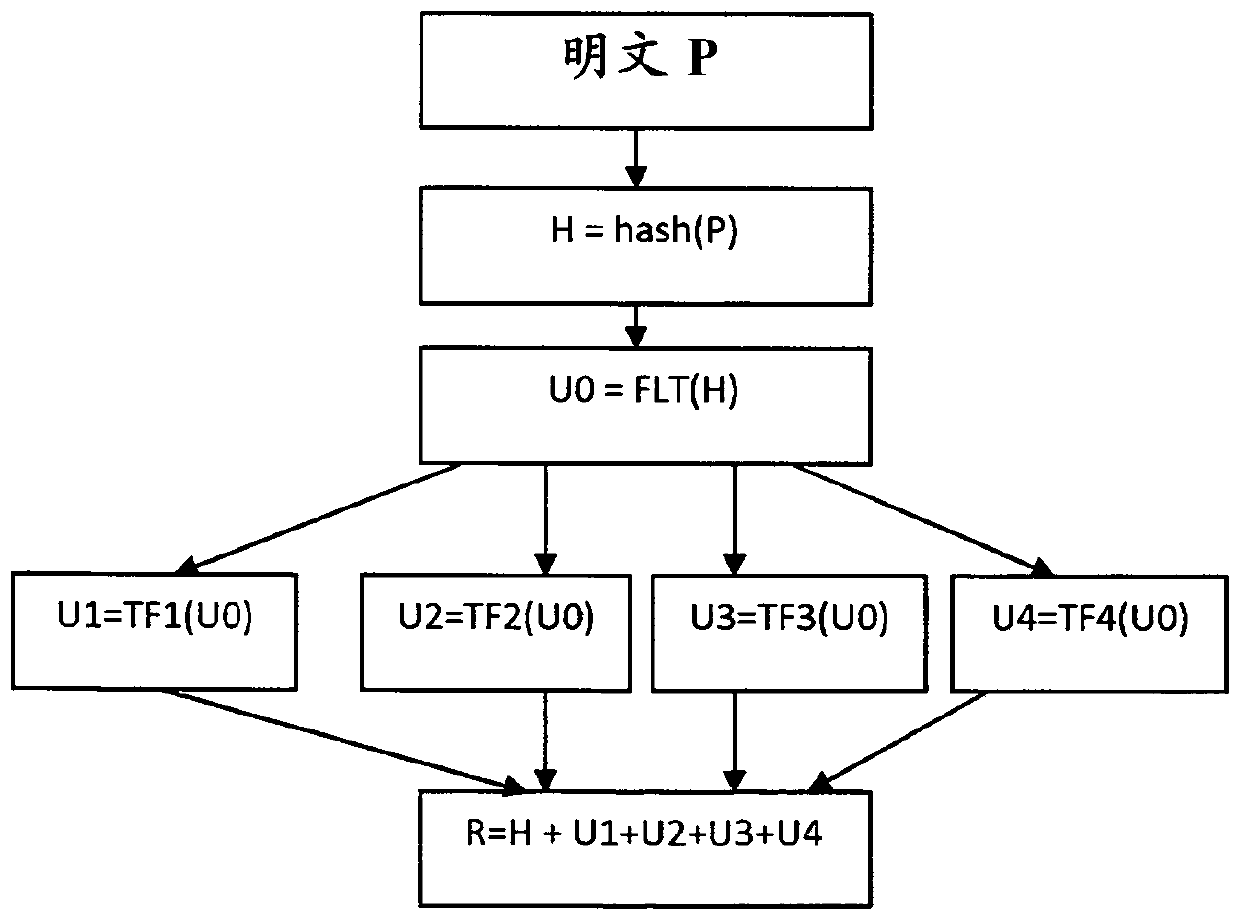
Method and device to produce secure hash value
ActiveCN110100409AEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesDigital data processing detailsPlaintextFloat Value
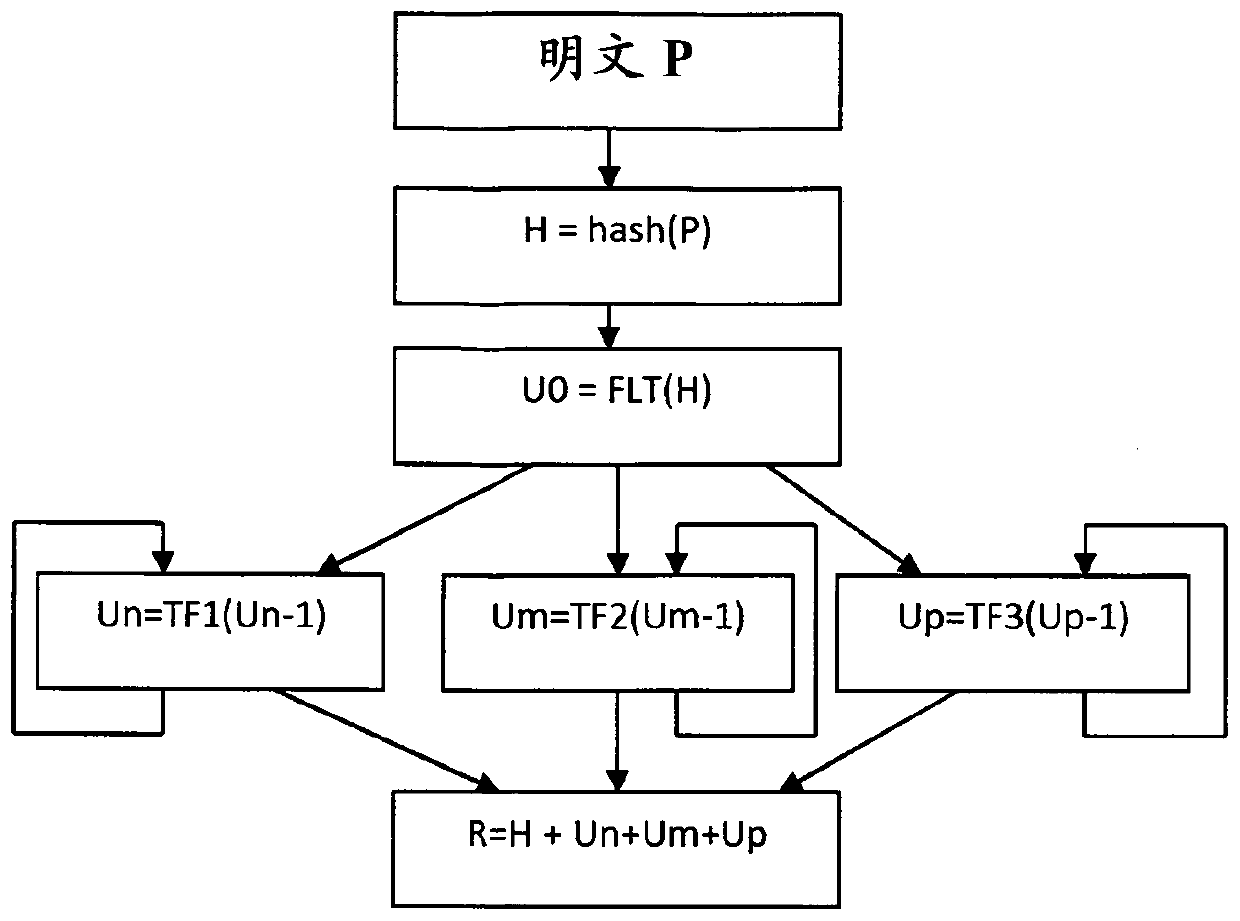
The generation of hash values become popular with the storage of pin code by an authentication server, since the authentication server knows only the result of the hash function and not the pin code itself. Each time an authentication is requested, a hash function is executed on the received pin code and then compared with the stored reference hash value of the initial pin code. In order to improve the security of the hash value, it is proposed a method to produce a secure hash value (R) from a plaintext (P), the method comprising: producing a first result (H) using an hash function of the plaintext (P), obtaining an initial floating value (U0) by converting the first result (H) into a floating number representation of the first value (H), updating a floating value (Un) by executing at least once a Transcendental function (TF) on the initial floating value (Un-1), obtaining the secure hash value (R) by mixing the first result (H) with the updated floating value (Un).
Owner:NAGRAVISION SA
Layered sculpturing method
ActiveCN104827815AReduce scrap rateAvoid missing engravingDecorative surface effectsReference modelFloat Value
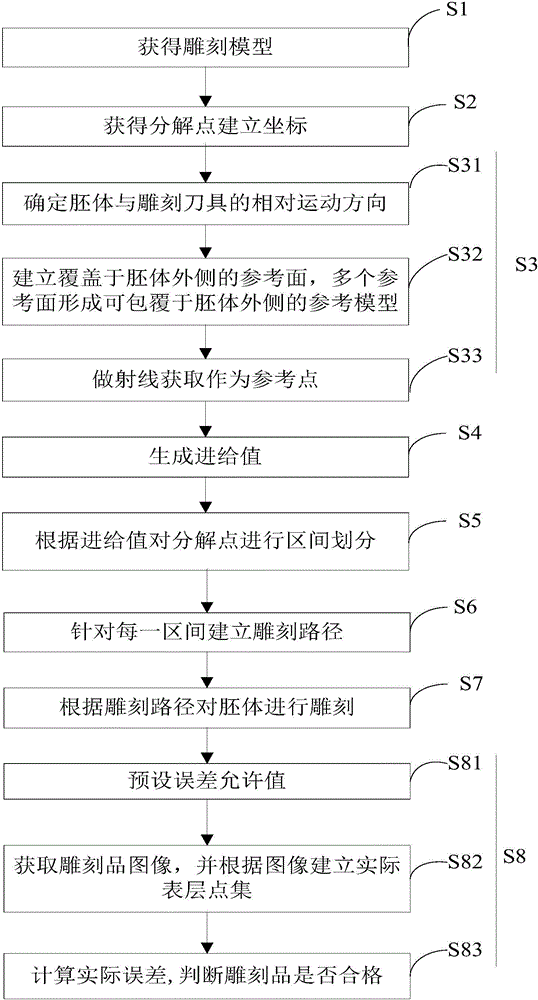
The invention discloses a layered sculpturing method. The layered sculpturing method comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring a sculpturing model; S2, selecting an original point, carrying out point decomposition on the surface layer of the sculpturing model, and establishing a coordinate according to the concentrated decomposed points of surface layer points; S3, establishing a reference model in a coordinate point in the step S2, wherein the reference model consists of not less than one reference point, and each concentrated decomposition point of the surface points corresponds to one reference point of the reference model; S4, generating a feeding value according to the corresponding relationship between each decomposition point and the reference point; S5, dividing the intervals of the decomposition points according to the feeding value, wherein the maximal difference of the feeding values of every two decomposition points in each interval is not greater than the preset floating value; S6, establishing a sculpturing path aiming at each interval; and S7, sculpturing a blank body according to the sculpturing path. According to the invention, the blank body is sculptured in a layered mode, and the blank body scrappage rate is reduced.
Owner:安徽华智智能卡科技有限公司
Method and device for quantising the floating value of a pixel in an image
The invention relates to a method and device for quantising the floating value of a pixel of an image by rounding either to a lesser whole number, to a greater whole number, or to the whole number closest to this floating value. The method is characterised in that the selection of rounding this floating value is determined based on a test value.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com