Human protein LT-alpha interacting with hepatitis g virus E2 protein
A technology of protein interaction and human protein, applied in the field of human protein LT-α that interacts with hepatitis G virus E2 protein, can solve the problems of changing T cell activity, ambiguity, and reducing T cell activity, and achieve omics The effect of mature technology and the simplicity and wide applicability of omics technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
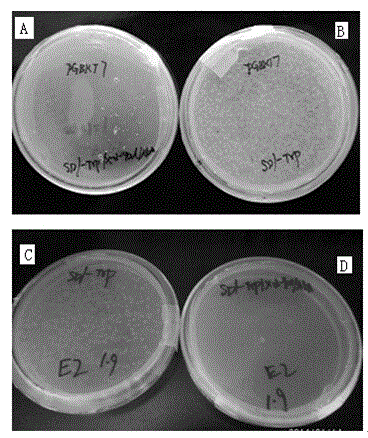
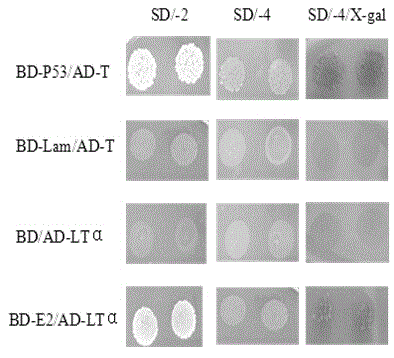
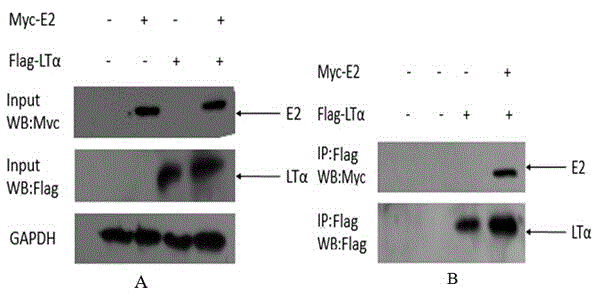
[0055] Example 1: Screening for Human Proteins Interacting with Hepatitis G Virus E2 Protein
[0056] 1. Cloning and identification of hepatitis G virus E2 gene
[0057] Analyze the target gene fragment sequence and the multiple cloning site information of the connected vector, and design primers: 5' end primer pGBKT7-E25'-CCG GAATTC GGCGCCCCGGCCTCGGTGCTAG, the underlined part is the EcoRI restriction site;
[0058] 3' end primer pGBKT7-E2 3'-ACG CGTCGA CCCTGCCCGAGGAGAGCCATGCGAAC, the underlined part is the SalⅠ restriction site;
[0059] PCR amplification of cDNA of hepatitis G virus type 7 to obtain gene fragments, 50 μl PCR system: 1 μl upstream primer, 1 μl downstream primer, 25 μl rTaq mixture, ddH 2 O2 1μl, template 2μl; PCR conditions: 94°C pre-denaturation for 5min, 35 cycles; 94°C for 30s, 50°C for 30s, 72°C for 2min, and final extension at 72°C for 7min; PCR products were identified by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis for fragment size .
[0060] 2. Construction...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com