Antifouling composition prepared from a pseudomonas pf-11 culture
一种PF-11、假单胞菌的技术,应用在植物学设备和方法、生物化学设备和方法、细菌等方向,能够解决大代谢差异寄生虫、宿主不同传播和感染策略、困难等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0165] Example 1 - Isolation, Characterization and Storage of Strain PF-11
[0166] Environmental Sampling and Bacterial Isolation
[0167] Soil and / or mud samples were collected in the Tagus River region around Lisbon, Portugal. The collected material (10 g) was homogenized with sterile water (50 mL). After gravity settling of the mixture, the liquid fraction was recovered. Then, the raw material suspension (including microorganisms) was collected by centrifugation (12000 g, 5 min). The resulting pellet was resuspended in sterile water. Primary growth was accomplished in LB (Luria Bertani) medium. These cultures were diluted (10-2 to 10-9) and grown on LA (LB+agar) or with ampicillin (8 μg / mL), amoxicillin (8 μg / mL) or cefotaxime (cefotaxime) (2 μg / mL) was grown in LA to select for resistant or reduced susceptibility strains. Colonies with significant size or morphology differences were selected. Each selected colony was subjected to successive plate passages (up to ...
Embodiment 2
[0174] Example 2 - PF-11 Culture Growth, Compound Preparation, Recovery and Characterization of Secreted Compounds
[0175] PF-11 growth conditions.
[0176]Frozen bacterial aliquots were grown overnight (16-18 h) at 30°C in LB agar medium. One colony was then used to transfer into a sterile flask containing M9 medium supplemented with glucose and grown in a bacterial constant temperature shaker at 120 r.p.m. for 16 h at 30°C.
[0177] Compounds are recovered from the culture.
[0178] Cells were removed by centrifugation (14.000 r.p.m., 4°C, 15 min) and the supernatant was collected. The supernatant was sterilized by filtration using a filter unit with a 0.22 μm DURAPORE filter (Millex GP, Millipore, Ireland). Sterility was verified by incubating 50 μl of the supernatant in LA dishes at 30° C. for at least 16 h.
[0179] Purification of original mixtures of compounds.
[0180] Supernatants were frozen at -80°C and dehydrated by lyophilization. It was then resuspended ...
Embodiment 3
[0187] Example 3 - Antimicrobials from Environmental Sources
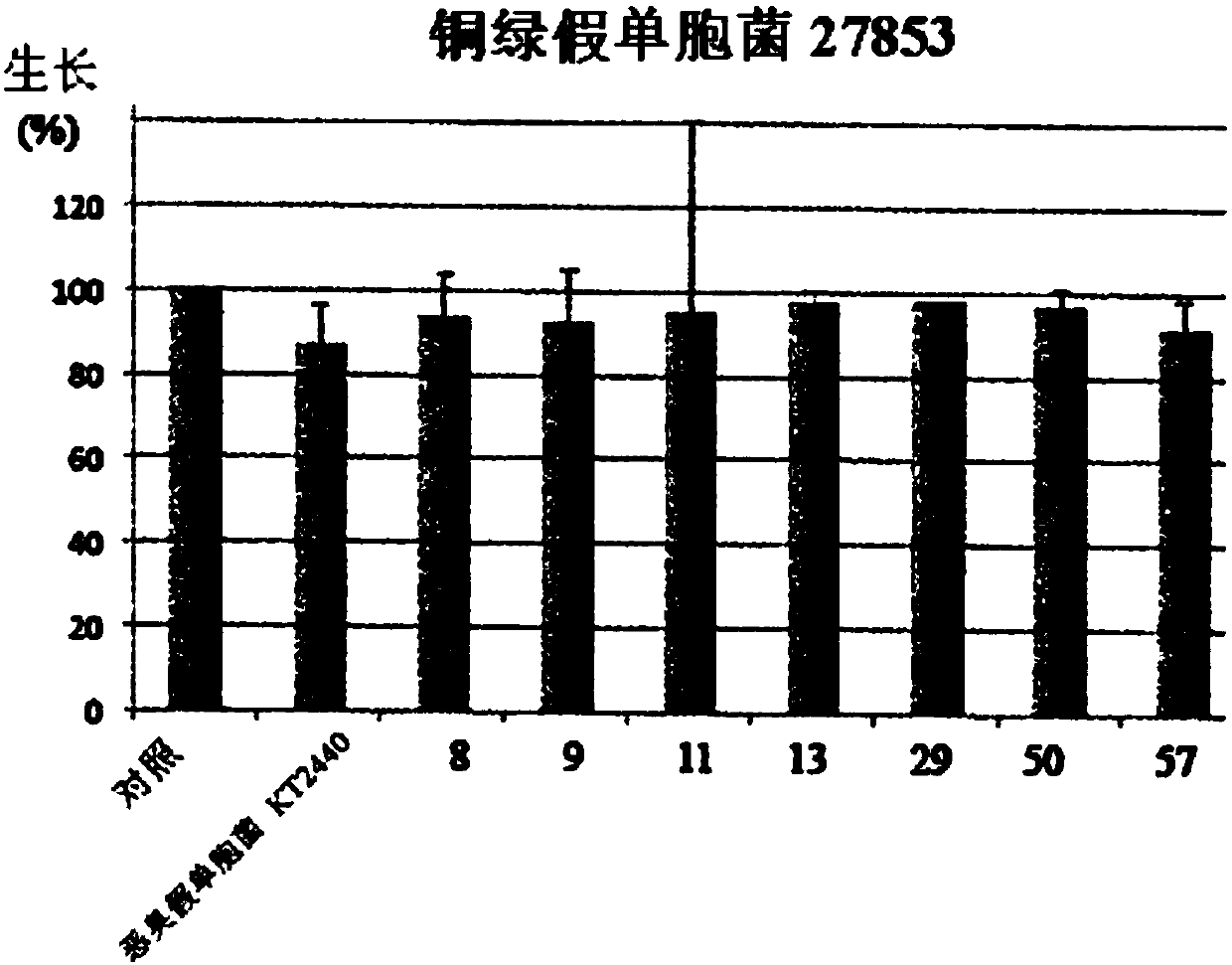
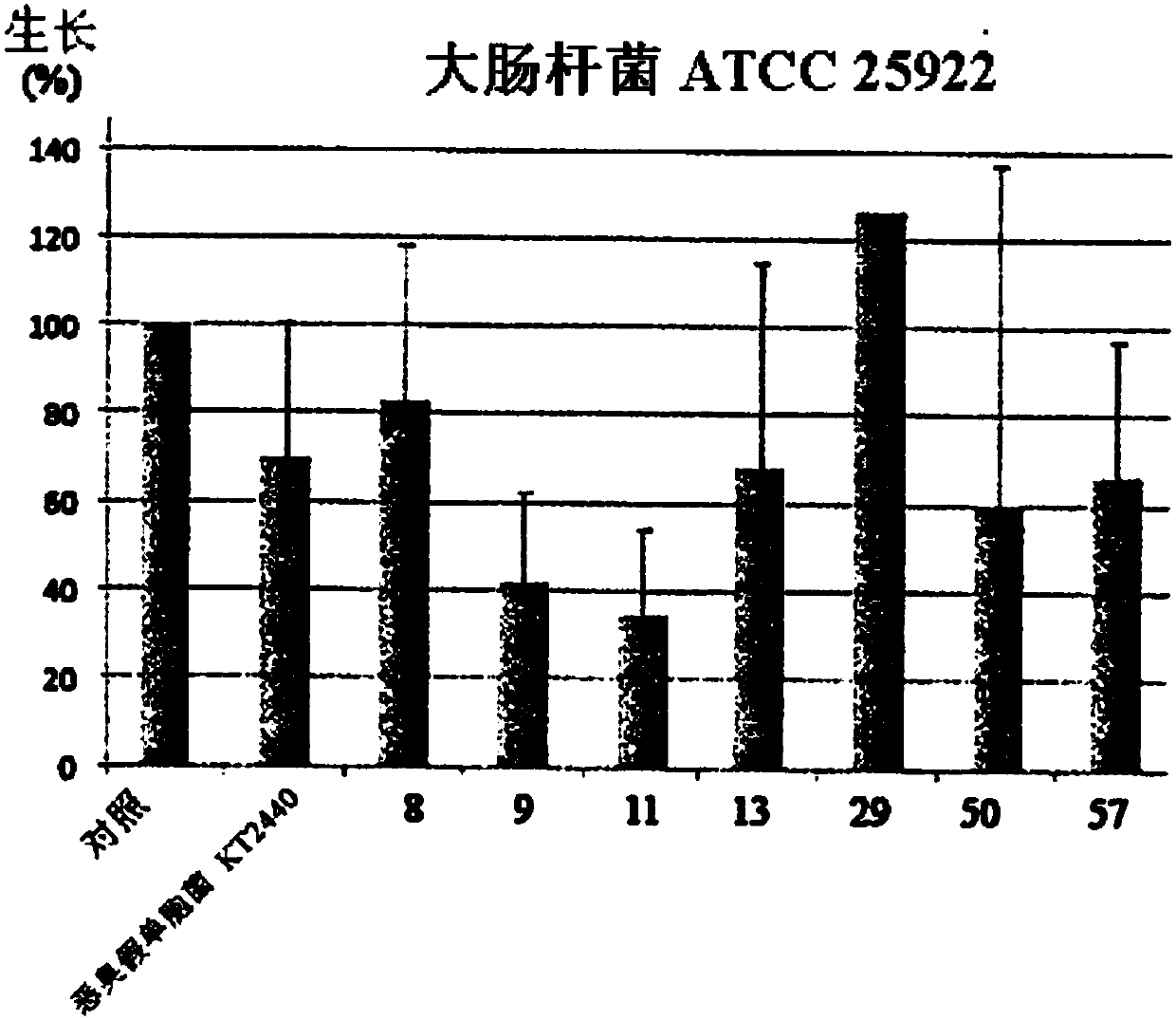
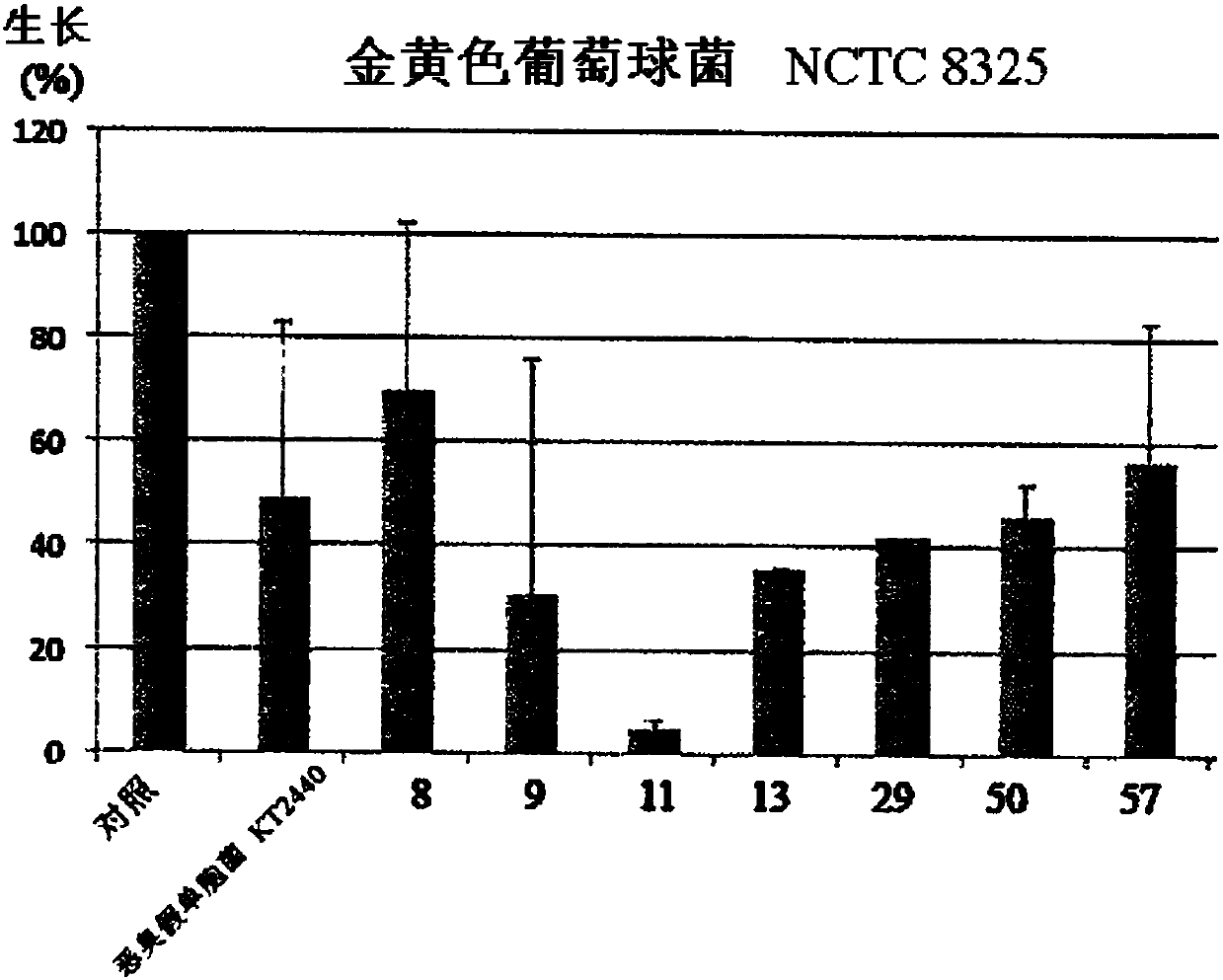
[0188] During a previous study, a heterogeneous collection of environmental Pseudomonas putida strains with strong adaptive skills collected through antibiotic resistance (Meireles 2013) was used to screen for secreted natural compounds Potential for microbial growth control. The content of Meireles 2013 is hereby incorporated by reference into this application. A set of P. putida isolates from this collection was selected based on its fitness level, antibiotic resistance and general fitness (data not shown), and aimed to collect multiple strain characteristics . . The secretome of these strains (ie the molecules they secrete) were collected and tested for the first time for effects on the growth of three model strain species E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. One strain, PF-11, showed significant antibacterial potential. This initial set was then extended to all P. putida strains fro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com