Cardiovascular stent coating material with endothelial cell selectivity and preparation and application method thereof
A technology of endothelial cells and coating materials, applied in coating, medical science, surgery, etc., can solve the problems of destroying the healing of endothelial layer, increasing the death of late thrombus, and achieving the effects of wide application range, growth inhibition, and good reactivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
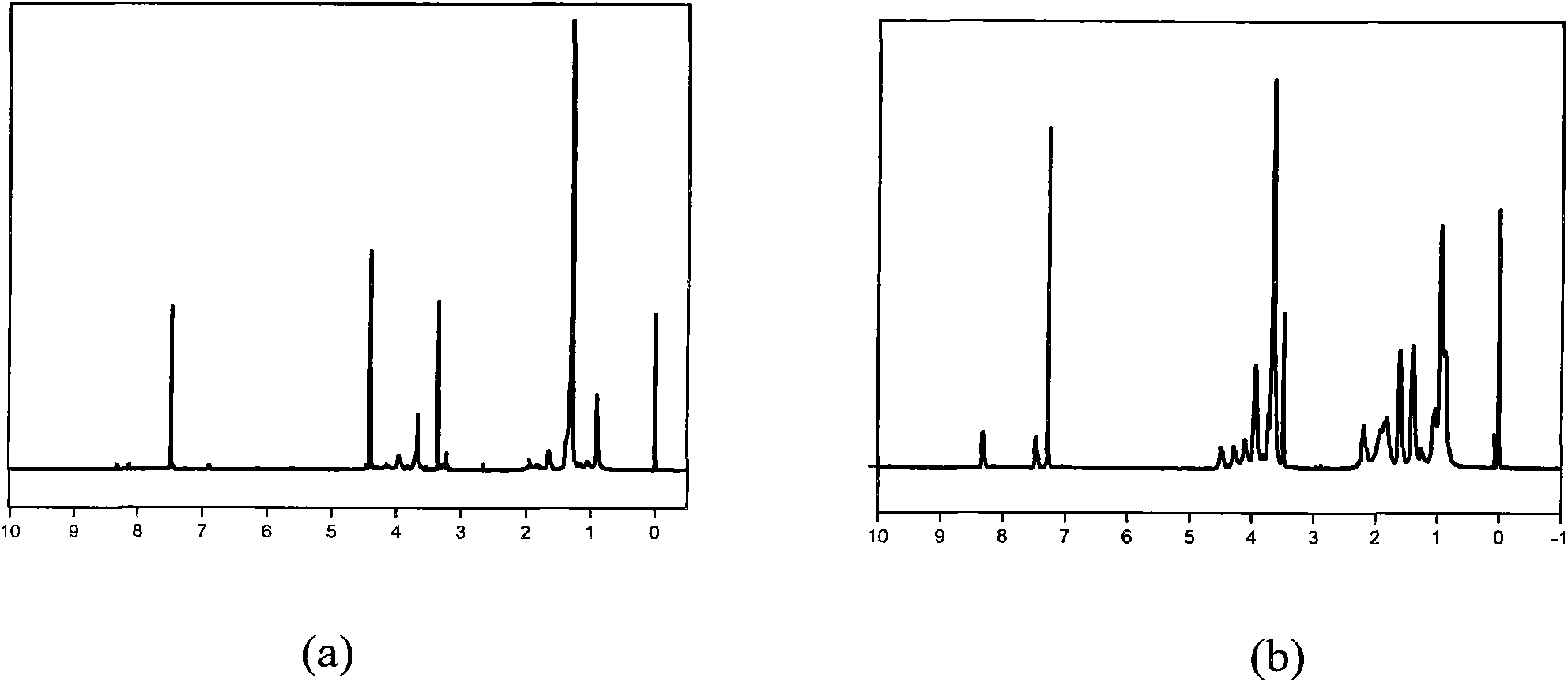
[0040] (1) Synthetic terpolymer
[0041] In a 50 mL polymerization tube, add 0.8 g MPC, 2.5 g SMA, 1.0 g MEONP (n=6) and 0.086 g initiator AIBN, and dissolve them with 30 ml ethanol. Freeze with liquid nitrogen until solid, vacuumize for 10 minutes, and then blow in argon; repeat the above steps three times to remove oxygen. Seal the tube with an alcohol blowtorch, put it in a 60°C oil bath and stir for 24 hours. After the reaction was completed, the polymerization tube was broken open, the polymerization solution was transferred to a 100ml single-necked flask, the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation under reduced pressure, and then precipitated with ice methanol. A light yellow solid was obtained by suction filtration, which was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran again, and the steps of rotary evaporation, precipitation and suction filtration were repeated three times. Finally, a light yellow solid was obtained, which was dried in a vacuum oven. NMR results confirmed that ...
Embodiment 2
[0055] (1) Synthetic terpolymer:
[0056] In a 50 mL polymerization tube, 0.6 g of MPC, 0.8 ml of BMA, 1.8 g of MEONP (n=10) and 0.067 g of initiator AIBN were added and dissolved in 10 ml of tetrahydrofuran. Freeze with liquid nitrogen until it is solid, vacuumize for 30 minutes, and then blow in nitrogen; repeat the above steps three times to remove oxygen. Seal the tube with an alcohol blowtorch, put it in a 90°C oil bath and stir for 48 hours. After the reaction was completed, the polymerization tube was broken open, the polymerization solution was transferred to a 100ml single-necked flask, the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation under reduced pressure, and then precipitated with ice methanol. A light yellow solid was obtained by suction filtration, which was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran again, and the steps of rotary evaporation, precipitation and suction filtration were repeated three times. Finally, a light yellow solid was obtained, which was dried in a vacuum...
Embodiment 3
[0070] (1) Synthetic terpolymer:
[0071] In a 50 mL polymerization tube, add 0.72 g PEGMA (n=6), 1.5 ml BMA, 1.2 g MEONP (n=1) and 0.05 g initiator AIBN, and dissolve with 50 ml isopropanol. Freeze with liquid nitrogen until solid, vacuumize for 30 minutes, and then blow in argon; repeat the above steps three times to remove oxygen. Seal the tube with an alcohol blowtorch, put it in a 65°C oil bath and stir for 20 hours. After the reaction was completed, the polymerization tube was broken open, the polymerization solution was transferred to a 100ml single-necked flask, the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation under reduced pressure, and then precipitated with ice methanol. A light yellow solid was obtained by suction filtration, which was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran again, and the steps of rotary evaporation, precipitation and suction filtration were repeated twice. Finally, a light yellow solid was obtained, which was dried in a vacuum oven. NMR results confirmed th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com