Antisense oligonucleotide directed removal of proteolytic cleavage sites, the hchwa-d mutation, and trinucleotide repeat expansions
a technology of proteolytic cleavage and antisense oligonucleotide, which is applied in the field of biotechnology and genetic and acquired diseases, can solve the problems of difficult implementation of such strategies in the clini
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
AON-Mediated Exon Skipping in Neurodegenerative Diseases to Remove Proteolytic Cleavage Sites
[0110]AON-mediated exon skipping in Huntington's disease to remove proteolytic cleavage sites from the huntingtin protein.
Methods
AONs and Primers
[0111]All AONs consisted of 2′-O-methyl RNA and full length phosphorothioate backbones.
Cell Cultures and AON Transfection
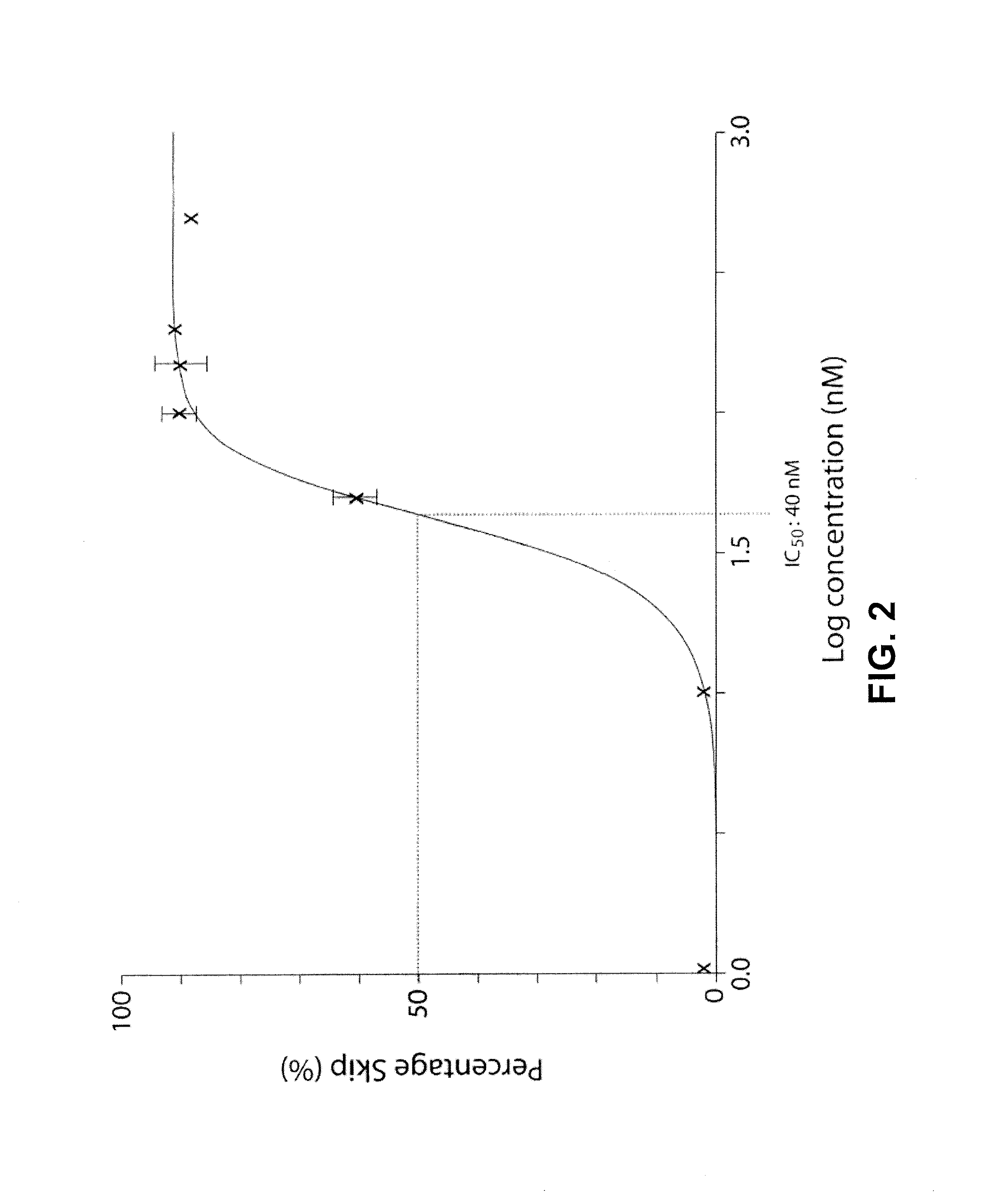
[0112]Patient fibroblast cells and human neuroblastoma cells were transfected with AONs at concentrations ranging between 1 and 1000 nM using Polyethylenemine (PEI) ExGen500 according to the manufacturer's instructions, with 3.3 μl PEI per μg of transfected AON. A second transfection was performed 24 hours after the first transfection. RNA was isolated 24 hours after the second transfection and cDNA was synthesized using random hexamer primers.
Cell Lines Used:
[0113]FLB73 Human Fibroblast Control
[0114]GM04022 Human Fibroblast HD
[0115]GMO2173 Human Fibroblast HD
[0116]SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Control
[0117]Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT...
example 2
AON Mediated Skipping of htt Exon 12 or 13 in Human Fibroblasts
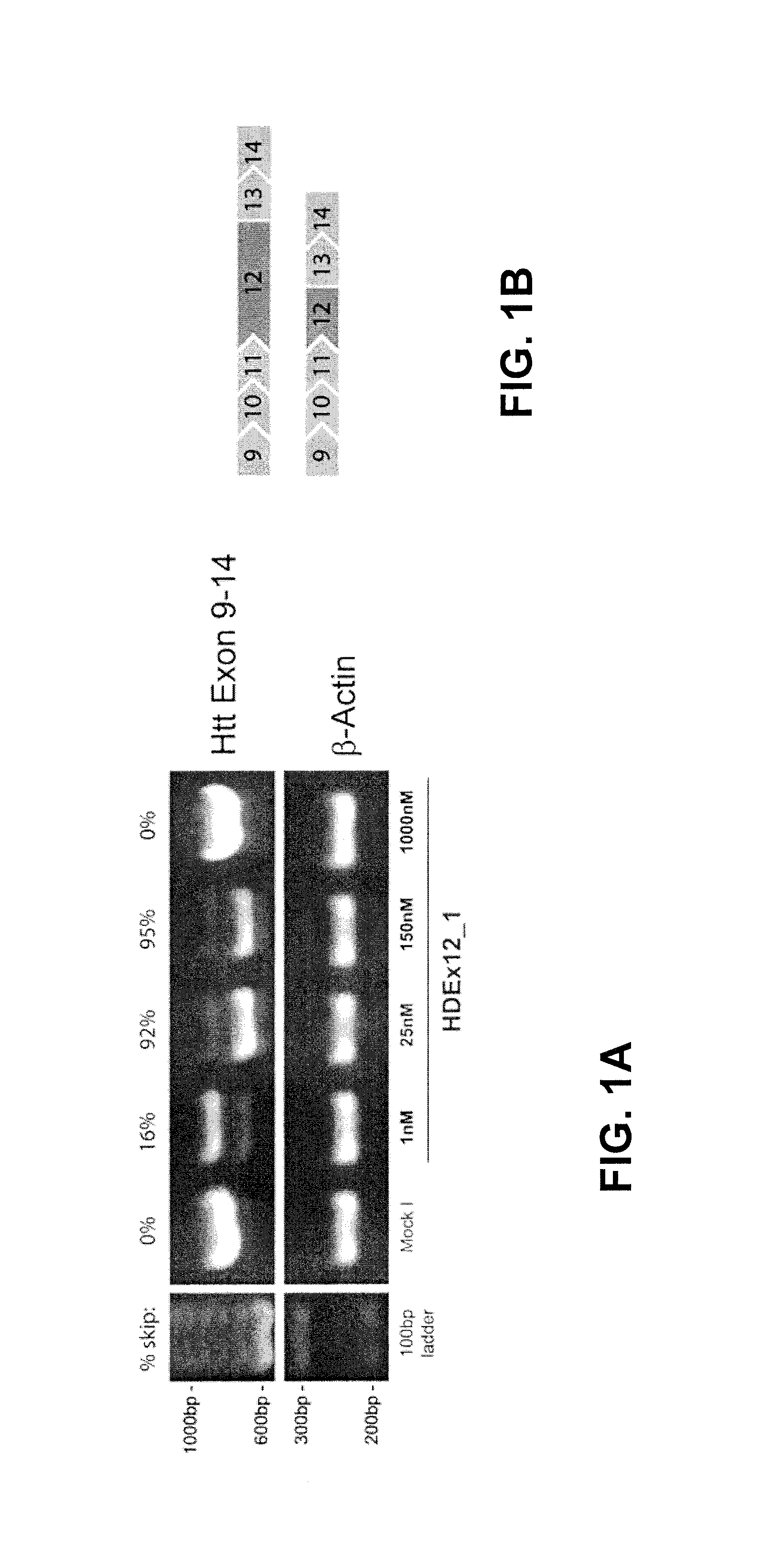
[0127]The caspase-6 site at amino acid position 586 previously shown to be important in disease pathology is encoded partly in exon 12 and partly in exon 13. Exon 12 also encodes two active caspase-3 sites at amino acids 513 and 552 (10, 33). Skipping of both exon 12 and 13 would maintain the open reading frame and therefore is anticipated to generate a shorter htt protein lacking these 3 caspase sites (see FIG. 6). The AONs used in this study are shown below.
AON Name Sequence (5′-3′):(SEQ ID NO: 182)hHTTEx12_7GUCCCAUCAUUCAGGUCCAU(SEQ ID NO: 178)hHTTEx12_5CUCAAGAUAUCCUCCUCAUC(SEQ ID NO: 190)hHTTEx13_1GGCUGUCCAAUCUGCAGG(SEQ ID NO: 238)Control AONUCCUUUCAUCUCUGGGCUC(SEQ ID NO: 239)mAON12.1GGCUCAAGAUGUCCUCCUCAUCC(SEQ ID NO: 240)mAON12.2UUUCAGAACUGUCCGAAGGAGUC(SEQ ID NO: 241)mAON13GGCUGUCCUAUCUGCAUG(SEQ ID NO: 242)Scrambled AONCUGAACUGGUCUACAGCUC(SEQ ID NO: 243)Alexa488 AONGGUACACCUAGCGGAACAAU
[0128]AONs were transfected in h...
example 3
Removal of the 586 Caspase-6 Cleavage Site from Mouse htt Protein In Vitro and in Vivo
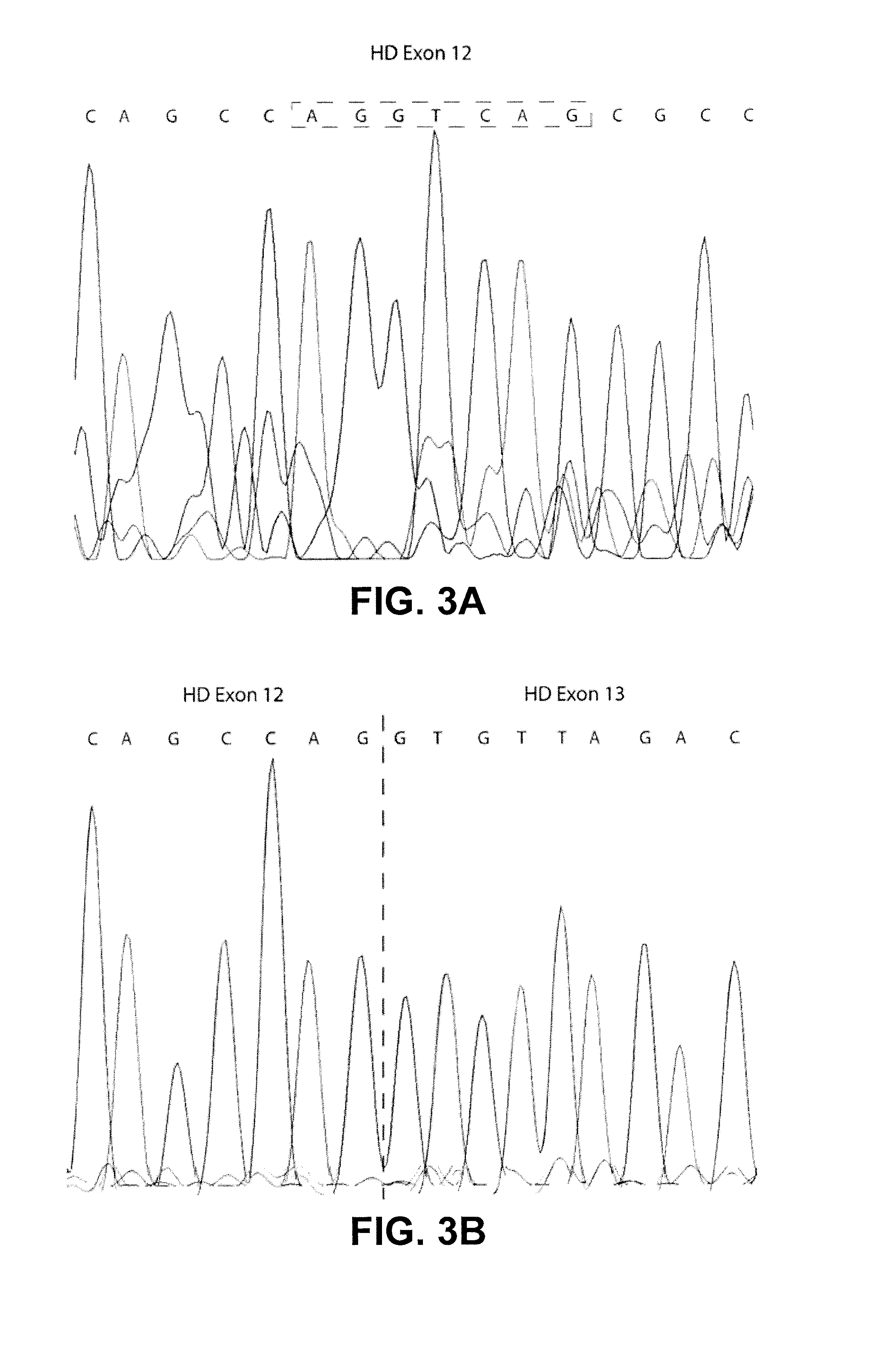
[0132]To investigate the potential of htt exon skipping in vivo and to test if removal of the amino acid sequence surrounding the 586 caspase-6 cleavage site could be harmful in vivo, AONs homologues to the mouse sequence was designed. Since mice do not exhibit the cryptic splice site that is responsible for the partial skip in human cells, the full skip of exon 12 and 13 as was described for the human cells was investigated. Transfection of 200 nM of each mouse specific htt AON targeting exon 12 and 13 in mouse C2C12 cells showed a skip of both exons with an efficiency of 86.8% (±5.6) (FIGS. 10A and 10B).
[0133]To investigate distribution of the AON in the mouse brain, 10 μg of Alexa Fluor 488 labeled control AON was injected bilaterally into the striatum of a control mouse. The mouse was sacrificed after one week, the brain was perfused, and sections were immunolabeled using the neuronal marker Ne...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com