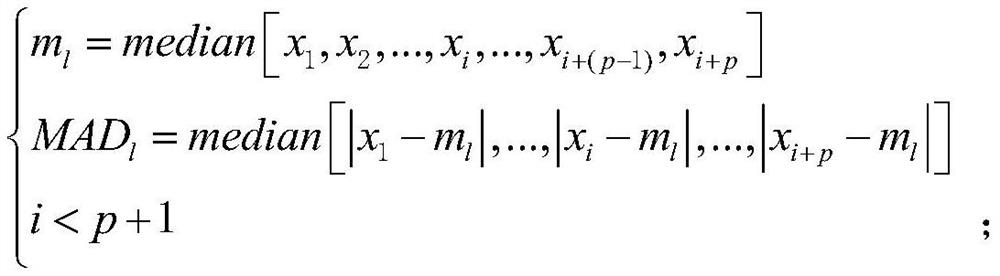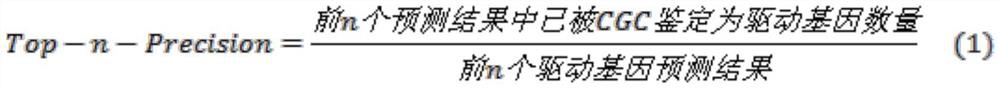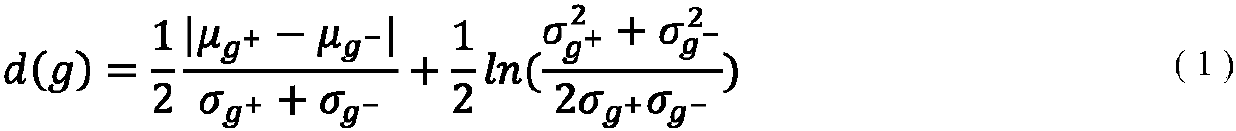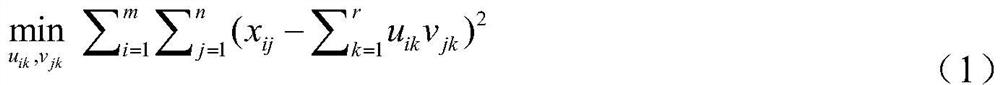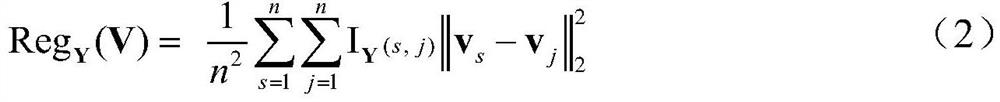Patents
Literature
45 results about "Gene recognition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
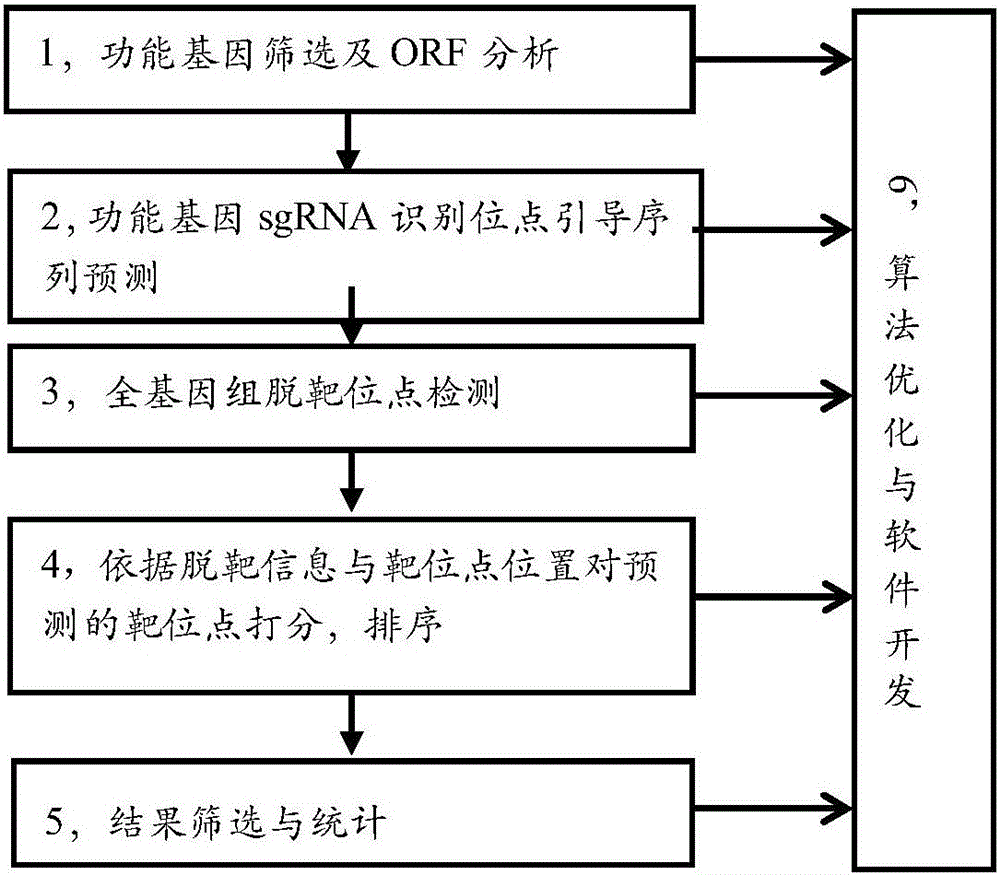
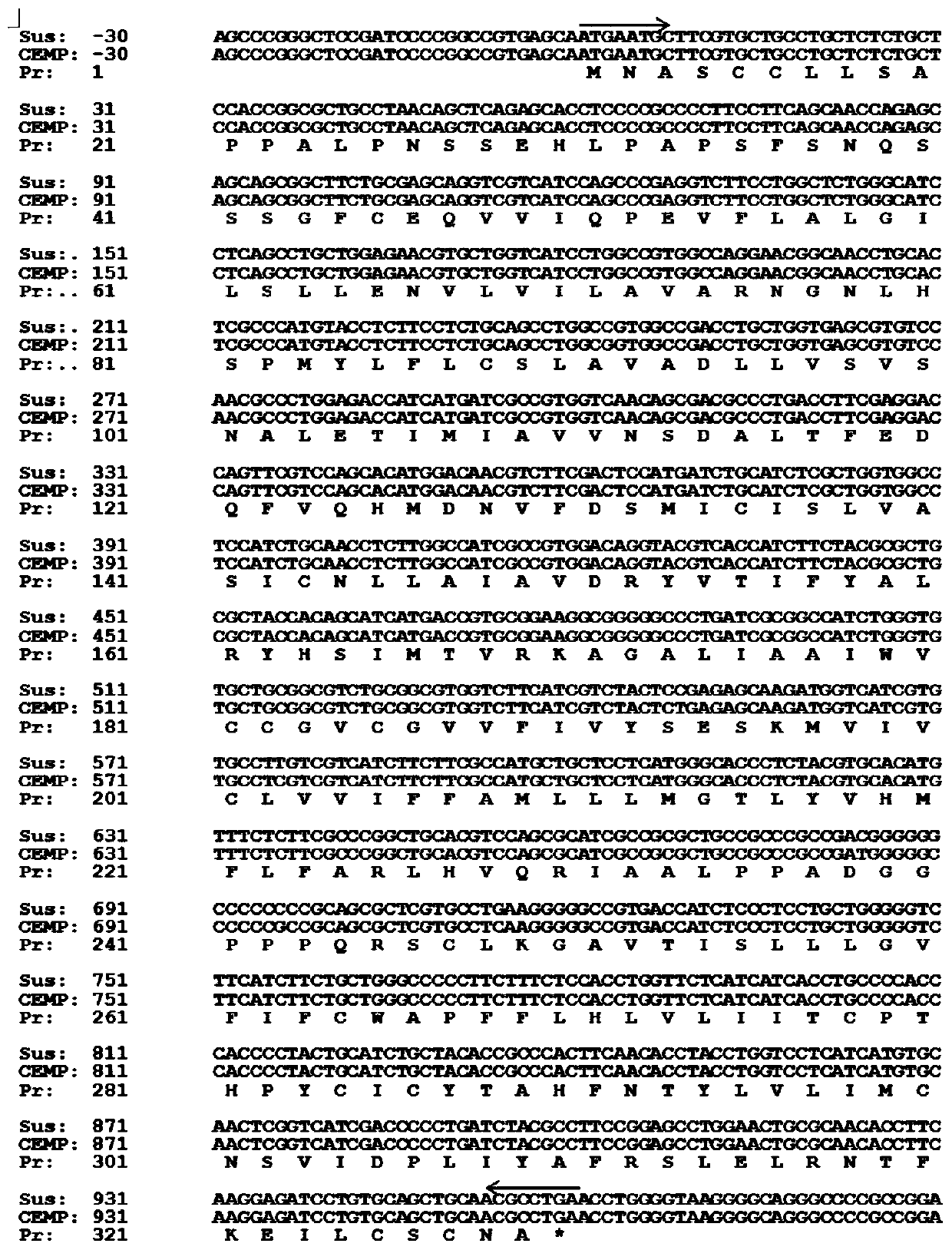
Efficient specific sgRNA recognition site guide sequence for pig gene editing and screening method thereof
ActiveCN105886616AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenome editingScreening method
The invention discloses an efficient specific sgRNA recognition site guide sequence for pig gene editing and a screening method thereof. The screening method includes: screening functional genes, performing ORF analysis, predicting a functional gene sgRNA recognition site guide sequence, detecting whole-genome off-target sites, grading predicted target sites according to off-target information and target site positions, sequencing, screening and statistically counting results, optimizing algorithms and developing software. The efficient specific sgRNA recognition site guide sequence and the screening method thereof have the advantages that the pig specific sgRNA recognition site guide sequence is obtained through strict screening and inspection and includes the sgRNA recognition site guide sequences, for CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing, of all pig protein encoding genes; the authenticating, grading and inspecting algorithms for specific sgRNA recognition and software corresponding to the algorithms and used for predicting and evaluating the pig functional gene sgRNA recognition site guide sequence are widely applicable to the sgRNA specific site prediction of non-model species with whole-genome sequences.
Owner:AGRO BIOLOGICAL GENE RES CENT GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
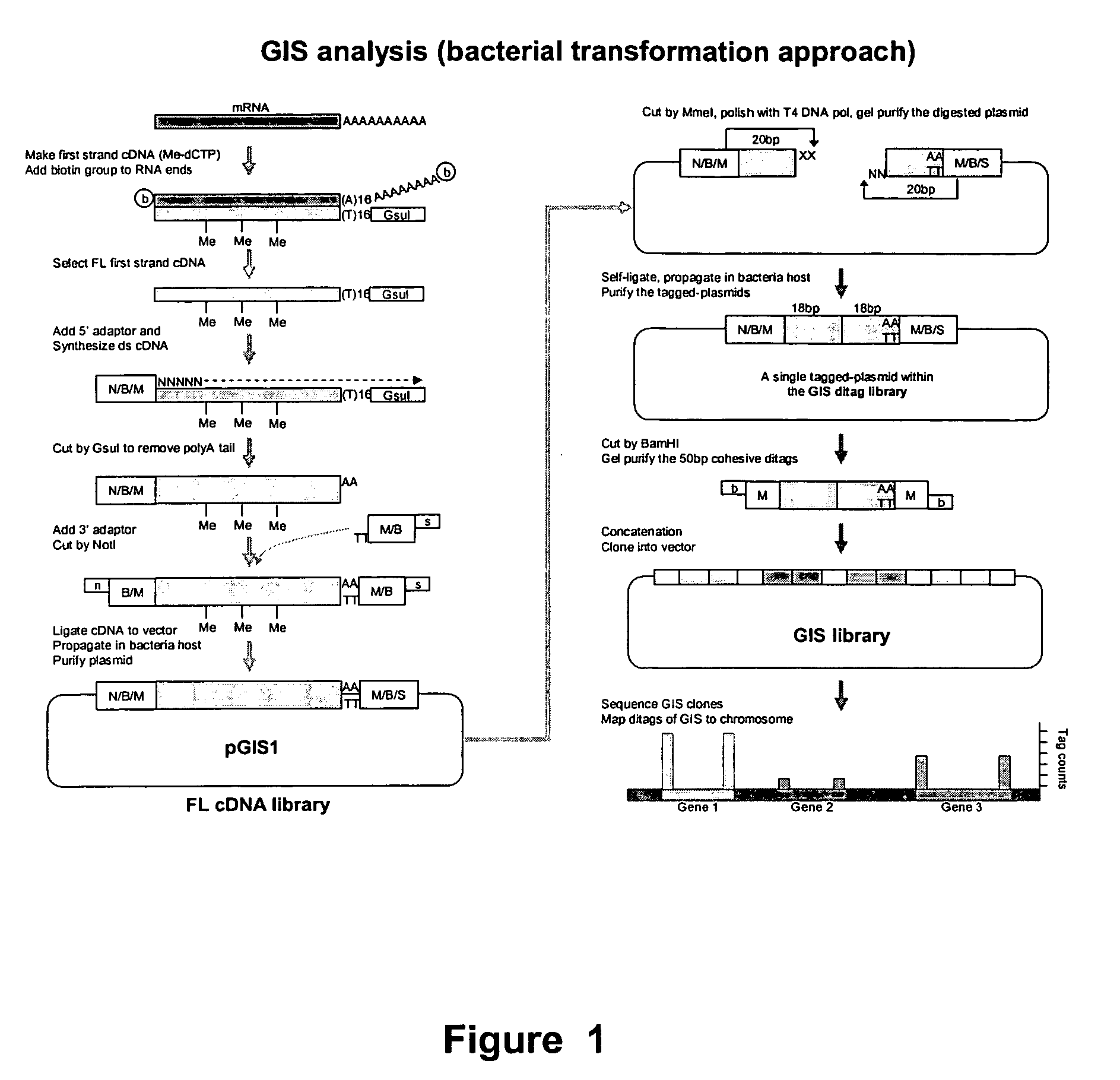
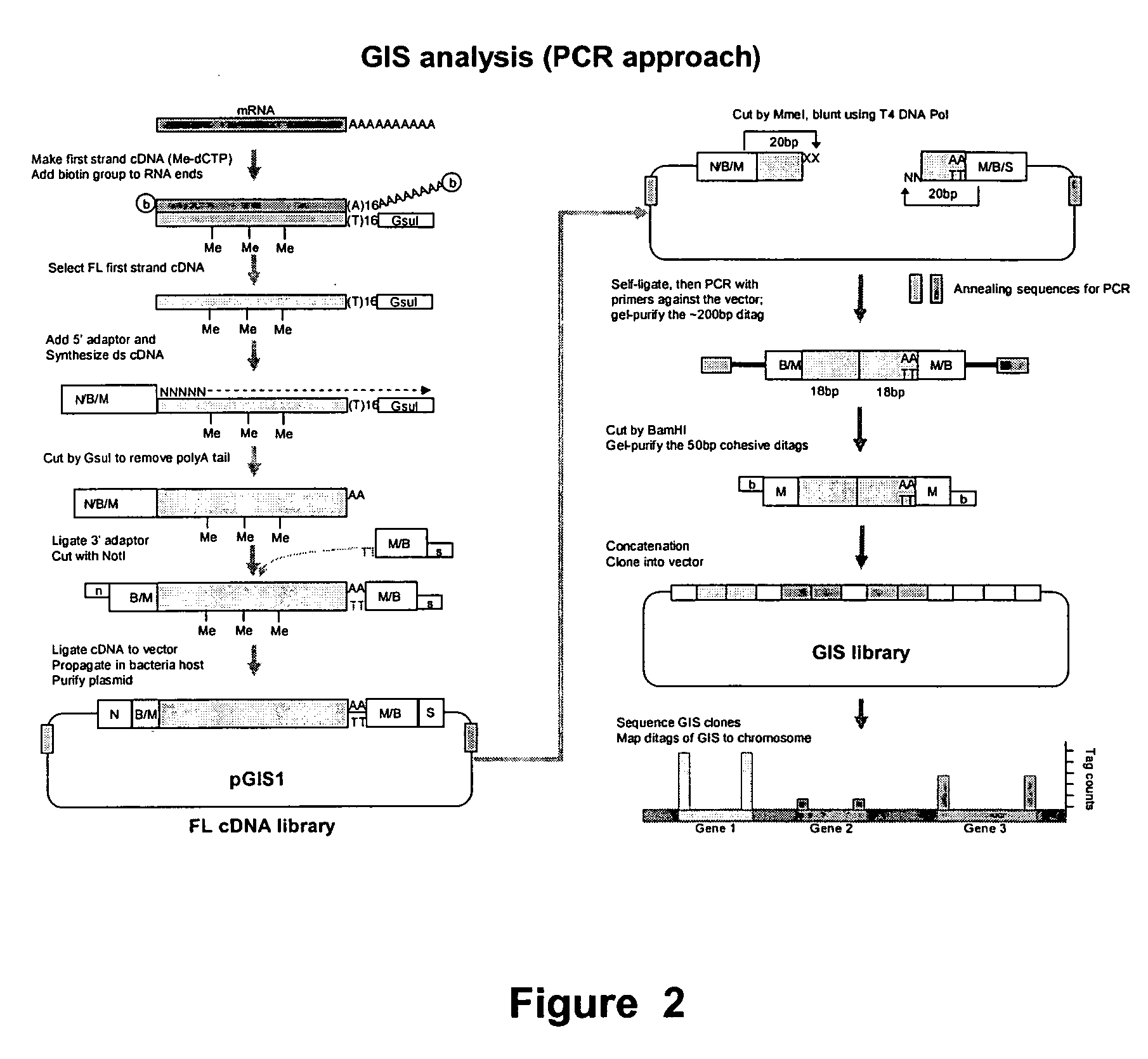
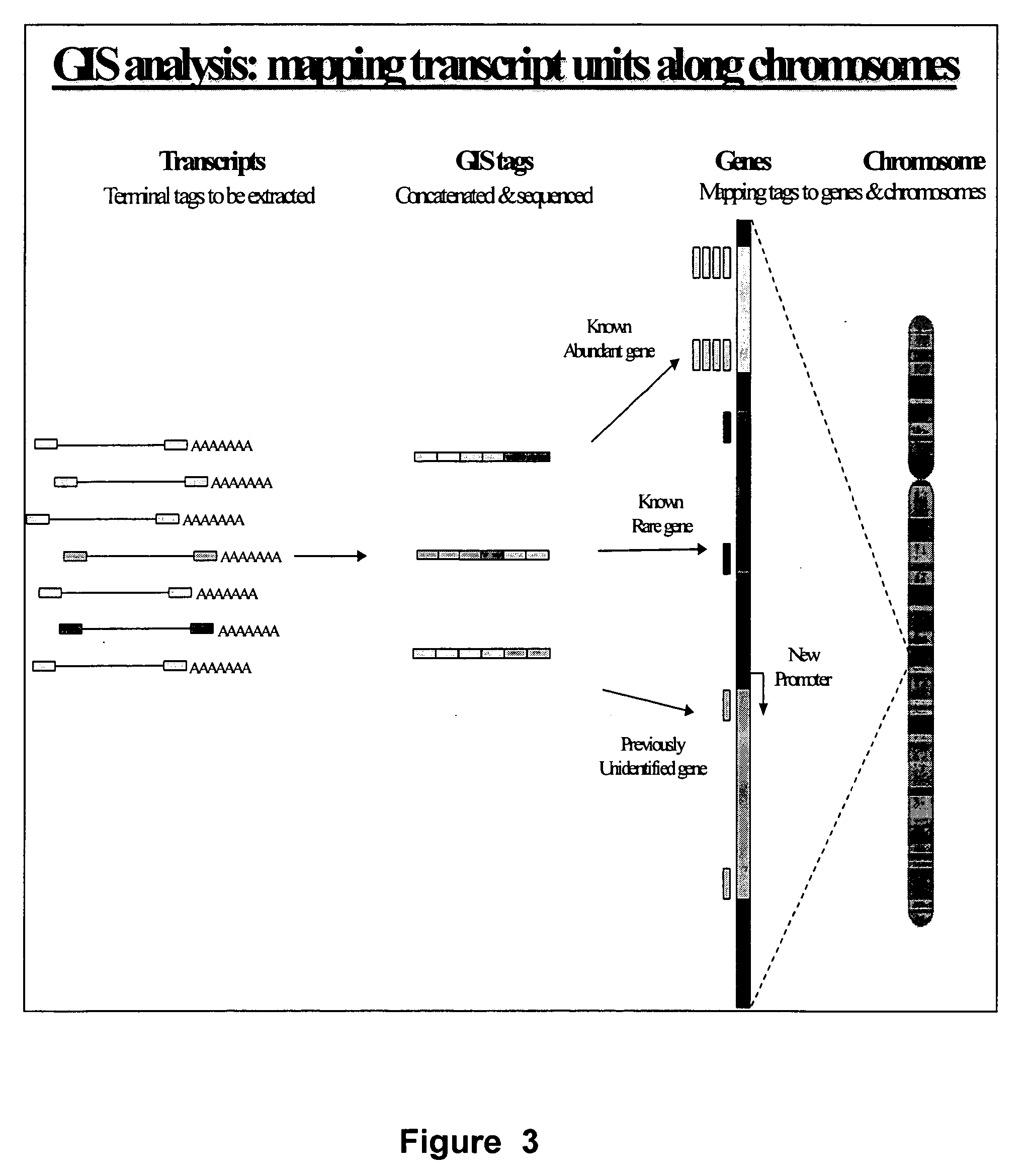
Method for gene identification signature (GIS) analysis
InactiveUS20050255501A1Strong specificityEasy to identifySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGene recognitionProtein
A method of identifying at least a nucleic acid molecule fragment to which a protein of interest binds, comprising: (i) preparing at least one nucleic acid molecule fragment to which a protein binds; (ii) isolating the 5′ terminus and the 3′ terminus of the nucleic acid fragment(s) and linking the 5′ terminus and 3′ terminus to create the at least one ditag; (iii) sequencing the ditag; and (iv) mapping the ditag sequence(s) to the genome.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Generation of biomaterial microarrays by laser transfer
InactiveUS6936311B2Wide rangeExcessive transferMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsGene recognitionBiological materials
A method for creating a microarray of biomaterial uses a source of laser energy, a receiving substrate, and a target substrate. The target substrate comprises a laser-transparent support having a laser-facing surface and a support surface. The target substrate also comprises a composite material having a back surface in contact with the support surface and a front surface. The composite material comprises a mixture of the biomaterial to be deposited and a matrix material. The matrix material is a material that has the property that, when it is exposed to laser energy, it desorbs from the laser-transparent support. The source of laser energy is positioned in relation to the target substrate so that laser energy is directed through the laser-facing surface of the target substrate and through the laser-transparent support to strike the composite material at a defined target location. The receiving substrate is positioned in a spaced relation to the target substrate. The source of laser energy has sufficient energy to desorb the composite material at the defined target location, causing the composite material to desorb from the defined target location and be lifted from the support surface of the laser-transparent support. The composite material is deposited at a defined receiving location on the receiving substrate. The steps are repeated at successive defined target locations and successive defined receiving locations such that the composite material is deposited in a microarray of deposited composite material. The method is useful for creating, for example, a gene recognition array,
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Human mitochondrial dna polymorphisms, haplogroups, associations with physiological conditions, and genotyping arrays
InactiveUS20050123913A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingNucleotidePhosphorylation
This invention provides human mtDNA polymorphisms that are diagnostic of all the major human haplogroups and methods of diagnosing those haplogroups and selected subhaplogroups. This invention also provides methods for identifying evolutionarily significant mitochondrial DNA genes, nucleotide alleles, and amino acid alleles. Evolutionarily significant genes and alleles are identified using one or two populations of a single species. The process of identifying evolutionarily significant nucleotide alleles involves identifying evolutionarily significant genes and then evolutionarily significant nucleotide alleles in those genes, and identifying evolutionarily significant amino acid alleles involves identifying amino acids encoded by all nonsynonymous alleles. Synonymous codings of the nucleotide alleles encoding evolutionarily significant amino acid alleles of this invention are equivalent to the evolutionarily significant amino acid alleles disclosed herein and are included within the scope of this invention. Synonymous codings include alleles at neighboring nucleotide loci that are within the same codon. This invention also provides methods for associating haplogroups and evolutionarily significant nucleotide and amino acid alleles with predispositions to physiological conditions. Methods for diagnosing predisposition to LHON, and methods for diagnosing increased likelihood of developing blindness, centenaria, and increased longevity that are not dependent on the geographical location of the individual being diagnosed are provided herein. Diagnosis of an individual with a predisposition to an energy metabolism-related physiological condition is dependent on the geographic region of the individual. Physiological conditions diagnosable by the methods of this invention include healthy conditions and pathological conditions. Physiological conditions that are associated with haplogroups and with alleles provided by this invention include energetic imbalance, metabolic disease, abnormal energy metabolism, abnormal temperature regulation, abnormal oxidative phosphorylation, abnormal electron transport, obesity, amount of body fat, diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
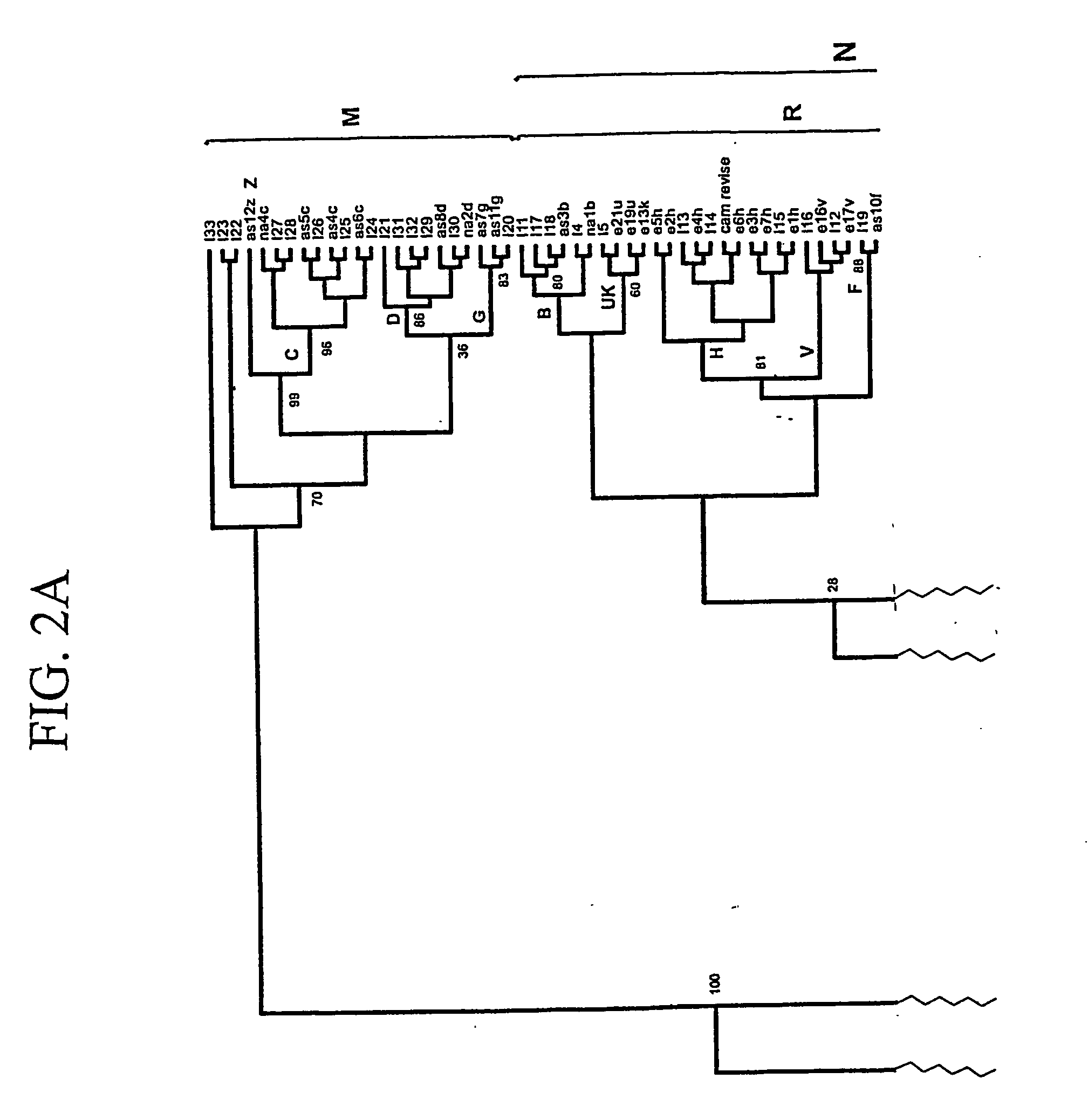
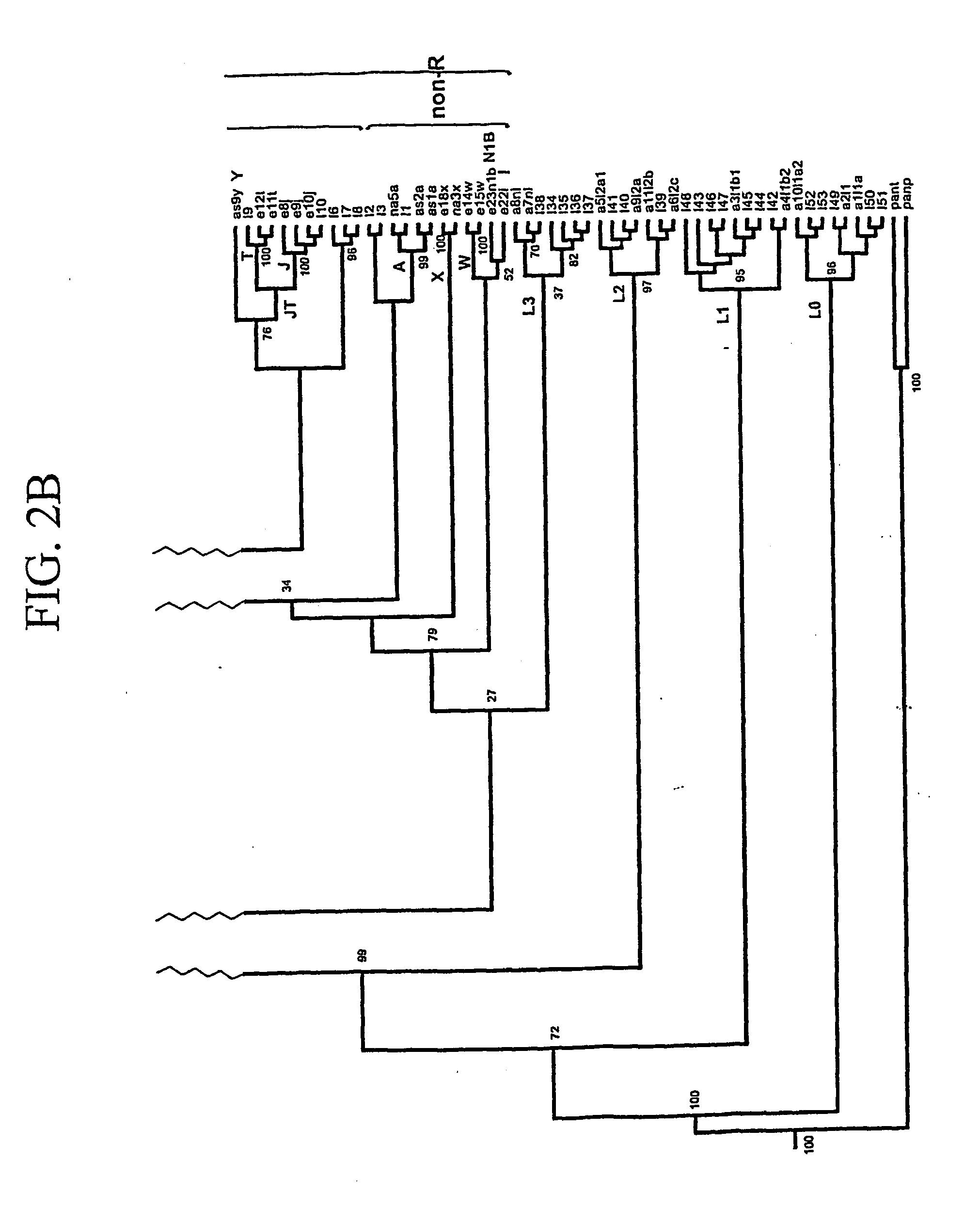
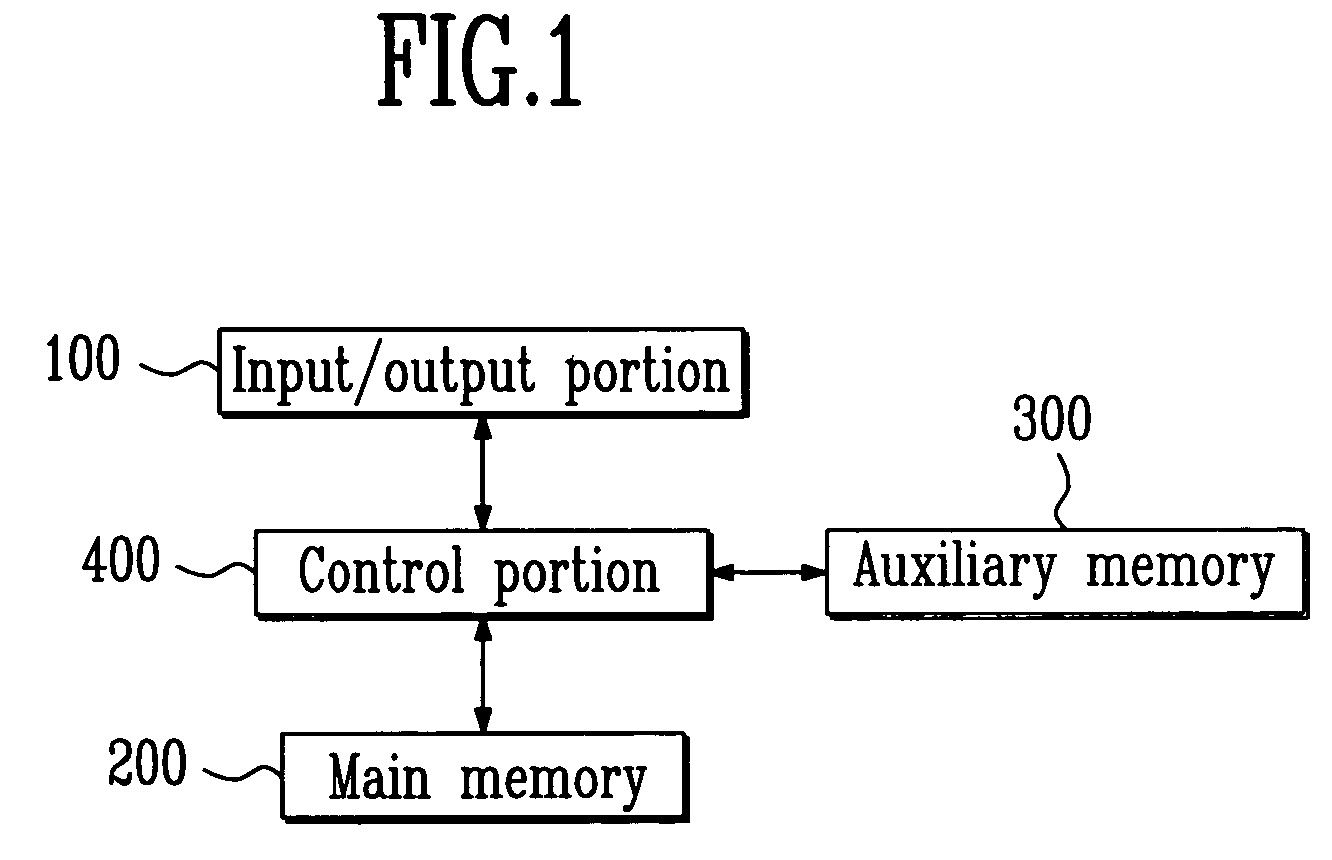
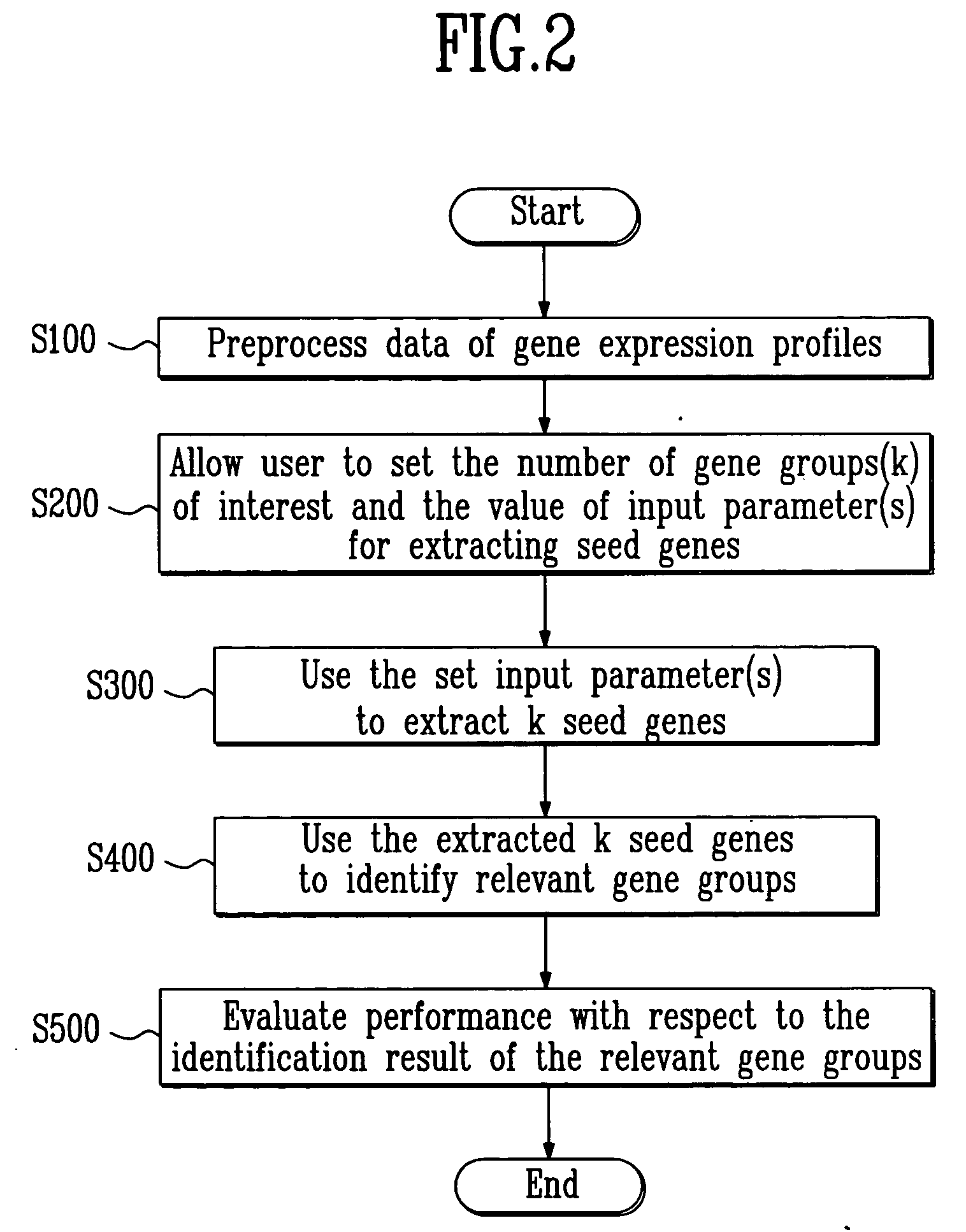
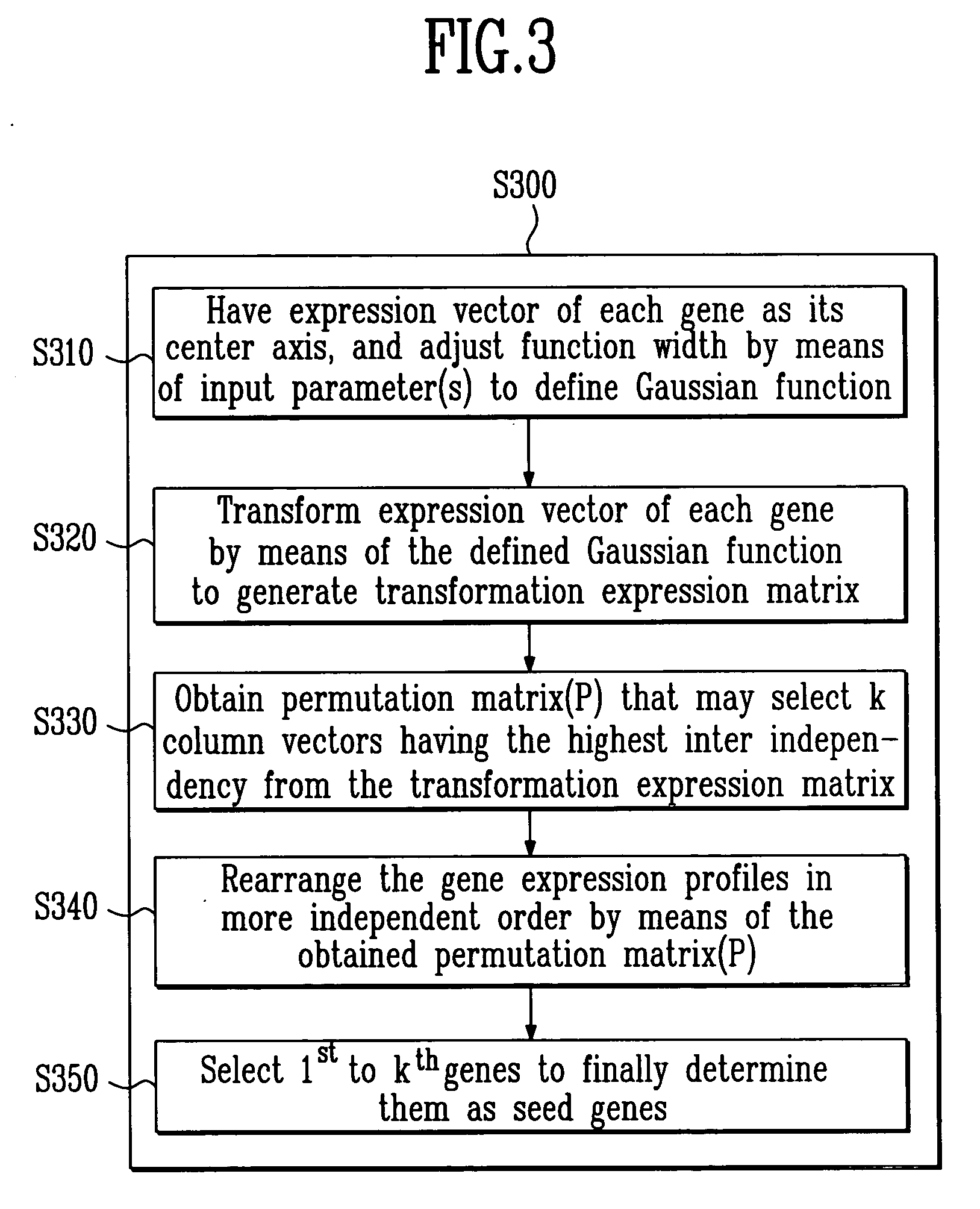
Method for identifying relevant groups of genes using gene expression profiles
InactiveUS20050130187A1Efficient identificationEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGeneticsGene recognition
Provided is a method for identifying relevant groups of genes using gene expression profiles. More particularly, it is provided a method for identifying relevant groups of genes using gene expression profiles, which analyzes the gene expression profiles obtained from microarray experiments to automatically extract seed genes of significance and identifies the relevant groups of genes based on the extracted seed genes, so that effective identification is possible regardless of the number of genes and a blind setting of initial input parameters are not required for users to readily use the method, wherein the method comprises the steps of (a) preprocessing the gene expression profiles; (b) setting the number of gene groups to be desired (k) and a input parameter(s); (c) extracting k seed genes (k=1, 2, 3, . . . ,n) based on the set input parameter(s); (d) identifying relevant groups of genes by means of the extracted seed genes; and (e) evaluating the identified relevant groups of genes.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Network gene recognition method based on entity self characteristics in information space
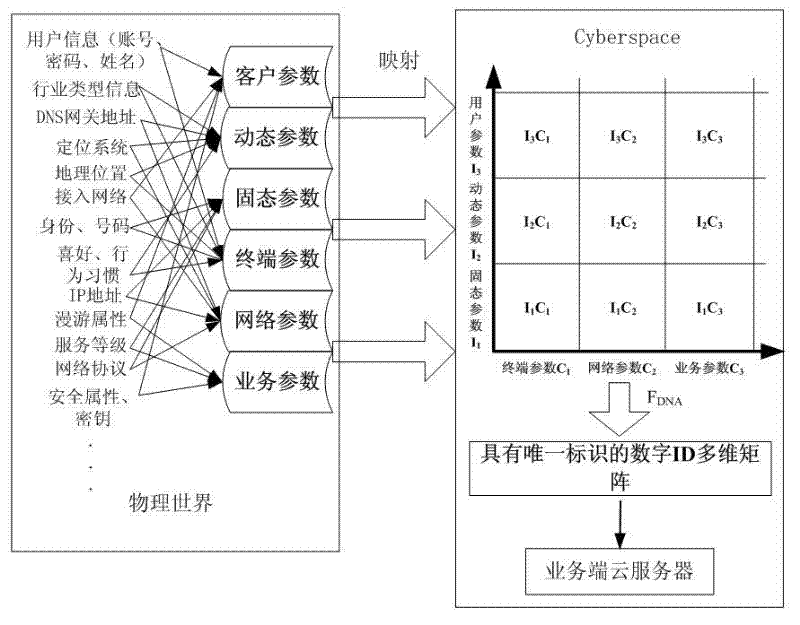
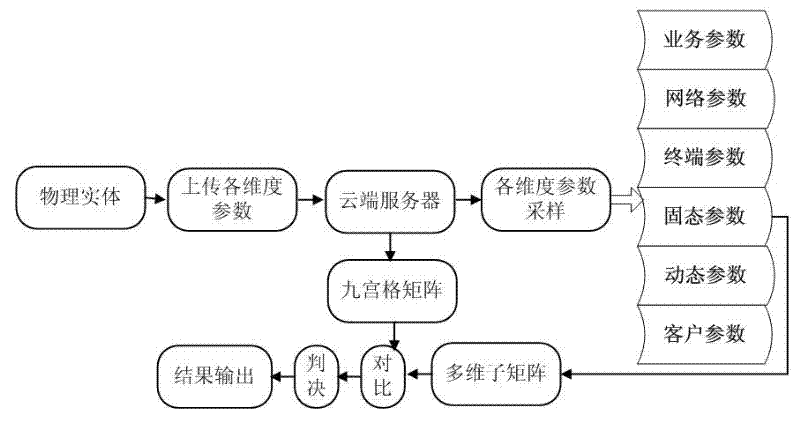
InactiveCN102594807ASolving the Trusted Identity ProblemEnhance the substantive functionTransmissionPattern recognitionInformation space
The invention discloses a network gene recognition method based on entity self characteristics in an information space. In the information space, a consistent identifier based on self characteristics is realized by using the physical or virtual objective attribute information of a cyber entity itself. The identifier is a unique structural data rule processed in the information space based on cyber entity self natural attribute and is used as a network gene identification and recognition method of an entity. With the adoption of the network gene recognition method, unique identification and unique mapping of the entity in a PS (Physical Space) and a CS (Cyber Space) can be realized, i.e. a self real name of the cyber entity in the CS, a real name in the CS and an anonymous name in the CS or the real name in the PS existing in anonymous name in the in the CS can be realized; and meanwhile, the switch and the mapping between the real name and the anonymous name are a principle and a mechanism uniquely corresponding to the cyber entity, so that any cyber entity possesses of a trusted identity.
Owner:JIANGSU DIGITAL DNA TECH CO LTD
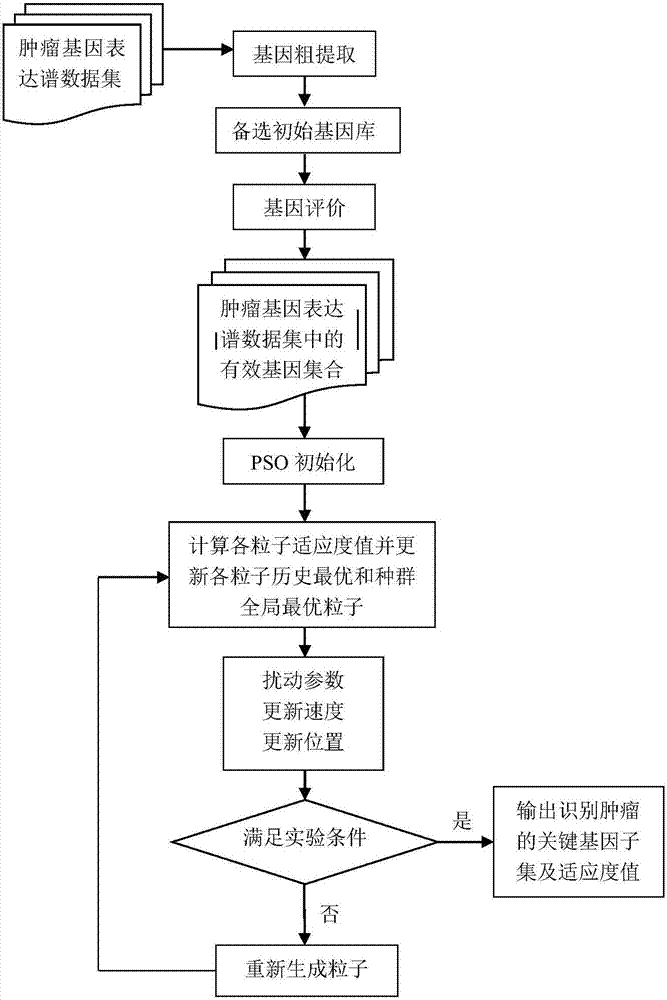
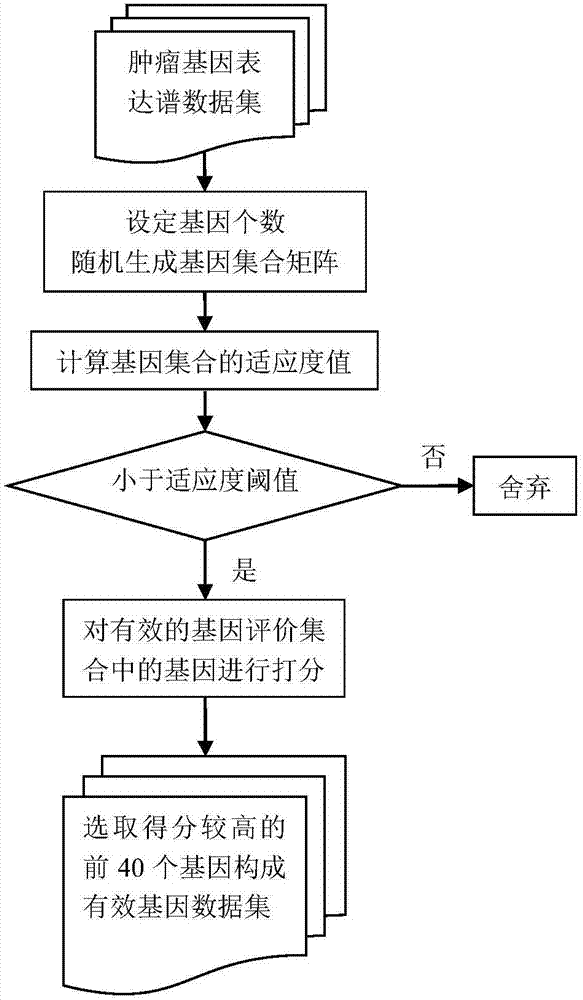
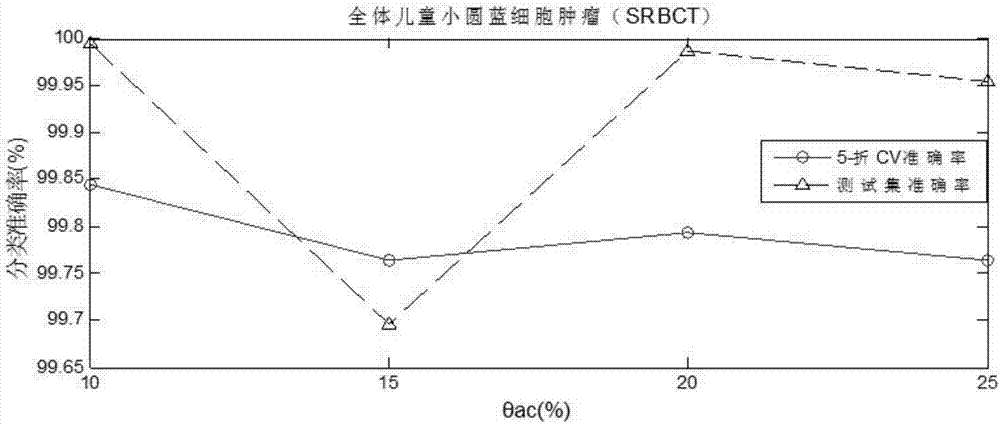
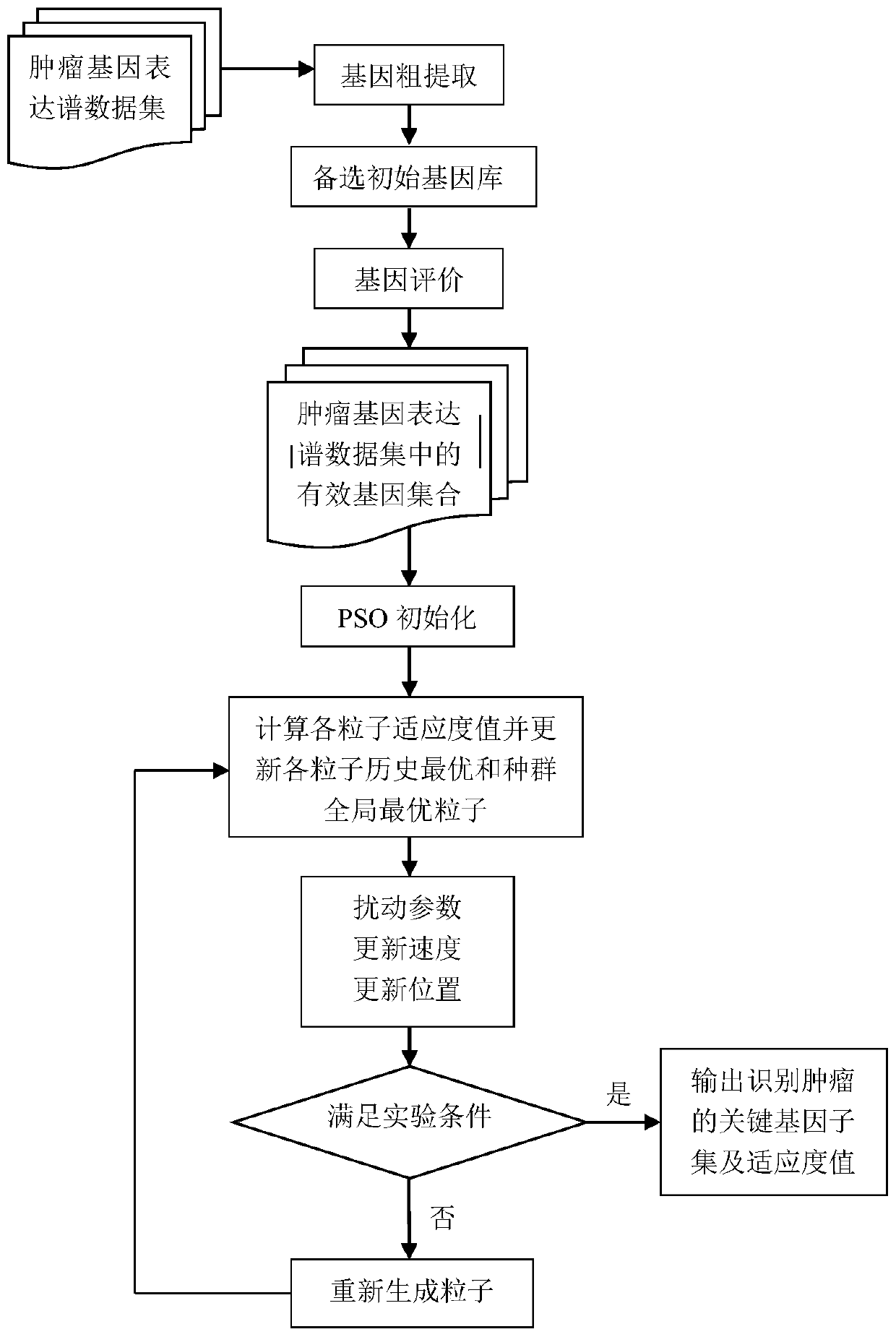
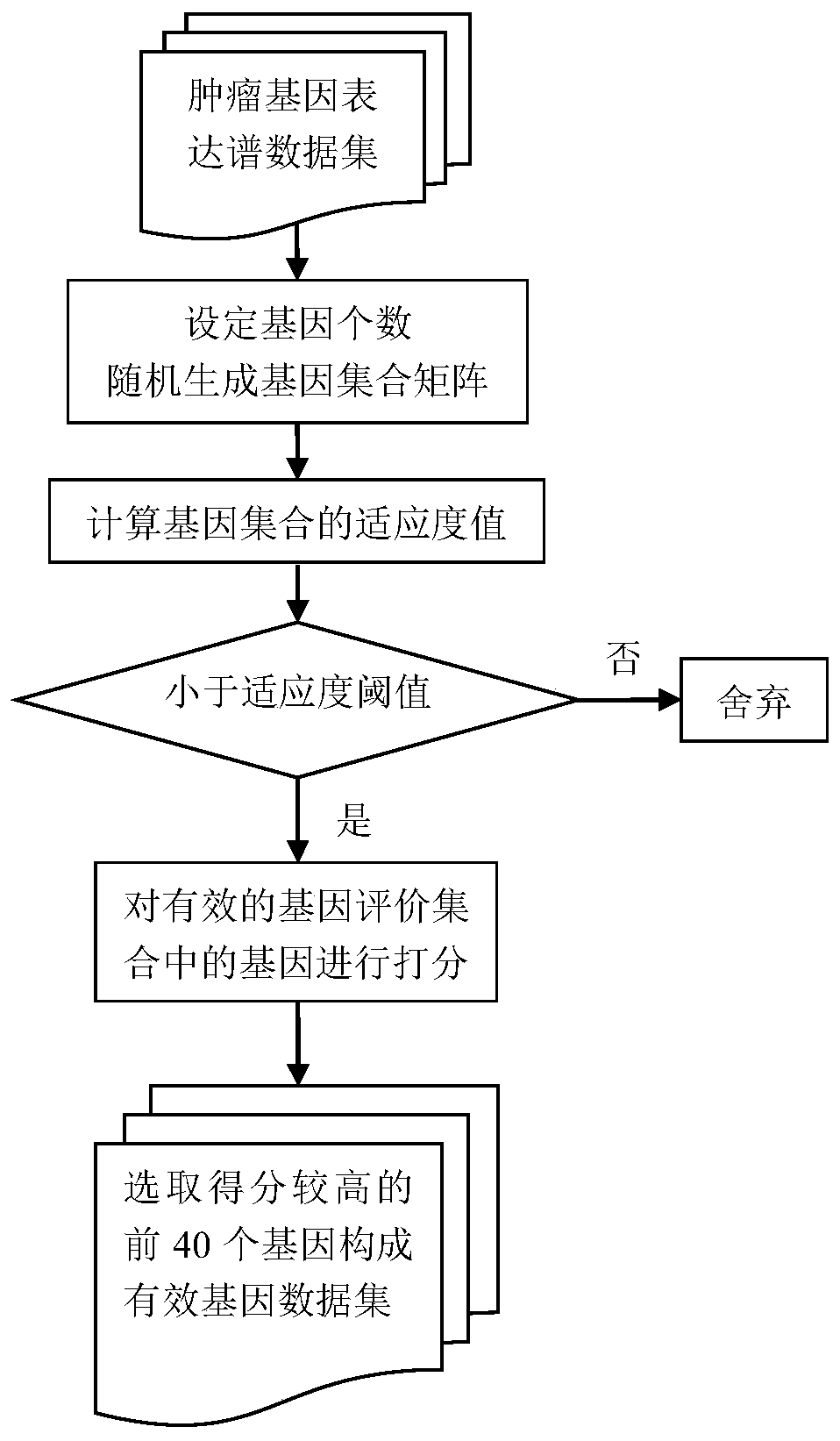
Tumor key gene identification method based on particle swarm optimization and marking criterion
ActiveCN106951728AAccurate identificationEffectively deleteProteomicsGenomicsLocal optimumMulti-swarm optimization
The invention discloses a tumor key gene identification method based on particle swarm optimization and a marking criterion. The method comprises the steps that one gene marking criterion is defined to acquire gene classification ability information so as to filter genes with a low correlation to a tumor category; and the Metropolis criterion is utilized to improve a particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm in combination with the gene classification ability information so as to realize identification of tumor key genes. The new method for gene classification information and PSO improvement overcomes the defect that a traditional method for identifying tumor key genes based on PSO is prone to fall into a locally optimal solution, gene subsets in a smaller number and with a high correlation to the tumor category can be selected, and therefore the method is beneficial for improving subsequent tumor identification.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
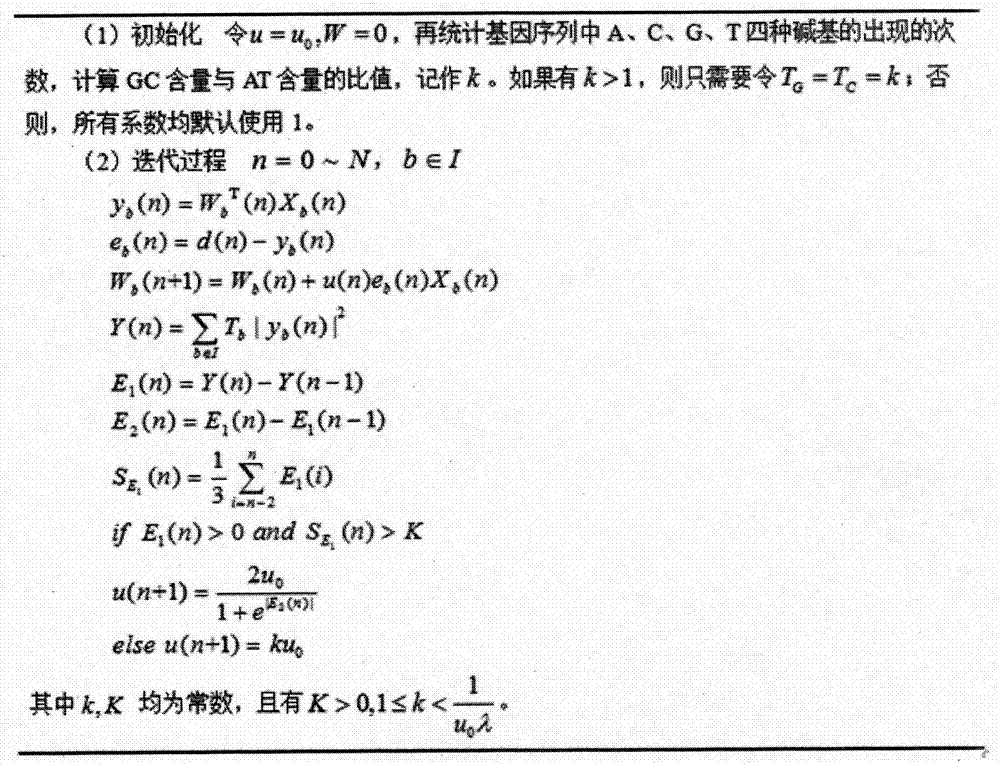
Gene recognition system of self-adaptation filter based on variable step size minimum mean square error
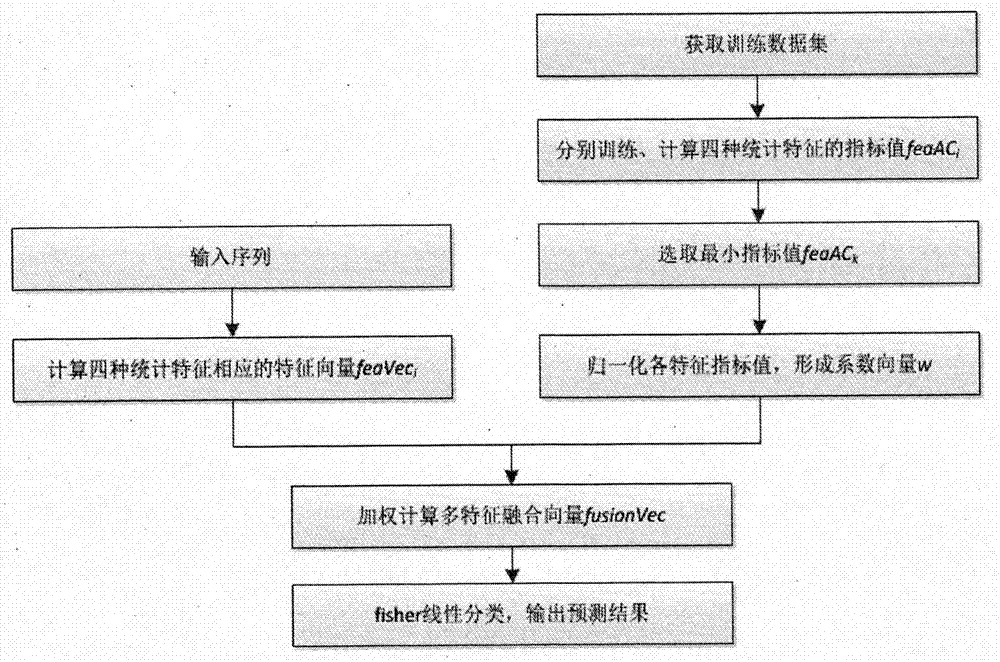
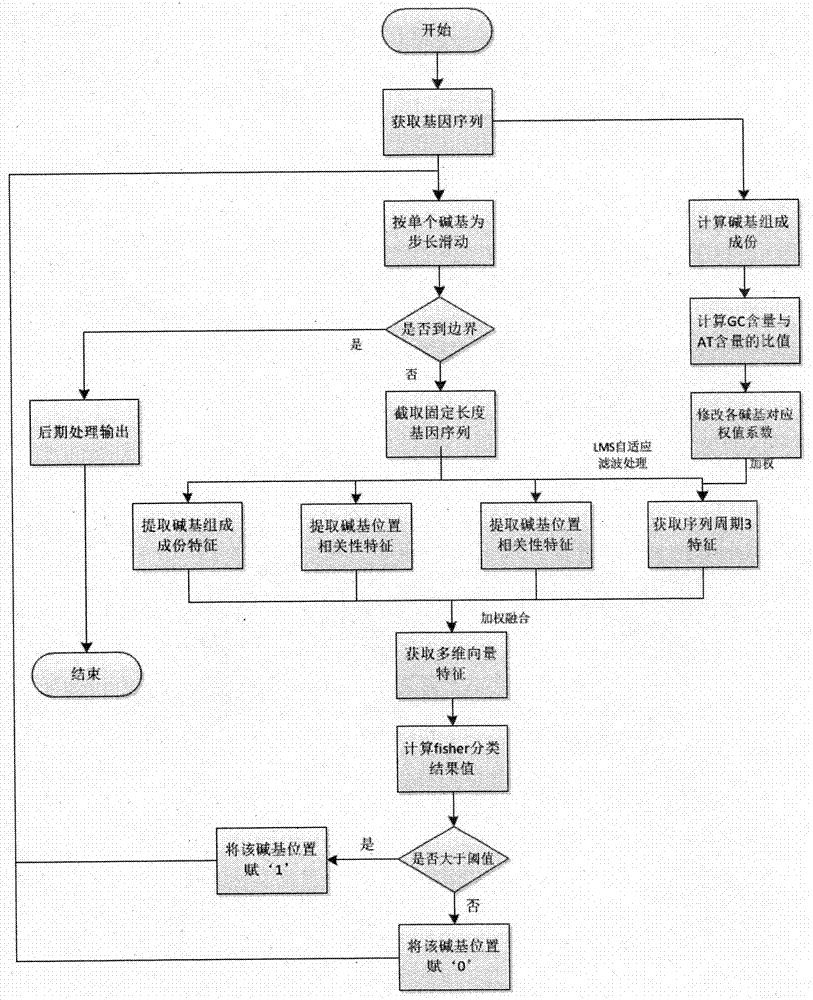
The invention discloses a gene recognition system of a self-adaptation filter based on a variable step size minimum mean square error. The system comprises an improvement unit of a variable step size LMS self-adaptation filter algorithm and a processing unit of a gene structure multi-characteristic weight fusion algorithm, wherein the improvement unit of the variable step size LMS self-adaptation filter algorithm is used to conduct filtering processing of a gene sequence by the variable step size LMS self-adaptation improvement algorithm, so gene characteristics in that random noise is rare, and cycle 3 behaviors are strong can be obtained; and the processing algorithm of the gene structure multi-characteristic weight fusion algorithm is used to extract characteristics of the gene sequence through a multi-characteristic weight fusion strategy, so that characteristic vectors with a higher expression ability can be obtained. The invention proposes the variable step size LMS self-adaptation filter improvement algorithm and the multi-characteristic weight fusion algorithm; and the two algorithms are integrated into the same gene recognition system, so recognition performance of the system is further improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Intelligent rail unmanned vehicle fault gene identification method and system
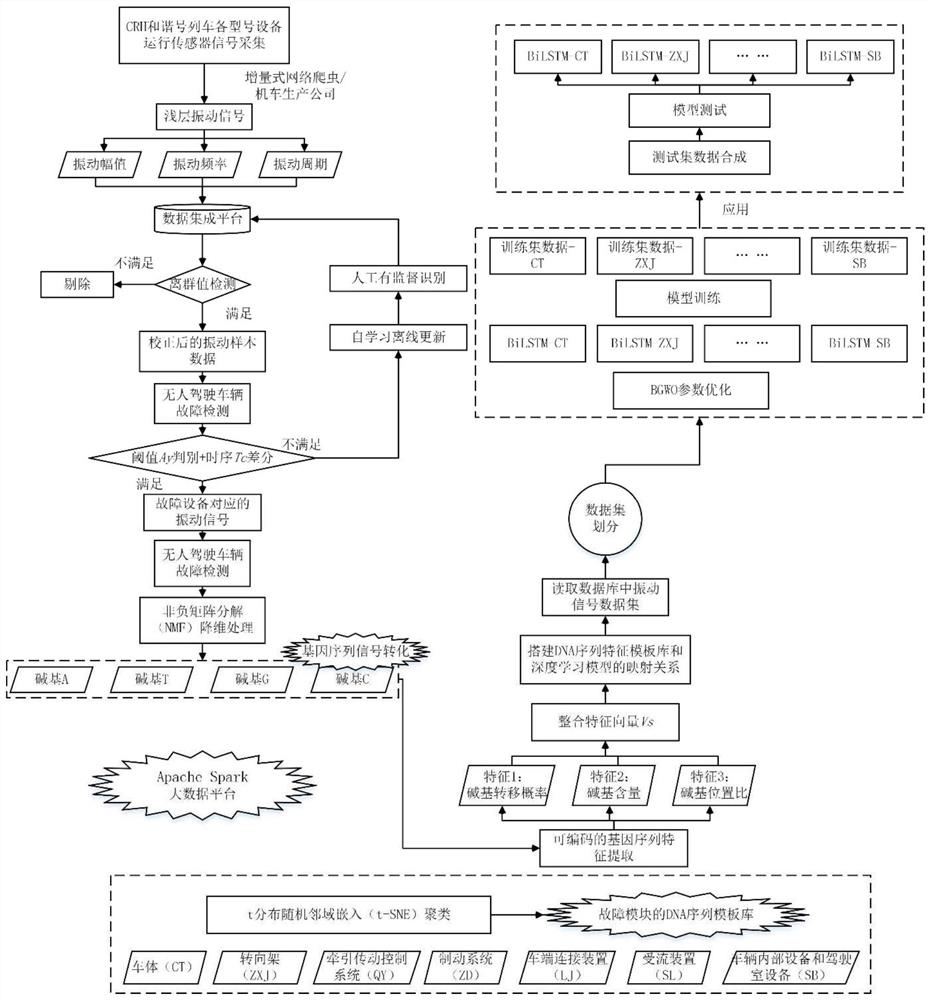
ActiveCN112650204AImplement fault diagnosisLower experience thresholdElectric testing/monitoringDimensionality reductionTerm memory
The invention discloses an intelligent rail unmanned vehicle fault gene identification method and system. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring historical vibration data of a train by adopting an incremental web crawler-based method; preprocessing the vibration amplitude EA and the vibration period ET of the vibration data, and outputting a new X; taking the X as the input of a fault detection module, and outputting fault sequence data E after detecting a fault sequence; taking the fault sequence data E as input of a dimension reduction model, and outputting encodable gene sequences I1, I2, I3 and I4; integrating the encodable gene sequences I1, I2, I3 and I4 into a DNA sequence S=S1, S2, S3,..., SN, extracting base characteristics of the DNA sequence, and permuting and combining the base characteristics to form a predictable pre-judged candidate vehicle part fault gene Vs; and training a bidirectional long-short-term memory network deep learning model by using the candidate vehicle part fault gene to obtain a classification model. The method can accurately identify the position and the type of the vehicle fault.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
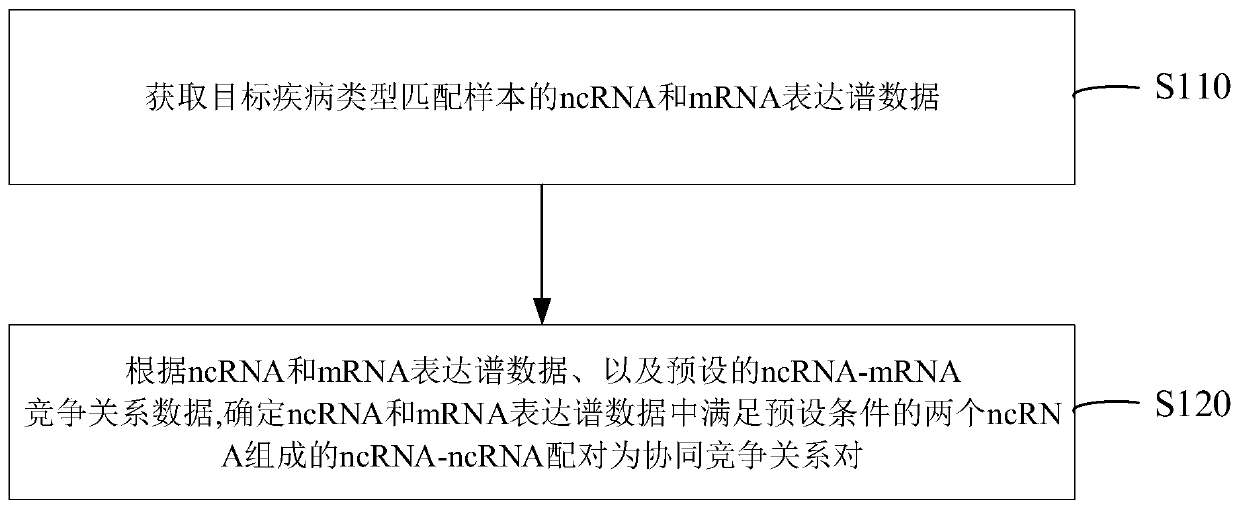
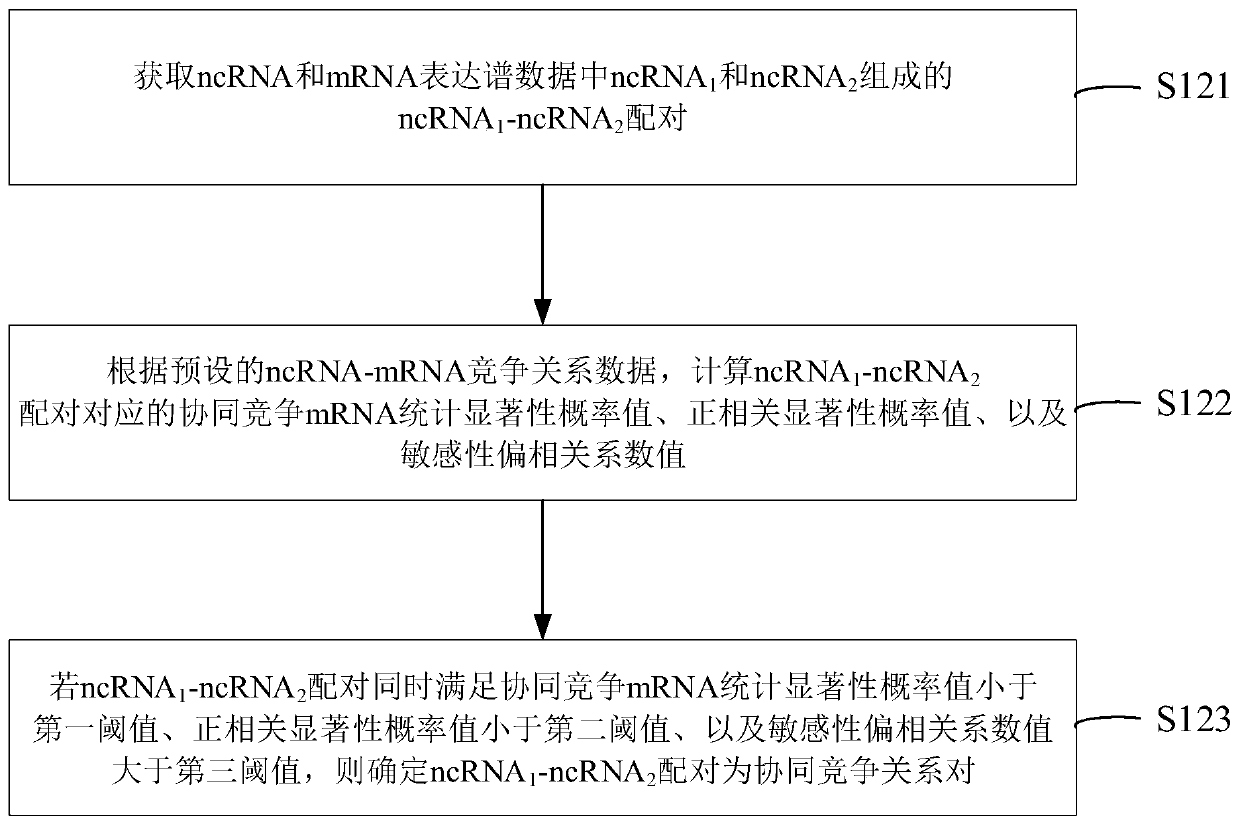
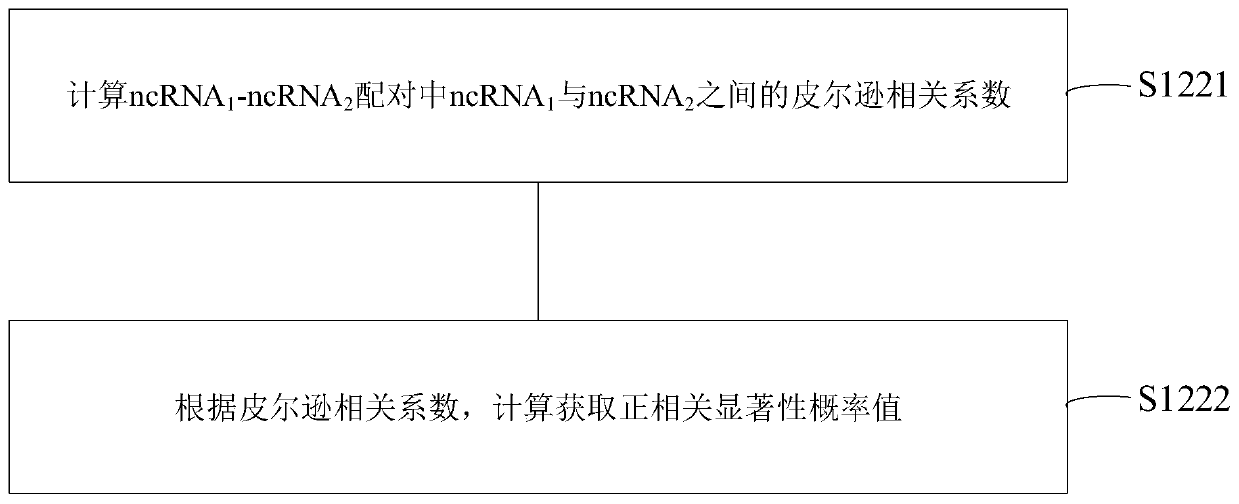
NcRNA collaborative competition network identification method and device
The invention provides an ncRNA collaborative competition network identification method and device, and relates to the technical field of gene identification. According to the method, ncRNA and mRNA expression profile data of a target disease type matching sample are obtained; and according to the ncRNA and mRNA expression profile data and preset ncRNA-mRNA competition relation data, an ncRNA-ncRNA pair consisting of two ncRNAs meeting a preset condition in the ncRNA and mRNA expression profile data is determined to be a cooperative competitive relationship pair. Thus, the ncRNA-ncRNA cooperative competition relation pair can be recognized an ncRNA cooperative competition network formed by competition of multiple ncRNAs and target gene mRNA can be recognized, and then reference can be provided for clinical diagnosis and targeted therapy of cancer and other human complex diseases.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
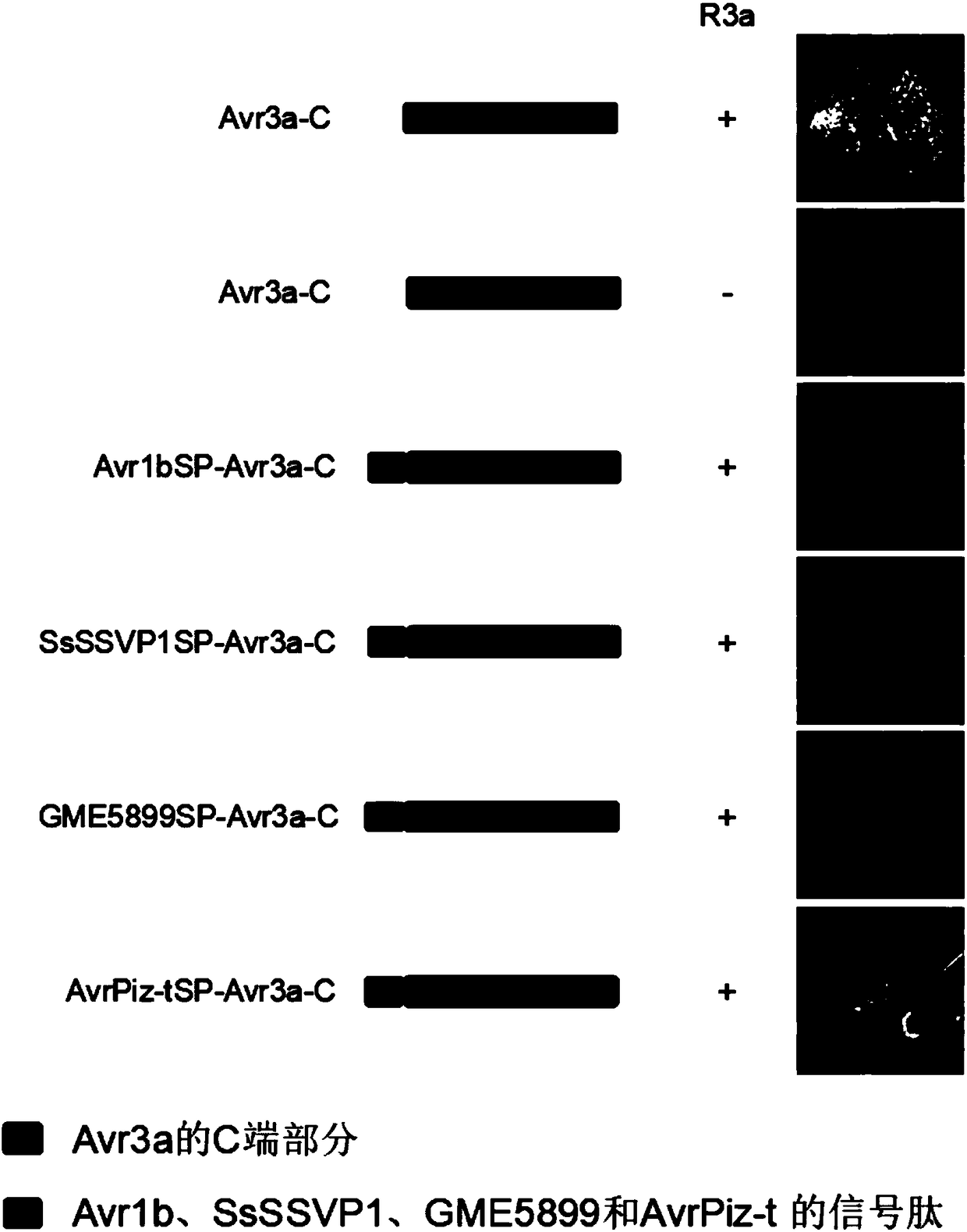
Method for indentifying non-toxic effect protein to identify signal peptide having secretion function by using anti-disease gene
ActiveCN108359689AShort timeLow costVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsSecretionSequence signal
The invention provides a method for indentifying non-toxic effect protein to identify signal peptide having a secretion function by using an anti-disease gene. The method comprises the following steps: 1) the to-be-identified signal peptide is connected with a C terminal construction expression carrier of phytophthora infestans nontoxic effect protein Avr3a, wherein the C terminal construction expression carrier of phytophthora infestans nontoxic effect protein Avr3a is shown as SEQ ID NO.3; 2) transforming the expression vector constructed in the step 1) to competent cell; and 3) injecting the competent cell in the step 2) and the competent cell containing the anti-disease gene in plant cells, and observing the necrotic condition of an injection site. If the injection site is necrotic, the to-be-detected signal peptide does not have the secretion function, and if the injection site has no necrotic condition, the to-be-detected signal peptide has the secretion function.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
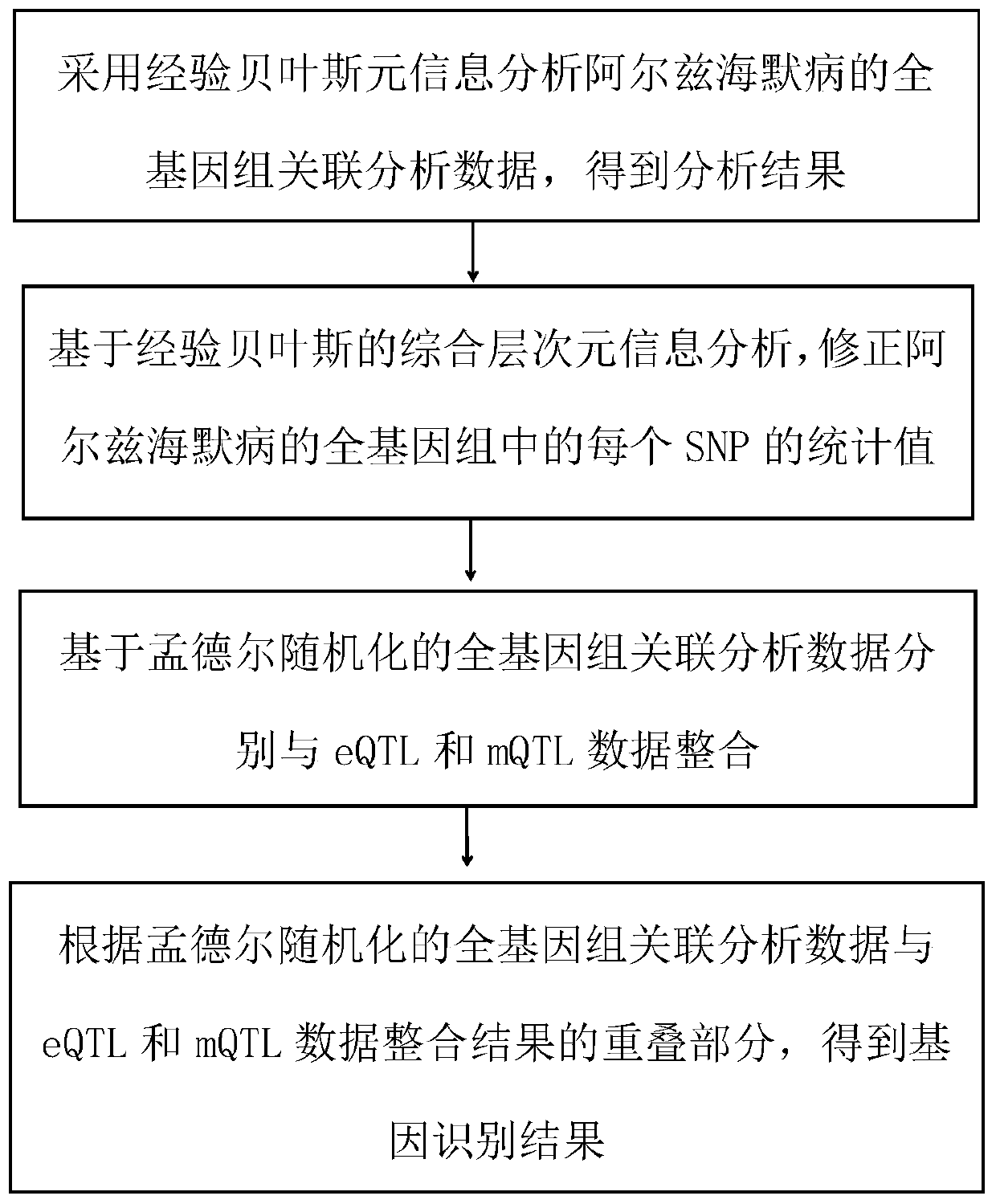
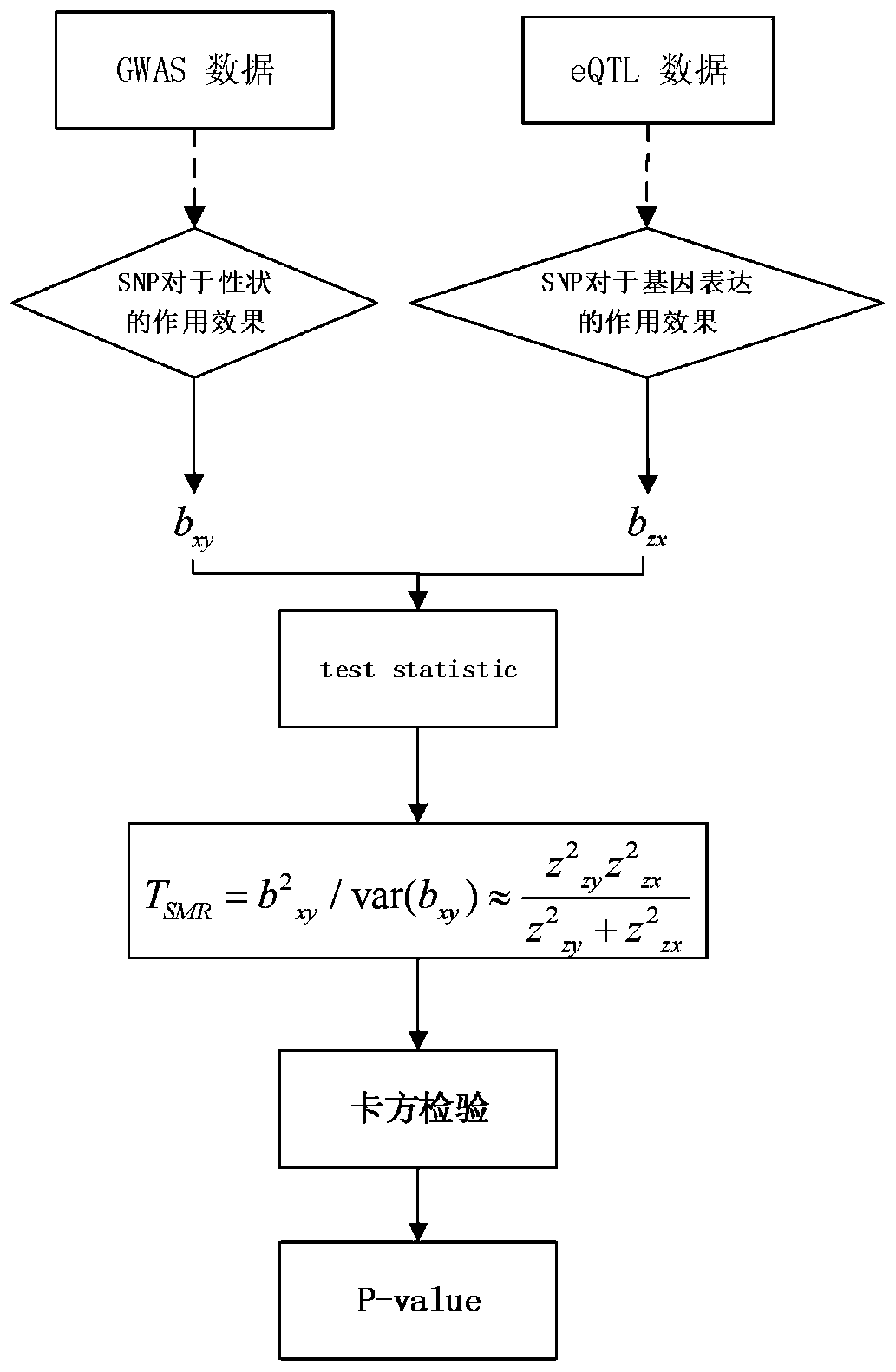
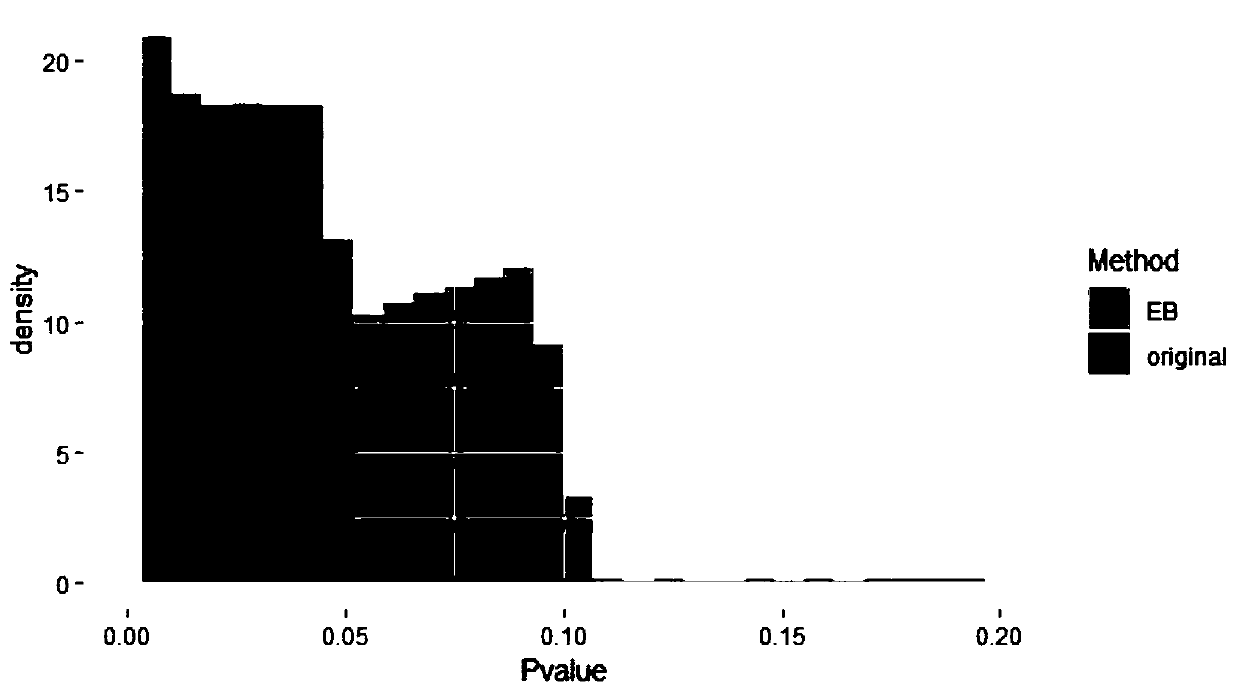
Gene recognition method based on empirical Bayesian and Mendel randomization fusion
PendingCN111180012AFast recognitionTake advantage ofBiostatisticsSequence analysisWhole Genome Association AnalysisMendelian randomization
The invention relates to a gene recognition method based on empirical Bayesian and Mendel randomization fusion. The method comprises the following steps: analyzing whole genome association analysis data by adopting empirical Bayesian meta-information to obtain an analysis result; correcting a statistical value of each SNP in the whole genome based on comprehensive hierarchical meta-information analysis of empirical Bayesian; integrating the whole genome association analysis data based on the Mendel randomization with the eQTL data and the mQTL data respectively, and obtaining a gene recognition result according to the overlapping part of the integration results of the whole genome association analysis data based on the Mendel randomization integrating with the eQTL data and the mQTL data.According to the method, the recognition speed of AD related genes can be greatly increased, existing data are fully utilized and the recognition speed of disease related genes is increased, and the research and development cost is saved; and the calculation result can screen out a great part of genes, so that a valuable research range is provided for subsequent biological experiments.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
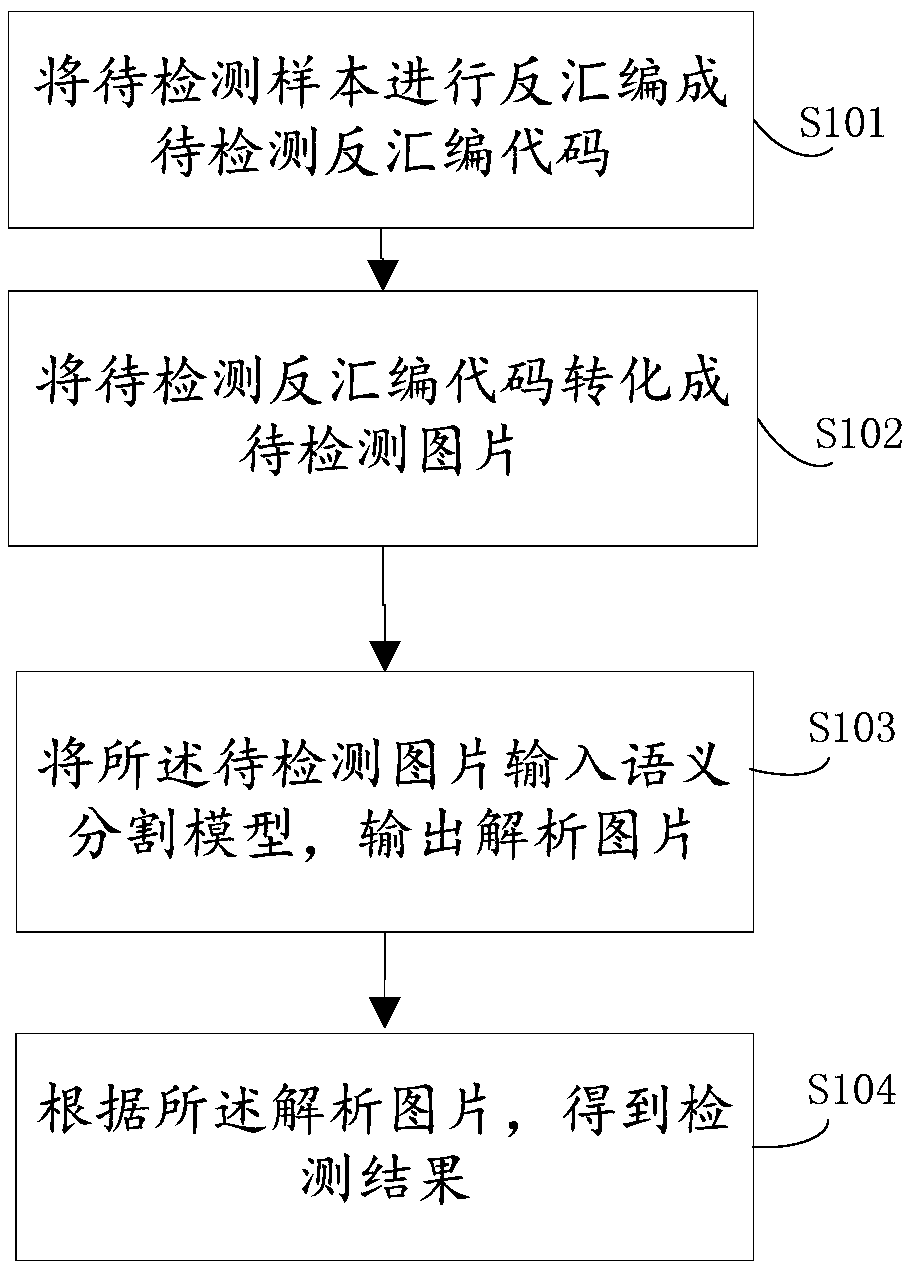
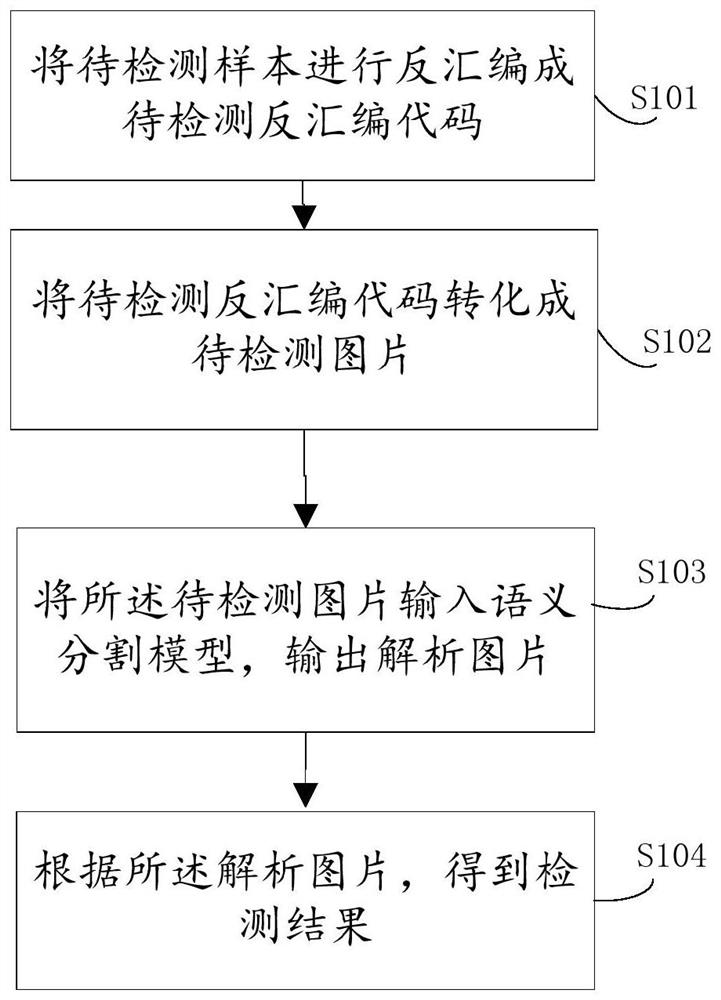
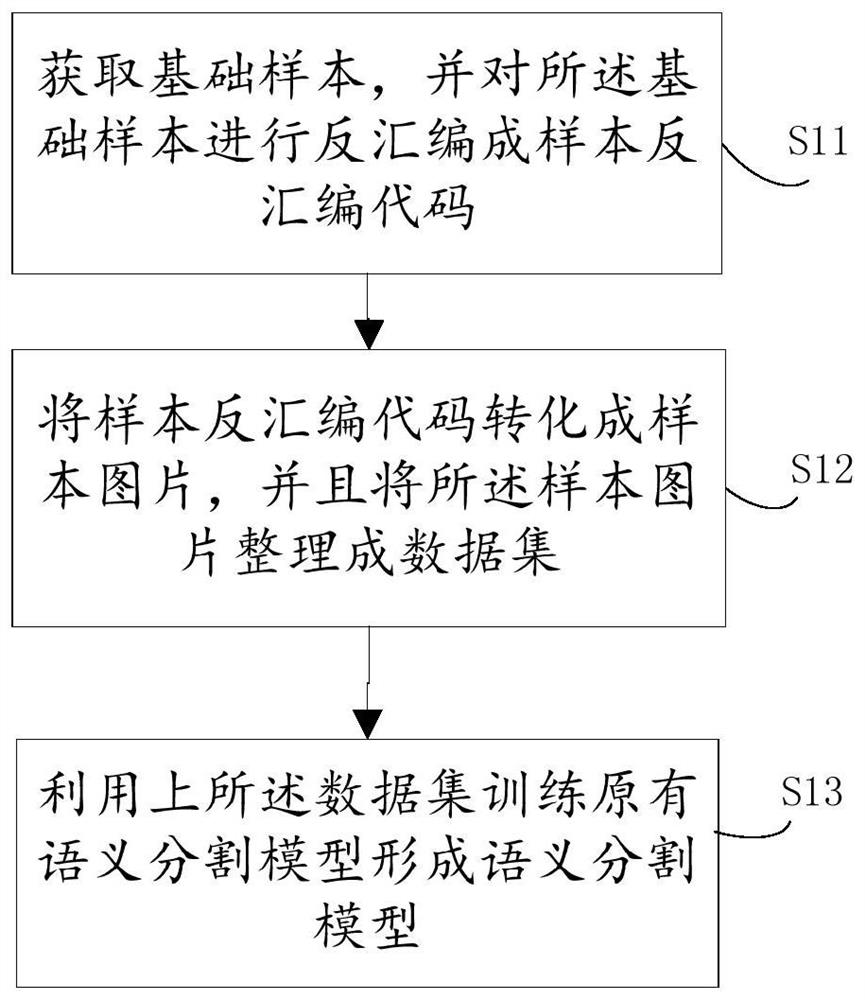
Rapid malware gene detection method and device based on semantic segmentation
ActiveCN109492396AImprove matching detection efficiencyImprove the accuracy of gene identificationCharacter and pattern recognitionPlatform integrity maintainanceFeature extractionGene bank
The invention provides a rapid malicious software gene detection method and device based on semantic segmentation, the matching detection efficiency of real-time samples can be greatly improved through a semantic segmentation model trained by a gene bank, and the trained semantic segmentation model does not need to carry the characteristics of the gene bank and even can be embedded into an offlinereal-time safety product; the gene recognition accuracy of malicious deformation can be improved through the automatic abstract feature extraction characteristic and the follow-up mature optimizationtechnology.
Owner:HANGZHOU ANHENG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Method for analyzing analgesic effect of active ingredients of nux vomica based on network pharmacology
The invention discloses a method for analyzing the analgesic effect of active ingredients of nux vomica based on network pharmacology. The method comprises the following steps: S1, obtaining chemicalcomponents and component action targets of nux vomica, wherein nux vomica is used as a keyword, and retrieving is performed by utilizing a BATMAN-TCM database to obtain a nux vomica active compound meeting conditions and a targeting gene thereof; S2, identifying a disease action target, wherein a virtual target gene related to pain is acquired by using a DisGeNET database, and intersection is performed on the nux vomica active compound and the target gene thereof to obtain a drug-disease intersection target gene; S3, constructing a nux vomica and disease network, and screening a core node; andS4, performing GO enrichment and KEGG pathway annotation analysis on the core node by using the DAVID, predicting target function distribution, analyzing the enrichment degree of the core pathway according to the enrichment factor, and analyzing the nux vomica analgesic action mechanism. With the method, the problems of long nux vomica research period, lack of systematicness, single research target and the like at present are solved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HOSPITAL OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
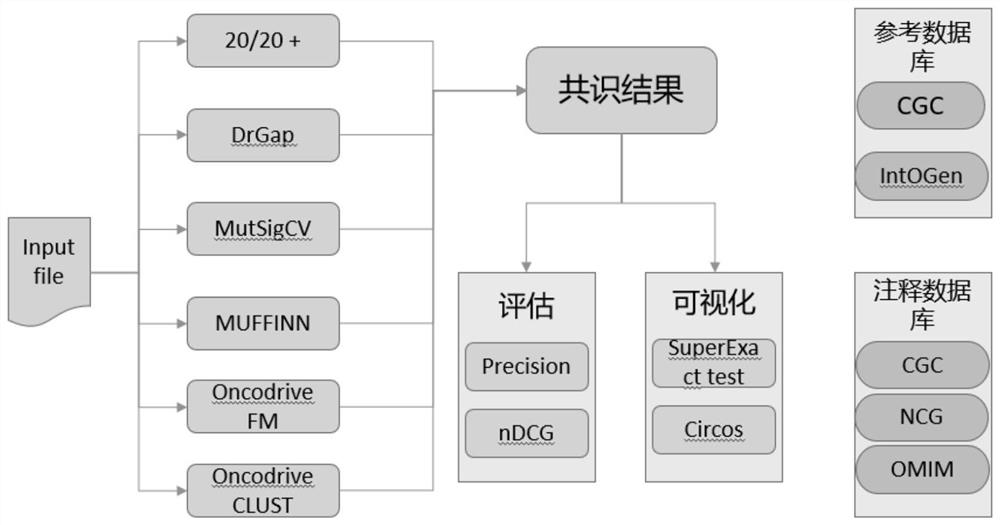
Method for identifying cancer driver gene by using consensus prediction result
The invention discloses a method for identifying a cancer driver gene by using a consensus prediction result. The method comprises the following steps: S1, receiving a mutation annotation format (MAF) file as input; S2, processing all the preprocessed input mutation data so as to respectively obtain a candidate driver gene list of each strategy; S3, on the basis of each differential driving gene list, obtaining a common driving gene list by using a rank integration method RobustRankAggreg; S4, evaluating the performance of the result by using Top-N-Precision and Top-N-nDCG, and carrying out KEGG pathway and gene ontology analysis on the common driver gene; S5, obtaining a consensus driving gene list by using an RAA algorithm; S6, employing the SuperExactTest and the Circos for organizing a visualization result. The method has certain superiority in driver gene prediction, although height difference exists between different driver gene identification strategies, not only can the most reliable driver gene be identified through cross analysis of results of each independent strategy, but also potential novel driver genes with undefined features can be found.
Owner:上海基绪康生物科技有限公司
Gene detection method, model training method, device, equipment and system
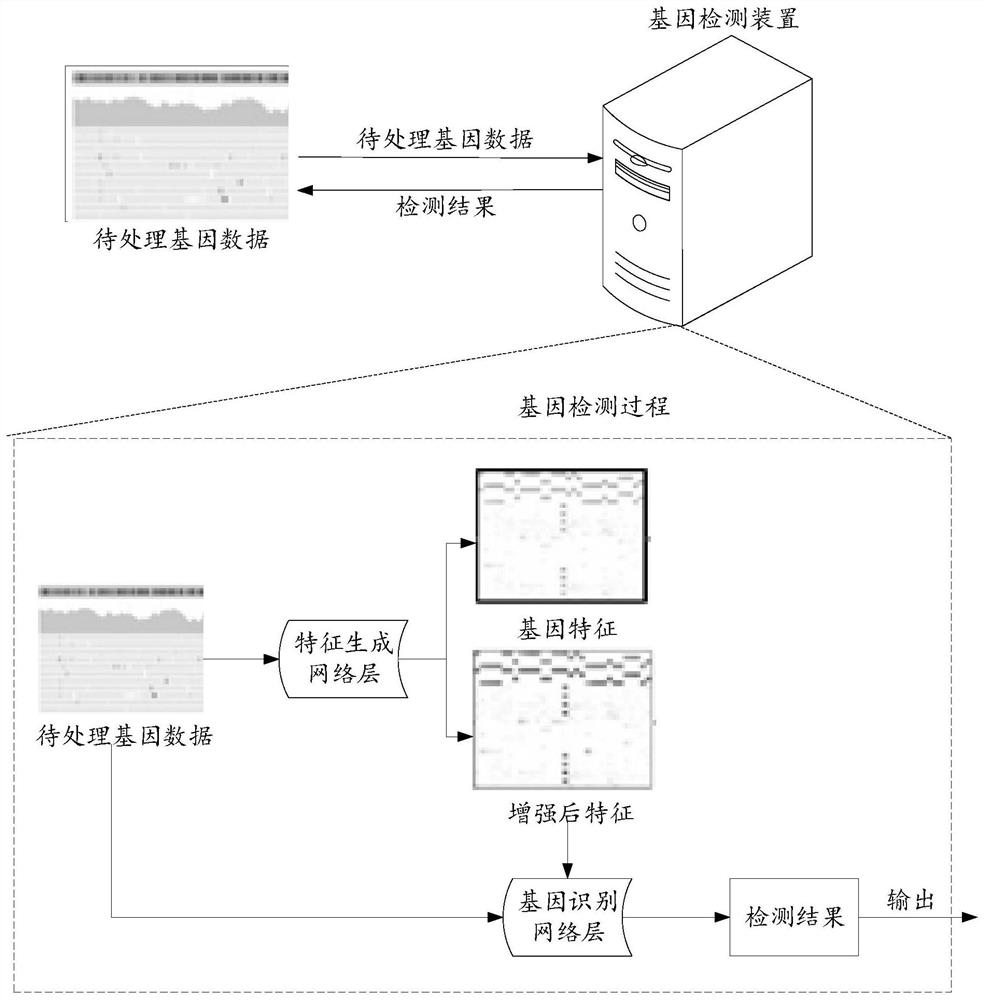
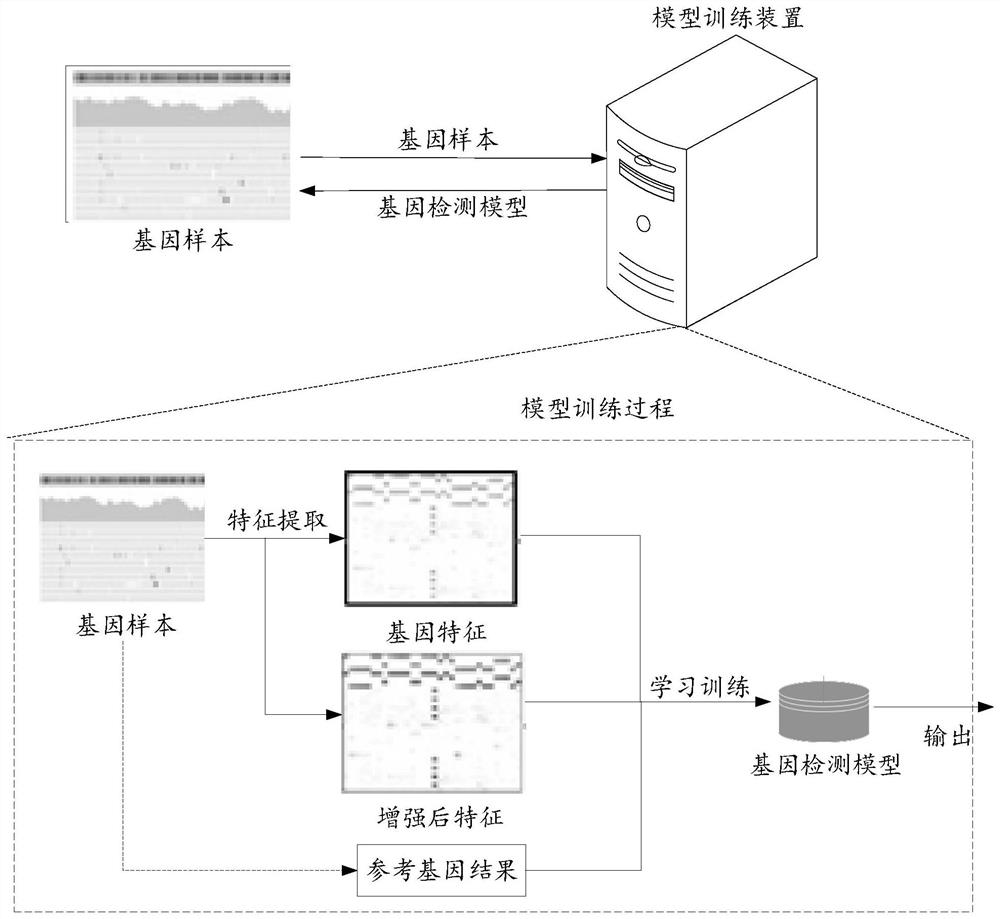
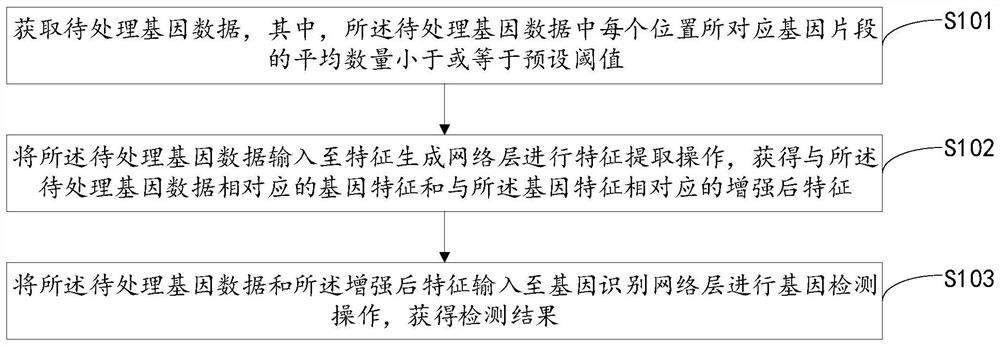
PendingCN113539357AGuaranteed accuracyImprove practicalityBiostatisticsProteomicsProcessed GenesFeature extraction
The embodiment of the invention provides a gene detection method, a model training method, a device, equipment and a system. The gene detection method comprises the following steps: acquiring to-be-processed gene data, wherein the average number of gene segments corresponding to each position in the to-be-processed gene data is smaller than or equal to a preset threshold value; inputting the to-be-processed gene data into a feature generation network layer for feature extraction operation to obtain gene features corresponding to the to-be-processed gene data and enhanced features corresponding to the gene features; and inputting the to-be-processed gene data and the enhanced features into a gene identification network layer for gene detection operation to obtain a detection result. According to the technical scheme provided by the embodiment, feature extraction operation is carried out through low-depth gene data, the gene features and the enhanced features corresponding to the gene features are obtained, and detection operation is carried out based on the enhanced features, so the accuracy of a gene detection result is ensured, and the data processing cost and the data processing amount are also reduced.
Owner:ALIBABA SINGAPORE HLDG PTE LTD
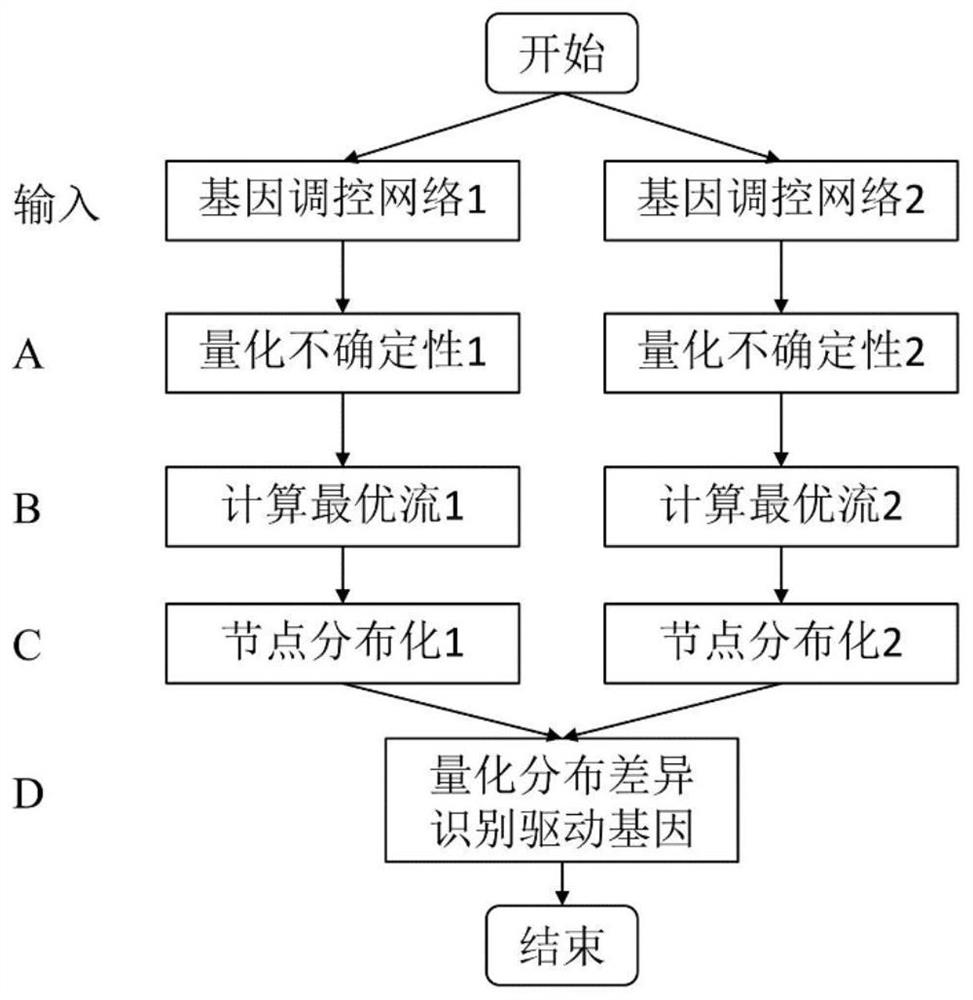
Method for identifying driver gene from differential network
The invention discloses a method for identifying a driver gene in a differential network. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: giving two gene regulation and control networksrepresenting two biological states; quantifying the uncertainty of edges in the networks, then calculating the strongest and most stable regulation relationship between any two nodes in the networks;then characterizing and expressing the nodes as the distribution of network flows; and finally, quantifying the network flow distribution difference of each gene in the two networks so as to identifythe driver gene. The method is different from other existing difference network analysis methods, and has the main contribution that the difference of network topology is described by combining network flow and information entropy. The combination has the advantages that the uncertainty of edges in the gene regulation and control networks can be quantified, and meanwhile, comprehensive topological characteristics (local and global, linear and nonlinear characteristics) in the network can be captured, so higher driver gene recognition accuracy and robustness can be achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
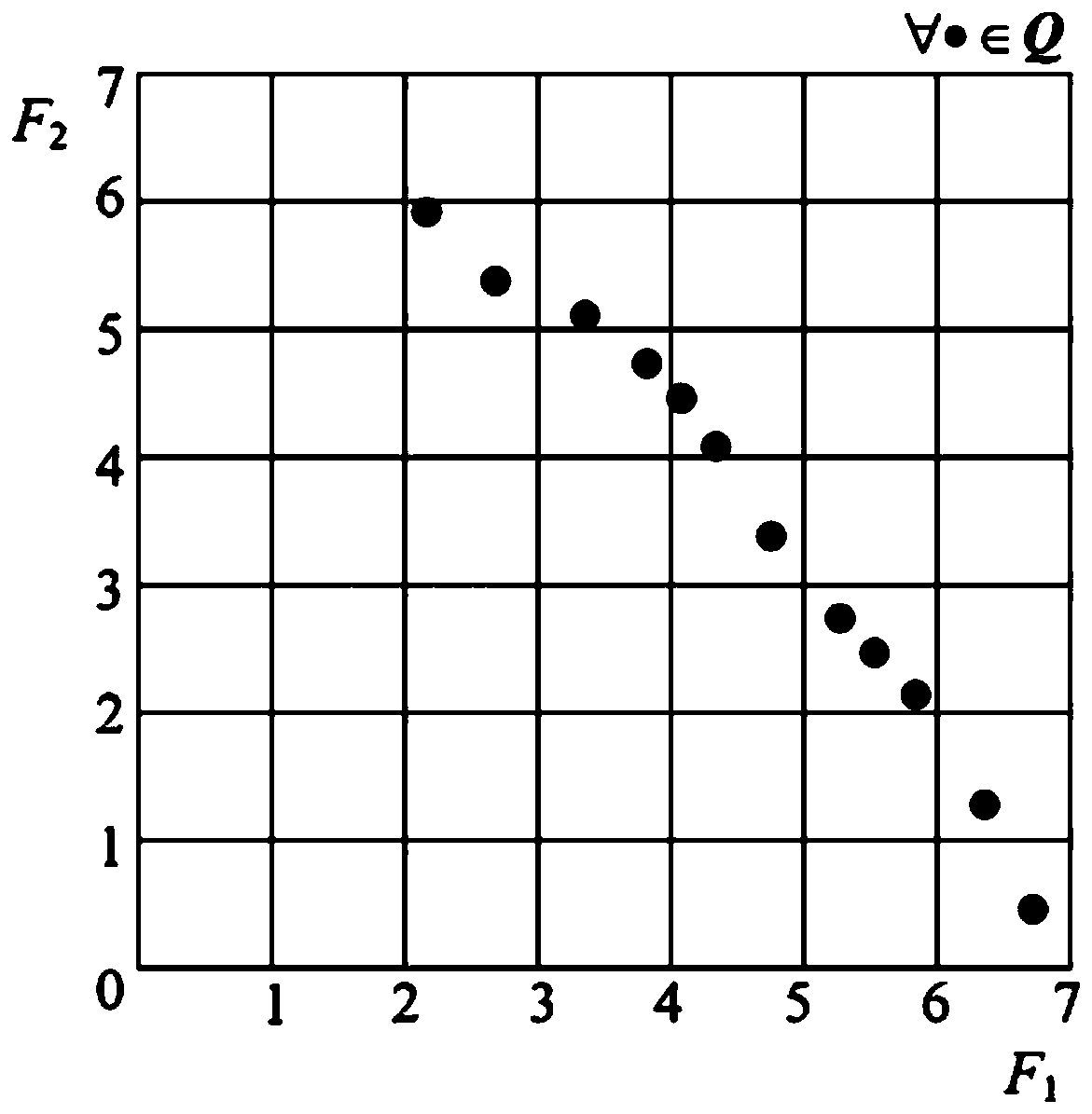
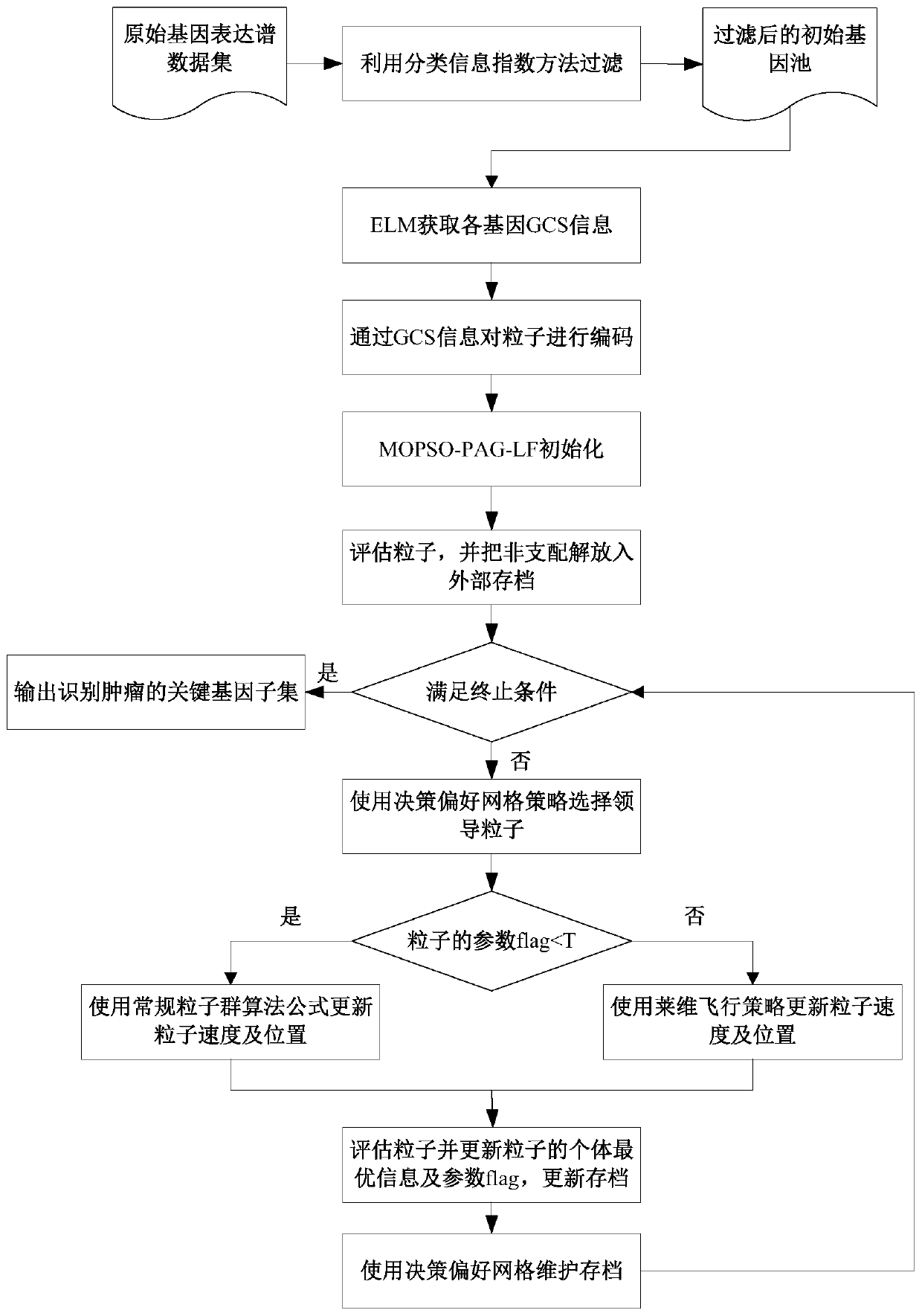
Tumor key gene identification method based on multi-objective particle swarm algorithm of preference grid and Levi flight
PendingCN110782950AImprove decision-making efficiencyFast convergenceBiostatisticsProteomicsLearning machineData set
The invention discloses a tumor key gene identification method based on a multi-objective particle swarm algorithm of a preference grid and Levi flight. The method comprises the steps that a classification information index is used to filter an original gene expression profile data set to acquire a primary gene pool; the GCS value of the gene category sensitivity information of each gene in the initial gene pool is calculated, and then particles are encoded by the GCS value; the classification accuracy of gene subsets on an extreme learning machine ELM and the size of the gene subsets are targeted to build a multi-objective optimization model; and the final gene subset is searched through the established multi-objective model, and then the key genes of a tumor are identified. In terms of the multi-objective optimization model, the method provided by the invention can quickly and efficiently identify a small number of key gene subsets with good classification performance in the primarygene pool through the multi-objective model.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
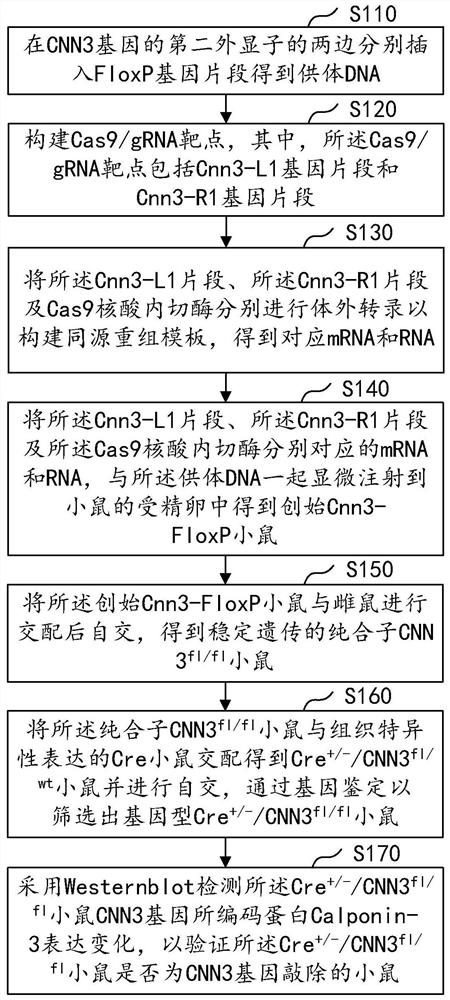
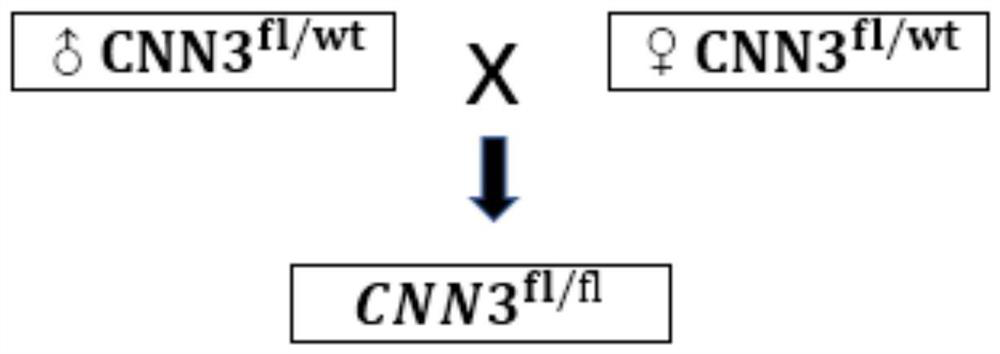
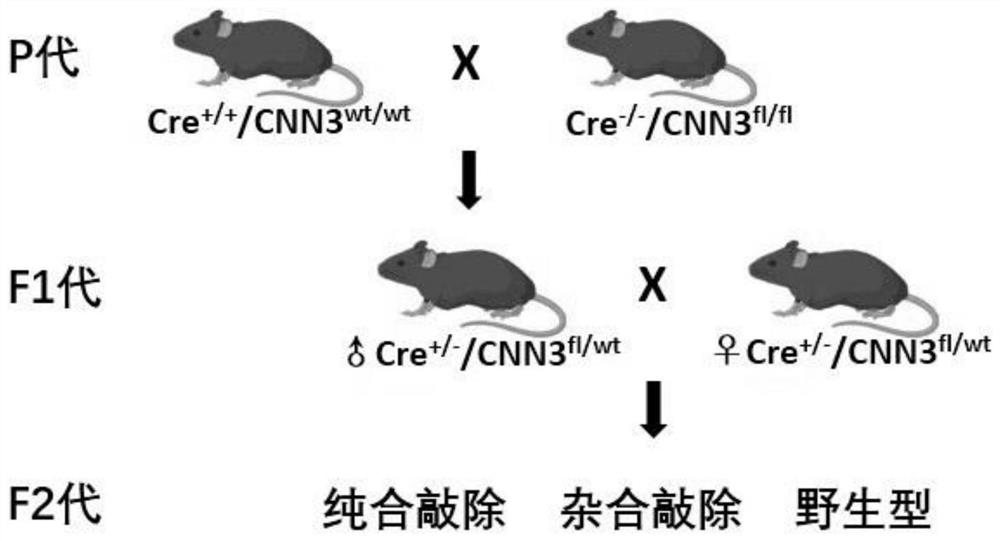
Construction method of CNN3 gene knockout mouse model based on Cre-FloxP system
PendingCN113584030AGenetic stabilityGenetically efficientHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAGenotypeGene recognition
The invention discloses a construction method of a CNN3 gene knockout mouse model based on a Cre-FloxP system, which comprises the following steps: respectively inserting FloxP gene segments at two sides of a second exon of a CNN3 gene, constructing a Cas9 / gRNA target and a homologous recombination template, carrying out microinjection on the homologous recombination template and donor DNA into a fertilized egg of a mouse to obtain a Cnn3-FloxP mouse, and carrying out Cre-FloxP system-based CNN3 gene knockout mouse model; after mating with a female mouse, conducting selfing to obtain a stably inherited homozygote CNN3fl / fl mouse; after the homozygote CNN3fl / fl mouse and a Cre mouse with tissue specific expression are copulated, conducting selfing, and screening out the mouse with the genotype of Cre + / - / CNN3fl / fl through gene recognition. The invention relates to the technical field of gene design, can efficiently construct a mouse with specific tissue or specific cell CNN3 gene knockout, and greatly improves the construction efficiency and the construction success rate of the mouse model with the selective CNN3 knockout function.
Owner:FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF KUNMING MEDICAL UNIV
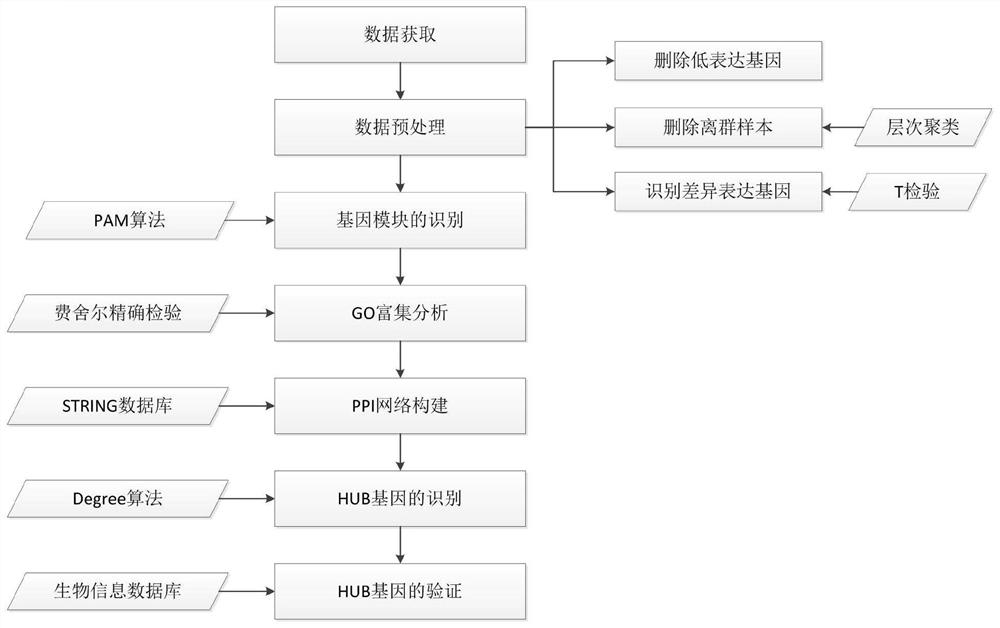
Gene expression data analysis method based on PAM clustering algorithm
PendingCN113380326AEasy to digEasy to analyzeBiostatisticsCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmGene recognition
The invention discloses a gene expression data analysis method based on a PAM clustering algorithm, and relates to the field of data analysis. The method comprises the steps of data acquisition, data preprocessing, gene module identification, GO enrichment analysis, PPI network construction, HUB gene identification and HUB gene verification. According to the method, on the basis of fully utilizing information contained in gene expression data, the optimal membership module can be searched for each gene through multiple iterations, so that the identified gene module is more reliable. The hidden information contained in the gene module can be better mined, so that the bioinformatics problem to be solved is comprehensively analyzed. According to the method, data preprocessing is performed on the gene expression data, so that the problems of much noise, many irrelevant genes, sparse data and the like in the gene expression data are solved. Through the downstream bioinformatics analysis process, a series of bioinformatics analysis can be completed, and the bioinformatics problems to be solved can be comprehensively analyzed and explained.
Owner:吉林省蒲川生物医药有限公司
Hepatitis B virus enrichment fluorescent PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection method
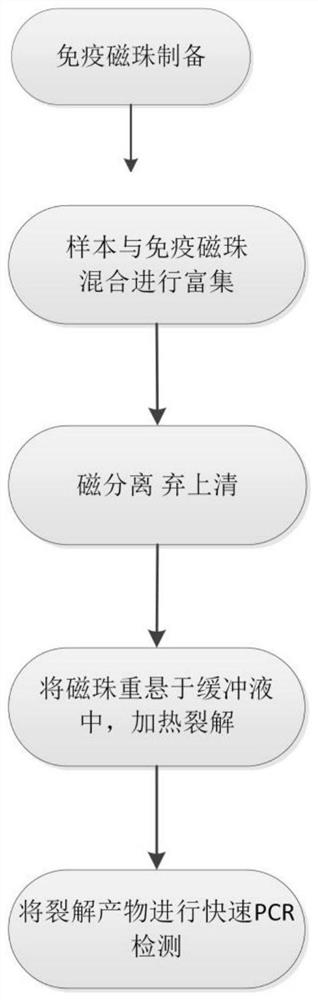
PendingCN114200127AEasy to storeEasy to transportMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisSuperparamagnetic beadsHepatitis B immunization
The invention relates to a hepatitis B virus enrichment fluorescent PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection method which comprises the following steps: S1, preparation of immunomagnetic beads: coupling hepatitis B virus antibodies to carboxyl modified superparamagnetic beads to obtain the immunomagnetic beads coupled with the hepatitis B virus antibodies, s2, enrichment of hepatitis B virus: mixing and incubating hepatitis B virus positive serum or plasma with the immunomagnetic beads coupled with the hepatitis B virus antibody; s3, separating the immunomagnetic bead-virus compound by using a magnetic tool, resuspending the immunomagnetic bead-virus compound in a salt ion buffer solution, and heating and cracking; and S4, separating the magnetic beads by using a magnetic tool to obtain enriched and concentrated hepatitis B virus, and directly detecting liquid in a split product by using a fluorescent PCR reagent. According to the invention, the detection sensitivity is greatly improved due to enrichment and concentration, the specificity is strong due to immune recognition and gene recognition, and the fluorescent PCR detection time is short due to the use of a rapid PCR reagent.
Owner:杭州丹威生物科技有限公司
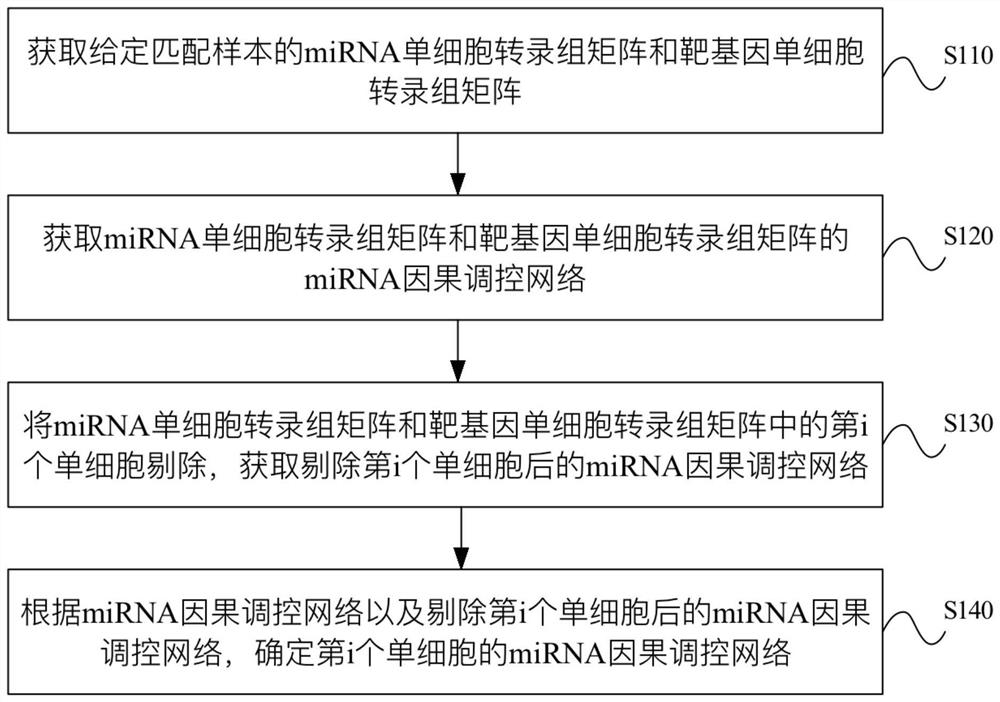
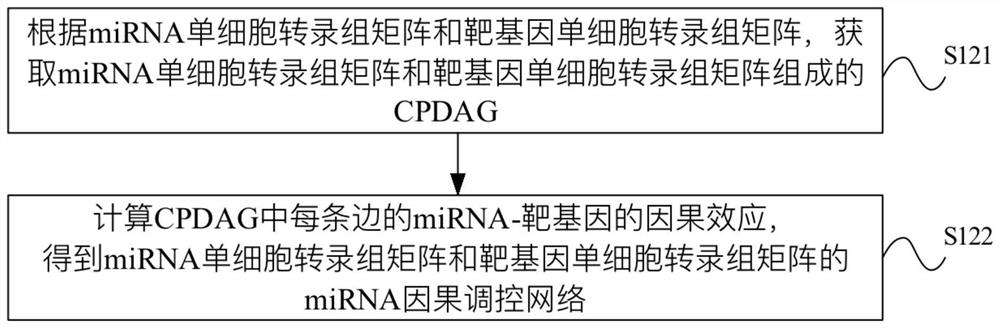
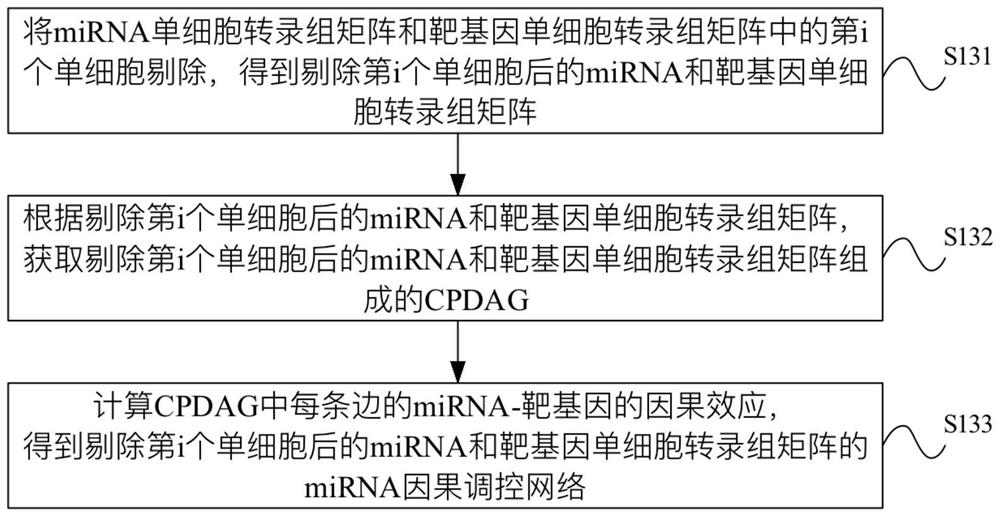
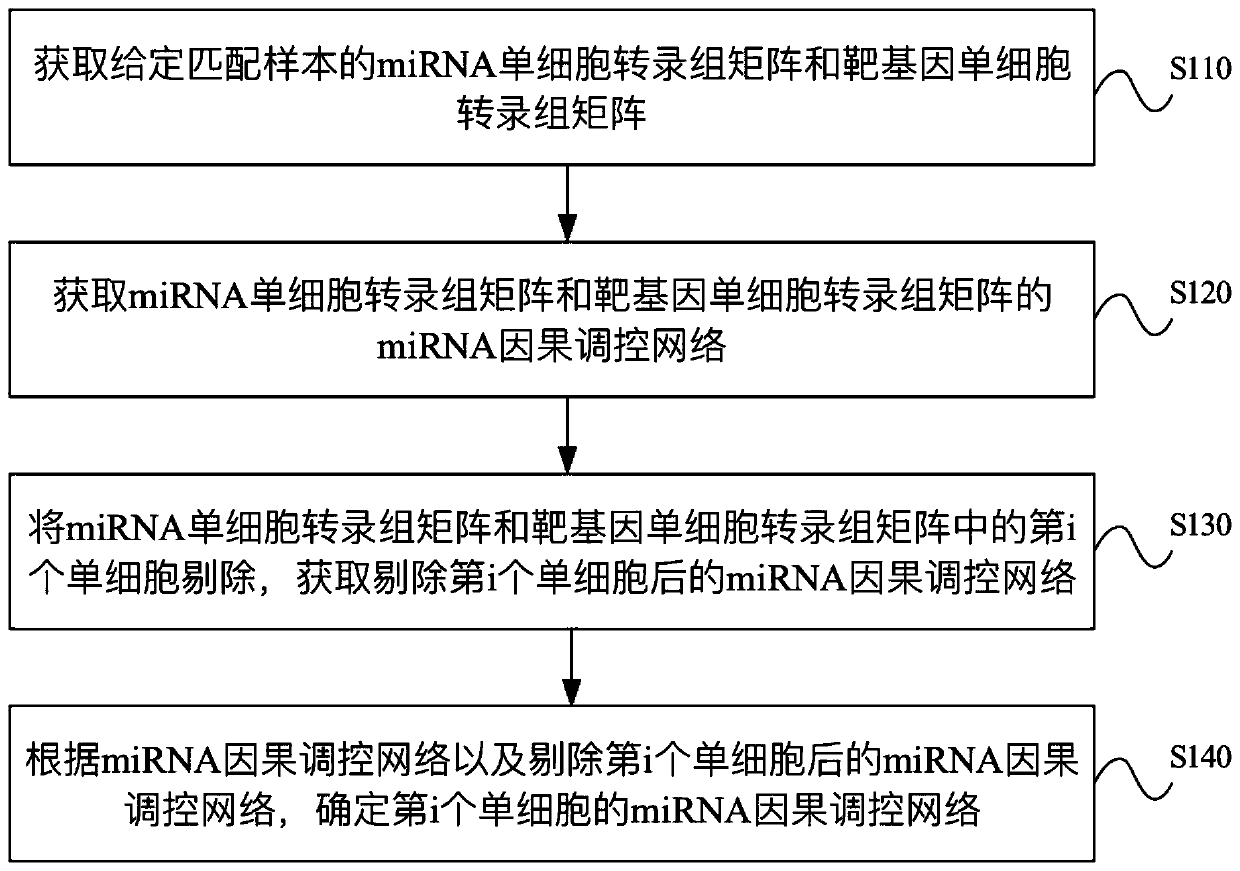
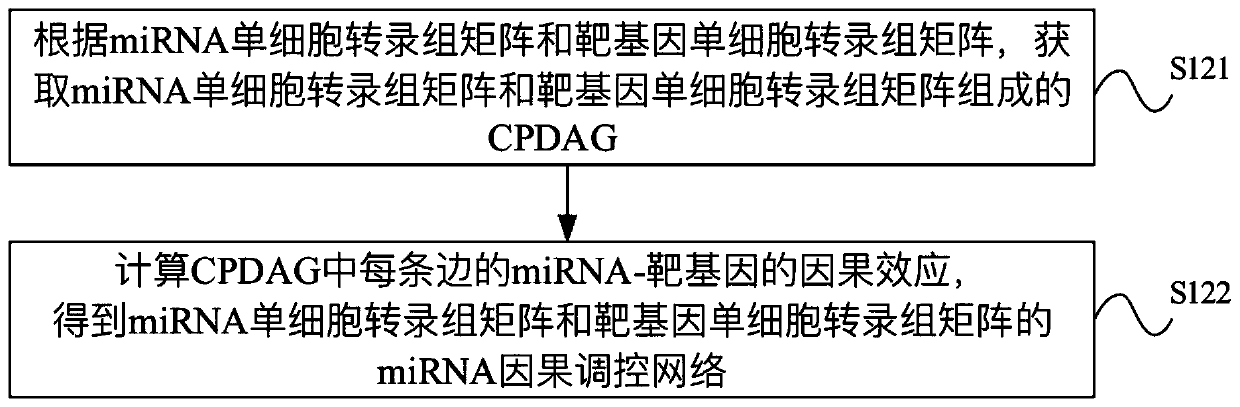
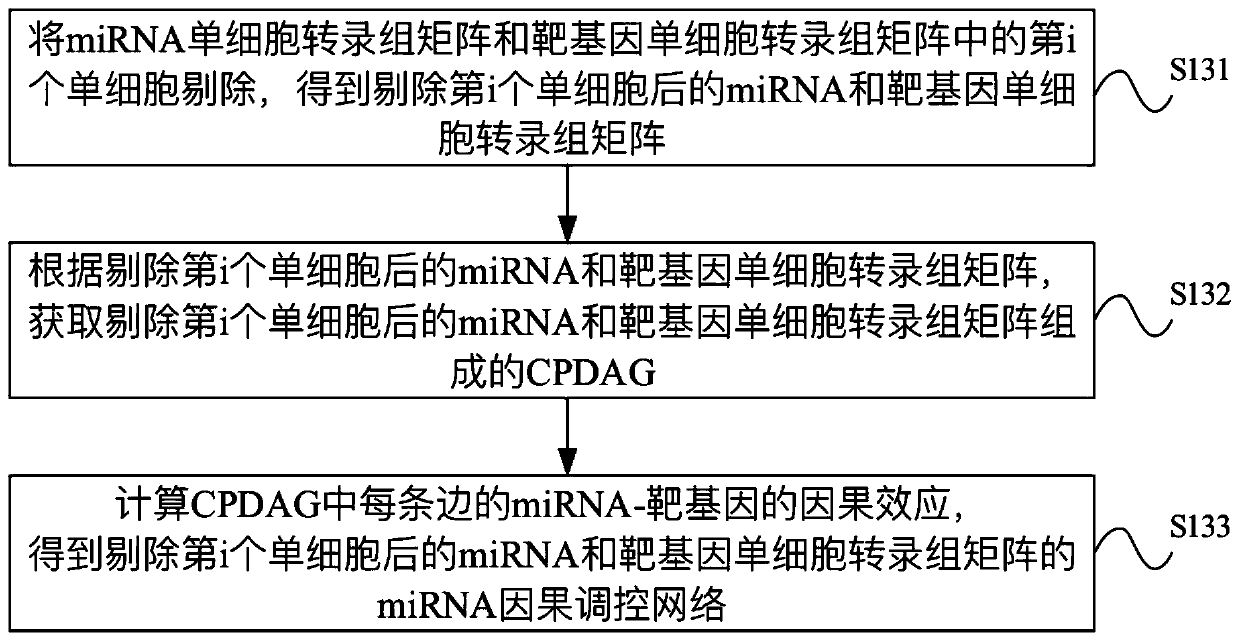
miRNA causal regulation network identification method, device, electronic equipment and storage medium
The invention provides a miRNA causal regulation network identification method and device, and relates to the technical field of gene identification. The miRNA causal regulatory network identification method includes: obtaining a miRNA single-cell transcriptome matrix and a target gene single-cell transcriptome matrix of a given matched sample. Obtain the miRNA causal regulatory network of miRNA single-cell transcriptome matrix and target gene single-cell transcriptome matrix. The i-th single cell in the miRNA single-cell transcriptome matrix and the target gene single-cell transcriptome matrix was eliminated to obtain the miRNA causal regulatory network after the i-th single cell was eliminated. According to the miRNA causal regulatory network and the miRNA causal regulatory network after removing the i-th single cell, the miRNA causal regulatory network of the i-th single cell was determined. Since the heterogeneity of each single cell is considered, the single-cell miRNA causal regulatory network is identified at the single-cell level, reflecting the effect of the real miRNA causal regulatory mechanism.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
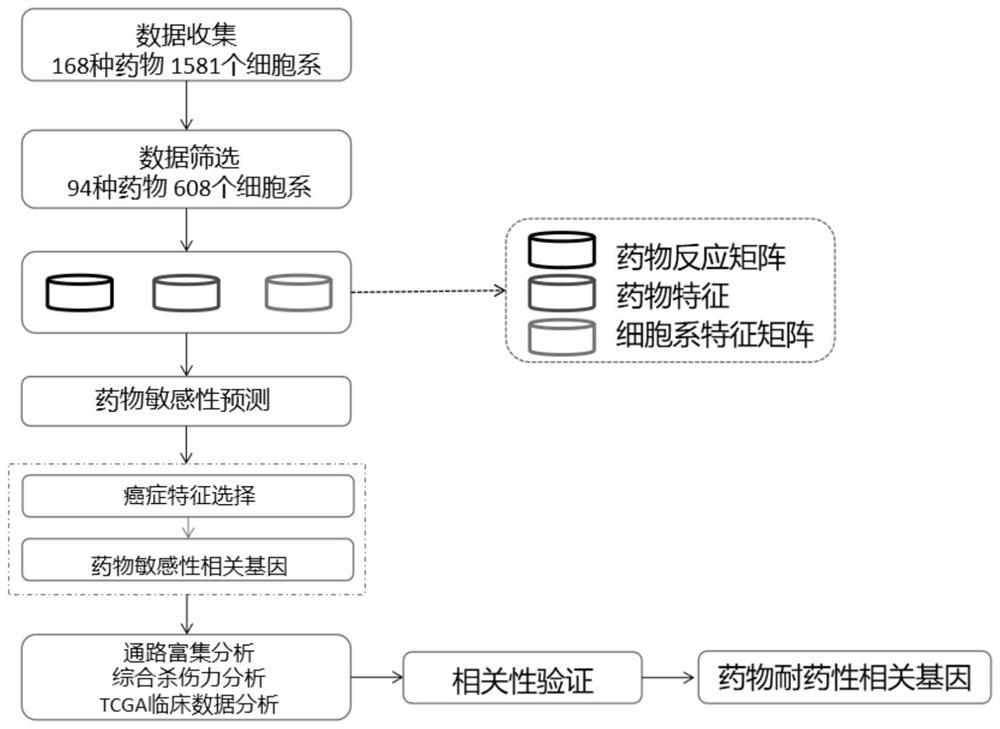
Comprehensive analysis method for predicting anti-cancer drug reaction related genes
PendingCN113362895AEasy to identifyAccurate prediction rateBiostatisticsHybridisationCancer cellCancer type
The invention relates to the technical field of drug research and development, and discloses a comprehensive analysis method for predicting anti-cancer drug reaction related genes, which comprises the following steps: 1) carrying out drug sensitivity prediction and feature gene identification; 2) carrying out drug sensitivity prediction based on a collaborative filtering method; and 3) identifying a drug sensitivity related gene of a specific cancer type. According to the method, a complete calculation pipeline is established to identify characteristic genes related to drug sensitivities and drug resistance of different cancer types, different drug sensitivities in a cancer cell line are predicted by using a collaborative filtering-based algorithm, and a group sparse model is used for selecting the characteristic genes of the drug sensitivities of a specific cancer type. The simultaneous integration of multiple drug cell line data and the expandability for further important gene identification can be realized, and meanwhile, the collaborative filtering algorithm has the advantage that the sensitivity of heterogeneous drug cell lines among multiple drugs can be modeled at the same time.
Owner:上海基绪康生物科技有限公司
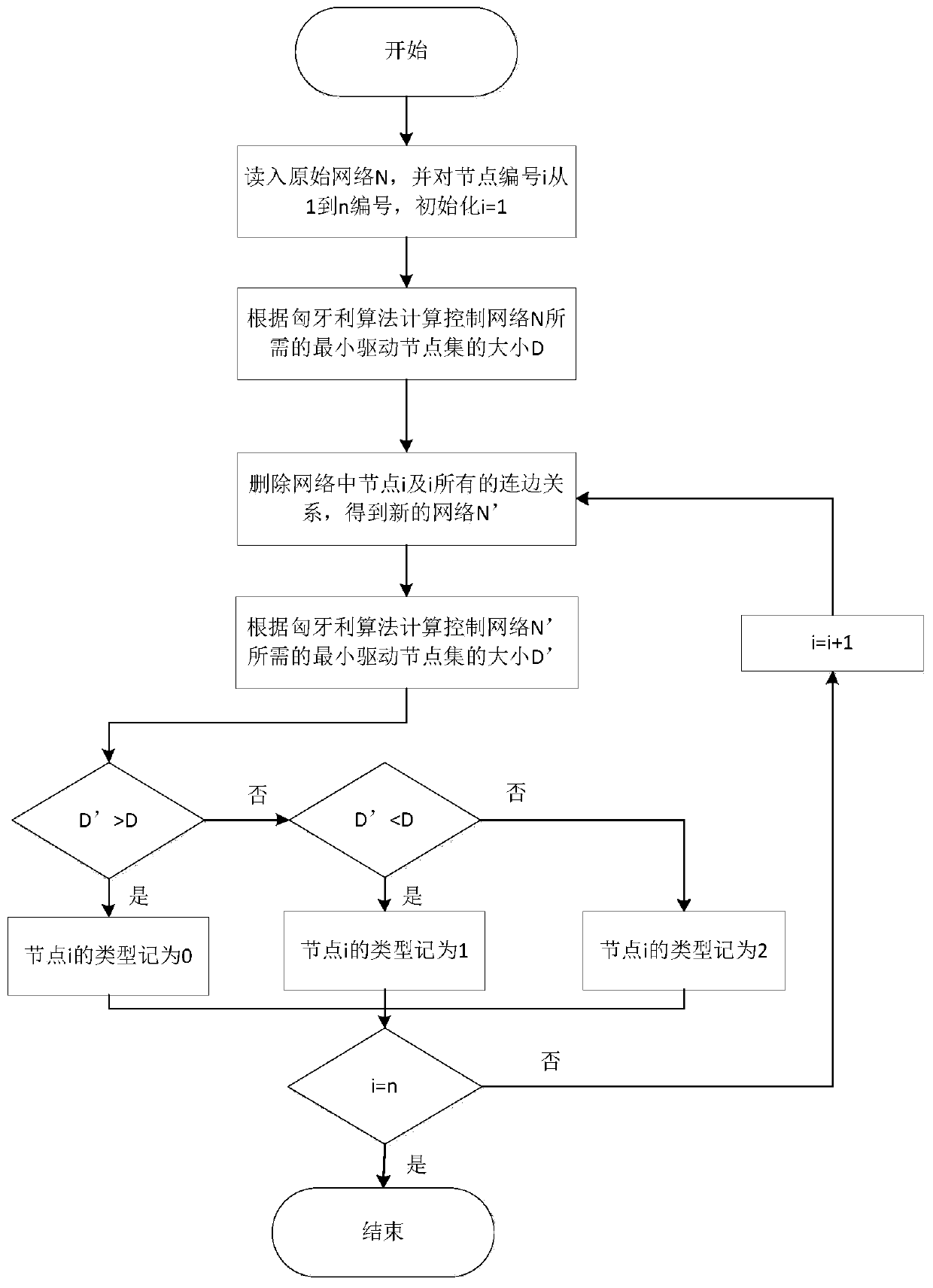
Method for identifying controllable gene based on complex network structure
The invention provides a method for identifying controllable gene based on complex network structure. A controllability node classification framework is constructed; genes are divided into different types for controlling role differences; a new gene is identified through statistical significance. According to the gene recognition method based on the controllable node classification framework, global information in a network is considered, gene classification is achieved from multiple control levels, the framework is applied to a tissue-specific regulation and control network, genes with remarkable biological significance can be systematically detected, and a tool platform is provided for further gene research.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
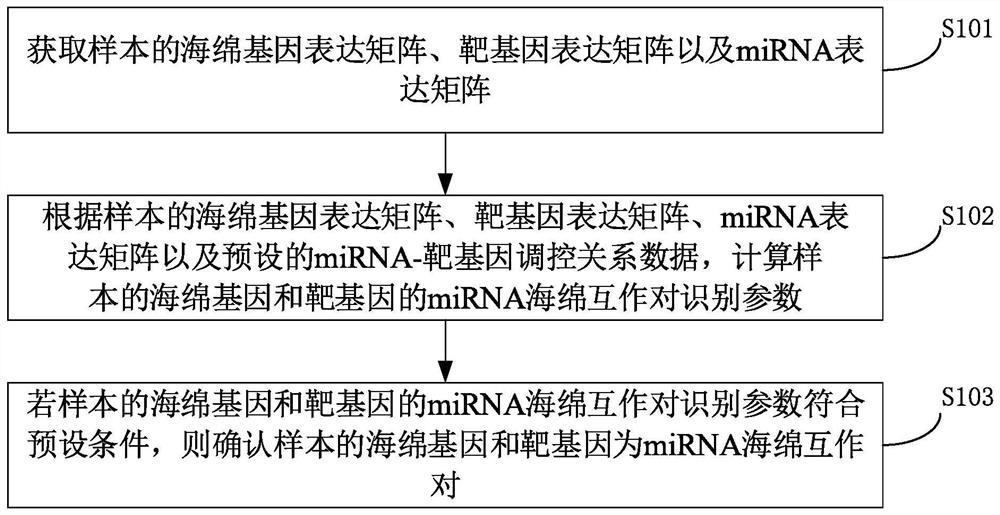
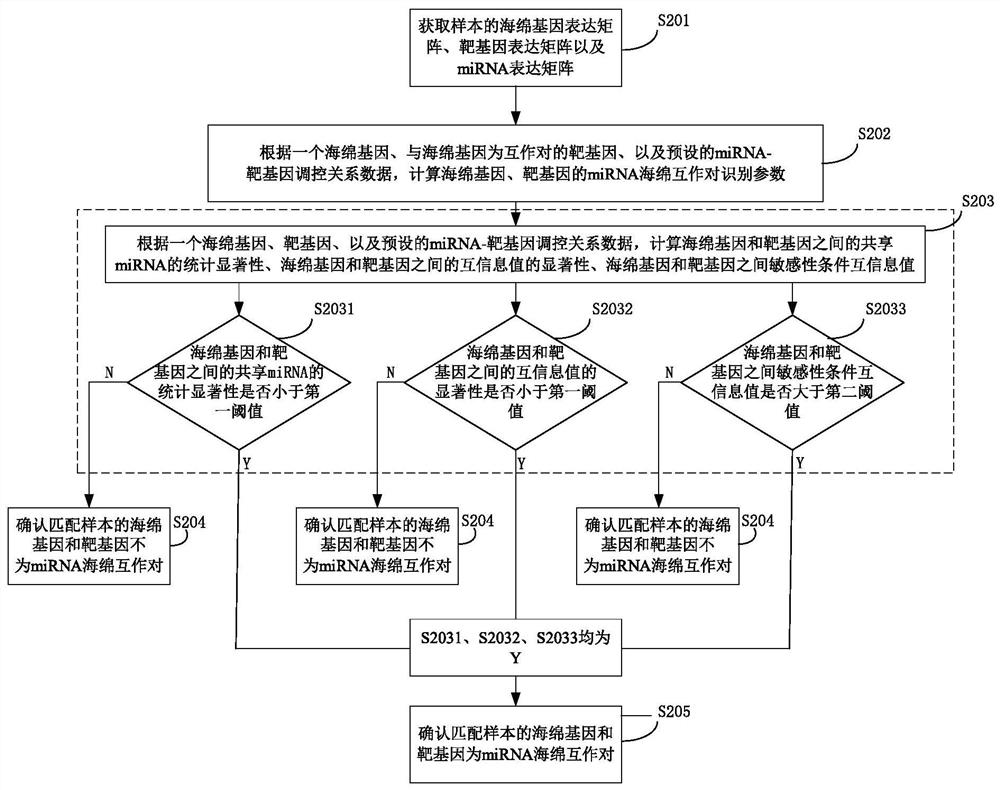
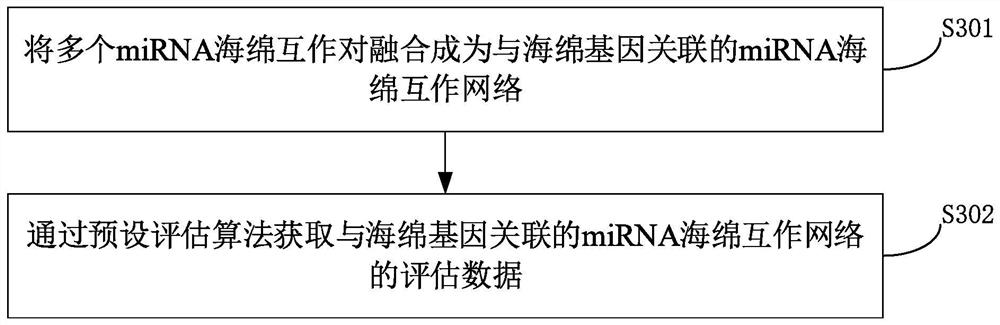
A method for identifying miRNA-sponge interaction pairs
ActiveCN110993020BAppropriate time complexityBiostatisticsProteomicsGene expression matrixData source
The invention provides a method for identifying miRNA sponge interaction pairs, and relates to the technical field of gene identification. The method for identifying the miRNA-sponge interaction pair includes: obtaining the sponge gene expression matrix, the target gene expression matrix and the miRNA expression matrix of the sample. And calculate the miRNA sponge interaction pair recognition parameters of the sponge gene of the matching sample and the target gene. If the identification parameters of the miRNA-sponge interaction pair between the sponge gene of the matching sample and the target gene meet the preset conditions, it is confirmed that the sponge gene and the target gene of the matching sample are miRNA-sponge interaction pairs. Due to the fusion of heterogeneous data sources in the calculation of miRNA-sponge interaction identification parameters, and when determining the miRNA-sponge interaction pair, it is based on the miRNA competition mechanism to measure the competition strength between miRNA sponges to identify the non-linearity between miRNA sponges Correlation relationship, and then determine miRNA sponge interaction pairs, realize the appropriate time complexity, and can identify the non-linear correlation relationship between miRNA sponges.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
Identification method and device for miRNA causal regulation and control network, electronic equipment and storage medium
The invention provides an identification method and device for a miRNA causal regulation and control network, belonging to the technical field of gene identification. The identification method for themiRNA causal regulation and control network comprises the following steps: acquiring a miRNA single-cell transcriptome matrix and a target gene single-cell transcriptome matrix of a given matching sample; acquiring a miRNA causal regulation and control network of the miRNA single-cell transcriptome matrix and the target gene single-cell transcriptome matrix; removing the i single cell in themiRNA single-cell transcriptome matrix and the target gene single-cell transcriptome matrix, and acquiring a miRNA causal regulation and control network after the i single cell is removed; and determining the miRNA causal control network of the i single cell according to the miRNA causal control network and the miRNA causal control network after the i single cell is removed. Because the heterogeneity of each single cell is taken into consideration, the single-cell miRNA causal regulation and control network is identified at a single-cell level, and the effect of a real miRNA causalregulation and control mechanism is reflected.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
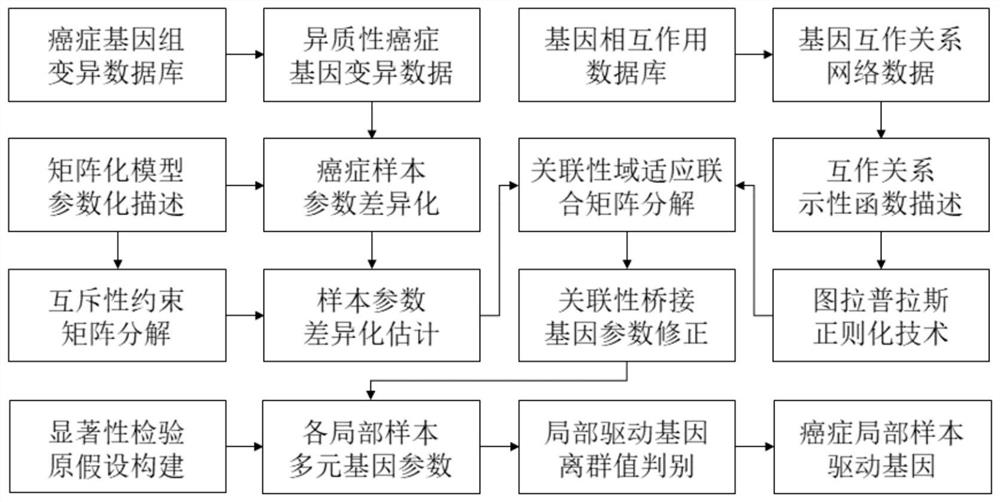
Mutually-exclusively constrained graph Laplacian approach to heterogeneous cancer driver gene identification
ActiveCN111785325BResolve indistinguishableRealize associative bridgingMedical automated diagnosisProteomicsCancer genomeGene recognition
The present invention provides a method for identifying heterogeneous cancer driver genes based on a mutually exclusive constrained graph Laplacian. First, obtain cancer genome variation data and gene interaction network; then, use a matrix model to describe the heterogeneity of cancer, and use mutually exclusive constraint matrix decomposition to estimate the sample parameters of heterogeneity cancer; Then, construct the mutual exclusion constraint matrix decomposition optimization function regularized by the joint association and interaction network, and correct the parameters of the driving genes affected by the interaction in the local samples through iterative solution; finally, use the outlier test method to identify the driving genes . The invention can solve the problem of differential estimation of parameters of cancer samples and effective identification of driver genes in local samples affected by interaction, and realizes the identification of driver genes mutated in local samples from gene variation data of heterogeneous cancer samples.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
A kind of preparation method of mc3r gene knockout pig
InactiveCN106191113BKnockout is fast and efficientPeptidesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyGene recognition
The invention discloses a preparing method for MC3R gene knockout pigs. The preparing method for MC3R gene knockout pigs includes the steps that a CRISPR / Cas9 system is adopted, the CRISPR / Cas9 system comprises an encoding gene of gRNA1 and an encoding gene of gRNA2, and the target sequence of a MC3R gene identified by the gRNA1 is a sequence 1 in a sequence table; the target sequence of the MC3R gene identified by the gRNA2 is a sequence 2 in a sequence table. An experiment shows that the MC3R gene knockout efficiency is 29.16% with the preparing method for MC3R gene knockout pigs; a target gene can be rapidly and efficiently knocked out in a large-fragment mode, exogenous gene fragments are not left, and the preparing method can be used for researching the action mode and mechanism of the MC3R gene, and can be further used for animal breeding.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
A method for identifying key tumor genes based on particle swarm optimization and scoring criteria
ActiveCN106951728BAccurate identificationEffectively deleteProteomicsGenomicsGene recognitionParticle swarm algorithm
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
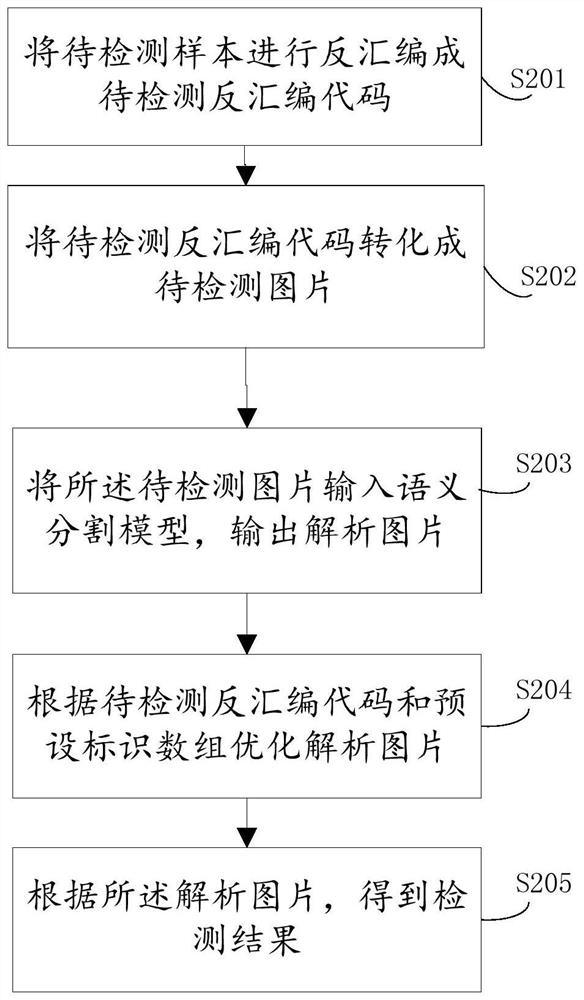
Method and device for rapid detection of malware genes based on semantic segmentation
ActiveCN109492396BImprove matching detection efficiencyImprove the accuracy of gene identificationCharacter and pattern recognitionPlatform integrity maintainanceFeature extractionGene recognition
The invention provides a method and device for rapid detection of malware genes based on semantic segmentation. The semantic segmentation model trained by the gene bank can greatly improve the matching detection efficiency of real-time samples, and the trained semantic segmentation model does not need to carry genes The features of the library can even be embedded in offline real-time security products; the features of automatic abstract feature extraction and subsequent mature optimization technology can improve the accuracy rate of genetic identification of malicious deformation.
Owner:HANGZHOU ANHENG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com