Encapsulated intestinal midgut endoderm cells
a technology of endoderm cells and endoderm cells, which is applied in the field of cell-based therapy for conditions, can solve the problems of inefficient process of differentiating enteroendocrine cells from these hesc-derived mid-/hindgut spheroids, and no incretin-based cell therapy option,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Method of Producing an Intestinal Midgut Endoderm Cell Population with CDX2 and FOXA2 Co-Presence / Co-Expression
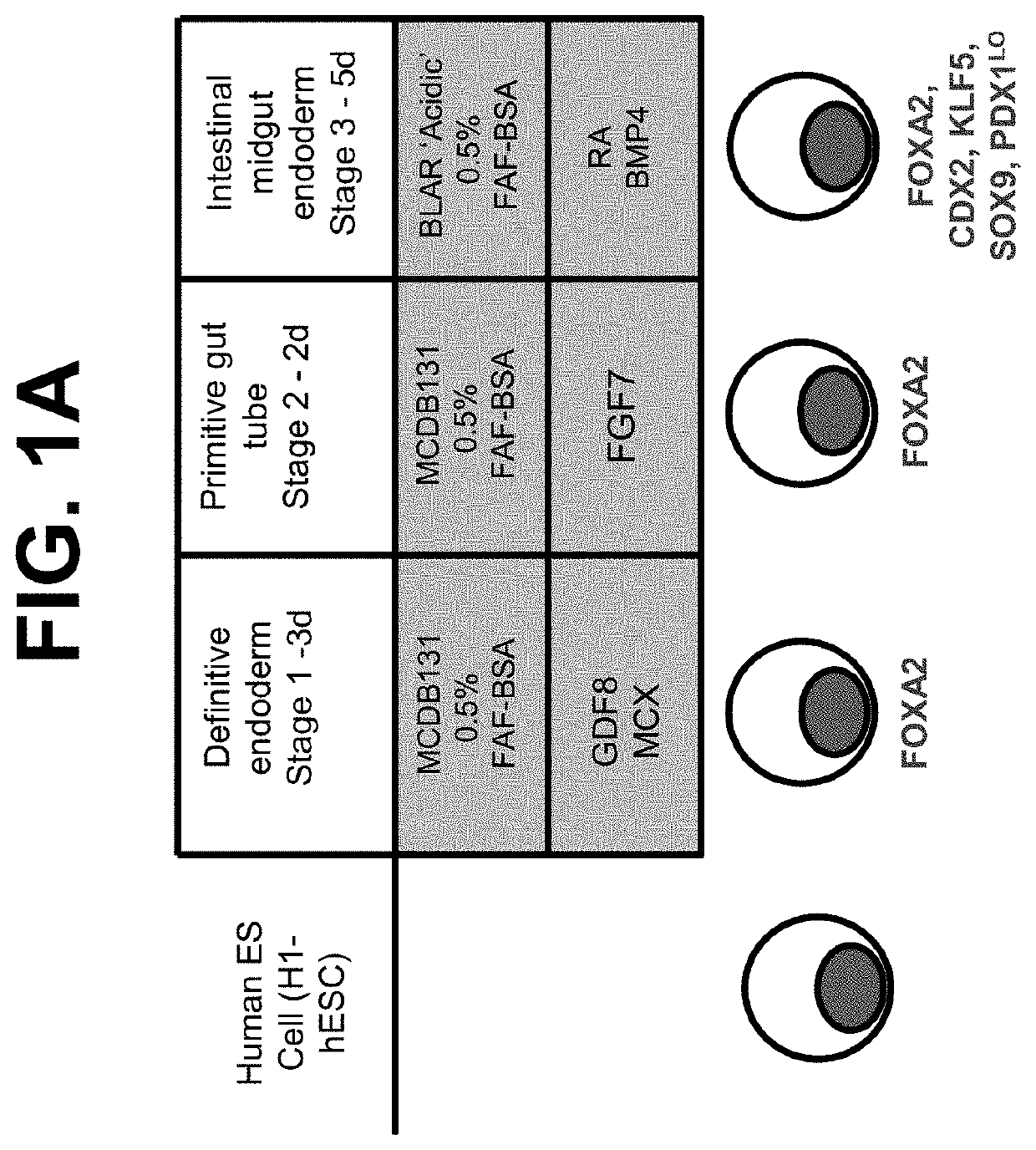
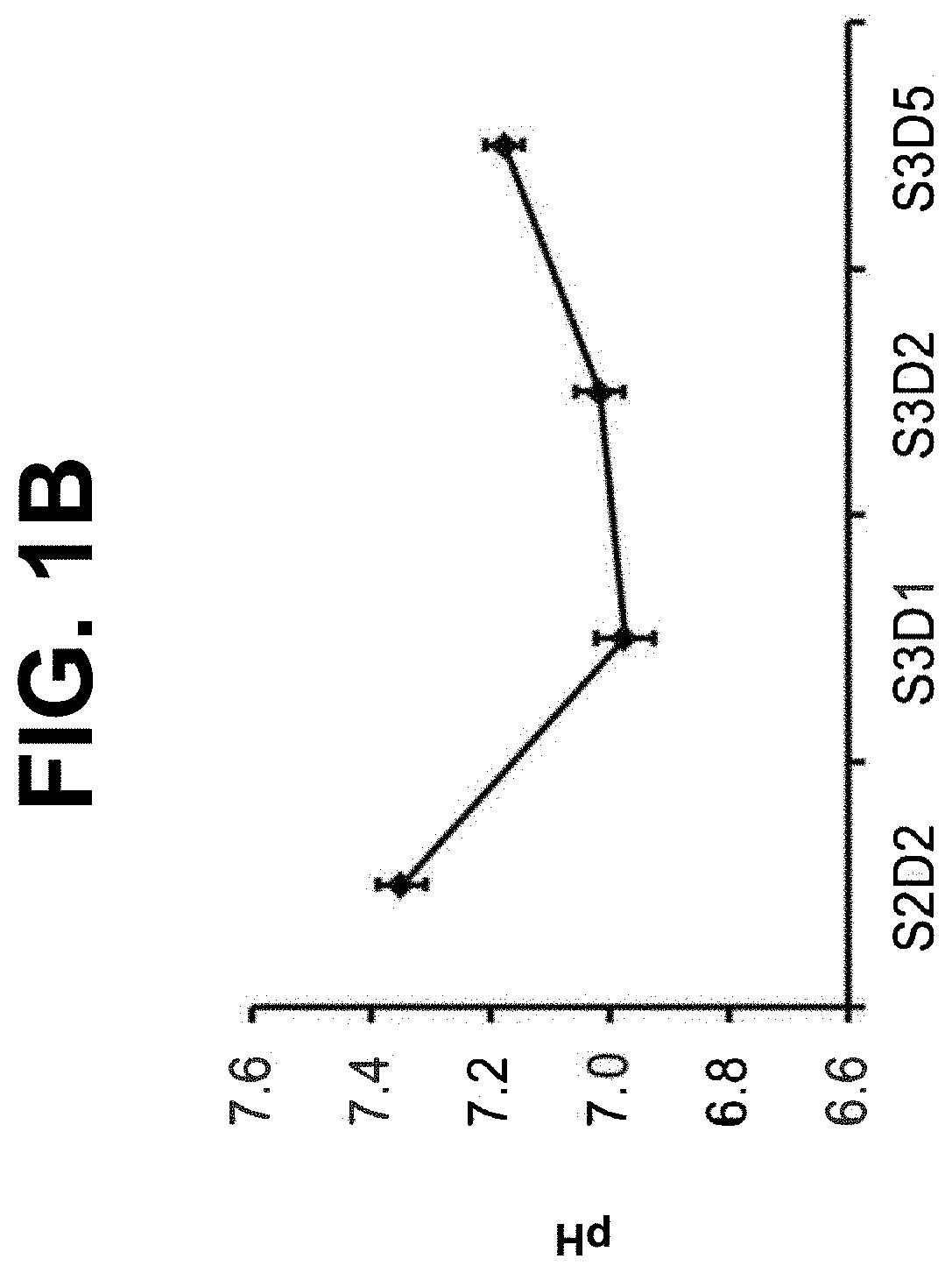
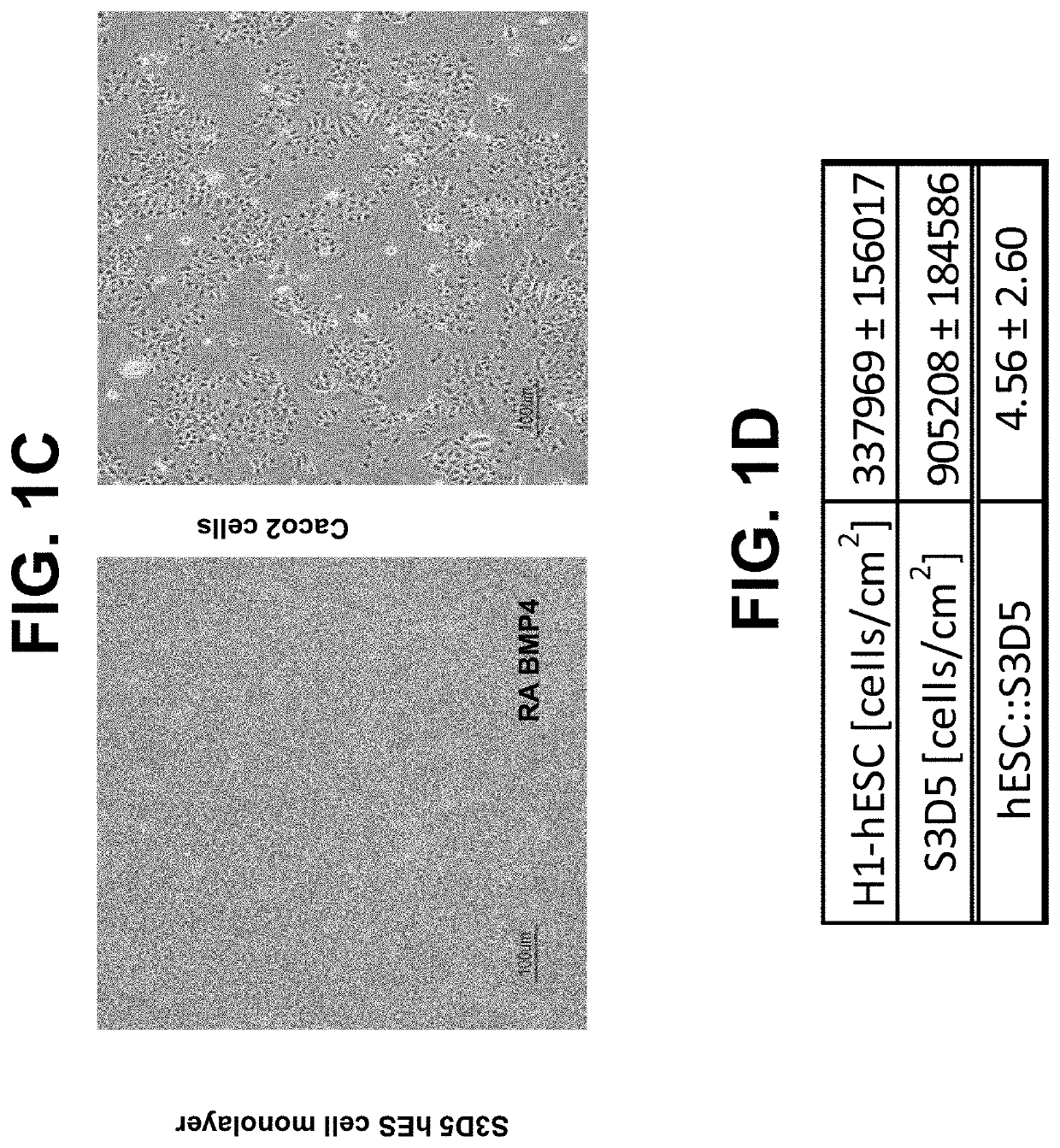
[0110]The following example describes a directed-based method to generate intestinal midgut endoderm cells from human embryonic stem cell (“hESC”). “Intestinal midgut endoderm” refers to a corresponding in vivo or in situ cell type which is CDX2-positive and FOXA2-positive endoderm cells present at about embryonic day 8.5 (“E8.5”) during mouse development, or at about the 3-4 week time point during human embryonic development.
Materials and Methods
[0111]Cell culture: Cells of the human embryonic stem cell line H1 (“H1-hESC”) (WA01 cells, WiCell Research Institute, Madison, Wis.) cultured with EZ8 media (Cat #A1516901 Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific) at passage 28 were seeded as single cells at 0.094×106 cells / cm2 on MATRIGEL™, at a 1:30 dilution, (Corning Incorporated, Corning, N.Y., Catalog #356231) coated dishes in a media of Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium Nutrient mix...
example 2
Intestinal Culturing Starting from the Definitive Endoderm, and Using FGF4 and WNT-Agonists, Generates an Endoderm-Mesenchyme Mixture of CDX2+ Mid- / Hindgut Cells
[0131]This example demonstrates the endoderm-mesenchyme-mixed quality of the CDX2+ mid- / hindgut cells generated from intestinal culturing beginning at the definitive endoderm stage using FGF4 and WNT-agonists (Spence et al., Nature, 2011; 470:105-109; Watson et al. Nature Med, 2014; 11:1310-1314). To examine the induction to midgut / hindgut endoderm cells described in Spence et al., infra, hESCs were differentiated using the protocol below. Note that the differentiation conditions outlined in this Example differ from Example 1 by the following: (i) intestinal condition starting point begins at the definitive endoderm stage; (ii) different growth factors and small molecules are used than RA and BMP4 or BMP2; and (iii) acidic culture conditions are not used.
Materials and Methods
[0132]Cell culture: H1-hESC cells were cultured an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com