Patents
Literature
115 results about "Cell selectivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Targeting proteins to cells expressing mannose receptors via expression in insect cells
The present invention is based on the discovery that proteins produced in insect cell cultures are glycosylated in a unique manner that causes them to be selectively imported by cells that express mannose receptors on their membranes, particularly macrophages. Proteins that are selectively imported into cells containing mannose receptors are provided, as well as pharmaceutical compositions containing such proteins and methods for producing such proteins. Application of the present invention to produce proteins useful for treating lysosomal storage disorders is also disclosed. Engineering of cells to express mannose receptors so that they will selectively import proteins produced in insect cells is also taught, as well as a protein targeting system using such cells and proteins. Finally, an improved elution buffer for the purification of proteins produced in insect cells from a Concanavalin A column is provided.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
Methods and compositions using peptides and proteins with c-terminal elements
ActiveUS20100322862A1Improve permeabilityInternalization of enhancedOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCell selectivityPeptide sequence
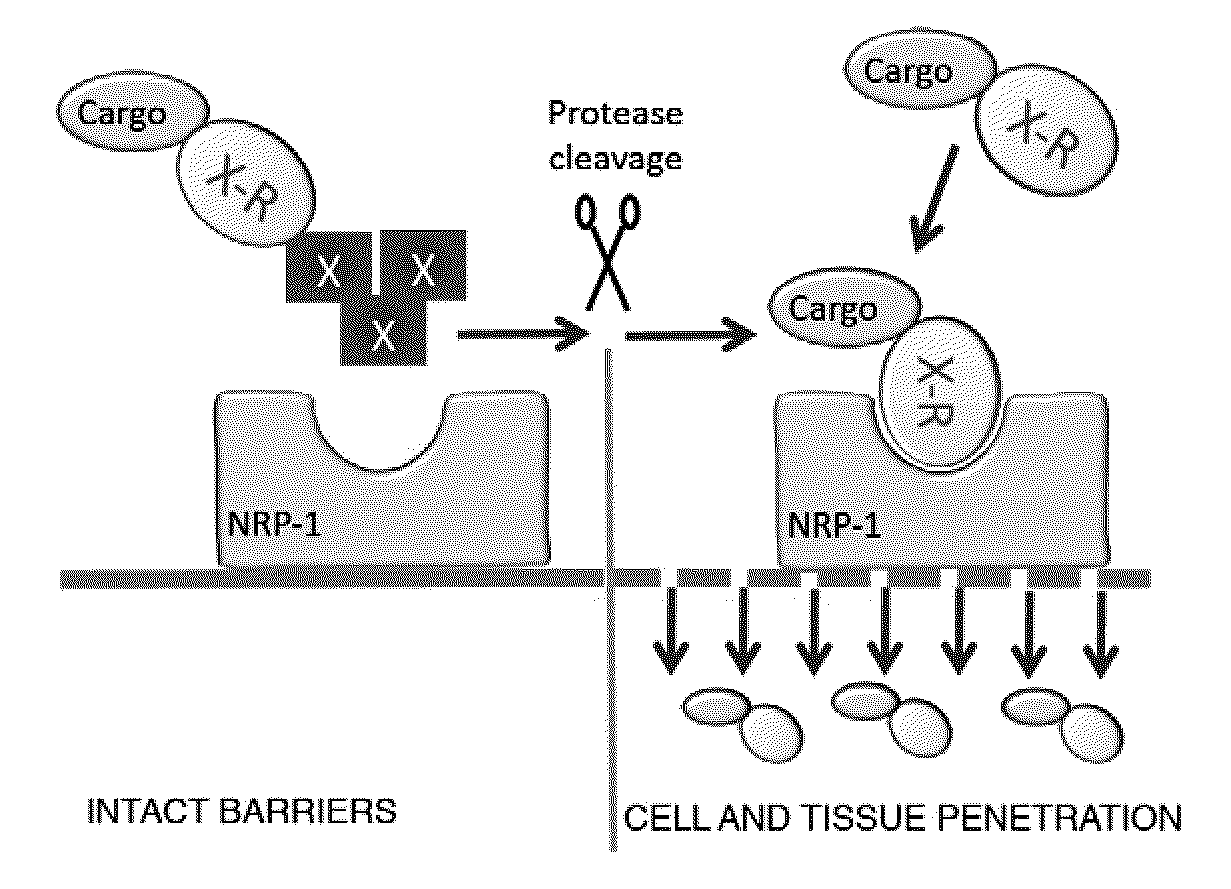
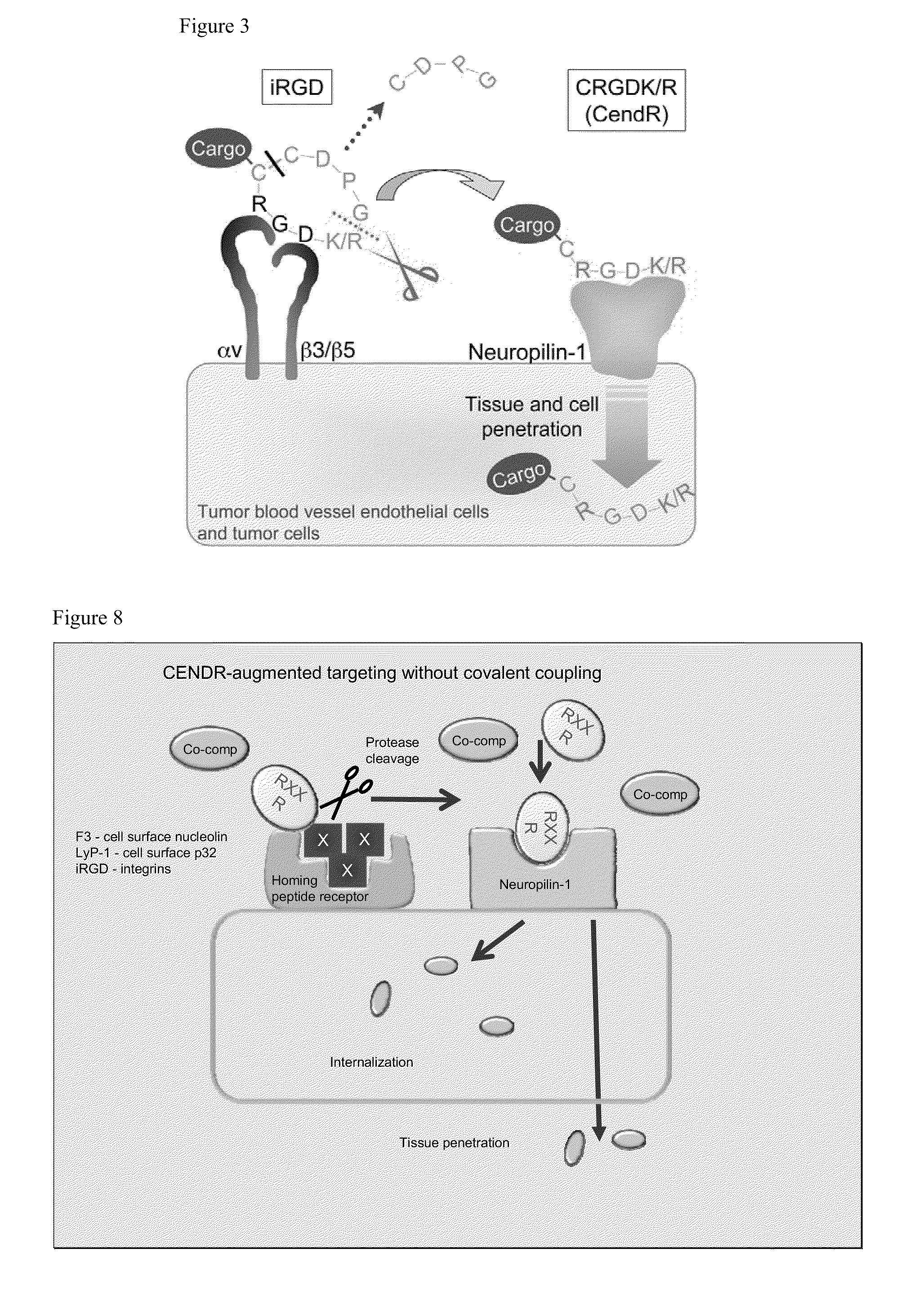
Disclosed are compositions and methods useful for targeting and internalizing molecules into cells of interest and for penetration by molecules of tissues of interest. The compositions and methods are based on peptide sequences that are selectively internalized by a cell, penetrate tissue, or both. The disclosed internalization and tissue penetration is useful for delivering therapeutic and detectable agents to cells and tissues of interest.
Owner:RICOH KK +1
Compound liposome containing anti-tumor drugs and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102091036ASolve the problem of poor wettabilityReduce harmMacromolecular non-active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsDiseaseLiposome
The invention belongs to a liposome, in particular relates to a compound liposome preparation with high targeting property of tumor tissues and efficient penetrability of tumor cells. The invention is characterized in that hyaluronic acid or sodium hyaluronate, tumor cell selective penetrating peptides and a liposome are used for together constructing a compound liposome. The compound liposome is characterized by utilizing the dual-tumor cell targeting property of the hyaluronic acid and tumor cell selective penetrating peptides to effectively solve the problem that because a conventional liposome and traditional cell penetrating peptides have no selectivity on normal cells and tumor cells, the toxicity is increased when the drug effect is increased in the therapeutic process, thereby fully meeting the clinical requirements of high efficiency and low toxicity when anti-tumor drugs are prepared into preparations for treating diseases.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
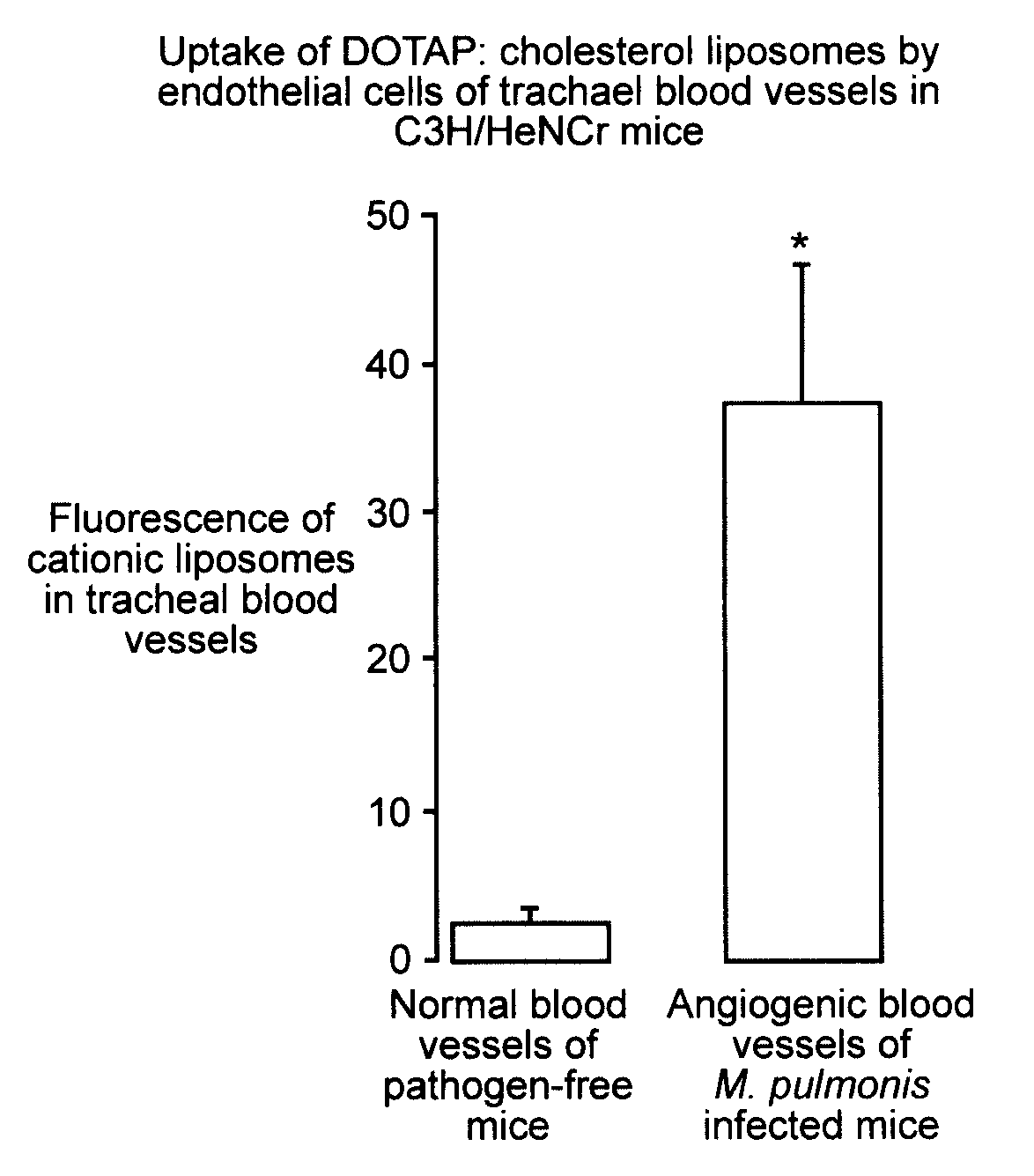
Cationic liposome delivery of taxanes to angiogenic blood vessels
InactiveUS7112338B2Precise deliveryOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsLipid formationCell selectivity
Angiogenic endothelial cells are selectively targeted with lipid / DNA complexes or cationic liposomes containing a substance which affects the targeted cells by inhibiting or promoting their growth. A site of angiogenesis can be precisely located by administering cationic liposomes containing a detectable label. The complexes may comprise nucleotide constructs which are comprised of promoters which are selectively and exclusively activated in the environment of an angiogenic endothelial cell.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Device for adhering various cells on same substrate orderly and adhering method
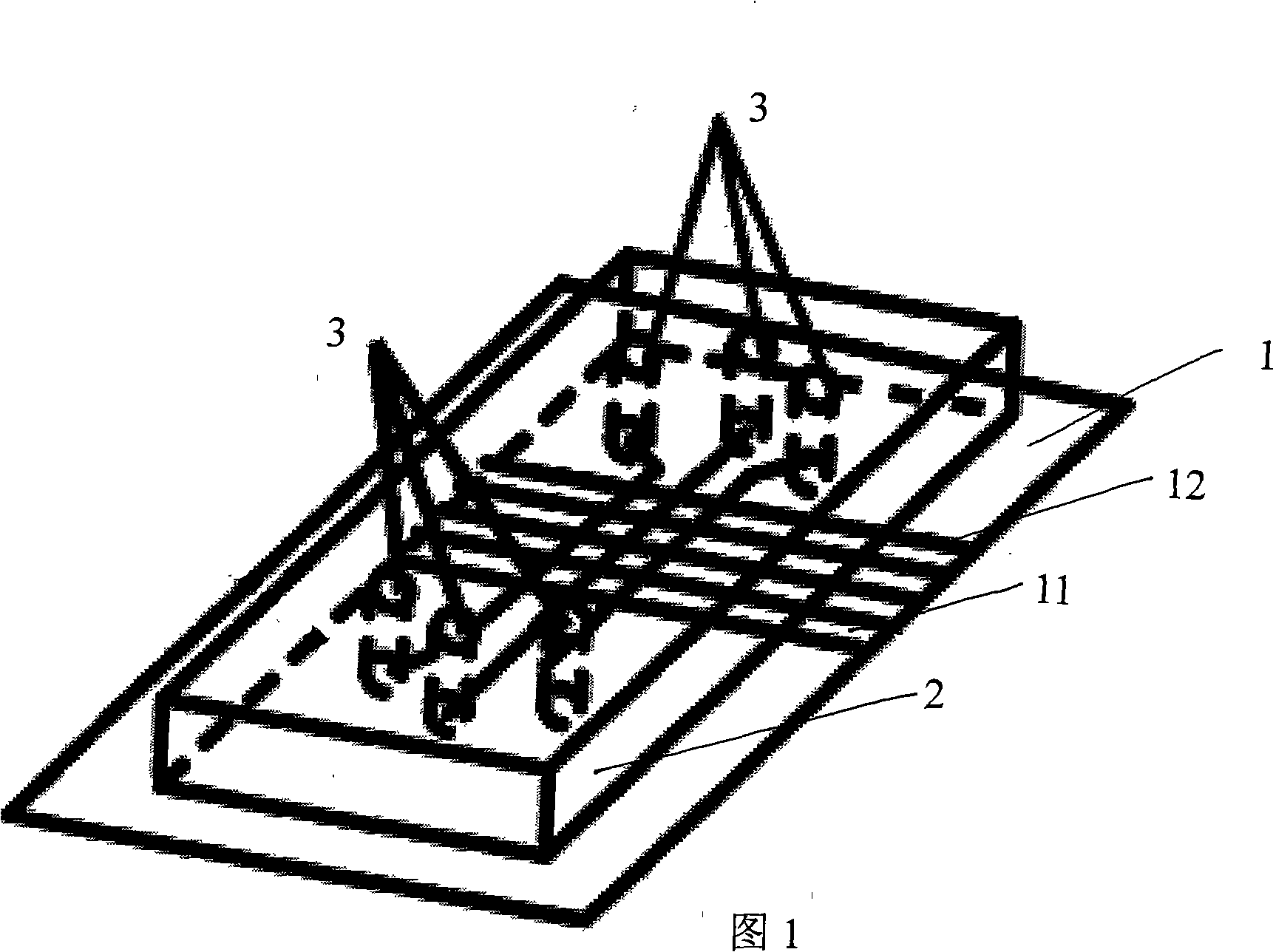
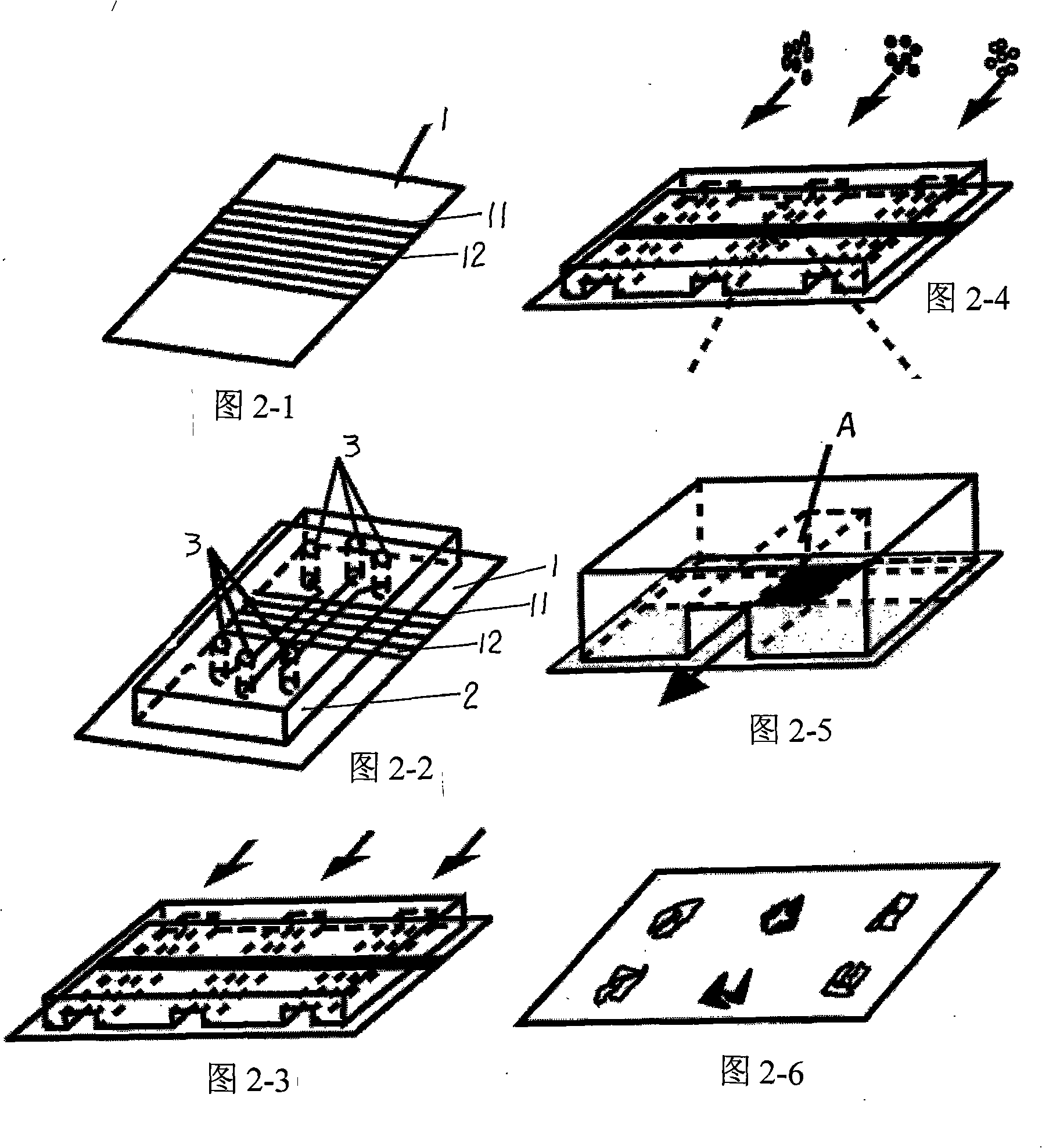
Disclosed is a device for sticking a plurality of cells to one basement in sequential arrays, which is characterized in that the upper surface of the basement is sequentially plated with a titanium adhesion layer, a golden layer, bands of mercaptan hydrophobic monolayer and bands of mercaptan hydrophilic monolayer, and the bands of mercaptan hydrophobic monolayer and the bands of mercaptan hydrophilic monolayer are parallel attached on the golden layer at intervals; the lower surface is provided with a second polydimethylsiloxane seal of a micro-groove unit; the micro-groove unit is composed of three parallel linear grooves; the ends of the grooves are provided with vertical through holes communicated with the grooves; the lower surface of the seal is coated on the surface of the basement with parallel bands of mercaptan hydrophobic monolayer and the bands of mercaptan hydrophilic monolayer; the linear grooves are perpendicular to the bands of mercaptan hydrophobic monolayer and the bands of mercaptan hydrophilic monolayer; and the golden surface of the basement is formed into a zone for the cells to be stuck on selectively. Substances (such as protein solution of the extra cellular matrix and polylysine solution, etc.), which facilitate the cells to be stuck, are injected into microflow pipes; after the cells are stuck selectively, different cell suspensions are injected into different pipes, and the cells are only stuck on the surfaces of the hydrophobic monolayer; then the seal is taken off, a plurality of different cell arrays are sequentially stuck on the basement.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
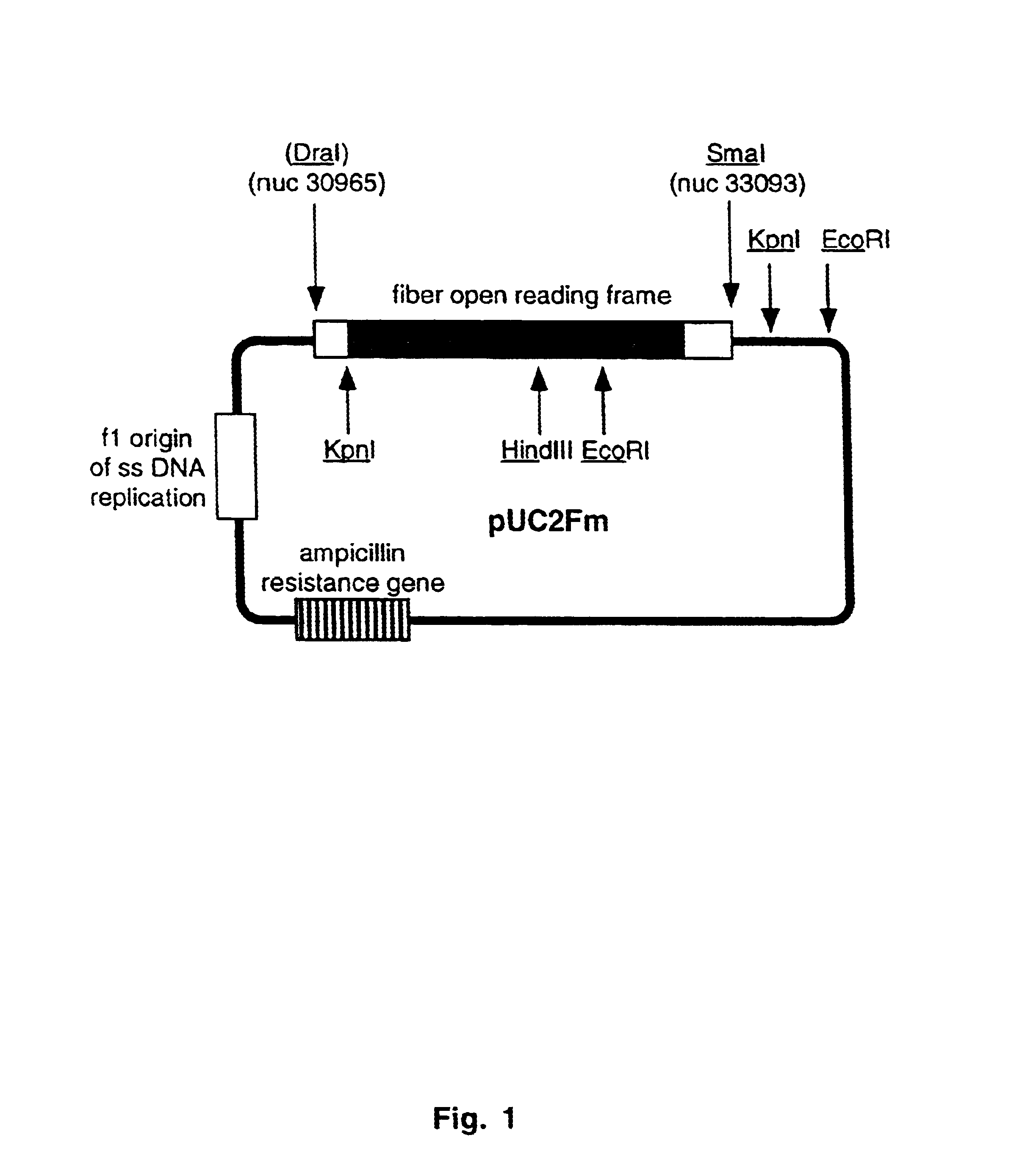
Ligands added to adenovirus fiber
InactiveUS6683170B2Avoid steric hindrance of bindingAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsFiberCell selectivity
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Truncated car peptides and methods and compositions using truncated car peptides
InactiveUS20120034164A1Reduce inflammationIncrease heightOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCell selectivityPeptide sequence
Disclosed are compositions and methods useful for targeting and internalizing molecules into cells of interest and for penetration by molecules of tissues of interest. The compositions and methods are based on peptide sequences, such as truncated CAR peptides, that are selectively internalized by a cell, penetrate tissue, or both. The disclosed internalization and tissue penetration is useful for delivering therapeutic and detectable agents to cells and tissues of interest.
Owner:SANFORD BURNHAM MEDICAL RES INST
Cell selective implant surface with controlled release of bioactive agents
InactiveUS20070190107A1Heal fastPreventing acuteMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic active ingredientsControlled releaseActive agent
The present invention relates to an implant (1) with at least partially a roughened surface (2), which is at least partially covered by an organic or polymeric intermediate layer (3) and attached thereto a top layer (4). The top layer (4) provides for a controlled release of at least one bioactive agent. A kit for preparing such an implant is also described.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH +1
Heterozygosis alpha spiral swine antibacterial peptide, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105777889AHigh antibacterial activityLow toxicityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsCell selectivityAntibacterial activity
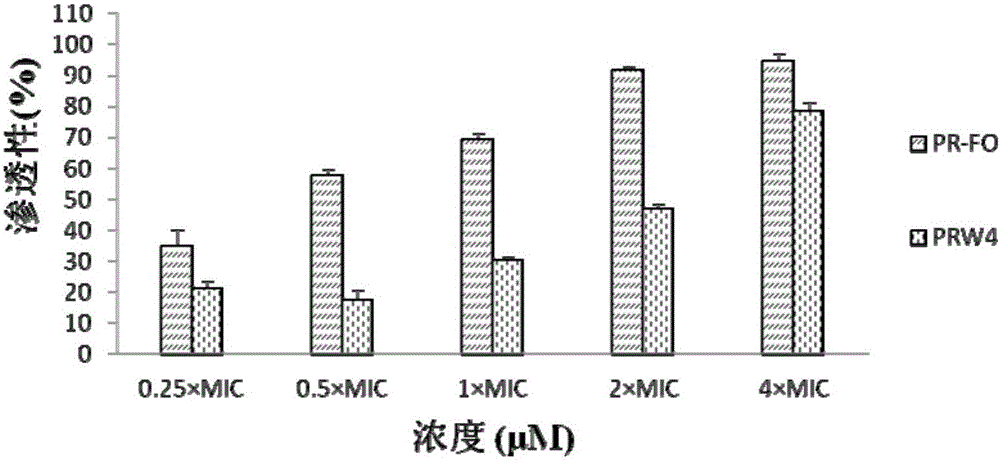
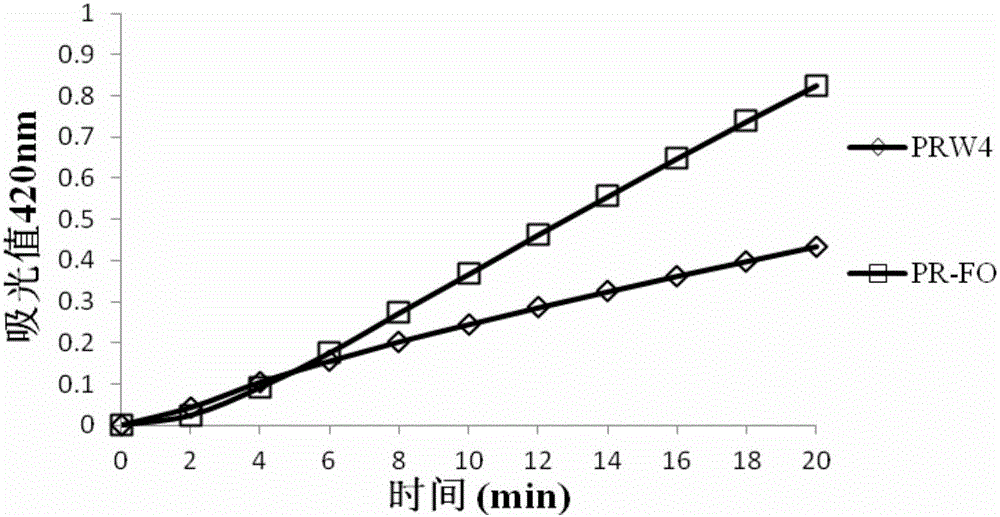
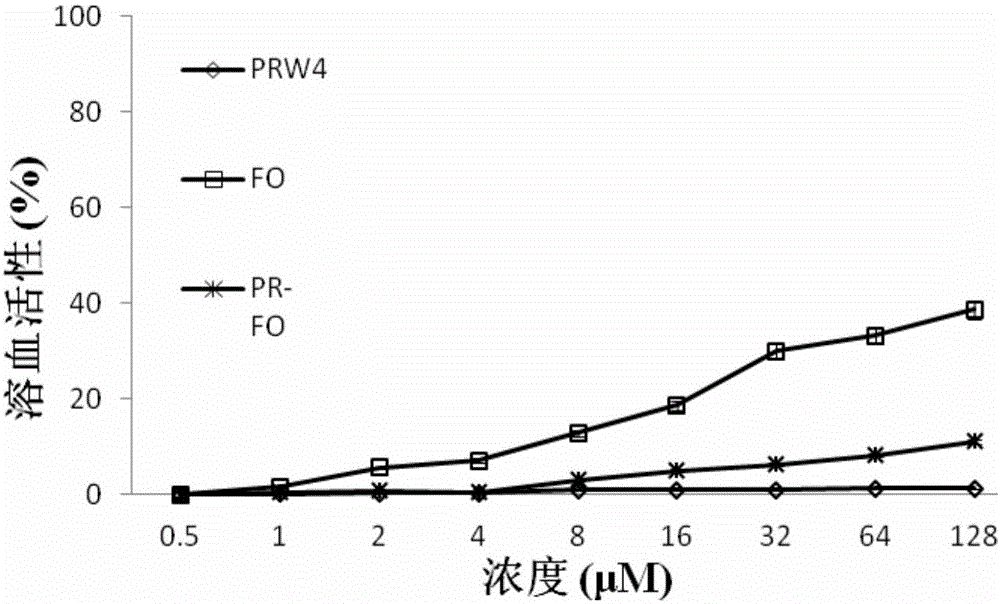
The invention provides a heterozygosis alpha spiral swine antibacterial peptide, and a preparation method and application thereof. The heterozygosis alpha spiral swine antibacterial peptide has the sequence shown as SEQ No.1 in a sequence table. According to the method, firstly, 16 amino acid residues before N- tail end in the swine antibacterial peptide PMAP-36 are modified, and are then subjected to heterozygosis with the front 15 amino acid of Fowlicidin-2 to obtain the antibacterial peptide PR-FO; the tail end of the carboxyl of the PR-FO is amidated so as to increase the positive charge and to improve the peptide stability; the sequence is shown as SEQ No. 1; then, a polypeptide synthesis instrument is used for synthesizing the antibacterial peptide PR-FO by a solid-phase synthesis method. The antibacterial peptide provided by the invention has higher antibacterial activity and low cell toxicity; the cell selectivity is greatly improved. The method can lay the feasible theoretical and practice foundation for making the antibacterial peptide into antibiotic substitutes.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
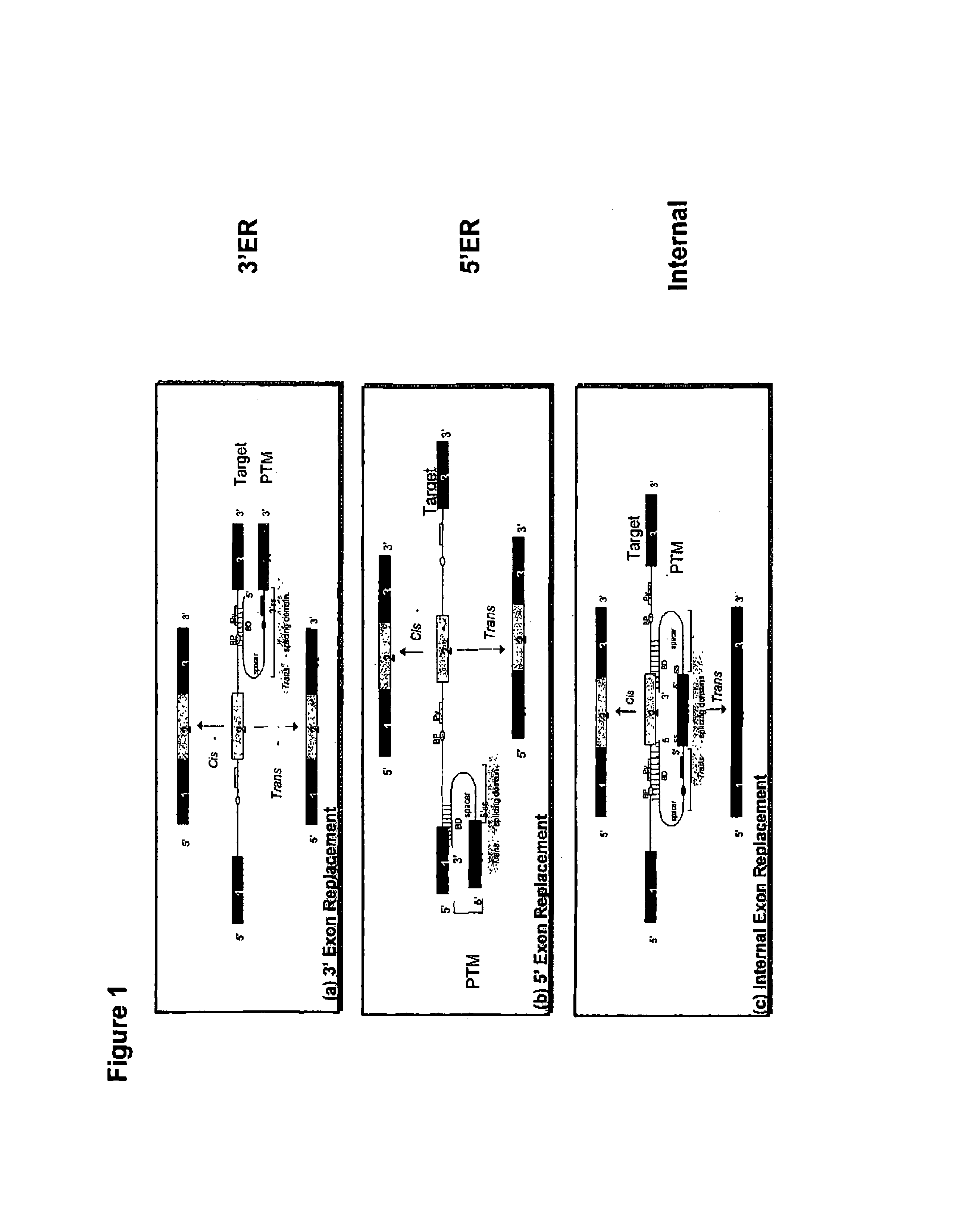
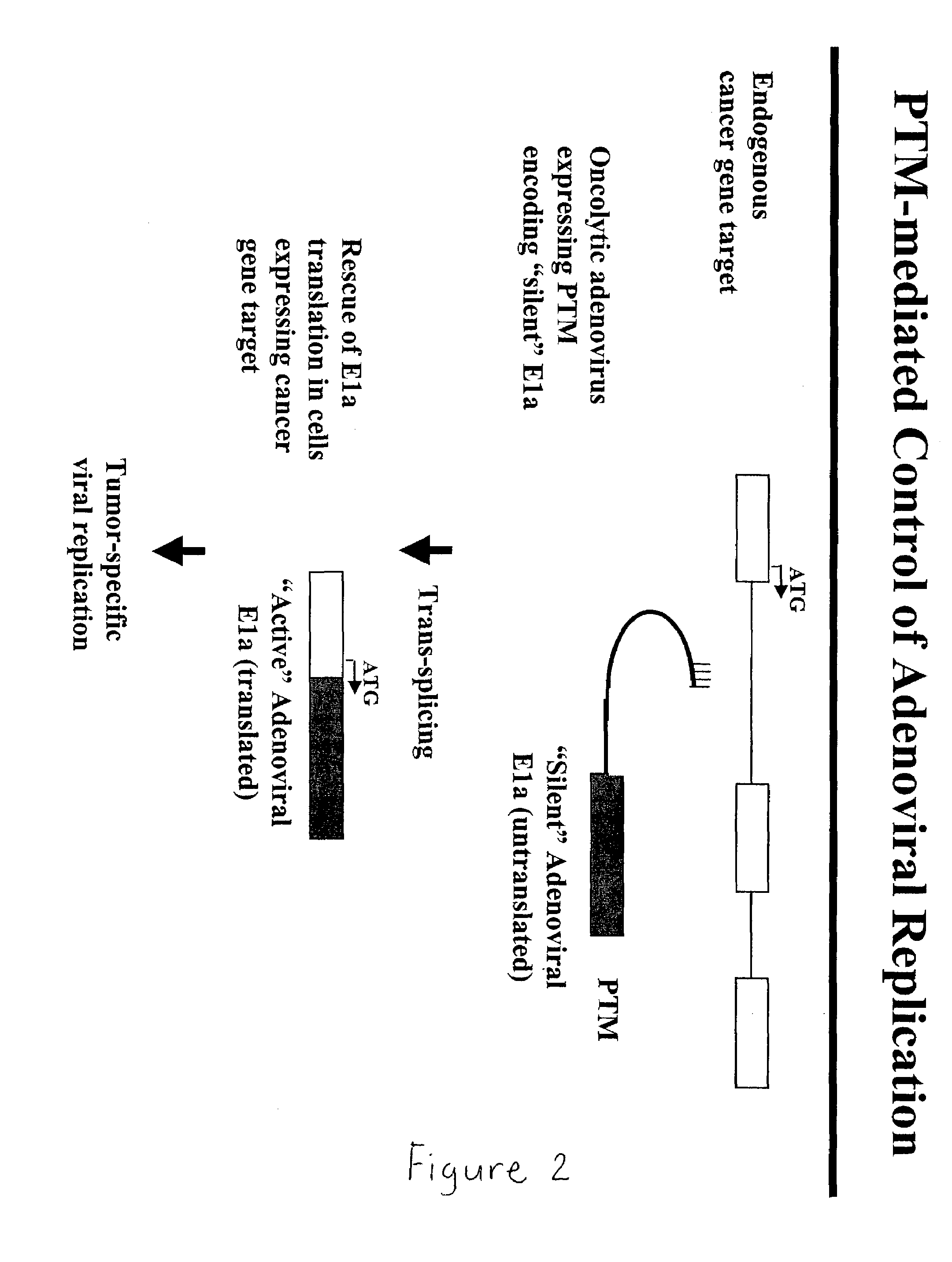
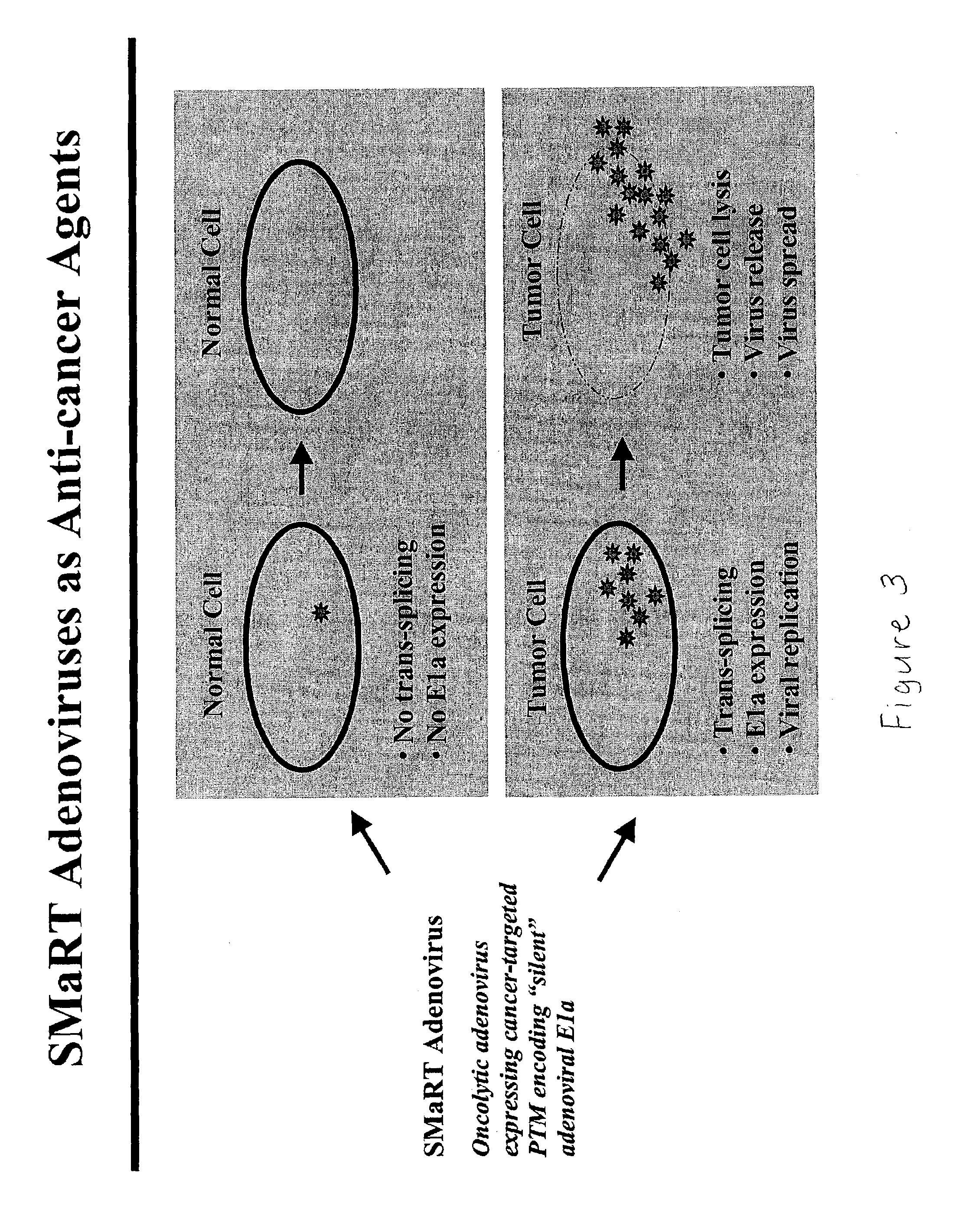
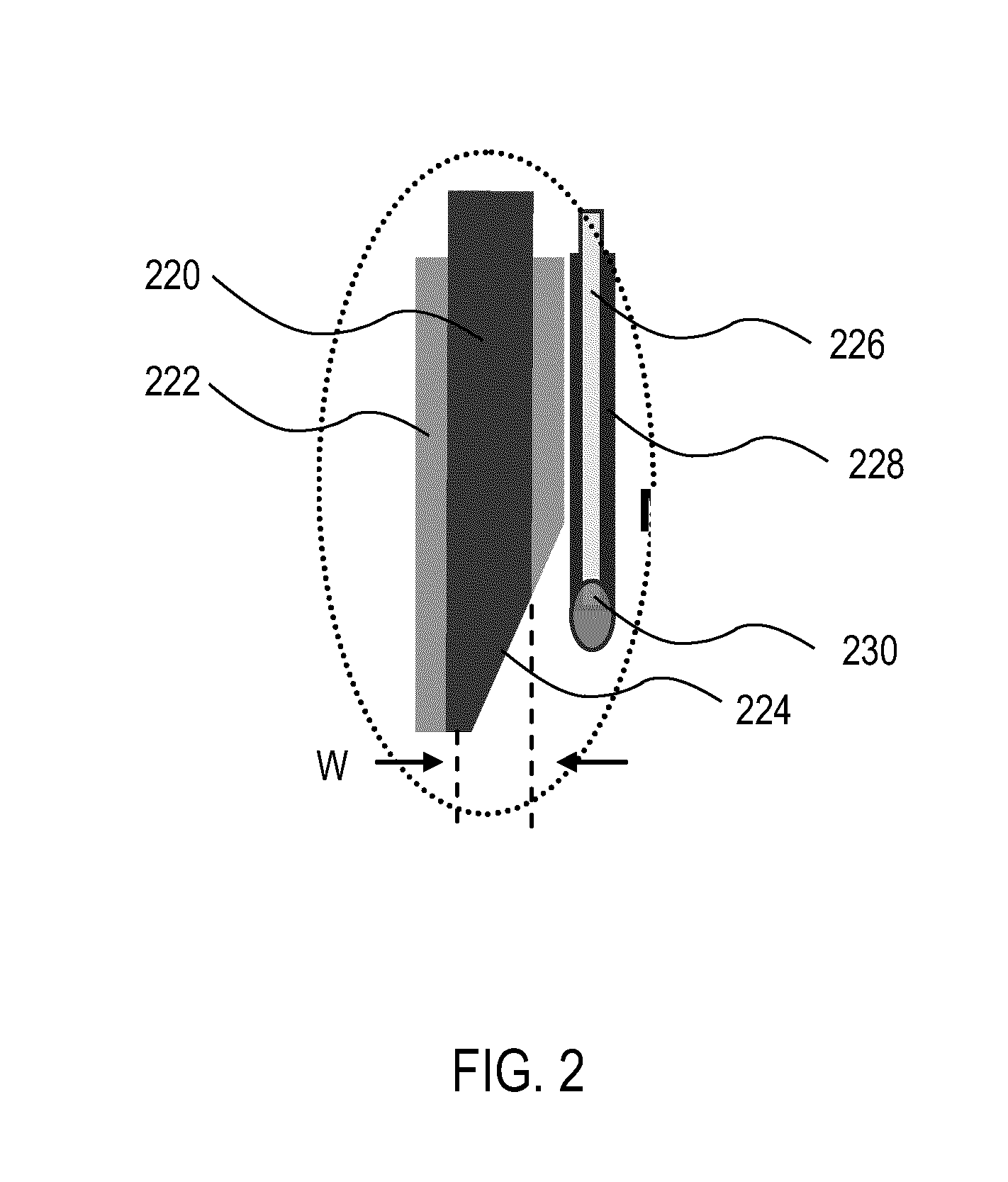
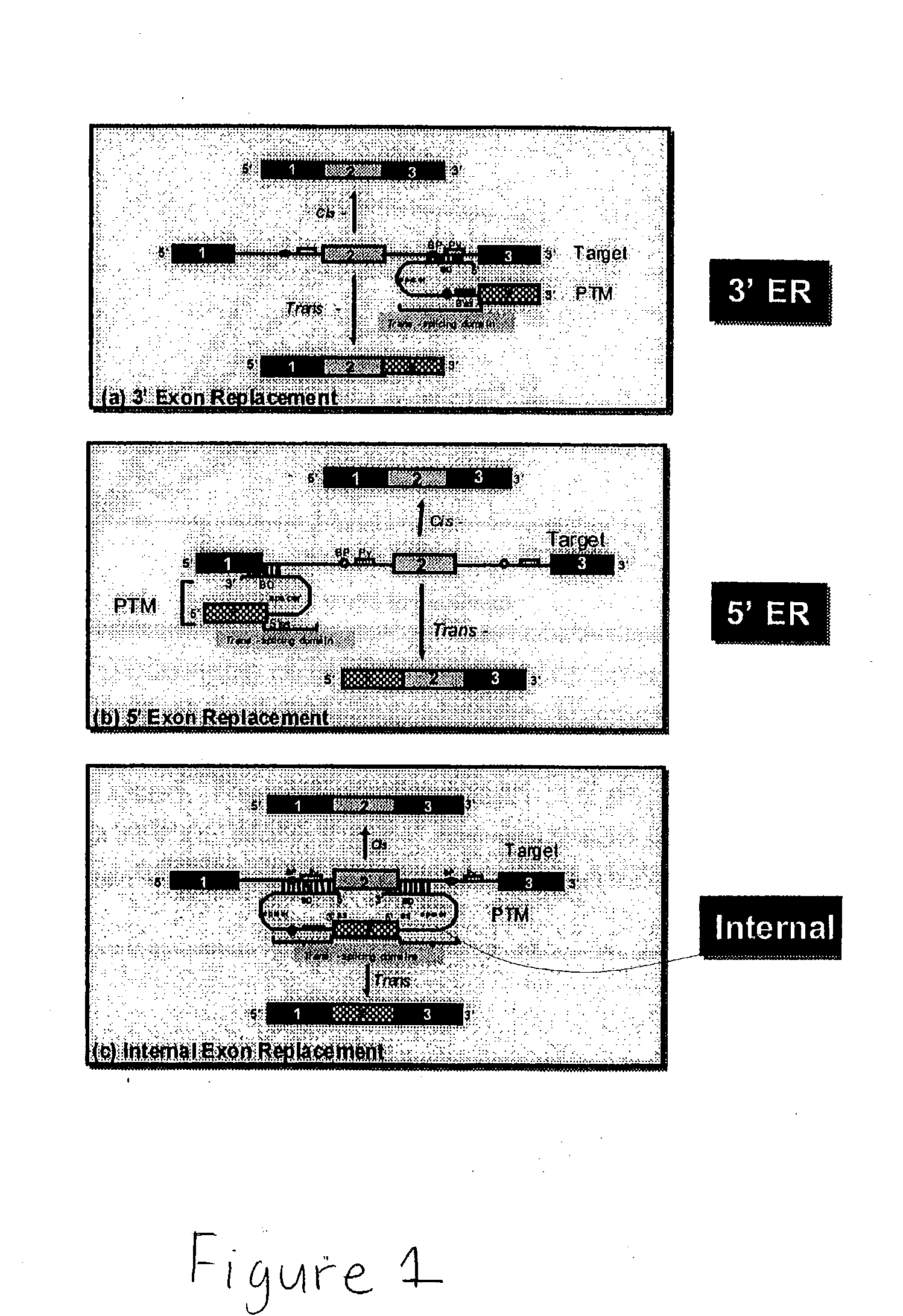
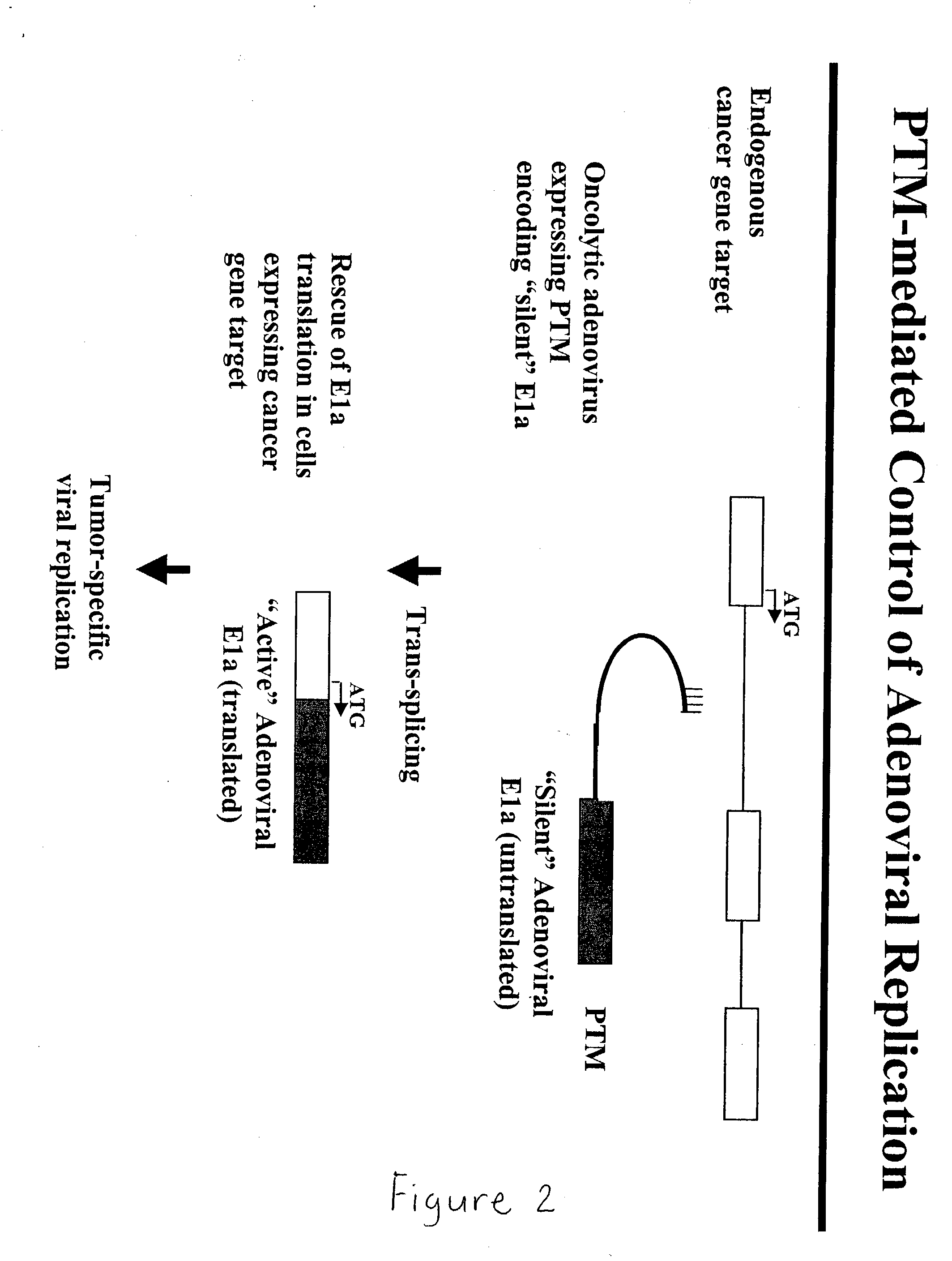
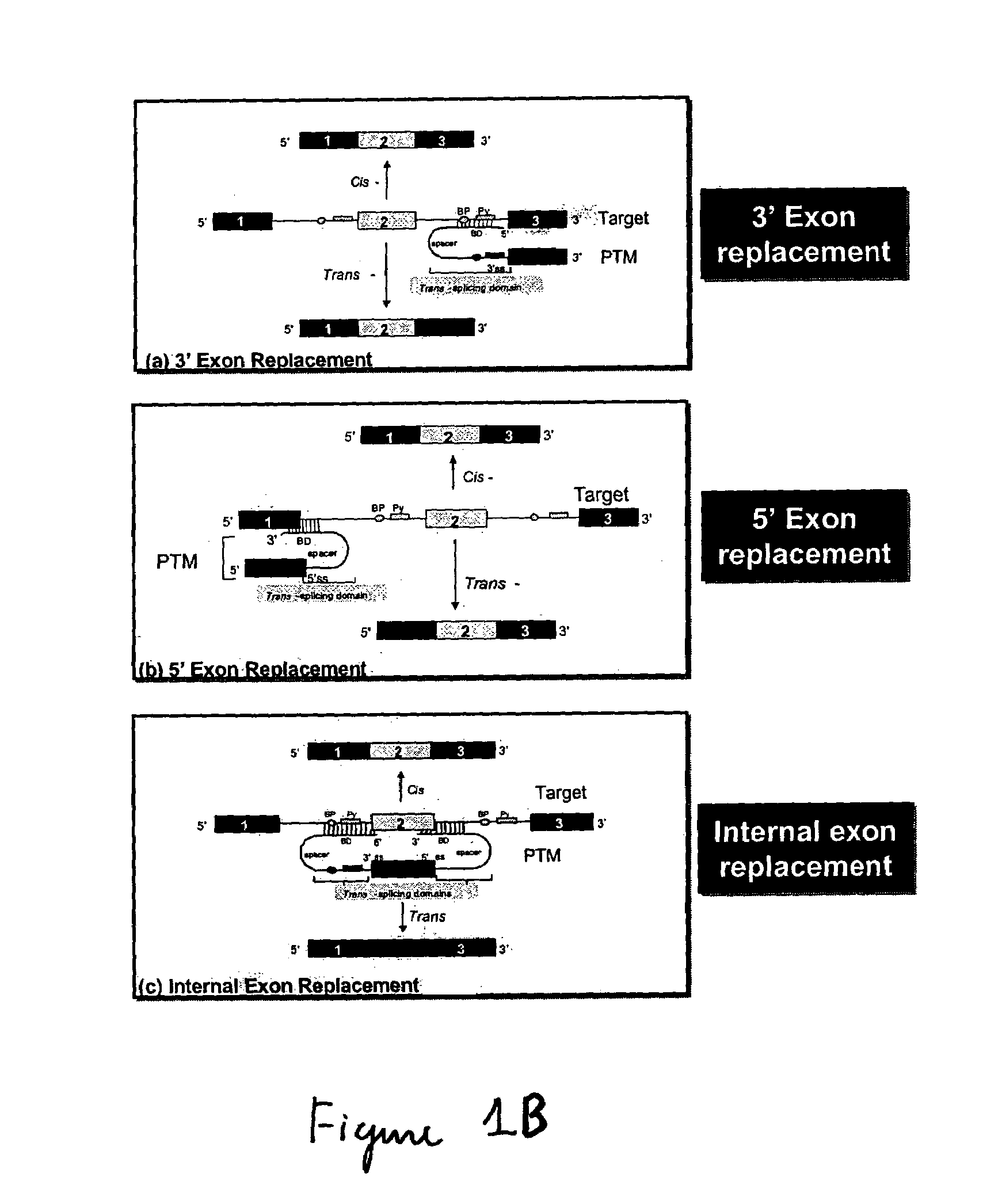
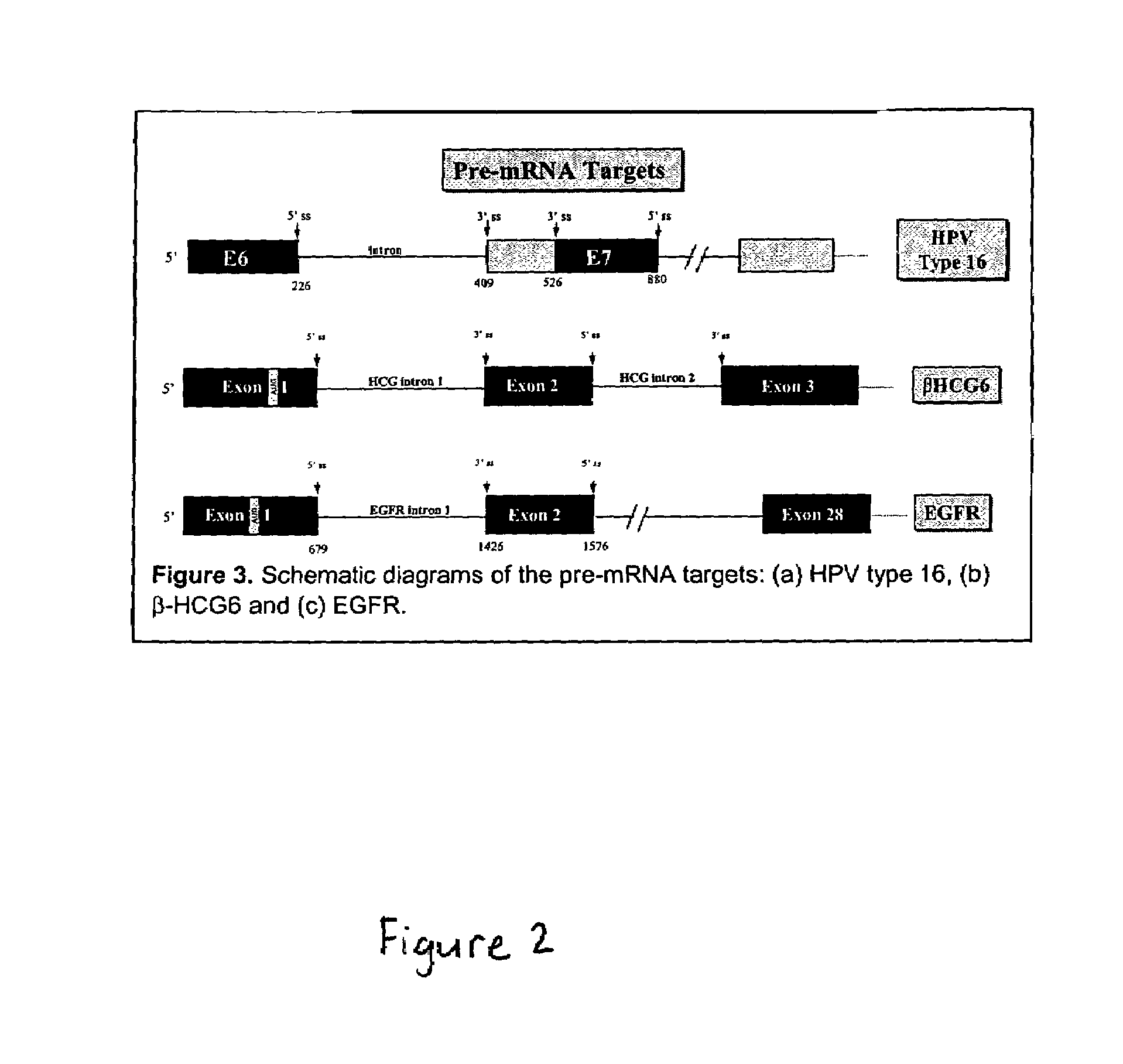
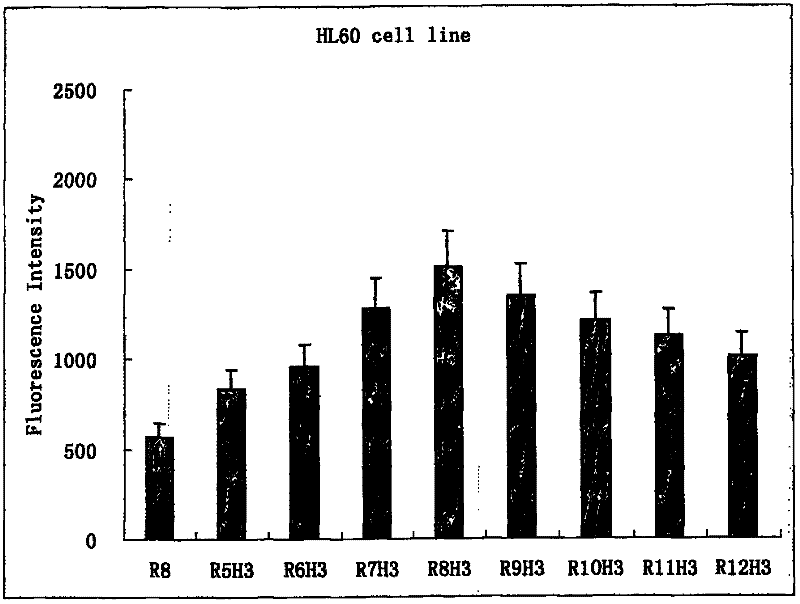
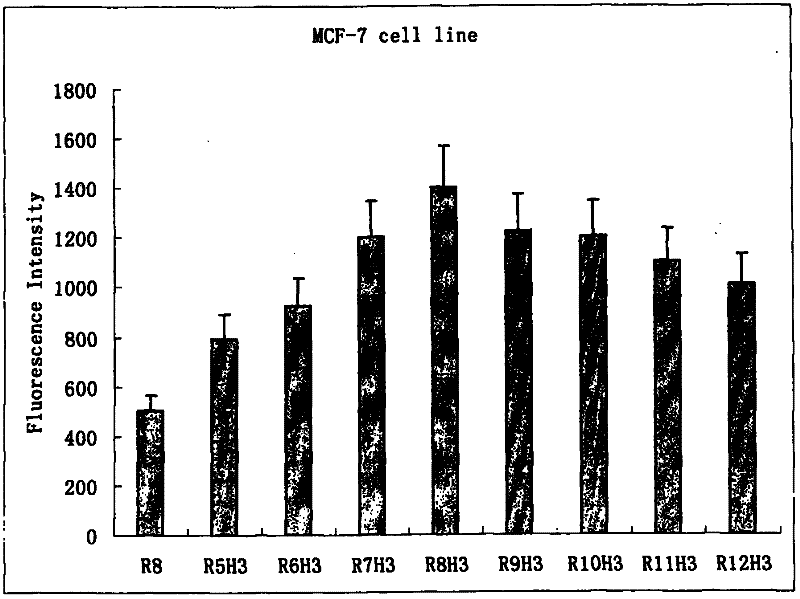
Use of spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing to confer cell selective replication to adenoviruses
The present invention provides methods and compositions for conferring tumor selective cell death on cancer cells expressing specific target precursor messenger RNA molecules (cancer cell selective target pre-mRNAs). The compositions of the invention include conditionally replicative adenoviruses that have been genetically engineered to express one or more pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs) designed to interact with one or more cancer cell target pre-mRNA and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of novel chimeric RNA molecules (chimeric RNA) capable of encoding adenovirus specific protein(s). Adenovirus specific proteins include those proteins complementing an essential activity necessary for replication of a defective adenovirus. The methods and compositions of the invention may be used to target a lytic adenovirus infection to cancer cells thereby providing a method for selective destruction of cancer cells. In addition, the adenoviruses of the invention may be engineered to encode PTMs designed to interact with target pre-mRNAs encoded by infectious agents within a cell, thereby targeting selective destruction of cells infected with such agents.
Owner:VIRXSYS
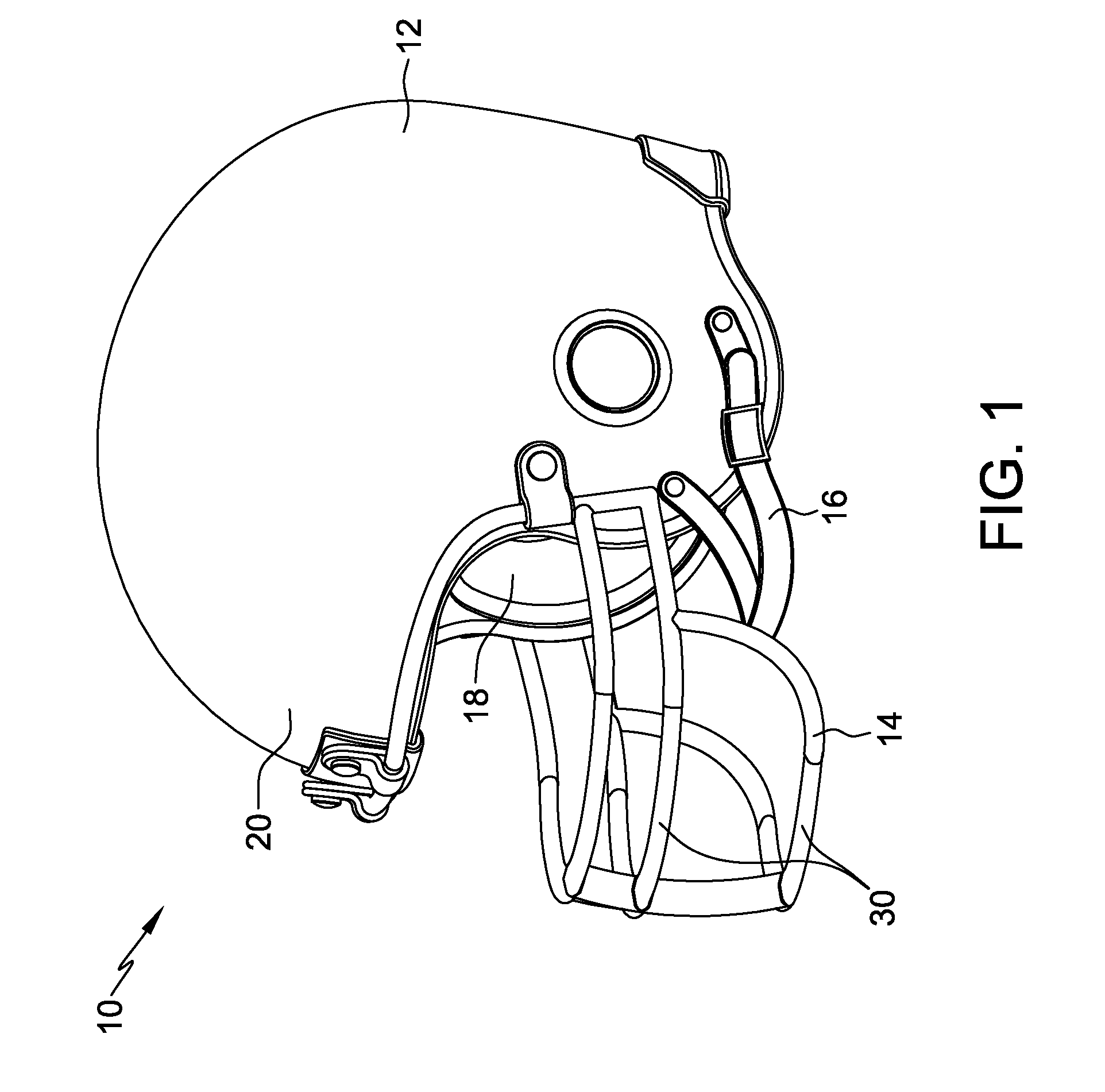
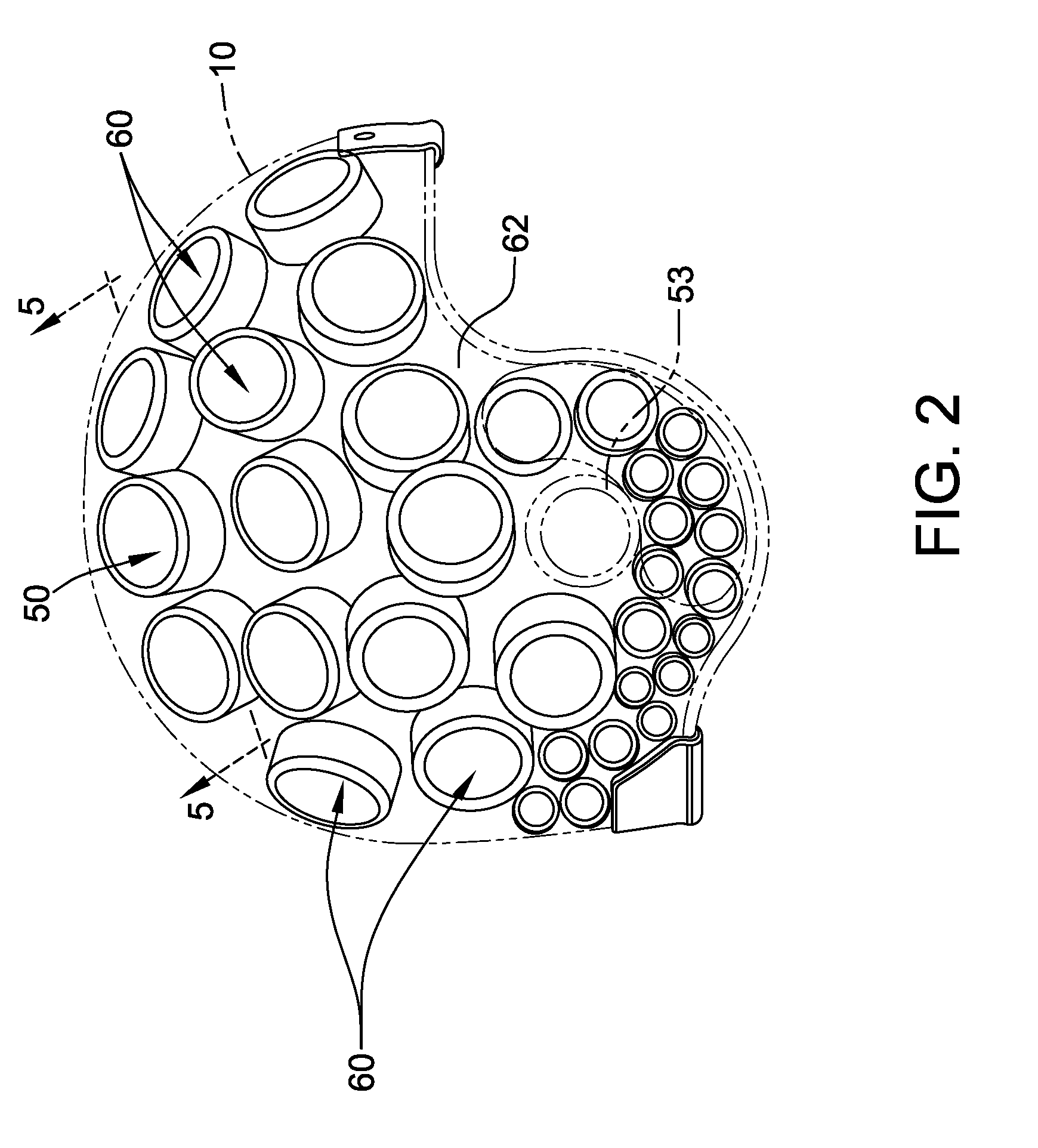
Protective headgear
A helmet including a shell and a support system is provided. The shell includes an outer surface and an inner surface. The support system includes a base and a plurality of hollow cells extending outward from the base. The support system substantially conforms to the shell inner surface. The cells are segmented into a plurality of regions wherein the cells within each of the regions are coupled together in flow communication via a plurality of channels extending therebetween. At least one cell within a first region is coupled in flow communication to at least one cell within a second region to enable fluid to be selectively transferred from at least some of the cells in the first region to at least some of the cells in the second region to facilitate reducing an amount of energy induced to a wearer of the helmet following an impact to the shell.
Owner:FRASER JANICE GERALDINE +1
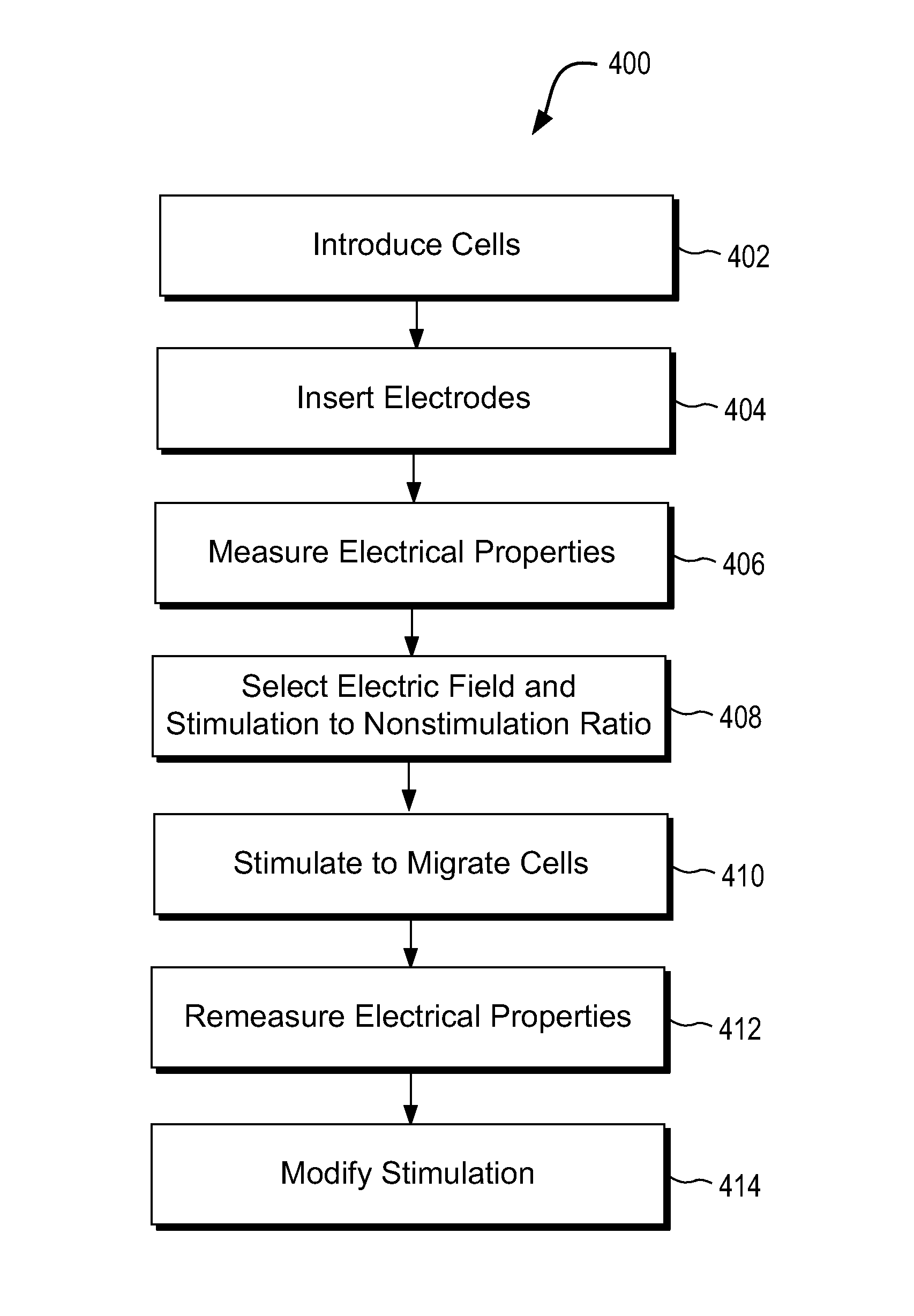
Systems and methods for selectively migrating cells using electric fields
Systems and methods are provided for migrating cells implanted or endogenous in tissue. The system may include first and second delivery electrodes configured for insertion in tissue and a direct current (DC) power source operatively coupled to the first and second delivery electrodes. The system further may include a programmable controller operatively coupled to the DC power source, wherein the programmable controller is programmed to direct the DC power source to deliver an electric field between the first delivery electrode and the second delivery electrode at a stimulation to nonstimulation ratio sufficient to cause the cells to migrate within tissue selectively.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Use of spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing to confer cell selective replication to adenoviruses
The present invention provides methods and compositions for conferring tumor selective cell death on cancer cells expressing specific target precursor messenger RNA molecules (cancer cell selective target pre-mRNAs). The compositions of the invention include conditionally replicative adenoviruses that have been genetically engineered to express one or more pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs) designed to interact with one or more cancer cell target pre-mRNA and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of novel chimeric RNA molecules (chimeric RNA) capable of encoding adenovirus specific protein(s). Adenovirus specific proteins include those proteins complementing an essential activity necessary for replication of a defective adenovirus. The methods and compositions of the invention may be used to target a lytic adenovirus infection to cancer cells thereby providing a method for selective destruction of cancer cells. In addition, the adenoviruses of the invention may be engineered to encode PTMs designed to interact with target pre-mRNAs encoded by infectious agents within a cell, thereby targeting selective destruction of cells infected with such agents.
Owner:VIRXSYS
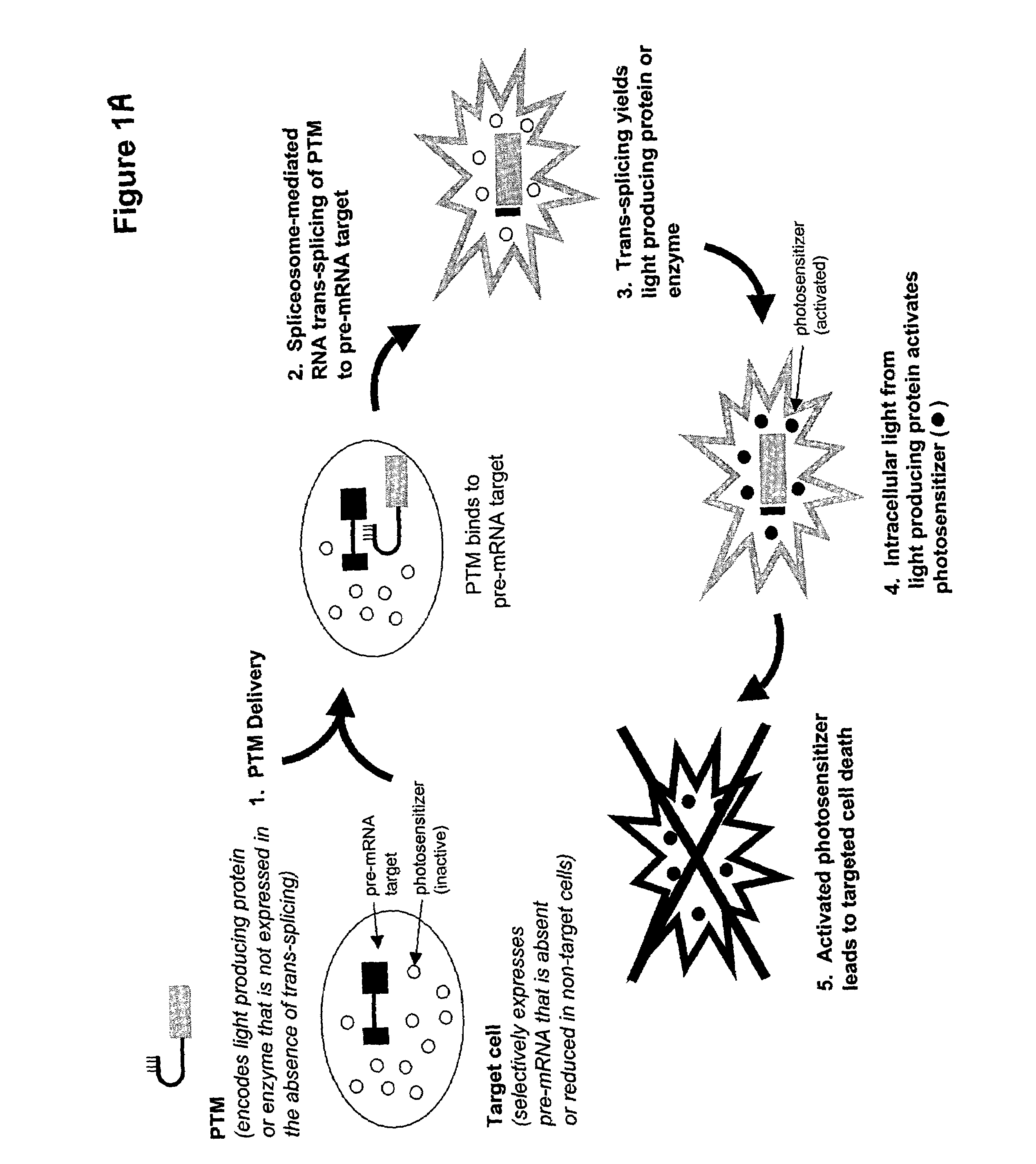
Trans-splicing mediated photodynamic therapy
The present invention provides methods and compositions for conferring selective death on cells expressing a specific target precursor messenger RNA (selective target pre-mRNA). The compositions of the invention include pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs) designed to interact with a target precursor messenger RNA molecule (target pre-mRNA) expressed within a cell and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of a novel chimeric mRNA molecule (chimeric mRNA) capable of encoding a light producing protein or enzyme. Cell death is further mediated by the presence of a photosensitizer which upon photoactivation produces cytotoxicity.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES SEC GOVERNMENT OF UNITED STATES +1
Application of tumor cell membrane selectively penetrating peptide
InactiveCN102174078AEfficient combinationImprove bindingPeptidesMacromolecular non-active ingredientsArginineCell selectivity
The invention belongs to the field of the membrane penetrating peptide and particularly relates to a tumor cell membrane selectively penetrating peptide and application thereof. The sequence of the tumor cell membrane selectively penetrating peptide comprises a basic amino acid cluster which is composed of 5 to 12 consecutive arginine residues. The tumor cell membrane selectively penetrating peptide is characterized in that the C or N end of the basic amino acid cluster is connected with three histidine residues. The tumor cell membrane selectively penetrating peptide has cell membrane penetration capacity, can distinguish tumor cells and normal tissue cells and can efficiently penetrate through the tumor cell membrane without penetrating through the normal tissue cell membrane basically.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Microfluidic device for cell motility screening and chemotaxis testing
InactiveUS20130244270A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMotilityCell locomotion
Owner:CAPITALBIO CORP +1
A kind of antibacterial peptide and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102276691ASimple experimental techniqueImprove therapeutic indexAntibacterial agentsPeptide preparation methodsCell selectivityArginine
The invention relates to antibacterial peptides and a preparation method thereof. An amino acid sequence of the antibacterial peptide is IleTrpArgIlePheArgArgIlePhe. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) designing a group of antibacterial peptides consisting of isoleucine, arginine and phenylalanine which serve as basic units by utilizing the bacteriostatic mechanism of the antibacterial peptides and the characteristic of amino acid composition; 2) synthesizing a polypeptide crude product by using a polypeptide synthesizer in a solid-phase synthetic process; 3) purifying the synthesized polypeptide by reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography, and identifying by electrospray mass spectrometry; and 4) performing an in-vitro activity test, wherein a result of the activity test indicates that antibacterial peptides B containing 3 basic units have high bacteriostatic activity and weak hemolytic activity, a treatment index is the highest, and cell selectivity is optimum, so the antibacterial peptides have high application value.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Multi-stranded beta-hairpin short-peptide with tolerant protease and preparation method and application
InactiveCN106749532ASimple experimental techniqueStable structureAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBeta hairpinCrystallography
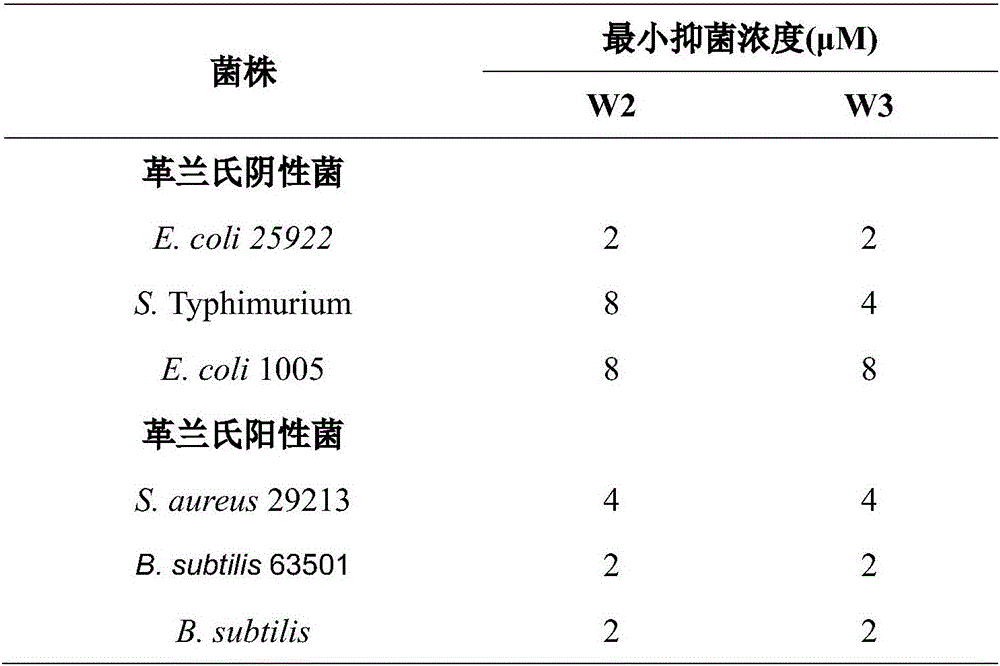
The invention provides a multi-stranded beta-hairpin short-peptide with tolerant protease and a preparation method and an application. A sequence is as shown in a SEQ ID No.1. The short-peptide provided by the invention fully exerts the structural advantages of a beta-hairpin structure to obtain a multi-stranded beta-hairpin structural antibacterial peptide. The stability is further improved while the activity is ensured by using a common amino, and composition of a corner amino acid is changed, so that a series of multi-stranded beta-hairpin antibacterial peptides of brand new structures: (WRXxRW)n-NH2, wherein n is 1, 2, 3 and 4; PG is selected as a corner to describe; when n is equal to 2, the antibacterial peptide is named W2; and when n is equal to 3, the antibacterial peptide is named W3. The peptide verifies relatively high cell selectivity and salt ion tolerance, and moreover, based on the activity of the antibacterial peptide with structural stability, the obtained antibacterial peptide is also relatively short, and relatively strong tolerance of in vivo protease is also represented.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method And Compositions For Improving Selective Catabolysis in Cells Of Keratin Surfaces
A skin care composition for stimulating selective catabolysis in cells of keratin surfaces comprising at least one autophagy activator and at least one proteasome activator, and a method for improving selective catabolysis in cells of keratin surfaces by treating with the composition.
Owner:ELC MANAGEMENT LLC
Tryptophan tension chain-beta-hairpin antibacterial peptide and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106749531ASimple experimental techniqueLow hemolytic activityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsCell selectivityCytotoxicity
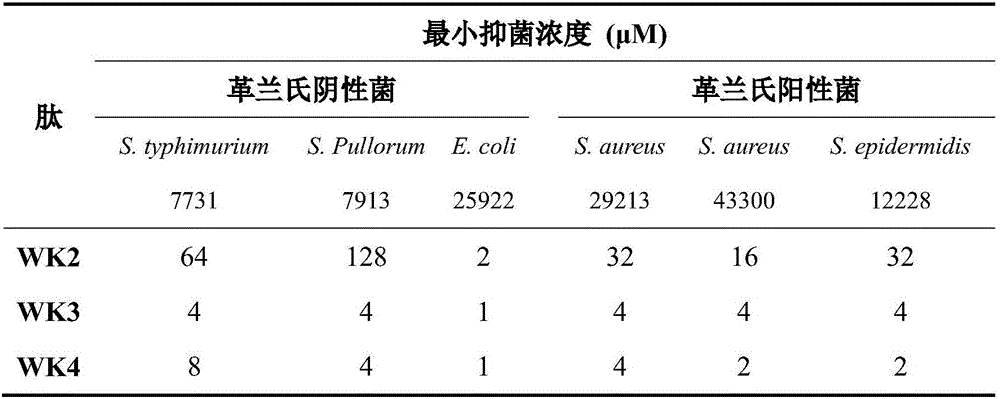
The invention provides a tryptophan tension chain-beta-hairpin antibacterial peptide and a preparation method and application thereof. A sequence of the antibacterial peptide is as shown in a sequence table SEQ ID No.1. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by taking a tryptophan tension chain structure as a template, combining amino acid composition and structural characteristics of the antibacterial peptide; and by using interaction of cross-chain W-W as a structural stable factor, symmetrically and circularly arranging an amino acid lysine with charges and a hydrophobic amino acid tryptophan as repeated binary sequence units on two arms of the beta-hairpin to obtain the antibacterial peptide WK3. The antibacterial peptide has relatively high bacteriostatic activity and cell selectivity, and the treatment index reaches up to 161.27. The antibacterial peptide designed by the method needs not to bind a disulfide bond but has extremely high structural stability, so that the selectivity of the antibacterial peptide between bacterial cells and mammalian cells is improved, and the antibacterial peptide has an application potential as an antibiotic substituent. The antibacterial peptide is relatively high in activity and relatively low in cytotoxicity.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for fixing biological macro molecule in common pattern on inorganic silicone material surface
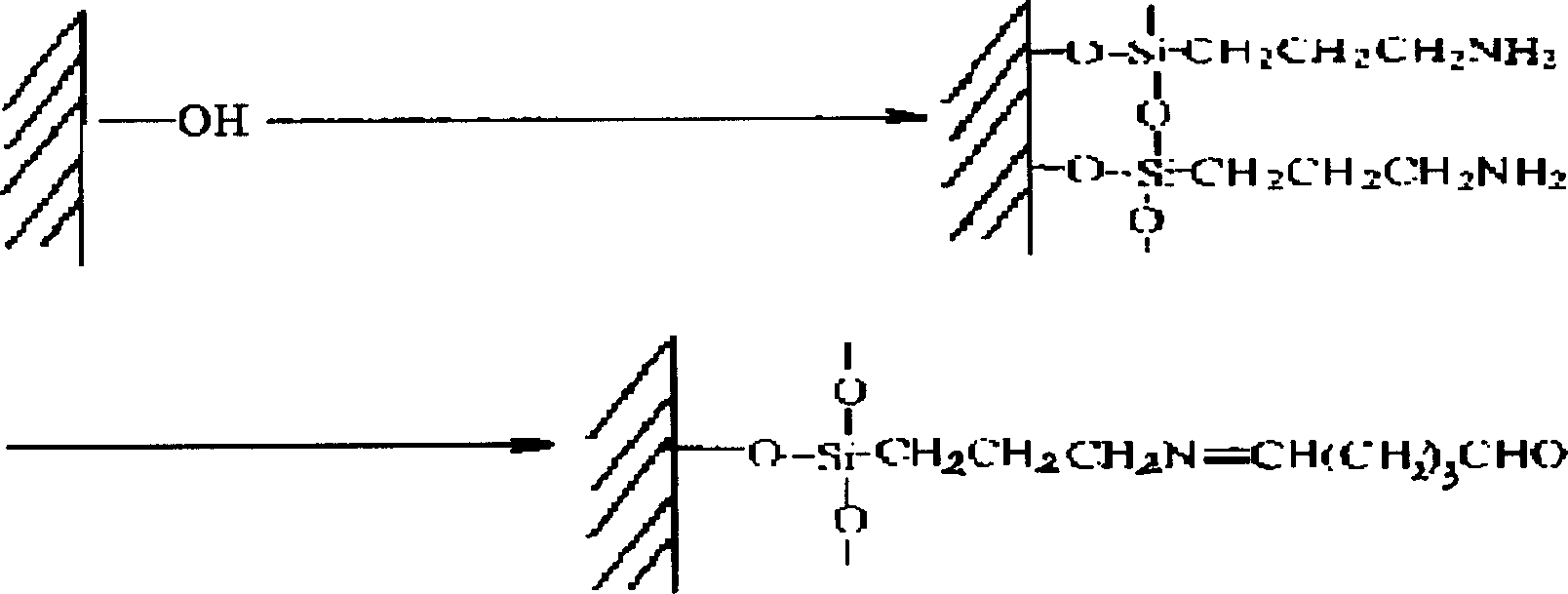
InactiveCN1425920AIncrease contrastImprove smoothnessMicrobiological testing/measurementLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingMicrocontact printingCell adhesion
The fixing process of biological macromolecule on inorganic silicon material surface in common pattern includes the following steps: amination and aldehydration treatment of the inorganic silicone material surface; polydimethyl siloxane stamp micro contact printing on the surface to form one biological macromolecule miro pattern; dropping one other biological macromolecule solution to fix in the uncovered area; and washing and ultrasonic treatment to form the co-pattern fixation of two kinds of biological macromolecules. The said process is simple, controllable and repeatable and has imld reaction condition. The present invention has excellent application foreground in selective cell adhesion, direction induction, cell-based biological device making, tissue engineering, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
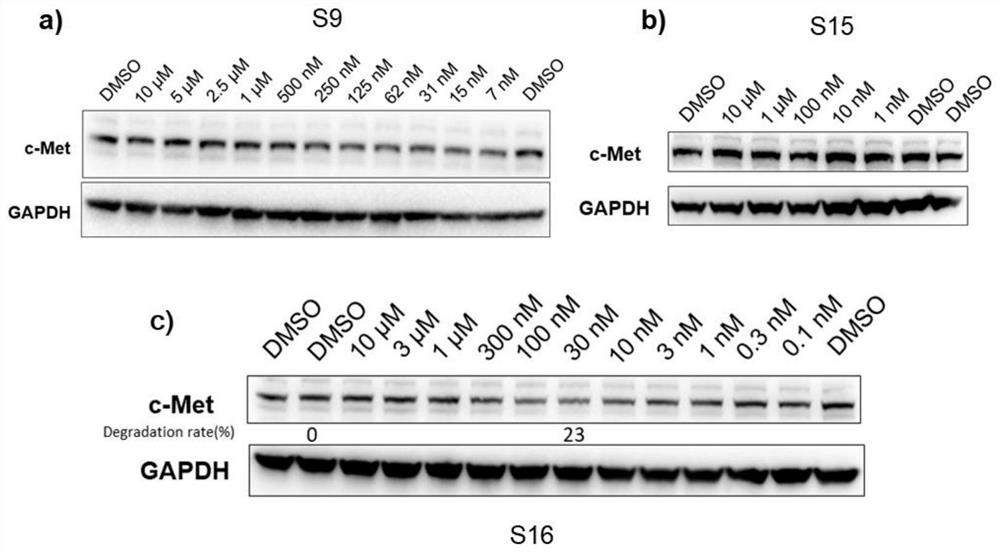
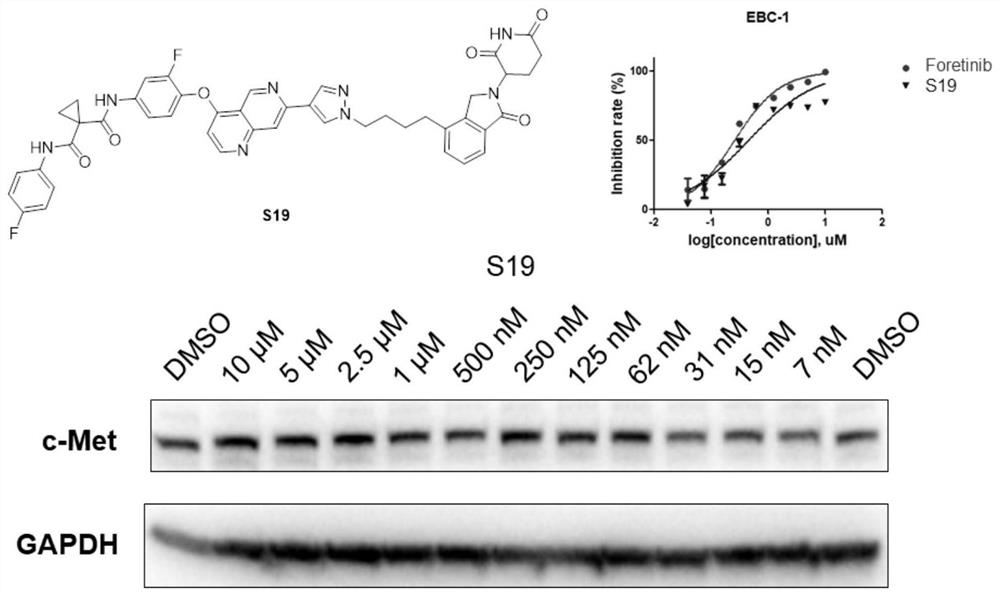
Targeted protein degradation c-Met degradation agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
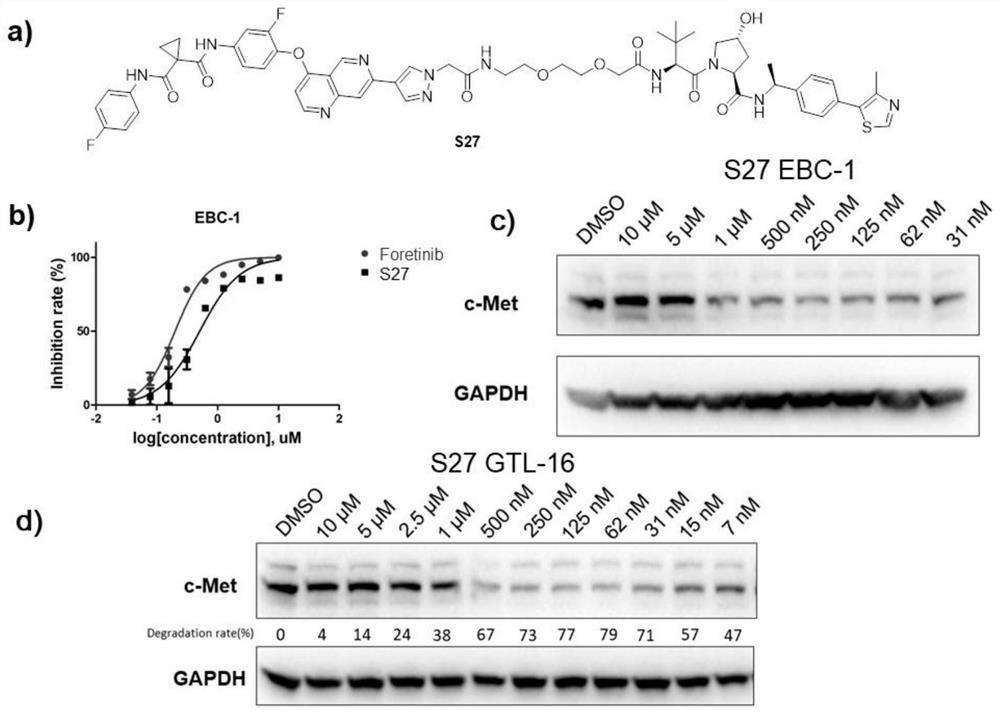
ActiveCN112239469AStrong growth inhibitory effectStrong antiproliferative activityOrganic active ingredientsDipeptide ingredientsProtein targetCell selectivity
The invention discloses a targeted protein degradation c-Met degradation agent as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The invention provides a c-Met degradation agent based on a targeted protein degradation PROTAC strategy, a preparation method thereof and application of the c-Met degradation agent in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer, gastric cancer and other cancers.The compound has a remarkable c-Met degradation effect and a remarkable cell proliferation inhibition effect, has the potential of serving as an anti-tumor drug to treat tumors, shows remarkable proliferation inhibition activity in an EBC1 drug-resistant cell strain constructed by lentiviral transfection, is obviously superior to a small molecule inhibitor LXM262. and obviously improves the cell selectivity. The compound has significant advantages in overcoming tumor c-Met acquired drug resistance, especially the compound S27 only provides good activity for c-Met dependent EBC-1 lung cancer cells, it is indicated that the compound S27 has good cell selectivity while the original small molecule inhibitor is multi-target, and the compound also has an inhibition effect on a c-Met non-dependent cell line.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Cationic liposome delivery of taxanes to angiogenic blood vessels
InactiveUS20100226970A1Precise deliveryInhibit angiogenesisBiocideOrganic active ingredientsNucleotideCell selectivity
Angiogenic endothelial cells are selectively targeted with lipid / DNA complexes or cationic liposomes containing a substance which affects the targeted cells by inhibiting or promoting their growth. A site of angiogenesis can be precisely located by administering cationic liposomes containing a detectable label. The complexes may comprise nucleotide constructs which are comprised of promoters which are selectively and exclusively activated in the environment of an angiogenic endothelial cell.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Novel brain targeting preparation for preventing and treating neurodegenerative disease
ActiveCN103372199AHigh activityEnhanced ability to penetrate the BBBNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsFreeze-dryingCell selectivity
The invention provides a novel brain targeting preparation for preventing and treating a neurodegenerative disease. The novel brain targeting preparation comprises effective dose of fusion protein of cell growth factor and TAT (transcriptional activator) cell-penetrating peptide, or fusion protein of the cell growth factor, TAT and a transferrin receptor monoclonal antibody, a protein activity protecting agent, and proper auxiliary material, wherein the fusion protein of cell growth factor and TAT cell-penetrating peptide or the fusion protein of the cell growth factor, TAT and transferrin receptor monoclonal antibody is an active ingredient. The novel brain targeting preparation disclosed by the invention has excellent performance of breaking through a blood brain barrier, and is specifically targeted to the brain; the defect that single TAT does not have cell selectivity can be overcome; a brain neurons microenvironment is regulated and controlled by the effects of neurotrophy, paracrine and the like, so as to play the roles of preventing and treating the neurodegenerative disease. The novel brain targeting preparation can be prepared into a freeze-drying preparation, a liquid preparation or an adhesive preparation and applied in an intravenous injection or nasal delivery manner.
Owner:BIOPHARM RES & DEV CENT JINAN +1
Method for producing proteins suitable for treating lysosomal storage disorders
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
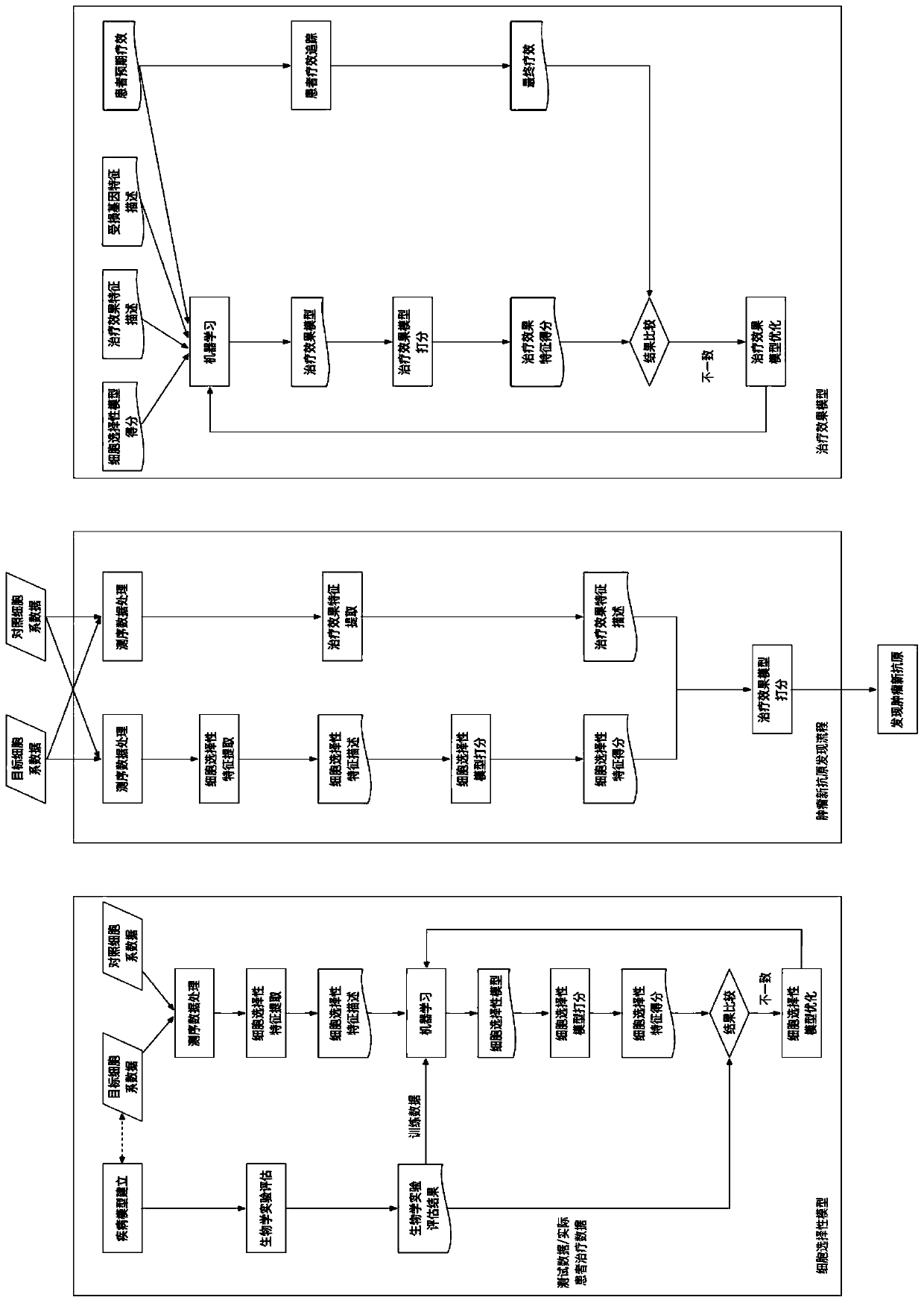
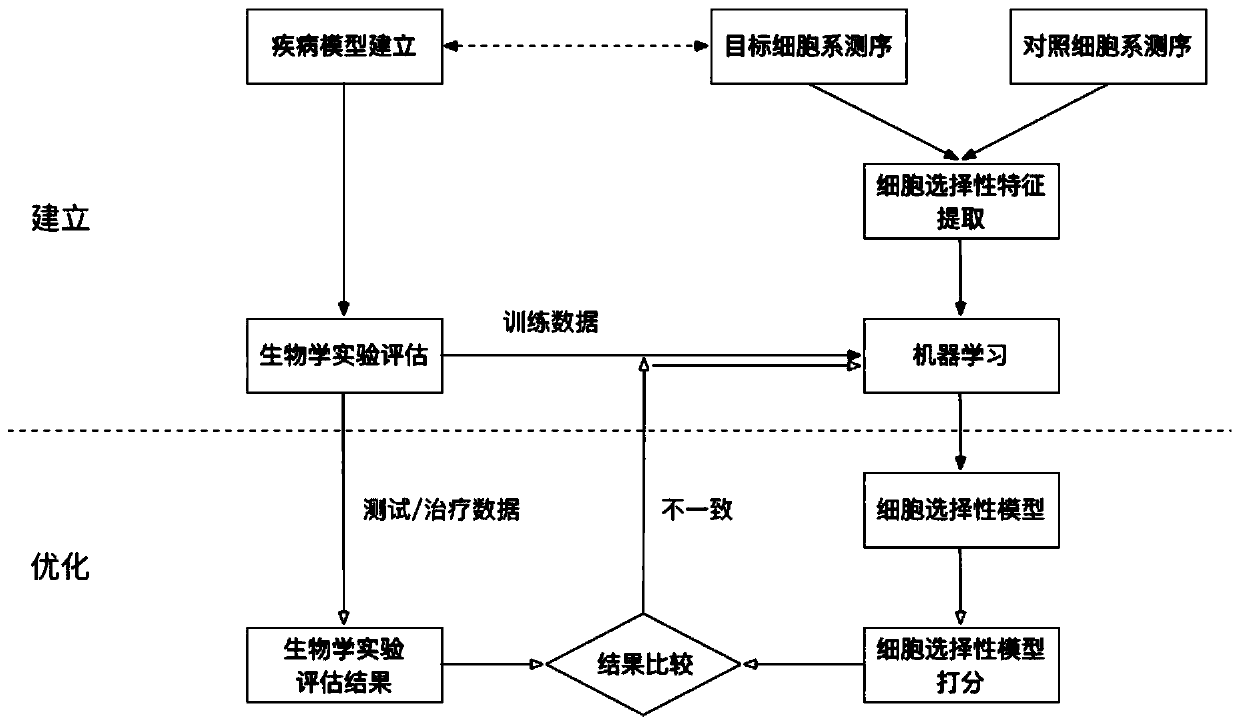
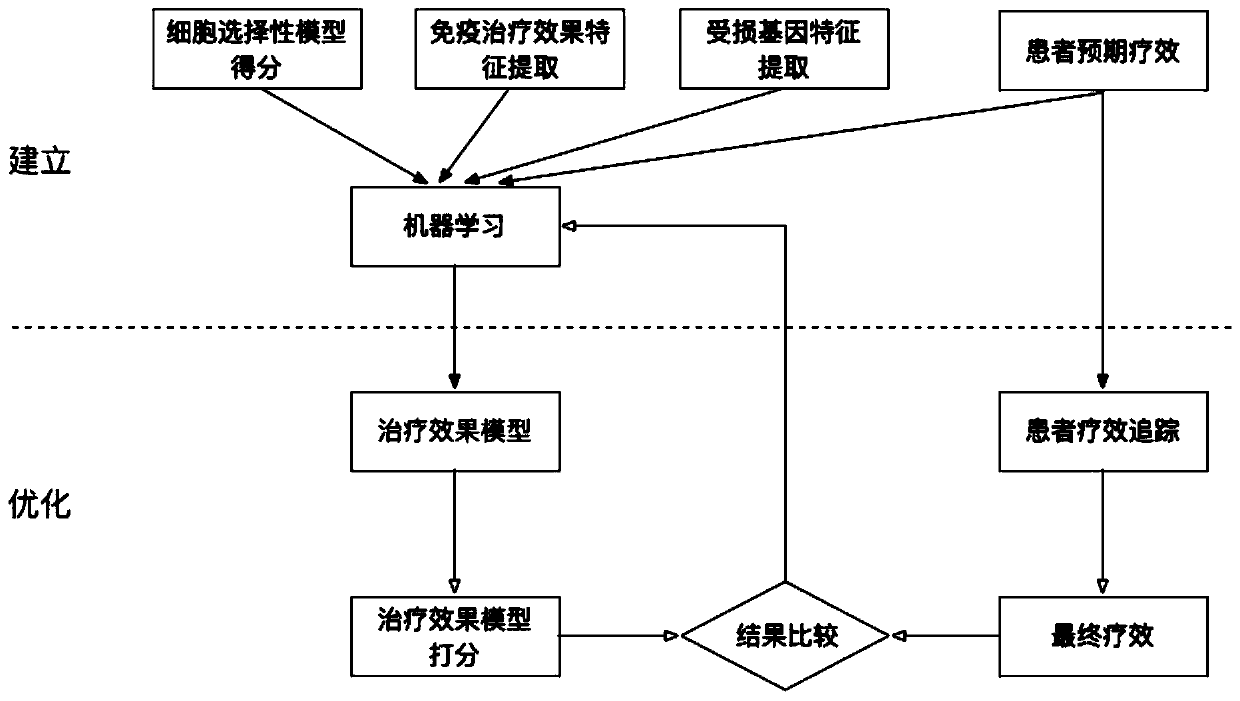
Method and system for selecting individualized tumor neoantigen based on expected curative effect
ActiveCN110277135AImprove effectivenessImprove forecast accuracyMedical automated diagnosisSystems biologyAntigenCell selectivity
The invention discloses a method and a system for selecting an individualized tumor neoantigen based on an expected curative effect. The method comprises the following steps: establishing and optimizing a cell selectivity model; establishing and optimizing a treatment effect model, carrying out auxiliary selection on individualized tumor neoantigens and the like, and can maximize the utilization of biological experiments to carry out trial and error, establish the most accurate cell selectivity model and maximize the utilization of the biological experiments to improve the effect on individual patients under the condition of not involving the patients; the method further considers the correlation between the selectivity of new antigen cells and the immune state of patients, builds a complete curative effect prediction model, evaluates the applicability of a specific new antigen to a specific patient according to an actual curative effect, provides high-value reference information for a doctor to select an appropriate new antigen for immunotherapy, utilizes the actual effect feedback of doctor treatment to the maximum extent, and continuously improves the prediction precision of the overall effectiveness of new antigen immunotherapy.
Owner:杭州新范式生物医药科技有限公司
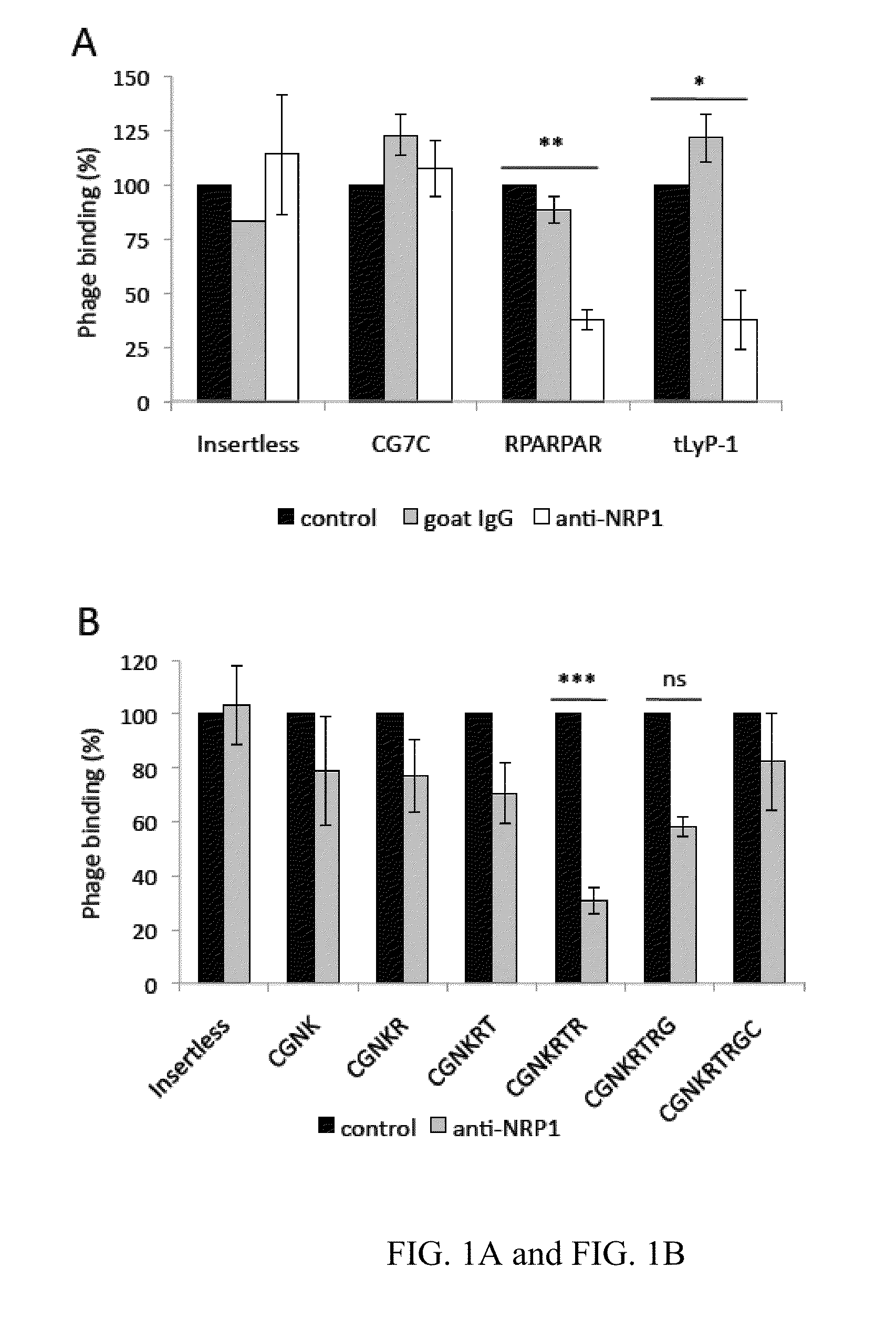
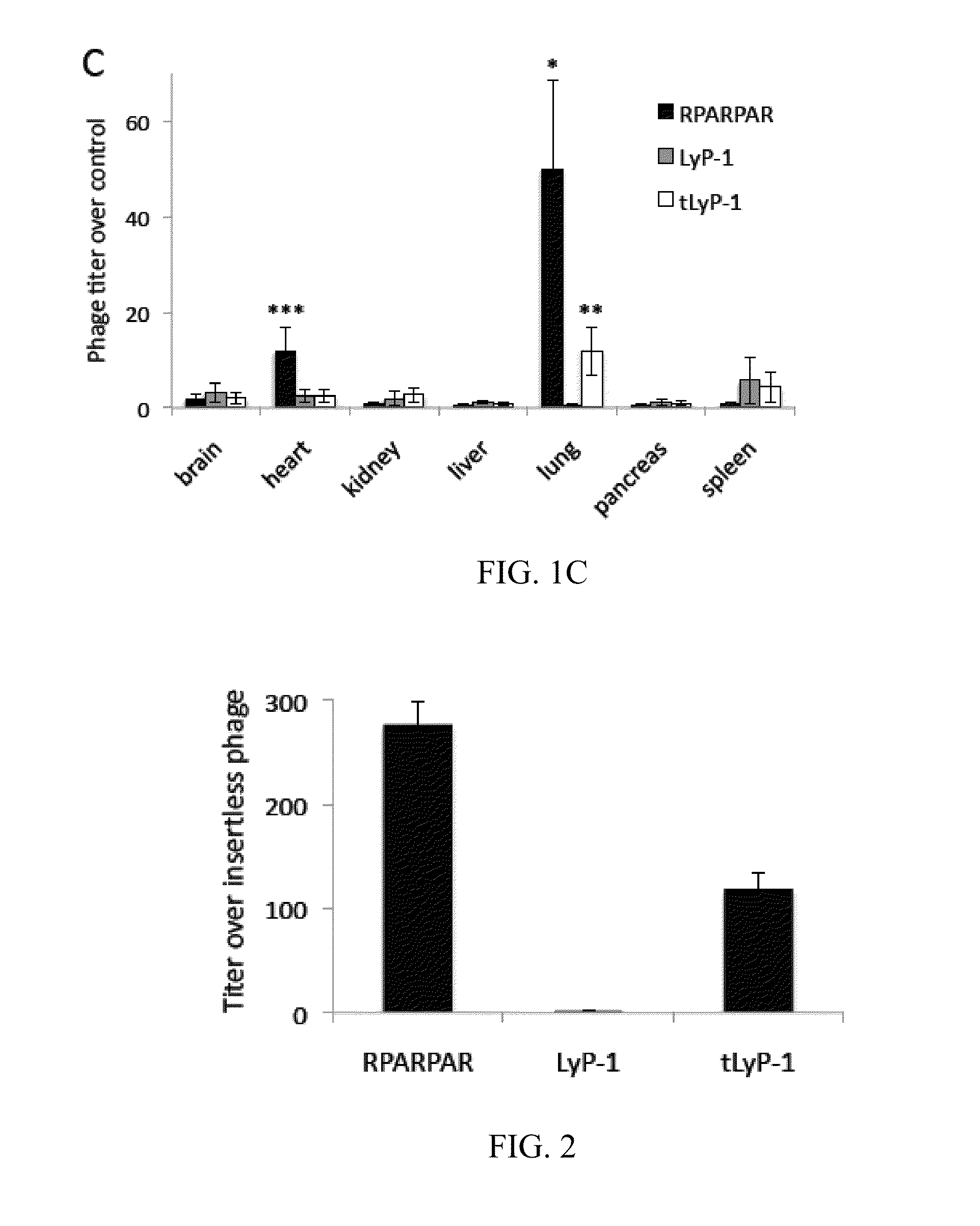
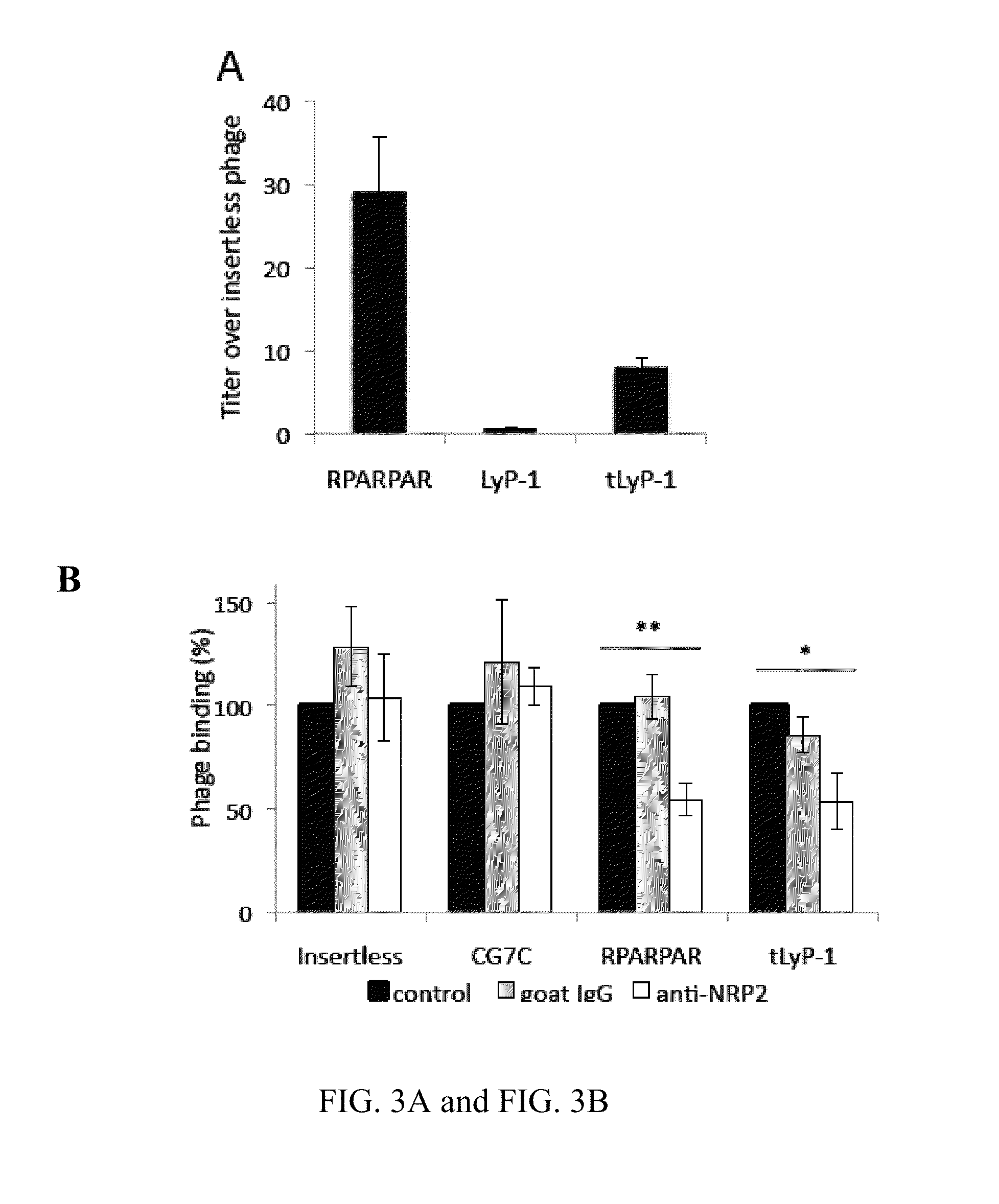
Truncated LYP-1 Peptides and Methods and Compositions Using Truncated LYP-1 Peptides
ActiveUS20150259380A1Reduce tumor burdenIncrease heightPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsCell selectivityPeptide sequence
Disclosed are compositions and methods useful for targeting and internalizing molecules into cells of interest and for penetration by molecules of tissues of interest. The compositions and methods are based on peptide sequences, such as truncated LyP-1 peptides, that are selectively internalized by a cell, penetrate tissue, or both. The disclosed internalization and tissue penetration is useful for delivering therapeutic and detectable agents to cells and tissues of interest.
Owner:SANFORD BURNHAM MEDICAL RES INST
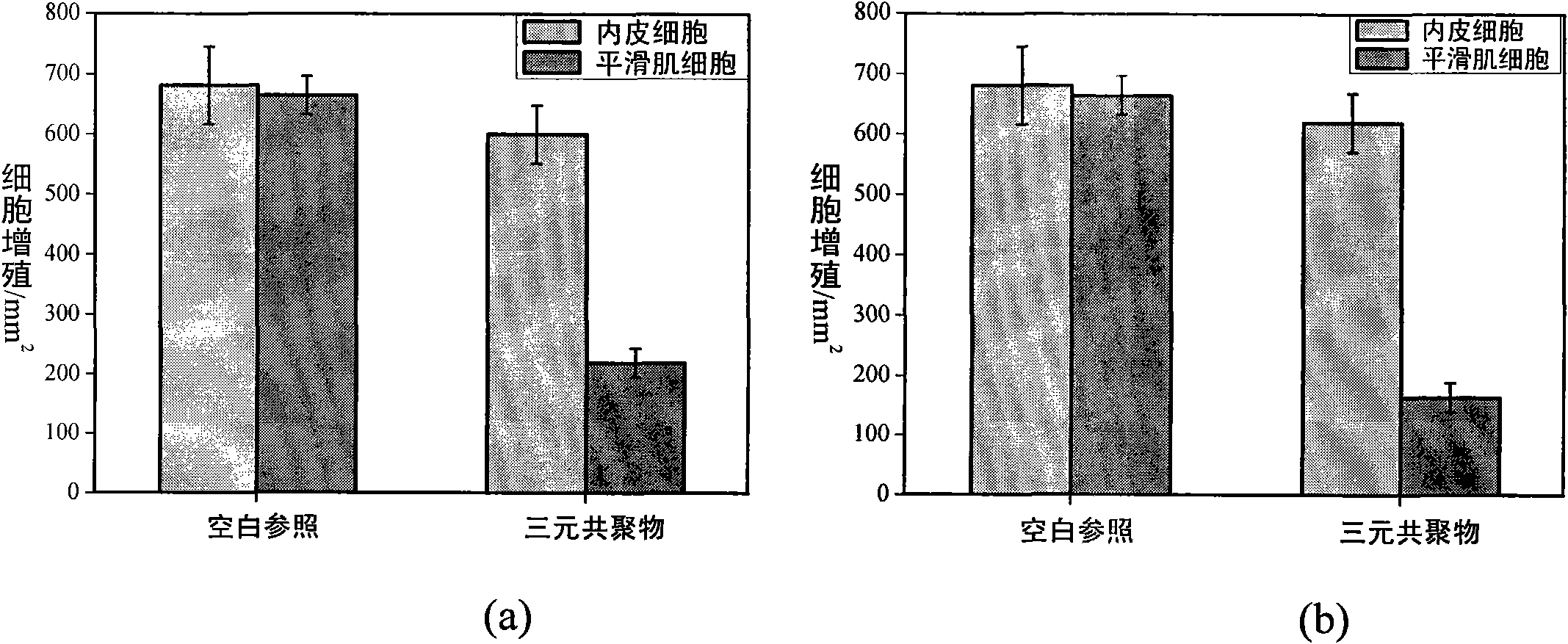
Cardiovascular stent coating material with endothelial cell selectivity and preparation and application method thereof
The invention discloses a cardiovascular stent coating material with endothelial cell selectivity and a preparation and application method thereof. The coating material is copolymerized by three monomers via free radicals, wherein the three monomers are as follows: a biocompatibility monomer containing cell membrane bionic structure, a polymerizable monomer containing hydrophobic functional groups and a polymerizable monomer containing reactive activity functional groups; the three monomers are synthesized into a terpolymer with reactive activity with a free radical copolymerization method; polypeptide sequence arginine-glutamic acid-aspartic acid-valine can be introduced in with a surface fixing method, and can specifically accelerate the adherency of endothelial cells to cause the coating to have endothelial cell selectivity. The cardiovascular stent coating material has good reactivity, can realize the immobilization and activity maintenance of biomolecules, such as polypeptide andthe like, and realizes the capture capability of in vivo in situ endothelial cells; and in addition, the obtained coating has stable structure, can adapt to the internal environment of human bodies and has good application prospect on cardiovascular diseases, cancers and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Antibodies for selective apoptosis of cells
InactiveUS20100062001A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsApoptosisVirology
A recombinant isolated antibody and a pharmaceutical composition containing same, capable of specifically recognizing an MHC-peptide complex with an affinity in a nanomolar range and of inducing apoptosis in cancer or pathogen infected cells is provided. Also provided are method for treating and diagnosing cancer or pathogen infection in a subject using the recombinant isolated antibody of the present invention.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Antibacterial peptide RW-P and preparation method and application thereof
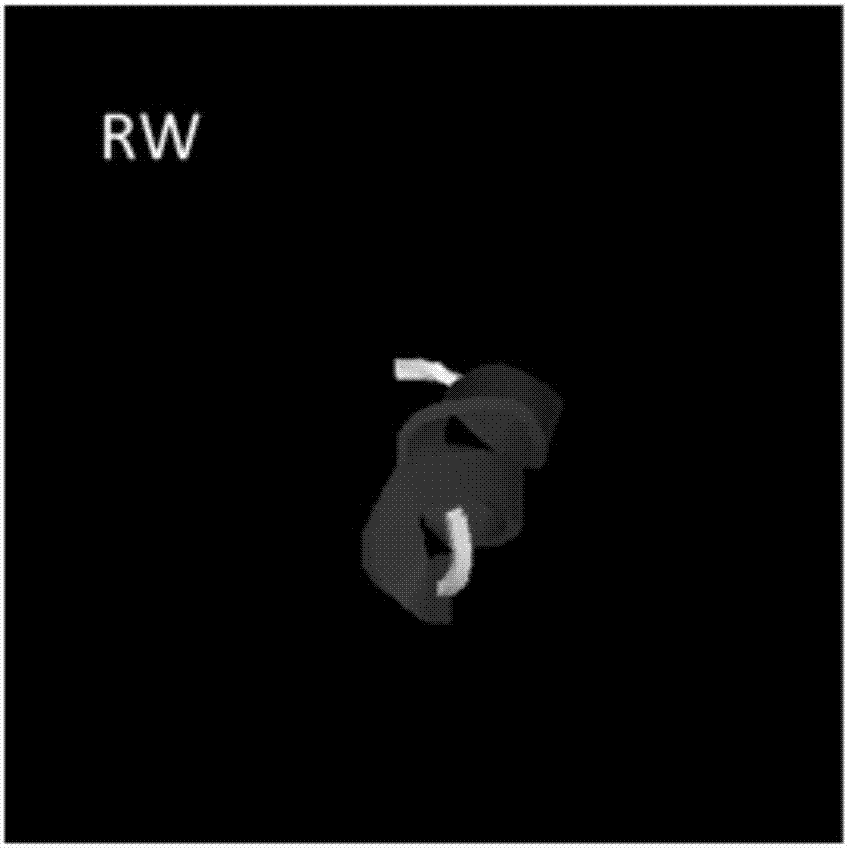
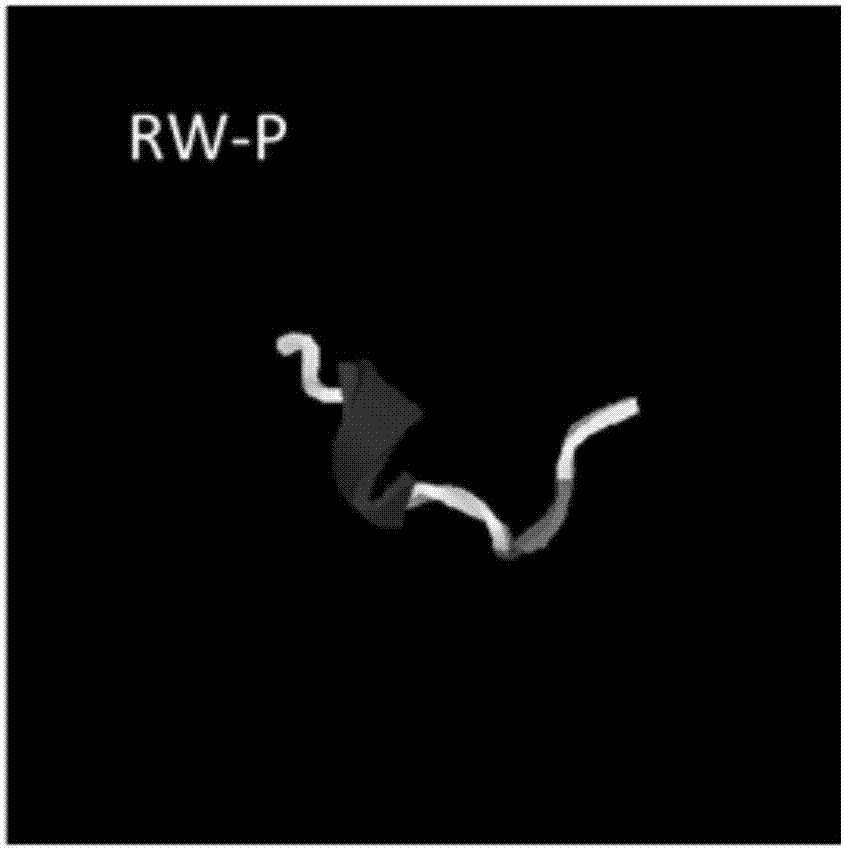
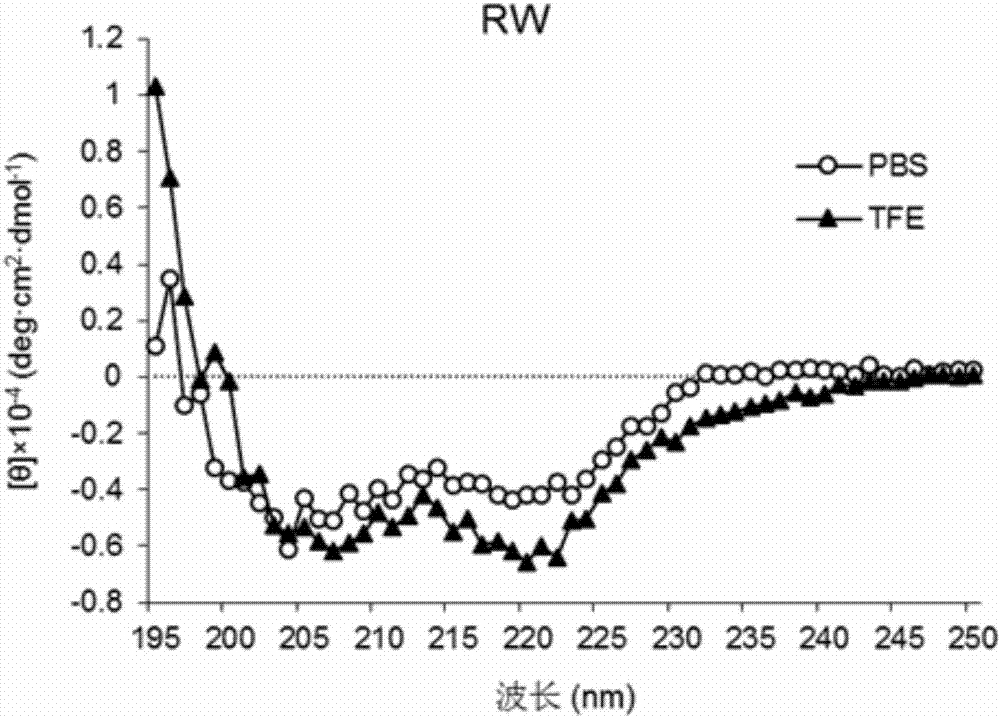
ActiveCN107141338AGood treatment effectImprove securityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsCell selectivityArginine
The invention provides an antibacterial peptide RW-P and a preparation method and an application thereof. The sequence of the antibacterial peptide RW-P is as shown in SEQ ID No.2. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by taking two simple amino acids as basic amino acids, repeating the amino acids in a sequence form of XXYY for three times to obtain alpha-spiral antibacterial peptide RW, wherein X is arginine and Y is tryptophan; and performing amino acid residue substitution at fixed sites on arginine at the 5th site and tryptophan at the 8th site of the RW antibacterial peptide, and introducing proline to obtain the antibacterial peptide RW-P. Computer structure prediction and circular dichroism spectrum structure determination verify that RW is of an alpha-spiral structure, and the spiral content of RW-P is reduced by introducing proline. Researches find that RW-P keeps a high antibacterial activity of RW, and meanwhile, the cytotoxicity is reduced and the cell selectivity is improved. The method provides a theoretical foundation for designing the efficient low-degree antibacterial peptide which is applied to animal production.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com