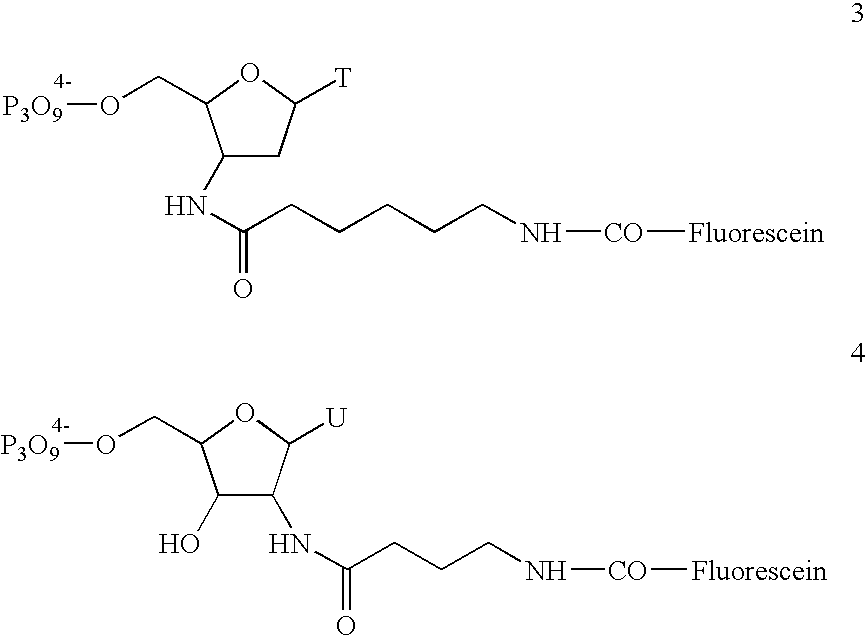
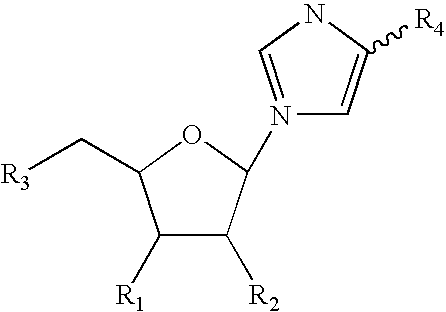
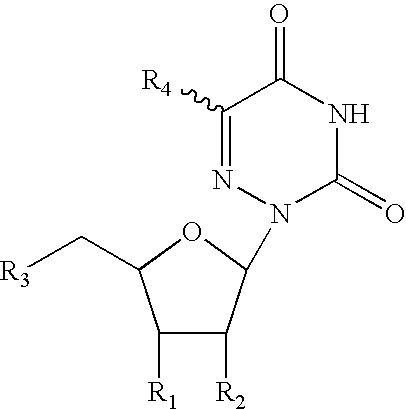
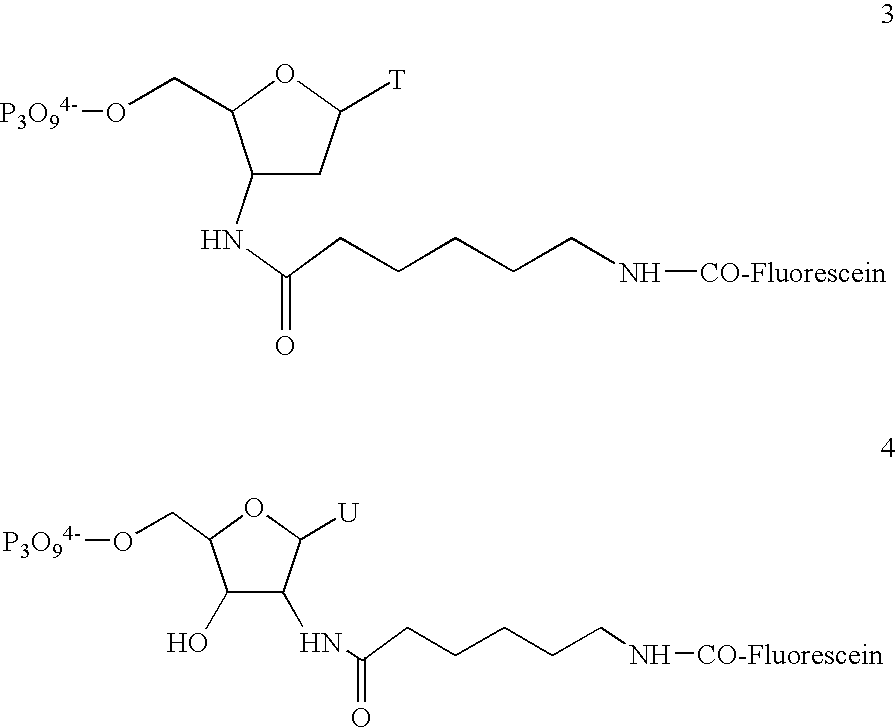
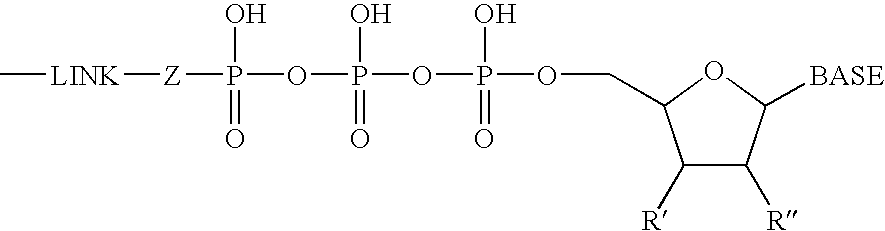
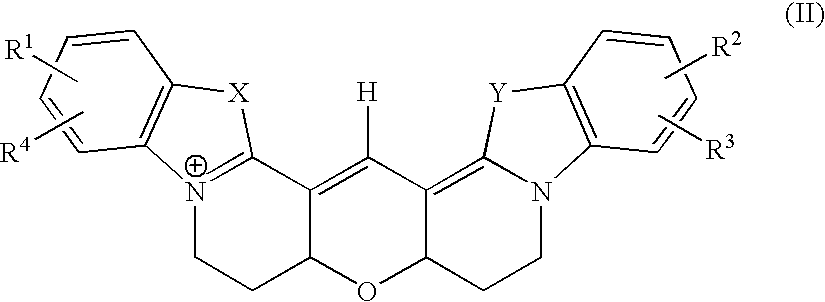
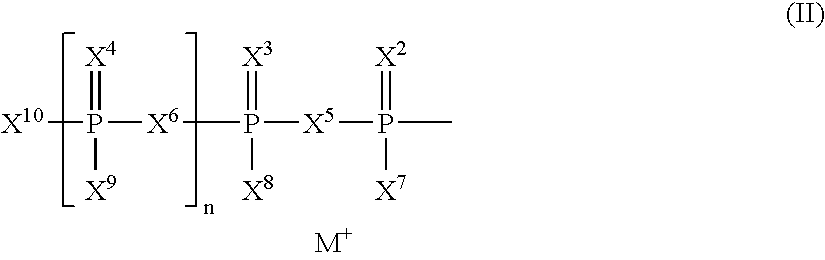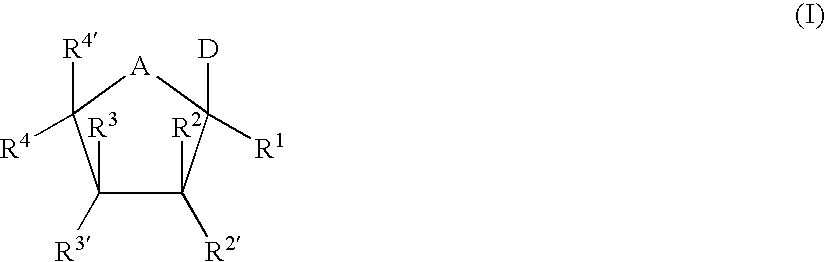Patents
Literature
118 results about "Nucleoside triphosphate synthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nucleoside triphosphates cannot be absorbed well, so they are typically synthesized within the cell. Synthesis pathways differ depending on the specific nucleoside triphosphate being made, but given the many important roles of nucleoside triphosphates, synthesis is tightly regulated in all cases.
Nucleotide mimics and their prodrugs
The present invention relates to nucleoside diphosphate mimics and nucleoside triphosphate mimics, which contain diphosphate or triphosphate moiety mimics and optionally sugar-modifications and / or base-modifications. The nucleotide mimics of the present invention, in a form of a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, a pharmaceutically acceptable prodrug, or a pharmaceutical formulation, are useful as antiviral, antimicrobial, and anticancer agents. The present invention provides a method for the treatment of viral infections, microbial infections, and proliferative disorders. The present invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of the present invention optionally in combination with other pharmaceutically active agents.
Owner:BIOTA SCI MANAGEMENT PTI LTD
Reagents for reversibly terminating primer extension
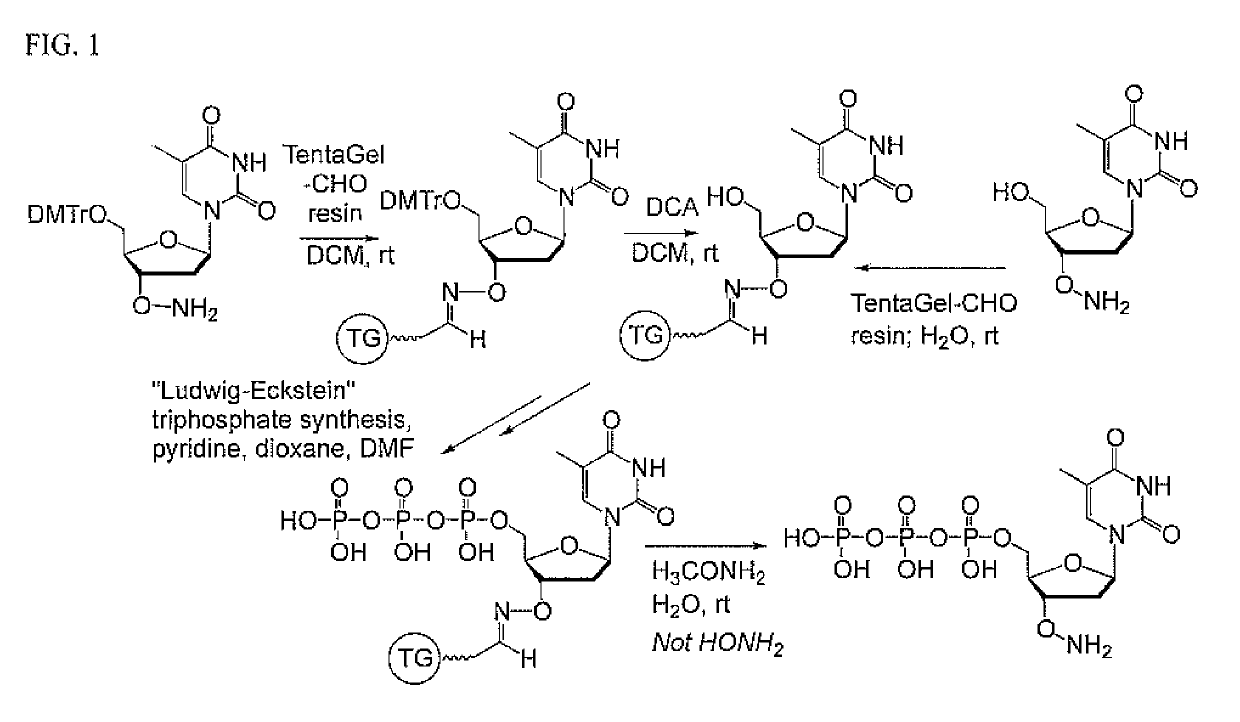
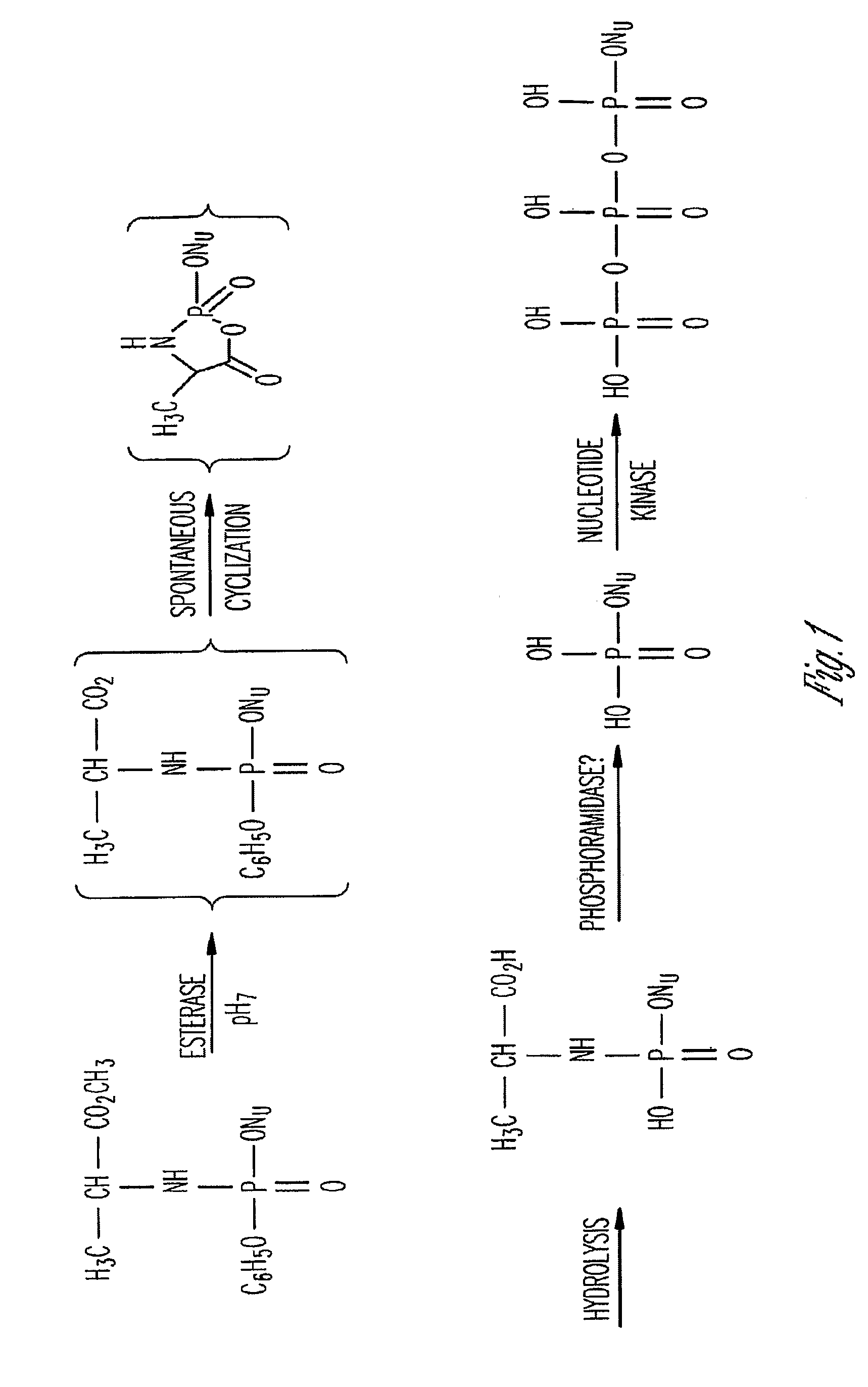
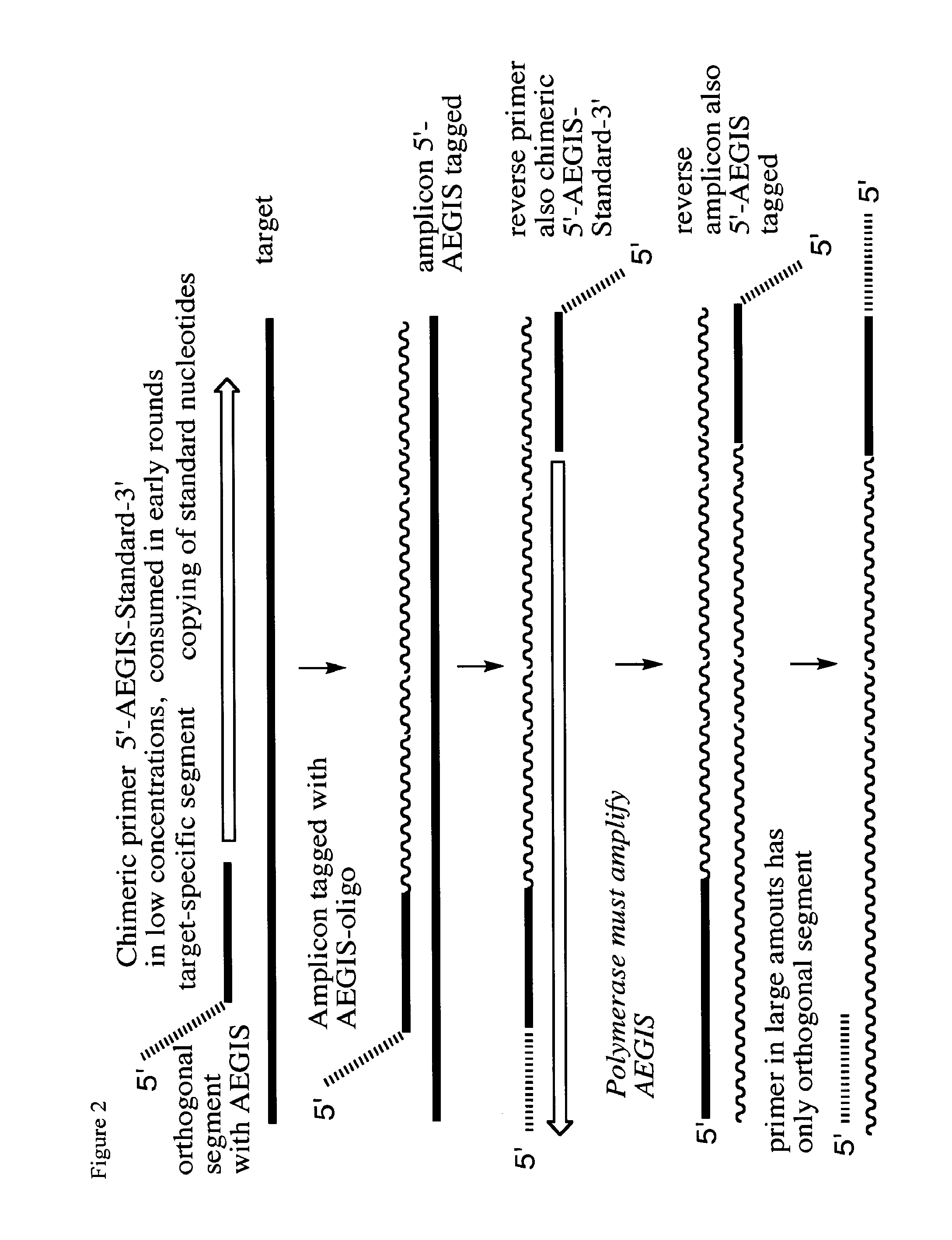
Processes are disclosed that use 3′-reversibly terminated nucleoside triphosphates to analyze DNA for purposes other than sequencing using cyclic reversible termination. These processes are based on the unexpected ability of terminal transferase to accept these triphosphates as substrates, the unexpected ability of polymerases to add reversibly and irreversibly terminated triphosphates in competition with each other, the development of cleavage conditions to remove the terminating group rapidly, in high yield, and without substantial damage to the terminated oligonucleotide product, and the ability of reversibly terminated primer extension products to capture groups. The presently preferred embodiments of the disclosed processes use a triphosphate having its 3′-OH group blocked as a 3′-ONH2 group, which can be removed in buffered NaNO2 and use variants of Taq DNA polymerase, including one that has a replacement (L616A).
Owner:BENNER STEVEN ALBERT +3
Mutation analysis using mass spectrometry
InactiveUS6503710B2Rapid and economic sample preparationAccurate massSamplingSugar derivativesChemical treatmentFree form
The invention presents a method for examining genetic material (deoxyribonucleic acid, DNA) to detect the presence of pre-known mutations, especially single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), using mass spectrometry with ionization by matrix-assisted laser desorption (MALDI). The invention uses nucleoside triphosphates with modified sites for the method of primer extension in a duplicating, enzymatic reaction and at least partially removal of primers from the extension product, in combination with product neutralization by chemical treatment of the modified sites, so that the resulting DNA products can be, by using special matrix materials, preferredly ionized in an adduct-free form over other constituents in the reaction solution without any further cleaning. The method is particularly suitable for simultaneous identification of several mutations by multiplexing.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH
Fluorescently labeled nucleoside triphosphates and analogs thereof for sequencing nucleic acids
InactiveUS20050170367A1Reducing background fluorescenceEfficient excitationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleoside triphosphateFluorescent labelling
The invention provides methods for sequencing a nucleic acid, and particularly methods for synthesizing fluorescently labeled nucleoside triphosphates and related analogs for sequencing nucleic acids.
Owner:HELICOS BIOSCIENCES CORPORATION +1
Mesoscale polynucleotide amplification device and method
InactiveUS6953676B1Quick testBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsTemperature controlPolymerase L
Disclosed are devices for amplifying a preselected polynucleotide in a sample by conducting a polynucleotide polymerization reaction. The devices comprise a substrate microfabricated to define a sample inlet port and a mesoscale flow system, which extends from the inlet port. The mesoscale flow system includes a polynucleotide polymerization reaction chamber in fluid communication with the inlet port which is provided with reagents required for polymerization and amplification of a preselected polynucleotide. In one embodiment the devices may be utilized to implement a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in the reaction chamber (PCR chamber). The PCR chamber is provided with the sample polynucleotide, polymerase, nucleoside triphosphates, primers and other reagents required for the polymerase chain reaction, and the device is provided with means for thermally controlling the temperature of the contents of the reaction chamber at a temperature controlled to dehybridize double stranded polynucleotide, to anneal the primers, and to polymerize and amplify the polynucleotide.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Fret-labeled compounds and uses therefor
ActiveUS20130071849A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCombinatorial chemistryNucleoside triphosphate
FRET-labeled compounds are provided for use in analytical reactions. In certain embodiments, FRET-labeled nucleotide analogs are used in place of naturally occurring nucleoside triphosphates or other analogs in analytical reactions comprising nucleic acids, for example, template-directed nucleic acid synthesis, DNA sequencing, RNA sequencing, single-base identification, hybridization, binding assays, and other analytical reactions.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Nucleotide mimics and their prodrugs
Owner:BIOTA SCI MANAGEMENT PTI LTD
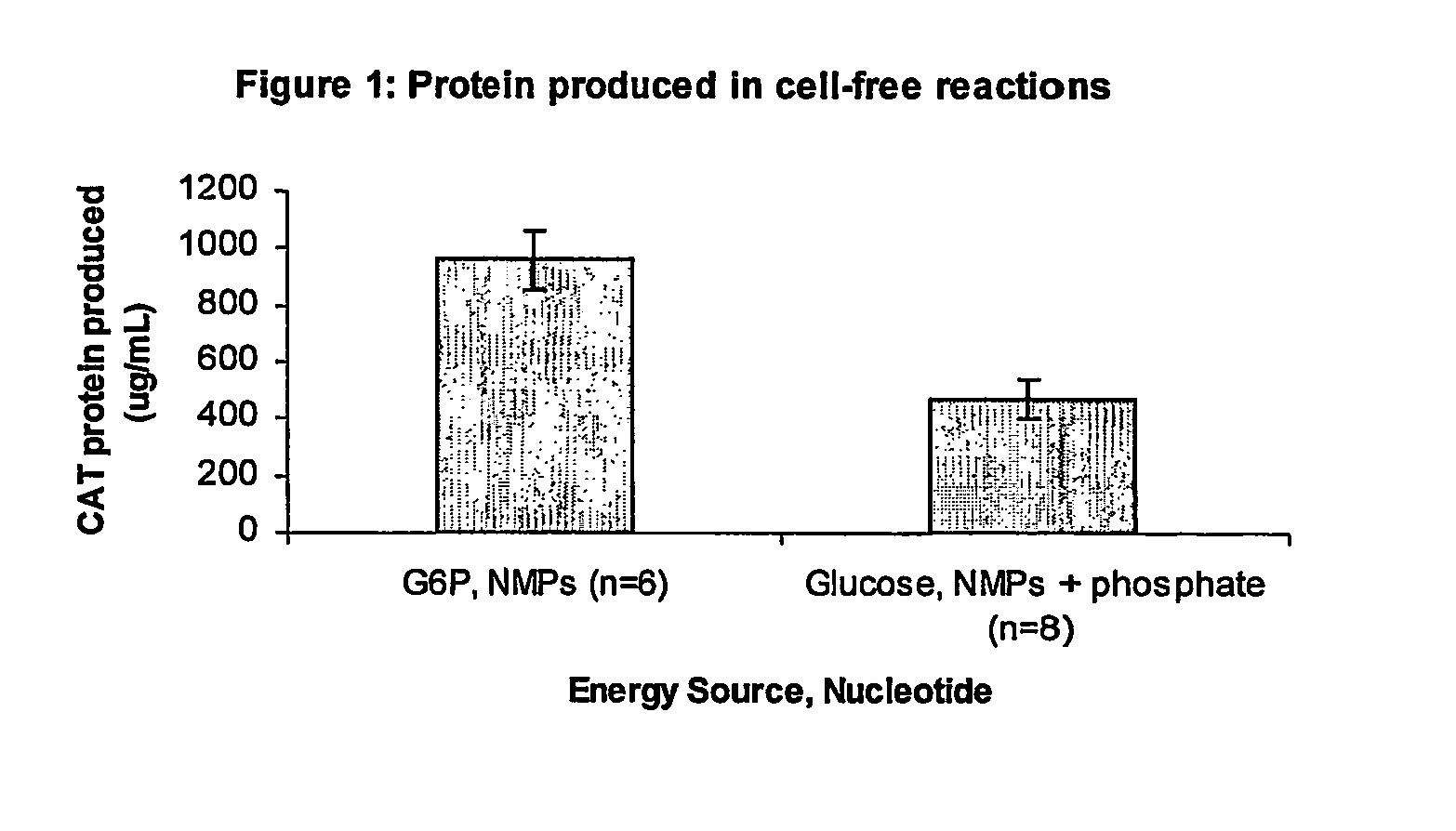
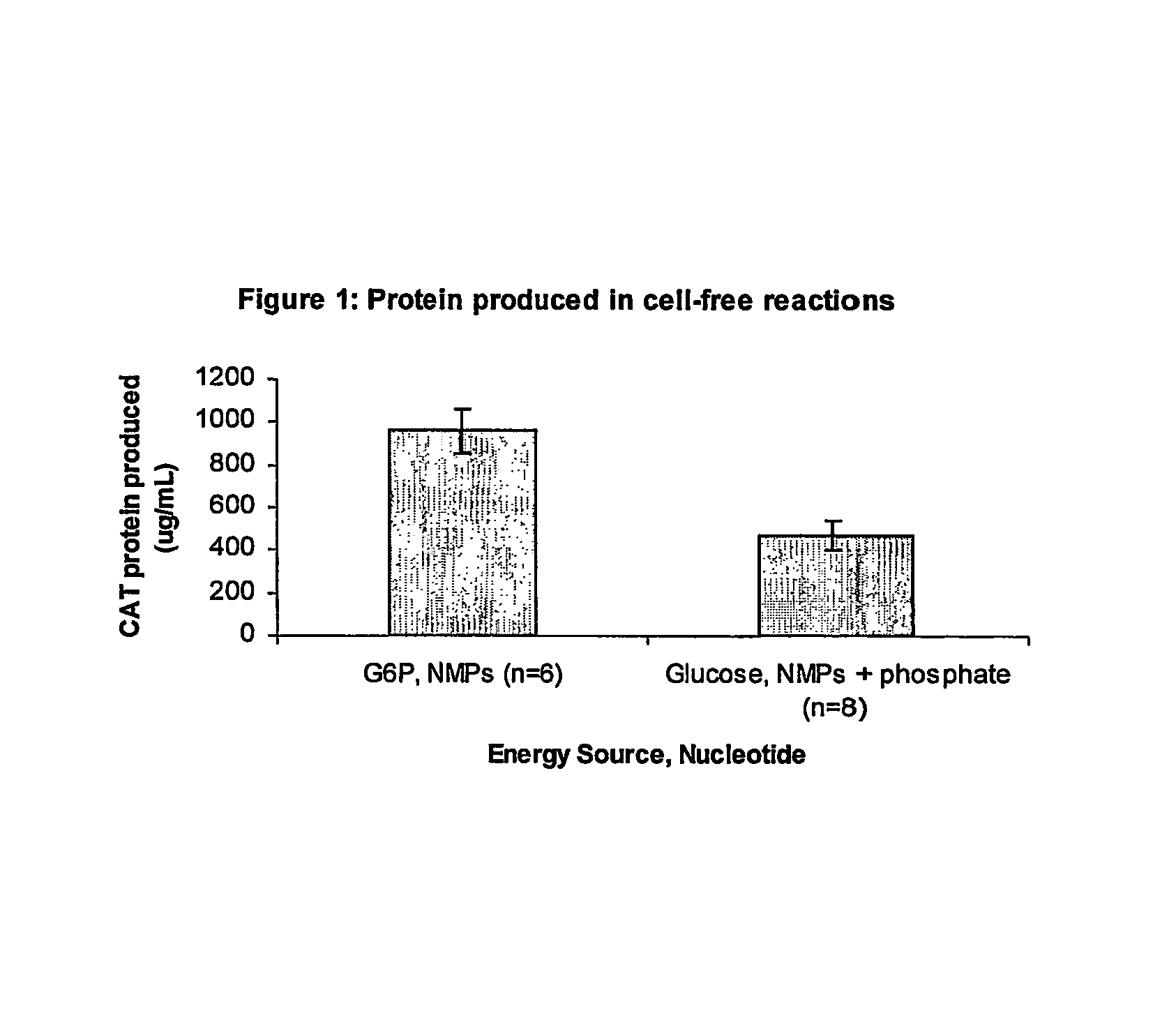
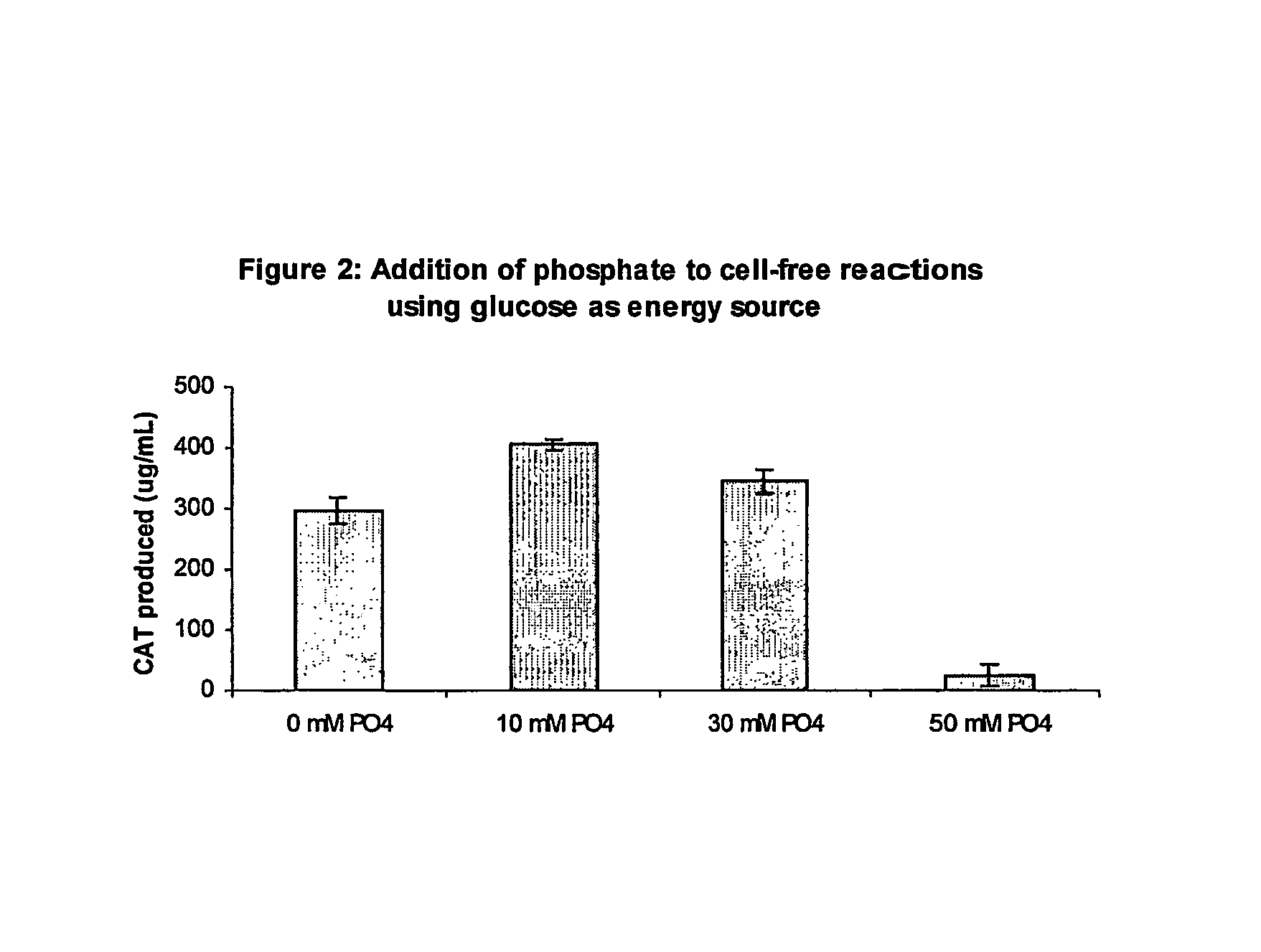
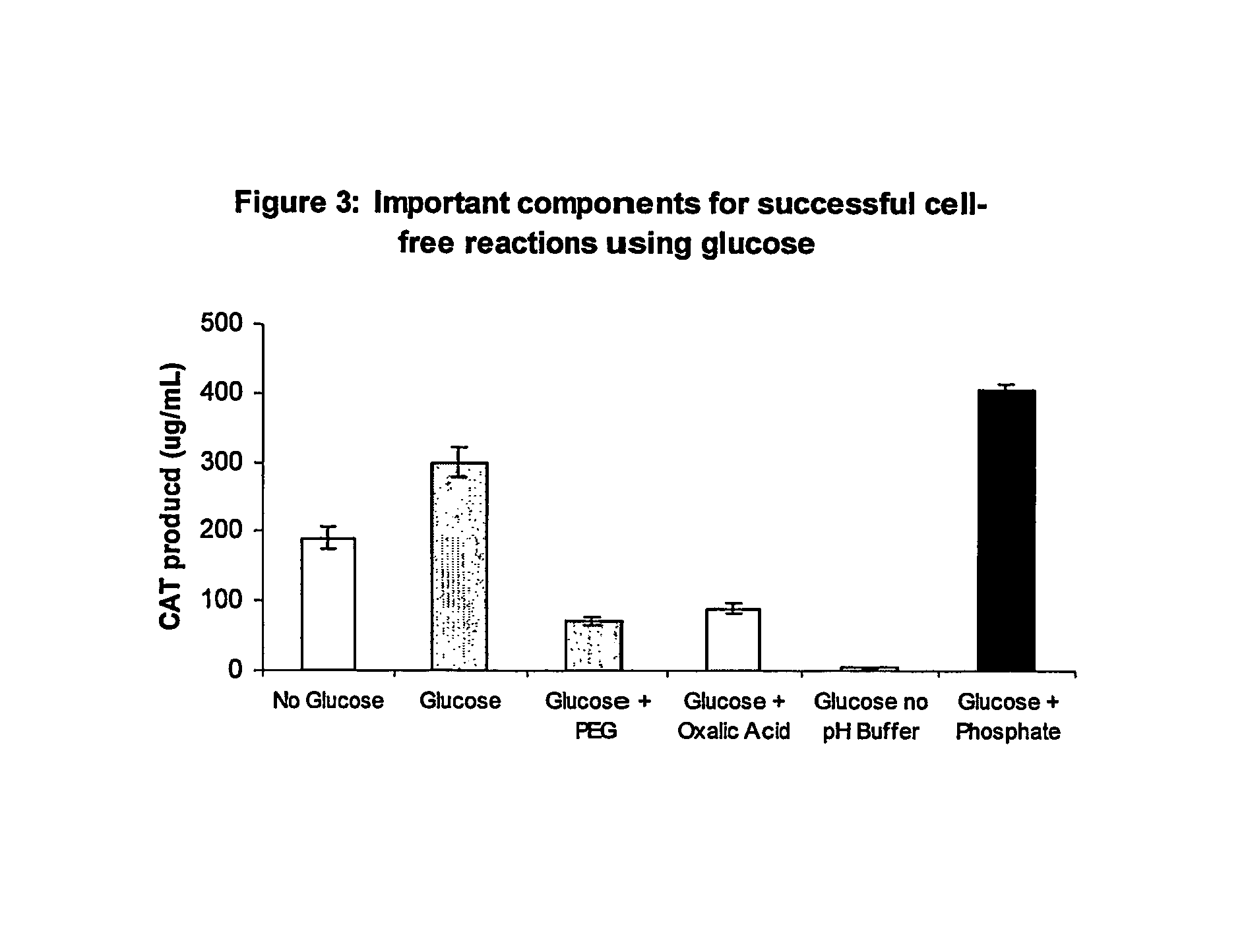
Methods of in vitro protein synthesis
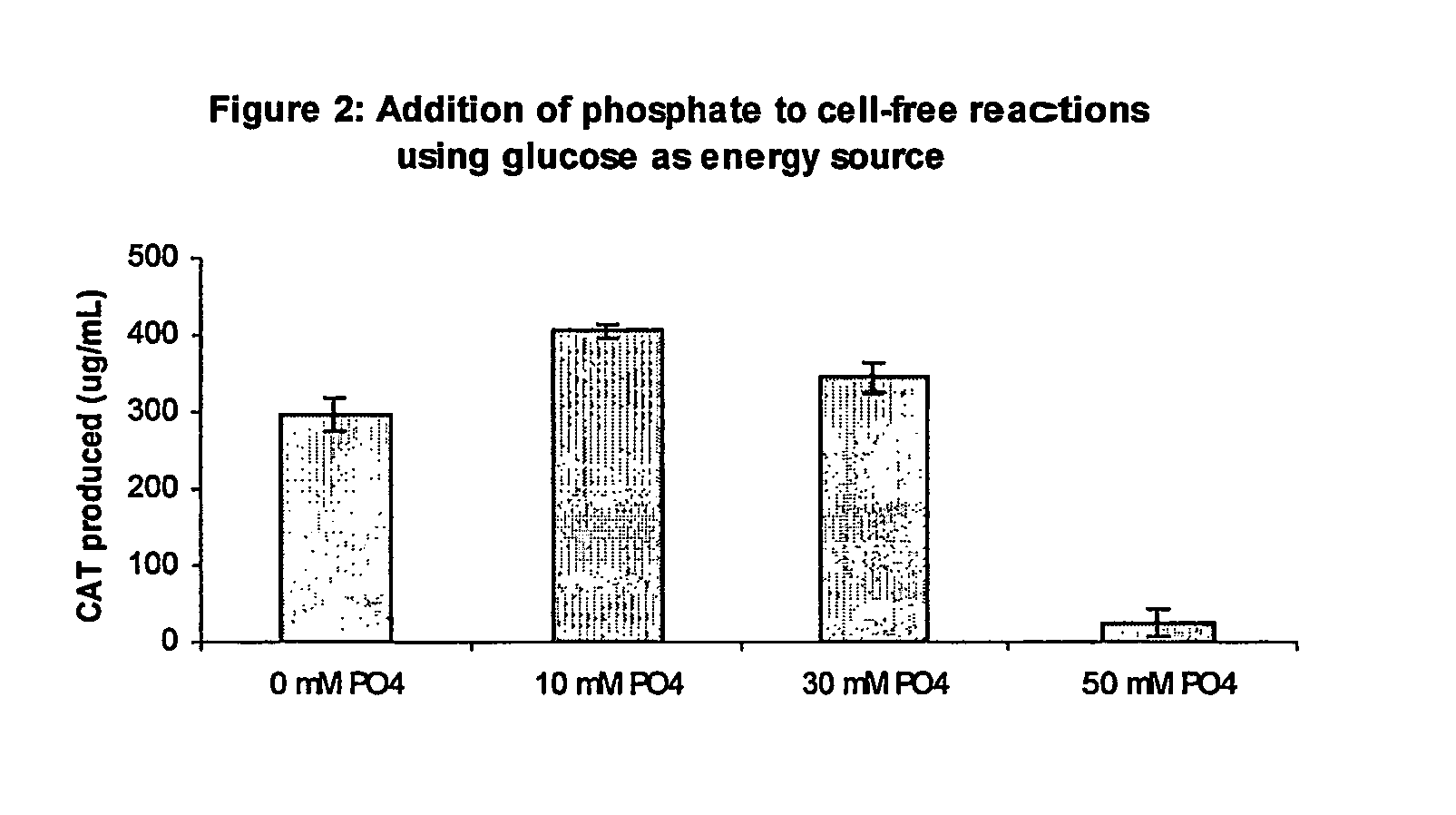
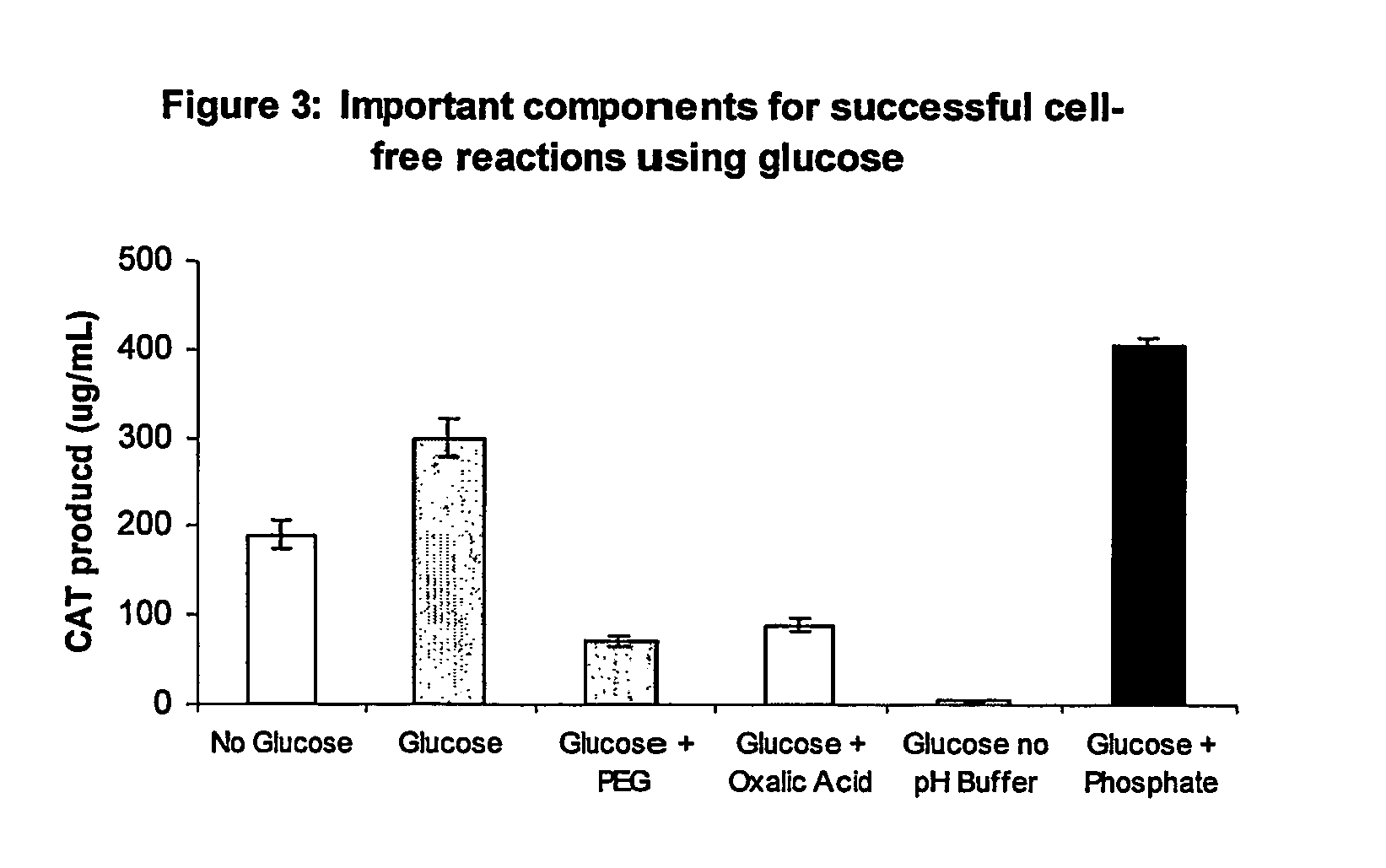
Improved methods are provided in vitro synthesis of biological molecules, providing for improved yields, lowered costs, and enhanced utility. Improved yield and lowered cost is obtained by the use of a phosphate free energy source in the presence of exogenous phosphate, and optionally in the absence of exogenous nucleoside triphosphates.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Nucleotide mimics and their prodrugs
The present invention relates to nucleoside diphosphate mimics and nucleoside triphosphate mimics, which contain diphosphate or triphosphate moiety mimics and optionally sugar-modifications and / or base-modifications. The nucleotide mimics of the present invention, in a form of a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, a pharmaceutically acceptable prodrug, or a pharmaceutical formulation, are useful as antiviral, antimicrobial, and anticancer agents. The present invention provides a method for the treatment of viral infections, microbial infections, and proliferative disorders. The present invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of the present invention optionally in combination with other pharmaceutically active agents.
Owner:BIOTA SCI MANAGEMENT PTI LTD
Nucleic acid analysis techniques
InactiveUS20050191646A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEnd labelingNucleoside triphosphate
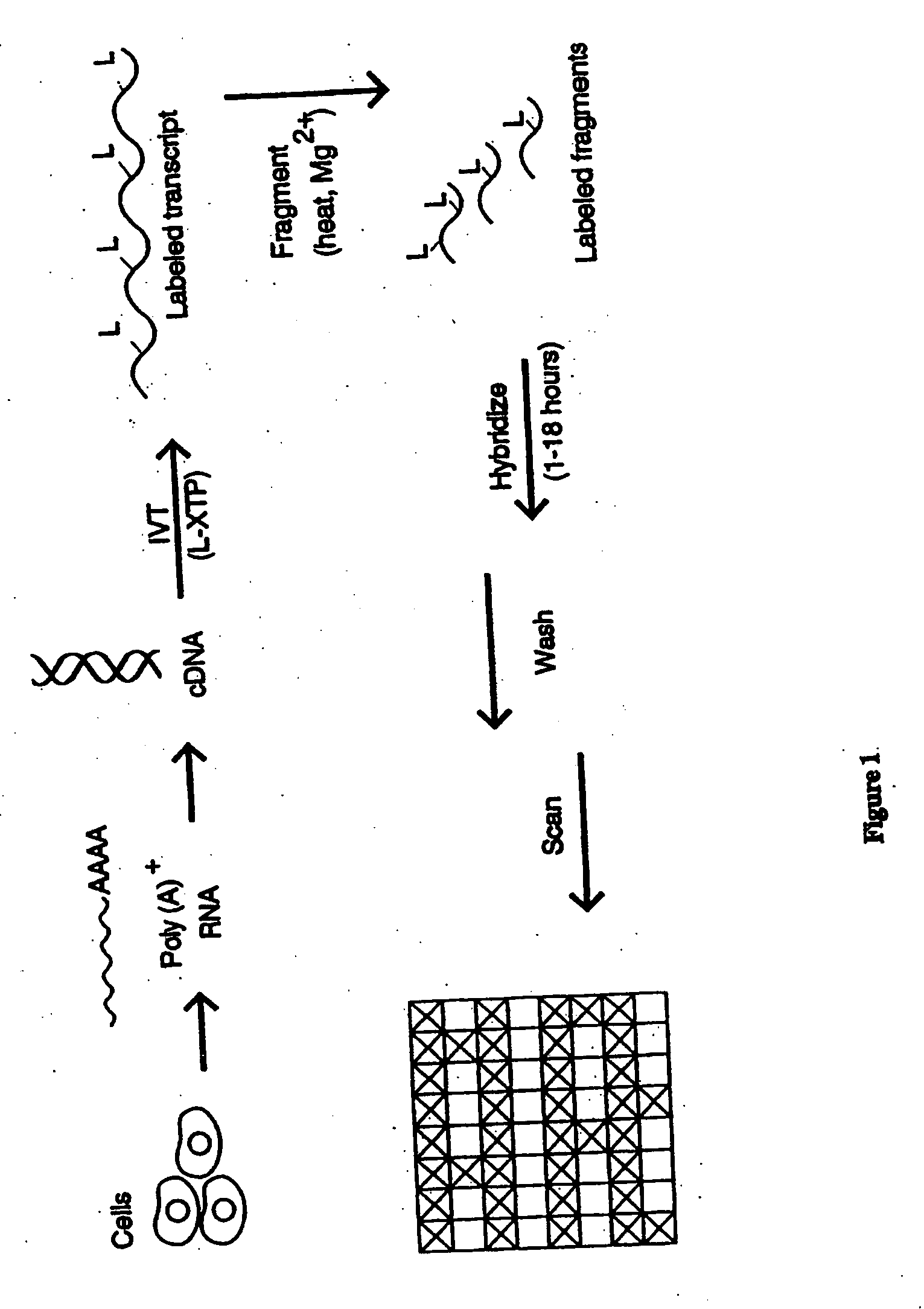
The present invention provides a simplified method for identifying differences in nucleic acid abundances (e.g., expression levels) between two or more samples. The methods involve providing an array containing a large number (e.g. greater than 1,000) of arbitrarily selected different oligonucleotide probes where the sequence and location of each different probe is known. Nucleic acid samples (e.g. mRNA) from two or more samples are hybridized to the probe arrays and the pattern of hybridization is detected. Differences in the hybridization patterns between the samples indicates differences in expression of various genes between those samples. This invention also provides a method of end-labeling a nucleic acid. In one embodiment, the method involves providing a nucleic acid, providing a labeled oligonucleotide and then enzymatically ligating the oligonucleotide to the nucleic acid. Thus, for example, where the nucleic acid is an RNA, a labeled oligoribonucleotide can be ligated using an RNA ligase. In another embodiment, the end labeling can be accomplished by providing a nucleic acid, providing labeled nucleoside triphosphates, and attaching the nucleoside triphosphates to the nucleic acid using a terminal transferase.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Nucleic acid analysis techniques
InactiveUS20050158772A1Easy and fast applicationBroaden applicationSugar derivativesOrganic chemistry methodsEnd labelingBiology
The present invention provides a simplified method for identifying differences in nucleic acid abundances (e.g., expression levels) between two or more samples. The methods involve providing an array containing a large number (e.g. greater than 1,000) of arbitrarily selected different oligonucleotide probes where the sequence and location of each different probe is known. Nucleic acid samples (e.g. mRNA) from two or more samples are hybridized to the probe arrays and the pattern of hybridization is detected. Differences in the hybridization patterns between the samples indicates differences in expression of various genes between those samples. This invention also provides a method of end-labeling a nucleic acid. In one embodiment, the method involves providing a nucleic acid, providing a labeled oligonucleotide and then enzymatically ligating the oligonucleotide to the nucleic acid. Thus, for example, where the nucleic acid is an RNA, a labeled oligoribonucleotide can be ligated using an RNA ligase. In another embodiment, the end labeling can be accomplished by providing a nucleic acid, providing labeled nucleoside triphosphates, and attaching the nucleoside triphosphates to the nucleic acid using a terminal transferase.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Compositions and Methods for RT-PCR
ActiveUS20140199699A1Rapid and efficient amplificationHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementTrehaloseBiology
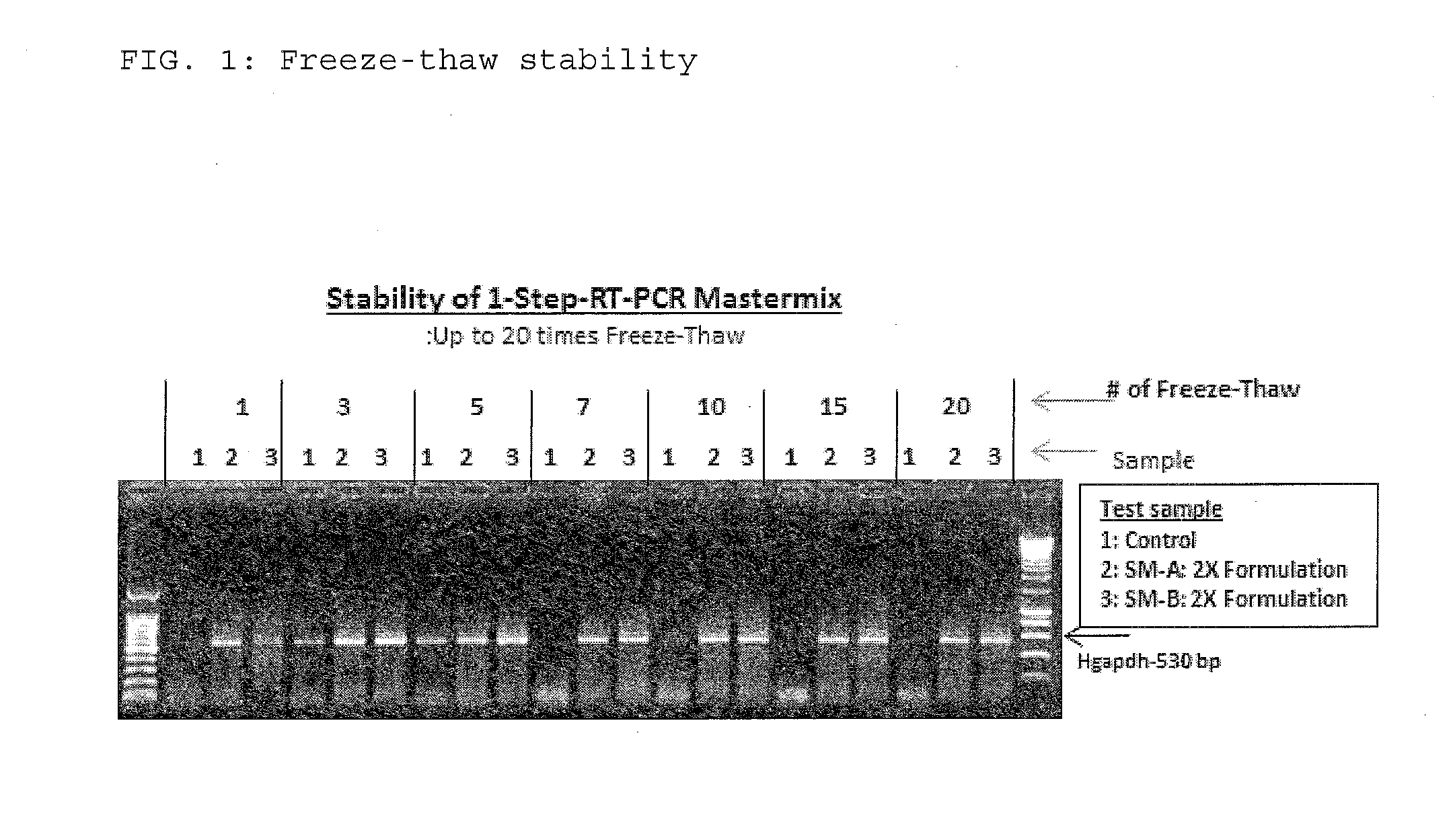
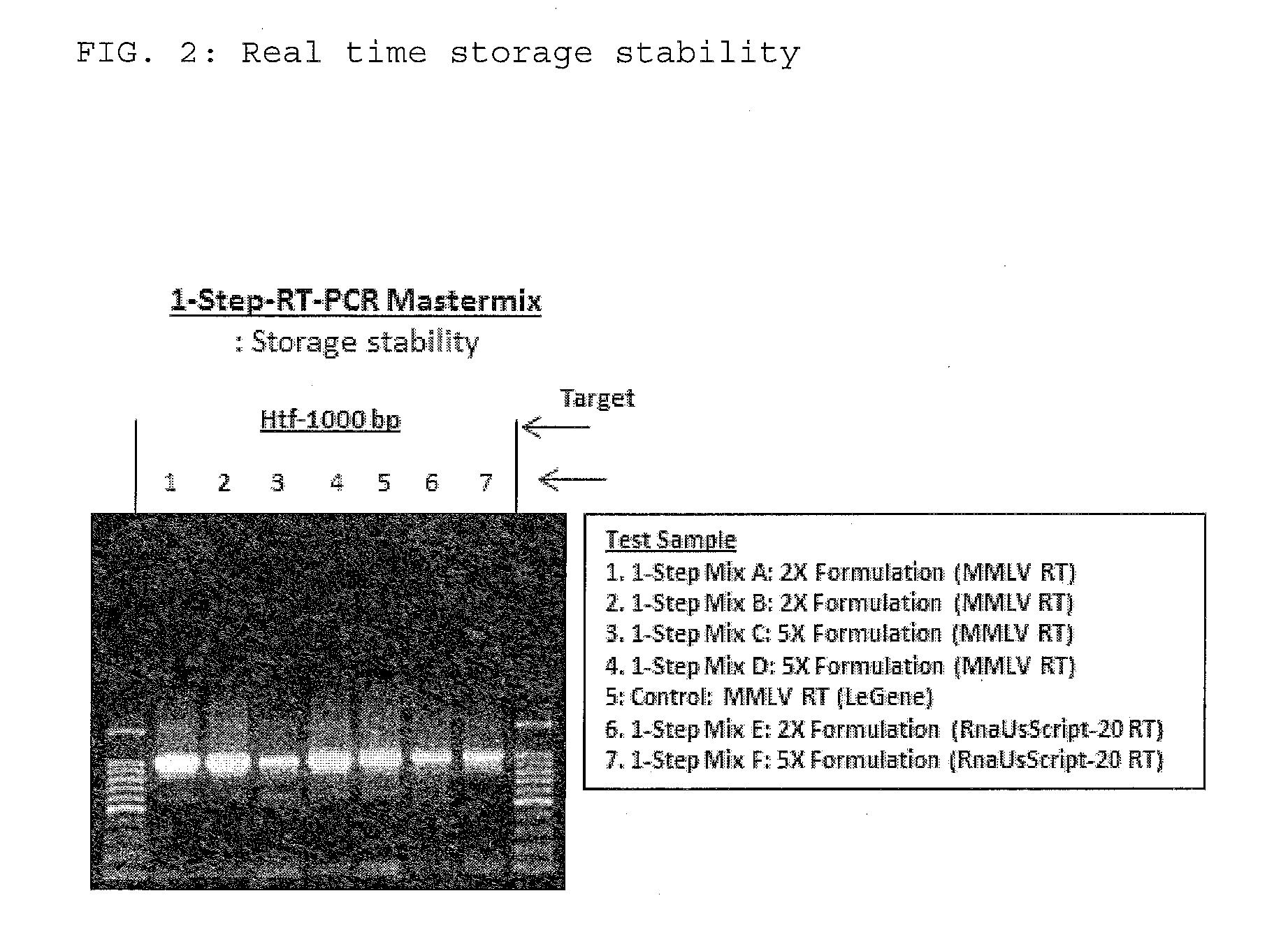
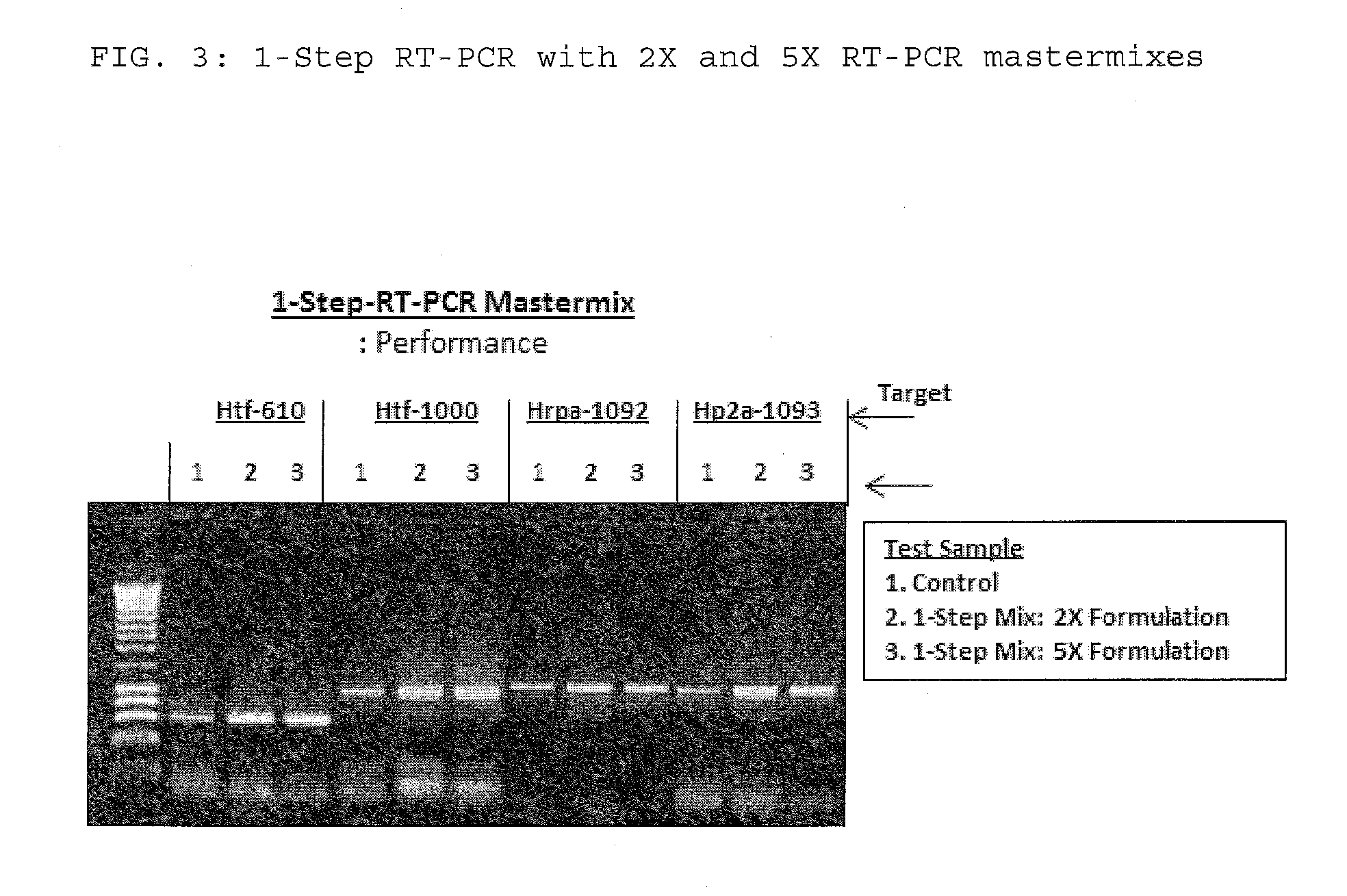
The present invention relates to methods and compositions having trehalose and DNA polymerase for facilitating the rapid and efficient amplification of nucleic acid molecules and the detection and quantitation of RNA molecules, and for increasing the detection sensitivity and reliability through generation of secure cDNA molecules prior to gene-specific primer dependent amplification. The reagent mixture comprises a ready to use reagent solution, wherein the solution comprises: (a) trehalose in a concentration between about 5% and about 35%; (b) a viral reverse transcriptase; and (c) at least one DNA polymerases, in a buffer suitable for use in a reverse transcription reaction, wherein the buffer comprises a co-factor metal ion and nucleoside triphosphates.
Owner:LEE JUN EUIHUM
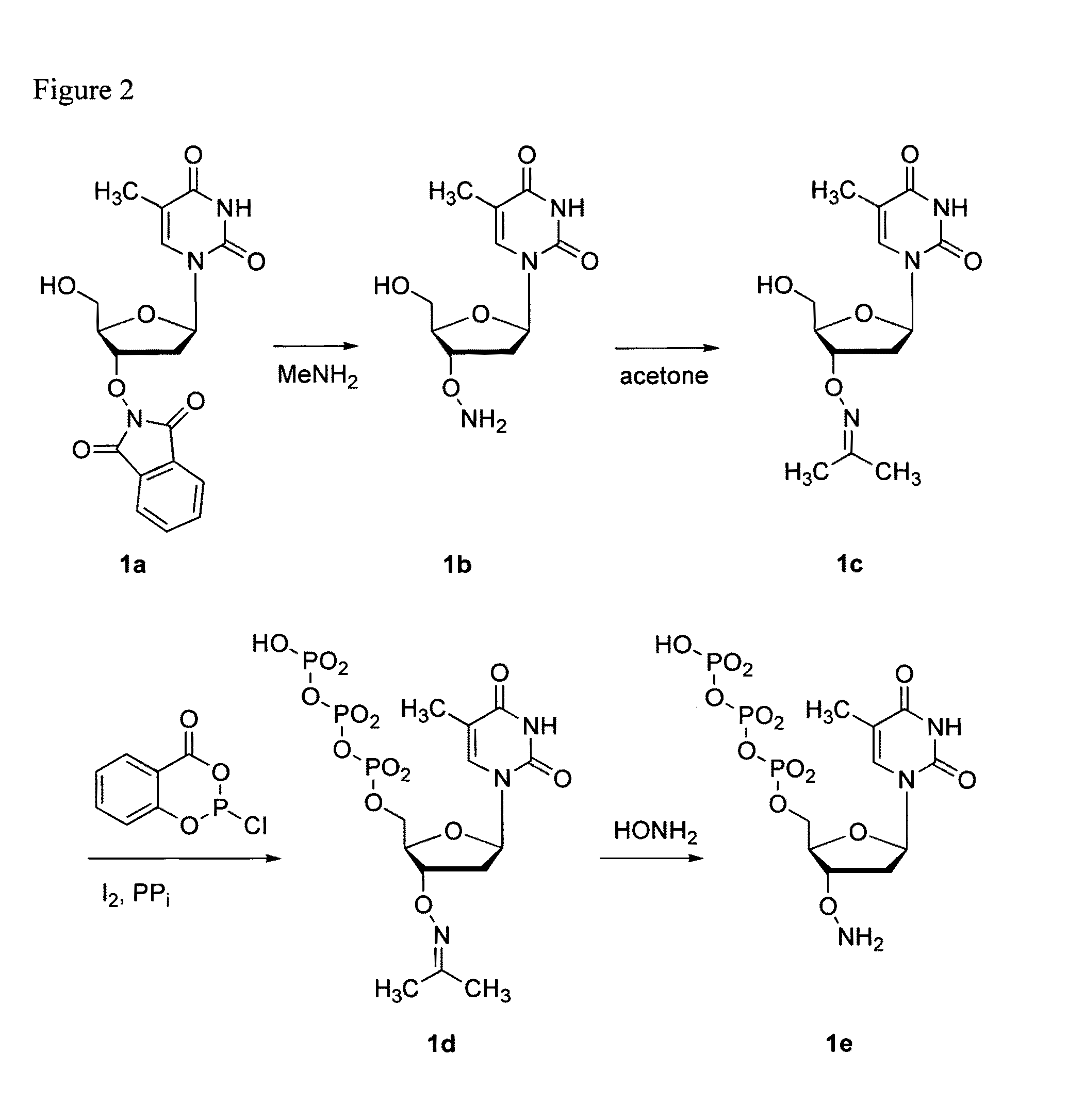
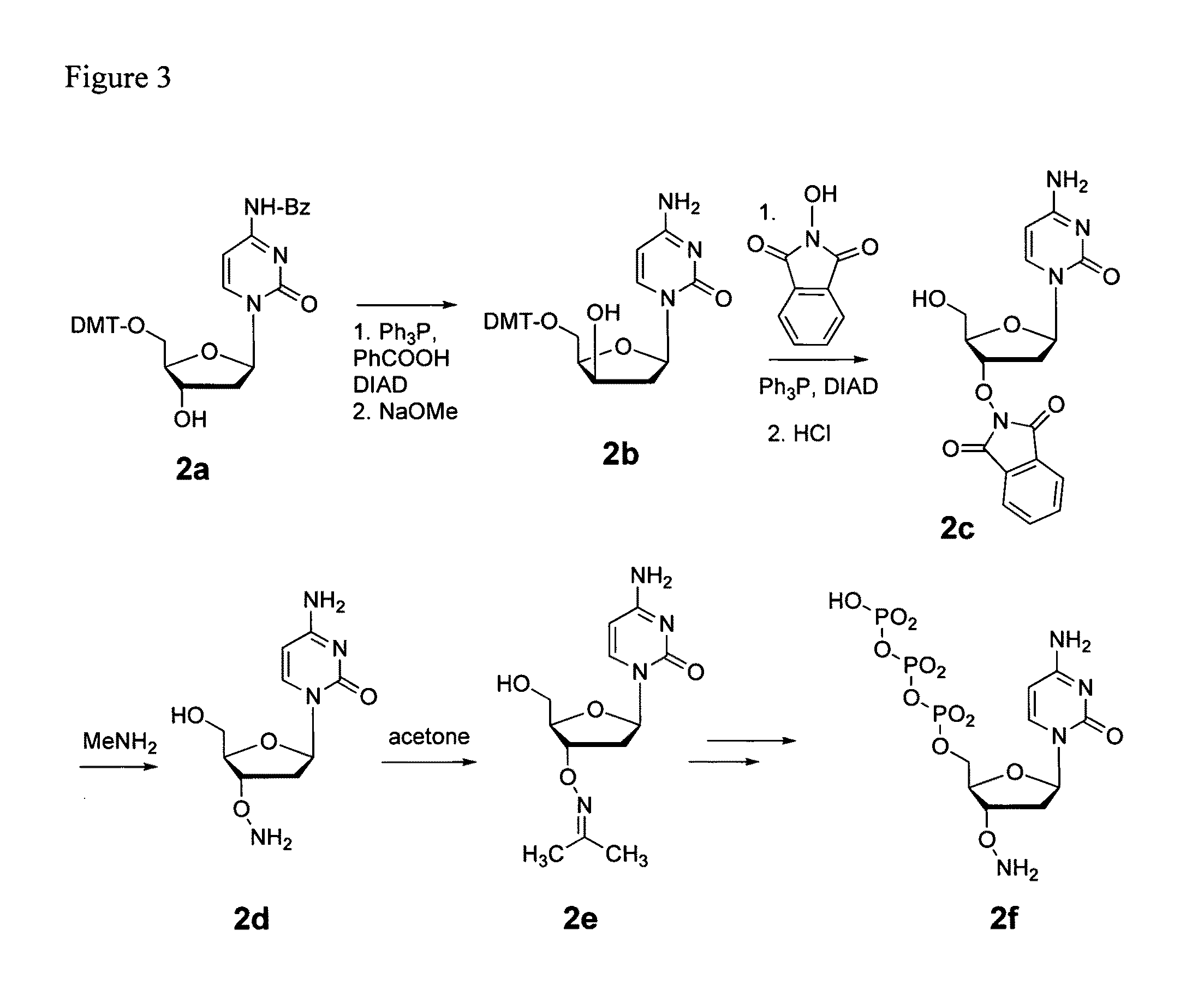
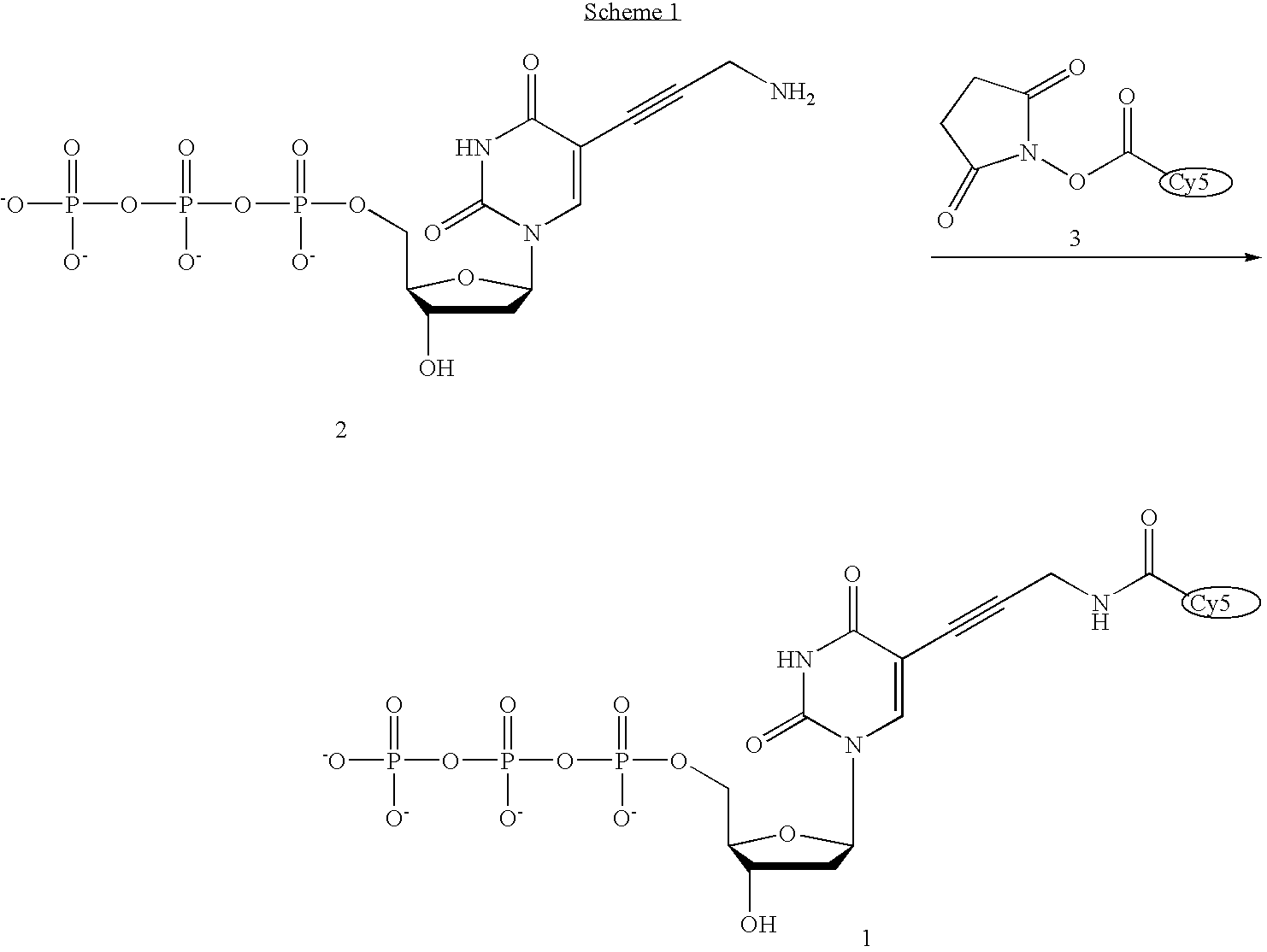
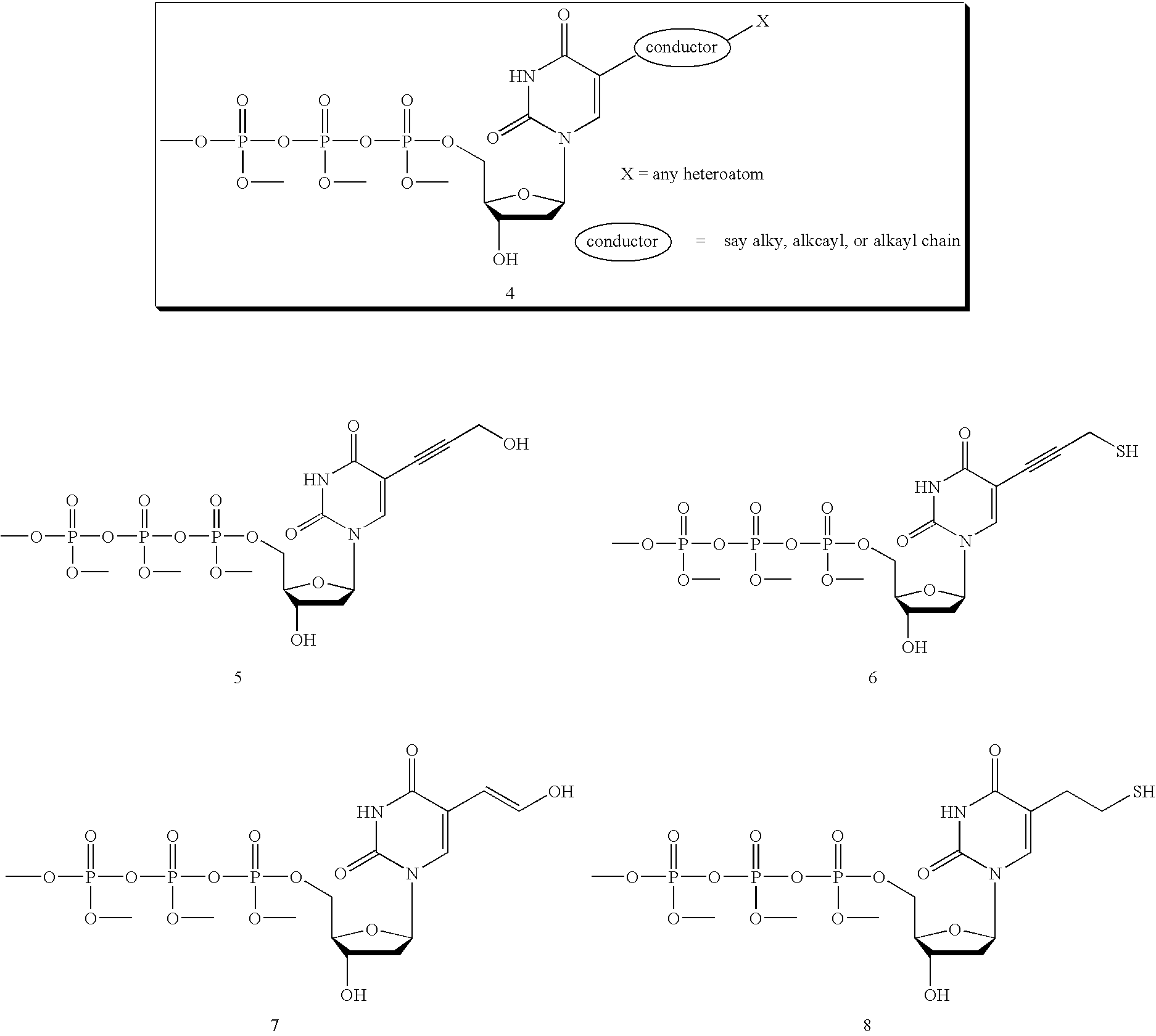
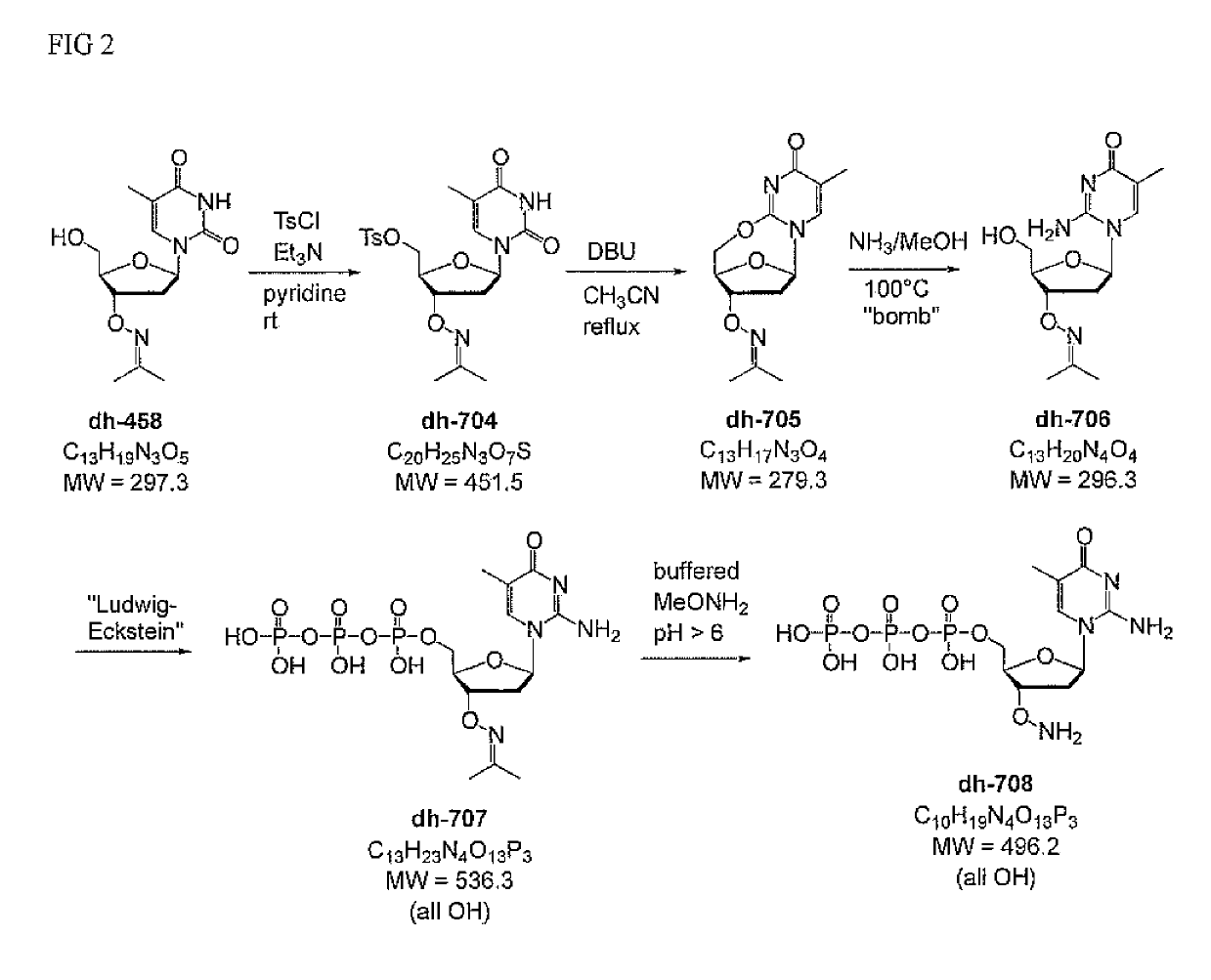
Nucleoside triphosphates with stable aminoxy groups
This invention claims aqueous compositions that comprise triphosphates of 2′-deoxynucleoside derivatives that have, instead of a 3′-OH moiety, a 3′-ONH2 moiety; wherein said compositions contain less than 0.5 mole percent contaminating triphosphate having a 3′-OH moiety, as well as processes for providing such compositions. The compositions further must contain insubstantial amounts of hydroxylamine.
Owner:BENNER STEVEN A
Phosphoramidate derivatives of FAU
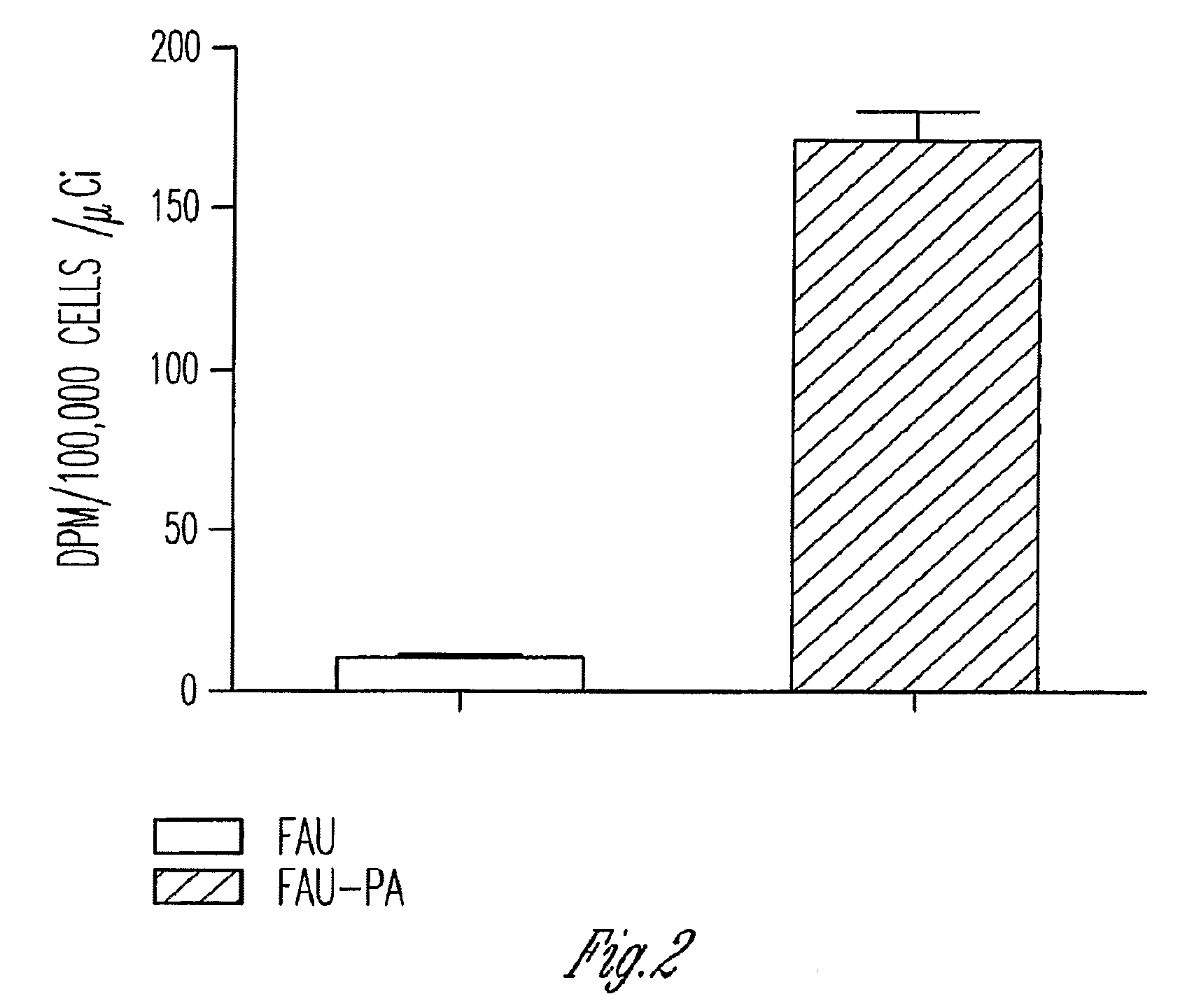
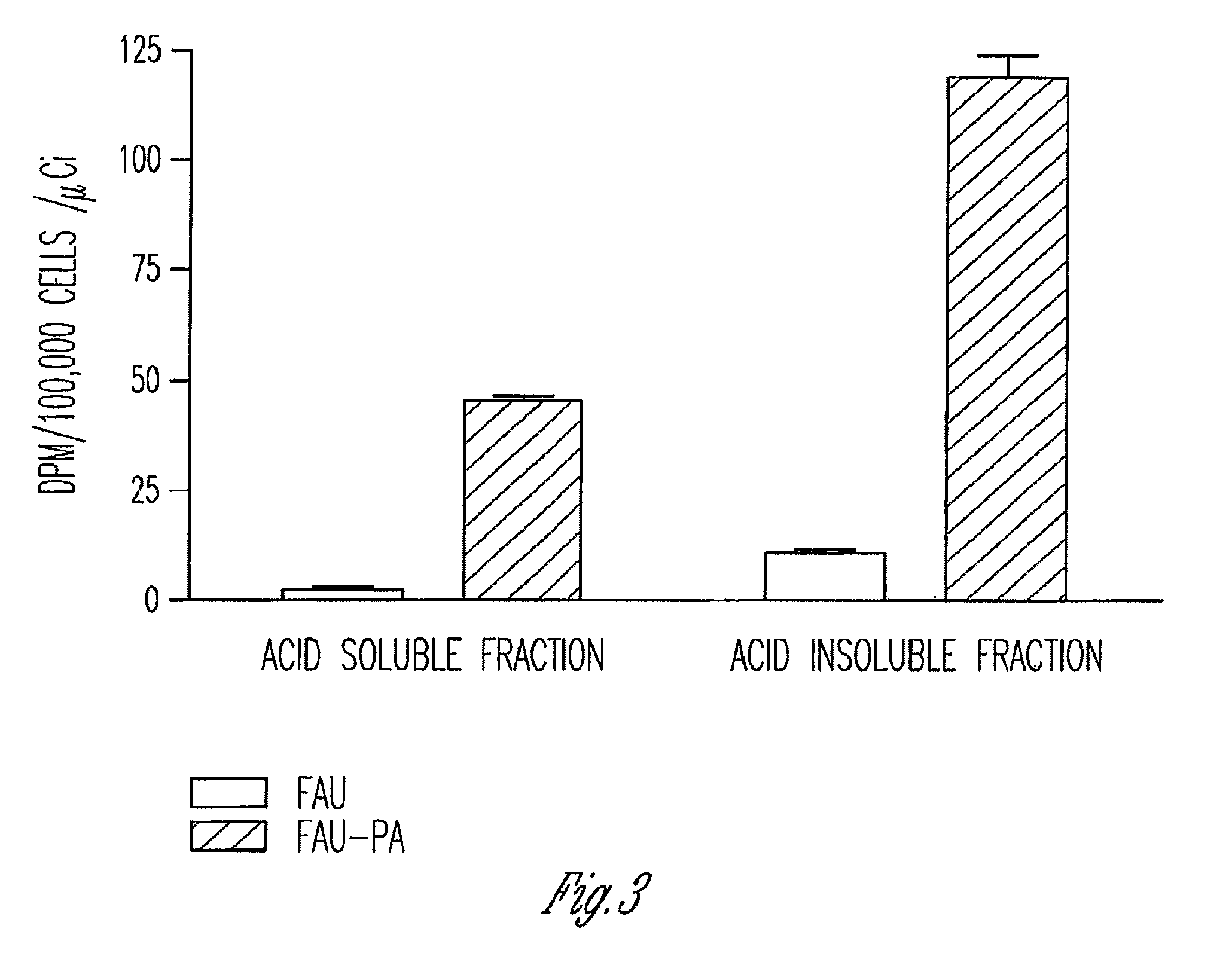
InactiveUS7888330B2Efficient deliveryIncreased formationBiocideIn-vivo radioactive preparationsNucleoside monophosphatePhosphorylation
The present invention provides phosphoramidate derivatives of a furanosyluracil analog, FAU, that can effectively deliver FAU monophosphate, or a derivative thereof, intracellularly. FAU-Phosphoramidate diesters can bypass the first step of phosphorylation and be activated intracellularly so as to be converted to nucleoside monophosphates. This results in improved formation of nucleoside triphosphates, and higher incorporation into DNA. The compounds of the invention can be used to treat cancer.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
Nucleoside Triphosphates with Stable Aminoxy Groups
This invention claims aqueous compositions that comprise triphosphates of 2′-deoxynucleoside derivatives that have, instead of a 3′-OH moiety, a 3′-ONH2 moiety; wherein said compositions contain less than 0.5 mole percent contaminating triphosphate having a 3′-OH moiety, as well as processes for providing such compositions. The compositions further must contain insubstantial amounts of hydroxylamine.
Owner:BENNER STEVEN A
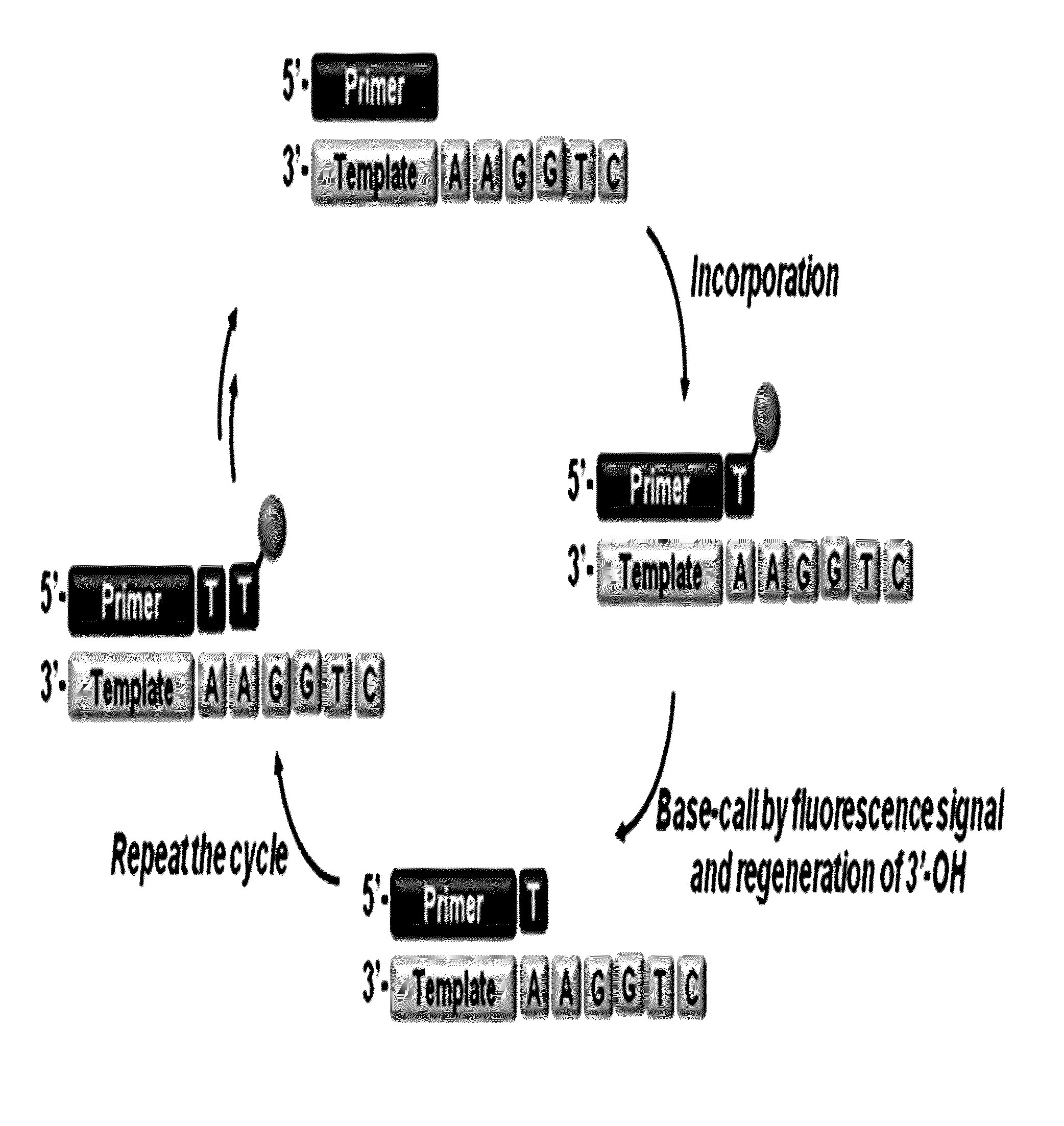
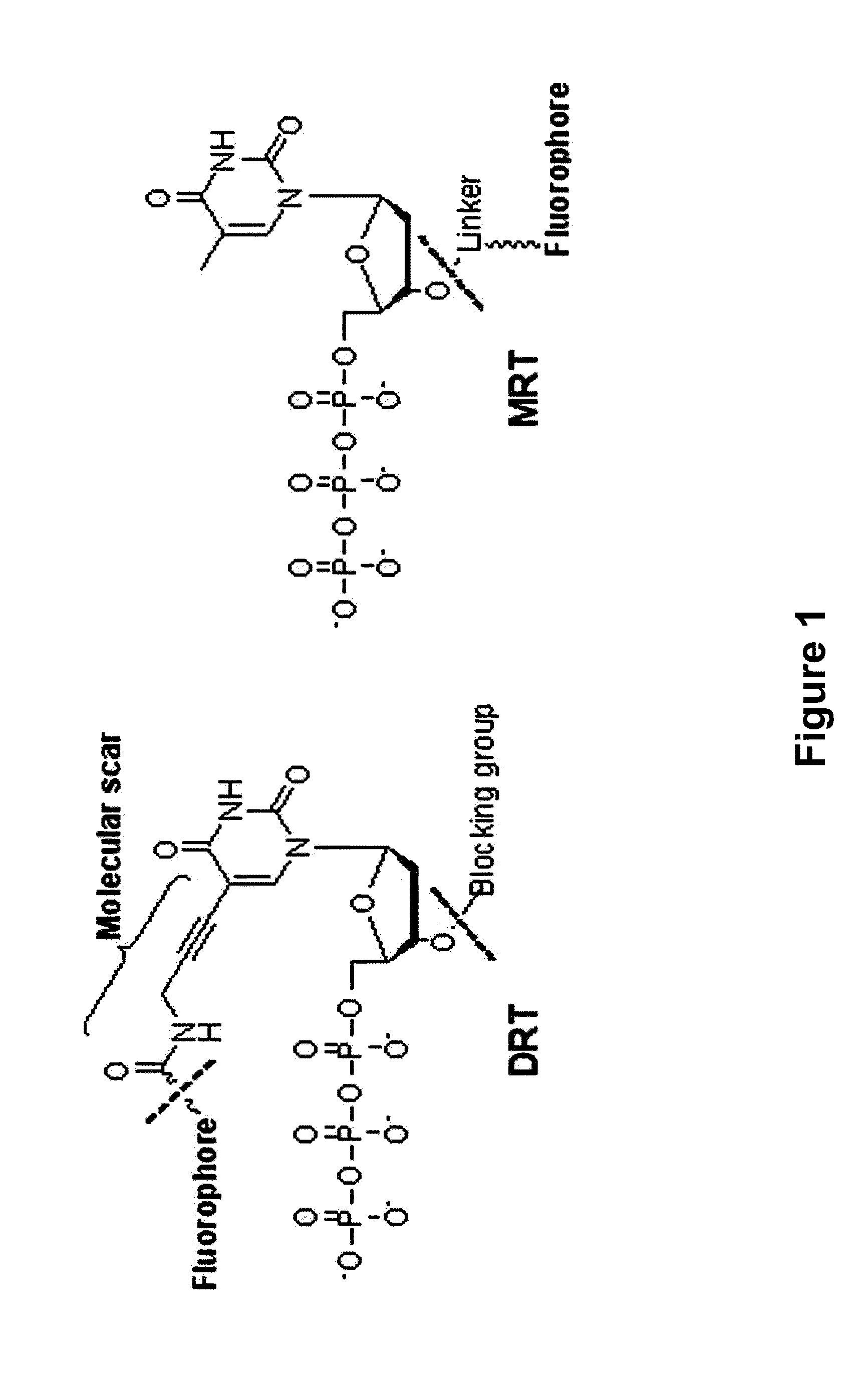
3'-o-fluorescently modified nucleotides and uses thereof
InactiveUS20110076679A1Improve efficiencyHigh yieldAnalysis using chemical indicatorsSugar derivativesFluorescenceA-DNA
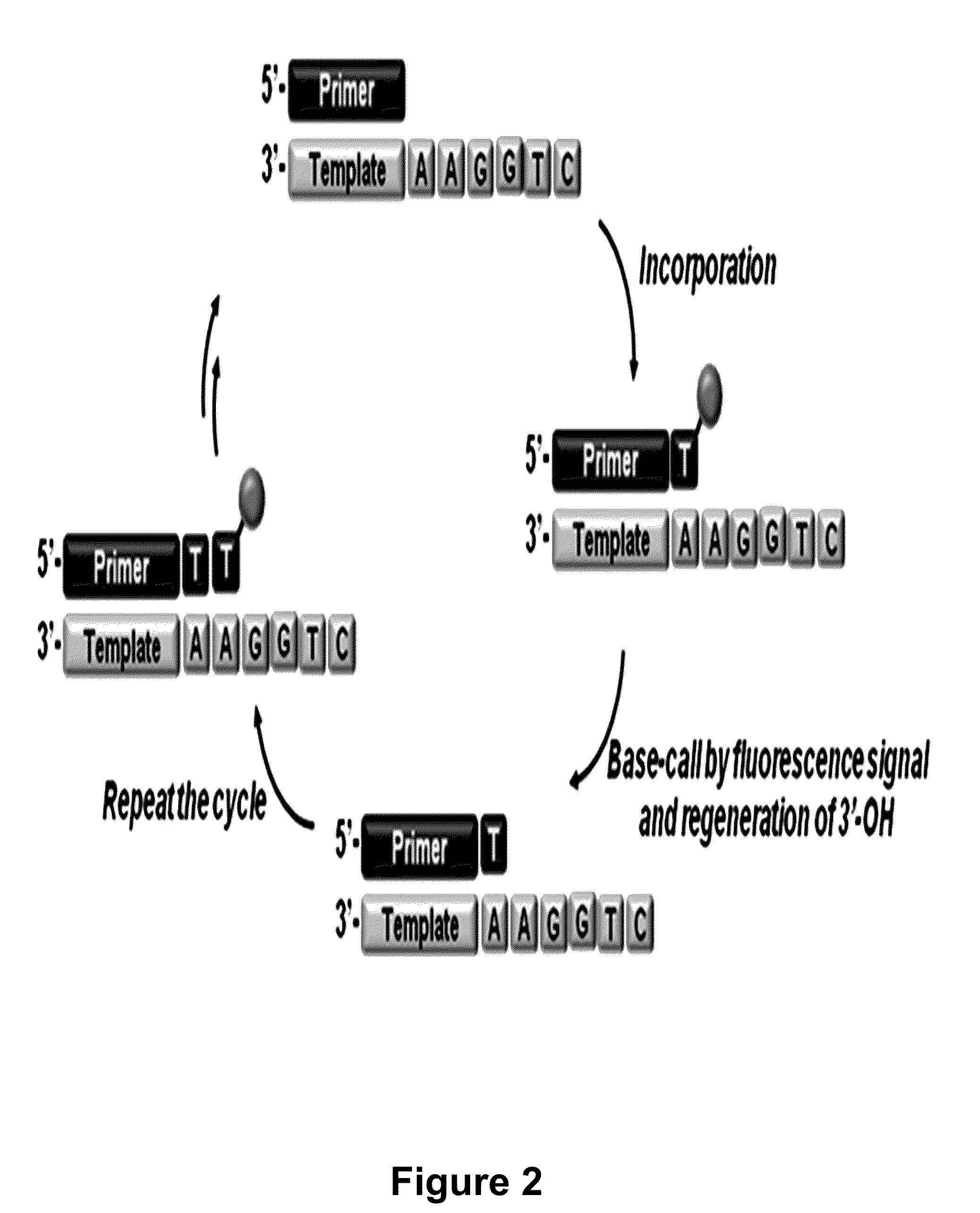
The present invention relates to a DNA sequencing method using a nucleoside triphosphate with a fluorescent blocking group on its 3′-OH end as a reversible terminator. Further, the present invention relates to sequencing-by-synthesis method using the mono-modified reversible terminator (MRT), the novel nucleotide monomer having a reversible fluorescent blocking group removable chemically or enzymatically at its 3′-OH end. The sequencing method of the present invention facilitates sequencing of bases inserted by terminating extension of a nucleotide chain by the nucleotide monomer and then detecting fluorescence signal from 3′-OH end. At this time, after analyzing the fluorescence signal, the blocking group conjugated to the 3′-OH end can be effectively removed, indicating that a free 3′-OH functional group can be successfully restored, so that the next monomer insertion is possible, making continuous sequencing possible.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Mesoscale polynucleotide amplification analysis
InactiveUS20060040309A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsTemperature controlPolymerase L
Disclosed are devices for amplifying a preselected polynucleotide in a sample by conducting a polynucleotide polymerization reaction. The devices comprise a substrate microfabricated to define a sample inlet port and a mesoscale flow system, which extends from the inlet port. The mesoscale flow system includes a polynucleotide polymerization reaction chamber in fluid communication with the inlet port which is provided with reagents required for polymerization and amplification of a preselected polynucleotide. In one embodiment the devices may be utilized to implement a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in the reaction chamber (PCR chamber). The PCR chamber is provided with the sample polynucleotide, polymerase, nucleoside triphosphates, primers and other reagents required for the polymerase chain reaction, and the device is provided with means for thermally controlling the temperature of the contents of the reaction chamber at a temperature controlled to dehybridize double stranded polynucleotide, to anneal the primers, and to polymerize and amplify the polynucleotide.
Owner:WILDING PETER +1
Post-synthesis labeling of nucleic acids, assays using nucleic acids that are labeled post-synthetically, single nucleotide polymorphism detection, and associated compounds and microarrays
InactiveUS20030119005A1Low specificityLess stringentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhosphoric acidNucleoside triphosphate
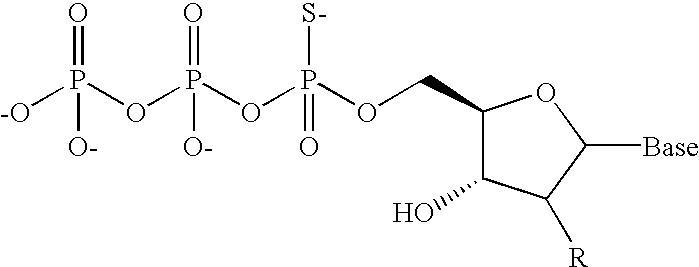
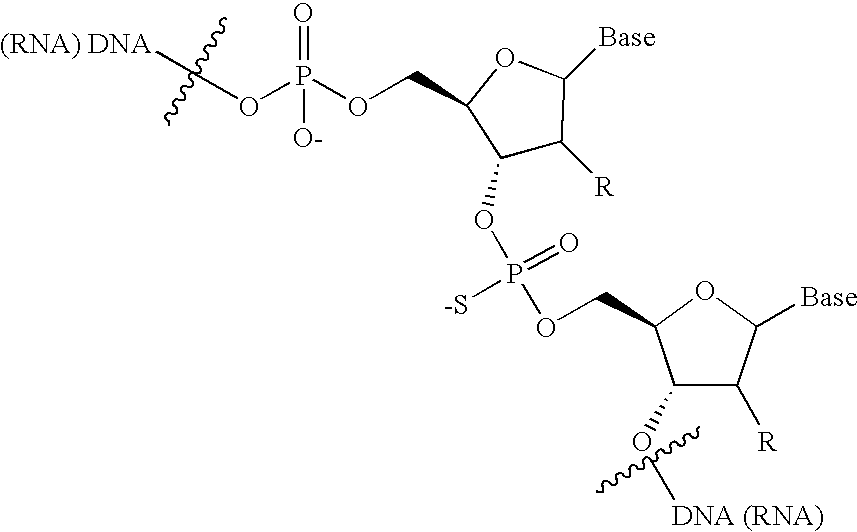
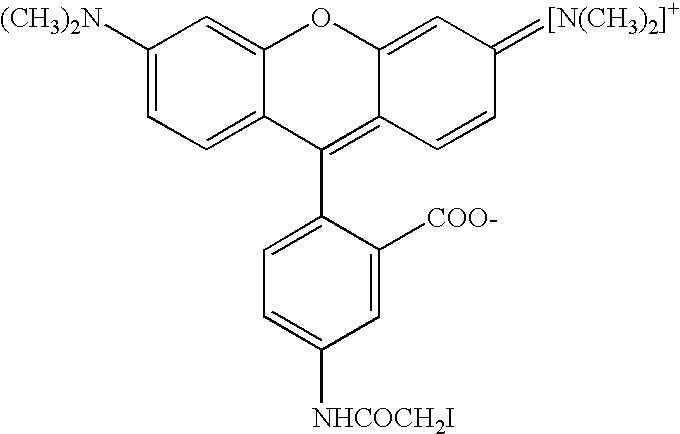
An assay is provided for nucleic acids that can be post-synthetically labeled, wherein modified nucleoside triphosphates are used that are more efficiently and specifically incorporated during nucleic acid synthesis than labeled nucleoside triphosphates. In a preferred embodiment, nucleoside alpha-thiotriphosphates are utilized. Maleimide or iodoacetamide conjugating moieties can be attached post-synthetically. The conjugating moieties may include a reporter group. Also disclosed are new methods for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Fluorescent quantitative detection kit of H1N1 influenza virus A and detection method thereof
ActiveCN101649356AStrong specificitySensitive detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesReverse transcriptasePolymerase L
The invention provides a nucleic-acid fluorescent quantitative RT-PCR detection kit of H1N1 influenza virus A and a detection method thereof. The detection kit mainly comprises a specific primer, a fluorescent probe, a PCR buffer solution, a deoxidized nucleoside triphosphate compound, a DNA polymerase, a reverse transcriptase and an RNA enzyme inhibitor, wherein the specific primer and the fluorescent probe have the following sequences: an upstream primer H1N1 A-FP:5'-AGGTTTGAGATATTCCCCAAGACA-3'; a downstream primer H1N1 A-RP:5'-AATTTTTGTAGAAGCTTTTTGCTCC-3'; and a specific probe H1N1 A-P:5'-F-CATGGCCCAATCATGACTCGAACA-Q-3', wherein F is a fluorescent reporter group; and Q is a fluorescent quenching group. The invention has the advantages that the nucleic-acid fluorescent quantitative RT-PCR detection kit of the H1N1 influenza virus A and the detection method thereof can be applied to the emergent detection and the monitoring of a lab where the H1N1 influenza virus A causes an outbreakepidemic.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
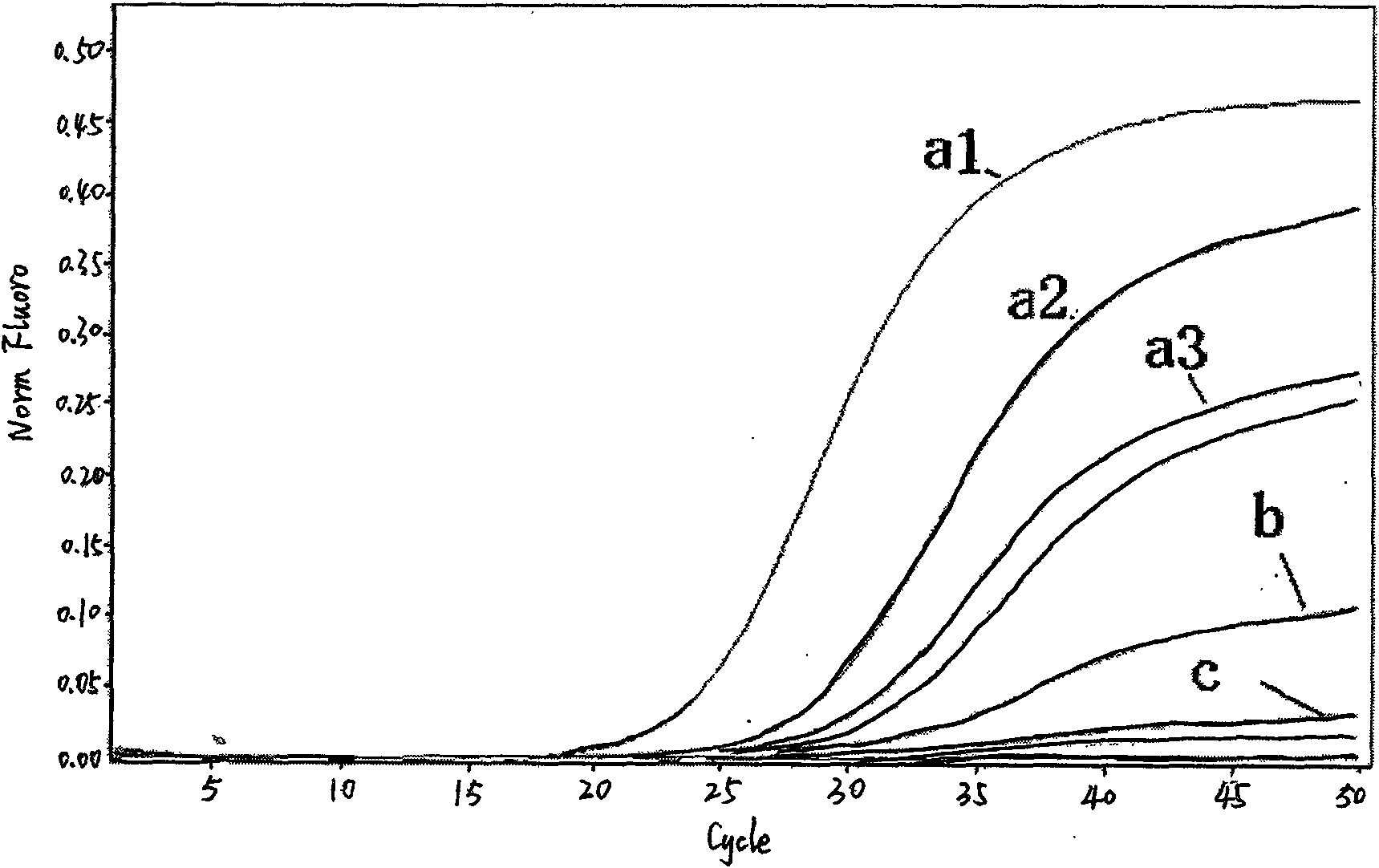
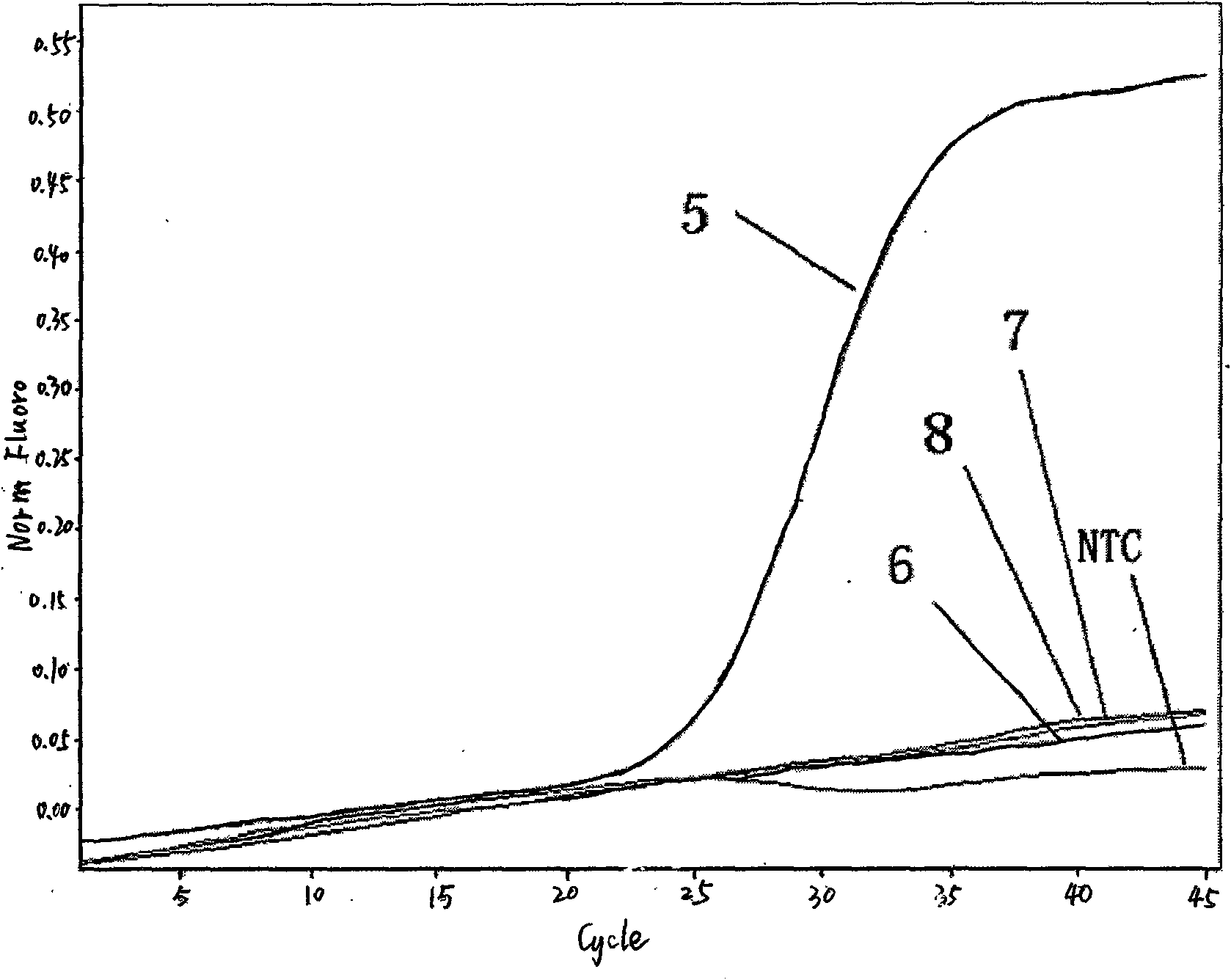
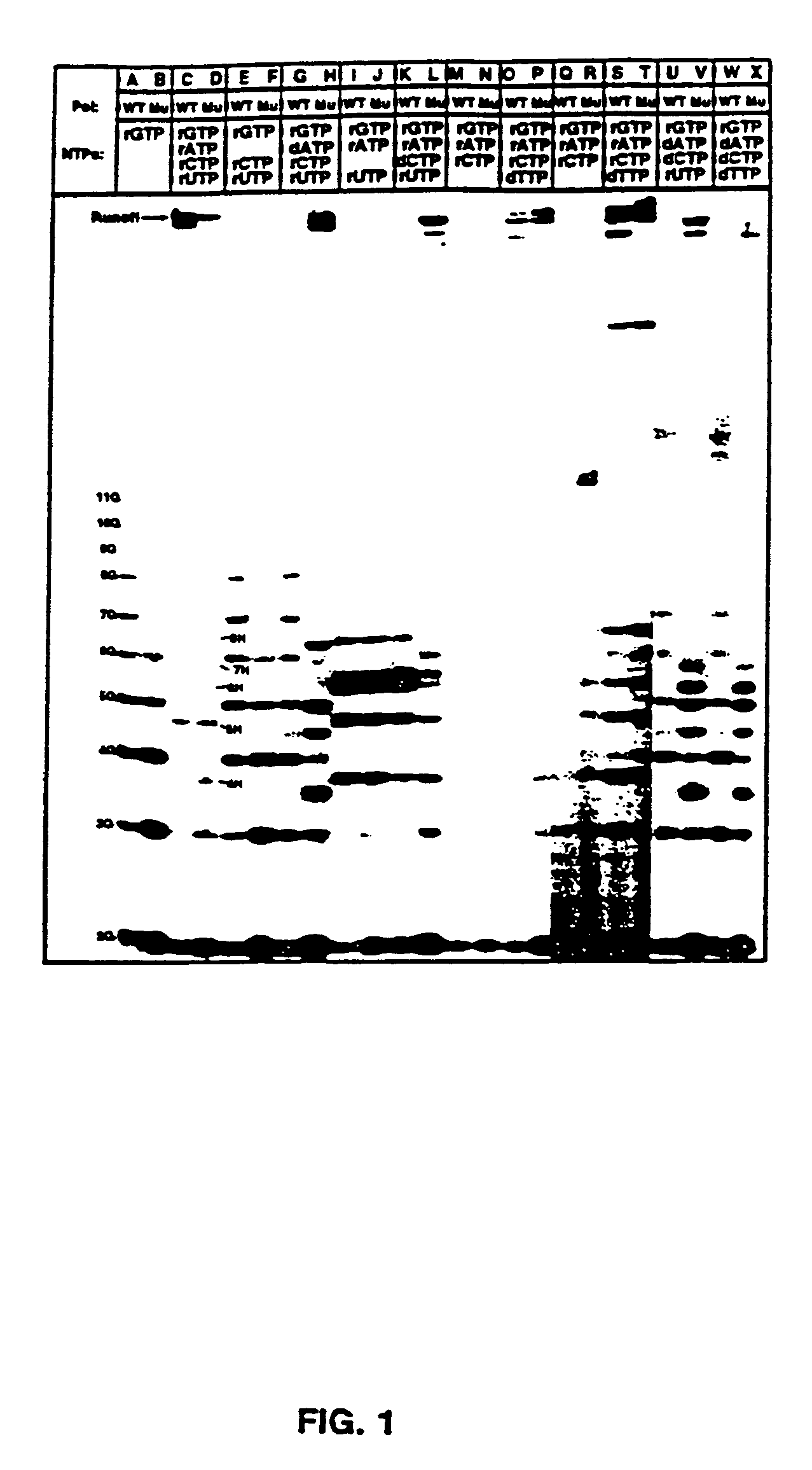
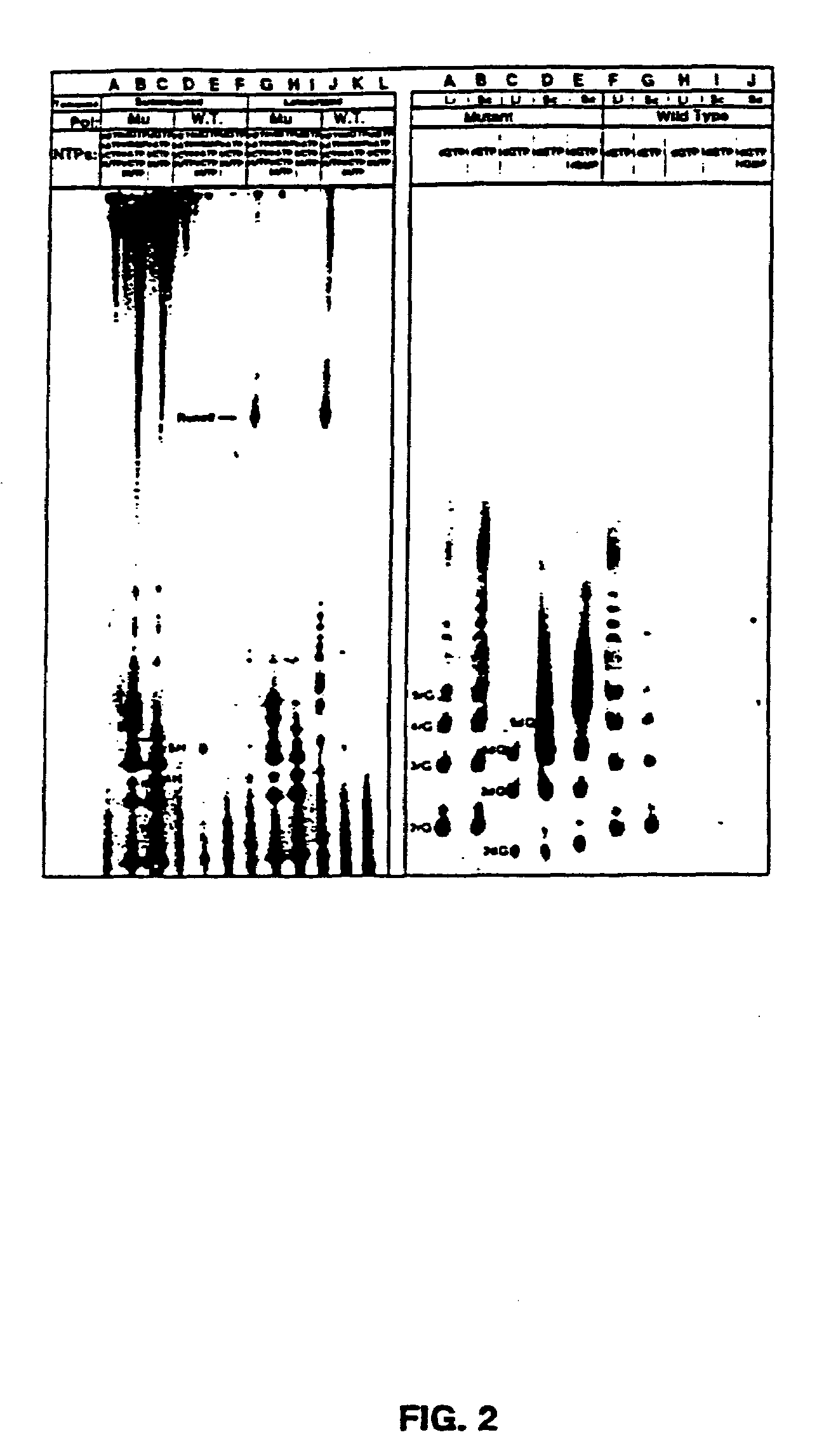
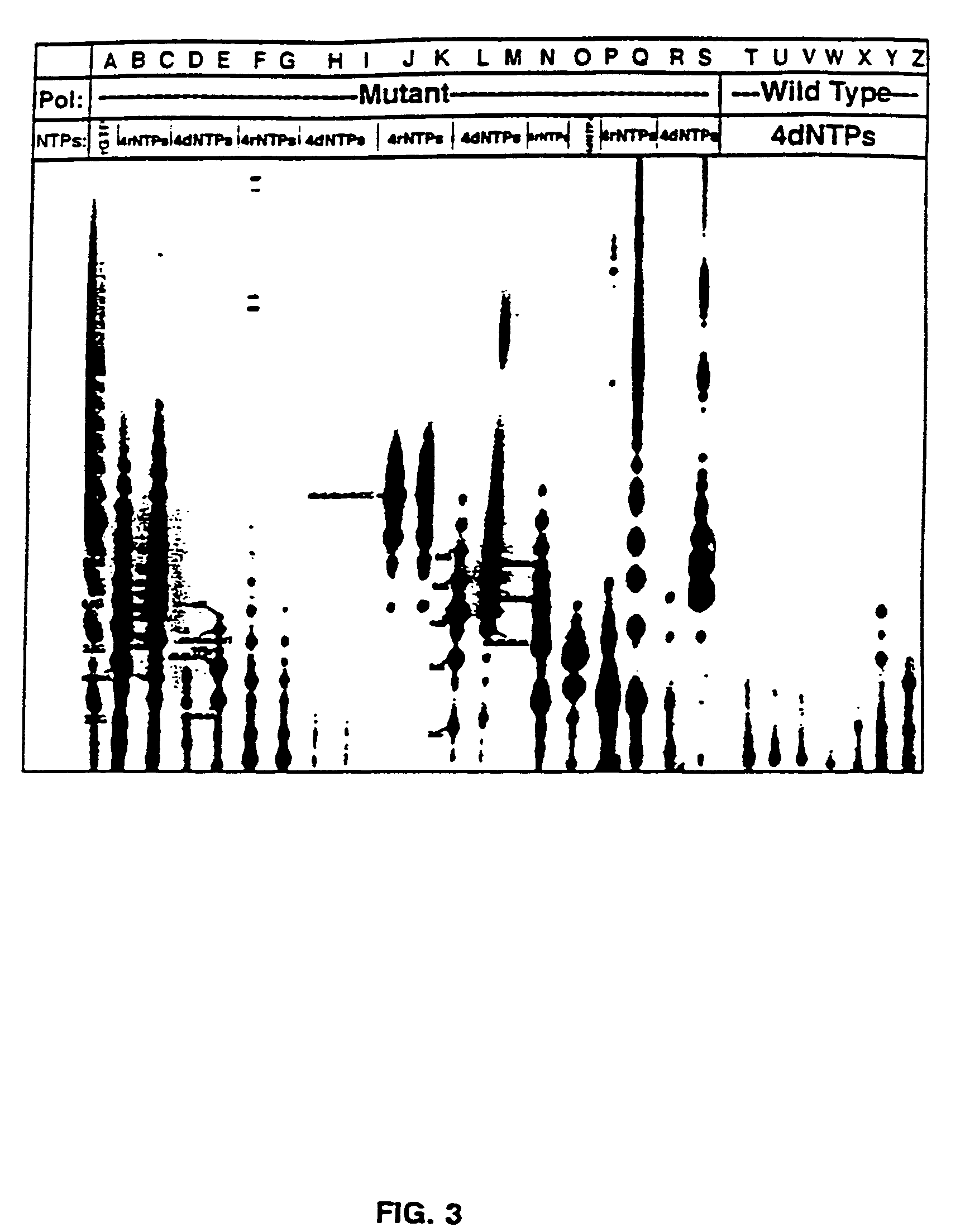
Methods for using double-mutant RNA polymerases with reduced discrimination between non-canonical and canonical nucleoside triphosphates
A method and kit for synthesizing a nucleic acid molecule comprising at least one non-canonical nucleoside triphosphate using a double-mutant polymerase having a reduced discrimination between canonical and non-canonical substrates is disclosed. The method comprises incubating a template nucleic acid in a reaction mixture comprising the mutant nucleic acid polymerase and the appropriate canonical and non-canonical nucleoside triphosphates which are desired substrates for the mutant nucleic acid polymerase. The present invention is also a method of determining the sequence of a nucleic acid molecule using the mutant polymerase to create a nucleic acid molecule comprising at least one non-canonical nucleoside triphosphate.
Owner:UNIV OF TEXAS
Nucleotide sequence for detecting listeria monocytogenes and detection method and detection kit
InactiveCN104450940AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses a nucleotide sequence for detecting listeria monocytogenes and a detection method and a detection kit, wherein the nucleotide sequence is expressed as SEQ ID NO. 1, the detection method is as follows: firstly, extracting the gene group DNA of the sample to be detected; secondly, taking the gene group DNA as the template, mixing with the specific primer Lm16, PCR buffer solution, MgCl2 solution, deoxidation nucleoside triphosphate mixture and Taq-DNA polymerase for preparing the PCR reaction system, carrying out the PCR reaction; finally, detecting whether the PCR product is the single amplification product, the size of which is 1623bp. The kit comprises the specific primer, PCR buffer solution, MgCl2 solution, deoxidation nucleoside triphosphate mixture and Taq-DNA polymerase. The kit can effectively detect the listeria monocytogenes in the food, and the detection sensitivity for the bacteria is high, the specificity is good and the antijamming capability is strong.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Polymerase incorporation of non-standard nucleotides
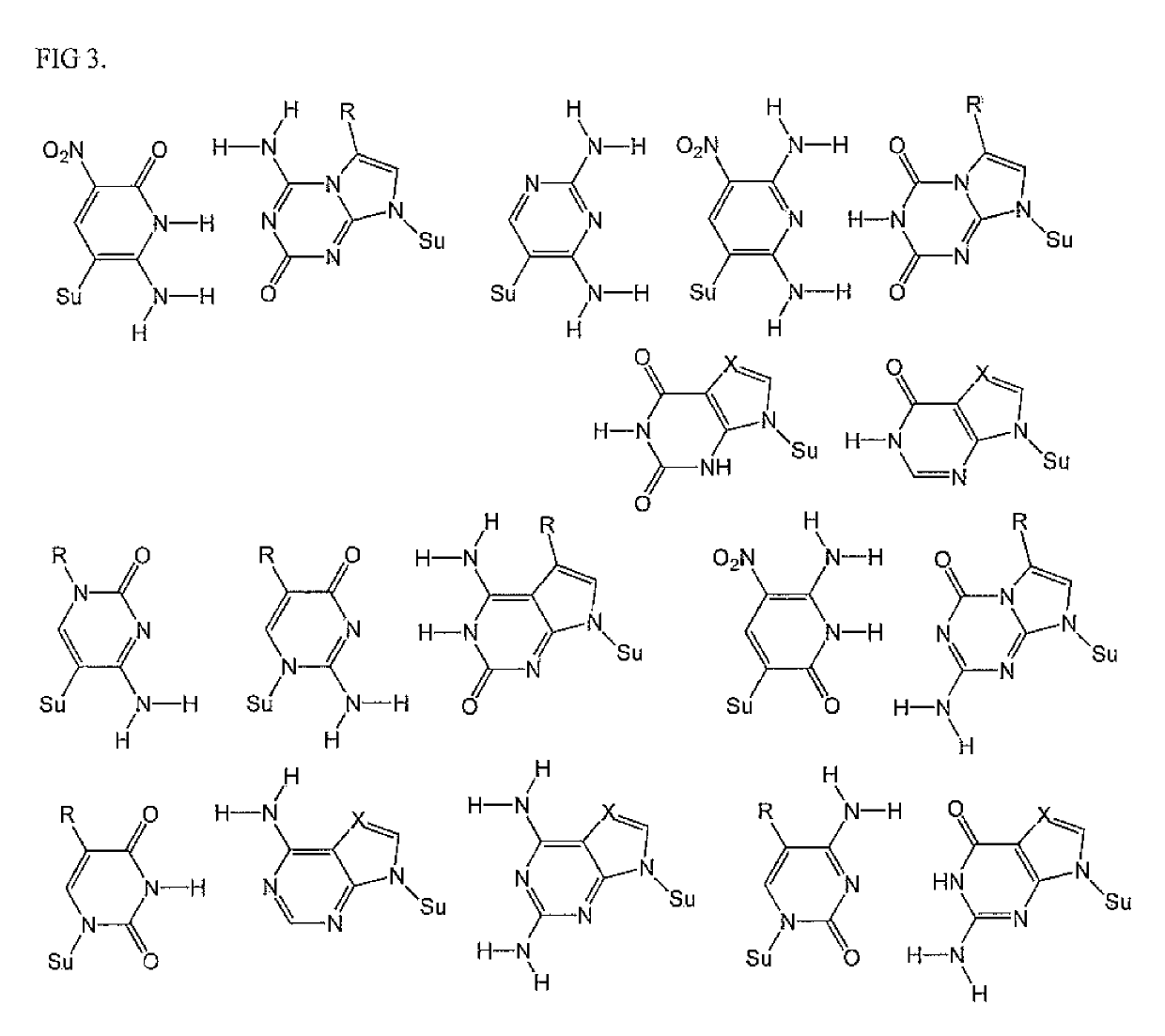
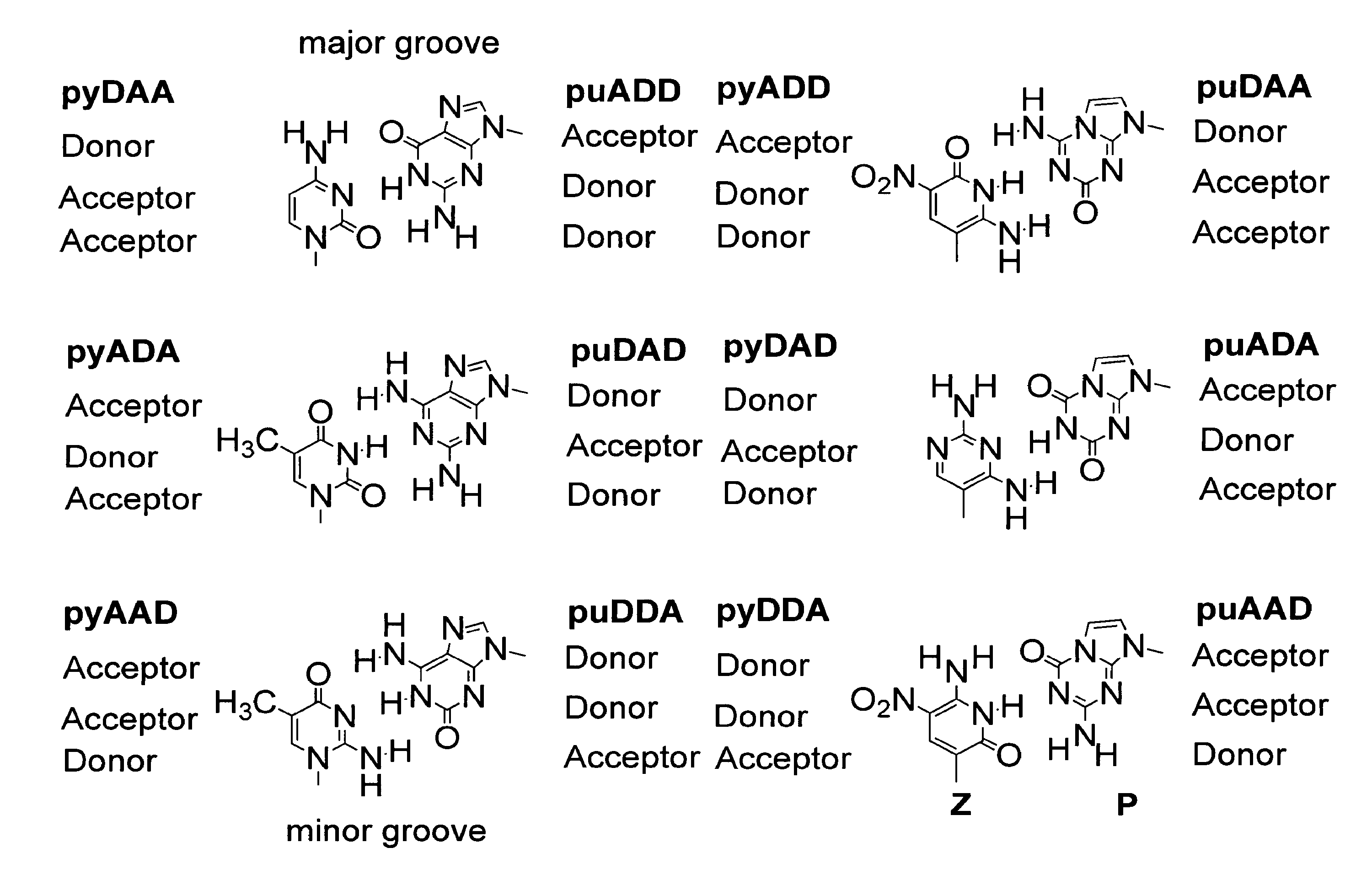
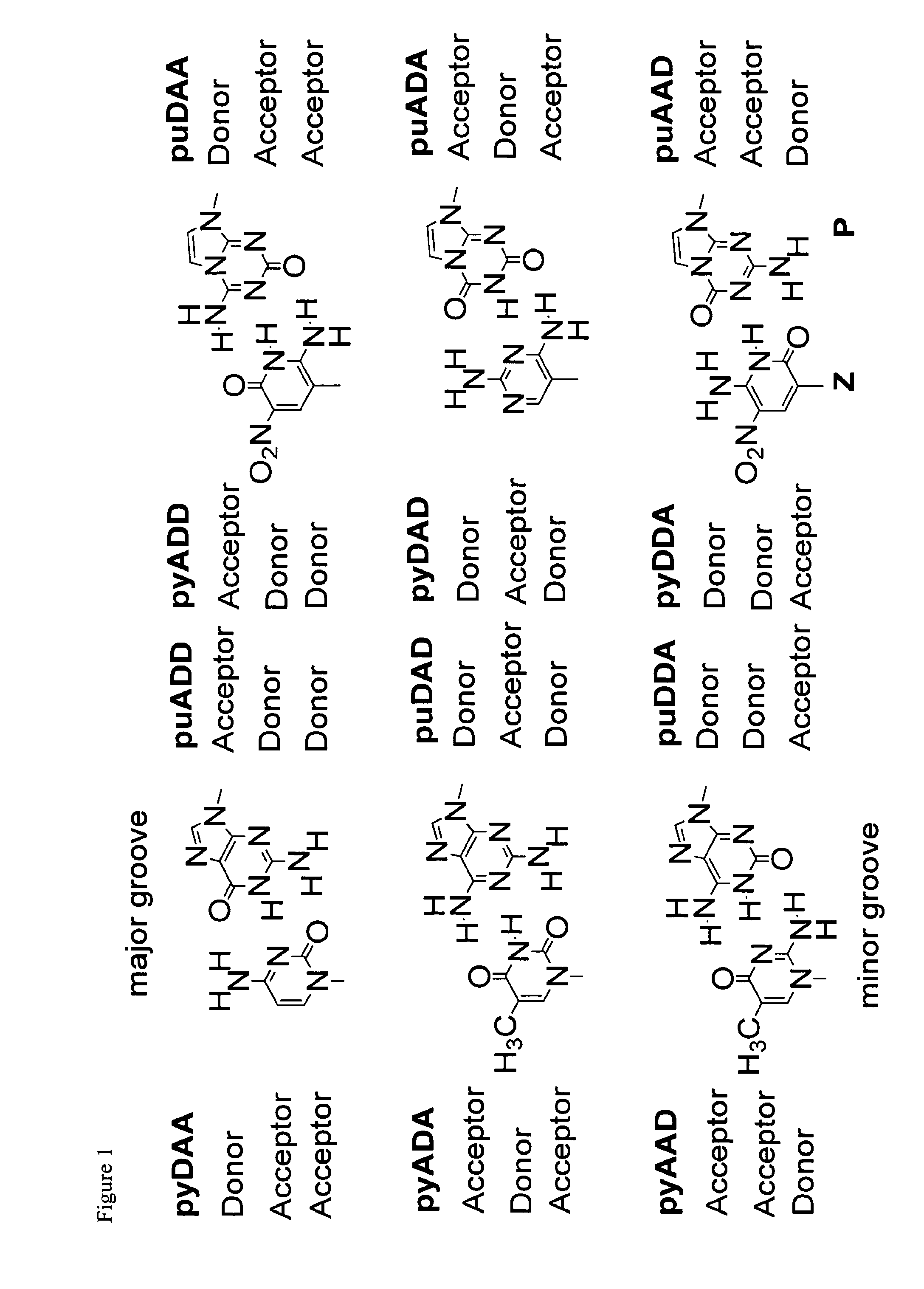
The disclosed invention teaches processes to amplify oligonucleotides by contacting templates and primers with DNA polymerases and triphosphates of non-standard nucleotides, which form nucleobase pairs fitting the standard Watson-Crick geometry, but joined by hydrogen bonding patterns different from those that join standard A:T and G:C pairs. Thus, this invention relates to nucleotide analogs and their derivatives that, when incorporated into DNA and RNA, expand the number of replicatable nucleotides beyond the four found in standard DNA and RNA. The invention further relates to polymerases that incorporate those non-standard nucleotide analogs into oligonucleotide products using the corresponding triphosphate derivatives, and more specifically, polymerases and non-standard nucleoside triphosphates that support the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), including PCR where the products contain more than one non-standard nucleotide unit.
Owner:BENNER STEVEN ALBERT +1
Method for purifying and preparing nucleoside triphosphate derivative
Purification of nucleoside triphosphate derivatives is improved in yield rate. It is carried out by: reacting nuleoside phosphate with dichlorophosphate derivative to obtain a treated liquid containing the target product, purifying it with anionic exchange resin to obtain a mixed product containing phosphate and triphosphate, separating them from each other with cationic exchange resin, necessarily, using hydrogen carbonate to preparing triphosphate directly. The target product yields above 6 times.
Owner:WUXI BIOLOGICS CO LTD +1
Nucleotide triphosphate with an electroactive label conjugated to the gamma phosphate
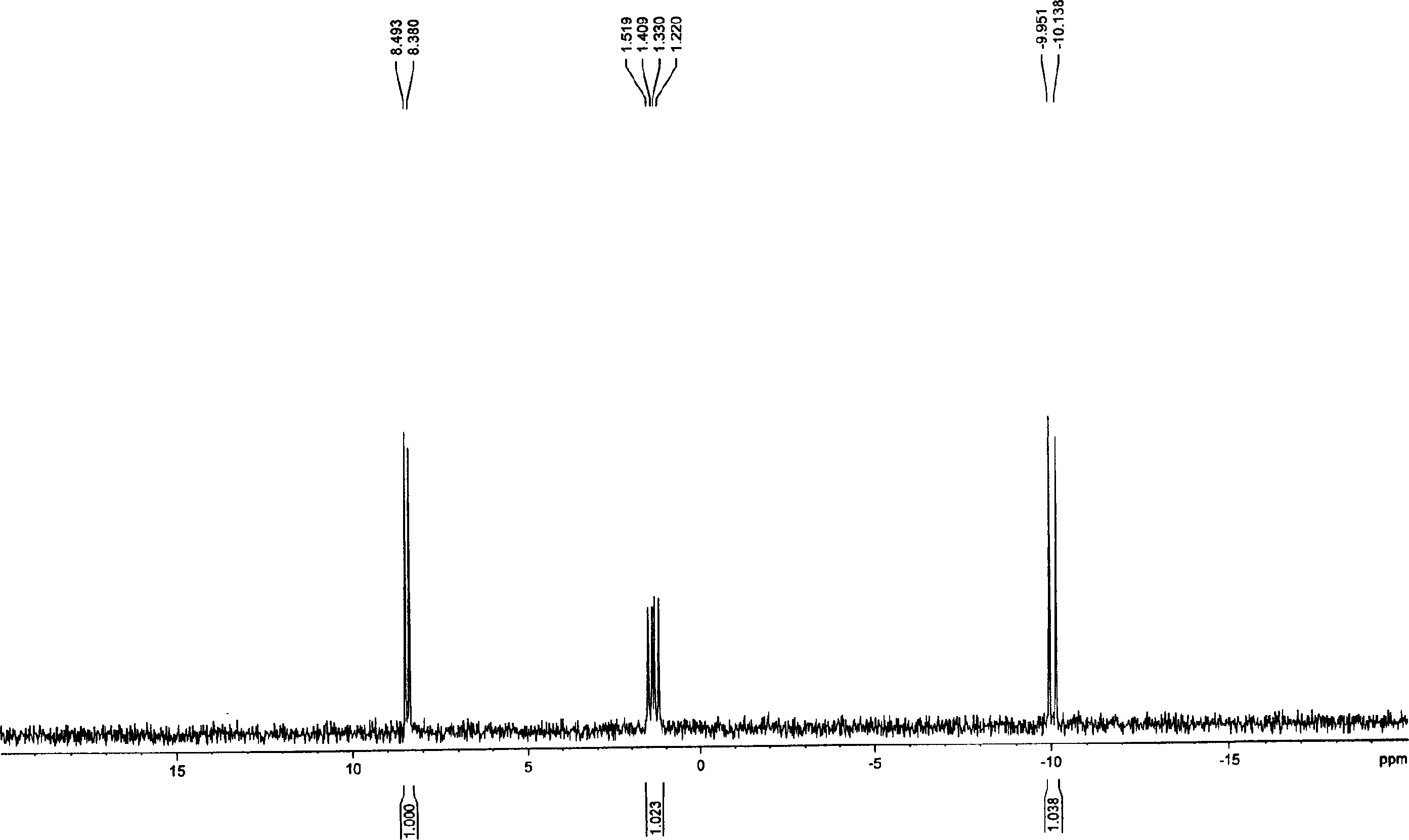
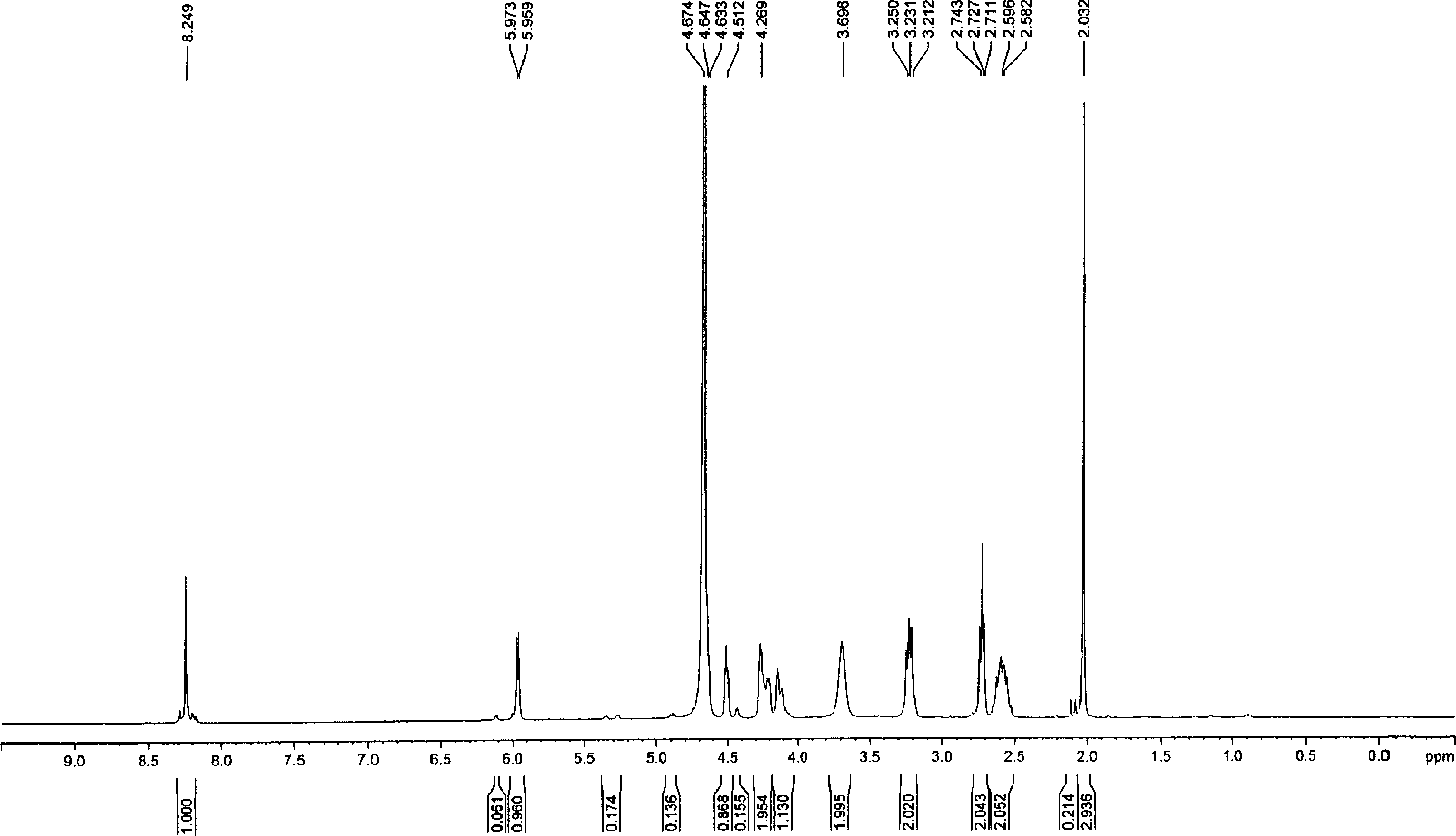
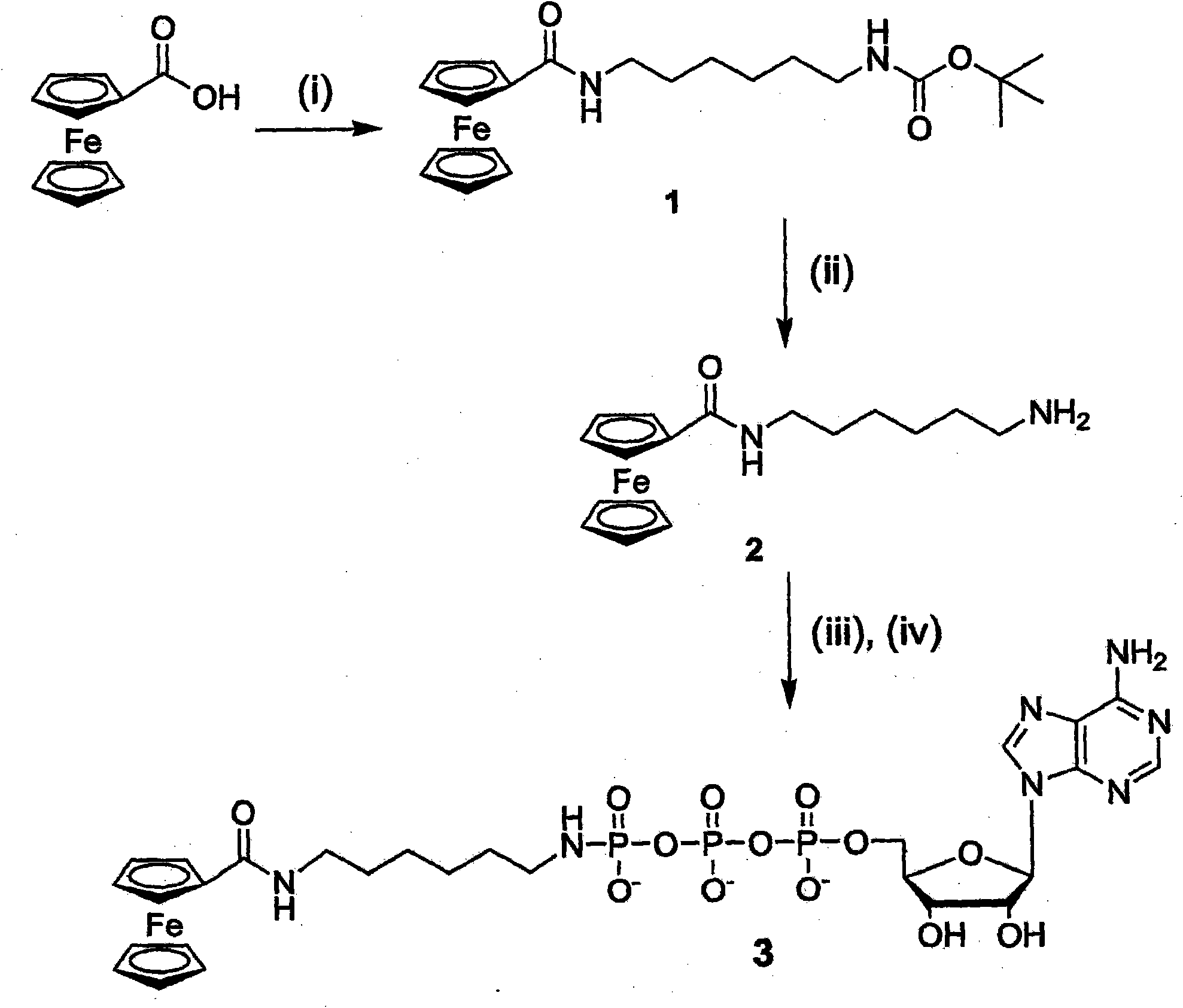
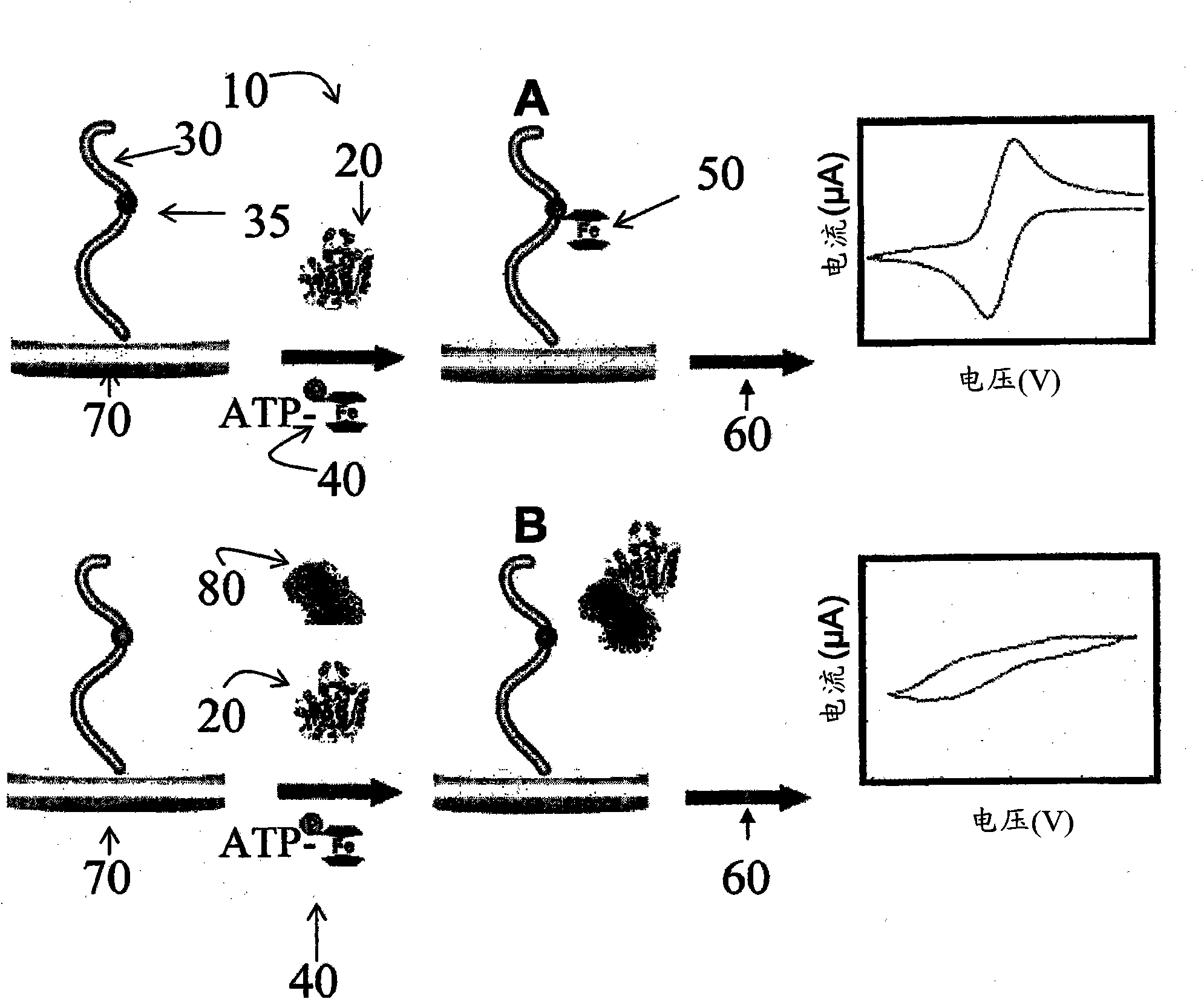
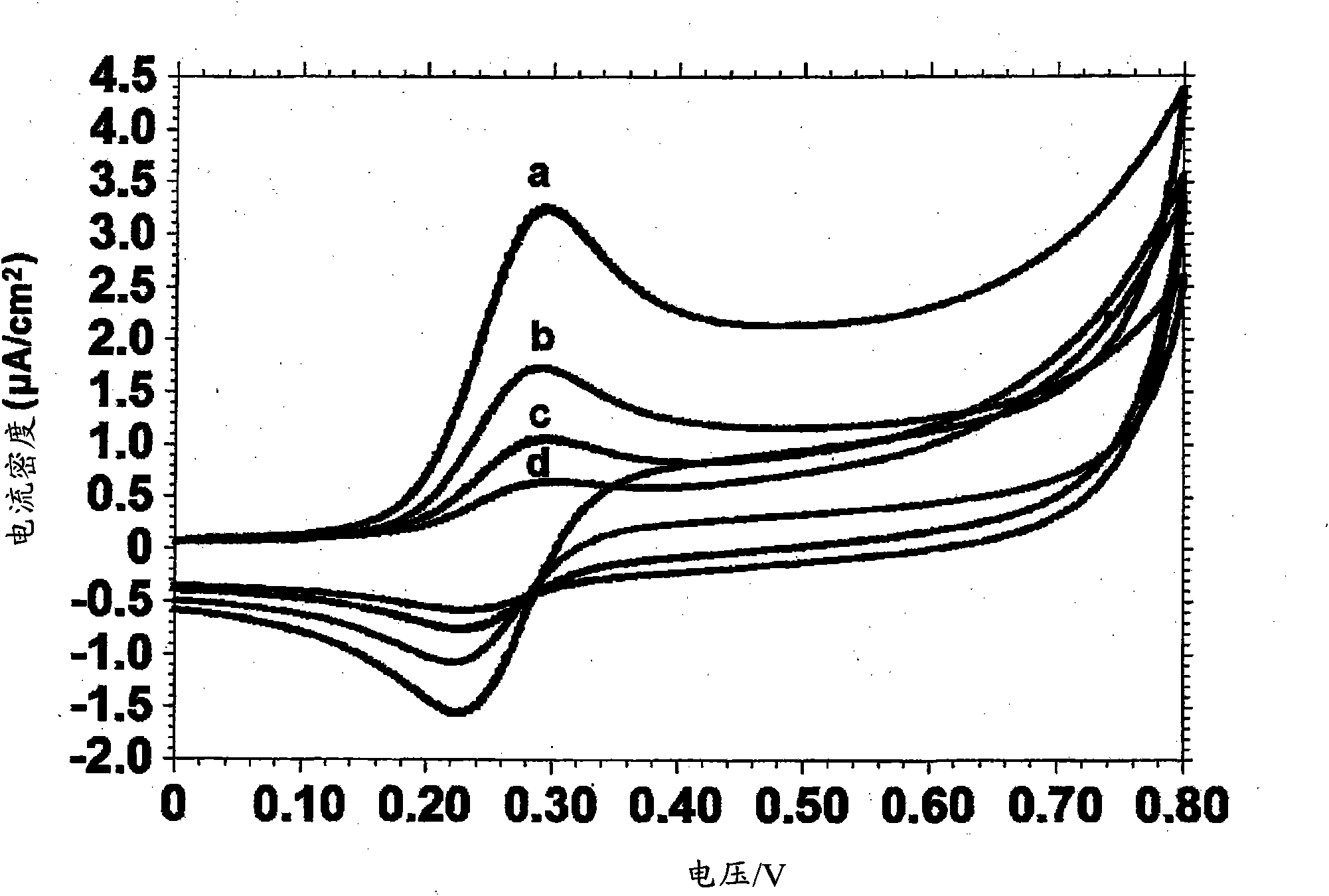
A nucleotide triphosphate (NTP) participates in a phosphorylation reaction, wherein a phosphate group is transferred from the NTP to a substrate by a kinase. Provision in a kinase reaction of a NTP whose gamma phosphate is conjugated to an electroactive label results in the transfer of the gamma phosphate-electroactive label conjugate from the NTP to the substrate. The electroactive label is an organic moiety such as a quinone or a mtrohetercycle, or is a metallocene such as a ferrocene or a cobaltocene. Upon transfer of the gamma phosphate-electroactive label conjugate to an electrode-bound substrate by a kinase, the phosphorylation event is detected electrochemically by cyclic voltammetry. Phosphorylation can also be detected by mass spectrometry of a substrate carrying the electroactive label-conjugated gamma phosphate. NTP comprising the gamma phosphate-electroactive label conjugate is used in methods of detecting the presence of a kinase in a sample, screening candidate compounds that modulate kinase activity, and in methods of diagnosing a disease associated with a kinase.
Owner:海因茨-伯恩哈德·克拉茨 +2
Methods of in vitro protein synthesis
Improved methods are provided in vitro synthesis of biological molecules, providing for improved yields, lowered costs, and enhanced utility. Improved yield and lowered cost is obtained by the use of a phosphate free energy source in the presence of exogenous phosphate, and optionally in the absence of exogenous nucleoside triphosphates.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Real time fluorescent PCR reagent kit for discriminating active Listeria monocytogenes and detection method
InactiveCN101463387AHigh detection sensitivityPrecise screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescent quenchingNucleoside triphosphate
Owner:ZHEJIANG CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Fluorescent Nucleotide Analogues
The present invention provides fluorescent cyanine dye-based nucleotide analogues, in which the cyanine dye is coupled to the γ-phosphate group of a nucleoside triphosphate. Preferred embodiments of the invention are directed to fluorescent cyanine dye-based GTP analogues which may be employed in an homogeneous FRET-based assay to measure the binding of guanine nucleotides to GPCR polypeptides, or alternatively, to measure the effect of an exogenous ligand on GPCR protein binding.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
RNA polymerase mutant capable of utilizing chemically modified nucleotides
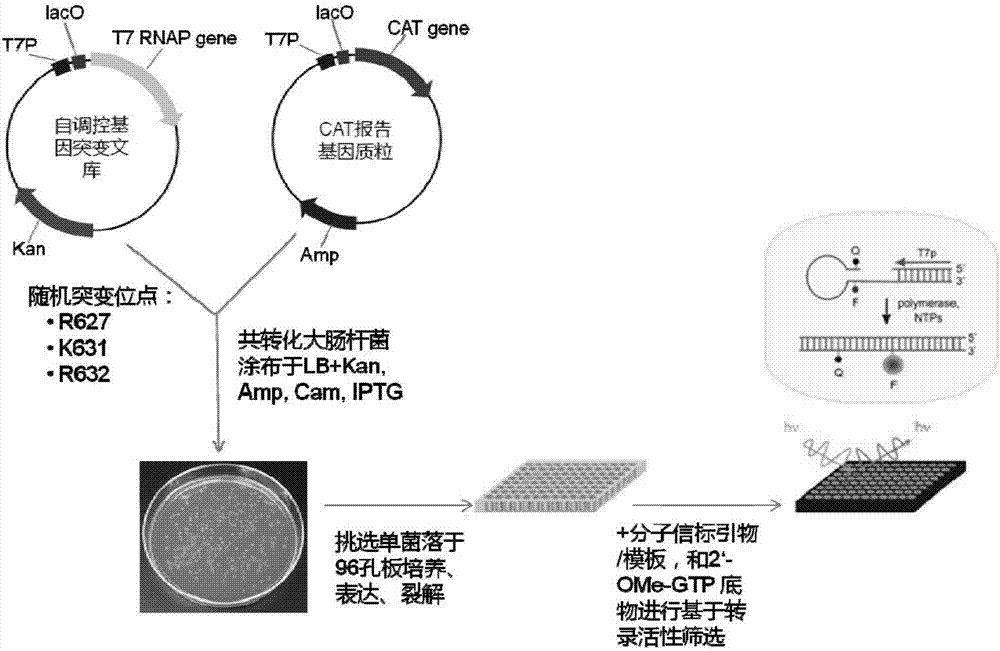
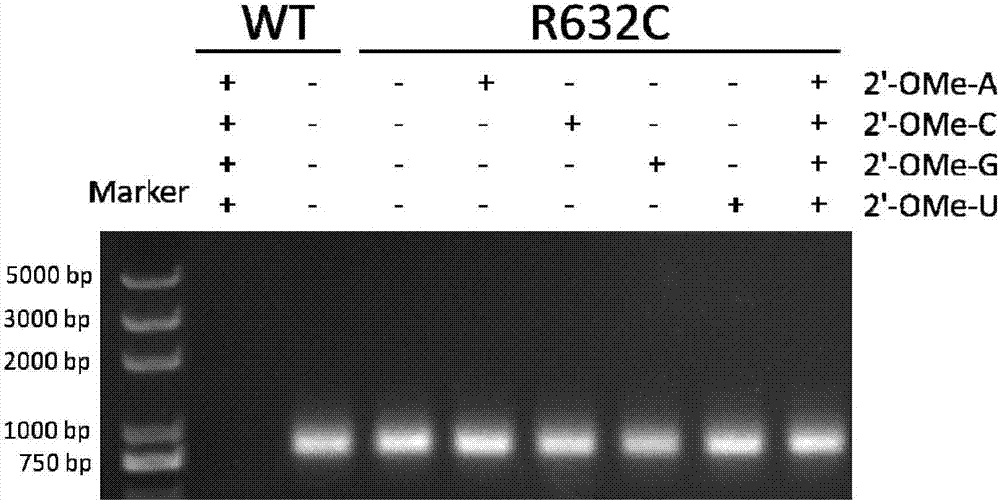
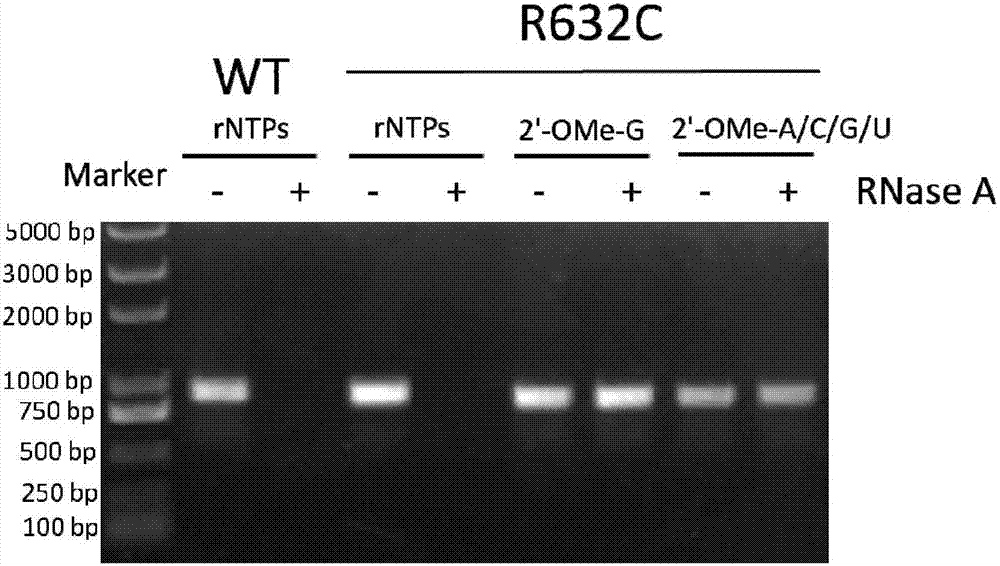
InactiveCN107460177AIncreased transcriptional activityHigh synthesis efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesT7 RNA polymeraseArginine
The invention provides a T7 RNA polymerase mutant by introducing a novel mutation. The T7 RNA polymerase mutant is selected from the mutant (R632C) with arginine at the position 632 in the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 constituting a wild type T7 RNA polymerase substituted by cysteine. The T7 RNA polymerase mutant has DNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity, and can use various 2'-modified nucleoside triphosphates as a synthetic substrate compared with the wild type T7 RNA polymerase. The invention further provides methods and kits for synthesizing the mutant and a nucleic acid containing one or more modified nucleotides.
Owner:张海生
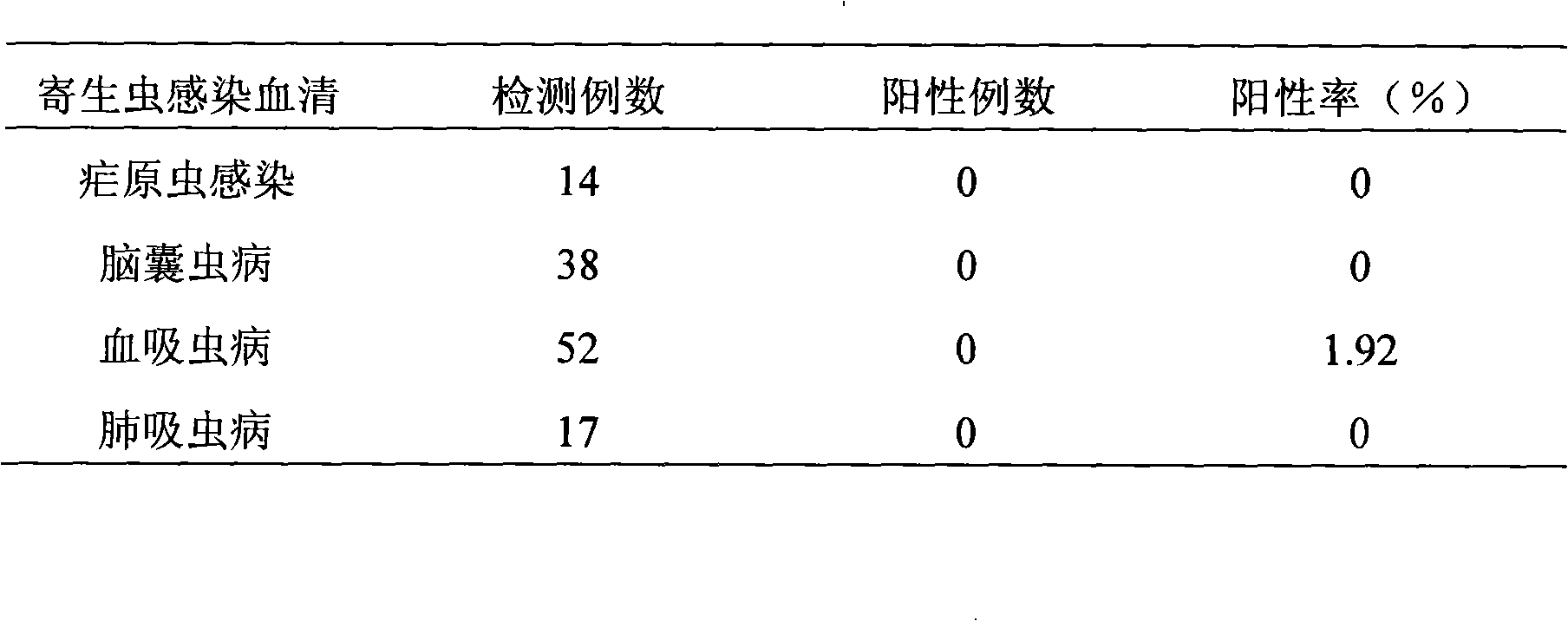
Early detection method for arch insect infection
The invention relates to a method for detecting toxoplasma infection early. The nucleoside triphosphate hydrolase-II (NTPase-II) of toxoplasma is an indispensable key enzyme in the process that purine is remedied and synthesized by the toxoplasma by utilizing host cells, play an important part in parasitism and propagation of the toxoplasma, and is a major antigen for causing a body to generate immune reaction in the acute infection stage of the toxoplasma. The gene of the toxoplasma nucleoside triphosphate hydrolase-II is expanded by utilizing a polymerase chain reaction through the invention, expression plasmids are constructed and recombined in a expression vector, the recombined expression plasmids are transferred to procaryotic cells for expression, recombined fusion protein NTPase-II is obtained, the recombined fusion protein NTPase-II is used as an indirect ELISA method to establish a coating antigen, and is used as the method for detecting the toxoplasma infection early.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Methods for using double-mutant RNA polymerases with reduced discrimination between non-canonical and canonical nucleoside triphosphates
ActiveUS20050069907A1Minimizes stepMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPolymerase LBiology
A method and kit for synthesizing a nucleic acid molecule comprising at least one non-canonical nucleoside triphosphate using a double-mutant polymerase having a reduced discrimination between canonical and non-canonical substrates is disclosed. The method comprises incubating a template nucleic acid in a reaction mixture comprising the mutant nucleic acid polymerase and the appropriate canonical and non-canonical nucleoside triphosphates which are desired substrates for the mutant nucleic acid polymerase. The present invention is also a method of determining the sequence of a nucleic acid molecule using the mutant polymerase to create a nucleic acid molecule comprising at least one non-canonical nucleoside triphosphate.
Owner:UNIV OF TEXAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com