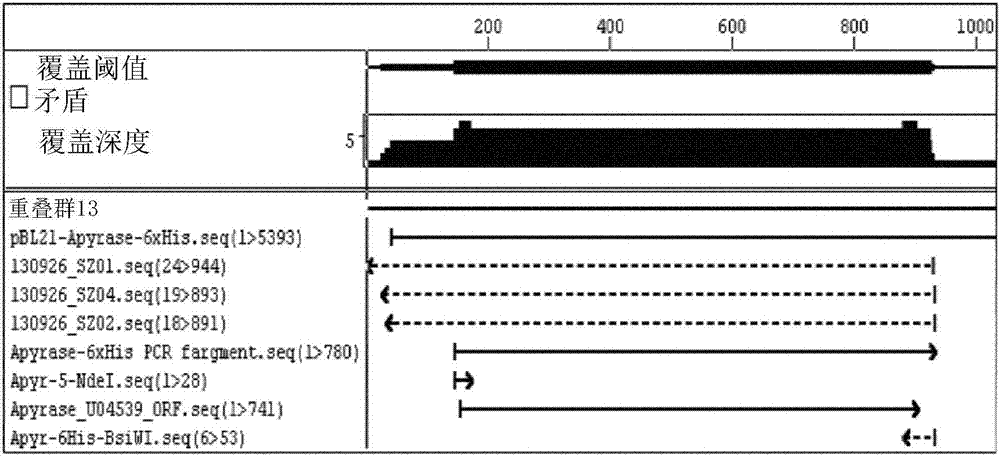
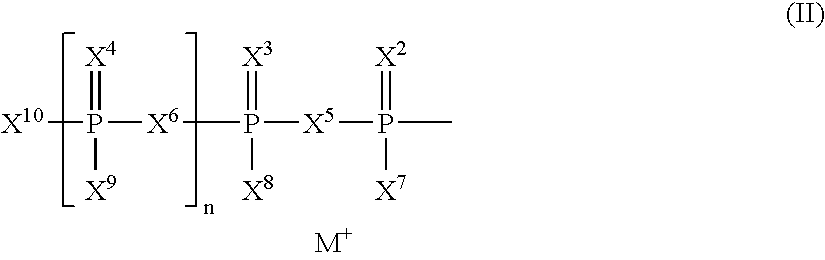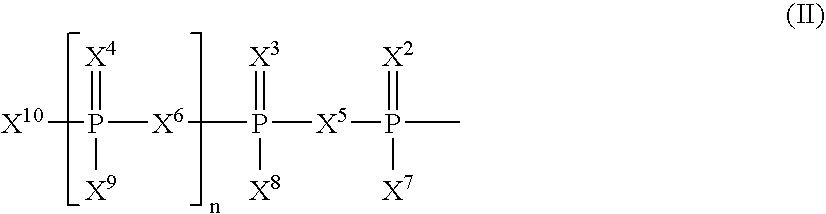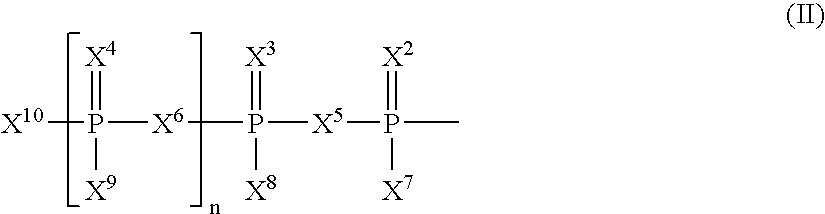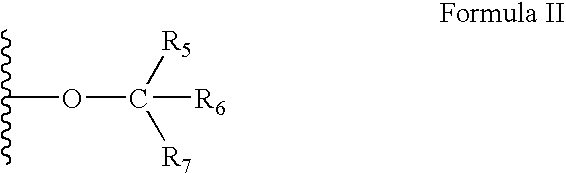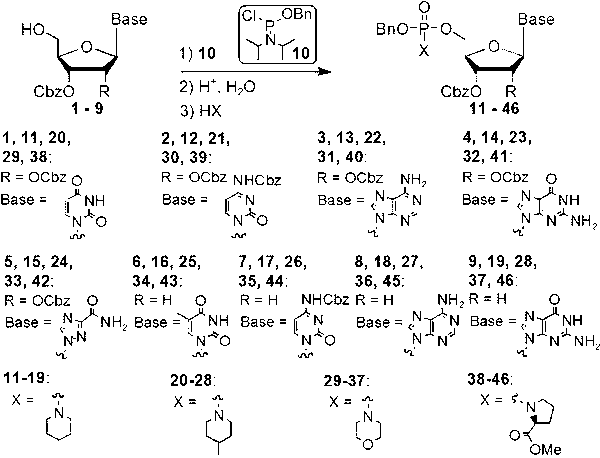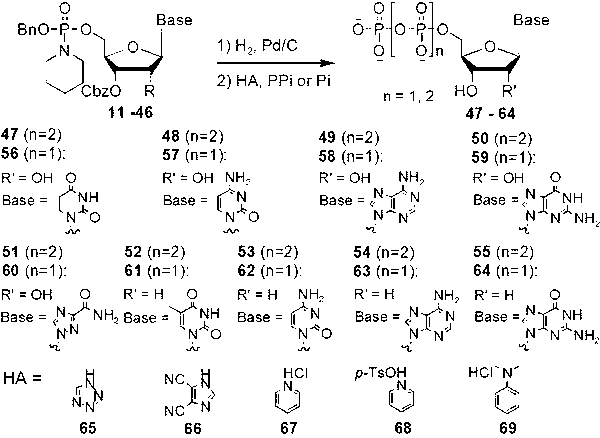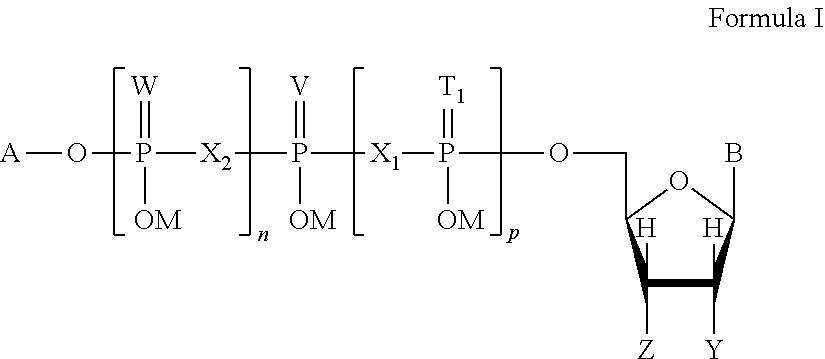Patents
Literature
36 results about "Nucleoside diphosphate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
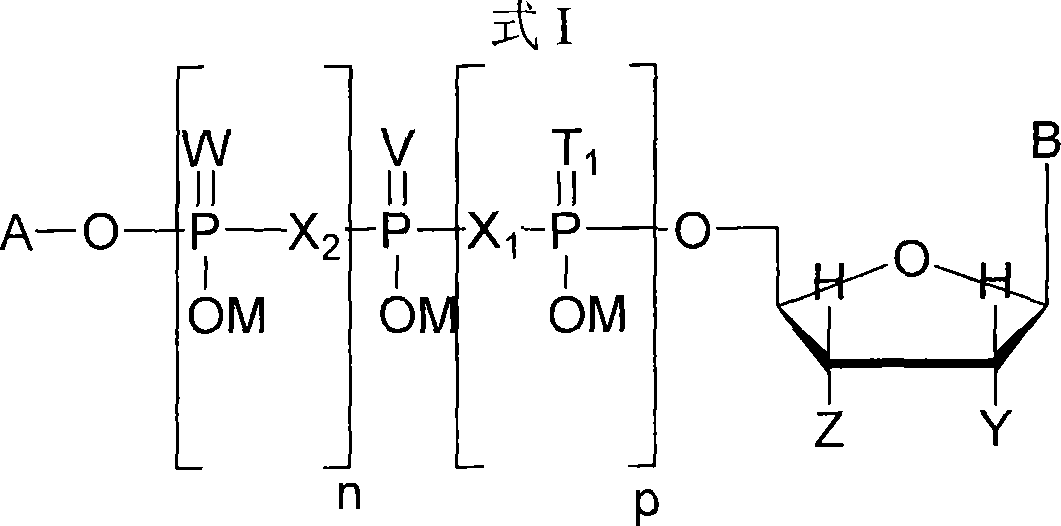
Nucleotide mimics and their prodrugs
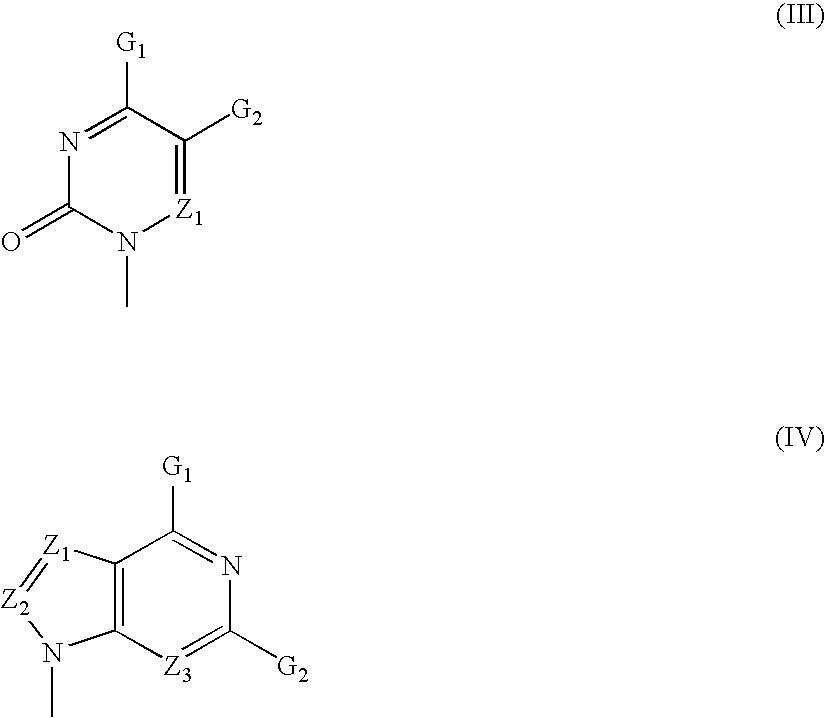
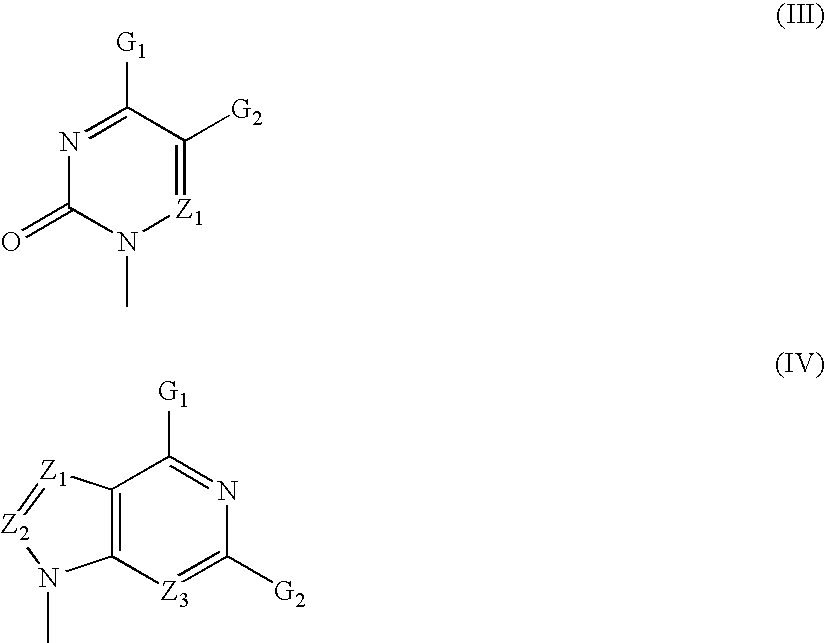
The present invention relates to nucleoside diphosphate mimics and nucleoside triphosphate mimics, which contain diphosphate or triphosphate moiety mimics and optionally sugar-modifications and / or base-modifications. The nucleotide mimics of the present invention, in a form of a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, a pharmaceutically acceptable prodrug, or a pharmaceutical formulation, are useful as antiviral, antimicrobial, and anticancer agents. The present invention provides a method for the treatment of viral infections, microbial infections, and proliferative disorders. The present invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of the present invention optionally in combination with other pharmaceutically active agents.
Owner:BIOTA SCI MANAGEMENT PTI LTD
Nucleotide mimics and their prodrugs
Owner:BIOTA SCI MANAGEMENT PTI LTD
Nucleotide mimics and their prodrugs
The present invention relates to nucleoside diphosphate mimics and nucleoside triphosphate mimics, which contain diphosphate or triphosphate moiety mimics and optionally sugar-modifications and / or base-modifications. The nucleotide mimics of the present invention, in a form of a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, a pharmaceutically acceptable prodrug, or a pharmaceutical formulation, are useful as antiviral, antimicrobial, and anticancer agents. The present invention provides a method for the treatment of viral infections, microbial infections, and proliferative disorders. The present invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of the present invention optionally in combination with other pharmaceutically active agents.
Owner:BIOTA SCI MANAGEMENT PTI LTD
P2Y6 receptor agonists for treating lung diseases
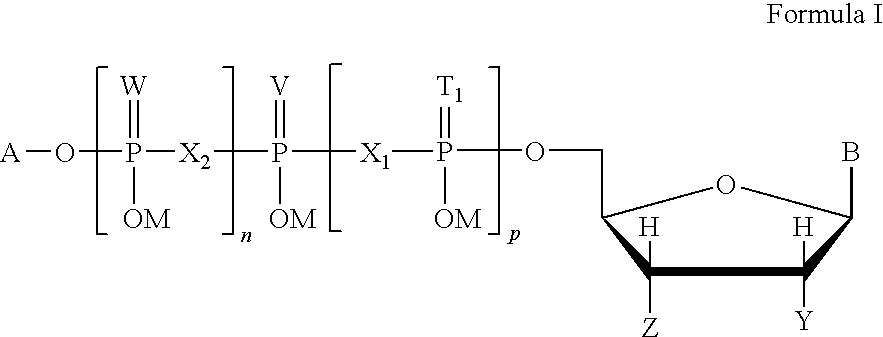
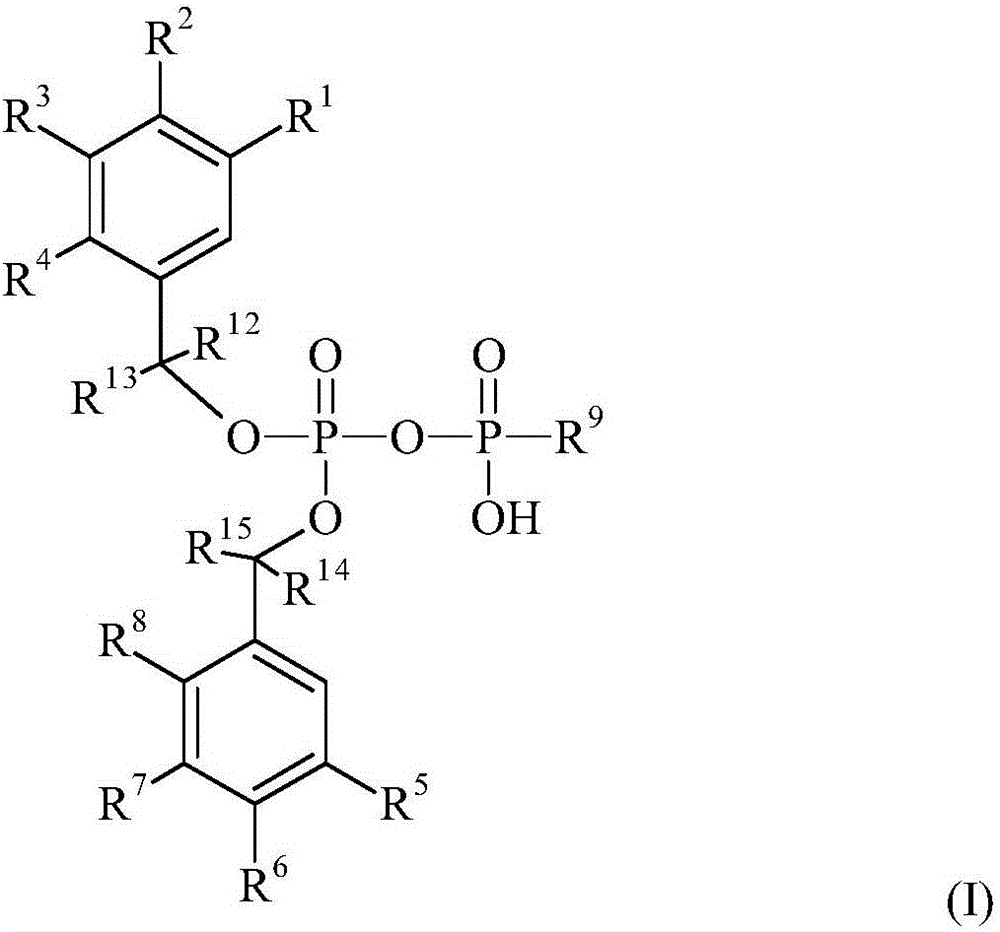
This invention is directed to a method of enhancing or facilitating the clearance of the lung mucus secretions in a subject. This invention is also directed to a method of facilitating the hydration of the lung mucus secretions in a subject. This invention is further directed to a method of preventing or treating diseases or conditions associated with impaired lung or airway function in a human or other mammal. The method comprises administering to a subject a pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutic effective amount of P2Y6 receptor agonist compound, wherein said amount is effective to activate the P2Y6 receptors on the luminal surface of lung epithelia. The P2Y6 receptor agonist compounds useful for this invention include mononucleoside 5′-diphosphates, dinucleoside monophosphate, dinucleoside diphosphates, or dinucleoside triphosphates of general Formula I, or salts, solvates, hydrates thereof.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
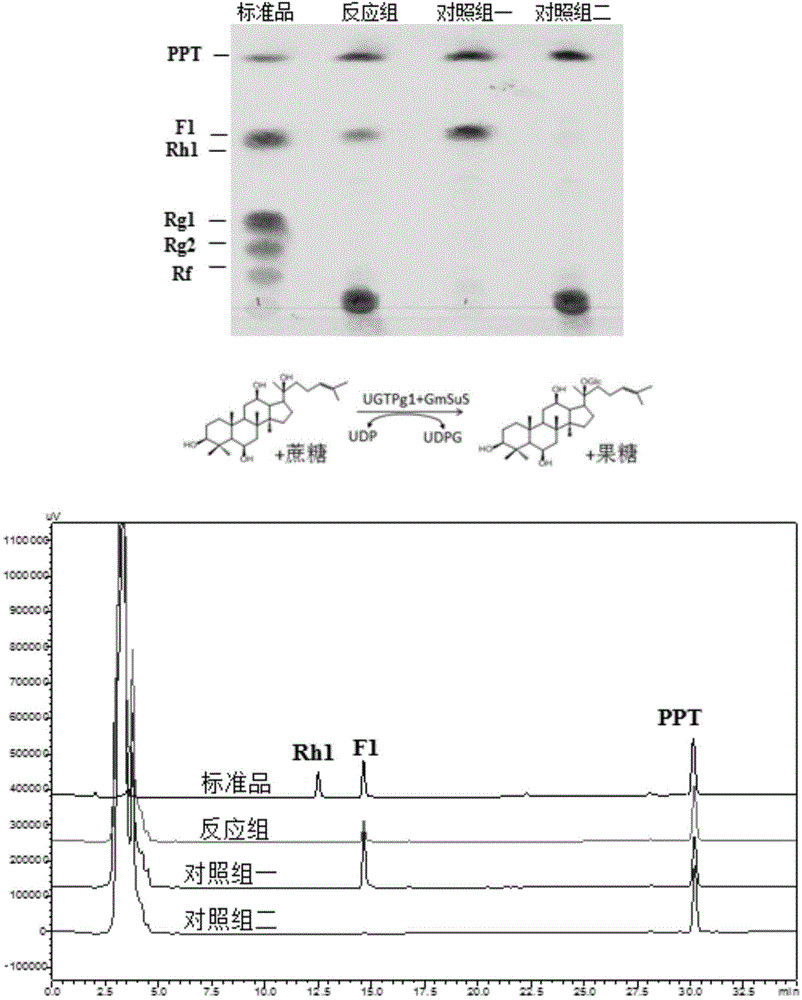
Novel catalytic system for preparing rare ginsenosides and application thereof
ActiveCN105087739AHigh catalytic efficiencyReduce use costFungiBacteriaSucrose synthetaseProtopanaxadiol
The invention discloses a co-catalytic reaction system for preparing rare ginsenosides. The co-catalytic reaction system comprises glycosyltransferase GT (a); sucrose synthase SUS (b); uridine diphosphate UDP (c); and saccharose (d). Experiments show that in the presence of the saccharose and little UDP, an enzyme combination composed of the glycosyltransferase and the saccharose is capable of replacing an in-vitro reaction system to synthesize UDP sugar, one of expensive materials for the rare ginsenosides, and efficiently and economically converting substrates such as protopanoxadiol or protopanaxatriol into the rare ginsenosides, wherein the UDP is about 1 / 4 of the UDP sugar in price and is 1% of its original dosage; thus, preparation cost of the rare ginsenosides is greatly saved, and large-scale commercial preparation of the ginsenosides is better facilitated.
Owner:SYNBIOTECH (SUZHOU) CO LTD
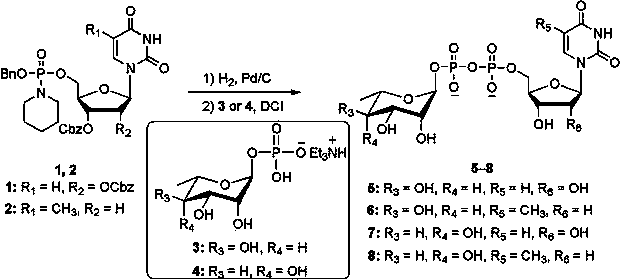
Method for synthesizing dinucleoside diphosphate and dinucleoside triphosphote
InactiveCN103910774AEasy to separateFast coupling reactionSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationChemical synthesisPhosphate
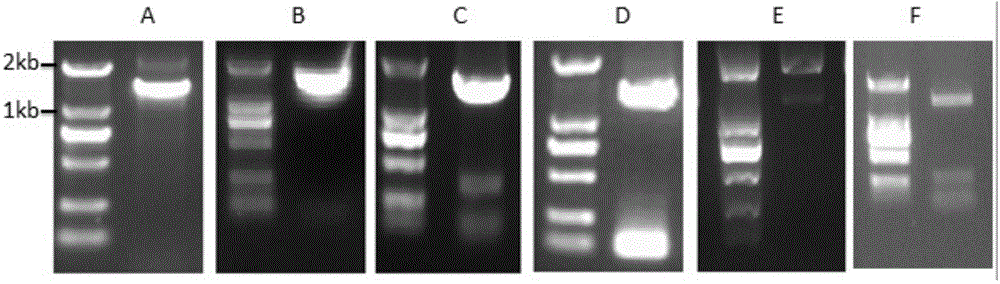
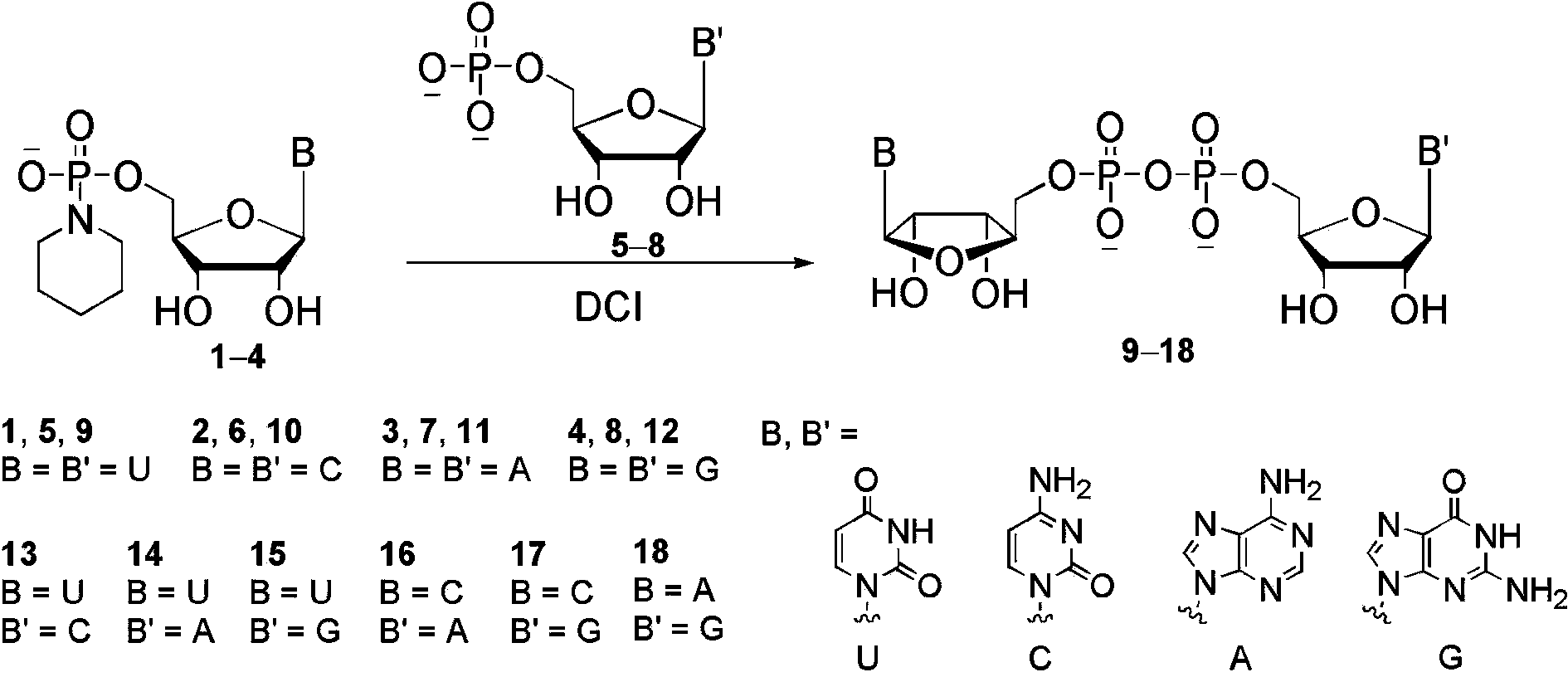
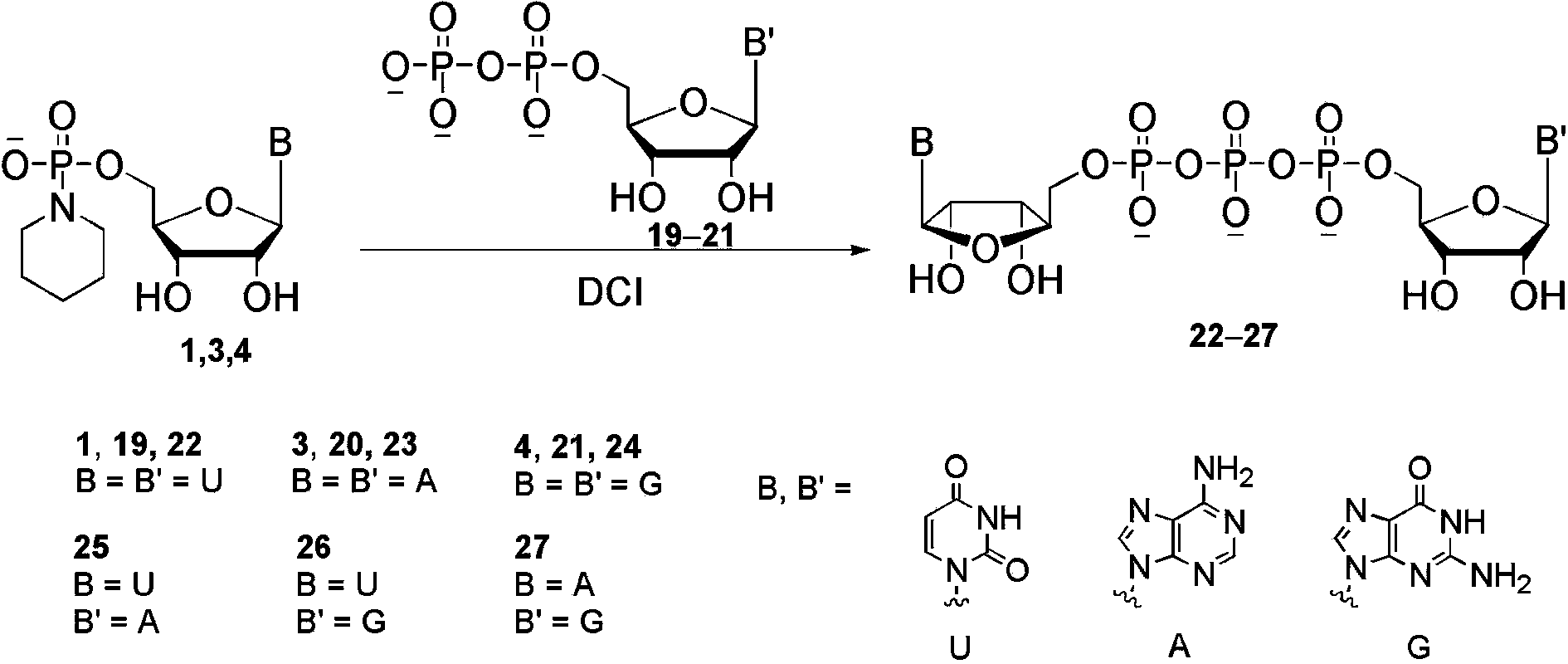
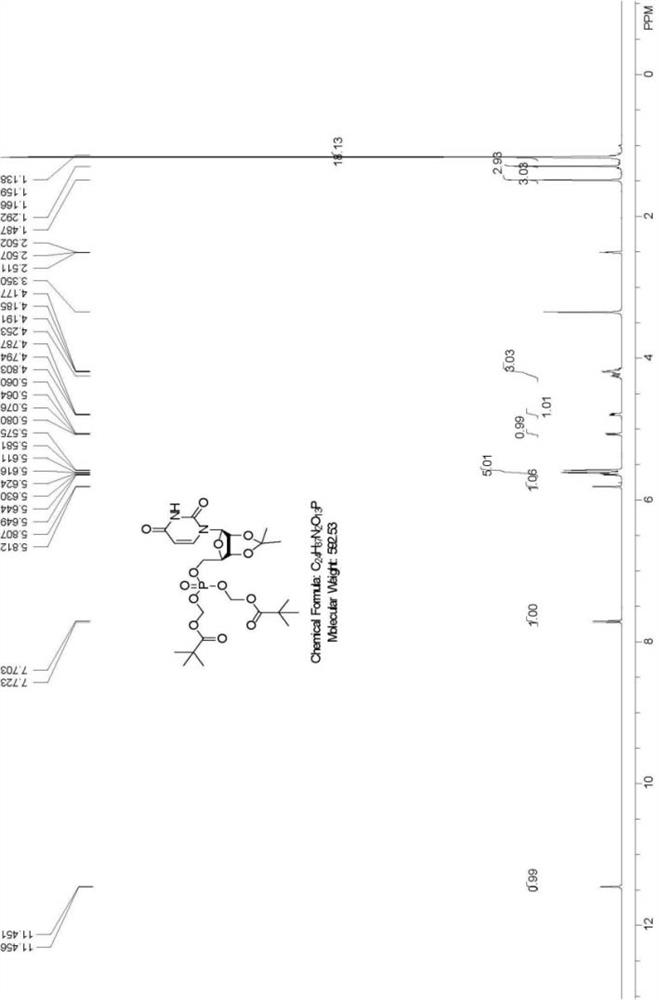
The invention belongs to the field of chemical synthesis and in particular relates to a method for synthesizing dinucleoside diphosphate and dinucleoside triphosphote. The method comprises the following steps: reacting nucleoside phosphoryl piperidine as a nucleoside phosphoryl donor, nucleoside phosphate or nucleoside diphosphate as a nucleoside phosphoryl receptor and 4,5-dicyanoimidazole (DCI) as an activating reagent in a high-polarity non-protonized solvent; purifying crude products through ion exchange chromatography to obtain dinucleoside diphosphate and dinucleoside triphosphote respectively. According to the method, the selected and used nucleoside phosphoryl piperidine raw material is simple and easily available, the coupling reaction speed is high in the presence of the activating reagent, the yield is high, few byproducts are generated, and the products are easily separated.
Owner:JIANGXI SCI & TECH NORMAL UNIV
Nucleoside phosphate and synthesis method thereof
ActiveCN112279877AAvoid it happening againAvoid corrosionSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationPhosphoric Acid EstersPhosphate
The invention discloses a synthesis method of nucleoside phosphate, which mainly comprises the following steps: mixing lithium diphosphate, nucleoside and a condensing agent in a solvent, stirring atroom temperature, adding a citric acid solution for washing after the reaction is finished, drying with anhydrous sodium sulfate to obtain a crude product, and carrying out column chromatography separation to obtain the product. According to the method disclosed by the invention, ion exchange resin does not need to be used for treatment in the process of synthesizing the raw material phosphodiester, the reaction can be carried out by directly using the lithium diphosphate, the method disclosed by the invention is simple to operate and low in equipment requirement, and the same meaningful method is provided for synthesizing nucleoside diphosphate.
Owner:南京颐媛生物医学研究院有限公司 +1
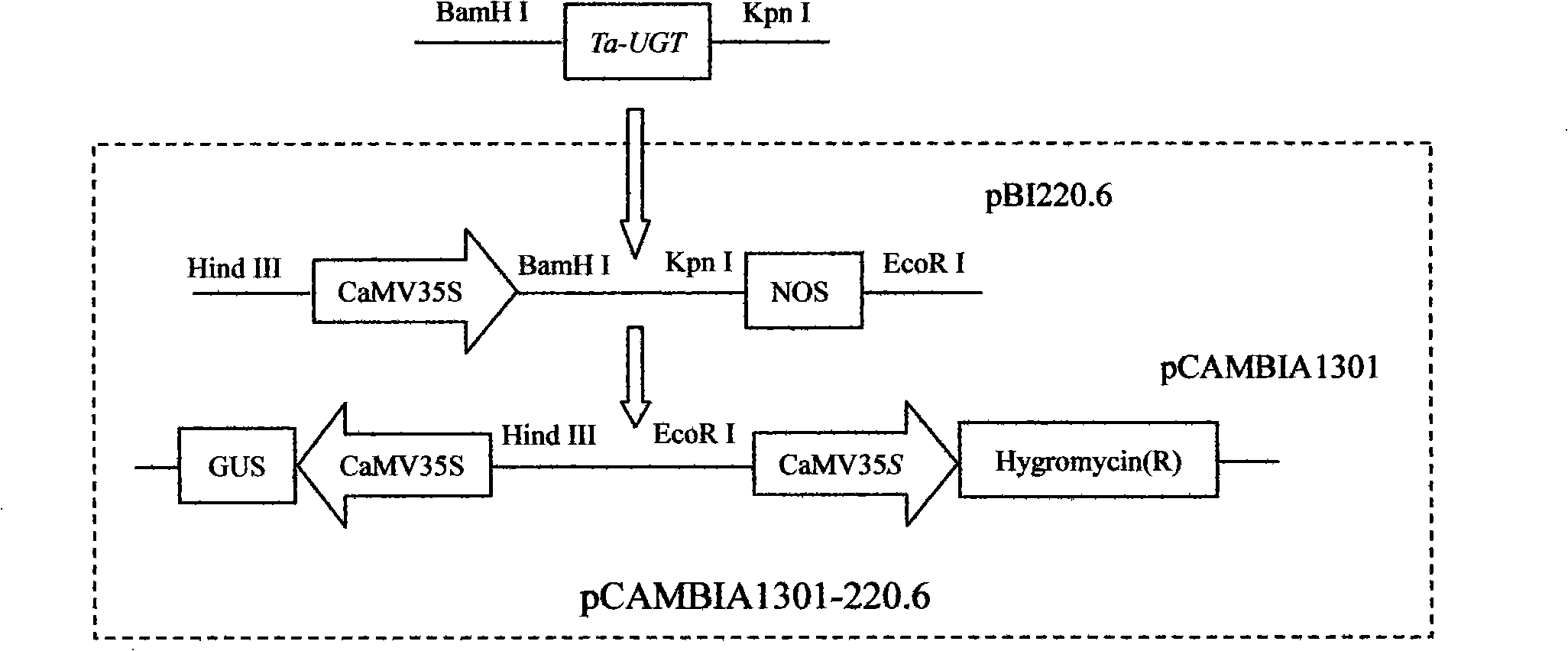
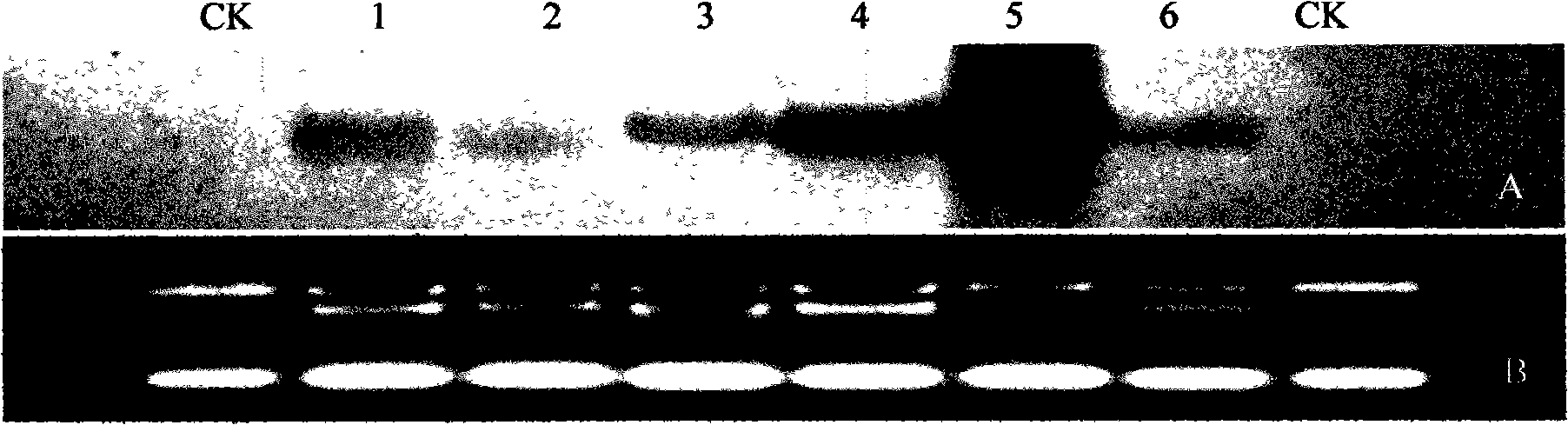
Diphosphoric uridine glucosyl transferase gene and encoded protein thereof
InactiveCN101314776AIncrease resistanceReduce contentTransferasesGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyDisease
The invention discloses a nucleoside diphosphate glucosyltransferase gene (Ta-UGT) and coded protein thereof, and belongs to the gene engineering field. The cDNA sequence of the nucleoside diphosphate glucosyltransferase gene (Ta-UGT) is SEQ ID NO.1, the sequence of coded amino acid thereof is SEQ ID NO.2, and the gene is from wheat scab (triticum asetivum L.), which is reported for the first time in the wheat and induced by deoxynivalenol (DON) to strengthen expression. An experiment shows that the over expression of the gene can improve the resistibility of plants to DON. The Ta-UGT is introduced into the wheat variety easily infected by gibberellic disease, so as to expect to reduce the content of the DON in the wheat grain.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for synthesizing nucleoside triphosphate and nucleoside diphosphate from all-protected nucleoside phosphoramidite intermediate through acid catalysis
InactiveCN103193843AImprove reaction speedHigh reaction yieldSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationPhosphorous acidChemical synthesis
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing nucleoside triphosphate and nucleoside diphosphate from an all-protected nucleoside phosphoramidite intermediate through acid catalysis. The method comprises the following steps of: generating a phosphoramidite intermediate crude product under an alkaline condition by taking carbobenzoxy protected nucleoside and benzyloxydiisopropylamino phosphorochloridite as raw materials, subjecting the phosphoramidite intermediate crude product to weak acid catalytic hydrolysis to obtain a nucleoside- H-phosphonate intermediate crude product, subjecting the nucleoside-H-phosphonate intermediate crude product and alkylamine to oxidative coupling, carrying out column chromatography on the resulting product to obtain an all-protected nucleoside phosphoramidite precursor, subjecting the nucleoside phosphoramidite precursor to catalysis and hydrogenation in an N-N-dimethylfomamide solution to remove all protective groups, filtering the resulting product to remove palladium on an activated carbon, and reacting the resulting product with pyrophosphate or monophosphoric acid alkyl ammonium salt under a condition in the presence of a weak acid catalyst to obtain a nucleoside triphosphate product and a nucleoside diphosphate product. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, reaction velocity and yield of the pyrophosphoric acid and monophosphoric acid reagents with the phosphoramidite intermediate are greatly improved, and an efficient, universal and novel method for the chemical synthesis of the nucleoside 5'- triphosphate and the nucleoside 5'-diphosphate is established.
Owner:JIANGXI SCI & TECH NORMAL UNIV
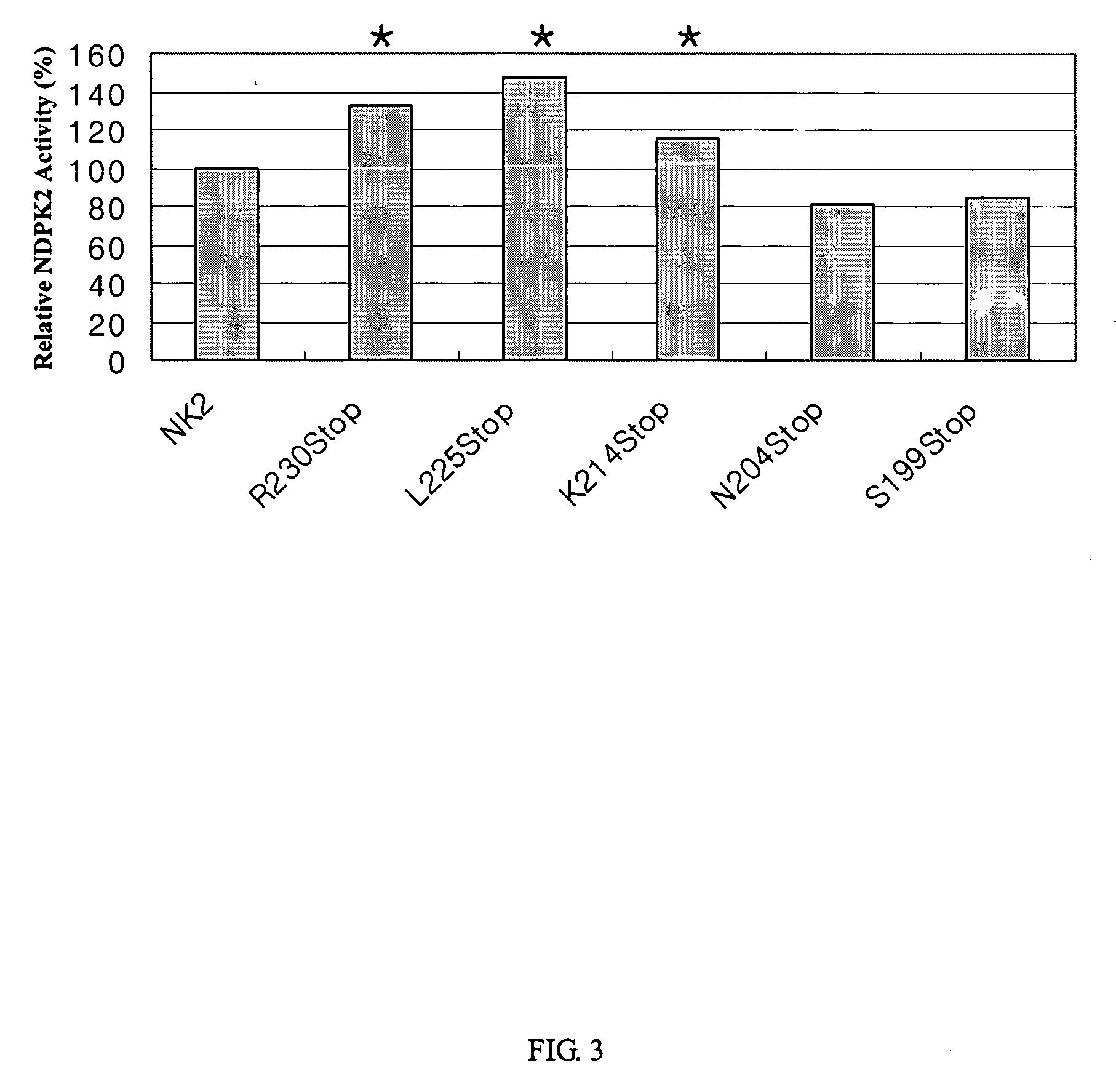
Nucleic acid molecules encoding hyperactive nucleoside di-phosphate kinase 2 and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070136897A1Efficient developmentImprove lighting efficiencySugar derivativesClimate change adaptationPhosphatePhytochrome
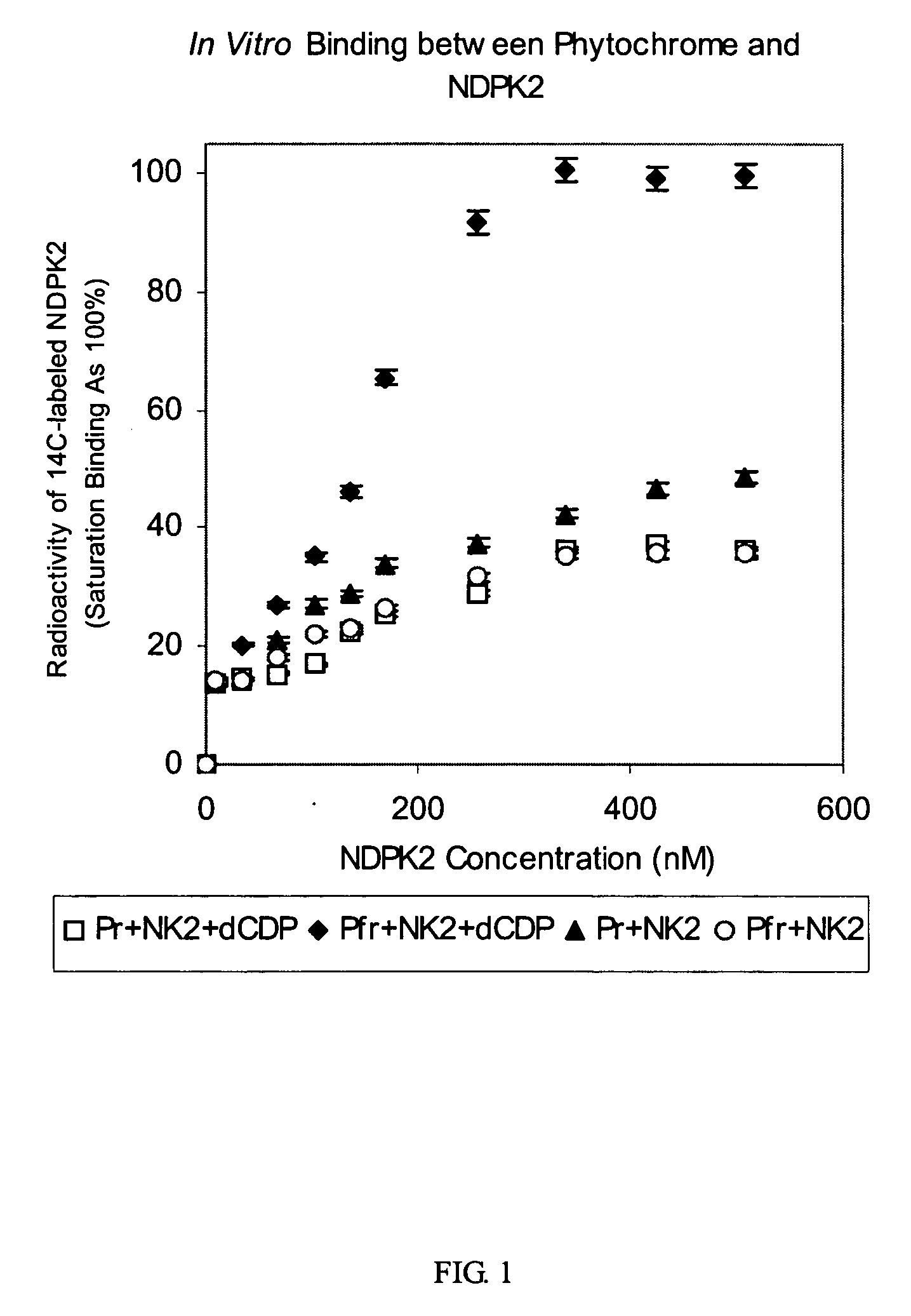
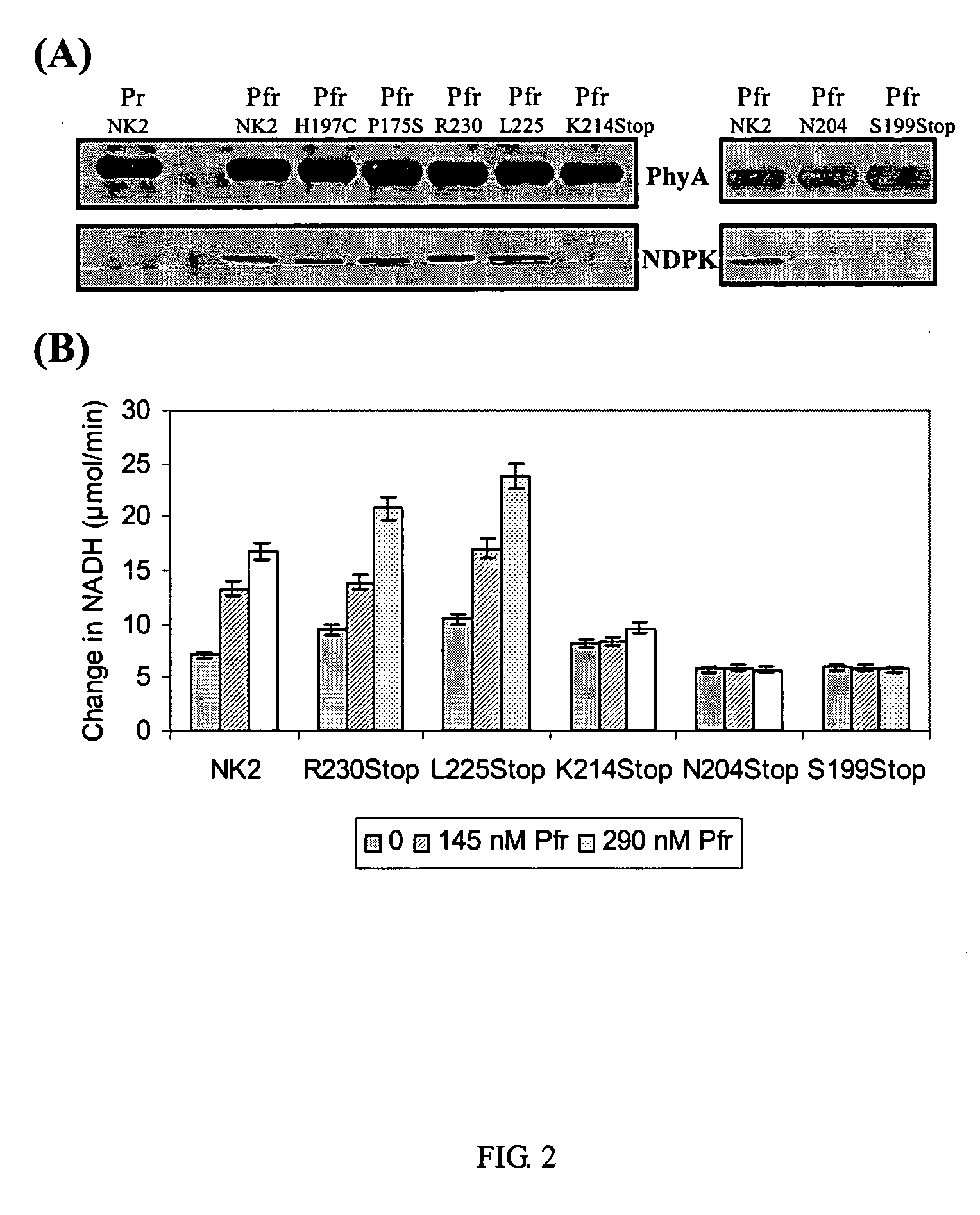
The present invention includes modified Arabidopsis Nucleoside Di-Phosphate Kinase 2 (NDPK2) nucleic acid molecules whose enzymatic activity have been increased (i.e. hyperactive). NDPKs are ubiquitous housekeeping enzymes that catalyze the transfer of γ-phosphoryl group from a nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) to a nucleoside diphosphate (NDP), and also multifunctional proteins that regulate a variety of eukaryotic cellular activities, including cell proliferation, development, and differentiation. In plants, NDPKs are reported to play a key role in the signaling of both stress and light. Among three NDPKs (NDPK1, NDPK2, NDPK3) in a model plant, Arabidopsis thaliana, NDPK2 was reported as a positive signal transducer of phytochrome-mediated plant light signaling and to regulate cellular redox state, which enhances multiple stress tolerance in transgenic plants. Thus, the plants with the hyperactive NDPK2 are expected to possess higher efficiency of light utilization and enhanced tolerance to various environmental stresses such as cold, salt, and oxidative stresses. Since abiotic stress is one of the most important factors to limit the productivity of many crops, the hyperactive NDPK2 can be used for the development of high-yielding multiple stress tolerant plants with higher efficiency of light utilization. In this invention, several hyperactive NDPK2 were generated by C-terminal deletion and site-directed mutagenesis. Therefore, the present invention can be utilized to develop multiple stress tolerant and efficiently light-utilizing plants, which can eventually increase crop yields. The invention also includes plants having at least one cell expressing the modified NDPK2, vectors comprising at least one portion of the modified NDPK2 nucleic acids, and methods using such vectors for producing plants with enhanced light sensitivity and stress tolerance.
Owner:KOREA KUMHO PETROCHEMICAL CO LTD
Composition and method for inhibiting platelet aggregation
This invention is directed to a method of preventing or treating diseases or conditions associated with platelet aggregation. The method is also directed to a method of treating thrombosis. The method comprises administering to a subject a pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutic effective amount of P2Y<12> receptor antagonist compound, wherein said amount is effective to bind the P2Y<12> receptors on platelets and inhibit ADP-induced platelet aggregation. The P2Y12 receptor antagonist compounds useful for this invention include mononucleoside 5'-monophosphates, mononucleoside polyphosphates, and dinucleoside polyphosphates of general Formula I, or salts thereof. The present invention also provides novel compounds of mononucleoside 5'-monophosphates and dinucleoside diphosphates. The present invention further provides pharmaceutical formulations comprising a pharmaceutical carrier and mononucleoside 5'-monophosphates or dinucleoside diphosphates.
Owner:INSPIRE PHARMA +1
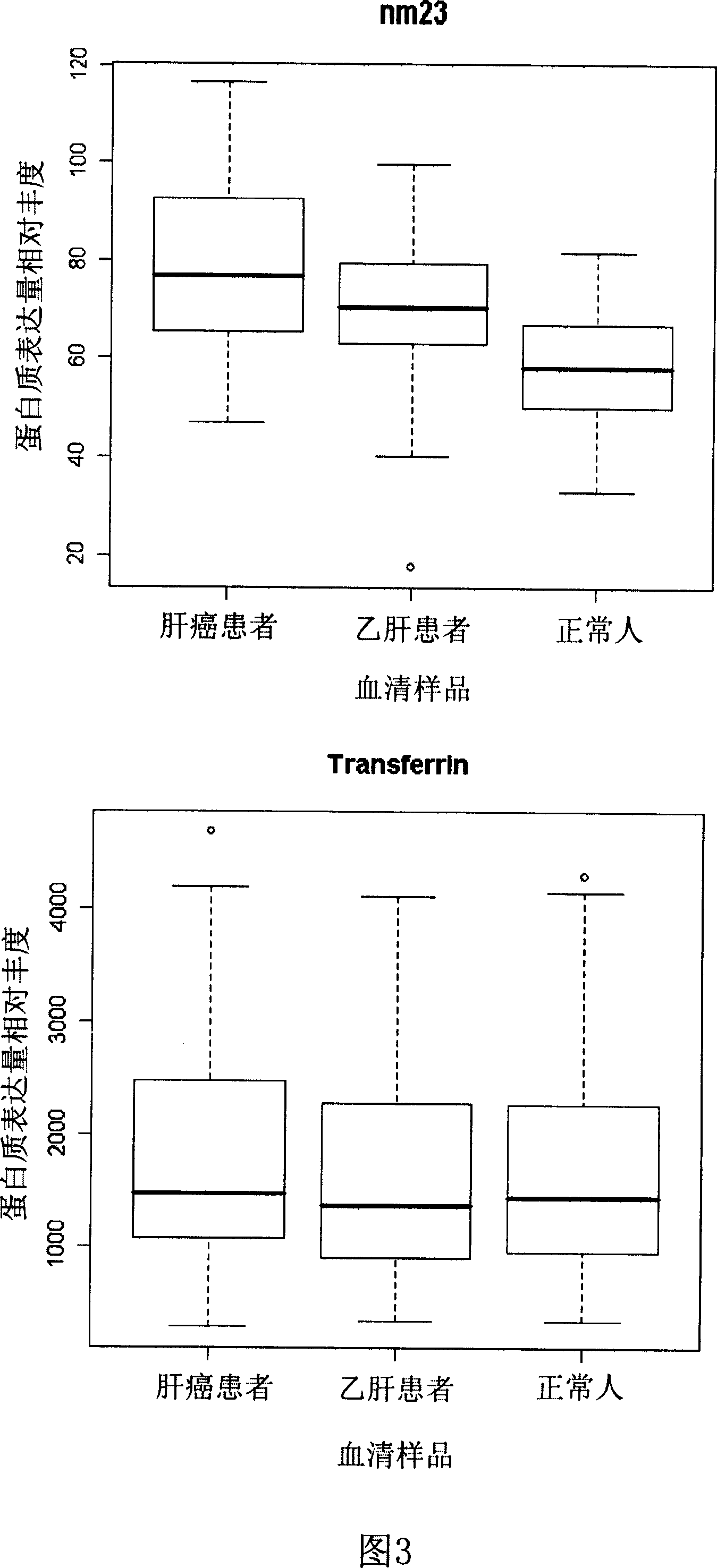
Application of nucleoside diphosphate kinase A
This invention relates to one method to filter liver cell cancer organism and side organism difference expression protein, which finds out one liver cell cancer organism expression protein, wherein, the immune experiment further proves G protein beta2 subunit in liver cell cancer organism different expression; The protein can be used as protein molecule label for liver cancer by the relative property.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
P2Y6 receptor agonists for treating lung diseases
The present invention relates to a method of increasing or facilitating the clearance of pulmonary mucus secretions in a subject. The present invention also relates to a method of facilitating hydration of pulmonary mucus secretions in a subject. The invention also relates to a method of preventing or treating a disease or condition associated with impaired lung or airway function in a human or other mammal. The method comprises administering to the subject a pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a P2Y6 receptor agonist compound, wherein said amount is effective to activate P2Y6 receptors on the luminal surface of the lung epithelium. The P2Y6 receptor agonist compounds used in the present invention include mononucleoside 5'-diphosphate, dinucleoside monophosphate, dinucleoside diphosphate or dinucleoside triphosphate of general formula I, or salts and solvates thereof , Hydrate.
Owner:INSPIRE PHARMA
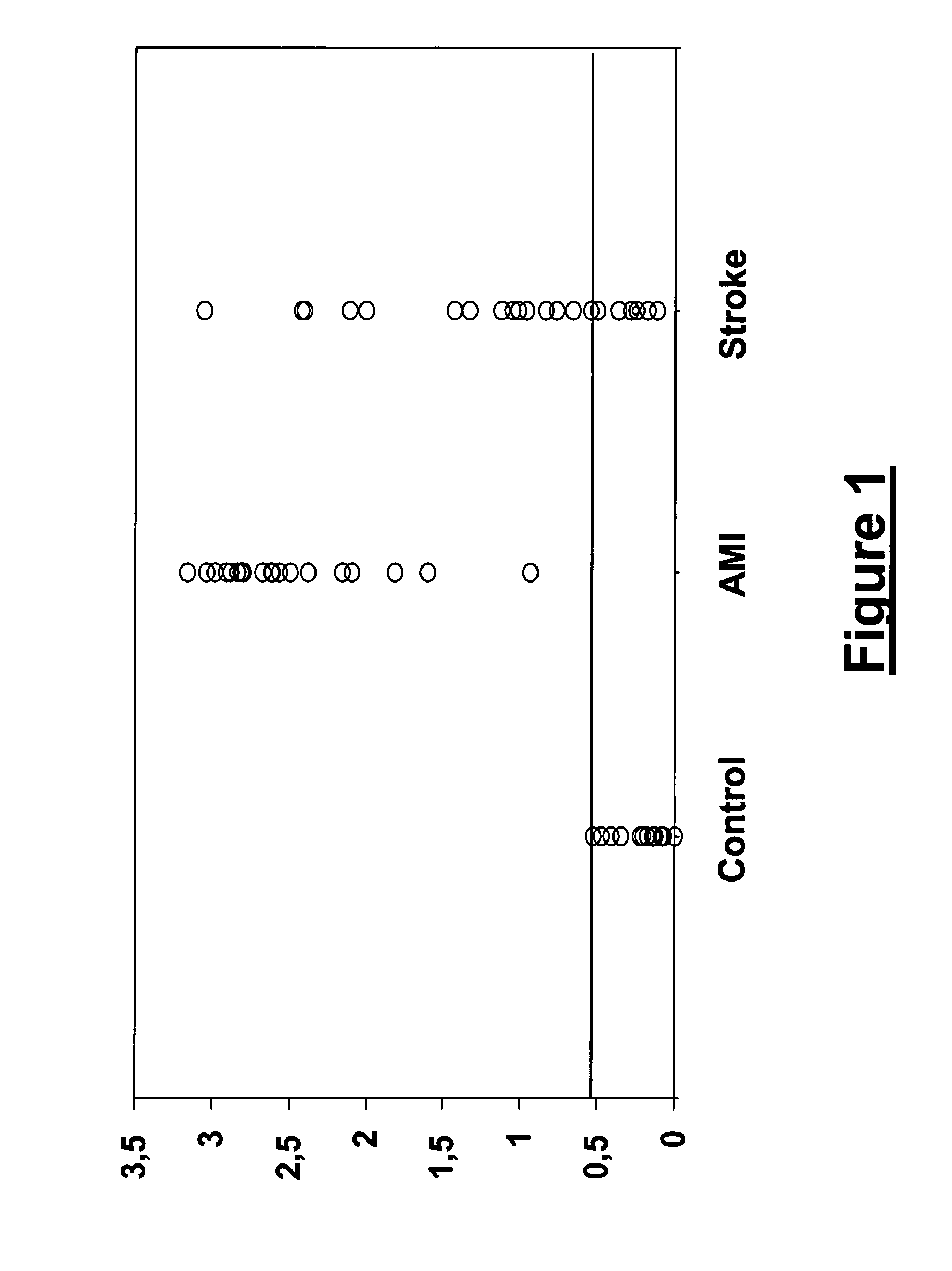
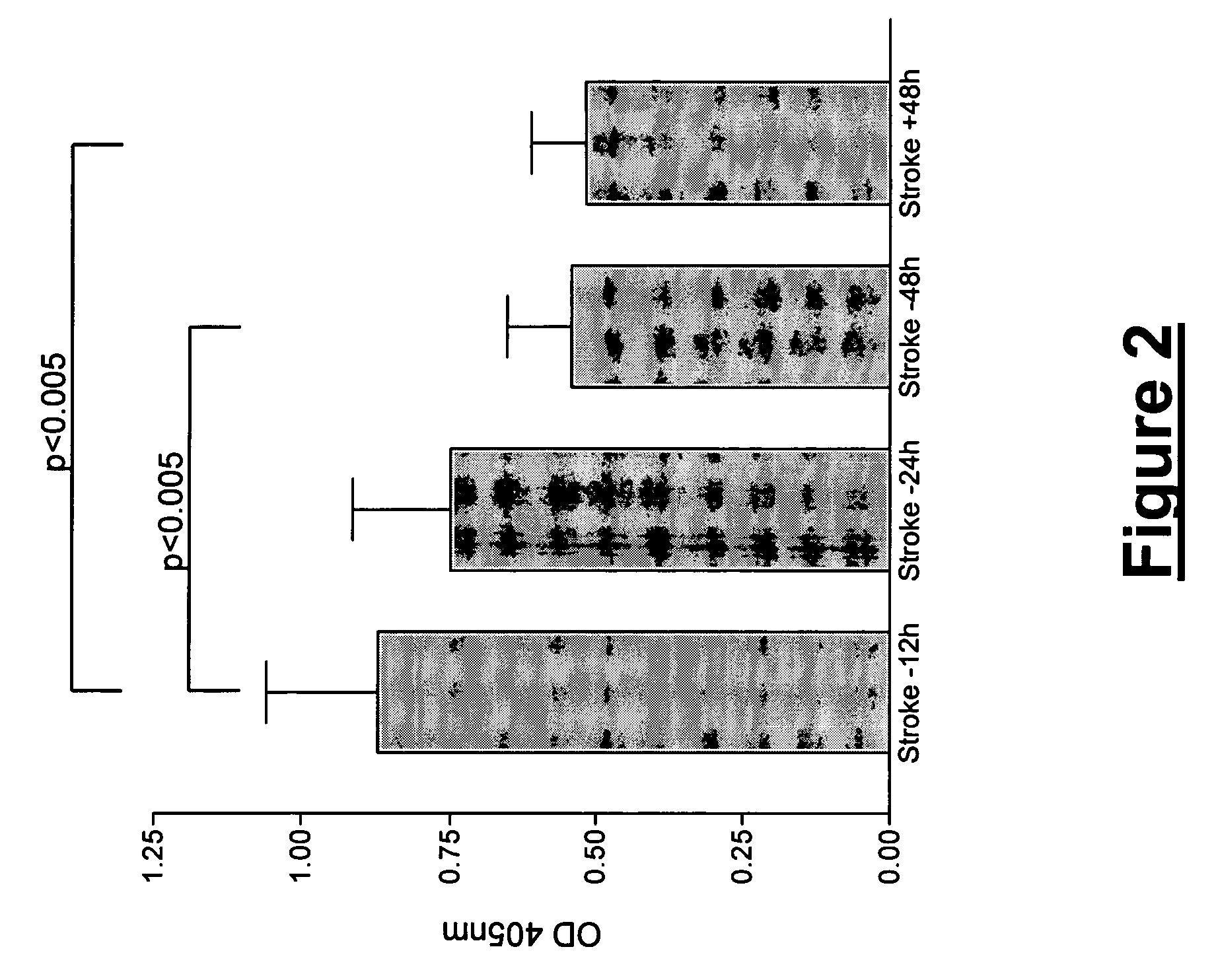
Method for the in vitro diagnosis of stroke
ActiveUS8486652B2Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningNucleoside diphosphate kinase ACut off value
Owner:BIO RAD EURO GMBH
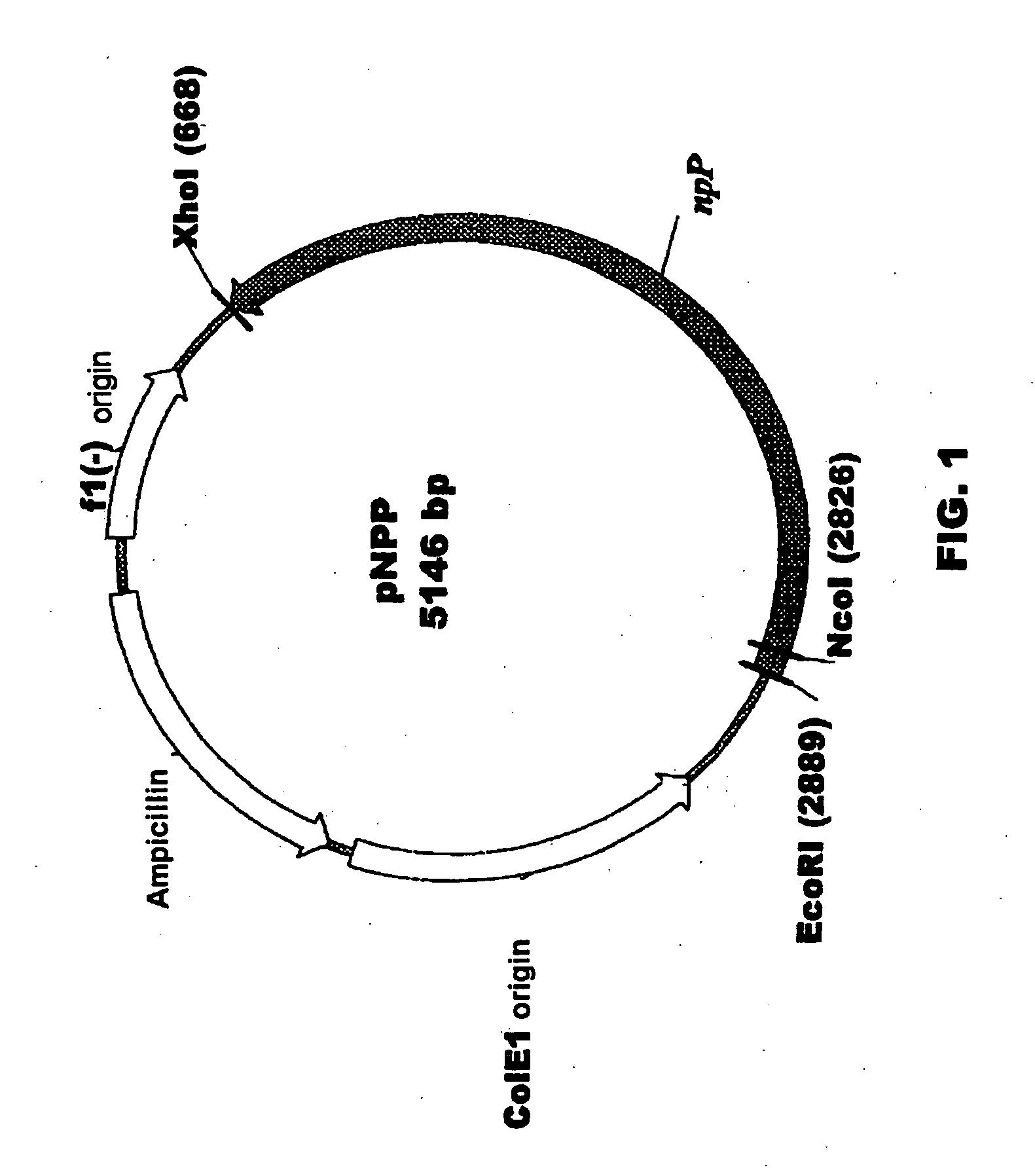
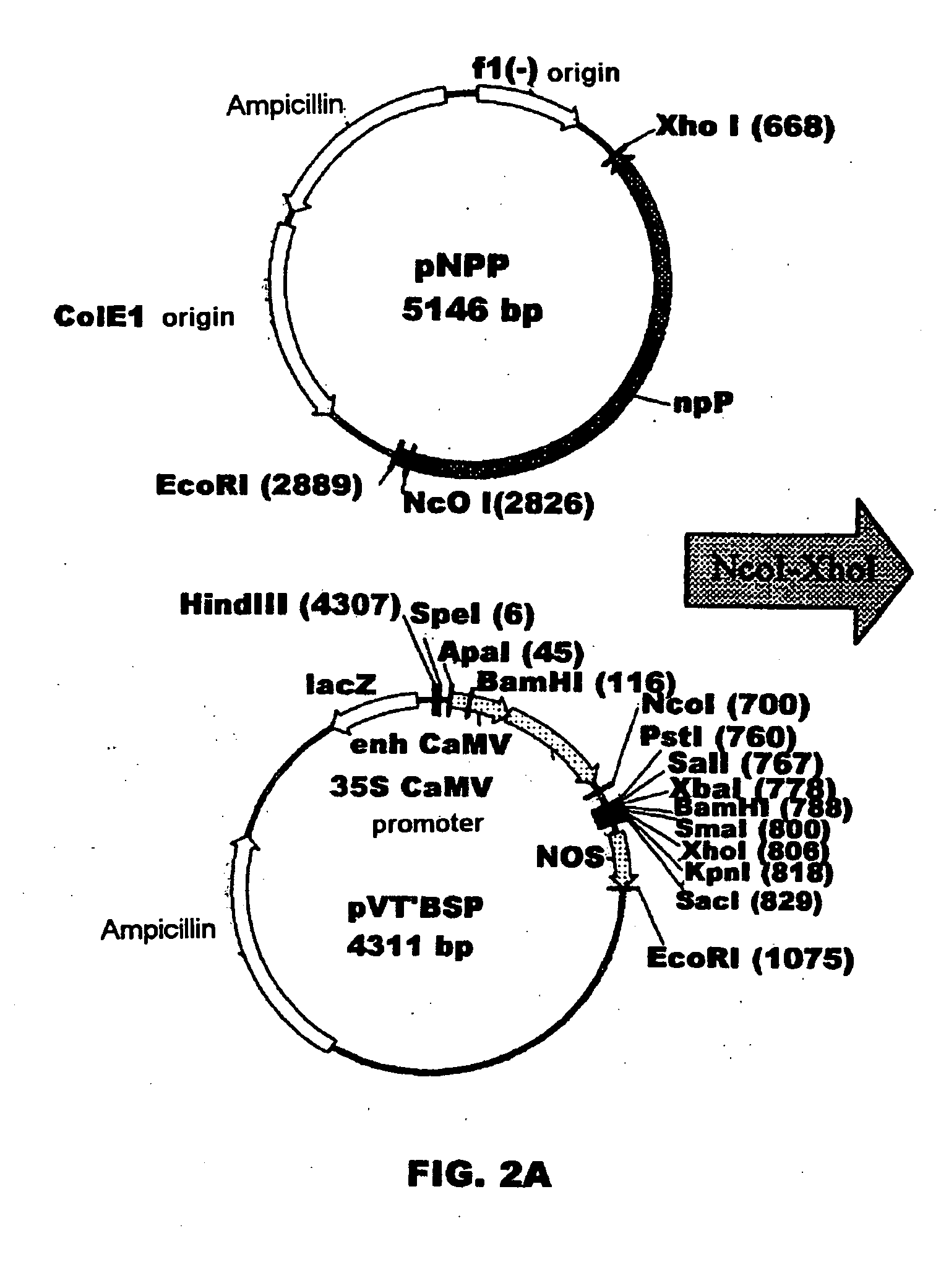
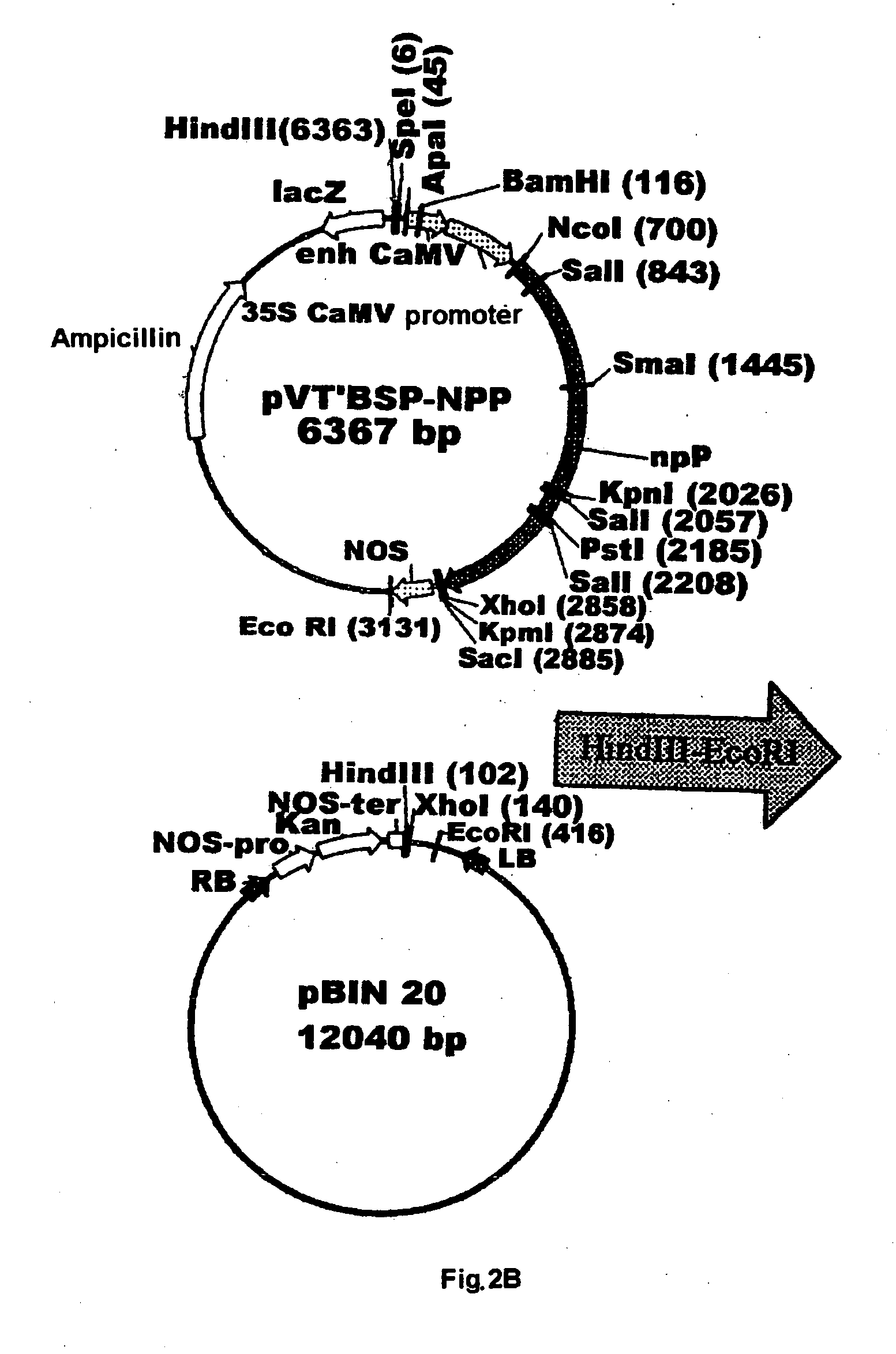
Plant nucleotide-sugar pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase (nppase), method of obtaining same and use of same in the production of assay devices and in the production of transgenic plants
InactiveUS20060242739A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh resistancePhosphate
Plant nucleotide pyrophosphatase / phosphodiesterase (NPPase), method of production, use in the manufacture of testing devices and in the production of transgenic plants. NPPase is an enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of a wide range of small molecules with phosphodiester and phosphosulphate bonds, in particular ADPG (adenosine diphosphate glucose) and APS (adenosine 5′-phosphosulphate). The enzyme obtained from plant extracts is used in assay devices for determining levels of nucleoside diphosphate sugars, based either on the sugar-1-phosphate released, or on the nucleoside monophosphate, both of which are products formed by the reaction catalysed by NPPase, as well as the detection of sulphonucleotides such as 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulphate (PAPS) and APS. The amino acid sequence of the enzyme is also described, as well as the nucleotide sequence of a complete cDNA and another incomplete cDNA. Finally, it describes the production of transgenic plants that overexpress NPPase and that have a high content of sugars, low content of starch and cell-wall polysaccharides and high resistance to high concentrations of salts and high temperature.
Owner:UNIV PUBLICA DE NAVARRA PAMPLONA +1
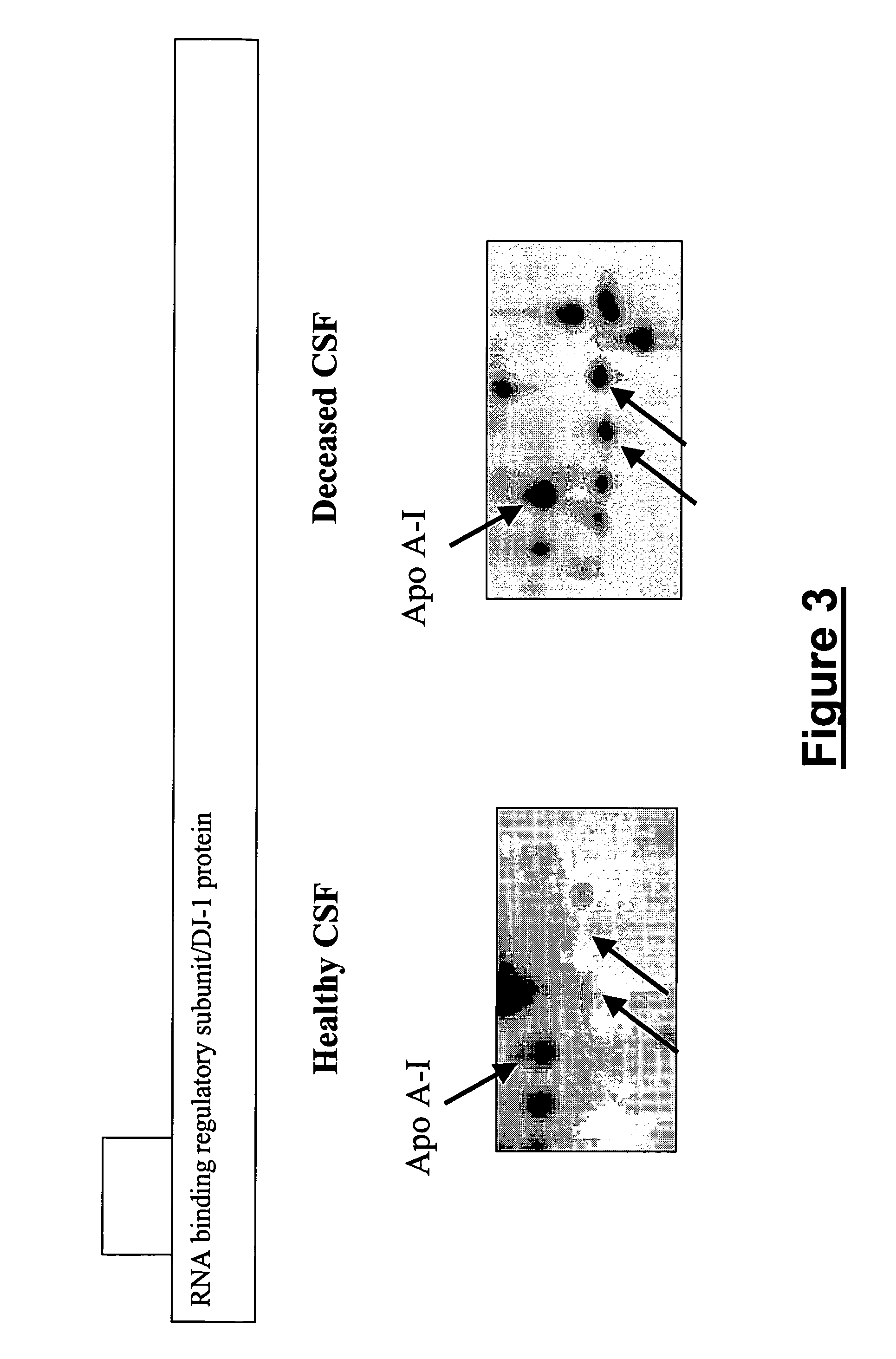
Diagnostic method for brain damage-related disorders
A brain damage-related disorder is diagnosed in a subject by detecting at least one polypeptide, or a variant or mutant thereof, selected from A-FABP, E-FABP, PGP 9.5, GFAP, Prostaglandin D synthase, Neuromodulin, Neurofilament L, Calcyphosine, RNA binding regulatory subunit, Ubiquitin fusion degradation protein 1 homolog, Nucleoside diphosphate kinase A, Glutathione S tranferase P, Cathepsin D, DJ-1 protein, Peroxiredoxin 5 and Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase A (Cyclophilin A) in a sample of body fluid taken from the subject.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GENEVA +1
Synthesis method of nucleoside diphosphate 6-deoxy-L-pyranose
InactiveCN103509074AShort reaction timeSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationPyranoseChemical synthesis
Owner:JIANGXI SCI & TECH NORMAL UNIV
Cordyceps Chinese Hirsutella uridylate-cytidylate kinase, coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN103031286AIncrease productionEnhance expressive abilityBacteriaTransferasesExpressivityCytidylate kinase
The invention relates to an enzyme from Bailing production bacterium Cordyceps Chinese Hirsutella for synthesizing metabolic pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphate from pyrimidine nucleoside, a gene for coding the enzyme and application thereof. The enzyme is uridylate-cytidylate kinase which has more than 90% of homology with amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.1; and the coding gene has more than 90% of homology with nucleotide sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.2. The invention researches the metabolic pathway of pyrimidine nucleotide synthesized pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphate in details in principle. The cloned DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) comprising the nucleotide sequence provided by the invention can be transformed into engineering bacterium by transduction, conversion and conjugal transfer. By adjusting the expression of the pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphate biosynthesized gene, the host pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphate is endowed with high expressivity, thereby providing an effective way for enhancing the yield of the pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphate and having great application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Nucleoside diphosphokinase A oxidation-reduction isomer
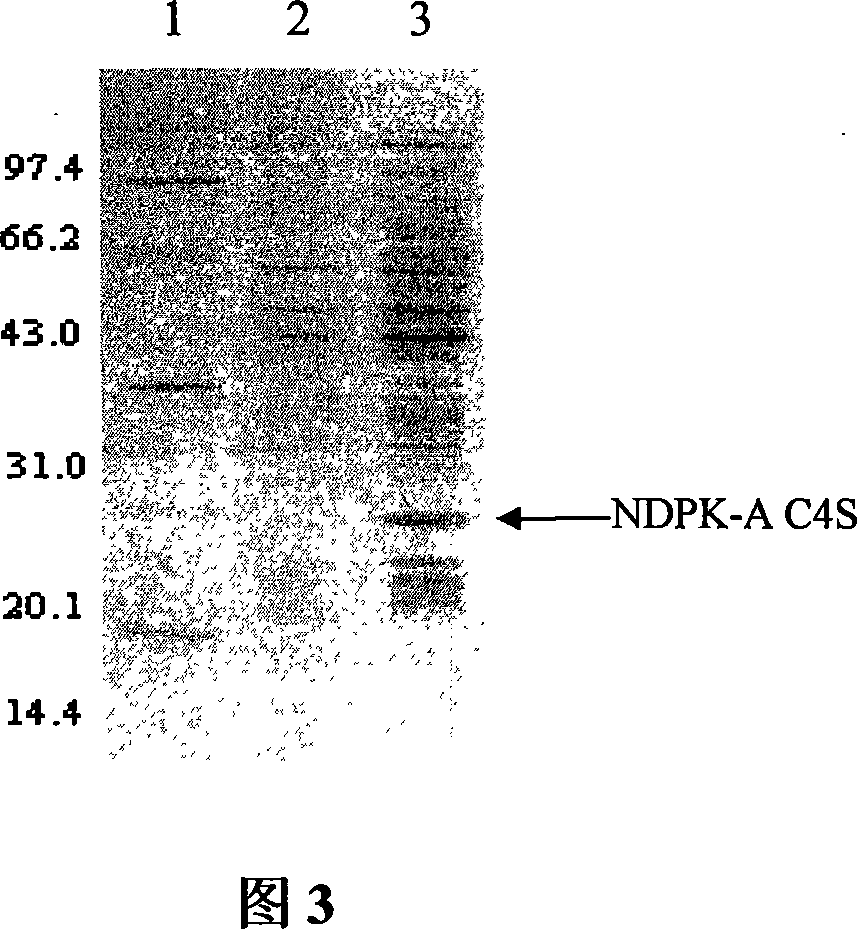
ActiveCN101063112AHigh activityUnchanged stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsTransferasesPhosphateNucleoside diphosphokinase
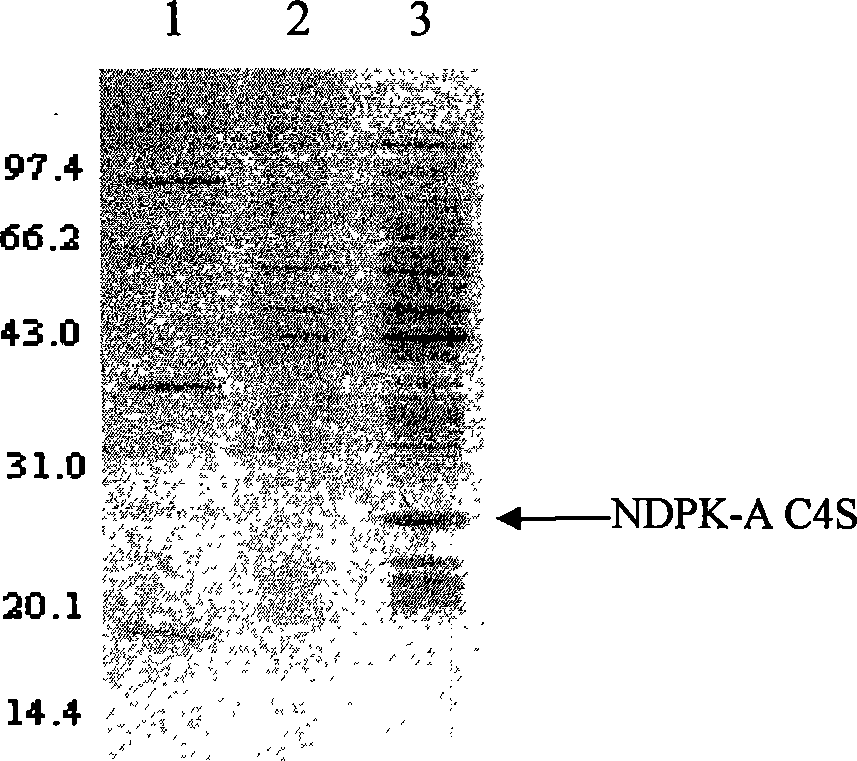
The invention discloses a method to get nucleic diphosphokinase A (NDPK-A) oxidation-reduction isomer through gene engineering in genetic engineering domain, which is characterized by the following: producing a amino acid abrupt change in NDPK-A; generating the oxidation-reduction isomer; abrupt-changing forth position cysteine to serine; getting amino acid abrupt change; setting the amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO. 2. This isomer possesses stronger activity, which can increase activity of phosphate group transferase of NDPK and DNase (inhibit cancer).
Owner:广州少伯控股集团有限公司
Cordyceps sinensis ribonucleotide reductase as well as coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN103045548AIncrease productionEnhance expressive abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideNucleoside diphosphate
The invention relates to ribonucleotide reductase from 'Bailing' producing strain cordyceps sinensis hirsutella sinensis for anabolism of deoxidized pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphate from pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphate, a gene coding the ribonucleotide reductase and application of the ribonucleotide reductase. The ribonucleotide reductase has over 90% of homology to the amino acid sequence shown by SEQ ID No.1 or SEQ ID No.3; and the coding gene has over 90% of homology to the nucleotide sequence shown by SEQ ID No.2 or SEQ ID No.4. According to the invention, the metabolic pathway for synthesizing deoxidized pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphate from pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphate is studied in details in principle, the cloning DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) comprising the nucleotide sequence provided by the invention can be transferred into engineering bacteria through transduction, transformation and combined transfer, high expressivity of the host deoxidized pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphate is obtained by adjusting the expression of the deoxidized pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphate biosynthesis gene, an effective means of increasing output of the deoxidized pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphate is provided, and a significant application prospect is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Cordyceps Chinese Hirsutella nucleoside diphosphokinase, coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN103031287BEnhance expressive abilityIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesBiosynthetic genesPhosphoric acid
The invention relates to an enzyme from Bailing production bacterium Cordyceps Chinese Hirsutella for synthesizing metabolic (desoxy) pyrimidine nucleoside triphosphate from (desoxy) pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphate, a gene for coding the enzyme and application thereof. The enzyme is nucleoside diphosphokinase which has more than 90% of homology with amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.1; and the coding gene has more than 90% of homology with nucleotide sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.2. The invention researches the metabolic pathway of (desoxy) pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphate synthesized (desoxy) pyrimidine nucleoside triphosphate in details in principle. The cloned DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) comprising the nucleotide sequence provided by the invention can be transformed into engineering bacterium by transduction, conversion and conjugal transfer. By adjusting the expression of the (desoxy) pyrimidine nucleoside triphosphate biosynthesized gene, the host (desoxy) pyrimidine nucleoside triphosphate is endowed with high expressivity, thereby providing an effective way for enhancing the yield of the (desoxy) pyrimidine nucleoside triphosphate and having great application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Method for producing polysaccharide
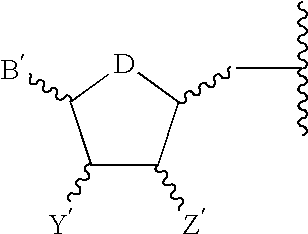
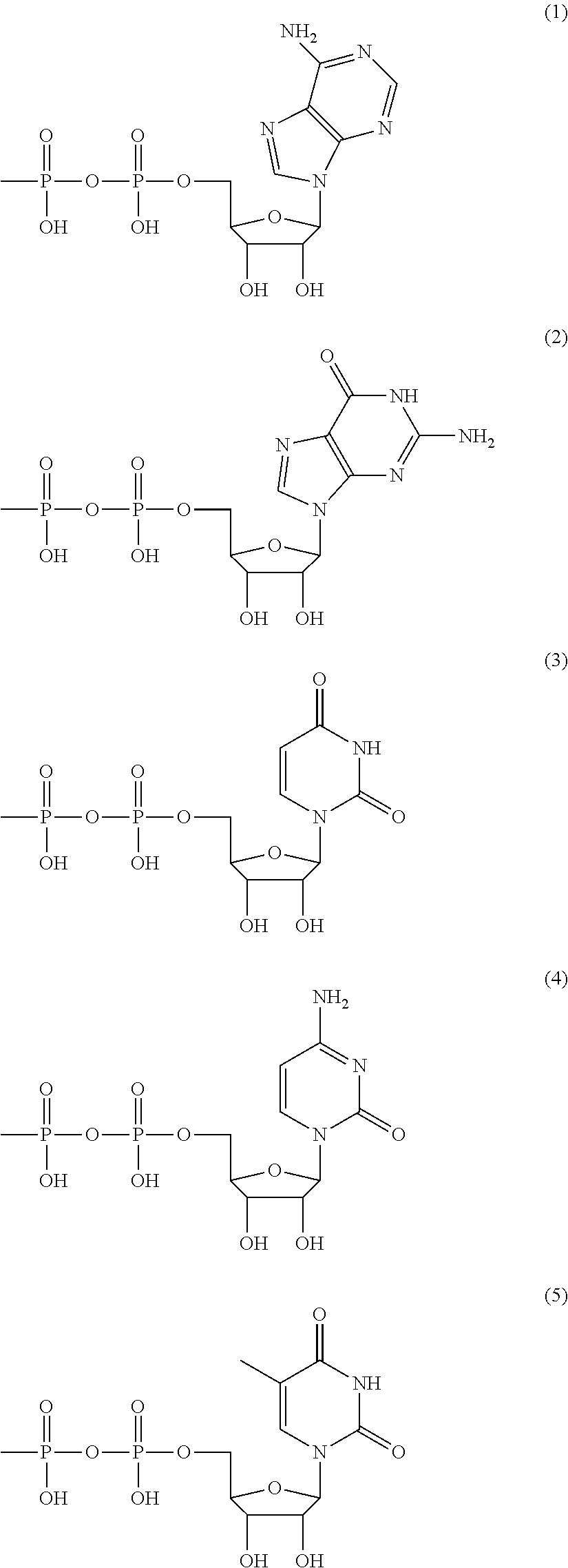
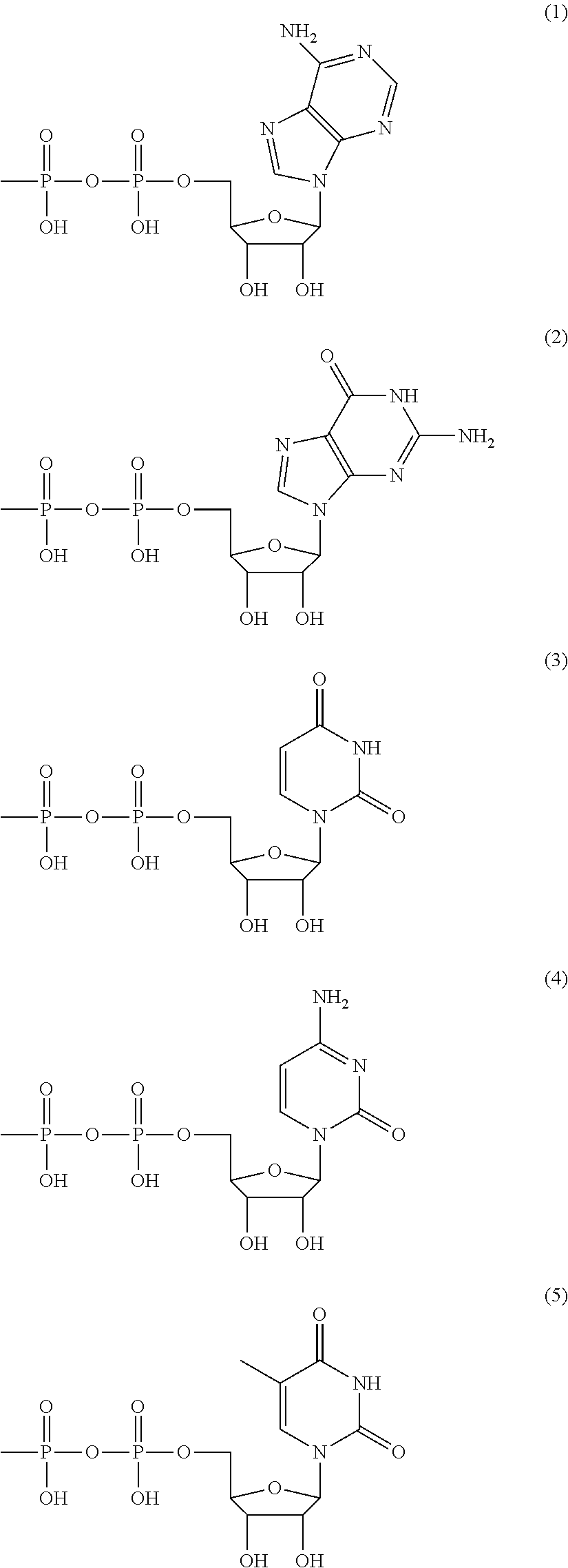
The present invention aims to provide a method for producing a polysaccharide with high efficiency using a polysaccharide synthase. The present invention provides a method for producing a polysaccharide, including allowing polysaccharide synthase (B) to act on ribonucleoside diphosphate-monosaccharide (A) shown below to produce a polysaccharide, wherein in 10 to 100% of the duration in which (B) acts on (A), the concentration of ribonucleoside diphosphate in a reaction solution is lower than 100 times an inhibitory concentration IC50 described below against polysaccharide synthase (B).Inhibitory concentration IC50: a concentration of ribonucleoside diphosphate at which an enzyme activity of polysaccharide synthase (B) is reduced by half while under a condition where (B) has a concentration at which (B) acts on ribonucleoside diphosphate-monosaccharide (A), wherein ribonucleoside diphosphate-monosaccharide (A) is used as a substrate and ribonucleoside diphosphate is used as an inhibitor.Ribonucleoside diphosphate-monosaccharide (A): a sugar nucleotide in which a proton of at least one hydroxyl group of at least one monosaccharide (a) selected from the group consisting of triose (a-1), tetrose (a-2), pentose (a-3), hexose (a-4), heptose (a-5), and monosaccharide (a-6) described below is substituted with a functional group represented by any one of chemical formulae (1) to (5) below.Monosaccharide (a-6): a monosaccharide selected from the group consisting of (a-1), (a-2), (a-3), (a-4), and (a-5), in which at least one member selected from the group consisting of a proton, a hydroxyl group, and a hydroxymethyl group of the monosaccharide is substituted with substituent (E) described below.Substituent (E) is at least one substituent selected from the group consisting of carboxyl, amino, N-acetylamino, sulfate, methylester, N-glycolyl, methyl, 1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl, phosphate, and 2-carboxy-2-hydroxyethyl groups.
Owner:SANYO CHEM IND LTD
Polyphosphate:AMP phosphotransferase
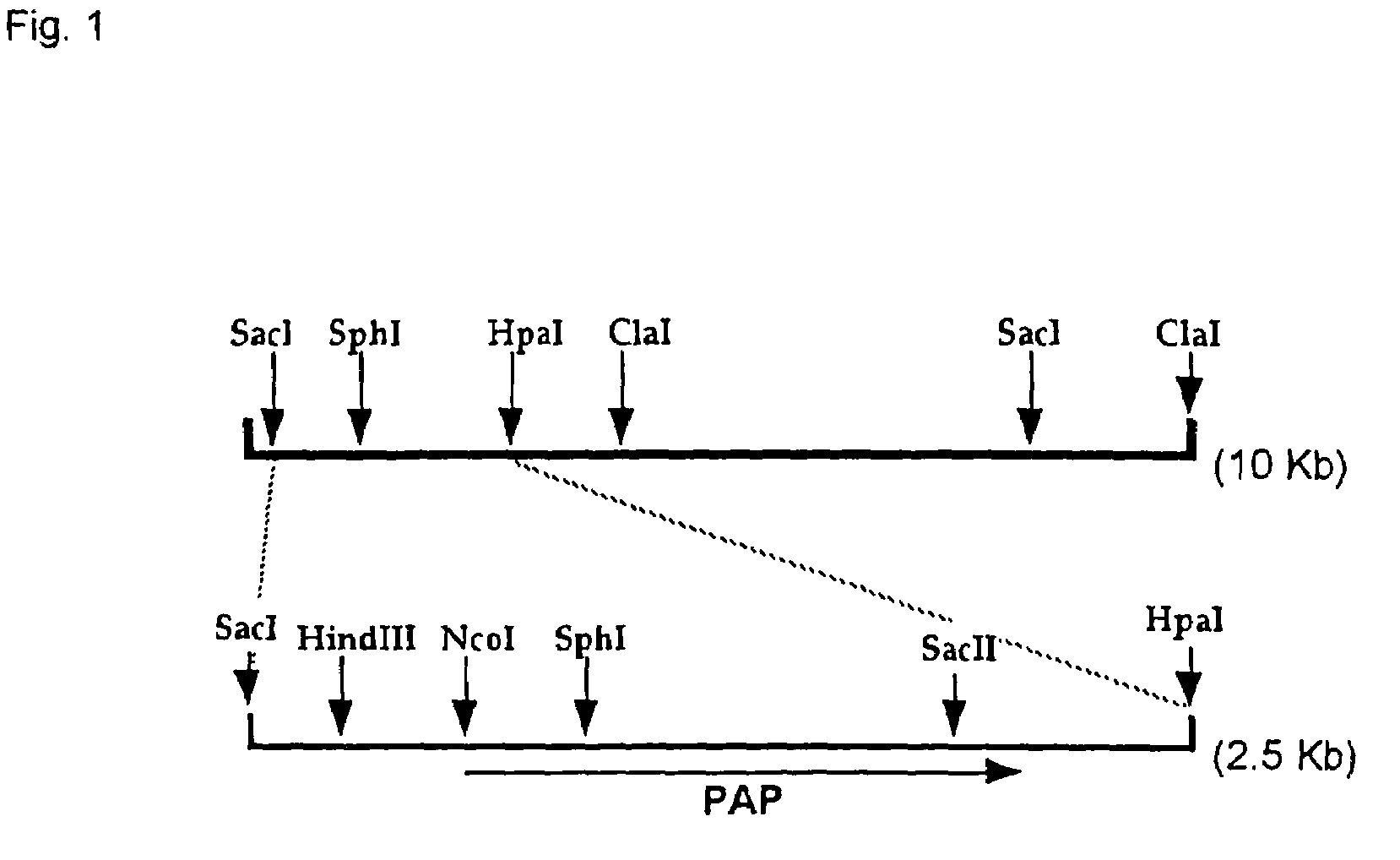
ActiveUS7329522B2High specific activityEfficient ATP generation/regeneration systemSugar derivativesBacteriaKilodaltonPhosphoric acid
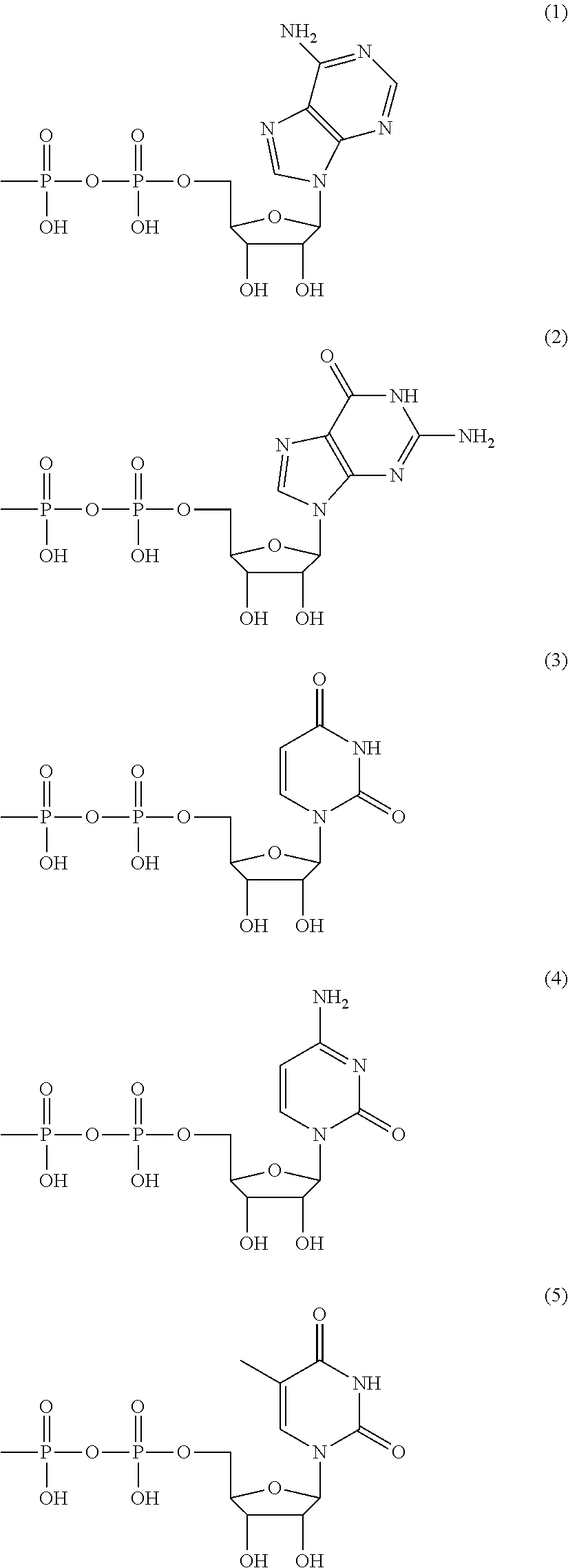
This invention relates to a novel polyphosphate: AMP phosphotransferase (PAP), a gene coding this PAP, and their use. The PAP has the following properties:(A) action: catalyzing of the following two reactions:NMP+PolyP(n)→NDP+PolyP(n-1) dNMP+POlyP(n)→dNDP+PolyP(n-1) (wherein NMP represents nucleoside monophosphate, NDP represents nucleoside diphosphate, dNMP represents deoxynucleoside monophosphate, dNDP represents deoxynucleoside diphosphate, n represents degree of polymerization of the polyphosphate which is an integer of up to 100);(B) substrate specificity: specific to AMP, GMP, IMP, dAMP, and dGMP, also acting with CMP, UMP, dCMP, and TMP;(C) molecular weight: about 55 to 56 Kd (kilodalton); and(D) specific activity: at least 70 units per 1 mg of enzyme protein.
Owner:YAMASA SHOYU CO LTD
Cordyceps Chinese Hirsutella nucleoside diphosphokinase, coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN103031287AEnhance expressive abilityIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesBiosynthetic genesPhosphoric acid
The invention relates to an enzyme from Bailing production bacterium Cordyceps Chinese Hirsutella for synthesizing metabolic (desoxy) pyrimidine nucleoside triphosphate from (desoxy) pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphate, a gene for coding the enzyme and application thereof. The enzyme is nucleoside diphosphokinase which has more than 90% of homology with amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.1; and the coding gene has more than 90% of homology with nucleotide sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.2. The invention researches the metabolic pathway of (desoxy) pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphate synthesized (desoxy) pyrimidine nucleoside triphosphate in details in principle. The cloned DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) comprising the nucleotide sequence provided by the invention can be transformed into engineering bacterium by transduction, conversion and conjugal transfer. By adjusting the expression of the (desoxy) pyrimidine nucleoside triphosphate biosynthesized gene, the host (desoxy) pyrimidine nucleoside triphosphate is endowed with high expressivity, thereby providing an effective way for enhancing the yield of the (desoxy) pyrimidine nucleoside triphosphate and having great application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Nucleoside diphosphokinase A oxidation-reduction isomer
ActiveCN101063112BUnchanged stabilityHigh activityPeptide/protein ingredientsTransferasesPhosphateNucleoside diphosphokinase
The invention discloses a method to get nucleic diphosphokinase A (NDPK-A) oxidation-reduction isomer through gene engineering in genetic engineering domain, which is characterized by the following: producing a amino acid abrupt change in NDPK-A; generating the oxidation-reduction isomer; abrupt-changing forth position cysteine to serine; getting amino acid abrupt change; setting the amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO. 2. This isomer possesses stronger activity, which can increase activity of phosphate group transferase of NDPK and DNase (inhibit cancer).
Owner:广州少伯控股集团有限公司
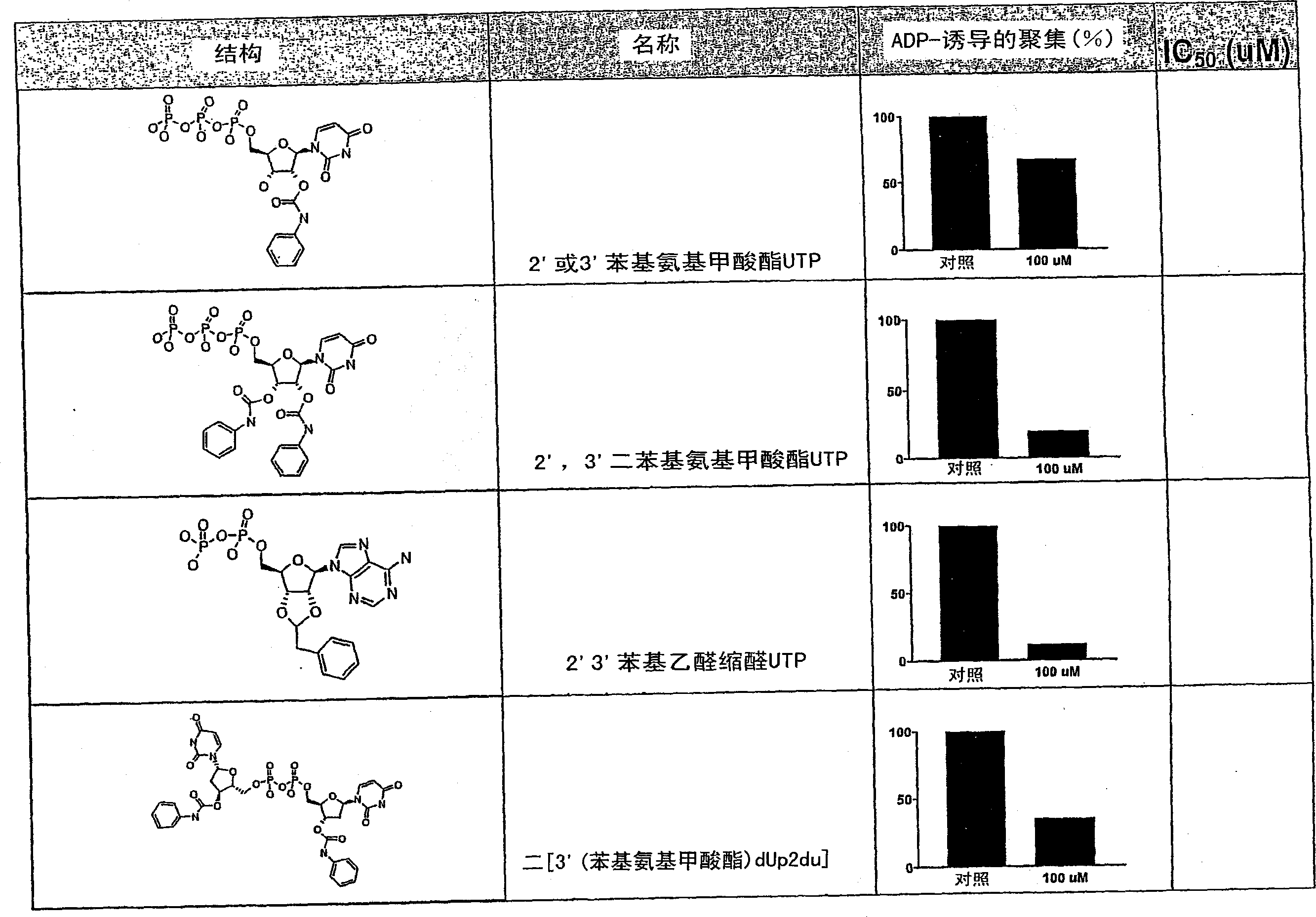
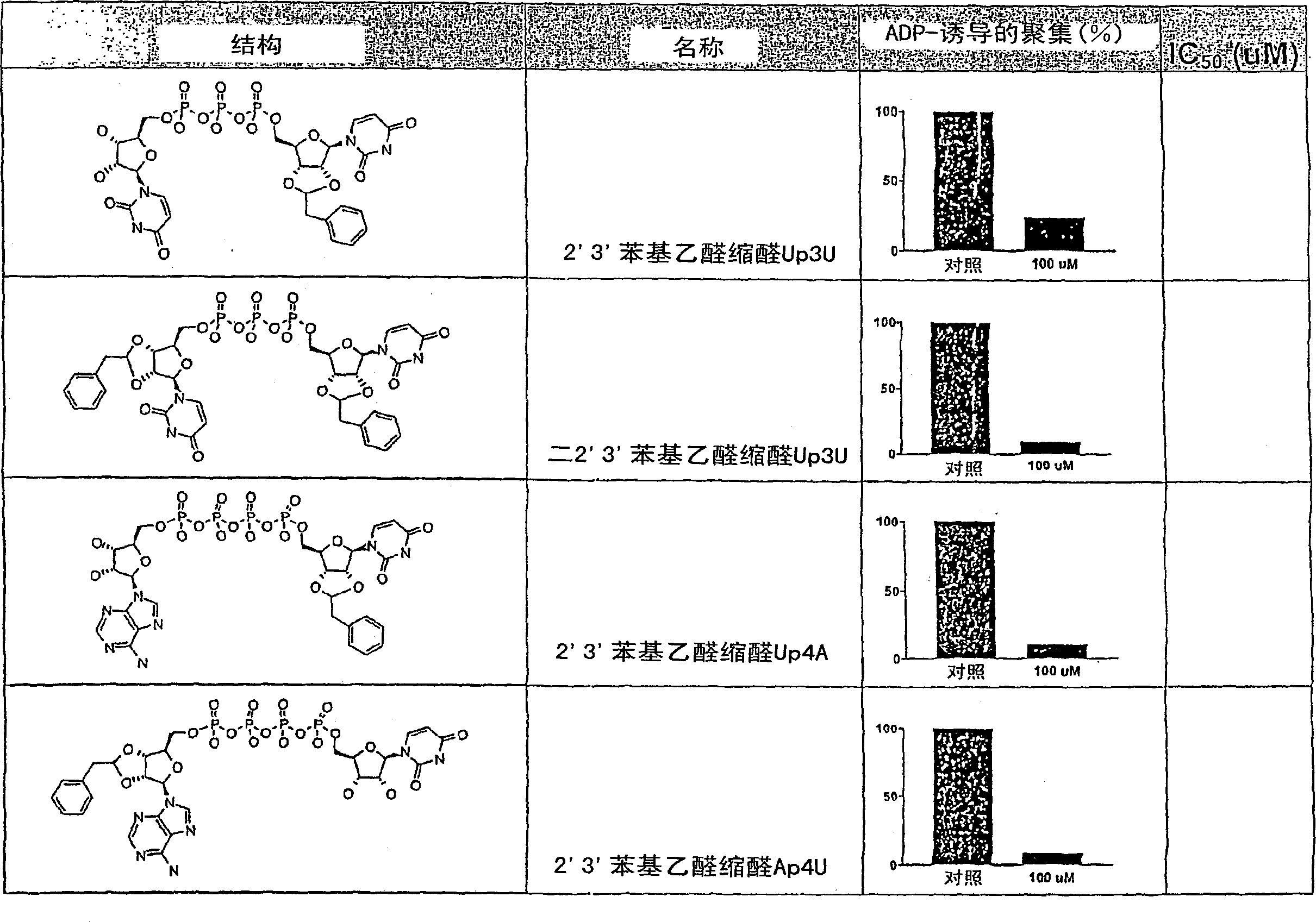
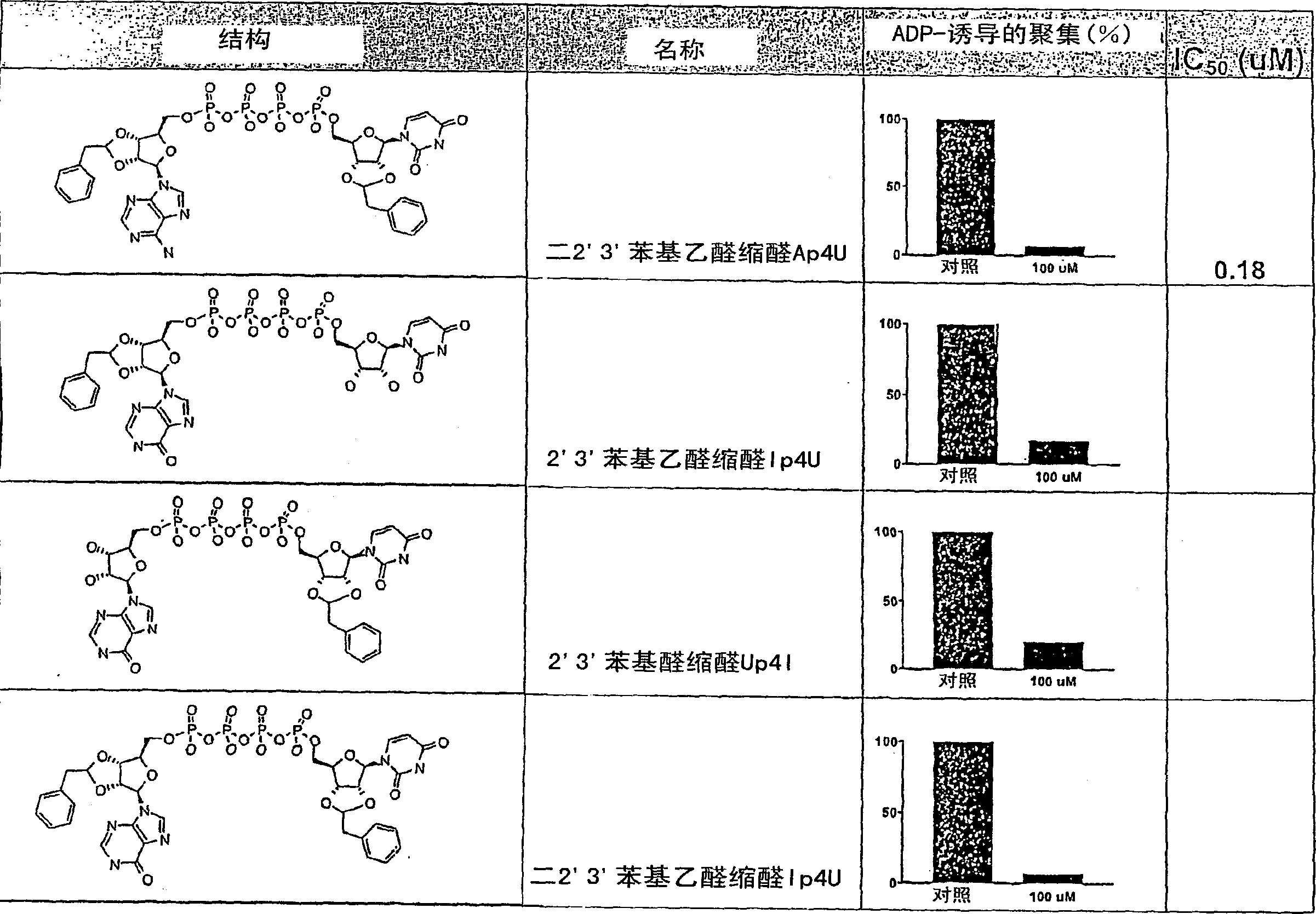
Di- and triphosphate prodrugs
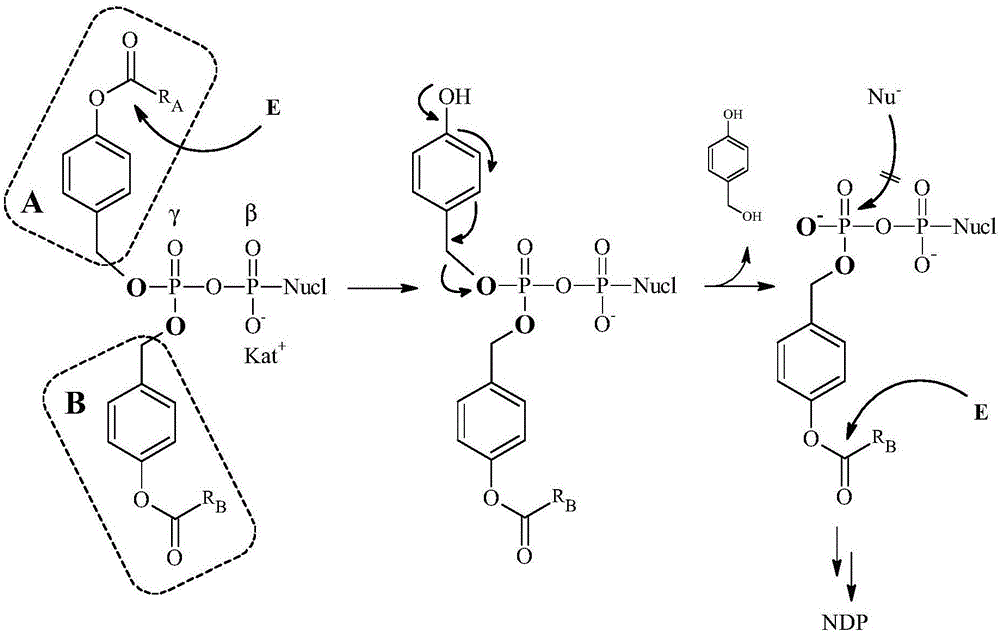
The invention relates to compounds which can be used as prodrugs, in particular nucleoside diphosphate and triphosphate prodrugs, and to a method for producing said compounds. The aim of the invention is to provide improved di- and / or triphosphate prodrugs, in particular nucleotide or nucleotide analog prodrugs. This is achieved in one aspect by providing bioreversibly and asymmetrically masked di- and triphosphate compounds, in particular nucleoside diphosphate and nucleoside triphosphate compounds or the analogs thereof. The masking only occurs at the terminal phosphate, i.e. at the Beta- or Gamma-phosphate, whereas the masking of the internal phosphate is omitted.
Owner:UNIV OF HAMBURG
Synthesis of 6-azido-6-deoxy-2-N-acetyl-hexosamine-nucleoside diphosphate
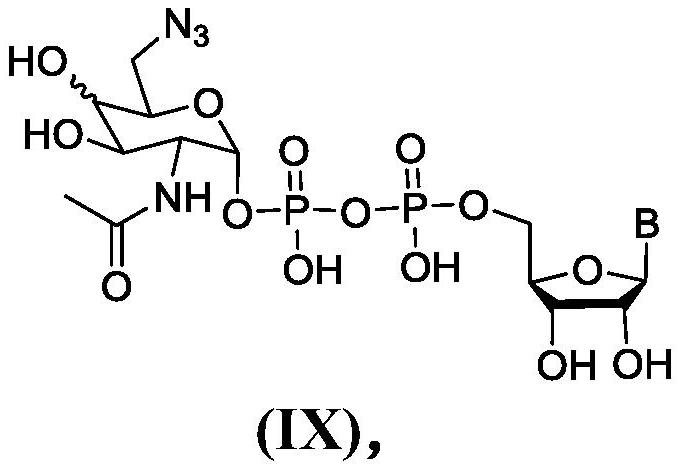
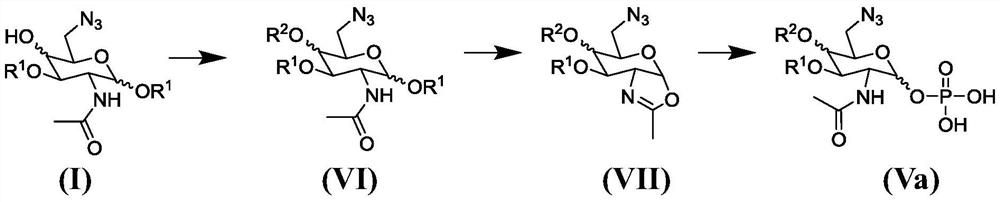
PendingCN114423773AImprove efficiencyHigh yieldEsterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesHexosaminesNucleoside diphosphate
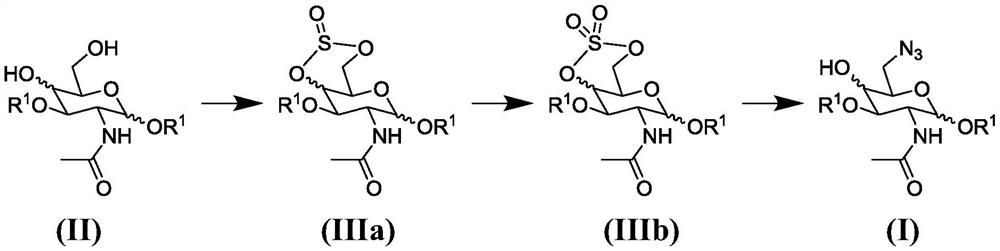
The present invention relates to a process for the synthesis of 6-azido-6-deoxy-2-N-acetyl-monosaccharide-nucleoside diphosphate, in particular 6-azido-6-deoxy-2-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine-nucleoside diphosphate or 6-azido-6-deoxy-2-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-nucleoside diphosphate, in particular to a process for the synthesis of 6-azido-6-deoxy-2-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine-nucleoside diphosphate or 6-azido-6-deoxy-2-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-nucleoside diphosphate. The synthesis method according to the invention is characterized by high efficiency and high yield. The other part of the invention is a key intermediate of the method.
Owner:SYNAFFIX
Analytical and diagnostic methods utilizing shigella flexneri apyrase
InactiveCN107075552AHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementShigella flexneriNucleoside diphosphate
A method, comprising the steps of providing a sample containing contaminating nucleoside diphosphates and / or nucleoside triphosphates, such as ATP and / or ATP analogues including deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates;reducing the amount of the contaminating nucleoside diphosphates and / or nucleoside triphosphates in the sample with an apyrase enzyme, wherein said apyrase enzyme is a Shigella flexneriapyrase; andperforming an analysis of the sample, wherein said analysis comprises an assay that would have been affected by the contaminating nucleoside diphosphates and / or nucleoside triphosphates had they not been reduced in the reduction step.
Owner:APIRAYS BIOSCI AB
P2y6 receptor agonists for treating lung diseases
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
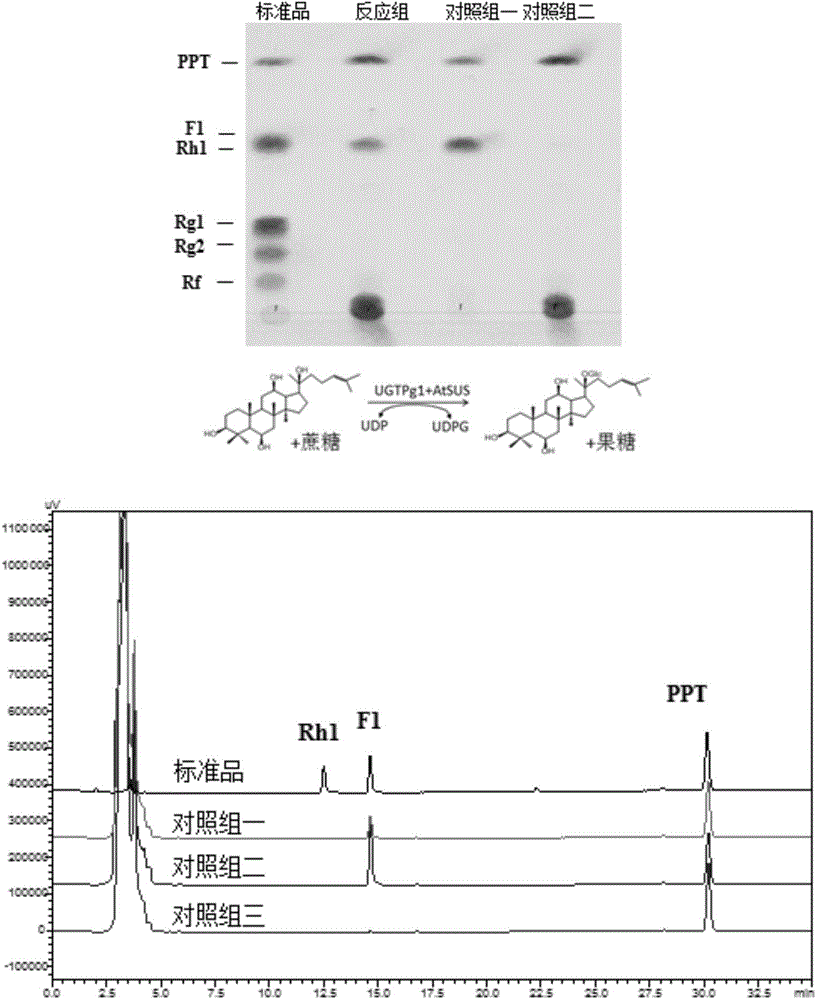
A new catalytic system for preparing rare ginsenosides and its application
ActiveCN105087739BHigh catalytic efficiencyReduce use costFungiBacteriaSucrose synthetaseProtopanaxadiol
The invention discloses a co-catalytic reaction system for preparing rare ginsenosides. The co-catalytic reaction system comprises glycosyltransferase GT (a); sucrose synthase SUS (b); uridine diphosphate UDP (c); and saccharose (d). Experiments show that in the presence of the saccharose and little UDP, an enzyme combination composed of the glycosyltransferase and the saccharose is capable of replacing an in-vitro reaction system to synthesize UDP sugar, one of expensive materials for the rare ginsenosides, and efficiently and economically converting substrates such as protopanoxadiol or protopanaxatriol into the rare ginsenosides, wherein the UDP is about 1 / 4 of the UDP sugar in price and is 1% of its original dosage; thus, preparation cost of the rare ginsenosides is greatly saved, and large-scale commercial preparation of the ginsenosides is better facilitated.
Owner:SYNBIOTECH (SUZHOU) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com