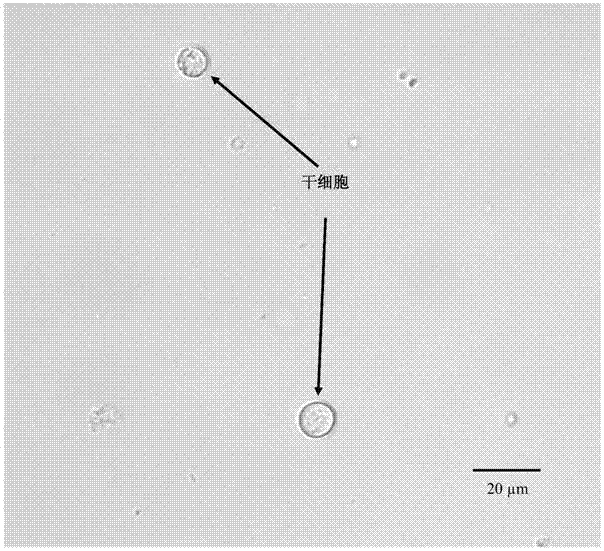
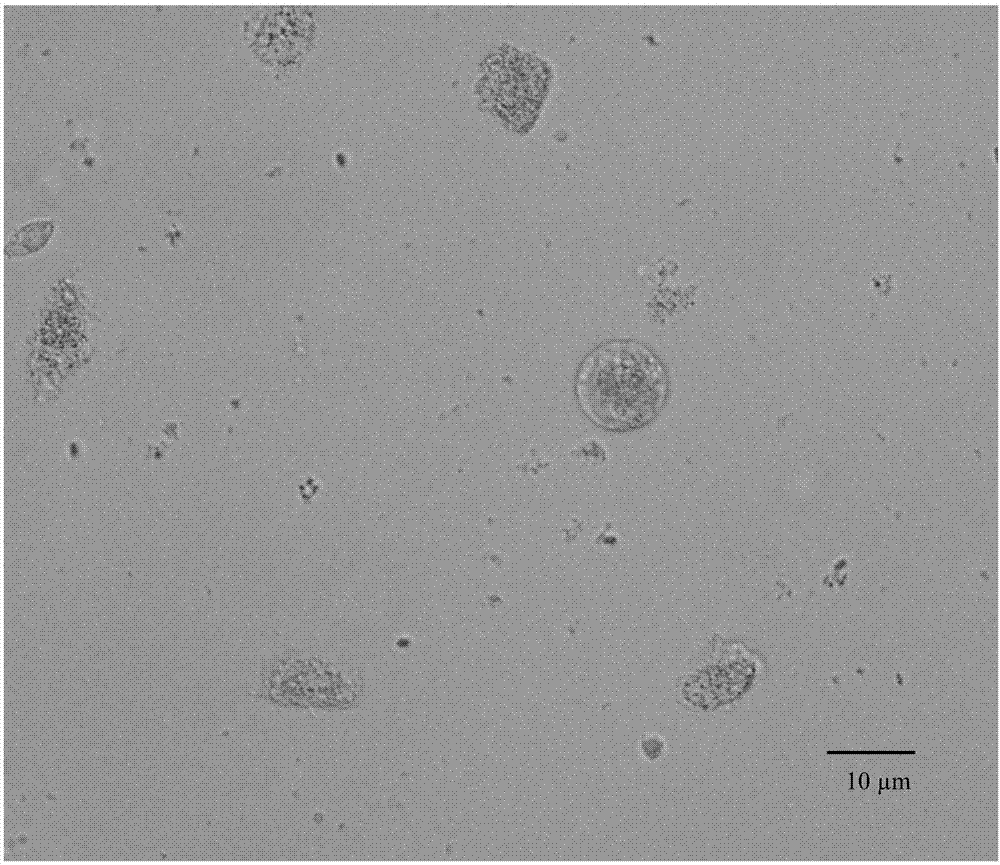
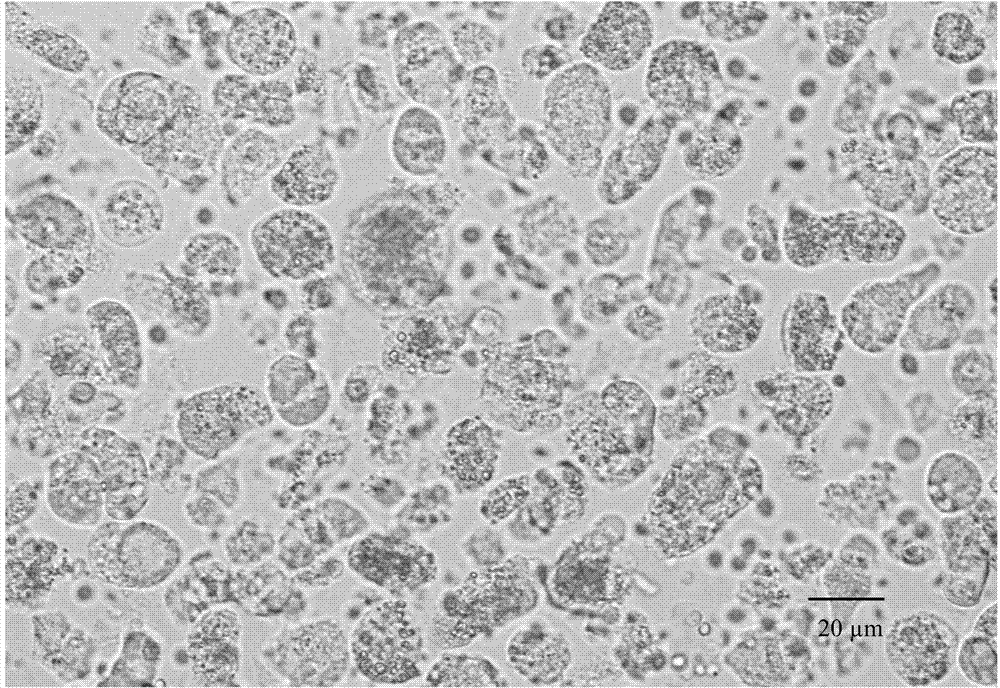
Method for extracting, separating and identifying chilo suppressalis midgut stem cells
A technology of intestinal stem cells and identification methods, applied in the field of extraction, separation and identification of midgut stem cells of C. To achieve the effect of inhibiting bacterial growth, avoiding cell contamination, and regular cell shape
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] In the absence of collagenase Ⅰ, Ficoll-Paque separation medium and density gradient centrifugation were used to extract, isolate and identify stem cells in the midgut of C. medinalis (taking 20 3rd instar larvae of C. medulla as an example);
[0045] 1.1 Under aseptic conditions, soak the 3rd instar larvae of Chilo borer in 2% sodium hypochlorite solution for 2 minutes, 75% ethanol for 2 minutes, and sterile dd H 2 In O for 2 minutes, carry out body surface disinfection;
[0046] 1.2 Put the worm body on a wax plate sterilized with 75% ethanol, and dissect the midgut of the larvae of Chilo suppressalis. Cut the ends of the thorax and abdomen separately, then cut along the worm body from the abdominal incision to the chest incision, and pull out the midgut side with tweezers;
[0047] 1.3 Take out the midgut, put it into a Petri dish filled with Ringer's solution, and use ophthalmic forceps to remove Malpighian tubes, peritrophic membranes and food residues, etc.;
[...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Collagenase I was added, and Ficoll-Paque separation solution and density gradient centrifugation were used to extract, separate and identify stem cells in the midgut of C. borer (taking the dissection of 40 third-instar larvae of C. borer as an example);
[0054] 2.1 Under sterile conditions, soak the 3rd instar larvae of Chilo borer in 2% sodium hypochlorite solution for 2 minutes, 75% ethanol for 5 minutes, and sterile dd H 2 In O for 2 minutes, carry out surface disinfection;
[0055] 2.2 Place the larvae in a wax plate sterilized with 75% ethanol, and dissect the midgut of the larvae of C. Cut the ends of the thorax and abdomen separately, then cut along the worm body from the abdominal incision to the chest incision, and pull out the midgut side with tweezers;
[0056] 2.3 Take out the midgut, put it into a petri dish filled with Ringer's solution, and use ophthalmic forceps to remove Malpighian tubes, peritrophic membranes and food residues, etc.;
[0057] 2.4 ...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Collagenase Ⅰ was added, and the midgut stem cells of C. borer were extracted, separated and identified by flow cytometry (take the dissection of 20 3rd instar larvae of C. borer as an example)
[0066] It is known from Example 2 that 0.1% collagenase I is beneficial to the extraction of midgut stem cells without damaging the cells, so in Example 3, 0.1% collagenase I was added to extract stem cells.
[0067] 3.1 Under aseptic conditions, soak the 3rd instar larvae of Chilo borer in 2% sodium hypochlorite solution for 2 minutes, 75% ethanol for 5 minutes, and sterile dd H 2 In O for 2 minutes, carry out surface disinfection;
[0068] 3.2 Put the worm body on a wax plate sterilized with 75% ethanol, and dissect the midgut of the larvae of Chilo suppressalis. Cut the ends of the thorax and abdomen separately, then cut along the worm body from the abdominal incision to the chest incision, and pull out the midgut side with tweezers;
[0069] 3.3 Take out the midgut, put i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com