GNSS signal processing methods and apparatus with ambiguity convergence indication
An ambiguity and signal technology, applied in the field of signals based on navigation satellite systems, which can solve the problems of erroneous solution convergence, incorrect positioning, and time-consuming
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0102] The present invention will now be described with reference to specific examples. It may be noted that the specific examples are intended to provide a better understanding to those skilled in the art and are not intended to limit the scope of the invention in any way, which is defined by the appended claims. In particular, embodiments described individually throughout this specification may be combined to form further embodiments to the extent they are not mutually exclusive.
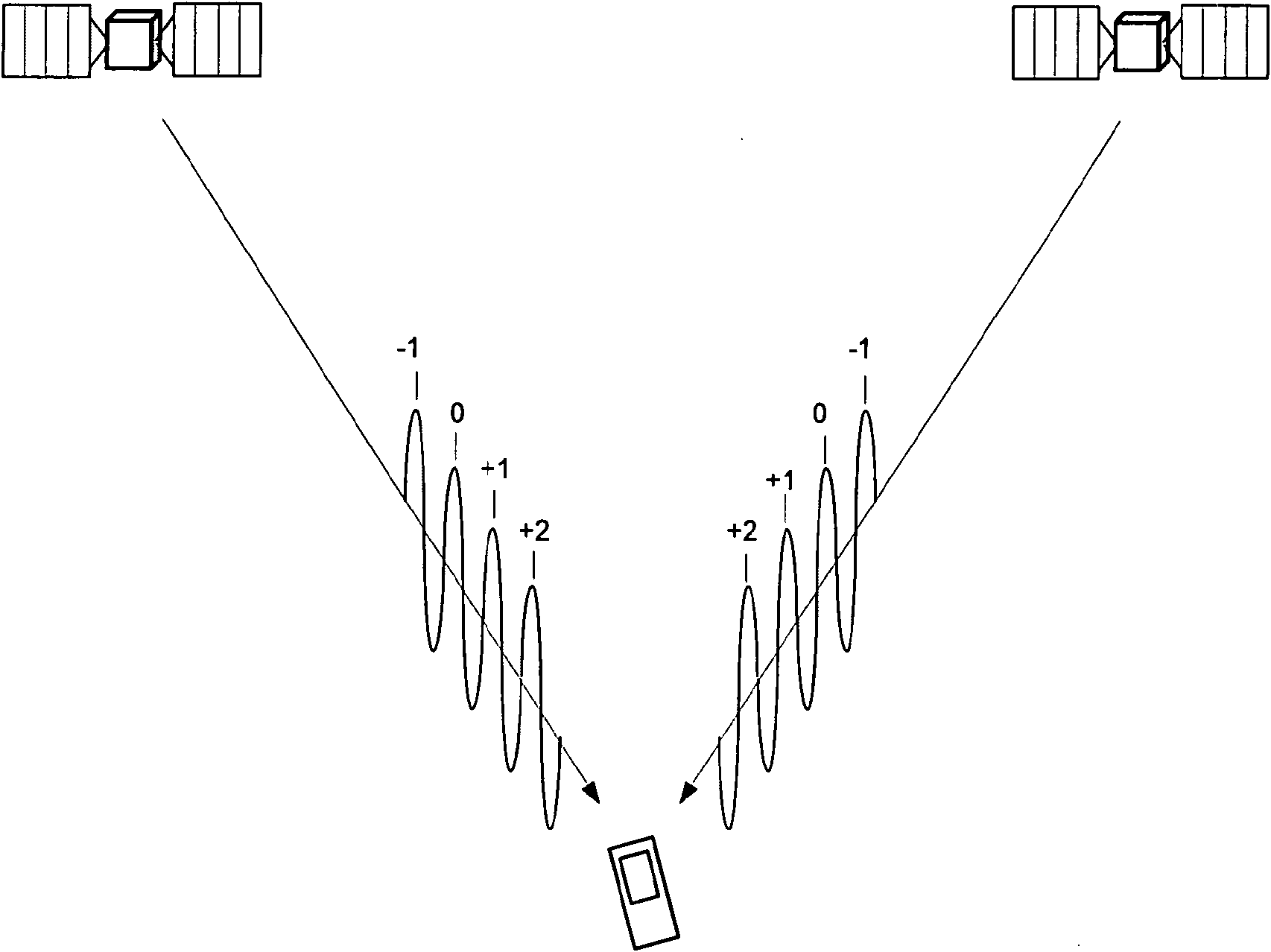
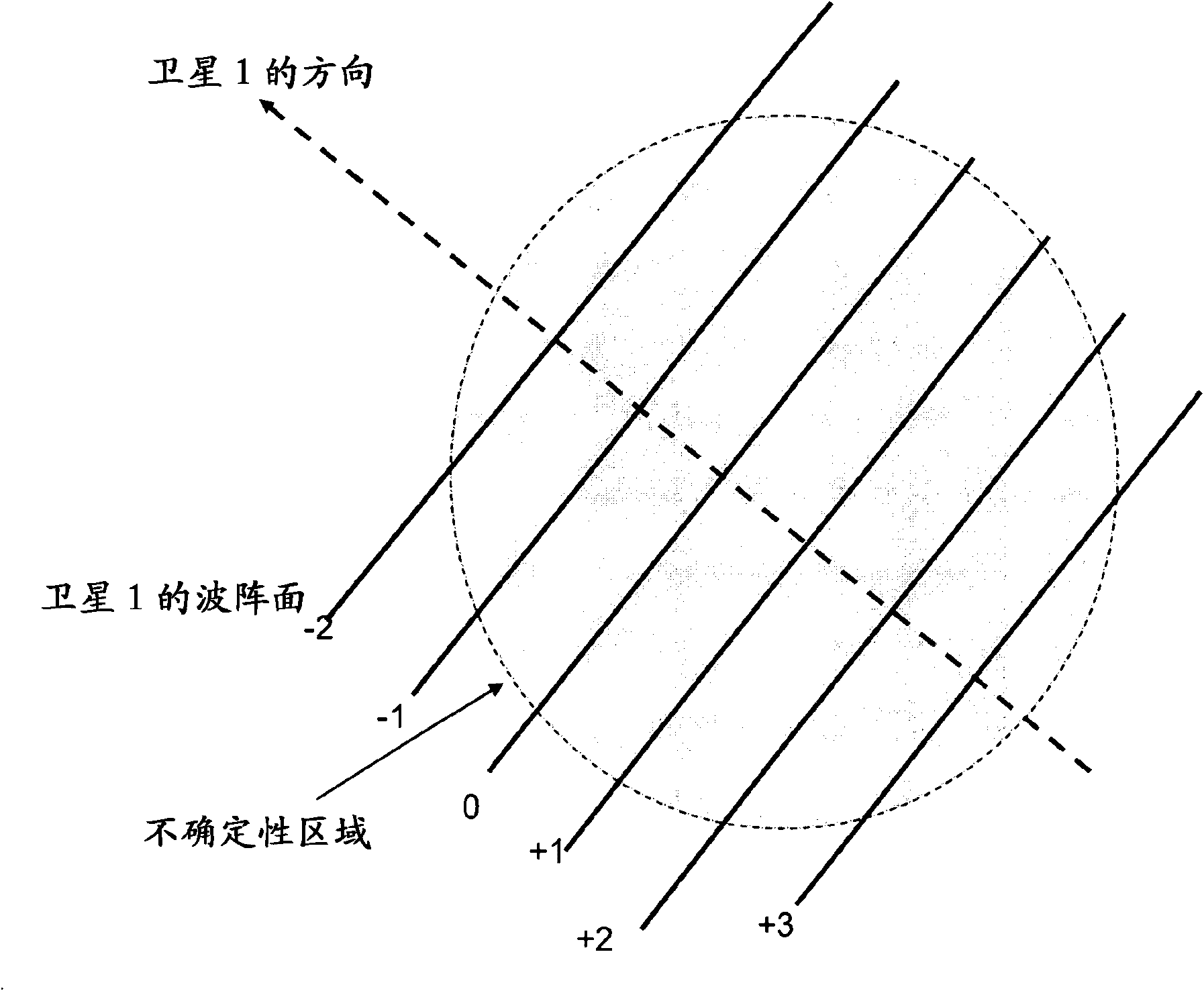
[0103] 1. Candidate set selection
[0104] The inventors have clearly realized that efficiently selecting the number of candidates for a weighted average can improve estimation with reduced processing requirements.
[0105] According to one embodiment, the integer solutions, ie integer candidate sets, for forming the weighted average are selected based on a quality measure. Rather, a candidate set may be selected that has a quality measure that is better than a threshold determined based on a re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com