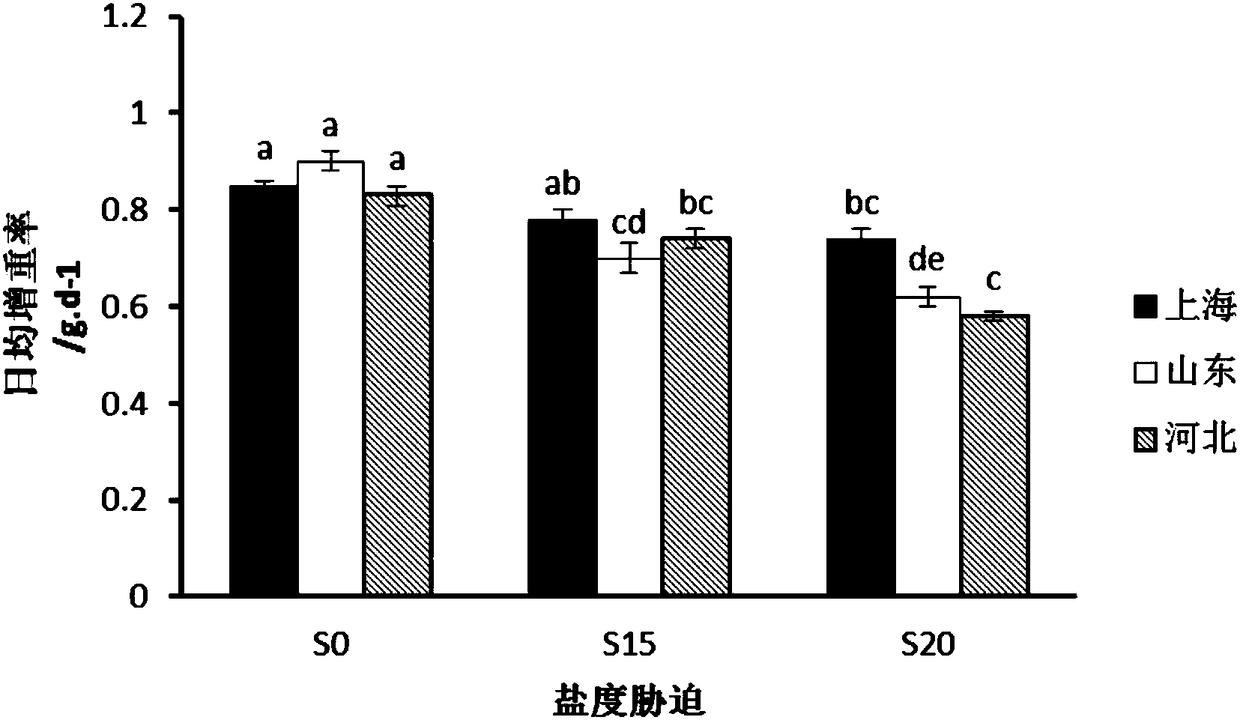
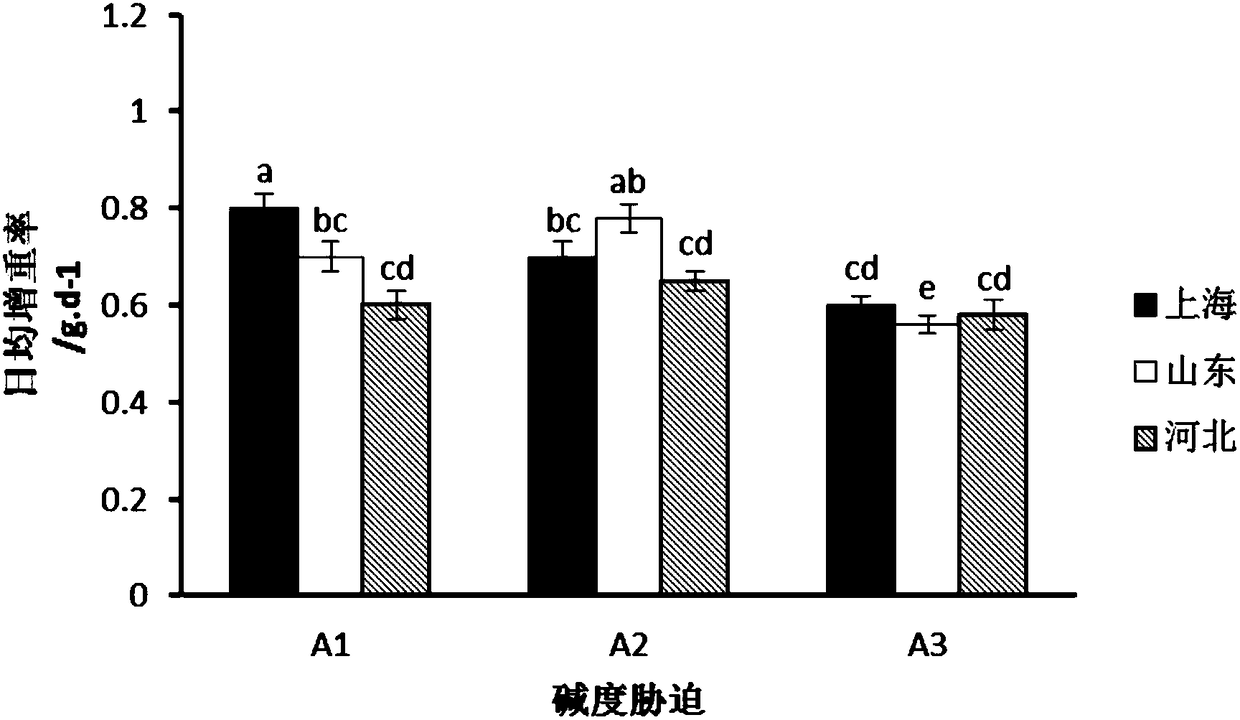
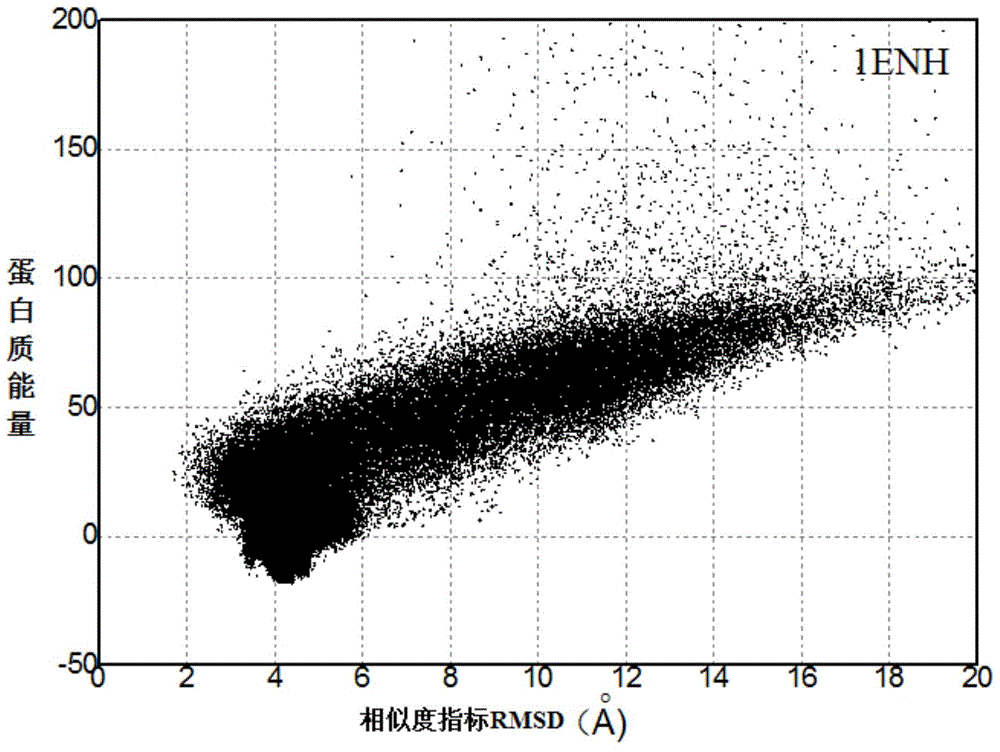
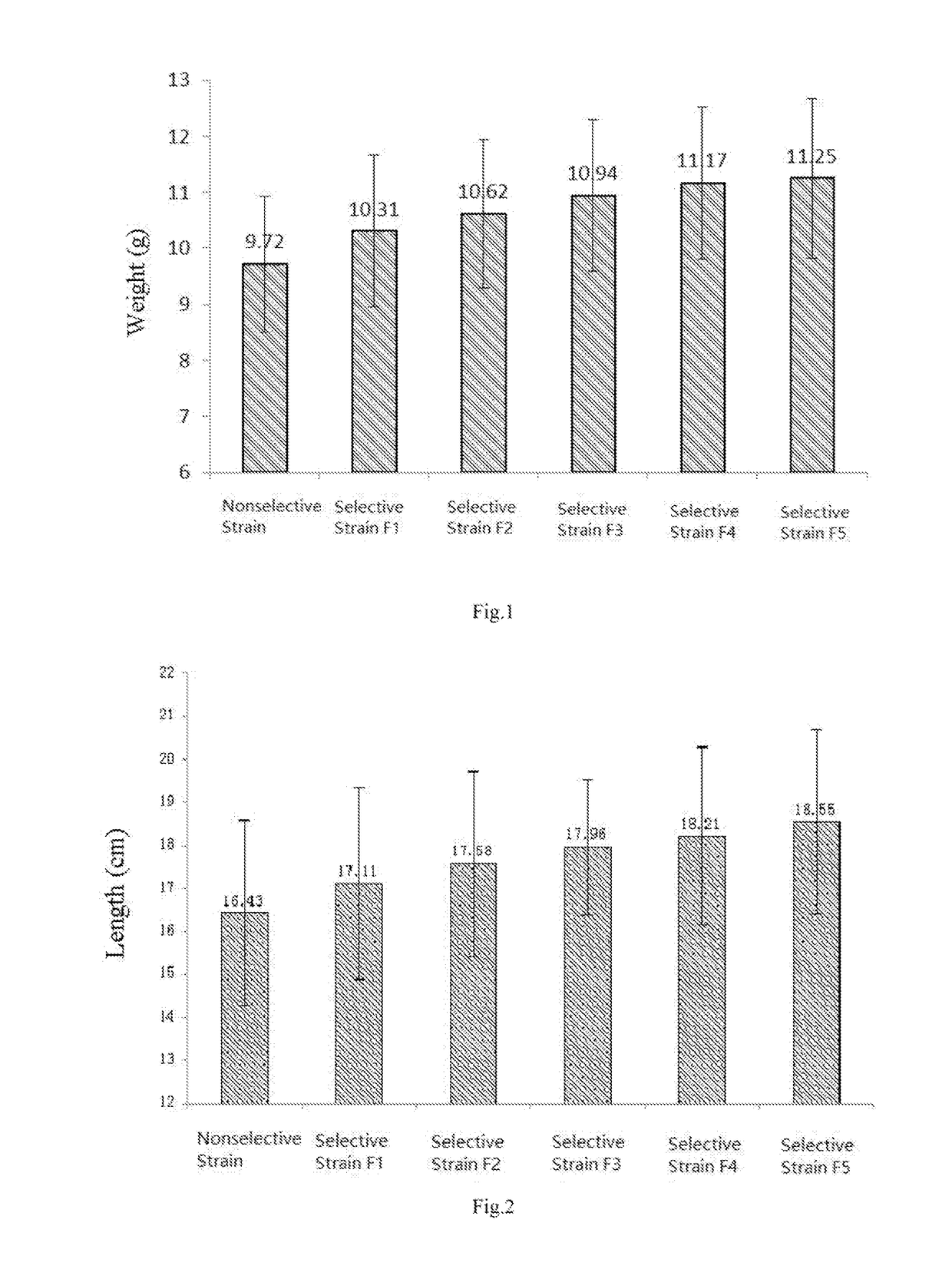
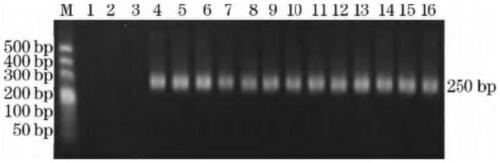
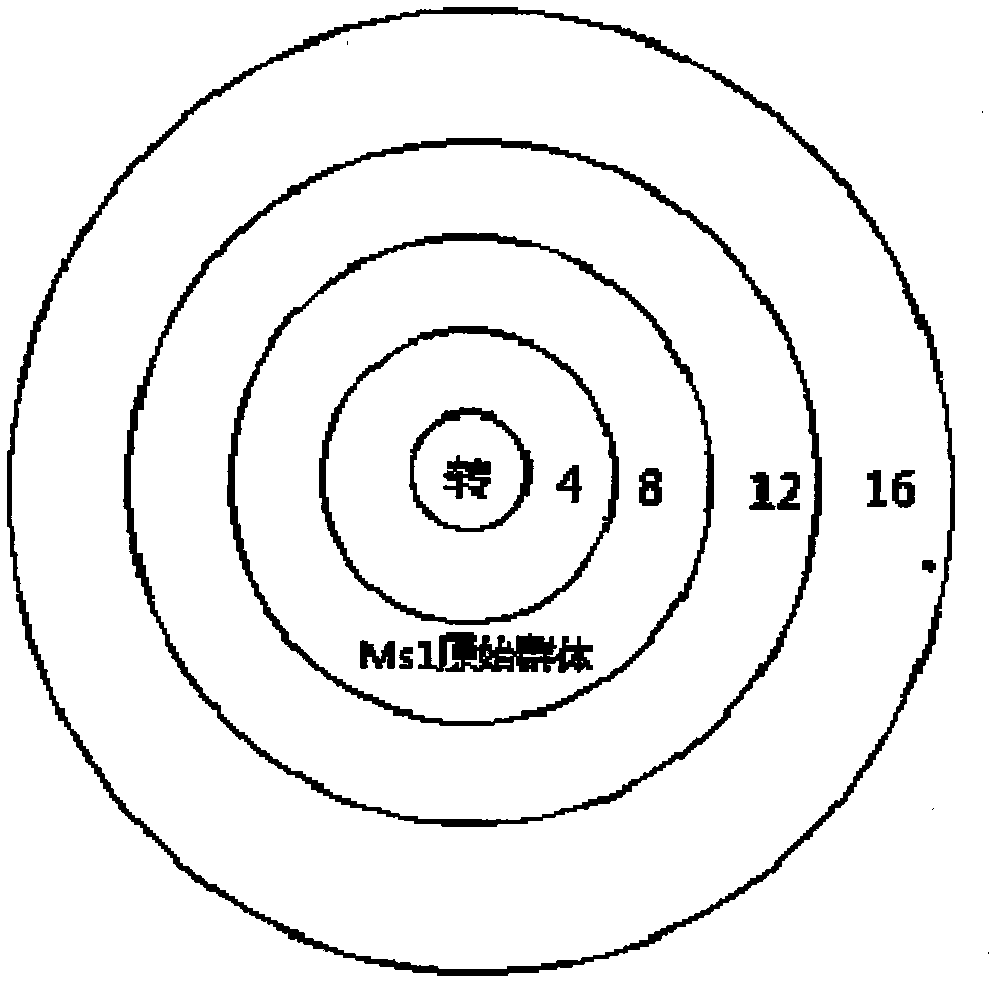
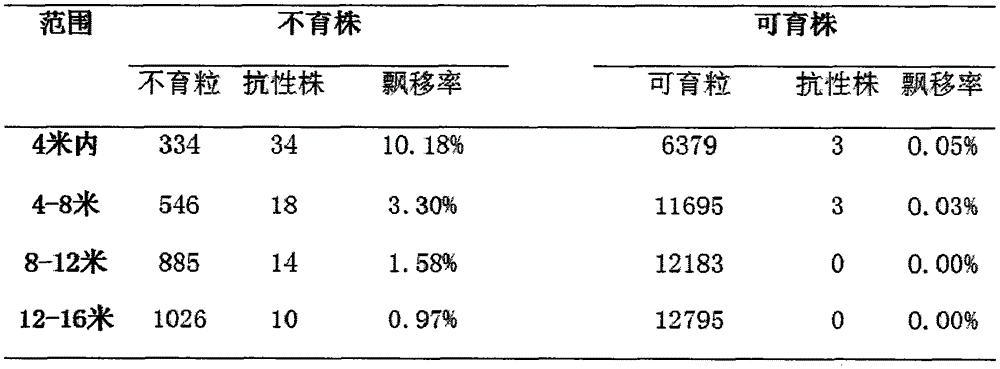
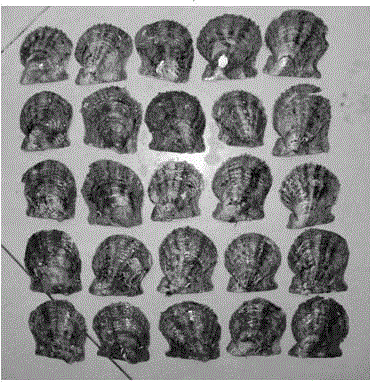
Patents
Literature
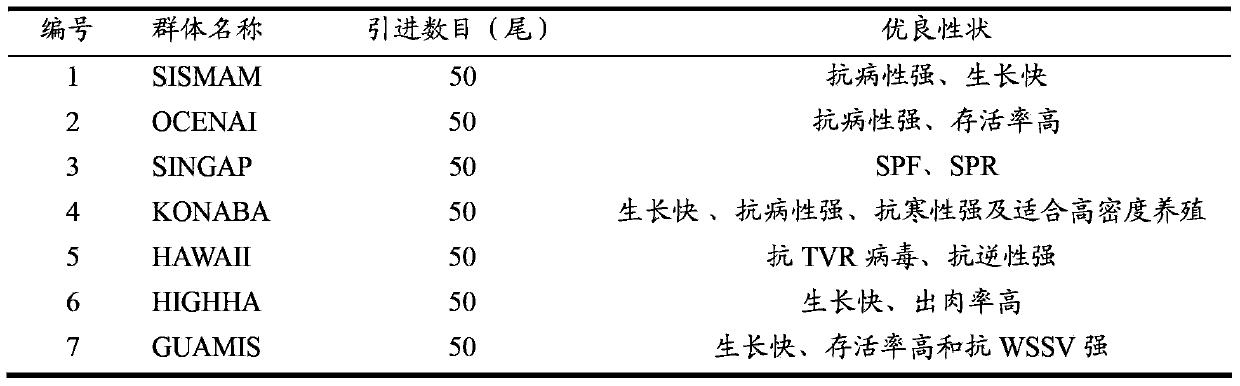
53 results about "Base population" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Definition: The base population refers to the number of people in a given area (e.g. a nation, province, city, etc) to which a specific vital rate applies, that is, the denominator of the crude birth rate or death rate; that population determined by a census. Source...
Intelligent searching method and device
InactiveCN102385636AConvenient and efficient accessEasy to pushDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsUser inputBase population
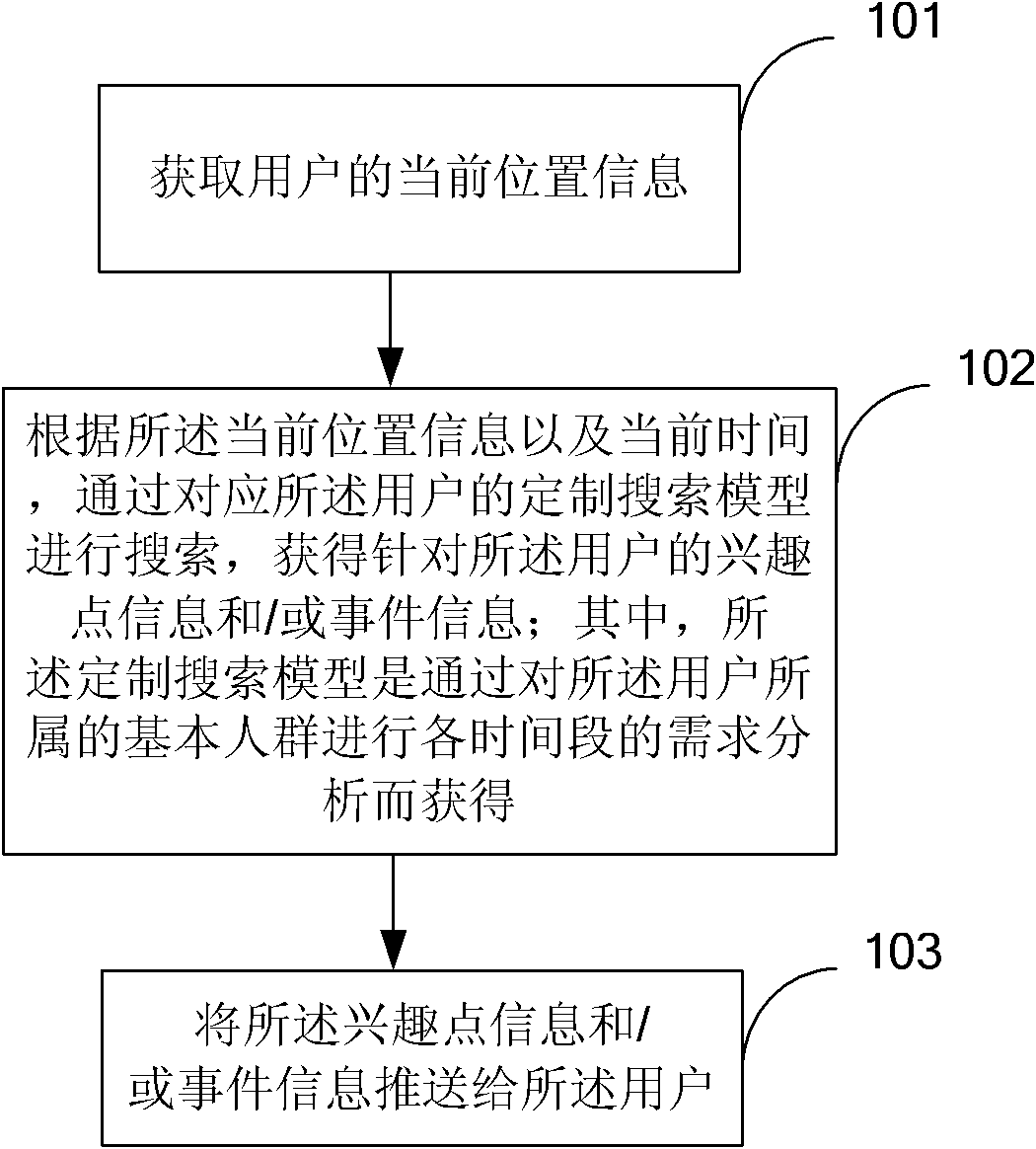
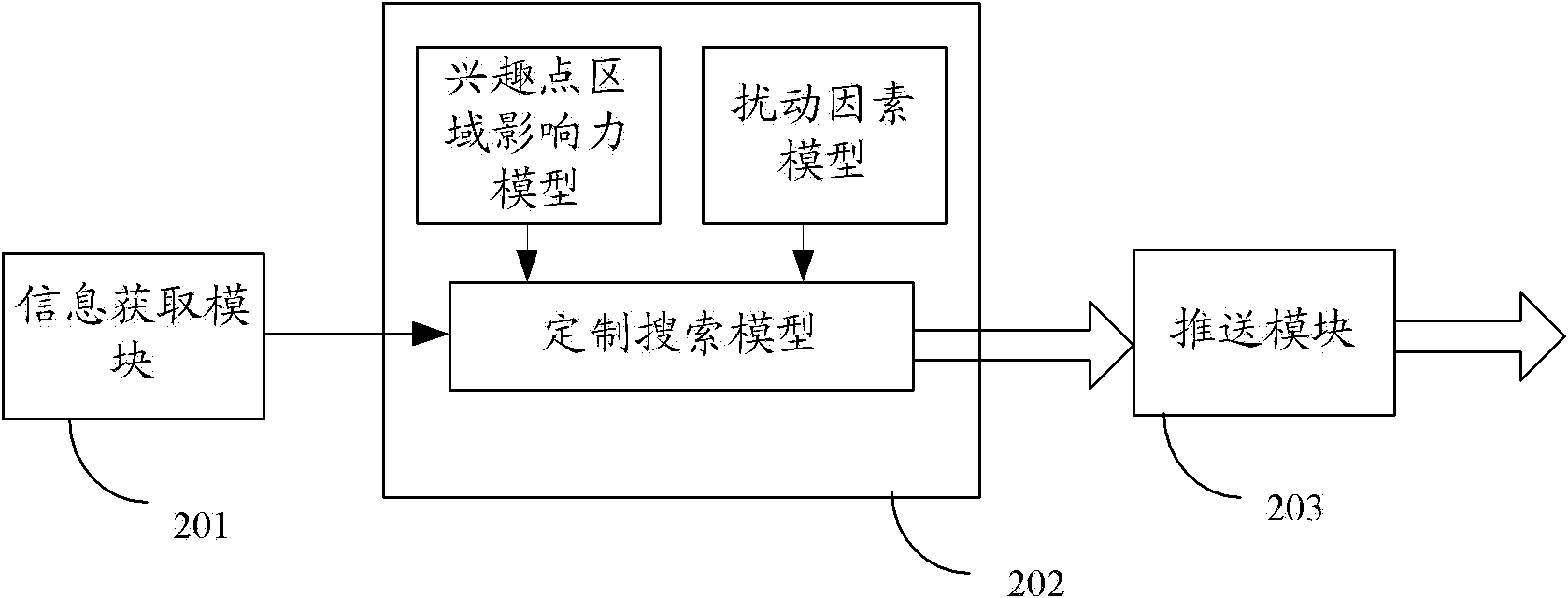
The invention discloses an intelligent searching method and device. The method comprises the following steps of: step 1, acquiring the current position information of a user; step 2, searching for interesting point information and / or event information directed at the user through a customized searching model corresponding to the user according to the current position information and the current time, wherein the customized searching model is obtained by executing demand analysis of each period of time on the base population of the user; and step 3, transferring the interesting point information and / or the event information to the user. Through the method and device disclosed by the invention, the user can get the interesting point information and the event information based on user characteristics without executing input operations, so that the life information demand of the user can be satisfied conveniently and accurately.
Owner:陈卫
Prawn low dissolved oxygen resistance family selection method
ActiveCN104686430ARich genetic diversityAvoid inbreedingClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaHigh densityPrawn
The invention relates to a prawn low dissolved oxygen resistance family selection method, and belongs to the technical field of prawn stress-resistance trait selection. The method comprises the steps of base population establishing; F1 generation family establishing; same pool culturing; low dissolved oxygen resistance testing; F2 generation family establishing; continuous generation selecting, wherein different sources of parent prawns are selected to establish a full / half-slib family through directional mating, common environmental breeding is performed, 94 h low dissolved oxygen stress is performed, parent selecting and remaining are performed according to the low dissolved oxygen resistance test result and the growth measure result, after four generations of continuous selection, the family of distant genetic relationship is selected from the families with excellent growth performance and strong low dissolved oxygen resistance performance, the male and female prawns which are big in individual, strong in vigor and normal in gonad development are selected to serve as parent to breed as good varieties. According to the method, the problem occurring in prawn high-density culturing that the prawns are dead caused by the fact that the prawn growth is influenced by low dissolved oxygen is solved, and the development of the prawn high-density culture industry is greatly promoted.
Owner:广东海威农业集团有限公司
NSGA-II algorithm-based multi-objective optimization method for mechanical arm in redundant space
ActiveCN105676636AIncrease load carrying capacityGuaranteed positioning accuracyAdaptive controlRedundant codeAngular velocity
The embodiment of the present invention provides an NSGA-II algorithm-based multi-objective optimization method for a mechanical arm in a redundant space. The method comprises the steps of converting the point-to-point transfer task of the mechanical arm in the operating space from a Cartesian space into a joint space, conducting the parameterized treatment on joint variables based on the sine seven-times polynomial interpolation method, adopting an obtained parameter sequence code as an individual in an NSGA-II algorithm-based population, figuring out an optimized solution for the motion trajectory of the mechanical arm based on the NSGA-II algorithm to enable the sum of the average values of all joint torques to be minimum, the torque of a largest joint to be minimum and the maximum angular velocity of joints to be minimum, and selecting a most optimal solution out of an obtained pareto non-dominated solution set. Based on the above method, the sum of the average values of all joint torques, the torque of the largest joint and the maximum angular velocity of joints are optimized according to the described motion trajectory. According to the technical scheme of the invention, when the point-to-point transfer task is executed in the operating space with the constraint conditions of the task to be met, multiple objects of the mechanical arm can be optimized at the same time according to the above described planning path.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
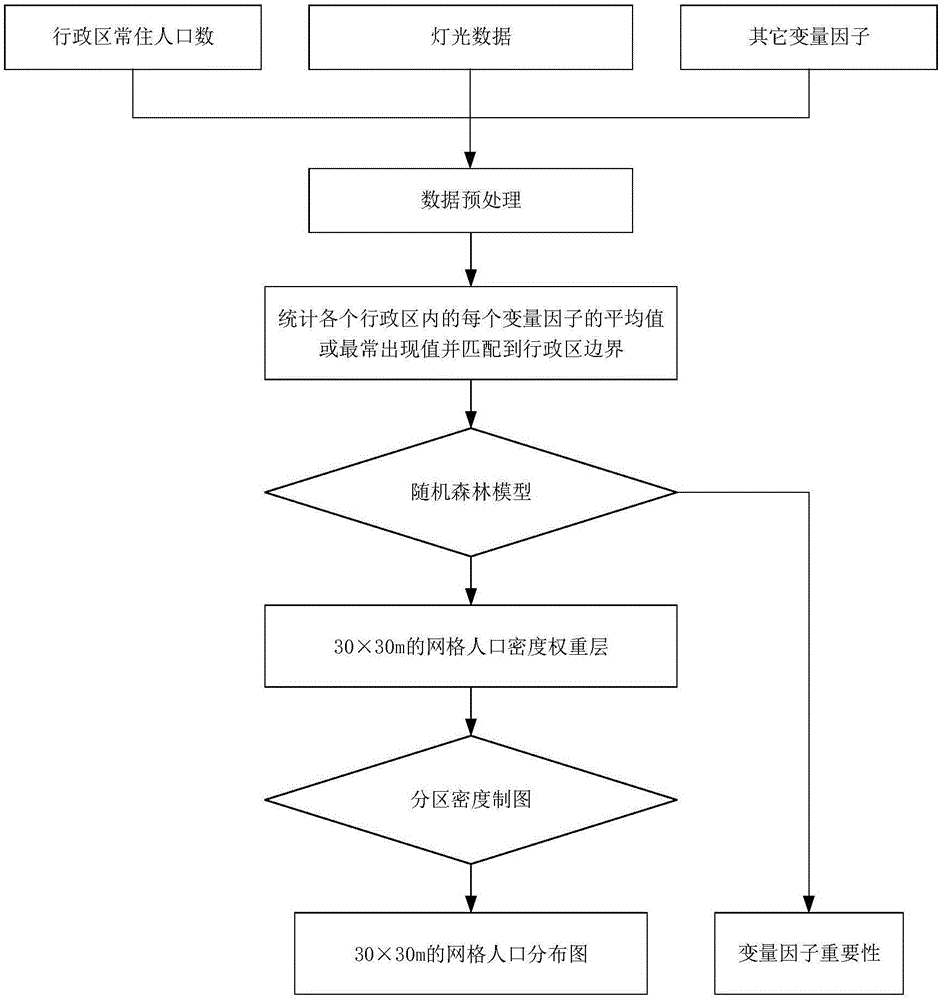
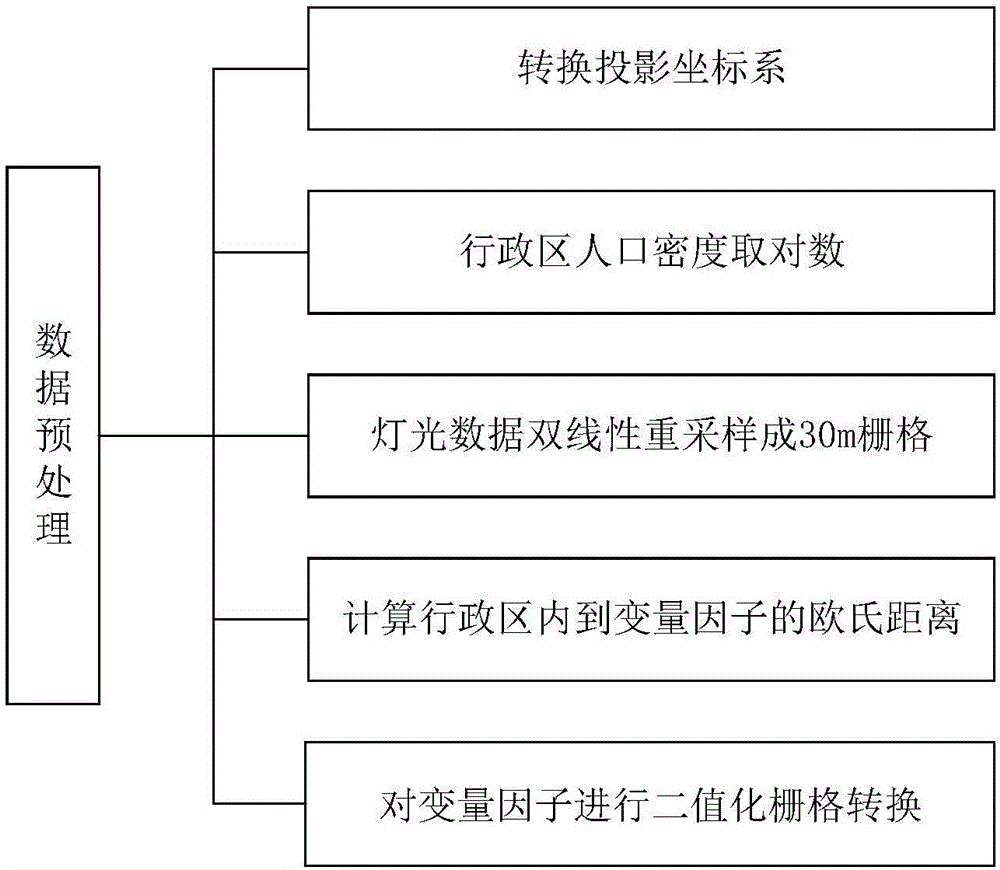
Random forest model-based population data spatialization method
InactiveCN106650618AImplementing Population Distribution EstimationCharacter and pattern recognitionHuman population distributionBase population
The invention discloses a random forest model-based population data spatialization method. According to the method, population distribution-related variable factors such as surface coverage data and lamp light data are selected; the population distribution-related variable factors are pre-processed, and the pre-processed population distribution-related variable factors are inputted into a random forest model; the relationship between population density and the variable factors, and the importance of the variable factors are determined through using the random forest model; the population density of each grid is obtained through inversion based on the relationship; and an estimation result is corrected through regional density charting, so that a gridded population distribution result can be obtained. With the method adopted, the precision of population data spatialization can be further improved, and the importance of the variable factors are interpreted.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
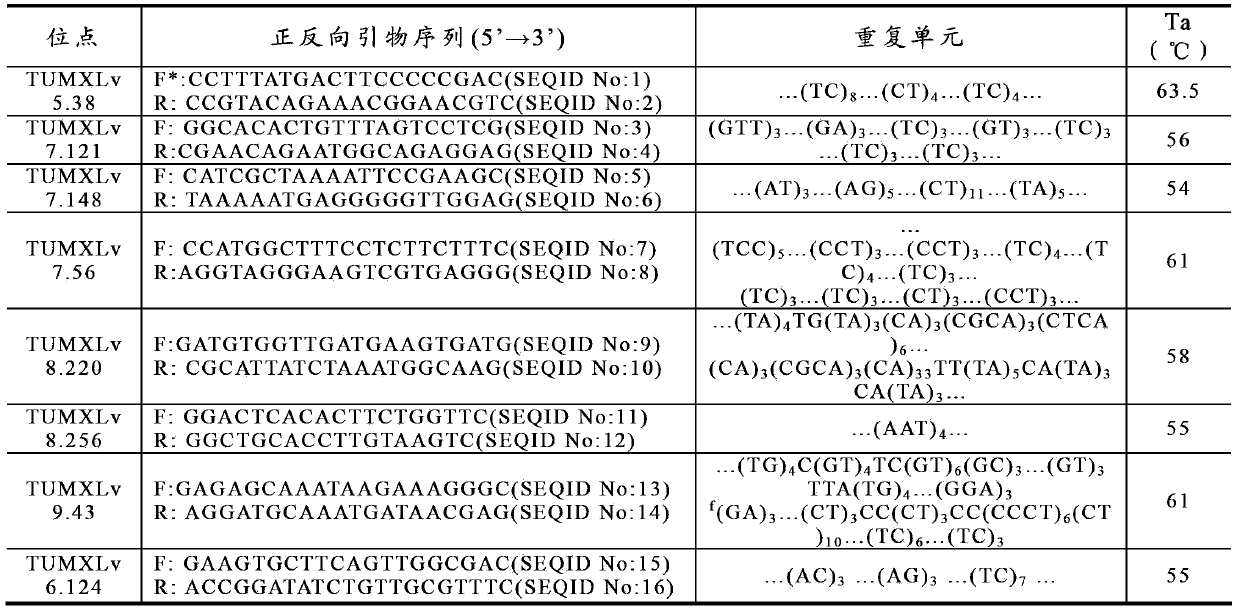
Litopenaeus vannamei base population establishing method based on genetic information and excellent properties
InactiveCN103416333AOvercoming diversityOvercome the loss of some good traitsMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationEconomic benefitsInformation design
The invention provides a Litopenaeus vannamei base population establishing method based on genetic information and excellent properties. The method comprises the following detail steps that multiple Litopenaeus vannamei populations with different excellent properties are selected, the genetic relationship among introduced individuals is analyzed by using molecular markers, a hybridization scheme is designed based on the genetic relationship information and excellent property information, and a great numbers of families are established to form a Litopenaeus vannamei base population with relative abundant heritable variation and excellent properties. According to the method, in the establishing process of the Litopenaeus vannamei base population, the molecular markers are used for detecting the genetic relationship among different individuals and designing the hybridization scheme, inbreeding can be avoided, genetic linkages can be broken through, sufficient recombination and orientated mating can be acquired, continuity and scientificity of breeding work are guaranteed, thus the acquisition of Litopenaeus vannamei base populations with the relative abundant heritable variation and excellent properties can be facilitated, therefore, genetic improvement and production performance improvement can be further carried out on the later generations of the Litopenaeus vannamei to a large extent, and better economic benefit is brought.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
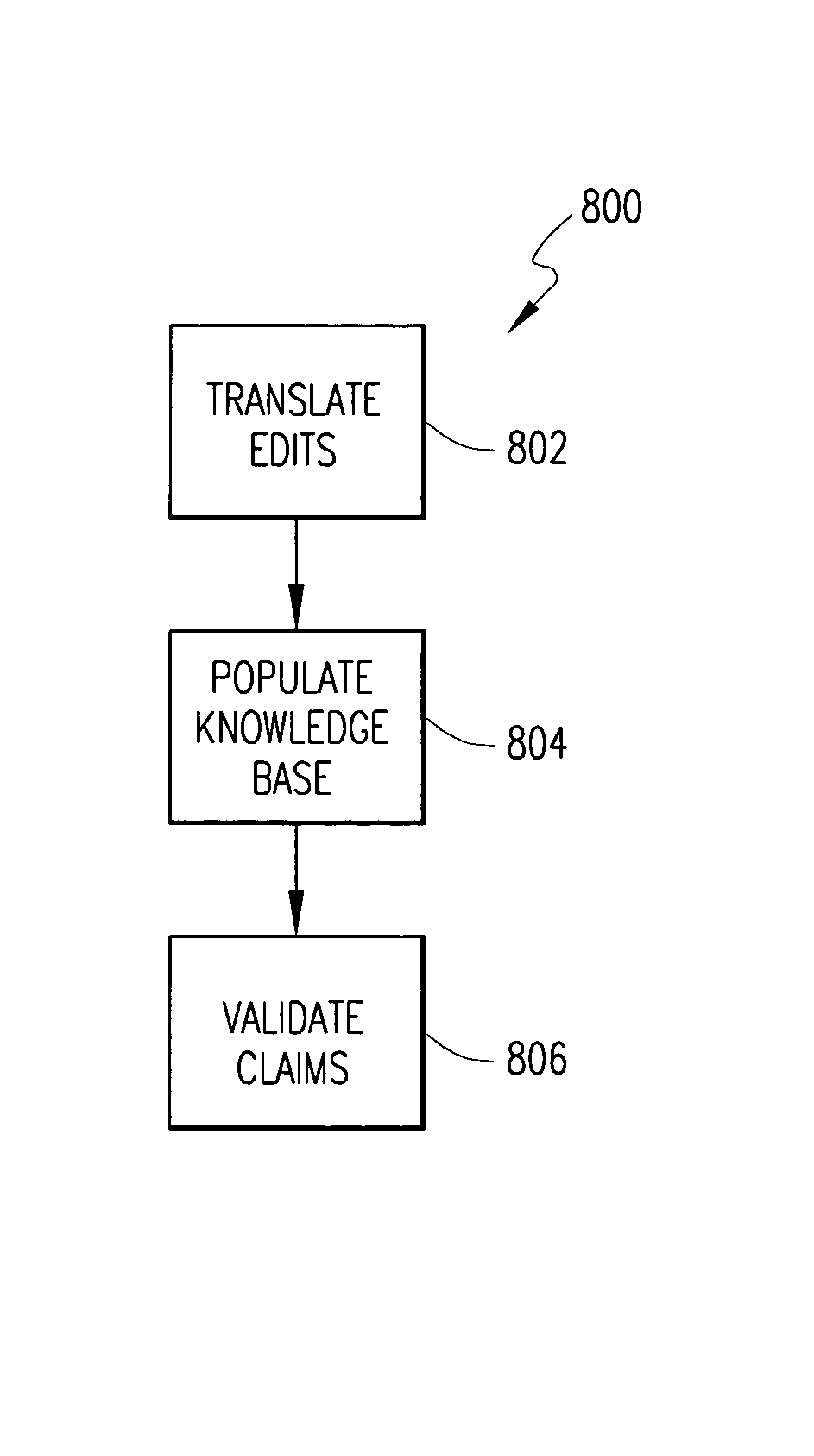
Method of and system for rules-based population of a knowledge base used for medical claims processing
A method of populating a knowledge base used in validating medical claims includes filtering a translated edit via at least one rule to determine a match between a syntax of the translated edit and a syntax of the rule. A method call is executed responsive to the filtering step resulting in at least one match being determined. The knowledge base is populated responsive to the executing step.
Owner:PEROT SYSTEMS
Breed conservation, screening and breed production method in tilapia complete set lines as well as between two lines of complete sets
ActiveCN102630617ALower conditionsEasy to operateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaTilapiaBase population
The invention relates to a breed conservation, screening and breed production method in tilapia complete set lines, comprising the following steps of: construction of complete set line base populations rich in hereditary variation, establishment of operation procedures of family production and management in the complete set lines, marking of individuals in the complete set lines, genetic evaluation analysis of important production traits and establishment of individual mating selection programs in the complete set lines. The invention also provides a hybrid breed production method between twolines of complete sets, which is established by utilizing the method. The method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of high pertinence, high selection breeding efficiency, capability of effectively preventing parent inbreeding depression of the complete set lines and the like; the harvest weight of the hybrid fine breed of tilapia is averagely increased by more than 30% than that of control groups; and the culture survival rate is also obviously higher than that of the control groups. According to the invention, a new technical approach is developed for cultivation of fish fine breeds; particularly a new selection breeding method is applied in the breed conservation, the screening and the breed production of the complete set lines in fish hybrid breeding; and the method isalso suitable for being popularized and applied in all cultured fishes and has broad popularization and application prospects.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Method for building pedigree of marsupenaeus japonicus and breeding
InactiveCN102405883ASimple designClarify blood relationshipClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaHybrid systemF1 generation
A method for building pedigree of marsupenaeus japonicus and breeding relates to the breeding of the penacus orientalis. The method comprises the following steps: building the base population; building the F1 generation pedigree; cultivating in a same pond; building the F2 generation close cousins pedigree; after growing to 3 cm, cultivating in the same pond, and selecting the breeding parents while reaching the specification of goods to generally build 8-16 close cousins pedigrees, wherein each close cousins pedigree retains 5-8 fullsibs family, the total number of the breeding pedigrees is 60-80, and the breeding parents in each pedigree are continuously bred to mature parents; and adopting a continuous multi-generation hybrid system to continuously build the close cousins pedigree of the next generation until to reach the breeding target and form the new fast growing variety. The invention is a method for building close cousins pedigree of marsupenaeus japonicus and breeding, especially can be applied to the inheritance breeding of the marsupenaeus japonicus, and has important significance for the breeding design of the marine animals which are not suitable for the fine breeding mode.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
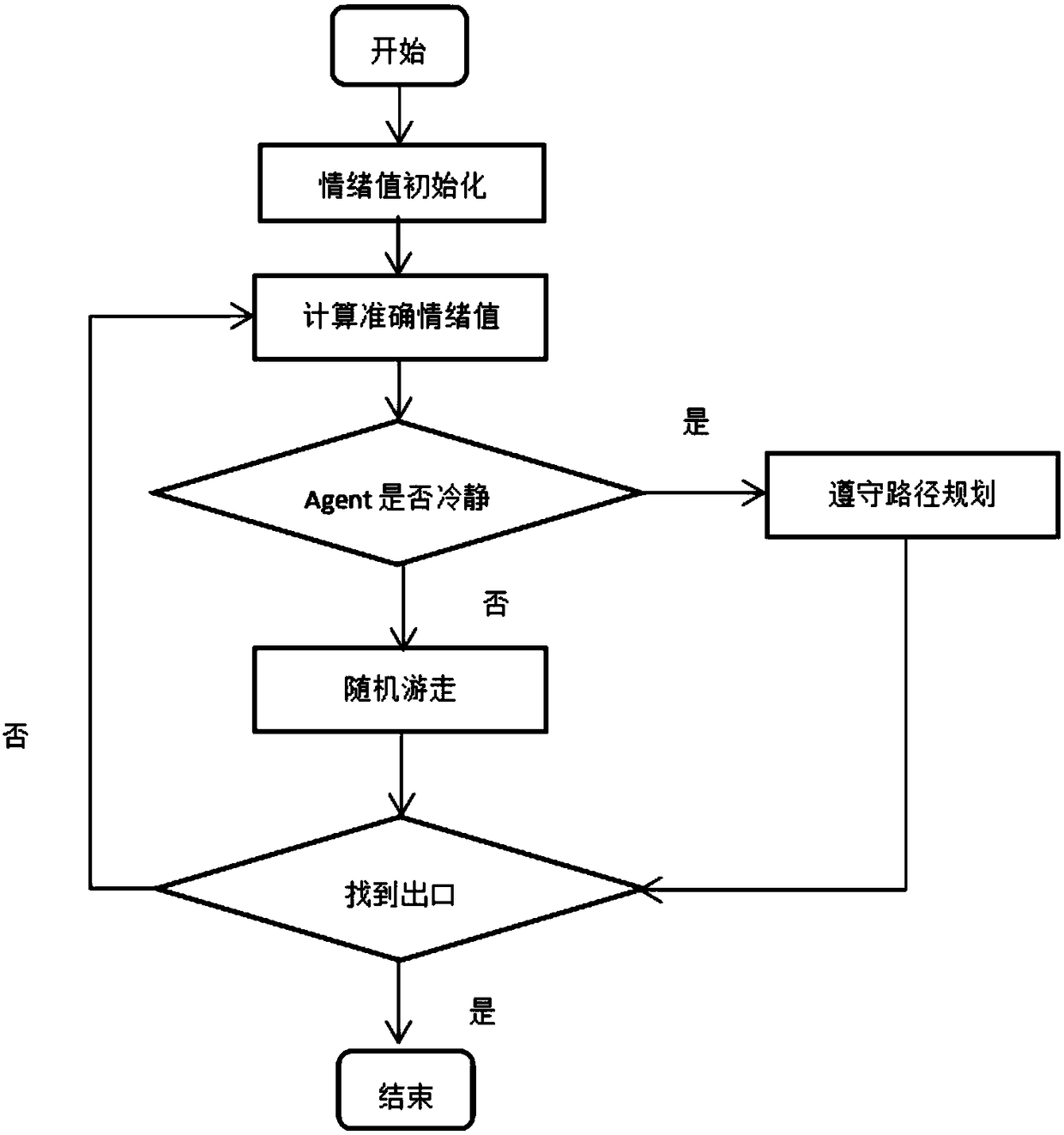
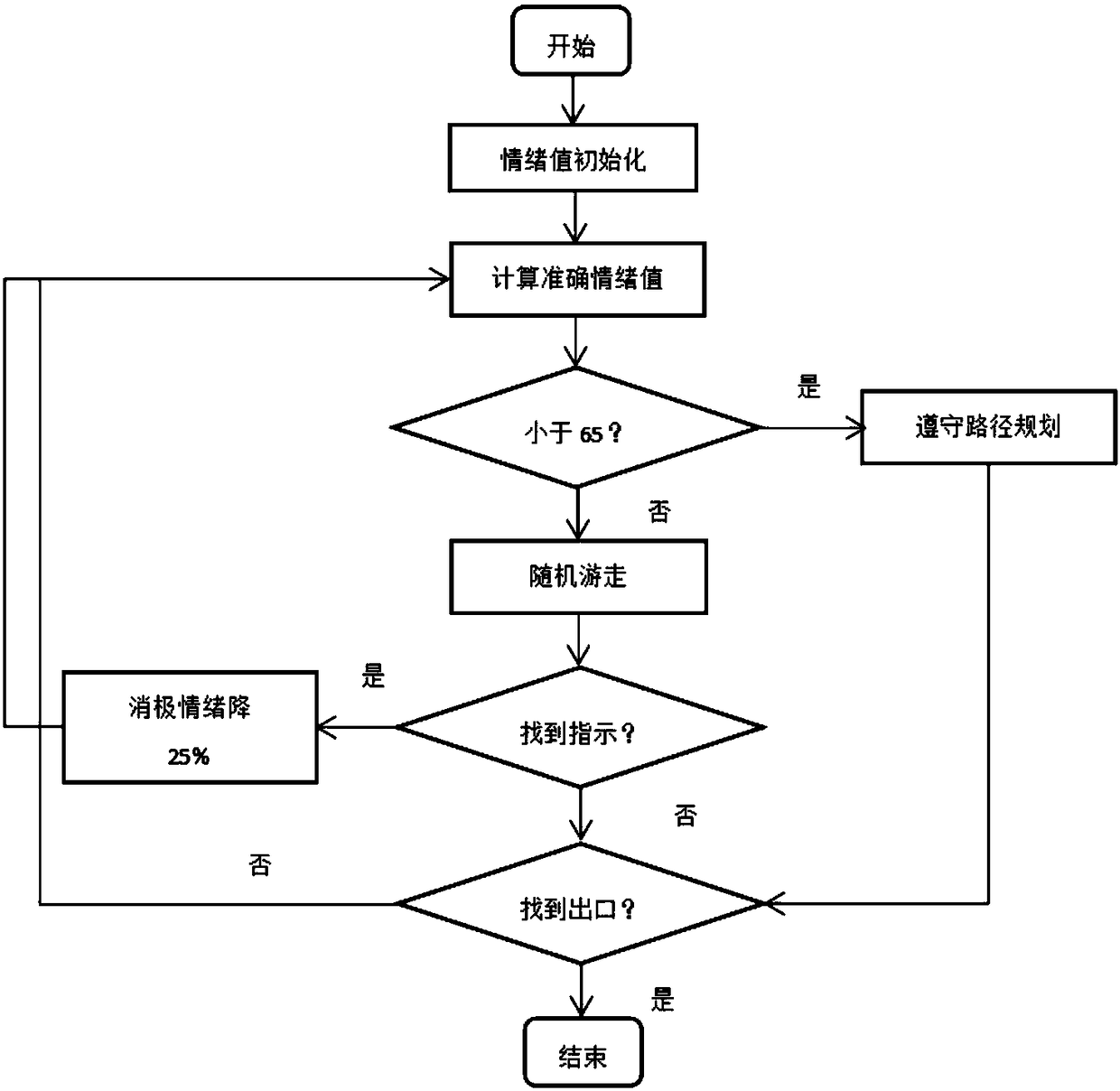
Multi-agent based population evacuation simulation model
InactiveCN108153945AReduce negative emotionsData processing applicationsDesign optimisation/simulationUnexpected eventsBase population
Provided is a multi-agent based population evacuation simulation model. The model includes a behavioral layer model, an emotion layer model and a guidance model; an emotion layer update mechanism anda behavior layer update mechanism are designed based on an X state machine idea, an emotion X state machine is refined, and the guidance model is added; the guidance model has an impact on emotions ofpedestrians, reduces the negative emotions of the pedestrians, helps the pedestrians find outlets, and updates the emotional layer update mechanism while updating emotions; a mechanism that the emotions react on behaviors is proposed, interactions between 'environment-emotions-behavior' are established, data output is calculated in the behavior layer and passed to the emotion layer, and feedbackgenerated by the emotions acts on the behavior layer. By applying the population evacuation simulation model to real life, the model solves the problem that the evacuation of population can be quicklyimplemented if an emergency occurs.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
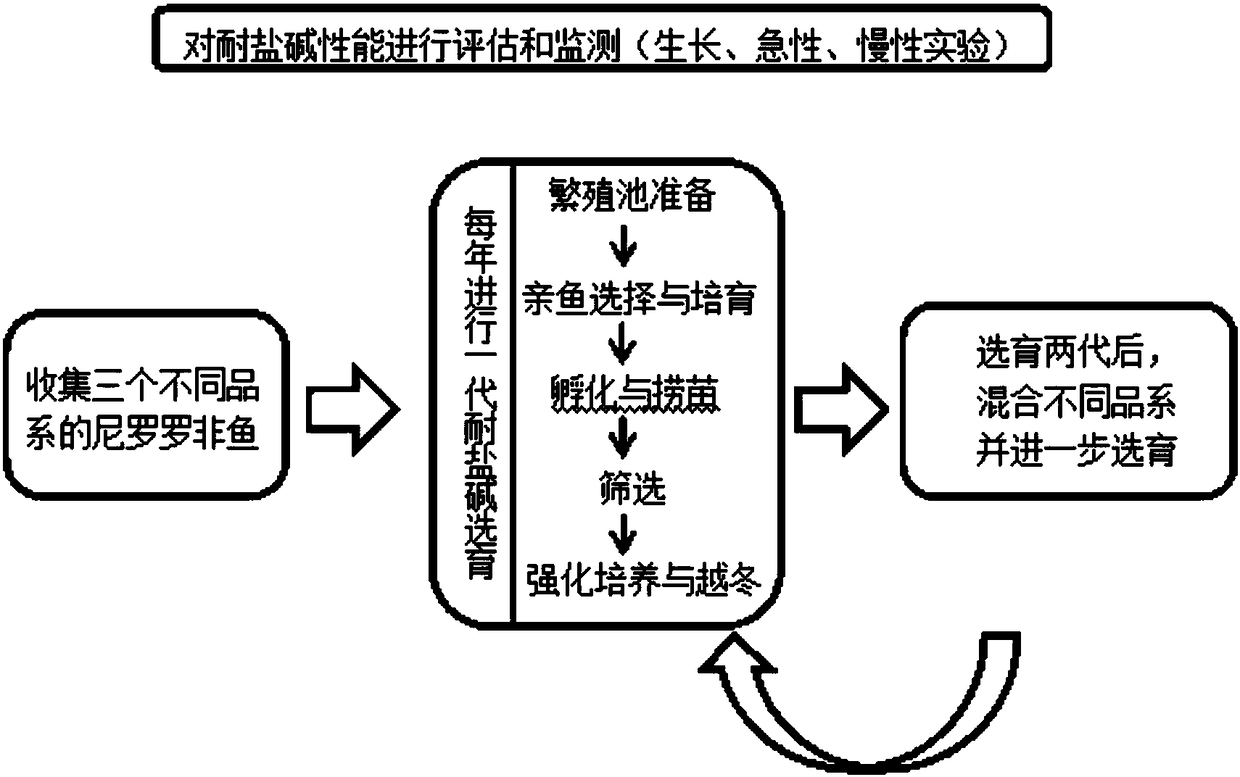
Method for selectively breeding excellent strains of saline-alkaline tolerant tilapia
ActiveCN108207712AImprove salt and alkali resistanceSalt-alkali tolerance gene pool is goodClimate change adaptationAgricultural fishingNile tilapiaBase population
The invention discloses a method for selectively breeding excellent strains of saline-alkaline tolerant tilapia. The method includes steps of collecting at least three different strains of Nile tilapia to be used as selective breeding base population and evaluating the saline-alkaline tolerance; carrying out one-generation saline-alkaline tolerant selective breeding on the different strains of Nile tilapia in every year and continuously selectively breeding at least two generations; mixing the different strains of saline-alkaline tolerant Nile tilapia with obvious growth superiority with one another after saline-alkaline tolerant selective breeding is carried out on the different strains of saline-alkaline tolerant Nile tilapia, then carrying out saline-alkaline tolerant selective breedingon the different strains of saline-alkaline tolerant Nile tilapia and continuously selectively breeding at least four generations to obtain the saline-alkaline tolerant Nile tilapia of the excellentstrains. Saline-alkaline tolerant selective breeding procedures include reproduction pond preparing, parent tilapia selecting and rearing, fry hatching and fishing, screening and intensified culture and overwintering. The method has the advantages that the method is high in reliability, operability and efficiency; novel technical ways can be developed for selectively breeding stress-resistant varieties of fish, and the method has important significance and application value in popularization of rearing of stress-resistant improved varieties of cultured fish.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Replica-exchanged-based population conformation space optimization method
ActiveCN104866733AIncrease diversityReduce complexitySpecial data processing applicationsStable stateAlgorithm
A replica-exchange-based population conformation space optimization method comprises the following steps: at first, performing random folding and transforming on an inquiry sequence on each temperature layer to generate an initial population; during population regeneration, taking Rosetta Score3 as an optimized objective function, sequentially taking each individual in the population as a targeted individual in each temperature layer, then randomly selecting two individuals different from the targeted individual for mutation operation and crossover operation to generate a variation individual, after that, randomly selecting one segment of another individual to exchange with the variation individual so as to generate a test individual, performing energy value comparison on the test individual and the targeted individual, judging whether the test individual is received or not according to the energy value, after population regeneration, carrying out replica-exchange on the population individuals between every two adjacent temperature layers to increase the diversity of the population, and through continuous population regeneration and replica-exchange, obtaining a series of semi-stable-state conformations. The conformation space optimization method provided by the invention is relatively high in prediction accuracy and relatively low in complexity.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for selective breeding of fast-growing strain of lined seahorse
InactiveUS20170105392A1Quality improvementHigh yieldClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaVitalityBase population
An method for selective breeding of a fast-growing strain of lined seahorse, including: (1) selecting high-quality lined seahorse parents as a base population for selective breeding; (2) performing prenatal intensified breeding; (3) performing pairing and mating, and rearing the juveniles thereof; (4) performing selective breeding in three junctures with different selection proportions; (5) pairing the saved adult lined seahorses, wherein those with low vitality, having injuries on the body surface, or having a dysplastic brood pouch or gonad are culled, and a selection proportion of 10% for every generation is maintained thereafter; (6) repeating steps (2) through (5) for at least four times to obtain a high-quality strain of lined seahorse with improved weight and body length and stable growth. The method can be used for selective breeding of a new strain with high quality and high yield.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
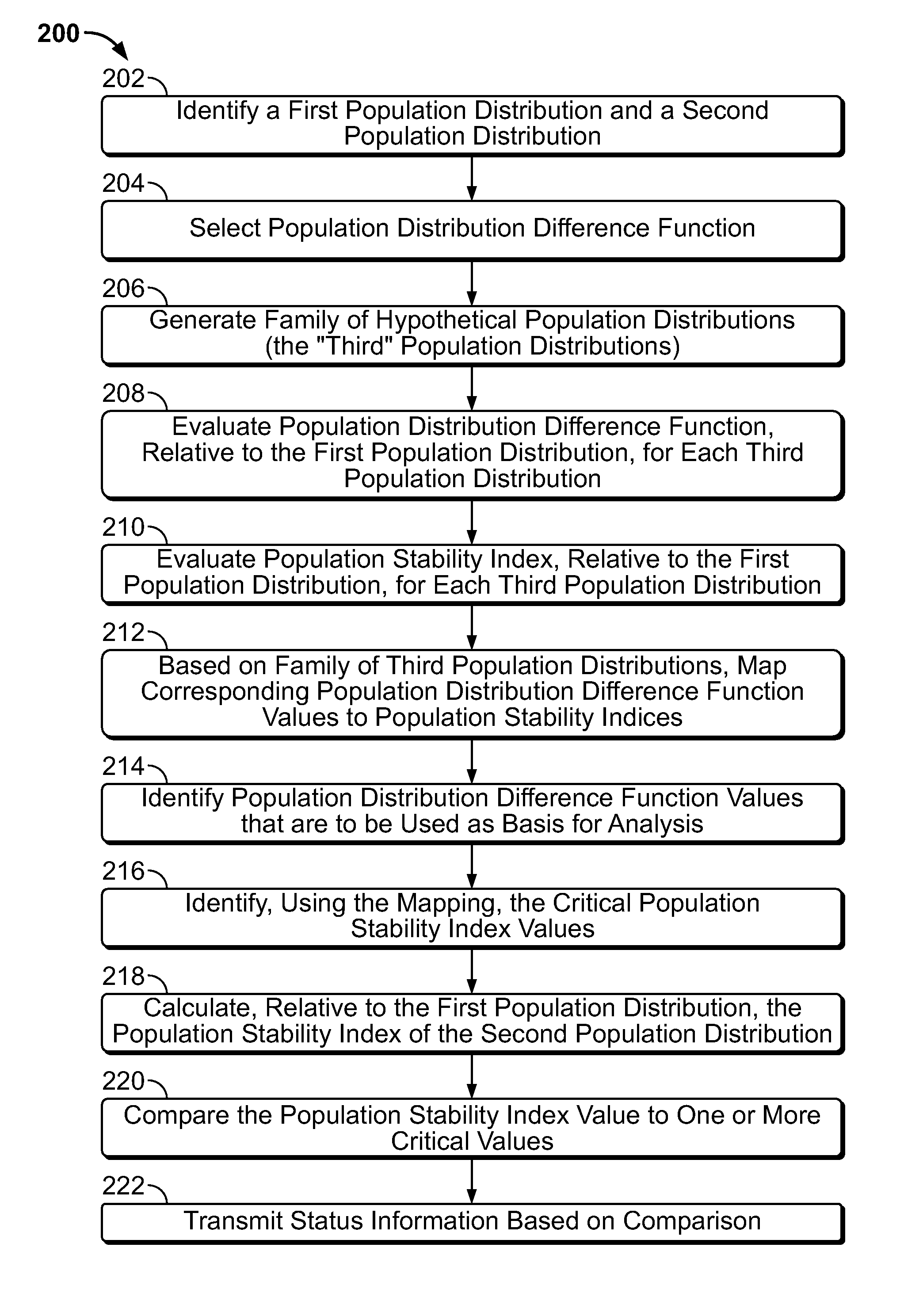
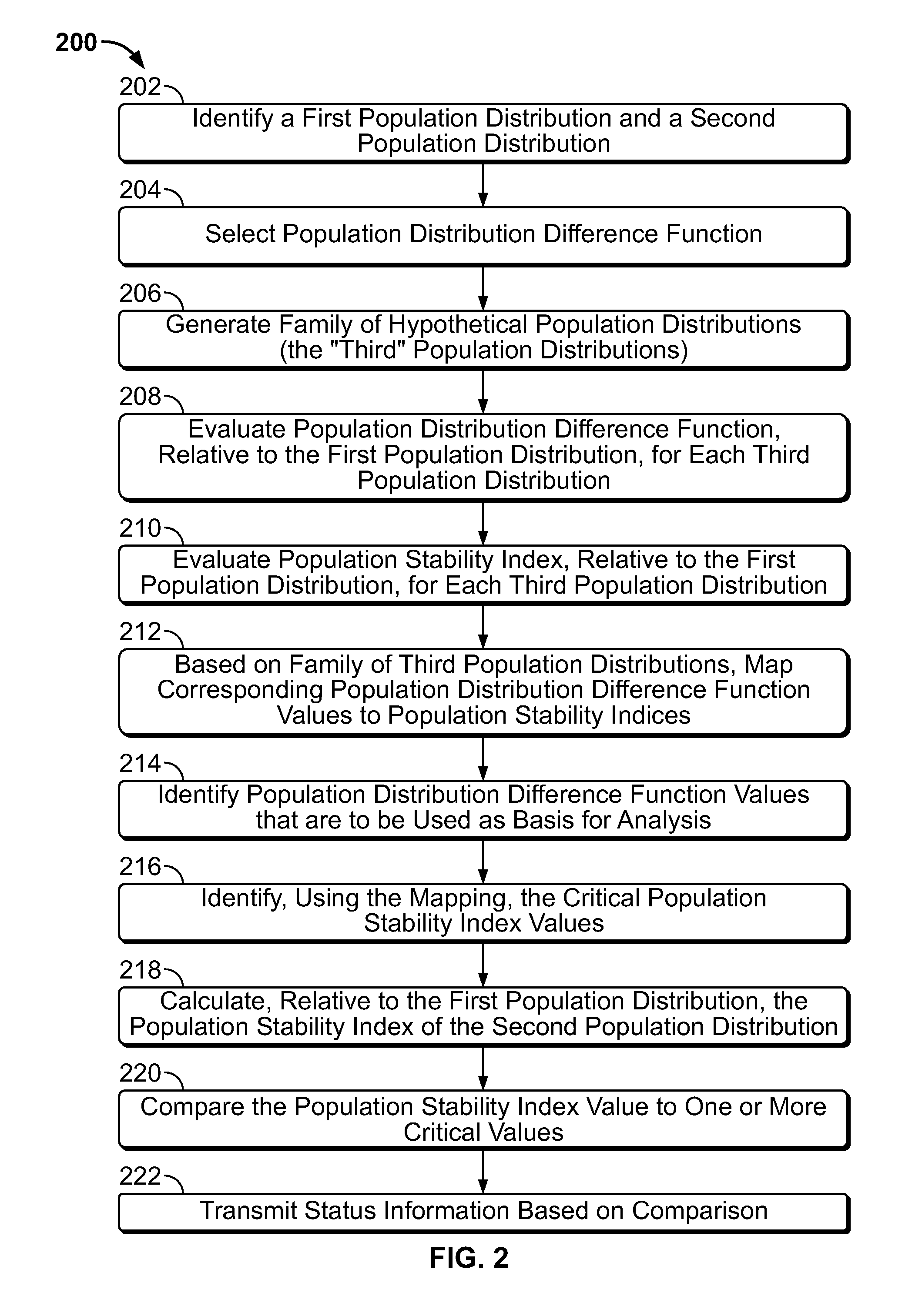
Machine-based population stability index selection
Apparatus and methods for quantifying a difference between a first population distribution data set and a second population distribution data set. The apparatus and methods may use randomly generated population distribution differences to generate a mapping of a population stability index to a population distribution difference function. The population distribution difference function may be more responsive to some differences between the first and second population distribution data sets than is the population stability index. The population distribution difference function thus may be used to identify differences between population distribution data sets. The differences may then be mapped to a corresponding population stability index. The population stability index may then be used to quantify a difference between the first and second data sets.
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA CORP
Breeding method for excellent new strain of stichopus japonicus
InactiveCN102687694AStable and heritableStable and heritable excellent traitsClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaDiseaseStichopus
The invention discloses a breeding method for new strain of stichopus japonicus, comprising the following steps of: 1) selecting excellent individuals in a wild stichopus japonicus population as parents, breeding at random, and selecting and remaining at high selection intensity, thereby establishing a base population; 2) carrying out blocked breeding to obtain single-character selected first filial generation, and continuing to select and remain at high selection pressure, and selecting stichopus japonicus individuals having excellent characters as parents for next generation; and 3) carrying out continuous progeny selection of the single-character population, and then carrying out a plurality of generations until the stichopus japonicus selected new strain having heritable excellent characters is obtained. The breeding method for excellent new strain of stichopus japonicus is high in strain selection teleonomy and most effective for quality characters; the scale of subculture blocked breeding of the population is large, the efficiency is high, the level of genetic polymorphism is kept well, the growth advantage and the volume increase effects are obvious, and the growth speed of stichopus japonicus is increased; and the obtained stichopus japonicus individuals are less in difference and have high stress resistance and disease resisting ability, and thereby having excellent economic benefit and wide breeding prospect.
Owner:AQUATIC PROD RES INST SHANDONG PROV
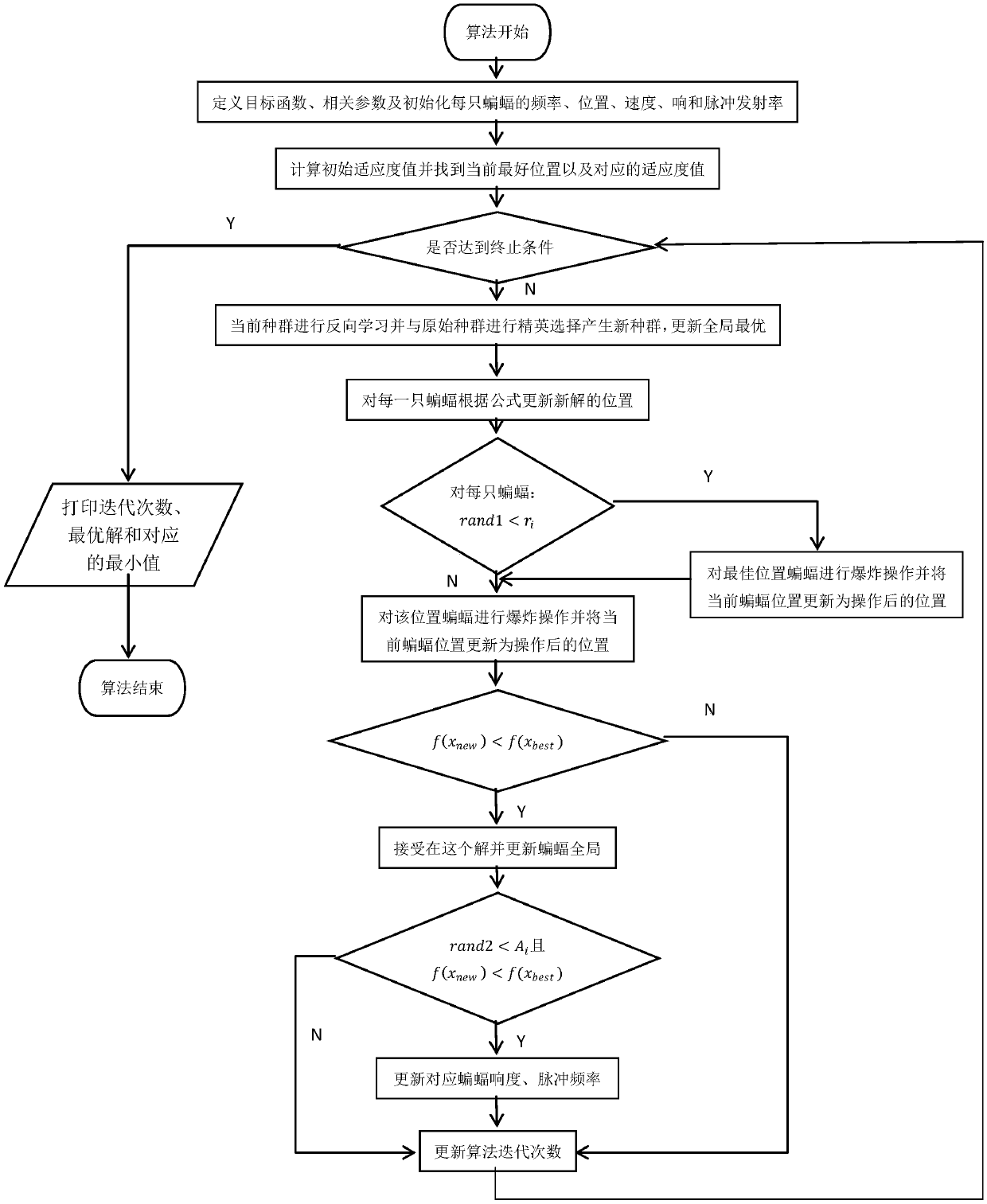
Single target optimization problem method integrating explosion strategy, opposition-based learning and bat algorithm and system
PendingCN108694438AImprove local exploration capabilitiesIncrease diversityArtificial lifeNeural learning methodsLocal optimumMicrochiroptera
The invention relates to a bat algorithm and a system, belonging to the field of data processing, and particularly relates to a single target optimization problem method integrating explosion strategy, opposition-based learning and bat algorithm and a system. In the optimization process, the opposition-based population of each bat in the bat algorithm is obtained by opposition-based learning, andthe elite selection is performed on the two populations, thus the diversity of the population is increased, and the global search ability is improved, the local optimal solution is avoided, the explosion strategy is added during the flight process, thus the local exploration ability of the algorithm is improved, and the optimal solution is more accurately searched. Through the simulation test of 12 typical test functions and knapsack problems, it is proved that DGOBA has higher efficiency for solving continuous and discrete optimization problems.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Big data intelligent marketing system and marketing method
InactiveCN108846700ALike to learn moreGood marketing effectMarket data gatheringBase populationData science
The invention discloses a big data intelligent marketing system and a marketing method, and the marketing steps are as follows: step 1, establishing a marketing platform; step 2, increasing the numberof consumers; step 3, guaranteeing stickiness of the consumers to the platform; step 4, analyzing platform consumer big data. According to the big data intelligent marketing system and the marketingmethod provided by the invention, through the age of big data, a marketing person can customize operation for each consumer according to hobbies and degree of accepting services of the consumers. Withsuch big data, an enterprise not only can determine basic population characteristics of target populations, but also can gain insight into the hobbies of the consumers.
Owner:山东外贸职业学院
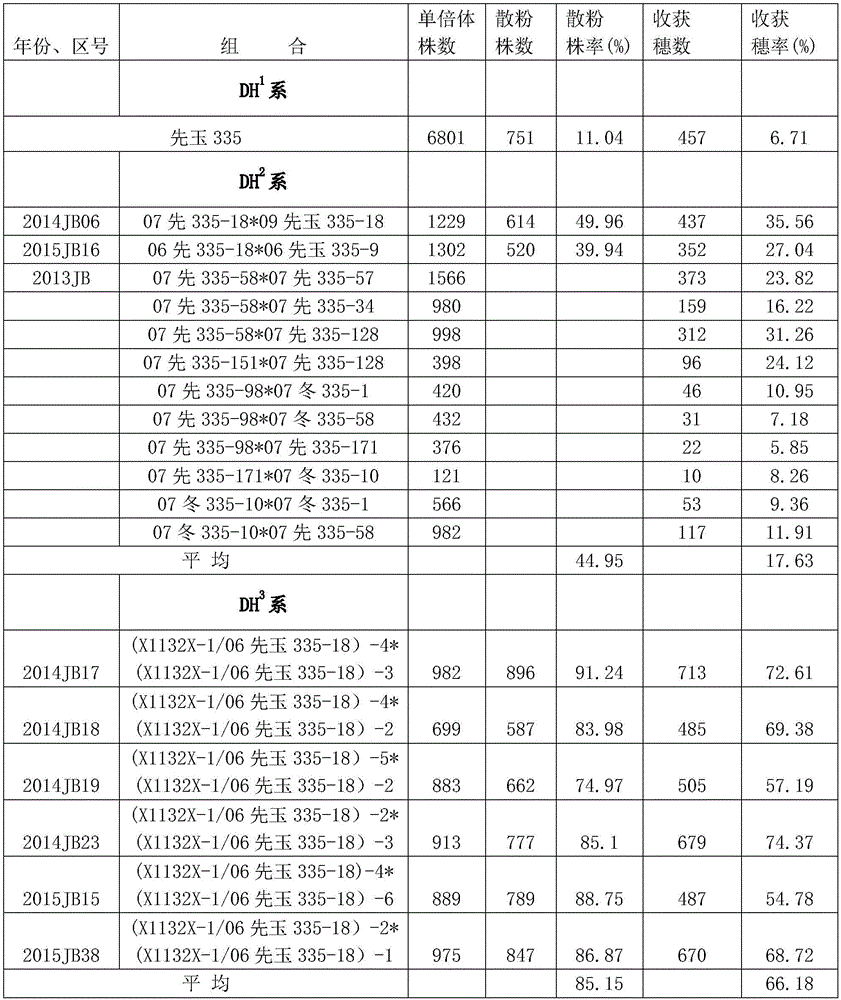
Breeding method for repairing and improving natural doubling rate of maize haploid male flower by utilizing recurrent selection
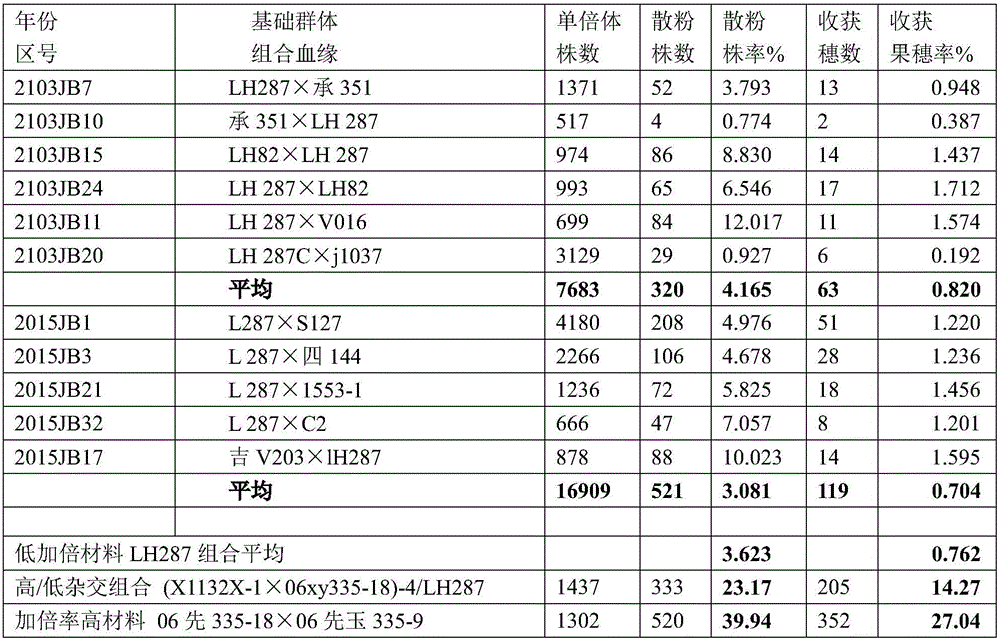
ActiveCN105918107AIncreased natural doubling rateHigh combination abilityAgriculturePlant genotype modificationBase populationRecurrent selection
The invention discloses a breeding method for repairing and improving a natural doubling rate of maize haploid male flower by utilizing recurrent selection, belonging to the field of maize breeding methods. The breeding method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: constructing an excellent base population, then generating a haploid by utilizing an inducing line, and carrying out doubling so as to obtain a double haploid (DH) line; and selecting a double haploid (DH) line hybridization group with complementary characters and strong pollinating ability so as to form a new round of a population, and carrying out recurrent selection so as to continuously improve the natural doubling rate of the haploid male flower. The method provided by the invention can significantly improve the natural doubling rate of the maize haploid male flower, wherein the natural doubling rate of the fourth round can maximally reach to 90% or above; moreover, the method provided by the invention overcomes the technical bottleneck of haploid breeding, and can increase the breeding efficiency of the double haploid (DH) line by a hundred times or above compared with the prior art; the method provided by the invention also has the advantages of no toxicity, rapidness, high efficiency, environmental protection, etc., and completely gets rid of a conventional highly-toxic, complicated and inefficient artificial doubling method; in addition, the excellent double haploid (DH) line selected from every round in the method provided by the invention can directly enter a commercial breeding procedure.
Owner:JILIN ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
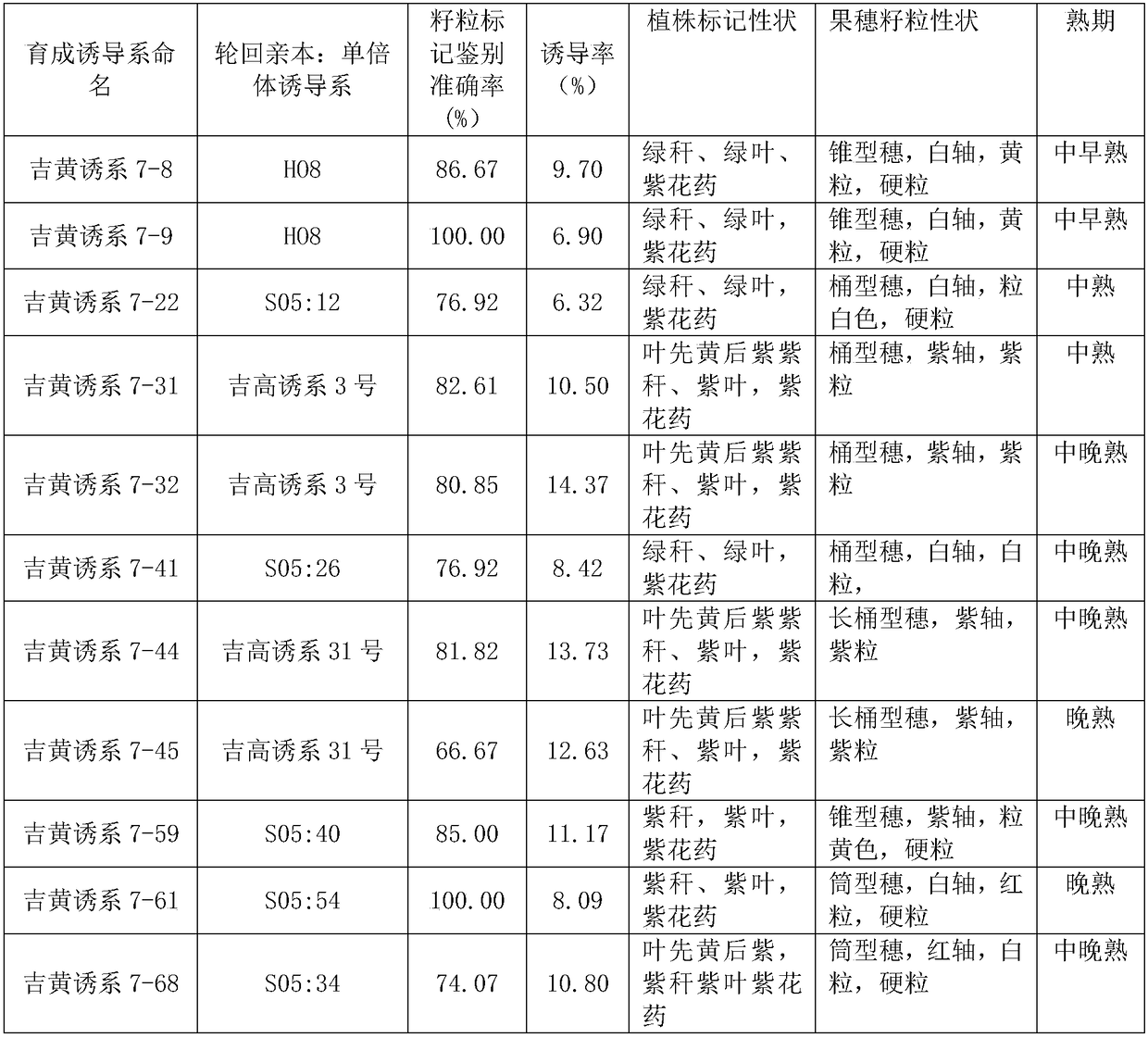
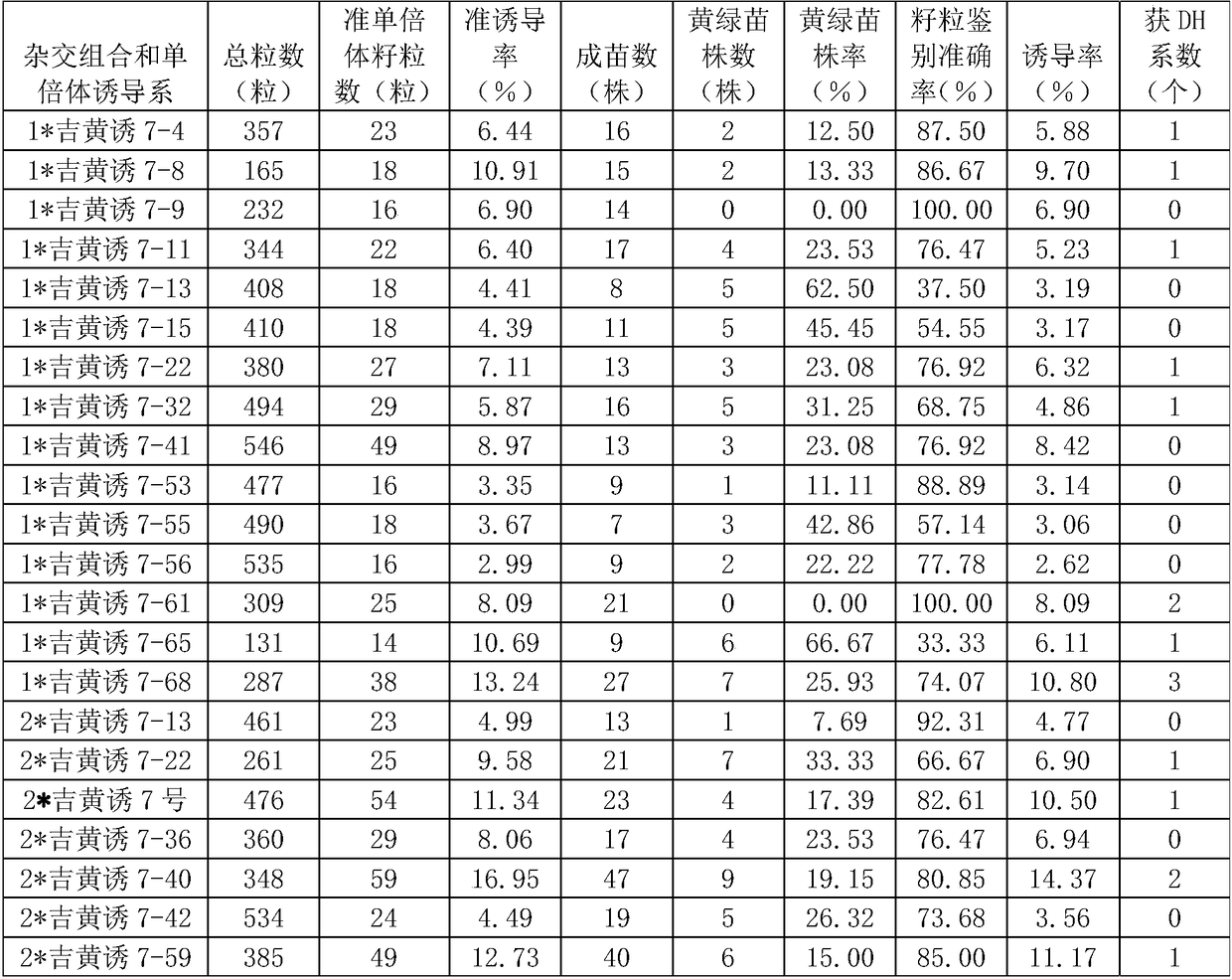
Breeding method for corn hybridization induced haploids by utilizing yellow-green seedling marker assisted selection
ActiveCN108377899AGenetically simpleStable traitsPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceBase population
The invention discloses a breeding method for corn hybridization induced haploids by utilizing yellow-green seedling marker assisted selection and belongs to the field of breeding methods. The breeding method comprises the following steps: pollinating a base population by utilizing an induction line with a yellow-green seedling marker, such as Jihuangyou No. 7; harvesting clusters; carrying out identification and screening on induced haploids at a seedling period according to leaf colors; weeding out hybrid diploid plants with seedling leaves which have a yellow-green color and keeping haploidplants with a green leaf color or early-period doubled haploid plants; carrying out selfing at a flowering period to obtain a new selfing line. According to the method disclosed by the invention, theused yellow-green seedling marker is controlled by a mono-dominant gene; compared with a grain marker and an adult-plant marker, the yellow-green seedling marker has the advantages of simple heredity, obvious distinctive features and accurate and reliable identification result, and special experience and technology are not needed; manpower and material resources are greatly reduced in an identification process at a seedling stage; the breeding method is suitable for carrying out large-scale induced haploid breeding and has high breeding efficiency; especially, the breeding method can be usedfor accurately identifying early-period doubled haploids and one-step line formation is realized.
Owner:JILIN ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
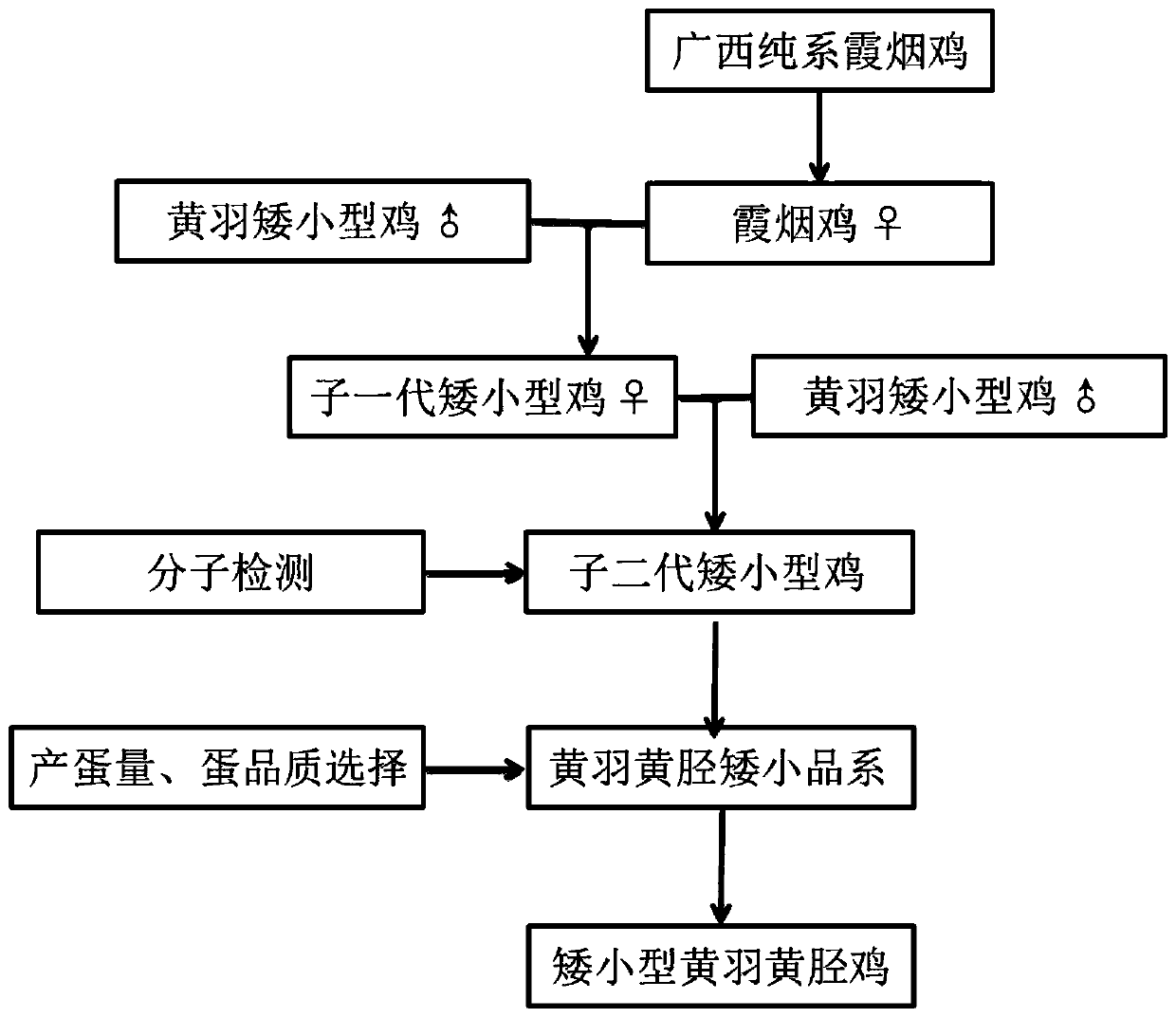
Breeding method for dwarf yellow-feather and yellow-shank chickens
ActiveCN109997788AIncrease egg productionIncrease profitMicrobiological testing/measurementAnimal husbandryGallus gallus gallusBroiler chick
The invention discloses a breeding method for dwarf yellow-feather and yellow-shank chickens, and belongs to the technical field of poultry breeding. The breeding method includes the following steps:step 1, establishing a pure line breeding base population; step 2, introducing dw genes into Xiayan chickens; step 3, establishing a dwarf yellow-feather and yellow-shank strain; step 4, breeding thechickens based on egg laying characters. The breeding method has the advantages that a modern genetic breeding method is applied, the local variety of Guangxi, the Xiayan chickens, is used as a basicmaterial, the dw genes are introduced, and accordingly, the local chicken strain combining the shape and flavor of local chickens with egg production and the taste of egg products, namely the dwarf yellow-feather and yellow-shank chickens, is bred; the risks brought by production and market fluctuations of strains and broilers can be handled, and high-quality materials are provided for breeding ofenterprises.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY
Breeding method of purple apostichopus japonicus
ActiveCN105613383AStrong selection purposeImprove efficiencyPisciculture and aquariaF1 generationPhenotypic trait
The invention provides a breeding method of purple apostichopus japonicus. The breeding method is characterized by collecting purely wild apostichopus japonicus individuals of which the back part and the abdomen part are totally purple, and transplanting the apostichopus japonicus individuals into a breeding pond for carrying out independent separation, temporary rearing and preserving; screening breeding base populations in the middle of May, and carrying out artificial spawning, hatching and breeding; when 30 percent of planktonic larvae develop to be doliolaria, feeding an adhering substrate, changing water and feeding fodder; recording the body color and the growth and development situation of the doliolaria at a fixed period, and screening and weeding out weak individuals; performing an overall breeding process in a purple environment, and strengthening the coloring of young purple apostichopus japonicus by feeding the fodder containing purple natural pigment components in an assisting manner; respectively carrying out selfing on bred F1-generation purple apostichopus japonicus and hybridization on the bred F1-generation purple apostichopus japonicus and preserved base populations, thus forming F2 filial generations, wherein a breeding technology and breeding conditions of the F2 filial generations are the same as those of F1 generations; carrying out three times of high-strength standard breeding, thus obtaining F3-generation new varieties of the purple apostichopus japonicus, wherein the selection and reservation rate is 90 percent or more, and no significant difference of the growing speed and the anti-capability is generated between the F3-generation new varieties of the purple apostichopus japonicus and original apostichopus japonicus.
Owner:MARINE BIOLOGY INST OF SHANDONG PROVINCE
Msl male sterile recurrent population of EPSPS gene transgenetic soybean and construction method thereof
InactiveCN104472367AEliminate multiple combinations of artificial hybridizationSave workAngiosperms/flowering plantsGlyphosateTransgenesis
The invention discloses an EPSPS gene transgenetic msl soybean population and its construction method. According to the invention, Shuang-Jin Zhao improved soybean msl male sterile recurrent base population is introduced; conventional PCR molecular biology analysis and field phenotypic identification are carried out while transgenic materials containing a herbicide-resistant gene EPSPS are determined; seeds from different varieties of EPSPS transgenetic gene materials are mixed according to the ratio of 1:1; after the mixed transgenetic seeds and seeds of the soybean msl male sterile recurrent base population are mixed according to the ratio of 1:1, the mixed seeds are planted in the field; when the soybean is ripened, seeds from sterile plants in the population are harvested; In the next year, the seeds from sterile plants are planted in the field and are sprayed with glyphosate to screen resistant strains; and during maturation, the resistant strains are mixed and harvested so as to preliminarily construct the population. According to the invention, wide hereditary basis of the msl male sterile recurrent base population and herbicide resistant characteristics of the transgenic materials are combined, and through natural crossing, multiple excellent genes can be polymerized and new multi-resistant high-quality soybean species can be cultivated. Work such as multiple combination of artificial crossing and genetic transformation of soybean EPSPS transgenetic genes are saved.
Owner:INST OF CEREAL & OIL CROPS HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Breeding method of pinctada martensi black-shell strain for sea pearl cultivation
ActiveCN103975883AIncrease productionIncreased survival rate during bead breeding periodClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaReciprocal crossBase population
The invention relates to a breeding method of a pinctada martensi black-shell strain for sea pearl cultivation and belongs to the technical field of pearl breeding. The breeding method includes taking two geographical populations, namely the wild population of Lingshui of Hainan and the cultured population of Leizhou of Beibuwan as the breeding base populations, selecting high-quality individualities as crossing parents from the two populations , breeding progeny by means of reciprocal cross and selfing of different geographical populations, and selecting the progeny of the combination of 'leizhou *lingshui' with remarkable growth superiority from the progeny to perform enclosed breeding of population so as to obtain a certain amount of the pinctada martensi black-shell strain with obvious feature of black shells, good economic character and stable heritability. The breeding method has the advantages of feasible principle, simple processes and low production cost, can improve the survival rate, growth rate, pearl quality and output of the pinctada martensi greatly, and accordingly can improve sustainable development of the national sea pearl cultivation field.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
Breeding method for novel polyembryony variety of mutton sheep
InactiveCN104585127AHigh reproductive rateReduce manufacturing costAnimal husbandryAnimal scienceEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a breeding method for a novel polyembryony variety of mutton sheep. The method comprises the following steps: selecting and collecting a polytocous mutton sheep base population and carrying out enclosed breeding; selecting excellent individual progeny and building another base population; carrying out enclosed breeding again, selecting excellent individuals from the enclosed-breeding progeny and building a core population; carrying out enclosed breeding of the core population and selecting excellent individuals from the enclosed-breeding progeny so as to obtain the novel polyembryony variety of mutton sheep; etc. The breeding method for the novel polyembryony variety of mutton sheep provided by the invention effectively improves the breeding rate of mutton sheep, reduces the breeding cost for ewes, enhances the economic benefits of mutton sheep breeding, is capable of reducing the breeding amount of ewes and saving grains for fodder, promotes the industrialized production of mutton sheep and accelerates the industrialization process of mutton sheep.
Owner:魏世年
Breeding method for pure white apostichopus japonicus
ActiveCN105706969AStrong selection purposeImprove efficiencyClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPlanktonBase population
The invention provides a breeding method for pure white apostichopus japonicas.The method is characterized by comprising the steps that pure wild apostichopus japonicas bodies with the white backs and abdomens are collected and transferred into an aquaculture pond for independent isolation temporary rearing and storage; breeding base populations are screened out starting from the last ten days of April, artificial spawning, incubation and breeding are performed; when 30% of plankton larvae are developed to doliolaria, a white corrugated plate frame is put in to be used as an adhering substrate; regular water changing and feed putting are performed, the apostichopus japonicas larva color and growth development situations are recorded, poor larvae are screened out and eliminated, and the overall breeding process is performed in the white culture pond on the basis of the apostichopus japonicas color changing apatetic principle; the bred generation F1 white apostichopus japonicas is used as parents to be subjected to selfing and hybridization with stored basic populations to form a filial generation F2, and the filial generation F2 and the generation F1 are the same in breeding technological process and breeding conditions.High-strength standardized breeding is performed three times, the pure white apostichopus japonicas novel line of the generation F3 is obtained, the selecting and remaining rate is 90% or above, and the growth speed and adverse resistance characters are not significantly different from those of protospecies apostichopus japonicas.
Owner:MARINE BIOLOGY INST OF SHANDONG PROVINCE
Breeding method for P-group maize inbred line Lx286
ActiveCN109197578AQuick judgment of cooperation abilityModerate maturityPlant genotype modificationDiseaseAgricultural science
The invention relates to a breeding method for a P-group maize inbred line Lx286. The method comprises the steps that a base material of an S0 generation of Y928 / C486 is constructed by taking Y928 andC486 as male and female parents in Jinan; the S0 generation is inbred in Hainan so as to obtain an S1 generation, and meanwhile, a tester C138 and the S0 generation thereof are combined so as to obtain a combination C138 / S0; according to the yield and the field performances (lodging resistance and disease resistance) of the hybridized combination C138 / S0 in Jinan, the Y928 / C486 is considered to establish base population offspring suitable for line selection; S1 offspring population of the Y928 / C486 is planted in Zhangye, Gansu, and early-maturing S2 single plants with good comprehensive characters are selected; the S2 single plants are planted into head progeny rows in Hainan, and the head progeny rows are subjected to test cross through the tester C138, and S3 head progeny rows with excellent comprehensive characters are selected in the harvesting process; S3 single plants of the selected head progeny rows are planted into head progeny rows and are inbred in Jinan so as to obtain S4,and S4 with higher combining ability is selected according to the field performances and the yield test result of a test cross combination and the comprehensive performances of the S3 head progeny rows; and bagging inbreeding is continuously carried out in Hainan and Jinan, and finally, the maize inbred line Lx286 is bred according to different test results of the tester.
Owner:MAIZE RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Technical method for continuous improvement of corn single cross hybrid
ActiveCN104026000AImprove bad traitsAvoid loss driftPlant genotype modificationBase populationTarget concentration
The invention discloses a technical method for continuous improvement of corn single cross hybrid. The method comprises the following steps: respectively selecting excellent individual plants from base population aiming at characters needing to be improved; planting the individual plants into panicle rows in the next season, performing selfing on superior plants in the panicle rows, and performing test cross on each excellent male parent panicle row and each excellent female parent panicle row; performing yield and improved character contrast test on the test cross combination and original single cross hybrid; planting the combined parent selfing clusters with excellent characters into panicle rows according to the identification result, carrying out mixed pollinating on the two parent cluster excellent panicle rows according to a one-superior-female parent multi-superior-male parent mode, mixing middle seeds of the clusters obtained by mixed pollinating so as to form a novel base population to enter the selection in the next selection. The technology has target concentration and can be applied to improvement of the comprehensive characters or single character of corn single cross hybrid and single cross hybrid parent population due to continuous cyclical selection, the yield is increased by over 5 percent compared with that of the original single cross hybrid, and the other comprehensive characters are obviously improved compared with those of the original single cross hybrid.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Dynamic fragment length based population protein structure prediction method
ActiveCN109147867ADiversity guaranteedEnhanced interactionProteomicsGenomicsAlgorithmBase population
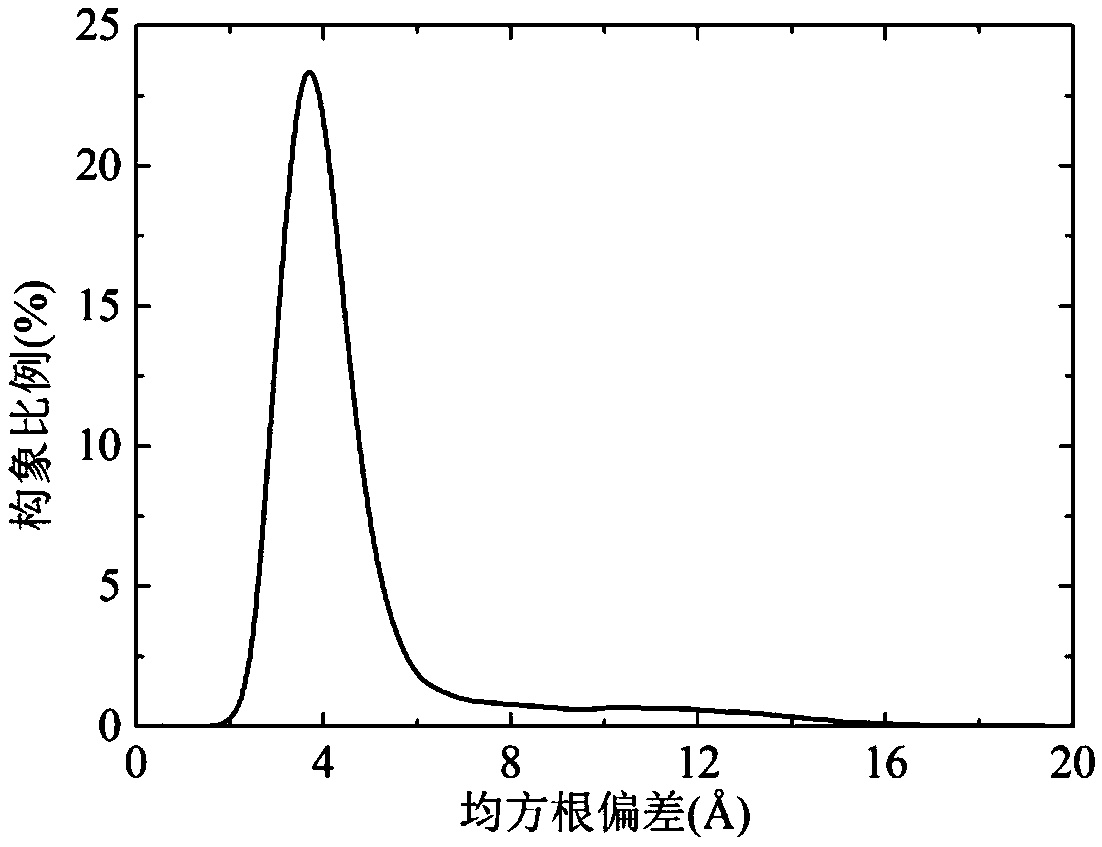
The invention discloses a dynamic fragment length based population protein structure prediction method. For each target conformation, half of conformation individuals can be randomly selected from a current population to establish a subpopulation, ordering can be performed on the population according to energy values, and a conformation can be randomly selected from top ranked conformations to guide variation; and during a variation process, multiple fragment lengths can be designed, selected probability can be calculated according to the previous success rate of each fragment length, and a fragment length can be selected to perform fragment exchange based on selection probability according to the way of roulette so that variation process can be realized. Thus, the dynamic fragment lengthbased population protein structure prediction method with high prediction precision and searching efficiency is provided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
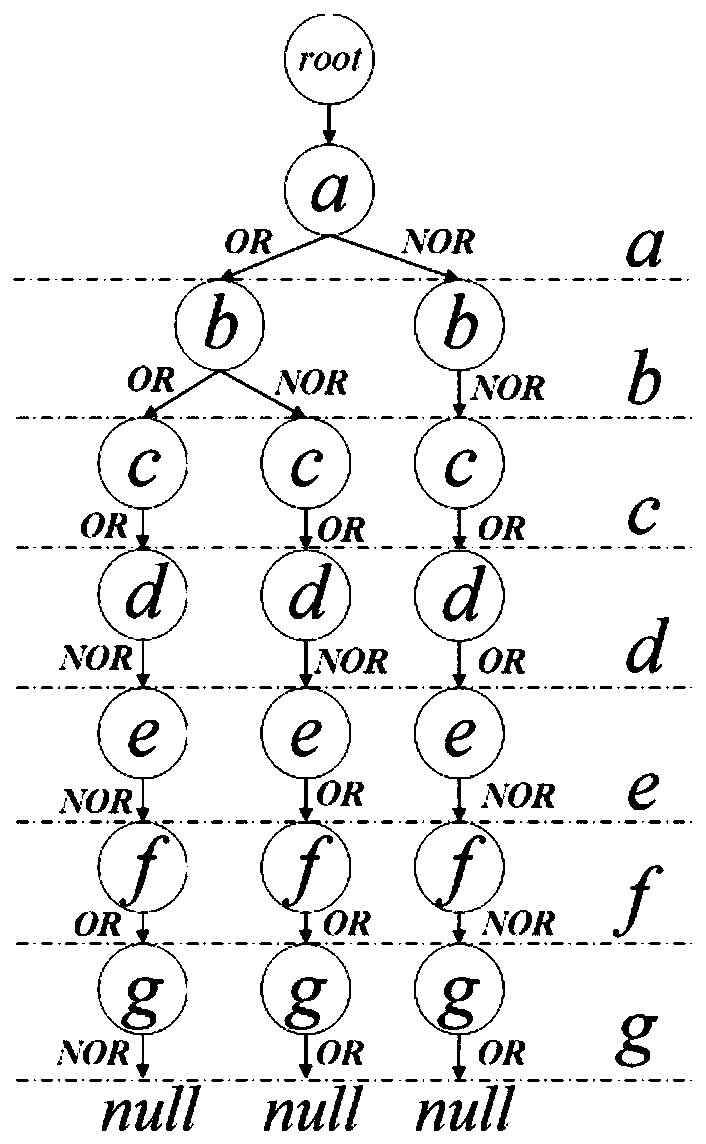
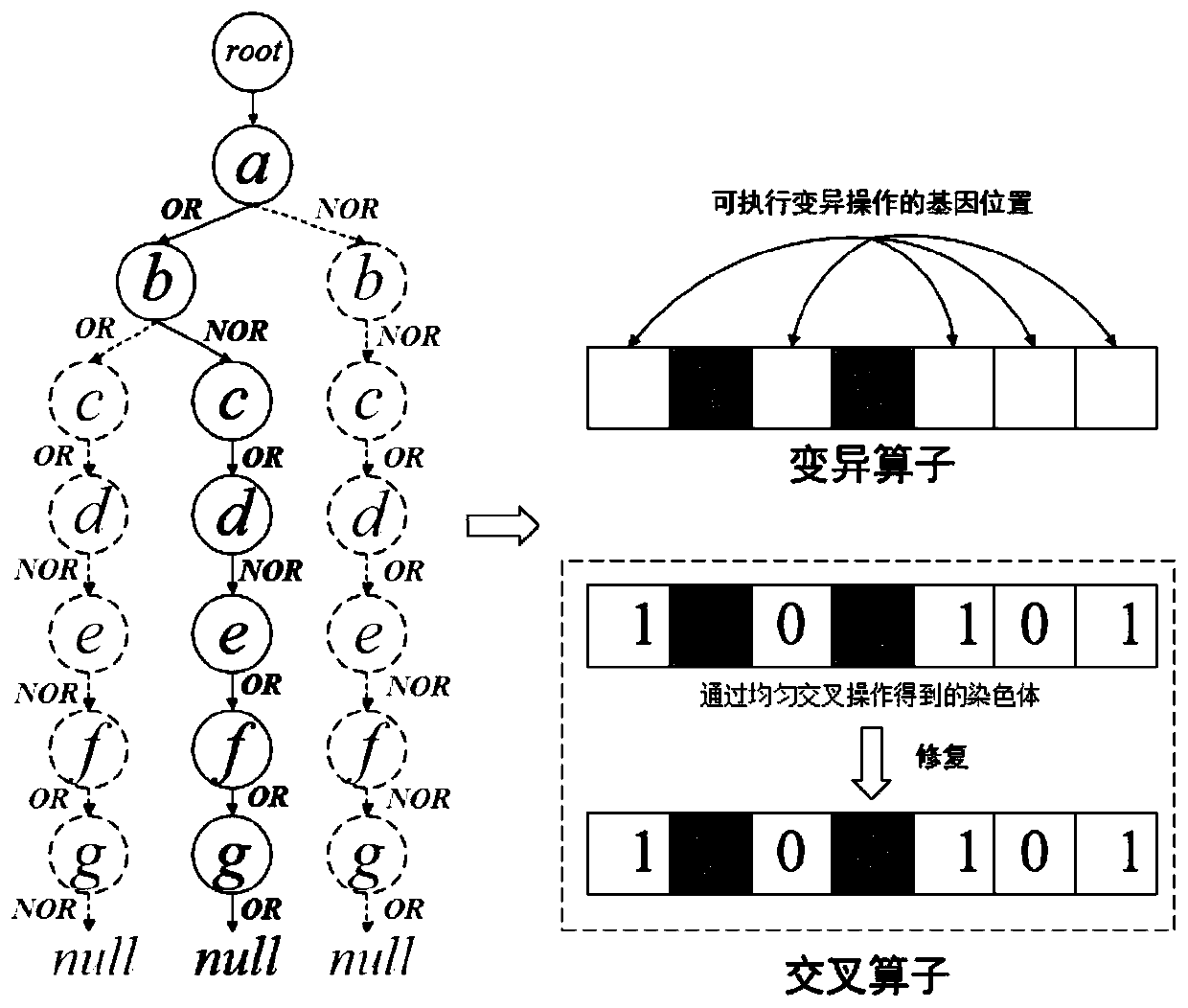
High-quality mode mining method based on multi-objective evolutionary algorithm
InactiveCN110069498AImprove solution efficiencySolution efficiency is not highArtificial lifeMachine learningMutation operatorOriginal data
The invention discloses a high-quality mode mining method based on a multi-objective evolutionary algorithm, and belongs to the technical field of data mining. According to the method, the problem that it is difficult for a user to set an appropriate parameter threshold value is solved by adopting a multi-objective evolutionary algorithm; OR / NOR-tree structure based population initialization strategy is combined with an original database which has been represented as a bitmap form to construct an initial population, and an improved cross operator and a mutation operator are adopted to set theNOR position and OR position in the OR / NOR-tree structure, so that the problem that the traditional random initialization method and crossover and mutation operator efficiency are not high due to thefact that the data is usually huge and sparse is solved; in addition, a worst individual search direction adjustment strategy is adopted to adjust the search direction, the optimization process and the optimization result are improved, and the convergence speed and the final solution quality are improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A kind of breeding method of purple Apostichopus japonicus
ActiveCN105613383BStrong selection purposeImprove efficiencyPisciculture and aquariaF1 generationBase population
The invention provides a breeding method of purple apostichopus japonicus. The breeding method is characterized by collecting purely wild apostichopus japonicus individuals of which the back part and the abdomen part are totally purple, and transplanting the apostichopus japonicus individuals into a breeding pond for carrying out independent separation, temporary rearing and preserving; screening breeding base populations in the middle of May, and carrying out artificial spawning, hatching and breeding; when 30 percent of planktonic larvae develop to be doliolaria, feeding an adhering substrate, changing water and feeding fodder; recording the body color and the growth and development situation of the doliolaria at a fixed period, and screening and weeding out weak individuals; performing an overall breeding process in a purple environment, and strengthening the coloring of young purple apostichopus japonicus by feeding the fodder containing purple natural pigment components in an assisting manner; respectively carrying out selfing on bred F1-generation purple apostichopus japonicus and hybridization on the bred F1-generation purple apostichopus japonicus and preserved base populations, thus forming F2 filial generations, wherein a breeding technology and breeding conditions of the F2 filial generations are the same as those of F1 generations; carrying out three times of high-strength standard breeding, thus obtaining F3-generation new varieties of the purple apostichopus japonicus, wherein the selection and reservation rate is 90 percent or more, and no significant difference of the growing speed and the anti-capability is generated between the F3-generation new varieties of the purple apostichopus japonicus and original apostichopus japonicus.
Owner:MARINE BIOLOGY INST OF SHANDONG PROVINCE
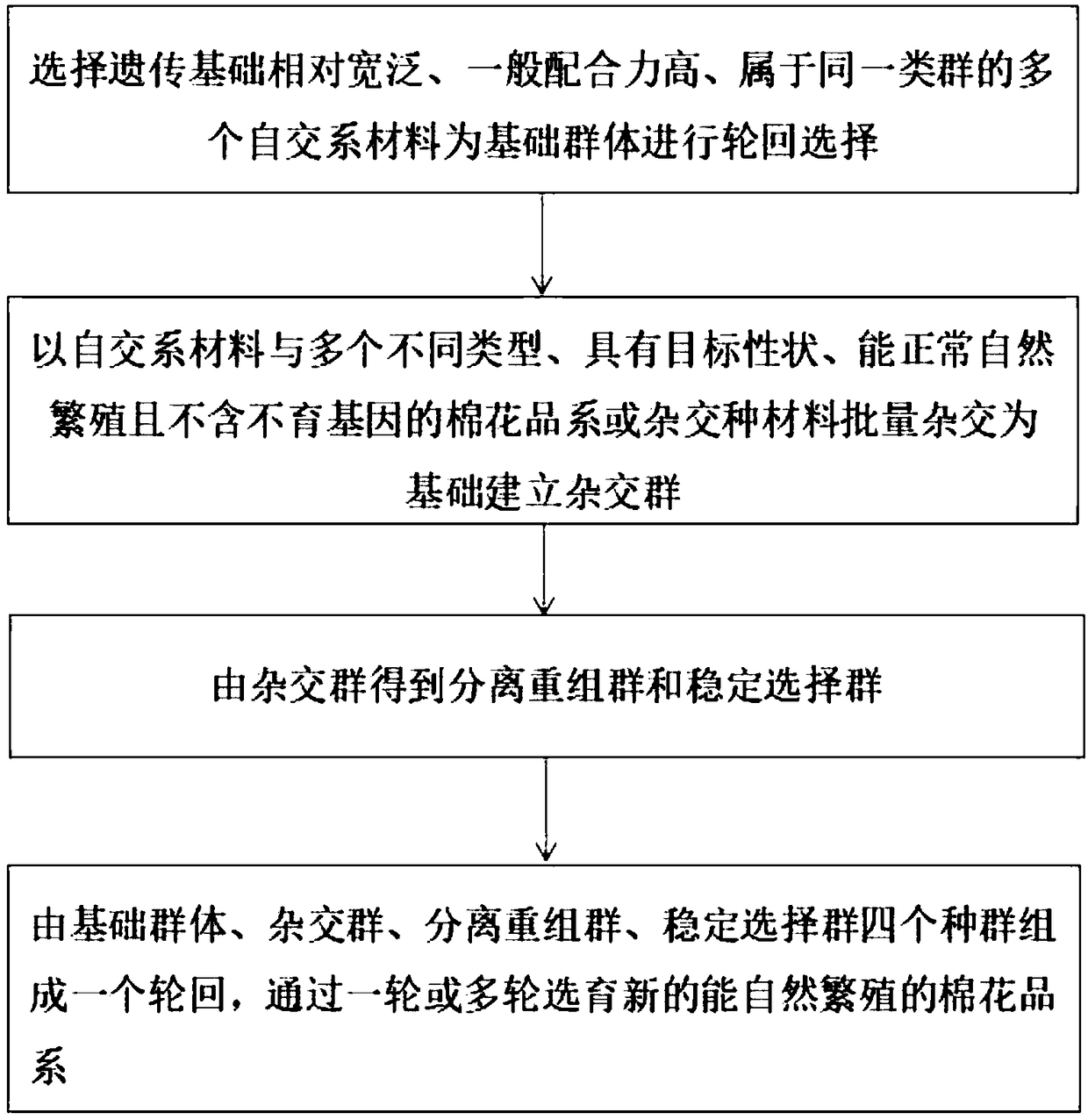
Recurrent breeding method of cotton variety
PendingCN109496837ASimple processReduce labor intensityPlant genotype modificationAgricultural sciencePollination
The invention discloses a recurrent breeding method of a cotton variety, and relates to the technical field of the breeding of cotton varieties. The recurrent breeding method of the cotton variety comprises the following steps of selecting multiple selfing-line materials, which are relatively broad in hereditary basis and high in general combining ability and belong to the same class group, as a base population to carry out recurrent selection; establishing a hybrid group on the basis of hybridizing the selfing-line materials with multiple cotton strains or coeno-species materials in a batch manner, wherein the cotton strains and the coeno-species materials belong to different types, have target traits, can normally and naturally reproduce and further do not contain sterile genes; obtaining an isolate recombination group and a stable selection group from the hybrid group; and forming one cycle by the four population groups of the base population, the hybrid group, the isolate recombination group and the stable selection group, and breeding a novel cotton strain which can naturally reproduce through one cycle or multiple cycles. Different types of breeding materials or resources meeting requirements can be obtained; the artificial castration, pollination and hybridization are not needed; the working procedure is simple; the labor intensity is low; and further, the work efficiency is high.
Owner:JIANGSU COASTAL AREA AGRI SCI RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com