Gene recognition method based on empirical Bayesian and Mendel randomization fusion
An identification method and randomization technology, applied in the field of gene identification, can solve the problems of missing rare variants, difficult biological functions of genetic variants, unable to fully reveal the genetic susceptibility factors of complex diseases, etc., to achieve the effect of improving the speed of identification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
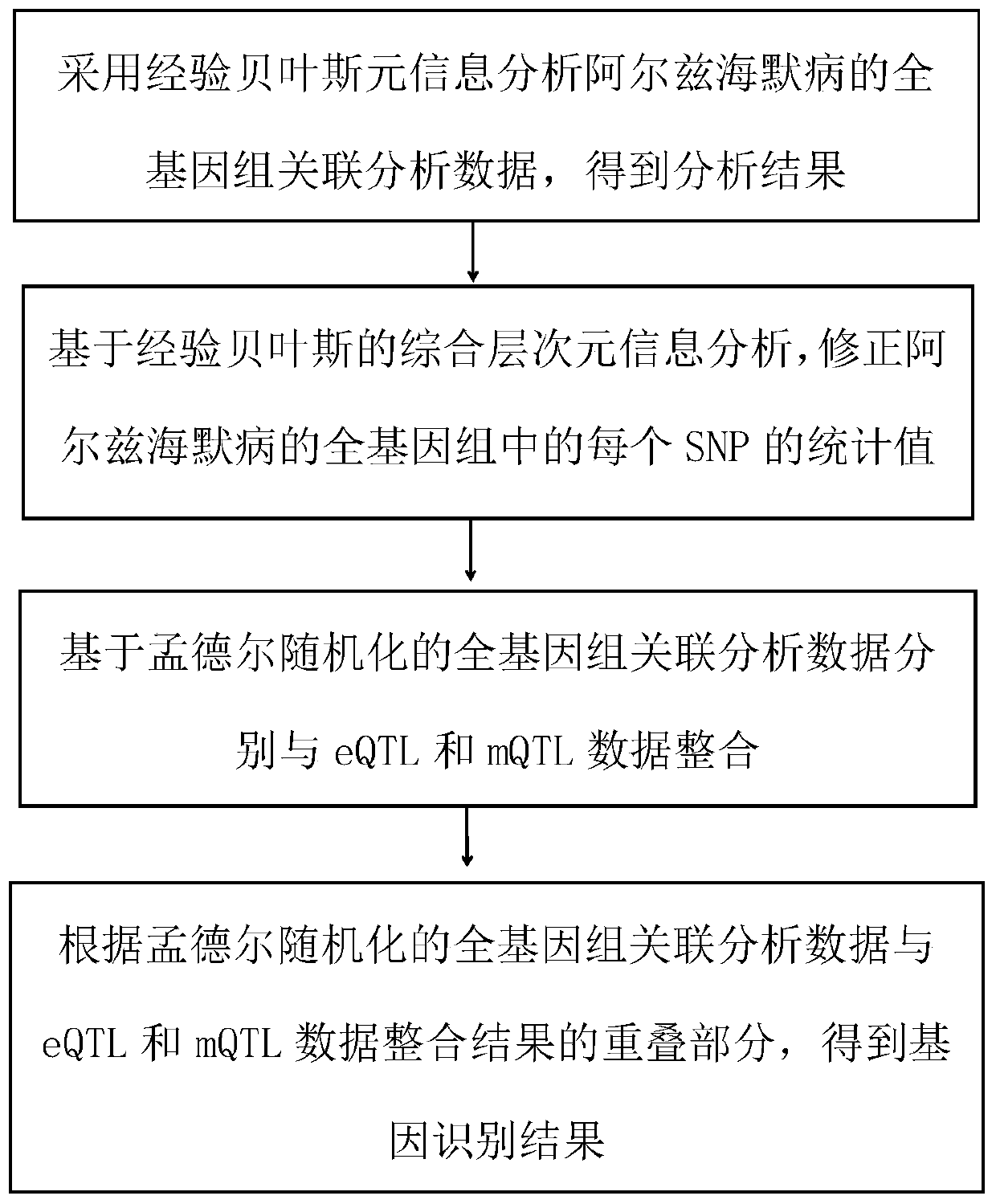
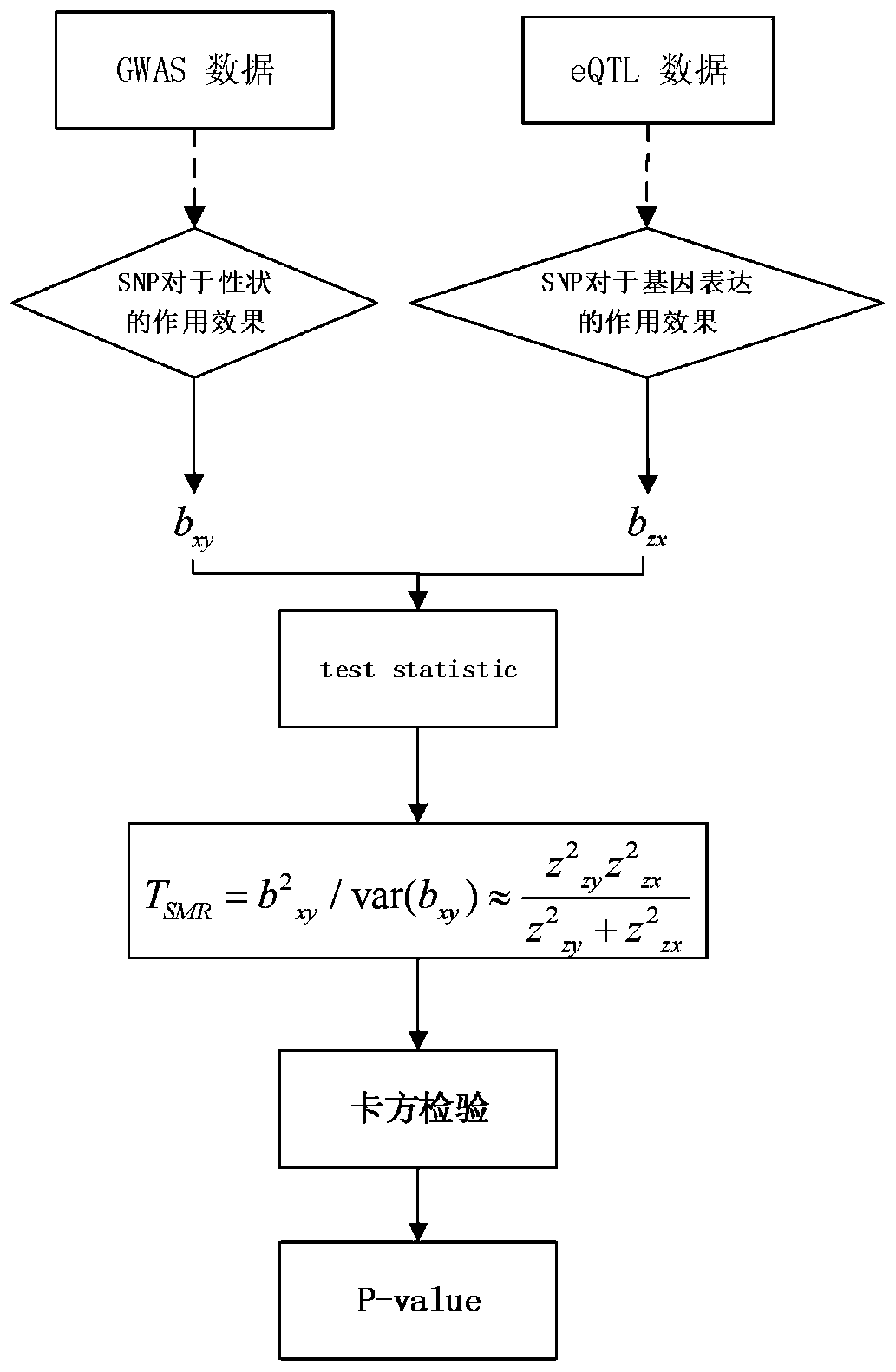
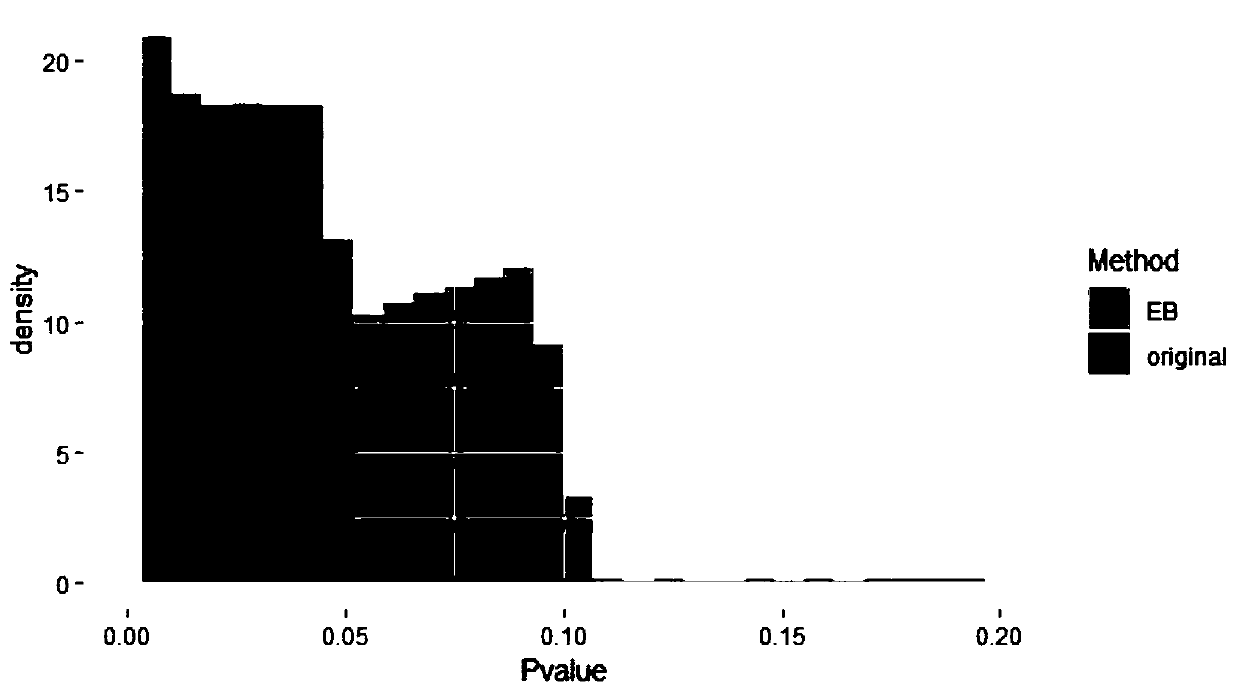
[0068] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a gene identification method based on the fusion of empirical Bayes and Mendelian randomization. Taking the whole gene analysis of Alzheimer's disease as an example, it specifically includes the following steps:
[0069] Step 1: Use empirical Bayesian meta-information to analyze the whole-genome association analysis data of Alzheimer's disease to obtain the analysis result; the step 1 specifically is:
[0070] Empirical Bayesian meta-information is used to analyze the genome-wide association analysis data of Alzheimer’s disease. The genome-wide association analysis data of Alzheimer’s disease includes the SE and Beta values. The SE value represents the standard error of each SNP to determine each Beta The weight of the value, the weight of each Beta value is expressed by the following formula:
[0071]
[0072] Where w i Is the weight of each Beta value, SE i Represents the standard deviation of each SNP, w i Represent...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com