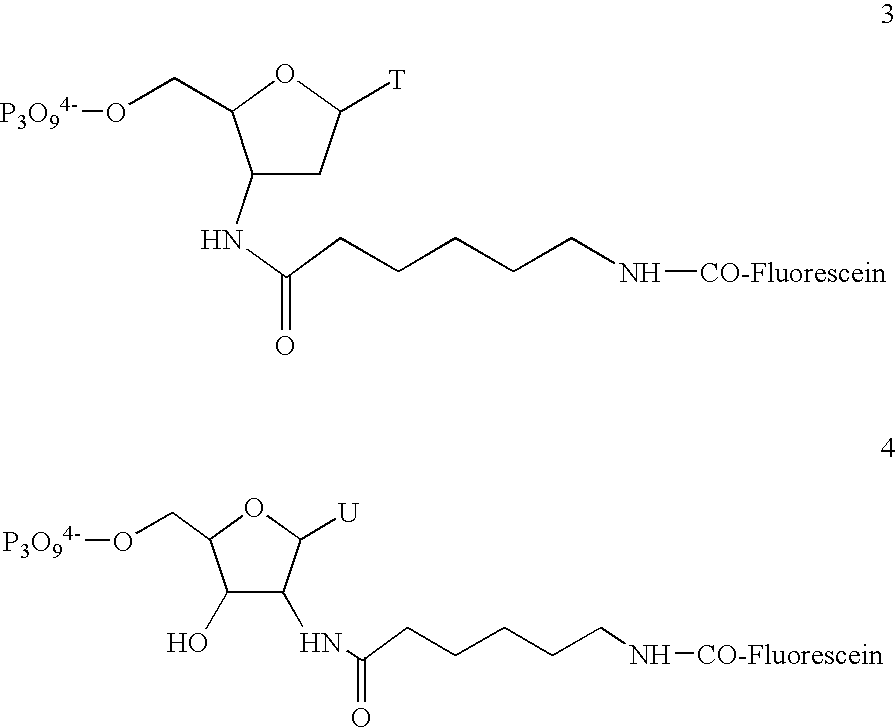
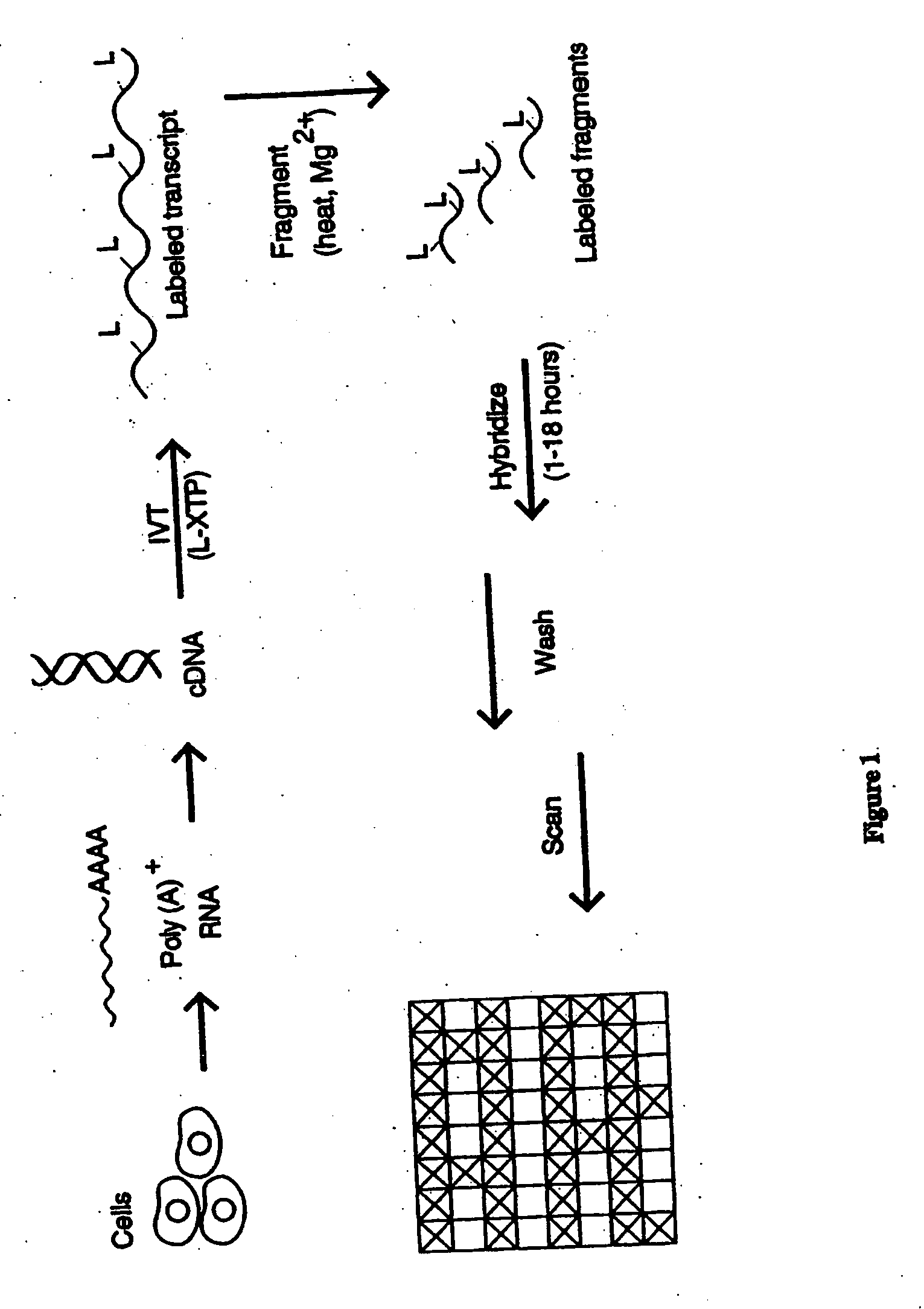
Nucleic acid analysis techniques
a technology of nucleic acid and analysis techniques, applied in the field of nucleic acid analysis techniques, can solve the problems of difficult or impossible to distinguish two or more gene products of approximately the same molecular weight, difficult to obtain an accurate and reliable measure of gene expression with one, or even a few, probes to the target gene, etc., and achieves the effect of simple application and rapidity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
First Generation Oligonucleotide Arrays Designed to Measure mRNA Levels for a Small Number of Murine Cytokines
A) Preparation of Labeled RNA.
[0479] 1) From Each of the Preselected Genes.
[0480] Fourteen genes (IL-2, IL-3, Il-4, IL-6, Il-10, IL-12p40, GM-CSF, IFN-γ, TNF-α, CTLA8, β-actin, GAPDH, IL-11 receptor, and Bio B) were each cloned into the p Bluescript II KS (+) phagemid (Stratagene, La Jolla, Calif., USA). The orientation of the insert was such that T3 RNA polymerase gave sense transcripts and T7 polymerase gave antisense RNA.
[0481] Labeled ribonucleotides in an in vitro transcription (IVT) reaction. Either biotin- or fluorescein-labeled UTP and CTP (1:3 labeled to unlabeled) plus unlabeled ATP and GTP were used for the reaction with 2500 units of T7 RNA polymerase (Epicentre Technologies, Madison, Wis., USA). In vitro transcription was done with cut templates in a manner like that described by Melton et al., Nucleic Acids Research, 12: 7035-7056 (1984). A typical in vitr...
example 2
T Cell Induction Experiments Measuring Cytokine mRNAs as a Function of Time Following Stimulation
[0525] The high density arrays of this invention were next used to monitor cytokine MRNA levels in murine T cells at different times following a biochemical stimulus. Cells from the murine T helper cell line (2D6) were treated with the phorbol ester 4-phorbol-12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and a calcium ionophore. Poly (A)+ MRNA was then isolated at 0, 2, 6 and 24 hours after stimulation. Isolated mRNA (approximately 1 μg) was converted to labeled antisense RNA using a procedure that combines a double-stranded cDNA synthesis step with a subsequent in vitro transcription reaction. This RNA synthesis and labeling procedure amplifies the entire mRNA population by 20 to 50-fold in an apparently unbiased and reproducible fashion (Table 2).
[0526] The labeled antisense T-cell RNA from the four time points was then hybridized to DNA probe arrays for 2 and 22 hours. A large increase in the γ-int...
example 3
Higher-Density Arrays Containing 65,000 Probes for Over 100 Murine Genes
[0528]FIG. 5 shows an array that contains over 65,000 different oligonucleotide probes (50 μm feature size) following hybridization with an entire murine B cell RNA population. Arrays of this complexity were read at a resolution of 7.5 μm in less than fifteen minutes. The array contains probes for 118 genes including 12 murine genes represented on the simpler array described above, 35 U.S.C. § 1020 additional murine genes, three bacterial genes and one phage gene. There are approximately 300 probe pairs per gene, with the probes chosen using the selection rules described herein. The probes were chosen from the 600 bases of sequence at the 3′ end of the translated region of each gene. A total of 21 murine RNAs were unambiguously detected in the B cell RNA population, at levels ranging from approximately 1:300,000 to 1:100.
[0529] Labeled RNA samples from the T cell induction experiments (FIG. 4) were hybridized ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fluorescence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com