Truncated car peptides and methods and compositions using truncated car peptides
a car peptide and car peptide technology, applied in the field of molecular medicine, can solve the problems of not selective, tissue penetration is a serious limitation in the delivery of compositions to cells, and does not appear to substantially mitigate this problem, so as to reduce the burden of tumors, slow down the increase or reduction of tumors, and increase or decrease tumors. the effect of burden
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
A. Example 1
Targeting of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension with CAR Pepetides
[0491]1. Introduction
[0492]Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a disease of the pulmonary vasculature defined by an elevated pulmonary vascular resistance, which eventually leads to right heart failure and premature death. The cause of this disease remains unknown. PAH can be idiopathic (IPAH) or associated with other conditions or exposures (secondary pulmonary hypertension), including connective tissue diseases, HIV infection, portal hypertension, and anorexigenic drug ingestion.
[0493]Most cases of severe PAH, especially IPAH, are associated with aberrant proliferation of pulmonary arterial endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells, leading to narrowing or even obliteration of the precapillary pulmonary vessel lumen (Humbert, M. et al. Cellular and molecular pathobiology of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 43, 13S-24S (2004)). Thus, intimal and medial thickening of resistant arteries ...
example 2
B. Example 2
Truncated CAR Peptide Mediates Heparin Sulfate (HS)-Dependent Tumor Homing
[0526]Several CAR peptides have been used in the present studies (Table 1).
TABLE 1Nomenclature of CAR peptidesPeptide sequenceNameCAR SKN KDCCAR(SEQ ID NO: 147)CAR SKN KtCAR(SEQ ID NO: 4)AR SKN KARSKNK(SEQ ID NO: 18)KNKSRAC-CARSKNKtCAR dimer(SEQ ID NO: 4)
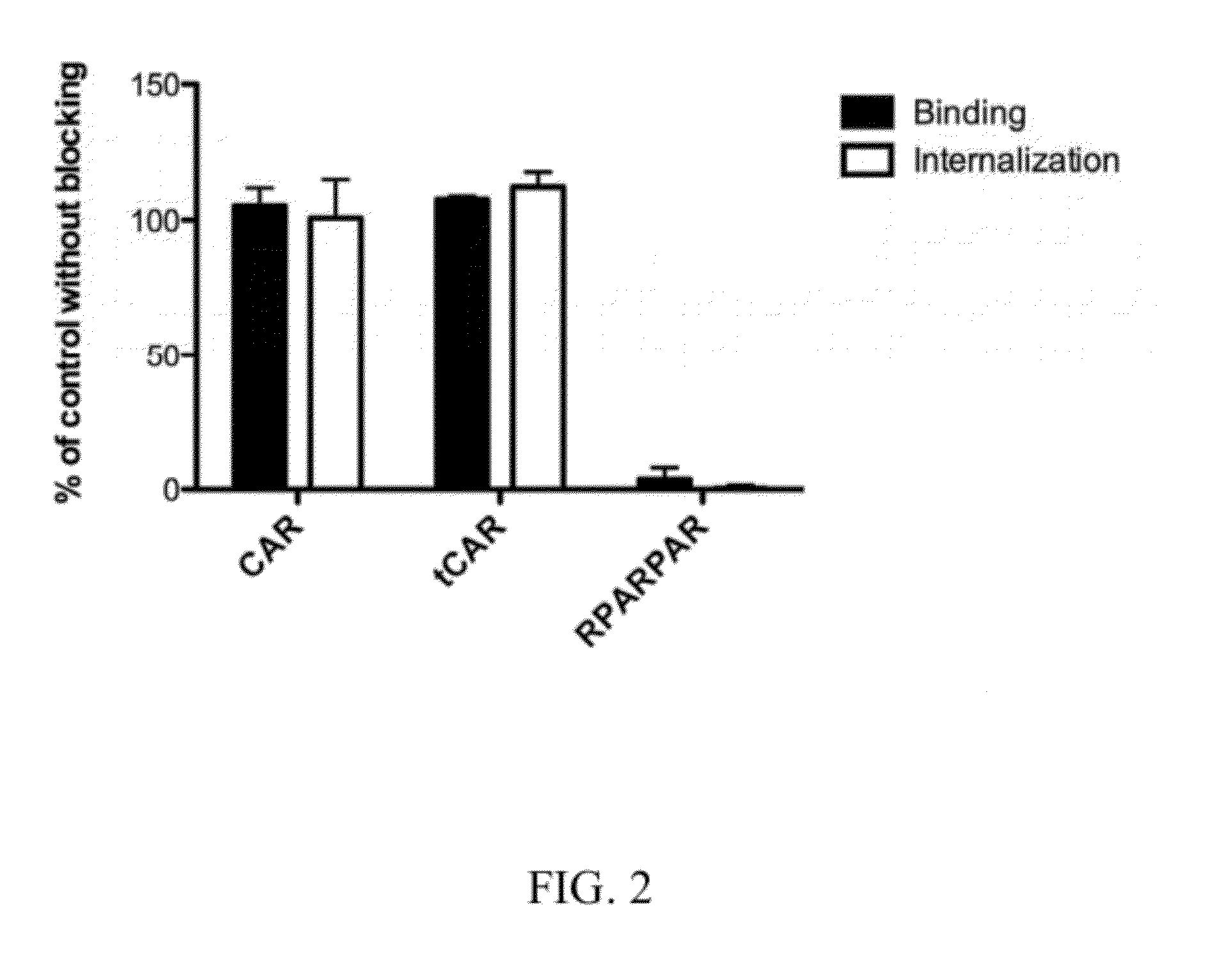
[0527]Multivalent complexes of the CendR peptide RPARPAR (SEQ ID NO:9) were used to block the neuropilin-1 binding site for peptides. RPARPAR inhibits the binding and internalization of RPARPAR phage (positive control) to cultured CHO-K cells, whereas the RPARPAR complexes have no effect on the binding and internalization of the CAR or tCAR phage (FIG. 2). These results show that the CAR and tCAR peptides do not use the CendR pathway (Teesalu et al., 2009) in their entry into cells.
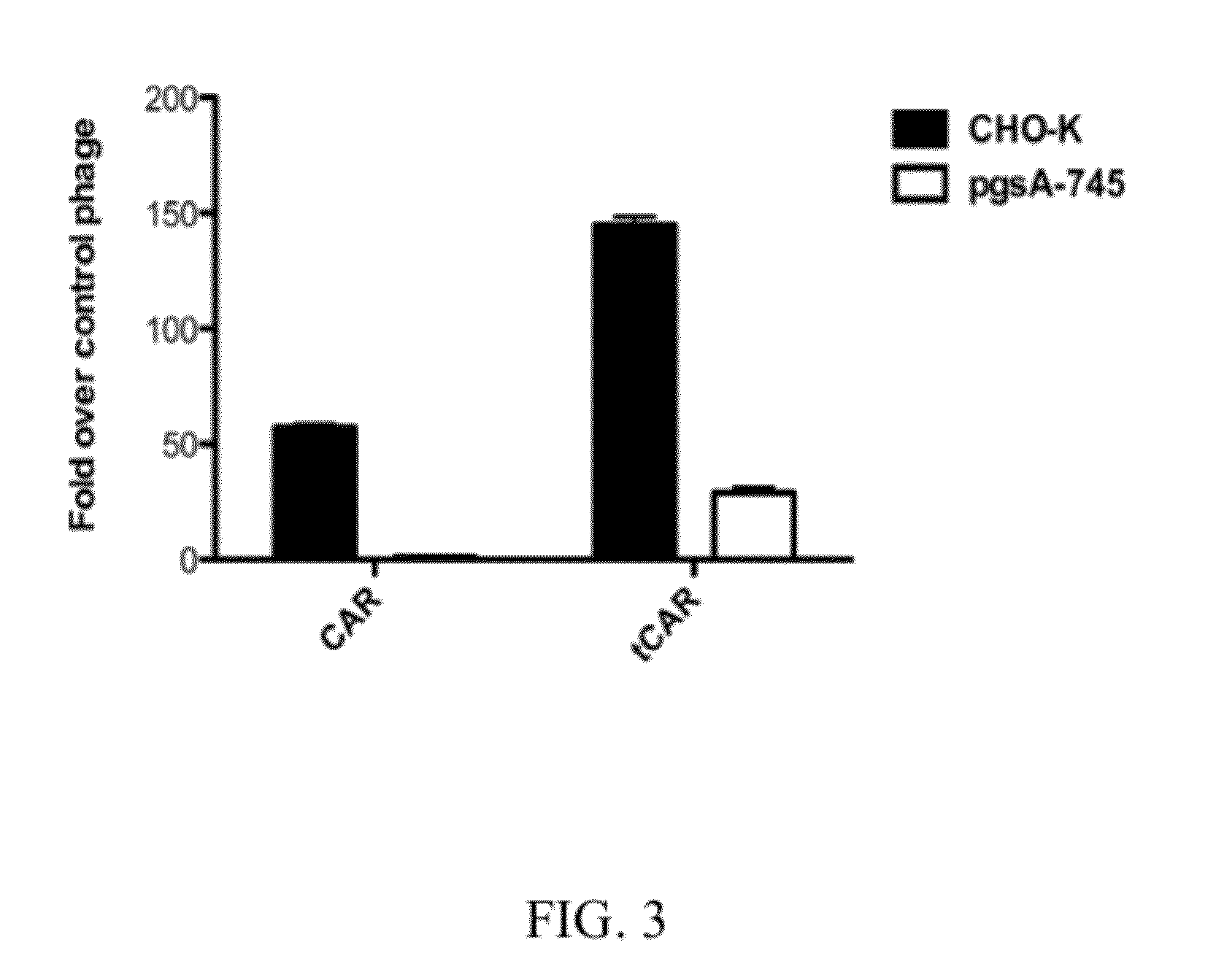
[0528]The phage internalize into CHO-K cells, whereas there is much less uptake into pgsA-745 mutant CHO-K cells, which are incapable of synthesizing glycosaminoglycans,...
example 3
C. Example 3
Monocrotaline Pulmonary Hypertension Model
[0536]1. Animal Model
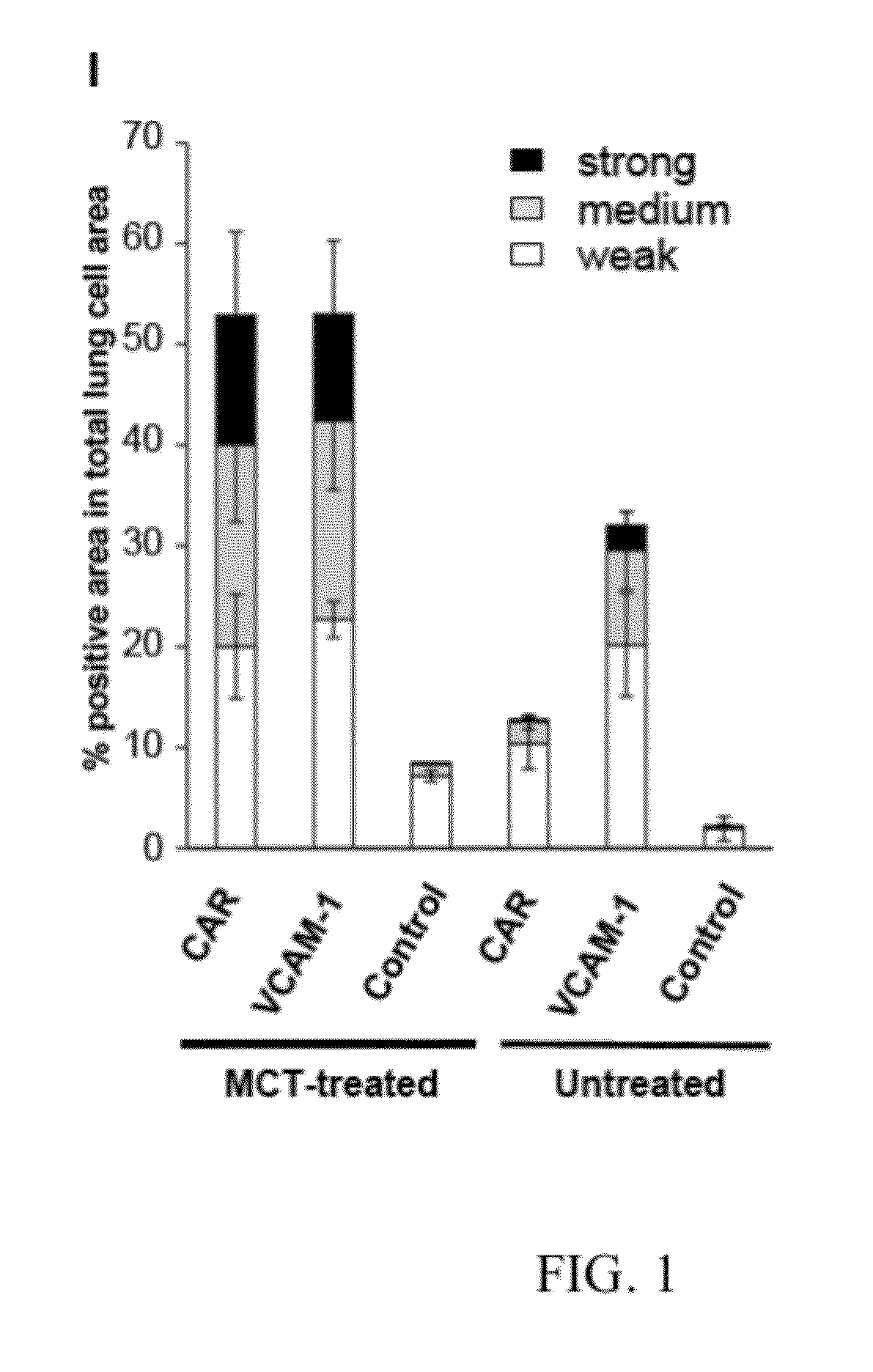
[0537]A rat model of monocrotaline (MCT)-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension was used for this study. Briefly, male Sprague-Dawley rats (150-200 g, Harlan Laboratories, IN) were administered with a single subcutaneous injection of monocrotaline at 60 mg / kg (Sigma-Aldrich, MO), while control rats administered 0.9% saline. Rats were randomly selected and studied for peptide distribution studies on 1, 3, 7, 14 or 21 days after the treatment of monocrotaline.
[0538]2. Peptides
[0539]The following peptides were labeled with 5-carboxyfluorescein (5FAM) and used for the lung targeting studies: CAR, 5FAM-CARSKNKDC; VCAM1, CVHSPNKKCGGSK-5FAM; Control, 5FAM-CGGGGGGGC. All peptides were synthesized by Anaspec (Anaspec Inc., CA). Peptides were resolved in PBS at the concentrations of 0.5 mg / mL.
[0540]3. Peptide Targeting Study
[0541]MCT-treated or untreated rats were injected with peptide solution at a dose of 3.3 mg / kg ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| swelling | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pulmonary pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com