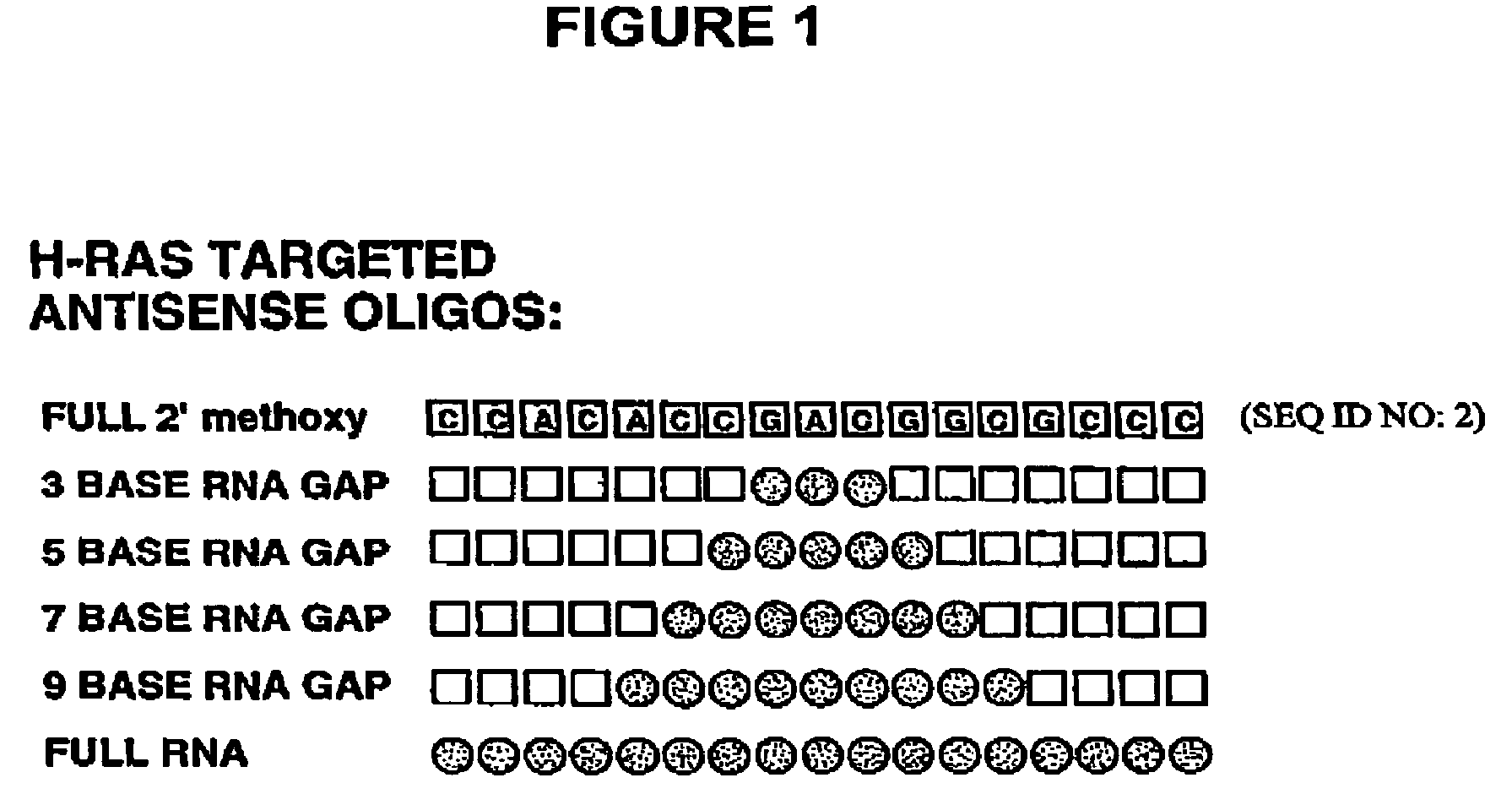
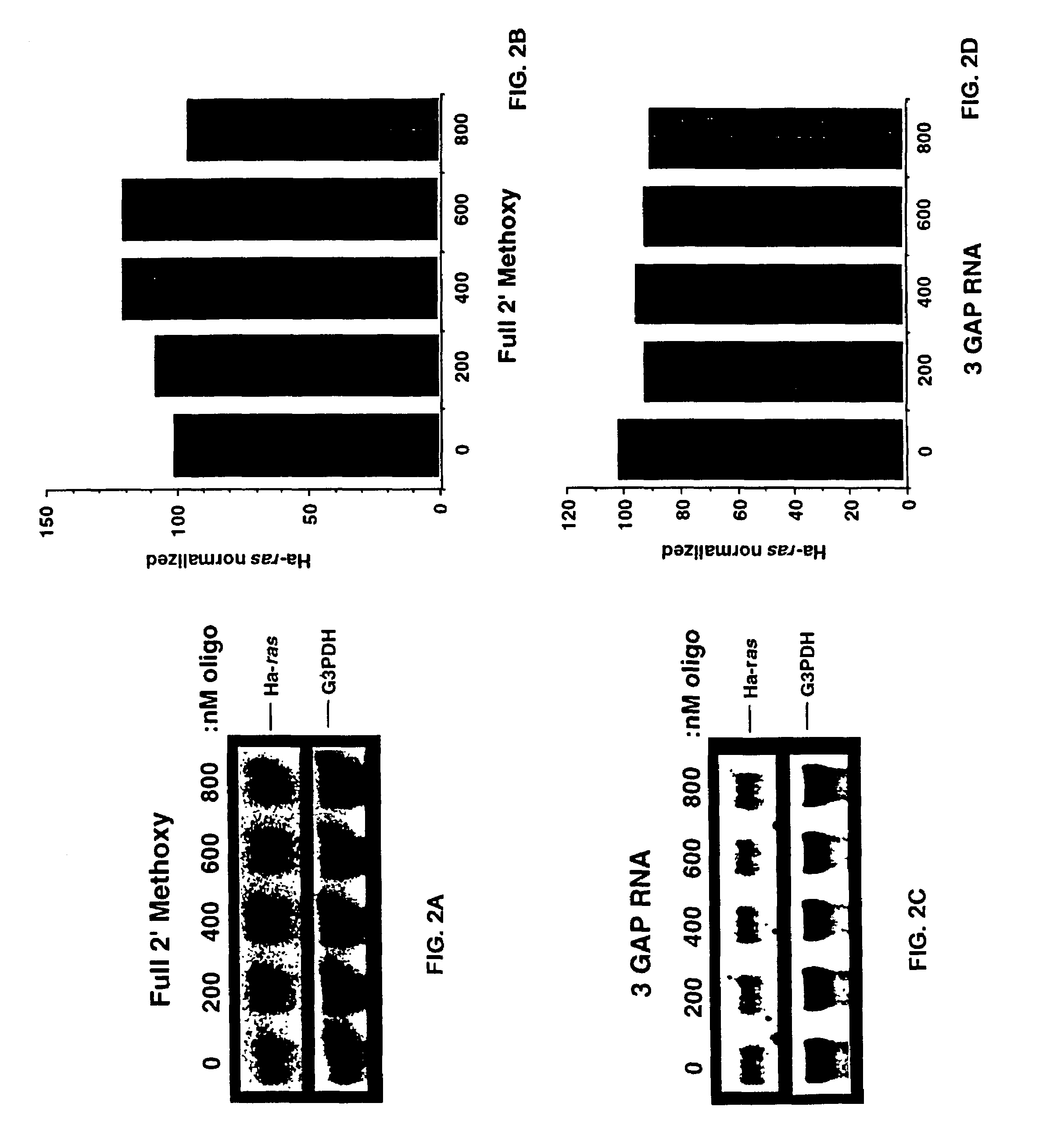
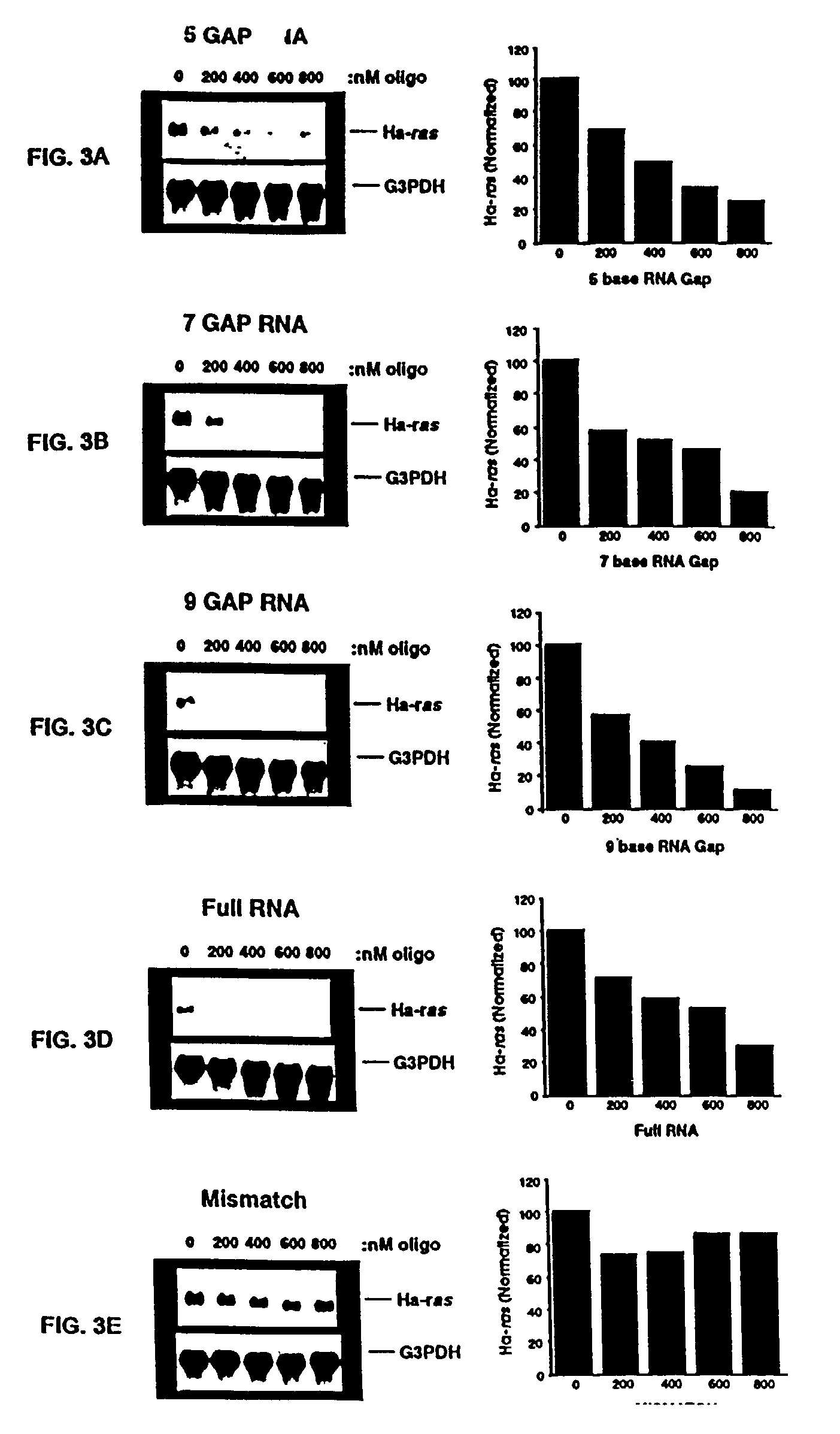
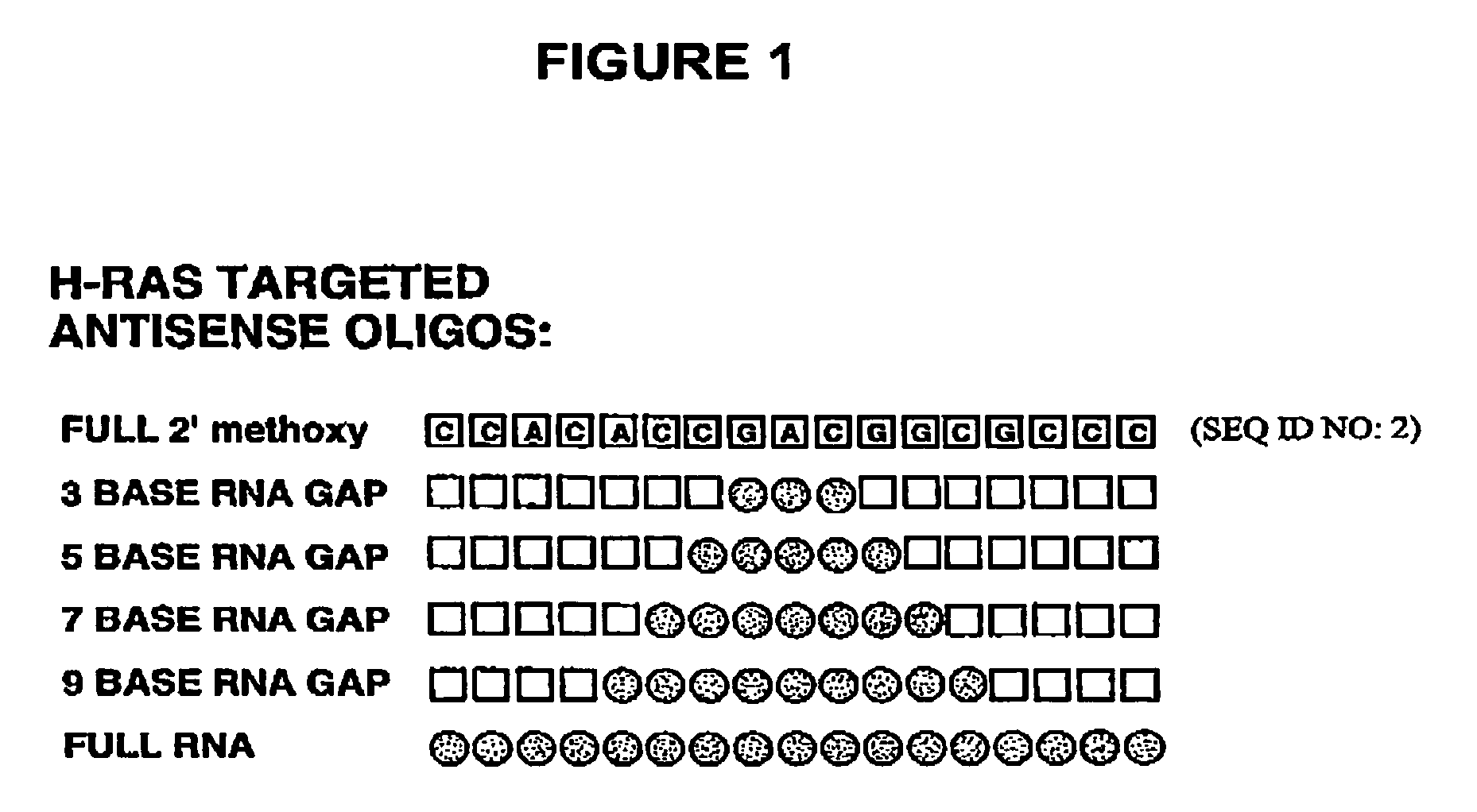
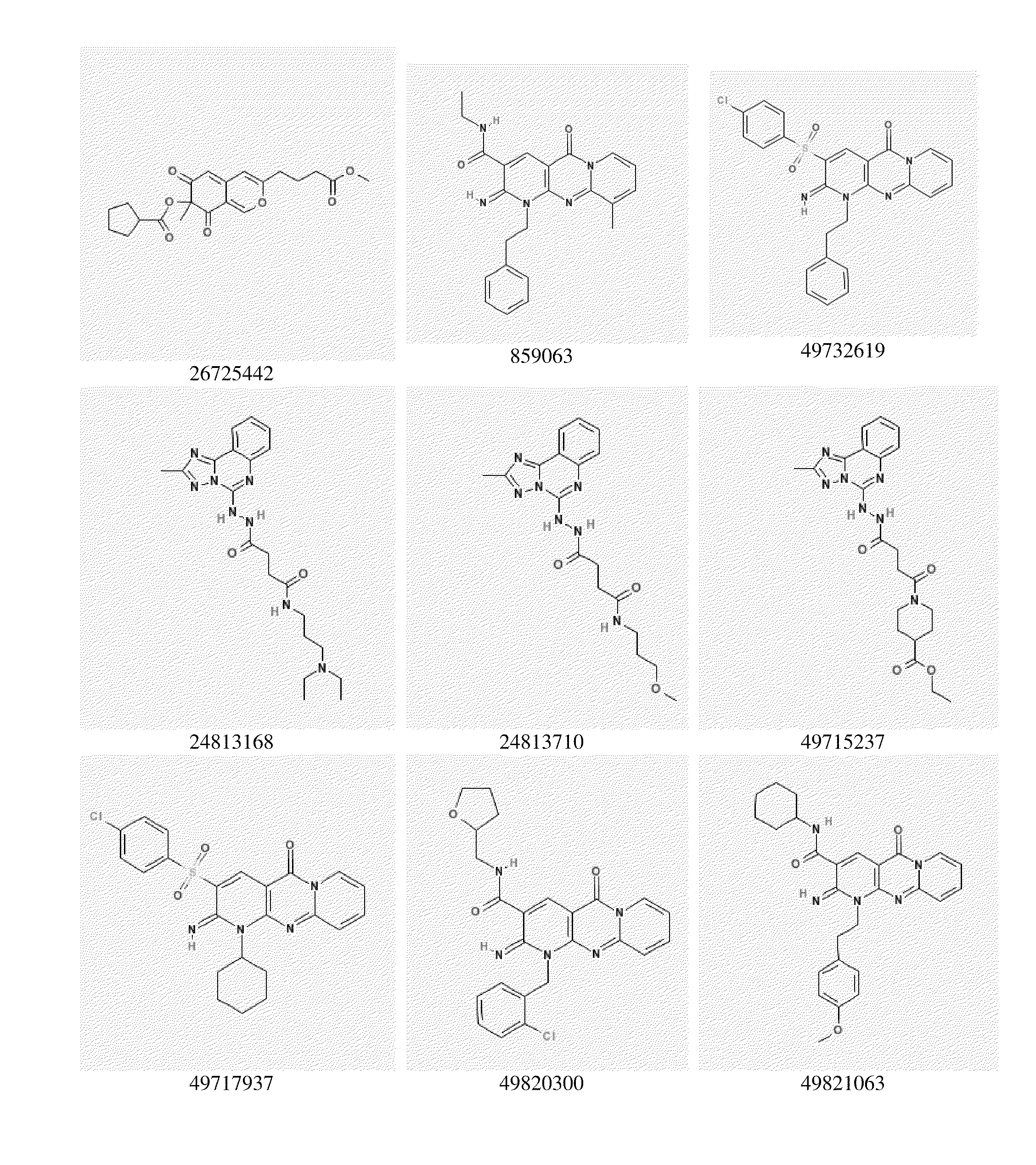
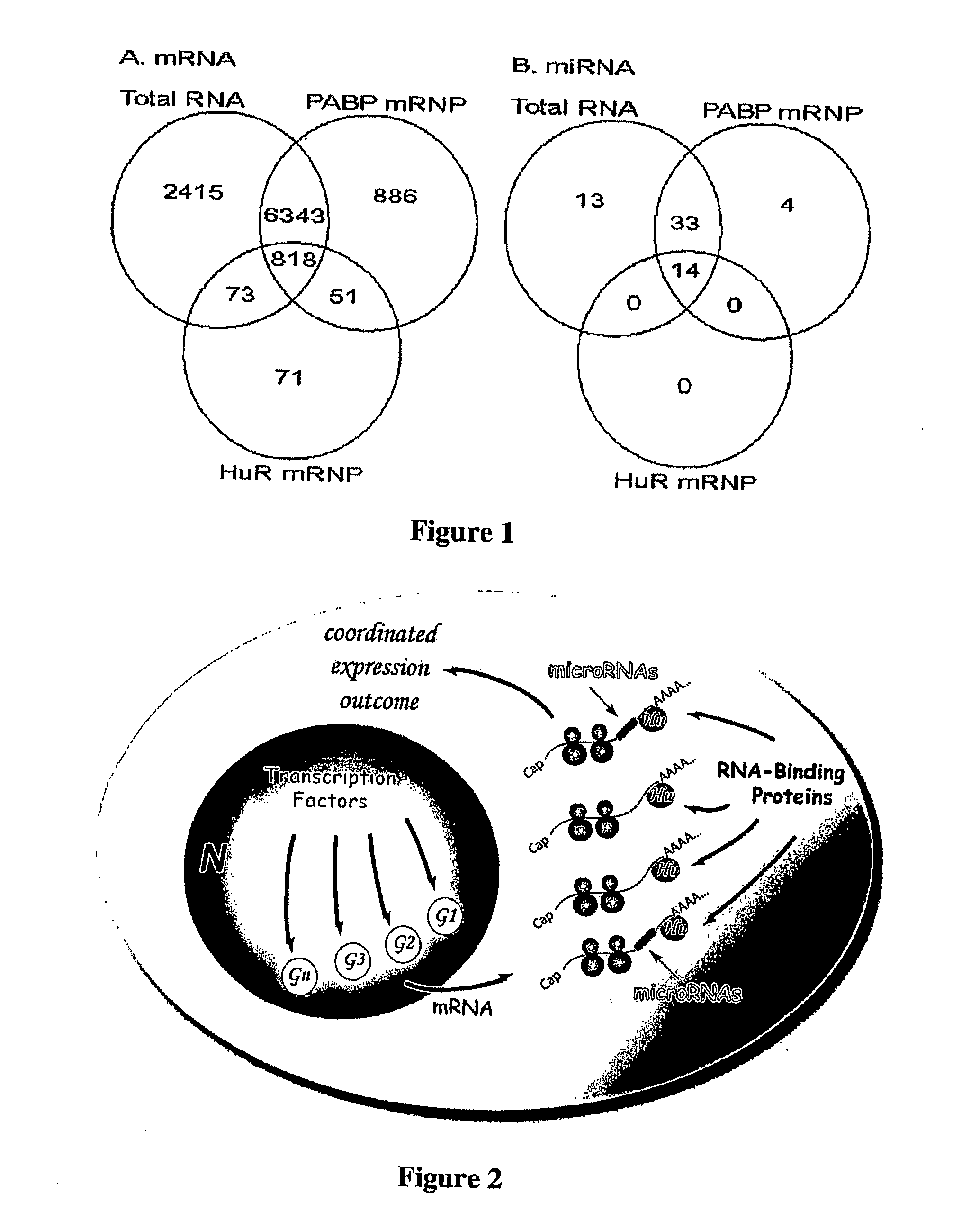
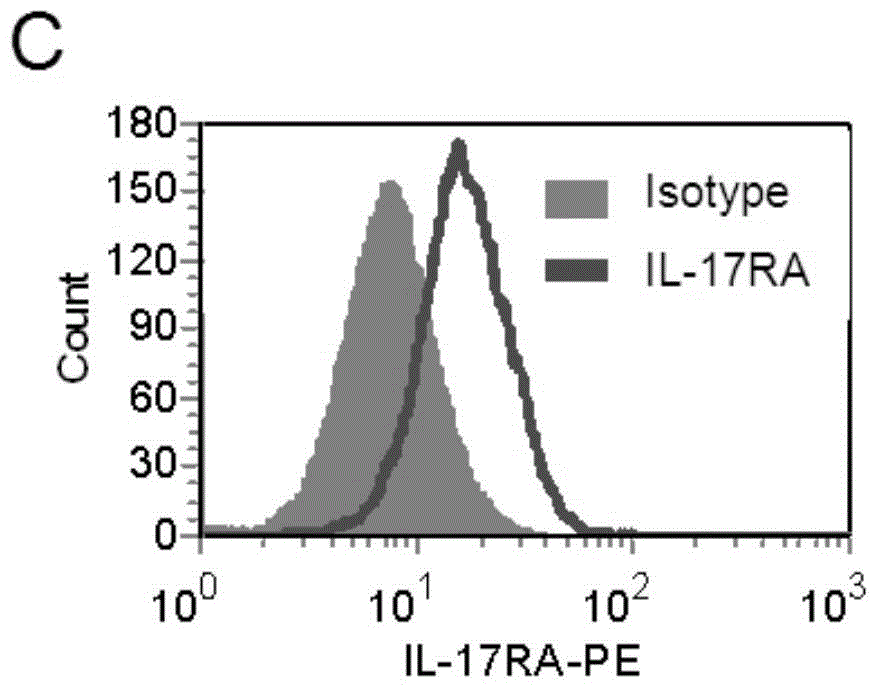
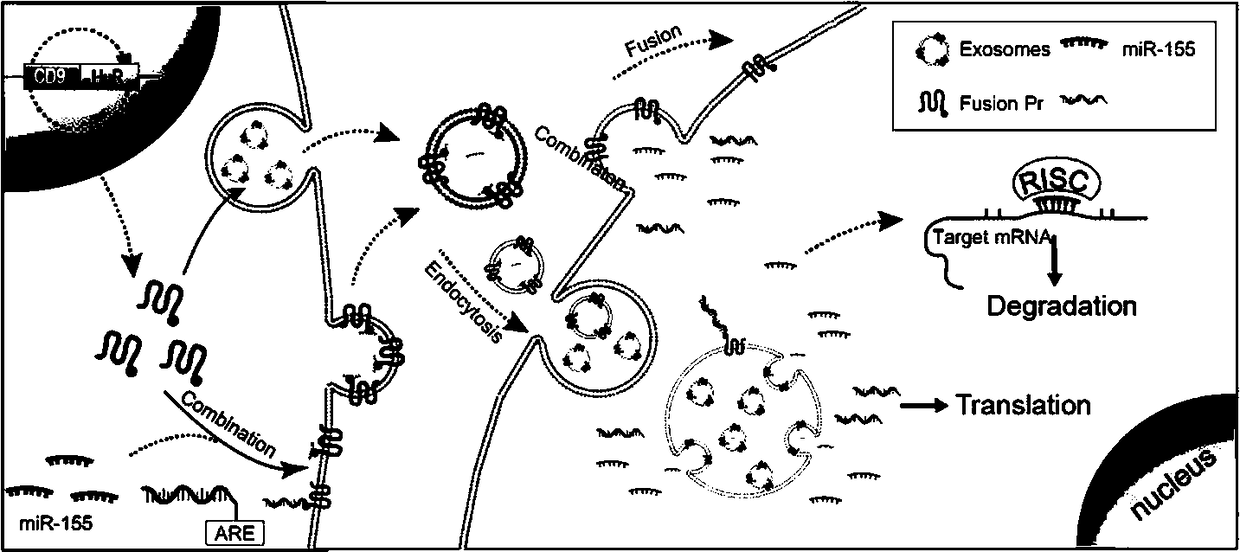
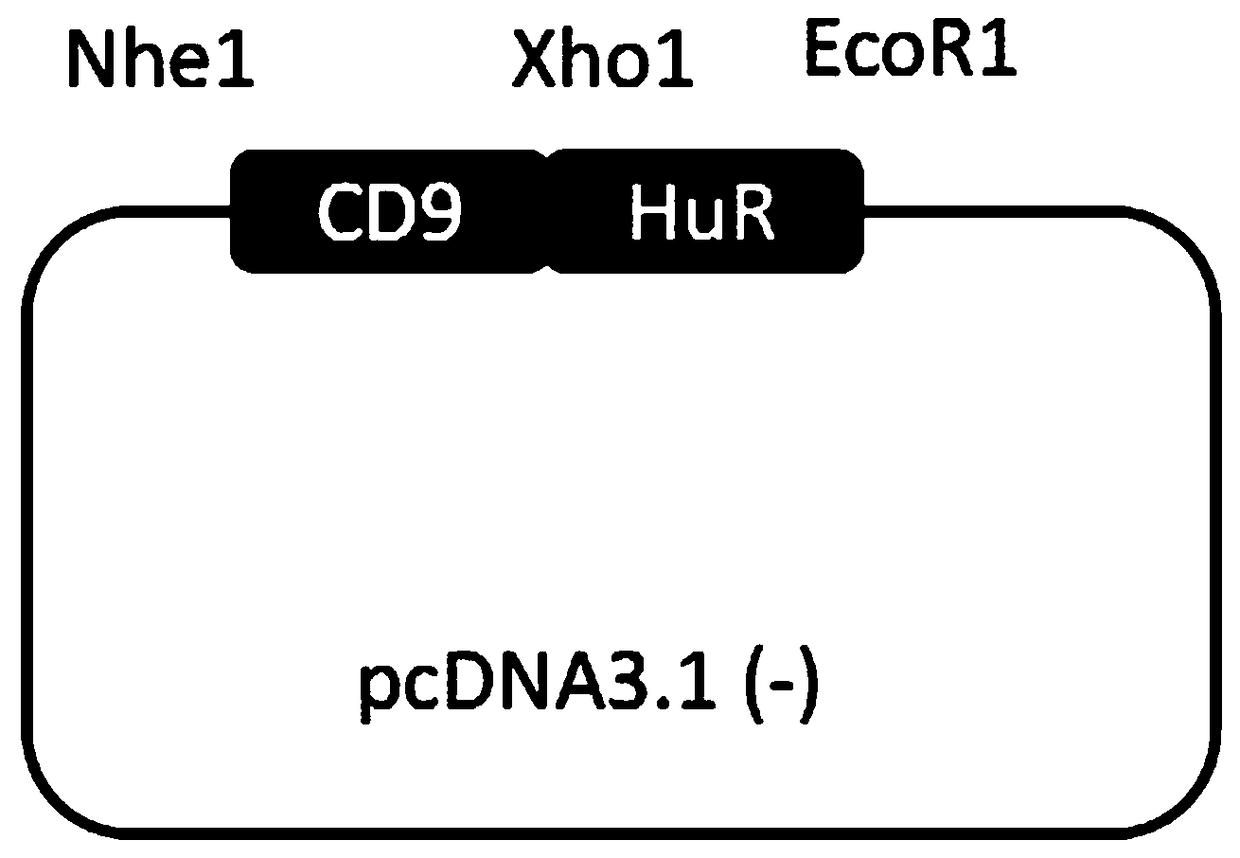
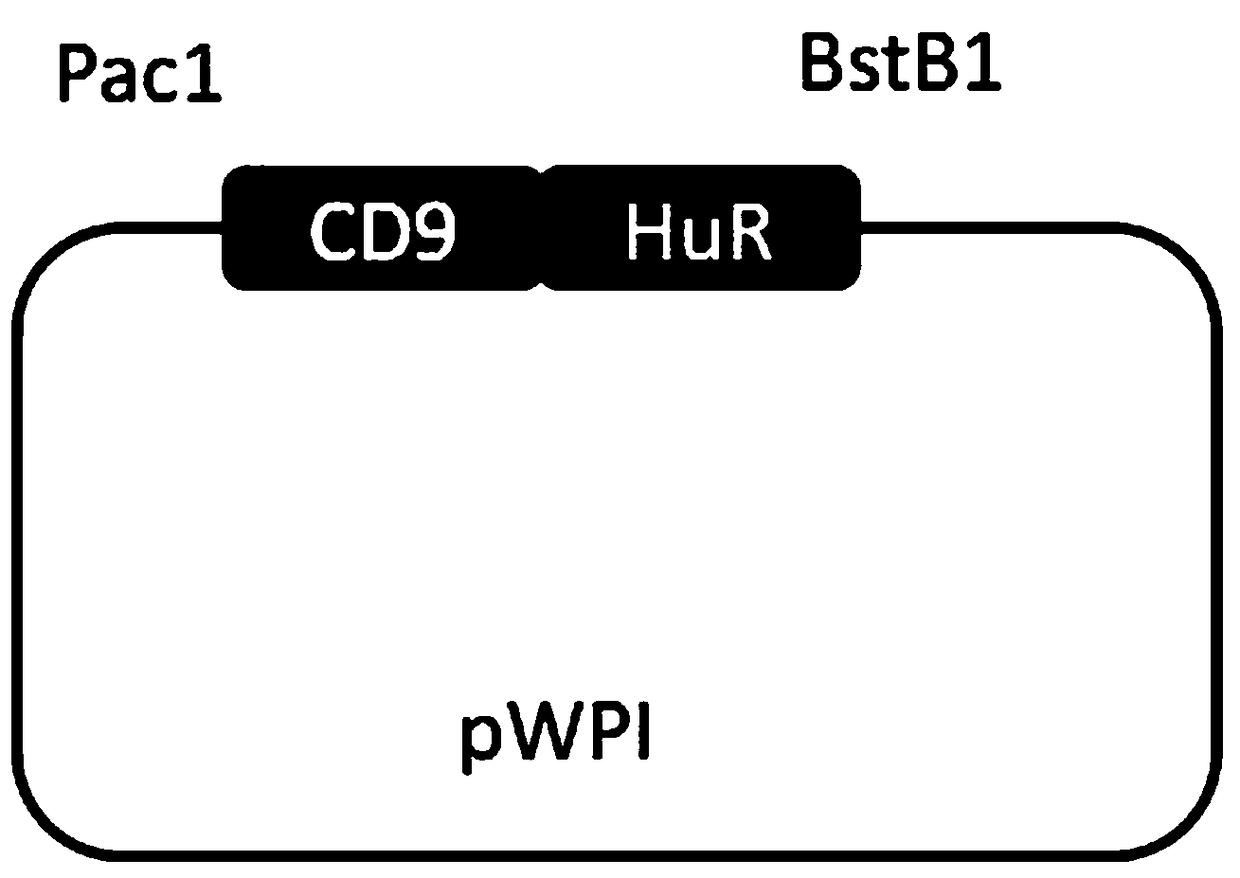
Patents
Literature
134 results about "RNA-Binding Motif" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
RNA-binding protein. RNA-binding proteins (often abbreviated as RBPs) are proteins that bind to the double or single stranded RNA in cells and participate in forming ribonucleoprotein complexes. RBPs contain various structural motifs, such as RNA recognition motif (RRM), dsRNA binding domain, zinc finger and others.
Oligoribonucleotides and ribonucleases for cleaving RNA
InactiveUS7432250B2High affinityStrong specificityHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsOrganismResearch purpose
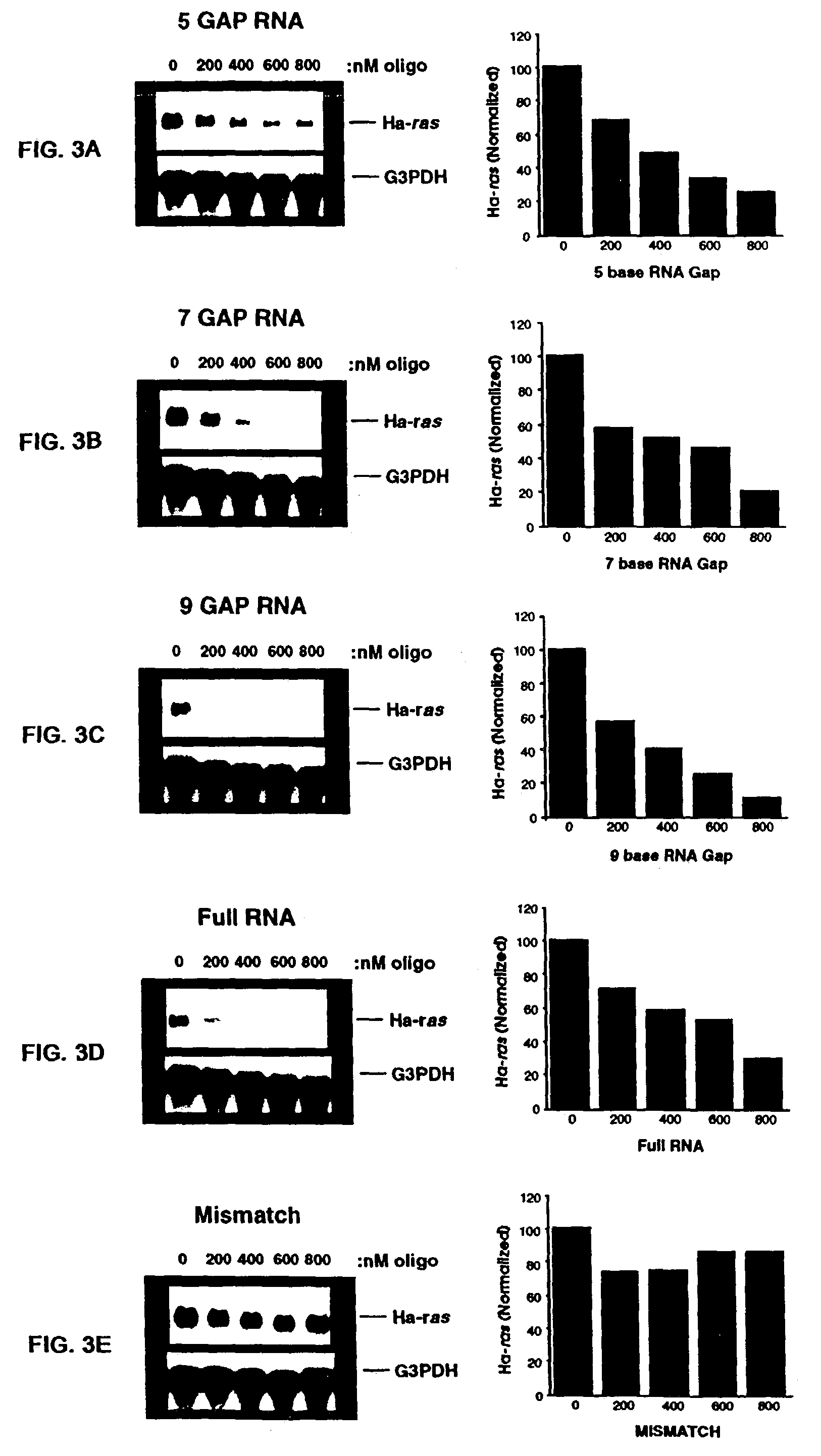
Oligomeric compounds including oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides are provided that have subsequences of 2′-pentoribofuranosyl nucleosides that activate dsRNase. The oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides can include substituent groups for increasing binding affinity to complementary nucleic acid strand as well as substituent groups for increasing nuclease resistance. The oligomeric compounds are useful for diagnostics and other research purposes, for modulating the expression of a protein in organisms, and for the diagnosis, detection and treatment of other conditions susceptible to oligonucleotide therapeutics. Also included in the invention are mammalian ribonucleases, i.e., enzymes that degrade RNA, and substrates for such ribonucleases. Such a ribonuclease is referred to herein as a dsRNase, wherein “ds” indicates the RNase's specificity for certain double-stranded RNA substrates. The artificial substrates for the dsRNases described herein are useful in preparing affinity matrices for purifying mammalian ribonuclease as well as non-degradative RNA-binding proteins.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Oligoribonucleotides and ribonucleases for cleaving RNA
InactiveUS7432249B2High affinityStrong specificityPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesADAMTS ProteinsOrganism
Oligomeric compounds including oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides are provided that have subsequences of 2′-pentoribofuranosyl nucleosides that activate dsRNase. The oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides can include substituent groups for increasing binding affinity to complementary nucleic acid strand as well as substituent groups for increasing nuclease resistance. The oligomeric compounds are useful for diagnostics and other research purposes, for modulating the expression of a protein in organisms, and for the diagnosis, detection and treatment of other conditions susceptible to oligonucleotide therapeutics. Also included in the invention are mammalian ribonucleases, i.e., enzymes that degrade RNA, and substrates for such ribonucleases. Such a ribonuclease is referred to herein as a dsRNase, wherein “ds” indicates the RNase's specificity for certain double-stranded RNA substrates. The artificial substrates for the dsRNases described herein are useful in preparing affinity matrices for purifying mammalian ribonuclease as well as non-degradative RNA-binding proteins.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Oligoribonucleotides and ribonucleases for cleaving RNA
InactiveUS7629321B2High affinityStrong specificityHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsOrganismResearch purpose
Oligomeric compounds including oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides are provided that have subsequences of 2′-pentoribofuranosyl nucleosides that activate dsRNase. The oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides can include substituent groups for increasing binding affinity to complementary nucleic acid strand as well as substituent groups for increasing nuclease resistance. The oligomeric compounds are useful for diagnostics and other research purposes, for modulating the expression of a protein in organisms, and for the diagnosis, detection and treatment of other conditions susceptible to oligonucleotide therapeutics. Also included in the invention are mammalian ribonucleases, i.e., enzymes that degrade RNA, and substrates for such ribonucleases. Such a ribonuclease is referred to herein as a dsRNase, wherein “ds” indicates the RNase's specificity for certain double-stranded RNA substrates. The artificial substrates for the dsRNases described herein are useful in preparing affinity matrices for purifying mammalian ribonuclease as well as non-degradative RNA-binding proteins.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Assays for measuring nucleic acid binding proteins and enzyme activities
InactiveUS6312896B1Simple and accurate and reliable assayEfficient transferSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein insertionNucleic acid binding protein
Owner:BIOVERIS CORP
Circular RNA for inhibition of microrna
InactiveUS20150299702A1Avoid interactionControl degradationOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDecoyCircular RNA
The present invention relates to inhibition of microRNAs (miRNA), other types of RNA and RNA-binding proteins. In particular the present invention relates to nucleic acid sequences that are circular and allow inhibition of the interactions between microRNAs and their RNA target and being resistant to degradation by exonucleases. Also, the present invention relates to nucleic acid sequence that are circular and acts as an RNA blocker or protein decoy.
Owner:AARHUS UNIV
Compounds for modulating RNA binding proteins and uses therefor
InactiveUS20110077250A1Reduce the burden onIncreases formation and stabilityBiocideLibrary screeningParasitic infectionProtein C
The invention relates to compositions and methods for inhibiting RNA binding proteins (e.g., MEX-3, MEX-5 and POS-1), as well as methods for treating and preventing disorders associated with parasitic infections and inflammatory disorders.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Methods for In Vivo Identification of Endogenous mRNA Targets of MicroRNAs
A method of generating a gene expression profile of noncoding regulatory RNA (ncRNA; e.g. a microRNA) in a cell in vivo, is carried out by: (a) partitioning from a cell at least one mRNA-protein (RNP) complex, the RNP complex comprising: (i) an RNA binding protein (RNABP) or RNA associated protein, (ii) at least one mRNA bound to or associated with said protein, and (iii) at least one ncRNA bound to or associated with said protein, and then (b) identifying at least one ncRNA in-at least one RNP complex, thereby to produce a gene expression profile comprising the identity of an ncRNA in an RNP complex.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
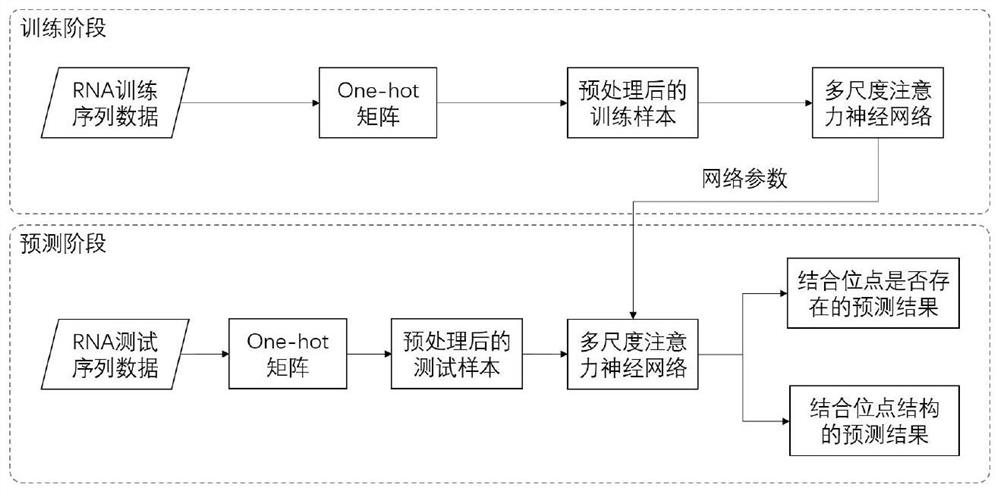
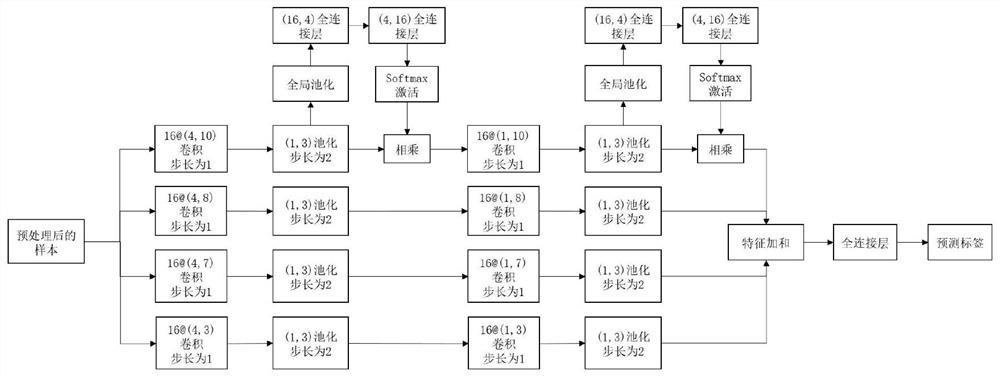
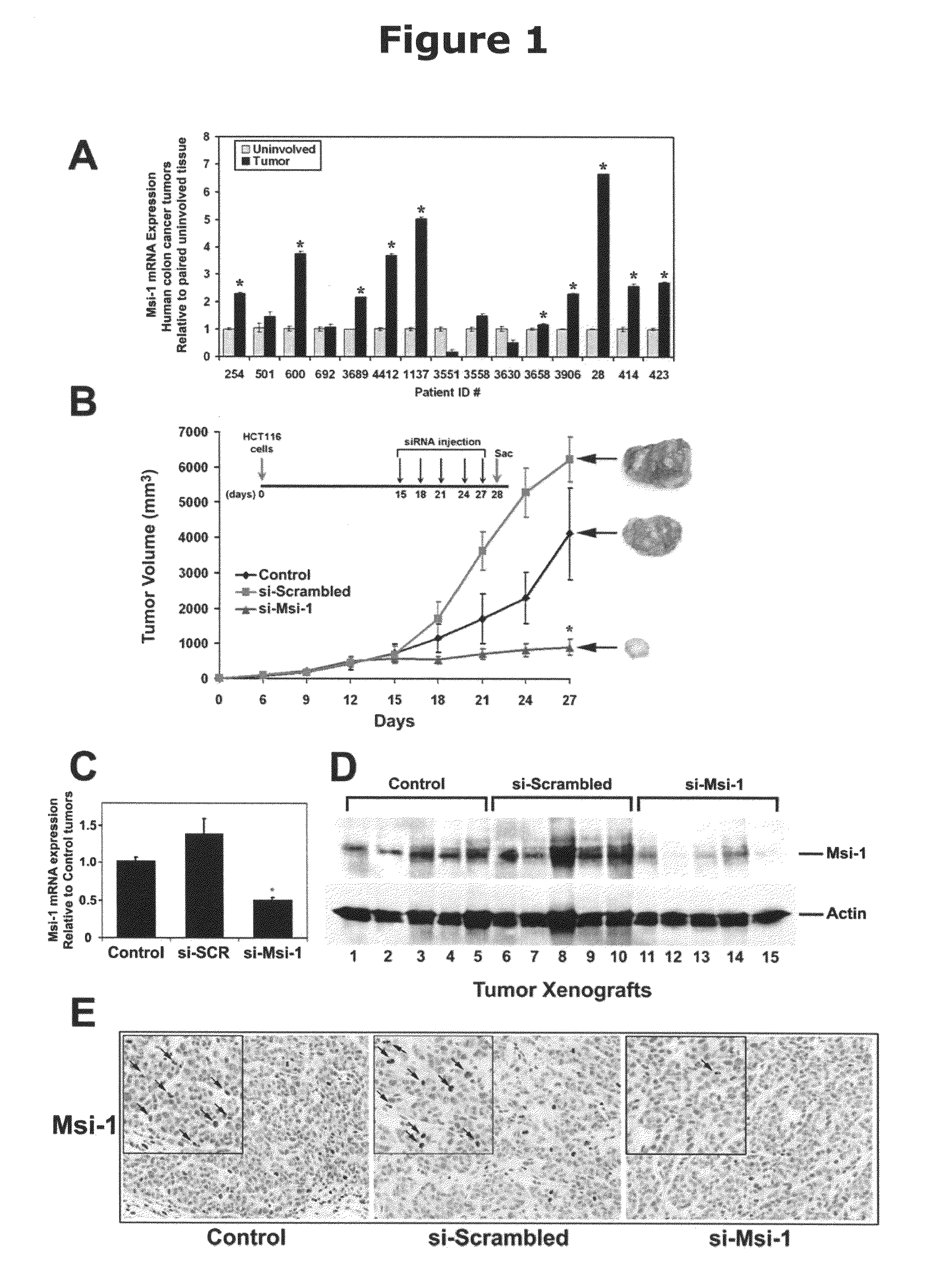
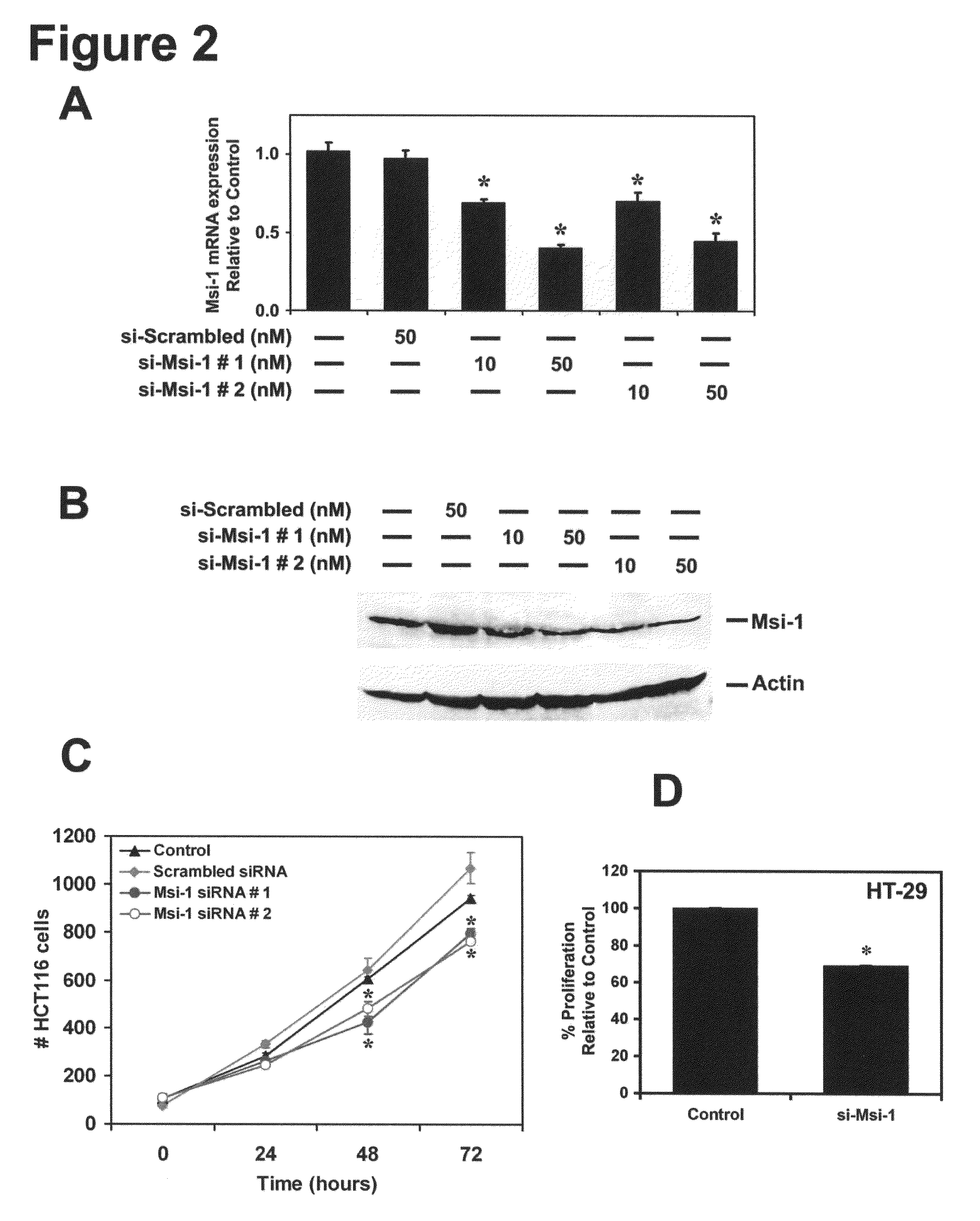
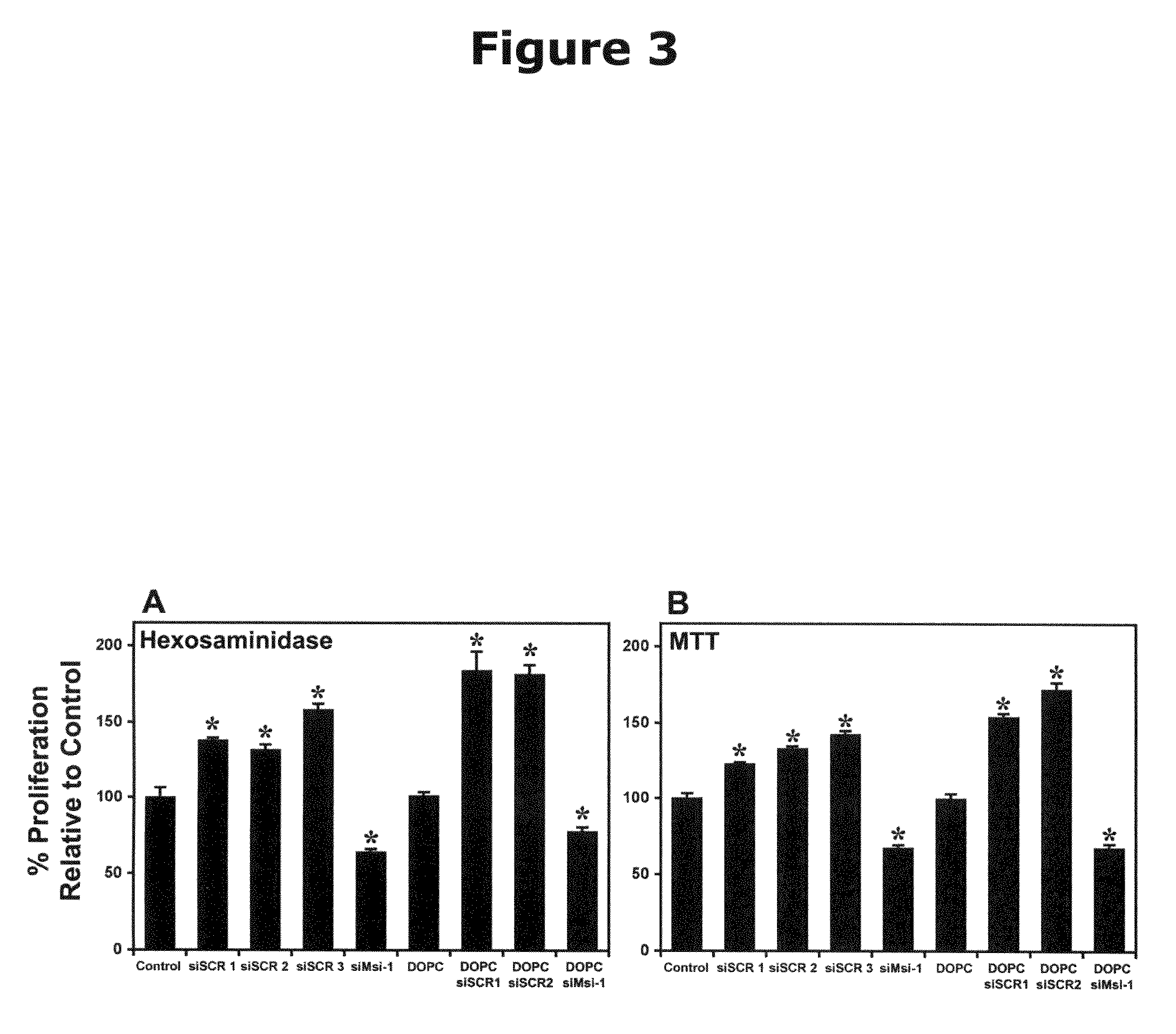
RNA binding protein prediction method and device based on multi-scale attention convolutional neural network
ActiveCN111798921AImprove forecast accuracyImprove robustnessBiostatisticsProteomicsBinding siteRNA Sequence
The invention discloses an RNA binding protein prediction method based on a multi-scale attention convolutional neural network. The RNA binding protein prediction method comprises a training stage anda prediction stage. The training stage comprises the following steps: preprocessing RNA data, encoding the RNA data, constructing a neural network and training network parameters. A mathematically abstract statistical mode of RNA is converted into a matrix form, the matrix form is input into a pre-designed attention mechanism-based multi-scale convolutional neural network, and parameters in the neural network are trained by using an Adam optimization method by minimizing a designed special cross entropy loss function. In the prediction stage, RNA sequence data with four basic groups as basicunits are input into the network, the probability of whether binding sites corresponding to binding proteins exist in the RNA data is output by the last layer of the neural network, and therefore theprediction result of the RNA sequence category is obtained. The method can improve the prediction precision.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Plants having enhanced yield-related traits and a method for making the same
The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for enhancing various yield-related traits and / or plant growth characteristics in plants by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a C3H-like polypeptide, or a SPATULA-like (SPT) polypeptide, or an IDI2 (Iron Deficiency Induced 2) polypeptide, or an elF4F-like protein complex subunit, or GR-RBP (Glycine Rich-RNA Binding Protein) polypeptide.; The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression and / or activity of a nucleic acid encoding a C3H-like polypeptide, or a SPATULA-like (SPT) polypeptide, or an IDI2 (Iron Deficiency Induced 2) polypeptide, or an elF4F-like protein complex subunit, or GR-RBP (Glycine Rich-RNA Binding Protein) polypeptide, which plants have enhanced yield-related traits and / or plant growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants or other control plants. The invention also provides constructs useful in the methods of the invention.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Methods for identifying therapeutic targets involved in glucose and lipid metabolism
The identification and evaluation of mRNA and protein targets associated with RNA binding proteins or mRNP complexes is described. In particular, the invention provides methods for identifying RNA binding proteins associated with physiological pathways that participate in glucose and lipid metabolism and mRNAs that exhibit coordinated gene regulation across those M pathways. Candidate targets are provided that are useful for the diagnosis or treatment of diseases related to diseases, such as disease related to aberrant glucose and lipid metabolism, such as, for example, obesity, diabetes, and hypoglycemia.
Owner:RIBONOMICS
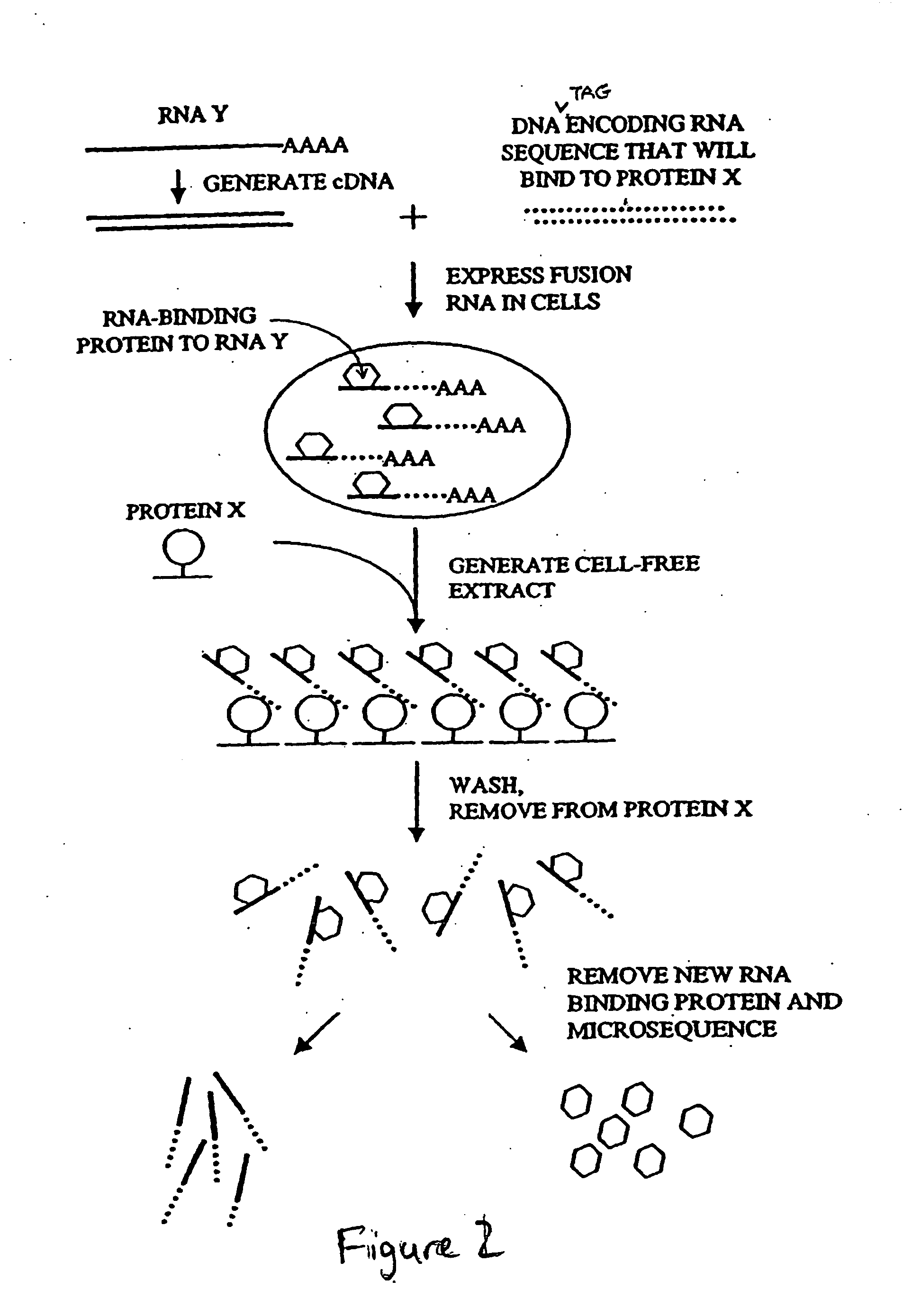
Translation driver system and methods for use thereof
InactiveUS6610508B1Preserving functionBacteriaSugar derivativesTranslational ActivationPresent method
The present method relates to the translational activation of genes using the ribosome recruitment protein, eIF4G or an eIF4G-like protein. The invention relates to the translation of RNA molecules containing heterologous protein-binding sites, which RNA molecules encode one, two, three or more proteins. The invention provides products and methods for the identification of RNA-binding proteins. The invention further provides a system by which protein-protein interactions and inhibitors or enhancers of these interactions may be identified. Further, the invention provides products and methods to provide a cell with one or more therapeutic proteins. The invention provides products and methods for controlling the levels of translation of such proteins. The invention provides products and methods to control the translation and stoichiometry of multiple subunit proteins. The invention provides products for and methods of screening for proteins which interact with an RNA binding site, and methods for identifying RNA binding sites.
Owner:ANDADYS PHARMA INC
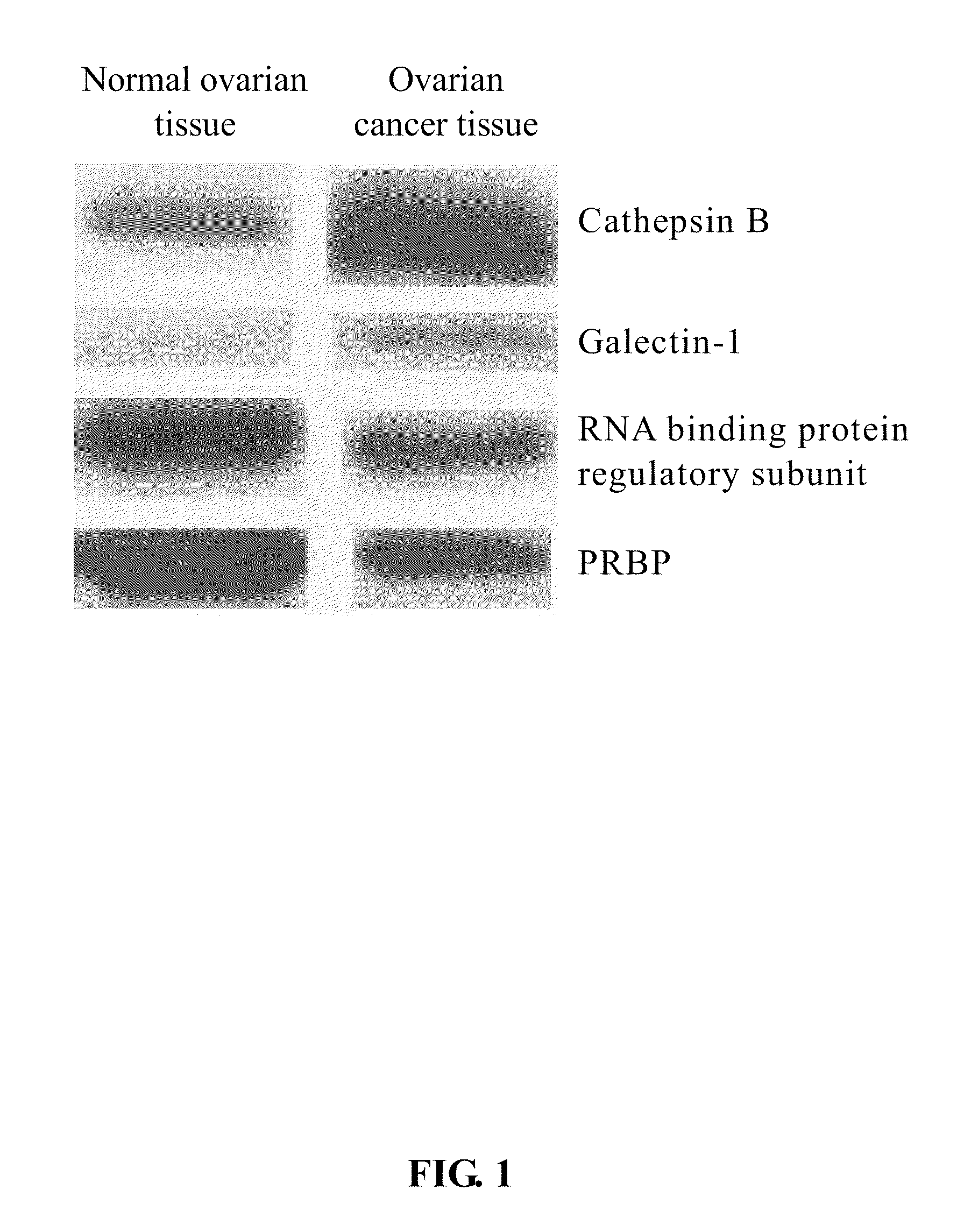
Tumor marker for ovarian cancer diagnosis
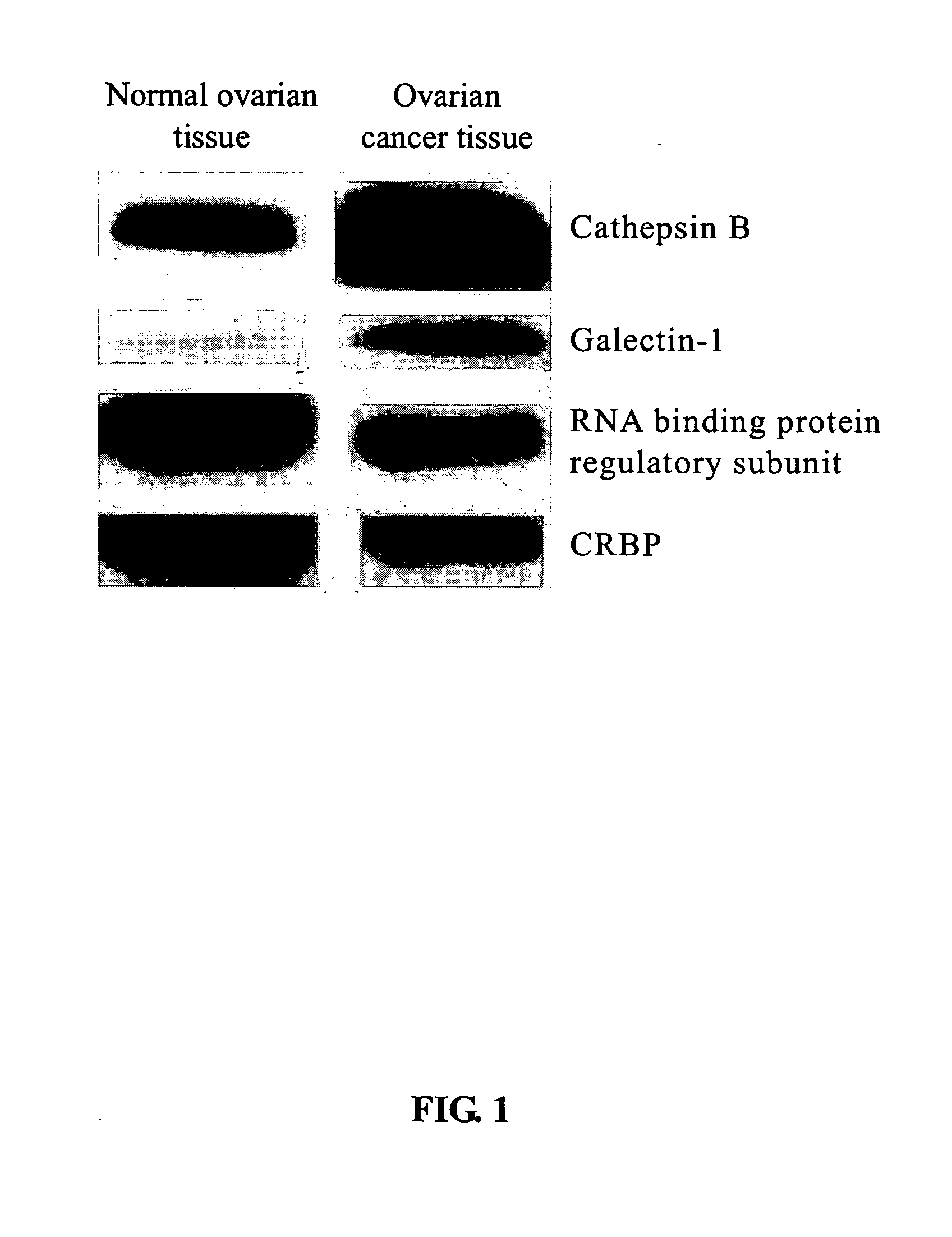
InactiveUS20070134689A1Accurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisAbnormal tissue growthCathepsin B
The present invention relates to a tumor marker for diagnosis of ovarian cancer, which is selected from the group consisting of alectin-1, cathepsin B, MHC class I antigen, heat shock protein (HSP) 27, ubiquitin carboxy-termal esterase L1, cellular retinol-binding protein (CRBP), transthyretin, SH3 binding glutamate-rich protein, tubulin-specific chaperone A, RNA binding protein regulatory subunit, γ-actin, tropomyosin and calcium / calmodulin-stimulated cyclic nucleotide phosphatase. The ovarian cancer is diagnosed effectively and efficiently based on detecting the expression levels of the tumor markers in the invention from the ovarian tissue sample of an individual to be diagnosed.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Compositions comprising inhibitors of RNA binding proteins and methods of producing and using same
Compositions for inhibiting RNA binding proteins, as well as methods of producing and using the same, are disclosed herein.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
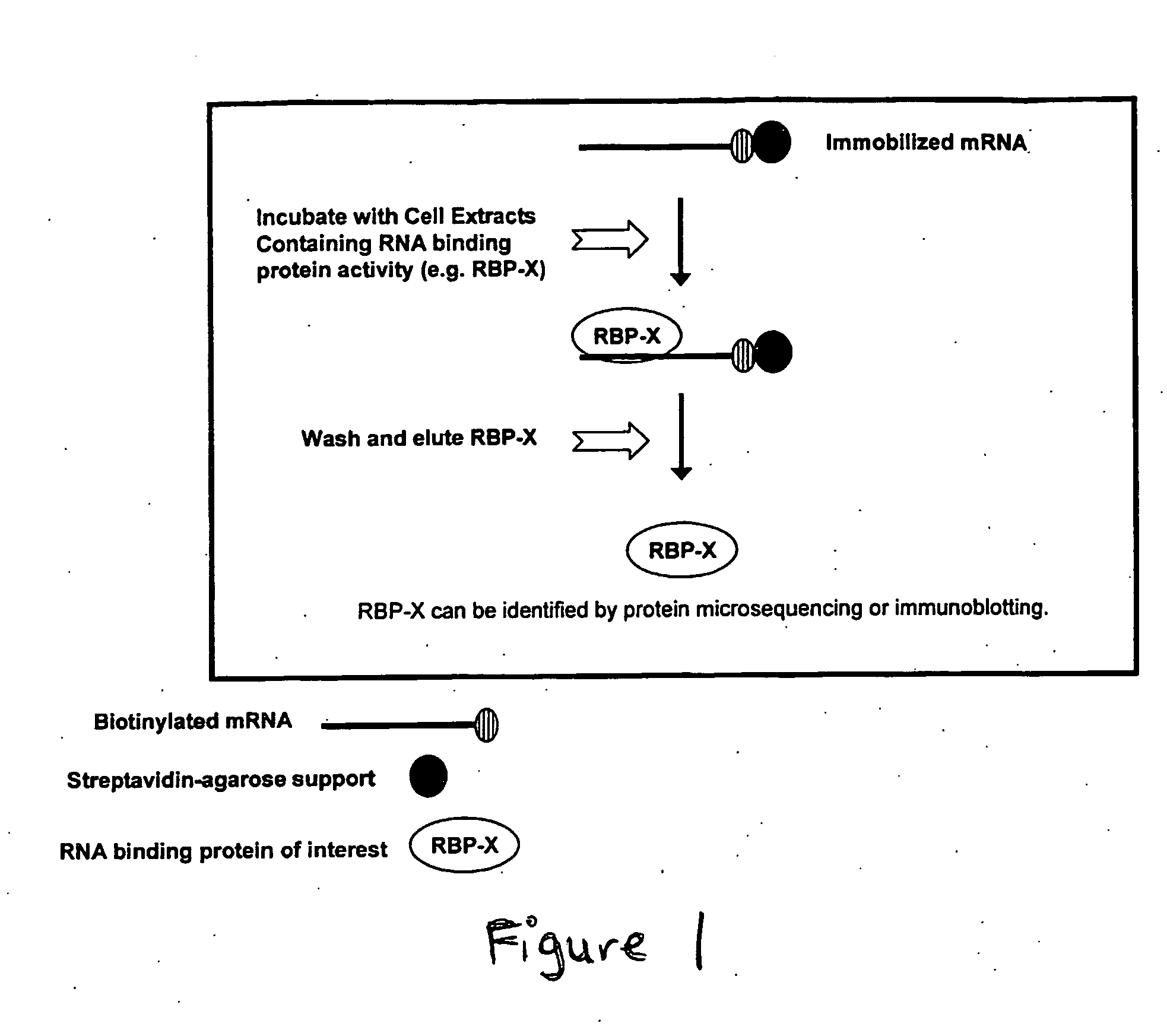
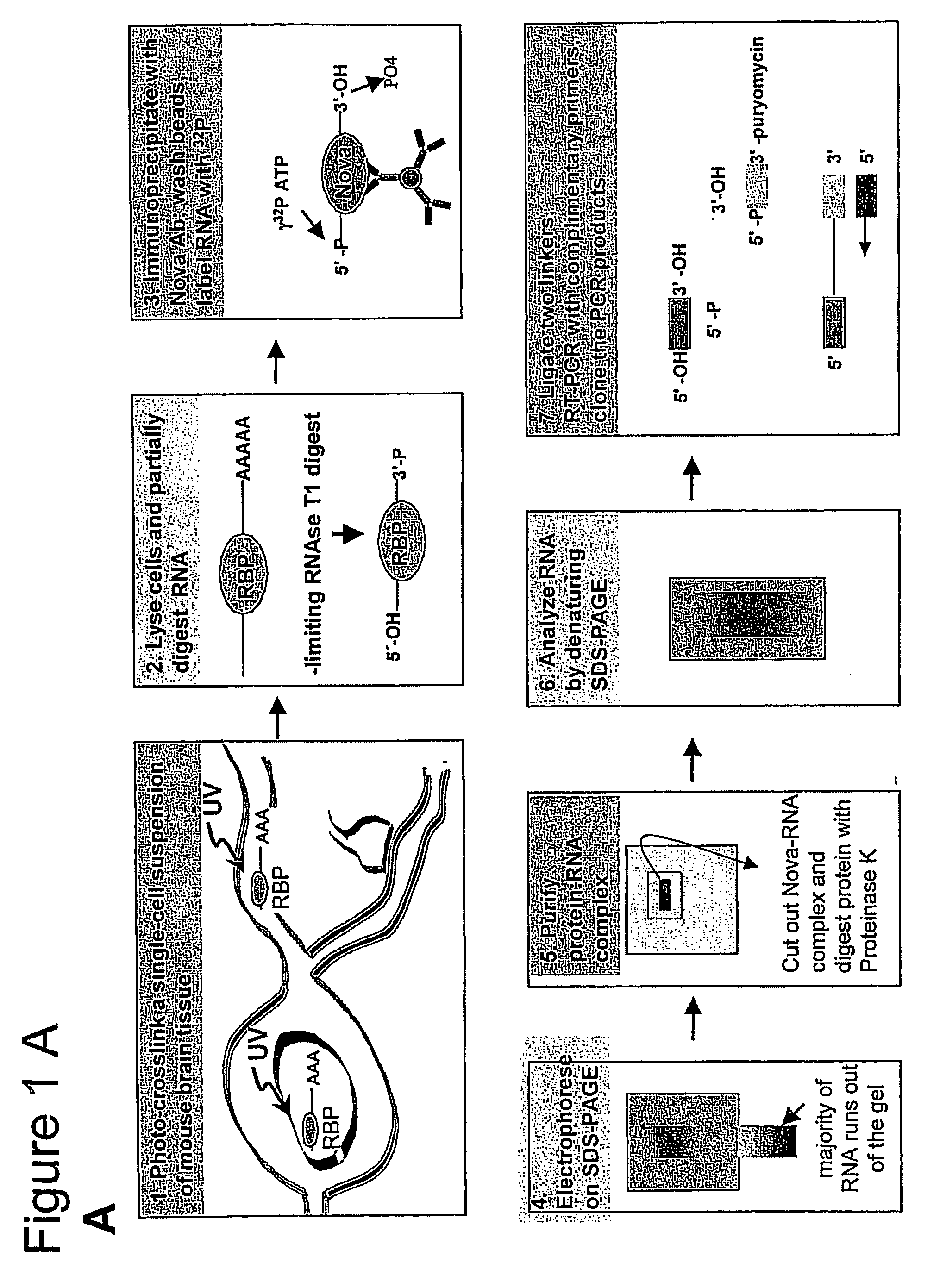
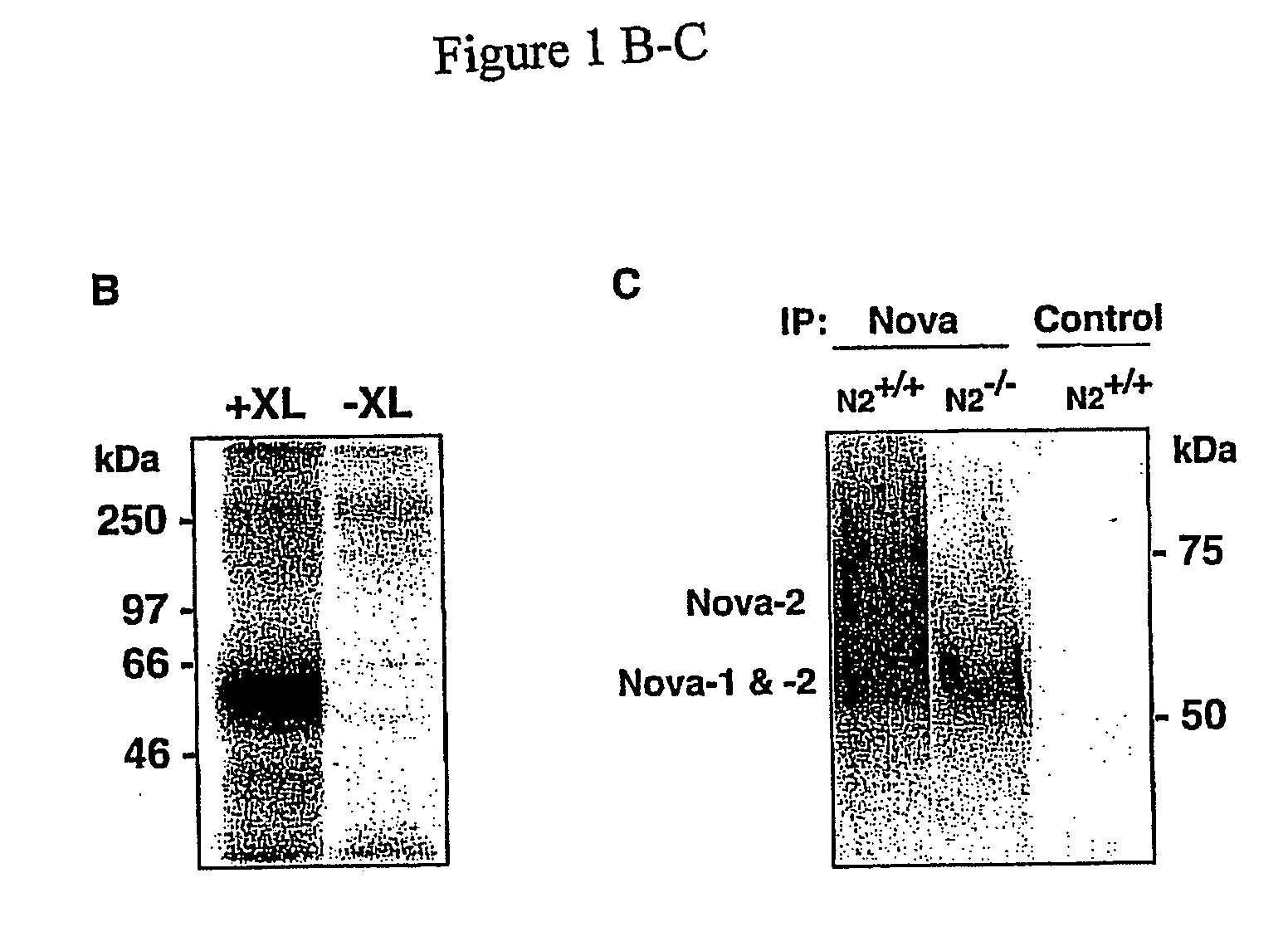
Methods for Identifying RNA Segments Bound by RNA-Binding Proteins or Ribonucleoprotein Complexes
ActiveUS20110287412A1Microbiological testing/measurementDNA preparationCross-linkRibonucleoprotein complex
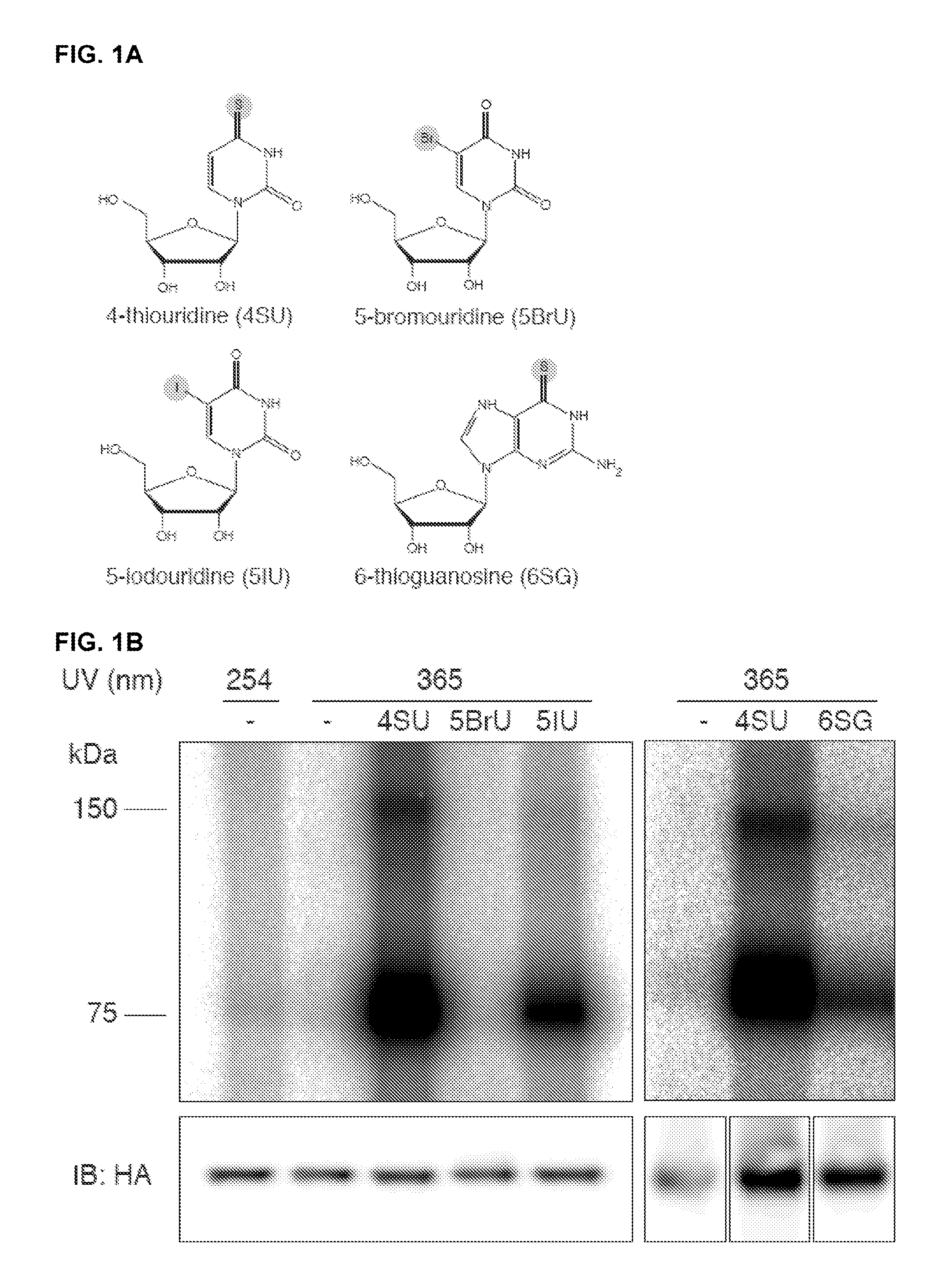
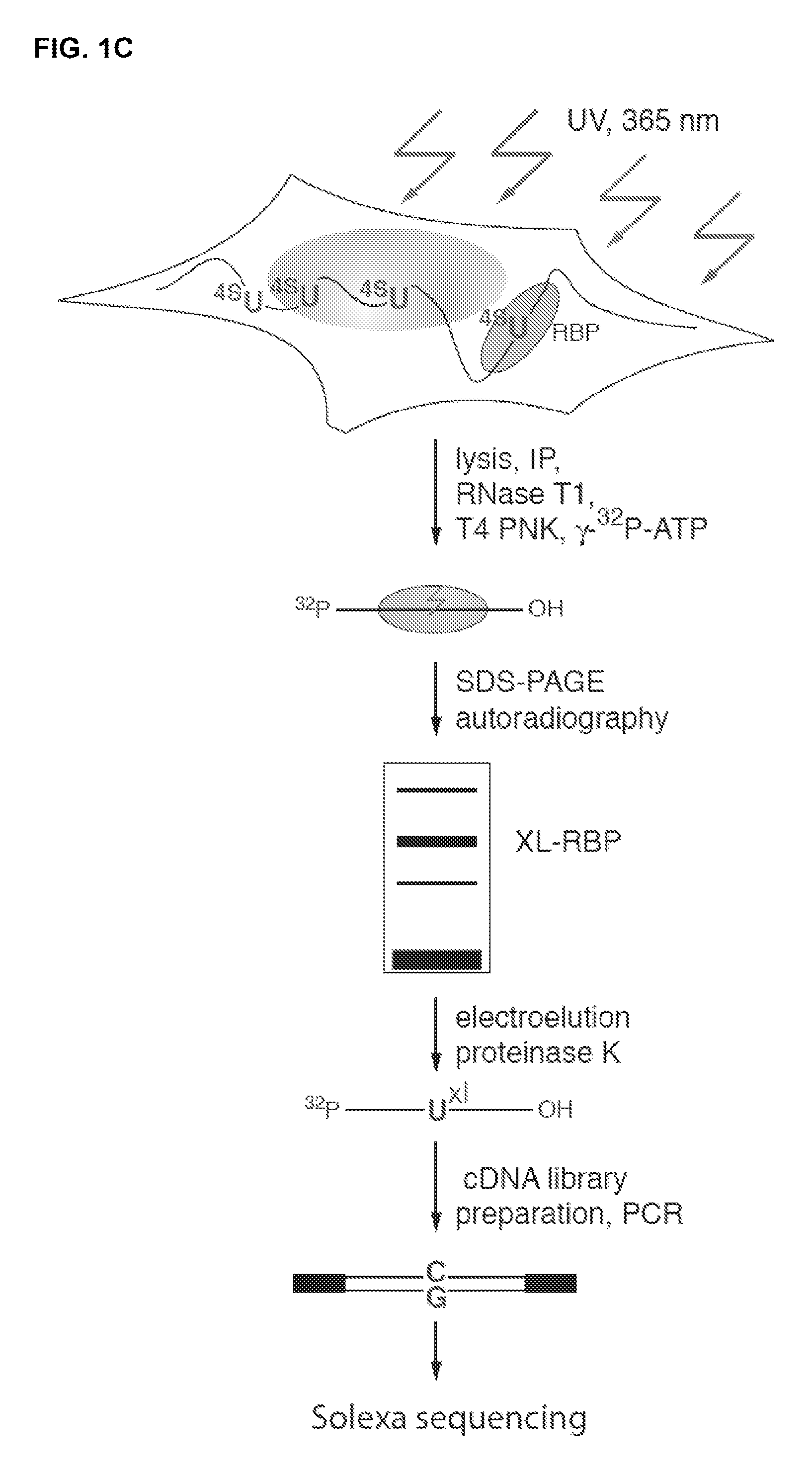
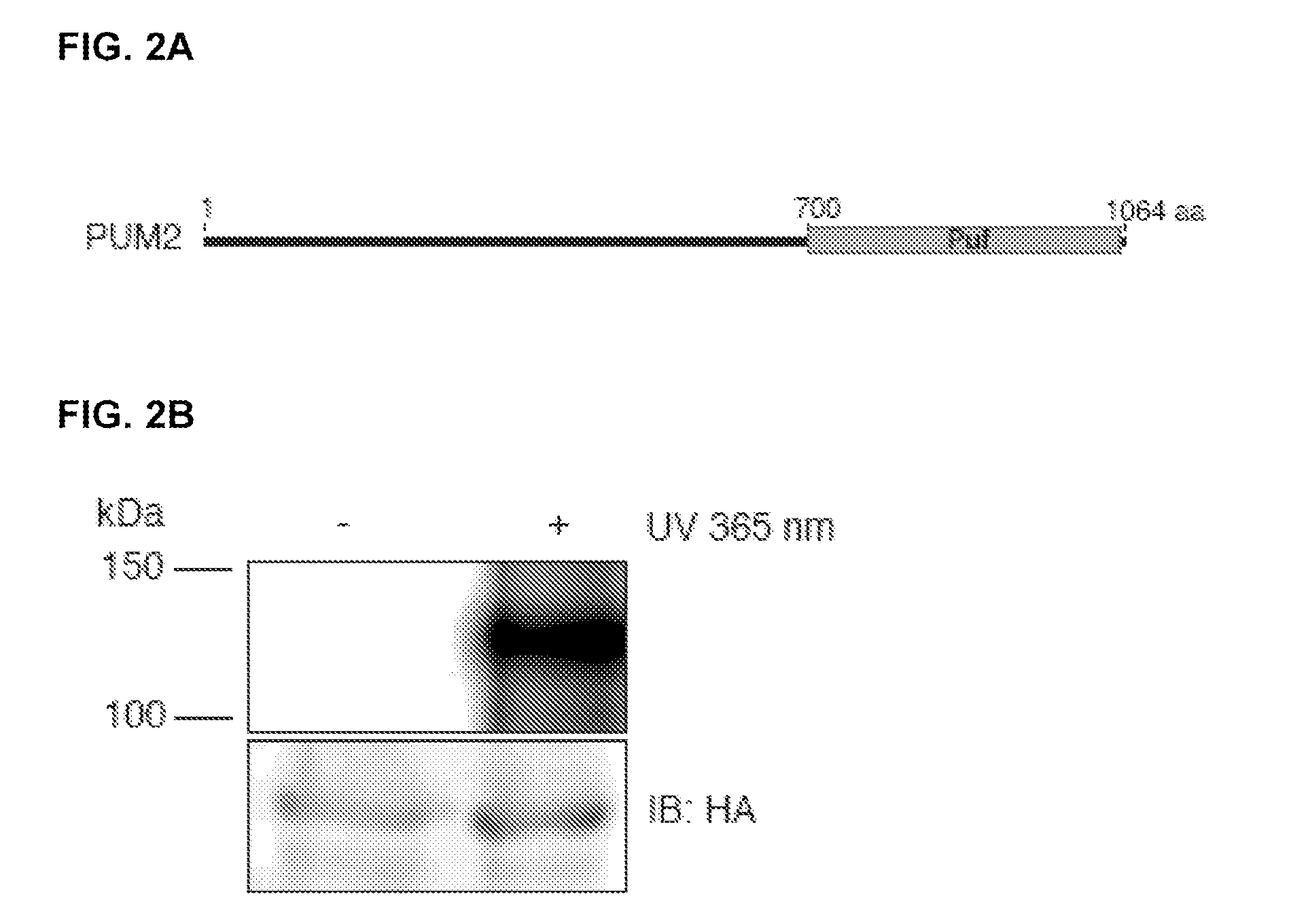
The present invention relates to a method for identifying a binding site on an RNA transcript, wherein the binding site binds to one or more binding moieties. The method includes, among other things, introducing a photoreactive nucleoside into living cells wherein the living cells incorporate the photoreactive nucleoside into RNA transcripts during transcription thereby producing modified RNA transcripts; reverse transcribing the RNA of isolated cross-linked segments thereby generating cDNA transcripts with one mutation wherein the photoreactive nucleoside is transcribed to a mismatched deoxynucleoside; amplifying the cDNA transcripts thereby generating amplicons; and analyzing the sequences of the amplicons aligned against the reference sequence so as to identify the binding site, wherein the sequences of each amplicon having a mutation resulting from the introduction of the photoreactive nucleoside is considered to be a valid amplicon comprising at least a portion of a binding site on the RNA transcript.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF BASEL +1
Assays for measuring nucleic acid binding proteins and enzyme activities
InactiveUS20020146722A1Simple and accurate and reliable assaySimple and accurate and reliableMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsAssayNucleic acid binding protein
Owner:BIOVERIS CORP
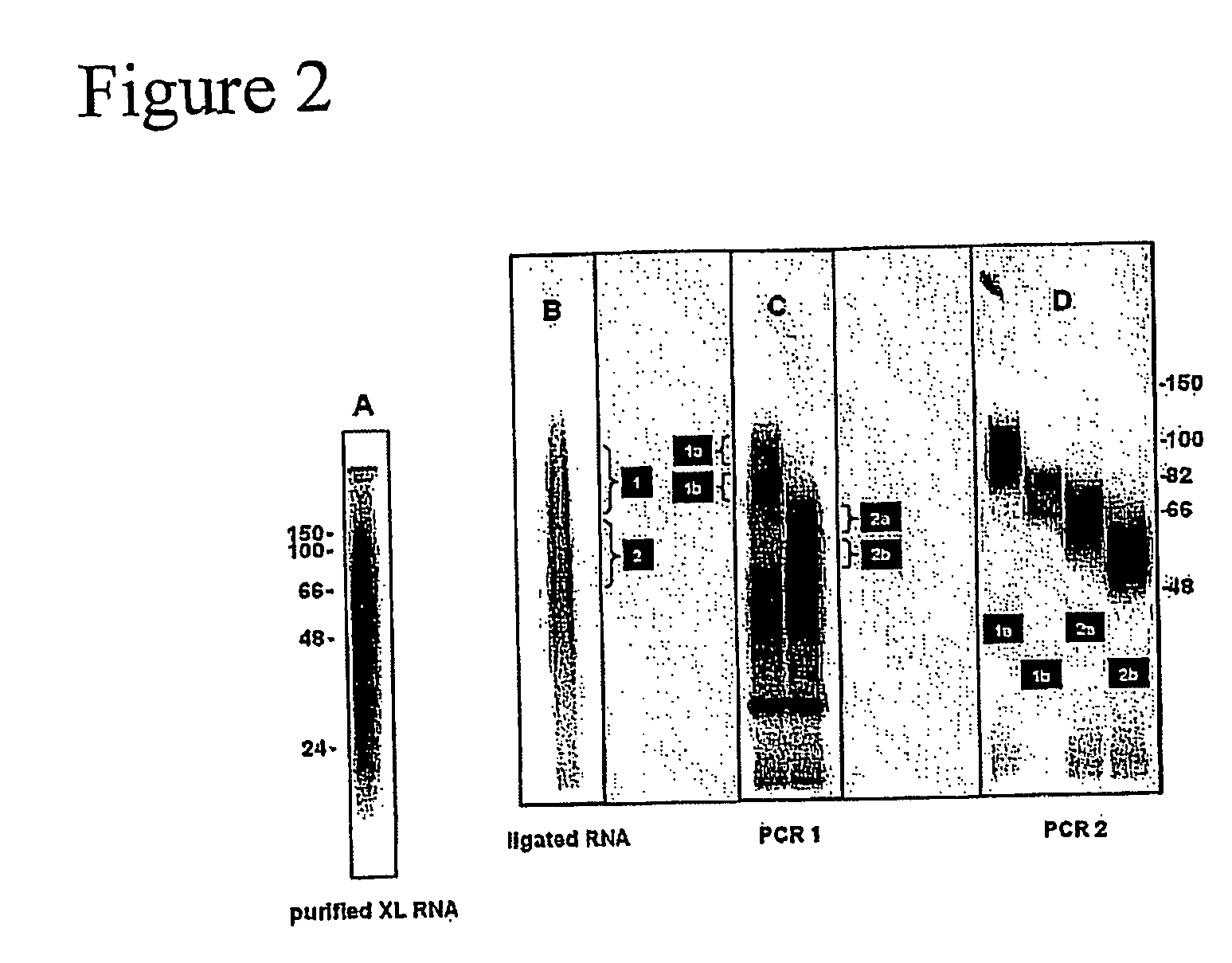
Method of purifying RNA binding protein-RNA complexes
InactiveUS20050227251A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationRNA MotifsGene expression profiling
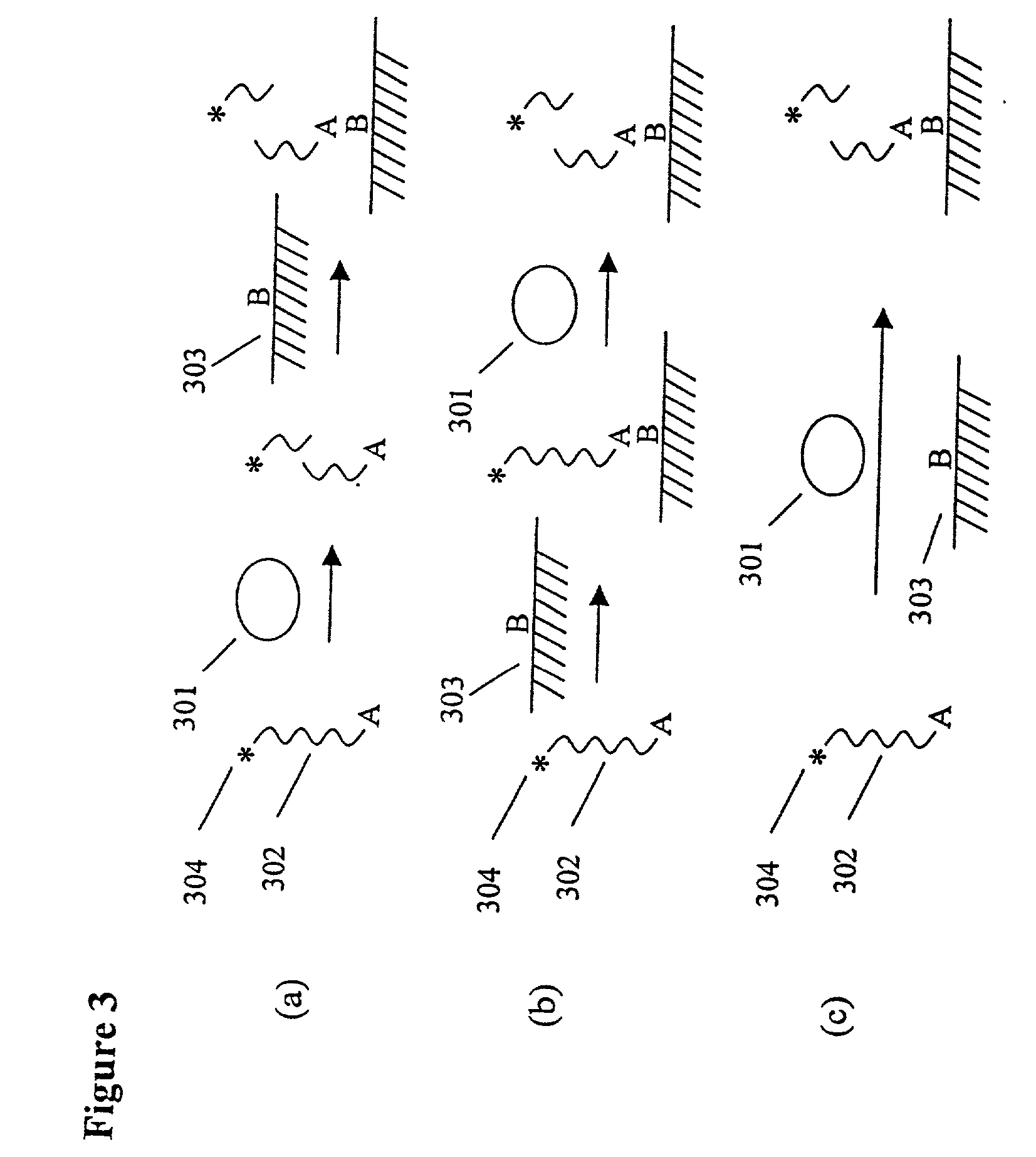
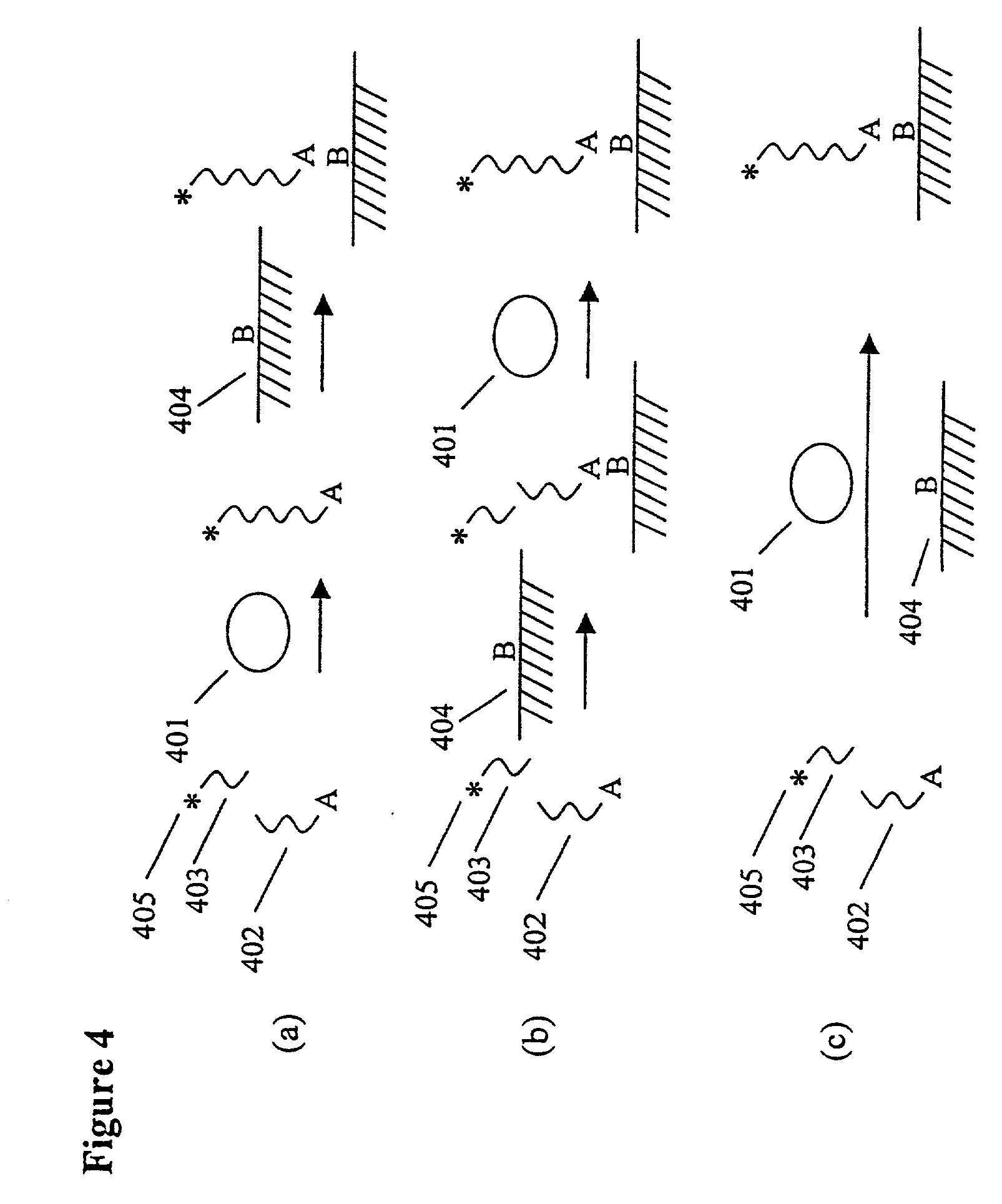
The present invention provides methods for purifying RNA molecules interacting with an RNA binding protein (RBP), and the use of such methods to analyze a gene expression profile of a cell. The invention also provides sequences of RNA molecules that mediate binding to an RBP, proteins encoded by the sequences, a method of identifying the sequences, and the use of the sequences in a screen to identify bioactive molecules. The invention also provides RNA motifs found among the sequences and compounds that bind the RNA motifs. In addition, the invention provides methods of treating diseases associated with a function of an RNA binding protein.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
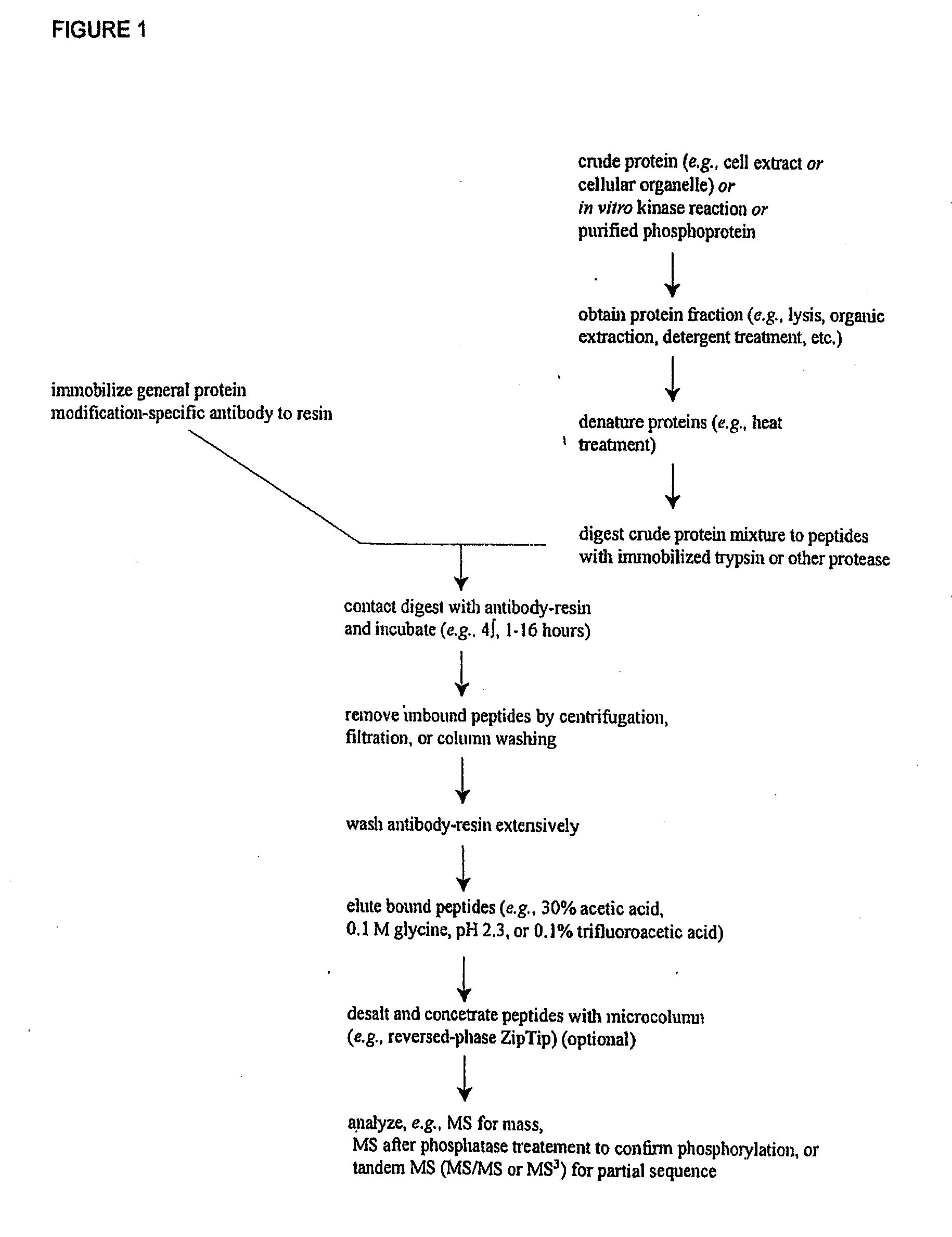
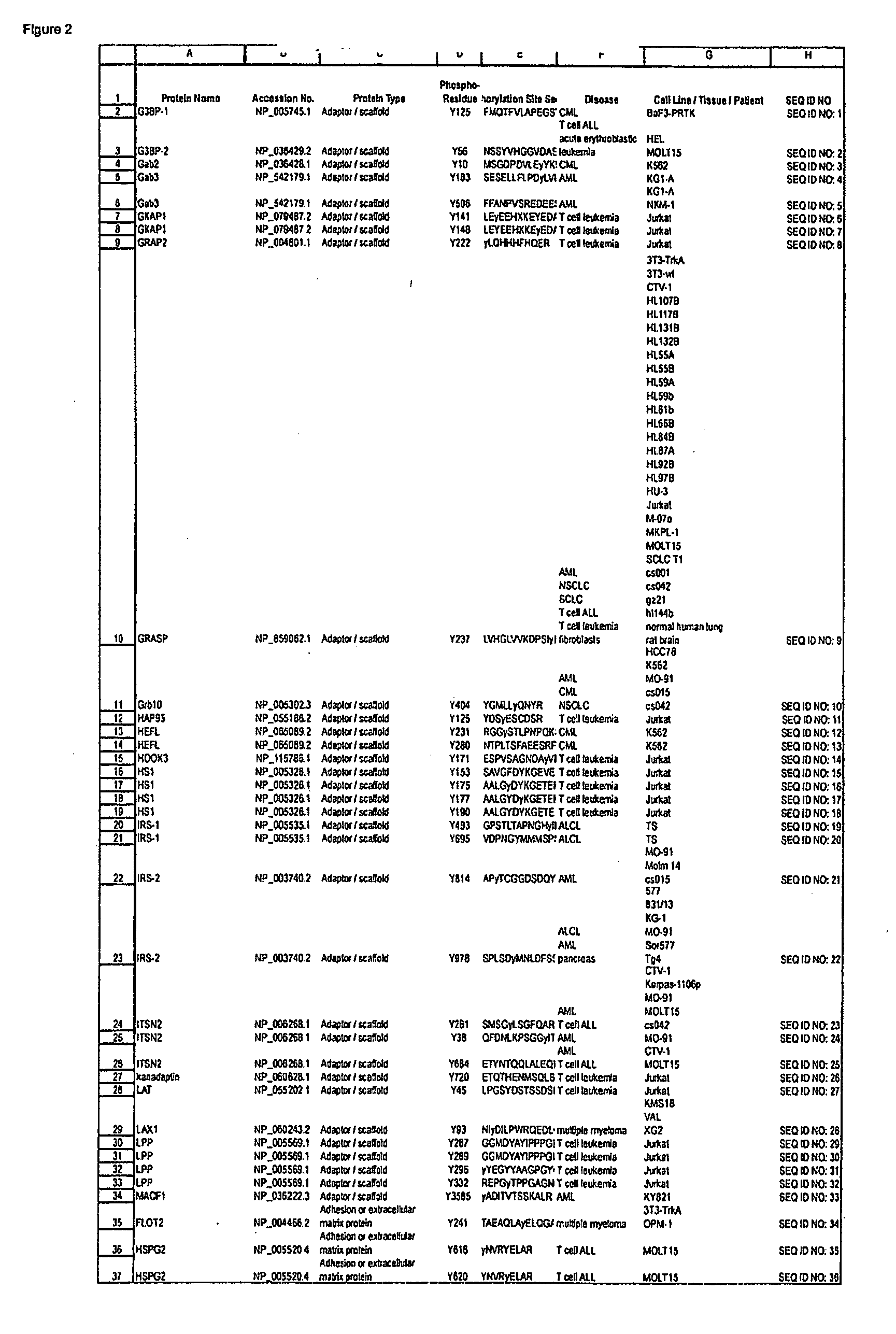
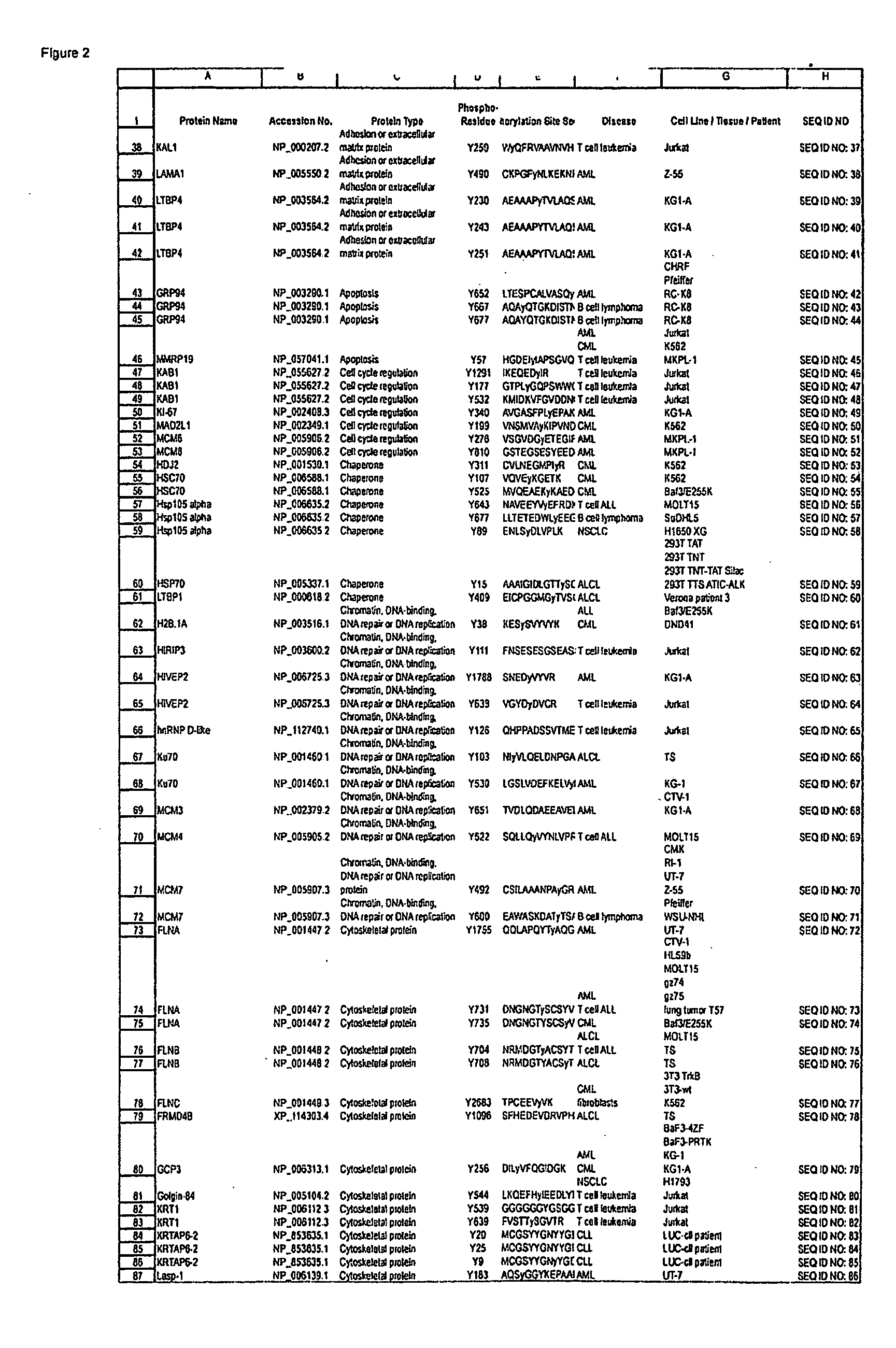
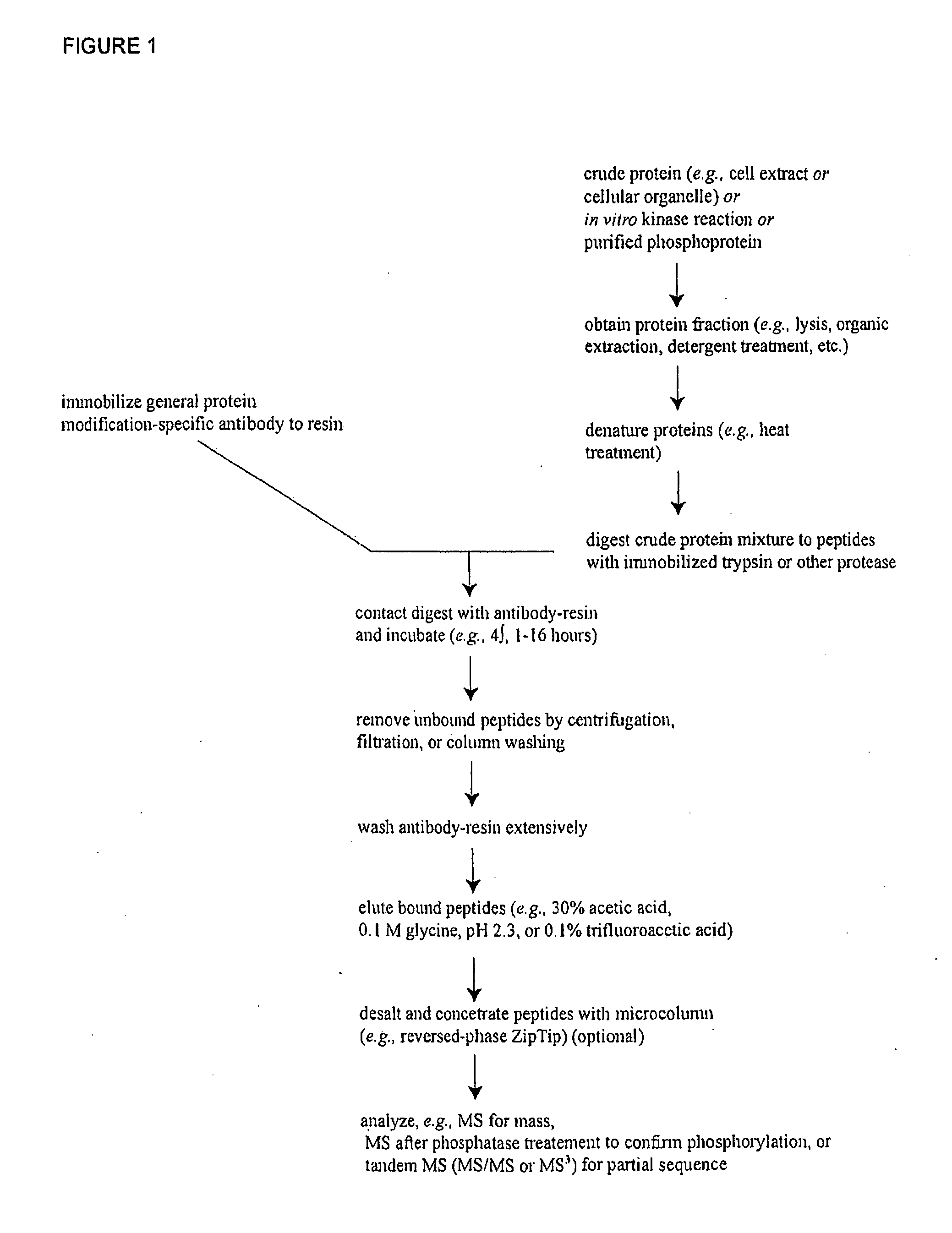
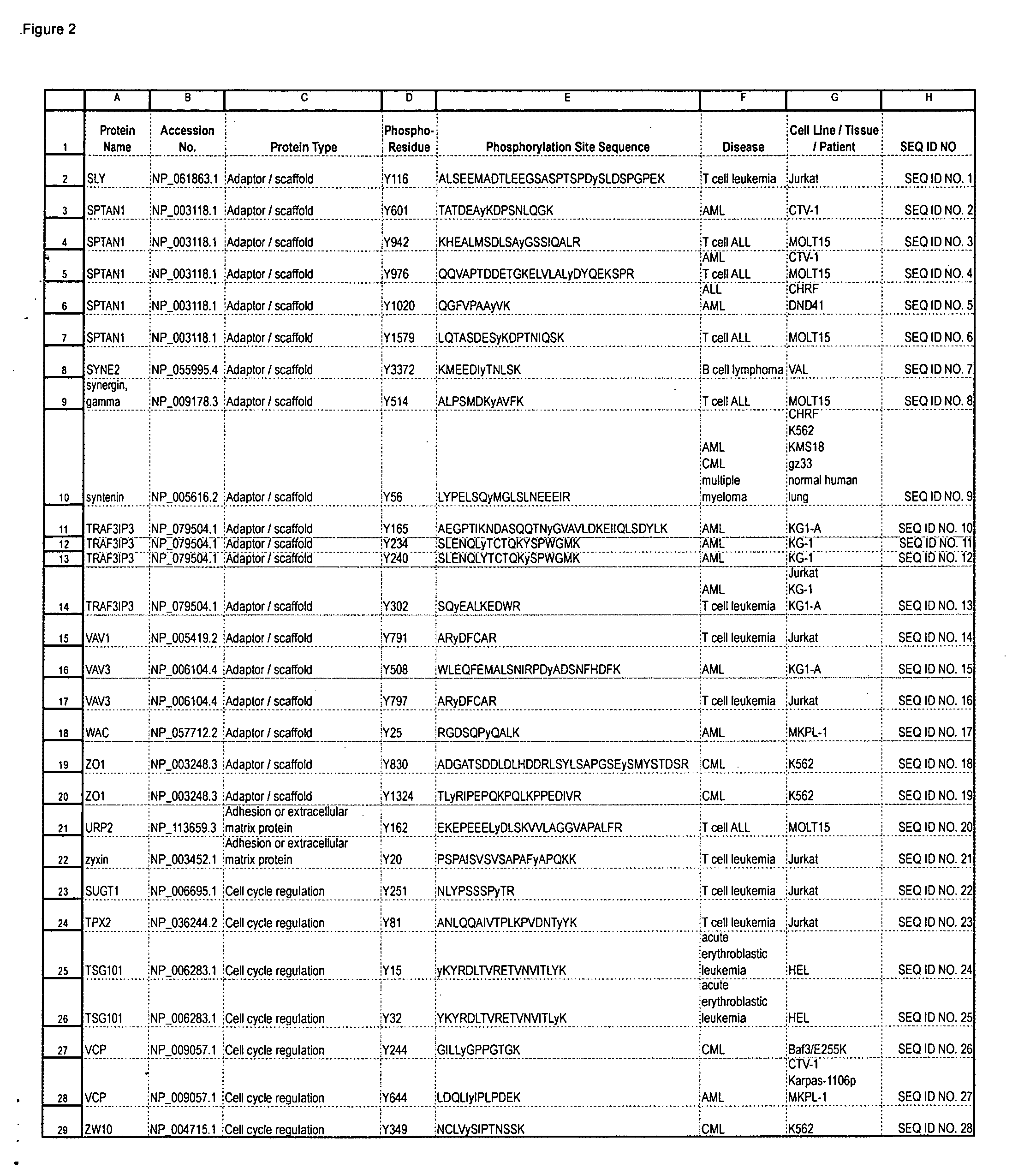
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in signaling pathways
InactiveUS20100009463A1Animal cellsIsotope introduction to peptides/proteinsCell Surface ProteinsPhosphorylation
The invention discloses novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: adaptor / scaffold proteins, adhesion / extracellular matrix protein, apoptosis proteins, calcium binding proteins, cell cycle regulation proteins, chaperone proteins, chromatin, DNA binding / repair / replication proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, endoplasmic reticulum or golgi proteins, enzyme proteins, G / regulator proteins, inhibitor proteins, motor / contractile proteins, phosphatase, protease, Ser / Thr protein kinases, protein kinase (Tyr)s, receptor / channel / cell surface proteins, RNA binding proteins, transcriptional regulators, tumor suppressor proteins, ubiquitan conjugating system proteins and proteins of unknown function.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
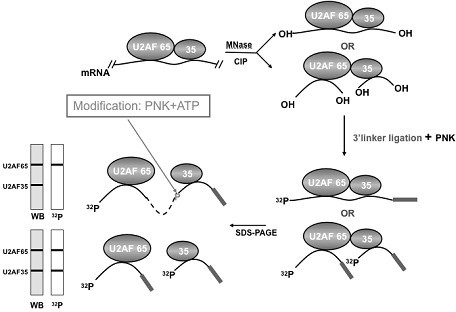
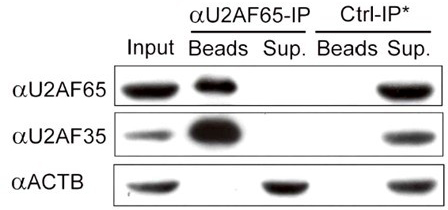
Improved method for identifying target RNA sequences of RNA-binding protein in cell sample
InactiveCN107674870ASimplify the experimental processLibrary creationDNA preparationCDNA libraryPhosphorylation
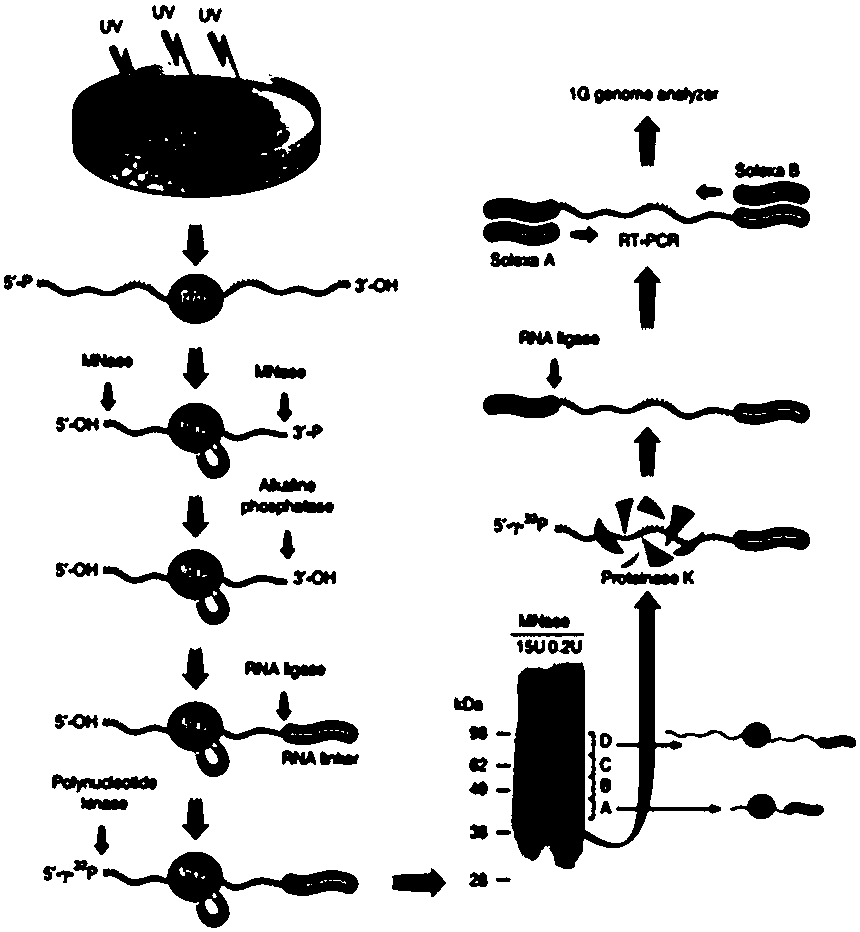
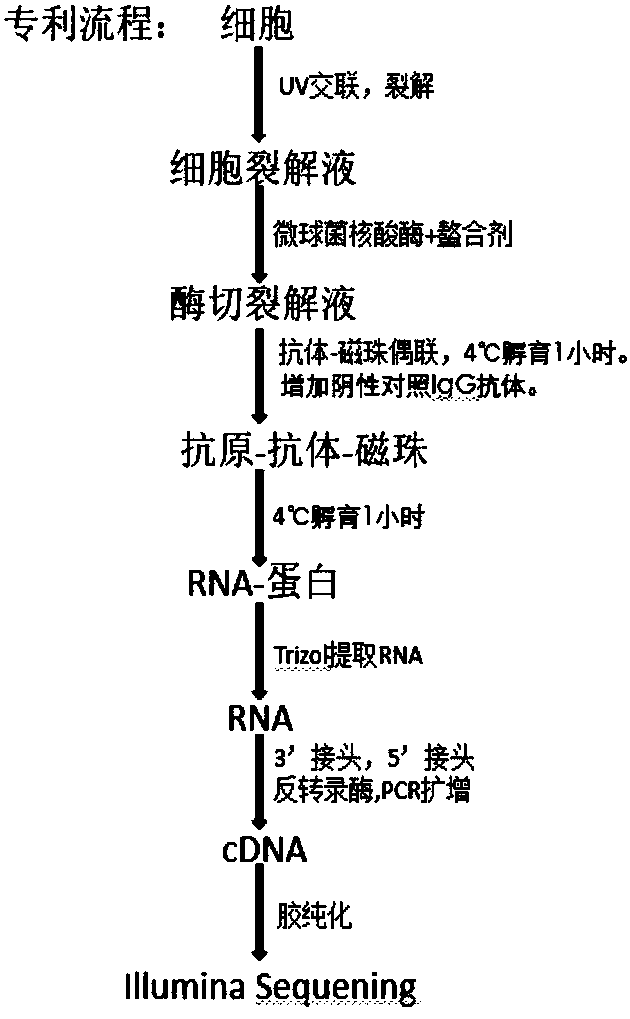
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, and provides improved identification for target RNA sequences bound to RNA-binding protein in cells. Through UV crosslinking-immunopricipitation, target RNA of RNA-binding protein is obtained, micrococcal nuclease is adopted for carrying out incomplete enzymolysis on the target RNA after ultraviolet crosslinking, after enzymolysis, a chelating agent capable of removing Ca<2+> is adopted for inactivating the enzyme, the 3' terminal of the target RNA obtained through the method is phosphorylated, the phosphorylated 3' terminal is ligated witha 3' RNA linker, then, the ligation product is phosphorylated, the phosphorylated ligation product is separated, the separated phosphorylated ligation product is recycled, then the 3' terminal is ligated with a 5' RNA linker, RT-PCR amplification is carried out, so that a cDNA library corresponding to the target RNA is obtained. With the technical scheme provided by the invention, the experiment flow is simplified, the step of isotope labelling is eliminated, due to the adding of an IgG antibody negative control sample, the influences of non-specific binding and background on the experimentalresult are eliminated, and the data result with the quality equal to that of Clip-seq is obtained.
Owner:武汉生命之美科技有限公司
Plants having improved growth characteristics and method for making the same
InactiveCN101040050AImprove growth characteristicsHigh yieldVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsAmino acid substitutionWild type
The present invention concerns a method for improving the growth characteristics of plants by increasing activity in a plant of an RNA-binding protein or a homologue thereof, wherein said RNA-binding protein or homologue thereof is either: (i) a polypeptide having RNA-binding activity and comprising either 2 or 3 RNA 10 recognition motifs (RRMs) and a motif having at least 75% sequence identity to motif I: PIYEAAVVALPVVVKERLVRILRLGIATRYD and / or a motif having at least 50% sequence identity to motif II: RFDPFTGEPYKFDP; or (ii) an RBP1 polypeptide or homologue thereof having (a) RNA-binding activity; (b) two RRM domains, (c) the following two motifs: (i) KIFVGGL; and (ii) 15 RPRGFGF, allowing for up to three amino acid substitutions and any conservative change in the motifs; and (d) having at least 20% sequence identity to the amino acid represented by SEQ ID NO: 15. The invention also concerns to transgenic plants having introduced therein an RNA-binding protein-encoding nucleic acid or variant thereof, which plants have improved growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants. The present invention also concerns constructs useful in the methods of the invention.
Owner:CROPDESIGN NV
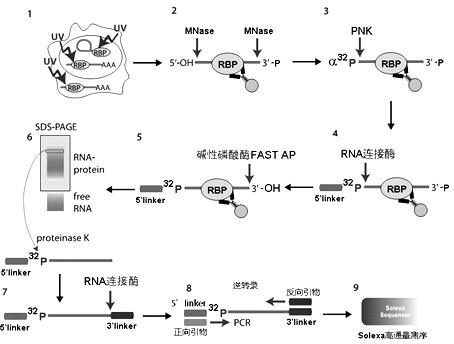
Method for identifying target RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of RNA binding protein through improved CLIP method
InactiveCN102628038AReduce degradationAvoid steric hindranceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationMicrococcal nucleaseBiology
The invention discloses a method for identifying a target RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of an RNA binding protein through an ultraviolet crosslinking-immune co-precipitation method. According to the method, micrococcalnuclease is used for performing incomplete enzymolysis instead of RNaseA and RNaseT1, and the micrococcalnuclease is completely inactivated by removing calcium ions (Ca<2+>) from a solution after enzymolysis is finished. Moreover, joints are arranged at the two ends of the target RNA in way of connecting 5'RNAlinker firstly and connecting 3'RNAlinker secondly after enzymolysis is finished. The micrococcalnuclease is used for clearing a part of RNAs, so that the degradation of the target RNA is effectively reduced; and due to the adoption of the scheme for connecting the 5'RNAlinker firstly, possible steric hindrance formed at a 3'end by a possibly-existing protein compound is overcome, and the successful rate of a CLIP technology is increased.
Owner:武汉生命之美科技有限公司
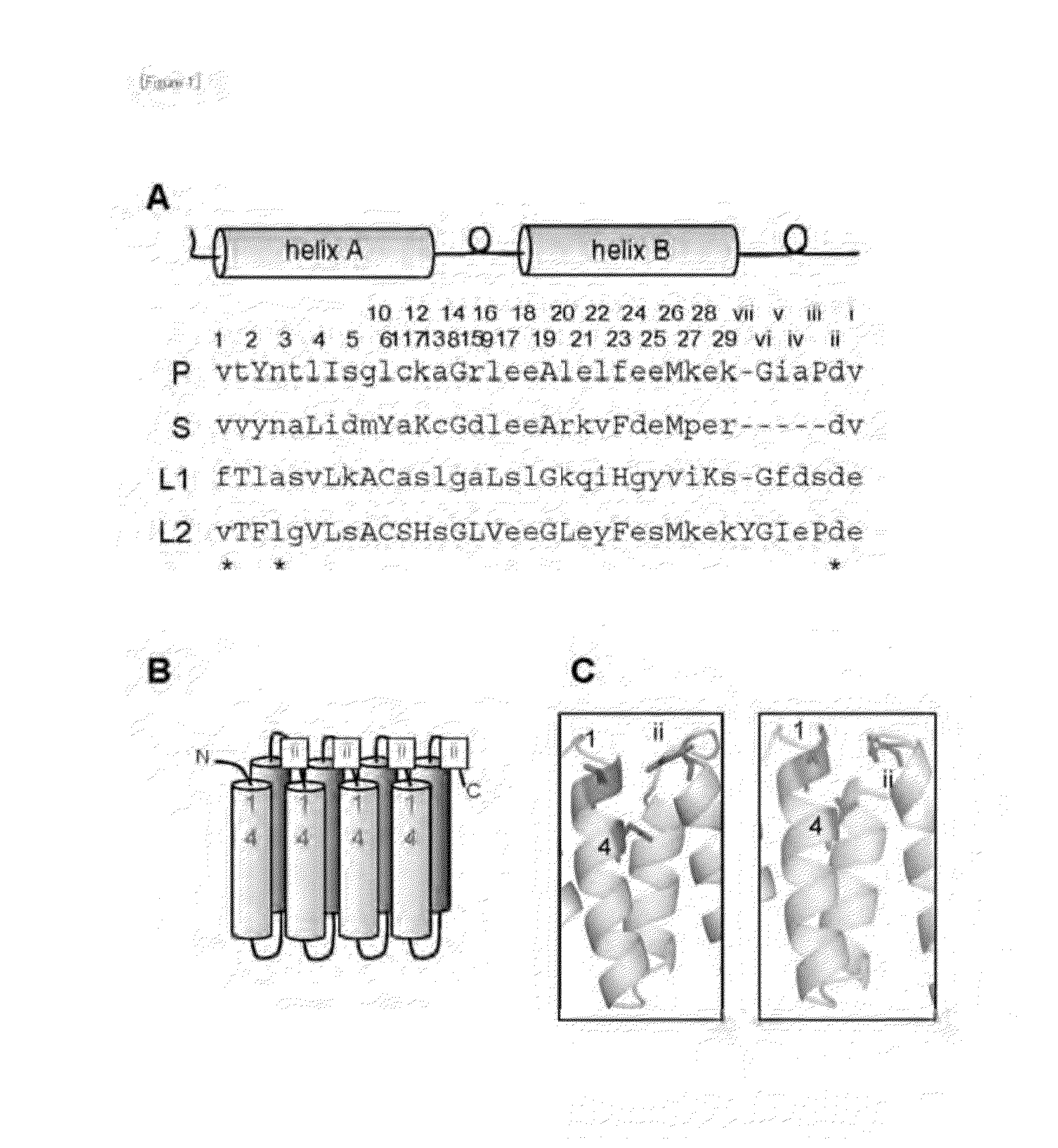
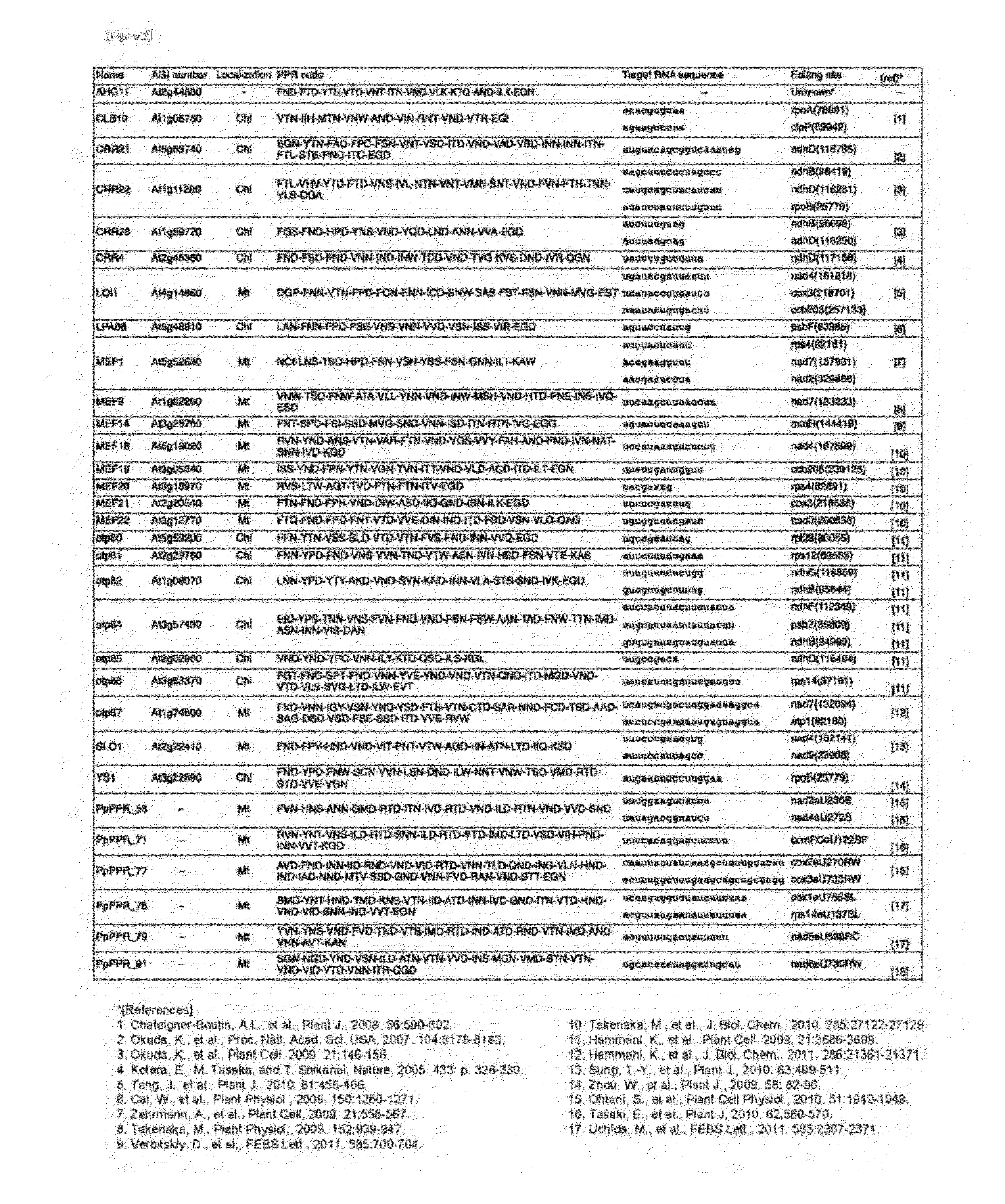
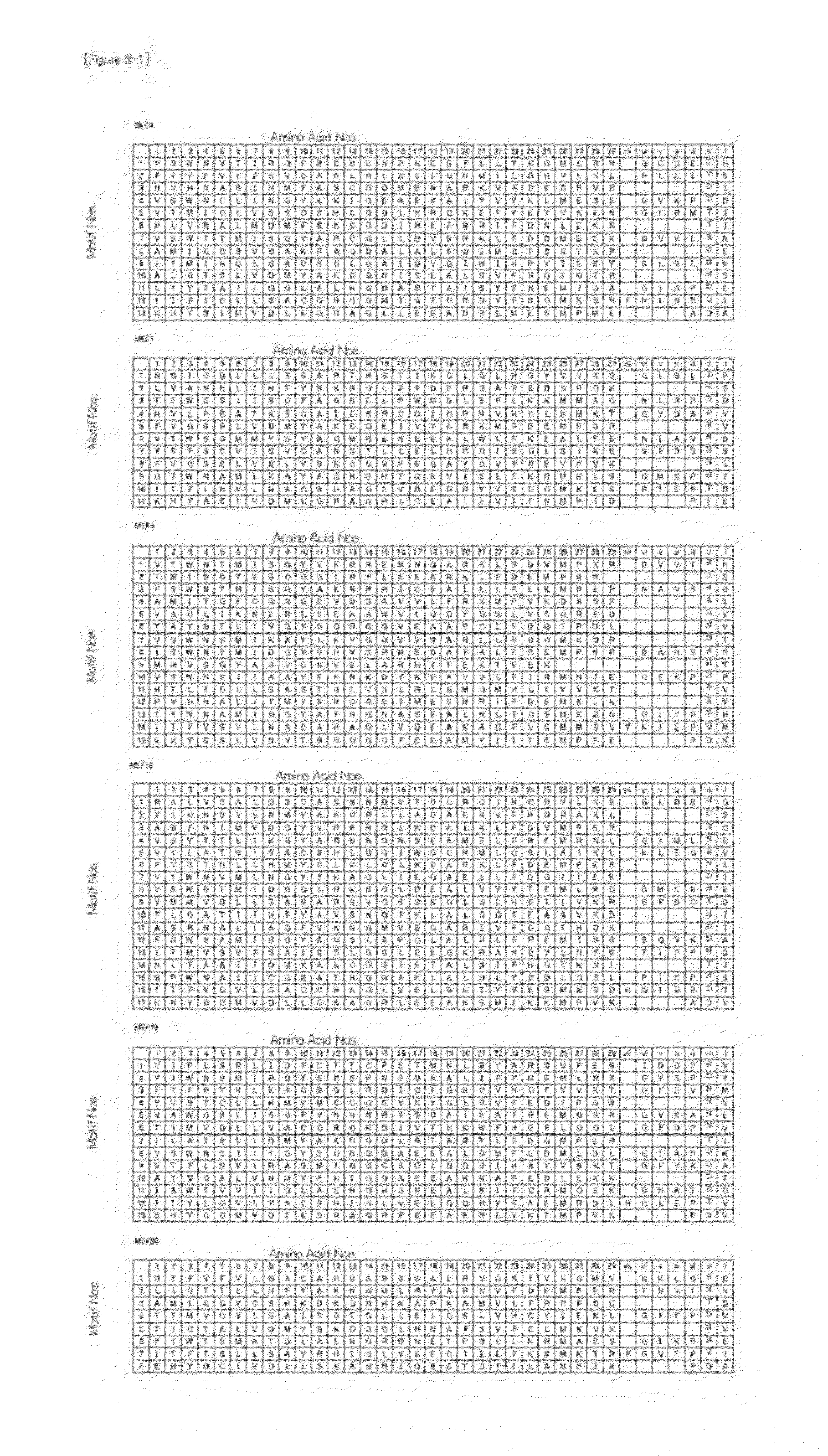
Method for Designing RNA Binding Protein Utilizing PPR Motif, and Use Thereof
ActiveUS20140335521A1Raise the possibilityFusion with RNA-binding domainMutant preparationProtein insertionC-terminus
A method for designing a protein capable of binding in an RNA base selective manner or RNA base sequence specific manner is provided. The protein of the present invention is a protein containing one or more of PPR motifs (preferably 2 to 14 PPR motifs) each consisting of a polypeptide of 30- to 38-amino acid length represented by the formula 1 (wherein Helix A is a moiety of 12-amino acid length capable of forming an α-helix structure, and is represented by the formula 2, wherein, in the formula 2, A1 to A12 independently represent an amino acid; X does not exist, or is a moiety of 1- to 9-amino acid length; Helix B is a moiety of 11- to 13-amino acid length capable of forming an α-helix structure; and L is a moiety of 2- to 7-amino acid length represented by the formula 3, wherein, in the formula 3, the amino acids are numbered “i” (-1), “ii” (-2), and so on from the C-terminus side, provided that Liii to Lvii may not exist), and combination of three amino acids A1, A4 and Lii, or combination of two amino acids A4, and Lii is a combination corresponding to a target RNA base or base sequence.
Owner:KYUSHU UNIV
Compounds for modulating RNA binding proteins and uses therefor
ActiveUS20110065704A1Increases formationImprove stabilityBiocideOrganic chemistryParasitic infectionInflammatory disorder
The invention relates to compositions and methods for inhibiting RNA binding proteins (e.g., MEX-3, MEX-5 and POS-1), as well as methods for treating and preventing disorders associated with parasitic infections and inflammatory disorders.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Kit for separating RNA (ribonucleic acid) bound in RNA binding protein
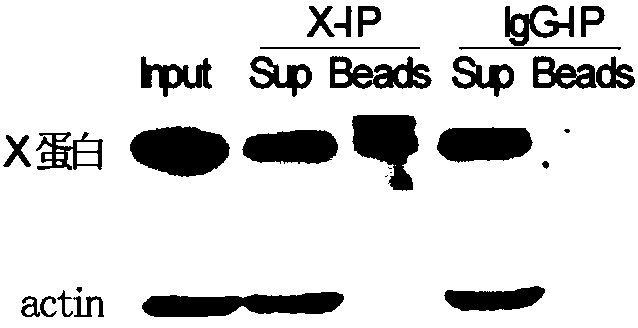
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology, particularly a kit for separating RNA (ribonucleic acid) bound in an RNA binding protein. The kit provided by the invention is used for separating, extracting and purifying RNA bound in a specific RNA binding protein. The kit comprises a lysis solution, a buffer solution and magnetic beads. The reagents in the kit are proportionally improved and optimized, and thus, can simply and stably obtain the mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) bound in the specific RNA binding protein in cells at higher yield through antibody antigen reaction and magnetic field principle. The kit is used for further cDNA real-time quantification, micro-array chip detection and other subsequent researches.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
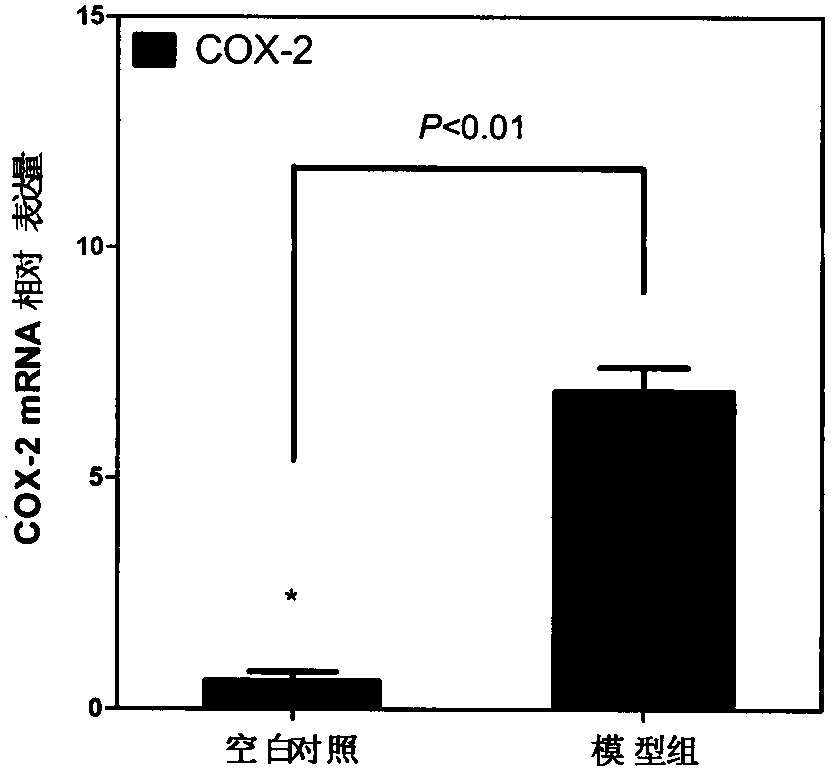
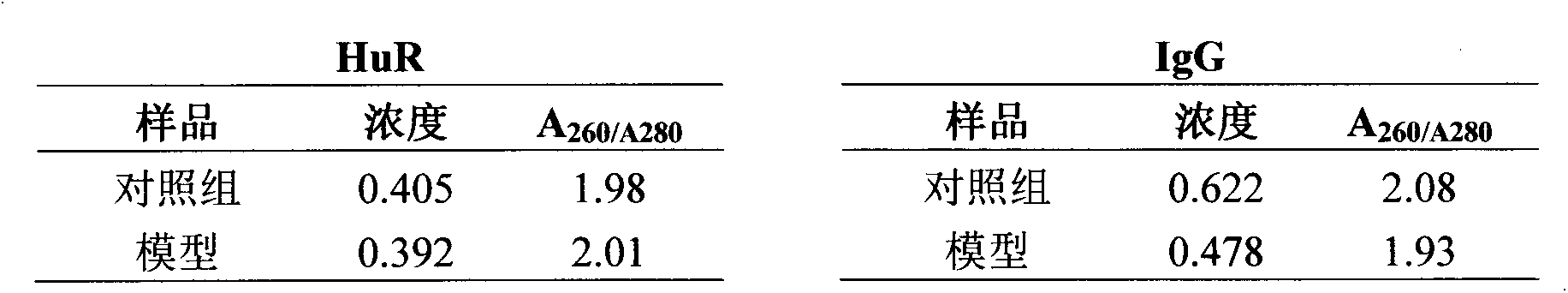
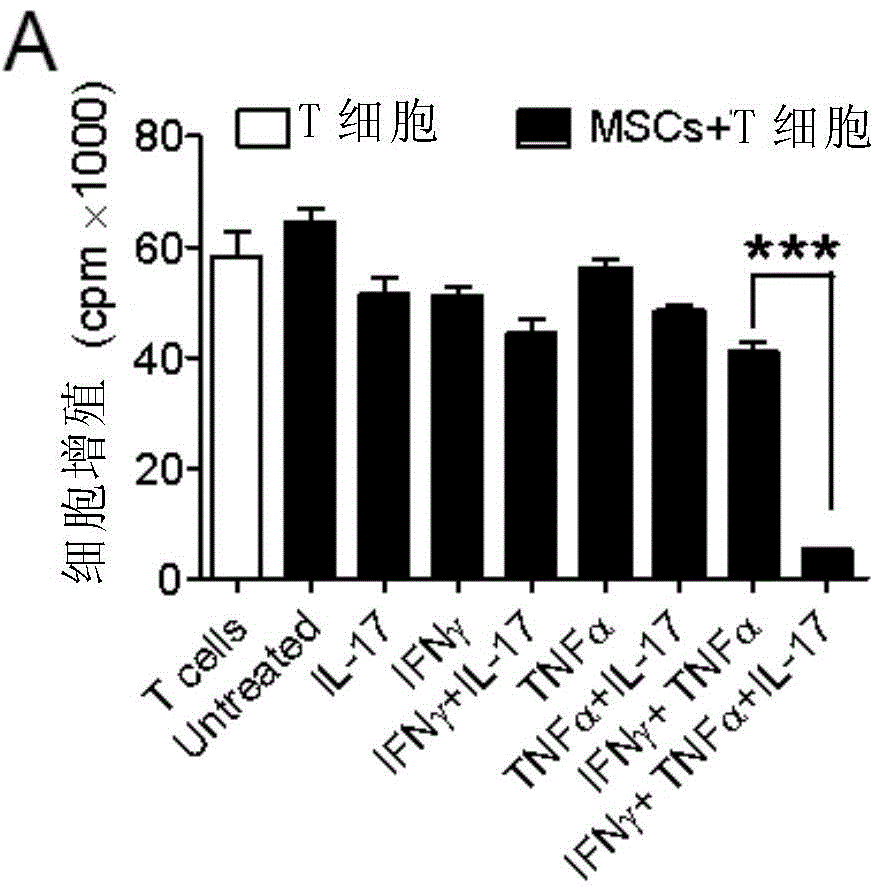
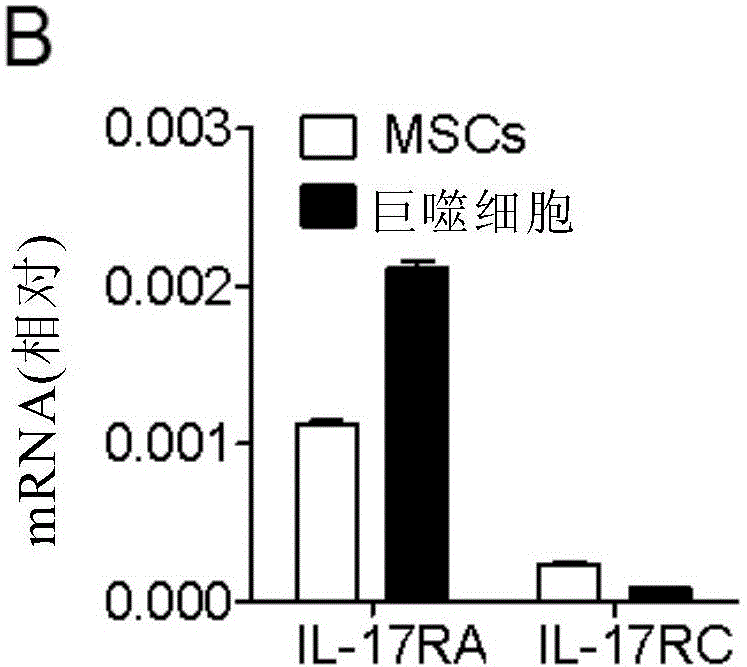
Application of IL-17 in improving mesenchymal stem cell immunity inhibition function
InactiveCN105079792AImprove immune suppressionPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemInterleukin 17Mesenchymal stem cell
Provided are uses of IL-17 in enhancing an immune-suppression function of mesenchymal stem cells. In particular, the present invention provides uses of an interleukin-17, a derivative of interleukin-17 or an agonist thereof for preparing a preparation or kit for enhancing an immune-suppression function of the mesenchymal stem cells; up-regulating the expression of imunosuppressive factors in the mesenchymal stem cells; enhancing the stability of mRNAs of the immunosuppressive factors; reducing the expression level of RNA-binding protein AUF1; inhibiting the proliferation of T cells; and treating hepatitis or liver damage.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
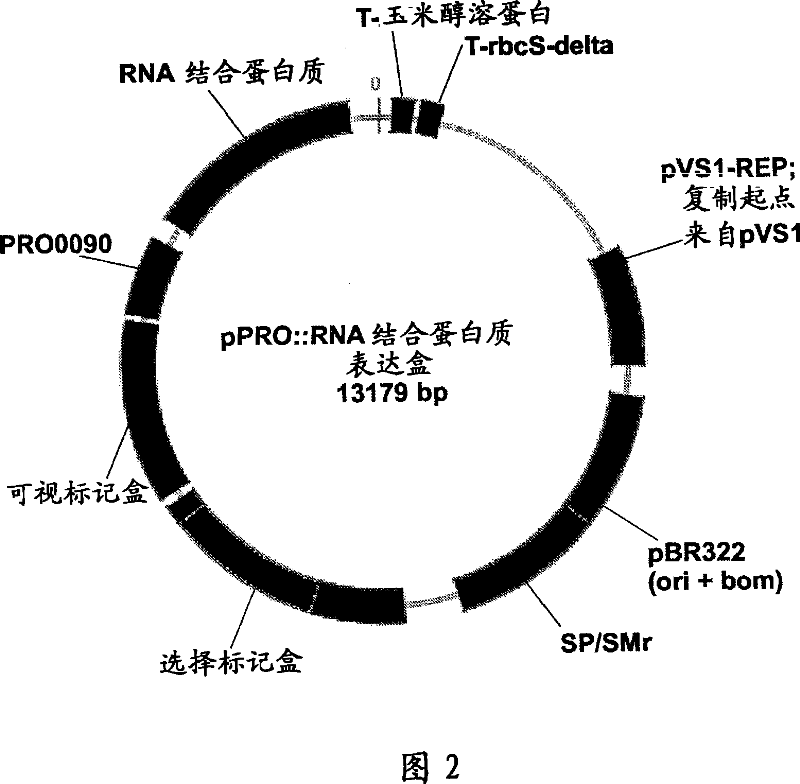
Expression vector of fusion protein for enhancing target RNA loading into exosome and establishment method and application thereof
InactiveCN108753806AEfficient deliveryImprove the efficiency of loading target RNAGenetic material ingredientsVector-based foreign material introductionDiseaseProtein target
The invention discloses an expression vector of a fusion protein for enhancing target RNA loading into an exosome and an establishment method and application thereof. The expression vector comprises atarget RNA binding protein sequence and an exosome membrane targeting protein sequence. The target RNA binding protein sequence comprises an RNA binding protein complete sequence or an RNA binding structural domain sequence. The exosome membrane targeting protein sequence can be localized in the exosome. In addition, the establishment method of the expression vector of the fusion protein for enhancing target RNA loading into the exosome is designed. The exosome containing the expression vector of the fusion protein for enhancing target RNA loading is prepared. The expression vector or the exosome is applied to targeting delivery of gene treatment and RNA regulated relevant disease treatment. Efficient candidate RNA molecule loading can be achieved, and meanwhile cellular endogenous RNA loading of the exosome is decreased. The expression vector can serve as an optimized vector for targeting delivery of gene treatment.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
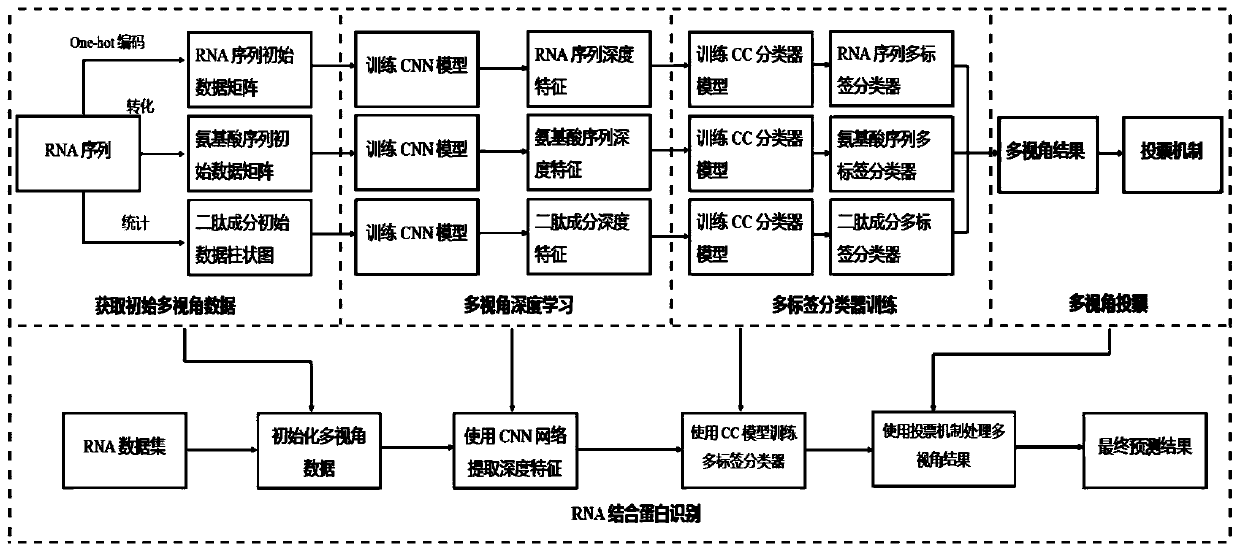
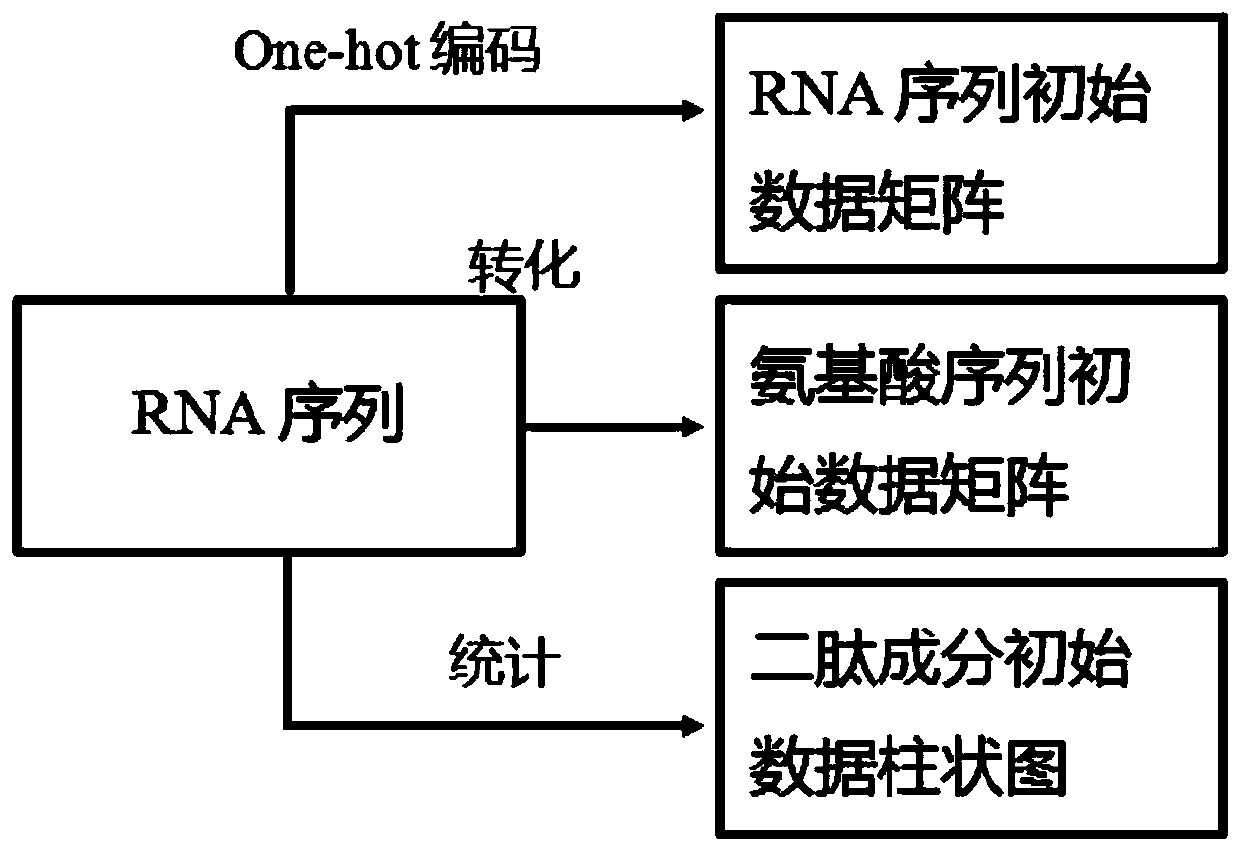
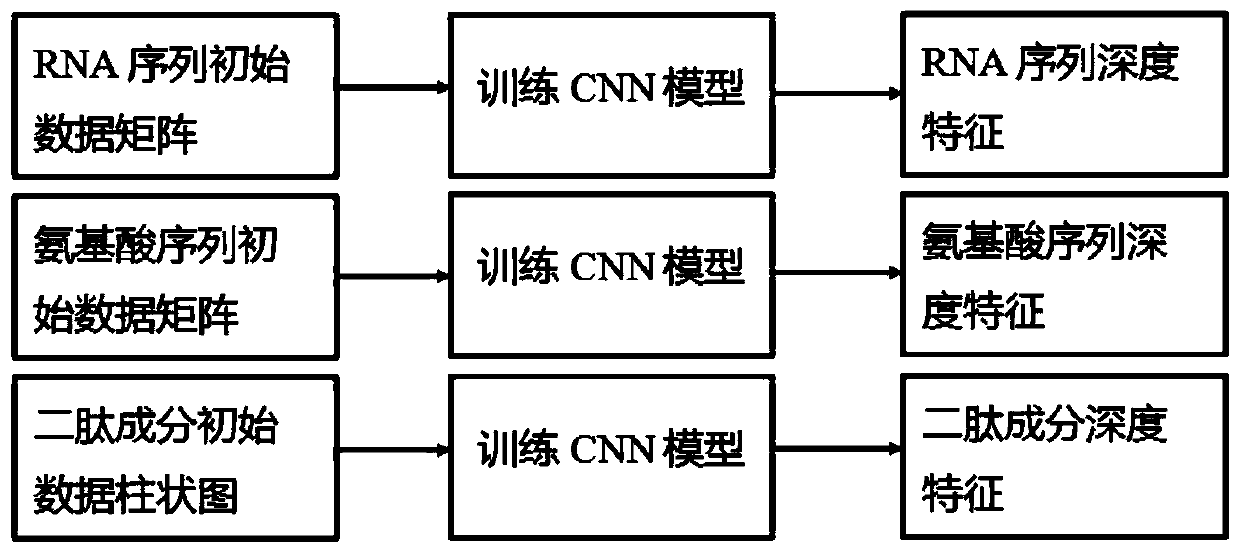
RNA binding protein recognition method based on multi-view depth features and multi-label learning
ActiveCN111445944AImprove bindingImprove classification performanceProteomicsGenomicsDipeptideMulti-label classification
The invention belongs to the field of intelligent cell biological recognition, and relates to an RNA binding protein recognition method based on multi-view depth features and multi-label learning. Themethod comprises a training stage and a use stage, wherein the training stage comprises initial multi-view data construction, a depth multi-view feature extraction model and multi-label classifier training, wherein the initial multi-view data construction comprises the following steps: converting an original RNA sequence into an amino acid sequence and a dipeptide component by using a molecular biology principle and a statistics principle to obtain the characteristics of the amino acid sequence and the dipeptide component, and then constructing an initial multi-view characteristic together with the original RNA sequence, and constructing a model for the initial multi-view characteristic. According to the method, based on the initial multi-view data, the CNN is used for deep learning to construct a deep multi-view characteristic, and compared with the original multi-view characteristic, the multi-view characteristic extracted based on the deep features have smaller data dimensions anda higher classification effect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Tumor markers for ovarian cancer diagnosis
The present invention relates to a tumor marker for diagnosis of ovarian cancer, which is selected from the group consisting of galectin-1, cathepsin B, MHC class I antigen, heat shock protein (HSP) 27, ubiquitin carboxy-termal esterase L1, plasma retinol-binding protein (PRBP), transthyretin, SH3 binding glutamate-rich protein, tubulin-specific chaperone A, RNA binding protein regulatory subunit, γ-actin, tropomyosin and calcium / calmodulin-stimulated cyclic nucleotide phosphatase. The ovarian cancer is diagnosed effectively and efficiently based on detecting the expression levels of the tumor markers in the invention from the ovarian tissue sample of an individual to be diagnosed.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Viral vector production system
The present invention relates to a nucleic acid sequence comprising a binding site operably linked to a nucleotide of interest, wherein the binding site is capable of interacting with an RNA-binding protein such that translation of the nucleotide of interest is repressed in a viral vector production cell.
Owner:MOREHOUSE SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Plant having enhanced yield-related trait and method for making same
The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for enhancing various yield-related traits and / or plant growth characteristics in plants by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a C3H-like polypeptide, or a SPATULA-like (SPT) polypeptide, or an IDI2 (Iron Deficiency Induced 2) polypeptide, or an eIF4F-like protein complex subunit, or GR-RBP (Glycine Rich-RNA Binding Protein) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression and / or activity of a nucleic acid encoding a C3H-like polypeptide, or a SPATULA-like (SPT) polypeptide, or an IDI2 (Iron Deficiency Induced 2) polypeptide, or an eIF4F-like protein complex subunit, or GR-RBP (Glycine Rich-RNA Binding Protein) polypeptide, which plants have enhanced yield-related traits and / or plant growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants or other control plants. The invention also provides constructs useful in the methods of the invention.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in signaling pathways
InactiveUS20100159477A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementGolgi componentCell Surface Proteins
The invention discloses novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: adaptor / scaffold proteins, adhesion / extracellular matrix protein, apoptosis proteins, calcium binding proteins, cell cycle regulation proteins, chaperone proteins, chromatin, DNA binding / repair / replication proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, endoplasmic reticulum or golgi proteins, enzyme proteins, G / regulator proteins, inhibitor proteins, motor / contractile proteins, phosphatase, protease, Ser / Thr protein kinases, Protein kinase (Tyr)s, receptor / channel / cell suface proteins, RNA binding proteins, transcriptional regulators, tumor suppressor proteins, ubiquitan conjugating system proteins and proteins of unknown function.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com