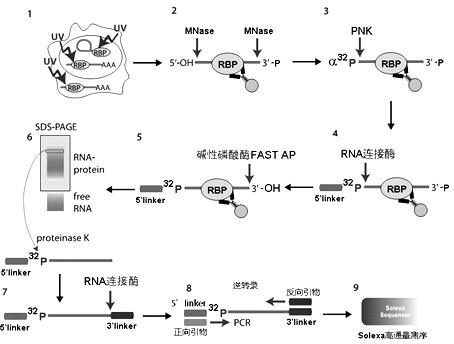
Method for identifying target RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of RNA binding protein through improved CLIP method
A technology for binding proteins and targets, which is applied in the fields of molecular biology and cell biology, can solve problems such as impact, and achieve the effects of overcoming steric hindrance, improving success rate, and reducing degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
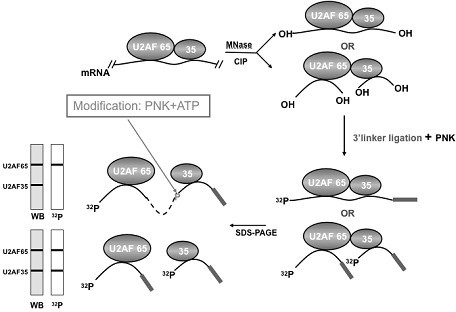
[0031] Example 1: Design and synthesis of RNA linker
[0032] The linker sequence used matches the UCSD Solexa sequencer. The sequence is 5'linker: 5'Biotin-AAU GAU ACG GCG ACC ACC GA 3'; 3'linker: 5'PO4-UCG UAU GCC GUC UUC UGC UUG-Puromycin. The biotin at the 5' end of the 5'linker and the puromycin at the 3' end of the 3'linker can block the end of the linker to prevent self-connection as described above. The reverse transcription primer is the reverse complementary DNA sequence of the 3' linker, namely: 5'CAA GCA GAA GAC GGC ATA CGA, the forward primer used in PCR is 5'AAT GAT ACG GCG ACC ACC GA, and the reverse primer is the reverse transcription primer.
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment 2: Preparation of ultraviolet cross-linking and cell lysate
[0034] 1) Use a 150mm cell culture dish to culture HeLa cells, use DMEM (Invitrogen) as the medium, discard the medium when the cell abundance reaches over 80%, rinse twice with 1xPBS buffer, then add an appropriate amount of PBS buffer to cover cell surface;
[0035] 2) Put the petri dish on ice, put it into the lower drawer of HL-2000 crosslinker (UVP), use 400mj / cm 2 The energy of 254nm ultraviolet light is irradiated for 1 to 1.5 minutes. Then take out the culture dish, pour off the PBS, add 15ml of PBS, and scrape off the cells with a cell scraper;
[0036] 3) Pipette the PBS suspension of all cells into a 15ml centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 4000rpm at 4°C for 5 minutes, and remove the supernatant. Add 1.5ml PBS, blow up the precipitate with a pipette, transfer to a clean 1.5ml centrifuge tube (DEPC treatment or use imported RNase free centrifuge tube), centrifuge again at 4000rpm for 5 min...
Embodiment 3
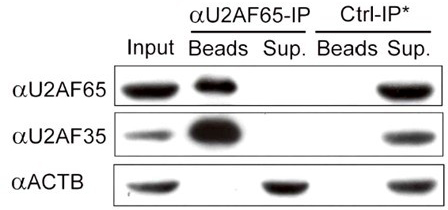
[0042] Example 3: Co-immunoprecipitation
[0043] 1) Couple 300 μl of protein A magnetic beads (Protein A beads, Dynal beads, Invitrogen 100.02) to U2AF65 monoclonal antibody (MC3, Abcam Company). Aspirate the supernatant after bead precipitation;
[0044] 2) Add 900 μl of elution buffer (same as Example 2) to resuspend the magnetic beads, put them on the magnetic separation rack until the magnetic beads are precipitated, and repeat this three times;
[0045] 3) Add 700 μl of the cell lysate in Example 1 to the magnetic beads in 2), resuspend the magnetic beads until they are completely suspended in the cell lysate, place them on a rotary mixer, and mix at 4°C for one hour;
[0046] 4) Take out the supernatant with a pipette and keep 50 μl for Western detection of IP efficiency ( image 3 ), the rest of the supernatant was discarded;
[0047] 5) Add 900 μl of elution buffer to the magnetic beads bound to U2AF65 protein, elute twice as described above, then add high-salt was...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com