Organic solvent resisting proteinase high-yield bacterium, gene and application of the organic solvent resisting proteinase
A technology resistant to organic solvents and proteases, used in applications, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve the problems of enzyme volatile inactivation, low tolerance concentration, low yield, etc., and achieve easy purification and organic solvent tolerance. Strong, high-yield effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] This experiment illustrates a screening procedure for the production of natural strains resistant to organic solvent proteases.
[0029] Extremophiles resistant to organic solvents were screened from oily soil samples using different concentrations of cyclohexane, toluene, acetone and other organic solvents as screening pressures. The milk agar plate medium was adopted, and the specific formula was: tryptone 5g / L, yeast powder 3g / L, skimmed milk powder 25g / L, agar 12g / L. The screened microorganisms resistant to organic solvents were inoculated on milk agar plates, and the strains with high protease production were initially screened according to the ratio of the colony to the size of the transparent circle. This method screened 10 strains of extremophile resistant to organic solvents with high protease production.
[0030] In order to further test the solvent tolerance of the secreted protease, the protease production ability of the 10 strains and the organic solvent r...
Embodiment 2
[0033] This experiment illustrates the biological properties of the organic solvent-resistant extremophile Pseudomonas aeruginosa PT121.
[0034] Physiological and biochemical properties
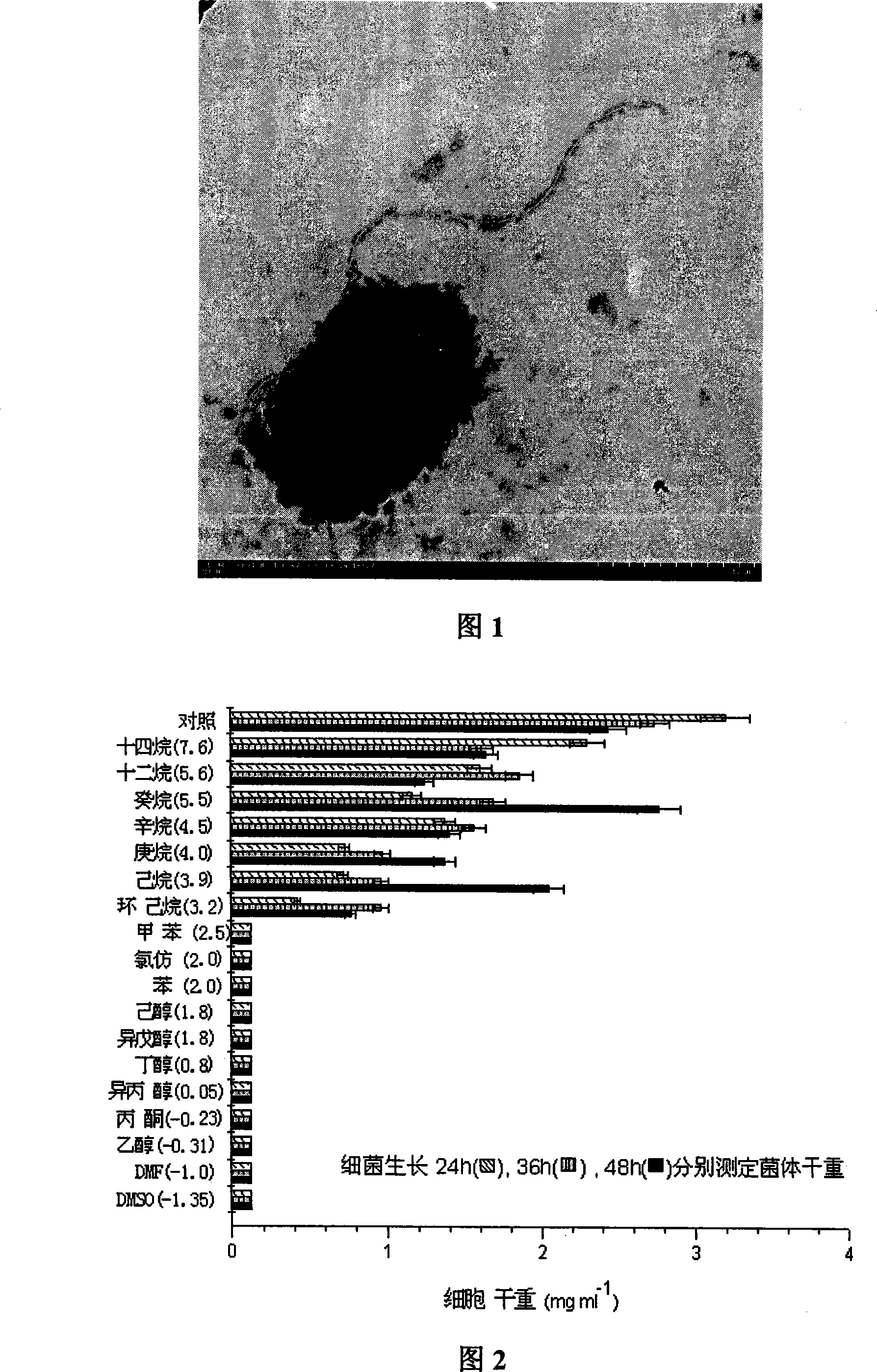
[0035] Gram staining of the strain showed that the strain was a Gram-negative strain without spores. Observation with a transmission electron microscope (Figure 1) showed that the strain was a monoflagellate bacterium with a size of 0.5 μm×1-2 μm. After growing in broth medium for 24 hours, the colony size is 2-3mm, the growth range is 30-40°C, the optimum growth temperature is 37°C, the growth pH is 6-11, and the optimum pH is 8.0. The characteristic is that the results of catalase reaction, oxidase reaction, nitric acid reduction reaction, gelatin reaction, glucose, D-xylose and D-fructose utilization are positive, and the results of lactose, maltose and mannose utilization are negative. grow under oxygen conditions. Some physiological and biochemical characteristics of the bacteria are ...
Embodiment 3
[0041] This experiment illustrates the purification procedure for organosolvent-tolerant proteases.
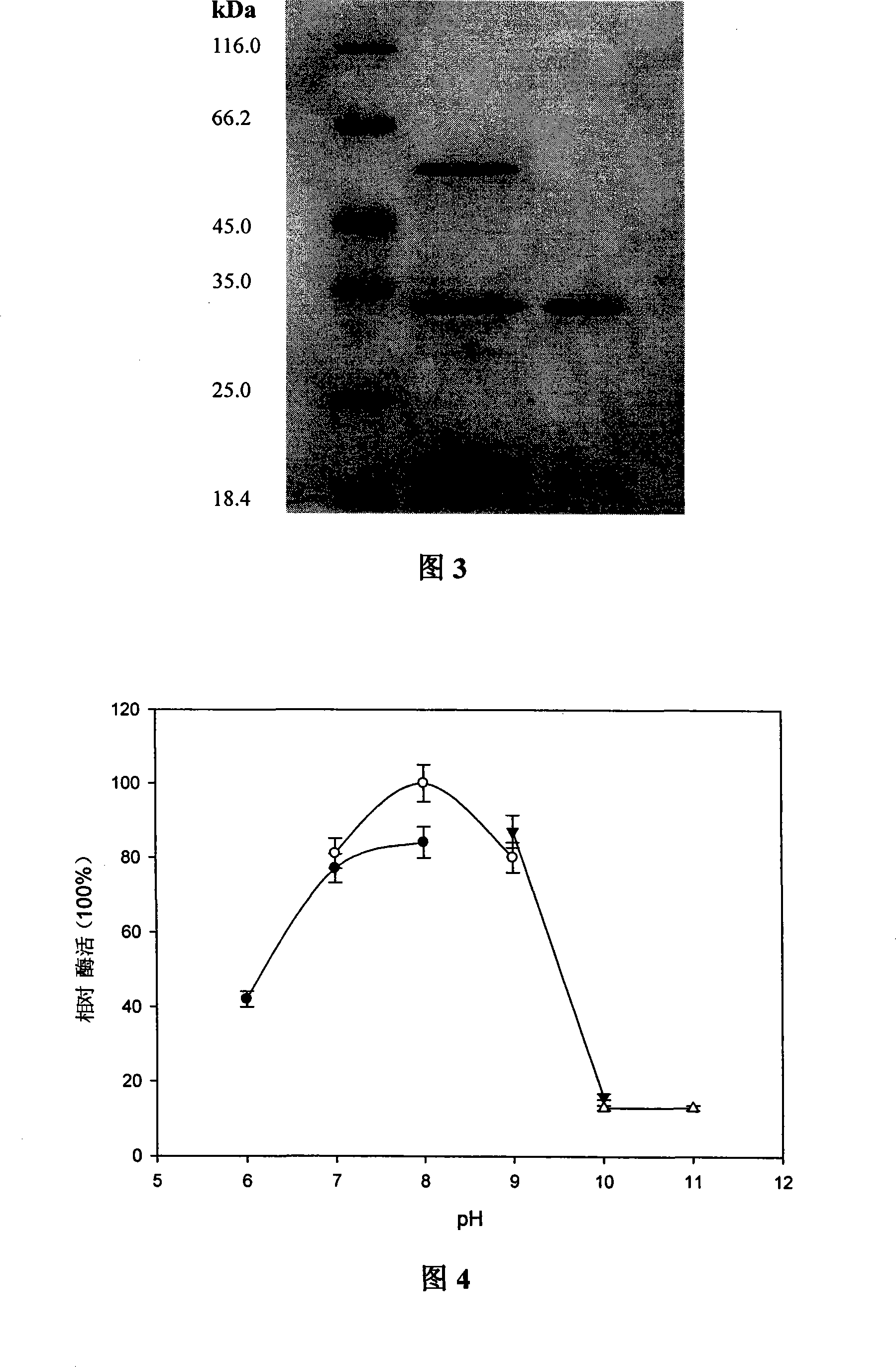
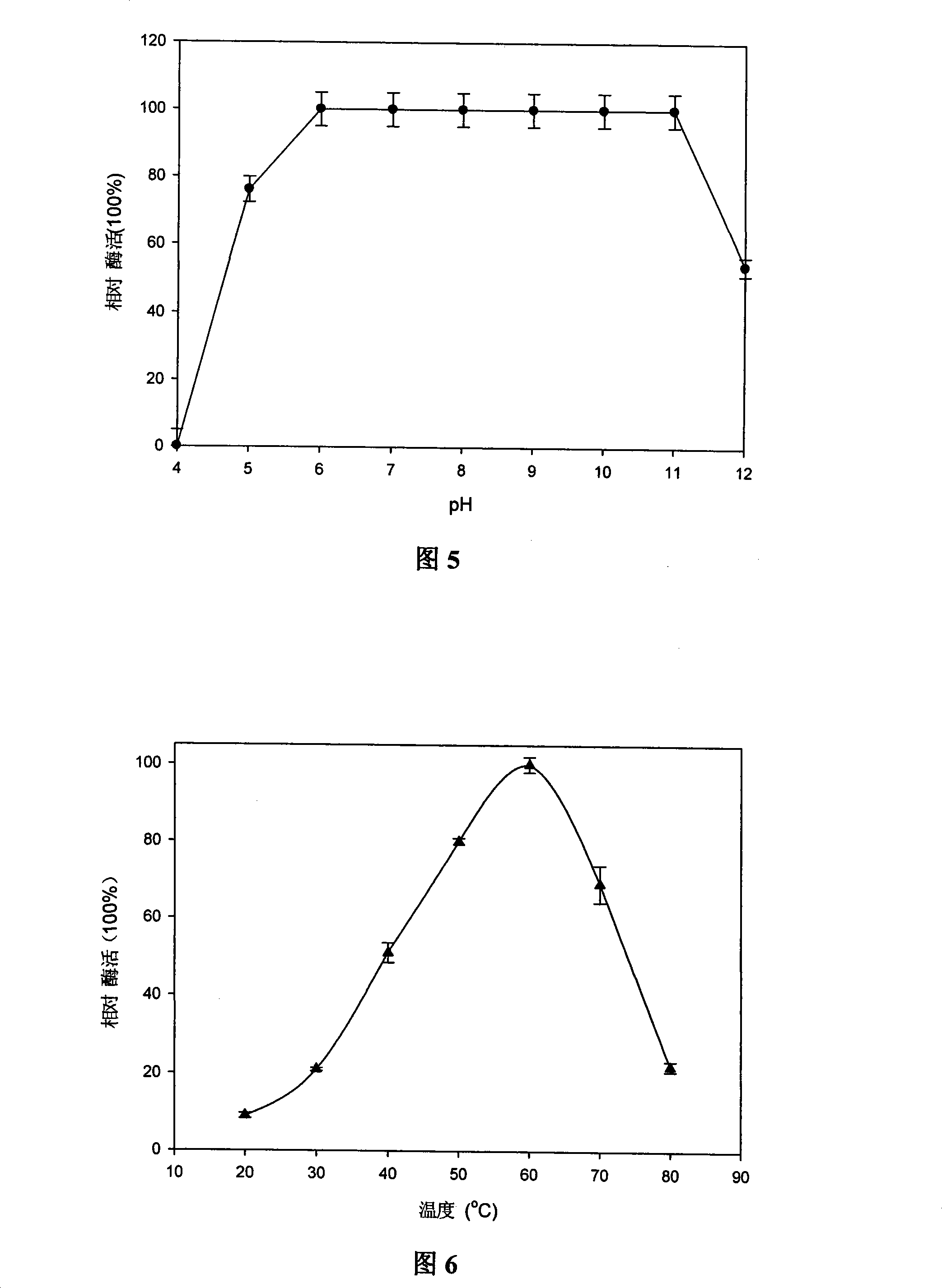
[0042] Firstly, culture the strain in the enzyme-producing medium for 72 hours, centrifuge at 10,000rmp at 4°C for 15 minutes, take the supernatant as the crude enzyme solution, put the crude enzyme solution in an ice bath, and slowly add NaCl while stirring to a final concentration of 1.6 mol / L. Add the treated supernatant to the Phenyl sepharose Fast Flow chromatography column equilibrated with 1.2mol / L NaCl, 0.05M Tris-HCl buffer (pH8.0), and use 0.05M Tris-HCl (pH8.0 , NaCl content is 1mol / L) buffer solution to carry out elution, collect eluate. The supernatant of the fermentation broth was only separated by one-step chromatographic column, and the analysis by SDS-PAGE (Figure 3) showed that the purified protease had reached electrophoretic purity. This protease subunit has a molecular weight of approximately 33 kDa. The recovery rate and purification multiple of protea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com