Patents
Literature
153 results about "Diabetes management" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The term diabetes includes several different metabolic disorders that all, if left untreated, result in abnormally high concentration of a sugar called glucose in the blood. Diabetes mellitus type 1 results when the pancreas no longer produces significant amounts of the hormone insulin, usually owing to the autoimmune destruction of the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas. Diabetes mellitus type 2, in contrast, is now thought to result from autoimmune attacks on the pancreas and/or insulin resistance. The pancreas of a person with type 2 diabetes may be producing normal or even abnormally large amounts of insulin. Other forms of diabetes mellitus, such as the various forms of maturity onset diabetes of the young, may represent some combination of insufficient insulin production and insulin resistance. Some degree of insulin resistance may also be present in a person with type 1 diabetes.
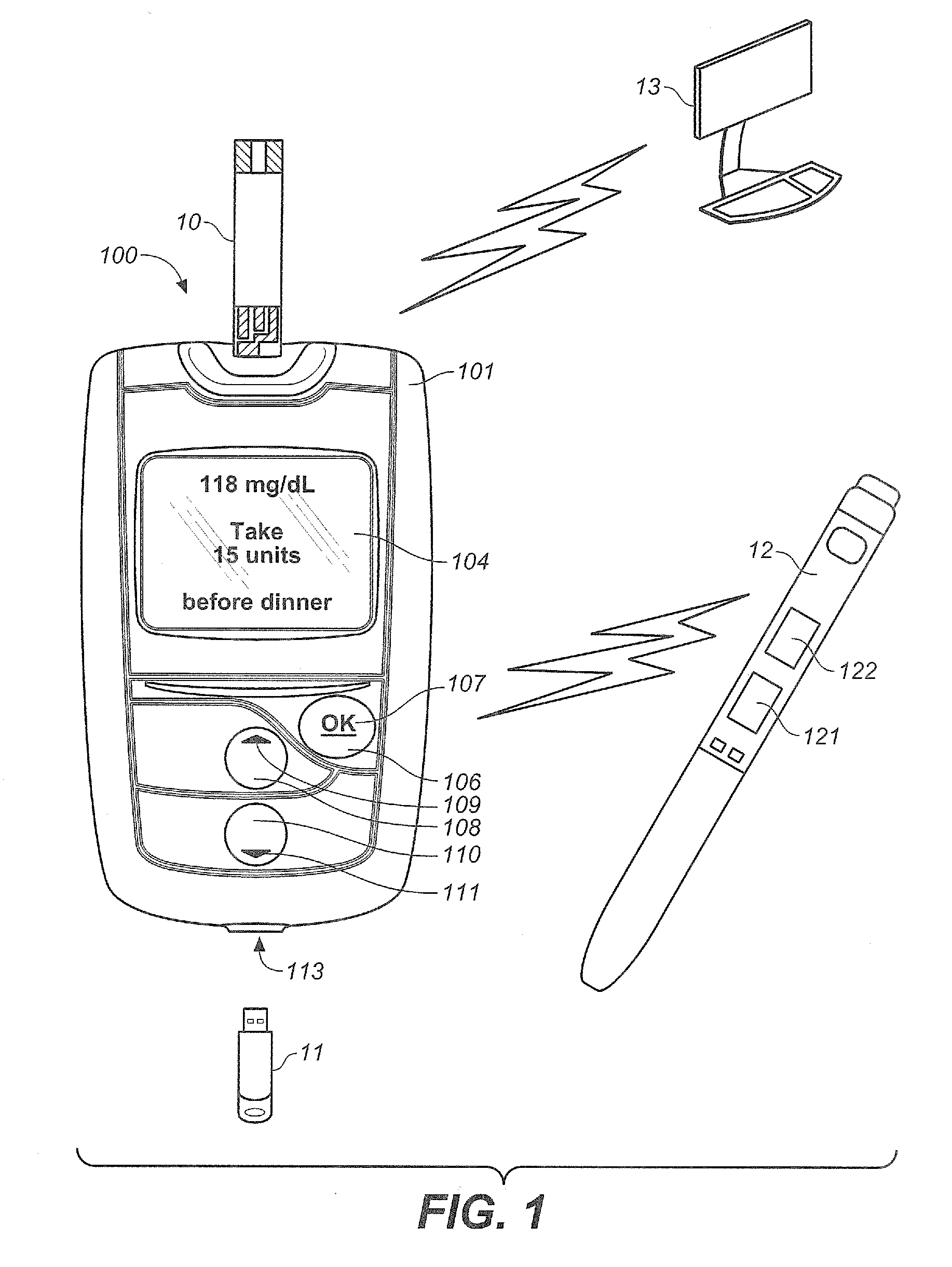
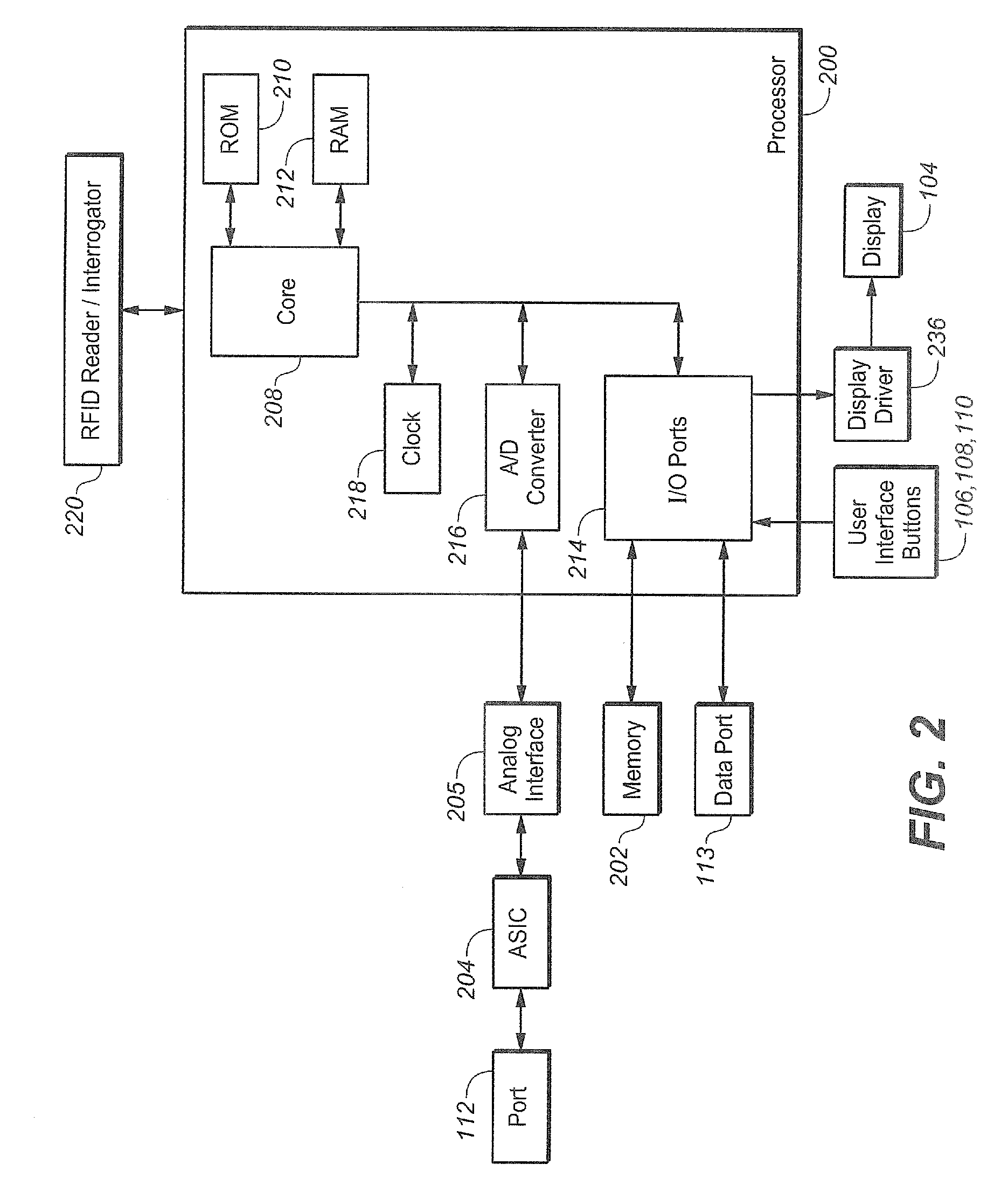
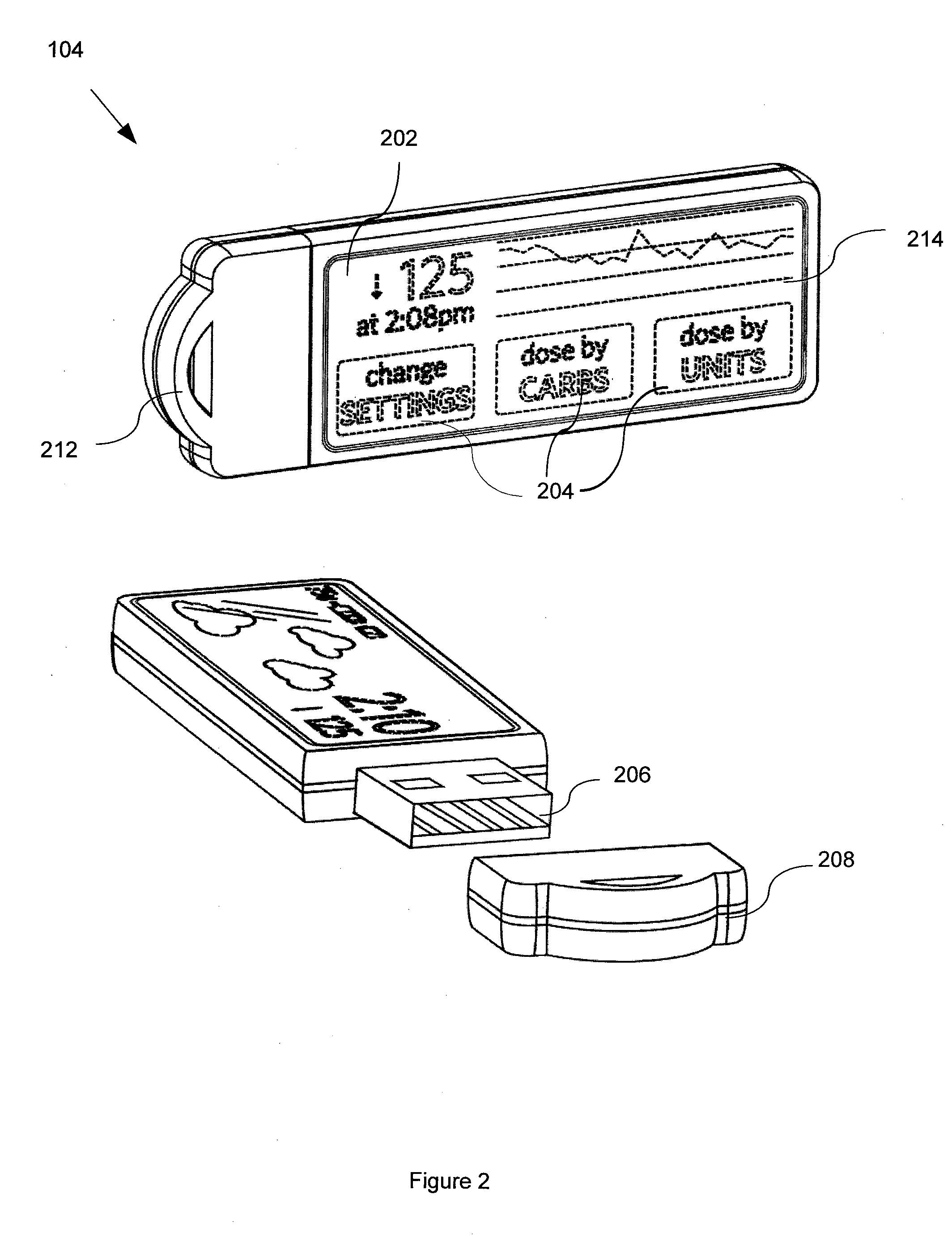
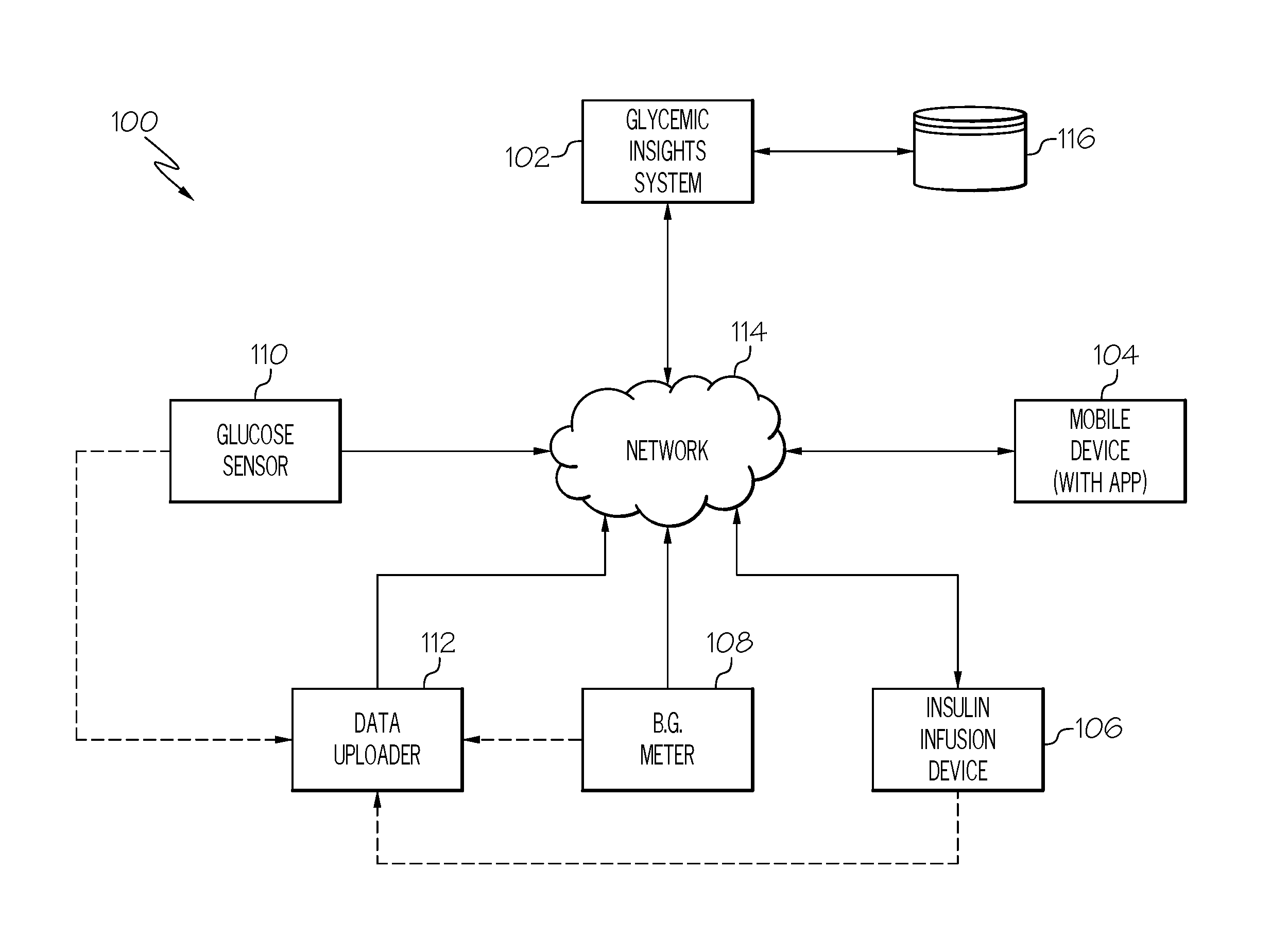
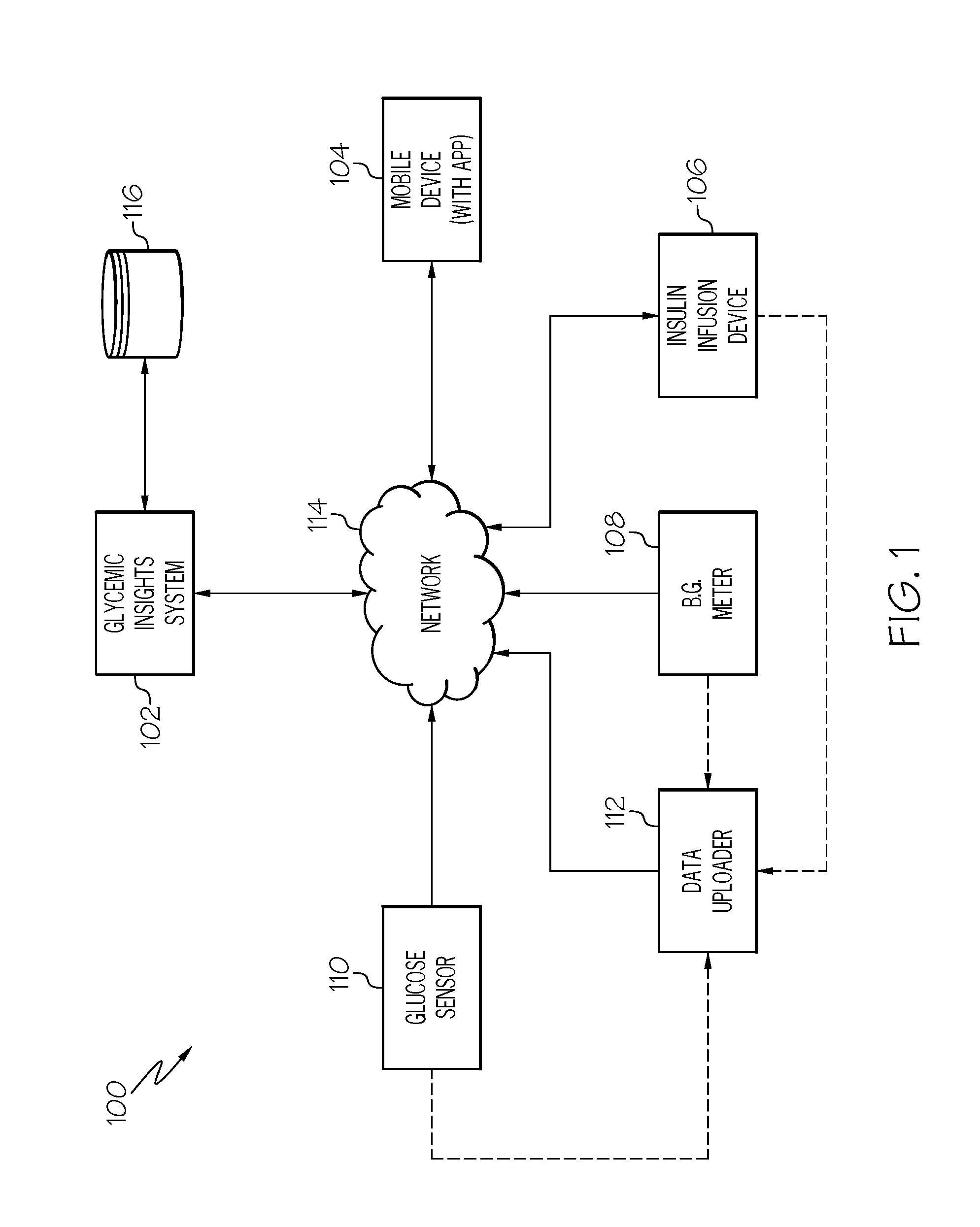
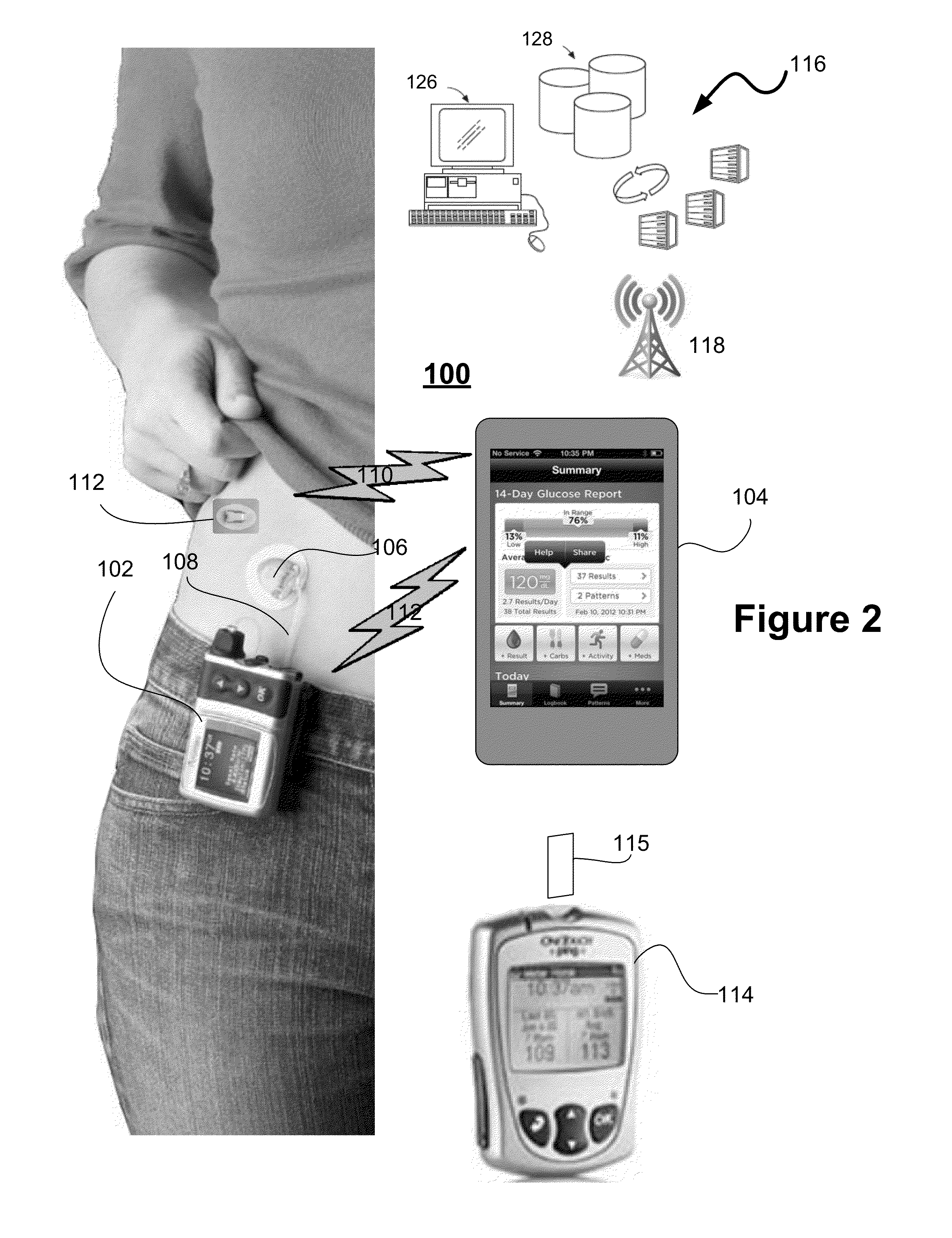
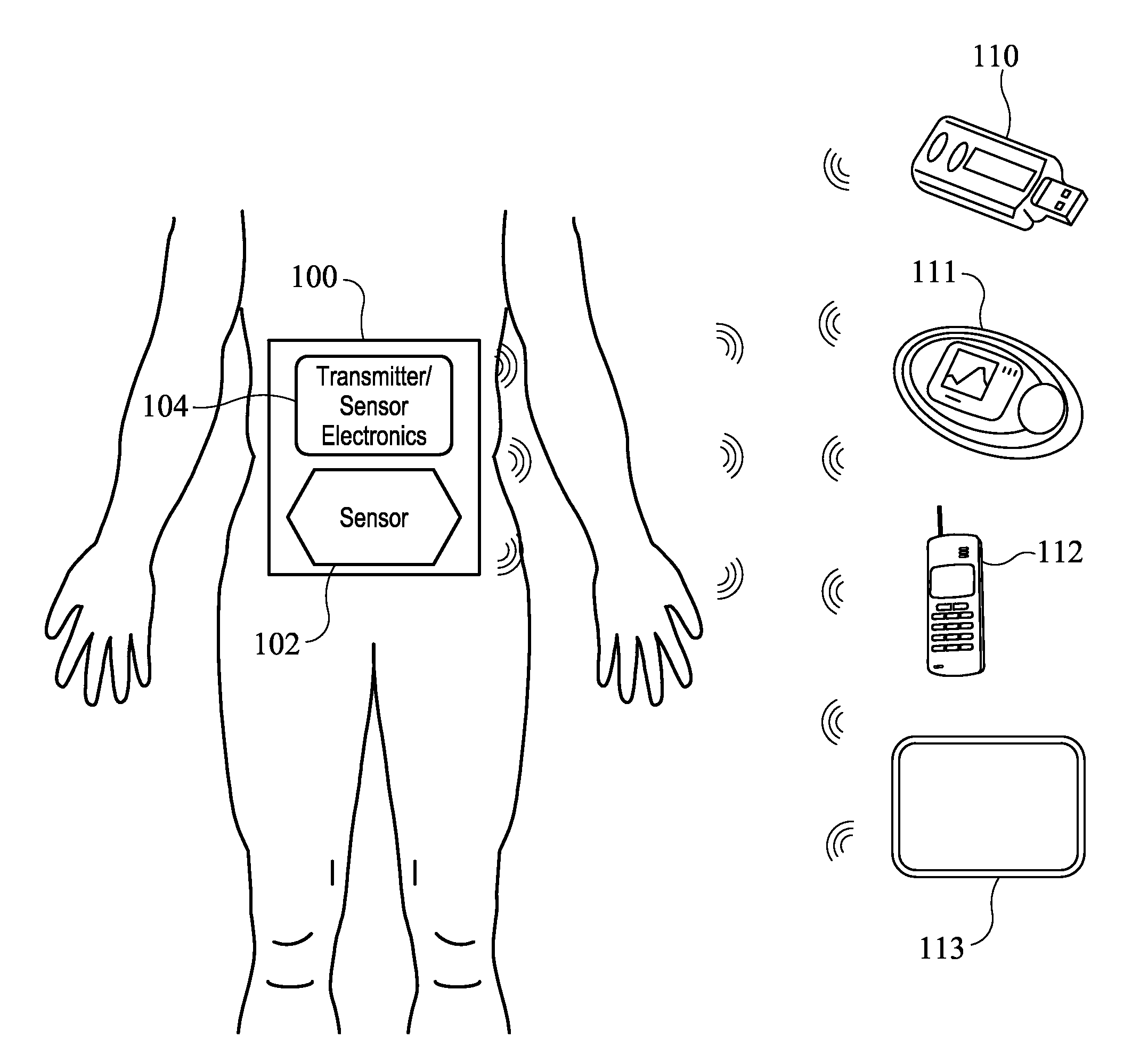
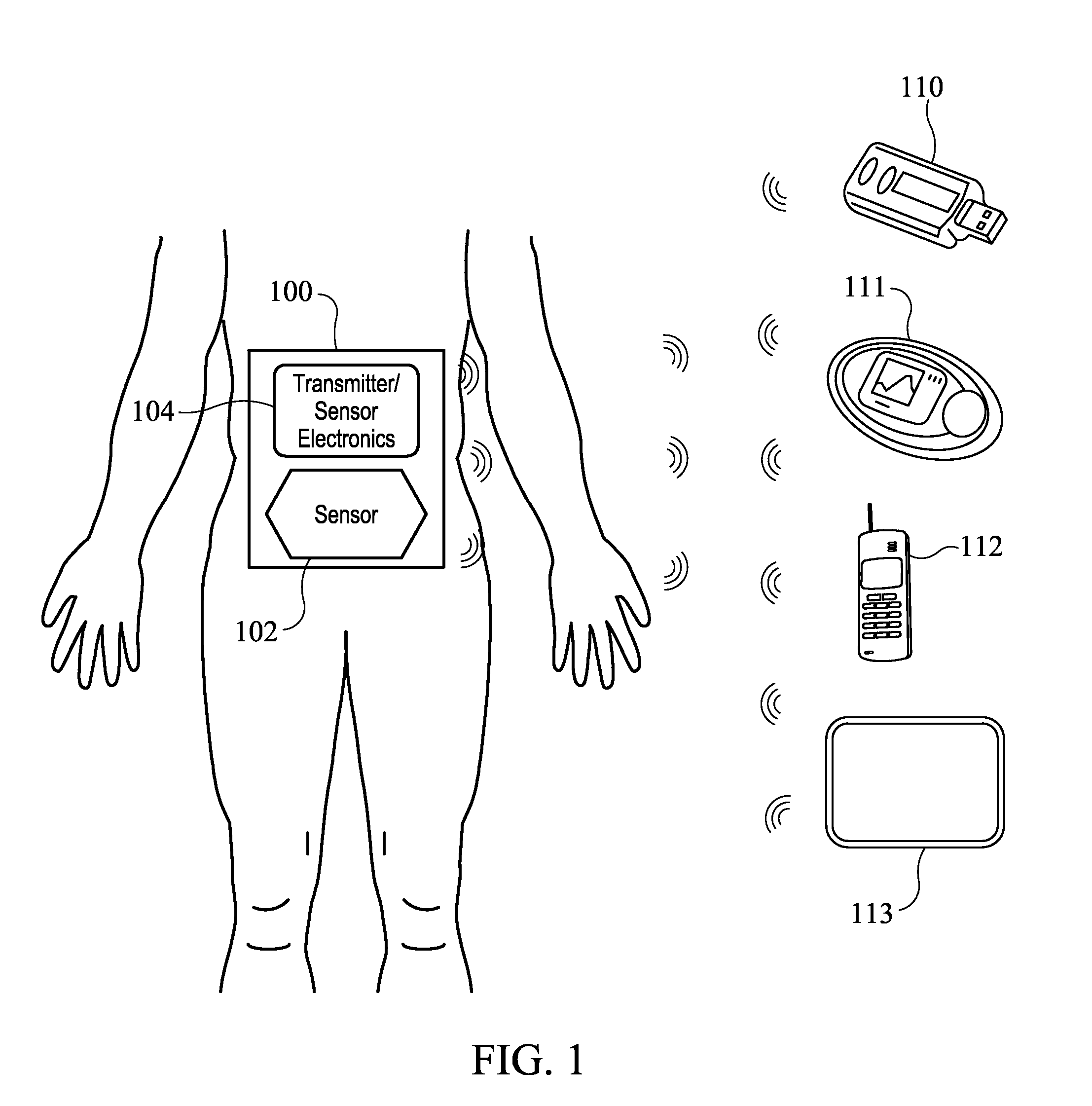
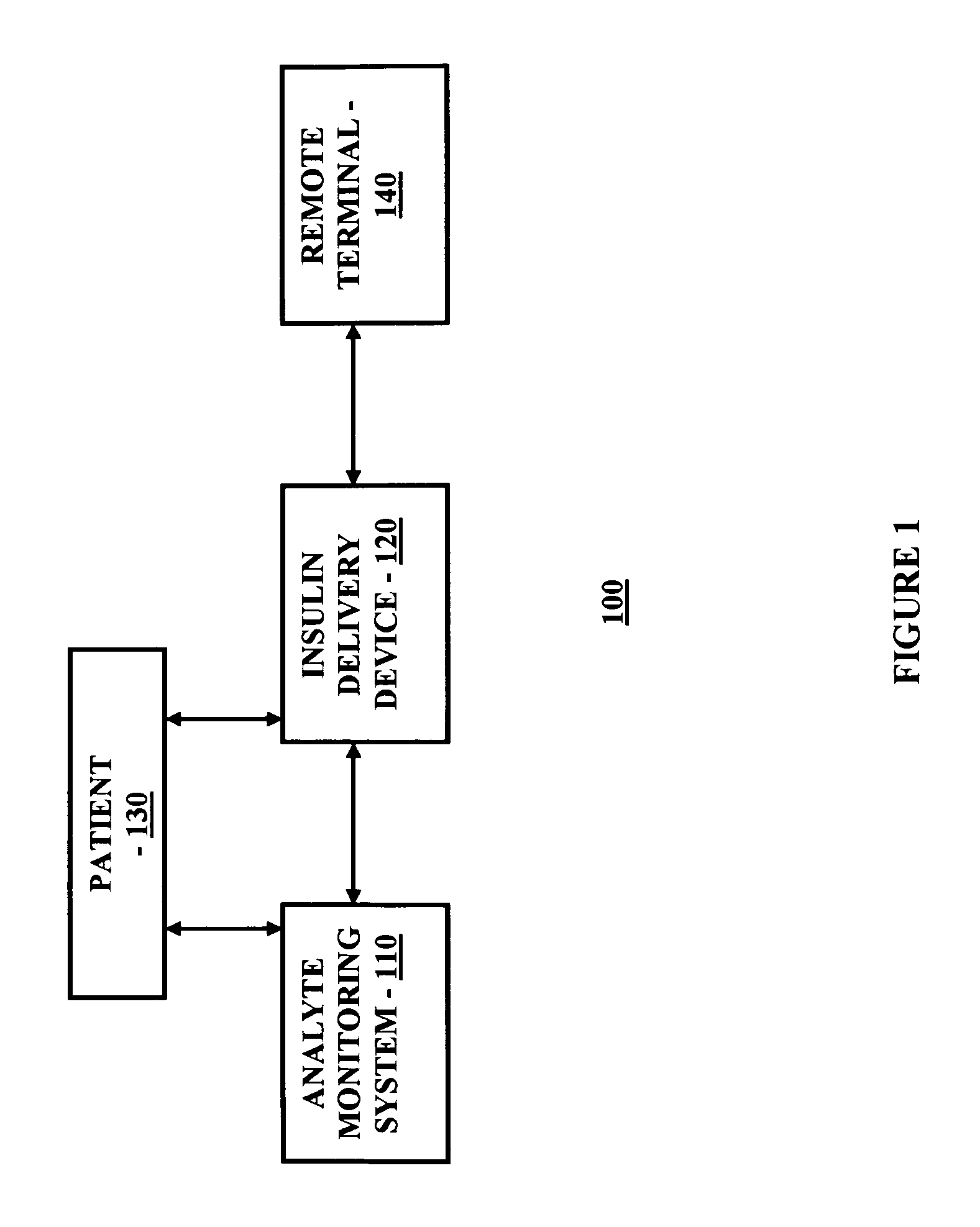
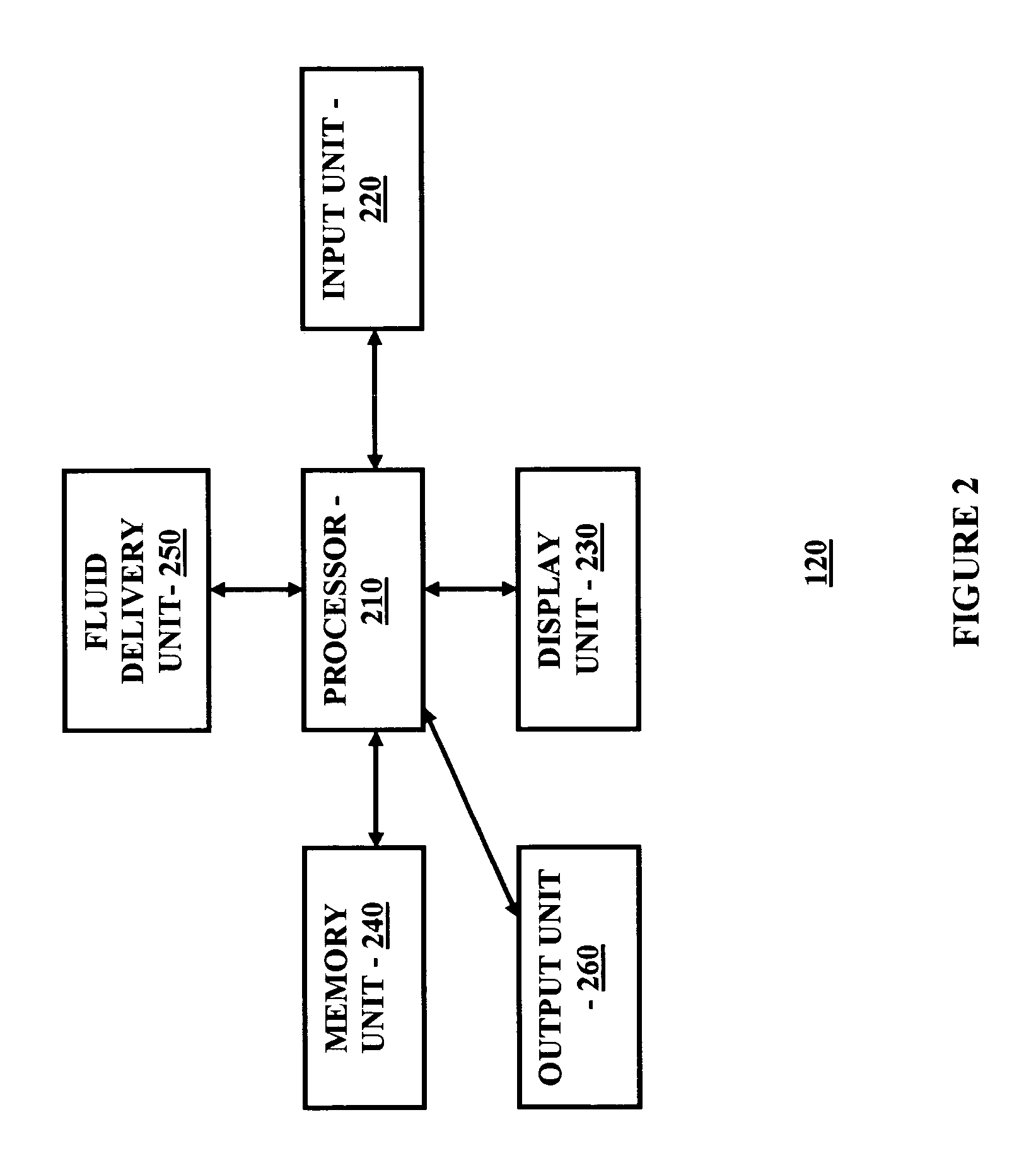
Systems and Methods for Diabetes Management Using Consumer Electronic Devices
InactiveUS20080119705A1Facilitate communicationDrug and medicationsNutrition controlDiabetes managementContinuous glucose monitoring
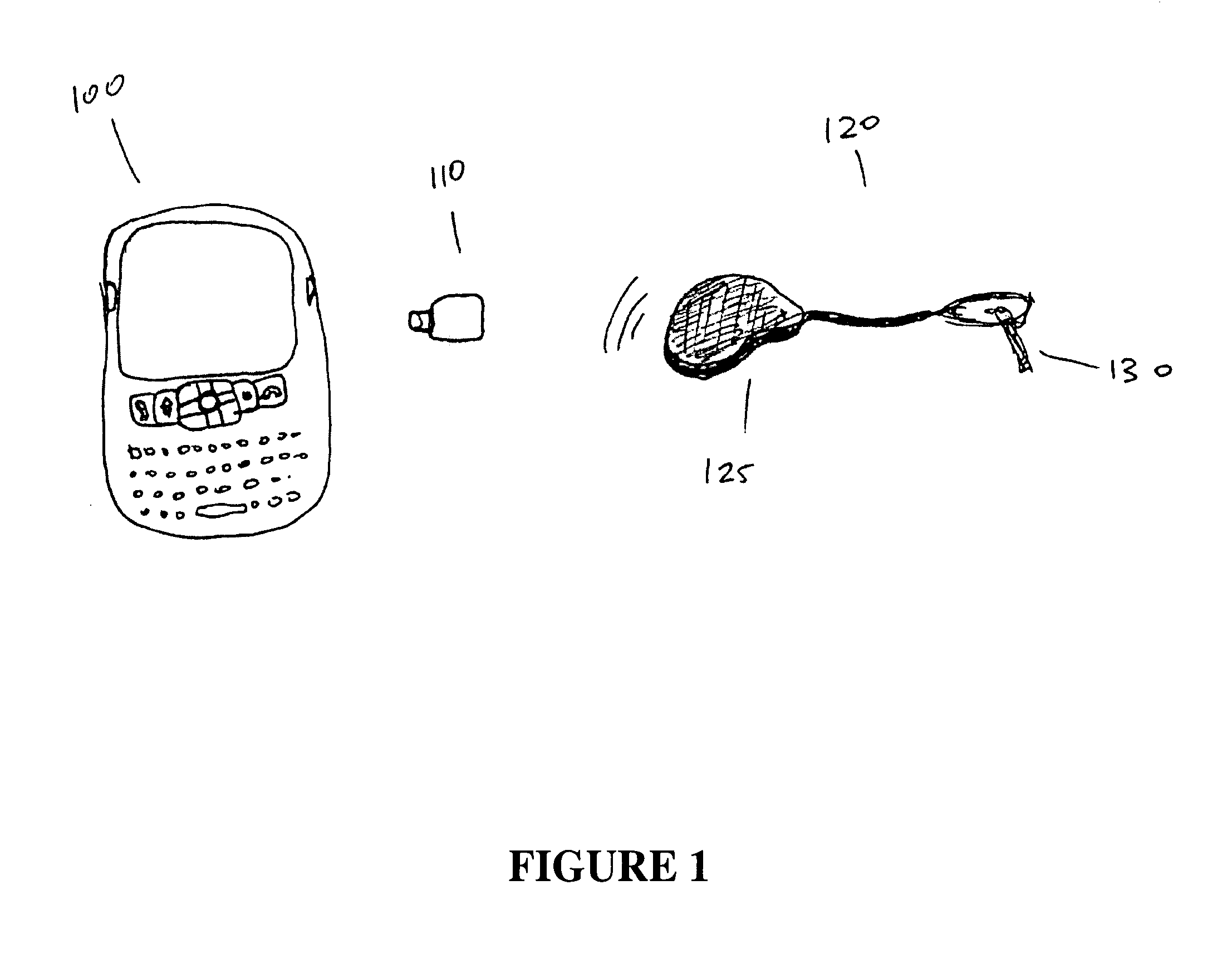
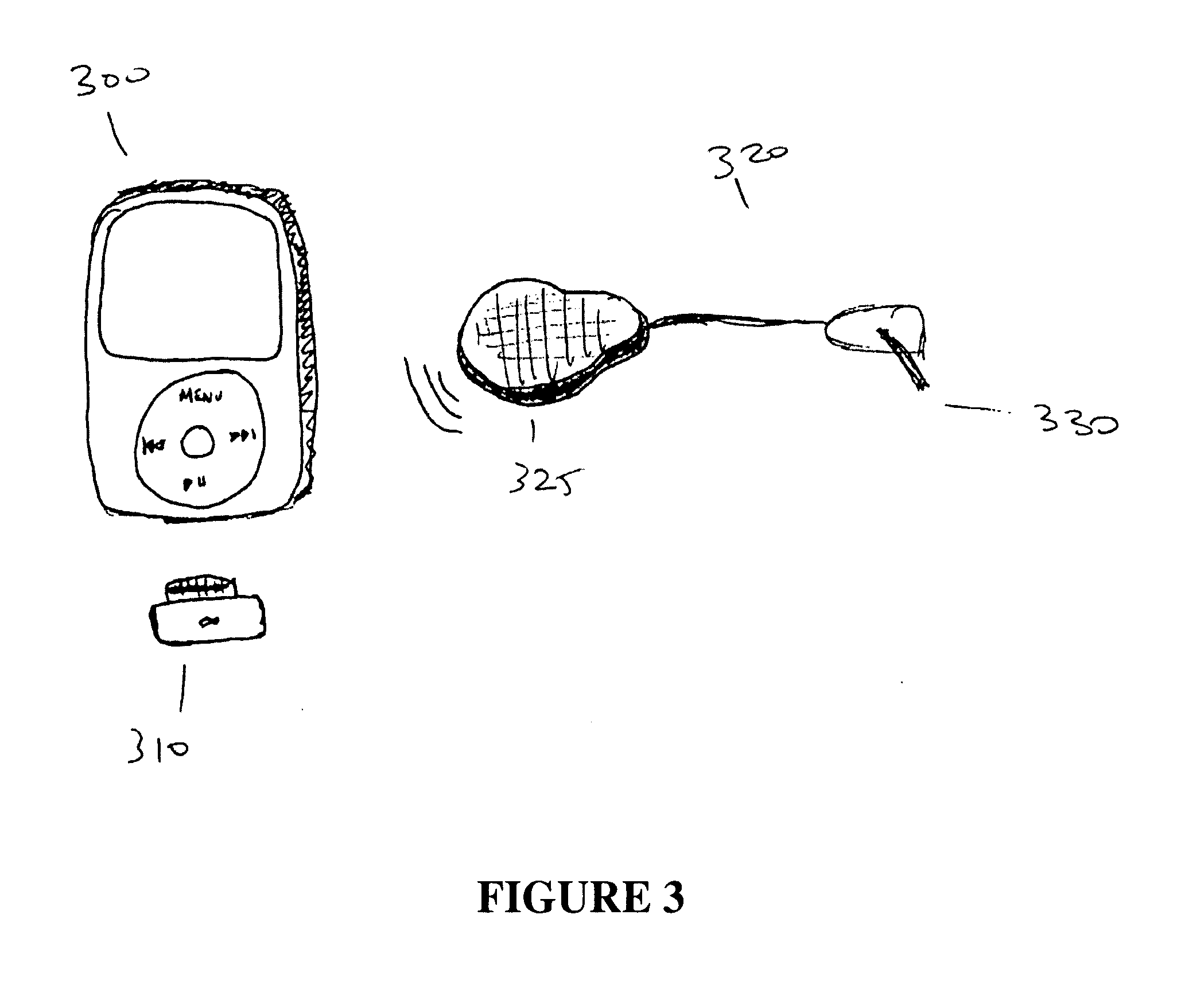
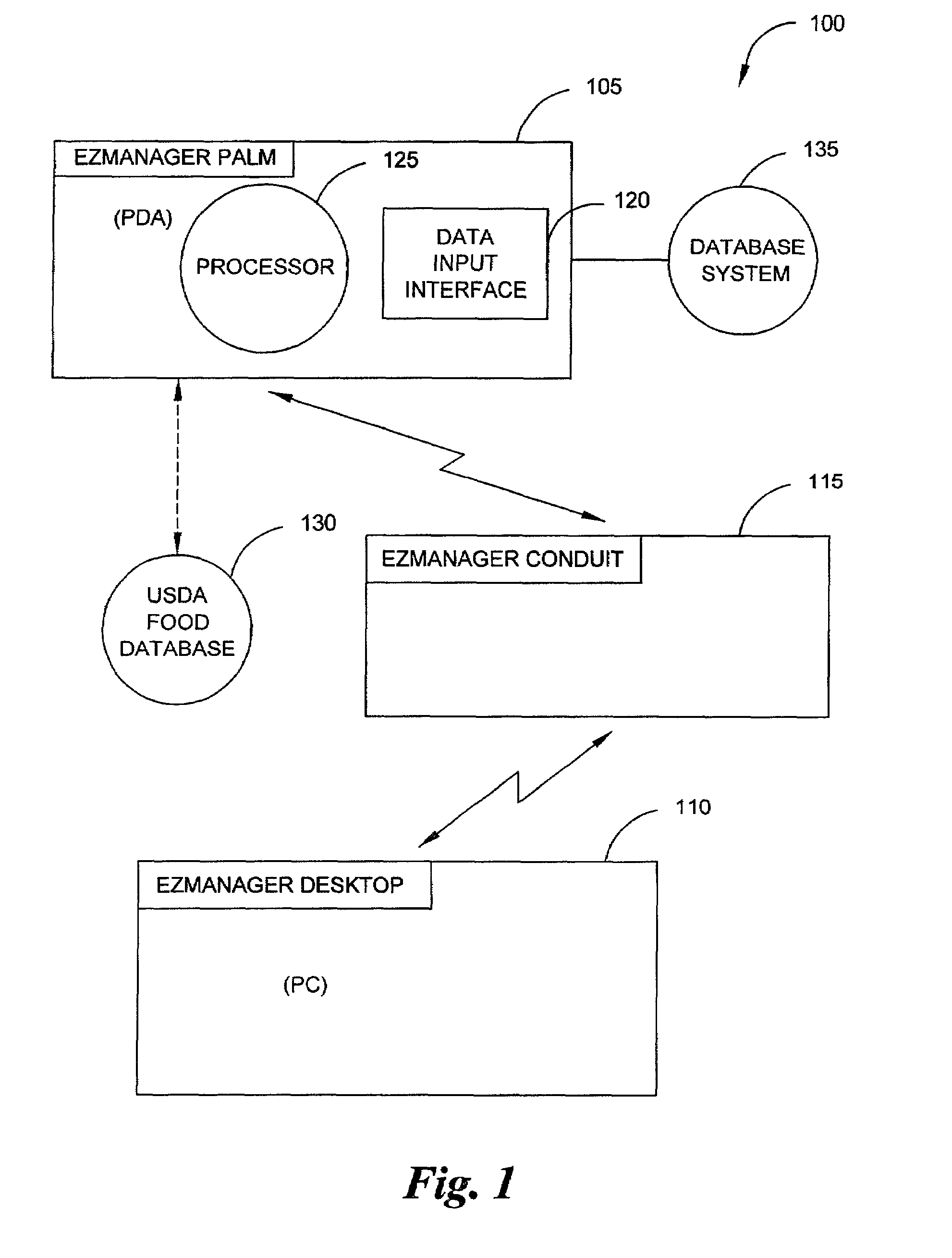
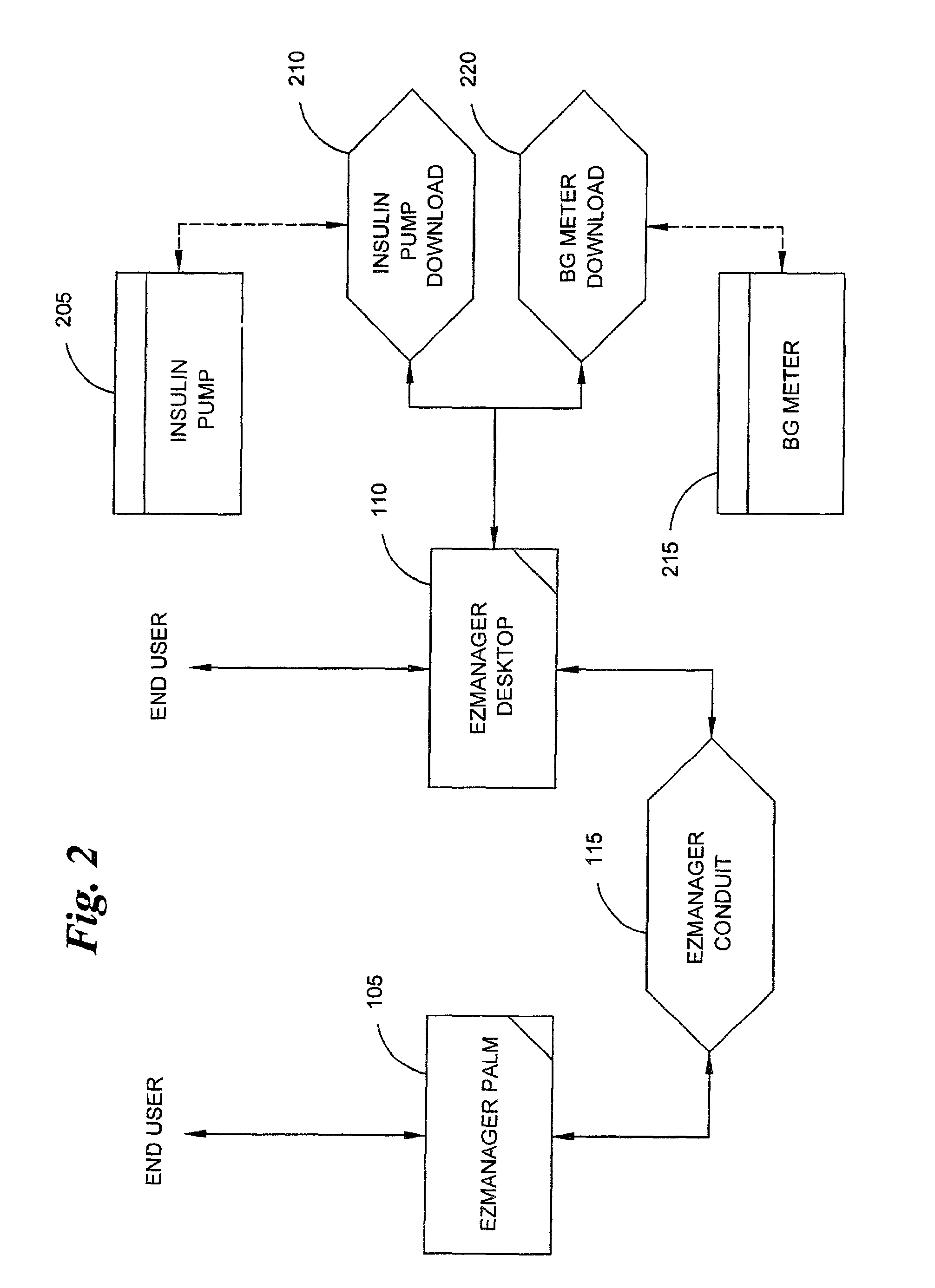
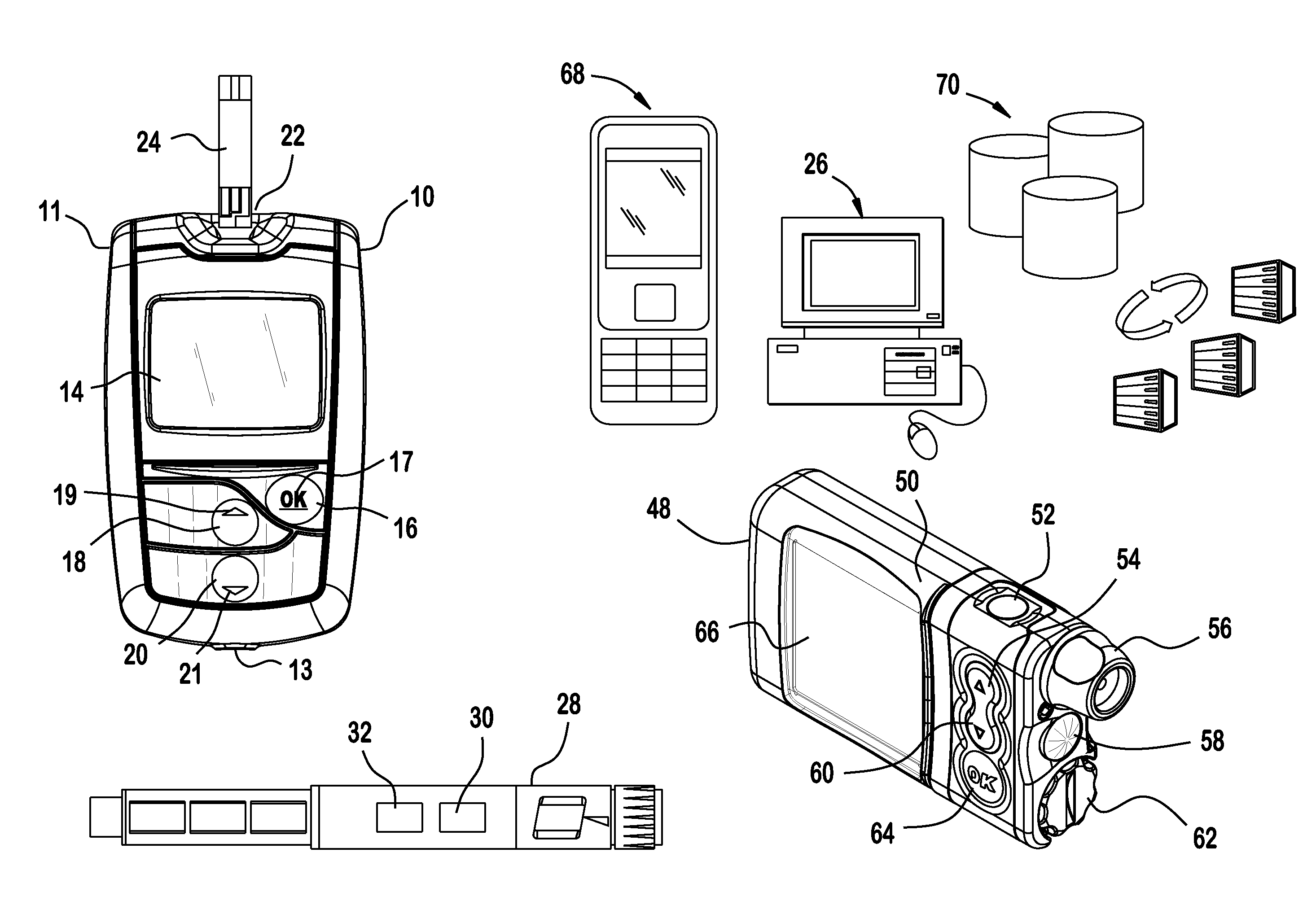
The invention is embodied in a system for diabetes management including a medical device (MD) and a consumer electronic device (CED). The CED may be used to monitor and / or control the MD. In particular embodiments, the system may include a connector that plugs into the CED to allow communication between the MD and the CED. The medical device may be an external infusion device, implantable pump, glucose meter, glucose monitor, continuous glucose monitoring system, or the like. The CED may be any type of consumer electronic device including, but not limited to, cellular phones, personal digital assistants (PDAs), BlackBerry, Smartphones, pocketpc phones, mp3 players, radios, CD players, and the like.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Smart messages and alerts for an infusion delivery and management system
ActiveUS20070213657A1Easy to controlIncrease motivationHealth-index calculationDrug and medicationsDiabetes mellitusDiabetes management
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Advanced diabetes management system (ADMS)
InactiveUS20070168224A1Eliminate useMedical communicationData processing applicationsDiseaseMedical treatment
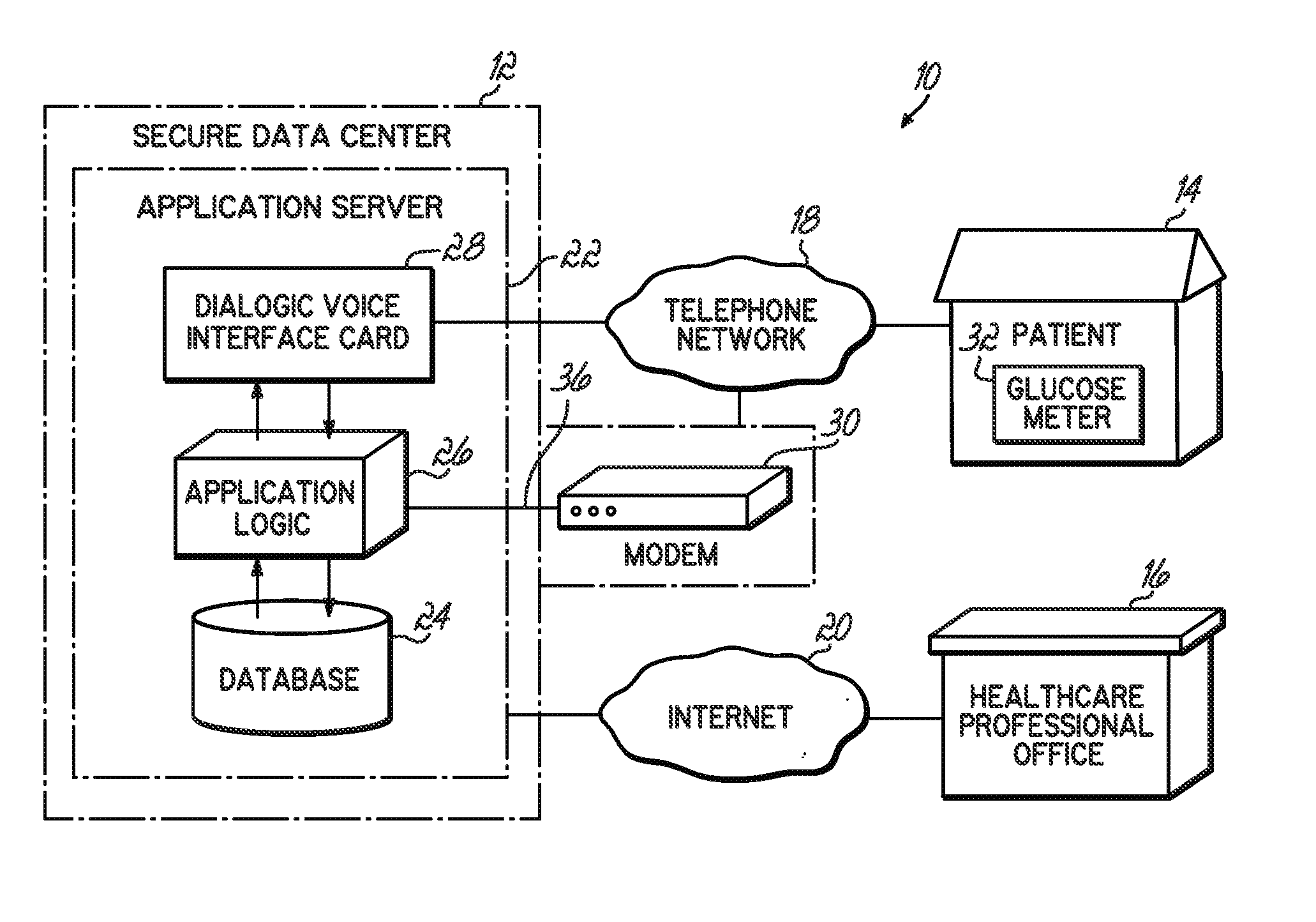
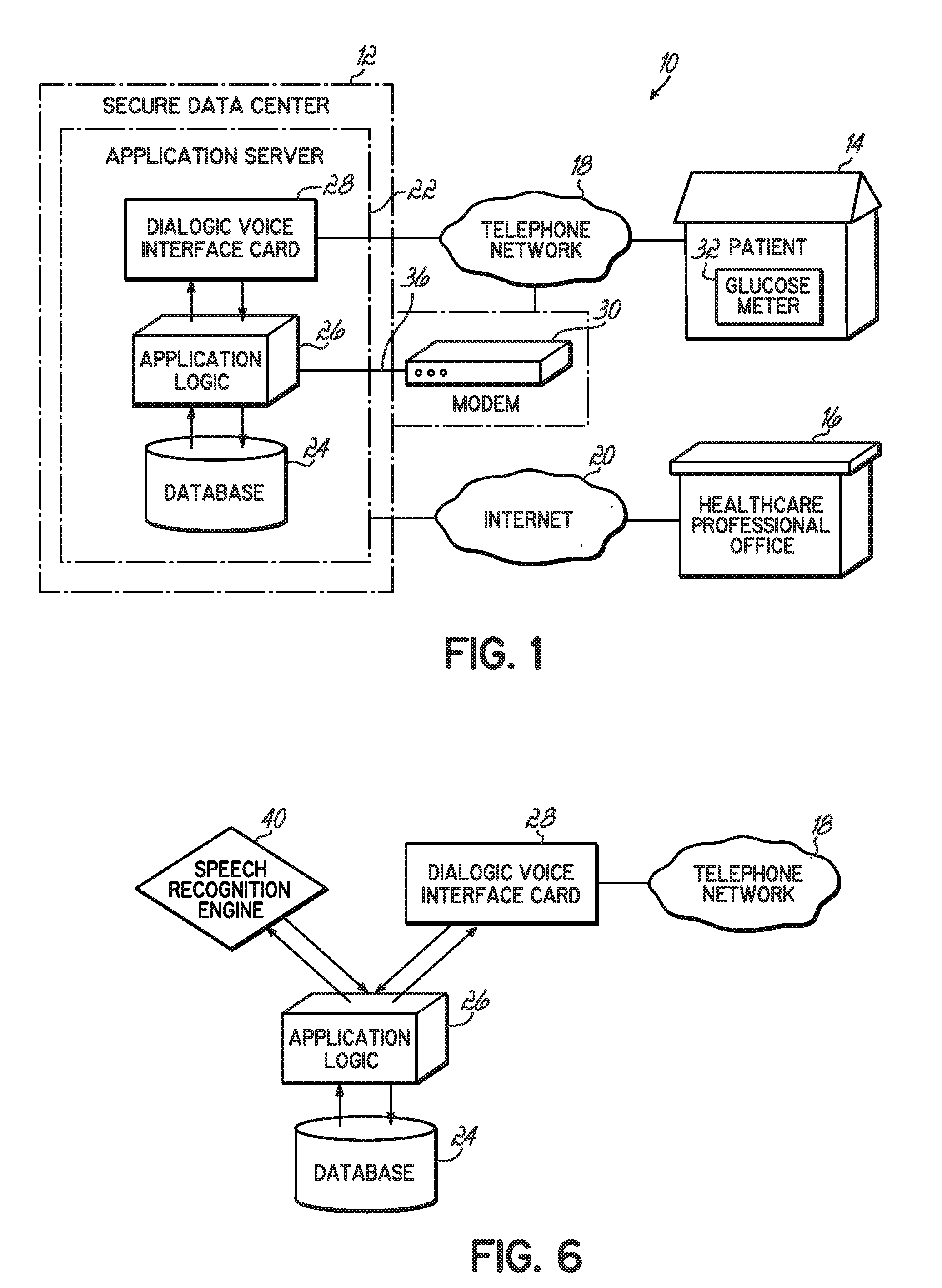
An automated healthcare communication system that facilitates communications between healthcare providers and patients and provides timely data to providers to help patients self manage their diabetes. Messages are presented to patients at pre-selected times to help them learn about the disease and develop appropriate behaviors that improve their health and to prompt them for data or for answers to specific questions or surveys. The system applies advanced speech recognition technology to make the system easy for patients to use and understand via a telephone network. Data collected from the patient is presented in real-time to healthcare providers so the patients' progress can be monitored and treatment plans adjusted accordingly.
Owner:AML & ASSOC LLC
System and method for managing diabetes
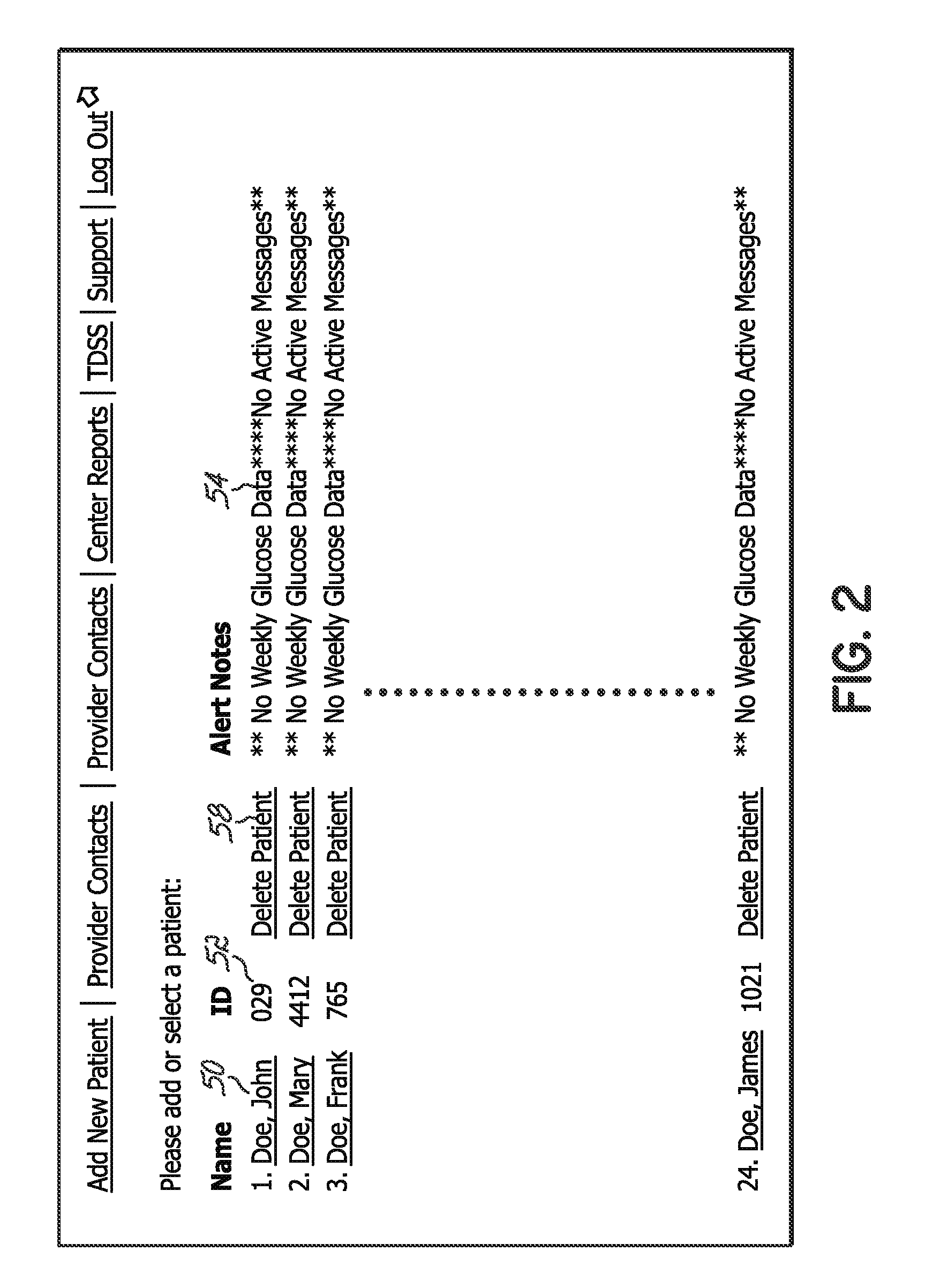
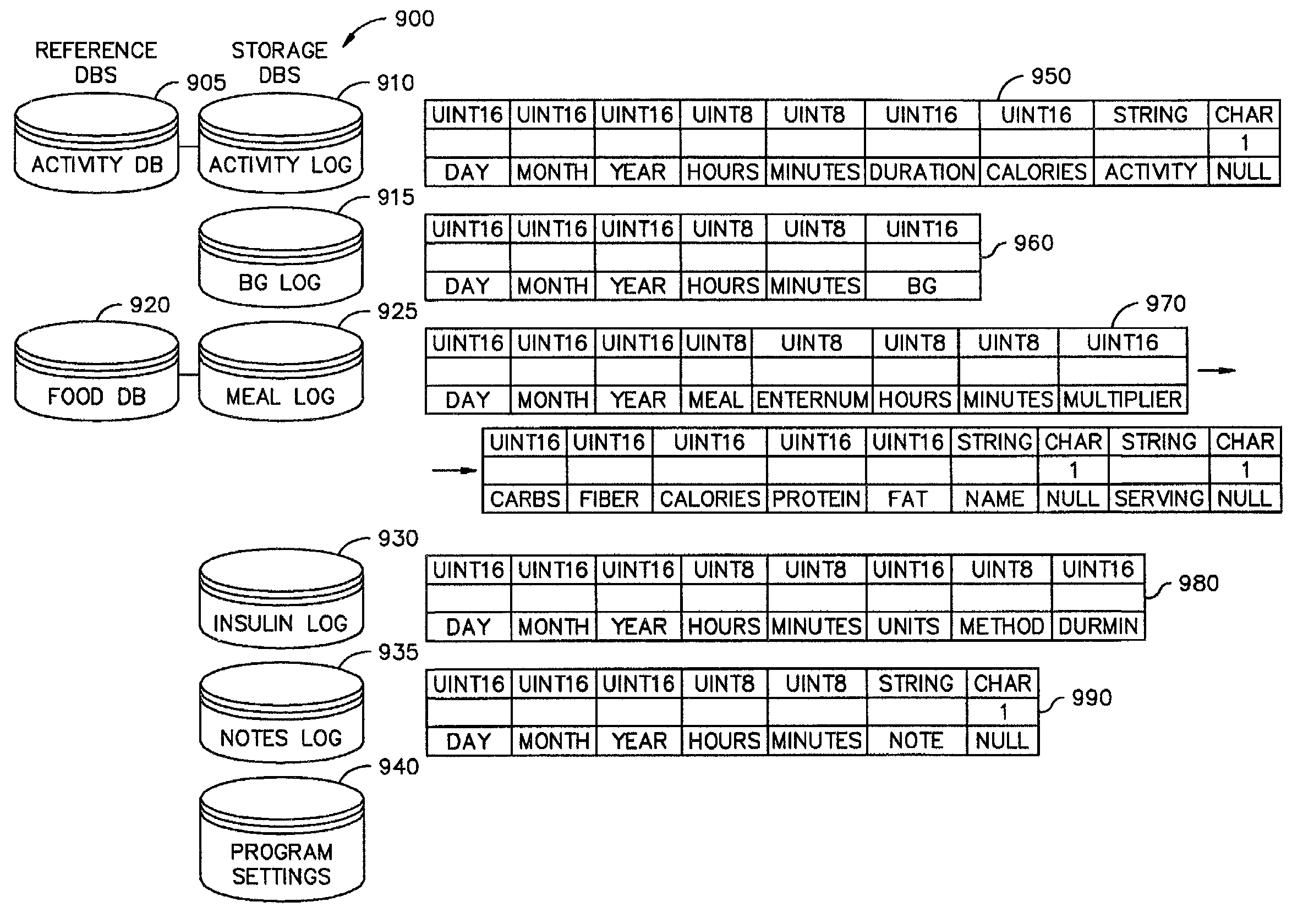
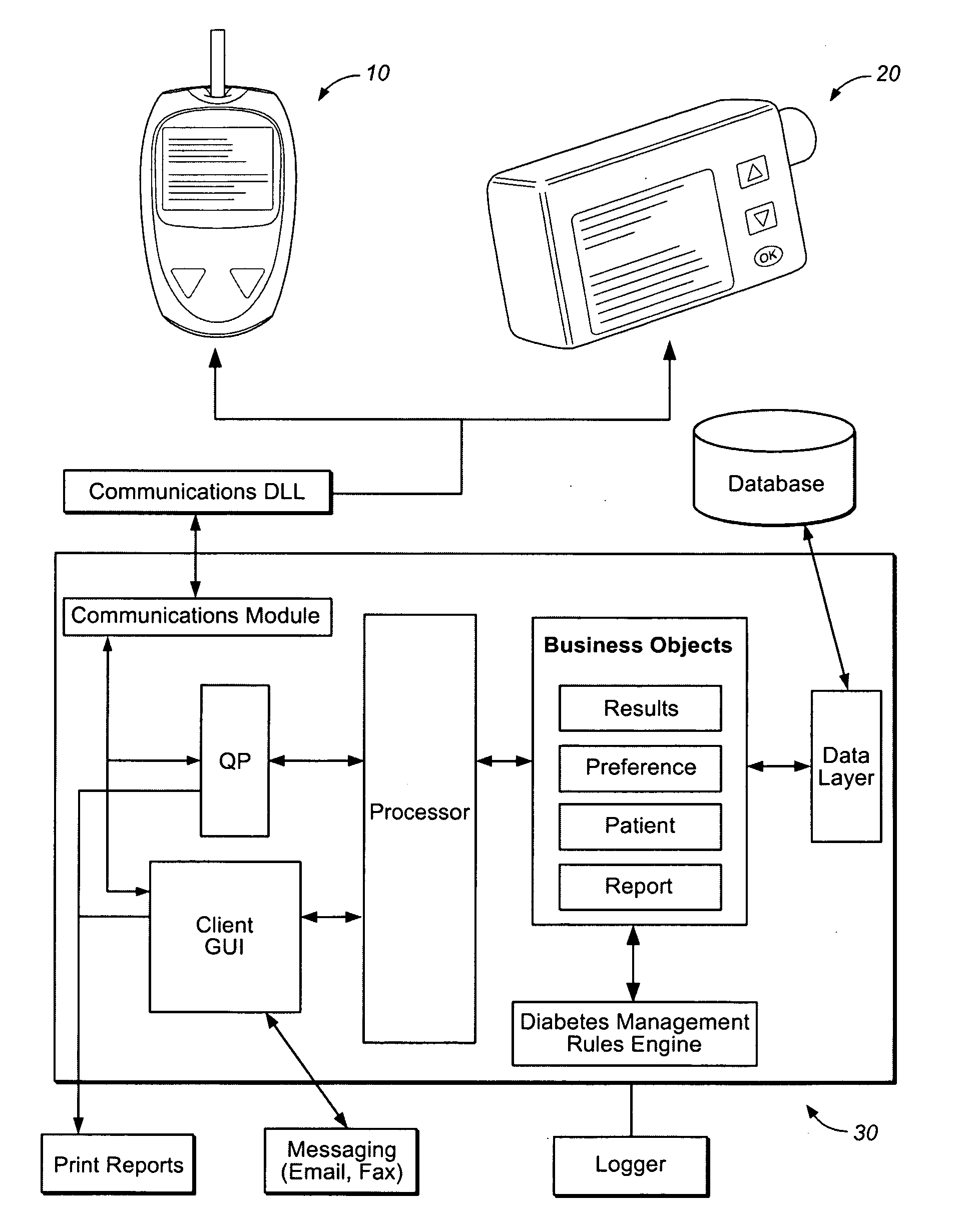
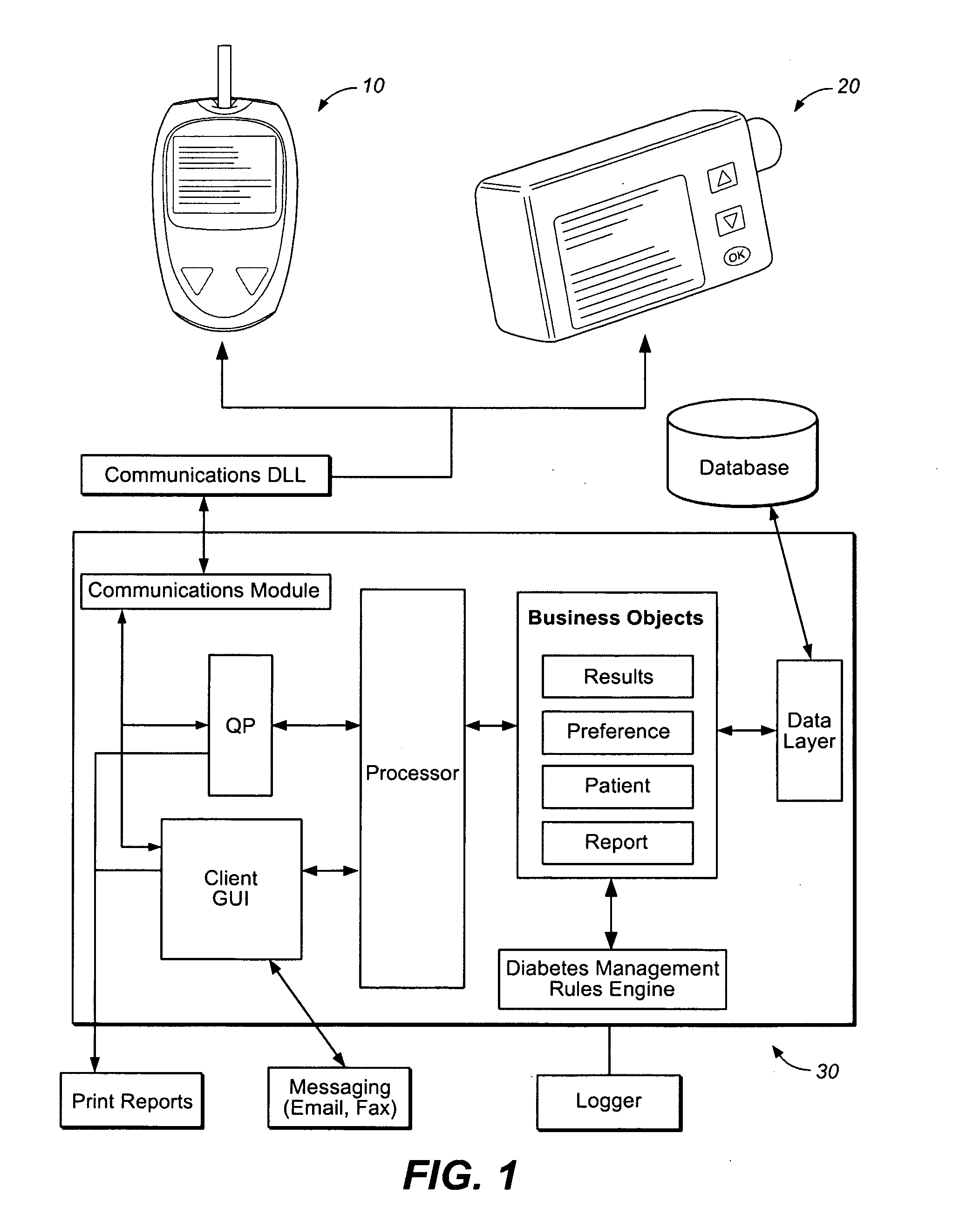
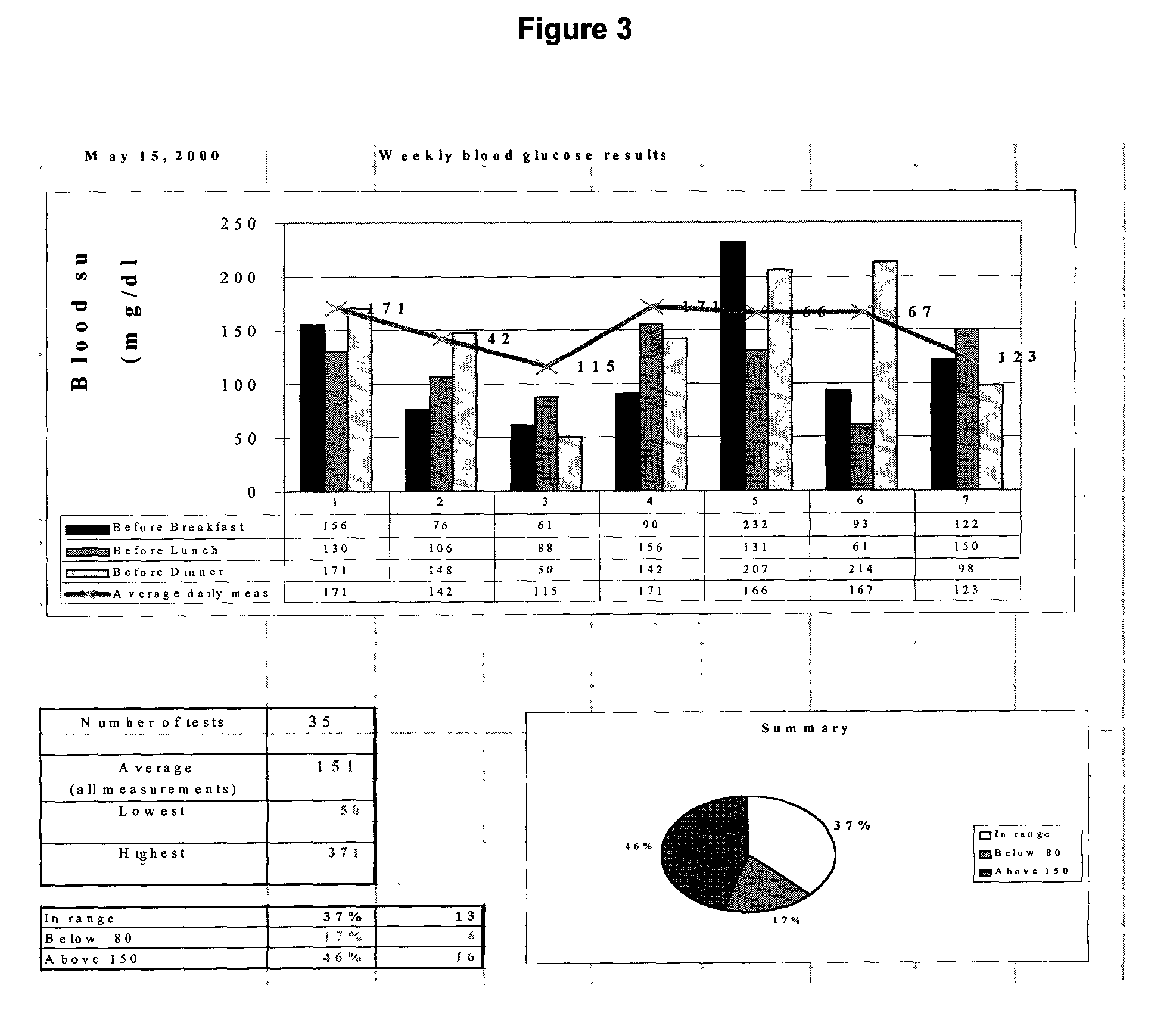
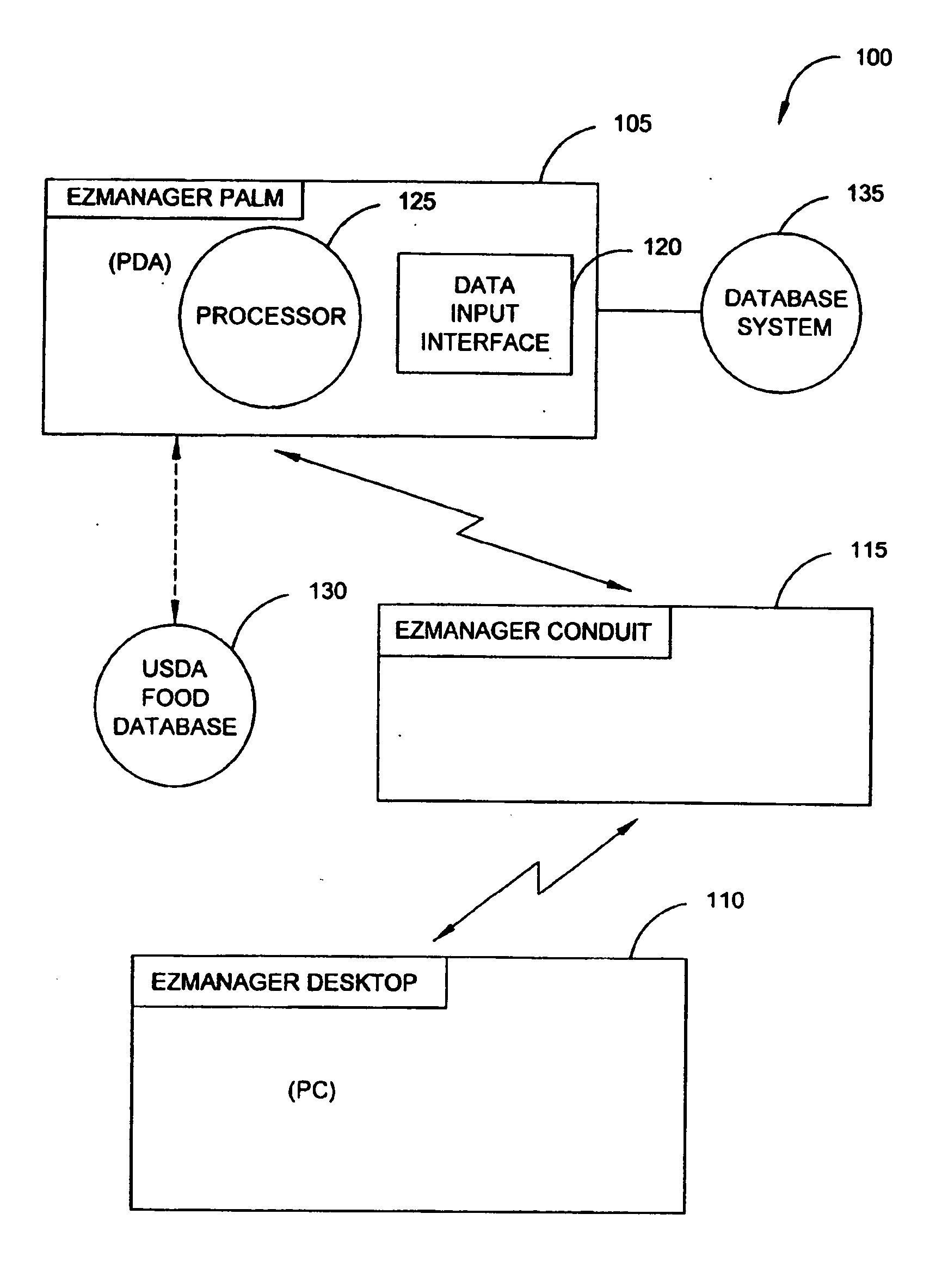
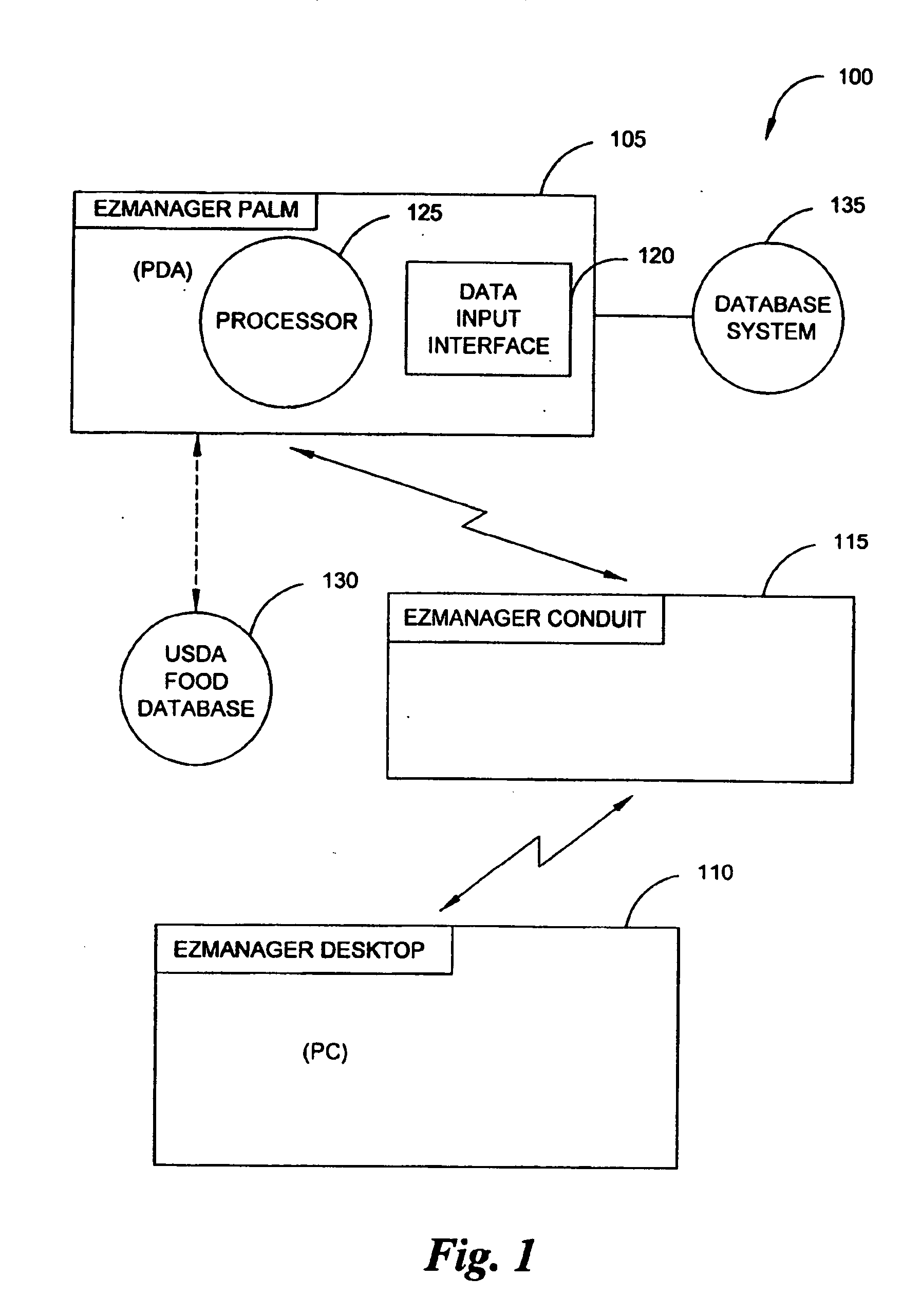
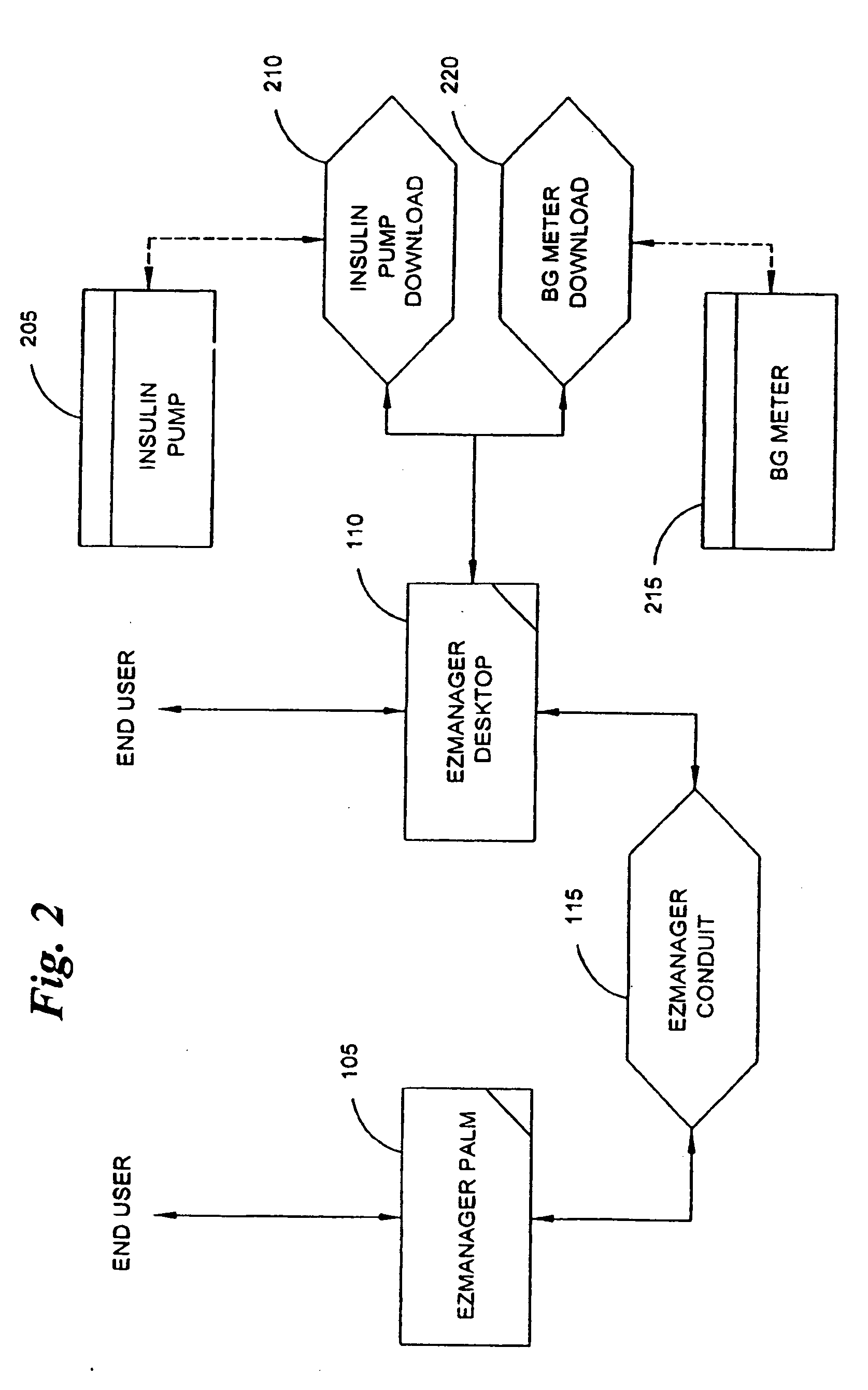
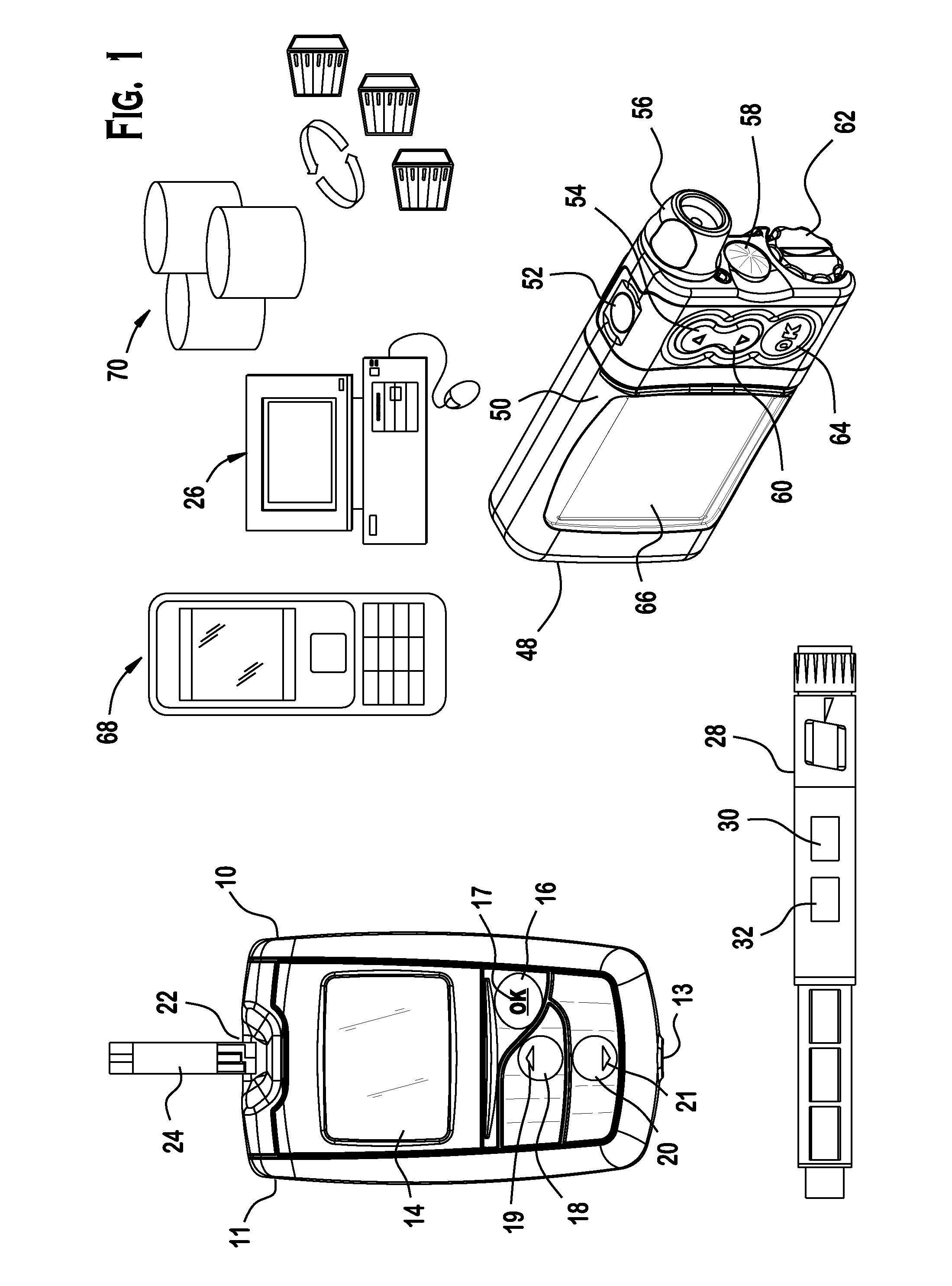
A diabetes management system and method used to manage the blood glucose level of a diabetes patient. The system includes at least one portable electronic device and a database system. The portable electronic device allows the patient to input different types of data into the processor to calculate insulin and carbohydrate intake recommendations for the patient. A time / date stamp is individually generated and stored for each type of data inputted by the patient. The diabetes management system also includes a database system which stores (i) activity data associated with the physical activity of the patient, (ii) blood glucose data associated with the blood glucose level of the patient, (iii) meal intake data associated with the food intake of the patient, and (iv) insulin intake data associated with the insulin intake of the patient.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Sensor systems having multiple probes and electrode arrays
ActiveUS20110319734A1Improve reliabilityImprove sensor accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSensor arrayDiabetes mellitus
Embodiments of the invention provide amperometric analyte sensors having multiple related structural elements (e.g. sensor arrays comprising a working, counter and reference electrode) and algorithms designed for use with such sensors. While embodiments of the innovation can be used in a variety of contexts, typical embodiments of the invention include glucose sensors used in the management of diabetes.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Analyte measurement and management device and associated methods
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
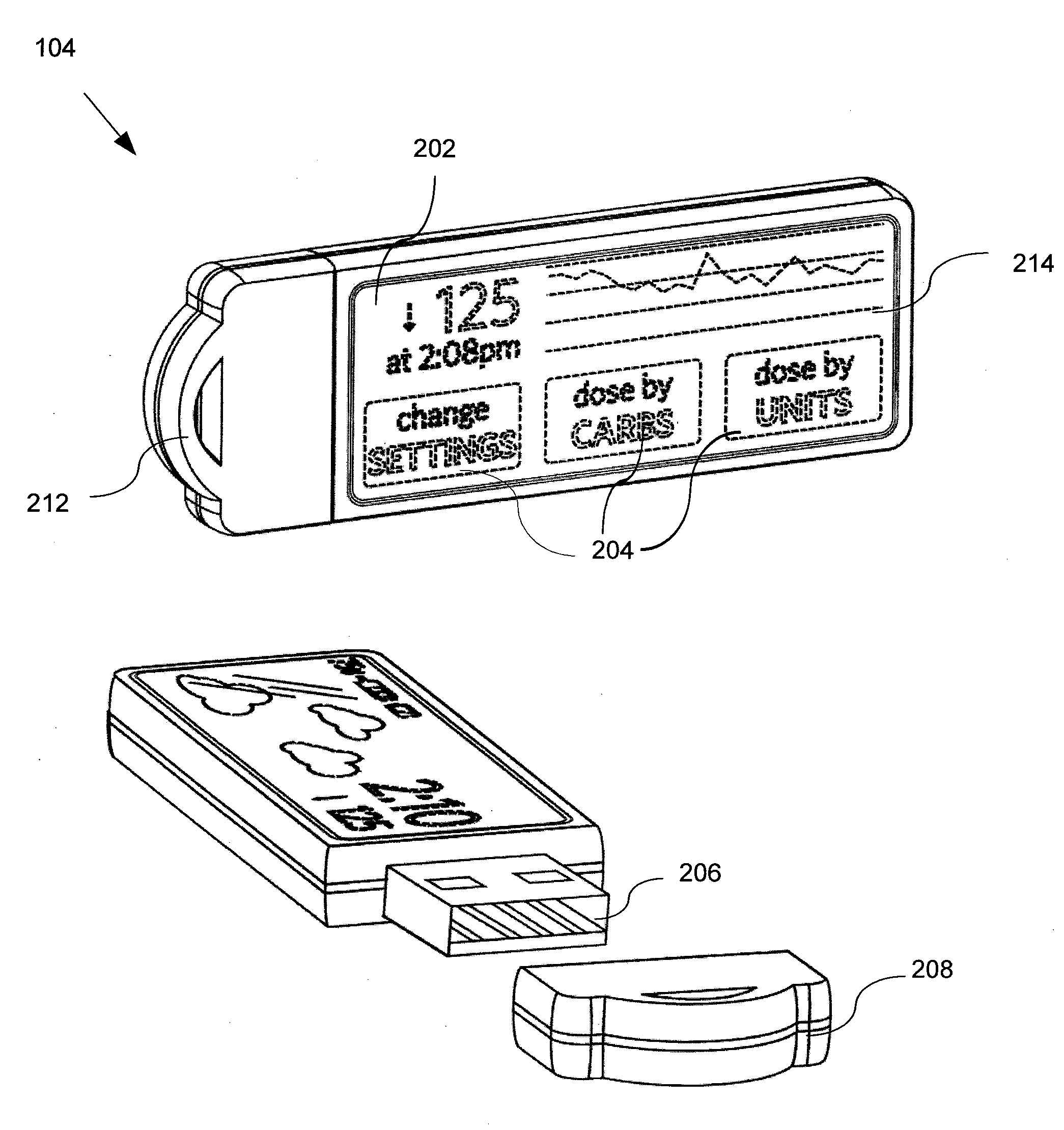
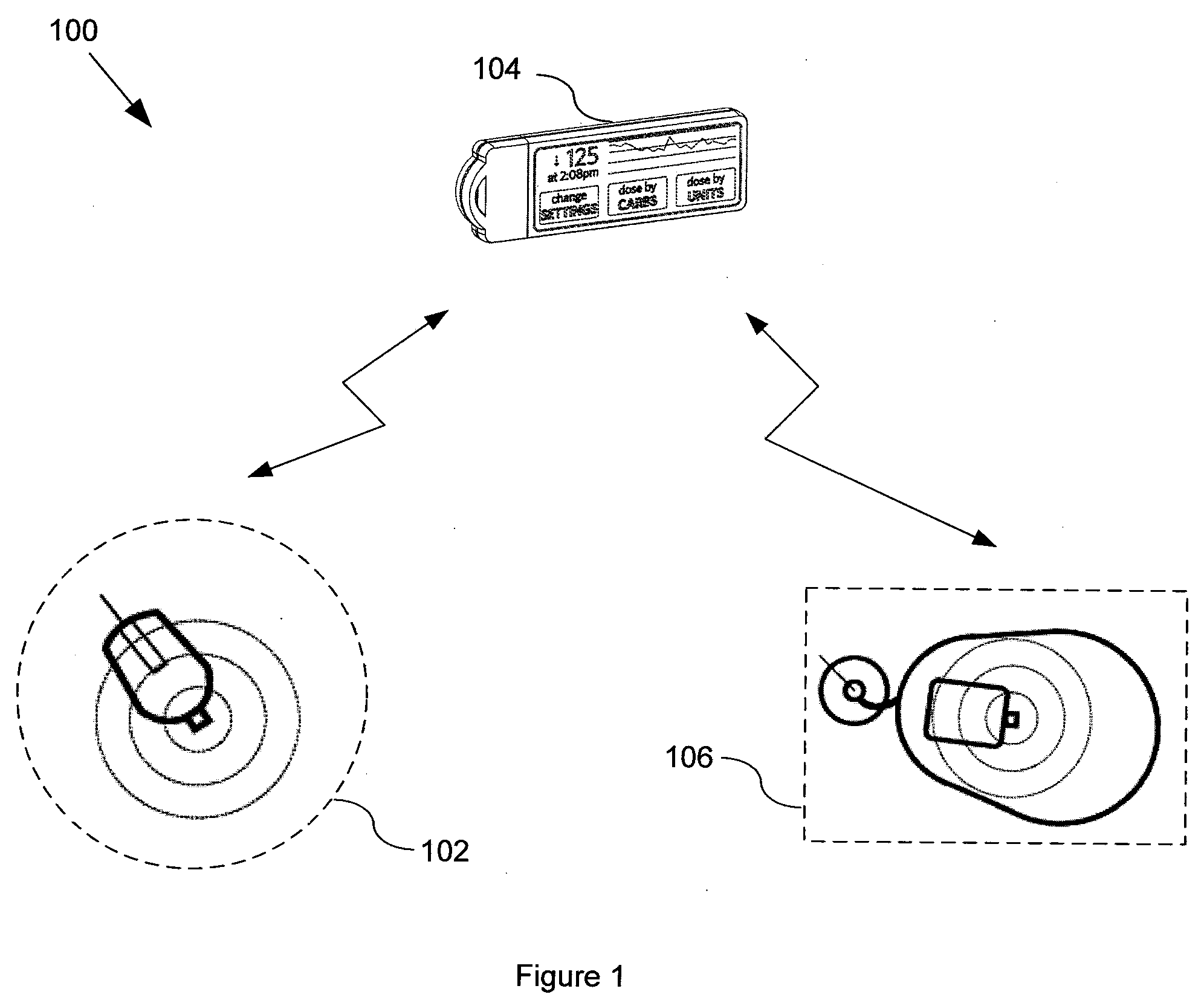
Diabetes Management System
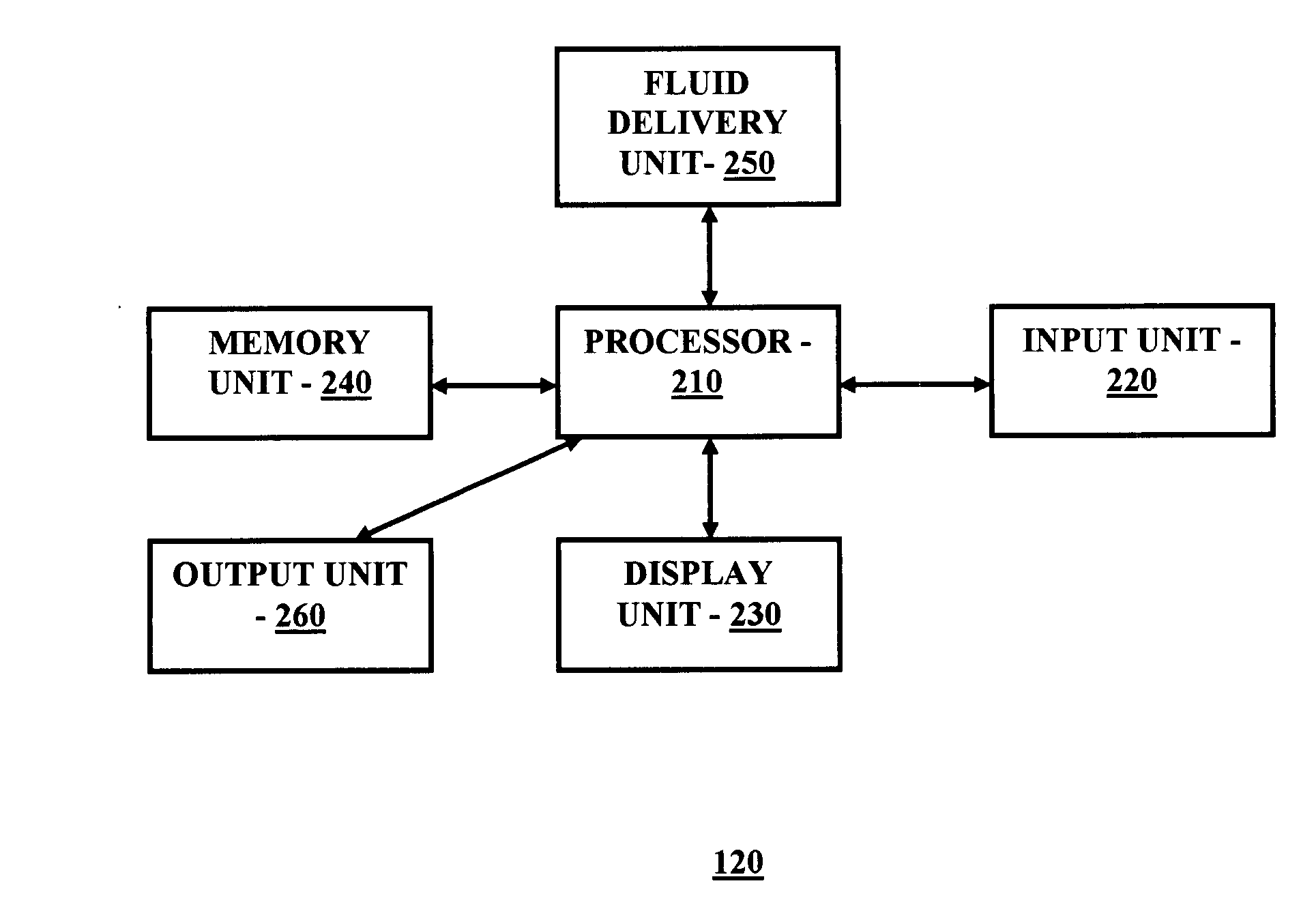
In one embodiment, a diabetes management system comprises a glucose monitoring system, a pump system, and a remote device. The glucose monitoring system and pump system are attached to a patient and covered by a soft shell. The glucose monitoring system and the pump system are controlled by the small, touch-screen remote device such a patient can discreetly monitor blood glucose levels and administer insulin dosages. The remote device has a small and durable form factor that can be worn or carried in various ways.
Owner:ADAPTIVE PATH
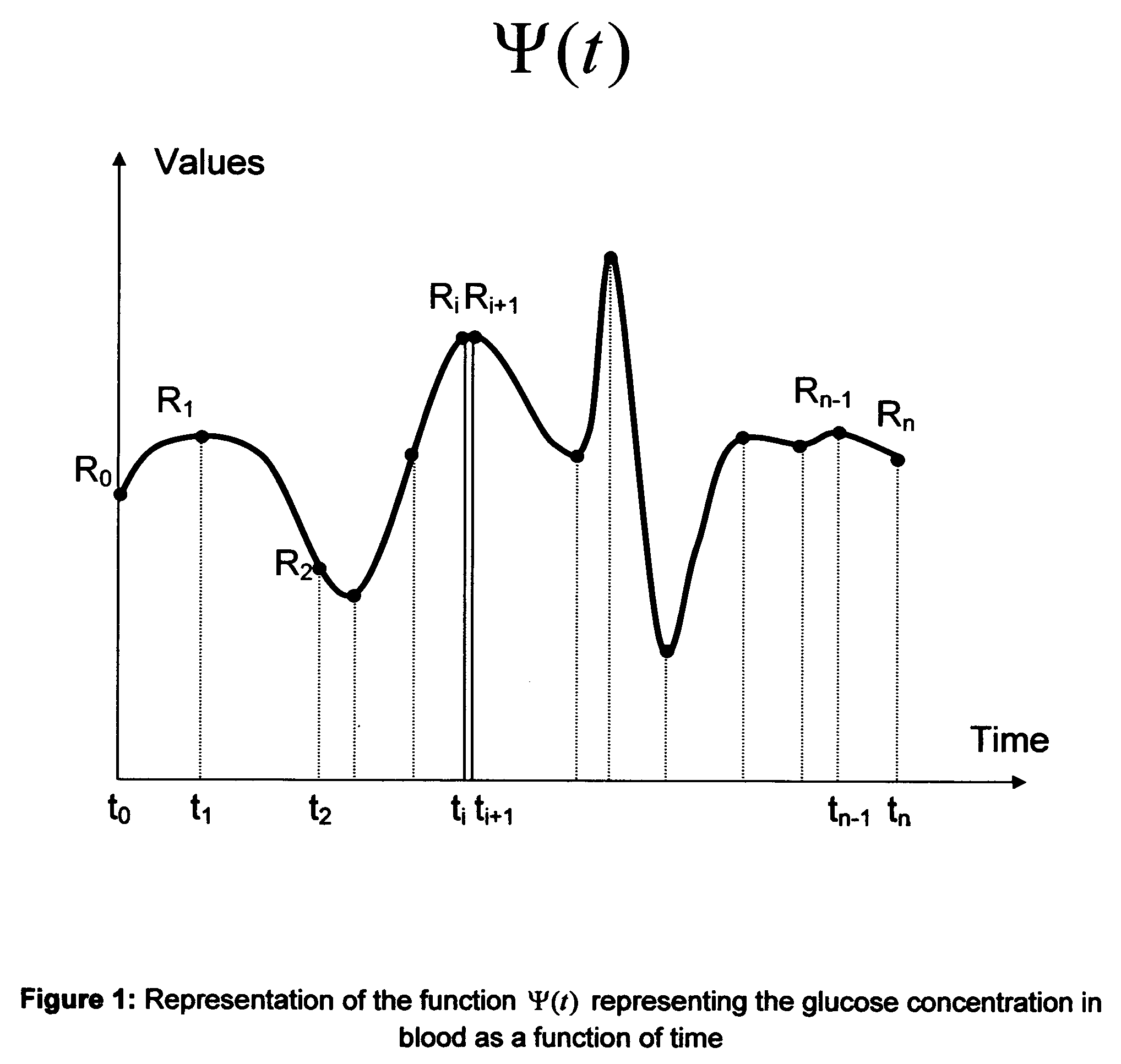
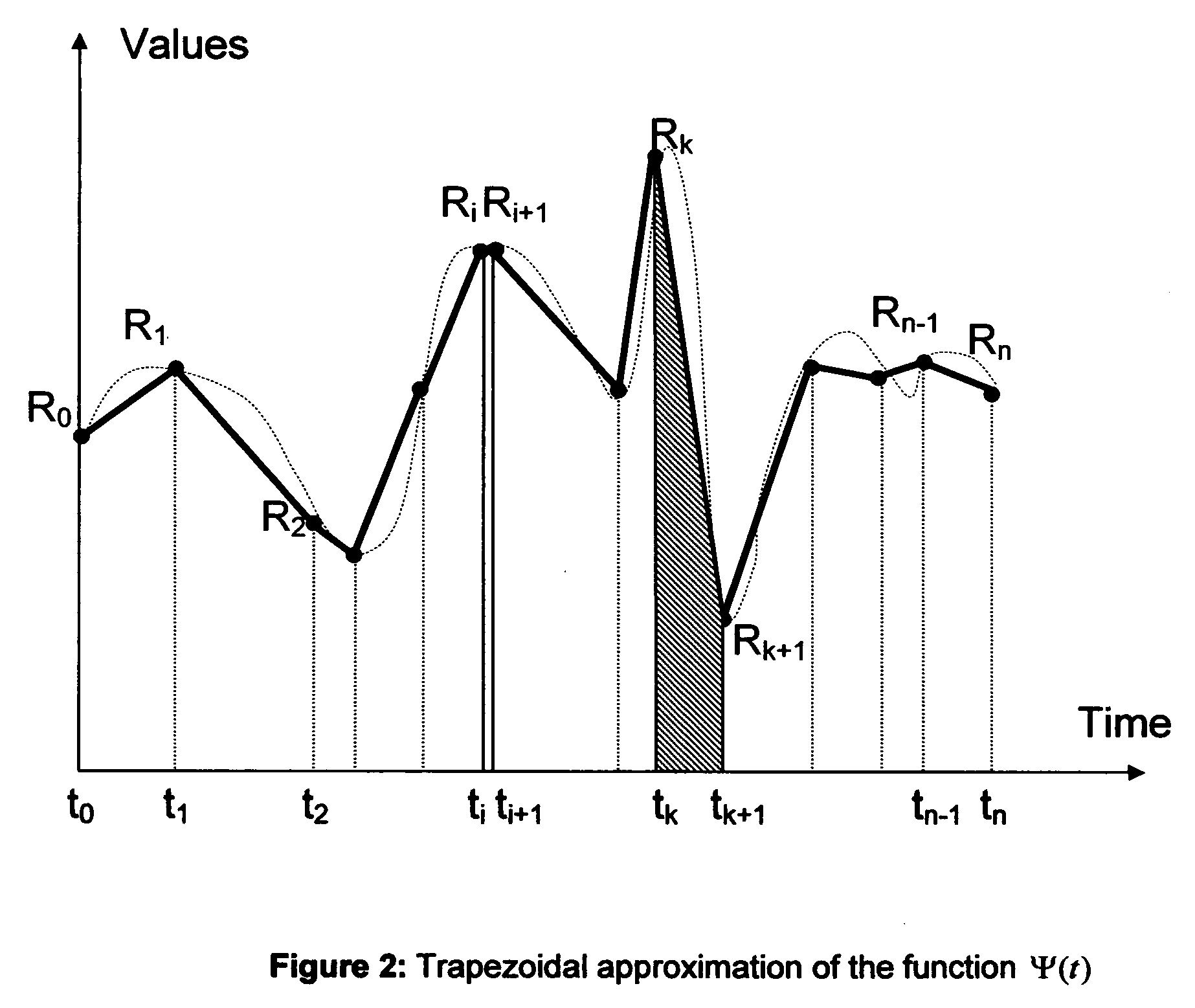
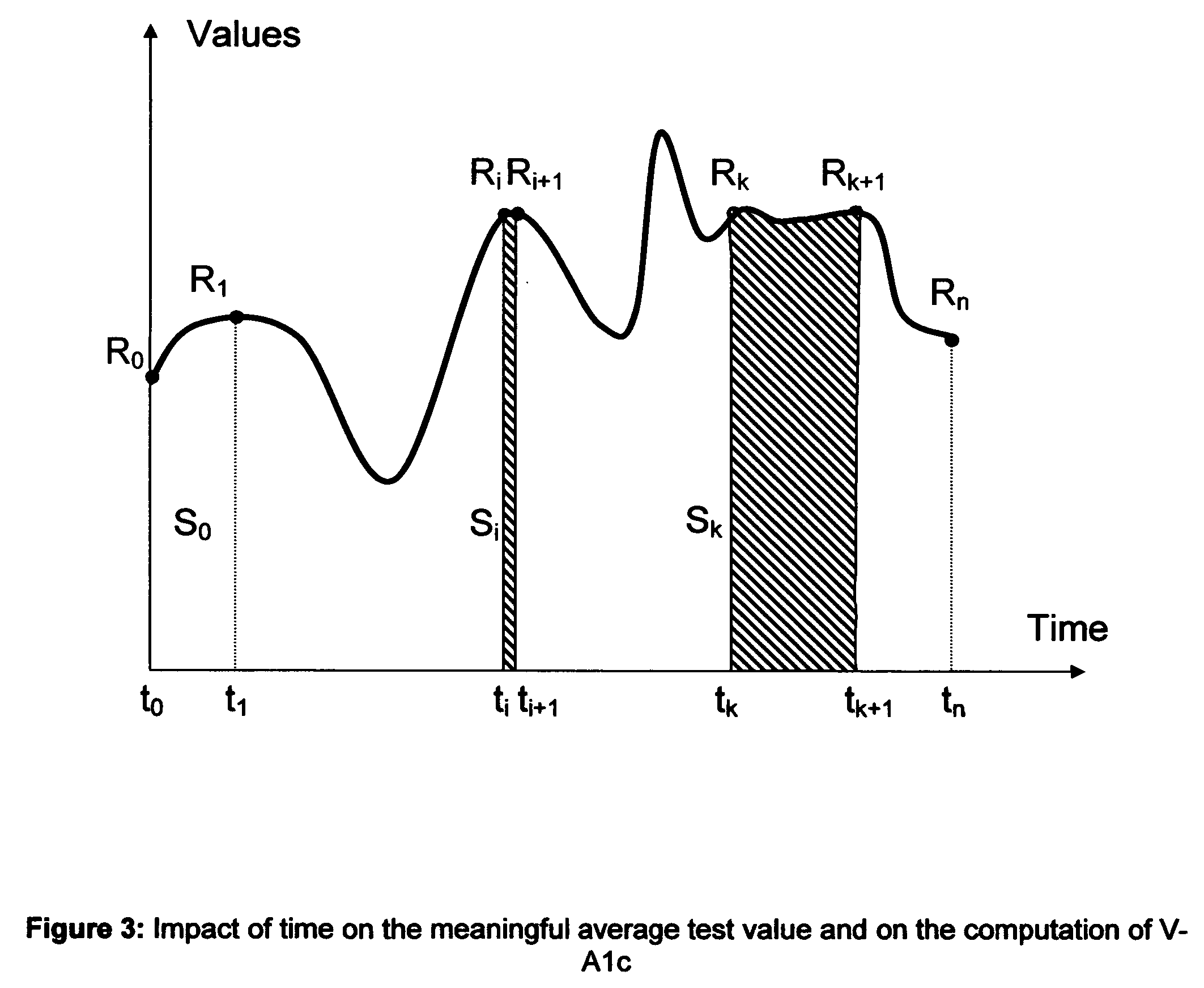
Method to determine the degree and stability of blood glucose control in patients with diabetes mellitus via the creation and continuous update of new statistical indicators in blood glucose monitors or free standing computers
InactiveUS20070010950A1Increase contributionShorten the timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsInstabilityGlucose control
Microvascular complications of diabetes mellitus are closely related to blood glucose levels and fluctuations. The Glycostator statistical package was created to allow patients and health care providers simple access to “glycemic indicators” which permit a “snapshot view” of the effectiveness of the patient's diabetes management program. Glycostator functions provide a simple way of enhancing the information already provided by home blood glucose monitoring devices. To this end, a set of new indices, including one called the Virtual A1c, are computed in a recursive fashion from blood glucose test results to provide a more meaningful day-to-day assessment of glycemic control. All indices can be made available at the meter user interface on request. The displayed indices allow patients to improve glycemic control by identifying problems with blood glucose control and lability that are less easily recognized in traditional blood glucose meter statistical packages. Virtual A1c emulates hemoglobin A1c continuously and provides better day-to-day assessment of long term glycemic control than does the traditional average blood glucose report. The method for computing each of these indices, including the Virtual A1c, allows for their implementation in commercial blood glucose monitors.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
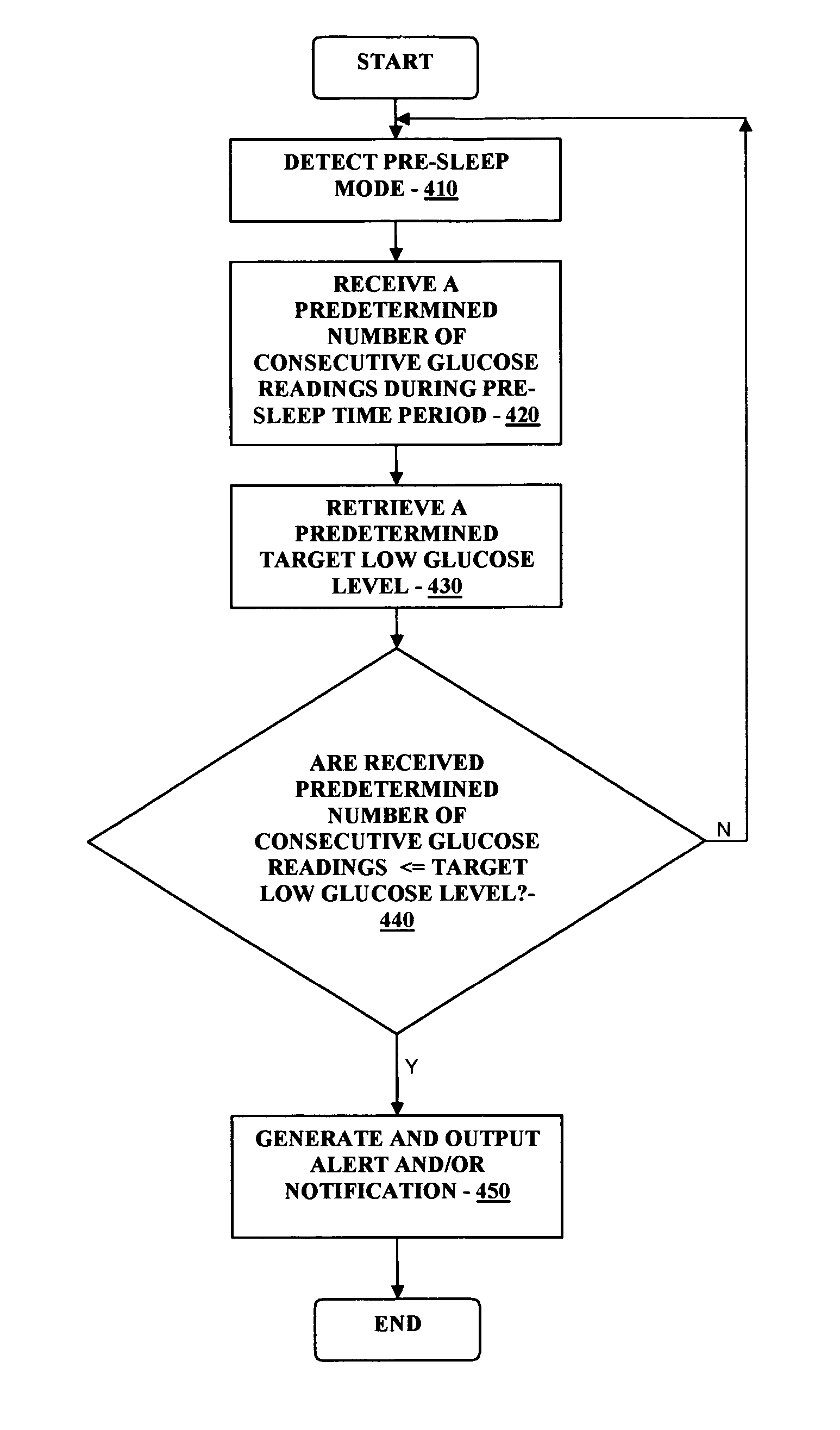
Methods of determining pre or post meal time slots or intervals in diabetes management
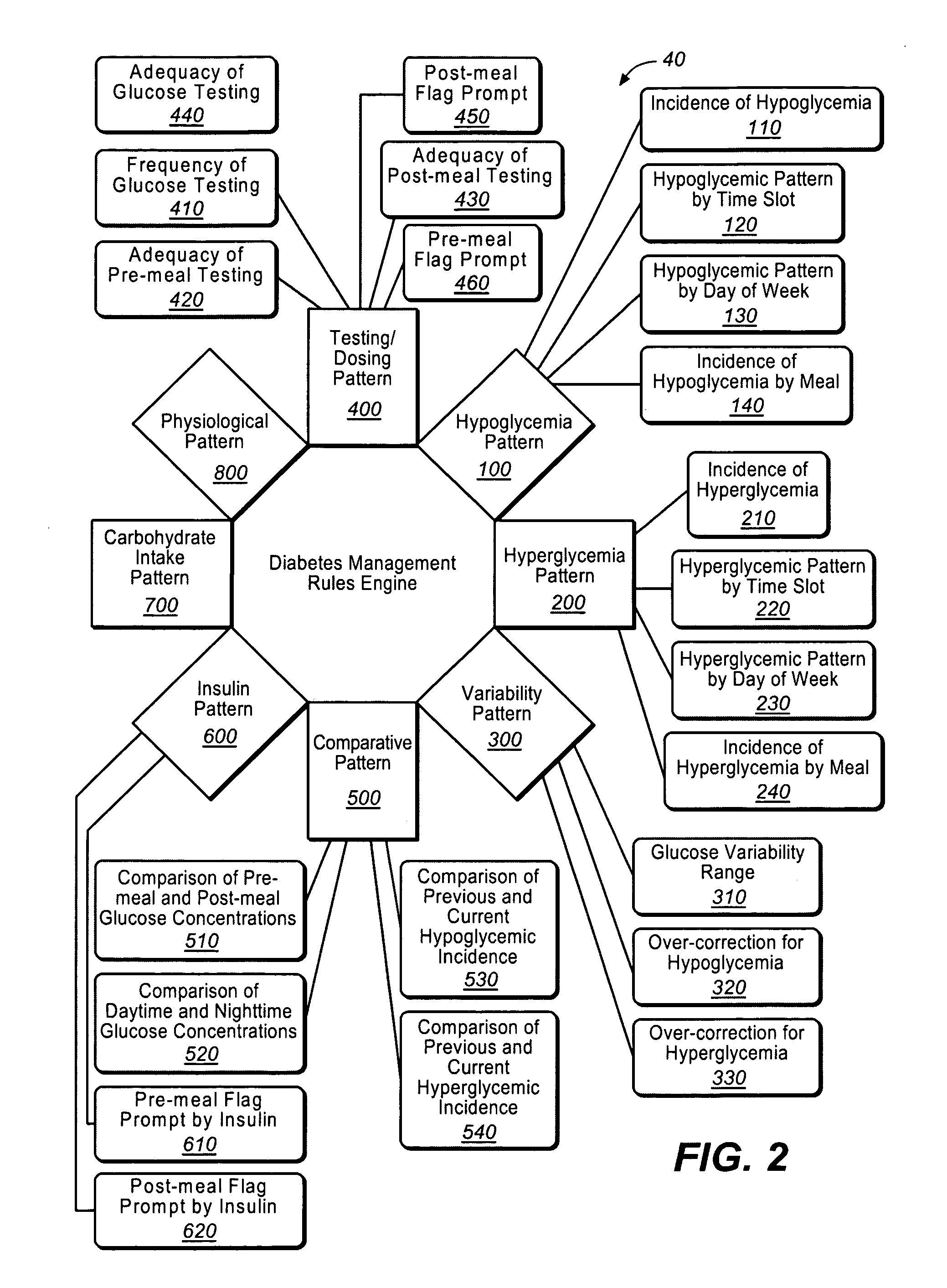
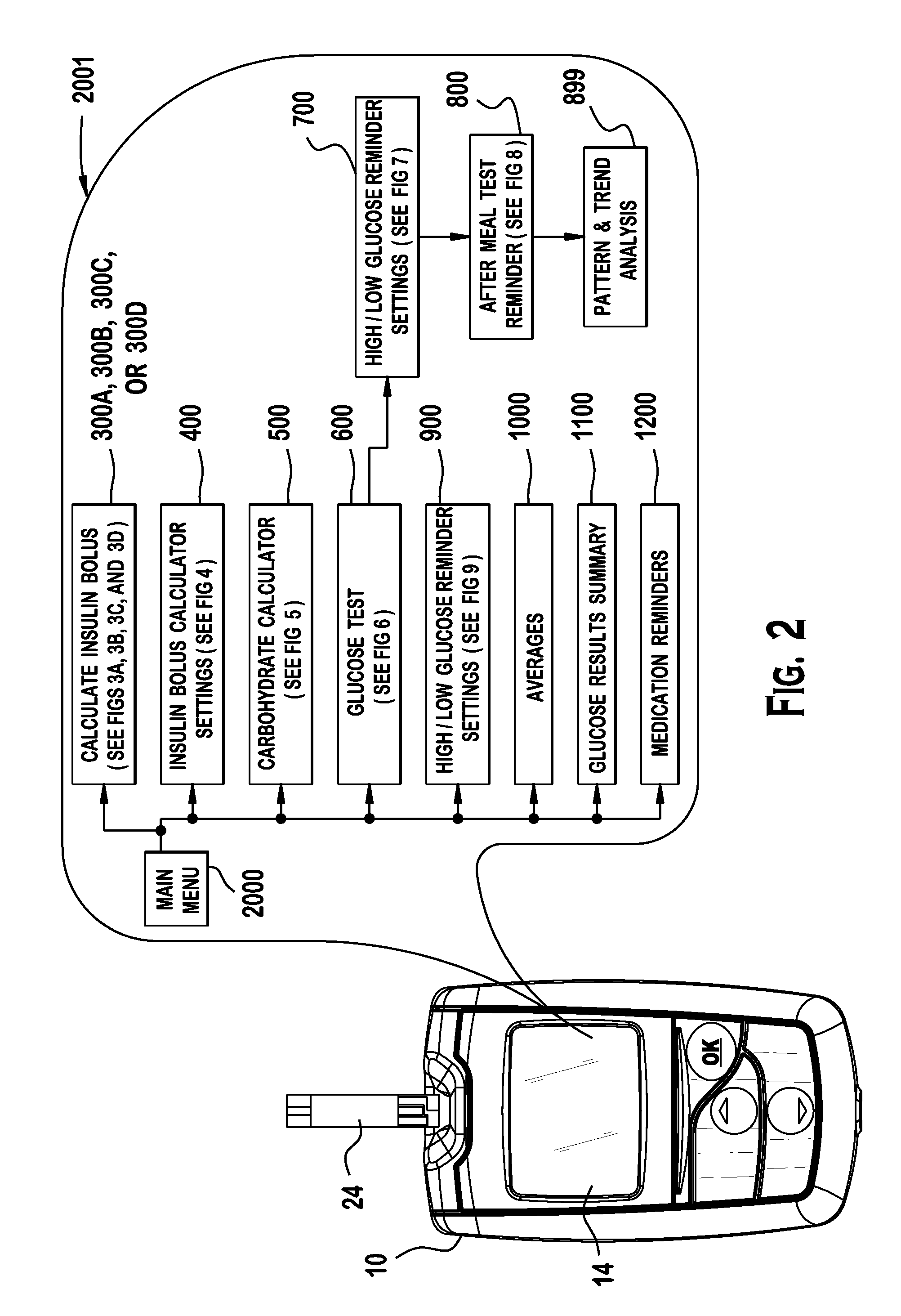
A diabetes management system or process is provided herein that may be used to analyze and recognize patterns for a large number of blood glucose concentration measurements and other physiological parameters related to the glycemia of a patient. In particular, a method of monitoring glycemia in a patient may include storing a patient's data on a suitable device, such as, for example, a blood glucose meter. The patient's data may include blood glucose concentration measurements. The diabetes management system or process may be installed on, but is not limited to, a personal computer, an insulin pen, an insulin pump, or a glucose meter. The diabetes management system or process may identify a plurality of pattern types from the data including a testing / dosing pattern, a hypoglycemic pattern, a hyperglycemic pattern, a blood glucose variability pattern, and a comparative pattern. After identifying a particular pattern with the data management system or process, a warning message may be displayed on a screen of a personal computer or a glucose meter. Other messages can also be provided to ensure compliance of any prescribed diabetes regiments or to guide the patient in managing the patient's diabetes.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
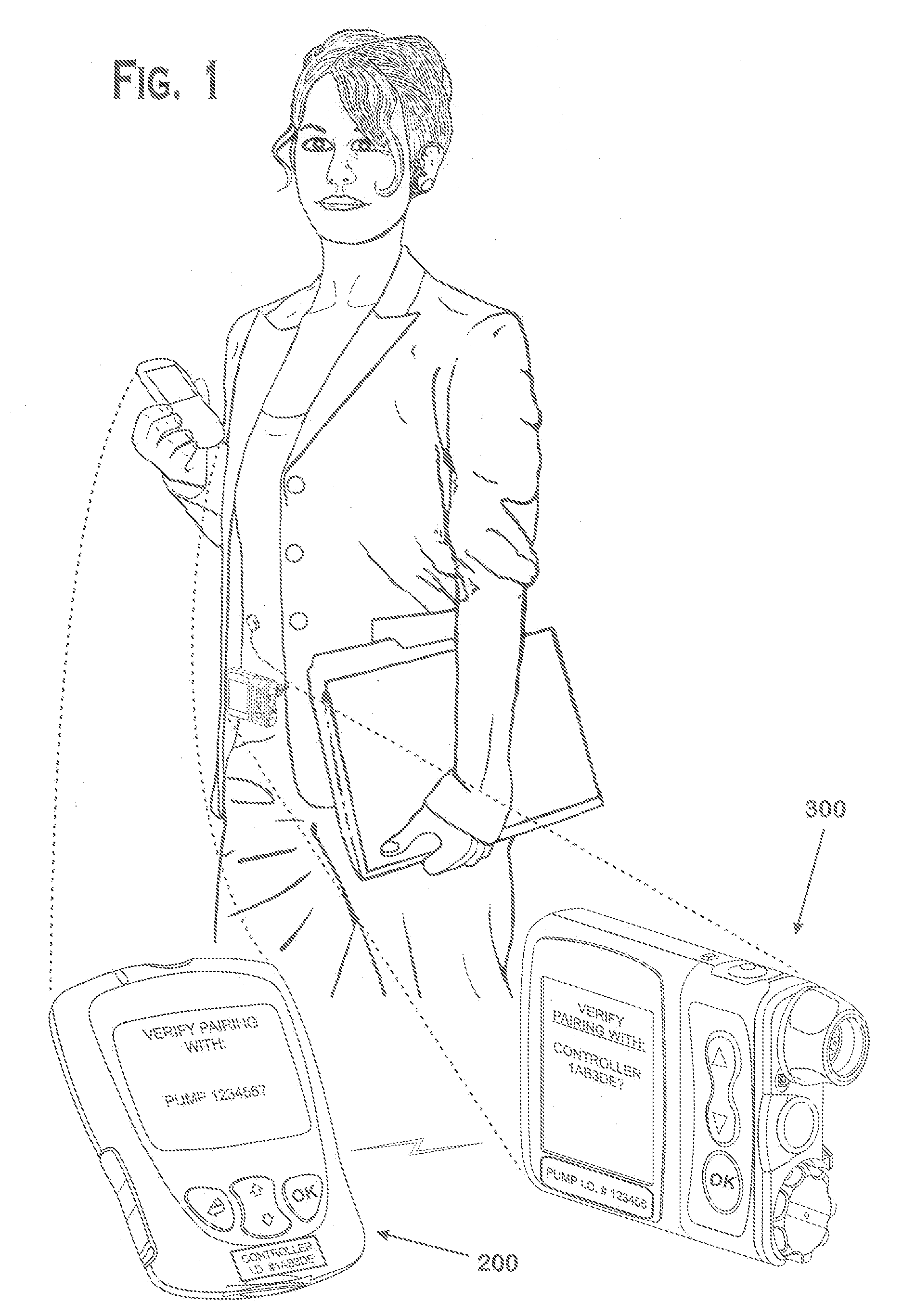
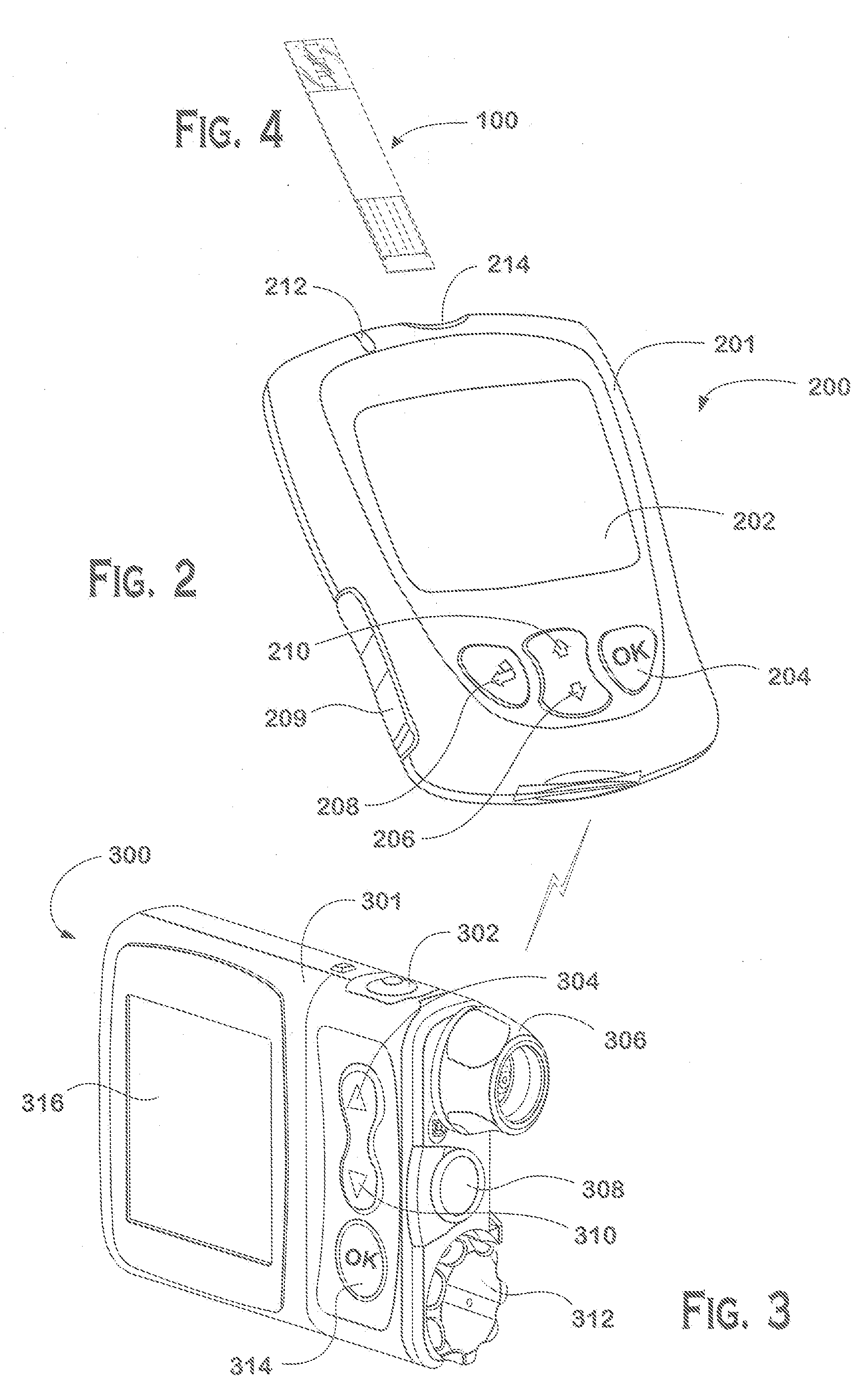
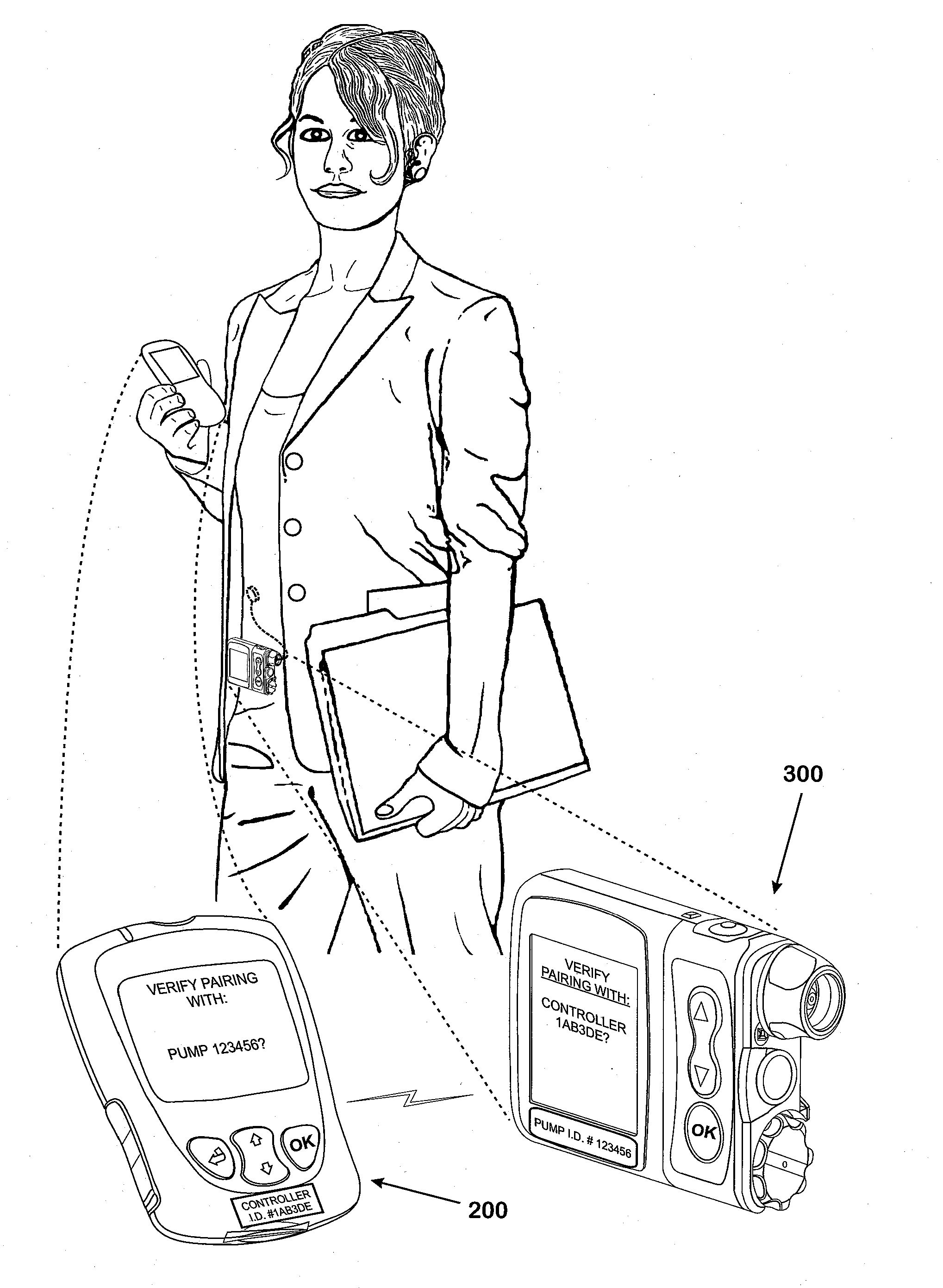
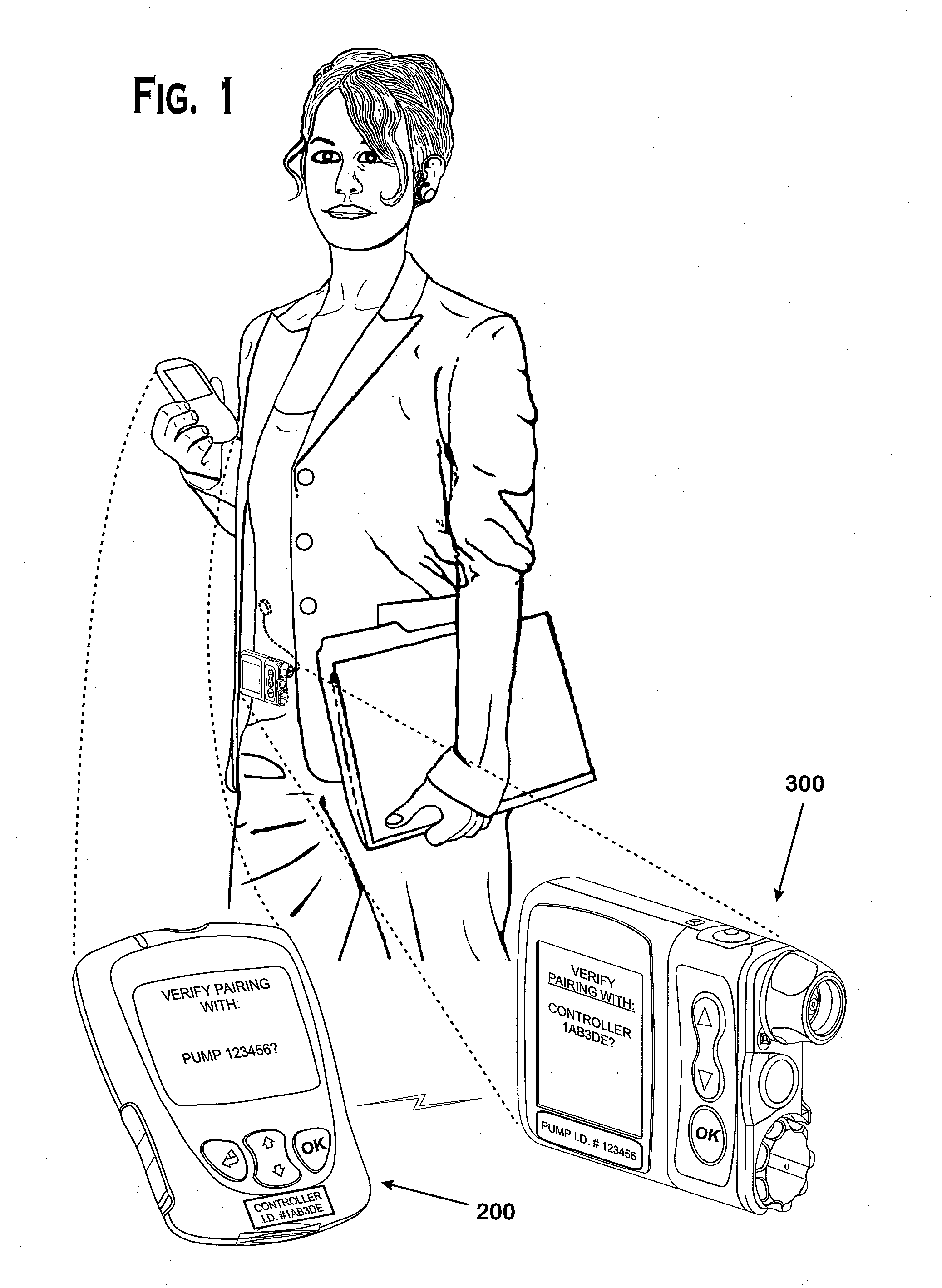
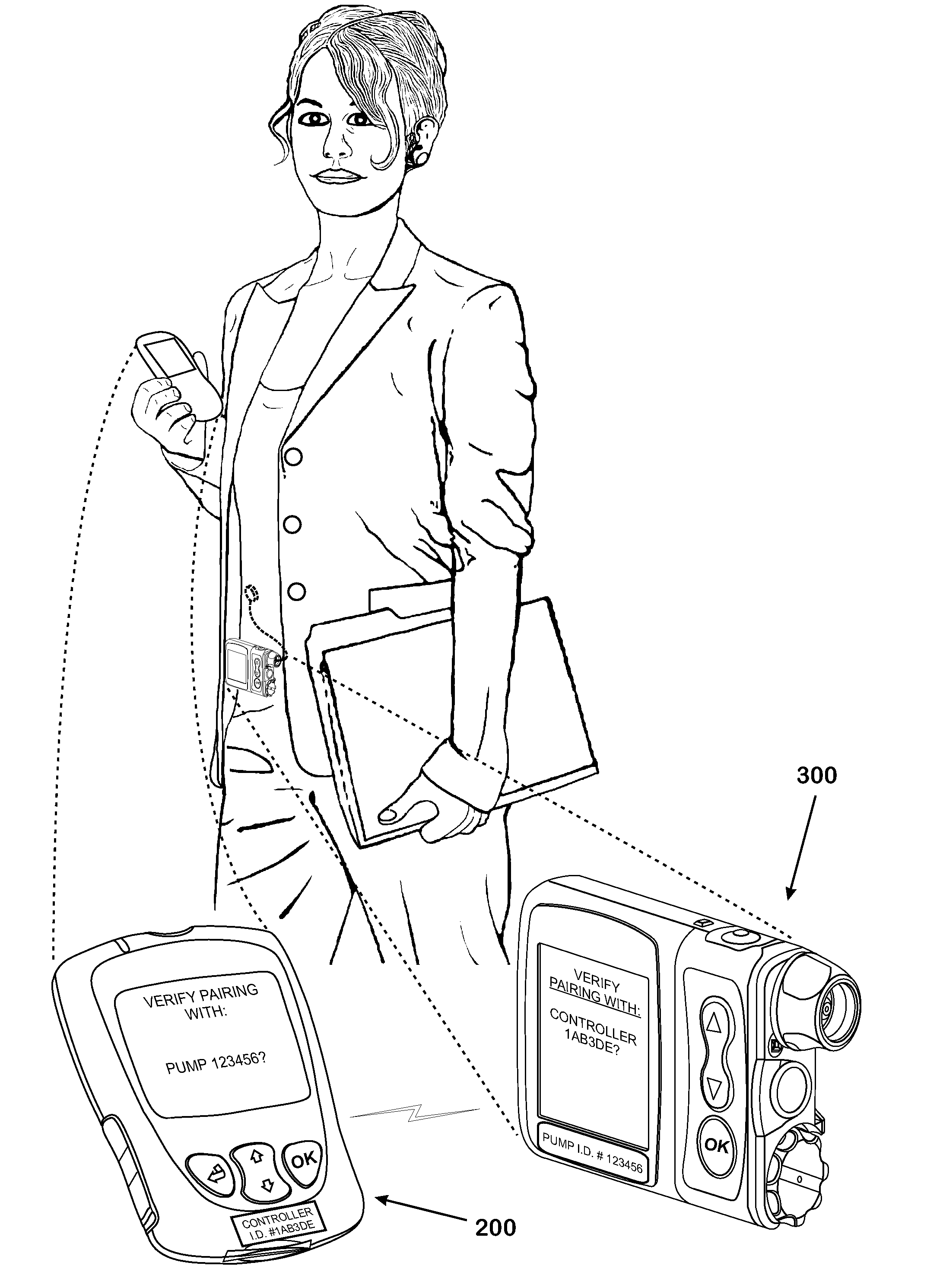
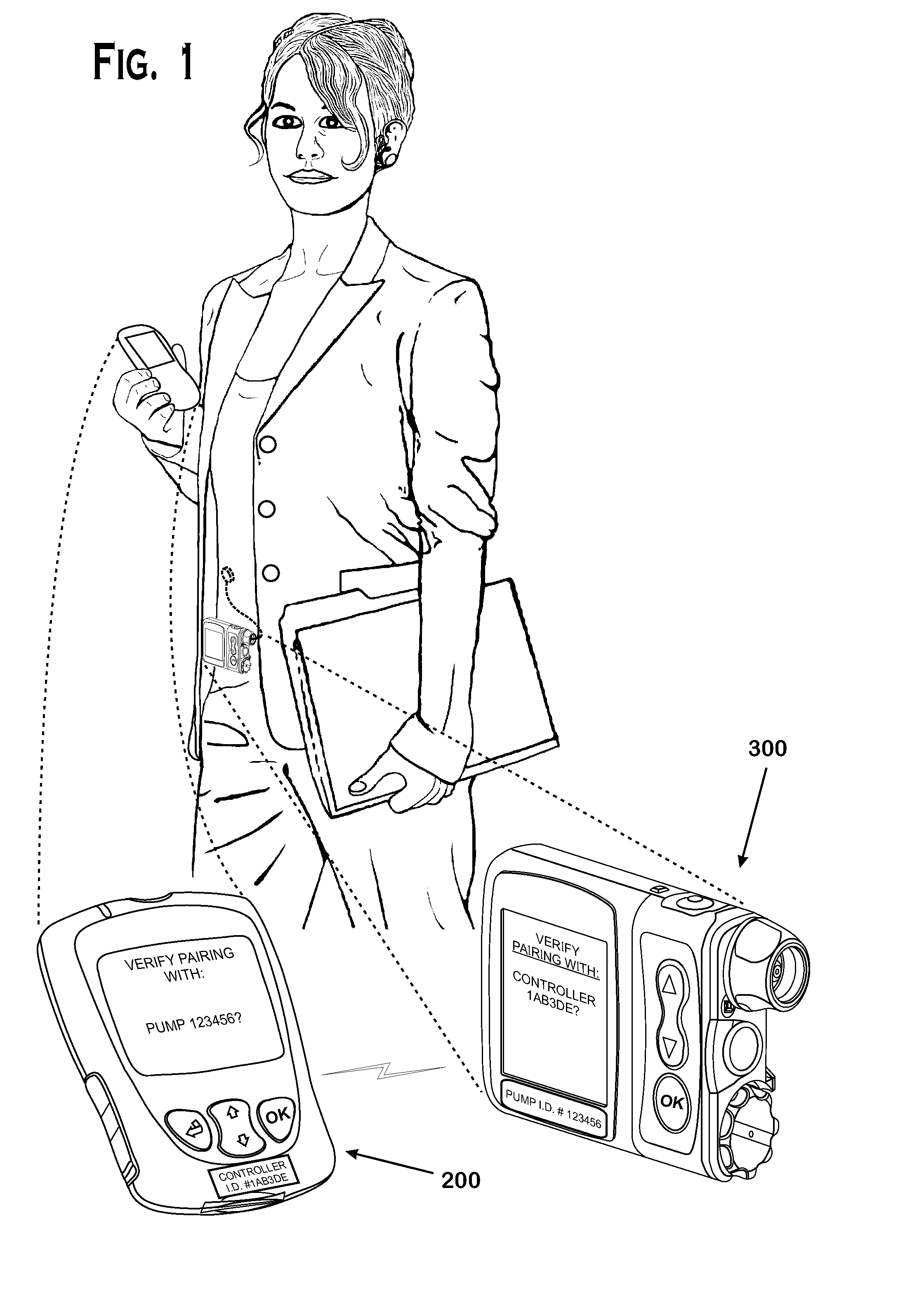
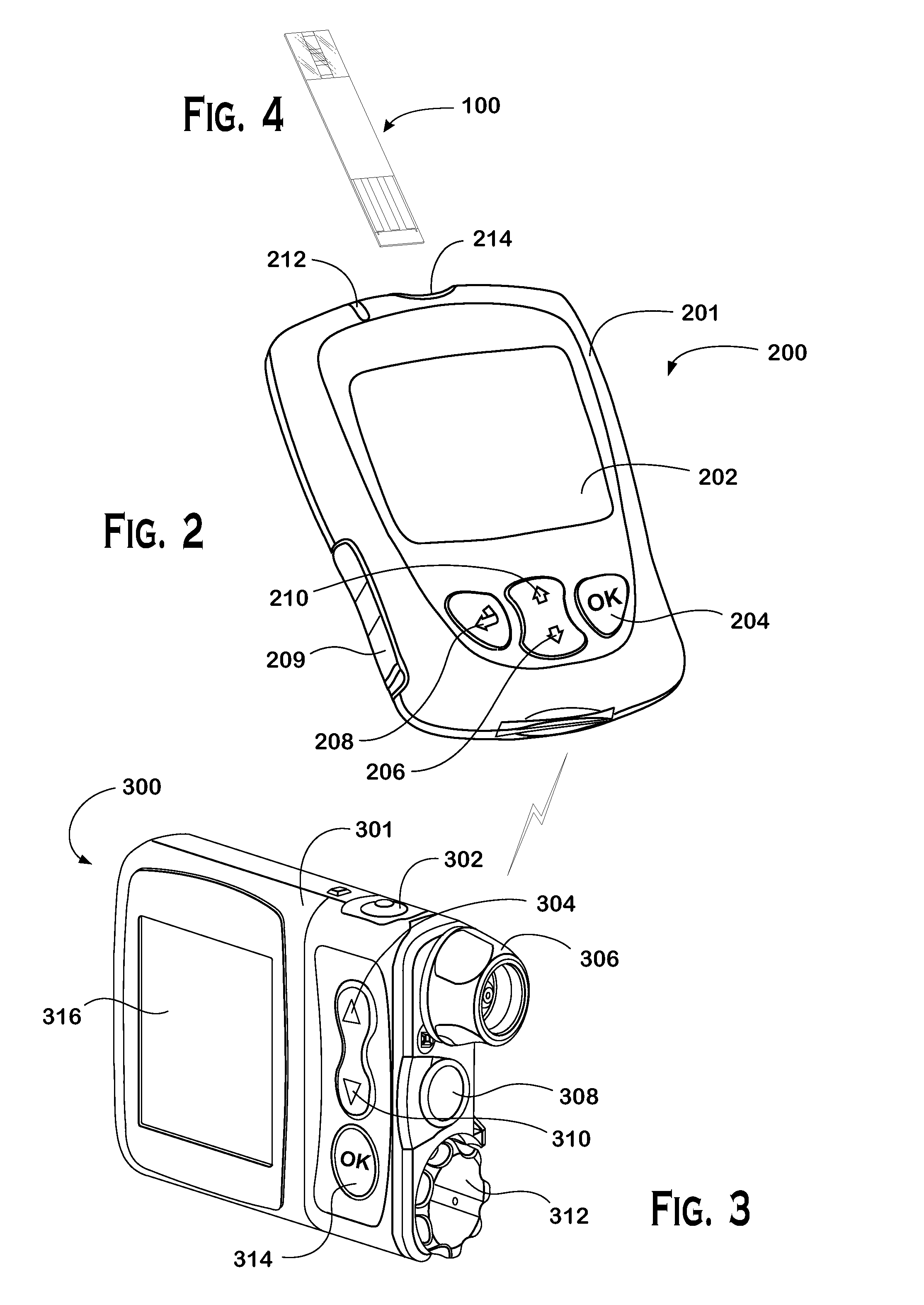
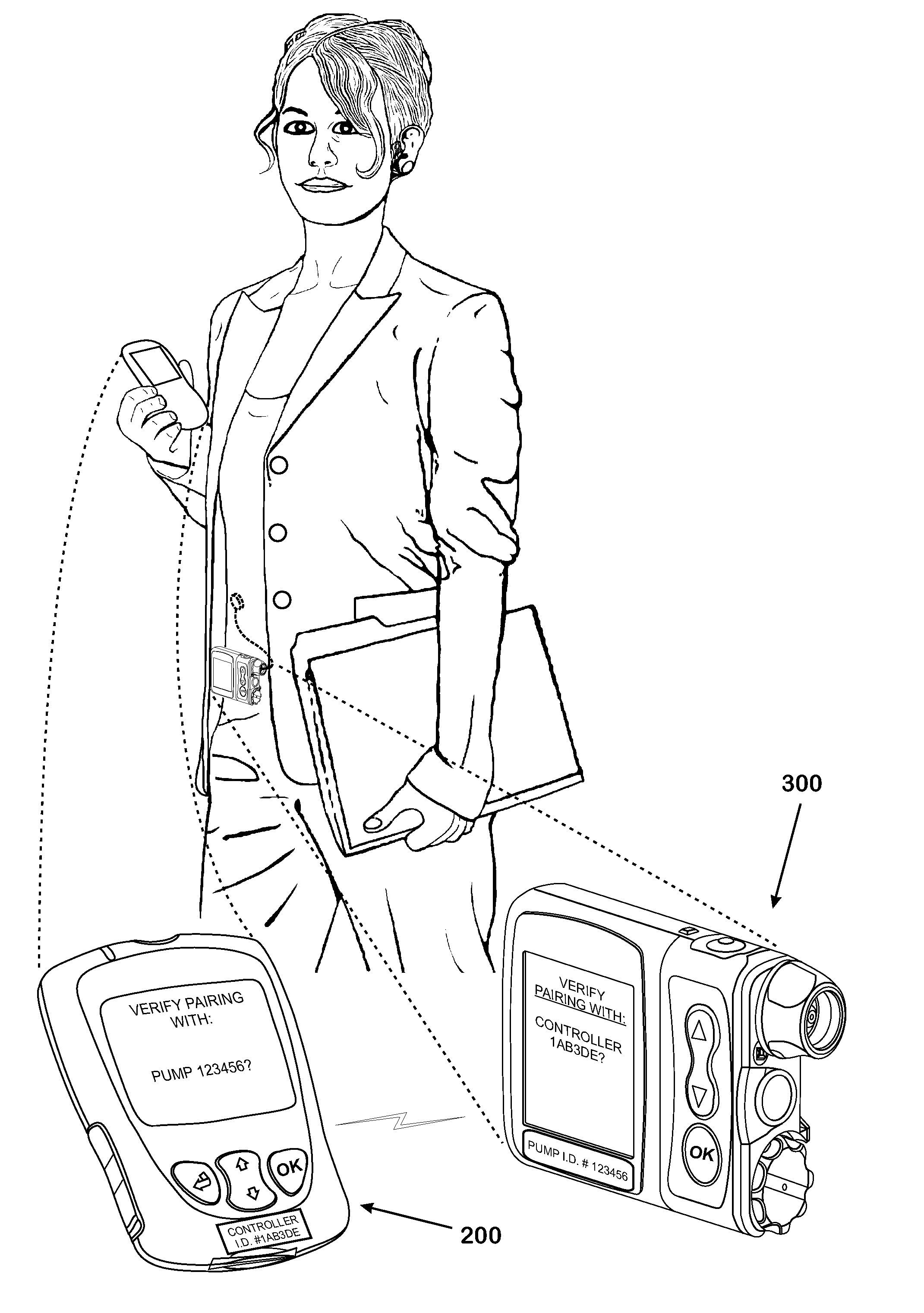
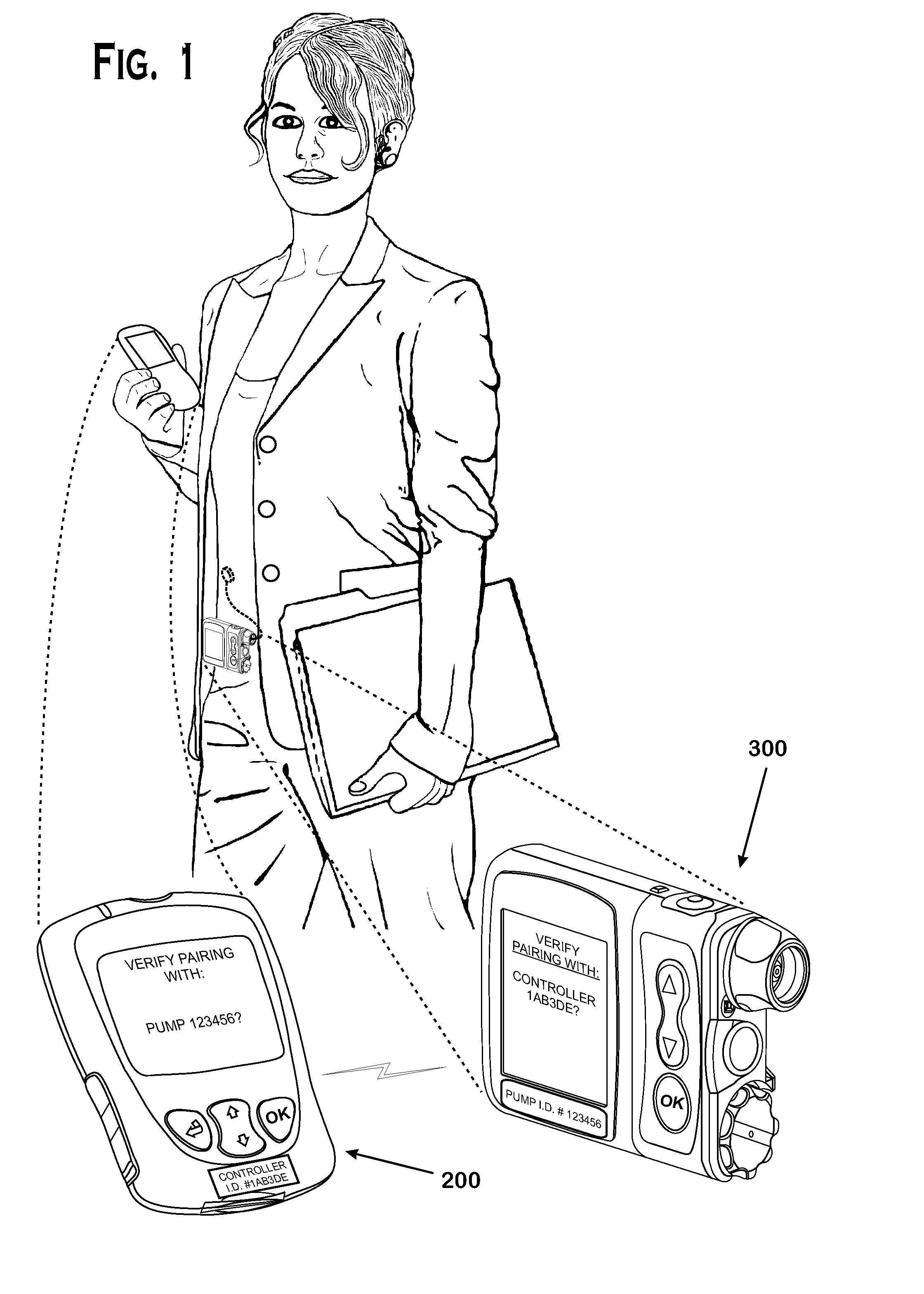
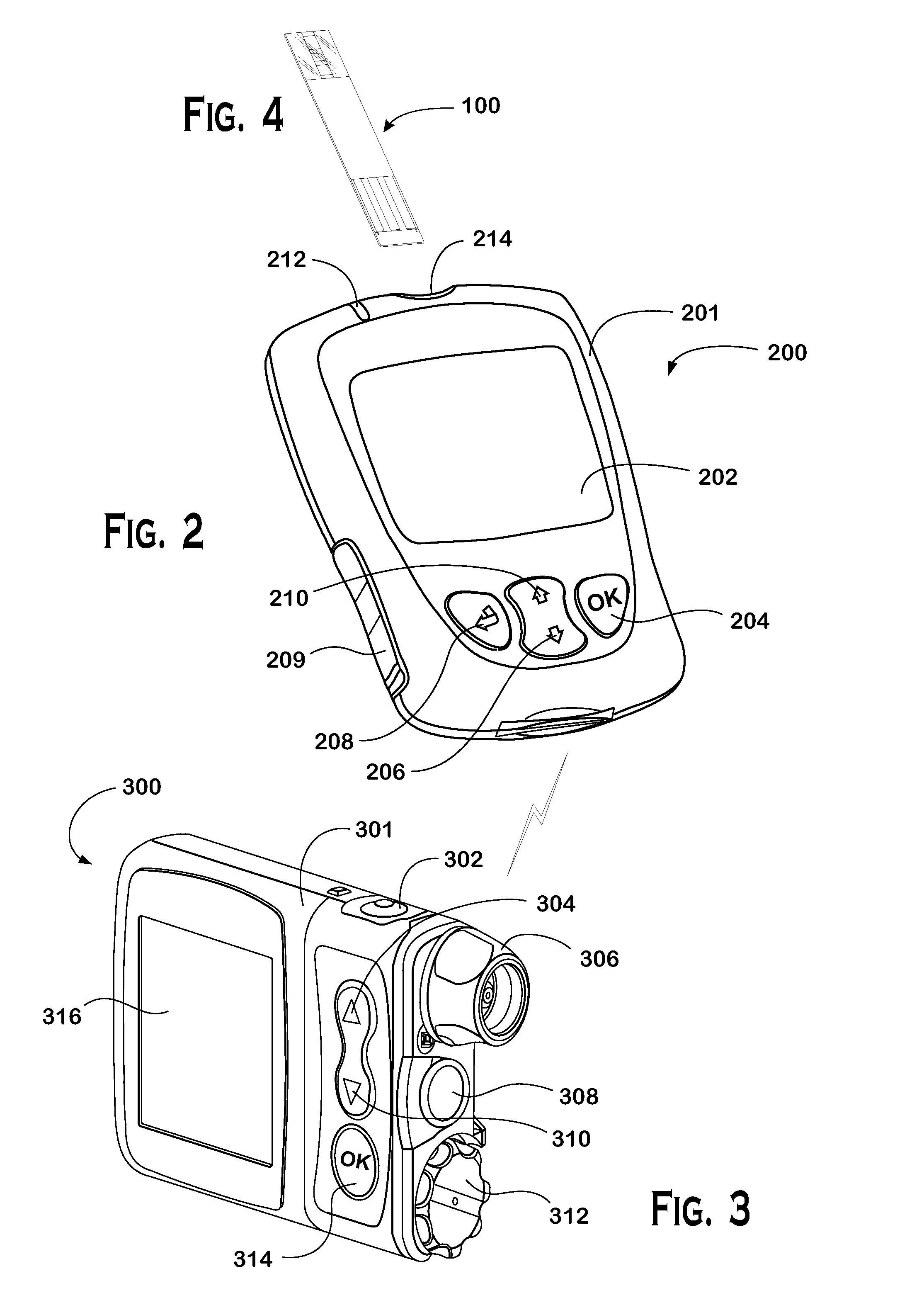
Systems and methods to pair a medical device and a remote controller for such medical device
ActiveUS20080312584A1Instances of incorrect device pairing are believed to be reducedTransmission systemsDrug and medicationsDiabetes mellitusDiabetes management
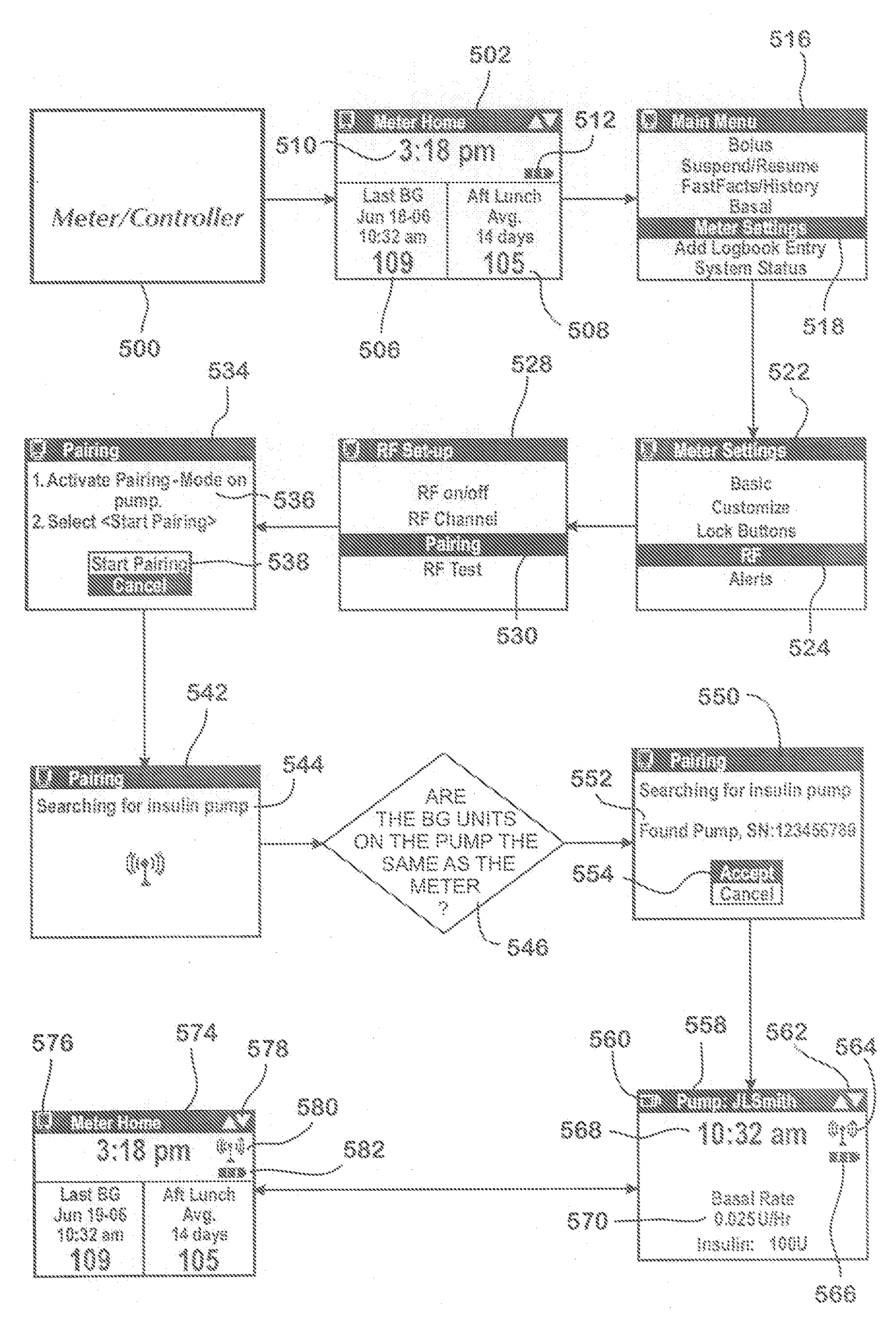
A disease management system, methods, and devices are shown and described. In one embodiment, the system includes an infusion pump and a remote controller with the ability to be paired to each other. A method to verify a wireless connection between an infusion pump and a remote controller is shown and described herein. In a further embodiment, a method to verify a wireless connection between an infusion pump and a remote controller is provided. In addition, a method of operating a diabetes management system is provided in which the system includes an infusion pump and at least a remote controller.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Methods to pair a medical device and at least a remote controller for such medical device
ActiveUS20080312512A1Instances of incorrect device pairing are believed to be reducedDrug and medicationsMedical devicesDiabetes mellitusDiabetes management
A disease management system, methods, and devices are shown and described. In one embodiment, the system includes an infusion pump and a remote controller with the ability to be paired to each other. A method to verify a wireless connection between an infusion pump and a remote controller is shown and described herein. In a further embodiment, a method to verify a wireless connection between an infusion pump and a remote controller is provided. In addition, a method of operating a diabetes management system is provided in which the system includes an infusion pump and at least a remote controller.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
System and Methods for Improved Diabetes Data Management and Use Employing Wireless Connectivity Between Patients and Healthcare Providers and Repository of Diabetes Management Information
ActiveUS20100069730A1Shorten development timeExtended service lifePhysical therapies and activitiesDrug and medicationsDiseaseInformation repository
Methods, devices and a system for disease management are provided that employ diagnostic testing devices (e.g., blood glucose meters) and medication delivery devices (e.g., insulin delivery devices) for providing data to a repository in real-time and automatically. Repository data can be analyzed to determine such information as actual test strip use, patient health parameters to outside prescribed ranges, testing and medication delivery compliance, patient profiles or stakeholders to receive promotional items or incentives, and so on. Connected meters and medication delivery devices and repository data analysis are also employed to associate a diagnostic test to a mealtime based on timing of a therapeutic intervention performed by an individual.
Owner:EMBECTA CORP
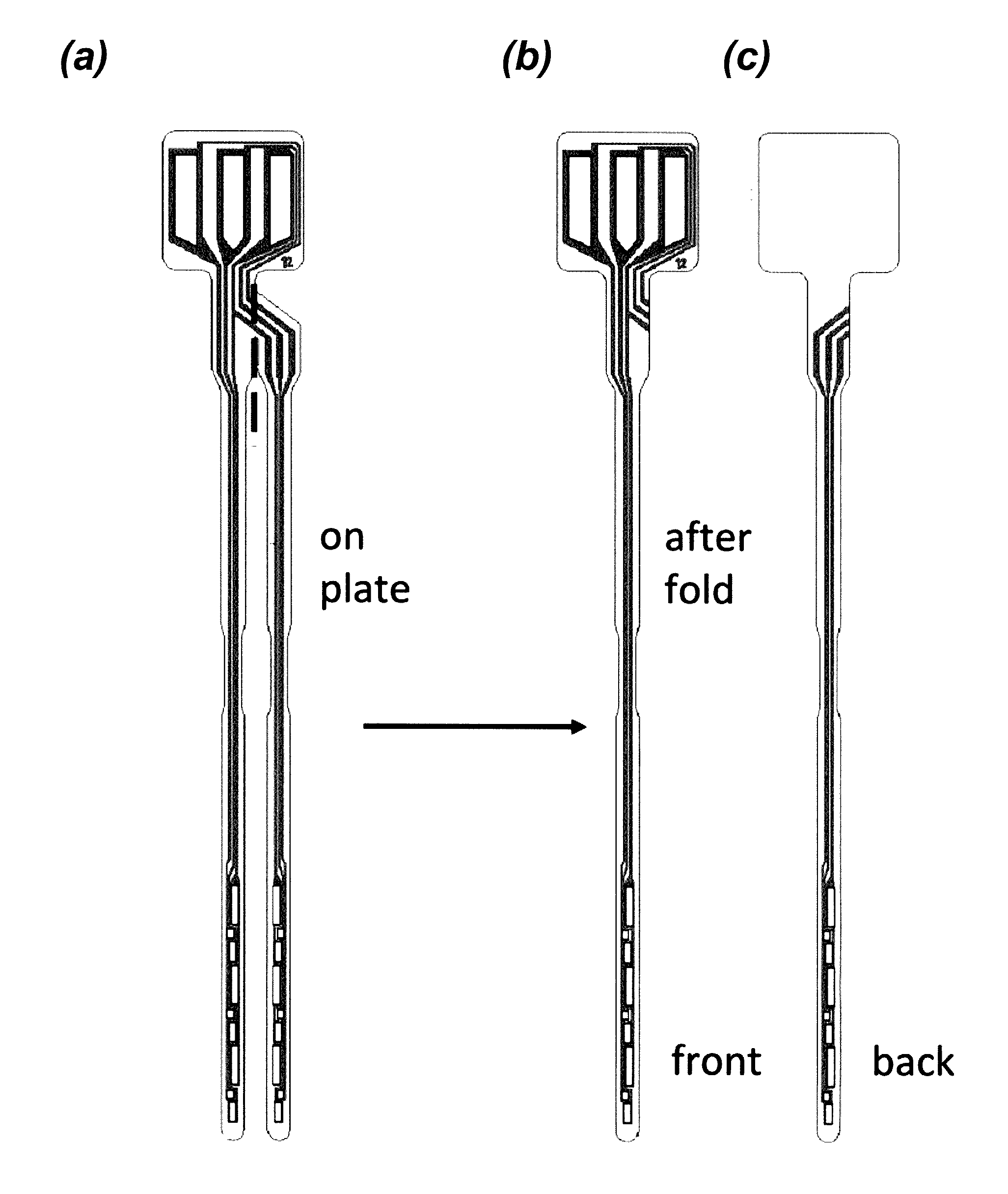
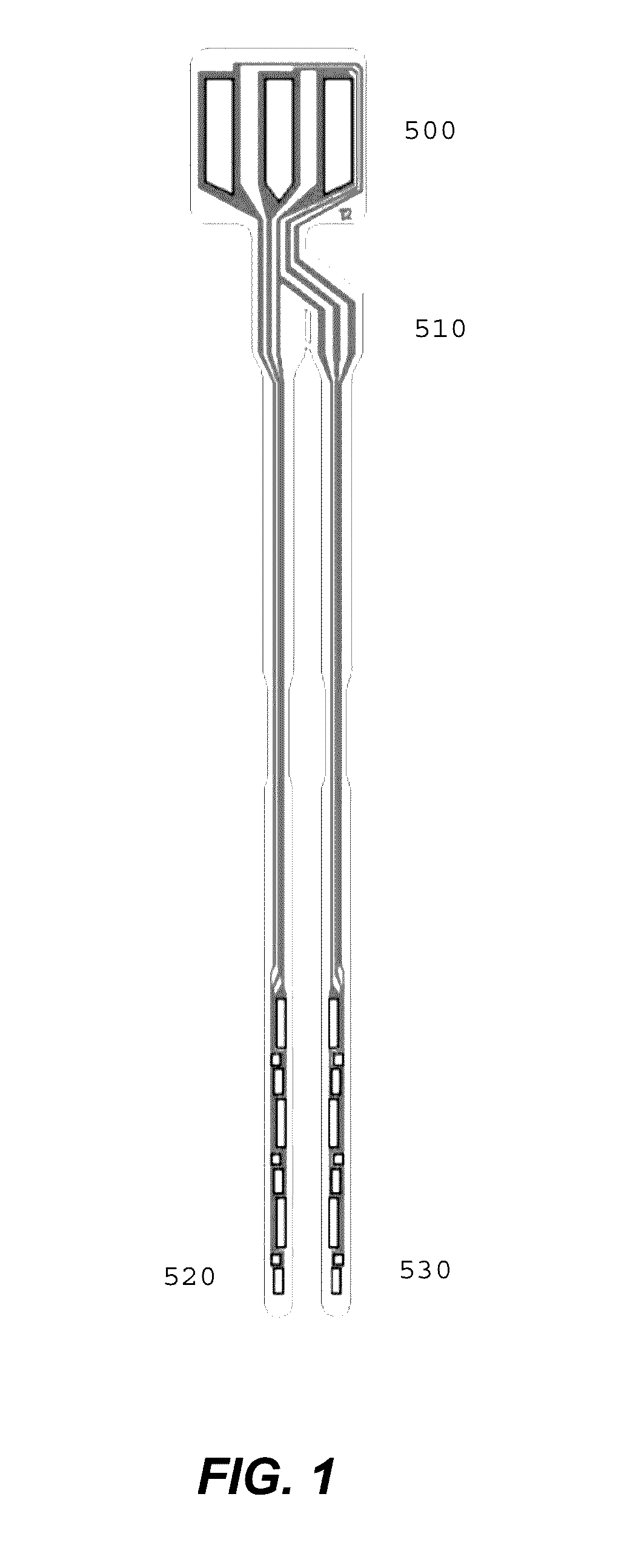
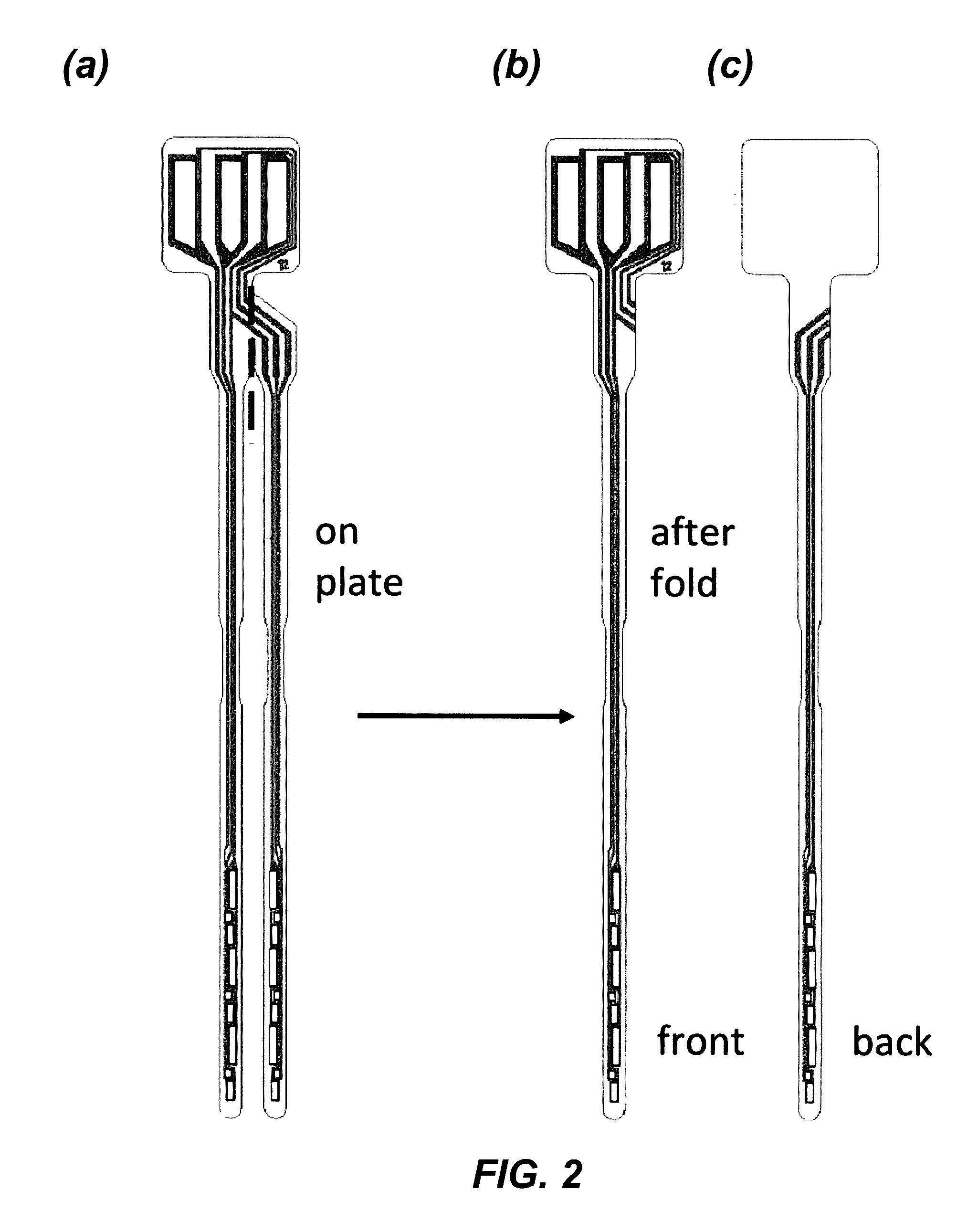
Foldover sensors and methods for making and using them
ActiveUS9493807B2Improve accuracyImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsGlucose sensorsAnalyte
The invention disclosed herein includes sensors having three dimensional configurations that allow expansive “360°” sensing (i.e. sensing analyte from multiple directions) in the environments in which such sensors are disposed. Embodiments of the invention provide analyte sensors having foldable substrates adapted to produce optimized configurations of electrode elements as well as methods for making and using such sensors. Typical embodiments of the invention include glucose sensors used in the management of diabetes.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Method of operating a medical device and at least a remote controller for such medical device
ActiveUS20080312585A1Instances of incorrect device pairing are believed to be reducedTransmission systemsDrug and medicationsDiabetes mellitusDiabetes management
A disease management system, methods, and devices are shown and described. In one embodiment, the system includes an infusion pump and a remote controller with the ability to be paired to each other. A method to verify a wireless connection between an infusion pump and a remote controller is shown and described herein. In a further embodiment, a method to verify a wireless connection between an infusion pump and a remote controller is provided. In addition, a method of operating a diabetes management system is provided in which the system includes an infusion pump and at least a remote controller.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
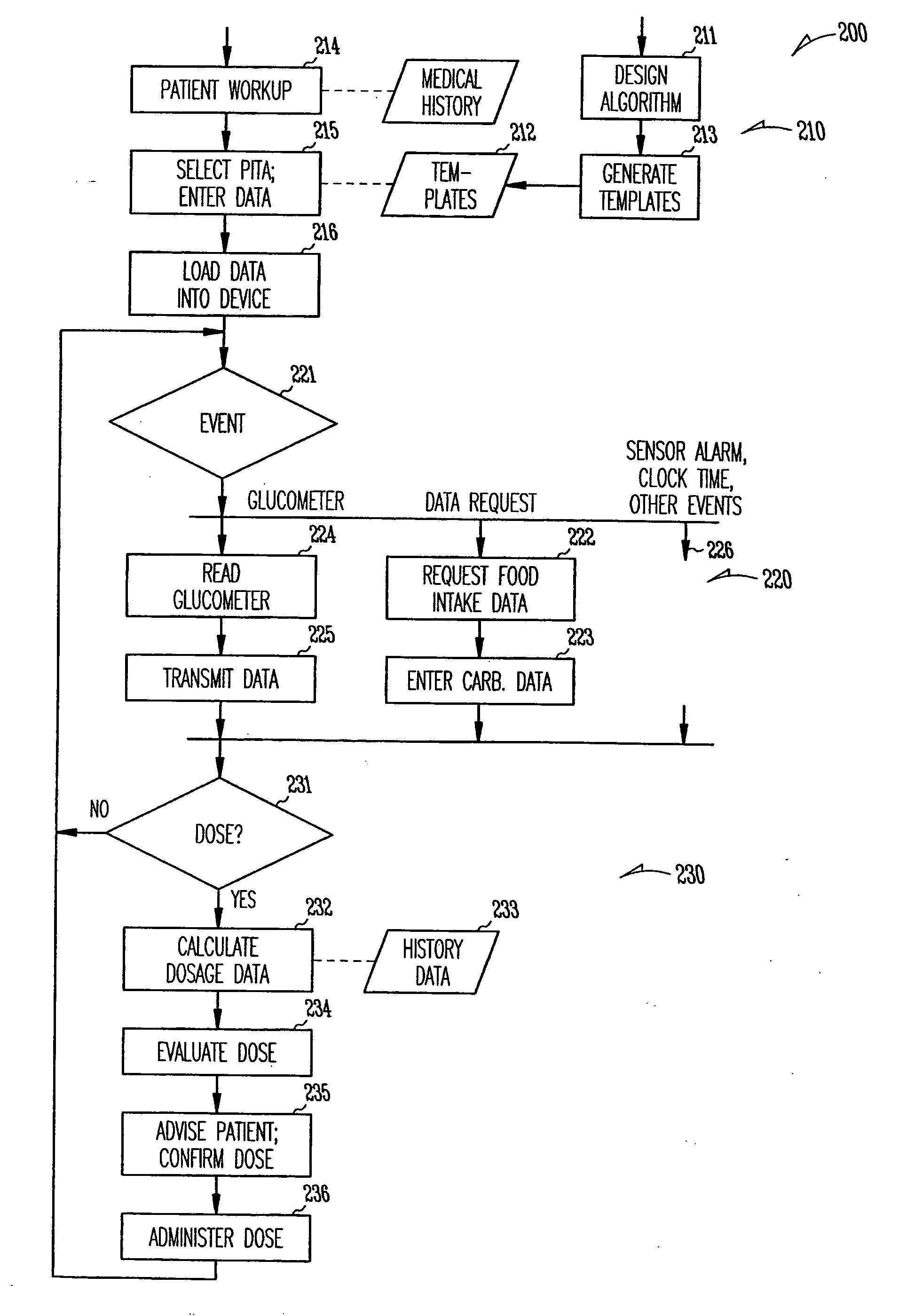
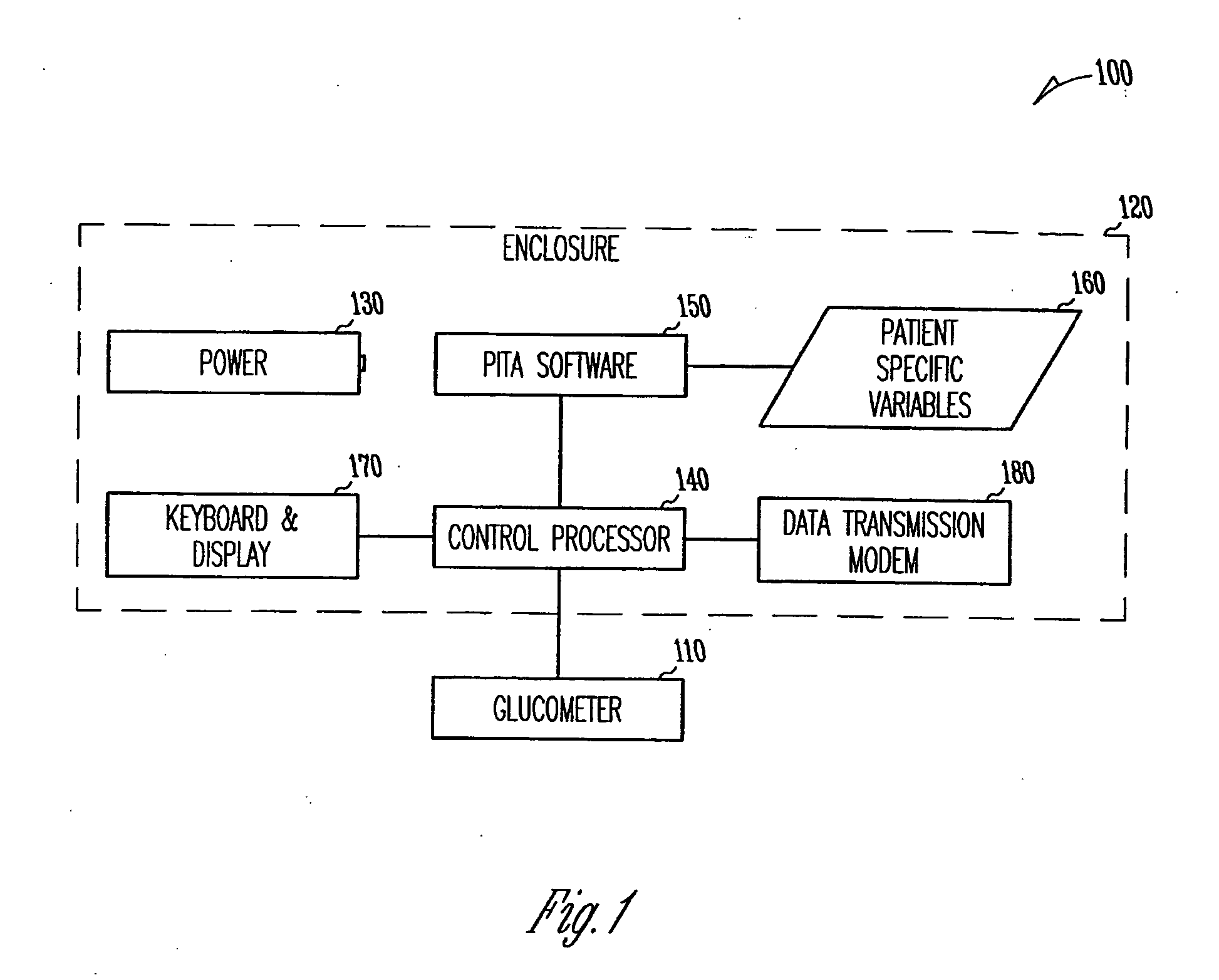
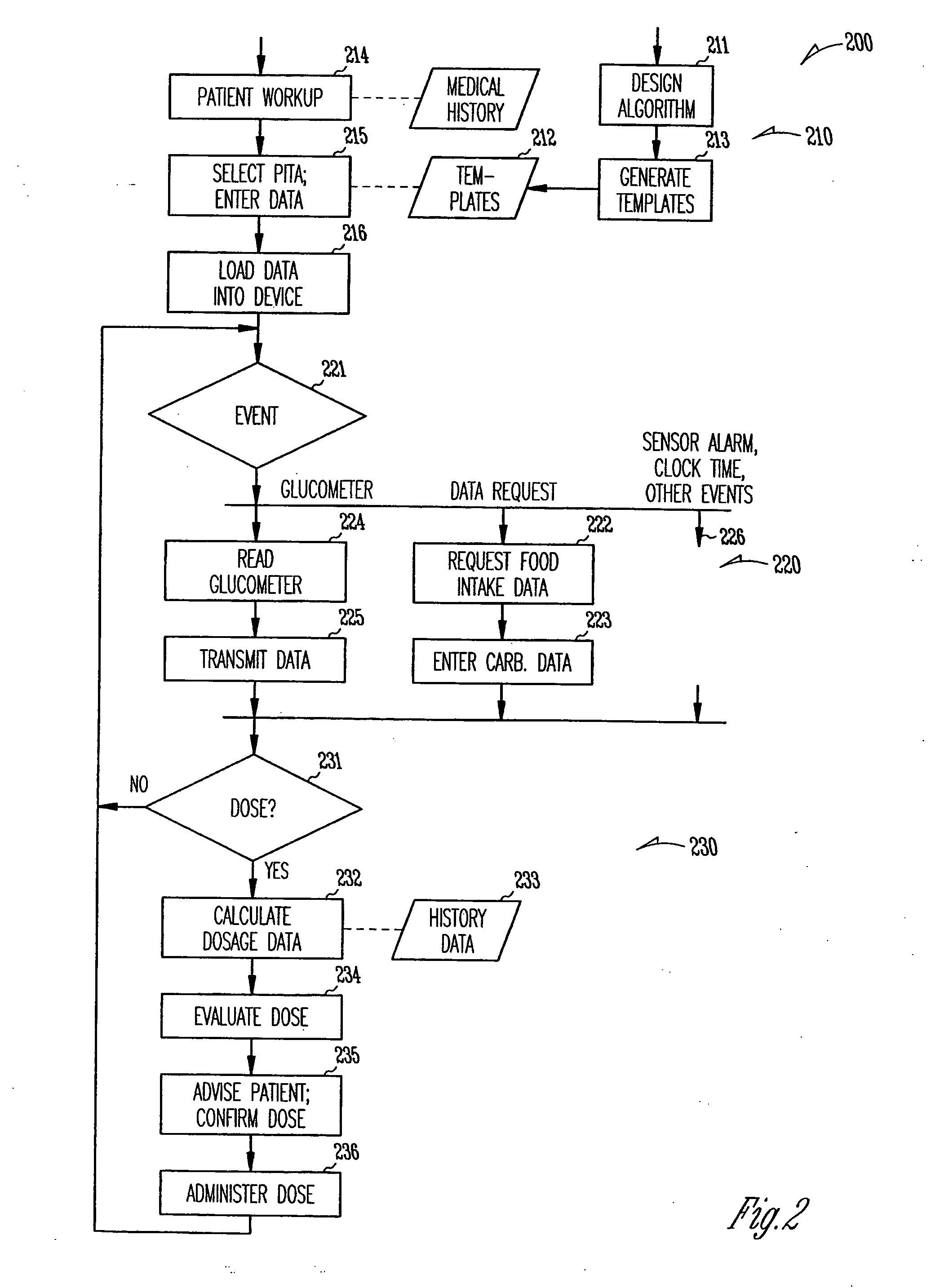
Patient management of diabetes treatment
InactiveUS20050197553A1Local control/monitoringDrug and medicationsPersonalizationPatient management
A portable diabetes management device calculates medication dosages from glucometer readings and data such as food intake entered by the patient, according to a management plan that can be personalized by a health-care professional using a template. The device may also store and communicate past data and plan revisions.
Owner:COOPER COLLEEN
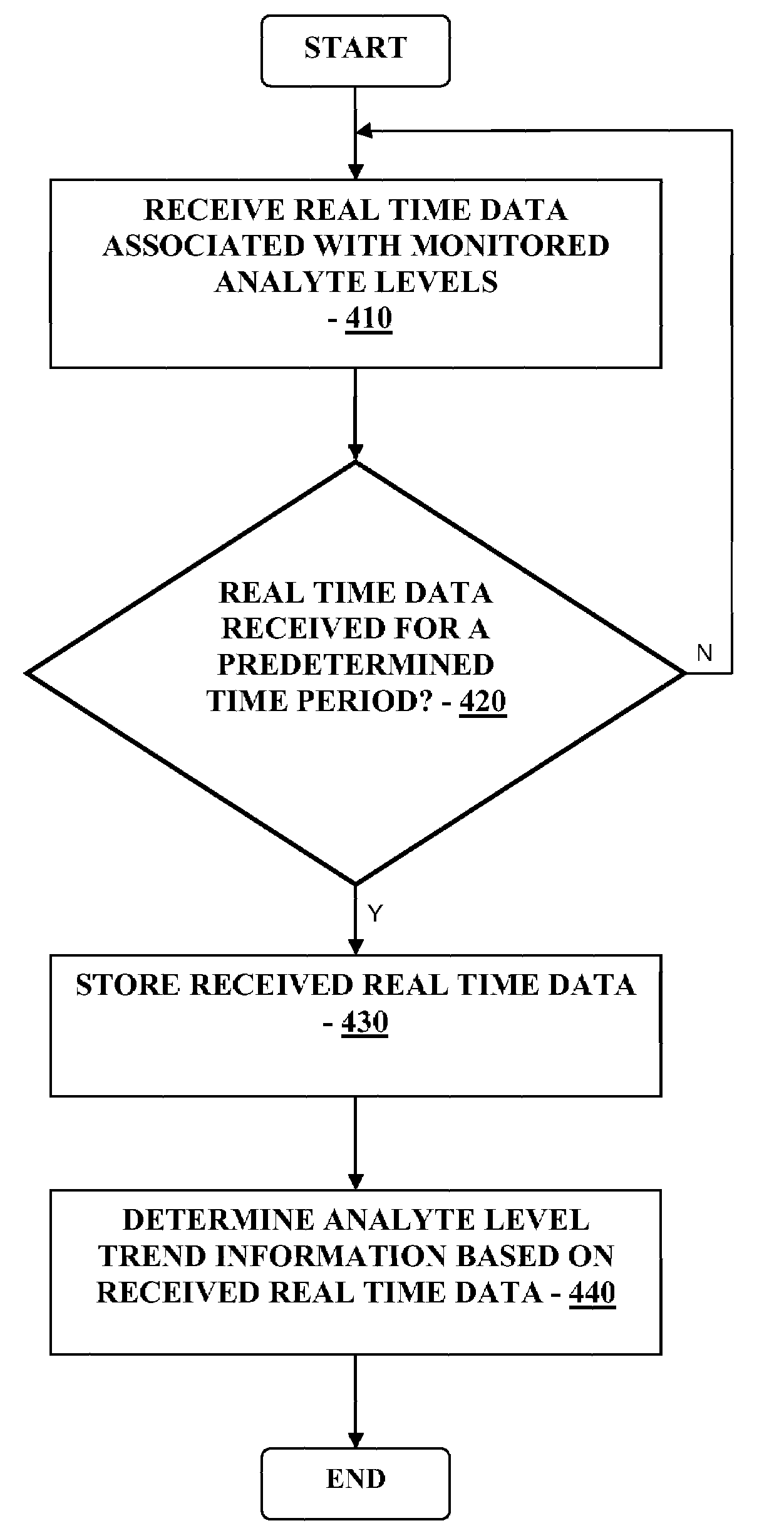
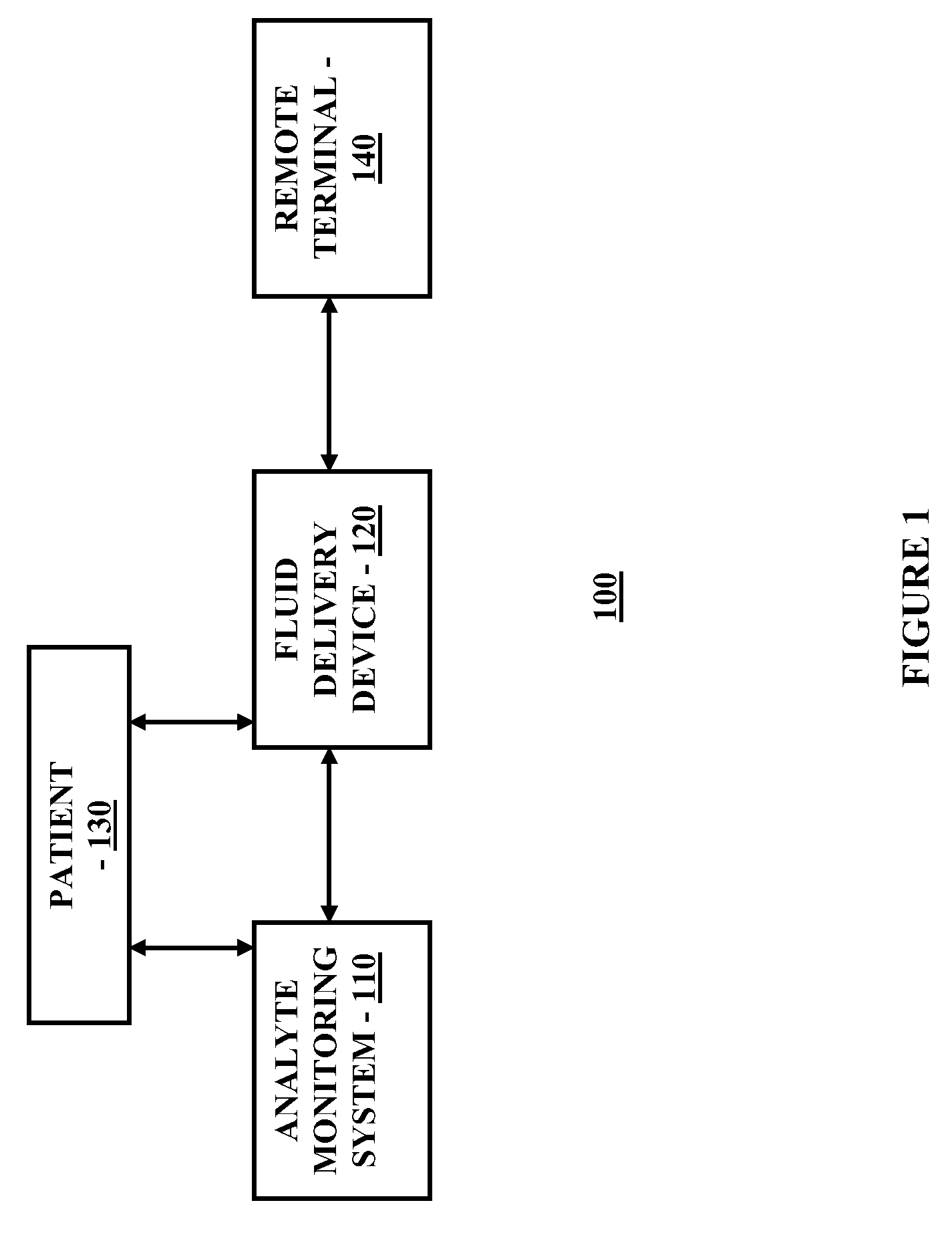
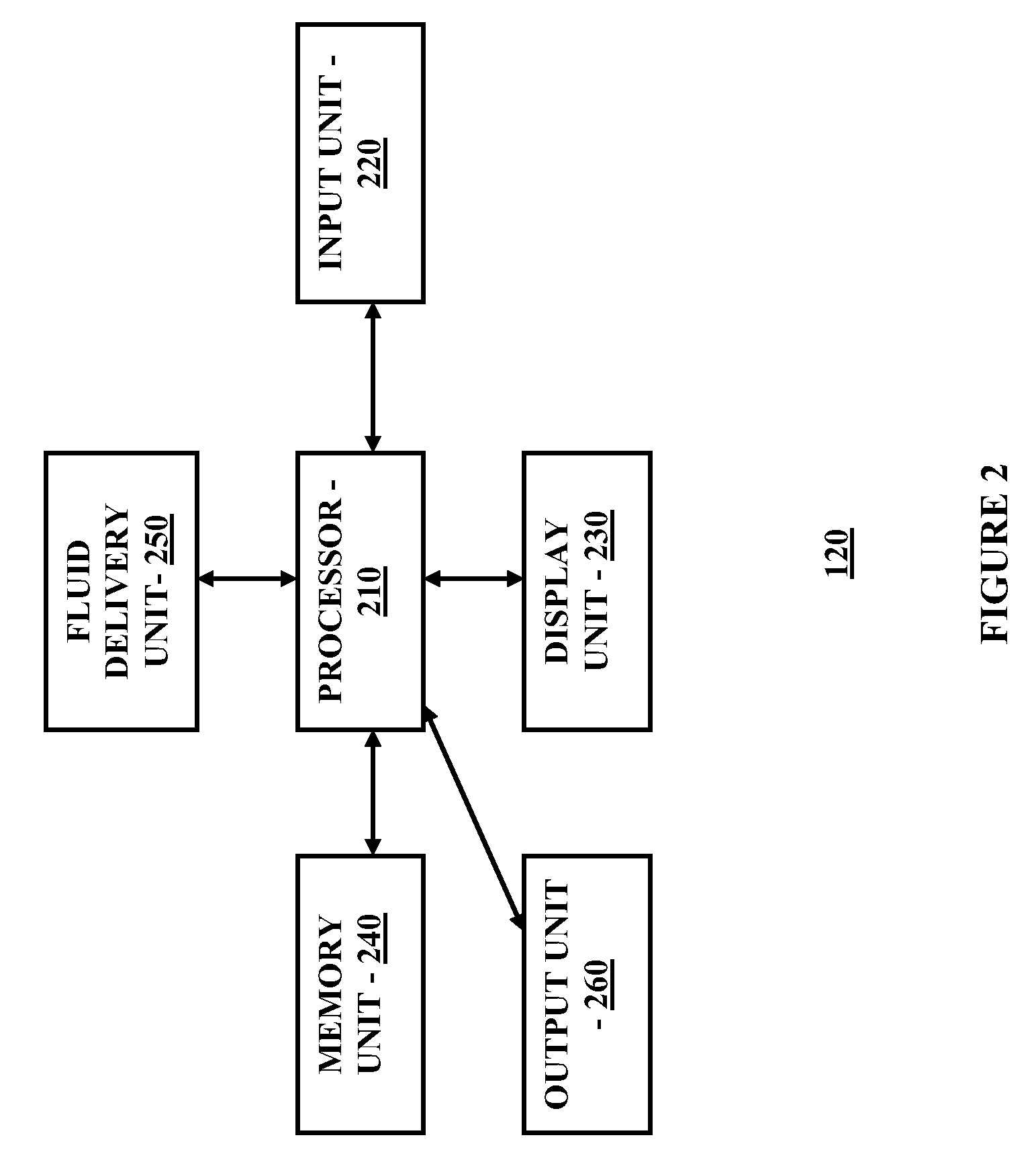
Method and System for Providing Integrated Analyte Monitoring and Infusion System Therapy Management
Method and system for providing diabetes management and insulin therapy based on substantially real time glucose monitoring system is provided.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Management and prioritization of the delivery of glycemic insight messages
InactiveUS20170053552A1Prevent and reduce and inputPrevent and reduce interactionMedical communicationMedical devicesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationUser device
A computer-implemented system and related method of managing use of a diabetes management device are presented here. An embodiment of the method obtains a number of glycemic insight messages for delivery to a user device associated with a user of the diabetes management device, each of the glycemic insight messages conveying information regarding a relationship between an insight event derived from patient-specific historical input data and a glycemic outcome. The glycemic insight messages are culled and prioritized to identify a group of insight messages intended for delivery. The method continues by queuing the group of insight messages based on the culling and prioritizing, and communicating at least one of the queued insight messages to the user device.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Method of operating a medical device and at least a remote controller for such medical device
ActiveUS8449523B2Instances of incorrect device pairing are believed to be reducedTransmission systemsDrug and medicationsDiabetes mellitusDiabetes management
A disease management system, methods, and devices are shown and described. In one embodiment, the system includes an infusion pump and a remote controller with the ability to be paired to each other. A method to verify a wireless connection between an infusion pump and a remote controller is shown and described herein. In a further embodiment, a method to verify a wireless connection between an infusion pump and a remote controller is provided. In addition, a method of operating a diabetes management system is provided in which the system includes an infusion pump and at least a remote controller.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Chronic disease management system
InactiveUS20060004603A1Data processing applicationsMedical equipmentDiabetes mellitusDiabetes management
A health care management system and method for chronic disease management such as diabetes management, hypertension management and like chronic diseases. The system is utilized by both patients and clinicians to manage the patients' chronic diseases and for clinicians to better manage a population of patients.
Owner:ANCHOR HLDG
Polypeptide formulations and methods for making, using and characterizing them
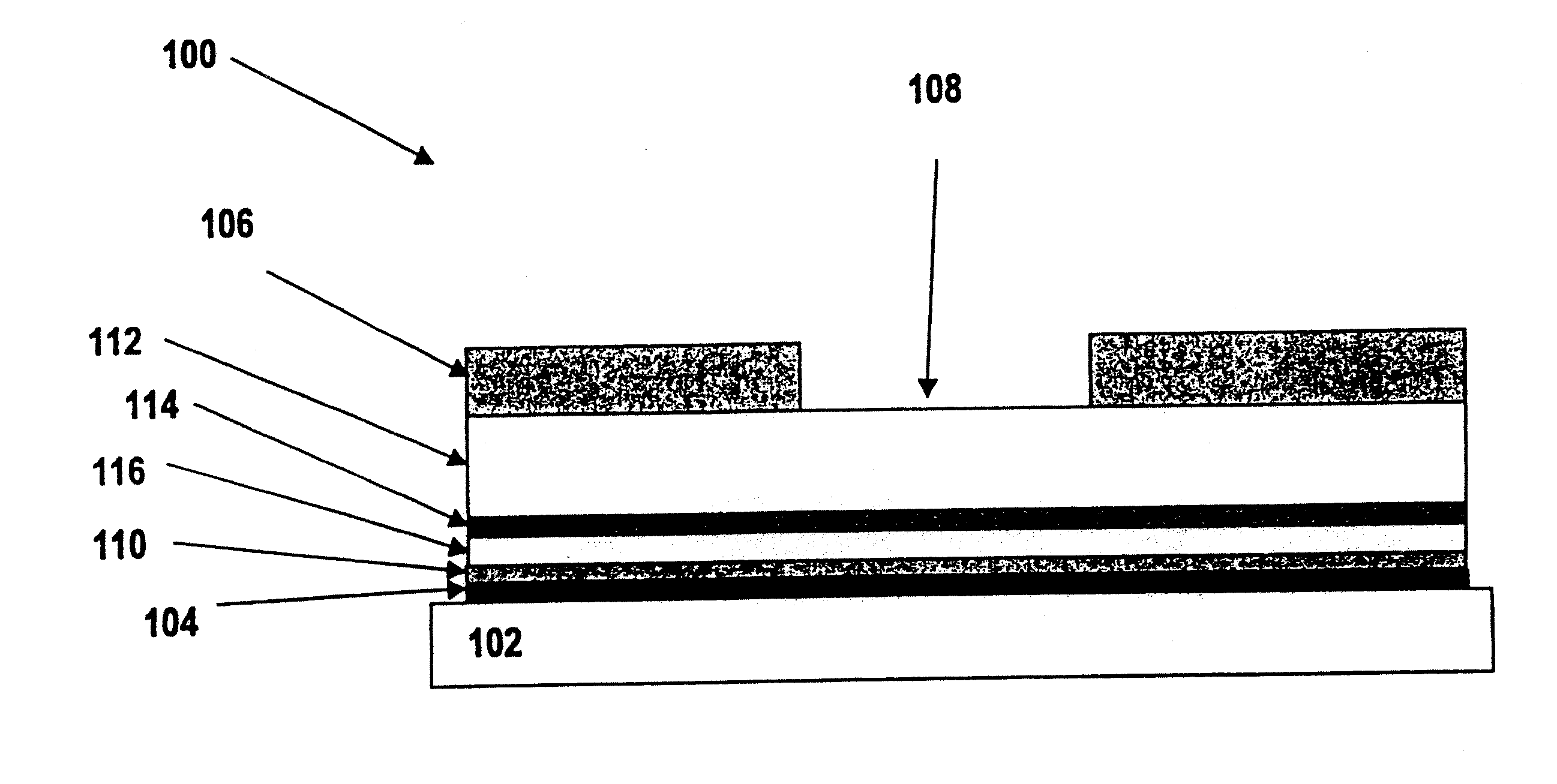
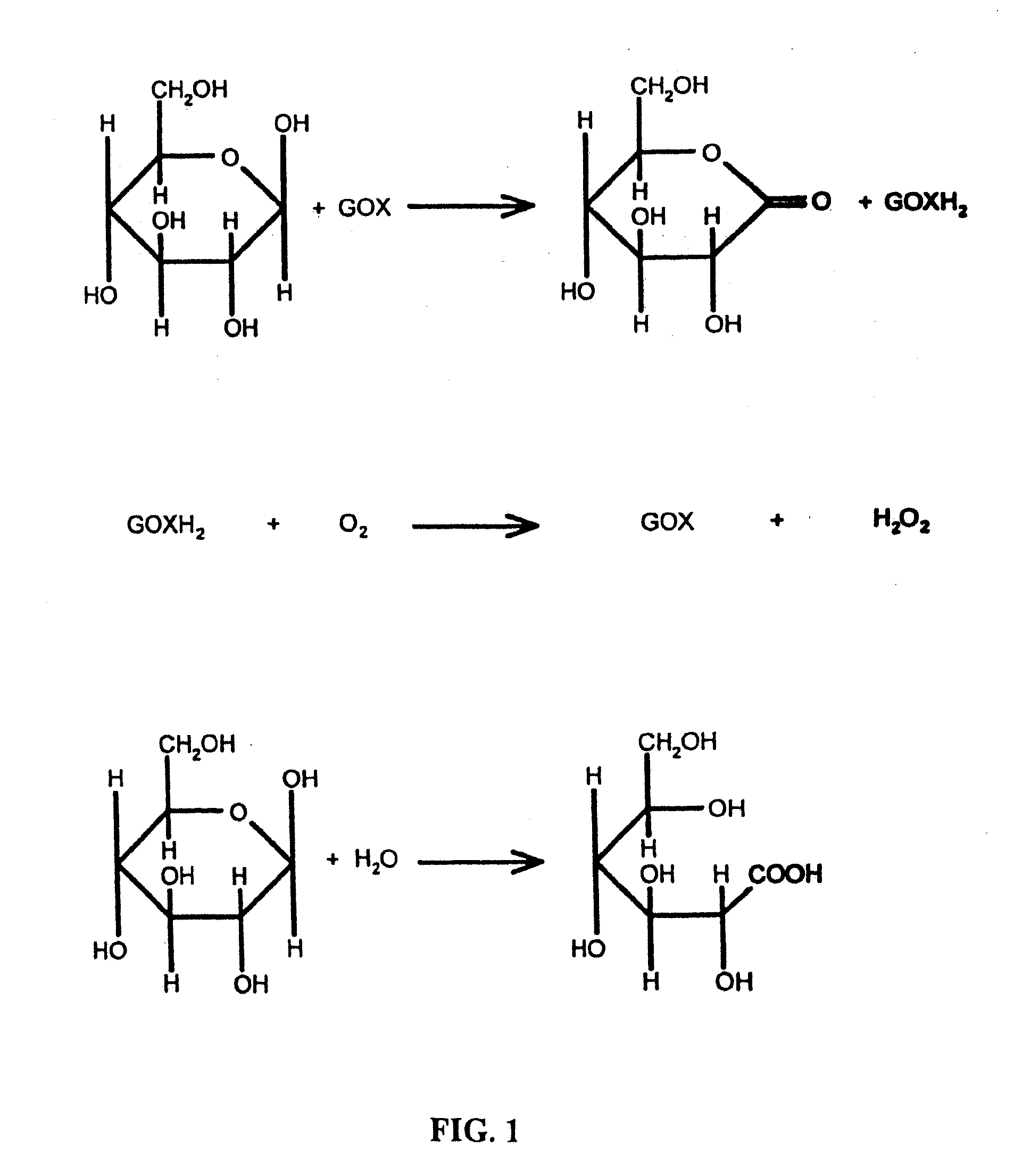
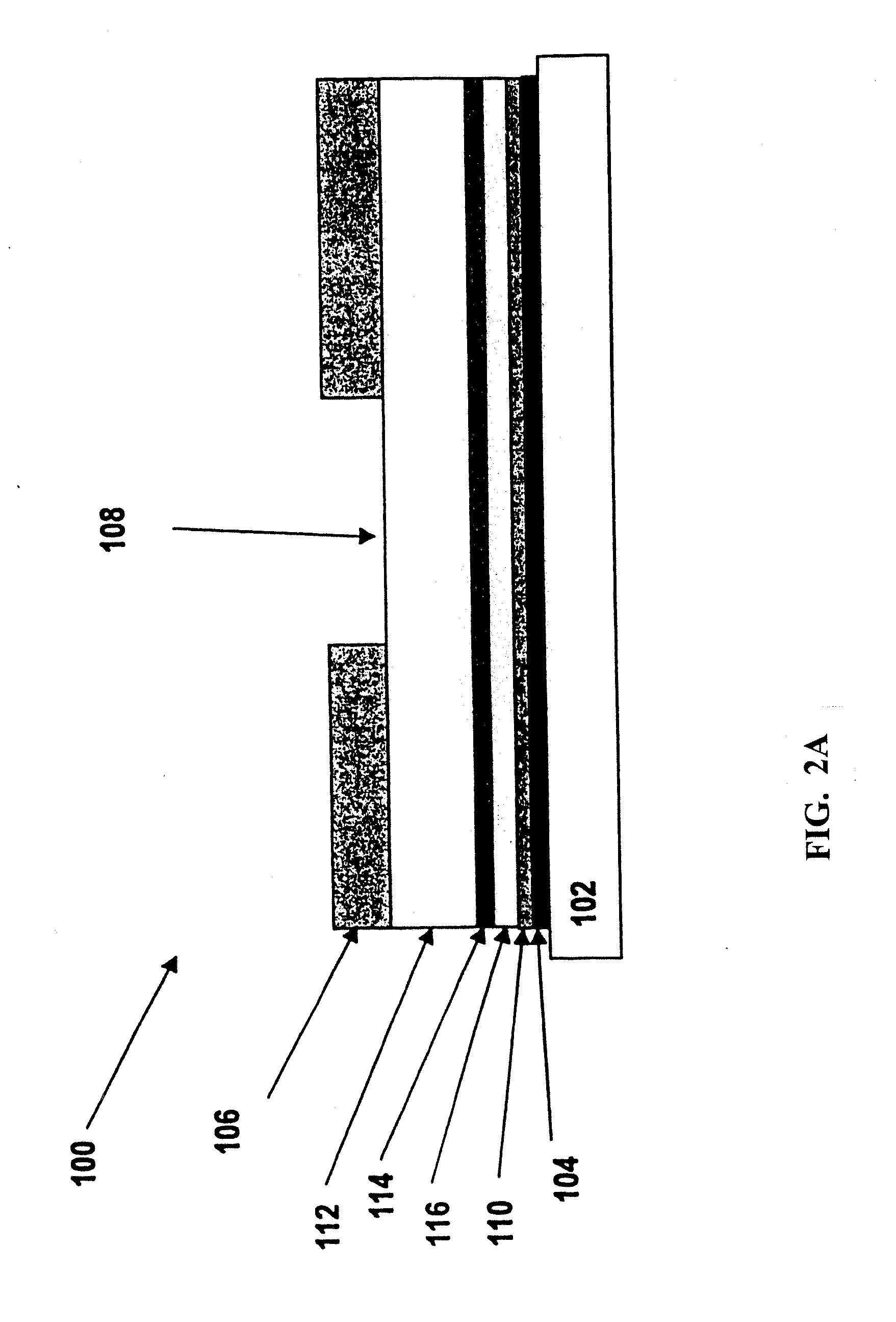
ActiveUS20060183178A1Improve performancePeptide/protein ingredientsComponent separationGlucose sensorsDiabetes management
Embodiments of the invention include polypeptide formulations and methods for making, using and characterizing them. Embodiment of the invention include stabilized polypeptide formulations, for example stable glucose oxidase formulations that can be used with glucose sensors used in the management of diabetes. Another embodiment of the invention includes methods to characterize the concentration of nonionic surfactants in stabilized polypeptide formulation for example stable insulin formulations that can be used in the treatment of diabetes.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Analyte sensor apparatuses having interference rejection membranes and methods for making and using them
InactiveUS20110082356A1Inhibited DiffusionReduce signalingImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsGlucose sensorsAnalyte
Embodiments of the invention provide amperometric analyte sensors having optimized elements such as interference rejection membranes as well as methods for making and using such sensors. While embodiments of the innovation can be used in a variety of contexts, typical embodiments of the invention include glucose sensors used in the management of diabetes.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Systems for diabetes management and methods
InactiveUS20100331654A1Local control/monitoringDrug and medicationsDiabetes mellitusDiabetes management
Owner:LIFESCAN SCOTLAND
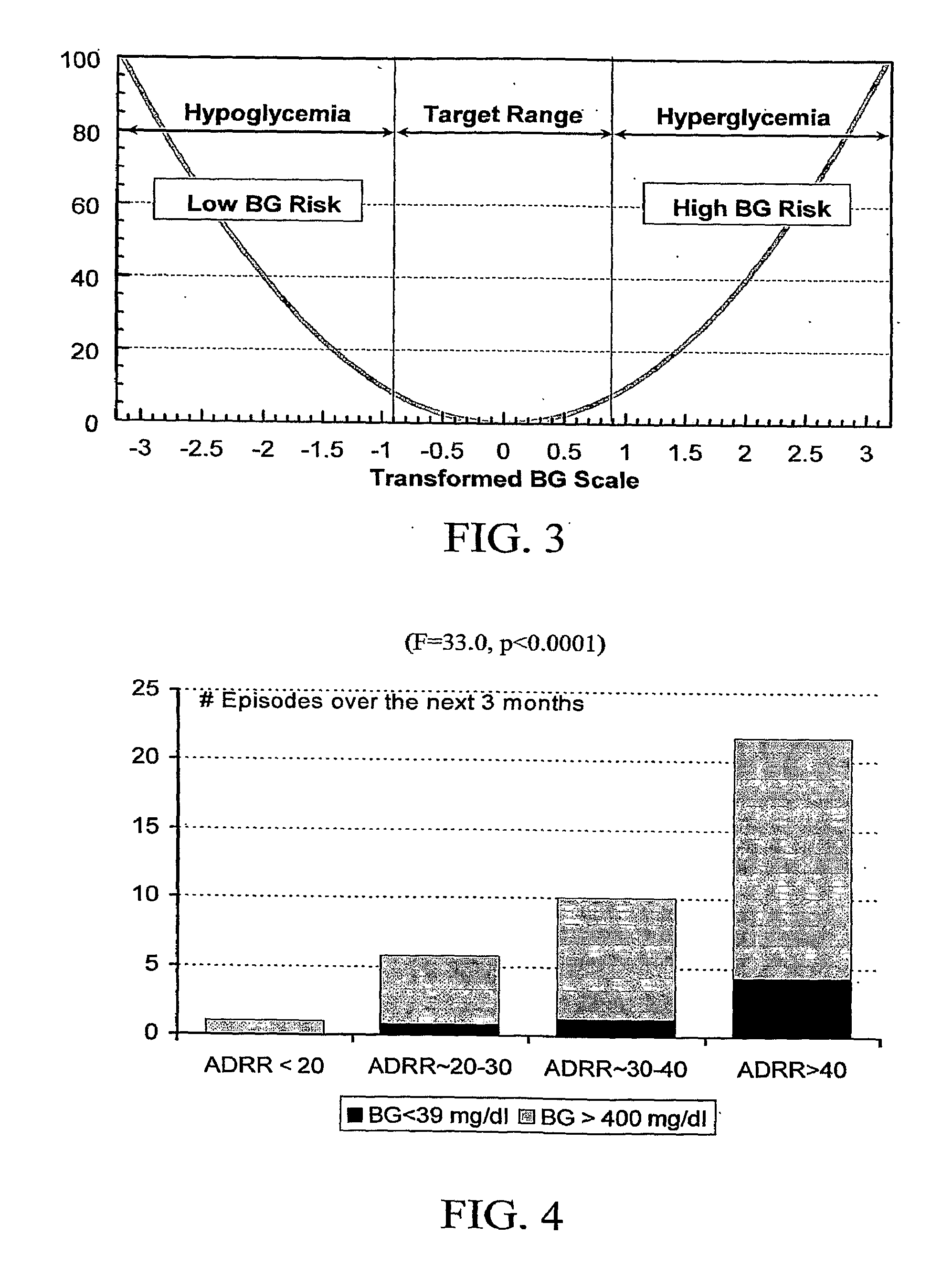
Method, System and Computer Program Product for Evaluation of Blood Glucose Variability In Diabetes From Self-Monitoring Data
ActiveUS20090171589A1Long-term riskEnhance existing SMBG devicesHealth-index calculationMedical automated diagnosisLow glucoseRisk profiling
A system, computer program product, method and algorithm for evaluation of blood glucose variability—one of the most important parameters of diabetes management. An embodiment of the method may use routine self-monitoring blood glucose (SMBG) data collected over a period of 2-6 weeks, for example, based on a theory of risk analysis of blood glucose data. One aspect may include a method, system and computer program product for computing the Average Daily Risk Range (ADRR)—a measure of overall glucose variability. Another aspect may include a method, system, and computer program product for estimating separately the glucose variability in the hypoglycemic range via a Low BG Index (LBGI) and the glucose variability in the high BG range via High BG Index (HBGI) followed by a combination of the two indices into a single variability display.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
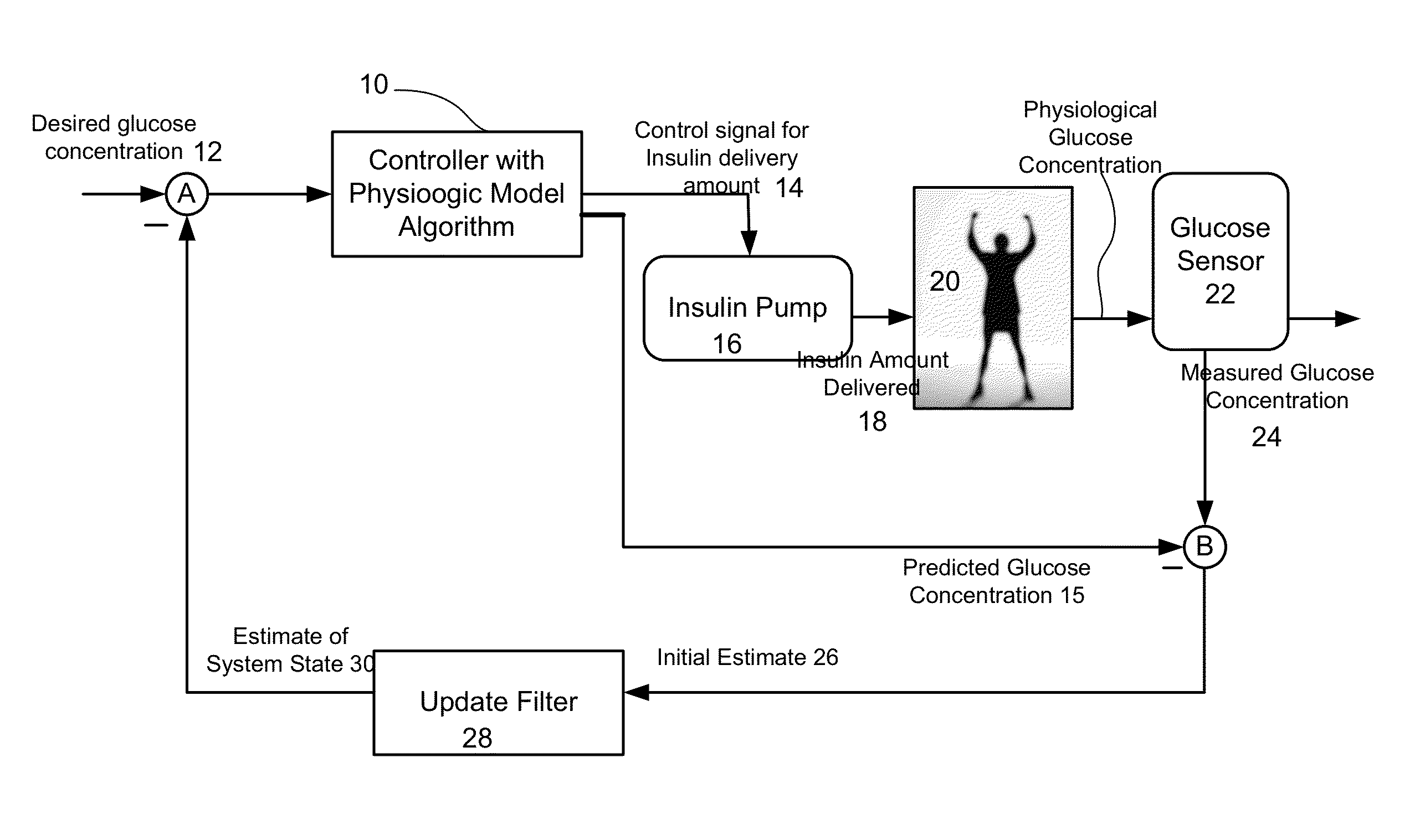
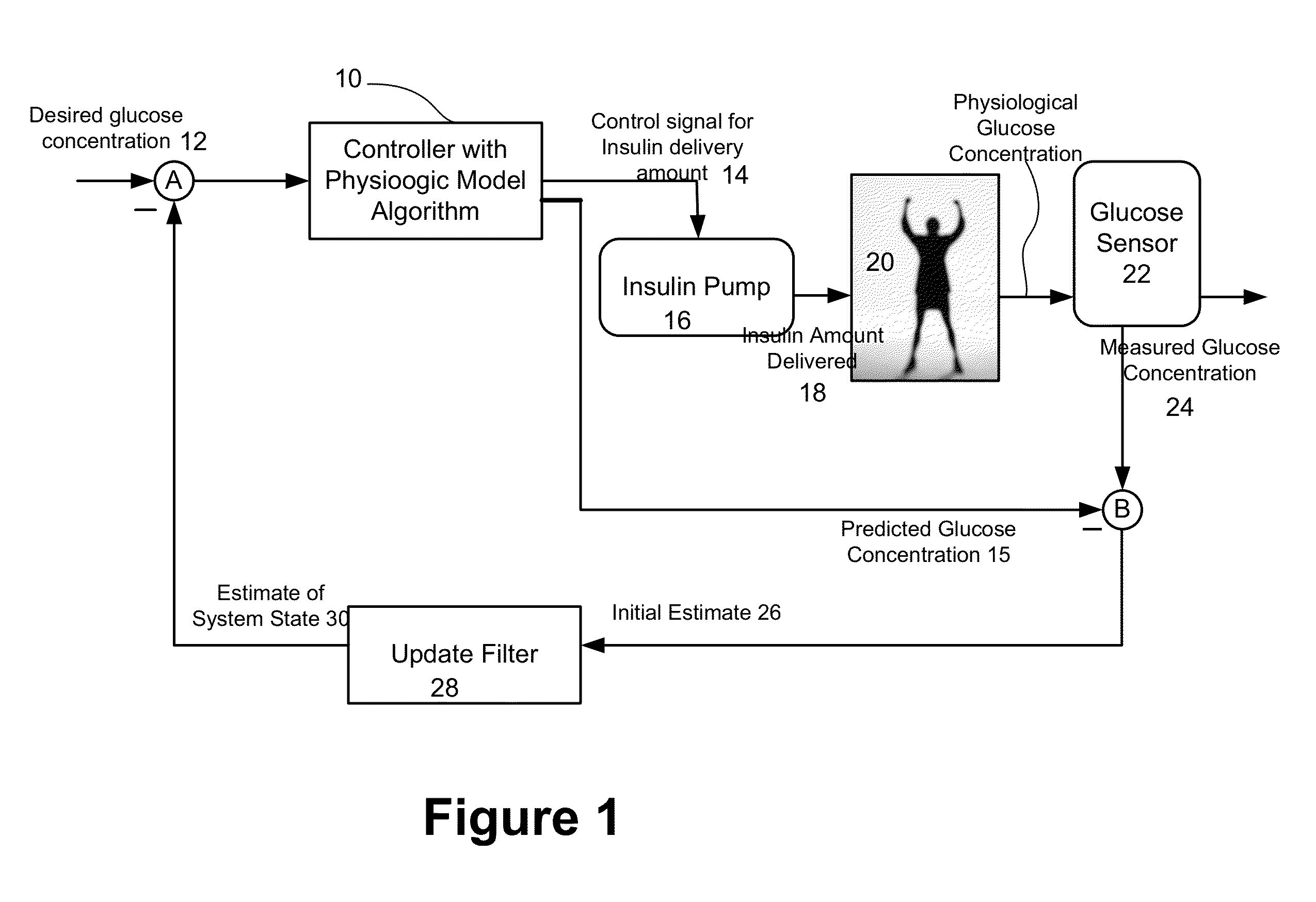
Method and system to handle manual boluses or meal events for closed-loop controllers
ActiveUS20140005633A1Negates portionReduce the impactDrug and medicationsMedical devicesGlucose sensorsDiabetes management
Described and illustrated is a diabetes management system that includes an infusion pump, glucose sensor and controller with a method programmed into the controller. The infusion pump is configured to deliver insulin to a subject. The glucose sensor is configured to sense glucose levels in the subject and provide output signals representative of the glucose levels in the subject. The controller is programmed to receive signals from at least one of the glucose sensor and the pump and configured to issue signals to the pump to deliver an amount of insulin determined by a feedback controller that utilizes a model predictive control and also configured to deliver at least the basal amount of insulin whenever the subject has initiated a manual bolus of insulin and a sensed or measured glucose level is at least a first threshold within a first duration of time.
Owner:JDRF INT +1
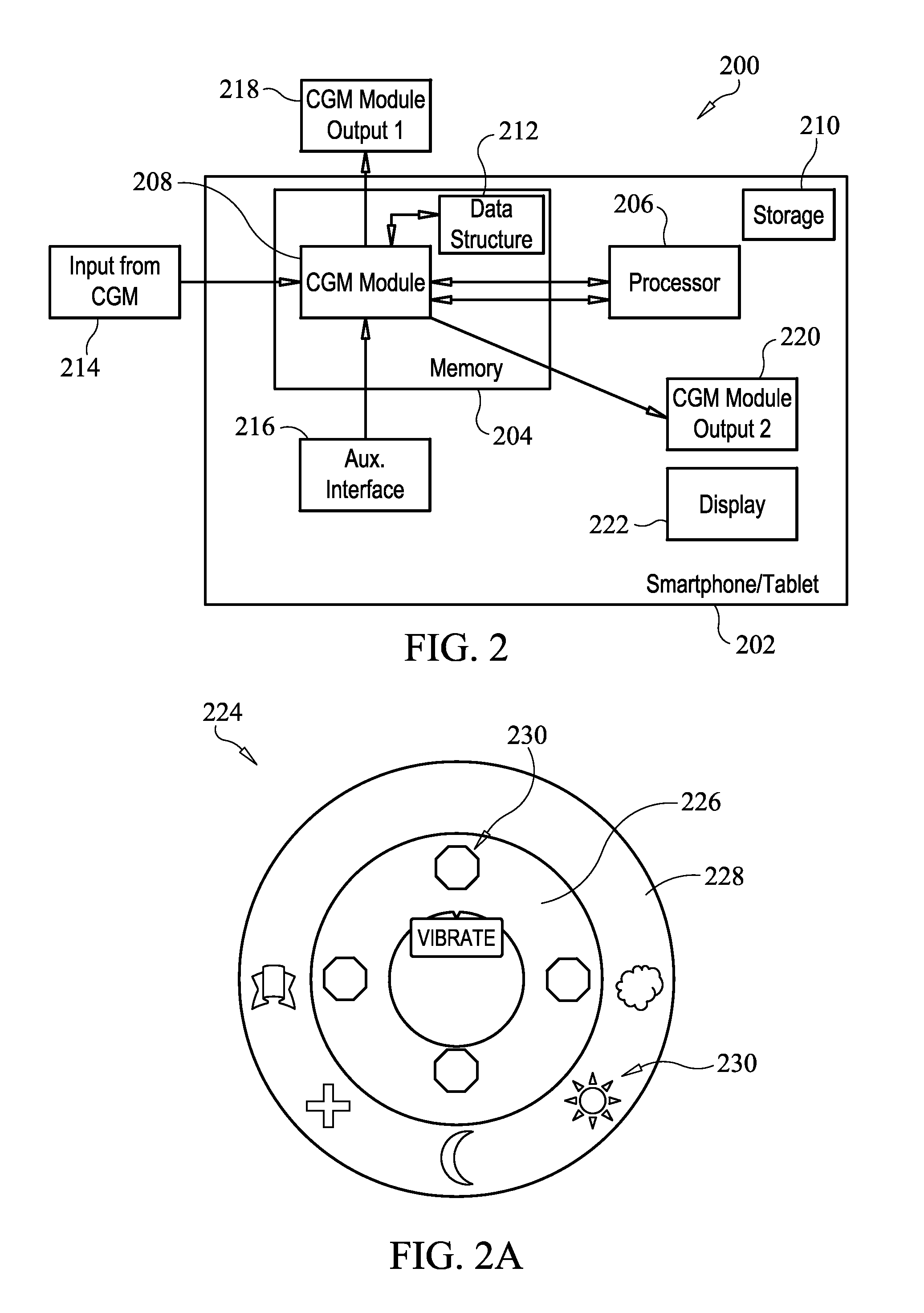
Systems and methods for leveraging smartphone features in continuous glucose monitoring
InactiveUS20140012118A1Strong alarmDiagnostic signal processingDrug and medicationsInternet privacyDiabetes management
The present embodiments harness a wide variety of capabilities of modern smartphones, and combine these capabilities with information from a continuous glucose monitor to provide diabetics and related people with more information than the continuous glucose monitor can provide by itself. The increased information provides the diabetic with an increased likelihood of good diabetes management for better health.
Owner:DEXCOM
Smart messages and alerts for an infusion delivery and management system
ActiveUS7981034B2Easy to controlHealth-index calculationDrug and medicationsDiabetes managementManagement system
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
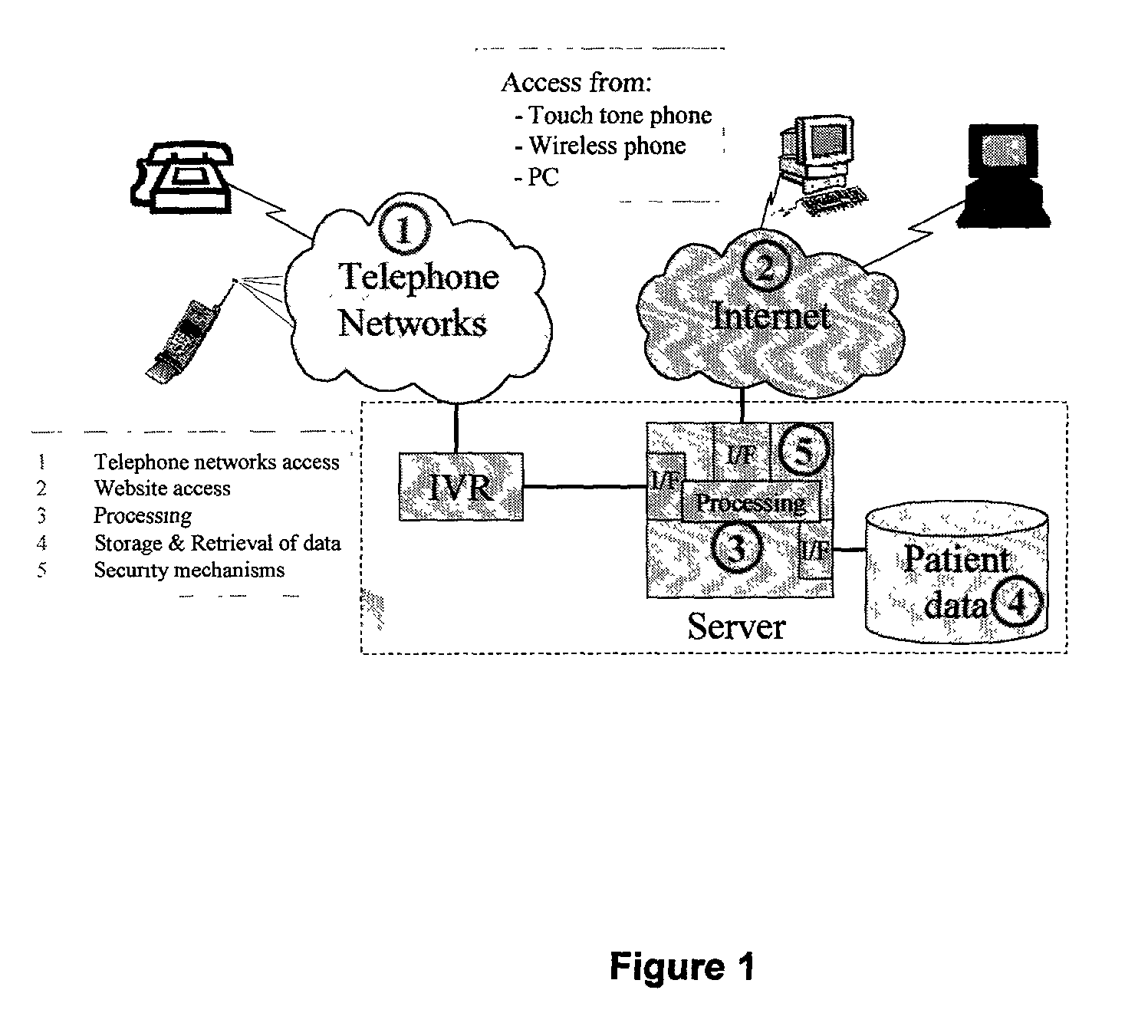
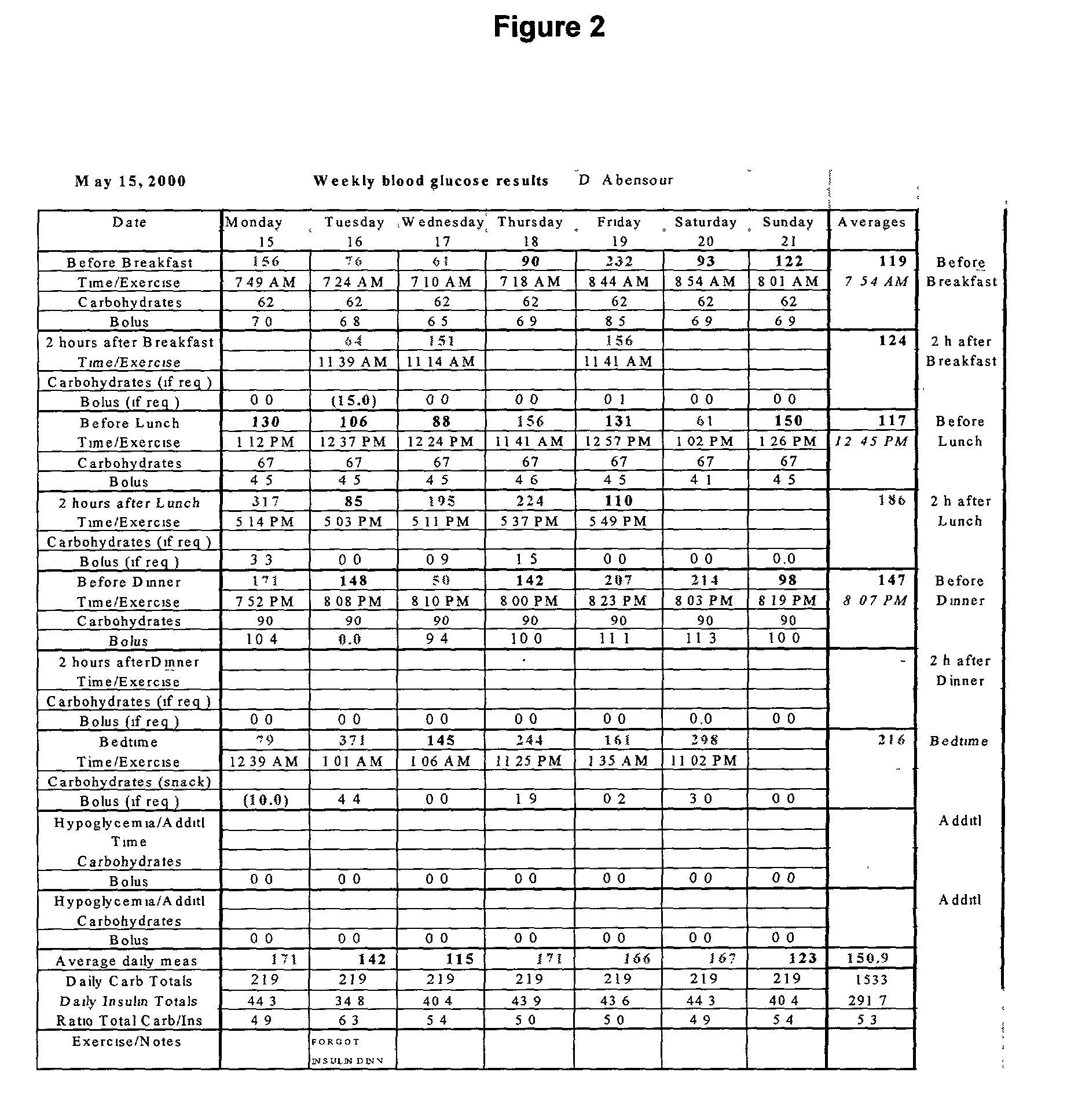
Method to determine insulin dosage requirements via a diabetic management internet web site which is also telephony accessible including extensions to general diet management
A computer system for ongoing monitoring and providing medication dosage recommendation to diabetic patients includes: a database for storing patient data; patient database access including one of web access, touch tone telephone access and speech recognition access; a server; a first set of programs contained within the server for processing the patient data and interfacing the data base accesses; a computer terminal connected to the server through the World Wide Web containing the set of programs including the specific interface to the system for a patient's physician to enter patient specific parameters relevant to compute one of the insulin and other medication dosage; a second set of programs contained within the server for diabetic management for interface by a patient and the patient physician by the patient means of database access; and the second set of programs to be used to enter the current blood glucose, the planned intake of carbohydrates, and to generate a recommendation of one of a dosage of diabetic medication and a quantity of glucose for intake.
Owner:ABENSOUR DANIEL +1
System and method for managing diabetes
A diabetes management system, an infusion pump, and methods for managing a blood glucose level of a diabetes patient. The infusion pump includes a processor for monitoring an amount of insulin delivered to a patient and an internal database in communication with the processor. The internal database is for storing food information. The diabetes management system includes a blood glucose monitor, a food database, and an infusion pump for delivering insulin to a patient. The food database comprises one or more records of information on various foods. The infusion pump of the diabetes management system includes (i) a processor for monitoring an amount of insulin delivered to the patient and (ii) a second database. The second database is for receiving at least a portion of the information from the food database.
Owner:CROTHALL KATHERINE D +2
Safety layer for integrated insulin delivery system
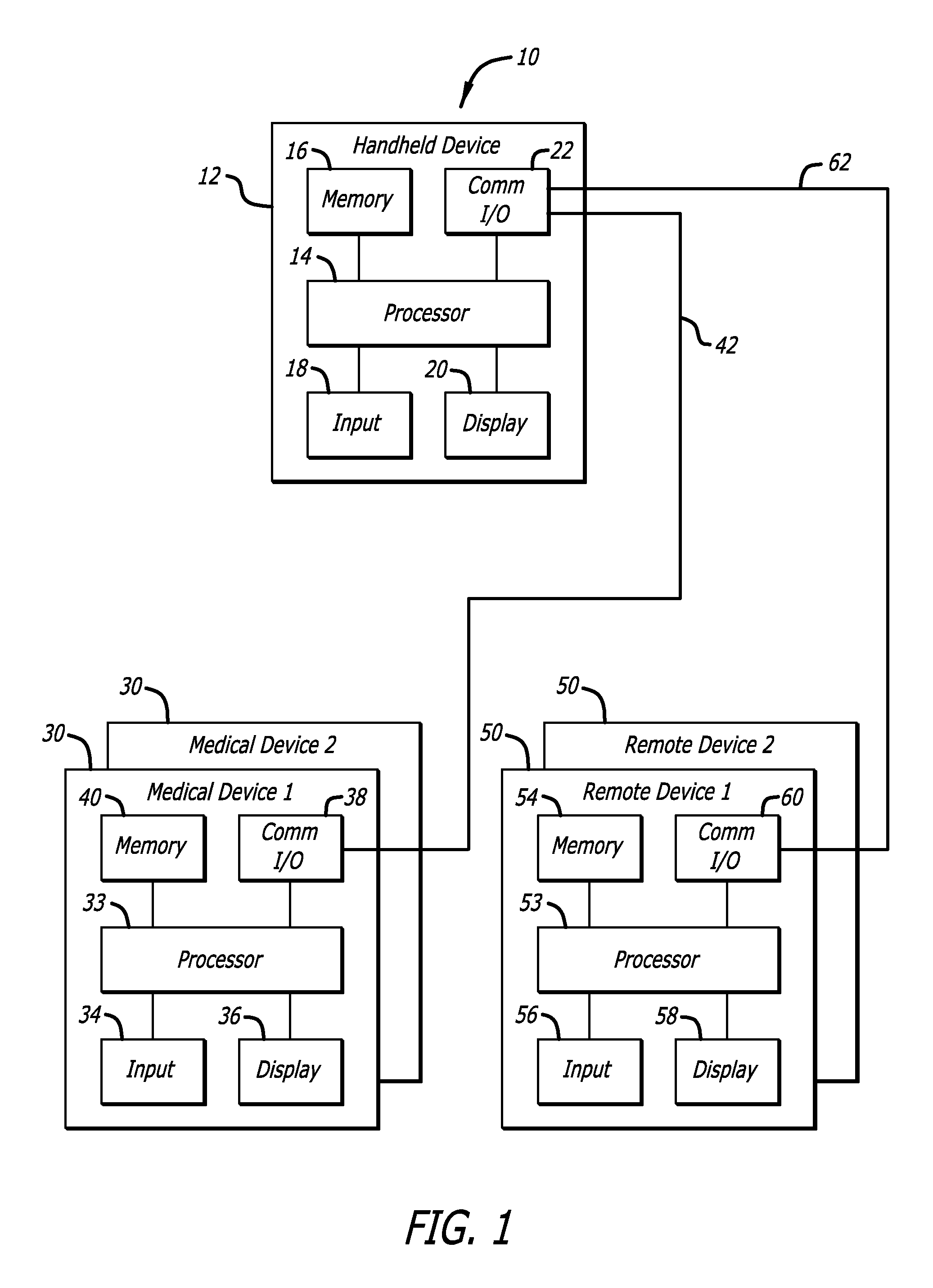
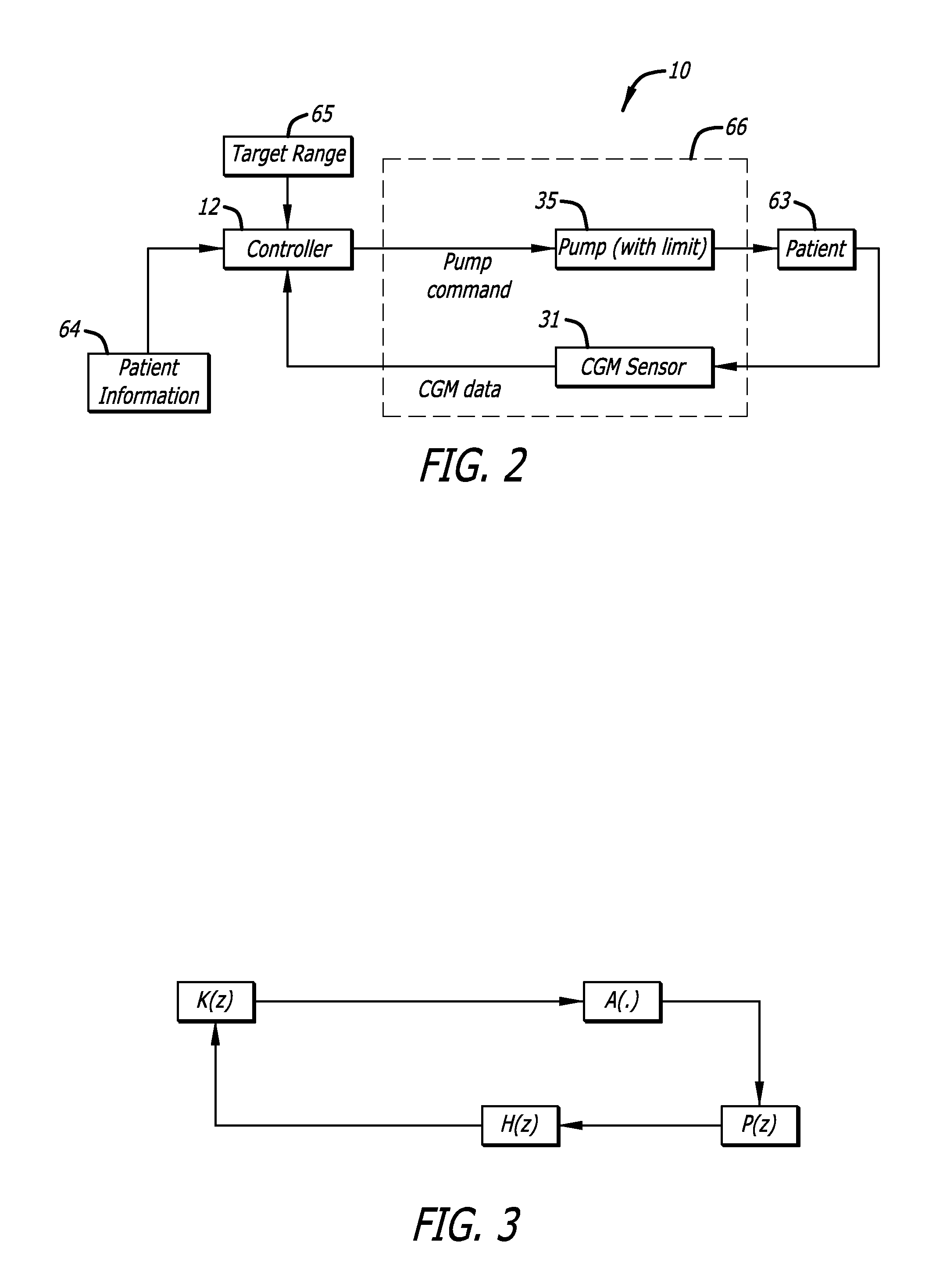
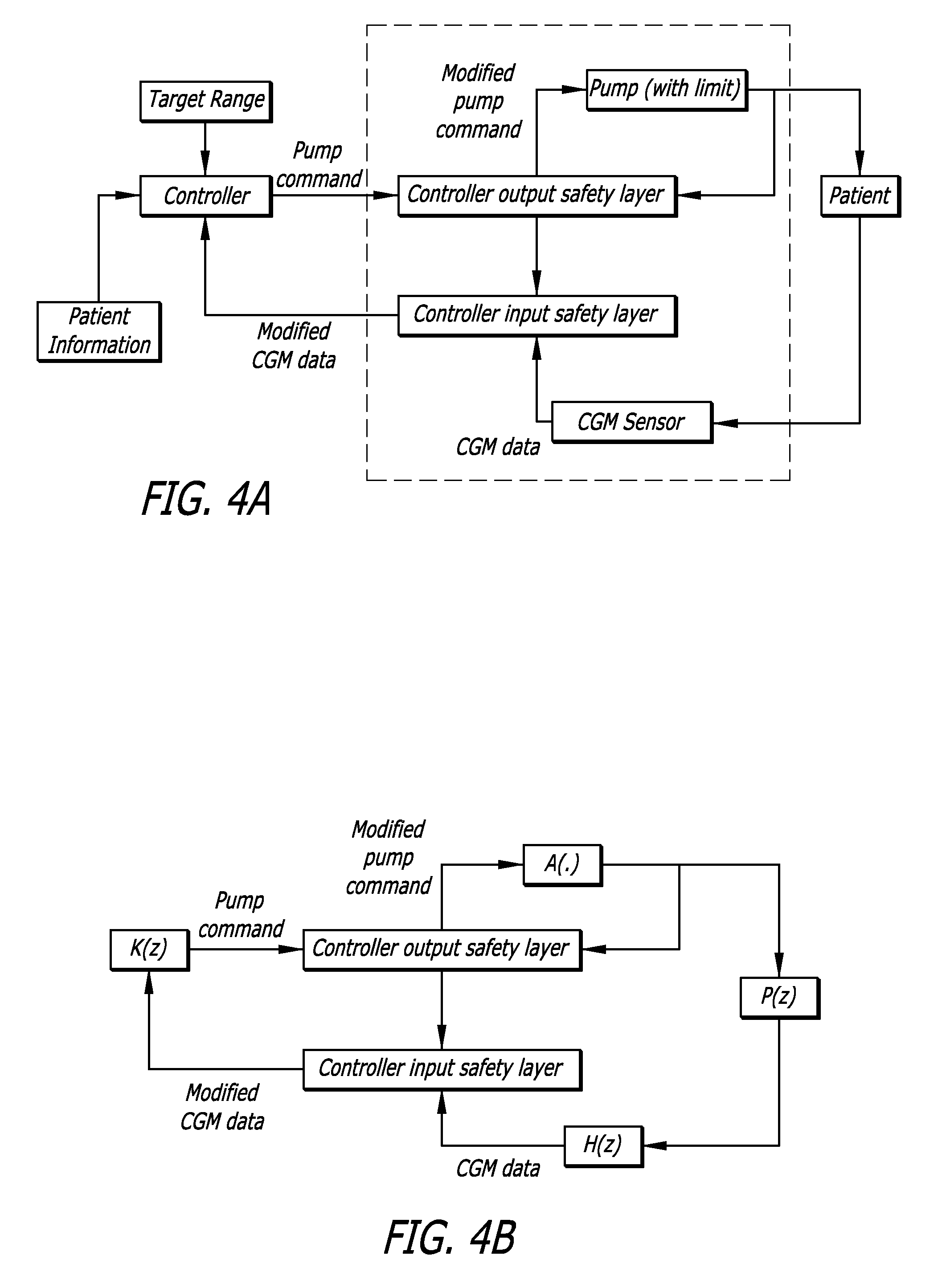
An integrated diabetes management (IDM) system includes a safety layer which, in one configuration has two components, one located between a glucose sensor and a controller and a second component located between a controller and a pump, to monitor various aspects of signals and modify those signals for compatibility and safety purposes. In one application, the safety layer receives output control signals from a controller and modifies those control signals as a function of an actual amount of insulin delivered to the user. The safety layer allows for an increased level of safety in the IDM system and permits development of separate hardware and software upgrades with the safety layer assuring that compatibility between components will continue.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com