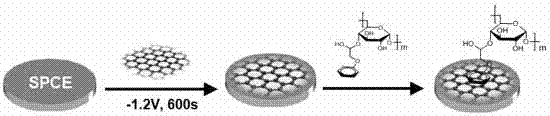
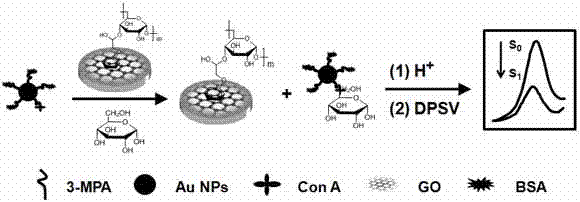
Patents
Literature
104 results about "Concanavalin A" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Concanavalin A (ConA) is a lectin (carbohydrate-binding protein) originally extracted from the jack-bean, Canavalia ensiformis. It is a member of the legume lectin family. It binds specifically to certain structures found in various sugars, glycoproteins, and glycolipids, mainly internal and nonreducing terminal α-D-mannosyl and α-D-glucosyl groups. ConA is a plant mitogen, and is known for its ability to stimulate mouse T-cell subsets giving rise to four functionally distinct T cell populations, including precursors to suppressor T-cell; one subset of human suppressor T-cells as well is sensitive to ConA. ConA was the first lectin to be available on a commercial basis, and is widely used in biology and biochemistry to characterize glycoproteins and other sugar-containing entities on the surface of various cells. It is also used to purify glycosylated macromolecules in lectin affinity chromatography, as well as to study immune regulation by various immune cells.
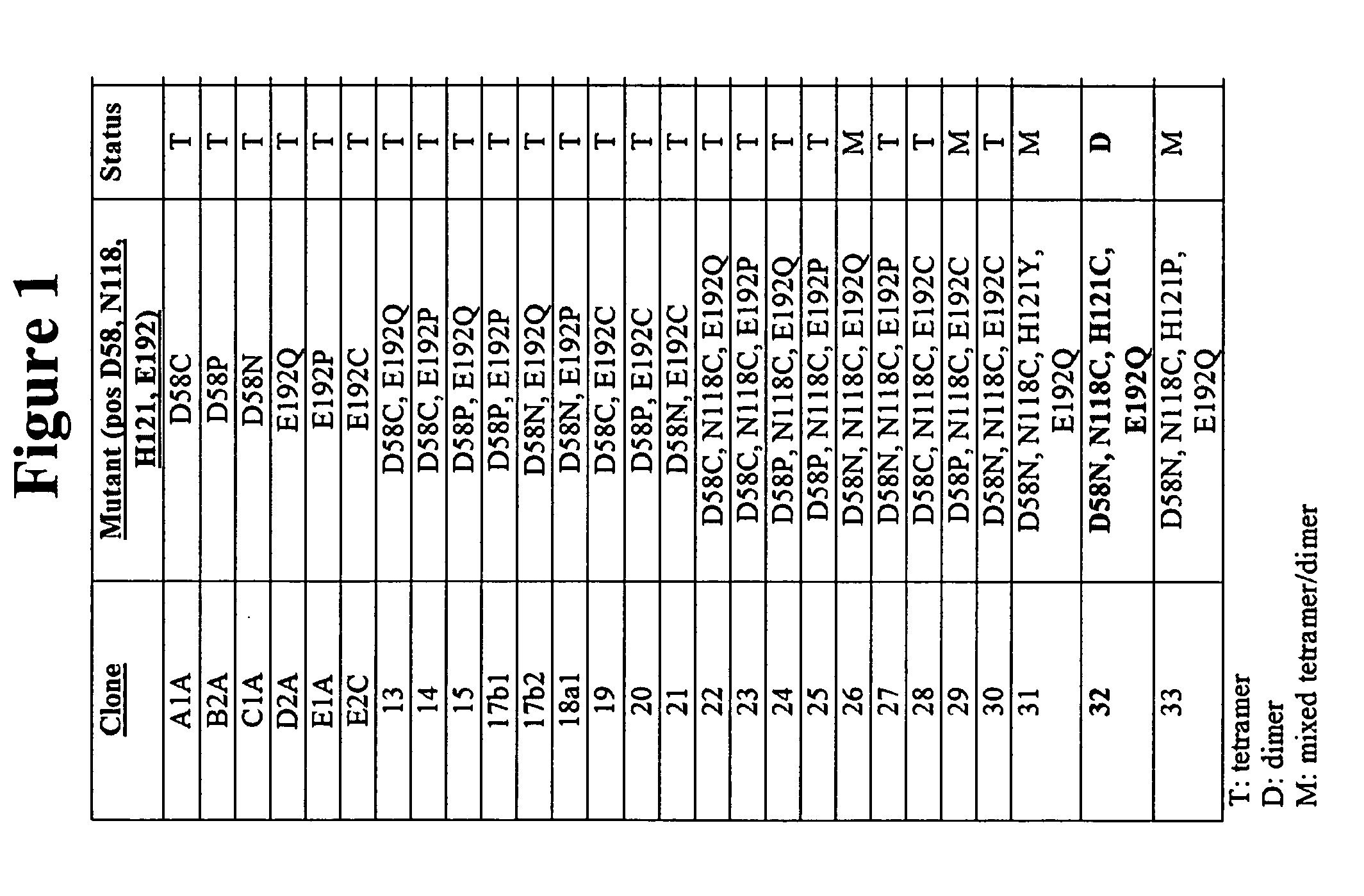
Design and construction of dimeric concanavalin a mutants
InactiveUS20070207498A1Retain biological activityDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsWild typeConcanavalin A assay
Embodiments of the invention provide for compositions comprising purified polypeptides such as purified Concanavalin A (ConA) mutants. In addition, embodiments provide for polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding those polypeptides, such as mutant ConA with reduced dimer-dimer interactions compared to wild type ConA. Some embodiments also provide for sensors comprising the polypeptides disclosed herein. The embodiments also provide an improved method of producing recombinant mutant ConA.
Owner:SENSOR TECH LLC
Targeting proteins to cells expressing mannose receptors via expression in insect cells
The present invention is based on the discovery that proteins produced in insect cell cultures are glycosylated in a unique manner that causes them to be selectively imported by cells that express mannose receptors on their membranes, particularly macrophages. Proteins that are selectively imported into cells containing mannose receptors are provided, as well as pharmaceutical compositions containing such proteins and methods for producing such proteins. Application of the present invention to produce proteins useful for treating lysosomal storage disorders is also disclosed. Engineering of cells to express mannose receptors so that they will selectively import proteins produced in insect cells is also taught, as well as a protein targeting system using such cells and proteins. Finally, an improved elution buffer for the purification of proteins produced in insect cells from a Concanavalin A column is provided.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
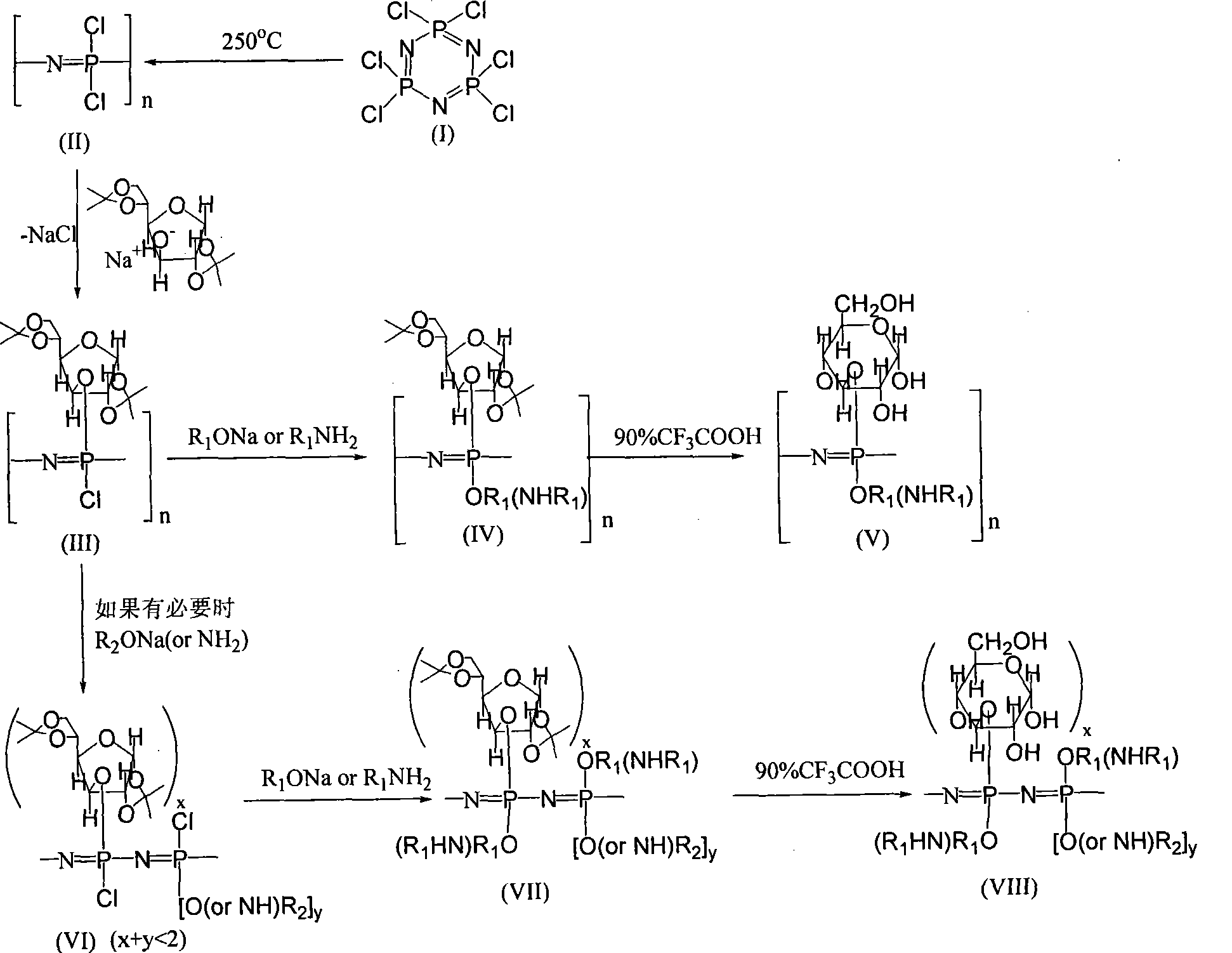
Glucose responding type polyphosphazene hydrogel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101450996ARaise the ratioGlucose responsiveMetabolism disorderPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolyphosphazeneBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to a glucose-responsive nitrile polyphosphine hydrogel and a method for preparing the same. The method utilizes interaction between nitrile polyphosphine containing glucose side groups and lectin concanavalin A (Concanavalin A, Con A) to obtain a hydrogel system with different crosslinking degrees and water contents through the proportion increase of the glucose side groups and the selection of a second proper substituting group and a third proper substituting group and other means; and the nitrile polyphosphine hydrogel system has glucose responsiveness, biocompatibility and biodegradability, and can be used for intelligent release of insulin.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Human immunosuppressive protein
InactiveUS7388076B2Prevent proliferationReduced viabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticEmbryonal Carcinoma CellsPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
A method for purifying an immunosuppressant protein (HISP) has the steps of obtaining supernatant from hNT cells; exposing the supernatant to preparative polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis to produce 20 isoelectric fractions, including active isoelectric fraction #10; placing the active isoelectric fraction on a Blue Sepharose column to bind albumin; and collecting the free fraction containing the concentrated, isolated HISP. Also disclosed is a method of treating inflammation, using an effective amount of an HISP. The HISP is anionic, has a molecular weight of 40-100 kDa, an isoelectric point of about 4.8 and is obtained from the supernatant of hNT cells, but not from NCCIT embryonal carcinoma cells, T98G glioblastoma cells or THP-1 monocytic leukemia cells. HISP can maintain T cells in a quiescent G0 / G1 state without lowering their viability. HISP loses activity when treated with heat, pH2, pH11, or mixed with trypsin or carboxypeptidase, but not with neuraminidase. HISP can suppress proliferation of responder peripheral blood mononuclear cells in allogeneic mixed lymphocyte cultures; HISP can suppress T-cell proliferation and IL-2 production in response to phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), ionomycin and concanavalin-A. HISP does not bind to heparin-sepharose CL-B gel; or to albumin-binding resin Blue Sepharose. HISP is concentrated with YM10 ultrafiltration. HISP does not act through the T-cell receptor-CD3 complex or via altered accessory signal cells. A method of treating inflammation comprises administering an effective amount of hNT neuronal cells.
Owner:SOUTH FLORIDA UNIVESITY OF
Method for in vitro preconditioning of myoblasts before transplantation
InactiveUS20020012657A1Increase secretionIncrease the number ofBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsFiberCell-Extracellular Matrix
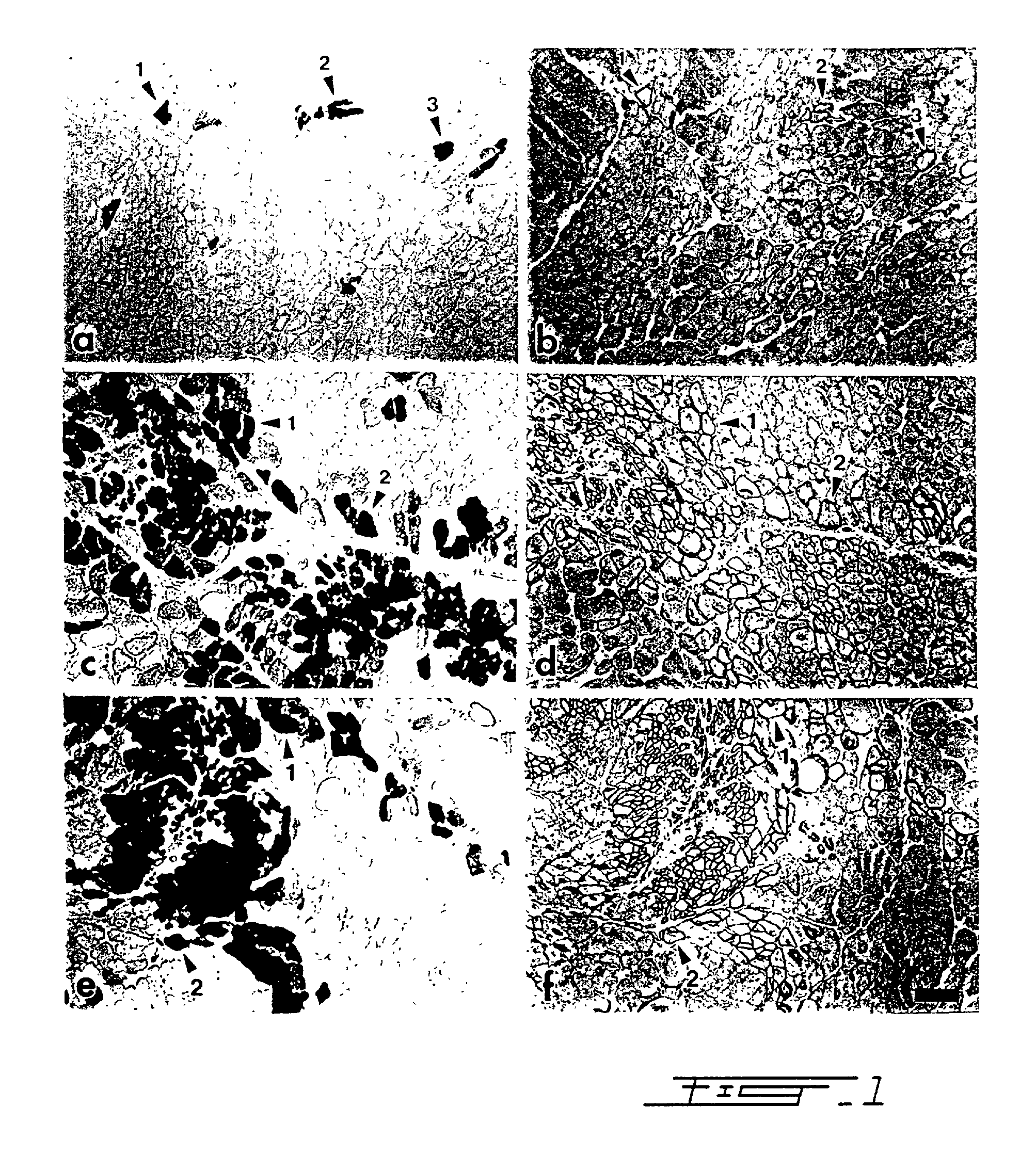
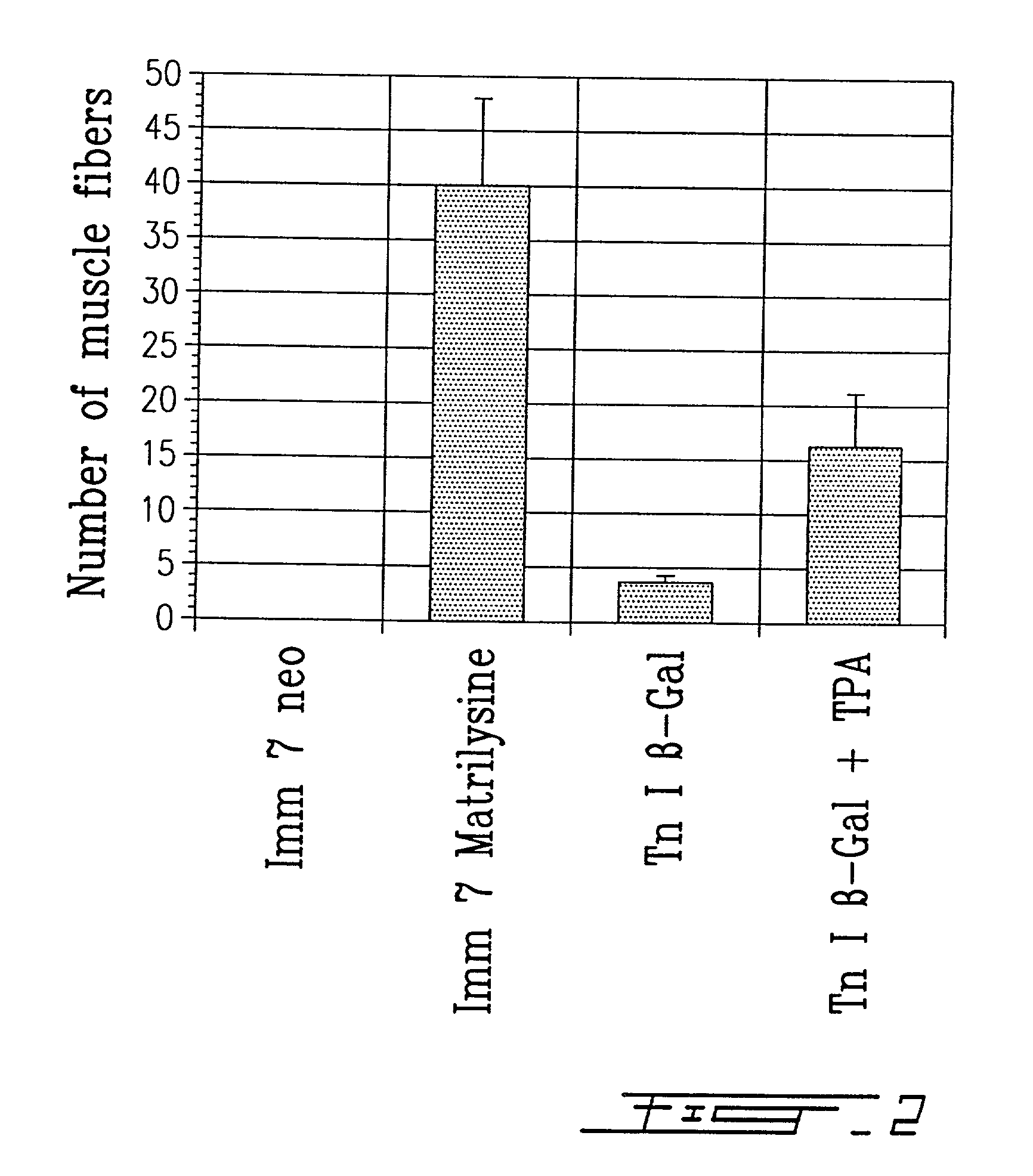
A method of pretreating healthy donor's myoblast cultures with growth or trophic factors like basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and with concanavalin A on transplantation to subjects suffering of myopathy like muscular dystrophy is disclosed and claimed. Recipient muscles show a higher percentage of functional cells, a four-fold increase, demonstrated by the higher incidence of dystrophin-positive fibers, and does not require previous preconditioning of recipient muscles by irradiation or toxin administration. The recipient subjects were immunosuppressed with FK 506. When growing myoblasts with 20 mug / ml concanavalin A or 100 ng / ml TPA for two to four days, migration of donor cells in recipient tissue was increased by 3-4 fold. This suggests that, when using primary cultures, metalloproteases are secreted by fibroblasts, resulting in a greater degradation of the extracellular matrix. Both metalloproteases and bFGF appear beneficial for the success of the transplantation. The use of recombinant myoblast expressing metalloproteases is also contemplated.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Process method of oxidized graphene directional immobilization glucose oxidase
The invention relates to a process method of oxidized graphene directional immobilization glucose oxidase. The process method comprises the following steps that 1) oxidized graphene is dissolved in distilled water, and oxidized graphene turbid liquid with the concentration being 1mg / mL is obtained through ultrasonic mixing; N-hydroxy sulfo-succinimide and 1-ethide-3-(3-dimethyl aminopropyl) carbodiimide are added into the turbid liquid, the washing and the separation are carried out after shaking, and esterified oxidized graphene is obtained; and 2) activated concanavalin A is added into the uniform esterified oxidized graphene, the centrifugation is carried out after reaction, and sediments are fully washed; and then, glucose oxidase solution is added, the full washing is carried out after reaction, and the directional immobilization glucose oxidase is obtained after the vacuum freeze-drying for 24 hours. The method for preparing the immobilized enzyme has the advantages that the immobilization efficiency is high, and the defects that the orientation of enzyme activity sites is inconsistent, or the enzyme activity sites are covered, and the like are avoided, so the activity of the immobilized enzyme is improved, the enzyme activity loss is low, and the enzyme activity can reach 150 to 195U / mg.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing glucose-sensitive insulin controlled-release biological material
ActiveCN101745114AIncreased sensitivityExcellent self-controlled release performancePeptide/protein ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsGlucose sensitivityDouble bond
The invention discloses a new method for preparing an intelligent glucose-sensitive insulin controlled-release biological material. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, dissolving glucose derivative monomers with C=C derivatives and concanavalin A derivative monomers with C=C double bonds in buffer solution to produce monomer solution; secondly, adding a catalyst in the monomer solution to perform free radical polymerization at a certain temperature; and finally, removing unreacted reactant through dialysis to obtain the glucose-sensitive insulin controlled-release biologicalmaterial. The preparation method has the advantages of convenient implementation, fast reaction process, mild reaction condition and easy production preparation on a large scale. The obtained glucan-concanavalin A insulin controlled-release biological carrier material has the advantages of good glucose-sensitive property and excellent insulin controlled-release performance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method and application of carrier-free combined cross-linked glucose oxidase/catalase enzyme aggregation
InactiveCN106929500ASmall particlesReduce mass transfer resistanceImmobilised enzymesOxidoreductasesCross-linkGluconic acid
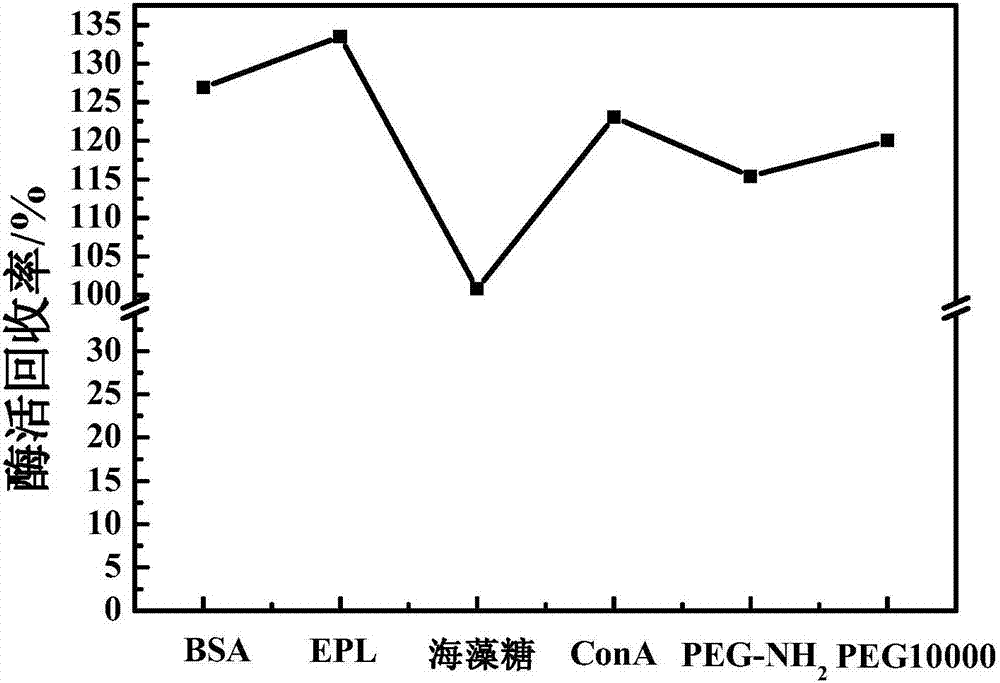
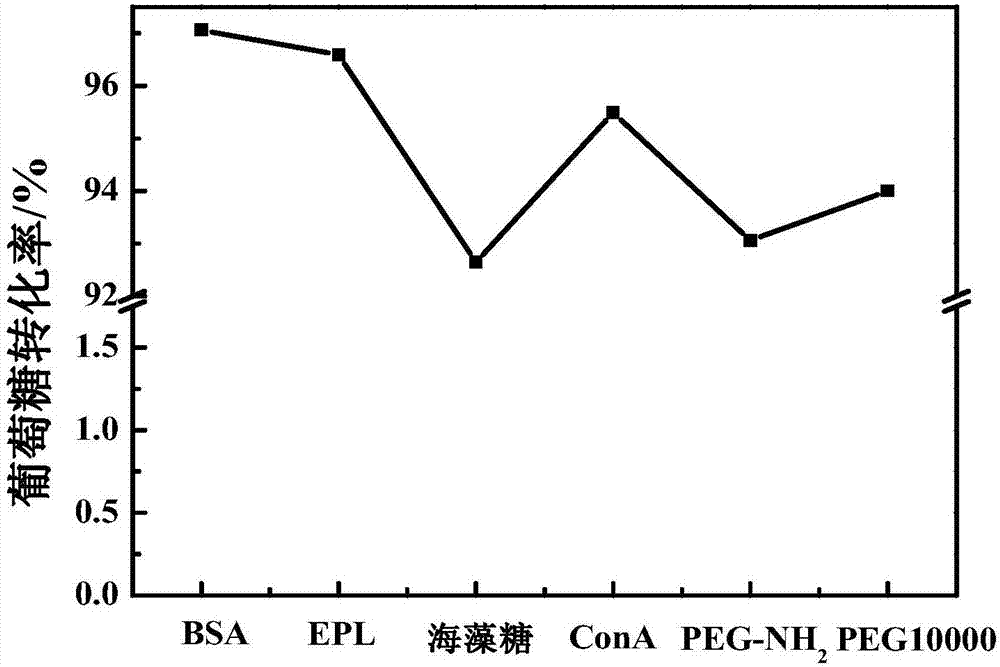
The invention discloses a preparation method of glucose oxidase / catalase cross-linked enzyme aggregation and application thereof for producing gluconic acid or salt. Concanavalin A (ConA), polylysine (EPL), PEG-NH2, bovine serum albumin (BSA) and trehalose or PEG10000 are added into the combined cross-linked enzyme aggregation Combi-CLEAs (CAT / GOx) to be adopted as a protective agent. According to the combined cross-linked enzyme aggregation, the enzyme activity recovery of immobilized enzyme is improved (by larger than 100%), the problem that the operation stability of the combined cross-linked enzyme aggregation is poor is effectively solved, and the service life of the combined cross-linked enzyme aggregation is prolonged. In the gluconic acid or salt producing process of the carrier-free combined cross-linked glucose oxidase / catalase enzyme aggregation, the glucose conversion rate is still kept to 90% or above after 20-batch repeated usage.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for producing proteins suitable for treating lysosomal storage disorders
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
Immunity inhibitor glycyrol
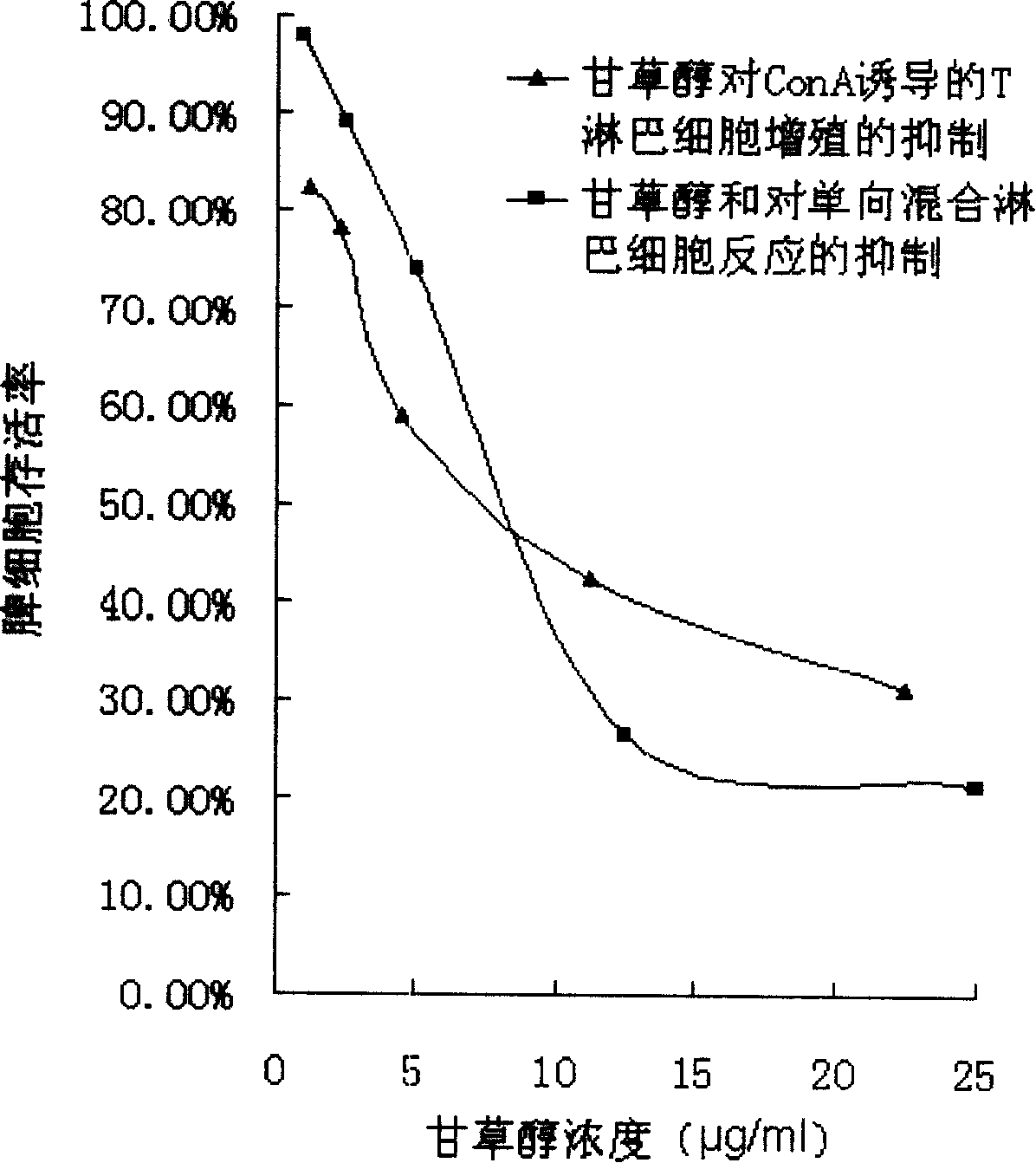
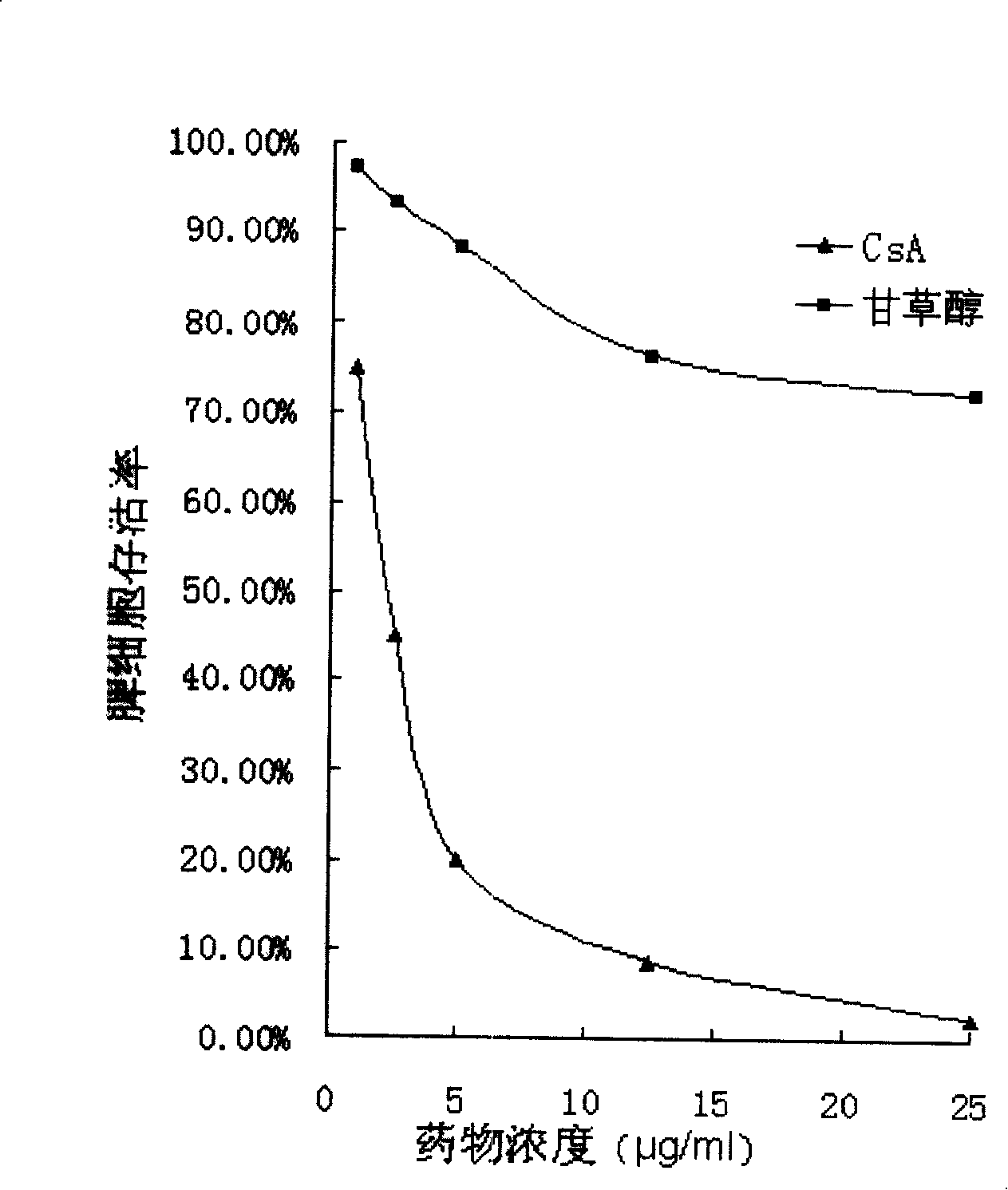
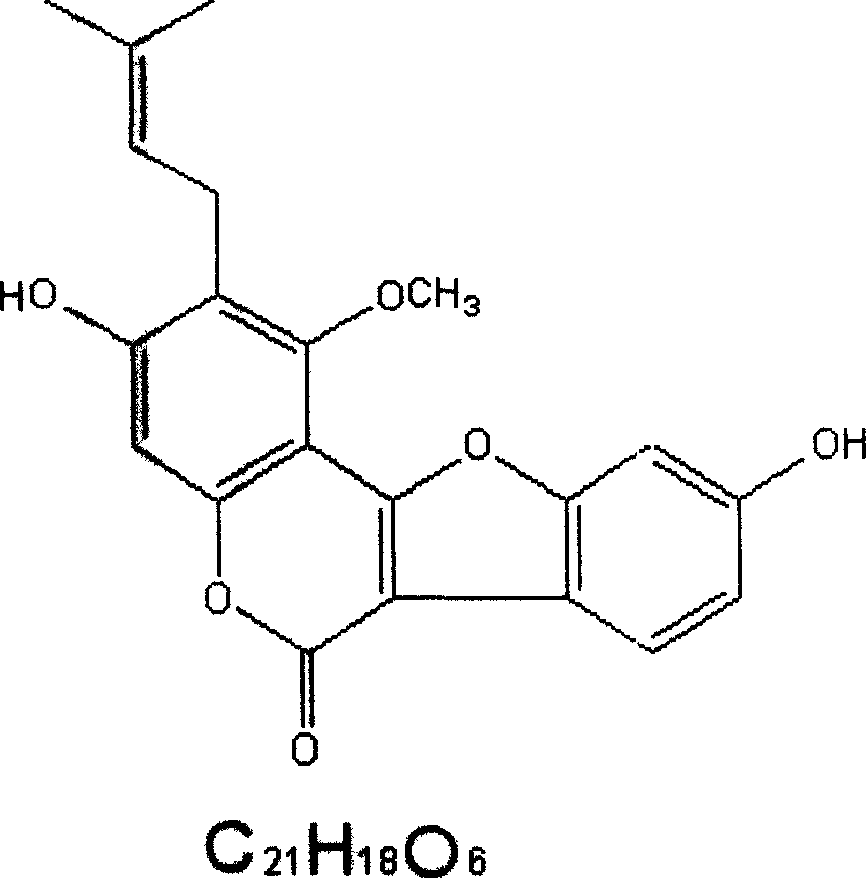
ActiveCN101235038ALow action doseSmall molecular weightOrganic chemistryImmunological disordersChemical structureDisease
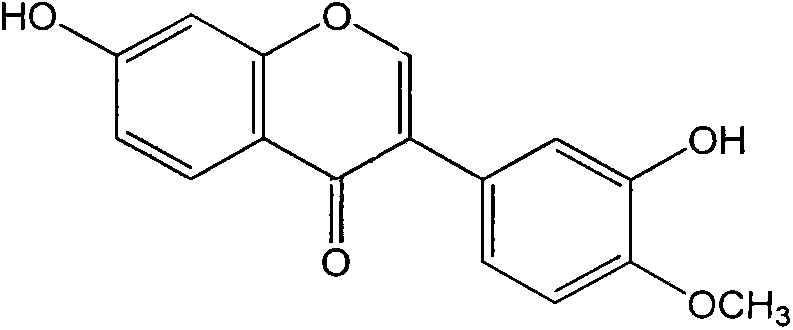
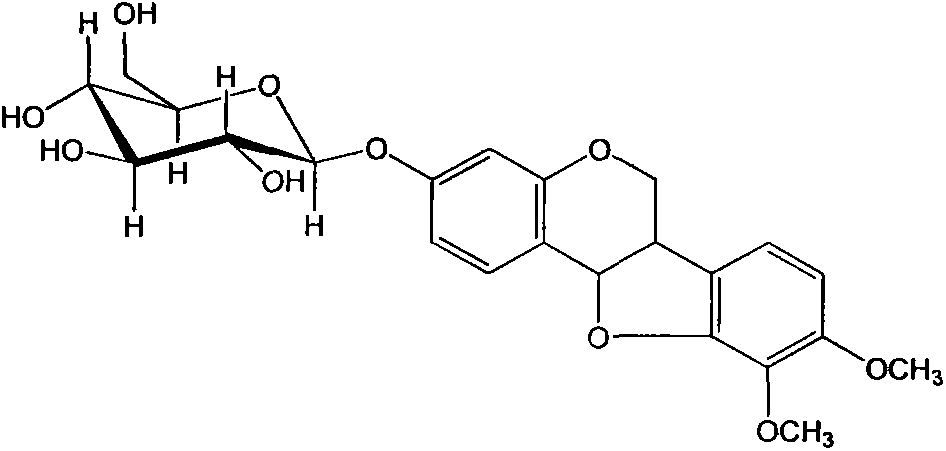
A new immunosuppressive agent as glycyrol has significant immunosuppressive activity, thus is useful as an immunosuppressive agent to treat relative diseases, wherein the glycyrol is a coumestrol compound extracted from glycyrrhiza, which is a small molecular compound with novel chemical structure. Tests prove that the glycyrol can inhibit the increment of T lymphocyte induced by canavaline A and inhibit one-way mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR), release the inflammatory symptom of delayed hypersensitivity and inhibit the homologous allogenic organ transplantation rejection. The glycyrol is a high-effective low-toxicity immunosuppressive agent, with small molecular weight and simple structure, which is easy to be modified and to prepare different drug agents, therefore, the compound is a new generation immunosuppressive agent.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
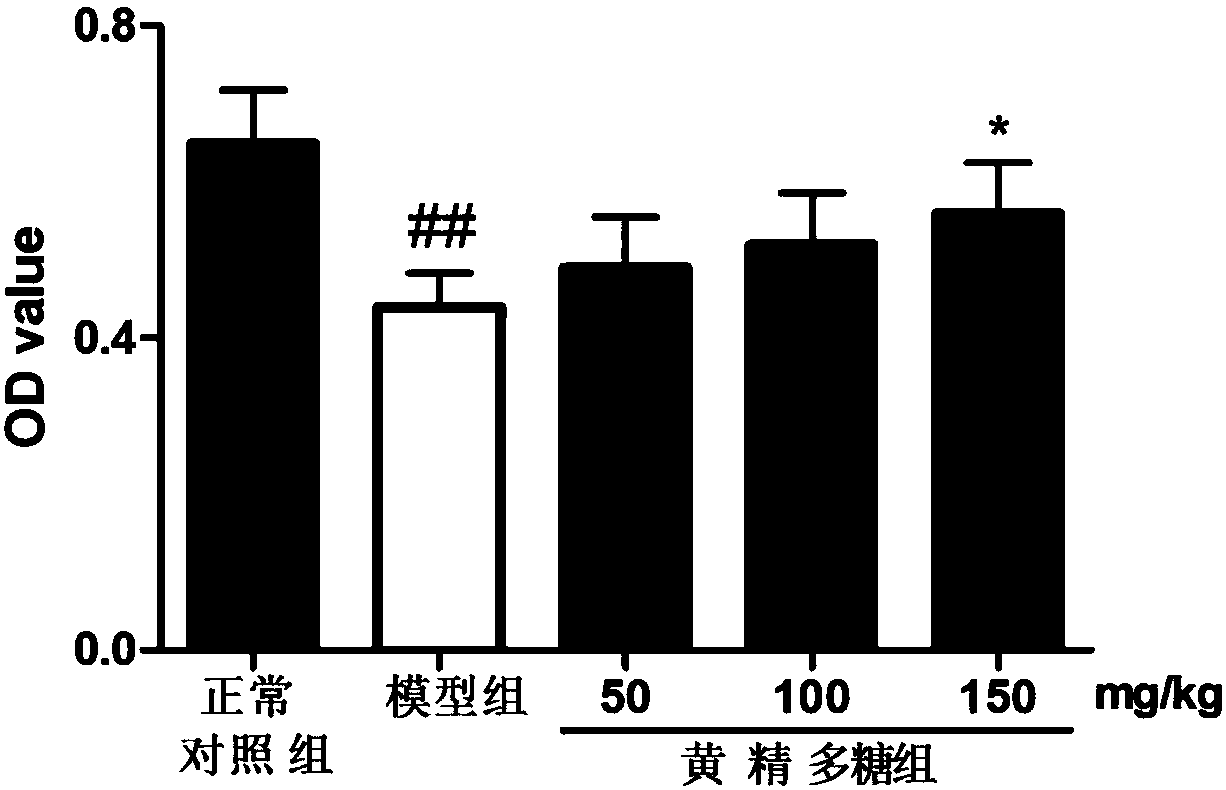
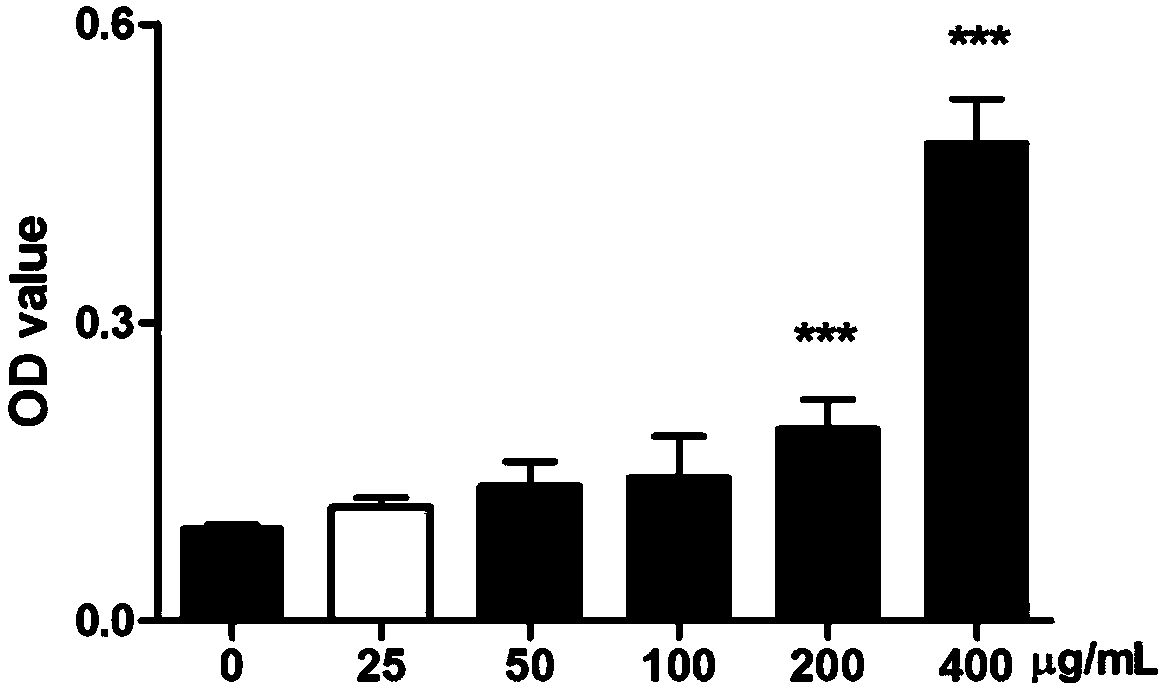
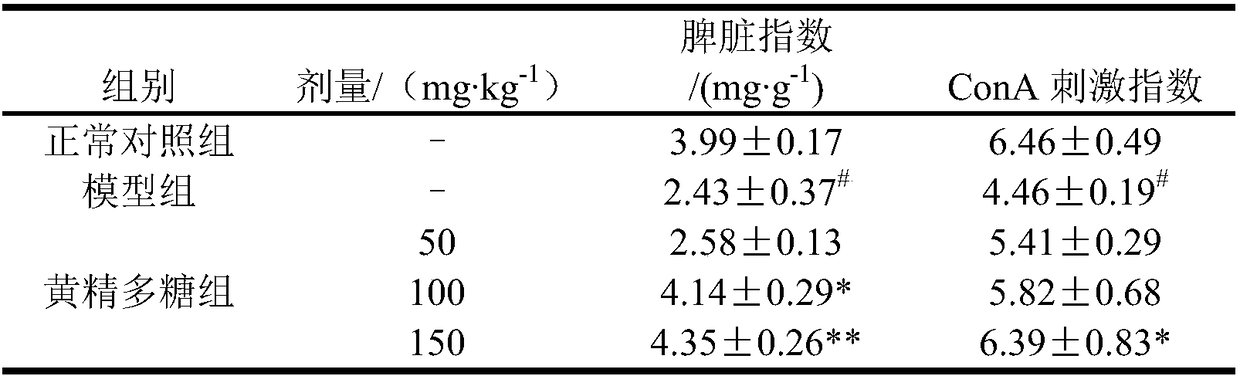
Preparation method and application of rhizoma polygonati polysaccharide
PendingCN108164615AIncrease proliferative activityImprove thymus indexOrganic active ingredientsImmunological disordersDiseaseMedicinal herbs
The invention relates to the field of a preparation method and application of a traditional Chinese medicine effective component and in particular relates to a preparation method of rhizoma polygonatipolysaccharide and application of the rhizoma polygonati polysaccharide to the preparation of an immunological enhancement medicine. The rhizoma polygonati polysaccharide is obtained by processing raw rhizoma polygonati, extracting and separating; when an extraction method provided by the invention is adopted, the extraction rate of the rhizoma polygonati polysaccharide is high and the content oftotal polysaccharide is high; the proliferation activity of the rhizoma polygonati polysaccharide on normal mouse spleen cells is improved; cyclophosphamide induced spleen and thymus gland index of mice with low immunity also can be improved; the in-vitro proliferation capability of spleen and thymus gland cells under the stimulation of concanavalin A is enhanced; the phagocytic function of macrophage of the mice with the low immunity and the capability of secreting IL-6 and TNF-alpha are enhanced; the rhizoma polygonati polysaccharide has actual application value in the aspect of treatment of diseases including immunodeficiency diseases, tumors and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Norovirus detection sensor and electrochemical sensing method using the same
ActiveUS20160061834A1Low costShorten the timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSignal detectorConcanavalin A
Disclosed herein are a norovirus detection sensor and an electrochemical sensing method using the sensor. Specifically, in the norovirus detection sensor including a bioreceptor and a signal detector, a three-dimensional gold nanosurface electrode is used as a substrate, and the bioreceptor employs concanavalin A as a sample capture agent immobilized to the substrate and capable of binding to norovirus. Therefore, the norovirus detection sensor has improved sensitivity by employing the three-dimensional gold nanosurface electrode having a wide surface area. In addition, the norovirus detection sensor has effects of reducing manufacturing costs using a non-antibody material, i.e., concanavalin A which is inexpensive and readily available.
Owner:KOREA BASIC SCI INST +2
Method for preparing AS-605240 and application thereof on preparing medicines for treating inflammatory diseases
InactiveCN101550135AGood curative effectMild reaction conditionsOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryQuinoxalineSodium bicarbonate
The invention relates to a method for preparing AS-605240 and an application thereof on medicines for treating inflammatory diseases. An improvement of the preparation method disclosed to the international patent is supplied to 5-quinoxaline methylene-2, 4-thiazolidinedione (AS-605240 with a structural formula I). 3, 4-diaminotoluene and glyoxal water solution as raw materials are relatively easy to obtain, reactive reagent, such as sodium bicarbonate, N-bromosuccinimide, carbon tetrachloride, and the like in each step is cheap and easy, and the reaction condition is mild. A great deal of mouse experimental curative effect observation of myocarditis, acute and chronic hepatitis, acute colitis and pancreatitis, which is induced by concanavalin A, is performed by the AS-605240, and the favorable curative effects of the AS-605240 are all confirmed. The prior TZDs, such as troglitazone, and the like are mainly used for aspects on treating diabetes mellitus, angiocardiopathy, and the like. In recent years, a study confirms that the AS-605240 protects the mouse joint and treats rheumatoid arthritis through restraining an osphatidylinositol 3 (PI3K) kinase gamma subtype signal way, therefore, the AS-605240 application on medicines for treating the inflammatory diseases opens up a new medical treatment field on the discovery of thiazolidinedione compound.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
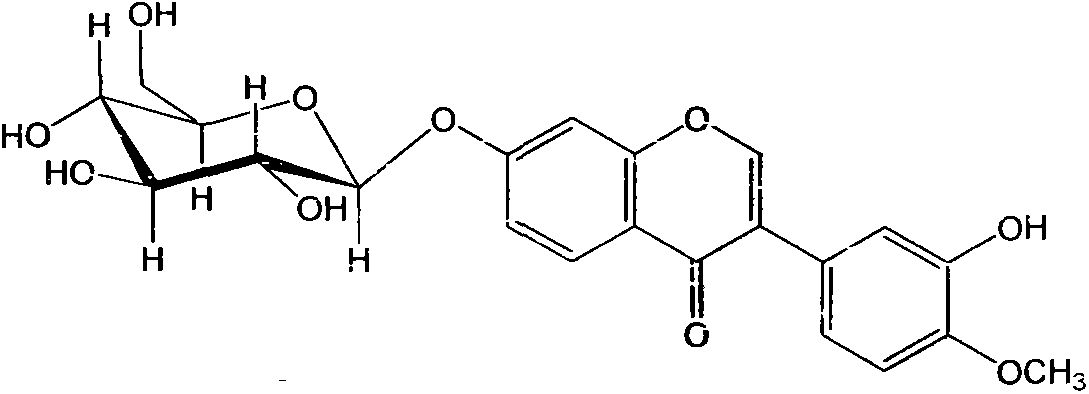
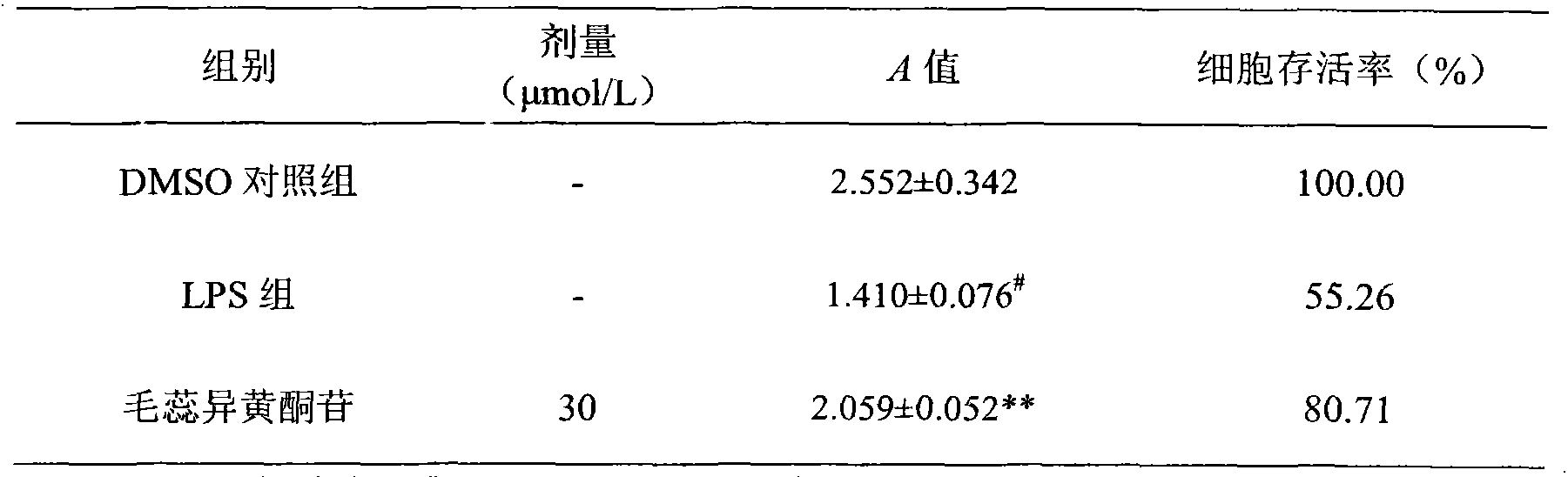
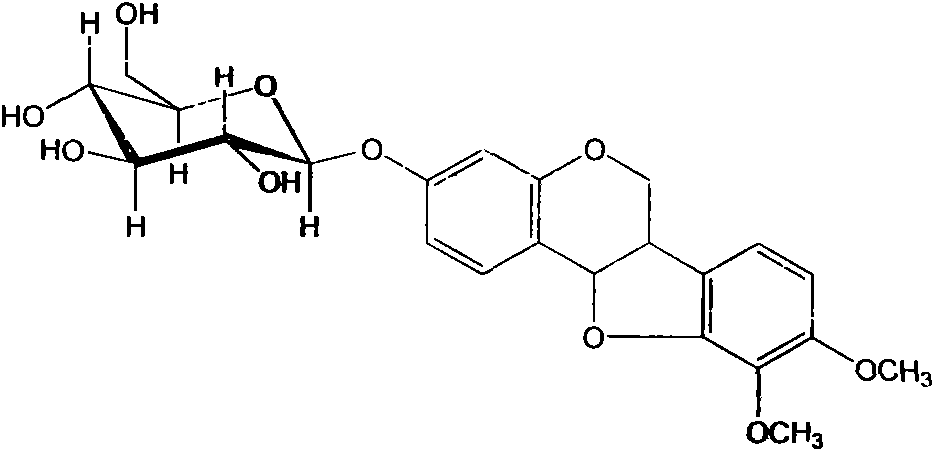
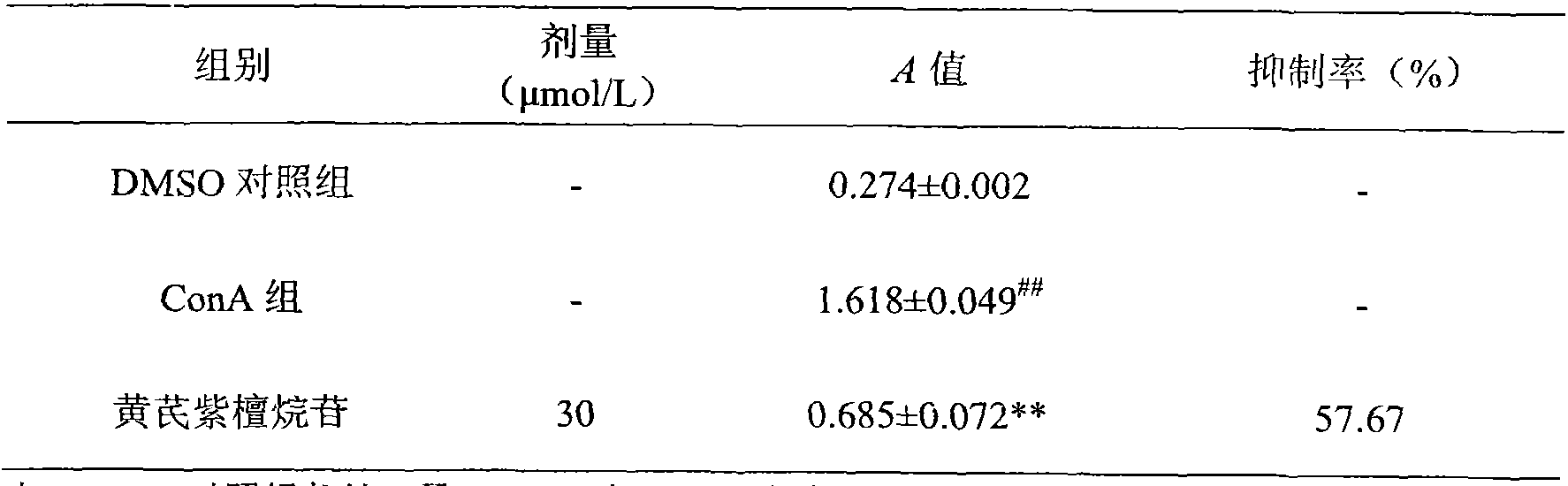
Application of calycosin in preparation of immunity inhibitors
InactiveCN104107175AHas inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsImmunological disordersLymphocyte proliferationCalycosin
Through the experiments and researches on calycosin, it has been found for the first time that calycosin can prominently inhibit the T lymphocyte proliferation induced by concanavalin A (Con A), has an immunity inhibiting effect, and is advantageously used to prepare immunity inhibitors.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Sensor for detecting bean protein A and preparation method and application thereof
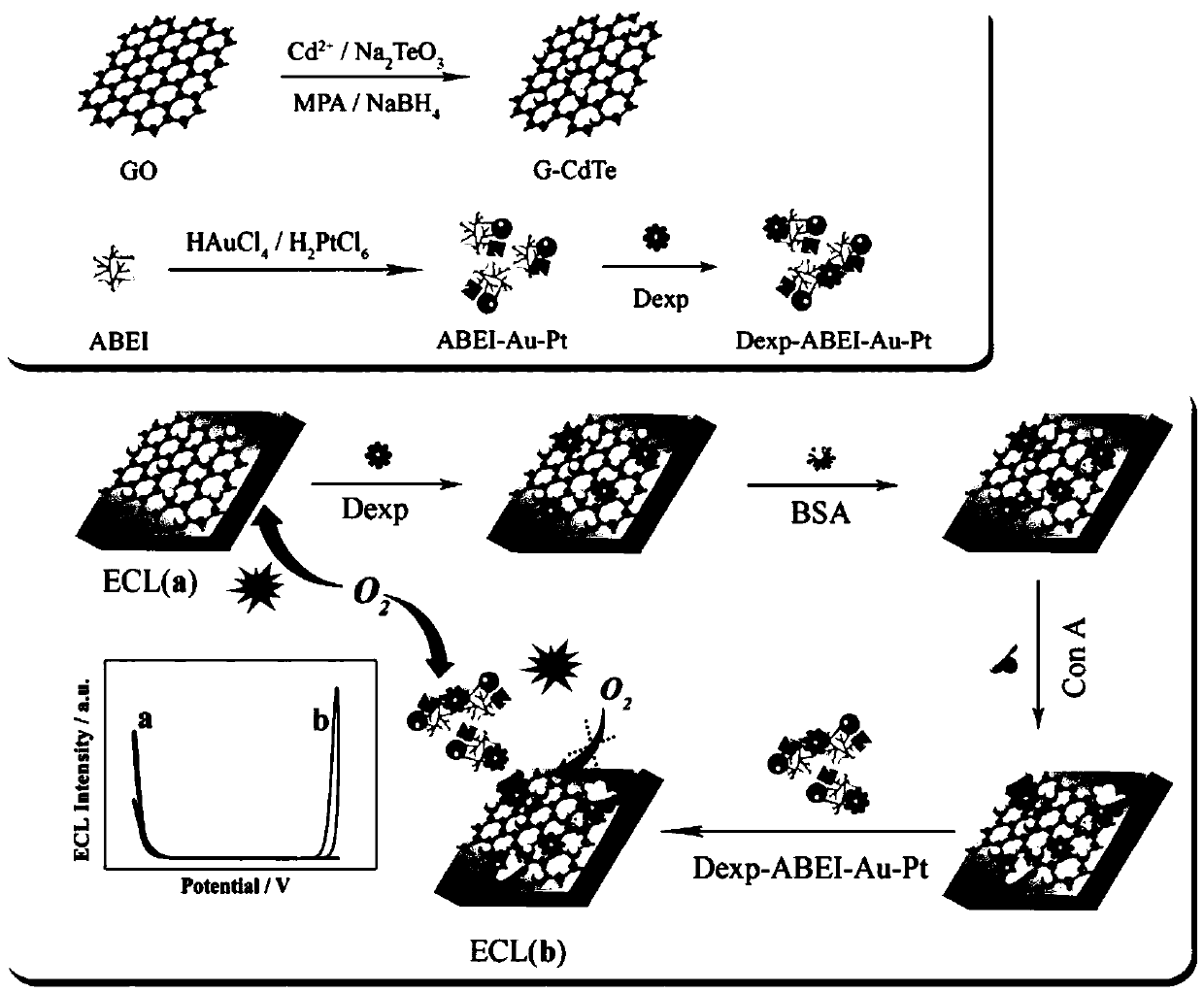
ActiveCN109100400ASolid load implementationECL signal enhancementMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemiluminescenceOxygen
The invention relates to the technical field of electrochemiluminescence sensors, in particular to a sensor for detecting bean protein A and a preparation method and application thereof. The sensor for detecting bean protein A comprises a cathode emitter, an anode emitter and a co-reagent. The cathode emitter comprises graphene oxide modified cadmium telluride quantum dots, the anode emitter comprises nanogold and nano-platinum modified N-(aminobutyl)-N-(ethylisoluminol). The preparation method comprises the following steps: combining graphene oxide modified cadmium telluride quantum dots anda recognition unit by pi-pi stacking, and modifying the surface of the pretreated electrode; modifying the anode emitter combined with the recognition unit and incubating to obtain the sensor. According to the sensor for detecting bean protein A and preparation method and application thereof, the ratio type electrochemiluminescence system is constructed on the basis of competitive consumption of oxygen, so that the signal to noise ratio is improved, and the detection result is high in reliability.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Method of proliferating LAK cell
InactiveCN101495620AMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsPlant LectinsPresent method
The present application aims at providing a treatment method effective for various cancers, immune deficiency diseases and infections, and a method of proliferating / activating cells associated therewith, which can be performed at such low costs that the methods can be applicable to nonhuman animals. A method of proliferating / activating cells of the present application comprises steps of, during the cell culture, supplementing a plant lectin (such as concanavalin A) and a growth factor having interleukin-2-like activity to the culture medium. Accordingly, the present method can proliferate / activate, on a preferential basis, a-type T cells associated with cell-mediated immunity for cancers, immunodeficiency diseases and infectious diseases.
Owner:ARIGEN PHARMA INC
Application of astraisoflavan-7-O-beta-D-glucoside in preparation of immunity inhibitors and vasodilators
InactiveCN104107182AHas inhibitory effectHas a vasodilation effectOrganic active ingredientsImmunological disordersVascular dilatationMedicine
Through the researches and experiments on astraisoflavan-7-O-beta-D-glucoside, it has been found for the first time that astraisoflavan-7-O-beta-D-glucoside can prominently inhibit T lymphocyte proliferation induced by concanavalin A (Con A) and rat isolated arterial ring contracts induced by potassium chloride (KCl), has immunity inhibiting and vasodilative effects, and is advantageously used to prepare immunity inhibitors and vasodilators.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Non-enzymatic electrochemical bio-sensing method facilitating glucose detection
ActiveCN107422009AEasy to detectAccurate measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesConsScreen printed electrode
The invention discloses a non-enzymatic electrochemical bio-sensing method facilitating glucose detection. A silk-screen printing electrode is modified with graphene, phenyl-glucan is subjected to pai-pai stacking and assembled on the surface of the silk-screen printing electrode, a sensor is prepared, a prepared Con A (concanavalin A) functionalized Au NP (gold nanoparticle) probe is directly mixed with a glucose solution to be used for competitive recognition of the sensor surface to capture an Au NP marker, the Au NP on the electrode surface is detected and specifically recognized through electrochemical stripping analysis for signal transduction of the sensor, and thus, the content of glucan in the glucan solution is detected. The method is convenient to operate, has the advantages of high sensitivity, wide linear range, low cost and the like and overcomes the defects that traditional enzymatic bioelectrochemical sensor preparation methods are complex, the analysis cost is higher and solutions are interfered by signals of electroactive substances in actual samples and the like.
Owner:HUBEI NORMAL UNIV
Application of calycosin-7-glucoside in preparation of immunity inhibitors and anti-inflammatory drugs
Through the experiments and researches on calycosin-7-glucoside, it has been found for the first time that calycosin-7-glucoside can prominently inhibit the T lymphocyte proliferation induced by concanavalin A (Con A) and reduce the macrophage toxicity induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS), has immunity inhibiting and anti-inflammatory effects, and is advantageously used to prepare immunity inhibitors and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Starch based segmented intestine targeting specific adhesion material, preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN101366946AGood biocompatibilityImprove colon targetingPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemDiseaseIntestinal structure
The invention discloses a starch based colon idiosyncratic adhesion material for coupling concanavalin A and a method for preparing the same. The anti-digestion starch undergoes the activating treatment by glutaraldehyde, couples with the concanavalin A and is subjected to centrifuge washing by phosphate buffer and inactivation by ethanolamine to obtain the starch based colon idiosyncratic adhesion material. The invention also discloses application of the starch based colon targeting idiosyncratic adhesion material in preparing biomacromolecule medicines of polypeptide protein or medicines of treating colon diseases. For the first time, the invention utilizes the characteristics of the idiosyncratic adsorption between the concanavalin A and the colon epithelial cell, successfully prepares the carrier material of the starch based colon idiosyncratic adhesion material by coupling the concanavalin A with the anti-digestion starch molecule by the glutaraldehyde and uses the starch based colon idiosyncratic adhesion material as an oral taking colon targeting control-release carrier material, so that starch based colon idiosyncratic adhesion material and the method have the characteristics of cell adsorption, enzymolysis triggering targeting, good biocompatibility, safety and non-toxin, good targeting slow-release effect, and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Application of astrapterocarpan in preparation of immunity inhibitor
InactiveCN104107183AHas inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsImmunological disordersImmunosuppressive effectConcanavalin A
Through the experiments and researches on astrapterocarpan, it has been found for the first time that astrapterocarpan can prominently inhibit the T lymphocyte proliferation induced by concanavalin A (Con A), has an immunity inhibiting effect, and thus can be advantageously used to prepare immunity inhibiting drug.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
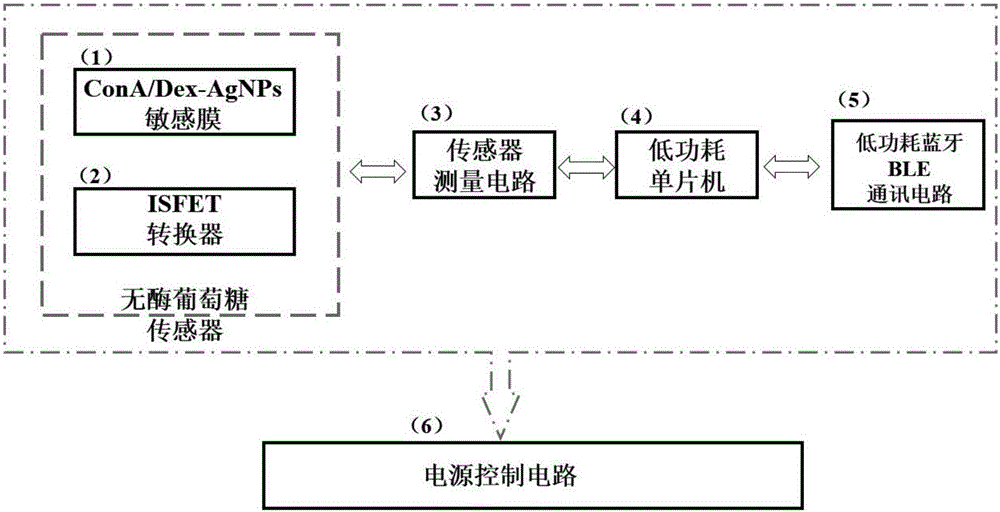
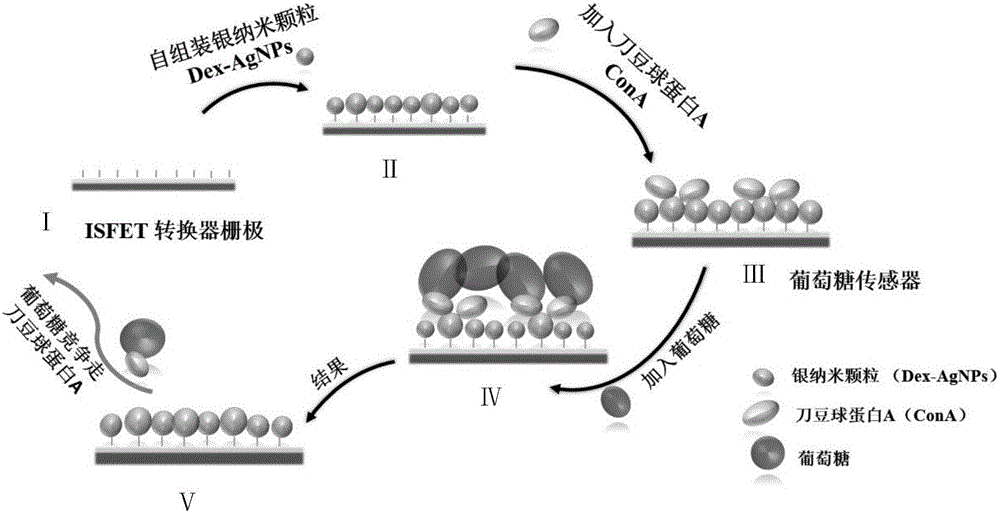
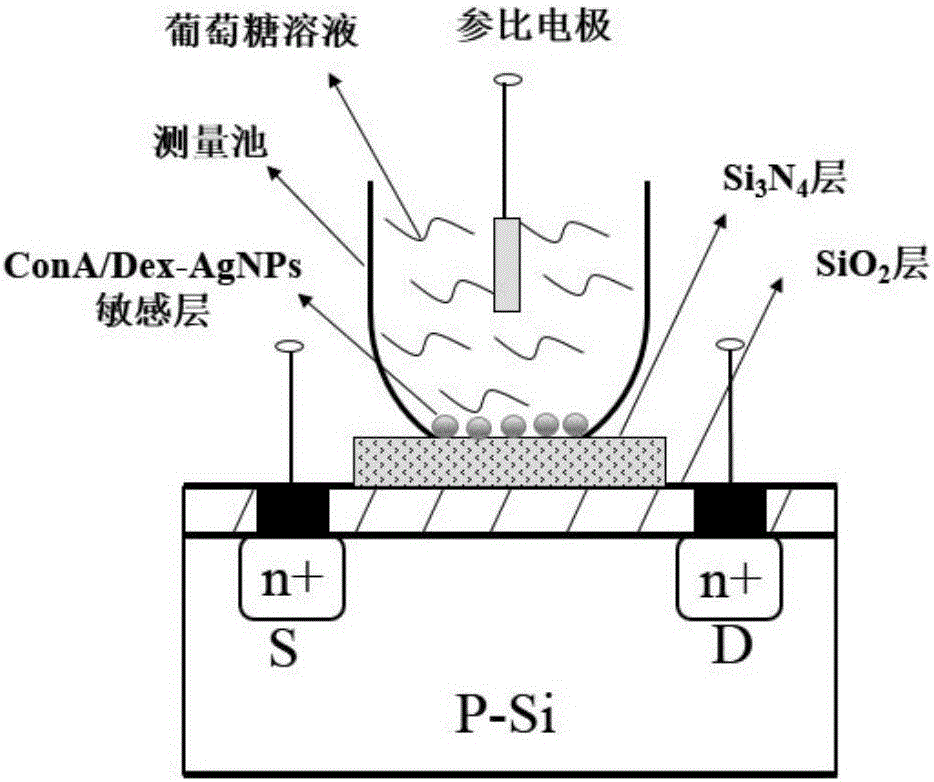
Glucose mobile detection device with low power consumption
The invention provides a glucose mobile detection device with low power consumption. The device comprises a ConA / Dex-AgNPs (concanavalin A / dextran-silver nanoparticles) sensitive membrane, an ISFET (insulator semiconductor field effect transistors) converter, a sensor measuring circuit, a low power consumption singlechip, a low power consumption BLE (Bluetooth low energy) communication circuit and a power supply control circuit, wherein ConA / Dex-AgNPs sensitive materials are combined with the ISFET converter; biochemical sensor detection of glucose is achieved based on the competitive relation among glucose, ConA and glucose; sensing signals are extracted, processed and packaged by the sensor measuring circuit and the low power consumption singlechip; the low power consumption BLE communication circuit carries out real-time communication with mobile equipment; the power supply control circuit is used for supplying power to each module and carrying out low power consumption control. The device has the advantages of low power consumption, small size, rapidness in detection, capability of being produced on a large scale by utilizing the integrated circuit technology, small sample solution quantity demand, capability of real-time communication with mobile phones, and the like.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Pharmaceutical composition for inducing damages of endothelial cells and treating tumor and method for treating tumor by using the same
InactiveUS20110144031A1Induced damageGood effectPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesAbnormal tissue growthEndothelial NOS
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for inducing damages of endothelial cells, a pharmaceutical composition for treating a tumor, and a method for treating a tumor by using the same. In addition, the pharmaceutical compositions for inducing damages of endothelial cells comprises: an effective amount of Concanavalin A (Con A).
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Method for preparing antibiotic peptide and transfer factor by in vitro culture and induction of lymphocyte
The invention discloses a method to prepare antibacterial peptide and transfer factor by culturing and inducing lymphocyte in vitro, which comprises: preparing and subculturing lymphocyte single layer by spleen or peripheral blood; using canavaline A to induce and culture the single layer, and obtaining the product. This invention needs just supersonic wave and frost-thaw treatment without purification, can apply the product directly on animal for antibiosis and antiviral, needs not to slay lots of live pigs, has high yield with low cost, and can prevent the product bringing extraneous virus.
Owner:DALIAN SANYI ANIMAL MEDICINE CO LTD +2
Novel method for separation of Gram-negative pathogenic bacteria in sepsis
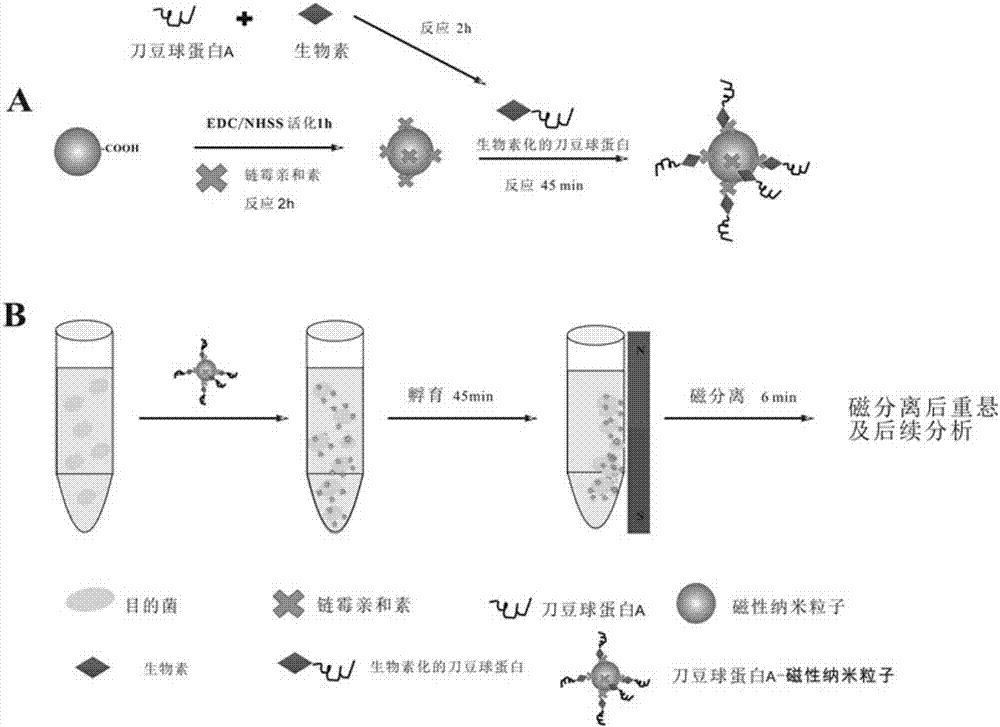
InactiveCN106916809ALow costQuality is easy to controlBacteriaMicroorganism separationBiotechnologyBiotin-streptavidin complex
The invention discloses separation of Gram-negative pathogenic bacteria. The method provides basis for subsequent research on the Gram-negative pathogenic bacteria and relates to the technical field of biology. The method includes the steps of: 1) conjugating magnetic nano-particles to streptavidin; 2) conjugating concanavalin A to long-chain biotin; 3) conjugating the biotinylated concanavalin A to the magnetic nano-particles coated with the streptavidin; 4) capturing the Gram-negative pathogenic bacteria in a sample solution by means of the streptavidin and long-chain biotin induced concanavalin A combined magnetic nano-particle composition; and 5) under effect of an external magnetic field, separating the captured Gram-negative pathogenic bacteria from the sample solution and performing re-suspension and the like. The Gram-negative pathogenic bacteria, captured through the magnetic separation, can be directly subjected to subsequent analysis. Compared with a conventional magnetic separation method for bacteria, the method can be used for magnetically separating the Gram-negative pathogenic bacteria from food substrates and blood. The method not only improves separation efficiency of the Gram-negative pathogenic bacteria in the sample solution but also reduces the cost.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Method for preparing glucose-responsive insulin-self-regulating-release carrier
InactiveCN103110956ASelf-regulating releaseRepeatablePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsCross-linkBiological materials
The invention relates to a method for preparing a glucose-responsive insulin-self-regulating-release microgel carrier, and belongs to the technical field of drug controlled release and biomaterials. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) dissolving glucose oxoethyl acrylate-modified chitosan CS-GEA into deionized water, and mixing dissolved liquid with activated Con A (Concanavalin A) liquid; (2) mixing cyclohexane with an emulsion stabilizer, namely tween 85, wherein the ratio of the volume of the cyclohexane in milliliter to the mass of the tween 85 in gram is (50-100):1; (3) dripping 1 part by volume of stirred mixed liquid obtained in the step (1) to 40-80 parts by volume of mixed liquid obtained in the step (2) so as to obtain dispersion liquid; and (4) dripping a cross-linking agent, namely genipin water liquid, to the dispersion liquid so as to obtain hardened microgel particles, standing after the reaction is completed, and carrying out centrifugation, water washing and drying on precipitates at a lower layer. The carrier prepared by the method has good glucose responsiveness and repeatable responsiveness, thereby being beneficial to the self-regulating release of insulin; and meanwhile, the method is simple and effective in Con A fixing, low in cost and convenient in implementation, thereby being beneficial to large-scale production.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Novel sugar-immobilized metal nanoparticle, method for measuring sugar-protein interaction using the same and method for recovering protein from sugar-protein interactant
ActiveUS20090240032A1Readily immobilize a sugar chainEasy to measureOrganic active ingredientsBiocideVisual observationSugar
It is intended to provide a stable novel sugar-immobilized metal nanoparticle capable of easily immobilizing a sugar chain, a method for measuring sugar-protein interaction easily and at a low cost using the same without labeling, and a method for simply recovering a protein from a sugar-protein interactant. A maltose-immobilized gold nanoparticle was obtained by binding a ligand complex, in which maltose and a linker compound had been bound to each other, to a gold nanoparticle. By adding this maltose-immobilized gold nanoparticle to a dilution series of concanavalin A, a sugar-protein interactant of maltose and ConA was formed, and red-purple color derived from a colloidal solution of maltose-immobilized gold nanoparticle disappeared. That is, sugar-protein interaction could be confirmed by visual observation without labeling.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +2
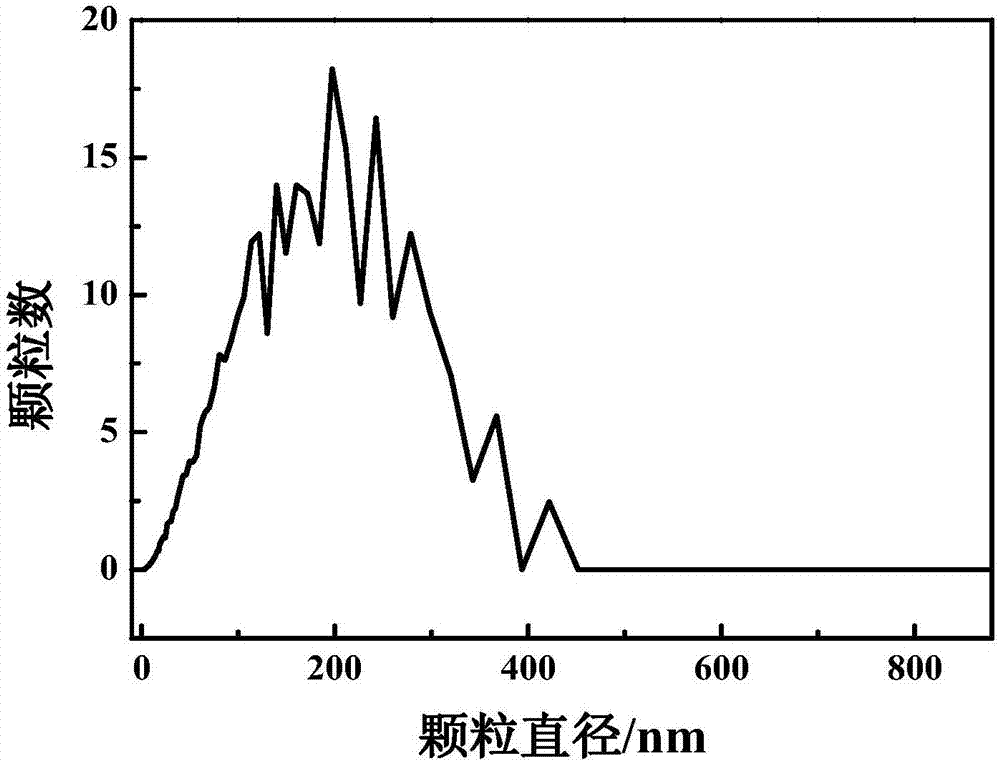
Insulin-loaded nanoparticles and application thereof
ActiveCN108721605AUniform sizeImprove thermal stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderNanoparticleGlucose lowering
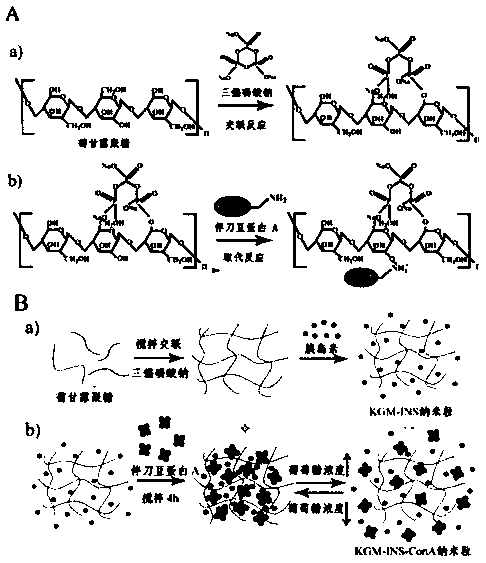
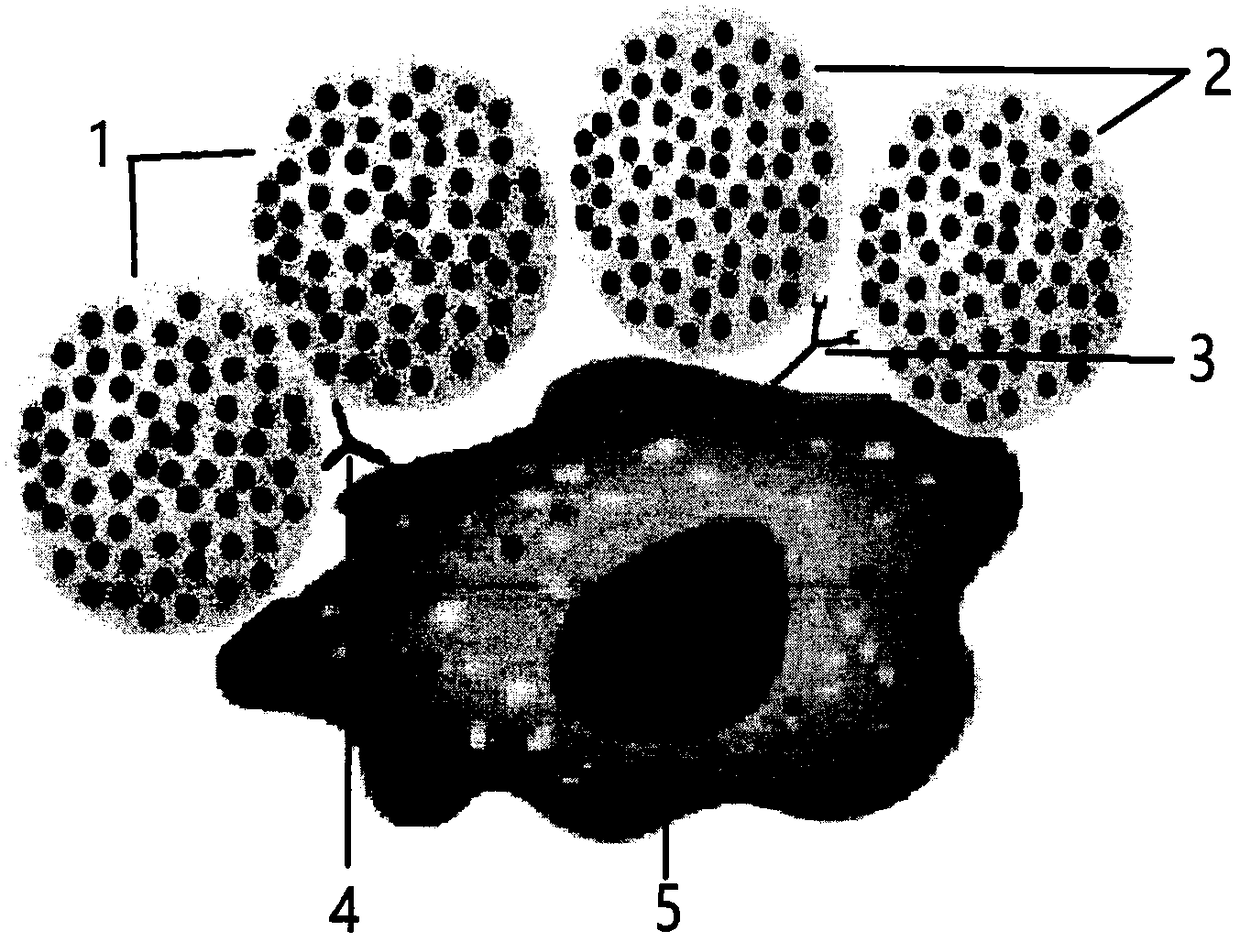
The invention discloses insulin-loaded nanoparticles. The insulin-loaded nanoparticles are obtained by carrying out reversible crosslinking reaction on glucomannan, concanavalin A and a crosslinking agent. The invention develops glucose induction type insulin oral nanoparticles prepared from a natural polymer; a glucose induction type insulin oral transportation system can be constructed by utilizing the nanoparticles; the system has basic properties of a transportation system which has glucose induction performance, can control blood glucose and has low toxin; the insulin-loaded nanoparticleshave a relatively good effect in bodies and have a slow glucose lowering effect for relatively long time; the blood glucose control curative effect of the glucose induction type insulin oral transportation system is improved, and the insulin-loaded nanoparticles have relatively great application potential in the fields of development of diabetes mellitus treatment, natural polymer medical functions and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing AIDS immunoadsorption therapeutic cell line
The invention discloses a method for preparing an AIDS immunoadsorption therapeutic cell line in the biomedical field. The method is characterized in that CD4+T cells and macrophages are sorted by animmunomagnetic bead method and are placed in a pre-fusion agent containing PHA, concanavalin A, IFN-gamma, SP2 / 0-IgG and CD4-IgG with myeloma cells (SP2 / 0), under combined action of PHA-activated T cells, concanavalin A for change of cell membrane solubility and an IFN-gamma activated macrophage IgGFc receptor, the IgGFab segment of CD4-IgG is bonded to CD4+T cells having CD4 epitope, the IgGFc segment is bonded to macrophages with IgGFc receptors, the IgGFab segment of SP2 / 0-IgG is bonded to the SP2 / 0 and the IgGFc segment is bonded to macrophages with IgGFc receptors so that a CD4+T cell-CD4-IgG-macrophage-IgG-SP2 / 0 conjugate is formed, three types of cells are fused under the action of a fusion agent, and the fused cells are cultured by a cell fusion selection medium (HAT) so that the AIDS immunoadsorption therapeutic cell line with effects of long-term passage, production of cytokines and HIV endocytosis is acquired.
Owner:翁炳焕
Liver protecting drug
The invention develops an anti-HBV drug, i.e., a hepatitis B granule, according to folk experience about treatment of hepatitis and the theory of traditional Chinese medicine. The hepatitis B granule is formed by combination of a plurality of Chinese herbal medicines consisting of glossy privet fruit, eclipta herba, spatholobus stem, Chinese thorowax root, red sage root, canton love-pea vine, Japanese climbing fern spore, common selfheal fruit-spike, virgate wormwood herb, European verbena herb and the like. The objective of the invention is to develop a novel natural medicinal preparation for treatment of hepatitis B. According to long-term considerable research of the inventor, the hepatitis B granule and drug serum thereof can inhibit propagation of hepatic HSC-T6 and collagen synthesis and exert obvious protection effects on acute chemical liver injury of mice caused by carbon tetrachloride, paracetamol, D-galactosamine and the like, immunological liver injury caused by concanavalin A and chronic hepatic fibrosis of rats. The hepatitis B granule provided by the invention may possibly become a novel liver protecting drug for patients with acute liver injury and chronic hepatic fibrosis. According to the invention, Guangxi characteristic crude drug resources are dug and systemized, and the novel natural medicinal preparation is provided for treatment of acute liver injury and chronic hepatic fibrosis.
Owner:GUANGXI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com