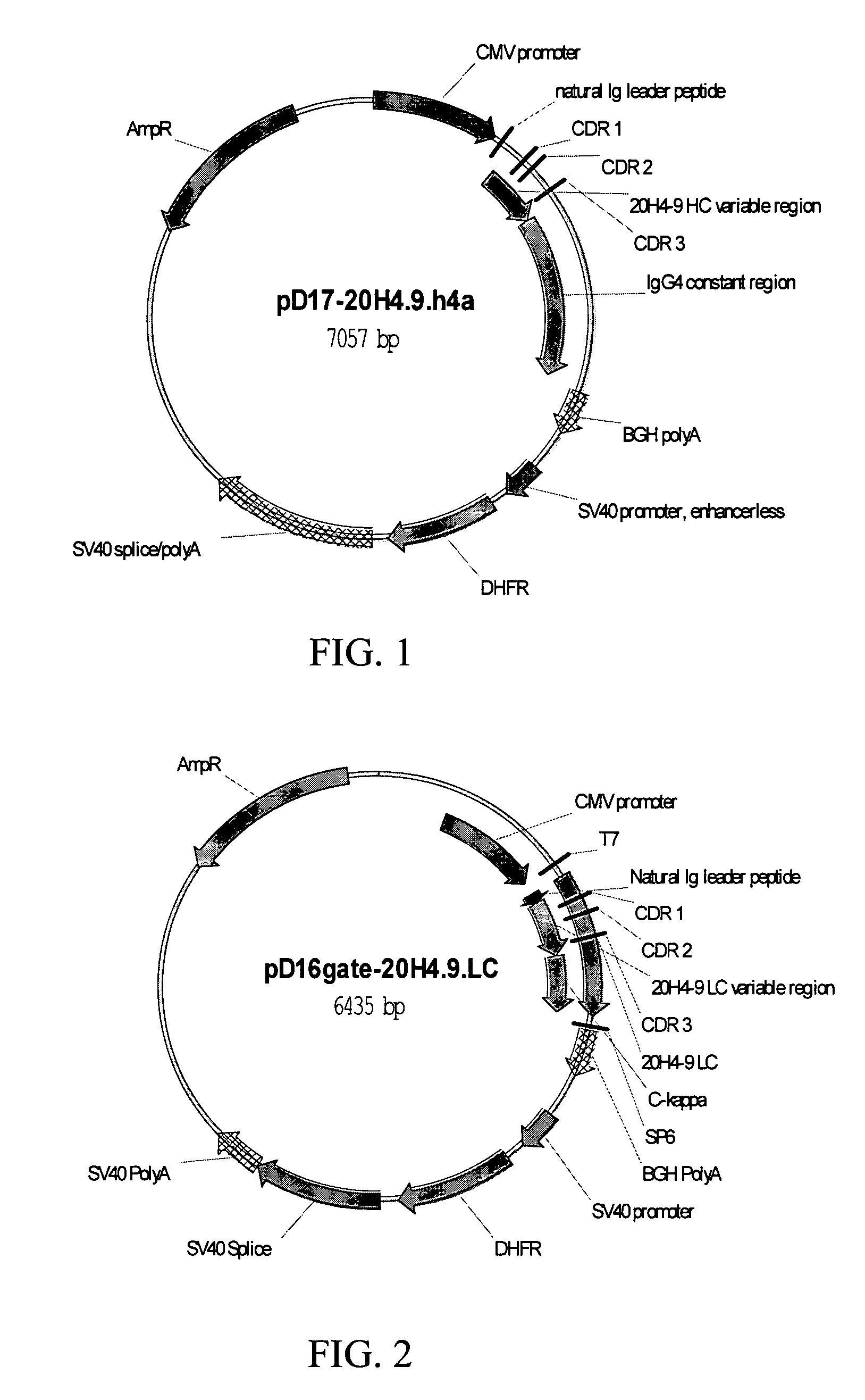
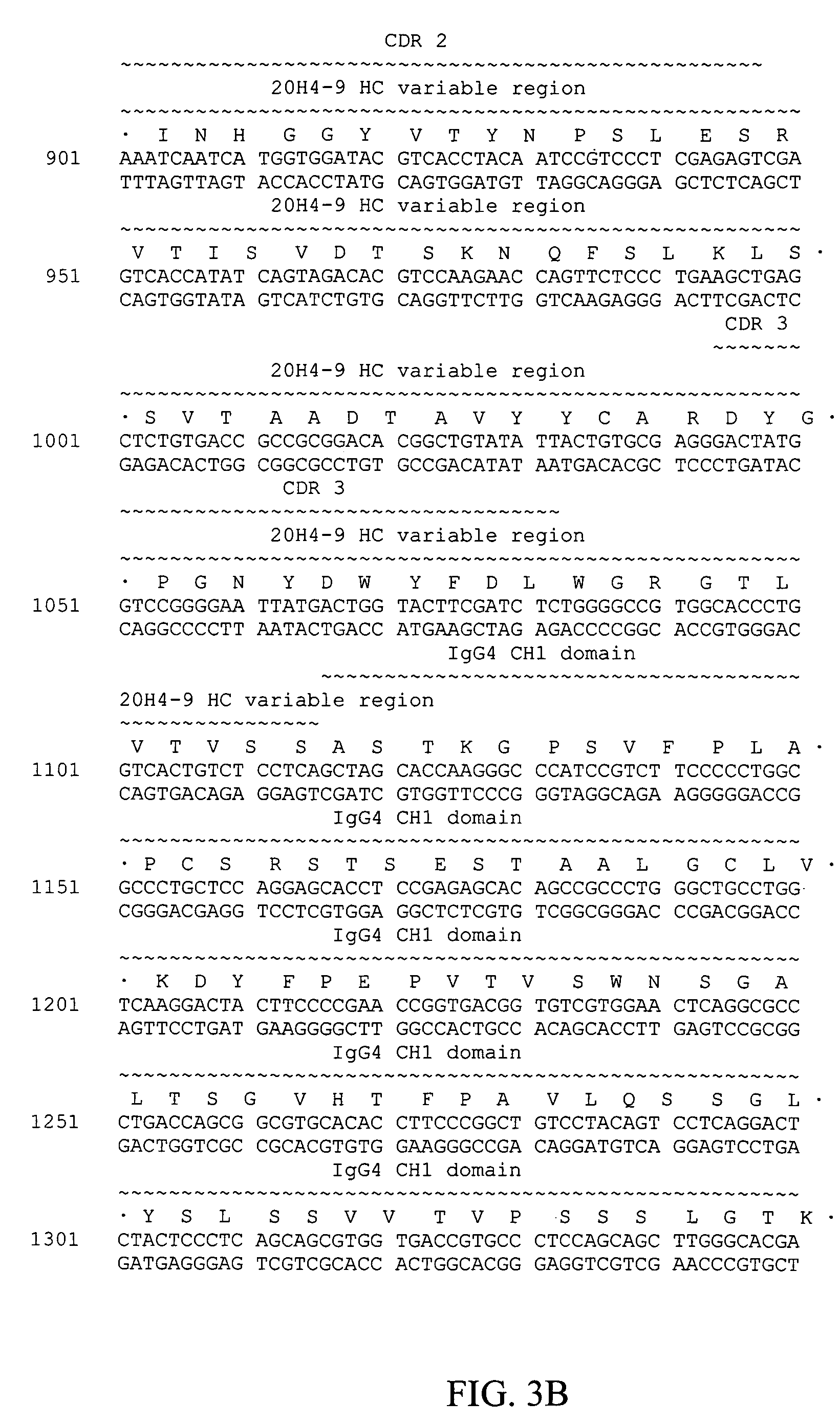
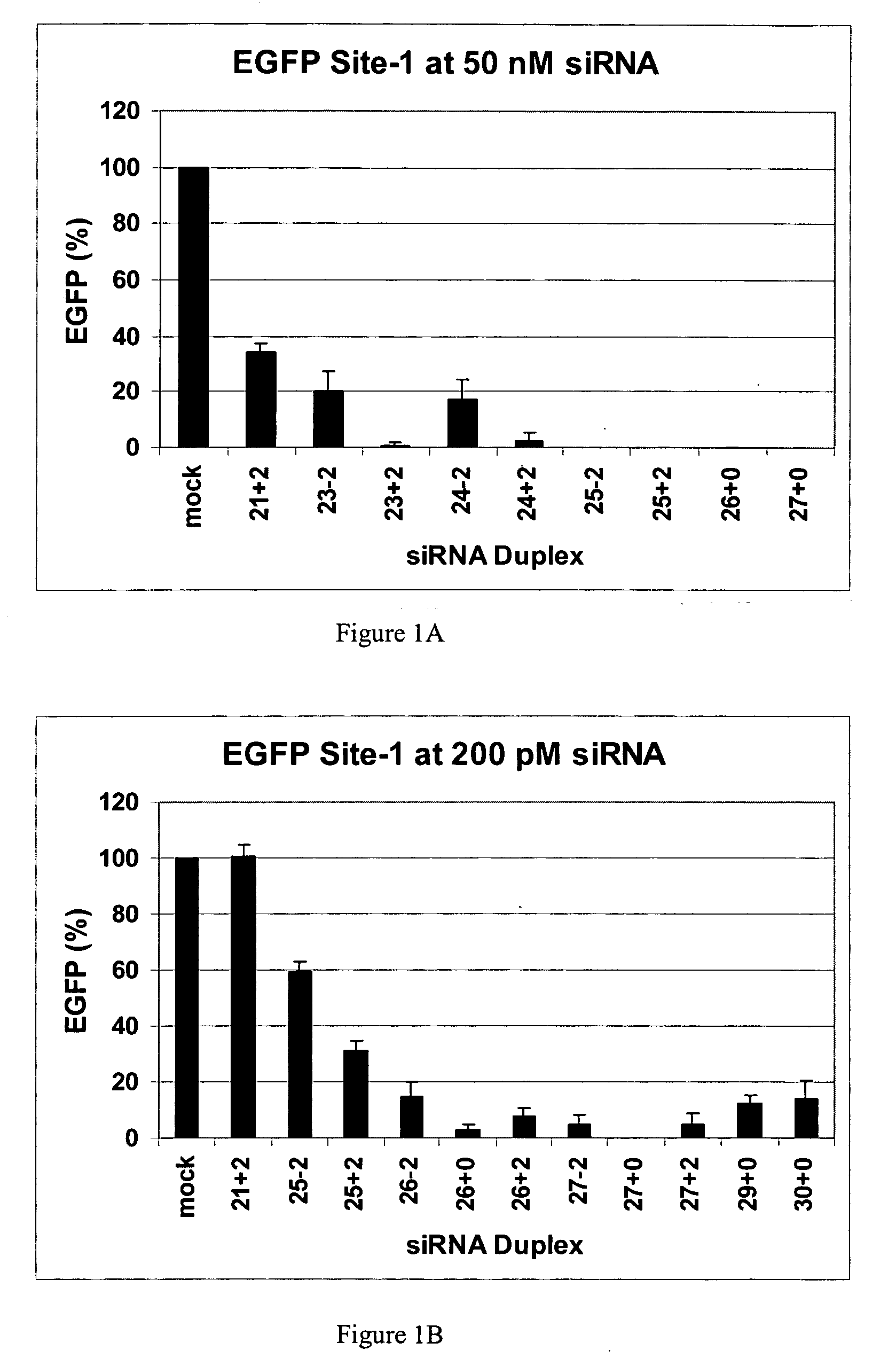
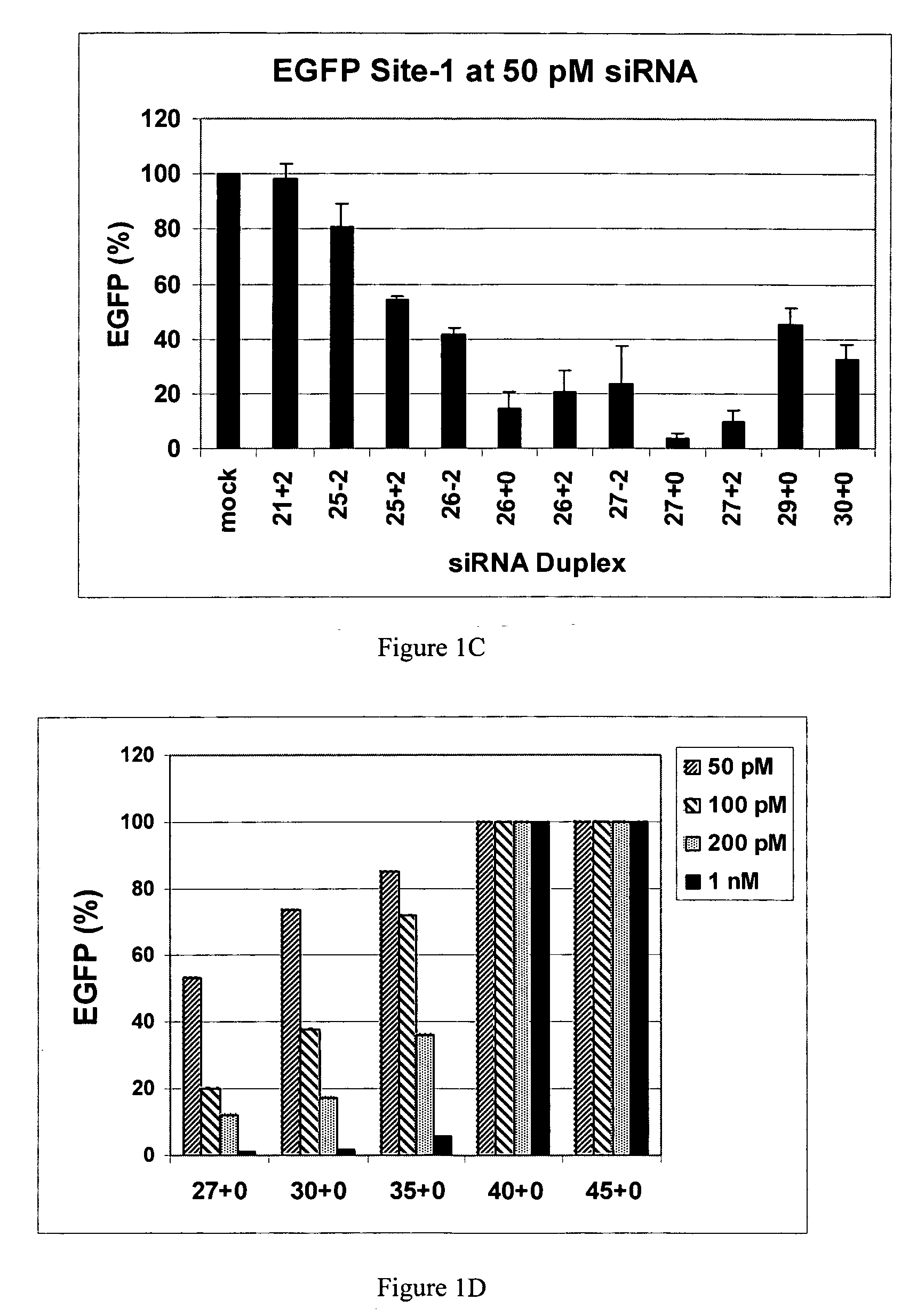
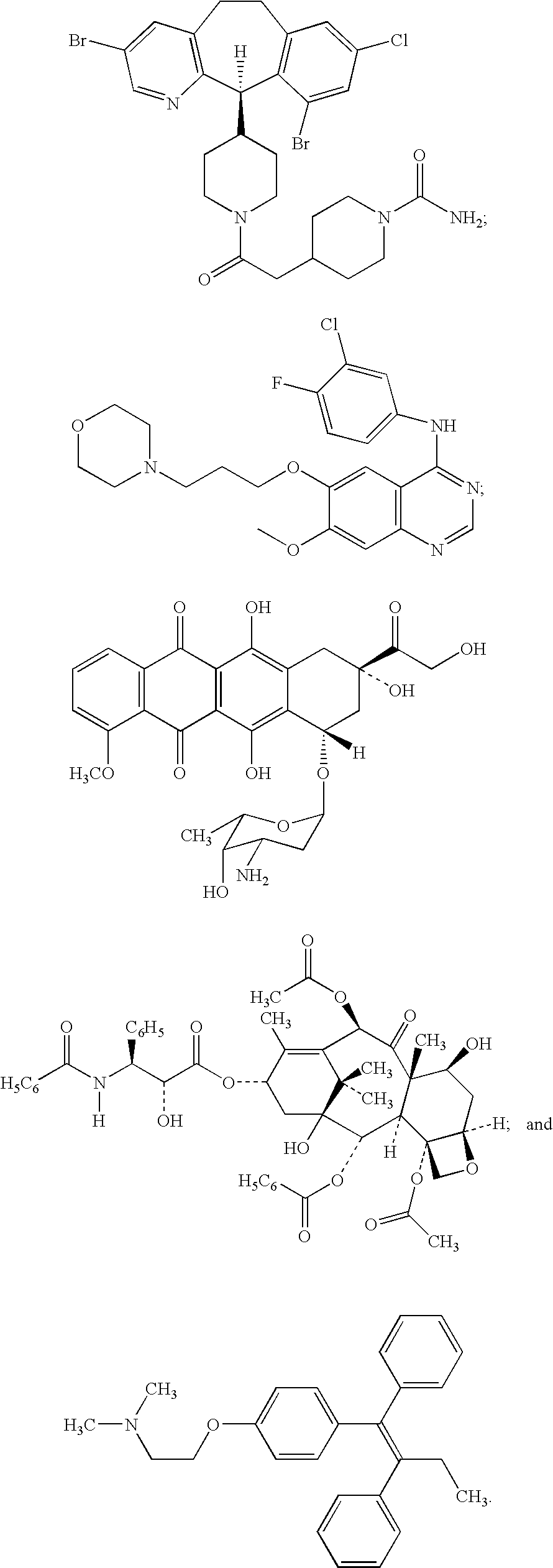
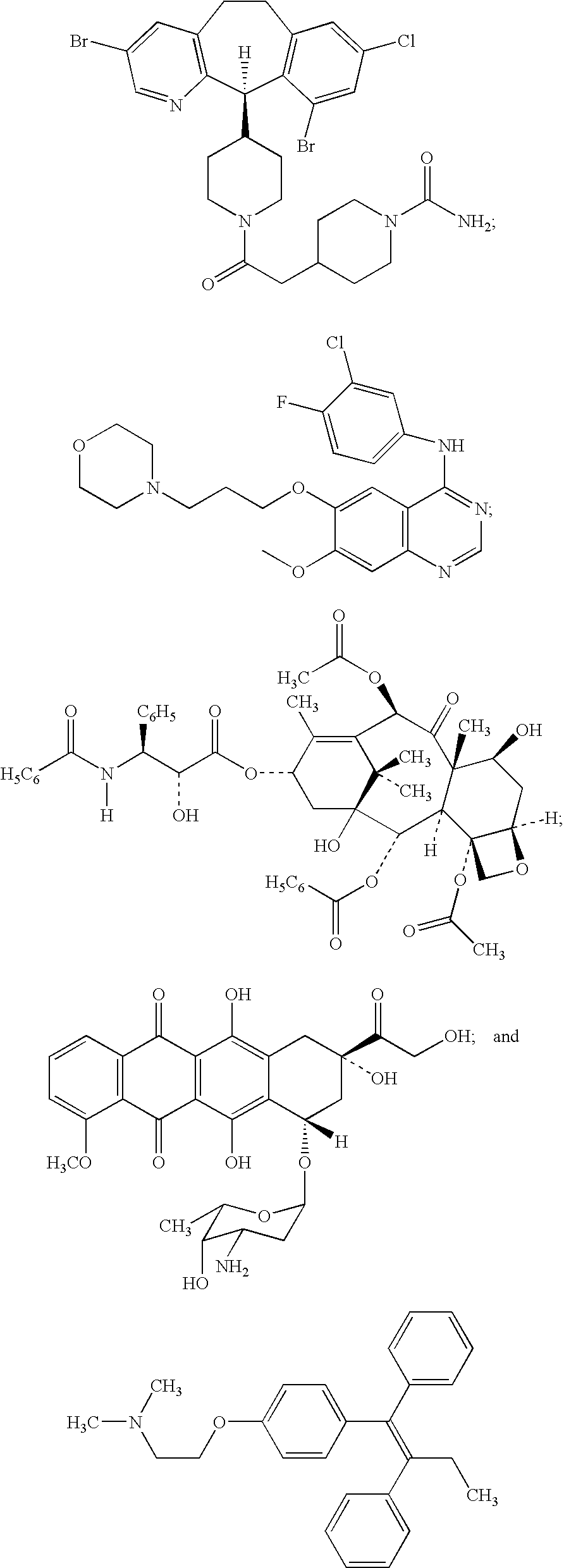
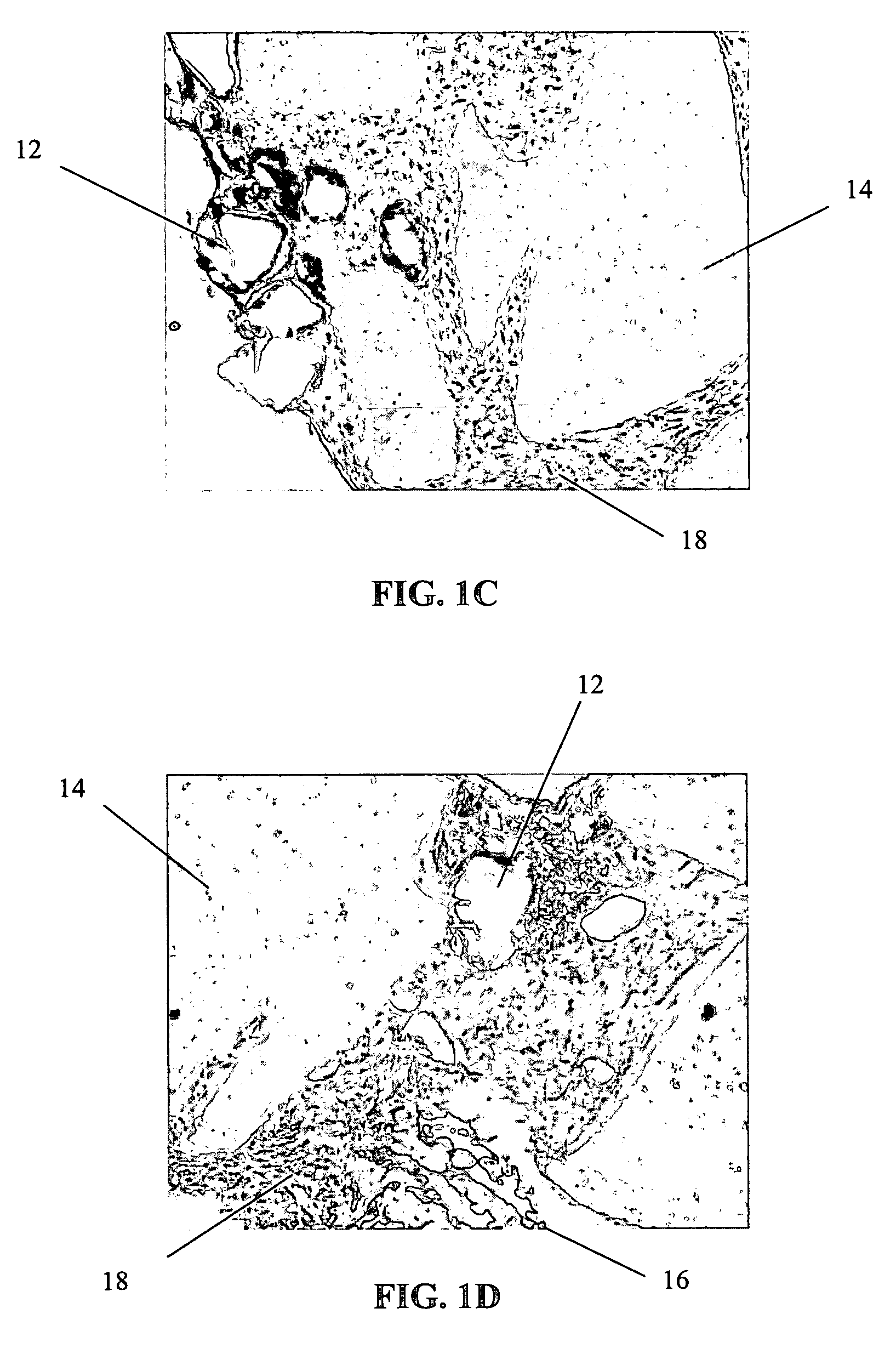
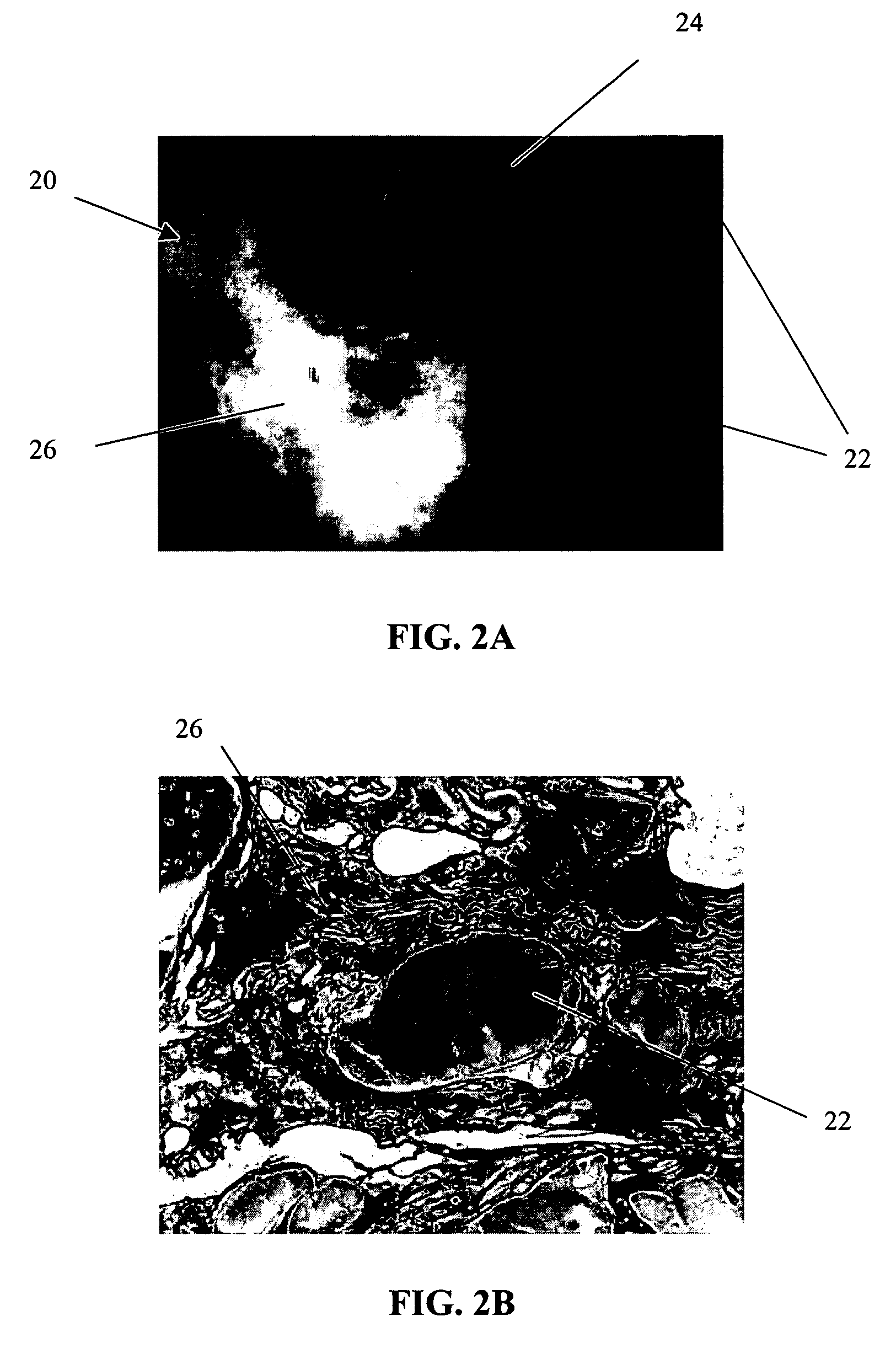
Patents
Literature
14550results about "Neuromuscular disorder" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
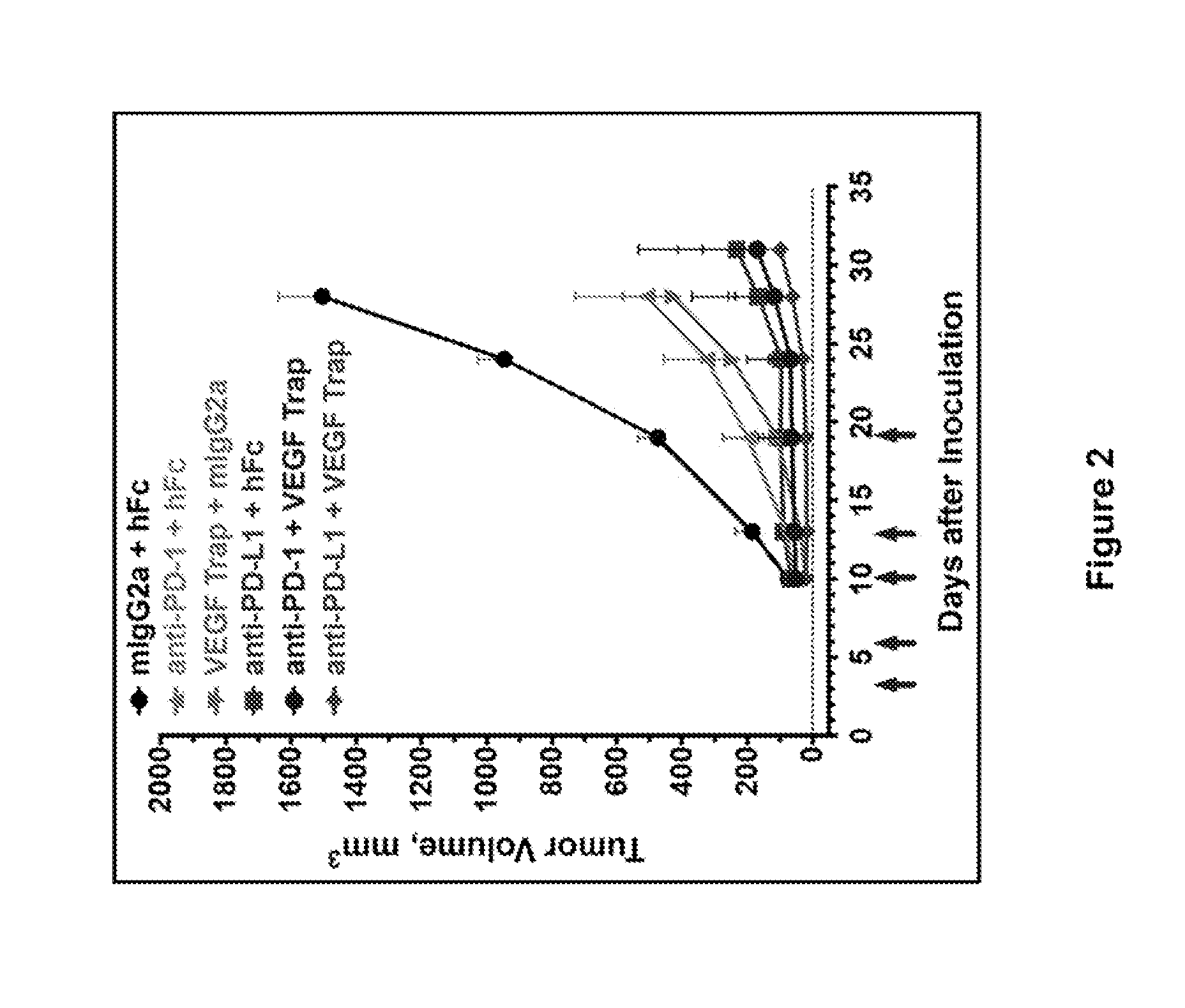
Anti-PD-L1 antibodies and uses therefor
The present invention is based, in part, on the identification of novel human anti-PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 antibodies. Accordingly, the invention relates to compositions and methods for diagnosing, prognosing, and treating conditions that would benefit from modulating PD-1, PD-L1, and / or PD-L2 activity (e.g., persistent infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases, asthma, transplant rejection, inflammatory disorders and tumors) using the novel human anti-PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 antibodies described herein.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC +2
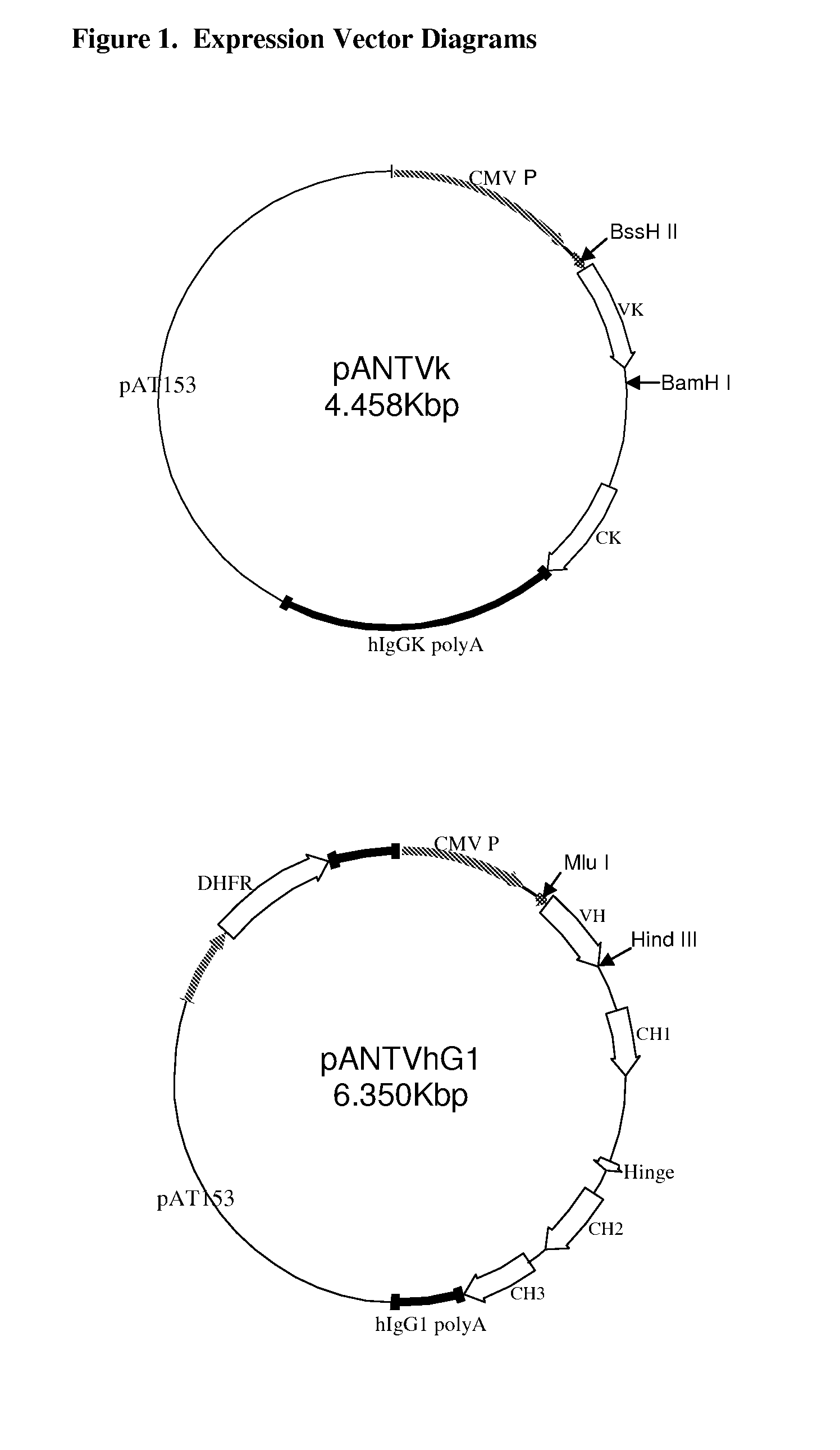
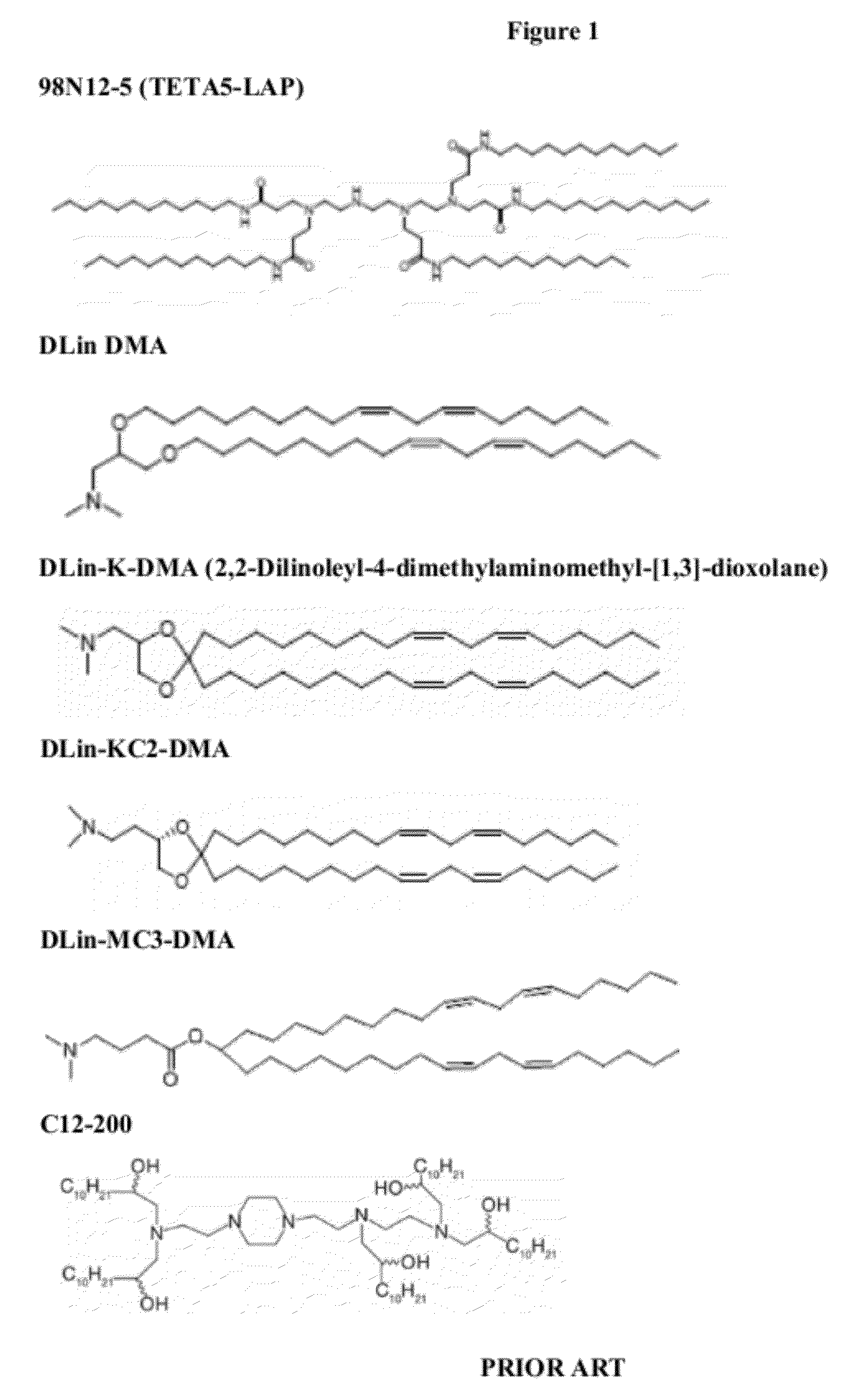
Delivery and formulation of engineered nucleic acids
ActiveUS20120251618A1Improve the level ofIncrease in level of polypeptideNervous disorderAntipyreticNucleic acidProtein expression
Provided are formulations, compositions and methods for delivering biological moieties such as modified nucleic acids into cells to modulate protein expression. Such compositions and methods include the delivery of biological moieties, and are useful for production of proteins.
Owner:MODERNATX INC
Humanized antibodies to gamma-interferon
The invention provides humanized immunoglobulins that bind to and neutralize gamma-interferon. The antibodies are useful for treatment of diseases of the immune system, particularly autoimmune diseases.
Owner:ABBOTT BIOTHERAPEUTICS CORP
Polynucleotides for causing RNA interference and method for inhibiting gene expression using the same
InactiveUS20080113351A1High RNA interference effectLittle riskOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderBase JNucleotide
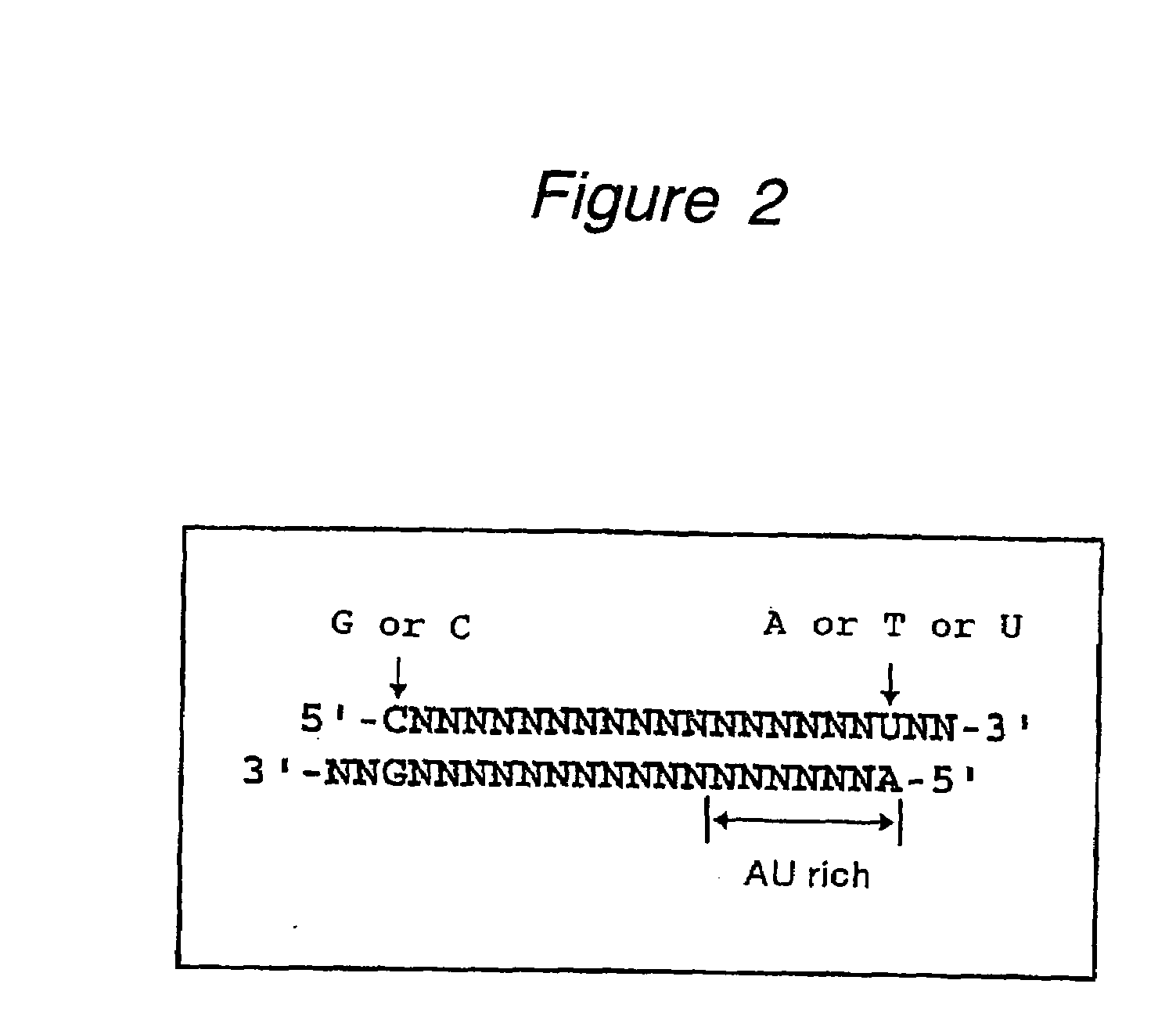
The present invention provides a polynucleotide that not only has a high RNA interference effect on its target gene, but also has a very small risk of causing RNA interference against a gene unrelated to the target gene. A sequence segment conforming to the following rules (a) to (d) is searched from the base sequences of a target gene for RNA interference and, based on the search results, a polynucleotide capable of causing RNAi is designed, synthesized, etc.:(a) The 3′ end base is adenine, thymine, or uracil,(b) The 5′ end base is guanine or cytosine,(c) A 7-base sequence from the 3′ end is rich in one or more types of bases selected from the group consisting of adenine, thymine, and uracil, and(d) The number of bases is within a range that allows RNA interference to occur without causing cytotoxicity.
Owner:ALPHAGEN
Fully human antibodies against human 4-1BB
Fully human antibodies and antigen-binding portions thereof that bind to human 4-1BB and that allow binding of human 4-1BB to a human 4-1BB ligand. In one aspect, the antibody is an IgG4 antibody. Also provided is a method for treating a disease in a subject comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of the antibody to said subject.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Methods and compositions for the specific inhibition of gene expression by double-stranded RNA
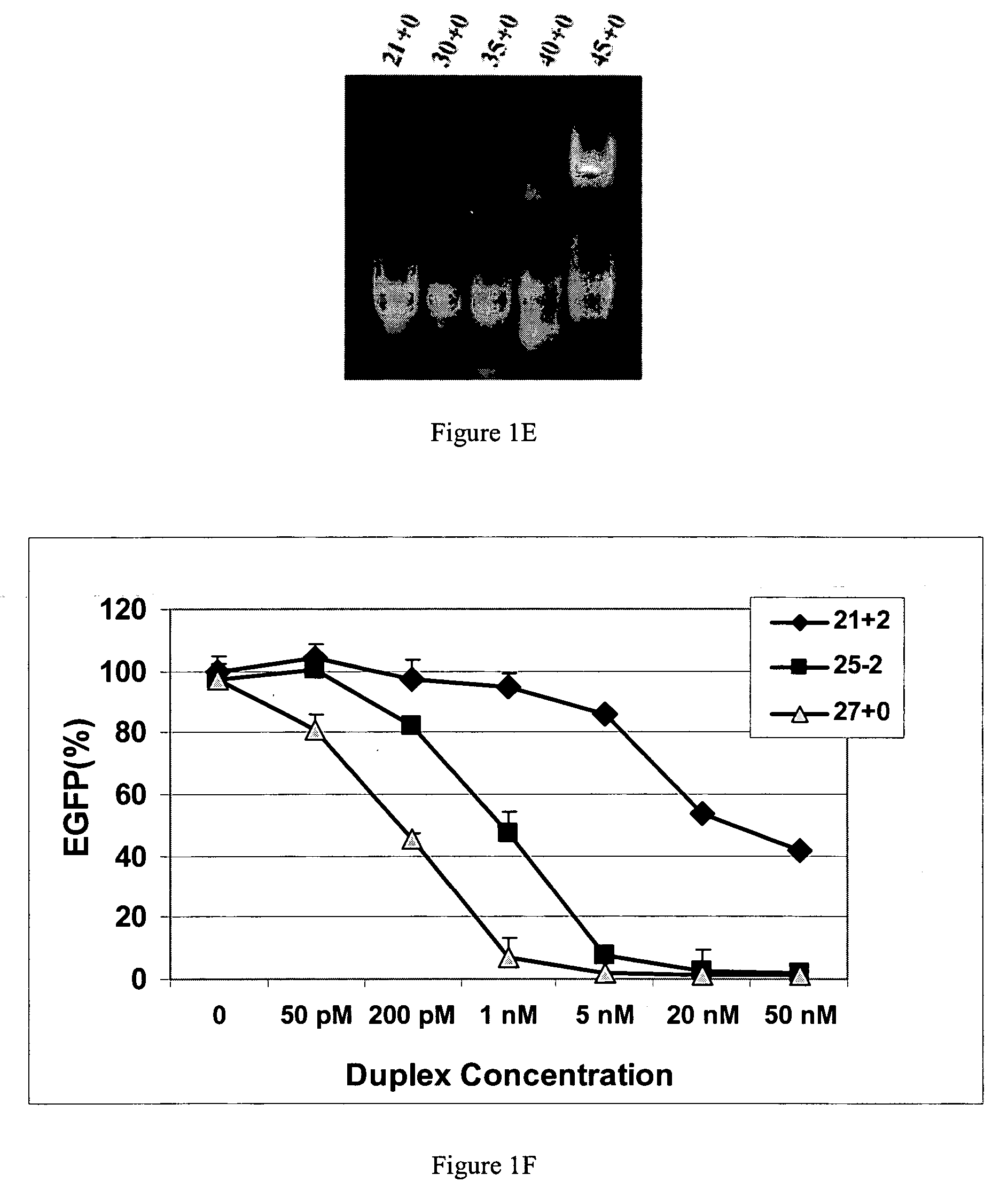
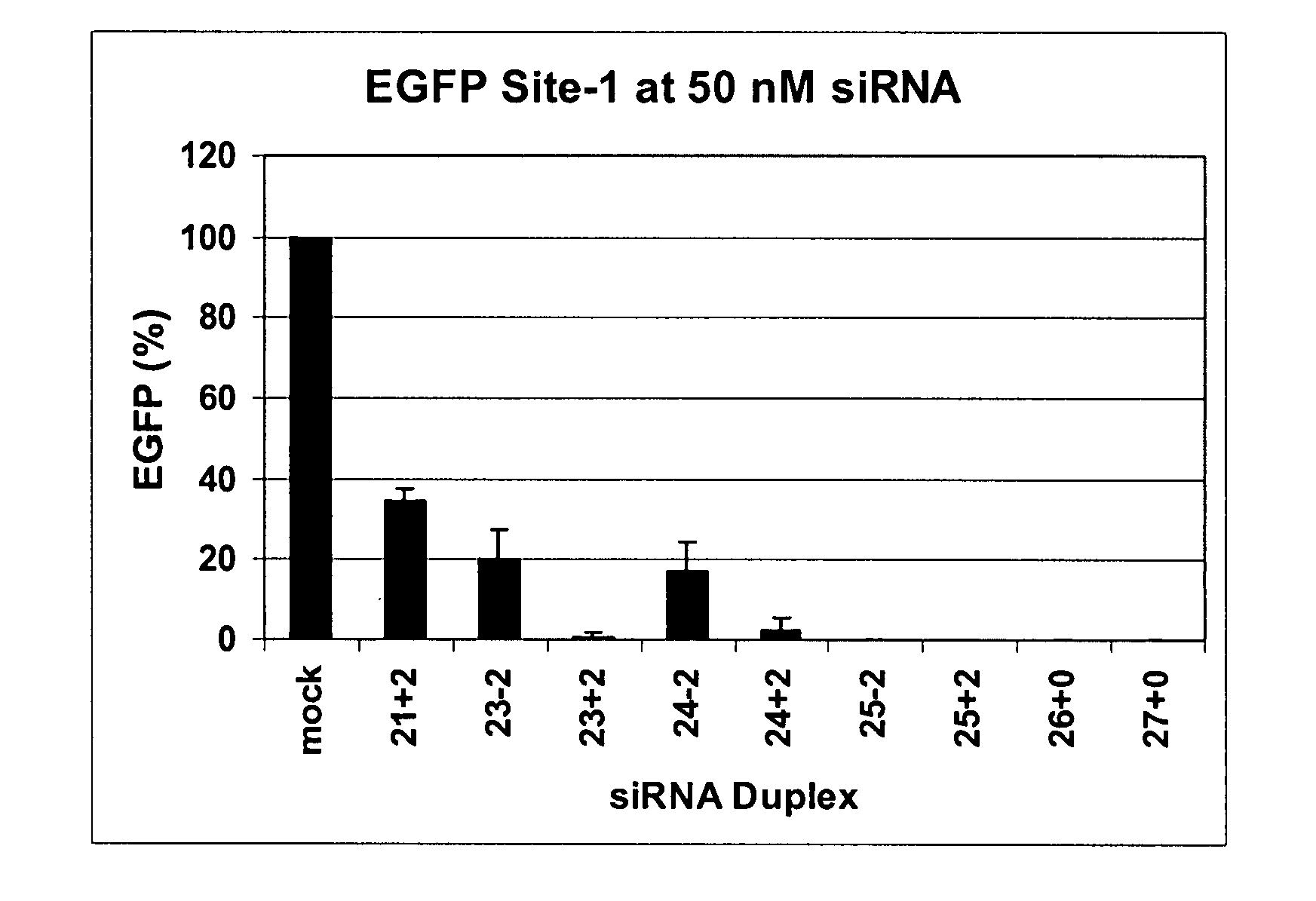
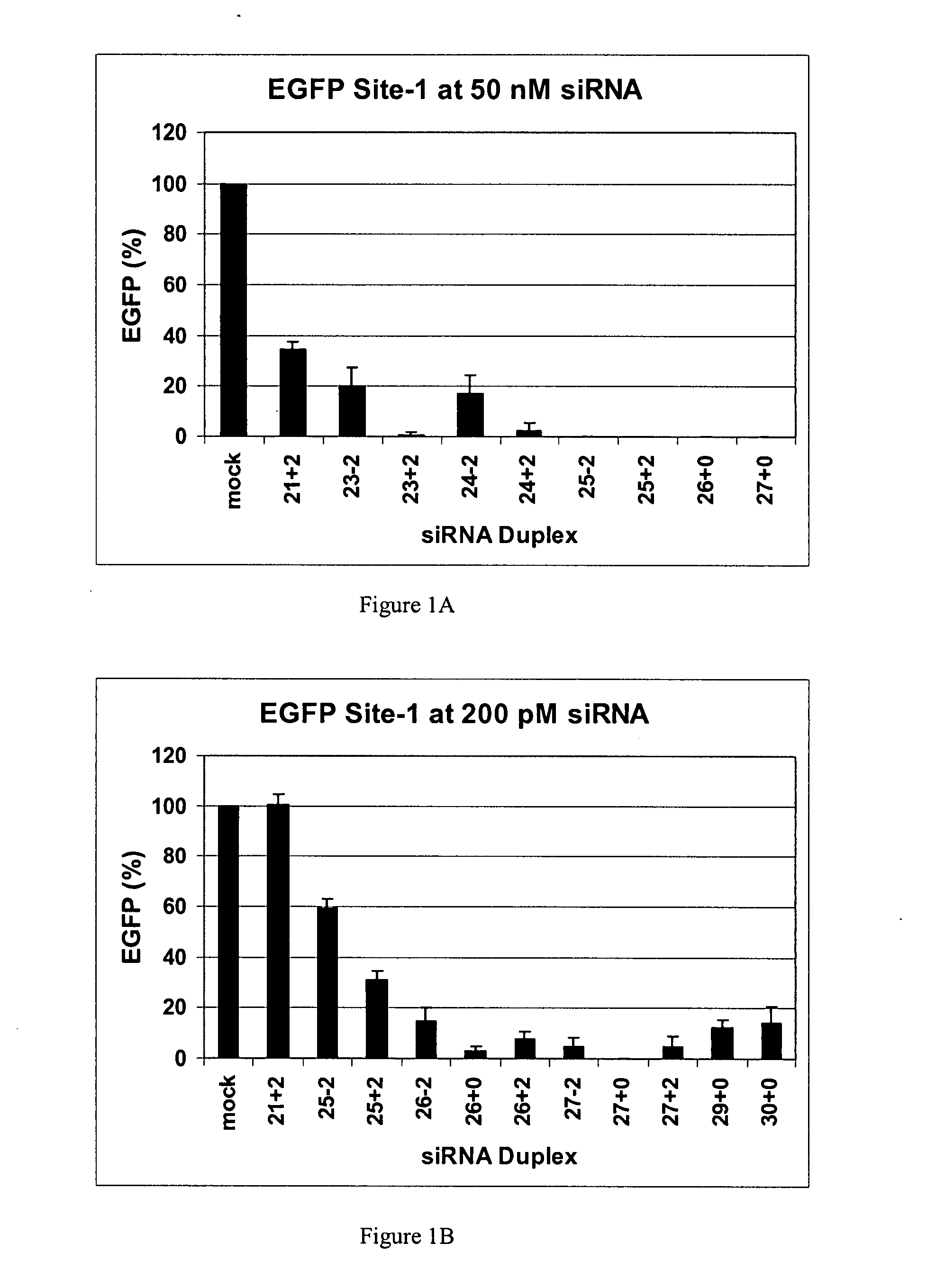
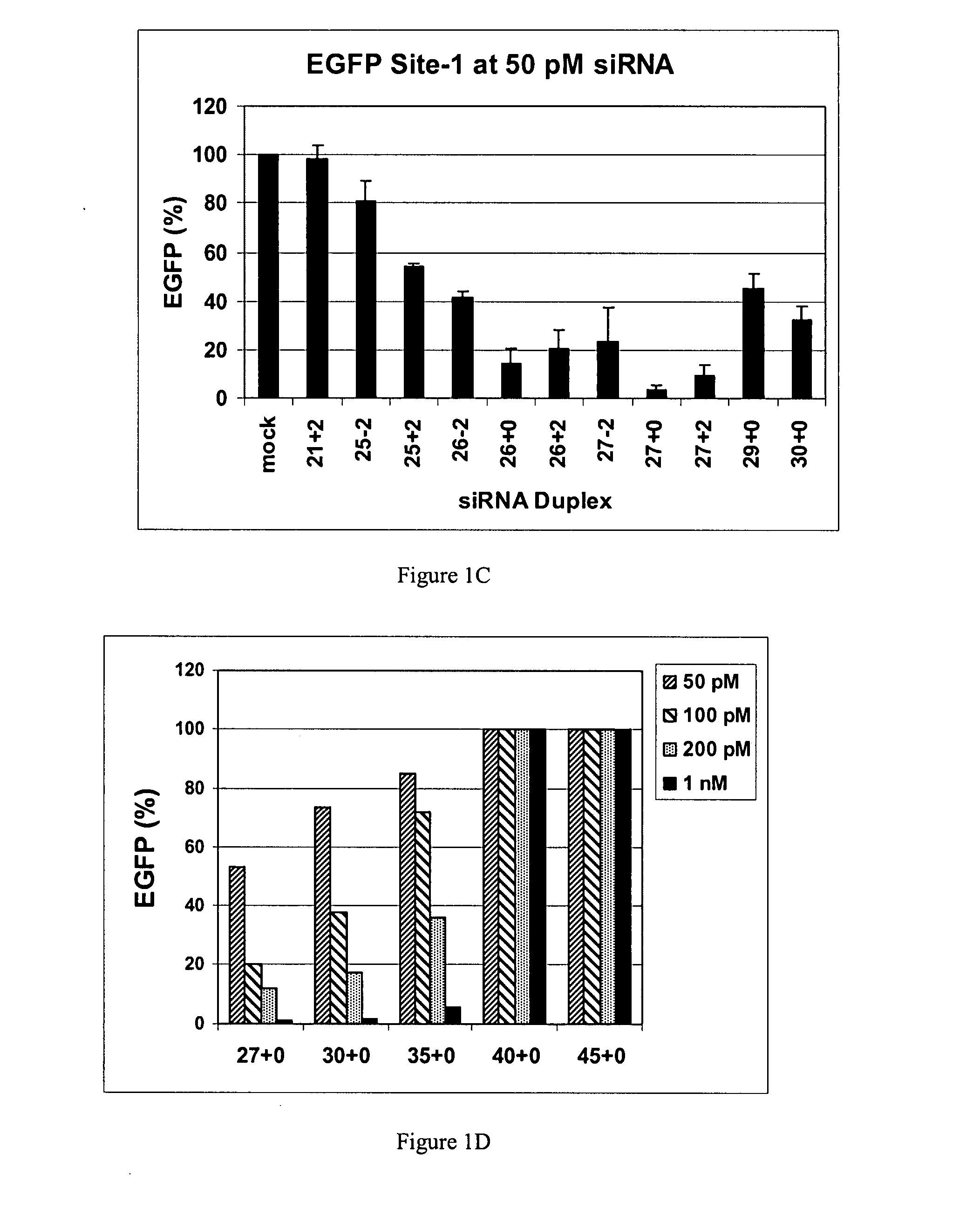
The invention is directed to compositions and methods for selectively reducing the expression of a gene product from a desired target gene in a cell, as well as for treating diseases caused by the expression of the gene. More particularly, the invention is directed to compositions that contain double stranded RNA (“dsRNA”), and methods for preparing them, that are capable of reducing the expression of target genes in eukaryotic cells. The dsRNA has a first oligonucleotide sequence that is between 25 and about 30 nucleotides in length and a second oligonucleotide sequence that anneals to the first sequence under biological conditions. In addition, a region of one of the sequences of the dsRNA having a sequence length of at least 19 nucleotides is sufficiently complementary to a nucleotide sequence of the RNA produced from the target gene to trigger the destruction of the target RNA by the RNAi machinery.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE +1
Methods and compositions for the specific inhibition of gene expression by double-stranded RNA
InactiveUS20070265220A1Improve stabilityConvenience to mergeSenses disorderAntipyreticDouble strandOligonucleotide
The invention is directed to compositions and methods for selectively reducing the expression of a gene product from a desired target gene in a cell, as well as for treating diseases caused by the expression of the gene. More particularly, the invention is directed to compositions that contain double stranded RNA (“dsRNA”), and methods for preparing them, that are capable of reducing the expression of target genes in eukaryotic cells. The dsRNA has a first oligonucleotide sequence that is between 25 and about 30 nucleotides in length and a second oligonucleotide sequence that anneals to the first sequence under biological conditions. In addition, a region of one of the sequences of the dsRNA having a sequence length of at least 19 nucleotides is sufficiently complementary to a nucleotide sequence of the RNA produced from the target gene to trigger the destruction of the target RNA by the RNAi machinery.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE +1
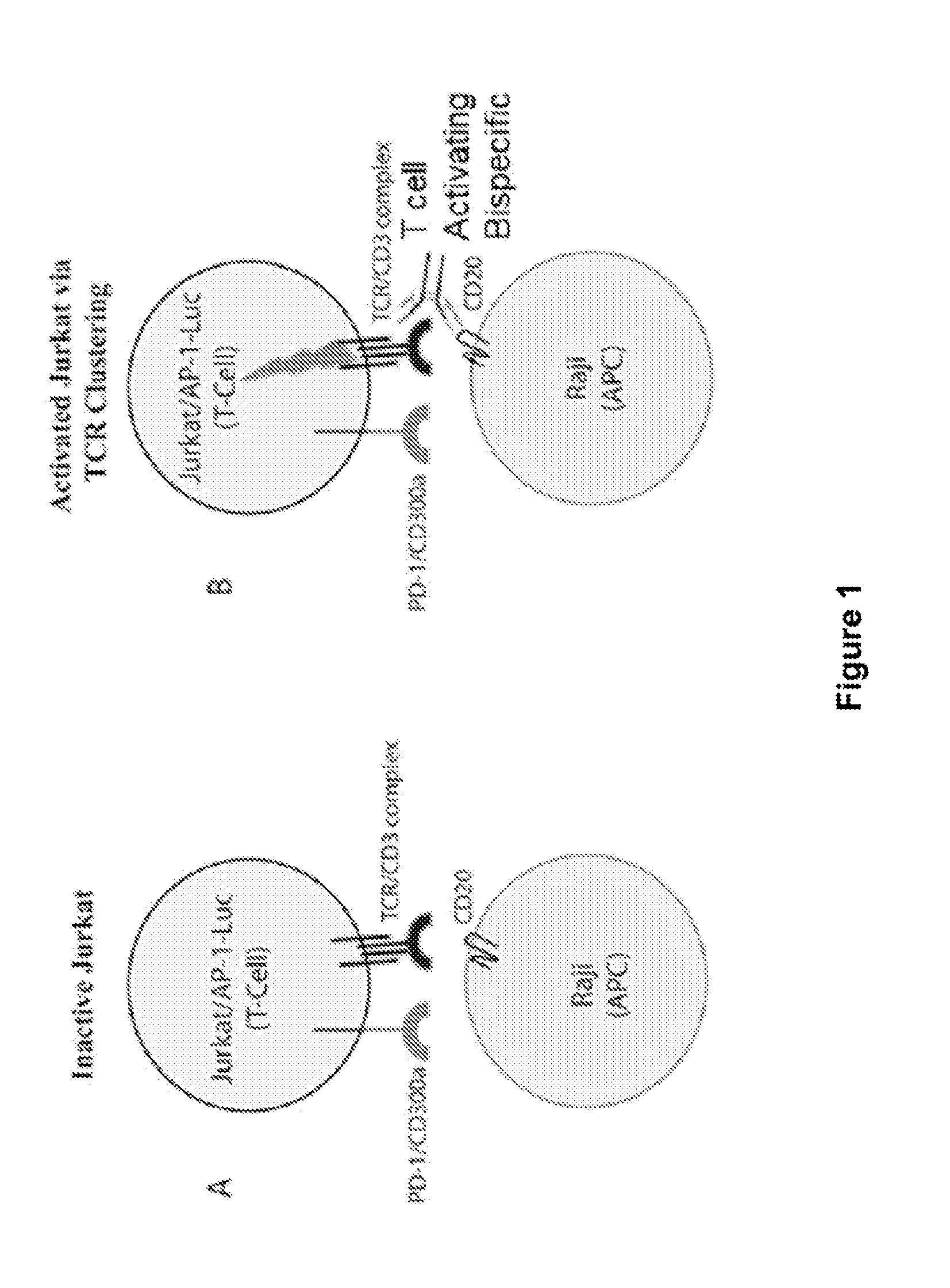
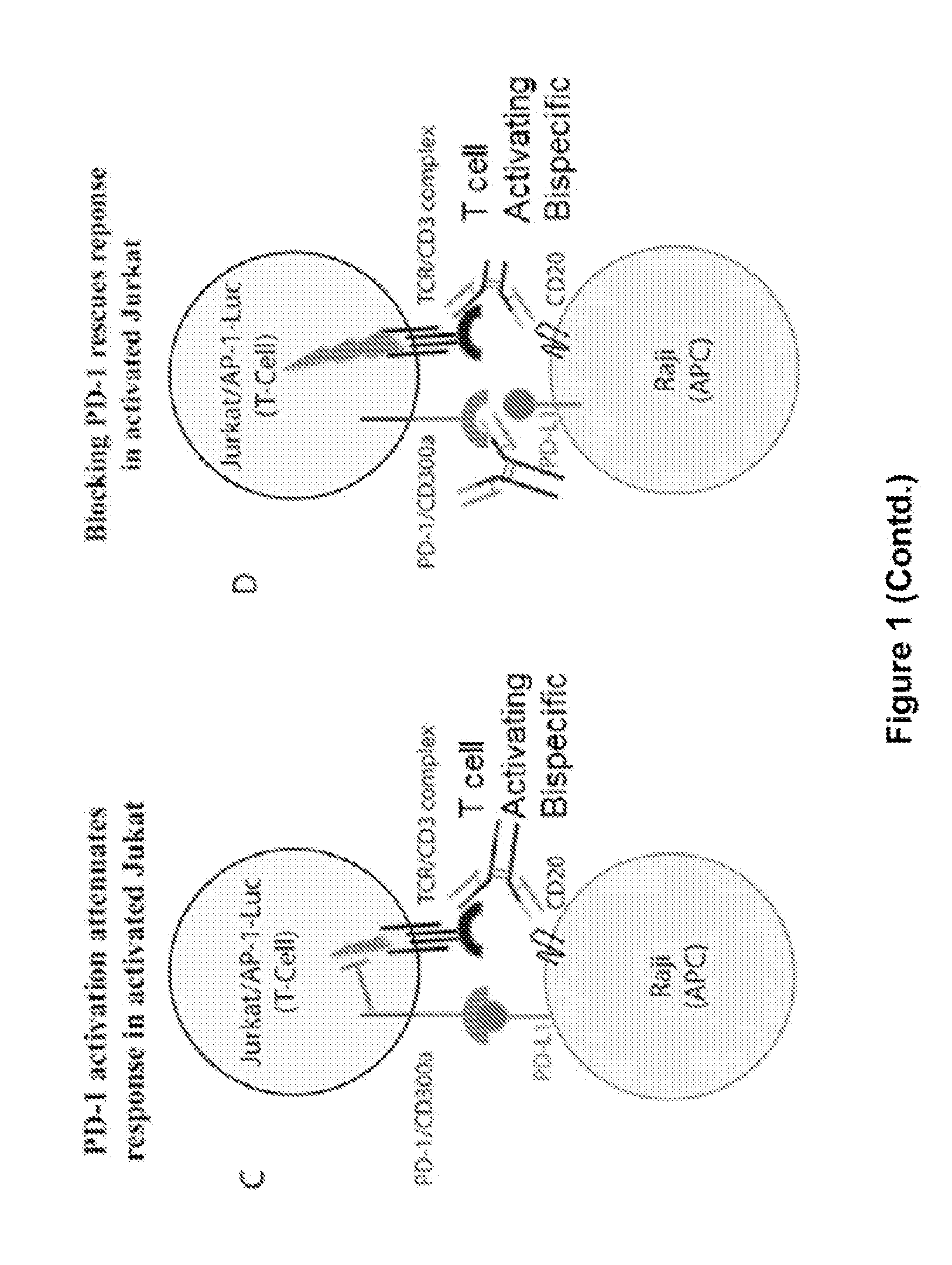
Human Antibodies to PD-1
ActiveUS20150203579A1Rescue T-cell signalingInhibit tumor growthNervous disorderAntipyreticFc(alpha) receptorDisease
The present invention provides antibodies that bind to the T-cell co-inhibitor programmed death-1 (PD-1) protein, and methods of use. In various embodiments of the invention, the antibodies are fully human antibodies that bind to PD-1. In certain embodiments, the present invention provides multi-specific antigen-binding molecules comprising a first binding specificity that binds to PD-1 and a second binding specificity that binds to an autoimmune tissue antigen, another T-cell co-inhibitor, an Fc receptor, or a T-cell receptor. In some embodiments, the antibodies of the invention are useful for inhibiting or neutralizing PD-1 activity, thus providing a means of treating a disease or disorder such as cancer or a chronic viral infection. In other embodiments, the antibodies are useful for enhancing or stimulating PD-1 activity, thus providing a means of treating, for example, an autoimmune disease or disorder.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Anti-IGFR antibody therapeutic combinations
InactiveUS20050136063A1Inhibit growthPrevent proliferationNervous disorderAntipyreticAnti-CEA AntibodyAntibody
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Polypeptide variants with altered effector function
InactiveUS20060067930A1High affinity bindingWeaker binding affinityCompound screeningNervous disorderEffector functionsMolecular biology
The invention provides polypeptides having IgG Fc regions with amino acid modifications that result in the polypeptides exhibiting altered Fc effector functions.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
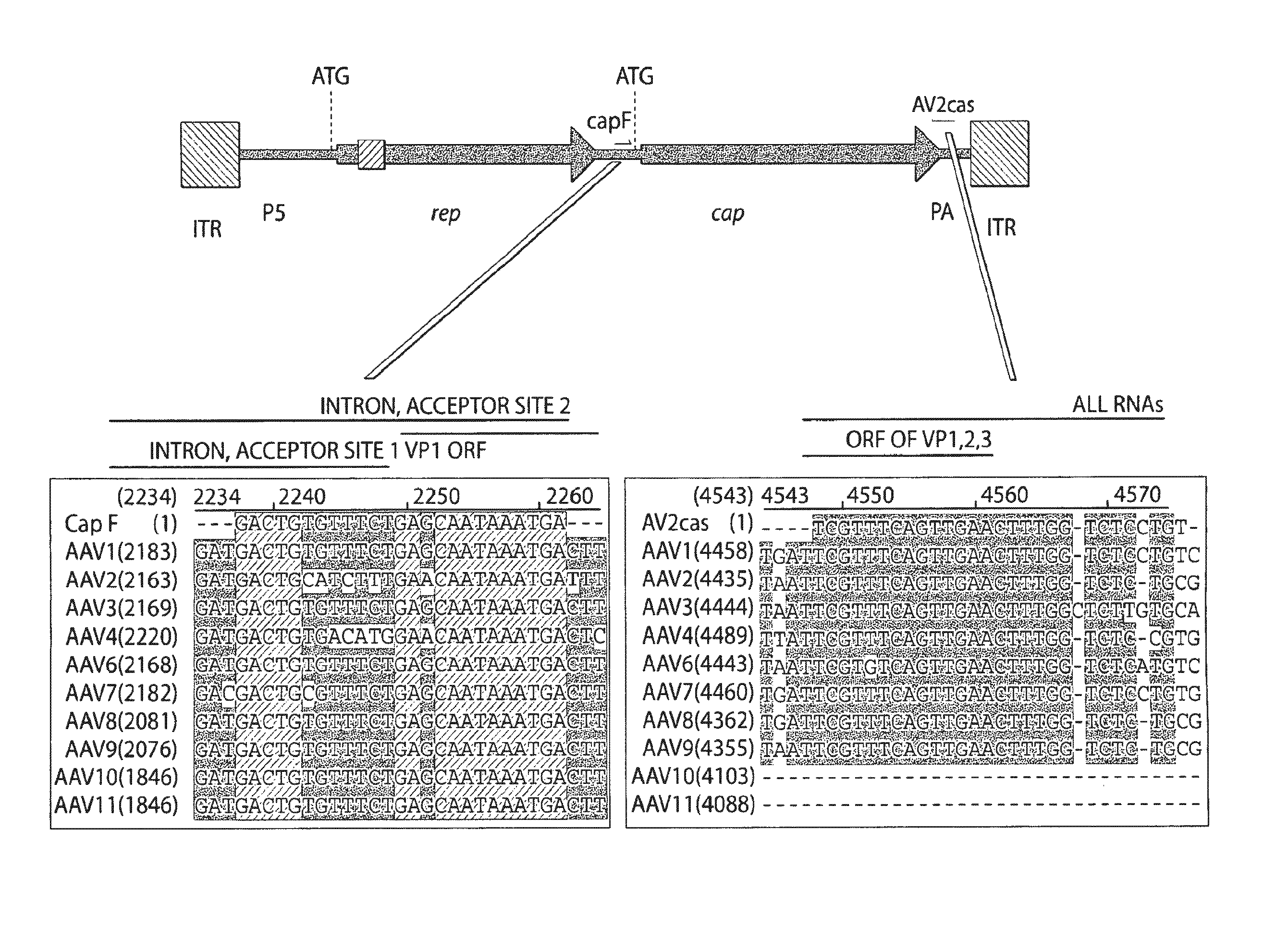
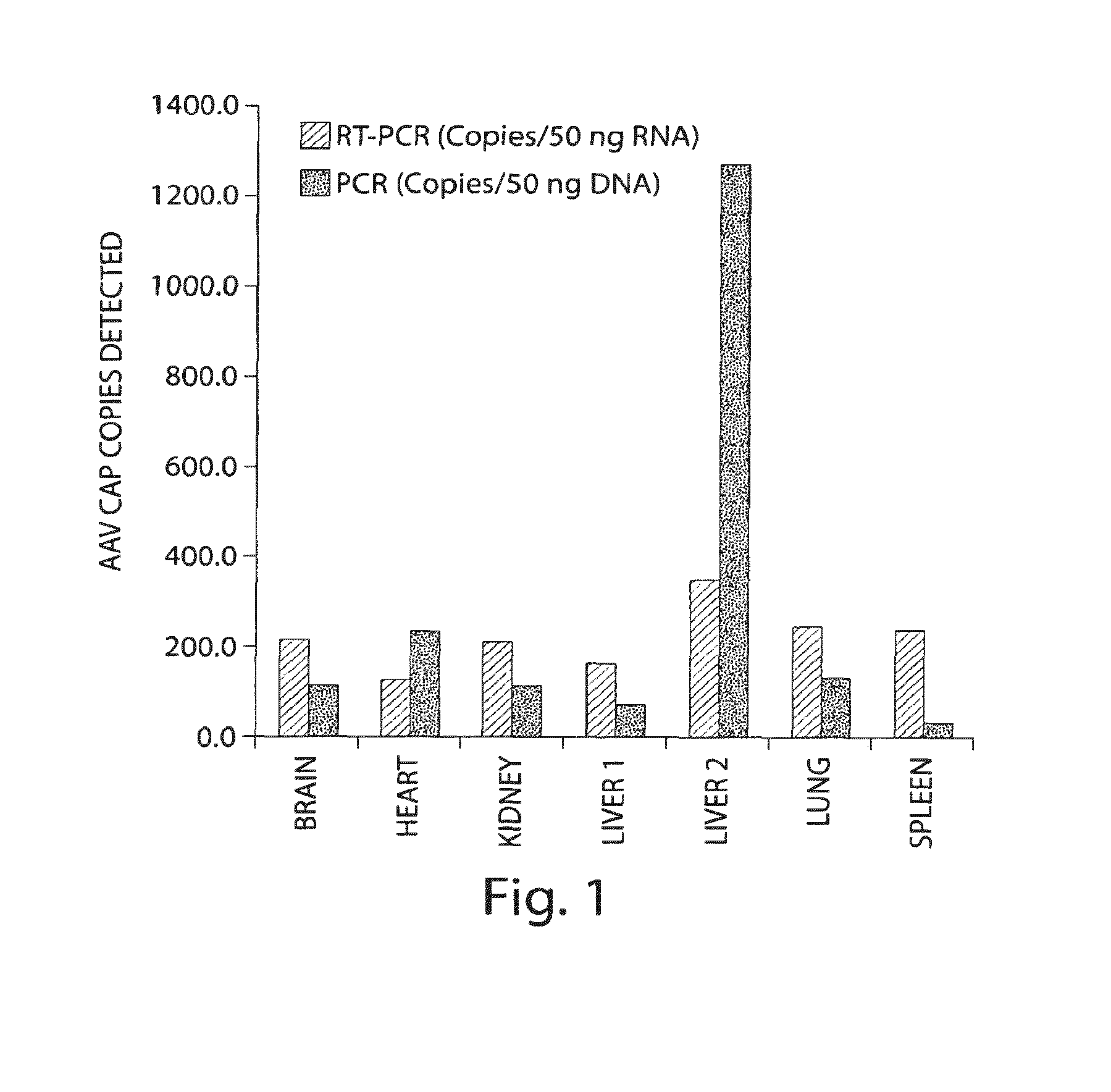
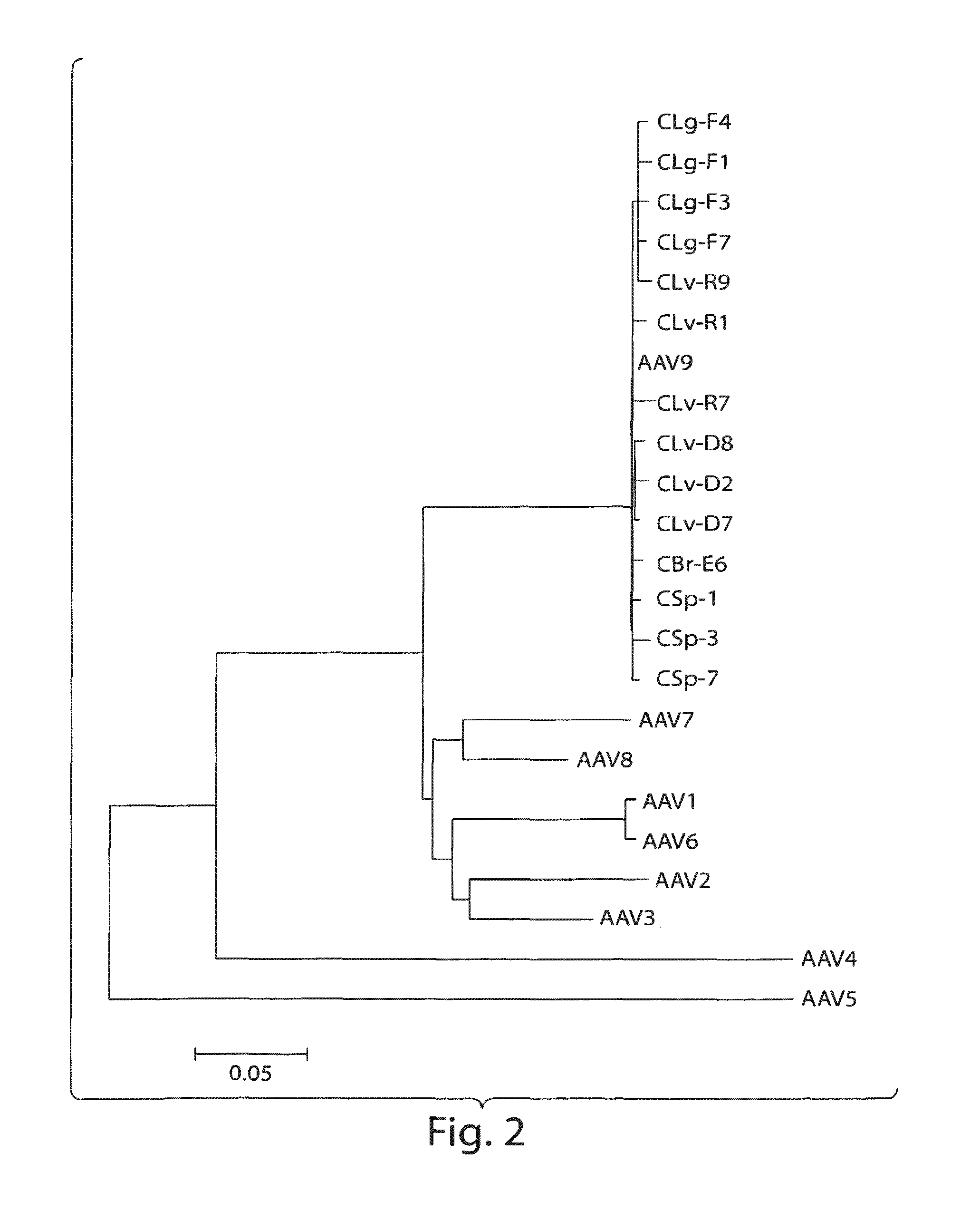
AAV's and uses thereof
The invention in some aspects relates to recombinant adeno-associated viruses having distinct tissue targeting capabilities. In some aspects, the invention relates to gene transfer methods using the recombinant adeno-associate viruses. In some aspects, the invention relates to isolated AAV capsid proteins and isolated nucleic acids encoding the same.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Embryonic-like stem cells derived from post-partum mammalian placenta, and uses and methods of treatment using said cells
Owner:CELULARITY INC
Compositions and methods for treating contracture
InactiveUS20050186261A1Prevent and minimize contracture formationPrevent relapseBiocideMuscular disorderPsychiatryContracture
A method for treating contracture is provided that includes administering to a patient in need thereof a composition that includes a therapeutic agent effective in treating contracture. Compositions, devices, and kits for use in treating contracture are also described.
Owner:ANGIOTECH INT AG (CH)
Compound and method for treating myotonic dystrophy
An antisense compound for use in treating myotonic dystrophy DM1 or DM2, a method of enhancing antisense targeting to heart and quadricep muscles, and a method for treating DM1 or DM2 in a mammalian subject are disclosed. The oligonucleotide has 8-30 bases, with at least 8 contiguous bases being complementary to the polyCUG or polyCCUG repeats in the 3′UTR region of dystrophia myotonica protein kinase (DMPK) mRNA in DM1 or DM2, respectively. Conjugated to the oligonucleotide is a cell-penetrating peptide having the sequence (RXRR(B / X)R)2XB, where R is arginine; B is β-alanine; and each X is —C(O)—(CH2)n—NH—, where n is 4-6. The antisense compound is effective to selectively block the sequestration of muscleblind-like 1 protein (MBNL1) and / or CUGBP, in heart and quadricep muscle in a myotonic dystrophy animal model.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
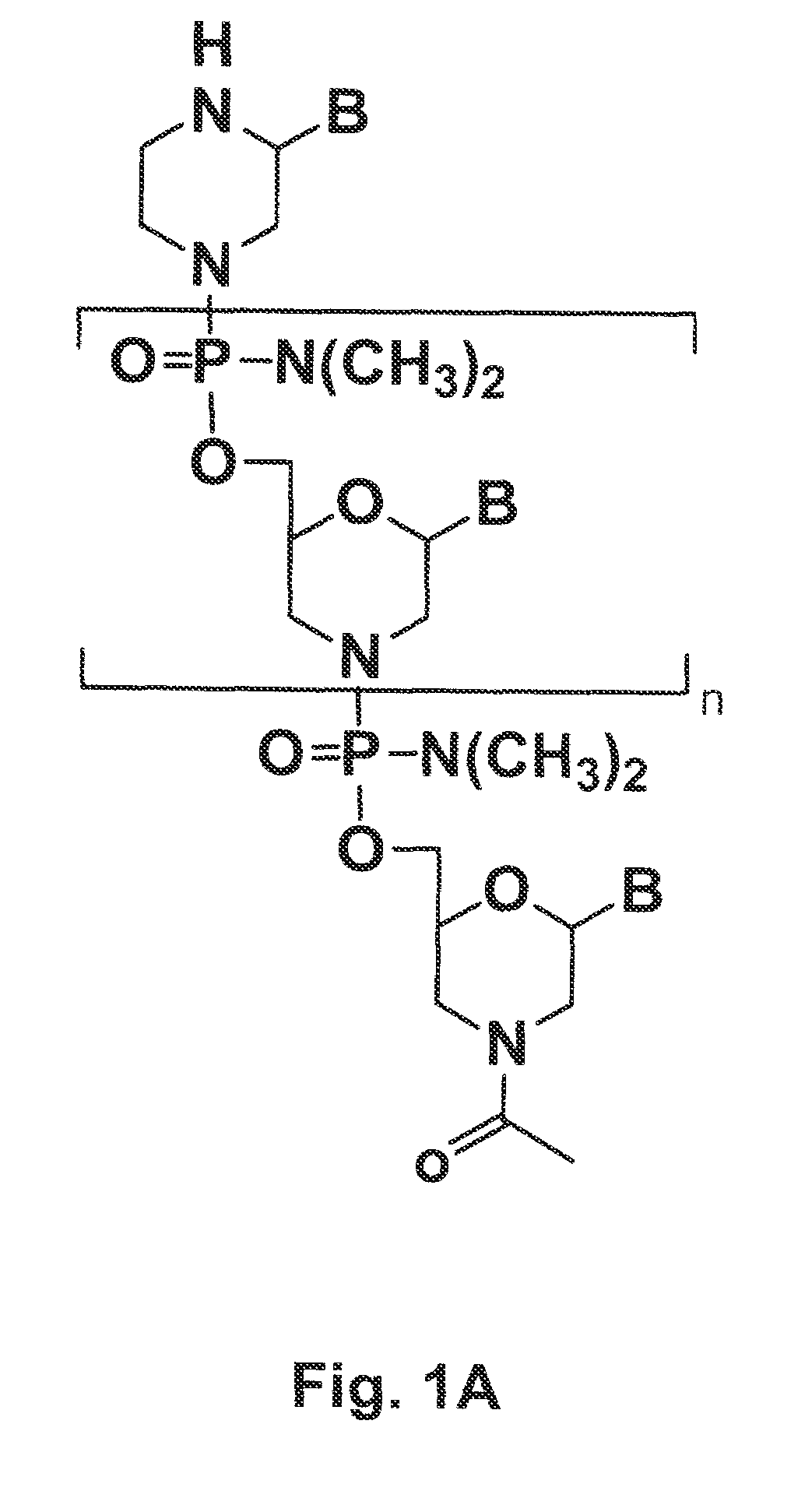
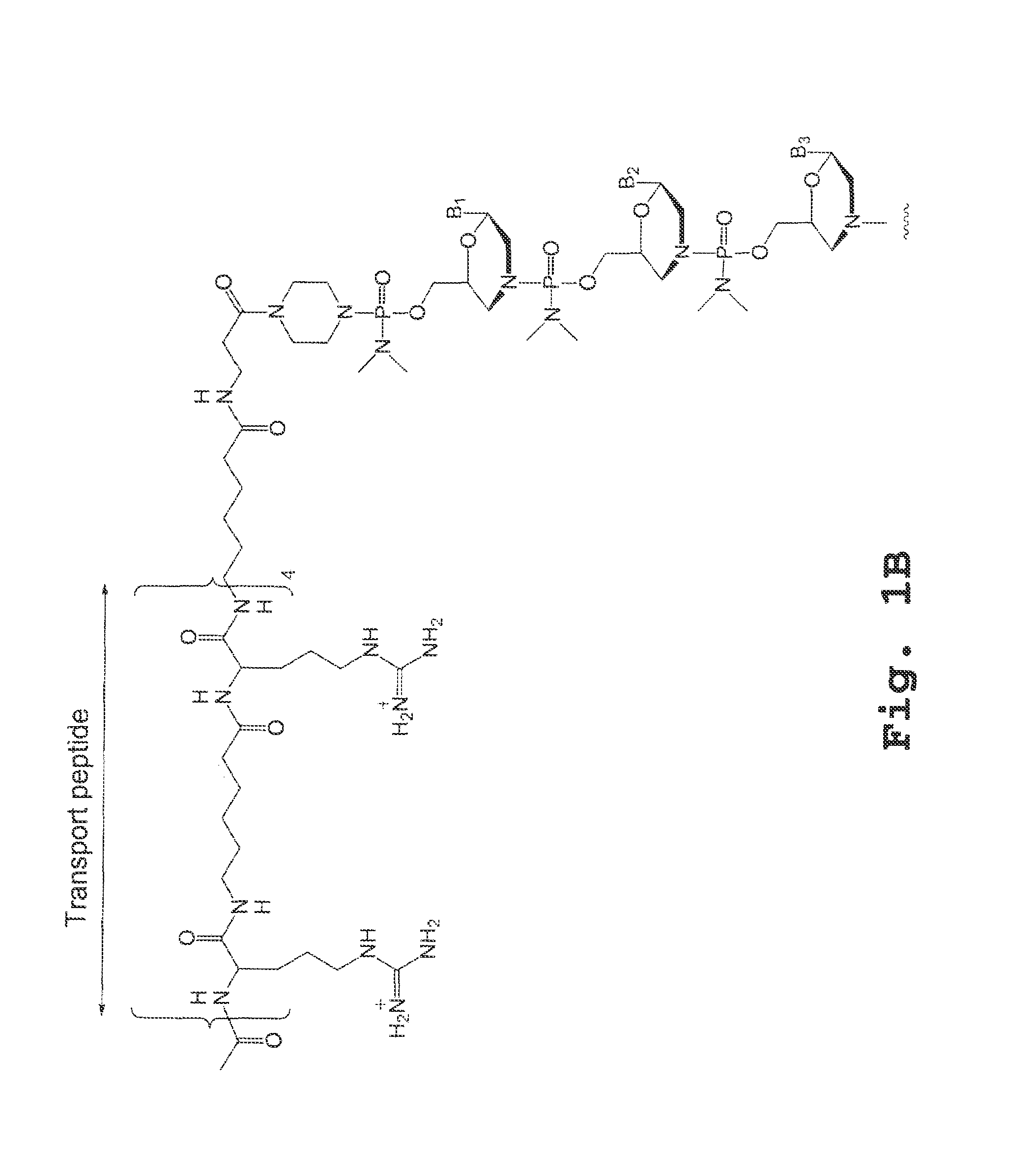
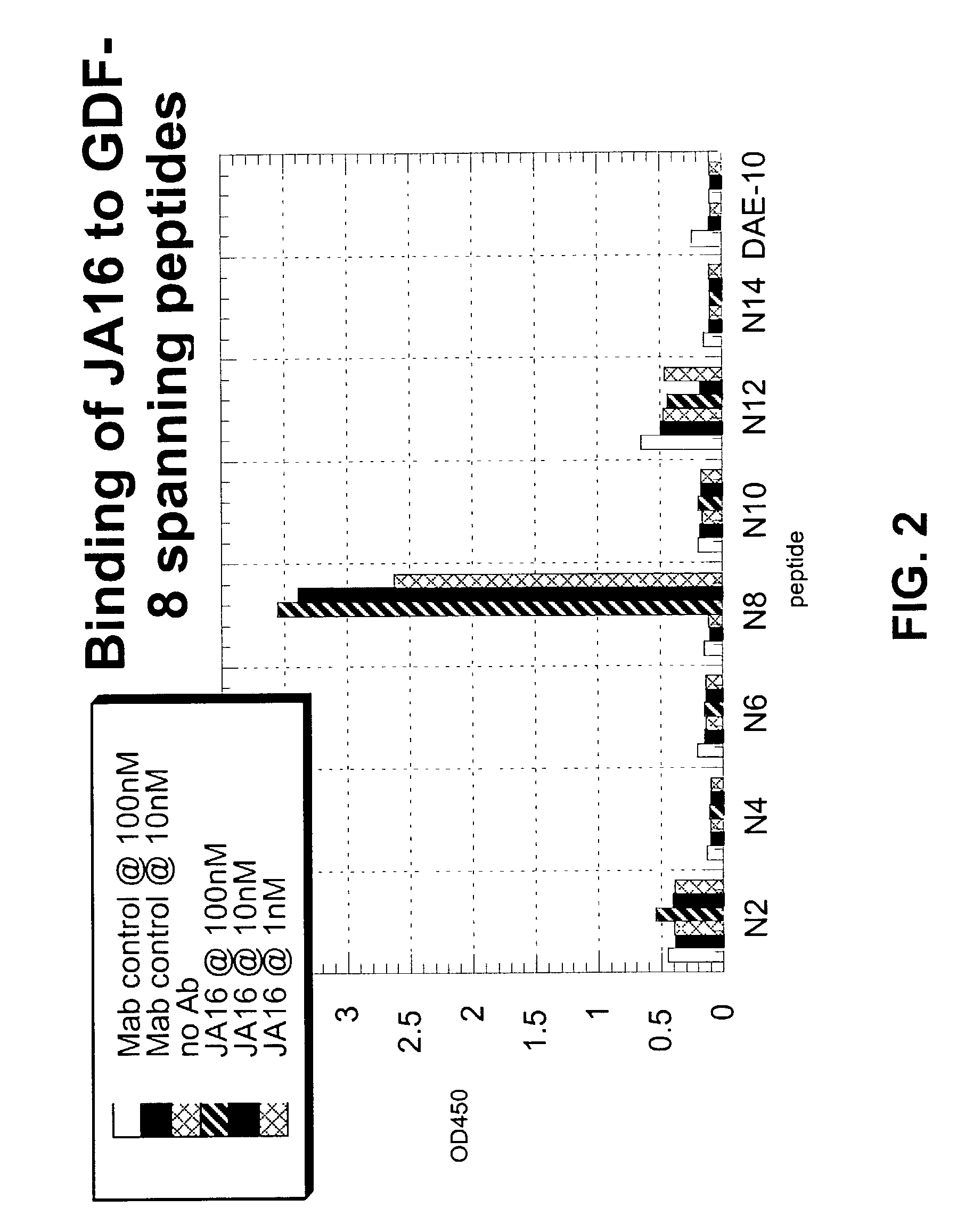
Antibody inhibitors of GDF-8 and uses thereof
ActiveUS7320789B2Reduction in one or more of the biological activitiesReduced activityNervous disorderMuscular disorderAntibody inhibitorAntibody fragments
The disclosure provides novel antibodies against growth and differentiation factor-8 (GDF-8), including antibody fragments, which inhibit GDF-8 activity in vitro and in vivo. The disclosure also provides methods for diagnosing, preventing, or treating degenerative disorders of muscle, bone, or insulin metabolism.
Owner:WYETH LLC
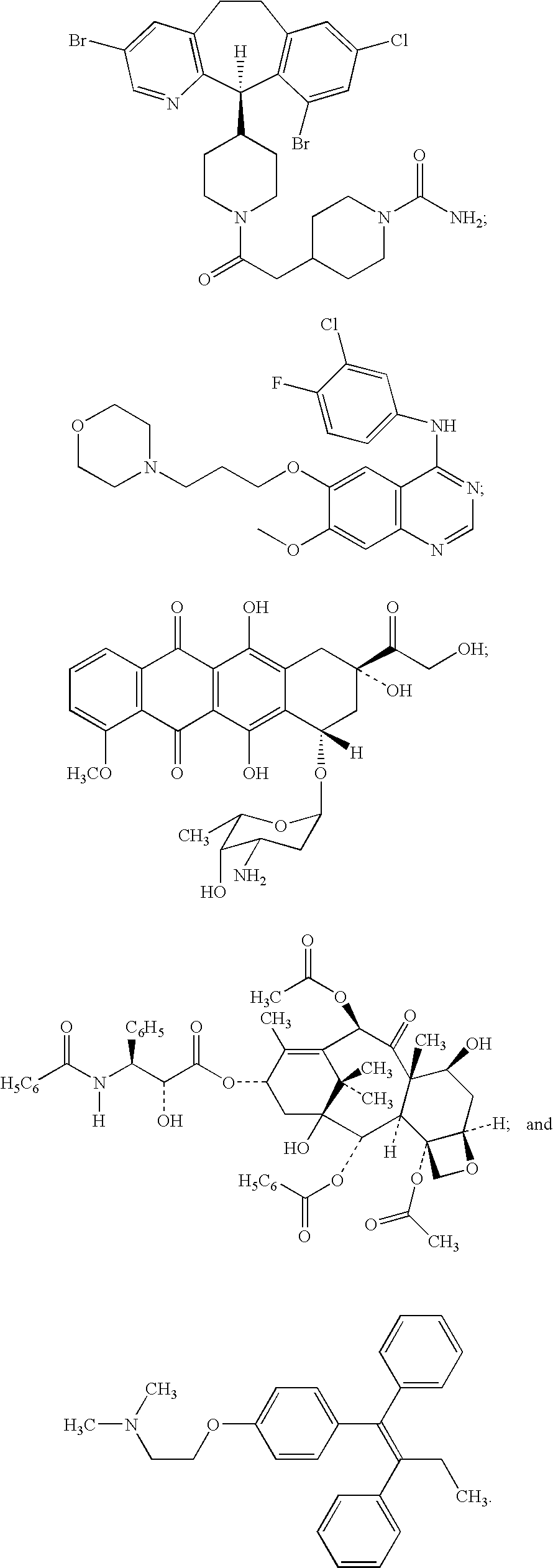
Small molecule toll-like receptor (TLR) antagonists
The invention provides methods and compositions useful for modulating signaling through Toll-like receptors. The methods involve contacting a TLR-expressing cell with a small molecule having a core structure including at least two rings. Certain of the compounds are 4-primary amino quinolines. Many of the compounds and methods are useful specifically for inhibiting immune stimulation involving at least one of TLR9, TLR8, TLR7, and TLR3. The methods may have use in the treatment of autoimmunity, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft versus host disease, infection, sepsis, cancer, and immunodeficiency.
Owner:COLEY PHARMA GMBH +1
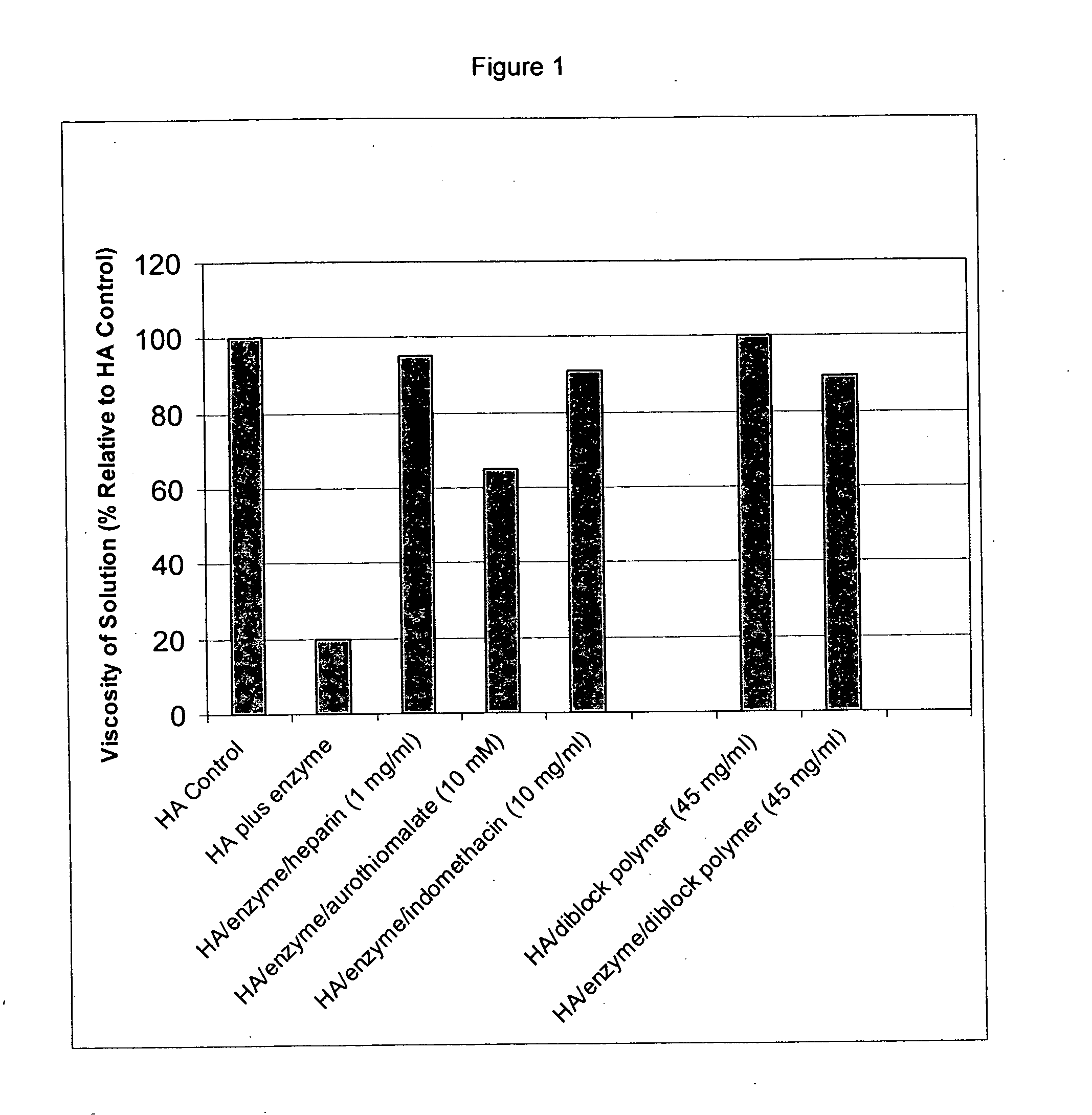
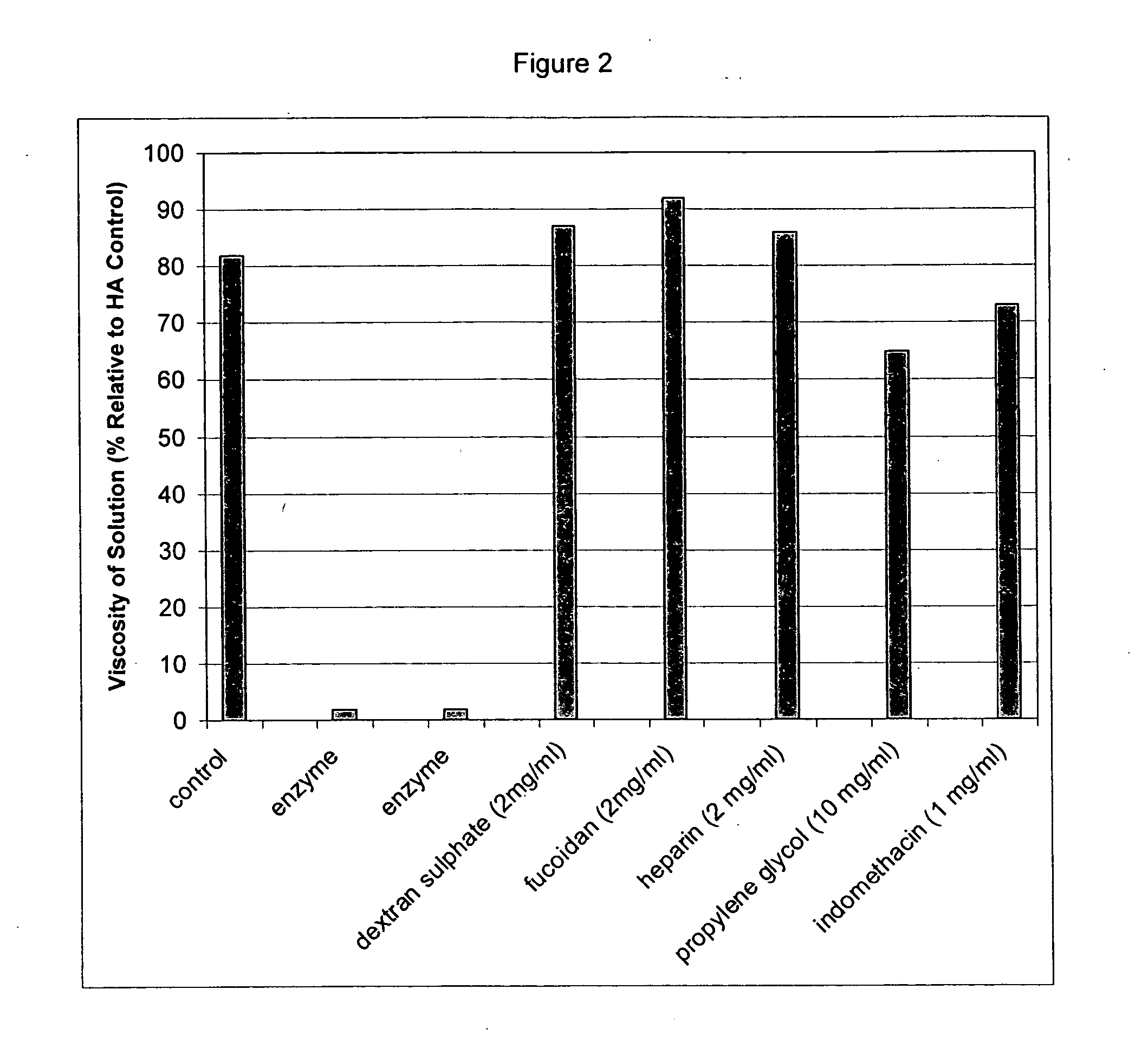
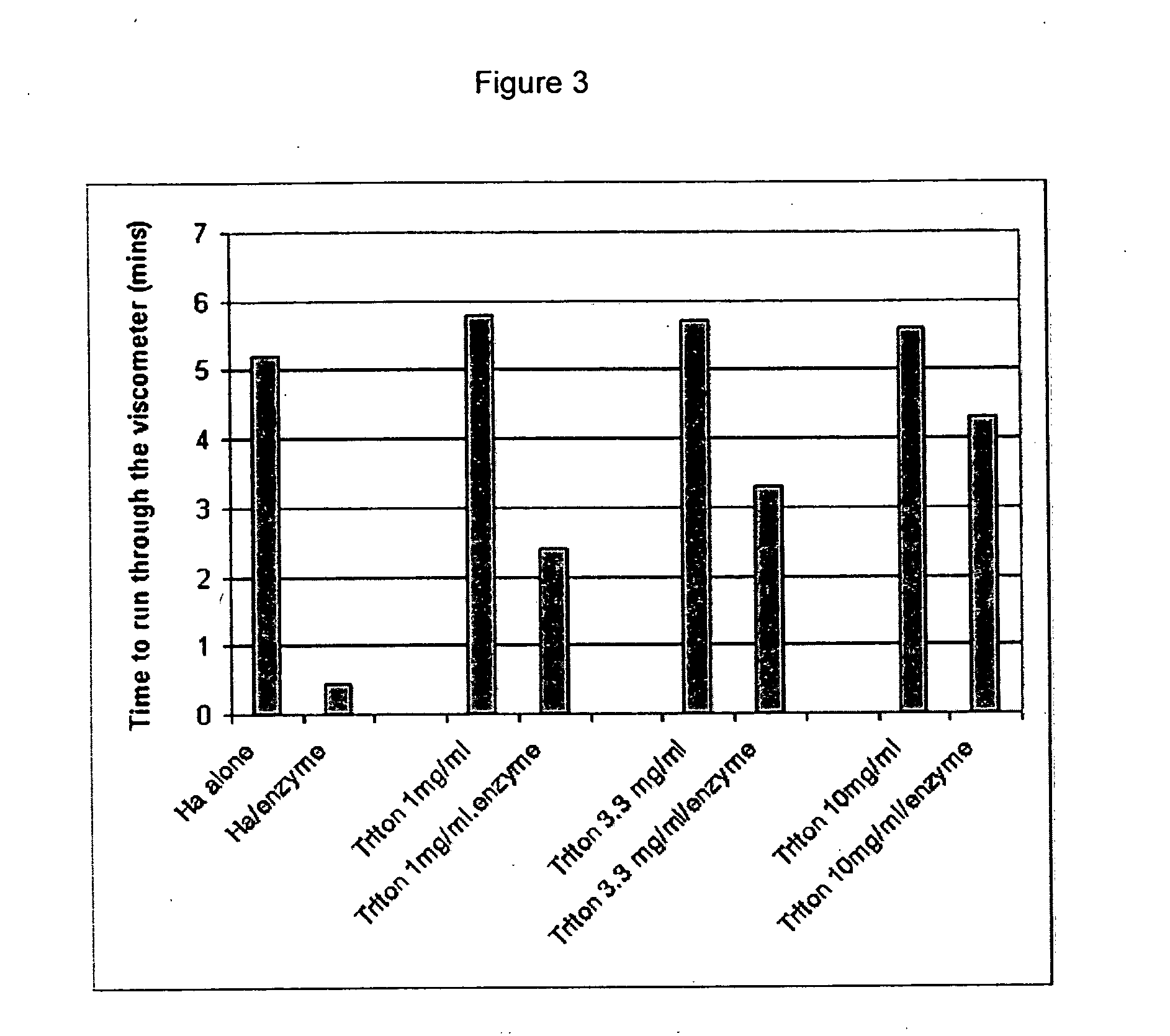
Compositions and methods using hyaluronic acid
InactiveUS20060040894A1Relieve painPreventing surgical adhesionBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsCompound (substance)Hyaluronic acid
Compositions and devices including hyaluronic acid and a compound that inhibits degradation of hyaluronic acid, and methods of making and using same.
Owner:ANGIOTECH INT AG (CH) +1
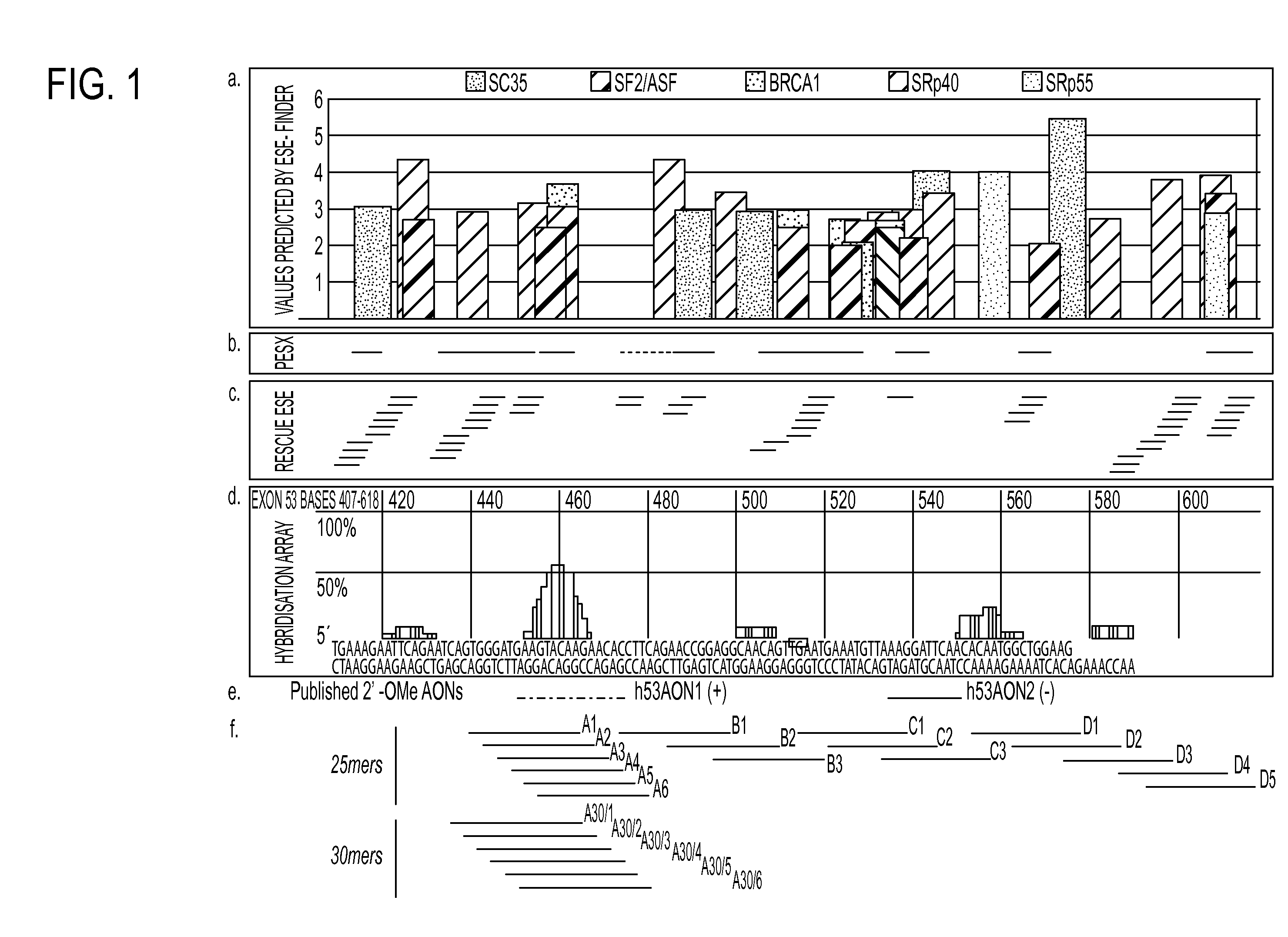
Oligomers
ActiveUS20100168212A1High degreeOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesMuscular dystrophyOligomer
Molecules are provided for inducing or facilitating exon skipping in forming spliced mRNA products from pre-mRNA molecules in cells. The molecules may be provided directly as oligonucleotides or expression products of vectors that are administered to a subject. High rates of skipping can be achieved. High rates of skipping reduce the severity of a disease like Duchene Muscular Dystrophy so that the disease is more like Becker Muscular Dystrophy. This is a severe reduction in symptom severity and mortality.
Owner:ROYAL HOLLOWAY & BEDFORD NEW COLLEGE
Specific kinase inhibitors
Resorcylic acid lactones having a C5-C6 cis double bond and a ketone at C7 and other compounds capable of Michael adduct formation are potent and stable inhibitors of a subset of protein kinases having a specific cysteine residue in the ATP binding site.
Owner:KOSAN BIOSCI
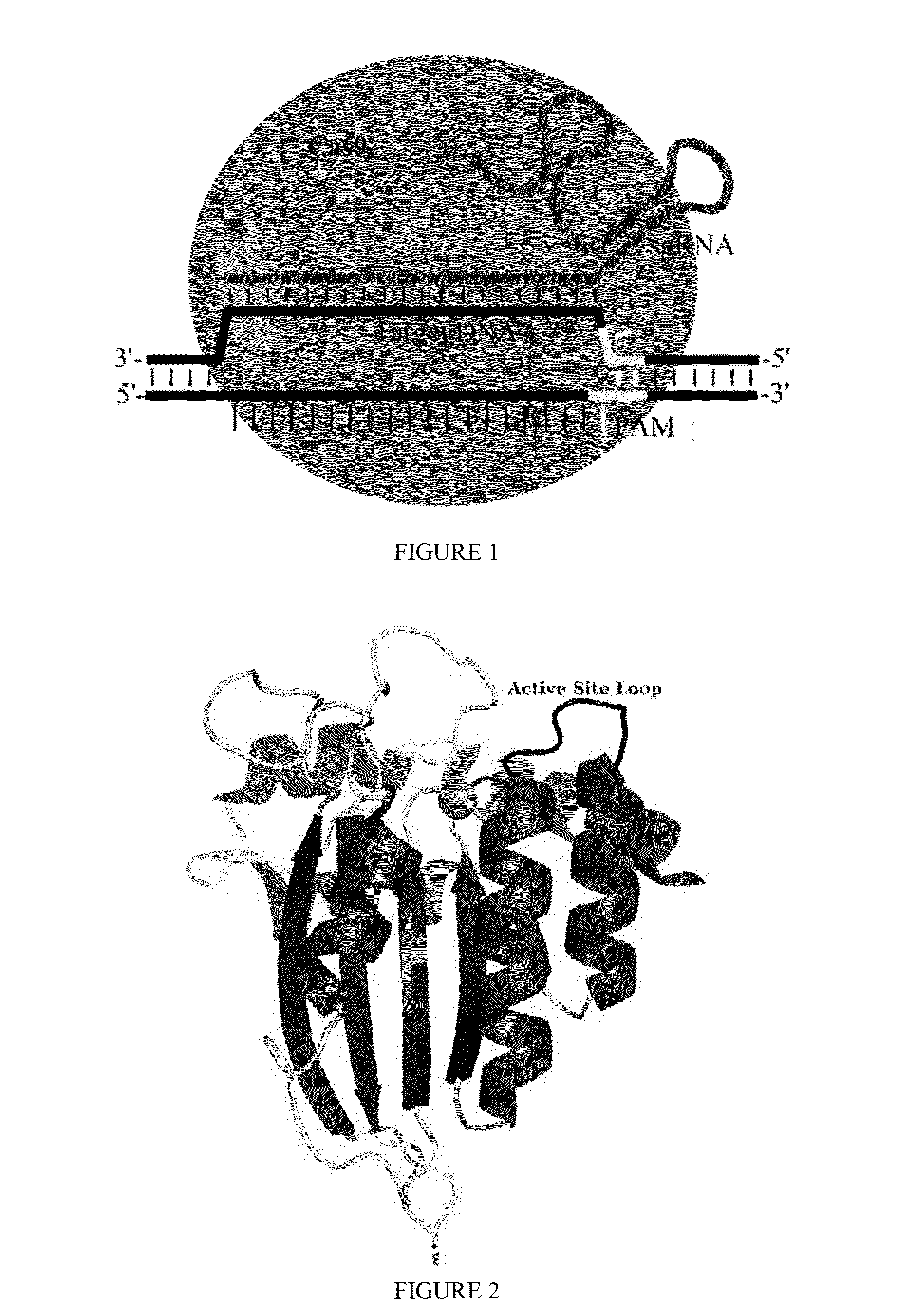
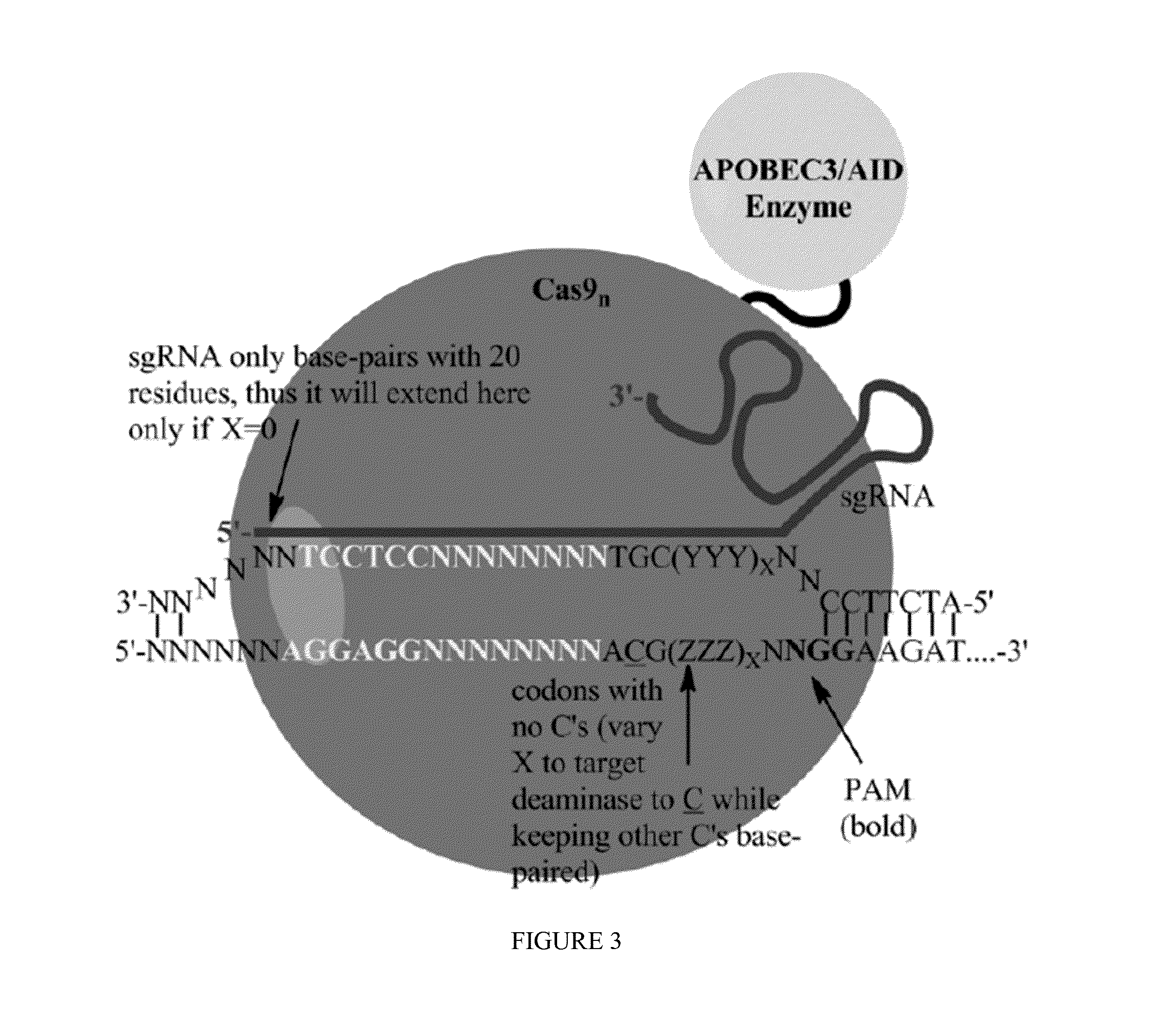
Fusions of cas9 domains and nucleic acid-editing domains
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a single site within the genome of a cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or enzyme domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, methods for targeted nucleic acid editing are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
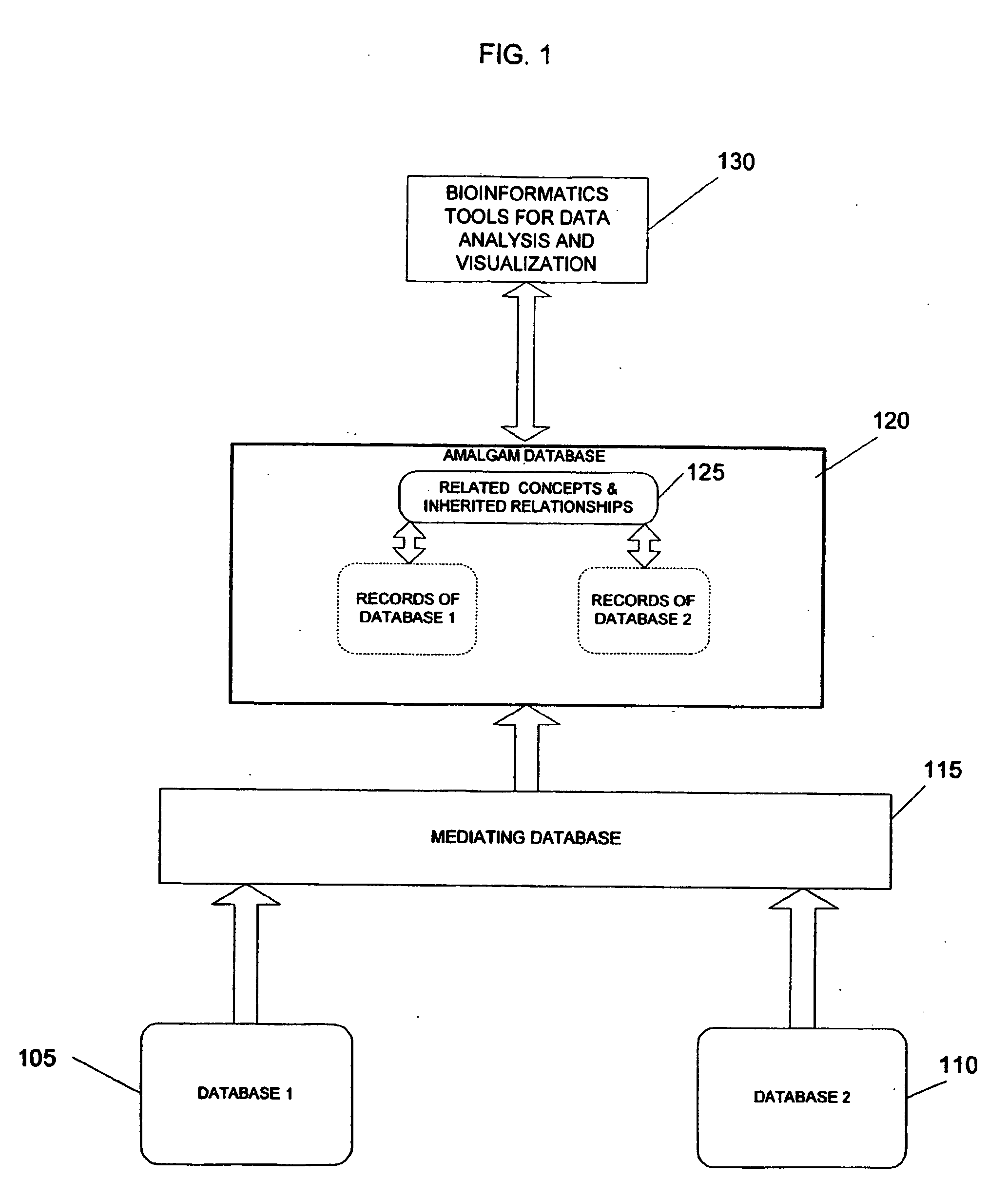
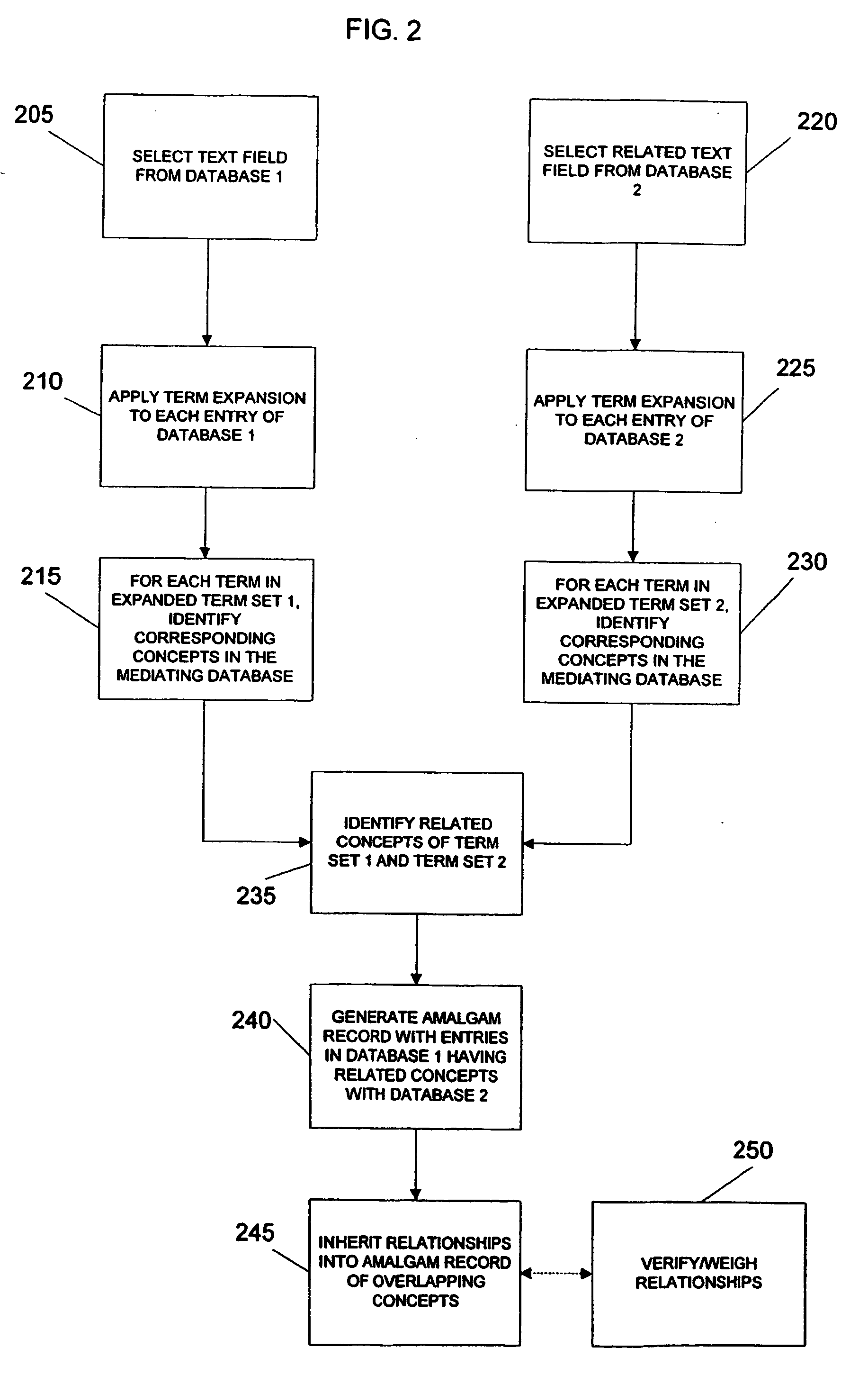
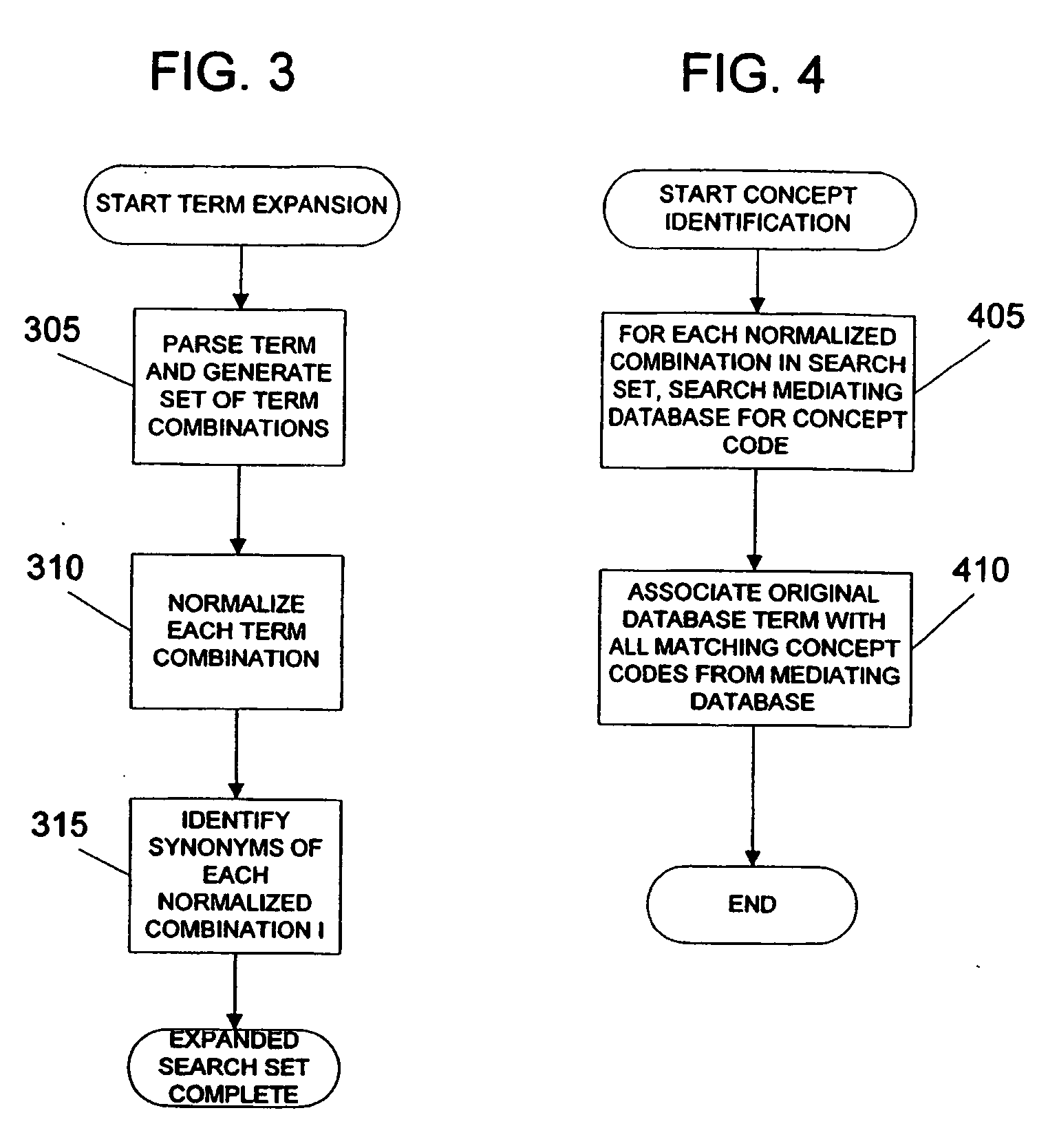
System and method for generating an amalgamated database
InactiveUS20060074991A1Organic active ingredientsNervous disorderInformaticsBioinformatics databases
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
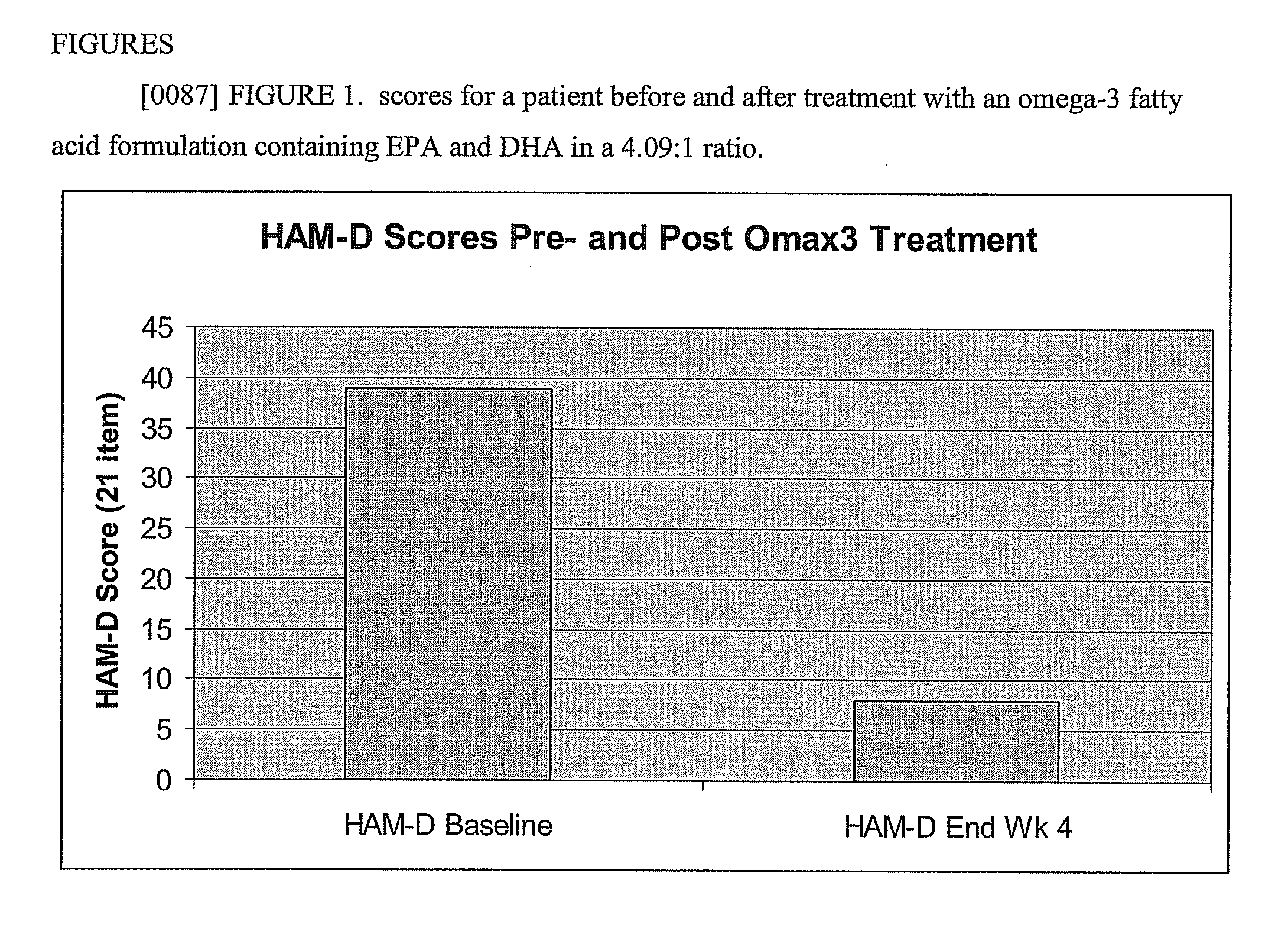
Omega 3 fatty acid formulations
The present invention provides highly purified omega-3 fatty acid formulations. Certain formulations provided herein have contain greater than 85% omega-3 fatty acids by weight. Certain other formulations provided herein contain EPA and DHA in a ratio of from about 4.01:1 to about 5:1. The invention also provides methods of using the dosage forms to treat a variety of cardiovascular, autoimmune, inflammatory, and central nervous system disorders by administering a formulation of the invention to a patient in need thereof.
Owner:CENESTRA
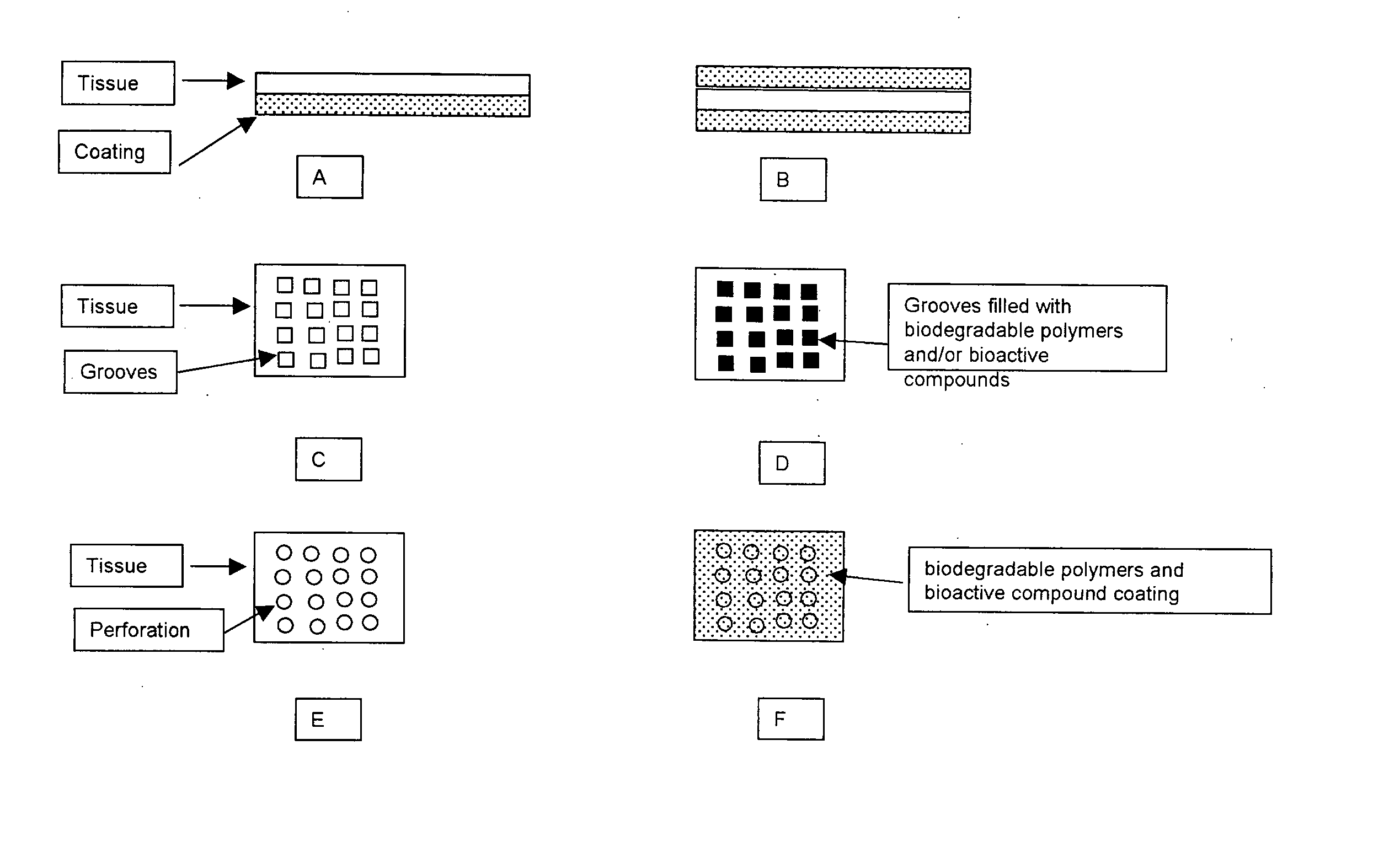
Implantable Tissue Compositions and Method
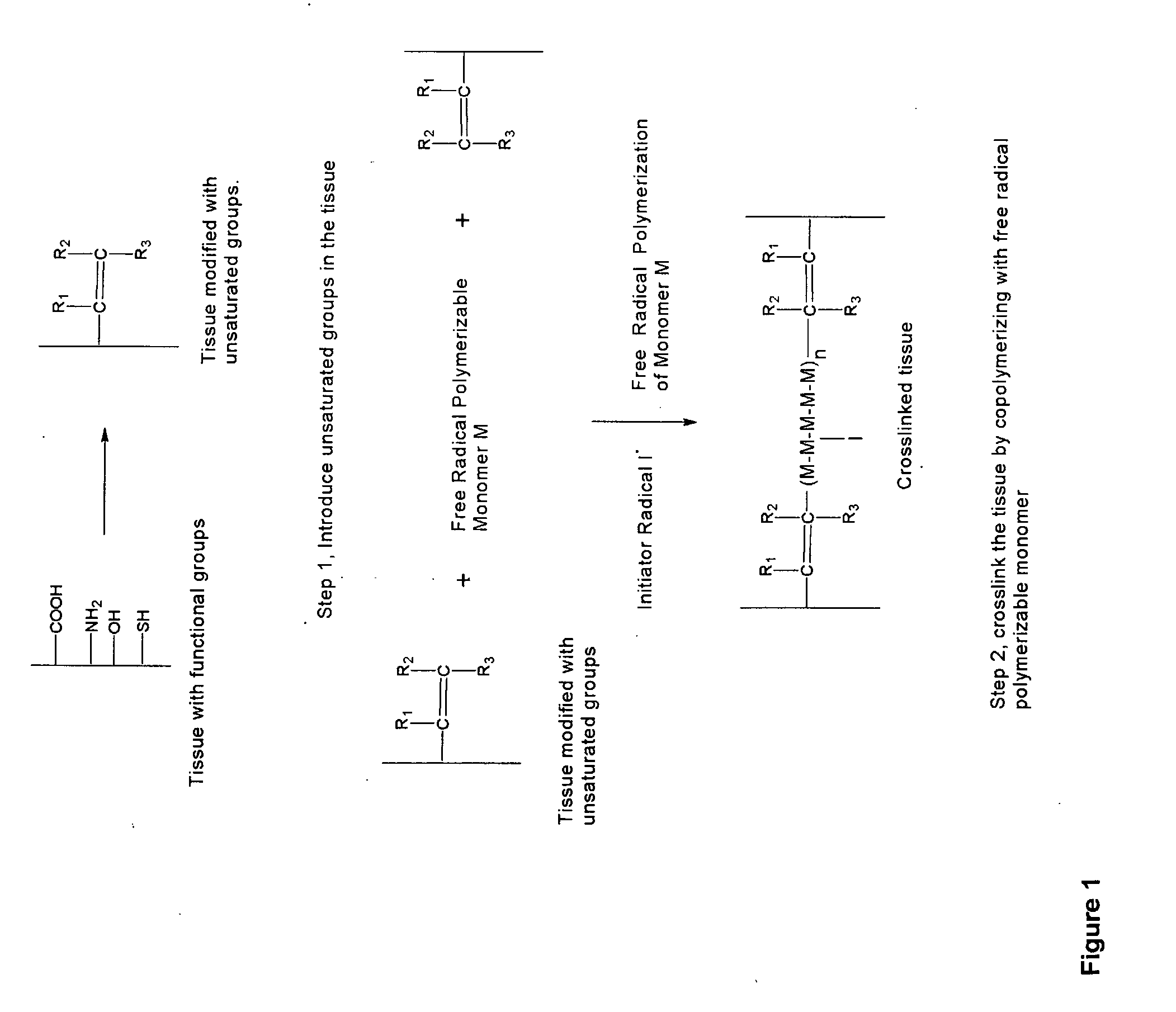
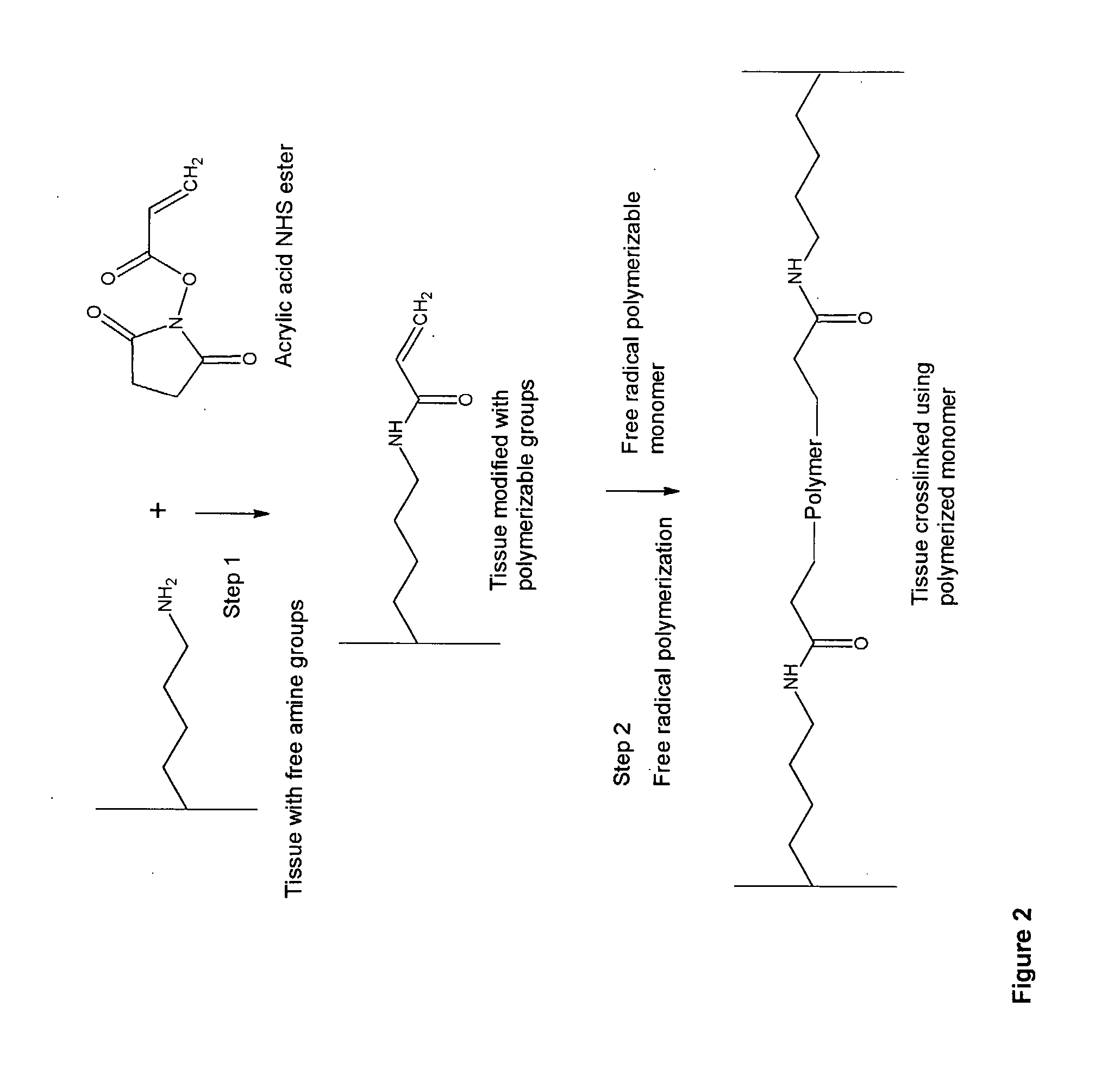
InactiveUS20070254005A1Promotes localized deliveryImprove overall lifespanNervous disorderAntipyreticWater insolubleFixation method
Novel implantable tissue fixation methods and compositions are disclosed. Methods and compositions of tissue, fixed using polymeric and / or variable length crosslinks, and di- or polymercapto compounds are described. Also described are the methods and compositions wherein the tissue is fixed using biodegradable crosslinkers. Methods and compositions for making radioopaque tissue are also described. Methods and compositions to obtain a degradable implantable tissue-synthetic biodegradable polymer composite are also described. Compositions and methods of incorporating substantially water-insoluble bioactive compounds in the implantable tissue are also disclosed. The use of membrane-like implantable tissue to make an implantable drug delivery patch are also disclosed. Also described are the compositions and methods to obtain a coated implantable tissue. Medical applications implantable tissue such as heart valve bioprosthesis, vascular grafts, meniscus implant, drug delivery patch are also disclosed.
Owner:PATHAK HLDG
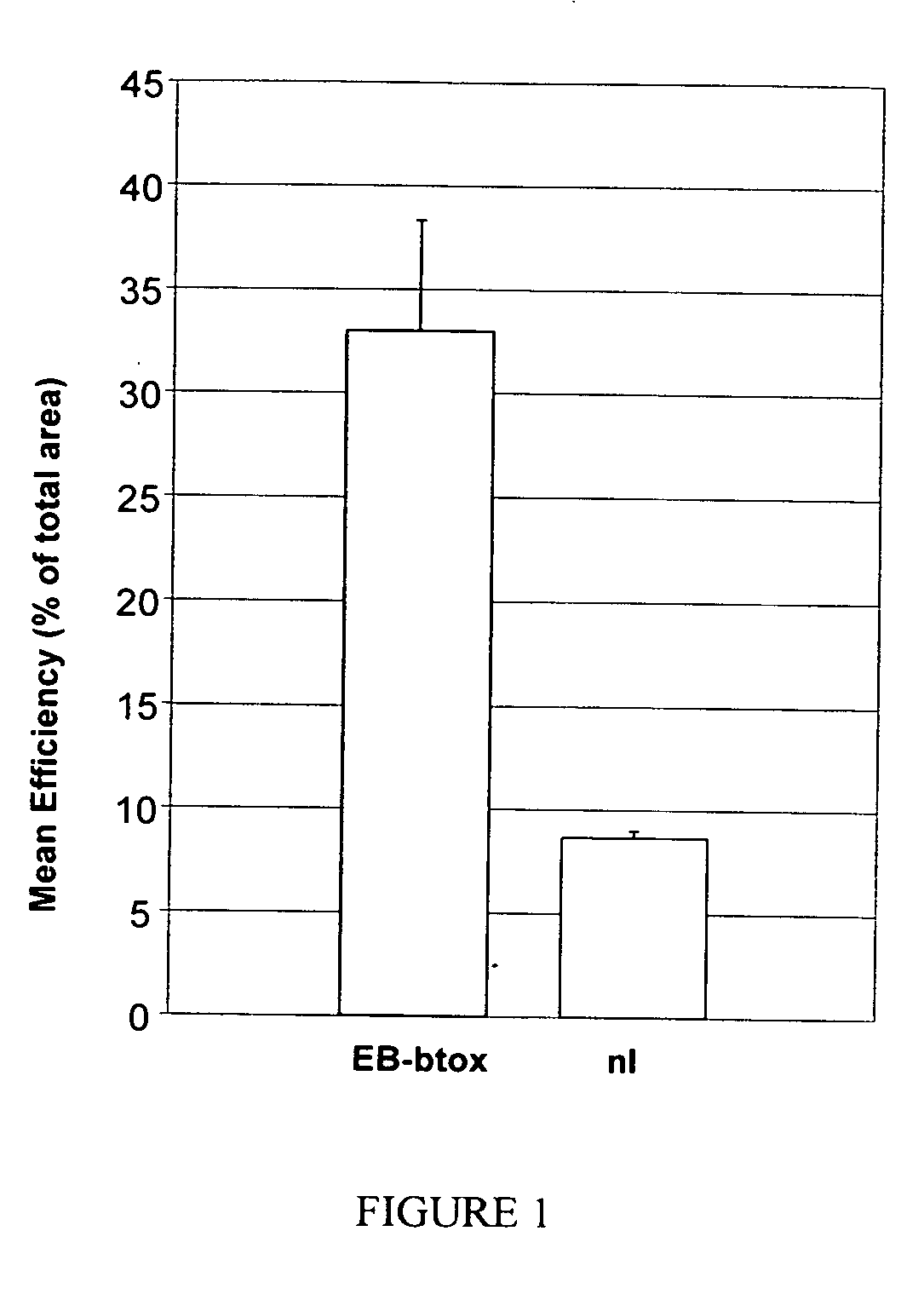
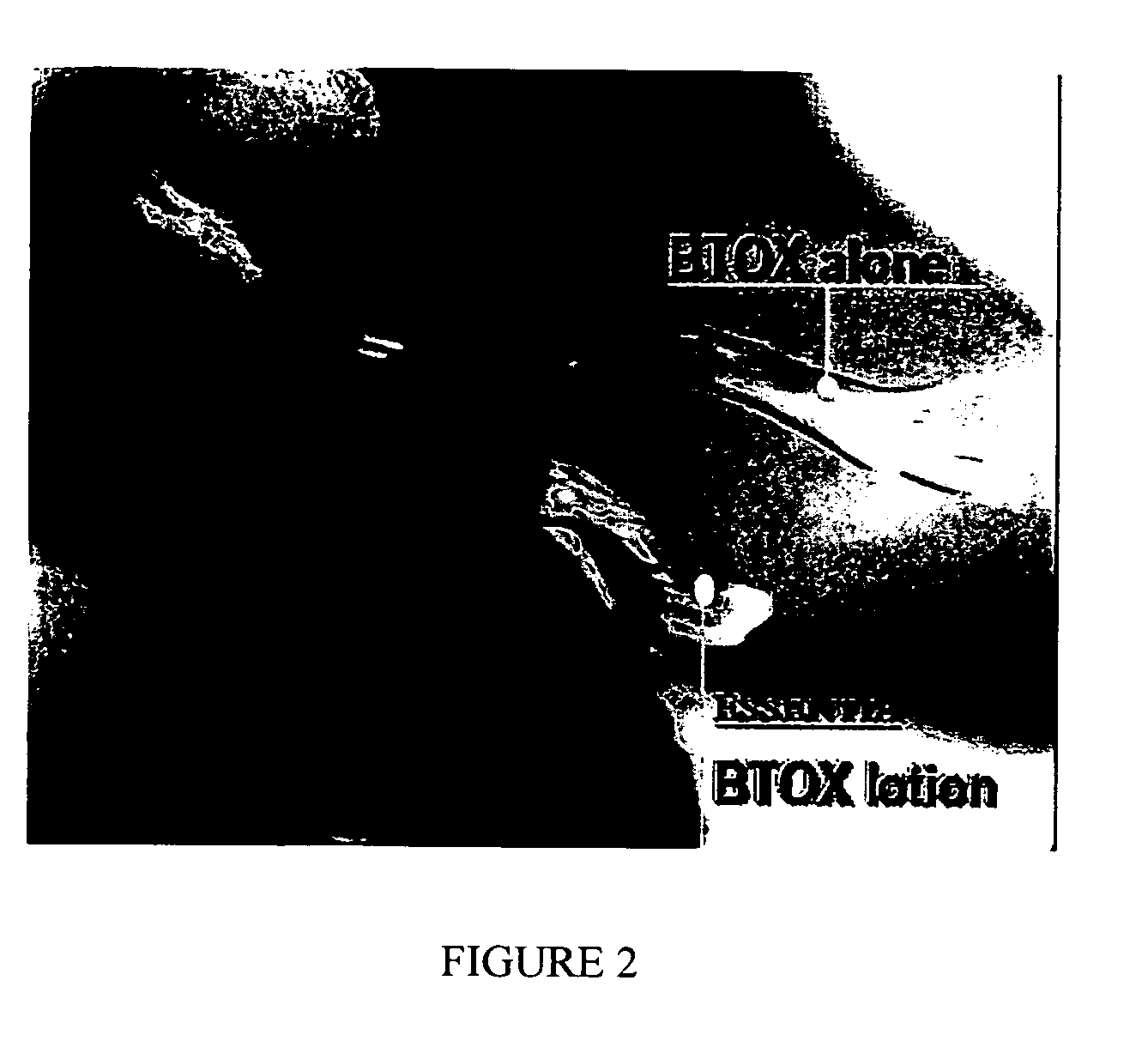
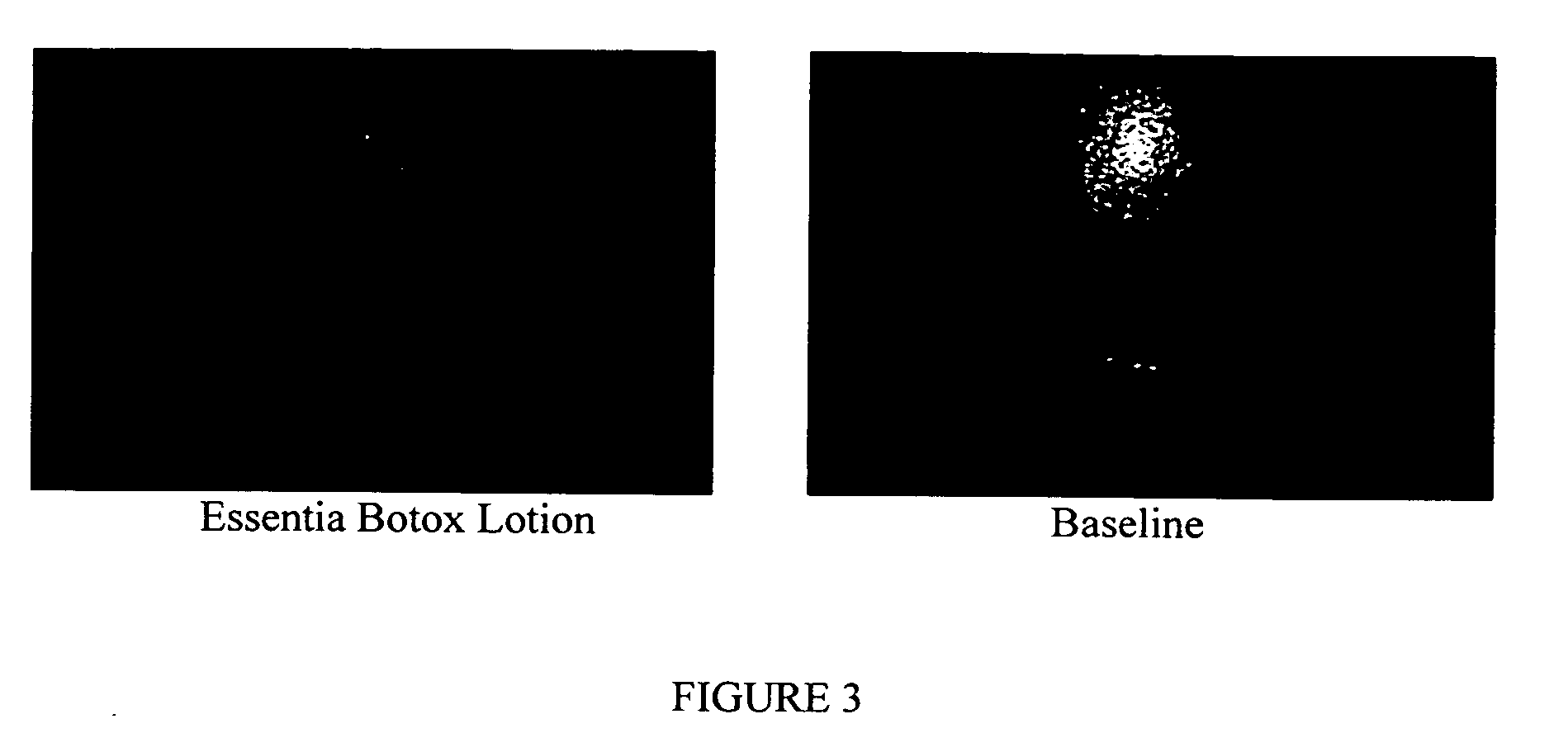
Compositions and methods for topical application and transdermal delivery of botulinum toxins
ActiveUS20050196414A1Reduce hypersecretionReduce sweatingCosmetic preparationsSenses disorderEpitheliumMedicine
A composition for topical application of a botulinum toxin (including botulinum toxin derivatives) comprises a botulinum toxin and a carrier comprising a polymeric backbone comprising a long-chain polypeptide or nonpeptidyl polymer having attached positively charged branching or “efficiency” groups. The invention also relates to methods for reducing muscle paralysis and other conditions that may be treated with a botulinum toxin, particularly paralysis of subcutaneous, and most particularly, facial, muscles, by topically applying an effective amount of the botulinum toxin and carrier, in conjunction, to the subject's skin or epithelium. Kits for administration are also described.
Owner:REVANCE THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods and compositions for the specific inhibition of gene expression by double-stranded RNA
Owner:CITY OF HOPE +1
Treatment of metabolic disorders using TNFalpha inhibitors
Methods for treating metabolic disorders, including diabetes and obesity, using TNFalpha inhibitors are described.
Owner:ABBOTT BIOTECHNOLOGY LTD
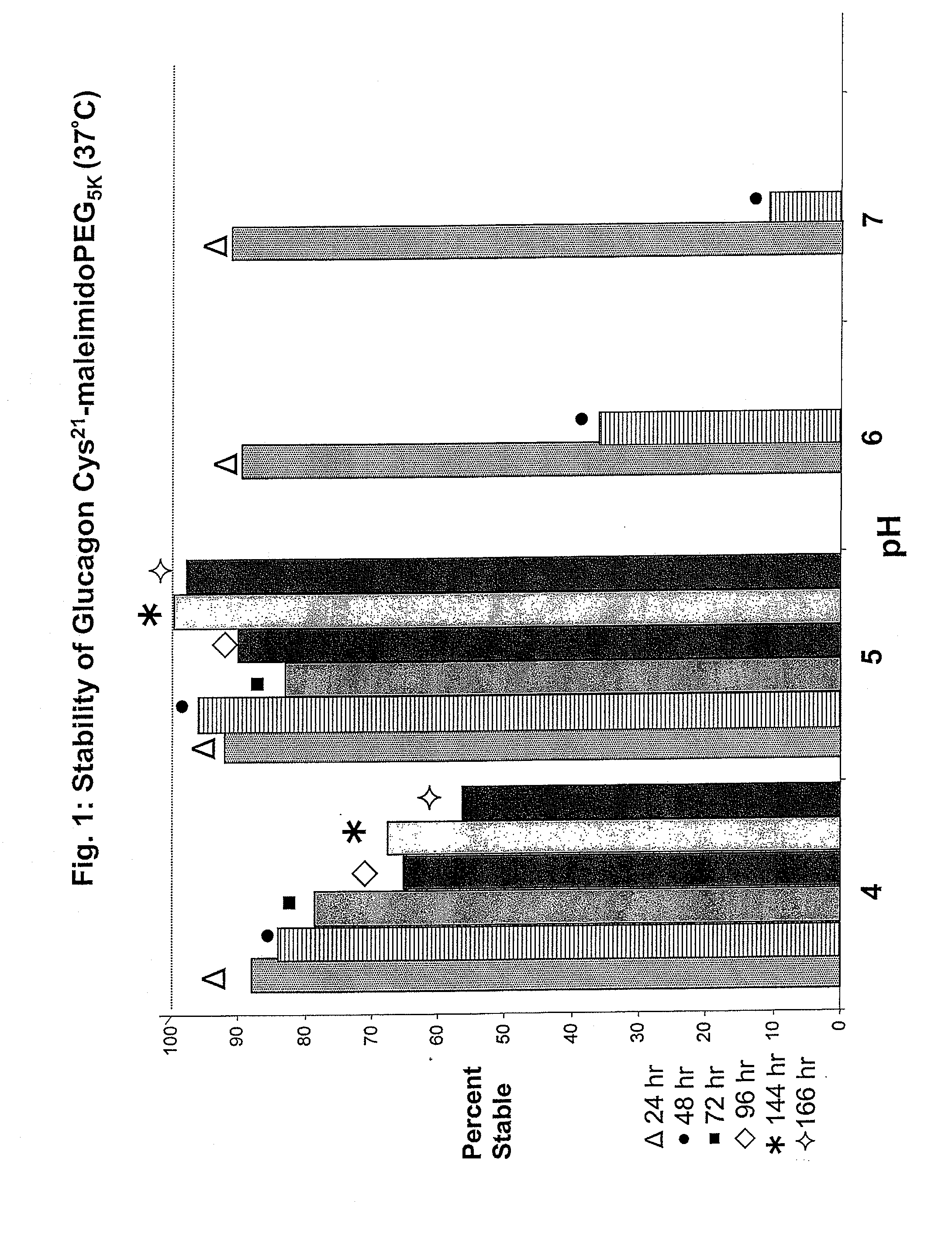
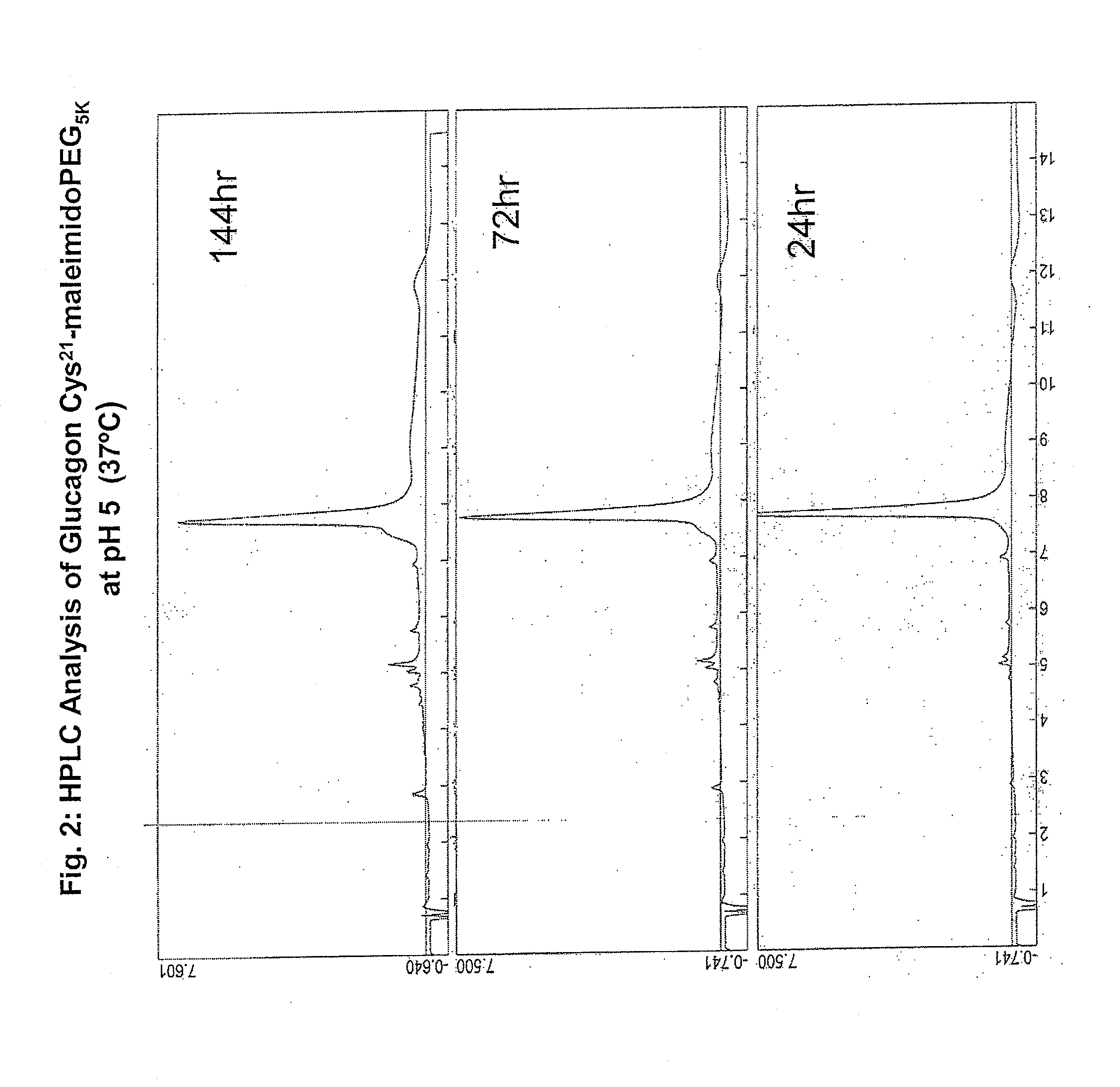
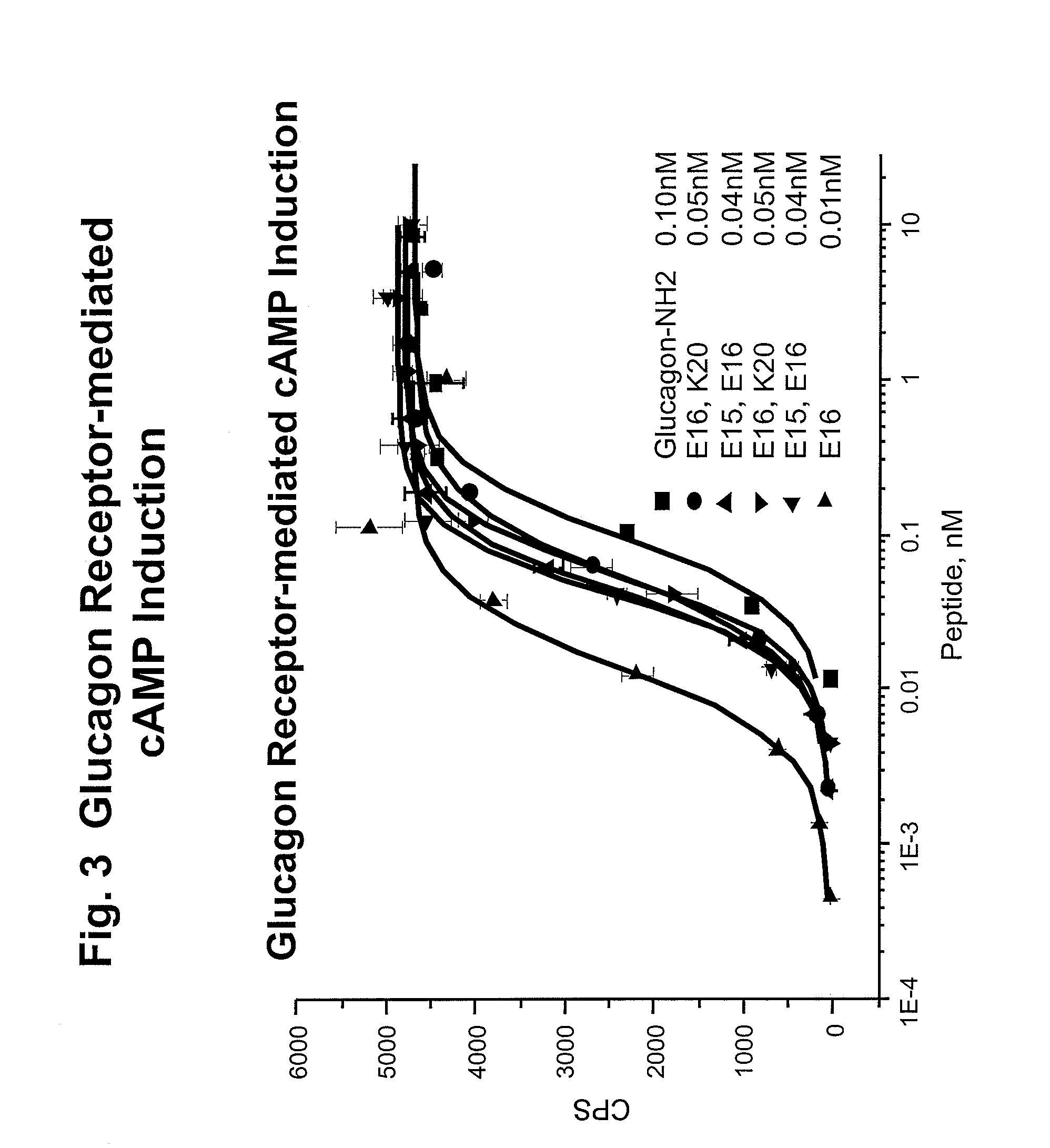
Glucagon/glp-1 receptor co-agonists
InactiveUS20100190701A1High activityEnhanced biophysical stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSolubilityCarboxylic acid
Modified glucagon peptides are disclosed having enhanced potency at the glucagon receptor relative to native glucagon. Further modification of the glucagon peptides by forming lactam bridges or the substitution of the terminal carboxylic acid with an amide group produces peptides exhibiting glucagon / GLP-1 receptor co-agonist activity. The solubility and stability of these high potency glucagon analogs can be further improved by modification of the polypeptides by pegylation, substitution of carboxy terminal amino acids, or the addition of a carboxy terminal peptide selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NO: 26 (GPSSGAPPPS), SEQ ID NO: 27 (K-RNRNNIA) and SEQ ID NO: 28 (KRNR).
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Conformable tissue repair implant capable of injection delivery
A conformable tissue implant is provided for use in repairing or augmenting a tissue defect or injury site. The tissue implant contains a tissue carrier matrix comprising a plurality of biocompatible, bioresorbable granules and at least one tissue fragment in association with the granules. The tissue fragment contains one or more viable cells that can migrate from the tissue and populate the tissue carrier matrix. Also provided is a method for injectably delivering the tissue implant.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
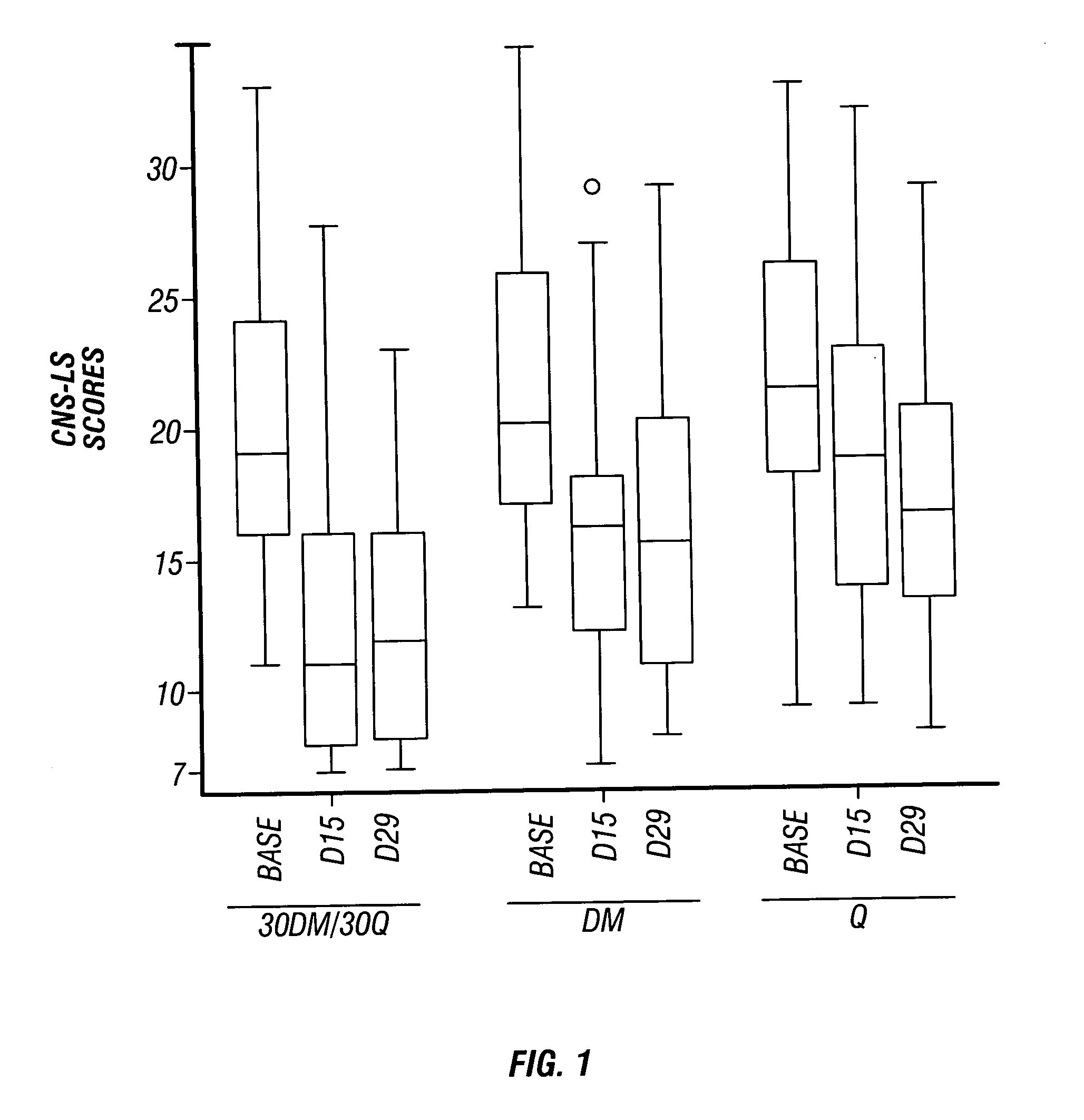
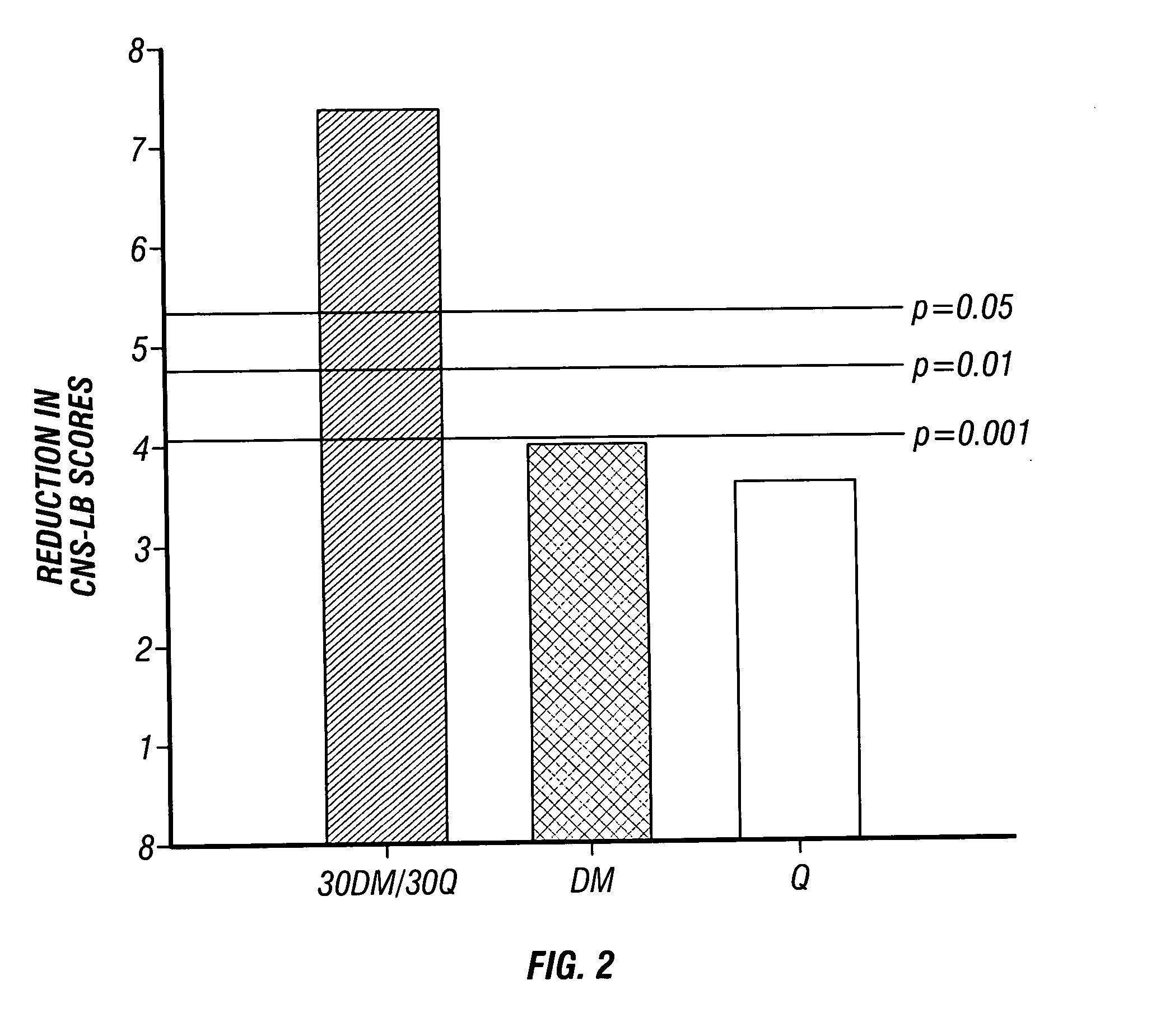
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising dextromethorphan and quinidine for the treatment of neurological disorders
Pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treating neurological disorders by administering same are provided. The compositions comprise dextromethorphan in combination with quinidine.
Owner:AVANIR PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com