Method for fixing biological macro molecule in common pattern on inorganic silicone material surface
A biomacromolecule and co-patterning technology, which is applied in the field of preparing templates for selective adhesion or orientation induction of cells, can solve the problems of difficulty in forming complementary patterns, easy contamination, and low pattern contrast, and achieve high contrast and firmness. Good controllability and repeatability, simple process effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
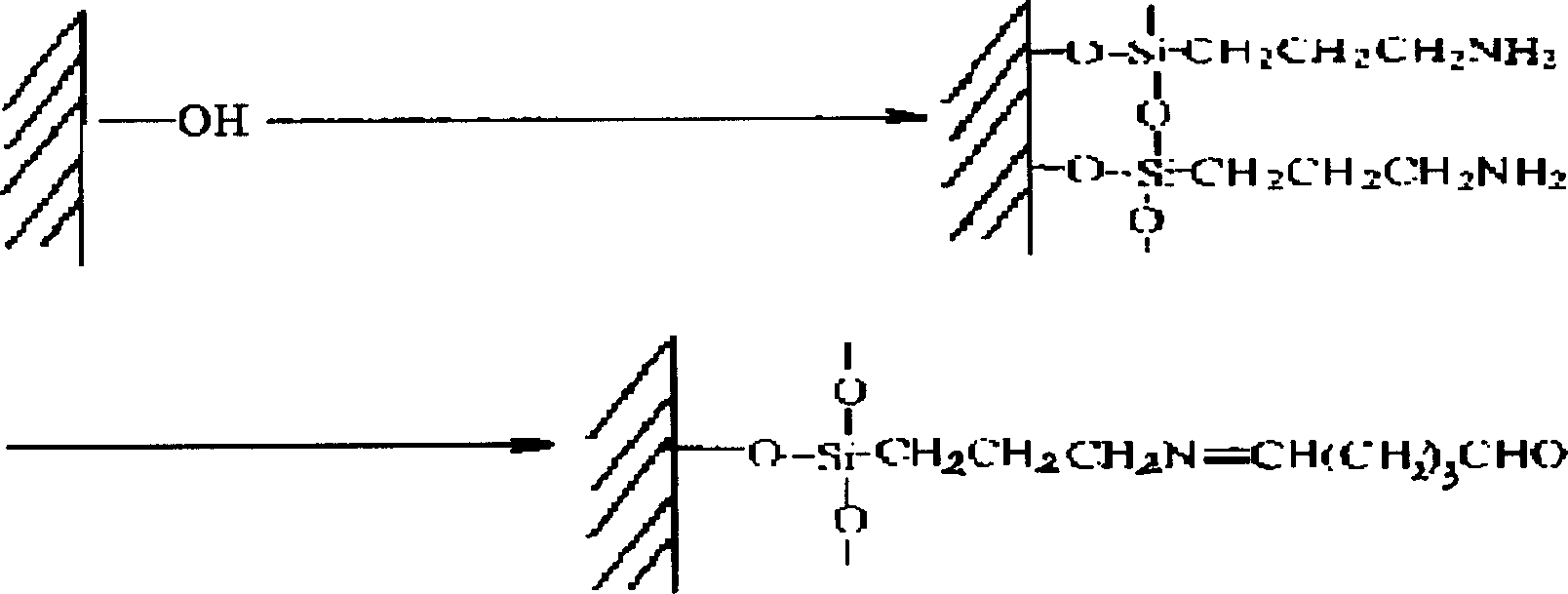
[0025] Preparation of PDMS stamps with microwells on the surface: first prepare an original bottom mold with conventional "photolithography" technology, that is, on a clean 3×3cm 2 The surface of the glass slide was spin-coated with BP218 UV positive photoresist at a speed of 2000 rpm, and then placed in an oven at 90°C for 30 minutes, and then exposed to a 1000-watt UV lamp and a photomask for 150 seconds. , and then developed in 2% NaOH solution for 45 seconds, pay attention to the uniformity of development. Because the photomask used contains the through holes of the microarray, the surface of the prepared base mold contains corresponding microwells of the microarray. On the surface of the original bottom mold, PDMS prepolymer was poured, and the prepolymer had been added with a cross-linking agent at a mass ratio of 10:1. After cross-linking and curing in an oven at 60°C for 12 hours, the positive-phase PDMS stamp was prepared, and the arrayed protruding pillars of the co...
example 2
[0029] Other conditions are the same as Example 1, but when preparing the PDMS stamp, the photomask used contains the blind hole of the microarray, thus finally obtained the PDMS reverse phase stamp containing the microwell on the surface ( figure 2 b). First use this stamp to micro-contact print albumin, and then drop chitosan solution to react to obtain albumin / chitosan co-pattern. CLSM observation shows that the dispersed chitosan pattern (dark color) is strong and fuzzy, and the continuous albumin The pattern (light color) is also not clear ( Figure 5 ), indicating that this co-patterning sequence is inappropriate.
example 3
[0031] Other conditions are the same as example 1, but the aldylated glass slide is replaced with only H 2 SO 4 :H 2 o 2 (7:3 V / V) treated blank slides (no amination and aldylation). Before sonication, a clear chitosan dispersion pattern and a layer of albumin can also be seen under the microscope, which is the result of the adsorption of biological macromolecules on the slide surface. After 10 minutes of sonication, the pattern became quite dim, and it was observed by CLSM that the fluorescence intensity of the albumin pattern on the surface of the blank slide ( Figure 4 b) only the fluorescence intensity of the albumin pattern on the surface of the formaldehyde slide slide in Example 1 ( Figure 4 One-third to one-fourth of a) proves that biomacromolecules are grafted on the surface of the glass slide after formylation through strong chemical bonds.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com